diff --git a/.github/workflows/ci-main.yml b/.github/workflows/ci-main.yml
index d49831f..a93dfee 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/ci-main.yml
+++ b/.github/workflows/ci-main.yml
@@ -49,6 +49,12 @@ jobs:
run: poetry run mypy src tests
- name: All tests (unit + integration + system)
- run: |
- poetry run pytest \
- --disable-warnings
+ run: poetry run pytest --disable-warnings --cov=asyncflow --cov-report=xml
+
+ - name: Upload coverage to Codecov
+ uses: codecov/codecov-action@v4
+ with:
+ files: coverage.xml
+ flags: tests
+ fail_ci_if_error: true
+ token: ${{ secrets.CODECOV_TOKEN }}
diff --git a/CHANGELOG.MD b/CHANGELOG.MD
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..20a987b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/CHANGELOG.MD
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+# Changelog
+
+All notable changes to this project will be documented in this file.
+
+The format is based on [Keep a Changelog](https://keepachangelog.com/en/1.1.0/).
+
+## \[Unreleased]
+
+### Planned
+
+* **Network baseline upgrade** (sockets, RAM per connection, keep-alive).
+* **New metrics and visualization improvements** (queue wait times, service histograms).
+* **Monte Carlo analysis** with confidence intervals.
+
+---
+
+## \[0.1.1] – 2025-08-29
+
+### Added
+
+* **Event Injection (runtime-ready):**
+
+ * Declarative events with `start` / `end` markers (server down/up, network spike start/end).
+ * Runtime scheduler integrated with SimPy, applying events at the right simulation time.
+ * Deterministic latency **offset handling** for network spikes (phase 1).
+
+* **Improved Server Model:**
+
+ * Refined CPU + I/O handling with clearer queue accounting.
+ * Ready queue length now explicitly updated on contention.
+ * I/O queue metrics improved with better protection against mis-counting edge cases.
+ * Enhanced readability and maintainability in endpoint step execution flow.
+
+### Documentation
+
+* Expanded examples on event injection in YAML.
+* Inline comments clarifying queue management logic.
+
+### Notes
+
+* This is still an **alpha-series** release, but now supports scenario-driven **event injection** and a more faithful **server runtime model**, paving the way for the upcoming network baseline upgrade.
+
+---
+
+## \[0.1.0a2] – 2025-08-17
+
+### Fixed
+
+* **Quickstart YAML in README**: corrected field to ensure a smooth first run for new users.
+
+### Notes
+
+* Minor docs polish only; no runtime changes.
+
+---
+
+## \[0.1.0a1] – 2025-08-17
+
+### Changed
+
+* Repository aligned with the **PyPI 0.1.0a1** build.
+* Packaging metadata tidy-up in `pyproject.toml`.
+
+### CI
+
+* Main workflow now also triggers on **push** to `main`.
+
+### Notes
+
+* No functional/runtime changes.
+
+---
+
+## \[v0.1.0-alpha] – 2025-08-17
+
+**First public alpha** of AsyncFlow — a SimPy-based, **event-loop-aware** simulator for async distributed systems.
+
+### Highlights
+
+* **Event-loop model** per server: explicit **CPU** (blocking), **I/O waits** (non-blocking), **RAM** residency.
+* **Topology graph**: generator → client → (LB, optional) → servers; multi-server via **round-robin**; **stochastic network latency** and optional dropouts.
+* **Workload**: stochastic traffic via simple RV configs (Poisson defaults).
+
+### Metrics & Analyzer
+
+* **Event metrics**: `RqsClock` (end-to-end latency).
+* **Sampled metrics**: `ready_queue_len`, `event_loop_io_sleep`, `ram_in_use`, `edge_concurrent_connection`.
+* **Analyzer API** (`ResultsAnalyzer`):
+
+ * `get_latency_stats()`, `get_throughput_series()`
+ * Plots: `plot_latency_distribution()`, `plot_throughput()`
+ * Per-server: `plot_single_server_ready_queue()`, `plot_single_server_io_queue()`, `plot_single_server_ram()`
+ * Compact dashboards.
+
+### Examples
+
+* YAML quickstart (single server).
+* Pythonic builder:
+
+ * Single server.
+ * **Load balancer + two servers** example with saved figures.
+
+### Tooling & CI
+
+* One-shot setup scripts (`dev_setup`, `quality_check`, `run_tests`, `run_sys_tests`) for Linux/macOS/Windows.
+* GitHub Actions: Ruff + MyPy + Pytest; **system tests gate merges** into `main`.
+
+### Compatibility
+
+* **Python 3.12+** (Linux/macOS/Windows).
+* Install from PyPI: `pip install asyncflow-sim`.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 4622987..b084df7 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
-# AsyncFlow — Event-Loop Aware Simulator for Async Distributed Systems
+# AsyncFlow: Scenario-Driven Simulator for Async Systems
Created and maintained by @GioeleB00.
[](https://pypi.org/project/asyncflow-sim/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/asyncflow-sim/)
[](LICENSE)
-[](#)
+[](https://codecov.io/gh/AsyncFlow-Sim/AsyncFlow)
[](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff)
[](https://mypy-lang.org/)
[](https://docs.pytest.org/)
@@ -14,27 +14,65 @@ Created and maintained by @GioeleB00.
-----
-AsyncFlow is a discrete-event simulator for modeling and analyzing the performance of asynchronous, distributed backend systems built with SimPy. You describe your system's topology—its servers, network links, and load balancers—and AsyncFlow simulates the entire lifecycle of requests as they move through it.
+**AsyncFlow** is a scenario-driven simulator for **asynchronous distributed backends**.
+You don’t “predict the Internet” — you **declare scenarios** (network RTT + jitter, resource caps, failure events) and AsyncFlow shows the operational impact: concurrency, queue growth, socket/RAM pressure, latency distributions. This means you can evaluate architectures before implementation: test scaling strategies, network assumptions, or failure modes without writing production code.
-It provides a **digital twin** of your service, modeling not just the high-level architecture but also the low-level behavior of each server's **event loop**, including explicit **CPU work**, **RAM residency**, and **I/O waits**. This allows you to run realistic "what-if" scenarios that behave like production systems rather than toy benchmarks.
+At its core, AsyncFlow is **event-loop aware**:
+
+* **CPU work** blocks the loop,
+* **RAM residency** ties up memory until release,
+* **I/O waits** free the loop just like in real async frameworks.
+
+With the new **event injection engine**, you can explore *what-if* dynamics: network spikes, server outages, degraded links, all under your control.
+
+---
### What Problem Does It Solve?
-Modern async stacks like FastAPI are incredibly performant, but predicting their behavior under real-world load is difficult. Capacity planning often relies on guesswork, expensive cloud-based load tests, or discovering bottlenecks only after a production failure. AsyncFlow is designed to replace that uncertainty with **data-driven forecasting**, allowing you to understand how your system will perform before you deploy a single line of code.
+Predicting how an async system will behave under real-world load is notoriously hard. Teams often rely on rough guesses, over-provisioning, or painful production incidents. **AsyncFlow replaces guesswork with scenario-driven simulations**: you declare the conditions (network RTT, jitter, resource limits, injected failures) and observe the consequences on latency, throughput, and resource pressure.
+
+---
+
+### Why Scenario-Driven? *Design Before You Code*
+
+AsyncFlow doesn’t need your backend to exist.
+You can model your architecture with YAML or Python, run simulations, and explore bottlenecks **before writing production code**.
+This scenario-driven approach lets you stress-test scaling strategies, network assumptions, and failure modes safely and repeatably.
+
+---
+
+### How Does It Work?
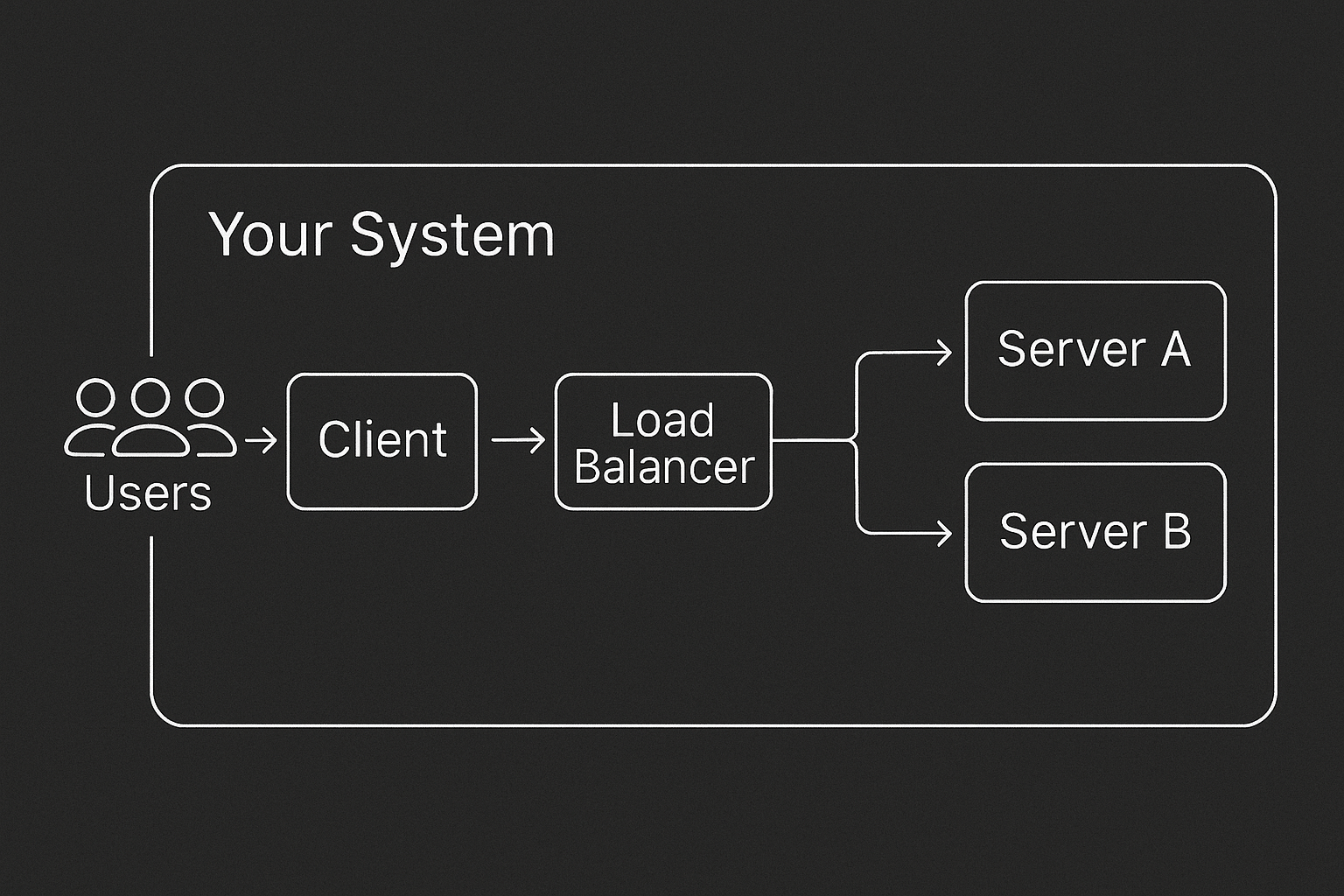
-### How Does It Work? An Example Topology
+AsyncFlow represents your system as a **directed graph of components**, for example: clients, load balancers, servers—connected by network edges with configurable latency models. Each server is **event-loop aware**: CPU work blocks, RAM stays allocated, and I/O yields the loop, just like real async frameworks. You can define topologies via **YAML** or a **Pythonic builder**.
-AsyncFlow models your system as a directed graph of interconnected components. A typical setup might look like this:
+
-
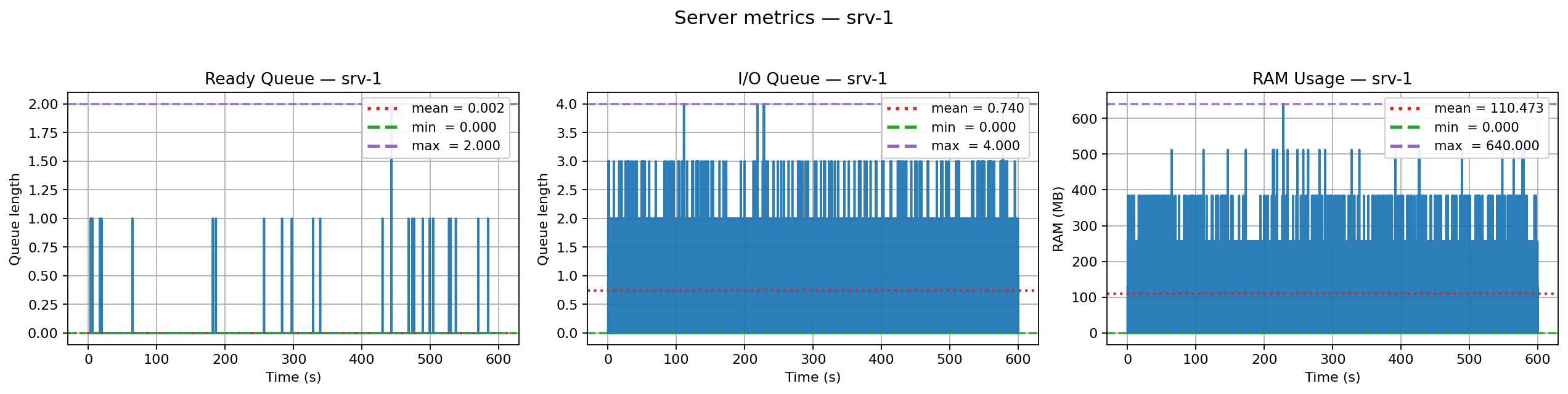
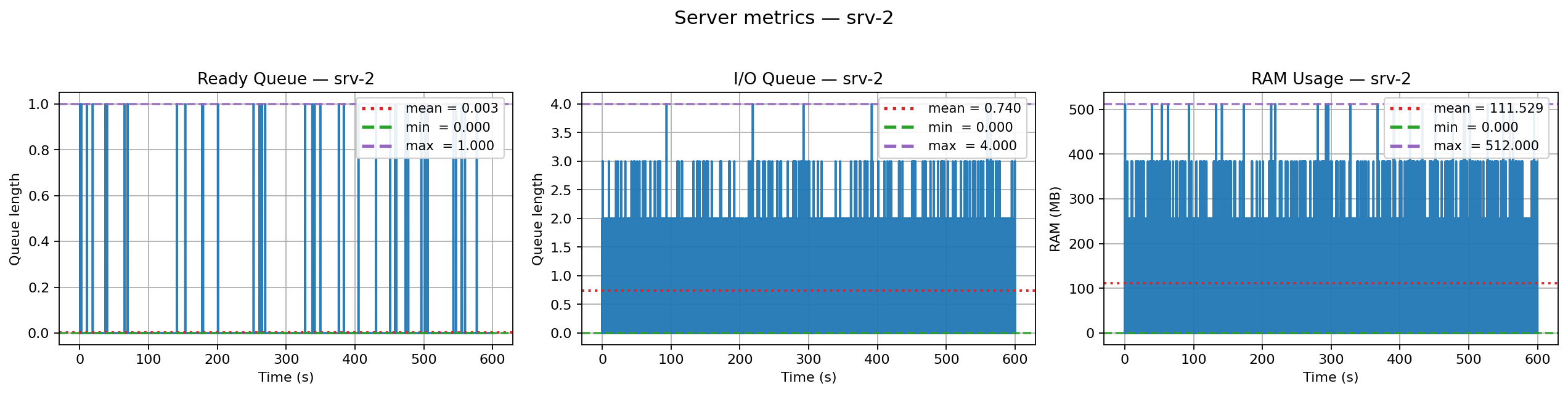
+Run the simulation and inspect the outputs:
+
+
+
+ 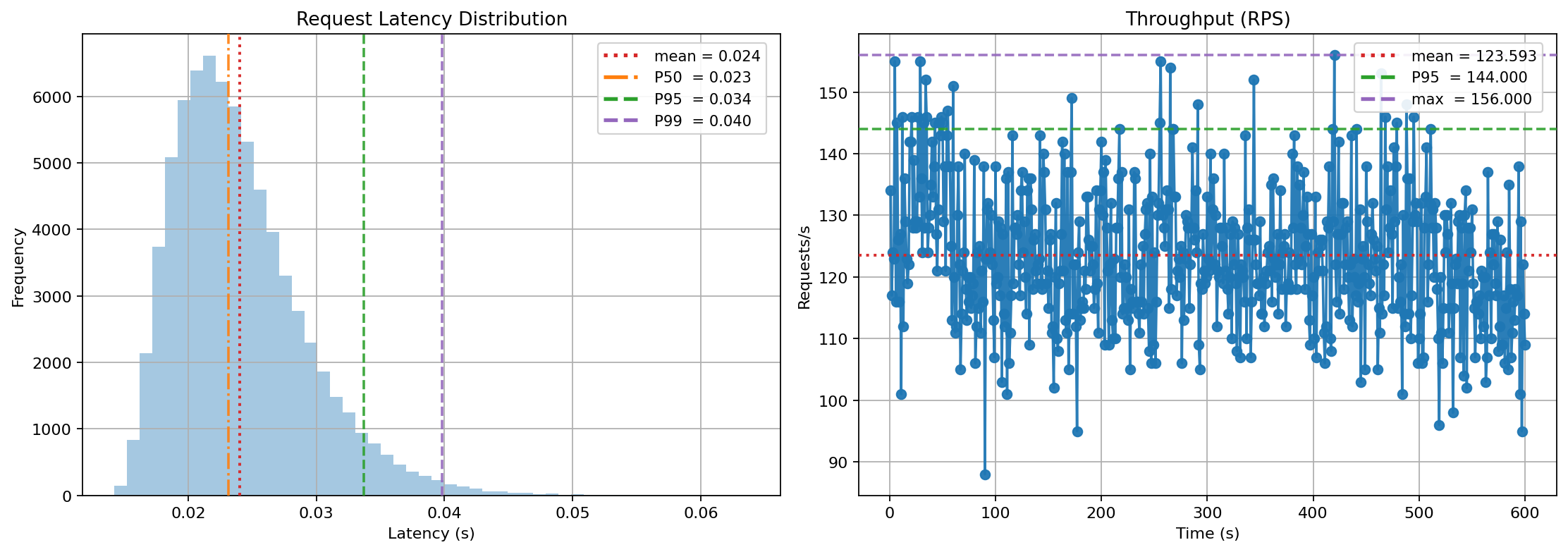 +
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+
+---
### What Questions Can It Answer?
-By running simulations on your defined topology, you can get quantitative answers to critical engineering questions, such as:
+With scenario simulations, AsyncFlow helps answer questions such as:
+
+* How does **p95 latency** shift if active users double?
+* What happens when a **client–server edge** suffers a 20 ms spike for 60 seconds?
+* Will a given endpoint pipeline — CPU parse → RAM allocation → DB I/O — still meet its **SLA at 40 RPS**?
+* How many sockets and how much RAM will a load balancer need under peak conditions?
- * How does **p95 latency** change if active users increase from 100 to 200?
- * What is the impact on the system if the **client-to-server network latency** increases by 3ms?
- * Will a specific API endpoint—with a pipeline of parsing, RAM allocation, and database I/O—hold its **SLA at a load of 40 requests per second**?
---
## Installation
@@ -167,7 +205,7 @@ You’ll get latency stats in the terminal and a PNG with four charts (latency d
**Want more?**
-For ready-to-run scenarios—including examples using the Pythonic builder and multi-server topologies—check out the `examples/` directory in the repository.
+For ready-to-run scenarios including examples using the Pythonic builder and multi-server topologies, check out the `examples/` directory in the repository.
## Development
@@ -279,97 +317,28 @@ bash scripts/run_sys_tests.sh
Executes **pytest** with a terminal coverage summary (no XML, no slowest list).
+## Current Limitations (v0.1.1)
+AsyncFlow is still in alpha. The current release has some known limitations that are already on the project roadmap:
-## What AsyncFlow Models (v0.1)
-
-AsyncFlow provides a detailed simulation of your backend system. Here is a high-level overview of the core components it models. For a deeper technical dive into the implementation and design rationale, follow the links to the internal documentation.
-
-* **Async Event Loop:** Simulates a single-threaded, non-blocking event loop per server. **CPU steps** block the loop, while **I/O steps** are non-blocking, accurately modeling `asyncio` behavior.
- * *(Deep Dive: `docs/internals/runtime-and-resources.md`)*
-
-* **System Resources:** Models finite server resources, including **CPU cores** and **RAM (MB)**. Requests must acquire these resources, creating natural back-pressure and contention when the system is under load.
- * *(Deep Dive: `docs/internals/runtime-and-resources.md`)*
-
-* **Endpoints & Request Lifecycles:** Models server endpoints as a linear sequence of **steps**. Each step is a distinct operation, such as `cpu_bound_operation`, `io_wait`, or `ram` allocation.
- * *(Schema Definition: `docs/internals/simulation-input.md`)*
-
-* **Network Edges:** Simulates the connections between system components. Each edge has a configurable **latency** (drawn from a probability distribution) and an optional **dropout rate** to model packet loss.
- * *(Schema Definition: `docs/internals/simulation-input.md` | Runtime Behavior: `docs/internals/runtime-and-resources.md`)*
-
-* **Stochastic Workload:** Generates user traffic based on a two-stage sampling model, combining the number of active users and their request rate per minute to produce a realistic, fluctuating load (RPS) on the system.
- * *(Modeling Details with mathematical explanation and clear assumptions: `docs/internals/requests-generator.md`)*
-
-* **Metrics & Outputs:** Collects two types of data: **time-series metrics** (e.g., `ready_queue_len`, `ram_in_use`) and **event-based data** (`RqsClock`). This raw data is used to calculate final KPIs like **p95/p99 latency** and **throughput**.
- * *(Metric Reference: `docs/internals/metrics`)*
-
-## Current Limitations (v0.1)
-
-* Network realism: base latency + optional drops (no bandwidth/payload/TCP yet).
-* Single event loop per server: no multi-process/multi-node servers yet.
-* Linear endpoint flows: no branching/fan-out within an endpoint.
-* No thread-level concurrency; modeling OS threads and scheduler/context switching is out of scope.”
-* Stationary workload: no diurnal patterns or feedback/backpressure.
-* Sampling cadence: very short spikes can be missed if `sample_period_s` is large.
-
-
-## Roadmap (Order is not indicative of priority)
-
-This roadmap outlines the key development areas to transform AsyncFlow into a comprehensive framework for statistical analysis and resilience modeling of distributed systems.
-
-### 1. Monte Carlo Simulation Engine
-
-**Why:** To overcome the limitations of a single simulation run and obtain statistically robust results. This transforms the simulator from an "intuition" tool into an engineering tool for data-driven decisions with confidence intervals.
-
-* **Independent Replications:** Run the same simulation N times with different random seeds to sample the space of possible outcomes.
-* **Warm-up Period Management:** Introduce a "warm-up" period to be discarded from the analysis, ensuring that metrics are calculated only on the steady-state portion of the simulation.
-* **Ensemble Aggregation:** Calculate means, standard deviations, and confidence intervals for aggregated metrics (latency, throughput) across all replications.
-* **Confidence Bands:** Visualize time-series data (e.g., queue lengths) with confidence bands to show variability over time.
-
-### 2. Realistic Service Times (Stochastic Service Times)
-
-**Why:** Constant service times underestimate tail latencies (p95/p99), which are almost always driven by "slow" requests. Modeling this variability is crucial for a realistic analysis of bottlenecks.
-
-* **Distributions for Steps:** Allow parameters like `cpu_time` and `io_waiting_time` in an `EndpointStep` to be sampled from statistical distributions (e.g., Lognormal, Gamma, Weibull) instead of being fixed values.
-* **Per-Request Sampling:** Each request will sample its own service times independently, simulating the natural variability of a real-world system.
-
-### 3. Component Library Expansion
-
-**Why:** To increase the variety and realism of the architectures that can be modeled.
-
-* **New System Nodes:**
- * `CacheRuntime`: To model caching layers (e.g., Redis) with hit/miss logic, TTL, and warm-up behavior.
- * `APIGatewayRuntime`: To simulate API Gateways with features like rate-limiting and authentication caching.
- * `DBRuntime`: A more advanced model for databases featuring connection pool contention and row-level locking.
-* **New Load Balancer Algorithms:** Add more advanced routing strategies (e.g., Weighted Round Robin, Least Response Time).
-
-### 4. Fault and Event Injection
-
-**Why:** To test the resilience and behavior of the system under non-ideal conditions, a fundamental use case for Site Reliability Engineering (SRE).
-
-* **API for Scheduled Events:** Introduce a system to schedule events at specific simulation times, such as:
- * **Node Down/Up:** Turn a server off and on to test the load balancer's failover logic.
- * **Degraded Edge:** Drastically increase the latency or drop rate of a network link.
- * **Error Bursts:** Simulate a temporary increase in the rate of application errors.
-
-### 5. Advanced Network Modeling
+* **Network model** — only base latency + jitter/spikes.
+ Bandwidth, queuing, and protocol-level details (HTTP/2 streams, QUIC, TLS handshakes) are not yet modeled.
-**Why:** To more faithfully model network-related bottlenecks that are not solely dependent on latency.
+* **Server model** — single event loop per server.
+ Multi-process or multi-threaded execution is not yet supported.
-* **Bandwidth and Payload Size:** Introduce the concepts of link bandwidth and request/response size to simulate delays caused by data transfer.
-* **Retries and Timeouts:** Model retry and timeout logic at the client or internal service level.
+* **Endpoint flows** — endpoints are linear pipelines.
+ Branching/fan-out (e.g. service calls to DB + cache) will be added in future versions.
-### 6. Complex Endpoint Flows
+* **Workload generation** — stationary workloads only.
+ No support yet for diurnal patterns, feedback loops, or adaptive backpressure.
-**Why:** To model more realistic business logic that does not follow a linear path.
+* **Overload policies** — no explicit handling of overload conditions.
+ Queue caps, deadlines, timeouts, rate limiting, and circuit breakers are not yet implemented.
-* **Conditional Branching:** Introduce the ability to have conditional steps within an endpoint (e.g., a different path for a cache hit vs. a cache miss).
-* **Fan-out / Fan-in:** Model scenarios where a service calls multiple downstream services in parallel and waits for their responses.
+* **Sampling cadence** — very short events may be missed if the `sample_period_s` is too large.
-### 7. Backpressure and Autoscaling
-**Why:** To simulate the behavior of modern, adaptive systems that react to load.
-* **Dynamic Rate Limiting:** Introduce backpressure mechanisms where services slow down the acceptance of new requests if their internal queues exceed a certain threshold.
-* **Autoscaling Policies:** Model simple Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) policies where the number of server replicas increases or decreases based on metrics like CPU utilization or queue length.
+📌 See the [ROADMAP](./ROADMAP.md) for planned features and upcoming milestones.
diff --git a/ROADMAP.md b/ROADMAP.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0fc9666
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ROADMAP.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+# **AsyncFlow Roadmap**
+
+AsyncFlow is designed as a **scenario-driven simulator for capacity planning**. Its purpose is not to “predict the Internet,” but to give engineers and researchers a way to test how backend systems behave under controlled, reproducible what-if conditions. The roadmap reflects a balance between realism, clarity, and usability: each step extends the tool while keeping its scope transparent and focused.
+
+---
+
+## **1. Network Baseline Upgrade**
+
+The first milestone is to move beyond a purely abstract latency model and introduce a more realistic network layer. Instead of only attaching a fixed RTT, AsyncFlow will account for socket capacity and per-connection memory usage at each node (servers and load balancers). This brings the simulator closer to operational limits, where resource saturation, rather than bandwidth, becomes the bottleneck.
+
+**Impact:** users will see how socket pressure and memory constraints affect latency, throughput, and error rates under different scenarios.
+
+---
+
+## **2. Richer Metrics and Visualization**
+
+Next, the focus shifts to **observability**. The simulator will expose finer metrics such as RAM queue lengths, CPU waiting times, and service durations. Visualizations will be improved with richer charts, event markers, and streamlined dashboards.
+
+**Impact:** enables clearer attribution of slowdowns whether they stem from CPU contention, memory limits, or network pressure and makes results easier to communicate.
+
+---
+
+## **3. Monte Carlo Analysis**
+
+Simulations are inherently variable. This milestone adds **multi-run Monte Carlo support**, allowing users to quantify uncertainty in latency, throughput, and utilization metrics. Results will be presented with confidence intervals and bands over time series, turning AsyncFlow into a decision-making tool rather than a single-run experiment.
+
+**Impact:** supports risk-aware capacity planning by highlighting ranges and probabilities, not just averages.
+
+---
+
+## **4. Databases and Caches**
+
+Once the core network and metric layers are mature, AsyncFlow will expand into modeling **stateful backends**. Simple but powerful abstractions for databases and caches will be introduced: connection pools, cache hit/miss dynamics, and latency distributions.
+
+**Impact:** this step unlocks realistic end-to-end scenarios, where system behavior is dominated not just by servers and edges, but by datastore capacity and caching efficiency.
