You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/2-app-scaffolding.md
+40-35Lines changed: 40 additions & 35 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -1,56 +1,59 @@
1
1
---
2
-
title: Create a new Android project
2
+
title: Set up the Development Environment
3
3
weight: 2
4
4
5
5
### FIXED, DO NOT MODIFY
6
6
layout: learningpathall
7
7
---
8
+
## Download Android Studio
8
9
9
-
This learning path will teach you to architect an app following [modern Android architecture](https://developer.android.com/courses/pathways/android-architecture) design with a focus on the [UI layer](https://developer.android.com/topic/architecture/ui-layer).
10
+
Start by downloading and installing the latest version of [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio/)on your host machine.
10
11
11
-
## Development environment setup
12
+
The instructions for this learning path were tested on a host machine running macOS, but you can use any of the supported hardware systems listed on the [Install Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio/install) webpage on the Android Developer website.
12
13
13
-
Download and install the latest version of [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio/) on your host machine.
14
+
After installation, open Android Studio and do the following:
14
15
15
-
The instructions for this learning path were tested on a Apple Silicon host machine running macOS, but you may choose any of the supported hardware systems as described [here](https://developer.android.com/studio/install).
16
+
* Accept license agreements.
17
+
* Download all the required assets.
18
+
* Select the default or recommended settings.
16
19
17
-
Upon first installation, open Android Studio and proceed with the default or recommended settings. Accept license agreements and let Android Studio download all the required assets.
20
+
{{% notice Tips %}}
21
+
Before you start coding, here are some useful tips:
18
22
19
-
Before you proceed to coding, here are some tips that might come handy:
23
+
1. To navigate to a file, simply press the Shift key twice, input the file name, select the correct result using the up and down arrow keys, and then press Enter.
20
24
21
-
{{% notice Tip %}}
22
-
1. To navigate to a file, simply double-tap `Shift` key and input the file name, then select the correct result using `Up` & `Down` arrow keys and then tap `Enter`.
23
-
24
-
2. Every time after you copy-paste a code block from this learning path, make sure you **import the correct classes** and resolved the errors. Refer to [this doc](https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/creating-and-optimizing-imports.html) to learn more.
25
+
2. Every time after you copy-and-paste a code block from this Learning Path, ensure that you import the correct classes and resolve any errors. For more information, see the [Auto import](https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/creating-and-optimizing-imports.html) web page.
25
26
{{% /notice %}}
26
27
27
28
## Create a new Android project
28
29
29
-
1. Navigate to File > New > New Project....
30
+
1. Navigate to **File** > **New** > **New Project**.
30
31
31
-
2. Select Empty Views Activity in the Phone and Tablet gallery as shown below, then click Next.
3. Enter a project name and use the default configurations as shown below. Make sure that Language is set to Kotlin, and that Build configuration language is set to Kotlin DSL.
[CameraX](https://developer.android.com/media/camera/camerax) is a Jetpack library, built to help make camera app development easier. It provides a consistent, easy-to-use API that works across the vast majority of Android devices with a great backward-compatibility.
40
+
## Add CameraX dependencies
40
41
41
-
1. Wait for Android Studio to sync project with Gradle files, this make take up to several minutes.
42
+
[CameraX](https://developer.android.com/media/camera/camerax) is a Jetpack library, built to help make camera app development easier. It provides a consistent, easy-to-use API that works across the vast majority of Android devices with great backward-compatibility.
42
43
43
-
2. Once project is synced, navigate to `libs.versions.toml` in your project's root directory as shown below. This file serves as the version catalog for all dependencies used in the project.
44
+
1. Wait for Android Studio to sync project with Gradle files. This might take several minutes.
2. Once the project is synced, navigate to `libs.versions.toml` in your project's root directory. See Figure 3. This file serves as the version catalog for all dependencies that the project uses.
47
+
48
+

46
49
47
50
{{% notice Info %}}
48
51
49
-
For more information on version catalogs, please refer to [this doc](https://developer.android.com/build/migrate-to-catalogs).
52
+
For more information on version catalogs, see [Migrate your build to version catalogs](https://developer.android.com/build/migrate-to-catalogs).
50
53
51
54
{{% /notice %}}
52
55
53
-
3. Append the following line to the end of `[versions]` section. This defines the version of CameraX libraries we will be using.
56
+
3. Append the following line to the end of `[versions]` section. This defines the version of CameraX libraries that you will be using.
