-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 385
Register your application with Azure Active Directory
Before using MSAL.NET you will have to register your applications with Azure AD.
Azure AD currently supports several kinds of applications, depending on what type of users they target:
- Azure AD v1.0 applications that allow users to sign-in with their work and school account use ADAL.NET and need to be registered in the Azure portal (https://portal.azure.com).
- Azure AD v2.0 applications that allow users to sign-in with either their work and school accounts or their personal accounts use MSAL.NET, which is a different library currently in preview. At the moment, the applications need to be registered in a different portal https://apps.dev.microsoft.com, unless they are Azure AD B2C applications.
If you are not familiar with v2.0 application registration, you might want to follow the following tutorials:
- Call the Microsoft Graph API from a Windows Desktop app.
- Add sign-in with Microsoft to an ASP.NET web app
Reading the following article will also be valuable: Type of Apps in the v2.0 endpoint
The picture below shows the scenarios where you want to use MSAL.NET:
when you want the users of the application to sign-in with Azure AD (work and school accounts), Microsoft (personal) accounts (MSA) or Azure AD B2C.
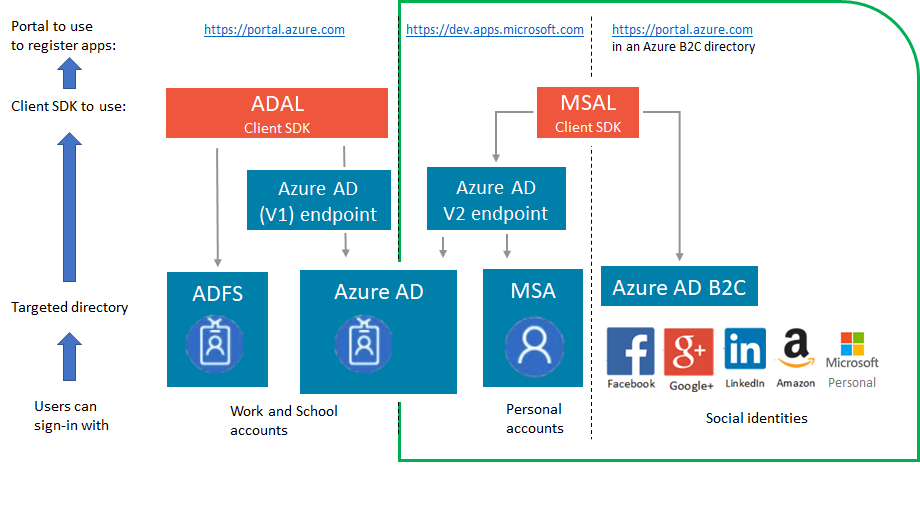
However, you still need to use ADAL.NET if your application needs to sign-in users with Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)
Also, before choosing to use MSAL.NET you might want to read Should I use the v2.0 endpoint?; in particular, the restrictions as of today.
If you are already familiar with the v1.0 endpoint (and ADAL.NET), you might want to read What's different about the v2.0 endpoint?
See also ADAL.NET to MSAL.NET, which explains how to port an application using ADAL.NET to MSAL.NET
Note that MSAL is work in progress.
- Home
- Why use MSAL.NET
- Is MSAL.NET right for me
- Scenarios
- Register your app with AAD
- Client applications
- Acquiring tokens
- MSAL samples
- Known Issues
- Acquiring a token for the app
- Acquiring a token on behalf of a user in Web APIs
- Acquiring a token by authorization code in Web Apps
- AcquireTokenInteractive
- WAM - the Windows broker
- .NET Core
- Maui Docs
- Custom Browser
- Applying an AAD B2C policy
- Integrated Windows Authentication for domain or AAD joined machines
- Username / Password
- Device Code Flow for devices without a Web browser
- ADFS support
- High Availability
- Regional
- Token cache serialization
- Logging
- Exceptions in MSAL
- Provide your own Httpclient and proxy
- Extensibility Points
- Clearing the cache
- Client Credentials Multi-Tenant guidance
- Performance perspectives
- Differences between ADAL.NET and MSAL.NET Apps
- PowerShell support
- Testing apps that use MSAL
- Experimental Features
- Proof of Possession (PoP) tokens
- Using in Azure functions
- Extract info from WWW-Authenticate headers
- SPA Authorization Code