You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/2-app-scaffolding.md
+6-6Lines changed: 6 additions & 6 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
1
1
---
2
-
title: Scaffold a new Android project
2
+
title: Create a new Android project
3
3
weight: 2
4
4
5
5
### FIXED, DO NOT MODIFY
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ This learning path will teach you to architect an app following [modern Android
12
12
13
13
Download and install the latest version of [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio/) on your host machine.
14
14
15
-
This learning path's instructions and screenshots are taken on macOS with Apple Silicon, but you may choose any of the supported hardware systems as described [here](https://developer.android.com/studio/install).
15
+
The instructions for this learning path were tested on a Apple Silicon host machine running macOS, but you may choose any of the supported hardware systems as described [here](https://developer.android.com/studio/install).
16
16
17
17
Upon first installation, open Android Studio and proceed with the default or recommended settings. Accept license agreements and let Android Studio download all the required assets.
18
18
@@ -26,12 +26,12 @@ Before you proceed to coding, here are some tips that might come handy:
26
26
27
27
## Create a new Android project
28
28
29
-
1. Navigate to **File > New > New Project...**.
29
+
1. Navigate to File > New > New Project....
30
30
31
-
2. Select **Empty Views Activity** in **Phone and Tablet** galary as shown below, then click **Next**.
31
+
2. Select Empty Views Activity in the Phone and Tablet gallery as shown below, then click Next.
3.Proceed with a cool project name and default configurations as shown below. Make sure that **Language** is set to **Kotlin**, and that **Build configuration language** is set to **Kotlin DSL**.
34
+
3.Enter a project name and use the default configurations as shown below. Make sure that Language is set to Kotlin, and that Build configuration language is set to Kotlin DSL.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/3-camera-permission.md
+11-11Lines changed: 11 additions & 11 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
1
1
---
2
-
title: Handle camera permission
2
+
title: Handle camera permissions
3
3
weight: 3
4
4
5
5
### FIXED, DO NOT MODIFY
@@ -8,18 +8,18 @@ layout: learningpathall
8
8
9
9
## Run the app on your device
10
10
11
-
1. Connect your Android device to your computer via a USB **data** cable. If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow [this guide](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/device#setting-up) and double check this checklist:
11
+
1. Connect your Android device to your computer via a USB data cable. If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow [this guide](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/device#setting-up) and double check this checklist:
12
12
13
-
1. You have enabled **USB debugging** on your Android device following [this doc](https://developer.android.com/studio/debug/dev-options#Enable-debugging).
13
+
1. You have enabled USB debugging on your Android device following [this doc](https://developer.android.com/studio/debug/dev-options#Enable-debugging).
14
14
15
-
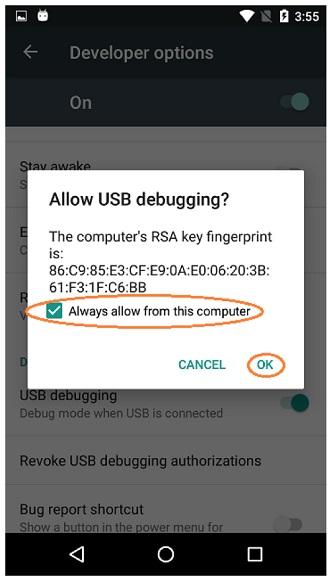
2. You have confirmed by tapping "OK" on your Android device when an **"Allow USB debugging"** dialog pops up, and checked "Always allow from this computer".
15
+
2. You have confirmed by tapping "OK" on your Android device when an "Allow USB debugging" dialog pops up, and checked "Always allow from this computer".
16
16
17
17
18
18
19
19
20
-
2. Make sure your device model name and SDK version correctly show up on the top right toolbar. Click the **"Run"** button to build and run, as described [here](https://developer.android.com/studio/run).
20
+
2. Make sure your device model name and SDK version correctly show up on the top right toolbar. Click the "Run" button to build and run the app.
21
21
22
-
3. After waiting for a while, you should be seeing success notification in Android Studio and the app showing up on your Android device.