54
57
```toml
55
58
camerax = "1.4.0"
56
59
```
@@ -64,7 +67,7 @@ camera-lifecycle = { group = "androidx.camera", name = "camera-lifecycle", versi
64
67
camera-view = { group = "androidx.camera", name = "camera-view", version.ref = "camerax" }
65
68
```
66
69
67
-
5. Navigate to `build.gradle.kts` in your project's `app` directory, then insert the following lines into `dependencies` block. This introduces the above dependencies into the `app` subproject.
70
+
5. Navigate to `build.gradle.kts` in your project's `app` directory, then insert the following lines into `dependencies` block. This introduces the dependencies listed above into the `app` subproject:
68
71
69
72
```kotlin
70
73
implementation(libs.camera.core)
@@ -75,32 +78,34 @@ camera-view = { group = "androidx.camera", name = "camera-view", version.ref = "
75
78
76
79
## Enable view binding
77
80
78
-
1. Within the above `build.gradle.kts` file, append the following lines to the end of `android` block to enable view binding feature.
81
+
1. Within the above `build.gradle.kts` file, append the following lines to the end of `android` block to enable the view binding feature:
79
82
80
83
```kotlin
81
84
buildFeatures {
82
85
viewBinding =true
83
86
}
84
87
```
85
88
86
-
2. You should be seeing a notification shows up, as shown below. Click **"Sync Now"** to sync your project.
89
+
2. You should see that a notification appears. See Figure 4. Click **Sync Now** to sync your project.
You may also click the __"Sync Project with Gradle Files"__ button in the toolbar or pressing the corresponding shortcut to start a sync.
95
+
You can also click the **Sync Project with Gradle Files** button in the toolbar, or enter the corresponding shortcut to start a sync.
93
96
94
97

95
98
{{% /notice %}}
96
99
97
-
3. Navigate to `MainActivity.kt` source file and make following changes. This inflates the layout file into a view binding object and stores it in a member variable within the view controller for easier access later.
100
+
3. Navigate to the `MainActivity.kt` source file and make the changes that Figure 5 shows in the View Binding screenshot.
101
+
102
+
This inflates the layout file into a view binding object, and stores it in a member variable within the view controller for easier access later.
1.**Replace** the placeholder "Hello World!" `TextView` within the layout file `activity_main.xml` with a camera preview view:
108
+
1.Within the layout file `activity_main.xml`, replace the placeholder "Hello World!" in `TextView` with a camera preview view:
104
109
105
110
```xml
106
111
<androidx.camera.view.PreviewView
@@ -111,7 +116,7 @@ You may also click the __"Sync Project with Gradle Files"__ button in the toolba
111
116
```
112
117
113
118
114
-
2. Add the following member variables to `MainActivity.kt` to store camerarelated objects:
119
+
2. Add the following member variables to `MainActivity.kt` to store camera-related objects:
115
120
116
121
```kotlin
117
122
// Camera
@@ -145,7 +150,7 @@ You may also click the __"Sync Project with Gradle Files"__ button in the toolba
145
150
}
146
151
```
147
152
148
-
4. Implement the above `bindCameraUseCases()` method:
153
+
4. Implement the `bindCameraUseCases()` method:
149
154
150
155
```kotlin
151
156
privatefunbindCameraUseCases() {
@@ -186,12 +191,12 @@ private fun bindCameraUseCases() {
186
191
}
187
192
```
188
193
189
-
5. Add a [companion object](https://kotlinlang.org/docs/object-declarations.html#companion-objects) to `MainActivity.kt` and declare a `TAG` constant value for `Log` calls to work correctly. This companion object comes handy for us to define all the constants and shared values accessible across the entire class.
194
+
5. Add a [companion object](https://kotlinlang.org/docs/object-declarations.html#companion-objects) to `MainActivity.kt`, and declare a `TAG` constant value for `Log` calls to work correctly. This companion object is useful in enabling you to define all the constants and shared values accessible across the entire class.
190
195
191
196
```kotlin
192
197
companionobject {
193
198
privateconstvalTAG="MainActivity"
194
199
}
195
200
```
196
201
197
-
In the next section, you will build and run the app to make sure the camera works well.
202
+
In the next section, you will build and run the app to ensure that the camera works as expected.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/learning-paths/smartphones-and-mobile/build-android-selfie-app-using-mediapipe-multimodality/3-camera-permission.md
+31-21Lines changed: 31 additions & 21 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -1,27 +1,29 @@
1
1
---
2
-
title: Handle camera permissions
2
+
title: Manage Camera Permissions
3
3
weight: 3
4
4
5
5
### FIXED, DO NOT MODIFY
6
6
layout: learningpathall
7
7
---
8
8
9
-
##Run the app on your device
9
+
### Connect your device to your machine with a USB data cable
10
10
11
-
1. Connect your Android device to your computer via a USB data cable. If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow [this guide](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/device#setting-up) and double check this checklist:
11
+
If this is your first time running and debugging Android apps, follow the guidance on the Android Developer website. See [Set up a device for development](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/device#setting-up), and check that you have completed these steps:
12
12
13
-
1. You have enabled USB debugging on your Android device following [this doc](https://developer.android.com/studio/debug/dev-options#Enable-debugging).