+
+---
+
+## **5. Overload Policies and Resilience**
+
+With the main components in place, the simulator will introduce **control policies**: queue caps, deadlines, circuit breakers, rate limiting, and similar mechanisms. These features make it possible to test how systems protect themselves under overload, and to compare resilience strategies side by side.
+
+**Impact:** users will gain insight into not just when a system fails, but how gracefully it degrades.
+
+---
+
+## **6. Reinforcement Learning Playground**
+
+The final planned milestone is a **research-oriented playground** where AsyncFlow serves as a training and evaluation environment for intelligent load-balancing and autoscaling strategies. With a Gym-like interface, researchers can train RL agents and benchmark them against established baselines in controlled, reproducible conditions.
+
+**Impact:** bridges capacity planning with modern adaptive control, turning AsyncFlow into both an educational tool and a research testbed.
+
+---
+
+## **Vision**
+
+At each step, AsyncFlow stays true to its philosophy: **clarity over exhaustiveness, scenarios over prediction**. The roadmap builds toward a platform that is useful across three domains:
+
+* **Education**, to illustrate principles of latency, concurrency, and resilience.
+* **Pre-production planning**, to evaluate system limits before deployment.
+* **Research**, to test new algorithms and policies in a safe, transparent environment.
+
+---
+
+
diff --git a/docs/api/event-injection.md b/docs/api/event-injection.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9156364
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/api/event-injection.md
@@ -0,0 +1,246 @@
+# EventInjection — Public API Documentation
+
+## Overview
+
+`EventInjection` declares a **time-bounded event** that affects a component in the simulation. Each event targets either a **server** or a **network edge**, and is delimited by a `start` marker and an `end` marker.
+
+Supported families (per code):
+
+* **Server availability**: `SERVER_DOWN` → `SERVER_UP`
+* **Network latency spike (deterministic offset in seconds)**: `NETWORK_SPIKE_START` → `NETWORK_SPIKE_END`
+ For network spikes, the `Start` marker carries the amplitude in seconds via `spike_s`.
+
+Strictness:
+
+* Models use `ConfigDict(extra="forbid", frozen=True)`
+ → unknown fields are rejected; instances are immutable at runtime.
+
+---
+
+## Data Model
+
+### `Start`
+
+* `kind: Literal[SERVER_DOWN, NETWORK_SPIKE_START]`
+ Event family selector.
+* `t_start: NonNegativeFloat`
+ Start time in **seconds** from simulation start; **≥ 0.0**.
+* `spike_s: PositiveFloat | None`
+ **Required** and **> 0** **only** when `kind == NETWORK_SPIKE_START`.
+ **Forbidden** (must be omitted/`None`) for any other kind.
+
+### `End`
+
+* `kind: Literal[SERVER_UP, NETWORK_SPIKE_END]`
+ Must match the start family (see invariants).
+* `t_end: PositiveFloat`
+ End time in **seconds**; **> 0.0**.
+
+### `EventInjection`
+
+* `event_id: str`
+ Unique identifier within the simulation payload.
+* `target_id: str`
+ Identifier of the affected component (server or edge) as defined in the topology.
+* `start: Start`
+ Start marker.
+* `end: End`
+ End marker.
+
+---
+
+## Validation & Invariants (as implemented)
+
+### Within `EventInjection`
+
+1. **Family coherence**
+
+ * `SERVER_DOWN` → `SERVER_UP`
+ * `NETWORK_SPIKE_START` → `NETWORK_SPIKE_END`
+ Any other pairing raises:
+
+ ```
+ The event {event_id} must have as value of kind in end {expected}
+ ```
+2. **Temporal ordering**
+
+ * `t_start < t_end` (with `t_start ≥ 0.0`, `t_end > 0.0`)
+ Error:
+
+ ```
+ The starting time for the event {event_id} must be smaller than the ending time
+ ```
+3. **Network spike parameter**
+
+ * If `start.kind == NETWORK_SPIKE_START` ⇒ `start.spike_s` **must** be provided and be a positive float (seconds).
+ Error:
+
+ ```
+ The field spike_s for the event {event_id} must be defined as a positive float (seconds)
+ ```
+ * Otherwise (`SERVER_DOWN`) ⇒ `start.spike_s` **must be omitted** / `None`.
+ Error:
+
+ ```
+ Event {event_id}: spike_s must be omitted for non-network events
+ ```
+
+### Enforced at `SimulationPayload` level
+
+4. **Unique event IDs**
+ Error:
+
+ ```
+ The id's representing different events must be unique
+ ```
+5. **Target existence & compatibility**
+
+ * For server events (`SERVER_DOWN`), `target_id` must refer to a **server**.
+ * For network spikes (`NETWORK_SPIKE_START`), `target_id` must refer to an **edge**.
+ Errors:
+
+ ```
+ The target id {target_id} related to the event {event_id} does not exist
+ ```
+
+ ```
+ The event {event_id} regarding a server does not have a compatible target id
+ ```
+
+ ```
+ The event {event_id} regarding an edge does not have a compatible target id
+ ```
+6. **Times within simulation horizon** (with `T = sim_settings.total_simulation_time`)
+
+ * `t_start >= 0.0` and `t_start <= T`
+ * `t_end <= T`
+ Errors:
+
+ ```
+ Event '{event_id}': start time t_start={t:.6f} must be >= 0.0
+ Event '{event_id}': start time t_start={t:.6f} exceeds simulation horizon T={T:.6f}
+ Event '{event_id}': end time t_end={t:.6f} exceeds simulation horizon T={T:.6f}
+ ```
+7. **Global liveness rule (servers)**
+ The payload is rejected if **all servers are down at the same moment**.
+ Implementation detail: the timeline is ordered so that, at identical timestamps, **`END` is processed before `START`** to avoid transient all-down states.
+ Error:
+
+ ```
+ At time {time:.6f} all servers are down; keep at least one up
+ ```
+
+---
+
+## Runtime Semantics (summary)
+
+* **Server events**: the targeted server is unavailable between the start and end markers; the system enforces that at least one server remains up at all times.
+* **Network spike events**: the targeted edge’s latency sampler is deterministically **shifted by `spike_s` seconds** during the event window (additive congestion model). The underlying distribution is not reshaped—samples are translated by a constant offset.
+
+*(This reflects the agreed model: deterministic additive offset on edges.)*
+
+---
+
+## Units & Precision
+
+* All times and offsets are in **seconds** (floating-point).
+* Provide values with the precision your simulator supports; microsecond-level precision is acceptable if needed.
+
+---
+
+## Authoring Guidelines
+
+* **Do not include `spike_s`** for non-network events.
+* Use **stable, meaningful `event_id`** values for auditability.
+* Keep events within the **simulation horizon**.
+* When multiple markers share the same timestamp, rely on the engine’s **END-before-START** ordering for determinism.
+
+---
+
+## Examples
+
+### 1) Valid — Server maintenance window
+
+```yaml
+event_id: ev-maint-001
+target_id: srv-1
+start: { kind: SERVER_DOWN, t_start: 120.0 }
+end: { kind: SERVER_UP, t_end: 240.0 }
+```
+
+### 2) Valid — Network spike on an edge (+8 ms)
+
+```yaml
+event_id: ev-spike-008ms
+target_id: edge-12
+start: { kind: NETWORK_SPIKE_START, t_start: 10.0, spike_s: 0.008 }
+end: { kind: NETWORK_SPIKE_END, t_end: 25.0 }
+```
+
+### 3) Invalid — Missing `spike_s` for a network spike
+
+```yaml
+event_id: ev-missing-spike
+target_id: edge-5
+start: { kind: NETWORK_SPIKE_START, t_start: 5.0 }
+end: { kind: NETWORK_SPIKE_END, t_end: 15.0 }
+```
+
+Error:
+
+```
+The field spike_s for the event ev-missing-spike must be defined as a positive float (seconds)
+```
+
+### 4) Invalid — `spike_s` present for a server event
+
+```yaml
+event_id: ev-bad-spike
+target_id: srv-2
+start: { kind: SERVER_DOWN, t_start: 50.0, spike_s: 0.005 }
+end: { kind: SERVER_UP, t_end: 60.0 }
+```
+
+Error:
+
+```
+Event ev-bad-spike: spike_s must be omitted for non-network events
+```
+
+### 5) Invalid — Mismatched families
+
+```yaml
+event_id: ev-bad-kinds
+target_id: edge-1
+start: { kind: NETWORK_SPIKE_START, t_start: 5.0, spike_s: 0.010 }
+end: { kind: SERVER_UP, t_end: 15.0 }
+```
+
+Error:
+
+```
+The event ev-bad-kinds must have as value of kind in end NETWORK_SPIKE_END
+```
+
+### 6) Invalid — Start not before End
+
+```yaml
+event_id: ev-bad-time
+target_id: srv-2
+start: { kind: SERVER_DOWN, t_start: 300.0 }
+end: { kind: SERVER_UP, t_end: 300.0 }
+```
+
+Error:
+
+```
+The starting time for the event ev-bad-time must be smaller than the ending time
+```
+
+---
+
+## Notes for Consumers
+
+* The schema is **strict**: misspelled fields (e.g., `t_strat`) are rejected.
+* The engine may combine multiple active network spikes on the same edge by **summing** their `spike_s` values while they overlap (handled by runtime bookkeeping).
+* This document describes exactly what is present in the provided code and validators; no additional fields or OpenAPI metadata are assumed.
diff --git a/docs/internals/edges-events-injection.md b/docs/internals/edges-events-injection.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..210d190
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/internals/edges-events-injection.md
@@ -0,0 +1,277 @@
+# Edge Event Injection: Architecture & Operations
+
+This document explains how **edge-level events** (e.g., deterministic latency spikes) are modeled, centralized, and injected into the simulation. It covers:
+
+* Data model (start/end markers & validation)
+* The **central event runtime** (timeline, cumulative offsets, live adapters)
+* How **SimulationRunner** wires everything
+* How **EdgeRuntime** consumes the adapters during delivery
+* Ordering, correctness guarantees, and trade-offs
+* Extension points and maintenance tips
+
+---
+
+## 1) Conceptual Model
+
+### What’s an “edge event”?
+
+An edge event is a **time-bounded effect** applied to a specific network edge (link). Today we support **latency spikes**: while the event is active, the edge’s transit time is increased by a fixed offset (`spike_s`) in seconds.
+
+### Event markers
+
+Events are defined with two **markers**:
+
+* `Start` (`kind` in `{NETWORK_SPIKE_START, SERVER_DOWN}`)
+* `End` (`kind` in `{NETWORK_SPIKE_END, SERVER_UP}`)
+
+Validation guarantees:
+
+* **Kind pairing** is coherent (e.g., `NETWORK_SPIKE_START` ↔ `NETWORK_SPIKE_END`).
+* **Time ordering**: `t_start < t_end`.
+* For network spike events, **`spike_s` is required** and positive.
+
+> These guarantees are enforced by the Pydantic models and their `model_validator`s in the schema layer, *before* runtime.
+
+---
+
+## 2) Centralized Event Registry: `EventInjectionRuntime`
+
+`EventInjectionRuntime` centralizes all event logic and exposes **live read-only views** (adapters) to edge actors.
+
+### Responsibilities & Data
+
+* **Input**:
+
+ * `events: list[EventInjection] | None`
+ * `edges: list[Edge]`, `servers: list[Server]`, `env: simpy.Environment`
+* **Internal state**:
+
+ * `self._edges_events: dict[event_id, dict[edge_id, float]]`
+ Mapping from event → edge → spike amplitude (`spike_s`).
+ This allows multiple events per edge and distinguishes overlapping events.
+ * `self._edges_spike: dict[edge_id, float]`
+ **Cumulative** spike currently active per edge (updated at runtime).
+ * `self._edges_affected: set[edge_id]`
+ All edges that are ever impacted by at least one event.
+ * `self._edges_timeline: list[tuple[time, event_id, edge_id, mark]]`
+ Absolute timestamps (`time`) with `mark ∈ {start, end}` for **edges**.
+ * (We also construct a server timeline, reserved for future server-side effects.)
+
+> If `events` is `None` or empty, the runtime initializes to empty sets/maps and **does nothing** when started.
+
+### Build step (performed in `__init__`)
+
+1. Early return if there are no events (keeps empty adapters).
+2. Partition events by **target type** (edge vs server).
+3. For each **edge** event:
+
+ * Record `spike_s` in `self._edges_events[event_id][edge_id]`.
+ * Append `(t_start, event_id, edge_id, start)` and `(t_end, event_id, edge_id, end)` to the **edge timeline**.
+ * Add `edge_id` to `self._edges_affected`.
+4. **Sort** timelines by `(time, mark == start, event_id, edge_id)` so that at equal time, **end** is processed **before start**.
+ (Because `False < True`, `end` precedes `start`.)
+
+### Runtime step (SimPy process)
+
+The coroutine `self._assign_edges_spike()`:
+
+* Iterates the ordered timeline of **absolute** timestamps.
+* Converts absolute `t_event` to relative waits via `dt = t_event - last_t`.
+* After waiting `dt`, applies the state change:
+
+ * On **start**: `edges_spike[edge_id] += delta`
+ * On **end**: `edges_spike[edge_id] -= delta`
+
+This gives a continuously updated, **cumulative** spike per edge, enabling **overlapping events** to stack linearly.
+
+### Public adapters (read-only views)
+
+* `edges_spike: dict[str, float]` — current cumulative spike per edge.
+* `edges_affected: set[str]` — edges that may ever be affected.
+
+These are **shared** with `EdgeRuntime` instances, so updates made by the central process are immediately visible to the edges **without any signaling or copying**.
+
+---
+
+## 3) Wiring & Lifecycle: `SimulationRunner`
+
+`SimulationRunner` orchestrates creation, wiring, and startup order.
+
+### Build phase
+
+1. Build node runtimes (request generator, client, servers, optional load-balancer).
+2. Build **edge runtimes** (`EdgeRuntime`) with their target boxes (stores).
+3. **Build events**:
+
+ * If `simulation_input.events` is empty/None → **skip** (no process, no adapters).
+ * Else:
+
+ * Construct **one** `EventInjectionRuntime`.
+ * Extract adapters: `edges_affected`, `edges_spike`.
+ * Attach these **same objects** to **every** `EdgeRuntime`.
+ (EdgeRuntime performs a membership check; harmless for unaffected edges.)
+
+> We deliberately attach adapters to all edges for simplicity. This is O(1) memory for references, and O(1) runtime per delivery (one membership + dict lookup). If desired, the runner could pass adapters **only** to affected edges—this would save a branch per delivery at the cost of more conditional wiring logic.
+
+### Start phase (order matters)
+
+* `EventInjectionRuntime.start()` — **first**
+ Ensures that the spike timeline is active before edges start delivering; the first edge transport will see the correct offset when due.
+* Start all other actors.
+* Start the metric collector (RAM / queues / connections snapshots).
+* `env.run(until=total_simulation_time)` to advance the clock.
+
+### Why this order?
+
+* Prevents race conditions where the first edge message observes stale (`0.0`) spike at time ≈ `t_start`.
+* Keeps the architecture deterministic and easy to reason about.
+
+---
+
+## 4) Edge Consumption: `EdgeRuntime`
+
+Each edge has:
+
+* `edges_affected: Container[str] | None`
+* `edges_spike: Mapping[str, float] | None`
+
+During `_deliver(state)`:
+
+1. Sample base latency from the configured RV.
+2. If adapters are present **and** `edge_id ∈ edges_affected`:
+
+ * Read `spike = edges_spike.get(edge_id, 0.0)`
+ * `effective = base_latency + spike`
+3. `yield env.timeout(effective)`
+
+No further coordination required: the **central** process updates `edges_spike` as time advances, so each delivery observes the **current** spike.
+
+---
+
+## 5) Correctness & Guarantees
+
+* **Temporal correctness**: Absolute → relative time conversion (`dt = t_event - last_t`) ensures the process applies changes at the exact timestamps. Sorting ensures **END** is processed before **START** when times coincide, so zero-length events won’t “leak” positive offset.
+* **Coherence**: Pydantic validators enforce event pairing and time ordering.
+* **Immutability**: Marker models are frozen; unknown fields are forbidden.
+* **Overlap**: Multiple events on the same edge stack linearly (`+=`/`-=`).
+
+---
+
+## 6) Performance & Trade-offs
+
+### Centralized vs Distributed
+
+* **Chosen**: one central `EventInjectionRuntime` with live adapters.
+
+ * **Pros**: simple mental model; single source of truth; O(1) read for edges; no per-edge coroutines; minimal memory traffic.
+ * **Cons**: single process to maintain (but it’s lightweight); edges branch on membership.
+
+* **Alternative A**: deliver the **full** event runtime object to each edge.
+
+ * **Cons**: wider API surface; tighter coupling; harder to evolve; edges would get capabilities they don’t need (SRP violation).
+
+* **Alternative B**: per-edge local event processes.
+
+ * **Cons**: one coroutine per edge (N processes), more scheduler overhead, duplicated logic & sorting.
+
+### Passing adapters to *all* edges vs only affected edges
+
+* **Chosen**: pass to all edges.
+
+ * **Pros**: wiring stays uniform; negligible memory; O(1) branch in `_deliver`.
+ * **Cons**: trivial per-delivery branch even for unaffected edges.
+* **Alternative**: only affected edges receive adapters.
+
+ * **Pros**: removes one branch at delivery.
+ * **Cons**: more conditional wiring, more moving parts for little gain.
+
+---
+
+## 7) Sequence Overview
+
+```
+SimulationRunner.run()
+ ├─ _build_rqs_generator()
+ ├─ _build_client()
+ ├─ _build_servers()
+ ├─ _build_load_balancer()
+ ├─ _build_edges()
+ ├─ _build_events()
+ │ └─ EventInjectionRuntime(...):
+ │ - build _edges_events, _edges_affected
+ │ - build & sort _edges_timeline
+ │
+ ├─ _start_events()
+ │ └─ start _assign_edges_spike() (central timeline process)
+ │
+ ├─ _start_all_processes() (edges, client, servers, etc.)
+ ├─ _start_metric_collector()
+ └─ env.run(until = T)
+```
+
+During `EdgeRuntime._deliver()`:
+
+```
+base = sample(latency_rv)
+if adapters_present and edge_id in edges_affected:
+ spike = edges_spike.get(edge_id, 0.0)
+ effective = base + spike
+else:
+ effective = base
+yield env.timeout(effective)
+```
+
+---
+
+## 8) Extensibility
+
+* **Other edge effects**: add new event kinds and store per-edge state (e.g., drop-rate bumps) in `_edges_events` and update logic in `_assign_edges_spike()`.
+* **Server outages**: server timeline is already scaffolded; add a server process to open/close resources (e.g., capacity=0 during downtime).
+* **Non-deterministic spikes**: swap `float` `spike_s` for a small sampler (callable) and apply the sampled value at each **start**, or at each **delivery** (define semantics).
+* **Per-edge filtering in runner** (micro-optimization): only wire adapters to affected edges.
+
+---
+
+## 9) Operational Notes & Best Practices
+
+* **Start order** matters: always start `EventInjectionRuntime` *before* edges.
+* **Adapters must be shared** (not copied) to preserve live updates.
+* **Keep `edges_spike` additive** (no negative values unless you introduce “negative spikes” intentionally).
+* **Time units**: seconds everywhere; keep it consistent with sampling.
+* **Validation first**: reject malformed events early (schema layer), *not* in runtime.
+
+---
+
+## 10) Glossary
+
+* **Adapter**: a minimal, read-only view (e.g., `Mapping[str, float]`, `Container[str]`) handed to edges to observe central state without owning it.
+* **Timeline**: sorted list of `(time, event_id, edge_id, mark)` where `mark ∈ {start, end}`.
+* **Spike**: deterministic latency offset to be added to the sampled base latency.
+
+---
+
+## 11) Example (end-to-end)
+
+**YAML (conceptual)**
+
+```yaml
+events:
+ - event_id: ev-spike-1
+ target_id: edge-42
+ start: { kind: NETWORK_SPIKE_START, t_start: 12.0, spike_s: 0.050 }
+ end: { kind: NETWORK_SPIKE_END, t_end: 18.0 }
+```
+
+**Runtime effect**
+
+* From `t ∈ [12, 18)`, `edge-42` adds **+50 ms** to its sampled latency.
+* Overlapping events stack: `edges_spike["edge-42"]` is the **sum** of active spikes.
+
+---
+
+## 12) Summary
+
+* We centralize event logic in **`EventInjectionRuntime`** and expose **live adapters** to edges.
+* Edges read **current cumulative spikes** at delivery time—**no coupling** and **no extra processes per edge**.
+* The runner keeps the flow simple and deterministic: **build → wire → start events → start actors → run**.
+* The architecture is **extensible**, **testable**, and **performant** for realistic workloads.
diff --git a/docs/internals/server-events-injection.md b/docs/internals/server-events-injection.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8bc7165
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/internals/server-events-injection.md
@@ -0,0 +1,203 @@
+# Server Event Injection — End-to-End Design & Rationale
+
+This document explains how **server-level events** (planned outages) are modeled and executed across all layers of the simulation stack. It complements the Edge Event Injection design.
+
+---
+
+## 1) Goals
+
+* Hide outage semantics from the load balancer algorithms: **they see only the current set of edges**.
+* Keep **runtime cost O(1)** per transition (down/up).
+* Preserve determinism and fairness when servers rejoin.
+* Centralize event logic; avoid per-server coroutines and ad-hoc flags.
+
+---
+
+## 2) Participants (layers)
+
+* **Schema / Validation (Pydantic)**: validates `EventInjection` objects (pairing, order, target existence).
+* **SimulationRunner**: builds runtimes; owns the **single shared** `OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]` used by the LB (`_lb_out_edges`).
+* **EventInjectionRuntime**: central event engine; builds the **server timeline** and a **reverse index** `server_id → (edge_id, EdgeRuntime)`; mutates `_lb_out_edges` at runtime.
+* **LoadBalancerRuntime**: reads `_lb_out_edges` to select the next edge (RR / least-connections). **No outage logic inside.**
+* **EdgeRuntime (LB→Server edges)**: unaffected by server outages; disappears from the LB’s choice set while the server is down.
+* **ServerRuntime**: unaffected structurally; no extra checks for “am I down?”.
+* **SimPy Environment**: schedules the central outage coroutine.
+* **Metric Collector**: optional; observes effects but is not part of the mechanism.
+
+---
+
+## 3) Data & Structures
+
+* **`_lb_out_edges: OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]`**
+ Single shared map of **currently routable** LB→server edges.
+
+ * Removal/Insertion/Move are **O(1)**.
+ * Aliased into both `LoadBalancerRuntime` and `EventInjectionRuntime`.
+
+* **`_servers_timeline: list[tuple[time, event_id, server_id, mark]]`**
+ Absolute timestamps, sorted by `(time, mark == start, event_id, server_id)` so **END precedes START** when equal.
+
+* **`_edge_by_server: dict[str, tuple[str, EdgeRuntime]]`**
+ Reverse index built from `_lb_out_edges` at initialization.
+
+---
+
+## 4) Build-time Responsibilities
+
+* **SimulationRunner**
+
+ 1. Build LB and pass it `_lb_out_edges` (empty at first).
+ 2. Build edges; when wiring LB→Server, insert that edge into `_lb_out_edges`.
+ 3. Build `EventInjectionRuntime`, passing:
+
+ * validated `events`
+ * `servers` and `edges` (IDs for sanity checks)
+ * aliased `_lb_out_edges`
+
+* **EventInjectionRuntime.**init****
+
+ * Partition events; construct ` _servers_timeline`.
+ * Sort timeline (END before START at equal `time`).
+ * Build ` _edge_by_server` by scanning `_lb_out_edges` (edge target → server\_id).
+
+---
+
+## 5) Run-time Responsibilities
+
+* **EventInjectionRuntime.\_assign\_server\_state()**
+
+ * Iterate the server timeline with absolute→relative waits: `dt = t_event − last_t`, then `yield env.timeout(dt)`.
+ * On `SERVER_DOWN` (START):
+ `lb_out_edges.pop(edge_id, None)`
+ * On `SERVER_UP` (END):
+
+ ```
+ lb_out_edges[edge_id] = edge_runtime
+ lb_out_edges.move_to_end(edge_id) # fairness on rejoin
+ ```
+
+* **LoadBalancerRuntime**
+
+ * For each request, read `_lb_out_edges` and apply the chosen algorithm. If a server is down, its edge simply **isn’t there**.
+
+* **EdgeRuntime & ServerRuntime**
+
+ * No additional work: outage is reflected entirely by presence/absence of the LB→server edge.
+
+---
+
+## 6) Sequence Overview (all layers)
+
+```
+User YAML ──► Schema/Validation
+ │ (pairing, ordering, target checks)
+ ▼
+ SimulationRunner
+ │ _lb_out_edges: OrderedDict[...] (shared object)
+ │ build LB, edges (LB→S inserted into _lb_out_edges)
+ │ build EventInjectionRuntime(..., lb_out_edges=alias)
+ │
+ ├─ _start_events()
+ │ └─ EventInjectionRuntime.start()
+ │ └─ start _assign_server_state() (SimPy proc)
+ │
+ ├─ _start_all_processes()
+ │ ├─ LoadBalancerRuntime.start()
+ │ ├─ EdgeRuntime.start() (if any process)
+ │ └─ ServerRuntime.start()
+ │
+ └─ env.run(until=T)
+
+Runtime progression (example):
+t=5s EventInjectionRuntime: SERVER_DOWN(S1)
+ └─ _edge_by_server[S1] -> (edge-S1, edge_rt)
+ └─ _lb_out_edges.pop("edge-S1") # O(1)
+
+t=7s LoadBalancerRuntime picks next edge
+ └─ "edge-S1" not present → never selected
+
+t=10s EventInjectionRuntime: SERVER_UP(S1)
+ └─ _lb_out_edges["edge-S1"] = edge_rt # O(1)
+ └─ _lb_out_edges.move_to_end("edge-S1") # fairness
+
+t>10s LoadBalancerRuntime now sees edge-S1 again
+ └─ RR/LC proceeds as usual
+```
+
+---
+
+## 7) Correctness & Determinism
+
+* **Exact timing**: absolute→relative conversion ensures transitions happen at precise timestamps.
+* **END before START** at identical times prevents spuriously “stuck down” outcomes for back-to-back events.
+* **Fair rejoin**: `move_to_end` reintroduces the server in a predictable RR position (least recently used).
+ (Least-connections remains deterministic because the edge reappears with its current connection count.)
+* **Availability constraint**: schema can enforce “at least one server up,” avoiding degenerate LB states.
+
+---
+
+## 8) Design Choices & Rationale
+
+* **Mutate the edge set, not the algorithm**
+ Removing/adding the LB→server edge keeps LB code **pure** and reusable; no conditional branches for “down servers”.
+* **Single shared `OrderedDict`**
+
+ * O(1) for remove/insert/rotate.
+ * Aliasing between LB and injector removes the need for signaling or copies.
+* **Centralized coroutine**
+ One SimPy process for server outages scales better than per-server processes; simpler mental model.
+* **Reverse index `server_id → edge`**
+ Constant-time resolution; avoids coupling servers to LB or vice-versa.
+
+---
+
+## 9) Performance
+
+* **Build**:
+
+ * Timeline construction: O(#server-events)
+ * Sort: O(#server-events · log #server-events)
+* **Run**:
+
+ * Each transition: O(1) (pop/set/move)
+ * LB pick: unchanged (RR O(1), LC O(n))
+* **Space**:
+
+ * Reverse index: O(#servers with LB edges)
+ * Timeline: O(#server-events)
+
+---
+
+## 10) Failure Modes & Guards
+
+* Unknown server in an event → rejected by schema (or ignored with a log if you prefer leniency).
+* Concurrent DOWN/UP at same timestamp → resolved by timeline ordering (END first).
+* All servers down → disallowed by schema (or handled by LB guard if you opt in later).
+* Missing reverse mapping (no LB) → injector safely no-ops.
+
+---
+
+## 11) Extensibility
+
+* **Multiple LB instances**: make the reverse index `(lb_id, server_id) → edge_id`, or pass per-LB `lb_out_edges`.
+* **Partial capacity**: instead of removing edges, attach capacity/weight and have the LB respect it (requires extending LB policy).
+* **Dynamic scale-out**: adding new servers at runtime is the same operation as “UP” with a previously unseen edge.
+
+---
+
+## 12) Operational Notes
+
+* Start the **event coroutine** before LB to avoid off-by-one delivery at `t_start`.
+* Keep `_lb_out_edges` the **only source of truth** for routable edges.
+* If you also use edge-level spikes, both coroutines can run concurrently; they are independent.
+
+---
+
+## 13) Summary
+
+We model server outages by **mutating the LB’s live edge set** via a centralized event runtime:
+
+* **O(1)** down/up transitions by `pop`/`set` on a shared `OrderedDict`.
+* LB algorithms remain untouched and deterministic.
+* A single SimPy coroutine drives the timeline; a reverse index resolves targets in constant time.
+* The design is minimal, performant, and easy to extend to richer failure models.
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers.py b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8af411f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers.py
@@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
+"""
+AsyncFlow builder example — LB + 2 servers (medium load) with events.
