|
| 1 | +# Queue |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +A queue is a linear data structure that restricts the order in which operations can be performed on its elements. |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +### Operation Orders |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +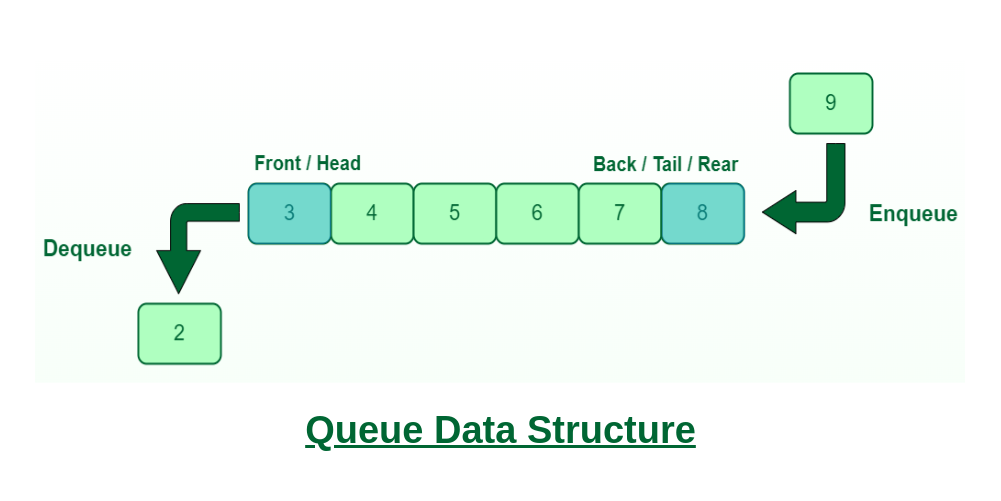 |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +*Source: GeeksForGeeks* |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +Queue follows a FIFO, first in first out order. |
| 12 | +This means the earliest element |
| 13 | +added to the stack is the one operations are conducted on first. |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +A [stack](../stack/README.md) is a queue with operations conducted in an opposite manner. |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +## Analysis |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +As a queue only interacts with either the first or last element regardless during its operations, |
| 20 | +it only needs to keep the pointers of the two element at hand, which is constantly updated as more |
| 21 | +elements are removed / added. This allows stack operations to only incur a *O(1)* time complexity. |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +## Notes |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +### Stack vs Queues |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +Stack and queues only differ in terms of operation order, you should aim to use a stack when |
| 28 | +you want the most recent elements to be operated on. |
| 29 | +Some situations where a stack would work well include build redo / undo systems and backtracking problems. |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +On the other hand, a queue allows you to operate on elements that enter first. Some situations where |
| 32 | +this would be useful include Breadth First Search algorithms and task / resource allocation systems. |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | +### Arrays vs Linked List |
| 35 | +It is worth noting that queues can be implemented with either a array or with a [linked list](../linkedList/README.md). |
| 36 | +In the context of ordered operations, the lookup is only restricted to the first element. |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | +Hence, there is not much advantage in using a array, which only has a better lookup speed (*O(1)* time complexity) |
| 39 | +to implement a queue. Especially when using a linked list to construct your queue |
| 40 | +would allow you to grow or shrink the queue as you wish. |
| 41 | + |
| 42 | +### Queue Variants |
| 43 | + |
| 44 | +These are some variants of queue that are commonly used. |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | +#### Double Ended Queue (Deque) |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | +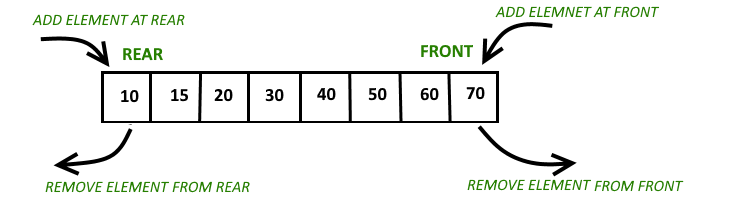 |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +*Source: GeeksForGeeks* |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +Deque is a variant of queue where elements can be removed or added from the head and tail of the queue. |
| 53 | +Deque could come in handy when trying to solve sliding window problems. |
| 54 | + |
| 55 | +However, it is important to note that when implementing a deque, unlike a queue, you would require a doubly linked list. |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +#### Monotonic Queue |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +This is a variant of queue where elements within the queue are either strictly increasing or decreasing. |
| 60 | +Monotonic queues are often implemented with a deque. |
| 61 | + |
| 62 | +Within a increasing monotonic queue, any element that is smaller than the current minimum is removed. |
| 63 | +Within a decreasing monotonic queue, any element that is larger than the current maximum is removed. |
| 64 | + |
| 65 | +It is worth mentioning that the most elements added to the monotonic queue would always be in a |
| 66 | +increasing / decreasing order, |
| 67 | +hence, we only need to compare down the monotonic queue from the back when adding new elements. |
| 68 | + |
0 commit comments