You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/2-app-scaffolding.md
+7-5Lines changed: 7 additions & 5 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -32,16 +32,18 @@ Before you start coding, here are some useful tips:
32
32
2. Select **Empty Views Activity** in the **Phone and Tablet** gallery as Figure 1 shows, then select **Next**.
3. Choose a project name, and select the default configurations as Figure 2 shows. Make sure that the **Language** field is set to **Kotlin**, and **Build configuration language** is set to **Kotlin DSL**.
35
+
3. Choose a project name, and select the default configurations as Figure 2 shows.
36
+
37
+
Make sure that the **Language** field is set to **Kotlin**, and the **Build configuration language** field is set to **Kotlin DSL**.
[CameraX](https://developer.android.com/media/camera/camerax) is a Jetpack library, built to help make camera app development easier. It provides a consistent, easy-to-use API that works across the vast majority of Android devices with great backward-compatibility.
41
43
42
-
1. Wait for Android Studio to sync project with Gradle files, this might take several minutes.
44
+
1. Wait for Android Studio to sync project with Gradle files. This might take several minutes.
43
45
44
-
2. Once the project is synced, navigate to `libs.versions.toml` in your project's root directory as Figure 3 shows. This file serves as the version catalog for all dependencies used in the project.
46
+
2. Once the project is synced, navigate to `libs.versions.toml` in your project's root directory. See Figure 3. This file serves as the version catalog for all dependencies that the project uses.
45
47
46
48

47
49
@@ -84,7 +86,7 @@ camera-view = { group = "androidx.camera", name = "camera-view", version.ref = "
84
86
}
85
87
```
86
88
87
-
2. You should see that a notification appears, as Figure 4 shows. Click **Sync Now** to sync your project.
89
+
2. You should see that a notification appears. See Figure 4. Click **Sync Now** to sync your project.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/3-camera-permission.md
+16-18Lines changed: 16 additions & 18 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -6,19 +6,15 @@ weight: 3
6
6
layout: learningpathall
7
7
---
8
8
9
-
##Run the app on your device
9
+
### Connect your device to your machine with a USB data cable
10
10
11
-
In this section, you will learn how to run the app on your device.
12
-
13
-
#### Connect your device to your machine with a USB data cable
14
-
15
-
If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow the guidance on the Android Developer website [Set up a device for development](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/device#setting-up), and check that you have completed these steps:
11
+
If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow the guidance on the Android Developer website. See [Set up a device for development](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/device#setting-up), and check that you have completed these steps:
16
12
17
-
1. You have followed the instructions [Enable USB debugging on your device](https://developer.android.com/studio/debug/dev-options#Enable-debugging) from the Android Developer website.
13
+
1. You have followed the instructions [Enable USB debugging on your device](https://developer.android.com/studio/debug/dev-options#Enable-debugging).
18
14
19
-
2. You have confirmed that you have enabled USB debugging by tapping **OK** on your device when the **Allow USB debugging** dialog appears, and that you have checked **Always allow from this computer**, as Figure 6 shows.
15
+
2. You have confirmed that you have enabled USB debugging by tapping **OK** on your device when the **Allow USB debugging** dialog appears, and that you have checked **Always allow from this computer**. See Figure 6.
20
16
21
-
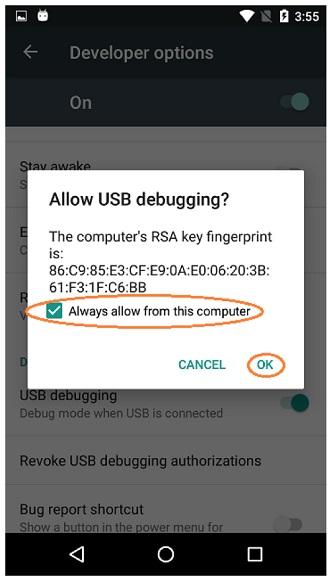 "Figure 6: Allow USB Debugging."