+
+Topology
+ generator → client → LB → srv-1
+ └→ srv-2
+ srv-1 → client
+ srv-2 → client
+
+Workload
+ ~40 rps (120 users × 20 req/min ÷ 60).
+
+Events
+ - Edge spike on client→LB (+15 ms) @ [100s, 160s]
+ - srv-1 outage @ [180s, 240s]
+ - Edge spike on LB→srv-2 (+20 ms) @ [300s, 360s]
+ - srv-2 outage @ [360s, 420s]
+ - Edge spike on gen→client (+10 ms) @ [480s, 540s]
+
+Outputs
+ PNGs saved under `lb_two_servers_events_plots/` next to this script:
+ - dashboard (latency + throughput)
+ - per-server plots: ready queue, I/O queue, RAM
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from pathlib import Path
+
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+import simpy
+
+# Public builder API
+from asyncflow import AsyncFlow
+from asyncflow.components import Client, Server, Edge, Endpoint, LoadBalancer
+from asyncflow.settings import SimulationSettings
+from asyncflow.workload import RqsGenerator
+
+# Runner + Analyzer
+from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+
+
+def build_and_run() -> ResultsAnalyzer:
+ """Build the scenario via the builder and run the simulation."""
+ # ── Workload (generator) ───────────────────────────────────────────────
+ generator = RqsGenerator(
+ id="rqs-1",
+ avg_active_users={"mean": 120},
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user={"mean": 20},
+ user_sampling_window=60,
+ )
+
+ # ── Client ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+
+ # ── Servers (identical endpoint: CPU 2ms → RAM 128MB → IO 12ms) ───────
+ endpoint = Endpoint(
+ endpoint_name="/api",
+ steps=[
+ {"kind": "initial_parsing", "step_operation": {"cpu_time": 0.002}},
+ {"kind": "ram", "step_operation": {"necessary_ram": 128}},
+ {"kind": "io_wait", "step_operation": {"io_waiting_time": 0.012}},
+ ],
+ )
+ srv1 = Server(
+ id="srv-1",
+ server_resources={"cpu_cores": 1, "ram_mb": 2048},
+ endpoints=[endpoint],
+ )
+ srv2 = Server(
+ id="srv-2",
+ server_resources={"cpu_cores": 1, "ram_mb": 2048},
+ endpoints=[endpoint],
+ )
+
+ # ── Load Balancer ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────
+ lb = LoadBalancer(
+ id="lb-1",
+ algorithms="round_robin",
+ server_covered=["srv-1", "srv-2"],
+ )
+
+ # ── Edges (exponential latency) ───────────────────────────────────────
+ e_gen_client = Edge(
+ id="gen-client",
+ source="rqs-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ )
+ e_client_lb = Edge(
+ id="client-lb",
+ source="client-1",
+ target="lb-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.002, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ )
+ e_lb_srv1 = Edge(
+ id="lb-srv1",
+ source="lb-1",
+ target="srv-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.002, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ )
+ e_lb_srv2 = Edge(
+ id="lb-srv2",
+ source="lb-1",
+ target="srv-2",
+ latency={"mean": 0.002, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ )
+ e_srv1_client = Edge(
+ id="srv1-client",
+ source="srv-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ )
+ e_srv2_client = Edge(
+ id="srv2-client",
+ source="srv-2",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ )
+
+ # ── Simulation settings ───────────────────────────────────────────────
+ settings = SimulationSettings(
+ total_simulation_time=600,
+ sample_period_s=0.05,
+ enabled_sample_metrics=[
+ "ready_queue_len",
+ "event_loop_io_sleep",
+ "ram_in_use",
+ "edge_concurrent_connection",
+ ],
+ enabled_event_metrics=["rqs_clock"],
+ )
+
+ # ── Assemble payload + events via builder ─────────────────────────────
+ payload = (
+ AsyncFlow()
+ .add_generator(generator)
+ .add_client(client)
+ .add_servers(srv1, srv2)
+ .add_load_balancer(lb)
+ .add_edges(
+ e_gen_client,
+ e_client_lb,
+ e_lb_srv1,
+ e_lb_srv2,
+ e_srv1_client,
+ e_srv2_client,
+ )
+ .add_simulation_settings(settings)
+ # Events
+ .add_network_spike(
+ event_id="ev-spike-1",
+ edge_id="client-lb",
+ t_start=100.0,
+ t_end=160.0,
+ spike_s=0.015, # +15 ms
+ )
+ .add_server_outage(
+ event_id="ev-srv1-down",
+ server_id="srv-1",
+ t_start=180.0,
+ t_end=240.0,
+ )
+ .add_network_spike(
+ event_id="ev-spike-2",
+ edge_id="lb-srv2",
+ t_start=300.0,
+ t_end=360.0,
+ spike_s=0.020, # +20 ms
+ )
+ .add_server_outage(
+ event_id="ev-srv2-down",
+ server_id="srv-2",
+ t_start=360.0,
+ t_end=420.0,
+ )
+ .add_network_spike(
+ event_id="ev-spike-3",
+ edge_id="gen-client",
+ t_start=480.0,
+ t_end=540.0,
+ spike_s=0.010, # +10 ms
+ )
+ .build_payload()
+ )
+
+ # ── Run ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+ runner = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+ results: ResultsAnalyzer = runner.run()
+ return results
+
+
+def main() -> None:
+ res = build_and_run()
+ print(res.format_latency_stats())
+
+ # Output directory next to this script
+ script_dir = Path(__file__).parent
+ out_dir = script_dir / "lb_two_servers_events_plots"
+ out_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+
+ # Dashboard (latency + throughput)
+ fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))
+ res.plot_base_dashboard(axes[0], axes[1])
+ fig.tight_layout()
+ dash_path = out_dir / "lb_two_servers_events_dashboard.png"
+ fig.savefig(dash_path)
+ print(f"Saved: {dash_path}")
+
+ # Per-server plots
+ for sid in res.list_server_ids():
+ # Ready queue
+ f1, a1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ res.plot_single_server_ready_queue(a1, sid)
+ f1.tight_layout()
+ p1 = out_dir / f"lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f1.savefig(p1)
+ print(f"Saved: {p1}")
+
+ # I/O queue
+ f2, a2 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ res.plot_single_server_io_queue(a2, sid)
+ f2.tight_layout()
+ p2 = out_dir / f"lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f2.savefig(p2)
+ print(f"Saved: {p2}")
+
+ # RAM usage
+ f3, a3 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ res.plot_single_server_ram(a3, sid)
+ f3.tight_layout()
+ p3 = out_dir / f"lb_two_servers_events_ram_{sid}.png"
+ f3.savefig(p3)
+ print(f"Saved: {p3}")
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ main()
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_dashboard.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_dashboard.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2177ffb
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_dashboard.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9c7ffba
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-2.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..678c839
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-2.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-1.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c8102f8
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-2.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ddf4a20
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-2.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3464e5f
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-2.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cfb8c0f
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/lb_two_servers_events_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-2.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server.py b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0c514b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server.py
@@ -0,0 +1,187 @@
+#!/usr/bin/env python3
+"""
+AsyncFlow builder example — build, run, and visualize a single-server async system
+with event injections (latency spike on edge + server outage).
+
+Topology (single server)
+ generator ──edge──> client ──edge──> server ──edge──> client
+
+Load model
+ ~100 active users, 20 requests/min each (Poisson-like aggregate).
+
+Server model
+ 1 CPU core, 2 GB RAM
+ Endpoint pipeline: CPU(1 ms) → RAM(100 MB) → I/O wait (100 ms)
+ Semantics:
+ - CPU step blocks the event loop
+ - RAM step holds a working set until request completion
+ - I/O step is non-blocking (event-loop friendly)
+
+Network model
+ Each edge has exponential latency with mean 3 ms.
+
+Events
+ - ev-spike-1: deterministic latency spike (+20 ms) on client→server edge,
+ active from t=120s to t=240s
+ - ev-outage-1: server outage for srv-1 from t=300s to t=360s
+
+Outputs
+ - Prints latency statistics to stdout
+ - Saves PNGs in `single_server_plot/` next to this script:
+ * dashboard (latency + throughput)
+ * per-server plots (ready queue, I/O queue, RAM)
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from pathlib import Path
+import simpy
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+
+# Public AsyncFlow API (builder)
+from asyncflow import AsyncFlow
+from asyncflow.components import Client, Server, Edge, Endpoint
+from asyncflow.settings import SimulationSettings
+from asyncflow.workload import RqsGenerator
+
+# Runner + Analyzer
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+
+
+def build_and_run() -> ResultsAnalyzer:
+ """Build the scenario via the Pythonic builder and run the simulation."""
+ # Workload (generator)
+ generator = RqsGenerator(
+ id="rqs-1",
+ avg_active_users={"mean": 100},
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user={"mean": 20},
+ user_sampling_window=60,
+ )
+
+ # Client
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+
+ # Server + endpoint (CPU → RAM → I/O)
+ endpoint = Endpoint(
+ endpoint_name="ep-1",
+ probability=1.0,
+ steps=[
+ {"kind": "initial_parsing", "step_operation": {"cpu_time": 0.001}}, # 1 ms
+ {"kind": "ram", "step_operation": {"necessary_ram": 100}}, # 100 MB
+ {"kind": "io_wait", "step_operation": {"io_waiting_time": 0.100}}, # 100 ms
+ ],
+ )
+ server = Server(
+ id="srv-1",
+ server_resources={"cpu_cores": 1, "ram_mb": 2048},
+ endpoints=[endpoint],
+ )
+
+ # Network edges (3 ms mean, exponential)
+ e_gen_client = Edge(
+ id="gen-client",
+ source="rqs-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ )
+ e_client_srv = Edge(
+ id="client-srv",
+ source="client-1",
+ target="srv-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ )
+ e_srv_client = Edge(
+ id="srv-client",
+ source="srv-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ )
+
+ # Simulation settings
+ settings = SimulationSettings(
+ total_simulation_time=500,
+ sample_period_s=0.05,
+ enabled_sample_metrics=[
+ "ready_queue_len",
+ "event_loop_io_sleep",
+ "ram_in_use",
+ "edge_concurrent_connection",
+ ],
+ enabled_event_metrics=["rqs_clock"],
+ )
+
+ # Assemble payload with events
+ payload = (
+ AsyncFlow()
+ .add_generator(generator)
+ .add_client(client)
+ .add_servers(server)
+ .add_edges(e_gen_client, e_client_srv, e_srv_client)
+ .add_simulation_settings(settings)
+ # Events
+ .add_network_spike(
+ event_id="ev-spike-1",
+ edge_id="client-srv",
+ t_start=120.0,
+ t_end=240.0,
+ spike_s=0.020, # 20 ms spike
+ )
+ ).build_payload()
+
+ # Run
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+ runner = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+ results: ResultsAnalyzer = runner.run()
+ return results
+
+
+def main() -> None:
+ # Build & run
+ res = build_and_run()
+
+ # Print concise latency summary
+ print(res.format_latency_stats())
+
+ # Prepare output dir
+ script_dir = Path(__file__).parent
+ out_dir = script_dir / "single_server_plot"
+ out_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+
+ # Dashboard (latency + throughput)
+ fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))
+ res.plot_base_dashboard(axes[0], axes[1])
+ fig.tight_layout()
+ dash_path = out_dir / "event_inj_single_server_dashboard.png"
+ fig.savefig(dash_path)
+ print(f"Saved: {dash_path}")
+
+ # Per-server plots
+ for sid in res.list_server_ids():
+ # Ready queue
+ f1, a1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ res.plot_single_server_ready_queue(a1, sid)
+ f1.tight_layout()
+ p1 = out_dir / f"event_inj_single_server_ready_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f1.savefig(p1)
+ print(f"Saved: {p1}")
+
+ # I/O queue
+ f2, a2 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ res.plot_single_server_io_queue(a2, sid)
+ f2.tight_layout()
+ p2 = out_dir / f"event_inj_single_server_io_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f2.savefig(p2)
+ print(f"Saved: {p2}")
+
+ # RAM usage
+ f3, a3 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ res.plot_single_server_ram(a3, sid)
+ f3.tight_layout()
+ p3 = out_dir / f"event_inj_single_server_ram_{sid}.png"
+ f3.savefig(p3)
+ print(f"Saved: {p3}")
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ main()
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_dashboard.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_dashboard.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1a81453
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_dashboard.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_io_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_io_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ed08233
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_io_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ram_srv-1.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ram_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..476bd79
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ram_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ready_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ready_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a6fcf29
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/builder_input/event_injection/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ready_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_dashboard.png b/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_dashboard.png
index 4d94cfe..dd6cc80 100644
Binary files a/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_dashboard.png and b/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_dashboard.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png b/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png
index 1665766..d7f57e6 100644
Binary files a/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png and b/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png b/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png
index cdda50f..f055ff4 100644
Binary files a/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png and b/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/two_servers.py b/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/two_servers.py
index fb2eb35..a57d090 100644
--- a/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/two_servers.py
+++ b/examples/builder_input/load_balancer/two_servers.py
@@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
-#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
Didactic example: AsyncFlow with a Load Balancer and two **identical** servers.
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/single_server/builder_service_plots.png b/examples/builder_input/single_server/builder_service_plots.png
index 22fc27d..31c230e 100644
Binary files a/examples/builder_input/single_server/builder_service_plots.png and b/examples/builder_input/single_server/builder_service_plots.png differ
diff --git a/examples/builder_input/single_server/single_server.py b/examples/builder_input/single_server/single_server.py
index bb54344..7fb7e99 100644
--- a/examples/builder_input/single_server/single_server.py
+++ b/examples/builder_input/single_server/single_server.py
@@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
-#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
AsyncFlow builder example — build, run, and visualize a single-server async system.
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/data/event_inj_lb.yml b/examples/yaml_input/data/event_inj_lb.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5d97bc8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/yaml_input/data/event_inj_lb.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+# AsyncFlow SimulationPayload — LB + 2 servers (medium load) with events
+#
+# Topology:
+# generator → client → LB → srv-1
+# └→ srv-2
+# srv-1 → client
+# srv-2 → client
+#
+# Workload targets ~40 rps (120 users × 20 req/min ÷ 60).
+
+rqs_input:
+ id: rqs-1
+ avg_active_users: { mean: 120 }
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user: { mean: 20 }
+ user_sampling_window: 60
+
+topology_graph:
+ nodes:
+ client: { id: client-1 }
+
+ load_balancer:
+ id: lb-1
+ algorithms: round_robin
+ server_covered: [srv-1, srv-2]
+
+ servers:
+ - id: srv-1
+ server_resources: { cpu_cores: 1, ram_mb: 2048 }
+ endpoints:
+ - endpoint_name: /api
+ steps:
+ - kind: initial_parsing
+ step_operation: { cpu_time: 0.002 } # 2 ms CPU
+ - kind: ram
+ step_operation: { necessary_ram: 128 } # 128 MB
+ - kind: io_wait
+ step_operation: { io_waiting_time: 0.012 } # 12 ms I/O wait
+
+ - id: srv-2
+ server_resources: { cpu_cores: 1, ram_mb: 2048 }
+ endpoints:
+ - endpoint_name: /api
+ steps:
+ - kind: initial_parsing
+ step_operation: { cpu_time: 0.002 }
+ - kind: ram
+ step_operation: { necessary_ram: 128 }
+ - kind: io_wait
+ step_operation: { io_waiting_time: 0.012 }
+
+ edges:
+ - { id: gen-client, source: rqs-1, target: client-1, latency: { mean: 0.003, distribution: exponential } }
+ - { id: client-lb, source: client-1, target: lb-1, latency: { mean: 0.002, distribution: exponential } }
+ - { id: lb-srv1, source: lb-1, target: srv-1, latency: { mean: 0.002, distribution: exponential } }
+ - { id: lb-srv2, source: lb-1, target: srv-2, latency: { mean: 0.002, distribution: exponential } }
+ - { id: srv1-client, source: srv-1, target: client-1, latency: { mean: 0.003, distribution: exponential } }
+ - { id: srv2-client, source: srv-2, target: client-1, latency: { mean: 0.003, distribution: exponential } }
+
+sim_settings:
+ total_simulation_time: 600
+ sample_period_s: 0.05
+ enabled_sample_metrics:
+ - ready_queue_len
+ - event_loop_io_sleep
+ - ram_in_use
+ - edge_concurrent_connection
+ enabled_event_metrics:
+ - rqs_clock
+
+# Events:
+# - Edge spikes (added latency in seconds) that stress different paths at different times.
+# - Server outages that never overlap (so at least one server stays up).
+events:
+ # Edge spike: client → LB gets +15 ms from t=100s to t=160s
+ - event_id: ev-spike-1
+ target_id: client-lb
+ start: { kind: network_spike_start, t_start: 100.0, spike_s: 0.015 }
+ end: { kind: network_spike_end, t_end: 160.0 }
+
+ # Server outage: srv-1 down from t=180s to t=240s
+ - event_id: ev-srv1-down
+ target_id: srv-1
+ start: { kind: server_down, t_start: 180.0 }
+ end: { kind: server_up, t_end: 240.0 }
+
+ # Edge spike focused on srv-2 leg (LB → srv-2) from t=300s to t=360s (+20 ms)
+ - event_id: ev-spike-2
+ target_id: lb-srv2
+ start: { kind: network_spike_start, t_start: 300.0, spike_s: 0.020 }
+ end: { kind: network_spike_end, t_end: 360.0 }
+
+ # Server outage: srv-2 down from t=360s to t=420s (starts right after the spike ends)
+ - event_id: ev-srv2-down
+ target_id: srv-2
+ start: { kind: server_down, t_start: 360.0 }
+ end: { kind: server_up, t_end: 420.0 }
+
+ # Late spike on generator → client from t=480s to t=540s (+10 ms)
+ - event_id: ev-spike-3
+ target_id: gen-client
+ start: { kind: network_spike_start, t_start: 480.0, spike_s: 0.010 }
+ end: { kind: network_spike_end, t_end: 540.0 }
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/data/event_inj_single_server.yml b/examples/yaml_input/data/event_inj_single_server.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9e7d2ec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/yaml_input/data/event_inj_single_server.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+# ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
+# AsyncFlow scenario: generator ➜ client ➜ server ➜ client
+# with event injection (edge spike + server outage)
+# ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
+
+# 1) Traffic generator (light load)
+rqs_input:
+ id: rqs-1
+ avg_active_users: { mean: 100 }
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user: { mean: 20 }
+ user_sampling_window: 60
+
+# 2) Topology
+topology_graph:
+ nodes:
+ client: { id: client-1 }
+ servers:
+ - id: srv-1
+ server_resources: { cpu_cores: 1, ram_mb: 2048 }
+ endpoints:
+ - endpoint_name: ep-1
+ probability: 1.0
+ steps:
+ # CPU-bound parse (~1ms)
+ - kind: initial_parsing
+ step_operation: { cpu_time: 0.001 }
+ # Hold 100 MB while processing
+ - kind: ram
+ step_operation: { necessary_ram: 100 }
+ # Non-blocking I/O wait (~100ms)
+ - kind: io_wait
+ step_operation: { io_waiting_time: 0.1 }
+
+ edges:
+ - id: gen-to-client
+ source: rqs-1
+ target: client-1
+ latency: { mean: 0.003, distribution: exponential }
+
+ - id: client-to-server
+ source: client-1
+ target: srv-1
+ latency: { mean: 0.003, distribution: exponential }
+
+ - id: server-to-client
+ source: srv-1
+ target: client-1
+ latency: { mean: 0.003, distribution: exponential }
+
+# 3) Simulation settings
+sim_settings:
+ total_simulation_time: 500
+ sample_period_s: 0.05
+ enabled_sample_metrics:
+ - ready_queue_len
+ - event_loop_io_sleep
+ - ram_in_use
+ - edge_concurrent_connection
+ enabled_event_metrics:
+ - rqs_clock
+
+# 4) Events (validated by Pydantic)
+# - ev-spike-1: deterministic latency spike (+20ms) on the client→server edge
+# from t=120s to t=240s
+# - ev-outage-1: server outage for srv-1 from t=300s to t=360s
+events:
+ - event_id: ev-spike-1
+ target_id: client-to-server
+ start:
+ kind: network_spike_start
+ t_start: 120.0
+ spike_s: 2.00
+ end:
+ kind: network_spike_end
+ t_end: 240.0
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/data/heavy_inj_single_server.yml b/examples/yaml_input/data/heavy_inj_single_server.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..839cf33
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/yaml_input/data/heavy_inj_single_server.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+# ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
+# AsyncFlow scenario (HEAVY): generator ➜ client ➜ server ➜ client
+# Edge-latency spike + heavier workload to provoke queue growth.
+# ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
+
+# 1) Traffic generator (heavier load)
+rqs_input:
+ id: rqs-1
+ # More concurrent users and higher per-user rate drive the system harder.
+ avg_active_users: { mean: 300 }
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user: { mean: 30 }
+ user_sampling_window: 60
+
+# 2) Topology
+topology_graph:
+ nodes:
+ client: { id: client-1 }
+ servers:
+ - id: srv-1
+ # Keep just 1 CPU core so the server becomes a bottleneck.
+ server_resources: { cpu_cores: 1, ram_mb: 8000 }
+ endpoints:
+ - endpoint_name: ep-1
+ probability: 1.0
+ steps:
+ # Heavier CPU (~5 ms) to increase service time
+ - kind: initial_parsing
+ step_operation: { cpu_time: 0.005 }
+ # Larger working set to keep RAM busy
+ - kind: ram
+ step_operation: { necessary_ram: 200 }
+ # Longer I/O wait (~200 ms) to create a noticeable I/O queue
+ - kind: io_wait
+ step_operation: { io_waiting_time: 0.2 }
+
+ edges:
+ - id: gen-to-client
+ source: rqs-1
+ target: client-1
+ latency: { mean: 0.003, distribution: exponential }
+
+ - id: client-to-server
+ source: client-1
+ target: srv-1
+ latency: { mean: 0.003, distribution: exponential }
+
+ - id: server-to-client
+ source: srv-1
+ target: client-1
+ latency: { mean: 0.003, distribution: exponential }
+
+# 3) Simulation settings
+sim_settings:
+ # Longer horizon so we clearly see pre-/during-/post-spike behavior.
+ total_simulation_time: 600
+ sample_period_s: 0.05
+ enabled_sample_metrics:
+ - ready_queue_len
+ - event_loop_io_sleep
+ - ram_in_use
+ - edge_concurrent_connection
+ enabled_event_metrics:
+ - rqs_clock
+
+# 4) Events (validated by Pydantic)
+# Large deterministic edge spike (+3.0 s) during [180, 300] s on the
+# client→server edge. With the heavier workload, this should help
+# exacerbate queue growth/oscillations around the spike window.
+events:
+ - event_id: ev-spike-heavy
+ target_id: client-to-server
+ start:
+ kind: network_spike_start
+ t_start: 180.0
+ spike_s: 3.0
+ end:
+ kind: network_spike_end
+ t_end: 300.0
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/data/two_servers_lb.yml b/examples/yaml_input/data/two_servers_lb.yml
index 100a46b..6adf5cb 100644
--- a/examples/yaml_input/data/two_servers_lb.yml
+++ b/examples/yaml_input/data/two_servers_lb.yml
@@ -9,11 +9,11 @@
# Each server runs: CPU(2 ms) → RAM(128 MB) → IO wait(12 ms)
# All network links use exponential latency with small means (2–3 ms).
#
-# Workload targets ~40 rps (120 users × 20 req/min ÷ 60).
+
rqs_input:
id: rqs-1
- avg_active_users: { mean: 120 }
+ avg_active_users: { mean: 400 }
avg_request_per_minute_per_user: { mean: 20 }
user_sampling_window: 60
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server.py b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..72605af
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server.py
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+"""
+Run the *heavy* YAML scenario with event injections and export charts.
+
+Scenario file:
+ data/heavy_event_inj_single_server.yml
+
+Outputs (saved under a folder next to this script):
+ examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/
+ - heavy_event_inj_single_server_dashboard.png
+ - heavy_event_inj_single_server_ready_queue_.png
+ - heavy_event_inj_single_server_io_queue_.png
+ - heavy_event_inj_single_server_ram_.png
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from pathlib import Path
+
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+
+
+def main() -> None:
+ """Defines paths, runs the simulation, and generates all outputs."""
+ # --- 1. Define File Paths ---
+ script_dir = Path(__file__).parent
+ yaml_path = script_dir.parent / "data" / "heavy_inj_single_server.yml"
+ output_base_name = "heavy_inj_single_server"
+
+ if not yaml_path.exists():
+ msg = f"YAML configuration file not found: {yaml_path}"
+ raise FileNotFoundError(msg)
+
+ # Create/ensure the output directory (overwrite files if present).
+ out_dir = script_dir / "heavy_single_server_plot"
+ out_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+
+ # --- 2. Run the Simulation ---
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+ runner = SimulationRunner.from_yaml(env=env, yaml_path=yaml_path)
+ results: ResultsAnalyzer = runner.run()
+
+ # --- 3. Dashboard (latency + throughput) ---
+ fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))
+ results.plot_base_dashboard(axes[0], axes[1])
+ fig.tight_layout()
+ dash_path = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_dashboard.png"
+ fig.savefig(dash_path)
+ print(f"Saved: {dash_path}")
+
+ # --- 4. Per-server plots ---
+ for sid in results.list_server_ids():
+ # Ready queue
+ f1, a1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ results.plot_single_server_ready_queue(a1, sid)
+ f1.tight_layout()
+ p1 = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_ready_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f1.savefig(p1)
+ print(f"Saved: {p1}")
+
+ # I/O queue
+ f2, a2 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ results.plot_single_server_io_queue(a2, sid)
+ f2.tight_layout()
+ p2 = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_io_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f2.savefig(p2)
+ print(f"Saved: {p2}")
+
+ # RAM usage
+ f3, a3 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ results.plot_single_server_ram(a3, sid)
+ f3.tight_layout()
+ p3 = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_ram_{sid}.png"
+ f3.savefig(p3)
+ print(f"Saved: {p3}")
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ main()
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_dashboard.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_dashboard.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4662ae0
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_dashboard.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_io_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_io_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..941a8db
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_io_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_ram_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_ram_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1efba07
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_ram_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_ready_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_ready_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..23f09f3
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/heavy_single_server_plot/heavy_inj_single_server_ready_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers.py b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a2b666c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers.py
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+"""
+Run the YAML scenario with LB + 2 servers and export charts.
+
+Scenario file:
+ data/lb_two_servers_events.yml
+
+Outputs (saved in subfolder next to this script):
+ - dashboard PNG (latency + throughput)
+ - per-server PNGs: ready queue, I/O queue, RAM
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from pathlib import Path
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+
+
+def main() -> None:
+ """Defines paths, runs the simulation, and generates all outputs."""
+ # --- 1. Define paths ---
+ script_dir = Path(__file__).parent
+ yaml_path = script_dir.parent / "data" / "event_inj_lb.yml"
+
+ out_dir = script_dir / "lb_two_servers_plots"
+ out_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True) # create if missing
+
+ output_base_name = "lb_two_servers_events"
+
+ if not yaml_path.exists():
+ msg = f"YAML configuration file not found: {yaml_path}"
+ raise FileNotFoundError(msg)
+
+ # --- 2. Run the simulation ---
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+ runner = SimulationRunner.from_yaml(env=env, yaml_path=yaml_path)
+ results: ResultsAnalyzer = runner.run()
+
+ # --- 3. Dashboard (latency + throughput) ---
+ fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))
+ results.plot_base_dashboard(axes[0], axes[1])
+ fig.tight_layout()
+ dash_path = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_dashboard.png"
+ fig.savefig(dash_path)
+ print(f"Saved: {dash_path}")
+
+ # --- 4. Per-server plots ---
+ for sid in results.list_server_ids():
+ # Ready queue
+ f1, a1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ results.plot_single_server_ready_queue(a1, sid)
+ f1.tight_layout()
+ p1 = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_ready_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f1.savefig(p1)
+ print(f"Saved: {p1}")
+
+ # I/O queue
+ f2, a2 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ results.plot_single_server_io_queue(a2, sid)
+ f2.tight_layout()
+ p2 = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_io_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f2.savefig(p2)
+ print(f"Saved: {p2}")
+
+ # RAM usage
+ f3, a3 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ results.plot_single_server_ram(a3, sid)
+ f3.tight_layout()
+ p3 = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_ram_{sid}.png"
+ f3.savefig(p3)
+ print(f"Saved: {p3}")
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ main()
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_dashboard.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_dashboard.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f23ee2a
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_dashboard.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7565139
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-2.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3531413
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_io_queue_srv-2.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b0ccfbc
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-2.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c0a9ddc
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ram_srv-2.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7cdbbcf
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-2.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8b732ab
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/lb_two_servers_plots/lb_two_servers_events_ready_queue_srv-2.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server.py b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..58d1603
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server.py
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+"""
+Run the YAML scenario with event injections and export charts.
+
+Scenario file:
+ data/event_inj_single_server.yml
+
+Outputs (saved under a folder next to this script):
+ examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/
+ - event_inj_single_server_dashboard.png
+ - event_inj_single_server_ready_queue_.png
+ - event_inj_single_server_io_queue_.png
+ - event_inj_single_server_ram_.png
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from pathlib import Path
+
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+
+
+def main() -> None:
+ """Defines paths, runs the simulation, and generates all outputs."""