22
+
3. After a while, you should see a success notification in Android Studio and the app showing up on your Android device.
23
23
24
24
4. However, the app shows only a black screen while printing error messages in your [Logcat](https://developer.android.com/tools/logcat) which looks like this:
25
25
@@ -30,11 +30,11 @@ layout: learningpathall
30
30
2024-11-20 11:43:03.408 2709-3807 PackageManager pid-2709 E Permission android.permission.CAMERA isn't requested by package com.example.holisticselfiedemo
31
31
```
32
32
33
-
5.Worry not. This is expected behavior because we haven't correctly configured this app's [permissions](https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/permissions/overview) yet, therefore Android OS restricts this app's access to camera features due to privacy reasons.
33
+
5.Do not worry. This is expected behavior because you haven't correctly configured this app's [permissions](https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/permissions/overview) yet. Android OS restricts this app's access to camera features due to privacy reasons.
34
34
35
35
## Request camera permission at runtime
36
36
37
-
1. Navigate to `manifest.xml` in your `app` subproject's `src/main` path. Declare camera hardware and permission by inserting the following lines into the `<manifest>` element. Make sure it's **outside** and **above**`<application>` element.
37
+
1. Navigate to `manifest.xml` in your `app` subproject's `src/main` path. Declare camera hardware and permission by inserting the following lines into the `<manifest>` element. Make sure it's declared outside and above `<application>` element.
38
38
39
39
```xml
40
40
<uses-feature
@@ -107,12 +107,12 @@ layout: learningpathall
107
107
108
108
## Verify camera permission
109
109
110
-
1. Rebuild and run the app. Now you should be seeing a dialog pops up requesting camera permissions!
110
+
1. Rebuild and run the app. Now you should see a dialog pop up requesting camera permissions!
111
111
112
-
2. Tap `Allow` or `While using the app` (depending on your Android OS versions), then you should be seeing your own face in the camera preview. Good job!
112
+
2. Tap `Allow` or `While using the app` (depending on your Android OS versions). Then you should see your own face in the camera preview. Good job!
113
113
114
114
{{% notice Tip %}}
115
115
Sometimes you might need to restart the app to observe the permission change take effect.
116
116
{{% /notice %}}
117
117
118
-
In the next chapter, we will introduce MediaPipe vision solutions.
118
+
In the next section, you will learn how to integrate MediaPipe vision solutions.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/4-introduce-mediapipe.md
+20-20Lines changed: 20 additions & 20 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -8,9 +8,9 @@ layout: learningpathall
8
8
9
9
[MediaPipe Solutions](https://ai.google.dev/edge/mediapipe/solutions/guide) provides a suite of libraries and tools for you to quickly apply artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques in your applications.
10
10
11
-
MediaPipe Tasks provides the core programming interface of the MediaPipe Solutions suite, including a set of libraries for deploying innovative ML solutions onto devices with a minimum of code. It supports multiple platforms, including Android, Web / JavaScript, Python, etc.
11
+
MediaPipe Tasks provides the core programming interface of the MediaPipe Solutions suite, including a set of libraries for deploying innovative ML solutions onto devices with a minimum of code. It supports multiple platforms, including Android, Web, JavaScript, Python, etc.
12
12
13
-
## Introduce MediaPipe dependencies
13
+
## Add MediaPipe dependencies
14
14
15
15
1. Navigate to `libs.versions.toml` and append the following line to the end of `[versions]` section. This defines the version of MediaPipe library we will be using.
16
16
@@ -19,57 +19,57 @@ mediapipe-vision = "0.10.15"
19
19
```
20
20
21
21
{{% notice Note %}}
22
-
Please stick with this version and do not use newer versions due to bugs and unexpected behaviors.
22
+
Please use this version and do not use newer versions as this introduces bugs and unexpected behavior.
23
23
{{% /notice %}}
24
24
25
-
2. Append the following lines to the end of `[libraries]` section. This declares MediaPipe's vision dependency.
25
+
2. Append the following lines to the end of `[libraries]` section. This declares MediaPipe's vision dependency:
26
26
27
27
```toml
28
28
mediapipe-vision = { group = "com.google.mediapipe", name = "tasks-vision", version.ref = "mediapipe-vision" }
29
29
```
30
30
31
-
3. Navigate to `build.gradle.kts` in your project's `app` directory, then insert the following line into `dependencies` block, ideally between `implementation` and `testImplementation`.
31
+
3. Navigate to `build.gradle.kts` in your project's `app` directory, then insert the following line into `dependencies` block, between `implementation` and `testImplementation`.