17
+

22
18
23
19
24
20
3. Make sure that your device model name and SDK version correctly show up in the top-right toolbar.
@@ -36,13 +32,13 @@ If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow the guidan
36
32
2024-11-20 11:43:03.408 2709-3807 PackageManager pid-2709 E Permission android.permission.CAMERA isn't requested by package com.example.holisticselfiedemo
37
33
```
38
34
39
-
6.This is the expected behavior from having not yet correctly configured the app's [permissions](https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/permissions/overview). Android OS restricts this app's access to camera features due to privacy constraints.
35
+
This is the expected behavior from having not yet correctly configured the app's permissions. See[Permissions](https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/permissions/overview) on the Android Developer website. Android OS restricts the app's access to camera features due to privacy constraints.
40
36
41
-
####Request camera permission at runtime
37
+
### Request camera permission at runtime
42
38
43
39
1. Navigate to `manifest.xml` in your `app` sub-project's `src/main` path.
44
40
45
-
Declare the camera hardware and set the permissions by inserting the following lines into the `<manifest>` element. Ensure that it is declared outside and above the `<application>` element.
41
+
Declare the camera hardware, and set the permissions by inserting the following lines into the `<manifest>` element, ensuring that it is declared outside and above the `<application>` element:
46
42
47
43
```xml
48
44
<uses-feature
@@ -52,7 +48,7 @@ If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow the guidan
52
48
```
53
49
54
50
2. Navigate to `strings.xml` in your `app` sub-project's `src/main/res/values` path.
55
-
Insert the following lines of text resources, which you will use at a later stage.
51
+
Insert the following lines of text resources, which you will use at a later stage:
56
52
57
53
```xml
58
54
<stringname="permission_request_camera_message">Camera permission is required to recognize face and hands</string>
@@ -77,8 +73,8 @@ If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow the guidan
77
73
}
78
74
```
79
75
80
-
5. Add a condition check in `onCreate()` wrapping `setupCamera()` method, to request camera
81
-
permission on runtime.
76
+
5. Add a condition check in on the `onCreate()` wrapping `setupCamera()` method, to request camera
77
+
permission on runtime:
82
78
83
79
```kotlin
84
80
if (!hasPermissions(baseContext)) {
@@ -117,14 +113,16 @@ If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow the guidan
117
113
}
118
114
```
119
115
120
-
####Verify camera permission
116
+
### Verify camera permission
121
117
122
118
1. Rebuild and run the app. Now you should see a dialog pop up requesting camera permissions.
123
119
124
-
2. Depending on your Android OS version, tap **Allow** or **While using the app**(). Then you should see your own face in the camera preview. Good job!
120
+
2. Depending on your Android OS version, tap **Allow** or **While using the app**().
121
+
122
+
You should then see your own face in the camera preview. Good job!
125
123
126
124
{{% notice Tip %}}
127
-
You might need to restart the app to observe the permission change take effect.
125
+
You might need to restart the app to ensure that the permission change takes effect.
128
126
{{% /notice %}}
129
127
130
128
In the next section, you will learn how to integrate MediaPipe vision solutions.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/4-introduce-mediapipe.md
+12-10Lines changed: 12 additions & 10 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -14,14 +14,14 @@ MediaPipe Tasks provides the core programming interface of the MediaPipe Solutio
14
14
15
15
1. Navigate to `libs.versions.toml` and append the following line to the end of the `[versions]` section.
16
16
17
-
This defines the version of MediaPipe library that you will be using.
17
+
This defines the version of MediaPipe library that you will be using:
18
18
19
19
```toml
20
20
mediapipe-vision = "0.10.15"
21
21
```
22
22
23
23
{{% notice Note %}}
24
-
Ensure that you use this version and not newer versions as they might introduce bugs and unexpected behavior.
24
+
Ensure that you use this particular version, and not later versions as they might produce unexpected behavior.
25
25
{{% /notice %}}
26
26
27
27
2. Append the following lines to the end of the `[libraries]` section. This declares MediaPipe's vision dependency:
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ In this app, you will use MediaPipe's [Face Landmark Detection](https://ai.googl
42
42
43
43
Choose one of the two options below that aligns best with your learning needs.