+ # --- 1. Define File Paths ---
+ script_dir = Path(__file__).parent # same folder as this file
+ yaml_path = script_dir.parent / "data" / "event_inj_single_server.yml"
+ output_base_name = "event_inj_single_server" # prefix for output files
+
+ if not yaml_path.exists():
+ msg = f"YAML configuration file not found: {yaml_path}"
+ raise FileNotFoundError(msg)
+
+ # Create/ensure the output directory:
+ out_dir = script_dir / "single_server_plot"
+ out_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+
+ # --- 2. Run the Simulation ---
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+ runner = SimulationRunner.from_yaml(env=env, yaml_path=yaml_path)
+ results: ResultsAnalyzer = runner.run()
+
+ # --- 3. Dashboard (latency + throughput) ---
+ fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))
+ results.plot_base_dashboard(axes[0], axes[1])
+ fig.tight_layout()
+ dash_path = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_dashboard.png"
+ fig.savefig(dash_path)
+ print(f"Saved: {dash_path}")
+
+ # --- 4. Per-server plots ---
+ for sid in results.list_server_ids():
+ # Ready queue
+ f1, a1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ results.plot_single_server_ready_queue(a1, sid)
+ f1.tight_layout()
+ p1 = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_ready_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f1.savefig(p1)
+ print(f"Saved: {p1}")
+
+ # I/O queue
+ f2, a2 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ results.plot_single_server_io_queue(a2, sid)
+ f2.tight_layout()
+ p2 = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_io_queue_{sid}.png"
+ f2.savefig(p2)
+ print(f"Saved: {p2}")
+
+ # RAM usage
+ f3, a3 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
+ results.plot_single_server_ram(a3, sid)
+ f3.tight_layout()
+ p3 = out_dir / f"{output_base_name}_ram_{sid}.png"
+ f3.savefig(p3)
+ print(f"Saved: {p3}")
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ main()
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_dashboard.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_dashboard.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c98a6a7
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_dashboard.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_io_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_io_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3a68e5e
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_io_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ram_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ram_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..404a2d9
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ram_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ready_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ready_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0ec5bbd
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/event_injections/single_server_plot/event_inj_single_server_ready_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/lb_dashboard.png b/examples/yaml_input/lb_dashboard.png
deleted file mode 100644
index dbe7d42..0000000
Binary files a/examples/yaml_input/lb_dashboard.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png b/examples/yaml_input/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6d3ac35..0000000
Binary files a/examples/yaml_input/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png b/examples/yaml_input/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 916c60f..0000000
Binary files a/examples/yaml_input/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers.py b/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers.py
index 1a01277..a6fb125 100644
--- a/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers.py
+++ b/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers.py
@@ -29,8 +29,11 @@
def main() -> None:
# Paths (same directory as this script)
- script_dir = Path(__file__).parent.parent
- yaml_path = script_dir / "data" / "two_servers_lb.yml"
+ script_dir = Path(__file__).parent
+ out_dir = script_dir / "two_servers_plot"
+ out_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+
+ yaml_path = script_dir.parent / "data" / "two_servers_lb.yml"
if not yaml_path.exists():
raise FileNotFoundError(f"YAML configuration not found: {yaml_path}")
@@ -49,8 +52,8 @@ def main() -> None:
results.plot_latency_distribution(axes_dash[0])
results.plot_throughput(axes_dash[1])
fig_dash.tight_layout()
- out_dashboard = script_dir / "lb_dashboard.png"
- fig_dash.savefig(out_dashboard)
+ out_dashboard = out_dir / "lb_dashboard.png"
+ fig_dash.savefig(out_dashboard, bbox_inches="tight")
print(f"🖼️ Dashboard saved to: {out_dashboard}")
# ---- Per-server metrics: one figure per server (Ready | I/O | RAM) ----
@@ -61,7 +64,7 @@ def main() -> None:
results.plot_single_server_ram(axes[2], sid)
fig_row.suptitle(f"Server metrics — {sid}", y=1.04, fontsize=14)
fig_row.tight_layout()
- out_path = script_dir / f"lb_server_{sid}_metrics.png"
+ out_path = out_dir / f"lb_server_{sid}_metrics.png"
fig_row.savefig(out_path, bbox_inches="tight")
print(f"🖼️ Server metrics for '{sid}' saved to: {out_path}")
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers_plot/lb_dashboard.png b/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers_plot/lb_dashboard.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..95c9a14
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers_plot/lb_dashboard.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers_plot/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png b/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers_plot/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..76ef6c5
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers_plot/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers_plot/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png b/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers_plot/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fac7f78
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/load_balancer/two_servers_plot/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server.py b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server.py
index ec14998..722de75 100644
--- a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server.py
+++ b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server.py
@@ -54,10 +54,12 @@
def main() -> None:
"""Defines paths, runs the simulation, and generates all outputs."""
# --- 1. Define File Paths ---
- script_dir = Path(__file__).parent # <-- same folder as this file
- out_dir = script_dir # <-- save outputs here
+ script_dir = Path(__file__).parent # same folder as this script
+ out_dir = script_dir / "single_server_plot" # outputs will go here
+ out_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # create if not exists
+
yaml_path = script_dir.parent / "data" / "single_server.yml"
- output_base_name = "single_server_results" # prefix for all output files
+ output_base_name = "single_server_results" # prefix for output files
if not yaml_path.exists():
raise FileNotFoundError(f"YAML configuration file not found: {yaml_path}")
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_dashboard.png b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_dashboard.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b54350d
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_dashboard.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_io_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_io_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c13b68e
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_io_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_ram_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_ram_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..511c132
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_ram_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_ready_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_ready_queue_srv-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4eaf2bd
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_plot/single_server_results_ready_queue_srv-1.png differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_dashboard.png b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_dashboard.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 0a6f994..0000000
Binary files a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_dashboard.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_io_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_io_queue_srv-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index f2bb1f0..0000000
Binary files a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_io_queue_srv-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_ram_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_ram_srv-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c7a33af..0000000
Binary files a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_ram_srv-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_ready_queue_srv-1.png b/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_ready_queue_srv-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 7539852..0000000
Binary files a/examples/yaml_input/single_server/single_server_results_ready_queue_srv-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/pyproject.toml b/pyproject.toml
index 3af003d..ca8f555 100644
--- a/pyproject.toml
+++ b/pyproject.toml
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
[tool.poetry]
name = "asyncflow-sim"
-version = "0.1.0a2"
+version = "0.1.1"
description = "Digital-twin simulator for distributed async systems. Build what-if scenarios and quantify capacity, latency and throughput offline, before you deploy."
authors = ["Gioele Botta"]
readme = "README.md"
diff --git a/readme_img/lb_dashboard.png b/readme_img/lb_dashboard.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..95c9a14
Binary files /dev/null and b/readme_img/lb_dashboard.png differ
diff --git "a/readme_img/lb_dashboard.png\357\200\272Zone.Identifier" "b/readme_img/lb_dashboard.png\357\200\272Zone.Identifier"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f46bcc4
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/readme_img/lb_dashboard.png\357\200\272Zone.Identifier"
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+[ZoneTransfer]
+ZoneId=3
diff --git a/readme_img/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png b/readme_img/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..76ef6c5
Binary files /dev/null and b/readme_img/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png differ
diff --git "a/readme_img/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png\357\200\272Zone.Identifier" "b/readme_img/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png\357\200\272Zone.Identifier"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f46bcc4
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/readme_img/lb_server_srv-1_metrics.png\357\200\272Zone.Identifier"
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+[ZoneTransfer]
+ZoneId=3
diff --git a/readme_img/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png b/readme_img/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fac7f78
Binary files /dev/null and b/readme_img/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png differ
diff --git "a/readme_img/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png\357\200\272Zone.Identifier" "b/readme_img/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png\357\200\272Zone.Identifier"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f46bcc4
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/readme_img/lb_server_srv-2_metrics.png\357\200\272Zone.Identifier"
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+[ZoneTransfer]
+ZoneId=3
diff --git a/readme_img/topology.png b/readme_img/topology.png
index bbb89e7..07fc170 100644
Binary files a/readme_img/topology.png and b/readme_img/topology.png differ
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/builder/asyncflow_builder.py b/src/asyncflow/builder/asyncflow_builder.py
index f6d2cea..ef33e7b 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/builder/asyncflow_builder.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/builder/asyncflow_builder.py
@@ -4,6 +4,8 @@
from typing import Self
+from asyncflow.config.constants import EventDescription
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import End, EventInjection, Start
from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
@@ -28,6 +30,7 @@ def __init__(self) -> None:
self._edges: list[Edge] | None = None
self._sim_settings: SimulationSettings | None = None
self._load_balancer: LoadBalancer | None = None
+ self._events: list[EventInjection] = []
def add_generator(self, rqs_generator: RqsGenerator) -> Self:
"""Method to instantiate the generator"""
@@ -88,6 +91,55 @@ def add_load_balancer(self, load_balancer: LoadBalancer) -> Self:
self._load_balancer = load_balancer
return self
+ # --------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+ # Events #
+ # --------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+
+ def add_network_spike(
+ self,
+ *,
+ event_id: str,
+ edge_id: str,
+ t_start: float,
+ t_end: float,
+ spike_s: float,
+ ) -> Self:
+ """Convenience: add a NETWORK_SPIKE on a given edge."""
+ event = EventInjection(
+ event_id=event_id,
+ target_id=edge_id,
+ start=Start(
+ kind=EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START,
+ t_start=t_start,
+ spike_s=spike_s,
+ ),
+ end=End(
+ kind=EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END,
+ t_end=t_end,
+ ),
+ )
+
+ self._events.append(event)
+ return self
+
+ def add_server_outage(
+ self,
+ *,
+ event_id: str,
+ server_id: str,
+ t_start: float,
+ t_end: float,
+ ) -> Self:
+ """Convenience: add a SERVER_DOWN → SERVER_UP window for a server."""
+ event = EventInjection(
+ event_id=event_id,
+ target_id=server_id,
+ start=Start(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, t_start=t_start),
+ end=End(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_UP, t_end=t_end),
+ )
+ self._events.append(event)
+ return self
+
def build_payload(self) -> SimulationPayload:
"""Method to build the payload for the simulation"""
if self._generator is None:
@@ -121,6 +173,7 @@ def build_payload(self) -> SimulationPayload:
"rqs_input": self._generator,
"topology_graph": graph,
"sim_settings": self._sim_settings,
+ "events": self._events or None,
})
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/components/__init__.py b/src/asyncflow/components/__init__.py
index 52d66c7..12e9e9e 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/components/__init__.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/components/__init__.py
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
"""Public components: re-exports Pydantic schemas (topology)."""
from __future__ import annotations
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
from asyncflow.schemas.topology.endpoint import Endpoint
from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import (
@@ -10,6 +11,14 @@
ServerResources,
)
-__all__ = ["Client", "Edge", "Endpoint", "LoadBalancer", "Server", "ServerResources"]
+__all__ = [
+ "Client",
+ "Edge",
+ "Endpoint",
+ "EventInjection",
+ "LoadBalancer",
+ "Server",
+ "ServerResources",
+ ]
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/config/constants.py b/src/asyncflow/config/constants.py
index de79a33..29b2229 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/config/constants.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/config/constants.py
@@ -175,6 +175,19 @@ class SystemEdges(StrEnum):
NETWORK_CONNECTION = "network_connection"
+# ======================================================================
+# CONSTANTS FOR THE EVENT TO INJECT IN THE SIMULATION
+# ======================================================================
+
+class EventDescription(StrEnum):
+ """Description for the events you may inject during the simulation"""
+
+ SERVER_UP = "server_up"
+ SERVER_DOWN = "server_down"
+ NETWORK_SPIKE_START = "network_spike_start"
+ NETWORK_SPIKE_END = "network_spike_end"
+
+
# ======================================================================
# CONSTANTS FOR SAMPLED METRICS
# ======================================================================
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/edge.py b/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/edge.py
index ee2131d..63c8f45 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/edge.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/edge.py
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
waits the sampled delay (and any resource wait) before delivering the
message to the target node's inbox.
"""
-from collections.abc import Generator
+from collections.abc import Container, Generator, Mapping
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
import numpy as np
@@ -23,25 +23,40 @@
from asyncflow.schemas.common.random_variables import RVConfig
-
class EdgeRuntime:
"""definining the logic to handle the edges during the simulation"""
- def __init__(
+ def __init__( # Noqa: PLR0913
self,
*,
env: simpy.Environment,
edge_config: Edge,
+
+ # ------------------------------------------------------------
+ # ATTRIBUTES FROM THE OBJECT EVENTINJECTIONRUNTIME
+ # We do not want to pass the full object EventInjectionRuntime
+ # we pass only the two structure necessary to add the spike
+ # in the case the edge is affected by increase latency
+ # We initiate both objects to None to dont break the API
+ # of SimulationRunner
+
+ edge_spike: Mapping[str, float] | None = None, # read-only view
+ edges_affected: Container[str] | None = None, # membership only
+ # -------------------------------------------------------------
+
rng: np.random.Generator | None = None,
target_box: simpy.Store,
settings: SimulationSettings,
+
) -> None:
"""Definition of the instance attributes"""
self.env = env
self.edge_config = edge_config
+ self.edges_spike = edge_spike
+ self.edges_affected = edges_affected
self.target_box = target_box
self.rng = rng or np.random.default_rng()
- self.setting = settings
+ self.settings = settings
self._edge_enabled_metrics = build_edge_metrics(
settings.enabled_sample_metrics,
)
@@ -73,7 +88,24 @@ def _deliver(self, state: RequestState) -> Generator[simpy.Event, None, None]:
self._concurrent_connections +=1
transit_time = general_sampler(random_variable, self.rng)
- yield self.env.timeout(transit_time)
+
+
+ # Logic to add if exists the event injection for the given edge
+ spike = 0.0
+ if (
+ self.edges_spike
+ and self.edges_affected
+ and self.edge_config.id in self.edges_affected
+ ):
+ spike = self.edges_spike.get(self.edge_config.id, 0.0)
+
+ # we do not use max(0.0, effective since) the transite time
+ # is positive, this condition is guaranteed from the pydantic
+ # validation
+
+ effective = transit_time + spike
+ yield self.env.timeout(effective)
+
state.record_hop(
SystemEdges.NETWORK_CONNECTION,
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/load_balancer.py b/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/load_balancer.py
index 498fb18..343cd84 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/load_balancer.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/load_balancer.py
@@ -1,16 +1,17 @@
"""Definition of the node represented by the LB in the simulation"""
+
+from collections import OrderedDict
from collections.abc import Generator
-from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+from typing import (
+ TYPE_CHECKING,
+)
import simpy
-from asyncflow.config.constants import LbAlgorithmsName, SystemNodes
+from asyncflow.config.constants import SystemNodes
from asyncflow.runtime.actors.edge import EdgeRuntime
-from asyncflow.runtime.actors.routing.lb_algorithms import (
- least_connections,
- round_robin,
-)
+from asyncflow.runtime.actors.routing.lb_algorithms import LB_TABLE
from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import LoadBalancer
if TYPE_CHECKING:
@@ -26,29 +27,38 @@ def __init__(
*,
env: simpy.Environment,
lb_config: LoadBalancer,
- out_edges: list[EdgeRuntime] | None,
+
+ # We use an OrderedDict because, for the RR algorithm,
+ # we rotate elements in O(1) by moving the selected key to the end.
+ # An OrderedDict also lets us remove an element by key in O(1)
+ # without implementing a custom doubly linked list + hashmap.
+ # Keys are the unique edge IDs that connect the LB to the servers.
+ # If multiple LBs are present, the SimulationRunner assigns
+ # the correct dict to each LB. Removals/insertions are performed
+ # by the EventInjectionRuntime.
+
+ lb_out_edges: OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime],
lb_box: simpy.Store,
) -> None:
"""
Descriprion of the instance attributes for the class
Args:
- env (simpy.Environment): env of the simulation
- lb_config (LoadBalancer): input to define the lb in the runtime
- rqs_state (RequestState): state of the simulation
- out_edges (list[EdgeRuntime]): list of edges that connects lb with servers
- lb_box (simpy.Store): store to add the state
-
+ env (simpy.Environment): Simulation environment.
+ lb_config (LoadBalancer): LB configuration for the runtime.
+ out_edges (OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]): Edges connecting
+ the LB to servers.
+ lb_box (simpy.Store): Queue (mailbox) from which the LB
+ consumes request states.
"""
self.env = env
self.lb_config = lb_config
- self.out_edges = out_edges
+ self.lb_out_edges = lb_out_edges
self.lb_box = lb_box
- self._round_robin_index: int = 0
+
def _forwarder(self) -> Generator[simpy.Event, None, None]:
"""Updtate the state before passing it to another node"""
- assert self.out_edges is not None
while True:
state: RequestState = yield self.lb_box.get() # type: ignore[assignment]
@@ -58,14 +68,7 @@ def _forwarder(self) -> Generator[simpy.Event, None, None]:
self.env.now,
)
- if self.lb_config.algorithms == LbAlgorithmsName.ROUND_ROBIN:
- out_edge, self._round_robin_index = round_robin(
- self.out_edges,
- self._round_robin_index,
- )
- else:
- out_edge = least_connections(self.out_edges)
-
+ out_edge = LB_TABLE[self.lb_config.algorithms](self.lb_out_edges)
out_edge.transport(state)
def start(self) -> simpy.Process:
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/routing/lb_algorithms.py b/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/routing/lb_algorithms.py
index 46078f7..47f950d 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/routing/lb_algorithms.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/routing/lb_algorithms.py
@@ -1,30 +1,45 @@
"""algorithms to simulate the load balancer during the simulation"""
+from collections import OrderedDict
+from collections.abc import Callable
-
+from asyncflow.config.constants import LbAlgorithmsName
from asyncflow.runtime.actors.edge import EdgeRuntime
-def least_connections(list_edges: list[EdgeRuntime]) -> EdgeRuntime:
- """We send the state to the edge with less concurrent connections"""
- concurrent_connections = [edge.concurrent_connections for edge in list_edges]
-
- idx_min = concurrent_connections.index(min(concurrent_connections))
-
- return list_edges[idx_min]
-
-def round_robin(edges: list[EdgeRuntime], idx: int) -> tuple[EdgeRuntime, int]:
+def least_connections(
+ edges: OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime],
+ ) -> EdgeRuntime:
+ """Return the edge with the fewest concurrent connections"""
+ # Here we use a O(n) operation, considering the amount of edges
+ # for the average simulation it should be ok, however, in the
+ # future we might consider to implement an heap structure to
+ # reduce the time complexity, especially if we will see
+ # during the Montecarlo analysis not good performances
+ name = min(edges, key=lambda k: edges[k].concurrent_connections)
+ return edges[name]
+
+def round_robin(
+ edges: OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime],
+ ) -> EdgeRuntime:
"""
We send states to different server in uniform way by
- rotating the list of edges that should transport the state
- to the correct server, we rotate the index and not the list
- to avoid aliasing since the list is shared by many components
+ rotating the ordered dict, given the pydantic validation
+ we don't have to manage the edge case where the dict
+ is empty
"""
- idx %= len(edges)
- chosen = edges[idx]
- idx = (idx + 1) % len(edges)
- return chosen, idx
+ # we use iter next creating all time a new iterator
+ # to be sure that we return always the first element
+ key, value = next(iter(edges.items()))
+ edges.move_to_end(key)
+
+ return value
+LB_TABLE: dict[LbAlgorithmsName,
+ Callable[[OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]], EdgeRuntime]] = {
+ LbAlgorithmsName.LEAST_CONNECTIONS: least_connections,
+ LbAlgorithmsName.ROUND_ROBIN: round_robin,
+}
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/server.py b/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/server.py
index 0572956..d83f94d 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/server.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/runtime/actors/server.py
@@ -113,27 +113,34 @@ def _handle_request( # noqa: PLR0915, PLR0912, C901
# CPU & RAM SCHEDULING
#
# RAM FIRST, CPU LATER
- # - The request reserves its full working set (total_ram) before
- # acquiring any CPU core. If memory isn't available, it stays
- # queued and leaves cores free for other requests.
+ # - The request reserves its full working set (total_ram) BEFORE
+ # trying to acquire a CPU core. If memory is not available, the
+ # request blocks on RAM and never enters the CPU/ready flow.
#
- # LAZY-CPU LOCK
- # - A core token is acquired only at the FIRST CPU step
- # (`if not core_locked`) and held for all consecutive CPU steps.
- # - As soon as an I/O step is encountered, the core is released
- # (`CPU.put(1)`) and remains free until the next CPU step,
- # which will re-acquire it.
+ # LAZY CPU-LOCK (CPU bursts)
+ # - A CPU token is acquired only at the FIRST CPU step of a burst
+ # (`if not core_locked`). Consecutive CPU steps reuse the same token.
+ # - As soon as an I/O step is encountered, the token is released
+ # (`CPU.put(1)`) and remains free until the next CPU step.
+ #
+ # READY QUEUE (new definition)
+ # - The ready queue tracks ONLY requests waiting for a core.
+ # - Increment ready when `CPU.get(1)` is NOT immediately satisfied
+ # (`event.triggered == False`).
+ # - Decrement ready right after the `yield cpu_req` succeeds,
+ # i.e. when the core is actually granted.
+ # - A request currently executing on a core (`core_locked=True`)
+ # is NOT counted in ready.
#
# WHY THIS IS REALISTIC
- # Prevents “core-hogging” during long I/O awaits.
- # Avoids redundant get/put calls for consecutive CPU steps
- # (one token for the entire sequence).
- # Mirrors a real Python async server: the GIL/worker thread is
- # held only during CPU-bound code and released on each await.
+ # - Prevents “core-hogging” during long I/O waits (the core is released).
+ # - Avoids redundant get/put calls on consecutive CPU steps.
+ # - Mirrors a real async server: a worker thread/GIL is held only
+ # during CPU-bound code and released on each `await` (I/O).
#
# END OF HANDLER
- # - If we still hold the core at the end (`core_locked == True`),
- # we put it back, then release the reserved RAM.
+ # - If the request still holds a core at the end, release it.
+ # - Then release the reserved RAM.
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Ask the necessary ram to the server
@@ -142,36 +149,49 @@ def _handle_request( # noqa: PLR0915, PLR0912, C901
self._ram_in_use += total_ram
- # Initial conditions of the server a rqs a priori is not in any queue
+ # Initial conditions of the server: a rqs a priori is not in any queue
# and it does not occupy a core until it started to be elaborated
+ # these are local variable so they are created for every request.
core_locked = False
is_in_io_queue = False
- is_in_ready_queue = False
+ waiting_cpu = False
- # --- Step Execution: Process CPU and IO operations ---
- # EDGE CASE
- # First-step I/O
- # A request could (in theory) start with an I/O step. In that case
- # it doesn't hold any core; we enter the
- # `not core_locked and not is_in_io_queue` branch and add +1
- # to the I/O queue without touching the ready queue.
+ # --- Step Execution: CPU & I/O dynamics ---
+ #
+ # EDGE CASE: First-step I/O
+ # - An endpoint can start with an I/O step: in that case the request
+ # holds no core (`core_locked=False`) and enters the I/O queue.
+ # Ready queue is unaffected. This is not realistic since the first
+ # step is usually related to the parsing of the requests however
+ # we prevent this case, since right now we dont have a pydantic
+ # validation to ensure the first step is CPU bounderd
#
# Consecutive I/O steps
- # The second I/O sees `is_in_io_queue == True`, so it does NOT
- # increment again—no double counting.
+ # - The second (and later) I/O step sees is_in_io_queue=True, so it
+ # does NOT increment again → no double-counting in I/O.
#
- # Transition CPU → I/O → CPU
- # - CPU step: `core_locked` becomes True, +1 ready queue
- # - I/O step: core is put back, -1 ready queue, +1 I/O queue
- # - Next CPU step: core is acquired, -1 I/O queue, +1 ready queue
+ # Transition CPU → I/O → CPU (with new ready semantics)
+ # - CPU step:
+ # * If no core is held, create cpu_req = CPU.get(1).
+ # * If cpu_req.triggered == False → the request is waiting → ready += 1.
+ # * After yield cpu_req (core granted) → ready -= 1, set core_locked=True.
+ # * A request currently executing on a core is NOT in ready.
+ # - I/O step:
+ # * If holding a core, release it (`CPU.put(1)`) and enter I/O queue (+1).
+ # * If already in I/O (consecutive step), do nothing (no double-counting).
+ # * Ready queue is never touched here.
+ # - Next CPU step:
+ # * Leave I/O queue (if counted) and repeat CPU acquisition logic.
+ # * If acquisition is not immediate, enter ready until the event resolves.
#
# Endpoint completion
- # If `core_locked == True` we were in the ready queue (-1)
- # Otherwise we were in the I/O queue (-1)
- # In both cases we clear the local flags so no “ghost” entries
- # remain in the global counters.
- # ------------------------------------------------------------------
+ # - If core_locked=True → release the core.
+ # - If is_in_io_queue=True → leave the I/O queue.
+ # - waiting_cpu should be False by now; if not, remove from ready defensively.
+ # - Invariant: the request must not remain counted in any queue once finished.
+ # -------------------------------------------------------------------
+
for step in selected_endpoint.steps:
@@ -183,19 +203,28 @@ def _handle_request( # noqa: PLR0915, PLR0912, C901
# in this configuration we are asking the cpu just in the
# first one
- if not core_locked:
- core_locked = True
+ if is_in_io_queue:
+ is_in_io_queue = False
+ self._el_io_queue_len -= 1
- if is_in_io_queue:
- is_in_io_queue = False
- self._el_io_queue_len -= 1
+ if not core_locked:
+ # simpy create an event and if it can be satisfied is triggered
+ cpu_req = self.server_resources[ServerResourceName.CPU.value].get(1)
- if not is_in_ready_queue:
- is_in_ready_queue = True
+ # no trigger ready queue without execution
+ if not cpu_req.triggered:
+ waiting_cpu = True
self._el_ready_queue_len += 1
+ # at this point wait for the cpu
+ yield cpu_req
- yield self.server_resources[ServerResourceName.CPU.value].get(1)
+ # here the cpu is free
+ if waiting_cpu:
+ waiting_cpu = False
+ self._el_ready_queue_len -= 1
+
+ core_locked = True
cpu_time = step.step_operation[StepOperation.CPU_TIME]
# Execute the step giving back the control to the simpy env
@@ -204,42 +233,40 @@ def _handle_request( # noqa: PLR0915, PLR0912, C901
# since the object is of an Enum class we check if the step.kind
# is one member of enum
elif step.kind in EndpointStepIO:
+ # define the io time
io_time = step.step_operation[StepOperation.IO_WAITING_TIME]
- # Same here with the boolean if we have multiple I/O steps
- # we release the core just the first time if the previous step
- # was a cpu bound step
-
- if not core_locked and not is_in_io_queue:
- is_in_io_queue = True
- self._el_io_queue_len += 1
-
if core_locked:
- # if the core is locked in the function it means that for sure
- # we had a cpu bound step so the if statement will be always
- # satisfy and we have to remove one element from the ready queue
-
- if is_in_ready_queue:
- is_in_ready_queue = False
- self._el_ready_queue_len -= 1
+ # release the core coming from a cpu step
+ yield self.server_resources[ServerResourceName.CPU.value].put(1)
+ core_locked = False
if not is_in_io_queue:
is_in_io_queue = True
self._el_io_queue_len += 1
+
+ # here is a sage check: the first step should always
+ # be a cpu bound (parsing of the request), if an user
+ # start with a I/O this allow to don't break the flux
+ elif not is_in_io_queue:
+ is_in_io_queue = True
+ self._el_io_queue_len += 1
- yield self.server_resources[ServerResourceName.CPU.value].put(1)
- core_locked = False
- yield self.env.timeout(io_time) # Wait without holding a CPU core
-
+ yield self.env.timeout(io_time)
if core_locked:
- is_in_ready_queue = False
- self._el_ready_queue_len -= 1
yield self.server_resources[ServerResourceName.CPU.value].put(1)
- else:
+ core_locked = False
+
+ if is_in_io_queue:
is_in_io_queue = False
self._el_io_queue_len -= 1
+ if waiting_cpu:
+ waiting_cpu = False
+ self._el_ready_queue_len -= 1
+
+
if total_ram:
self._ram_in_use -= total_ram
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/runtime/events/injection.py b/src/asyncflow/runtime/events/injection.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..753c5d3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/asyncflow/runtime/events/injection.py
@@ -0,0 +1,254 @@
+"""
+Centralized runtime object to inject events into the simulation.
+This covers, for example, deterministic network latency spikes on edges and
+scheduled server outages over a defined time window.
+"""
+from collections import OrderedDict
+from collections.abc import Generator
+from typing import cast
+
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow.runtime.actors.edge import EdgeRuntime
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import Server
+
+# Helpers to distinguish when the event start and when the event finish
+START_MARK = "start"
+END_MARK = "end"
+
+# definition of indexes for the tuple to be assigned for the timeline
+TIME = 0
+EVENT_ID = 1
+TARGET_ID = 2
+START_END = 3
+
+class EventInjectionRuntime:
+ """
+ Runtime container responsible for applying event effects.