32
32
33
33
```kotlin
34
34
implementation(libs.mediapipe.vision)
35
35
```
36
36
37
37
## Prepare model asset bundles
38
38
39
-
In this app, we will be using MediaPipe's [Face Landmark Detection](https://ai.google.dev/edge/mediapipe/solutions/vision/face_landmarker) and [Gesture Recognizer](https://ai.google.dev/edge/mediapipe/solutions/vision/gesture_recognizer) solutions, which requires their model asset bundle files to initialize.
39
+
In this app, you will use MediaPipe's [Face Landmark Detection](https://ai.google.dev/edge/mediapipe/solutions/vision/face_landmarker) and [Gesture Recognizer](https://ai.google.dev/edge/mediapipe/solutions/vision/gesture_recognizer) solutions, which requires their model asset bundle files to initialize.
40
40
41
41
Choose one of the two options below that aligns best with your learning needs.
42
42
43
-
### Basic approach: manual downloading
43
+
### Basic approach: manual download
44
44
45
-
Simply download the following two files, then move them into the default asset directory: `app/src/main/assets`.
45
+
Download the following two files, then move them into the default asset directory: `app/src/main/assets`.
Gradle doesn't come with a convenient [Task](https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/tutorial_using_tasks.html) type to manage downloads, therefore we will introduce[gradle-download-task](https://github.com/michel-kraemer/gradle-download-task) dependency.
59
+
Gradle doesn't come with a convenient [Task](https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/tutorial_using_tasks.html) type to manage downloads, so you will use the[gradle-download-task](https://github.com/michel-kraemer/gradle-download-task) dependency.
60
60
61
-
1.Again, navigate to `libs.versions.toml`. Append `download = "5.6.0"` to `[versions]` section, and `de-undercouch-download = { id = "de.undercouch.download", version.ref = "download" }` to `[plugins]` section.
61
+
1.Navigate to `libs.versions.toml`. Append `download = "5.6.0"` to `[versions]` section, and `de-undercouch-download = { id = "de.undercouch.download", version.ref = "download" }` to `[plugins]` section.
62
62
63
-
2.Again, navigate to `build.gradle.kts` in your project's `app` directory and append `alias(libs.plugins.de.undercouch.download)` to the `plugins` block. This enables the aforementioned_Download_ task plugin in this `app` subproject.
63
+
2.Navigate to `build.gradle.kts` in your project's `app` directory and append `alias(libs.plugins.de.undercouch.download)` to the `plugins` block. This enables the _Download_ task plugin in this `app` subproject.
64
64
65
-
4. Insert the following lines between `plugins` block and `android` block to define the constant values, including: asset directory path and the URLs for both models.
65
+
3. Insert the following lines between `plugins` block and `android` block to define the constant values, including: asset directory path and the URLs for both models.
66
66
```kotlin
67
67
val assetDir ="$projectDir/src/main/assets"
68
68
val gestureTaskUrl ="https://storage.googleapis.com/mediapipe-models/gesture_recognizer/gesture_recognizer/float16/1/gesture_recognizer.task"
69
69
val faceTaskUrl ="https://storage.googleapis.com/mediapipe-models/face_landmarker/face_landmarker/float16/1/face_landmarker.task"
70
70
```
71
71
72
-
5. Insert `import de.undercouch.gradle.tasks.download.Download`into **the top of this file**, then append the following code to **the end of this file**, which hooks two _Download_ tasks to be executed before `preBuild`:
72
+
4. Insert `import de.undercouch.gradle.tasks.download.Download`to the top of this file, then append the following code to the end of this file, which hooks two _Download_ tasks to be executed before `preBuild`:
3.Now you are ready to import MediaPipe's Face Landmark Detection and Gesture Recognizer into the project. Actually, we have already implemented the code below for you based on [MediaPipe's sample code](https://github.com/google-ai-edge/mediapipe-samples/tree/main/examples). Simply create a new file `HolisticRecognizerHelper.kt` placed in the source directory along with `MainActivity.kt`, then copy paste the code below into it.
104
+
3.You are ready to import MediaPipe's Face Landmark Detection and Gesture Recognizer into the project. Example code is already implemented for ease of use based on [MediaPipe's sample code](https://github.com/google-ai-edge/mediapipe-samples/tree/main/examples). Simply create a new file `HolisticRecognizerHelper.kt` placed in the source directory along with `MainActivity.kt`, then copy paste the code below into it.