13
+
1. You have followed the instructions [Enable USB debugging on your device](https://developer.android.com/studio/debug/dev-options#Enable-debugging).
14
14
15
-
2. You have confirmed by tapping "OK" on your Android device when an "Allow USB debugging" dialog pops up, and checked "Always allow from this computer".
15
+
2. You have confirmed that you have enabled USB debugging by tapping **OK** on your device when the **Allow USB debugging** dialog appears, and that you have checked **Always allow from this computer**. See Figure 6.
16
16
17
-
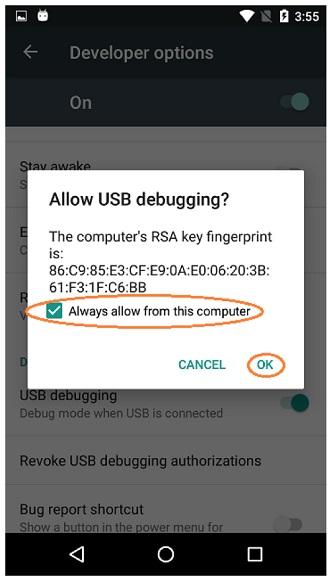
17
+

18
18
19
19
20
-
2. Make sure your device model name and SDK version correctly show up on the topright toolbar. Click the "Run" button to build and run the app.
20
+
3. Make sure that your device model name and SDK version correctly show up in the top-right toolbar.
21
21
22
-
3. After a while, you should see a success notification in Android Studio and the app showing up on your Android device.
22
+
Click the **Run** button to build and run the app.
23
23
24
-
4. However, the app shows only a black screen while printing error messages in your [Logcat](https://developer.android.com/tools/logcat) which looks like this:
24
+
4. After a while, you should see a notification of a successful build in Android Studio and the new app will be displayed on your Android device.
25
+
26
+
5. However, you will also see that the app shows a black screen while printing error messages in your [Logcat](https://developer.android.com/tools/logcat), which looks like this:
25
27
26
28
```
27
29
2024-11-20 11:15:00.398 18782-18818 Camera2CameraImpl com.example.holisticselfiedemo E Camera reopening attempted for 10000ms without success.
@@ -30,11 +32,13 @@ layout: learningpathall
30
32
2024-11-20 11:43:03.408 2709-3807 PackageManager pid-2709 E Permission android.permission.CAMERA isn't requested by package com.example.holisticselfiedemo
31
33
```
32
34
33
-
5. Do not worry. This is expected behavior because you haven't correctly configured this app's [permissions](https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/permissions/overview) yet. Android OS restricts this app's access to camera features due to privacy reasons.
35
+
This is the expected behavior from having not yet correctly configured the app's permissions. See[Permissions](https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/permissions/overview) on the Android Developer website. Android OS restricts the app's access to camera features due to privacy constraints.
36
+
37
+
### Request camera permission at runtime
34
38
35
-
## Request camera permission at runtime
39
+
1. Navigate to `manifest.xml` in your `app` sub-project's `src/main` path.
36
40
37
-
1. Navigate to `manifest.xml` in your `app` subproject's `src/main` path. Declare camera hardware and permission by inserting the following lines into the `<manifest>` element. Make sure it's declared outside and above `<application>` element.
41
+
Declare the camera hardware, and set the permissions by inserting the following lines into the `<manifest>` element, ensuring that it is declared outside and above the `<application>` element:
2. Navigate to `strings.xml` in your `app` subproject's `src/main/res/values` path. Insert the following lines of text resources, which will be used later.
50
+
2. Navigate to `strings.xml` in your `app` sub-project's `src/main/res/values` path.
51
+
Insert the following lines of text resources, which you will use at a later stage:
47
52
48
53
```xml
49
54
<stringname="permission_request_camera_message">Camera permission is required to recognize face and hands</string>
50
55
<stringname="permission_request_camera_rationale">To grant Camera permission to this app, please go to system settings</string>
51
56
```
52
57
53
-
3. Navigate to `MainActivity.kt` and add the following permission related values to companion object:
58
+
3. Navigate to `MainActivity.kt` and add the following permission-related values to companion
0 commit comments