+ It ingests validated EventInjection objects plus the current topology
+ (edges and servers) and exposes the state needed to activate/deactivate
+ event effects during the simulation.
+ """
+
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ *,
+ events: list[EventInjection] | None,
+ edges: list[Edge],
+ env: simpy.Environment,
+ servers: list[Server],
+ # This is initiated in the simulation runner to understand
+ # the process there are extensive comments in that file
+ lb_out_edges: OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime],
+ ) -> None:
+ """
+ Definition of the attributes of the instance for
+ the object EventInjectionRuntime
+
+ Args:
+ events (list[EventInjection]): input data of all events
+ edges (list[Edge]): input data for the edges
+ env (simpy.Environment): simpy env for the simulation
+ servers (list[Server]): input data of the server
+ lb_out_edges: OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]:
+ ordered dict to handle server events
+
+ """
+ self.events = events
+ self.edges = edges
+ self.env = env
+ self.servers = servers
+ self.lb_out_edges = lb_out_edges
+
+ # Nested mapping for edge spikes:
+ # edges_events: Dict[event_id, Dict[edge_id, float]]
+ # The outer key is the globally unique event_id. The inner mapping
+ # uses the target edge_id. Because multiple events can apply to the
+ # same edge, we use event_id as the primary key. The inner value
+ # stores the spike amplitude (in seconds) to apply while the event
+ # is active. It is necessary to compute superoposition of spike
+ # on the same target
+
+ self._edges_events: dict[str, dict[str, float]] = {}
+
+ # ---------------------------------------------------------
+ # THE FOLLOWING TWO INSTANCES ARE THE ONE NECESSARY TO ADD
+ # THE SPIKE DURING THE SIMULATION AND THEY WILL BE USED
+ # IN THE EDGERUNTIME CLASS
+ # ---------------------------------------------------------
+
+ # definition of a dictionary that will be useful in the
+ # Edge runtime to track the cumulative spike for a given edge
+ # alone, we need this in combination with the above nested map
+ # becuase as we said since we allow the superposition of spike
+ # we need the nested map to calculate the correct cumulative
+ # spike, in this way in the edge runtime we will need just
+ # the information of the edge id to have the correct cumulative
+ # spike
+ # The idea is a nested map to calculate and a suitable dict
+ # to be imported in edge runtime that with just the information
+ # of the edge id is able to assign the correct delay even
+ # with superposition of spike
+
+ self._edges_spike: dict[str, float] = {}
+
+ # We need a set for a fast lookup to determine if a given edge
+ # identifid with its own id is affected by an event
+
+ self._edges_affected: set[str] = set()
+
+ # ---------------------------------------------------------------
+
+ # Definition of timeline object, they represent a time
+ # ordered list of tuple that we will use to iterate to track
+ # and inject the events in the simulation
+
+ self._edges_timeline: list[tuple[float, str, str, str]] = []
+ self._servers_timeline: list[tuple[float, str, str, str]] = []
+
+ # No events we do not have to do any operation
+ if not self.events:
+ return
+
+ # Set for a fast lookup to fill the nested map and
+ self._servers_ids = {server.id for server in self.servers}
+ self._edges_ids = {edge.id for edge in self.edges}
+
+ for event in self.events:
+ start_event = (
+ event.start.t_start, event.event_id, event.target_id, START_MARK,
+ )
+ end_event = (
+ event.end.t_end, event.event_id, event.target_id, END_MARK,
+ )
+
+ if event.target_id in self._edges_ids:
+ spike = event.start.spike_s
+ assert spike is not None
+ self._edges_events.setdefault(
+ event.event_id,
+ {})[event.target_id] = spike
+
+ self._edges_timeline.append(start_event)
+ self._edges_timeline.append(end_event)
+ self._edges_affected.add(event.target_id)
+ elif event.target_id in self._servers_ids:
+ self._servers_timeline.append(start_event)
+ self._servers_timeline.append(end_event)
+
+ # Order the two timeline with lambda functions
+ self._edges_timeline.sort(
+ key=lambda e: (
+ e[TIME], e[START_END] == START_MARK, e[EVENT_ID], e[TARGET_ID],
+ ),
+ )
+ self._servers_timeline.sort(
+ key=lambda e: (
+ e[TIME], e[START_END] == START_MARK, e[EVENT_ID], e[TARGET_ID],
+ ),
+ )
+
+ # This function is useful to assign to connect the server id
+ # that will be down to the edge runtime that we have to remove
+ # from the ordered dict
+
+ # Build reverse index: server_id -> (edge_id, EdgeRuntime)
+ self._edge_by_server: dict[str, tuple[str, EdgeRuntime]] = {}
+
+ for edge_id, edge_runtime in lb_out_edges.items():
+ # Each EdgeRuntime has an associated Edge config.
+ # The .edge_config.target corresponds to the server_id.
+ server_id = edge_runtime.edge_config.target
+ self._edge_by_server[server_id] = (edge_id, edge_runtime)
+
+
+ def _assign_edges_spike(self) -> Generator[simpy.Event, None, None]:
+ """
+ Function to manage the assignment of the cumulative spikes
+ during the simulation.
+ The timeline contains absolute timestamps (seconds since t=0).
+ SimPy expects relative waits, so we advance by dt = t_event - last_t.
+ After waiting up to the event time, we apply the state change.
+ END comes before START at identical timestamps thanks to sorting.
+ """
+ last_t: float = float(self.env.now) # usually 0.0 at start
+
+ for event in self._edges_timeline:
+ # Explicit type for mypy
+ t: float = cast("float", event[TIME])
+ event_id: str = cast("str", event[EVENT_ID])
+ edge_id: str = cast("str", event[TARGET_ID])
+ mark: str = cast("str", event[START_END])
+
+ dt: float = t - last_t
+ if dt > 0.0:
+ yield self.env.timeout(dt)
+ last_t = t
+
+ # Apply the effect at the instant when the event start
+ if mark == START_MARK:
+ current = self._edges_spike.get(edge_id, 0.0)
+ delta = self._edges_events[event_id][edge_id]
+ self._edges_spike[edge_id] = current + delta
+ else: # END_MARK
+ current = self._edges_spike.get(edge_id, 0.0)
+ delta = self._edges_events[event_id][edge_id]
+ self._edges_spike[edge_id] = current - delta
+
+
+ def _assign_server_state(self) -> Generator[simpy.Event, None, None]:
+ last_t: float = float(self.env.now)
+ for ev in self._servers_timeline:
+ t = cast("float", ev[TIME])
+ server_id = cast("str", ev[TARGET_ID])
+ mark = cast("str", ev[START_END])
+
+ dt = t - last_t
+ if dt > 0.0:
+ yield self.env.timeout(dt)
+ last_t = t
+
+ edge_info = self._edge_by_server.get(server_id)
+ if not edge_info:
+ continue
+ edge_id, edge_runtime = edge_info
+
+ if mark == START_MARK:
+ # server DOWN: remove edge from the ordered dict
+ self.lb_out_edges.pop(edge_id, None)
+ else:
+ # server UP: put the edge server lb
+ # back in the ordered dict with the
+ # policy to move it at the end
+ self.lb_out_edges[edge_id] = edge_runtime
+ self.lb_out_edges.move_to_end(edge_id)
+
+
+
+
+
+ def start(self) -> tuple[simpy.Process, simpy.Process]:
+ """Start both edge-spike and server-outage timelines."""
+ p1 = self.env.process(self._assign_edges_spike())
+ p2 = self.env.process(self._assign_server_state())
+ return p1, p2
+
+ @property
+ def edges_spike(self) -> dict[str, float]:
+ """
+ Expose the value of the private dict, this will be
+ used in the edge runtime to determine the current,
+ if exist, network spike
+ """
+ return self._edges_spike
+
+ @property
+ def edges_affected(self) -> set[str]:
+ """
+ Expose the value of the private set, this will be
+ used in the edge runtime to determine the current,
+ if exist, network spike
+ """
+ return self._edges_affected
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/runtime/simulation_runner.py b/src/asyncflow/runtime/simulation_runner.py
index 5d112ae..08ae0df 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/runtime/simulation_runner.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/runtime/simulation_runner.py
@@ -1,7 +1,11 @@
"""Components to run the whole simulation given specific input data"""
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from collections import OrderedDict
from itertools import chain
from pathlib import Path
+from types import MappingProxyType
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Protocol, cast
import numpy as np
@@ -16,11 +20,13 @@
from asyncflow.runtime.actors.load_balancer import LoadBalancerRuntime
from asyncflow.runtime.actors.rqs_generator import RqsGeneratorRuntime
from asyncflow.runtime.actors.server import ServerRuntime
+from asyncflow.runtime.events.injection import EventInjectionRuntime
from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
if TYPE_CHECKING:
from collections.abc import Iterable
+ from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import (
Client,
@@ -63,18 +69,51 @@ def __init__(
# instantiation of object needed to build nodes for the runtime phase
self.servers: list[Server] = simulation_input.topology_graph.nodes.servers
self.client: Client = simulation_input.topology_graph.nodes.client
+ self.events: list[EventInjection] | None = None
self.rqs_generator: RqsGenerator = simulation_input.rqs_input
self.lb: LoadBalancer | None = None
self.simulation_settings = simulation_input.sim_settings
self.edges: list[Edge] = simulation_input.topology_graph.edges
self.rng = np.random.default_rng()
- # Object needed to start the simualation
+ # Object needed to start the simulation
self._servers_runtime: dict[str, ServerRuntime] = {}
self._client_runtime: dict[str, ClientRuntime] = {}
self._rqs_runtime: dict[str, RqsGeneratorRuntime] = {}
- self._lb_runtime: dict[str, LoadBalancerRuntime] = {}
+ # right now we allow max one LB per simulation so we don't need a dict
+ self._lb_runtime: LoadBalancerRuntime | None = None
self._edges_runtime: dict[tuple[str, str], EdgeRuntime] = {}
+ self._events_runtime: EventInjectionRuntime | None = None
+
+ # Initialization of the OrderedDict used for event injection.
+ # This structure allows us to temporarily shut down servers by removing
+ # their edges from the load balancer during the simulation. The choice
+ # of OrderedDict is motivated by its mutability and O(1) operations for
+ # both removal (by key) and moving an element to the end.
+ #
+ # Advantages of this approach:
+ # 1) We allocate a single shared object in memory.
+ # 2) The same object is aliased in both LoadBalancerRuntime and
+ # EventInjectionRuntime, so updates are reflected dynamically.
+ #
+ # Workflow:
+ # - Instantiate the OrderedDict here.
+ # - Remove edges (LB→server connections) in EventInjectionRuntime
+ # when a server goes down.
+ # - Pass the same OrderedDict to LoadBalancerRuntime, which will
+ # apply its algorithm (RR, LeastConnections) only to the currently
+ # available edges.
+ #
+ # Notes:
+ # - Pydantic ensures that at least one server remains available, so the
+ # condition "all servers down" is not allowed.
+ # - Shutting down a server by cutting its edge reduces the number of
+ # SimPy processes to manage, because we skip transport to a down
+ # server entirely.
+ # - This also avoids extra conditions or policies on the server side to
+ # check whether the server is up or down.
+
+ self._lb_out_edges: OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime] = OrderedDict()
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
@@ -144,7 +183,7 @@ def _build_load_balancer(self) -> None:
"""
Build given the input data the load balancer runtime we will
use a dict because we may have multiple load balancer and we
- will be usefull to assign outer edges
+ will be useful to assign outer edges
"""
# Topologies without a LB are perfectly legal (e.g. the “minimal”
# integration test). Early-return instead of asserting.
@@ -153,14 +192,16 @@ def _build_load_balancer(self) -> None:
self.lb = self.simulation_input.topology_graph.nodes.load_balancer
- self._lb_runtime[self.lb.id] = LoadBalancerRuntime(
+ self._lb_runtime = LoadBalancerRuntime(
env=self.env,
lb_config=self.lb,
- out_edges= [],
+ lb_out_edges = self._lb_out_edges,
lb_box=self._make_inbox(),
)
+
+
def _build_edges(self) -> None:
"""Initialization of the edges runtime dictionary from the input data"""
# We need to merge all previous dictionary for the nodes to assign
@@ -168,9 +209,11 @@ def _build_edges(self) -> None:
all_nodes: dict[str, object] = {
**self._servers_runtime,
**self._client_runtime,
- **self._lb_runtime,
**self._rqs_runtime,
-}
+ }
+
+ if self._lb_runtime is not None:
+ all_nodes[self._lb_runtime.lb_config.id] = self._lb_runtime
for edge in self.edges:
@@ -186,6 +229,7 @@ def _build_edges(self) -> None:
msg = f"Unknown runtime for {edge.target!r}"
raise TypeError(msg)
+
self._edges_runtime[(edge.source, edge.target)] = (
EdgeRuntime(
env=self.env,
@@ -208,18 +252,49 @@ def _build_edges(self) -> None:
edge.target)
]
elif isinstance(source_object, LoadBalancerRuntime):
- assert source_object.out_edges is not None
- source_object.out_edges.append(self._edges_runtime[(
- edge.source,
- edge.target,
- )
- ])
-
+ self._lb_out_edges[edge.id] = (
+ self._edges_runtime[(edge.source, edge.target)]
+ )
else:
msg = f"Unknown runtime for {edge.source!r}"
raise TypeError(msg)
+
+ def _build_events(self) -> None:
+ """
+ Function to centralize the events logic: with this function
+ we attach all events to the components affected
+ """
+ if not self.simulation_input.events or self._events_runtime is not None:
+ return
+
+ self.events = self.simulation_input.events
+ self._events_runtime = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=self.events,
+ edges=self.edges,
+ env=self.env,
+ servers=self.servers,
+ lb_out_edges=self._lb_out_edges,
+ )
+
+ # container only readable
+ edges_affected_view = self._events_runtime.edges_affected
+
+ # only readable map
+ edges_spike_view = MappingProxyType(self._events_runtime.edges_spike)
+
+ # We assign the two objects to all edges even though there are no
+ # events affecting them, this case is managed in the EdgeRuntime
+ # In the future we may control here if an edge is affected from an
+ # event this should have some advantage at the level of ram
+
+ for edge in self._edges_runtime.values():
+ edge.edges_affected = edges_affected_view
+ edge.edges_spike = edges_spike_view
+
+
+
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# RUN phase #
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
@@ -242,7 +317,7 @@ def _start_all_processes(self) -> None:
self._rqs_runtime.values(),
self._client_runtime.values(),
self._servers_runtime.values(),
- self._lb_runtime.values(),
+ ([] if self._lb_runtime is None else [self._lb_runtime]),
)
# Here we are saying to mypy that those object are of
@@ -250,6 +325,7 @@ def _start_all_processes(self) -> None:
for rt in cast("Iterable[Startable]", runtimes):
rt.start()
+
def _start_metric_collector(self) -> None:
"""One coroutine that snapshots RAM / queues / connections."""
SampledMetricCollector(
@@ -259,6 +335,14 @@ def _start_metric_collector(self) -> None:
sim_settings=self.simulation_settings,
).start()
+
+ def _start_events(self) -> None:
+ """Function to start the process to build events"""
+ if self._events_runtime is not None:
+ self._events_runtime.start()
+
+
+
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
# Public entry-point #
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
@@ -273,7 +357,11 @@ def run(self) -> ResultsAnalyzer:
# 2. WIRE
self._build_edges()
+ # 3 ATTACH EVENTS TO THE COMPONENTS
+ self._build_events()
+
# 3. START ALL COROUTINES
+ self._start_events()
self._start_all_processes()
self._start_metric_collector()
@@ -296,7 +384,7 @@ def from_yaml(
*,
env: simpy.Environment,
yaml_path: str | Path,
- ) -> "SimulationRunner":
+ ) -> SimulationRunner:
"""
Quick helper so that integration tests & CLI can do:
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/schemas/events/injection.py b/src/asyncflow/schemas/events/injection.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..266f920
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/asyncflow/schemas/events/injection.py
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
+"""Pydantic model to inject event during the simulation"""
+
+from typing import Literal
+
+from pydantic import (
+ BaseModel,
+ ConfigDict,
+ NonNegativeFloat,
+ PositiveFloat,
+ model_validator,
+)
+
+from asyncflow.config.constants import EventDescription
+
+# Event input schema:
+# - Each event has its own identifier (event_id) and references the affected
+# component via target_id.
+# - The event window is represented by two markers, Start and End.
+# - We constrain kind with Literal[...] over EventDescription (a StrEnum),
+# so Pydantic enforces allowed values automatically for both Start and End.
+# - Both marker models use ConfigDict(extra="forbid", frozen=True):
+# extra="forbid" rejects unknown fields (e.g., catches t_strat vs t_start);
+# frozen=True makes instances immutable at runtime for stability.
+
+class Start(BaseModel):
+ """Start marker for an event window."""
+
+ model_config = ConfigDict(extra="forbid", frozen=True)
+
+ # Only "start" kinds allowed here
+ kind: Literal[
+ EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN,
+ EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START,
+ ]
+ t_start: NonNegativeFloat # seconds from simulation start
+ spike_s: None | PositiveFloat = None
+
+
+
+class End(BaseModel):
+ """End marker for an event window."""
+
+ model_config = ConfigDict(extra="forbid", frozen=True)
+
+ # Only "end" kinds allowed here
+ kind: Literal[
+ EventDescription.SERVER_UP,
+ EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END,
+ ]
+ t_end: PositiveFloat # strictly > 0
+
+class EventInjection(BaseModel):
+ """Definition of the input structure to define an event in the simulation"""
+
+ event_id: str
+ target_id: str
+ start: Start
+ end: End
+
+ # Yaml example:
+ # event_id: ev-1
+ # target_id: srv-1
+ # start: { kind: SERVER_DOWN, t_start: 120.0 }
+ # end: { kind: SERVER_UP, t_end: 240.0 }
+
+ @model_validator(mode="after") # type: ignore[arg-type]
+ def ensure_start_end_compatibility(
+ cls, # noqa: N805
+ model: "EventInjection",
+ ) -> "EventInjection":
+ """
+ Check the compatibility between Start and End both at level
+ of time interval and kind
+ """
+ # Ensure kind for Start and End are compatible
+ start_to_end = {
+ EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN: EventDescription.SERVER_UP,
+ EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START: EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END,
+ }
+
+ expected = start_to_end[model.start.kind]
+ if model.end.kind != expected:
+ msg = (f"The event {model.event_id} must have "
+ f"as value of kind in end {expected}")
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+ # Ensure the time sequence is well defined
+ if model.start.t_start >= model.end.t_end:
+ msg=(f"The starting time for the event {model.event_id} "
+ "must be smaller than the ending time")
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+ return model
+
+
+ @model_validator(mode="after") # type: ignore[arg-type]
+ def ensure_spike_exist_on_network_event(
+ cls, # noqa: N805
+ model: "EventInjection",
+ ) -> "EventInjection":
+ """
+ When a network event is selected the spike must be
+ indicated
+ """
+ if (model.start.kind == EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START
+ and model.start.spike_s is None):
+ msg = (
+ f"The field spike_s for the event {model.event_id} "
+ "must be defined as a positive float"
+ )
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+ if (model.start.kind != EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START
+ and model.start.spike_s is not None):
+ msg = f"Event {model.event_id}: spike_s must be omitted"
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+
+ return model
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/schemas/payload.py b/src/asyncflow/schemas/payload.py
index 3c889e4..cd5cf7d 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/schemas/payload.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/schemas/payload.py
@@ -1,7 +1,9 @@
"""Definition of the full input for the simulation"""
-from pydantic import BaseModel
+from pydantic import BaseModel, field_validator, model_validator
+from asyncflow.config.constants import EventDescription
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
from asyncflow.schemas.topology.graph import TopologyGraph
from asyncflow.schemas.workload.rqs_generator import RqsGenerator
@@ -13,3 +15,240 @@ class SimulationPayload(BaseModel):
rqs_input: RqsGenerator
topology_graph: TopologyGraph
sim_settings: SimulationSettings
+ events: list[EventInjection] | None = None
+
+ @field_validator("events", mode="after")
+ def ensure_event_id_is_unique(
+ cls, # noqa: N805
+ v: list[EventInjection] | None,
+ ) -> list[EventInjection] | None:
+ """Ensure the id uniqueness of the events id"""
+ if v is None:
+ return v
+
+ event_id = [event.event_id for event in v]
+ set_event_id = set(event_id)
+
+ if len(event_id) != len(set_event_id):
+ msg = "The id's representing different events must be unique"
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+ return v
+
+ @model_validator(mode="after") # type: ignore[arg-type]
+ def ensure_components_ids_is_compatible(
+ cls, # noqa: N805
+ model: "SimulationPayload",
+ ) -> "SimulationPayload":
+ """
+ Ensure the id related to the target component of the event
+ exist
+ """
+ if model.events is None:
+ return model
+
+ servers_list = model.topology_graph.nodes.servers
+ edges_list = model.topology_graph.edges
+ valid_ids = (
+ {server.id for server in servers_list}
+ | {edge.id for edge in edges_list}
+ )
+
+ for event in model.events:
+ if event.target_id not in valid_ids:
+ msg = (f"The target id {event.target_id} related to "
+ f"the event {event.event_id} does not exist")
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+ return model
+
+ @model_validator(mode="after") # type: ignore[arg-type]
+ def ensure_event_time_inside_simulation_horizon(
+ cls, # noqa: N805
+ model: "SimulationPayload",
+ ) -> "SimulationPayload":
+ """
+ The time interval associated to each event must be in
+ the simulation horizon
+ """
+ if model.events is None:
+ return model
+
+ horizon = float(model.sim_settings.total_simulation_time)
+
+ for ev in model.events:
+ t_start = ev.start.t_start
+ t_end = ev.end.t_end
+
+ if t_start < 0.0:
+ msg = (
+ f"Event '{ev.event_id}': start time t_start={t_start:.6f} "
+ "must be >= 0.0"
+ )
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+ if t_start > horizon:
+ msg = (
+ f"Event '{ev.event_id}': start time t_start={t_start:.6f} "
+ f"exceeds simulation horizon T={horizon:.6f}"
+ )
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+ # t_end is PositiveFloat by schema, but still guard the horizon.
+ if t_end > horizon:
+ msg = (
+ f"Event '{ev.event_id}': end time t_end={t_end:.6f} "
+ f"exceeds simulation horizon T={horizon:.6f}"
+ )
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+ return model
+
+ @model_validator(mode="after") # type: ignore[arg-type]
+ def ensure_compatibility_event_kind_target_id(
+ cls, # noqa: N805
+ model: "SimulationPayload",
+ ) -> "SimulationPayload":
+ """
+ The kind of the event must be compatible with the target id
+ type, for example we cannot have an event regarding a server
+ with a target id associated to an edge
+ """
+ if model.events is None:
+ return model
+
+ servers_list = model.topology_graph.nodes.servers
+ edges_list = model.topology_graph.edges
+
+ # We need just the Start or End kind because
+ # we have a validation for the coherence between
+ # the starting event kind and the finishing event kind
+ server_kind = {EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN}
+ edge_kind = {EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START}
+
+ servers_ids = {server.id for server in servers_list}
+ edges_ids = {edge.id for edge in edges_list}
+
+ for event in model.events:
+ if event.start.kind in server_kind and event.target_id not in servers_ids:
+ msg = (f"The event {event.event_id} regarding a server does not have "
+ "a compatible target id")
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+ if event.start.kind in edge_kind and event.target_id not in edges_ids:
+ msg = (f"The event {event.event_id} regarding an edge does not have "
+ "a compatible target id")
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+
+ return model
+
+
+ @model_validator(mode="after") # type: ignore[arg-type]
+ def ensure_not_all_servers_are_down_simultaneously(
+ cls, # noqa: N805
+ model: "SimulationPayload",
+ ) -> "SimulationPayload":
+ """
+ We will not accept the condition to have all server down
+ at the same moment, always at least one server must be up
+ and running
+ """
+ if model.events is None:
+ return model
+
+ # First let us build a list of events related to the servers
+ servers_list = model.topology_graph.nodes.servers
+ servers_ids = {server.id for server in servers_list}
+ server_events = [
+ event for event in model.events
+ if event.target_id in servers_ids
+ ]
+
+ # Helpers needed in the algorithm to define a specific ordering
+ # procedure
+ start = "start"
+ end = "end"
+
+ # Let us define a list of tuple as a timeline, this approach ensure
+ # the possibility to have different servers going up or down at the
+ # same time, a more elegant approach through an hashmap has been
+ # considered however it would require an extra assumption that all
+ # the times had to be different, we thought that this would be too
+ # strict
+ timeline: list[tuple[float, str, str]] = []
+ for event in server_events:
+ timeline.append((event.start.t_start, start, event.target_id))
+ timeline.append((event.end.t_end, end, event.target_id))
+
+ # Let us order the timeline by time if there are multiple events at the
+ # same time process first the end type events
+ timeline.sort(key=lambda x: (x[0], x[1] == start))
+
+ # Definition of a set to verify the condition that at least one server must
+ # be up
+ server_down = set()
+ for time, kind, server_id in timeline:
+ if kind == end:
+ server_down.discard(server_id)
+ else: # "start"
+ server_down.add(server_id)
+ if len(server_down) == len(servers_ids):
+ msg = (
+ f"At time {time:.6f} all servers are down; keep at least one up"
+ )
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+
+ return model
+
+
+ @model_validator(mode="after") # type: ignore[arg-type]
+ def forbid_overlapping_server_outages(
+ cls, # noqa: N805
+ model: "SimulationPayload",
+ ) -> "SimulationPayload":
+ """
+ Forbid overlapping SERVER_DOWN intervals targeting the same server.
+
+ Rationale:
+ - Keeps runtime simple (no reference counting).
+ - Allows back-to-back windows (END at t and START at t) thanks to sorting
+ END before START at the same timestamp.
+ """
+ events = model.events
+ if not events:
+ return model
+
+ servers_ids = {s.id for s in model.topology_graph.nodes.servers}
+
+ # Build per-server timelines with (time, kind) marks only for server outages
+ per_server: dict[str, list[tuple[float, str]]] = {}
+ for ev in events:
+ if (
+ ev.target_id in servers_ids
+ and ev.start.kind == EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN
+ ):
+ per_server.setdefault(
+ ev.target_id, []).append((ev.start.t_start, "start"),
+ )
+ per_server[ev.target_id].append((ev.end.t_end, "end"))
+
+ # Sweep-line per server: sort by (time, END first), ensure active<=1
+ for srv_id, timeline in per_server.items():
+ if not timeline:
+ continue
+ # END before START at same t
+ timeline.sort(key=lambda x: (x[0], x[1] == "start"))
+ active = 0
+ for t, mark in timeline:
+ if mark == "end":
+ if active > 0:
+ active -= 1
+ else: # START
+ if active >= 1:
+ msg = (f"Overlapping events for server '{srv_id}' at t={t:.6f};"
+ " server outage windows must not overlap.")
+ raise ValueError(msg)
+ active += 1
+
+ return model
+
+
diff --git a/src/asyncflow/schemas/topology/nodes.py b/src/asyncflow/schemas/topology/nodes.py
index d742421..5ada69b 100644
--- a/src/asyncflow/schemas/topology/nodes.py
+++ b/src/asyncflow/schemas/topology/nodes.py
@@ -141,6 +141,8 @@ class TopologyNodes(BaseModel):
servers: list[Server]
client: Client
+ # Right now we accept just one LB, in the future we
+ # will change this
load_balancer: LoadBalancer | None = None
@model_validator(mode="after") # type: ignore[arg-type]
diff --git a/tests/conftest.py b/tests/conftest.py
index 80955f0..6834764 100644
--- a/tests/conftest.py
+++ b/tests/conftest.py
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
"""Pytest configuration file for setting up test fixtures and plugins."""
-
import pytest
+import simpy
from numpy.random import Generator as NpGenerator
from numpy.random import default_rng
@@ -150,4 +150,13 @@ def payload_base(
rqs_input=rqs_input,
topology_graph=topology_minimal,
sim_settings=sim_settings,
+
)
+
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+# Simpy env #
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+@pytest.fixture
+def env() -> simpy.Environment:
+ """Return a fresh SimPy environment per test."""
+ return simpy.Environment()
diff --git a/tests/integration/event_injection/lb_two_servers.py b/tests/integration/event_injection/lb_two_servers.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4272719
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/event_injection/lb_two_servers.py
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+"""Integration test: LB with two servers and concurrent event injections.
+
+Topology:
+
+ rqs-1 → client-1 → lb-1 → {srv-1, srv-2}
+ srv-* → client-1
+
+Events:
+- NETWORK_SPIKE on 'client-to-lb' in [0.20, 0.35].
+- SERVER_DOWN/UP on 'srv-1' in [0.40, 0.55].
+
+Assertions:
+- Simulation completes.