105
105
106
106
```kotlin
107
107
packagecom.example.holisticselfiedemo
@@ -426,9 +426,9 @@ data class GestureResultBundle(
426
426
```
427
427
428
428
{{% notice Info %}}
429
-
In this learning path we are only configuring the MediaPipe vision solutions to recognize one person with at most two hands in the camera.
429
+
In this learning path you are only configuring the MediaPipe vision solutions to recognize one person with at most two hands in the camera.
430
430
431
-
If you'd like to experiment with more people, simply change the `FACES_COUNT` constant to be your desired value.
431
+
If you'd like to experiment with more people, change the `FACES_COUNT` constant to be your desired value.
432
432
{{% /notice %}}
433
433
434
-
In the next chapter, we will connect the dots from this helper class to the UI layer via a ViewModel.
434
+
In the next section, you will connect the dots from this helper class to the UI layer via a ViewModel.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/6-flow-data-to-view-1.md
+7-7Lines changed: 7 additions & 7 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ layout: learningpathall
8
8
9
9
[SharedFlow](https://developer.android.com/kotlin/flow/stateflow-and-sharedflow#sharedflow) and [StateFlow](https://developer.android.com/kotlin/flow/stateflow-and-sharedflow#stateflow) are [Kotlin Flow](https://developer.android.com/kotlin/flow) APIs that enable Flows to optimally emit state updates and emit values to multiple consumers.
10
10
11
-
In this learning path, you will have the opportunity to experiment with both `SharedFlow` and `StateFlow`. This chapter will focus on SharedFlow while the next chapter will focus on StateFlow.
11
+
In this learning path, you will experiment with both `SharedFlow` and `StateFlow`. This section will focus on SharedFlow while the next chapter will focus on StateFlow.
12
12
13
13
`SharedFlow` is a general-purpose, hot flow that can emit values to multiple subscribers. It is highly configurable, allowing you to set the replay cache size, buffer capacity, etc.
14
14
@@ -54,9 +54,9 @@ This `SharedFlow` is initialized with a replay size of `1`. This retains the mos
54
54
55
55
## Visualize face and gesture results
56
56
57
-
To visualize the results of Face Landmark Detection and Gesture Recognition tasks, we have prepared the following code for you based on [MediaPipe's samples](https://github.com/google-ai-edge/mediapipe-samples/tree/main/examples).
57
+
To visualize the results of Face Landmark Detection and Gesture Recognition tasks, based on [MediaPipe's samples](https://github.com/google-ai-edge/mediapipe-samples/tree/main/examples) follow the intructions in this section.
58
58
59
-
1. Create a new file named `FaceLandmarkerOverlayView.kt` and fill in the content below:
59
+
1. Create a new file named `FaceLandmarkerOverlayView.kt` and copy the content below:
60
60
61
61
```kotlin
62
62
/*
@@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ class FaceLandmarkerOverlayView(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) :
180
180
```
181
181
182
182
183
-
2. Create a new file named `GestureOverlayView.kt` and fill in the content below:
183
+
2. Create a new file named `GestureOverlayView.kt` and copy the content below:
184
184
185
185
```kotlin
186
186
/*
@@ -302,7 +302,7 @@ class GestureOverlayView(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) :
302
302
303
303
## Update UI in the view controller
304
304
305
-
1. Add the above two overlay views to `activity_main.xml` layout file:
305
+
1. Add the two overlay views to `activity_main.xml` layout file:
@@ -316,7 +316,7 @@ class GestureOverlayView(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) :
316
316
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
317
317
```
318
318
319
-
2. Collect the new SharedFlow `uiEvents` in `MainActivity` by appending the code below to the end of `onCreate` method, **below**`setupCamera()` method call.
319
+
2. Collect the new SharedFlow `uiEvents` in `MainActivity` by appending the code below to the end of `onCreate` method, below `setupCamera()` method call.
320
320
321
321
```kotlin
322
322
lifecycleScope.launch {
@@ -363,7 +363,7 @@ class GestureOverlayView(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) :
363
363
}
364
364
```
365
365
366
-
4. Build and run the app again. Now you should be seeing face and gesture overlays on top of the camera preview as shown below. Good job!
366
+
4. Build and run the app again. Now you should see face and gesture overlays on top of the camera preview as shown below. Good job!
0 commit comments