-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 385
Register your application with Azure Active Directory
Jean-Marc Prieur edited this page Mar 6, 2018
·
20 revisions
Before using MSAL.NET you will have to register you applications with Azure AD.
Azure AD currently supports several kinds of applications, depending on type of users they target:
- Azure AD v1 applications, let users sign-in with their work and school account use ADAL.NET and need to be registered in the Azure portal (https://portal.azure.com).
- Azure AD v2 application let users sign-in with their work and school accounts or their personal accounts use MSAL.NET, which is a different library, currently in Preview. Currently the applications need to be registered in a different portal https://dev.apps.microsoft.com, unless they are Azure AD B2C applications.
If you are not familiar with v2 application registration, you might want to follow the following tutorials:
- Call the Microsoft Graph API from a Windows Desktop app. Reading the following article will also be valuable: Type of Apps in the V2 endpoint
- Add sign-in with Microsoft to an ASP.NET web app
The picture below shows in which case you want to use MSAL.NET: when you want the users of the application to sign-in with Azure AD (work and school accounts) or Microsoft (personal) accounts (MSA), or with Azure AD B2C.
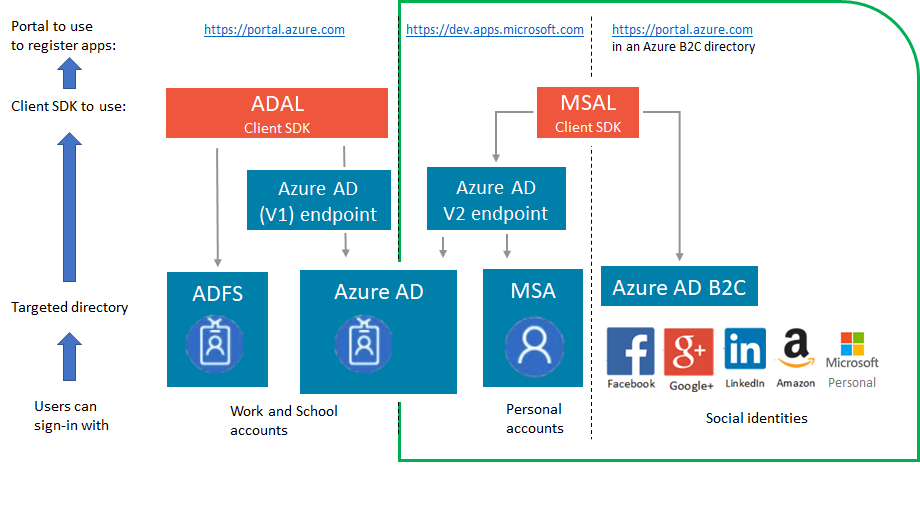
But you still need to use ADAL.NET if your application needs to sign-in users with Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)
Also, before choosing to use MSAL.NET you might also want to read:
Note that MSAL is work in progress.
- Home
- Why use MSAL.NET
- Is MSAL.NET right for me
- Scenarios
- Register your app with AAD
- Client applications
- Acquiring tokens
- MSAL samples
- Known Issues
- Acquiring a token for the app
- Acquiring a token on behalf of a user in Web APIs
- Acquiring a token by authorization code in Web Apps
- AcquireTokenInteractive
- WAM - the Windows broker
- .NET Core
- Maui Docs
- Custom Browser
- Applying an AAD B2C policy
- Integrated Windows Authentication for domain or AAD joined machines
- Username / Password
- Device Code Flow for devices without a Web browser
- ADFS support
- High Availability
- Regional
- Token cache serialization
- Logging
- Exceptions in MSAL
- Provide your own Httpclient and proxy
- Extensibility Points
- Clearing the cache
- Client Credentials Multi-Tenant guidance
- Performance perspectives
- Differences between ADAL.NET and MSAL.NET Apps
- PowerShell support
- Testing apps that use MSAL
- Experimental Features
- Proof of Possession (PoP) tokens
- Using in Azure functions
- Extract info from WWW-Authenticate headers
- SPA Authorization Code