+- Latency stats and throughput exist.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow.config.constants import Distribution, EventDescription, LatencyKey
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+from asyncflow.schemas.common.random_variables import RVConfig
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
+from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
+from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.graph import TopologyGraph
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import (
+ Client,
+ LoadBalancer,
+ Server,
+ ServerResources,
+ TopologyNodes,
+)
+from asyncflow.schemas.workload.rqs_generator import RqsGenerator
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+
+
+def _server(sid: str) -> Server:
+ return Server(id=sid, server_resources=ServerResources(), endpoints=[])
+
+
+def _edge(eid: str, src: str, tgt: str, mean: float = 0.002) -> Edge:
+ return Edge(
+ id=eid,
+ source=src,
+ target=tgt,
+ latency=RVConfig(mean=mean, distribution=Distribution.POISSON),
+ )
+
+
+def test_lb_two_servers_with_events_end_to_end() -> None:
+ """Round-robin LB with events; check that KPIs are produced."""
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+ rqs = RqsGenerator(
+ id="rqs-1",
+ avg_active_users=RVConfig(mean=1.0),
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user=RVConfig(mean=2.0),
+ user_sampling_window=10.0,
+ )
+ sim = SimulationSettings(total_simulation_time=0.8)
+
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+ lb = LoadBalancer(id="lb-1")
+ srv1 = _server("srv-1")
+ srv2 = _server("srv-2")
+
+ edges = [
+ _edge("gen-to-client", "rqs-1", "client-1"),
+ _edge("client-to-lb", "client-1", "lb-1"),
+ _edge("lb-to-srv1", "lb-1", "srv-1"),
+ _edge("lb-to-srv2", "lb-1", "srv-2"),
+ _edge("srv1-to-client", "srv-1", "client-1"),
+ _edge("srv2-to-client", "srv-2", "client-1"),
+ ]
+ nodes = TopologyNodes(servers=[srv1, srv2], client=client, load_balancer=lb)
+ topo = TopologyGraph(nodes=nodes, edges=edges)
+
+ events = [
+ EventInjection(
+ event_id="spike",
+ target_id="client-to-lb",
+ start={
+ "kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START,
+ "t_start": 0.20,
+ "spike_s": 0.02,
+ },
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END, "t_end": 0.35},
+ ),
+ EventInjection(
+ event_id="outage-srv1",
+ target_id="srv-1",
+ start={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, "t_start": 0.40},
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_UP, "t_end": 0.55},
+ ),
+ ]
+
+ payload = SimulationPayload(rqs_input=rqs, topology_graph=topo, sim_settings=sim)
+ payload.events = events
+
+ runner = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+ results: ResultsAnalyzer = runner.run()
+
+ stats = results.get_latency_stats()
+ assert stats
+ assert stats[LatencyKey.TOTAL_REQUESTS] > 0
+ ts, rps = results.get_throughput_series()
+ assert len(ts) == len(rps) > 0
diff --git a/tests/integration/event_injection/single_server.py b/tests/integration/event_injection/single_server.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1698305
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/event_injection/single_server.py
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+"""Integration test: single server with edge spike and server outage.
+
+Topology:
+
+ rqs-1 → client-1 → lb-1 → srv-1
+ srv-1 → client-1
+
+Events:
+- NETWORK_SPIKE on 'client-to-lb' during a small window.
+- SERVER_DOWN/UP on 'srv-1' during a small window.
+
+Assertions focus on end-to-end KPIs; the fine-grained event sequencing is
+covered by unit tests in the event injection suite.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow.config.constants import Distribution, EventDescription, LatencyKey
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+from asyncflow.schemas.common.random_variables import RVConfig
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
+from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
+from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.graph import TopologyGraph
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import (
+ Client,
+ LoadBalancer,
+ Server,
+ ServerResources,
+ TopologyNodes,
+)
+from asyncflow.schemas.workload.rqs_generator import RqsGenerator
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+
+
+def _server(sid: str) -> Server:
+ return Server(id=sid, server_resources=ServerResources(), endpoints=[])
+
+
+def _edge(eid: str, src: str, tgt: str, mean: float = 0.002) -> Edge:
+ return Edge(
+ id=eid,
+ source=src,
+ target=tgt,
+ latency=RVConfig(mean=mean, distribution=Distribution.POISSON),
+ )
+
+
+def test_single_server_with_spike_and_outage_end_to_end() -> None:
+ """Run with both edge spike and server outage; verify KPIs exist."""
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+ rqs = RqsGenerator(
+ id="rqs-1",
+ avg_active_users=RVConfig(mean=1.0),
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user=RVConfig(mean=2.0),
+ user_sampling_window=10.0,
+ )
+ sim = SimulationSettings(total_simulation_time=1.0)
+
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+ lb = LoadBalancer(id="lb-1")
+ srv = _server("srv-1")
+
+ edges = [
+ _edge("gen-to-client", "rqs-1", "client-1"),
+ _edge("client-to-lb", "client-1", "lb-1"),
+ _edge("lb-to-srv1", "lb-1", "srv-1"),
+ _edge("srv1-to-client", "srv-1", "client-1"),
+ ]
+ nodes = TopologyNodes(servers=[srv], client=client, load_balancer=lb)
+ topo = TopologyGraph(nodes=nodes, edges=edges)
+
+ # Events in a short (but disjoint) schedule to avoid cross-process ties
+ events = [
+ EventInjection(
+ event_id="spike",
+ target_id="client-to-lb",
+ start={
+ "kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START,
+ "t_start": 0.2,
+ "spike_s": 0.01,
+ },
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END, "t_end": 0.4},
+ ),
+ EventInjection(
+ event_id="outage",
+ target_id="srv-1",
+ start={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, "t_start": 0.5},
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_UP, "t_end": 0.7},
+ ),
+ ]
+
+ payload = SimulationPayload(rqs_input=rqs, topology_graph=topo, sim_settings=sim)
+ payload.events = events
+
+ runner = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+ results: ResultsAnalyzer = runner.run()
+
+ stats = results.get_latency_stats()
+ assert stats
+ assert stats[LatencyKey.TOTAL_REQUESTS] > 0
diff --git a/tests/integration/load_balancer/test_lb_basic.py b/tests/integration/load_balancer/test_lb_basic.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..293f5ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/load_balancer/test_lb_basic.py
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+"""Integration test: one LB and two servers (round-robin by default).
+
+We build a minimal but functional topology:
+
+ rqs-1 → client-1 → lb-1 → {srv-1, srv-2}
+ srv-* → client-1
+
+Assertions:
+- Simulation completes without error.
+- Latency stats and throughput time-series are non-empty.
+- Sampled metrics include edge/server series.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow.config.constants import (
+ Distribution,
+ EndpointStepCPU,
+ LatencyKey,
+ SampledMetricName,
+ StepOperation,
+)
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+from asyncflow.schemas.common.random_variables import RVConfig
+from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
+from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.endpoint import (
+ Endpoint,
+ Step,
+)
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.graph import TopologyGraph
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import (
+ Client,
+ LoadBalancer,
+ Server,
+ ServerResources,
+ TopologyNodes,
+)
+from asyncflow.schemas.workload.rqs_generator import RqsGenerator
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+
+
+def _server(server_id: str) -> Server:
+ """Minimal server with a single CPU-bound endpoint."""
+ ep = Endpoint(
+ endpoint_name="get",
+ steps=[
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepCPU.CPU_BOUND_OPERATION,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.CPU_TIME: 0.001},
+ ),
+ ],
+ )
+ return Server(
+ id=server_id,
+ server_resources=ServerResources(), # defaults are fine
+ endpoints=[ep],
+ )
+
+
+def _edge(eid: str, src: str, tgt: str, mean: float = 0.001) -> Edge:
+ """Low-latency edge to keep tests fast/deterministic enough."""
+ return Edge(
+ id=eid,
+ source=src,
+ target=tgt,
+ latency=RVConfig(mean=mean, distribution=Distribution.POISSON),
+ )
+
+
+def test_lb_two_servers_end_to_end_smoke() -> None:
+ """Run end-to-end with LB and two servers; check basic KPIs exist."""
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+
+ # Stronger workload to avoid empty stats due to randomness:
+ # ~5 active users generating ~60 rpm each → ~5 rps expected.
+ rqs = RqsGenerator(
+ id="rqs-1",
+ avg_active_users=RVConfig(mean=5.0),
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user=RVConfig(mean=60.0),
+ user_sampling_window=5.0,
+ )
+ # Horizon must be >= 5 (schema), use a bit more to accumulate samples.
+ sim = SimulationSettings(total_simulation_time=8.0)
+
+ # Topology: rqs→client→lb→srv{1,2} and back srv→client
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+ lb = LoadBalancer(id="lb-1")
+
+ srv1 = _server("srv-1")
+ srv2 = _server("srv-2")
+
+ edges = [
+ _edge("gen-to-client", "rqs-1", "client-1"),
+ _edge("client-to-lb", "client-1", "lb-1"),
+ _edge("lb-to-srv1", "lb-1", "srv-1"),
+ _edge("lb-to-srv2", "lb-1", "srv-2"),
+ _edge("srv1-to-client", "srv-1", "client-1"),
+ _edge("srv2-to-client", "srv-2", "client-1"),
+ ]
+ nodes = TopologyNodes(servers=[srv1, srv2], client=client, load_balancer=lb)
+ topo = TopologyGraph(nodes=nodes, edges=edges)
+
+ payload = SimulationPayload(rqs_input=rqs, topology_graph=topo, sim_settings=sim)
+
+ runner = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+ results: ResultsAnalyzer = runner.run()
+
+ # Assertions: latency and throughput are present
+ stats = results.get_latency_stats()
+ assert stats
+ assert stats[LatencyKey.TOTAL_REQUESTS] > 0
+ assert stats[LatencyKey.MEAN] > 0.0
+
+ ts, rps = results.get_throughput_series()
+ assert len(ts) == len(rps) > 0
+ assert any(val > 0 for val in rps)
+
+ sampled = results.get_sampled_metrics()
+ assert SampledMetricName.RAM_IN_USE in sampled
+ assert sampled[SampledMetricName.RAM_IN_USE]
+ assert SampledMetricName.EDGE_CONCURRENT_CONNECTION in sampled
+ assert sampled[SampledMetricName.EDGE_CONCURRENT_CONNECTION]
diff --git a/tests/integration/single_server/test_int_single_server.py b/tests/integration/single_server/test_int_single_server.py
index 4d55310..efb1ef9 100644
--- a/tests/integration/single_server/test_int_single_server.py
+++ b/tests/integration/single_server/test_int_single_server.py
@@ -12,6 +12,7 @@
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+import numpy as np
import pytest
from asyncflow.config.constants import LatencyKey, SampledMetricName
@@ -26,7 +27,19 @@
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
@pytest.mark.integration
def test_single_server_happy_path(runner: SimulationRunner) -> None:
- """Run the simulation and ensure that *something* was processed."""
+ """Run the simulation and ensure that *something* was processed.
+
+ Make the test deterministic and sufficiently loaded so at least one request
+ is generated and measured.
+ """
+ # Deterministic RNG for the whole runner
+ runner.rng = np.random.default_rng(0)
+
+ # Increase horizon and load to avoid zero-request realizations
+ runner.simulation_settings.total_simulation_time = 30
+ runner.rqs_generator.avg_active_users.mean = 5.0
+ runner.rqs_generator.avg_request_per_minute_per_user.mean = 30.0
+
results: ResultsAnalyzer = runner.run()
# ── Latency stats must exist ───────────────────────────────────────────
@@ -43,10 +56,8 @@ def test_single_server_happy_path(runner: SimulationRunner) -> None:
# ── Sampled metrics must include *one* server and *one* edge ───────────
sampled = results.get_sampled_metrics()
- # Server RAM & queues
assert SampledMetricName.RAM_IN_USE in sampled
assert sampled[SampledMetricName.RAM_IN_USE], "Server RAM time-series missing."
- # Edge concurrent-connection metric
assert SampledMetricName.EDGE_CONCURRENT_CONNECTION in sampled
- assert sampled[SampledMetricName.EDGE_CONCURRENT_CONNECTION], "Edge metric missing."
+
diff --git a/tests/system/test_sys_ev_inj_lb_two_servers.py b/tests/system/test_sys_ev_inj_lb_two_servers.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..15e978b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/system/test_sys_ev_inj_lb_two_servers.py
@@ -0,0 +1,237 @@
+"""System test: client + LB + 2 servers with edge spike and server outage.
+
+Topology:
+ generator → client → lb-1 → {srv-1, srv-2} → client
+
+Endpoint on both servers:
+ CPU(1 ms) → RAM(64 MB) → IO(10 ms)
+
+Edges (baseline):
+ exponential latency ~ 2-3 ms per hop.
+
+Events injected:
+ - NETWORK_SPIKE on edge 'lb-srv-1': +50 ms, t ∈ [2.0, 12.0] s
+ - SERVER_DOWN on 'srv-2': t ∈ [5.0, 20.0] s
+
+Checks:
+- mean latency with events > baseline by a safe margin;
+- throughput stays > 30% of baseline (LB still routes to srv-1),
+ and not more than +5% above baseline;
+- sampled metrics present for both servers.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+import os
+import random
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+
+import numpy as np
+import pytest
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow import AsyncFlow
+from asyncflow.components import Client, Edge, Endpoint, LoadBalancer, Server
+from asyncflow.config.constants import LatencyKey
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+from asyncflow.settings import SimulationSettings
+from asyncflow.workload import RqsGenerator
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+ from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
+
+pytestmark = [
+ pytest.mark.system,
+ pytest.mark.skipif(
+ os.getenv("ASYNCFLOW_RUN_SYSTEM_TESTS") != "1",
+ reason=(
+ "System tests disabled "
+ "(set ASYNCFLOW_RUN_SYSTEM_TESTS=1 to run)."
+ ),
+ ),
+]
+
+SEED = 7778
+# LB re-routing and stochasticity can raise throughput
+REL_TOL_TPUT_UPPER = 0.25 # allow up to +25% increase;
+REL_TOL_TPUT_LOWER = 0.30 # must keep at least 30% throughput
+
+
+def _seed_all(seed: int = SEED) -> None:
+ """Seed Python, NumPy, and hashing for reproducibility."""
+ random.seed(seed)
+ np.random.seed(seed) # noqa: NPY002
+ os.environ["PYTHONHASHSEED"] = str(seed)
+
+
+def _build_payload(*, with_events: bool) -> SimulationPayload:
+ """Build payload for client + LB + two servers; optionally add events."""
+ # Workload: ~26.7 rps (80 users * 20 rpm / 60).
+ gen = RqsGenerator(
+ id="rqs-1",
+ avg_active_users={"mean": 80},
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user={"mean": 20},
+ user_sampling_window=60,
+ )
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+ lb = LoadBalancer(id="lb-1", algorithm="round_robin")
+
+ ep = Endpoint(
+ endpoint_name="/api",
+ steps=[
+ {"kind": "initial_parsing", "step_operation": {"cpu_time": 0.001}},
+ {"kind": "ram", "step_operation": {"necessary_ram": 64}},
+ {"kind": "io_wait", "step_operation": {"io_waiting_time": 0.010}},
+ ],
+ )
+
+ srv1 = Server(
+ id="srv-1",
+ server_resources={"cpu_cores": 1, "ram_mb": 2048},
+ endpoints=[ep],
+ )
+ srv2 = Server(
+ id="srv-2",
+ server_resources={"cpu_cores": 1, "ram_mb": 2048},
+ endpoints=[ep],
+ )
+
+ # Edges: generator→client, client→lb, lb→srv-{1,2}, srv-{1,2}→client.
+ edges = [
+ Edge(
+ id="gen-client",
+ source="rqs-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ ),
+ Edge(
+ id="client-lb",
+ source="client-1",
+ target="lb-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.002, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ ),
+ Edge(
+ id="lb-srv-1",
+ source="lb-1",
+ target="srv-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ ),
+ Edge(
+ id="lb-srv-2",
+ source="lb-1",
+ target="srv-2",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ ),
+ Edge(
+ id="srv1-client",
+ source="srv-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ ),
+ Edge(
+ id="srv2-client",
+ source="srv-2",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ ),
+ ]
+
+ settings = SimulationSettings(
+ total_simulation_time=100.0, # >= 5 s
+ sample_period_s=0.05,
+ enabled_sample_metrics=[
+ "ready_queue_len",
+ "event_loop_io_sleep",
+ "ram_in_use",
+ "edge_concurrent_connection",
+ ],
+ enabled_event_metrics=["rqs_clock"],
+ )
+
+ flow = (
+ AsyncFlow()
+ .add_generator(gen)
+ .add_client(client)
+ .add_load_balancer(lb)
+ .add_servers(srv1, srv2)
+ .add_edges(*edges)
+ .add_simulation_settings(settings)
+ )
+
+ if with_events:
+ # Edge spike on lb→srv-1: +50 ms between 2s and 12s.
+ flow = flow.add_network_spike(
+ event_id="edge-spike-1",
+ edge_id="lb-srv-1",
+ t_start=2.0,
+ t_end=12.0,
+ spike_s=0.050,
+ )
+
+ # Server outage on srv-2 between 5s and 20s.
+ flow = flow.add_server_outage(
+ event_id="srv2-outage",
+ server_id="srv-2",
+ t_start=5.0,
+ t_end=20.0,
+ )
+
+ return flow.build_payload()
+
+
+def _run(payload: SimulationPayload) -> ResultsAnalyzer:
+ """Run one simulation and return the analyzer."""
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+ runner = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+ return runner.run()
+
+
+def test_lb_two_servers_spike_and_outage() -> None:
+ """LB keeps serving via srv-1; latency rises; throughput remains non-zero."""
+ _seed_all(SEED)
+
+ # Baseline
+ res_base = _run(_build_payload(with_events=False))
+ stats_base = res_base.get_latency_stats()
+ assert stats_base, "Expected non-empty latency stats (baseline)."
+ mean_base = float(stats_base.get(LatencyKey.MEAN, 0.0))
+ assert mean_base > 0.0
+
+ # With events (spike on lb→srv-1 and outage on srv-2)
+ _seed_all(SEED)
+ res_evt = _run(_build_payload(with_events=True))
+ stats_evt = res_evt.get_latency_stats()
+ assert stats_evt, "Expected non-empty latency stats (events)."
+ mean_evt = float(stats_evt.get(LatencyKey.MEAN, 0.0))
+ assert mean_evt > 0.0
+
+ # Expect a noticeable increase in mean latency with events.
+ # Spike is +50 ms for 10 s out of 40 s on half of LB routes ≈ few ms avg.
+ assert mean_evt >= mean_base + 0.003
+
+ # Throughput should remain within reasonable bounds:
+ # not zero (LB routes to srv-1), and not spuriously higher than baseline.
+ _, rps_base = res_base.get_throughput_series()
+ _, rps_evt = res_evt.get_throughput_series()
+
+ assert rps_base, "No throughput series produced (baseline)."
+ assert rps_evt, "No throughput series produced (events)."
+
+ rps_mean_base = float(np.mean(rps_base))
+ rps_mean_evt = float(np.mean(rps_evt))
+ denom = max(rps_mean_base, 1e-9)
+
+ # Lower bound: at least 30% of baseline throughput.
+ assert (rps_mean_evt / denom) >= REL_TOL_TPUT_LOWER
+ # Upper bound: at most +5% above baseline.
+ assert (abs(rps_mean_evt - rps_mean_base) / denom) <= REL_TOL_TPUT_UPPER
+
+ # Sampled metrics present for both servers.
+ sampled = res_evt.get_sampled_metrics()
+ for key in ("ready_queue_len", "event_loop_io_sleep", "ram_in_use"):
+ assert key in sampled
+ assert "srv-1" in sampled[key]
+ assert "srv-2" in sampled[key]
+ assert len(sampled[key]["srv-1"]) > 0
+ assert len(sampled[key]["srv-2"]) > 0
diff --git a/tests/system/test_sys_ev_inj_single_server.py b/tests/system/test_sys_ev_inj_single_server.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e1132c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/system/test_sys_ev_inj_single_server.py
@@ -0,0 +1,199 @@
+"""System test: single server with a deterministic network spike on an edge.
+
+Topology:
+ generator → client → srv-1 → client
+
+Endpoint:
+ CPU(1 ms) → RAM(64 MB) → IO(10 ms)
+
+Edges (baseline):
+ exponential latency ~ 2-3 ms per hop.
+
+Event injected:
+ NETWORK_SPIKE on edge 'client-srv' adding +50 ms between t=[0.5, 2.5] s.
+
+Checks:
+- mean latency with spike > mean latency without spike by a safe margin;
+- throughput stays roughly similar (the spike increases latency, not λ);
+- sampled metrics present.
+
+This test runs *two* short simulations (same seed):
+ (A) baseline (no events)
+ (B) with edge spike
+Then compares their metrics.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+import os
+import random
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+
+import numpy as np
+import pytest
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow import AsyncFlow
+from asyncflow.components import Client, Edge, Endpoint, Server
+from asyncflow.config.constants import LatencyKey
+from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+from asyncflow.settings import SimulationSettings
+from asyncflow.workload import RqsGenerator
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ from asyncflow.metrics.analyzer import ResultsAnalyzer
+ from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
+
+pytestmark = [
+ pytest.mark.system,
+ pytest.mark.skipif(
+ os.getenv("ASYNCFLOW_RUN_SYSTEM_TESTS") != "1",
+ reason=(
+ "System tests disabled "
+ "(set ASYNCFLOW_RUN_SYSTEM_TESTS=1 to run)."
+ ),
+ ),
+]
+
+SEED = 4240
+REL_TOL_TPUT = 0.20 # throughput should be within ±20%
+
+
+def _seed_all(seed: int = SEED) -> None:
+ """Seed Python, NumPy, and hashing for reproducibility."""
+ random.seed(seed)
+ np.random.seed(seed) # noqa: NPY002
+ os.environ["PYTHONHASHSEED"] = str(seed)
+
+
+def _build_payload(*, with_spike: bool) -> SimulationPayload:
+ """Build a single-server payload; optionally inject an edge spike."""
+ # Workload: ~26.7 rps (80 users * 20 rpm / 60).
+ gen = RqsGenerator(
+ id="rqs-1",
+ avg_active_users={"mean": 80},
+ avg_request_per_minute_per_user={"mean": 20},
+ user_sampling_window=60,
+ )
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+
+ ep = Endpoint(
+ endpoint_name="/api",
+ steps=[
+ {"kind": "initial_parsing", "step_operation": {"cpu_time": 0.001}},
+ {"kind": "ram", "step_operation": {"necessary_ram": 64}},
+ {"kind": "io_wait", "step_operation": {"io_waiting_time": 0.010}},
+ ],
+ )
+ srv = Server(
+ id="srv-1",
+ server_resources={"cpu_cores": 1, "ram_mb": 2048},
+ endpoints=[ep],
+ )
+
+ # Edges: baseline exponential latencies around a few milliseconds.
+ edges = [
+ Edge(
+ id="gen-client",
+ source="rqs-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ ),
+ Edge(
+ id="client-srv",
+ source="client-1",
+ target="srv-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.002, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ ),
+ Edge(
+ id="srv-client",
+ source="srv-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency={"mean": 0.003, "distribution": "exponential"},
+ ),
+ ]
+
+ # Simulation horizon covers the whole spike window.
+ settings = SimulationSettings(
+ total_simulation_time=100.0, # >= 5 (schema lower bound)
+ sample_period_s=0.05,
+ enabled_sample_metrics=[
+ "ready_queue_len",
+ "event_loop_io_sleep",
+ "ram_in_use",
+ "edge_concurrent_connection",
+ ],
+ enabled_event_metrics=["rqs_clock"],
+ )
+
+ flow = (
+ AsyncFlow()
+ .add_generator(gen)
+ .add_client(client)
+ .add_servers(srv)
+ .add_edges(*edges)
+ .add_simulation_settings(settings)
+ )
+
+ if with_spike:
+ # Add +50 ms to client→server between t=[0.5, 2.5] seconds.
+ flow = flow.add_network_spike(
+ event_id="net-spike-1",
+ edge_id="client-srv",
+ t_start=0.5,
+ t_end=2.5,
+ spike_s=0.050,
+ )
+
+ return flow.build_payload()
+
+
+def _run(payload: SimulationPayload) -> ResultsAnalyzer:
+ """Run one simulation and return the analyzer."""
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+ runner = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+ return runner.run()
+
+
+def test_edge_latency_spike_increases_mean_latency() -> None:
+ """The injected edge spike must measurably increase mean latency."""
+ _seed_all(SEED)
+
+ # Baseline.
+ res_base = _run(_build_payload(with_spike=False))
+ stats_base = res_base.get_latency_stats()
+ assert stats_base, "Expected non-empty latency stats (baseline)."
+ mean_base = float(stats_base.get(LatencyKey.MEAN, 0.0))
+ assert mean_base > 0.0
+
+ # With spike.
+ _seed_all(SEED) # identical workload chronology, only edge differs
+ res_spike = _run(_build_payload(with_spike=True))
+ stats_spike = res_spike.get_latency_stats()
+ assert stats_spike, "Expected non-empty latency stats (spike)."
+ mean_spike = float(stats_spike.get(LatencyKey.MEAN, 0.0))
+ assert mean_spike > 0.0
+
+ # The spike window covers part of the horizon and adds +50 ms on
+ # the client→server hop; expect a noticeable average increase.
+ assert mean_spike >= mean_base * 1.02
+
+ # Throughput should remain roughly similar (spike adds latency, not λ).
+ _, rps_base = res_base.get_throughput_series()
+ _, rps_spike = res_spike.get_throughput_series()
+
+ assert rps_base, "No throughput series produced (baseline)."
+ assert rps_spike, "No throughput series produced (spike)."
+
+ rps_mean_base = float(np.mean(rps_base))
+ rps_mean_spike = float(np.mean(rps_spike))
+ denom = max(rps_mean_base, 1e-9)
+ rel_diff = abs(rps_mean_spike - rps_mean_base) / denom
+ assert rel_diff <= REL_TOL_TPUT
+
+ # Basic sampled metrics should be present.
+ sampled = res_spike.get_sampled_metrics()
+ for key in ("ready_queue_len", "event_loop_io_sleep", "ram_in_use"):
+ assert key in sampled
+ assert "srv-1" in sampled[key]
+ assert len(sampled[key]["srv-1"]) > 0
diff --git a/tests/unit/public_api/test_import.py b/tests/unit/public_api/test_import.py
index cd708bc..2bea333 100644
--- a/tests/unit/public_api/test_import.py
+++ b/tests/unit/public_api/test_import.py
@@ -14,6 +14,7 @@
Client,
Edge,
Endpoint,
+ EventInjection,
LoadBalancer,
Server,
ServerResources,
@@ -43,6 +44,7 @@ def test_components_public_symbols() -> None:
"Client",
"Edge",
"Endpoint",
+ "EventInjection",
"LoadBalancer",
"Server",
"ServerResources",
@@ -57,6 +59,7 @@ def test_components_symbols_are_importable_classes() -> None:
(Client, "Client"),
(Edge, "Edge"),
(Endpoint, "Endpoint"),
+ (EventInjection, "EventInjection"),
(LoadBalancer, "LoadBalancer"),
(Server, "Server"),
(ServerResources, "ServerResources"),
diff --git a/tests/unit/runtime/actors/test_load_balancer.py b/tests/unit/runtime/actors/test_load_balancer.py
index 1905543..94c372d 100644
--- a/tests/unit/runtime/actors/test_load_balancer.py
+++ b/tests/unit/runtime/actors/test_load_balancer.py
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
from __future__ import annotations
+from collections import OrderedDict
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, cast
-import pytest
import simpy
from asyncflow.config.constants import LbAlgorithmsName, SystemNodes
@@ -15,7 +15,6 @@
from asyncflow.runtime.actors.edge import EdgeRuntime
-
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
# Dummy objects (lightweight test doubles) #
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
@@ -23,7 +22,7 @@ class DummyState:
"""Tiny substitute for ``RequestState`` - only ``history`` is needed."""
def __init__(self) -> None:
- """Instance of the state history"""
+ """Inizialization of the attributes"""
self.history: list[str] = []
def record_hop(self, comp_type: SystemNodes, comp_id: str, _: float) -> None:
@@ -35,27 +34,21 @@ class DummyEdge:
"""Stub that mimics just the pieces `LoadBalancerRuntime` relies on."""
def __init__(self, edge_id: str, concurrent: int = 0) -> None:
- """Instance for the dummy edge"""
+ """Inizialization of the attributes"""
self.edge_config = type("Cfg", (), {"id": edge_id})
self.concurrent_connections = concurrent
self.received: list[DummyState] = []
# Signature compatible with EdgeRuntime.transport
def transport(self, state: DummyState) -> None:
- """Collect the state for later assertions."""
+ """Function to simulate the transport"""
self.received.append(state)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
-# Fixtures #
+# Helpers #
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
-@pytest.fixture
-def env() -> simpy.Environment:
- """Return a fresh SimPy environment per test."""