44
44
45
-
### Basic approach: manual download
45
+
### 1. Basic approach: manual download
46
46
47
47
Download the following two files, then move them into the default asset directory `app/src/main/assets`:
Gradle does not come with a convenient [Task](https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/tutorial_using_tasks.html) type to manage downloads, so you will use the [gradle-download-task](https://github.com/michel-kraemer/gradle-download-task) dependency.
61
+
As Gradle does not come with a convenient [Task](https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/tutorial_using_tasks.html) type to manage downloads, you will need to use the [gradle-download-task](https://github.com/michel-kraemer/gradle-download-task) dependency.
62
62
63
63
1. Navigate to `libs.versions.toml`. Then:
64
64
65
65
* Append `download = "5.6.0"` to the `[versions]` section, and append `de-undercouch-download = { id = "de.undercouch.download", version.ref = "download" } to `[plugins]` section.
66
66
67
-
2. Navigate to `build.gradle.kts` in your project's `app` directory. Then append `alias(libs.plugins.de.undercouch.download)` to the `plugins` block. This enables the _Download_ task plugin in this `app` subproject.
67
+
2. Navigate to `build.gradle.kts` in your project's `app` directory. Then:
68
+
69
+
* Append `alias(libs.plugins.de.undercouch.download)` to the `plugins` block. This enables the _Download_ task plugin in this `app` subproject.
68
70
69
71
3. Insert the following lines between the `plugins` block and the `android` block to define the constant values, including the asset directory path and the URLs for both models:
70
72
@@ -99,7 +101,7 @@ tasks.named("preBuild") {
99
101
1. Sync the project again.
100
102
101
103
{{% notice Tip %}}
102
-
Refer to [this section](2-app-scaffolding.md#enable-view-binding) if you need help.
104
+
See the previous section[Set up the Development Environment](2-app-scaffolding.md#enable-view-binding), as a reminder on how to do this.
103
105
{{% /notice %}}
104
106
105
107
2. Now you should see both model asset bundles in your `assets` directory, as shown below:
@@ -110,7 +112,7 @@ Refer to [this section](2-app-scaffolding.md#enable-view-binding) if you need he
110
112
111
113
Example code is already implemented for ease of use based on [MediaPipe's sample code](https://github.com/google-ai-edge/mediapipe-samples/tree/main/examples).
112
114
113
-
Simply create a new file `HolisticRecognizerHelper.kt` placed in the source directory along with `MainActivity.kt`, then copyandpaste the code below into it.
115
+
Simply create a new file called `HolisticRecognizerHelper.kt`, and place it in the source directory along with `MainActivity.kt`, then copy-and-paste the code below into it:
114
116
115
117
```kotlin
116
118
packagecom.example.holisticselfiedemo
@@ -435,9 +437,9 @@ data class GestureResultBundle(
435
437
```
436
438
437
439
{{% notice Info %}}
438
-
The scope of this Learning Path is limited to the recognition of at most one person with two hands in the camera using the MediaPipe vision solutions.
440
+
The scope of this Learning Path is limited to the recognition of one person with two hands in the camera using the MediaPipe vision solutions.
439
441
440
-
If you do want to experiment with a greater number of people, change the `FACES_COUNT` constant to a different value.
442
+
If you would like to experiment with a greater number of people, change the `FACES_COUNT` constant to a higher value.
441
443
{{% /notice %}}
442
444
443
445
In the next section, you will connect the dots from this helper class to the UI layer through a ViewModel.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/_index.md
+1-1Lines changed: 1 addition & 1 deletion
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ minutes_to_complete: 120
6
6
who_is_this_for: This is an introductory topic for mobile application developers interested in learning how to build an Android selfie application with Modern MediaPipe Multimodal AI, Kotlin flows, and CameraX, using the Modern Android Development (MAD) architecture design.
7
7
8
8
learning_objectives:
9
-
- Architect a modern Android app focussing on the UI layer.
9
+
- Architect a modern hands-free selfie Android app with MediaPipe.
10
10
- Leverage lifecycle-aware components within the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) architecture.
11
11
- Combine MediaPipe's face landmark detection and gesture recognition for integration in a multimodel selfie solution.
0 commit comments