- return simpy.Environment()
-
-
-def _make_lb_runtime(
+def make_lb_runtime(
env: simpy.Environment,
algorithm: LbAlgorithmsName,
edges: list[DummyEdge],
@@ -64,26 +57,30 @@ def _make_lb_runtime(
lb_cfg = LoadBalancer(
id="lb-1",
algorithms=algorithm,
- server_covered={e.edge_config.id for e in edges}, # type: ignore[attr-defined]
+ server_covered={e.edge_config.id for e in edges}, # type: ignore[attr-defined]
)
inbox: simpy.Store = simpy.Store(env)
+
+ # Build the OrderedDict[id -> DummyEdge]
+ od: OrderedDict[str, DummyEdge] = OrderedDict((e.edge_config.id, e) for e in edges) # type: ignore[attr-defined]
+
lb = LoadBalancerRuntime(
env=env,
lb_config=lb_cfg,
- # ② cast DummyEdge list to the expected interface type
- out_edges=cast("list[EdgeRuntime]", edges),
+ lb_out_edges=cast("OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]", od),
lb_box=inbox,
)
lb.start()
return lb
+
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
# Tests #
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
def test_round_robin_rotation(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
"""Three requests, two edges ⇒ order must be edge-0, edge-1, edge-0."""
edge0, edge1 = DummyEdge("srv-A"), DummyEdge("srv-B")
- lb = _make_lb_runtime(env, LbAlgorithmsName.ROUND_ROBIN, [edge0, edge1])
+ lb = make_lb_runtime(env, LbAlgorithmsName.ROUND_ROBIN, [edge0, edge1])
for _ in range(3):
lb.lb_box.put(DummyState())
@@ -103,7 +100,7 @@ def test_least_connections_picks_lowest(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
busy = DummyEdge("busy", concurrent=10)
idle = DummyEdge("idle", concurrent=1)
- lb = _make_lb_runtime(env, LbAlgorithmsName.LEAST_CONNECTIONS, [busy, idle])
+ lb = make_lb_runtime(env, LbAlgorithmsName.LEAST_CONNECTIONS, [busy, idle])
lb.lb_box.put(DummyState())
env.run()
@@ -112,20 +109,23 @@ def test_least_connections_picks_lowest(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
assert not busy.received
-def test_start_raises_if_no_edges(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
- """`start()` followed by `env.run()` with `out_edges=None` must assert."""
+def test_no_edges_is_noop(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """
+ With an empty mapping of lb_out_edges, starting the LB and running the env
+ should be a no-op (no assertions raised).
+ """
lb_cfg = LoadBalancer(
- id="lb-bad",
+ id="lb-empty",
algorithms=LbAlgorithmsName.ROUND_ROBIN,
server_covered=set(),
)
lb = LoadBalancerRuntime(
env=env,
lb_config=lb_cfg,
- out_edges=None,
+ lb_out_edges=cast("OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]", OrderedDict()),
lb_box=simpy.Store(env),
)
lb.start()
- with pytest.raises(AssertionError):
- env.run()
+ # No events in the env; this should simply return without error.
+ env.run()
diff --git a/tests/unit/runtime/actors/test_server.py b/tests/unit/runtime/actors/test_server.py
index 4c915ac..f5ff2ef 100644
--- a/tests/unit/runtime/actors/test_server.py
+++ b/tests/unit/runtime/actors/test_server.py
@@ -1,18 +1,18 @@
-"""Unit-tests for ServerRuntime concurrency, resource handling and metrics.
+"""Unit tests for ServerRuntime concurrency, resources, and metrics.
-Each test spins up an isolated SimPy environment containing:
+Each test spins up an isolated SimPy environment with:
* one ServerRuntime
* one mock edge with zero-latency delivery (InstantEdge)
* an inbox (simpy.Store) for incoming requests
-* a sink (simpy.Store) that receives the request after the server
+* a sink (simpy.Store) receiving the RequestState after the server
-The server exposes:
- RAM = 1024 MB, CPU cores = 2
-and a single endpoint with the step sequence:
- RAM(128 MB) ➜ CPU(5 ms) ➜ I/O(20 ms).
+Default server:
+ RAM = 1024 MB, CPU cores = 2
+Default endpoint:
+ RAM(128 MB) → CPU(5 ms) → I/O(20 ms)
-All timings are in **seconds** because SimPy's clock is unit-agnostic.
+All timings are in seconds (SimPy is unit-agnostic).
"""
from __future__ import annotations
@@ -34,77 +34,92 @@
from asyncflow.runtime.rqs_state import RequestState
from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
from asyncflow.schemas.topology.endpoint import Endpoint, Step
-from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import (
- Server,
- ServerResources,
-)
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import Server, ServerResources
if TYPE_CHECKING:
-
- from collections.abc import Generator
+ from collections.abc import Generator, Iterable
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Helpers #
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
+
+
class InstantEdge:
"""Stub EdgeRuntime with zero latency and no drops."""
def __init__(self, env: simpy.Environment, sink: simpy.Store) -> None:
- """Attribute"""
+ """Store environment and sink."""
self._env = env
self._sink = sink
def transport(self, state: RequestState) -> simpy.Process:
- """Transport function"""
+ """Schedule the zero-latency delivery."""
return self._env.process(self._deliver(state))
- def _deliver(self, state: RequestState) -> Generator[simpy.Event, None, None]:
- """Deliver function"""
+ def _deliver(
+ self, state: RequestState,
+ ) -> Generator[simpy.Event, None, None]:
+ """Put the state into the sink immediately."""
yield self._sink.put(state)
+def _mk_endpoint(steps: Iterable[Step]) -> Endpoint:
+ """Build a single endpoint with the provided steps."""
+ return Endpoint(endpoint_name="/predict", steps=list(steps))
+
+
+def _default_steps() -> tuple[Step, Step, Step]:
+ """RAM → CPU → I/O default pipeline."""
+ return (
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepRAM.RAM,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.NECESSARY_RAM: 128},
+ ),
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepCPU.CPU_BOUND_OPERATION,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.CPU_TIME: 0.005},
+ ),
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepIO.DB,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.IO_WAITING_TIME: 0.020},
+ ),
+ )
+
+
def _make_server_runtime(
env: simpy.Environment,
+ *,
+ cpu_cores: int = 2,
+ ram_mb: int = 1024,
+ steps: Iterable[Step] | None = None,
) -> tuple[ServerRuntime, simpy.Store]:
"""Return a (ServerRuntime, sink) ready for injection tests."""
- # Resources
- res_spec = ServerResources(cpu_cores=2, ram_mb=1024)
+ res_spec = ServerResources(cpu_cores=cpu_cores, ram_mb=ram_mb)
containers = build_containers(env, res_spec)
- # Endpoint: RAM → CPU → I/O
- endpoint = Endpoint(
- endpoint_name="/predict",
- steps=[
- Step(
- kind=EndpointStepRAM.RAM,
- step_operation={StepOperation.NECESSARY_RAM: 128},
- ),
- Step(
- kind=EndpointStepCPU.CPU_BOUND_OPERATION,
- step_operation={StepOperation.CPU_TIME: 0.005},
- ),
- Step(
- kind=EndpointStepIO.DB,
- step_operation={StepOperation.IO_WAITING_TIME: 0.020},
- ),
- ],
+ endpoint = _mk_endpoint(steps if steps is not None else _default_steps())
+ server_cfg = Server(
+ id="api_srv",
+ endpoints=[endpoint],
+ server_resources=res_spec,
)
- server_cfg = Server(id="api_srv", endpoints=[endpoint], server_resources=res_spec)
-
inbox: simpy.Store = simpy.Store(env)
sink: simpy.Store = simpy.Store(env)
edge = InstantEdge(env, sink)
- settings = SimulationSettings(total_simulation_time=1900, sample_period_s=0.1)
+ settings = SimulationSettings(
+ total_simulation_time=60,
+ sample_period_s=0.01,
+ )
runtime = ServerRuntime(
env=env,
server_resources=containers,
server_config=server_cfg,
- out_edge=edge, # type: ignore[arg-type]
+ out_edge=edge, # type: ignore[arg-type]
server_box=inbox,
settings=settings,
rng=default_rng(seed=0),
@@ -113,8 +128,10 @@ def _make_server_runtime(
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
-# Tests #
+# Tests (ready queue = only requests waiting for a CPU core) #
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
+
+
def test_ram_is_released_at_end() -> None:
"""RAM tokens must return to capacity once the request finishes."""
env = simpy.Environment()
@@ -129,52 +146,217 @@ def test_ram_is_released_at_end() -> None:
assert len(sink.items) == 1
-def test_cpu_core_held_only_during_cpu_step() -> None:
- """Exactly one core is busy during the CPU-bound window (0 5ms)."""
+def test_cpu_core_held_only_during_cpu_step_single_request() -> None:
+ """Single request with 2 cores holds a core only during CPU time."""
env = simpy.Environment()
- server, _ = _make_server_runtime(env)
+ server, _ = _make_server_runtime(env, cpu_cores=2)
cpu = server.server_resources["CPU"]
server.server_box.put(RequestState(id=2, initial_time=0.0))
server.start()
- env.run(until=0.004) # mid-CPU step
- assert cpu.level == 1 # 2-1
+ # Mid CPU step (5 ms total).
+ env.run(until=0.003)
+ # One core in use: level = 2 - 1 = 1
+ assert cpu.level == 1
+ # No ready-wait, acquisition was immediate.
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+ assert server.io_queue_len == 0
- env.run(until=0.006) # after CPU step
+ # After CPU step, during I/O.
+ env.run(until=0.008)
assert cpu.level == 2 # released
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+ assert server.io_queue_len == 1 # now in I/O
+ # End.
+ env.run()
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+ assert server.io_queue_len == 0
-def test_ready_and_io_queue_counters() -> None:
- """ready_queue_len and io_queue_len should toggle as CPU⇄I/O phases alternate."""
+
+def test_ready_increases_only_when_cpu_contention_exists() -> None:
+ """With 1 core and overlap, the second request waits in ready."""
env = simpy.Environment()
- server, _ = _make_server_runtime(env)
+ server, _ = _make_server_runtime(env, cpu_cores=1)
+
+ # First request at t=0.0
+ server.server_box.put(RequestState(id=10, initial_time=0.0))
+ # Second overlaps during the first CPU window.
+ server.server_box.put(RequestState(id=11, initial_time=0.001))
- server.server_box.put(RequestState(id=3, initial_time=0.0))
server.start()
- # 1) before start queues are empty
+ # During first CPU, second should be in ready.
+ env.run(until=0.004)
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 1
+
+ # After first CPU is done, second should start CPU → ready back to 0.
+ env.run(until=0.0065)
assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
- assert server.io_queue_len == 0
- # 2) during CPU (0 5ms) ready queue+1
- env.run(until=0.003)
- assert server.ready_queue_len == 1
+ env.run()
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
assert server.io_queue_len == 0
- # 3) during I/O (5 25ms) ready 0, io+1
- env.run(until=0.010)
+
+def test_consecutive_io_steps_do_not_double_count() -> None:
+ """Two consecutive I/O steps count as a single presence in I/O queue."""
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+
+ steps = (
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepRAM.RAM,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.NECESSARY_RAM: 64},
+ ),
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepIO.DB,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.IO_WAITING_TIME: 0.010},
+ ),
+ # Use another valid I/O category (e.g., CACHE) to simulate consecutive I/O.
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepIO.CACHE,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.IO_WAITING_TIME: 0.015},
+ ),
+ )
+ server, _ = _make_server_runtime(env, steps=steps)
+
+ server.server_box.put(RequestState(id=20, initial_time=0.0))
+ server.start()
+
+ # During first I/O.
+ env.run(until=0.005)
+ assert server.io_queue_len == 1
+
+ # Still I/O during second consecutive I/O step; stays 1.
+ env.run(until=0.020)
+ assert server.io_queue_len == 1
+
+ env.run()
+ assert server.io_queue_len == 0
assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+
+
+def test_first_step_io_enters_io_queue_without_touching_ready() -> None:
+ """First-step I/O enters I/O queue and leaves ready untouched."""
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+
+ steps = (
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepRAM.RAM,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.NECESSARY_RAM: 64},
+ ),
+ # Valid I/O category for first-step I/O (e.g., WAIT).
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepIO.WAIT,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.IO_WAITING_TIME: 0.010},
+ ),
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepCPU.CPU_BOUND_OPERATION,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.CPU_TIME: 0.005},
+ ),
+ )
+ server, _ = _make_server_runtime(env, steps=steps, cpu_cores=1)
+
+ server.server_box.put(RequestState(id=30, initial_time=0.0))
+ server.start()
+
+ # During first I/O window.
+ env.run(until=0.005)
assert server.io_queue_len == 1
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+
+ # When switching to CPU: with a single request, acquisition is immediate.
+ env.run(until=0.012)
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+
+ env.run()
+ assert server.io_queue_len == 0
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+
+
+def test_cpu_burst_reuses_single_token_no_extra_ready() -> None:
+ """Consecutive CPU steps reuse the same token; no extra ready bumps."""
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+
+ steps = (
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepRAM.RAM,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.NECESSARY_RAM: 64},
+ ),
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepCPU.CPU_BOUND_OPERATION,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.CPU_TIME: 0.004},
+ ),
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepCPU.CPU_BOUND_OPERATION,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.CPU_TIME: 0.004},
+ ),
+ )
+ server, _ = _make_server_runtime(env, steps=steps, cpu_cores=1)
+ cpu = server.server_resources["CPU"]
+
+ server.server_box.put(RequestState(id=40, initial_time=0.0))
+ server.start()
+
+ # During first CPU step.
+ env.run(until=0.002)
+ assert cpu.level == 0 # 1 core total, 1 in use
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+
+ # During second CPU step (same token).
+ env.run(until=0.006)
+ assert cpu.level == 0
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+
+ env.run()
+ assert cpu.level == 1
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
+ assert server.io_queue_len == 0
+
+
+def test_ram_gating_blocks_before_ready() -> None:
+ """When RAM is scarce, blocks on RAM and must NOT inflate ready."""
+ env = simpy.Environment()
+
+ # Respect ServerResources(min RAM = 256).
+ # Endpoint needs 256 MB → second request waits on RAM (not in ready).
+ steps = (
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepRAM.RAM,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.NECESSARY_RAM: 256},
+ ),
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepCPU.CPU_BOUND_OPERATION,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.CPU_TIME: 0.005},
+ ),
+ Step(
+ kind=EndpointStepIO.DB,
+ step_operation={StepOperation.IO_WAITING_TIME: 0.020},
+ ),
+ )
+ server, _ = _make_server_runtime(
+ env,
+ cpu_cores=2,
+ ram_mb=256,
+ steps=steps,
+ )
+
+ server.server_box.put(RequestState(id=50, initial_time=0.0))
+ server.server_box.put(RequestState(id=51, initial_time=0.0))
+ server.start()
+
+ # Shortly after start: first runs; second is blocked on RAM, not in ready.
+ env.run(until=0.002)
+ assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
- # 4) completed both back to 0
env.run()
assert server.ready_queue_len == 0
assert server.io_queue_len == 0
def test_enabled_metrics_dict_populated() -> None:
- """ServerRuntime must create lists for every mandatory sampled metric."""
+ """ServerRuntime creates lists for every mandatory sampled metric."""
env = simpy.Environment()
server, _ = _make_server_runtime(env)
diff --git a/tests/unit/runtime/events/test_injection_edges.py b/tests/unit/runtime/events/test_injection_edges.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1bb76a6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/runtime/events/test_injection_edges.py
@@ -0,0 +1,296 @@
+"""Step-by-step tests for edge spike handling in EventInjectionRuntime."""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from collections import OrderedDict
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+
+import pytest
+
+from asyncflow.config.constants import EventDescription
+from asyncflow.runtime.actors.edge import EdgeRuntime
+from asyncflow.runtime.events.injection import (
+ END_MARK,
+ START_MARK,
+ EventInjectionRuntime,
+)
+from asyncflow.schemas.common.random_variables import RVConfig
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ import simpy
+
+
+# ----------------------------- Helpers ------------------------------------- #
+
+def _edge(edge_id: str, source: str, target: str) -> Edge:
+ """Minimal edge with negligible latency."""
+ return Edge(id=edge_id, source=source, target=target, latency=RVConfig(mean=0.001))
+
+
+def _spike_event(
+ *, event_id: str, edge_id: str, t_start: float, t_end: float, spike_s: float,
+) -> EventInjection:
+ """NETWORK_SPIKE event for a specific edge."""
+ return EventInjection(
+ event_id=event_id,
+ target_id=edge_id,
+ start={
+ "kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START,
+ "t_start": t_start,
+ "spike_s": spike_s,
+ },
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END, "t_end": t_end},
+ )
+
+
+def _drain_zero_time(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """Consume *all* events scheduled at the current time (typically t=0)"""
+ while env.peek() == env.now:
+ env.step()
+
+# ----------------------------- Tests (edge spike) --------------------------- #
+
+def test_single_spike_start_and_end_step_by_step(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """Single spike: +0.5 at t=1.0, gives 0.0 a t=3.0."""
+ edges = [_edge("edge-1", "A", "B")]
+ ev = _spike_event(
+ event_id="ev1", edge_id="edge-1", t_start=1.0, t_end=3.0, spike_s=0.5,
+ )
+
+ rt = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[ev],
+ edges=edges,
+ env=env,
+ servers=[],
+ lb_out_edges=OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime](),
+ )
+ rt.start()
+
+ # Drena tutti gli 'start events' a t=0 dei processi registrati
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+
+ # Ora il prossimo evento deve essere a 1.0 (START)
+ assert env.peek() == pytest.approx(1.0)
+
+ # Step @1.0 → applica START(ev1)
+ env.step()
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(1.0)
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.5)
+
+ # Prossimo evento a 3.0 (END)
+ assert env.peek() == pytest.approx(3.0)
+
+ # Step @3.0 → applica END(ev1)
+ env.step()
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(3.0)
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.0)
+
+
+def test_spike_superposition_on_same_edge(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """Due spike sovrapposti si sommano nell'intervallo comune."""
+ edges = [_edge("edge-1", "A", "B")]
+ ev1 = _spike_event(
+ event_id="ev1", edge_id="edge-1", t_start=1.0, t_end=4.0, spike_s=0.3,
+ )
+ ev2 = _spike_event(
+ event_id="ev2", edge_id="edge-1", t_start=2.0, t_end=3.0, spike_s=0.2,
+ )
+
+ rt = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[ev1, ev2],
+ edges=edges,
+ env=env,
+ servers=[],
+ lb_out_edges=OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime](),
+ )
+ rt.start()
+
+ _drain_zero_time(env) # next should be 1.0
+ env.step() # @1.0 START ev1
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(1.0)
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.3)
+
+ env.step() # @2.0 START ev2
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(2.0)
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.5)
+
+ env.step() # @3.0 END ev2
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(3.0)
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.3)
+
+ env.step() # @4.0 END ev1
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(4.0)
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.0)
+
+
+def test_end_before_start_at_same_timestamp(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """A t=5.0 devono avvenire END(evA) poi START(evB), spike finale 0.6."""
+ edges = [_edge("edge-1", "X", "Y")]
+ ev_a = _spike_event(
+ event_id="evA", edge_id="edge-1", t_start=1.0, t_end=5.0, spike_s=0.4,
+ )
+ ev_b = _spike_event(
+ event_id="evB", edge_id="edge-1", t_start=5.0, t_end=6.0, spike_s=0.6,
+ )
+
+ rt = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[ev_a, ev_b],
+ edges=edges,
+ env=env,
+ servers=[],
+ lb_out_edges=OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime](),
+ )
+ rt.start()
+
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ env.step()
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(1.0)
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.4)
+
+ env.step()
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(5.0)
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.6)
+
+
+def test_only_targeted_edges_are_marked_affected(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """Solo l'edge con evento è marcato e riceve spike."""
+ edges = [_edge("edge-1", "A", "B"), _edge("edge-2", "A", "C")]
+ ev = _spike_event(
+ event_id="ev1", edge_id="edge-1", t_start=1.0, t_end=2.0, spike_s=0.4,
+ )
+
+ rt = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[ev],
+ edges=edges,
+ env=env,
+ servers=[],
+ lb_out_edges=OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime](),
+ )
+ rt.start()
+
+ assert "edge-1" in rt.edges_affected
+ assert "edge-2" not in rt.edges_affected
+
+ _drain_zero_time(env) # next 1.0
+ env.step() # @1.0 START ev1
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.4)
+ assert rt.edges_spike.get("edge-2", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.0)
+
+
+def test_internal_timeline_order_at_same_time(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """Controllo diretto della timeline: a 5.0 → [END, START]."""
+ edges = [_edge("edge-1", "S", "T")]
+ ev_a = _spike_event(
+ event_id="a", edge_id="edge-1", t_start=1.0, t_end=5.0, spike_s=0.4,
+ )
+ ev_b = _spike_event(
+ event_id="b", edge_id="edge-1", t_start=5.0, t_end=6.0, spike_s=0.6,
+ )
+
+ rt = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[ev_a, ev_b],
+ edges=edges,
+ env=env,
+ servers=[],
+ lb_out_edges=OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime](),
+ )
+
+ times_at_5 = [tpl for tpl in rt._edges_timeline if tpl[0] == 5.0] # noqa: SLF001
+ assert len(times_at_5) == 2
+ marks_at_5 = [tpl[3] for tpl in times_at_5]
+ assert marks_at_5 == [END_MARK, START_MARK]
+
+
+def test_no_events_is_noop(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """When events=None, the runtime should not alter any edge state."""
+ edges = [_edge("e1", "A", "B")]
+
+ inj = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=None,
+ edges=edges,
+ env=env,
+ servers=[],
+ lb_out_edges=OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime](),
+ )
+ # Should start without scheduling edge changes.
+ inj.start()
+
+ assert inj.edges_affected == set()
+ assert inj.edges_spike == {}
+
+
+def test_end_then_multiple_starts_same_timestamp(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """At the same timestamp, END must be applied before multiple STARTs.
+
+ Scenario on edge 'E':
+ ev1: +0.4 active [1, 5]
+ ev2: +0.3 active [5, 6]
+ ev3: +0.2 active [5, 7]
+
+ At t=5.0:
+ - END(ev1) applies first (removes +0.4 → 0.0),
+ - then START(ev2) and START(ev3) (+0.3 + 0.2),
+ Final spike at t=5.0 is +0.5.
+ """
+ e = _edge("E", "S", "T")
+ ev1 = _spike_event(
+ event_id="ev1", edge_id=e.id, t_start=1.0, t_end=5.0, spike_s=0.4,
+ )
+ ev2 = _spike_event(
+ event_id="ev2", edge_id=e.id, t_start=5.0, t_end=6.0, spike_s=0.3,
+ )
+ ev3 = _spike_event(
+ event_id="ev3", edge_id=e.id, t_start=5.0, t_end=7.0, spike_s=0.2,
+ )
+
+ inj = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[ev1, ev2, ev3],
+ edges=[e],
+ env=env,
+ servers=[],
+ lb_out_edges=OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime](),
+ )
+ inj.start()
+
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+
+ # @1.0 → START ev1 → +0.4
+ env.step()
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(1.0)
+ assert inj.edges_spike[e.id] == pytest.approx(0.4)
+
+ # @5.0 → END ev1, then START ev2 & START ev3 → 0.0 + 0.3 + 0.2 = 0.5
+ env.step()
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(5.0)
+ assert inj.edges_spike[e.id] == pytest.approx(0.5)
+
+
+def test_zero_time_batch_draining_makes_first_event_visible(
+ env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """After start(), draining zero-time events reveals the first real timestamp.
+
+ Without draining, the next scheduled item may still be an activation at t=0.
+ After draining, the next event should be the edge spike START (e.g., 1.0s).
+ """
+ e = _edge("E", "S", "T")
+ ev = _spike_event(event_id="ev", edge_id=e.id, t_start=1.0, t_end=2.0, spike_s=0.1)
+
+ inj = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[ev],
+ edges=[e],
+ env=env,
+ servers=[],
+ lb_out_edges=OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime](),
+ )
+ inj.start()
+
+ # Drain zero-time activations so the next event is 1.0s.
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.peek() == pytest.approx(1.0)
+
+ # Step to 1.0s and confirm activation.
+ env.step()
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(1.0)
+ assert inj.edges_spike[e.id] == pytest.approx(0.1)
diff --git a/tests/unit/runtime/events/test_injection_servers.py b/tests/unit/runtime/events/test_injection_servers.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7347fb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/runtime/events/test_injection_servers.py
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
+"""Server-outage tests for EventInjectionRuntime (using real `Server` model)."""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from collections import OrderedDict
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+
+import pytest
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow.config.constants import EventDescription
+from asyncflow.runtime.actors.edge import EdgeRuntime
+from asyncflow.runtime.events.injection import EventInjectionRuntime
+from asyncflow.schemas.common.random_variables import RVConfig
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import Server, ServerResources
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
+
+
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+# Helpers #
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+
+def _edge(edge_id: str, source: str, target: str) -> Edge:
+ """Create a minimal LB→server edge with negligible latency."""
+ return Edge(
+ id=edge_id,
+ source=source,
+ target=target,
+ latency=RVConfig(mean=0.001),
+ )
+
+
+def _srv(server_id: str) -> Server:
+ """Create a minimal, fully-typed Server instance for tests."""
+ return Server(
+ id=server_id,
+ server_resources=ServerResources(), # uses defaults
+ endpoints=[], # empty list is valid
+ )
+
+def _srv_event(
+ server_id: str, ev_id: str, t_start: float, t_end: float) -> EventInjection:
+ """Create a SERVER_DOWN/UP event for the given server id."""
+ return EventInjection(
+ event_id=ev_id,
+ target_id=server_id,
+ start={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, "t_start": t_start},
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_UP, "t_end": t_end},
+ )
+
+
+def _drain_zero_time(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """Consume all events scheduled at the current time (typically t=0)."""
+ while env.peek() == env.now:
+ env.step()
+
+
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+# Tests #
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+
+def test_outage_removes_and_restores_edge_order(
+ env: simpy.Environment, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """DOWN removes the LB→server edge; reinserts it at the end (OrderedDict policy)"""
+ # Two distinct LB→server edges
+ lb_e1 = _edge("lb-e1", "lb-1", "srv-1")
+ lb_e2 = _edge("lb-e2", "lb-1", "srv-2")
+
+ er1 = EdgeRuntime(
+ env=env, edge_config=lb_e1, target_box=simpy.Store(env), settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+ er2 = EdgeRuntime(
+ env=env, edge_config=lb_e2, target_box=simpy.Store(env), settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+
+ lb_out = OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]([("lb-e1", er1), ("lb-e2", er2)])
+
+ outage = _srv_event("srv-1", "ev-out", 5.0, 7.0)
+ servers = [_srv("srv-1"), _srv("srv-2")]
+
+ inj = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[outage], edges=[], env=env, servers=servers, lb_out_edges=lb_out,
+ )
+ inj.start()
+
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e1", "lb-e2"]
+
+ # @5.0 → remove lb-e1
+ env.step()
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(5.0)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2"]
+ assert "lb-e1" not in lb_out
+
+ # @7.0 → reinsert lb-e1 at the end
+ env.step()
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(7.0)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2", "lb-e1"]
+ assert lb_out["lb-e1"] is er1
+
+
+def test_outage_for_server_not_in_lb_is_noop(
+ env: simpy.Environment, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """DOWN/UP for a server with no LB edges should not change the LB mapping."""
+ lb_e2 = _edge("lb-e2", "lb-1", "srv-2")
+ er2 = EdgeRuntime(
+ env=env, edge_config=lb_e2, target_box=simpy.Store(env), settings=sim_settings)
+ lb_out = OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]([("lb-e2", er2)])
+
+ outage = _srv_event("srv-3", "ev-out", 5.0, 6.0) # srv-3 not in LB
+ inj = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[outage],
+ edges=[],
+ env=env,
+ servers=[_srv("srv-2"), _srv("srv-3")],
+ lb_out_edges=lb_out,
+ )
+ inj.start()
+
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2"]
+
+ env.step() # @5.0
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2"]
+
+ env.step() # @6.0
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2"]
diff --git a/tests/unit/runtime/events/test_injection_servers_edges.py b/tests/unit/runtime/events/test_injection_servers_edges.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..966a9f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/runtime/events/test_injection_servers_edges.py
@@ -0,0 +1,237 @@
+"""Mixed timeline tests: edge spikes and server outages in the same run."""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from collections import OrderedDict
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+
+import pytest
+import simpy
+
+from asyncflow.config.constants import EventDescription
+from asyncflow.runtime.actors.edge import EdgeRuntime
+from asyncflow.runtime.events.injection import EventInjectionRuntime
+from asyncflow.schemas.common.random_variables import RVConfig
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import Server, ServerResources
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
+
+
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+# Helpers #
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+
+def _edge(edge_id: str, source: str, target: str) -> Edge:
+ """Create a minimal edge with negligible latency."""
+ return Edge(id=edge_id, source=source, target=target, latency=RVConfig(mean=0.001))
+
+
+def _srv(server_id: str) -> Server:
+ """Create a minimal, fully-typed Server instance for tests."""
+ return Server(id=server_id, server_resources=ServerResources(), endpoints=[])
+
+
+def _spike_event(
+ *, ev_id: str,
+ edge_id: str,
+ t0: float,
+ t1: float,
+ spike_s: float,
+ ) -> EventInjection:
+ """Build a NETWORK_SPIKE_START → NETWORK_SPIKE_END event for an edge."""
+ return EventInjection(
+ event_id=ev_id,
+ target_id=edge_id,
+ start={
+ "kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START,
+ "t_start": t0,
+ "spike_s": spike_s,
+ },
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END, "t_end": t1},
+ )
+
+
+def _srv_event(server_id: str, ev_id: str, t0: float, t1: float) -> EventInjection:
+ """Build a SERVER_DOWN → SERVER_UP event for a server."""
+ return EventInjection(
+ event_id=ev_id,
+ target_id=server_id,
+ start={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, "t_start": t0},
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_UP, "t_end": t1},
+ )
+
+
+def _drain_zero_time(env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
+ """Consume all events at the current time (typically t=0)."""
+ while env.peek() == env.now:
+ env.step()
+
+
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+# Tests #
+# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
+
+def test_edge_spike_and_server_outage_independent_timelines(
+ env: simpy.Environment, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """Edge spikes evolve independently from server outages on LB edges."""
+ # Topology pieces:
+ net_e = _edge("net-1", "X", "Y") # edge that will receive the spike
+ lb_e1 = _edge("lb-e1", "lb-1", "srv-1")
+ lb_e2 = _edge("lb-e2", "lb-1", "srv-2")
+
+ # Edge runtimes only for LB edges (spike is handled by injection runtime state)
+ er1 = EdgeRuntime(
+ env=env,
+ edge_config=lb_e1,
+ target_box=simpy.Store(env),
+ settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+ er2 = EdgeRuntime(
+ env=env,
+ edge_config=lb_e2,
+ target_box=simpy.Store(env),
+ settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+ lb_out = OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]([("lb-e1", er1), ("lb-e2", er2)])
+
+ # Events:
+ # - Server outage on srv-1: [1.0, 3.0] → lb-e1 removed at 1.0, reinserted at 3.0.
+ # - Edge spike on net-1: [2.0, 4.0] → +0.3 during [2.0, 4.0].
+ ev_srv = _srv_event("srv-1", "out-1", 1.0, 3.0)
+ ev_spk = _spike_event(
+ ev_id="spk-1", edge_id="net-1", t0=2.0, t1=4.0, spike_s=0.3,
+ )
+
+ inj = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[ev_srv, ev_spk],
+ edges=[net_e],
+ env=env,
+ servers=[_srv("srv-1"), _srv("srv-2")],
+ lb_out_edges=lb_out,
+ )
+ inj.start()
+
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e1", "lb-e2"]
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.0)
+
+ # @1.0 → server DOWN (srv-1) → remove lb-e1
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(1.0)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2"]
+ assert "lb-e1" not in lb_out
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.0)
+
+ # @2.0 → spike START on net-1 → +0.3
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(2.0)
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.3)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2"] # still down for srv-1
+
+ # @3.0 → server UP (srv-1) → reinsert lb-e1 at the end
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(3.0)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2", "lb-e1"]
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.3)
+
+ # @4.0 → spike END on net-1 → 0.0
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(4.0)
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-1", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.0)
+
+
+def test_interleaved_multiple_spikes_with_single_outage(
+ env: simpy.Environment, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """Multiple spikes can interleave with a single outage on a different component."""
+ # Components:
+ net_e = _edge("net-2", "S", "T")
+ lb_e1 = _edge("lb-e1", "lb-1", "srv-1")
+ lb_e2 = _edge("lb-e2", "lb-1", "srv-2")
+
+ er1 = EdgeRuntime(
+ env=env,
+ edge_config=lb_e1,
+ target_box=simpy.Store(env),
+ settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+ er2 = EdgeRuntime(
+ env=env,
+ edge_config=lb_e2,
+ target_box=simpy.Store(env),
+ settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+ lb_out = OrderedDict[str, EdgeRuntime]([("lb-e1", er1), ("lb-e2", er2)])
+
+ # Events timeline no equal timestamps across server/edge to
+ # avoid cross-process order assumptions):
+ # 1.0 server DOWN (srv-1) → remove lb-e1
+ # 2.0 spike A START on net-2 (+0.2) → +0.2
+ # 3.0 server UP (srv-1) → reinsert lb-e1 at the end
+ # 4.0 spike B START on net-2 (+0.1) → +0.3
+ # 5.0 spike A END on net-2 → +0.1
+ # 6.0 spike B END on net-2 → +0.0
+ ev_down = _srv_event("srv-1", "out-1", 1.0, 3.0)
+ spk_a = _spike_event(ev_id="spk-A", edge_id="net-2", t0=2.0, t1=5.0, spike_s=0.2)
+ spk_b = _spike_event(ev_id="spk-B", edge_id="net-2", t0=4.0, t1=6.0, spike_s=0.1)
+
+ inj = EventInjectionRuntime(
+ events=[ev_down, spk_a, spk_b],
+ edges=[net_e],
+ env=env,
+ servers=[_srv("srv-1"), _srv("srv-2")],
+ lb_out_edges=lb_out,
+ )
+ inj.start()
+
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e1", "lb-e2"]
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-2", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.0)
+
+ # @1.0 server DOWN → remove lb-e1
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(1.0)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2"]
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-2", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.0)
+
+ # @2.0 spike A START → +0.2
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(2.0)
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-2", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.2)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2"]
+
+ # @3.0 server UP → reinsert lb-e1 at the end
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(3.0)
+ assert list(lb_out.keys()) == ["lb-e2", "lb-e1"]
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-2", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.2)
+
+ # @4.0 spike B START → +0.3
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(4.0)
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-2", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.3)
+
+ # @5.0 spike A END → +0.1
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(5.0)
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-2", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.1)
+
+ # @6.0 spike B END → +0.0
+ env.step()
+ _drain_zero_time(env)
+ assert env.now == pytest.approx(6.0)
+ assert inj.edges_spike.get("net-2", 0.0) == pytest.approx(0.0)
+
diff --git a/tests/unit/runtime/test_simulation_runner.py b/tests/unit/runtime/test_simulation_runner.py
index 3a352f5..9ec9299 100644
--- a/tests/unit/runtime/test_simulation_runner.py
+++ b/tests/unit/runtime/test_simulation_runner.py
@@ -14,14 +14,30 @@
import simpy
import yaml
+from asyncflow.config.constants import Distribution, EventDescription
from asyncflow.runtime.simulation_runner import SimulationRunner
+from asyncflow.schemas.common.random_variables import RVConfig
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import EventInjection
+from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
+from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.graph import TopologyGraph
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import (
+ Client,
+ LoadBalancer,
+ Server,
+ ServerResources,
+ TopologyNodes,
+)
if TYPE_CHECKING:
from pathlib import Path
from asyncflow.runtime.actors.client import ClientRuntime
from asyncflow.runtime.actors.rqs_generator import RqsGeneratorRuntime
- from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
+ from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
+ from asyncflow.schemas.workload.rqs_generator import RqsGenerator
+
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
@@ -43,7 +59,7 @@ def runner(
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
-# Builder-level tests #
+# Builder-level tests (original) #
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
def test_build_rqs_generator_populates_dict(runner: SimulationRunner) -> None:
"""_build_rqs_generator() must register one generator runtime."""
@@ -77,13 +93,13 @@ def test_build_servers_keeps_empty_with_minimal_topology(
def test_build_load_balancer_noop_when_absent(
runner: SimulationRunner,
) -> None:
- """No LB in the payload → builder leaves dict empty."""
+ """No LB in the payload → builder leaves runtime as None."""
runner._build_load_balancer() # noqa: SLF001
- assert runner._lb_runtime == {} # noqa: SLF001
+ assert runner._lb_runtime is None # noqa: SLF001
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
-# Edges builder #
+# Edges builder (original) #
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
def test_build_edges_with_stub_edge(runner: SimulationRunner) -> None:
"""
@@ -91,14 +107,14 @@ def test_build_edges_with_stub_edge(runner: SimulationRunner) -> None:
to the single stub edge (generator → client) present in the minimal
topology fixture.
"""
- runner._build_rqs_generator() # noqa: SLF001
- runner._build_client() # noqa: SLF001
- runner._build_edges() # noqa: SLF001
+ runner._build_rqs_generator() # noqa: SLF001
+ runner._build_client() # noqa: SLF001
+ runner._build_edges() # noqa: SLF001
assert len(runner._edges_runtime) == 1 # noqa: SLF001
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
-# from_yaml utility #
+# from_yaml utility (original) #
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
def test_from_yaml_minimal(tmp_path: Path, env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
"""from_yaml() parses YAML, validates via Pydantic and returns a runner."""
@@ -124,3 +140,141 @@ def test_from_yaml_minimal(tmp_path: Path, env: simpy.Environment) -> None:
assert isinstance(runner, SimulationRunner)
assert runner.rqs_generator.id == "gen-yaml"
assert runner.client.id == "cli-yaml"
+
+
+def _payload_with_lb_one_server_and_edges(
+ *,
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator,
+ sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> SimulationPayload:
+ """Build a small payload with LB → server wiring and one net edge."""
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+ server = Server(id="srv-1", server_resources=ServerResources(), endpoints=[])
+ lb = LoadBalancer(id="lb-1")
+ nodes = TopologyNodes(servers=[server], client=client, load_balancer=lb)
+
+ e_gen_lb = Edge(
+ id="gen-lb",
+ source=rqs_input.id,
+ target=lb.id,
+ latency=RVConfig(mean=0.001, distribution=Distribution.POISSON),
+ )
+ e_lb_srv = Edge(
+ id="lb-srv",
+ source=lb.id,
+ target=server.id,
+ latency=RVConfig(mean=0.002, distribution=Distribution.POISSON),
+ )
+ e_net = Edge(
+ id="net-edge",
+ source=rqs_input.id,
+ target=client.id,
+ latency=RVConfig(mean=0.003, distribution=Distribution.POISSON),
+ )
+ graph = TopologyGraph(nodes=nodes, edges=[e_gen_lb, e_lb_srv, e_net])
+
+ return SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=graph,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+
+
+def test_make_inbox_bound_to_env_and_fifo(runner: SimulationRunner) -> None:
+ """_make_inbox() binds to runner.env and behaves FIFO."""
+ box = runner._make_inbox() # noqa: SLF001
+ assert isinstance(box, simpy.Store)
+
+ # Put two items and consume them in order using `run(until=...)`.
+ env = runner.env
+ env.run(until=box.put("first"))
+ env.run(until=box.put("second"))
+ got1 = env.run(until=box.get())
+ got2 = env.run(until=box.get())
+ assert got1 == "first"
+ assert got2 == "second"
+
+
+def test_build_load_balancer_when_present(
+ env: simpy.Environment,
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator,
+ sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """_build_load_balancer() should create `_lb_runtime` if LB exists."""
+ payload = _payload_with_lb_one_server_and_edges(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input, sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+ sr = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+
+ sr._build_load_balancer() # noqa: SLF001
+ assert sr._lb_runtime is not None # noqa: SLF001
+ assert sr._lb_runtime.lb_config.id == "lb-1" # noqa: SLF001
+
+
+def test_build_edges_populates_lb_out_edges_and_sources(
+ env: simpy.Environment,
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator,
+ sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """_build_edges() wires generator→LB and populates `_lb_out_edges`."""
+ payload = _payload_with_lb_one_server_and_edges(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input, sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+ sr = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+
+ sr._build_rqs_generator() # noqa: SLF001
+ sr._build_client() # noqa: SLF001
+ sr._build_servers() # noqa: SLF001
+ sr._build_load_balancer() # noqa: SLF001
+ sr._build_edges() # noqa: SLF001
+
+ assert "lb-srv" in sr._lb_out_edges # noqa: SLF001
+ assert len(sr._edges_runtime) >= 2 # noqa: SLF001
+ gen_rt = next(iter(sr._rqs_runtime.values())) # noqa: SLF001
+ assert gen_rt.out_edge is not None
+
+
+def test_build_events_attaches_shared_views(
+ env: simpy.Environment,
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator,
+ sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """_build_events() attaches shared `edges_affected` and `edges_spike` views."""
+ payload = _payload_with_lb_one_server_and_edges(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input, sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ )
+ spike = EventInjection(
+ event_id="ev-spike",
+ target_id="net-edge",
+ start={
+ "kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START,
+ "t_start": 0.2,
+ "spike_s": 0.05,
+ },
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END, "t_end": 0.4},
+ )
+ outage = EventInjection(
+ event_id="ev-out",
+ target_id="srv-1",
+ start={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, "t_start": 0.1},
+ end={"kind": EventDescription.SERVER_UP, "t_end": 0.3},
+ )
+ payload.events = [spike, outage]
+
+ sr = SimulationRunner(env=env, simulation_input=payload)
+ sr._build_rqs_generator() # noqa: SLF001
+ sr._build_client() # noqa: SLF001
+ sr._build_servers() # noqa: SLF001
+ sr._build_load_balancer() # noqa: SLF001
+ sr._build_edges() # noqa: SLF001
+ sr._build_events() # noqa: SLF001
+
+ assert sr._events_runtime is not None # noqa: SLF001
+ events_rt = sr._events_runtime # noqa: SLF001
+
+ assert "net-edge" in events_rt.edges_affected
+ for er in sr._edges_runtime.values(): # noqa: SLF001
+ assert er.edges_spike is not None
+ assert er.edges_affected is events_rt.edges_affected
+
+
diff --git a/tests/unit/schemas/test_event_injection.py b/tests/unit/schemas/test_event_injection.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5593fd7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/schemas/test_event_injection.py
@@ -0,0 +1,196 @@
+"""Unit tests for the EventInjection Pydantic models.
+
+This suite verifies:
+- Family coherence: SERVER_DOWN→SERVER_UP and
+ NETWORK_SPIKE_START→NETWORK_SPIKE_END.
+- Temporal ordering: t_start < t_end, with field constraints.
+- Spike semantics: spike_s is required only for NETWORK_SPIKE_START
+ and forbidden otherwise.
+- Strictness: unknown fields are rejected; models are frozen.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+import re
+from typing import Any
+
+import pytest
+from pydantic import ValidationError
+
+from asyncflow.config.constants import EventDescription
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import End, EventInjection, Start
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Helpers
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+def _mk_server_down(start_t: float, end_t: float) -> EventInjection:
+ """Build a minimal server down/up event with the given times."""
+ start = Start(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, t_start=start_t)
+ end = End(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_UP, t_end=end_t)
+ return EventInjection(
+ event_id="ev-server-1",
+ target_id="srv-1",
+ start=start,
+ end=end,
+ )
+
+
+def _mk_network_spike(
+ start_t: float,
+ end_t: float,
+ spike_s: float | None,
+) -> EventInjection:
+ """Build a minimal network spike event with the given times and spike."""
+ start = Start(
+ kind=EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START,
+ t_start=start_t,
+ spike_s=spike_s,
+ )
+ end = End(kind=EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END, t_end=end_t)
+ return EventInjection(
+ event_id="ev-spike-1",
+ target_id="edge-1",
+ start=start,
+ end=end,
+ )
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Start/End family coherence
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+def test_family_coherence_server_ok() -> None:
+ """SERVER_DOWN followed by SERVER_UP should validate."""
+ model = _mk_server_down(start_t=10.0, end_t=20.0)
+ assert model.start.kind is EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN
+ assert model.end.kind is EventDescription.SERVER_UP
+
+
+def test_family_coherence_network_ok() -> None:
+ """NETWORK_SPIKE_START followed by NETWORK_SPIKE_END should validate."""
+ model = _mk_network_spike(start_t=1.0, end_t=2.0, spike_s=0.005)
+ assert model.start.kind is EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START
+ assert model.end.kind is EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END
+
+
+def test_family_mismatch_raises() -> None:
+ """Mismatched start/end families must raise a ValueError."""
+ start = Start(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, t_start=1.0)
+ end = End(kind=EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END, t_end=2.0)
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=r"must have .* kind in end"):
+ EventInjection(
+ event_id="ev-bad",
+ target_id="srv-1",
+ start=start,
+ end=end,
+ )
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Temporal ordering & per-field constraints
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+def test_time_ordering_start_before_end() -> None:
+ """t_start must be strictly less than t_end."""
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=r"smaller than the ending time"):
+ _mk_server_down(start_t=10.0, end_t=10.0)
+
+
+def test_start_non_negative_enforced() -> None:
+ """Start.t_start is NonNegativeFloat; negatives raise ValidationError."""
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError):
+ Start(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, t_start=-1.0)
+
+
+def test_end_positive_enforced() -> None:
+ """End.t_end is PositiveFloat; non-positive values raise ValidationError."""
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError):
+ End(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_UP, t_end=0.0)
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Spike semantics
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+def test_network_spike_requires_spike_s() -> None:
+ """NETWORK_SPIKE_START requires spike_s (seconds) to be present."""
+ # Define the event id for the matching condition.
+ event_id = "ev-spike-1"
+
+ # Define the full message to be matched
+ expected_message = (
+ f"The field spike_s for the event {event_id} "
+ "must be defined as a positive float"
+ )
+
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError, match=re.escape(expected_message)):
+ _mk_network_spike(start_t=0.5, end_t=1.5, spike_s=None)
+
+
+def test_network_spike_positive_spike_s_enforced() -> None:
+ """spike_s uses PositiveFloat; negative values raise ValidationError."""
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError):
+ _mk_network_spike(start_t=0.0, end_t=1.0, spike_s=-0.001)
+
+
+def test_spike_s_forbidden_for_server_events() -> None:
+ """For non-network events, spike_s must be omitted."""
+ event_id = "ev-bad-spike"
+ expected_message = f"Event {event_id}: spike_s must be omitted"
+ start = Start(
+ kind=EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN,
+ t_start=0.0,
+ spike_s=0.001,
+ )
+ end = End(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_UP, t_end=1.0)
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=re.escape(expected_message)):
+ EventInjection(
+ event_id="ev-bad-spike",
+ target_id="srv-1",
+ start=start,
+ end=end,
+ )
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Strictness (extra fields) and immutability (frozen models)
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+def test_extra_fields_forbidden_in_start() -> None:
+ """Unknown fields in Start must be rejected due to extra='forbid'."""
+ payload: dict[str, Any] = {
+ "kind": EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN,
+ "t_start": 0.0,
+ "unknown_field": 123,
+ }
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError):
+ Start.model_validate(payload)
+
+
+def test_extra_fields_forbidden_in_end() -> None:
+ """Unknown fields in End must be rejected due to extra='forbid'."""
+ payload: dict[str, Any] = {
+ "kind": EventDescription.SERVER_UP,
+ "t_end": 1.0,
+ "unknown_field": True,
+ }
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError):
+ End.model_validate(payload)
+
+
+def test_start_is_frozen_and_immutable() -> None:
+ """Start is frozen; attempting to mutate fields must raise an error."""
+ start = Start(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, t_start=0.0)
+ # Cast to Any to avoid mypy's read-only property check; runtime must fail.
+ start_any: Any = start
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError, match="Instance is frozen"):
+ start_any.t_start = 1.0
+
+
+def test_end_is_frozen_and_immutable() -> None:
+ """End is frozen; attempting to mutate fields must raise an error."""
+ end = End(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_UP, t_end=1.0)
+ end_any: Any = end
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError, match="Instance is frozen"):
+ end_any.t_end = 2.0
diff --git a/tests/unit/schemas/test_payload.py b/tests/unit/schemas/test_payload.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8547f83
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/schemas/test_payload.py
@@ -0,0 +1,374 @@
+"""Unit tests for the SimulationPayload Pydantic model.
+
+This suite verifies:
+- Unique event IDs constraint.
+- Target existence against the topology graph.
+- Event times inside the simulation horizon.
+- Kind/target compatibility (server vs. edge).
+- Global liveness: not all servers down simultaneously.
+
+All tests are ruff- and mypy-friendly (short lines, precise raises, and
+single statements inside raises blocks). They reuse fixtures from
+conftest.py where convenient and build custom topologies when needed.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
+
+import pytest
+
+from asyncflow.config.constants import Distribution, EventDescription
+from asyncflow.schemas.common.random_variables import RVConfig
+from asyncflow.schemas.events.injection import End, EventInjection, Start
+from asyncflow.schemas.payload import SimulationPayload
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.edges import Edge
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.graph import TopologyGraph
+from asyncflow.schemas.topology.nodes import (
+ Client,
+ Server,
+ TopologyNodes,
+)
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ from asyncflow.schemas.settings.simulation import SimulationSettings
+ from asyncflow.schemas.workload.rqs_generator import RqsGenerator
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Helpers
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+
+def _mk_network_spike(
+ event_id: str,
+ target_id: str,
+ start_t: float,
+ end_t: float,
+ spike_s: float,
+) -> EventInjection:
+ """Build a NETWORK_SPIKE event for the given target edge."""
+ start = Start(
+ kind=EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_START,
+ t_start=start_t,
+ spike_s=spike_s,
+ )
+ end = End(kind=EventDescription.NETWORK_SPIKE_END, t_end=end_t)
+ return EventInjection(
+ event_id=event_id,
+ target_id=target_id,
+ start=start,
+ end=end,
+ )
+
+
+def _mk_server_window(
+ event_id: str,
+ target_id: str,
+ start_t: float,
+ end_t: float,
+) -> EventInjection:
+ """Build a SERVER_DOWN → SERVER_UP event for the given server."""
+ start = Start(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_DOWN, t_start=start_t)
+ end = End(kind=EventDescription.SERVER_UP, t_end=end_t)
+ return EventInjection(
+ event_id=event_id,
+ target_id=target_id,
+ start=start,
+ end=end,
+ )
+
+
+def _topology_with_min_edge() -> TopologyGraph:
+ """Create a tiny topology with one client and one minimal edge."""
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+ edge = Edge(
+ id="gen-to-client",
+ source="rqs-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency=RVConfig(mean=0.001, distribution=Distribution.POISSON),
+ )
+ nodes = TopologyNodes(servers=[], client=client)
+ return TopologyGraph(nodes=nodes, edges=[edge])
+
+
+def _topology_with_two_servers_and_edge() -> TopologyGraph:
+ """Create a topology with two servers and a minimal edge."""
+ client = Client(id="client-1")
+ servers = [
+ Server(id="srv-1", server_resources={"cpu_cores": 1}, endpoints=[]),
+ Server(id="srv-2", server_resources={"cpu_cores": 1}, endpoints=[]),
+]
+ edge = Edge(
+ id="gen-to-client",
+ source="rqs-1",
+ target="client-1",
+ latency=RVConfig(mean=0.001, distribution=Distribution.POISSON),
+ )
+ nodes = TopologyNodes(servers=servers, client=client)
+ return TopologyGraph(nodes=nodes, edges=[edge])
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Unique event IDs
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+
+def test_unique_event_ids_ok(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """Different event_id values should validate."""
+ topo = _topology_with_min_edge()
+ ev1 = _mk_network_spike(
+ "ev-a", "gen-to-client", start_t=0.0, end_t=1.0, spike_s=0.001,
+ )
+ ev2 = _mk_network_spike(
+ "ev-b", "gen-to-client", start_t=2.0, end_t=3.0, spike_s=0.002,
+ )
+ payload = SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev1, ev2],
+ )
+ assert payload.events is not None
+ assert len(payload.events) == 2
+
+
+def test_duplicate_event_ids_rejected(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """Duplicate event_id values must be rejected."""
+ topo = _topology_with_min_edge()
+ ev1 = _mk_network_spike(
+ "ev-dup", "gen-to-client", start_t=0.0, end_t=1.0, spike_s=0.001,
+ )
+ ev2 = _mk_network_spike(
+ "ev-dup", "gen-to-client", start_t=2.0, end_t=3.0, spike_s=0.002,
+ )
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=r"must be unique"):
+ SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev1, ev2],
+ )
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Target existence
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+
+def test_target_id_must_exist(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """Target IDs not present in the topology must be rejected."""
+ topo = _topology_with_min_edge()
+ ev = _mk_network_spike(
+ "ev-x", "missing-edge", start_t=0.0, end_t=1.0, spike_s=0.001,
+ )
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=r"does not exist"):
+ SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev],
+ )
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Event times within horizon
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+
+def test_start_time_exceeds_horizon_rejected(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """Start time greater than the horizon must be rejected."""
+ topo = _topology_with_min_edge()
+ horizon = float(sim_settings.total_simulation_time)
+ ev = _mk_network_spike(
+ "ev-hz-start",
+ "gen-to-client",
+ start_t=horizon + 0.1,
+ end_t=horizon + 0.2,
+ spike_s=0.001,
+ )
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=r"exceeds simulation horizon"):
+ SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev],
+ )
+
+
+def test_end_time_exceeds_horizon_rejected(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """End time greater than the horizon must be rejected."""
+ topo = _topology_with_min_edge()
+ horizon = float(sim_settings.total_simulation_time)
+ ev = _mk_network_spike(
+ "ev-hz-end",
+ "gen-to-client",
+ start_t=horizon - 0.1,
+ end_t=horizon + 0.1,
+ spike_s=0.001,
+ )
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=r"exceeds simulation horizon"):
+ SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev],
+ )
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Kind/target compatibility
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+
+def test_server_event_cannot_target_edge(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """SERVER_DOWN should not target an edge ID."""
+ topo = _topology_with_min_edge()
+ ev = _mk_server_window(
+ "ev-srv-bad",
+ target_id="gen-to-client",
+ start_t=0.0,
+ end_t=1.0,
+ )
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=r"regarding a server .* compatible"):
+ SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev],
+ )
+
+
+def test_edge_event_ok_on_edge(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """NETWORK_SPIKE event is valid when it targets an edge ID."""
+ topo = _topology_with_min_edge()
+ ev = _mk_network_spike(
+ "ev-edge-ok", "gen-to-client", start_t=0.0, end_t=1.0, spike_s=0.001,
+ )
+ payload = SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev],
+ )
+ assert payload.events is not None
+ assert payload.events[0].target_id == "gen-to-client"
+
+
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+# Global liveness: not all servers down simultaneously
+# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+
+def test_reject_when_all_servers_down_at_same_time(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """
+ It should raise a ValidationError if there is any time interval during which
+ all servers are scheduled to be down simultaneously.
+ """
+ topo = _topology_with_two_servers_and_edge()
+
+ # --- SETUP: Use a longer simulation horizon for this specific test ---
+ # The default `sim_settings` fixture has a short horizon (e.g., 5s) to
+ # keep most tests fast. For this test, we need a longer horizon to
+ # ensure the event times themselves are valid.
+ sim_settings.total_simulation_time = 30 # e.g., 30 seconds
+
+ # The event times are now valid within the new horizon.
+ # srv-1 is down [10, 20), srv-2 is down [15, 25).
+ # This creates an overlap in [15, 20) where both are down.
+ ev_a = _mk_server_window("ev-a", "srv-1", start_t=10.0, end_t=20.0)
+ ev_b = _mk_server_window("ev-b", "srv-2", start_t=15.0, end_t=25.0)
+
+ # Now the test will bypass the time horizon validation and trigger
+ # the correct validator that checks for server downtime overlap.
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=r"all servers are down"):
+ SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev_a, ev_b],
+ )
+
+
+def test_accept_when_never_all_down(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """Payload is valid when at least one server stays up at all times."""
+ topo = _topology_with_two_servers_and_edge()
+
+ # --- SETUP: Use a longer simulation horizon for this specific test ---
+ # As before, we need to ensure the event times are valid within the
+ # simulation's total duration.
+ sim_settings.total_simulation_time = 30 # e.g., 30 seconds
+
+ # Staggered windows: srv-1 down [10, 15), srv-2 down [15, 20).
+ # There is no point in time where both are down.
+ ev_a = _mk_server_window("ev-a", "srv-1", start_t=10.0, end_t=15.0)
+ ev_b = _mk_server_window("ev-b", "srv-2", start_t=15.0, end_t=20.0)
+
+ # This should now pass validation without raising an error.
+ payload = SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev_a, ev_b],
+ )
+ assert payload.events is not None
+ assert len(payload.events) == 2
+
+
+def test_server_outage_back_to_back_is_valid(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """Back-to-back outages on the same server (END==START) must be accepted."""
+ topo = _topology_with_two_servers_and_edge()
+ sim_settings.total_simulation_time = 30 # ensure timestamps are within horizon
+
+ # srv-1: [10, 15] followed immediately by [15, 20] → no overlap
+ ev_a = _mk_server_window("ev-a", "srv-1", start_t=10.0, end_t=15.0)
+ ev_b = _mk_server_window("ev-b", "srv-1", start_t=15.0, end_t=20.0)
+
+ payload = SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev_a, ev_b],
+ )
+ assert payload.events is not None
+ assert len(payload.events) == 2
+
+
+def test_server_outage_overlap_same_server_is_rejected(
+ rqs_input: RqsGenerator, sim_settings: SimulationSettings,
+) -> None:
+ """Overlapping outages on the same server must be rejected by validation."""
+ topo = _topology_with_two_servers_and_edge()
+ sim_settings.total_simulation_time = 30 # ensure timestamps are within horizon
+
+ # srv-1: [10, 15] and [14, 20] → overlap in [14, 15]
+ ev_a = _mk_server_window("ev-a", "srv-1", start_t=10.0, end_t=15.0)
+ ev_b = _mk_server_window("ev-b", "srv-1", start_t=14.0, end_t=20.0)
+
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=r"Overlapping events for"):
+ SimulationPayload(
+ rqs_input=rqs_input,
+ topology_graph=topo,
+ sim_settings=sim_settings,
+ events=[ev_a, ev_b],
+ )
 +
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+