Peak-to-gene correlation analysis using an FDR emprically-derived via permutation #1149
RegnerM2015
started this conversation in
Show and tell
Replies: 3 comments 13 replies
-
|
better late than never? This has now been incorporated into |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
3 replies
-
|
Hi @rcorces , how can I use this approach currently with ArchR? |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
6 replies
-
|
Hi @RegnerM2015 - thanks for this method. I was wondering if you get the above error or not?
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
4 replies
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
-
Peak-to-gene correlation analysis with an empirically derived FDR via permutation
Hi ArchR users and @rcorces,
In Regner et al. "A multi-omic single-cell landscape of human gynecologic malignancies", the authors use an empirically-derived FDR for assessing statistical significance of peak-to-gene associations. This is similar to the concept implemented by the
addEmpiricalPvalparameter inaddPeak2GeneLinks. The idea is to find background or null peak-to-gene associations and use this background to estimate the false discovery rate for a chosen alpha. Instead of finding null associations between peaks and genes located on different chromosomes, you can also induce the null condition by permuting the scATAC aggregate/metacell labels (Figure 1). In some cases, this may offer increased statistical power to detect peak-to-gene associations.Figure 1 | Peak-to-gene correlation analysis with an empirically derived FDR.
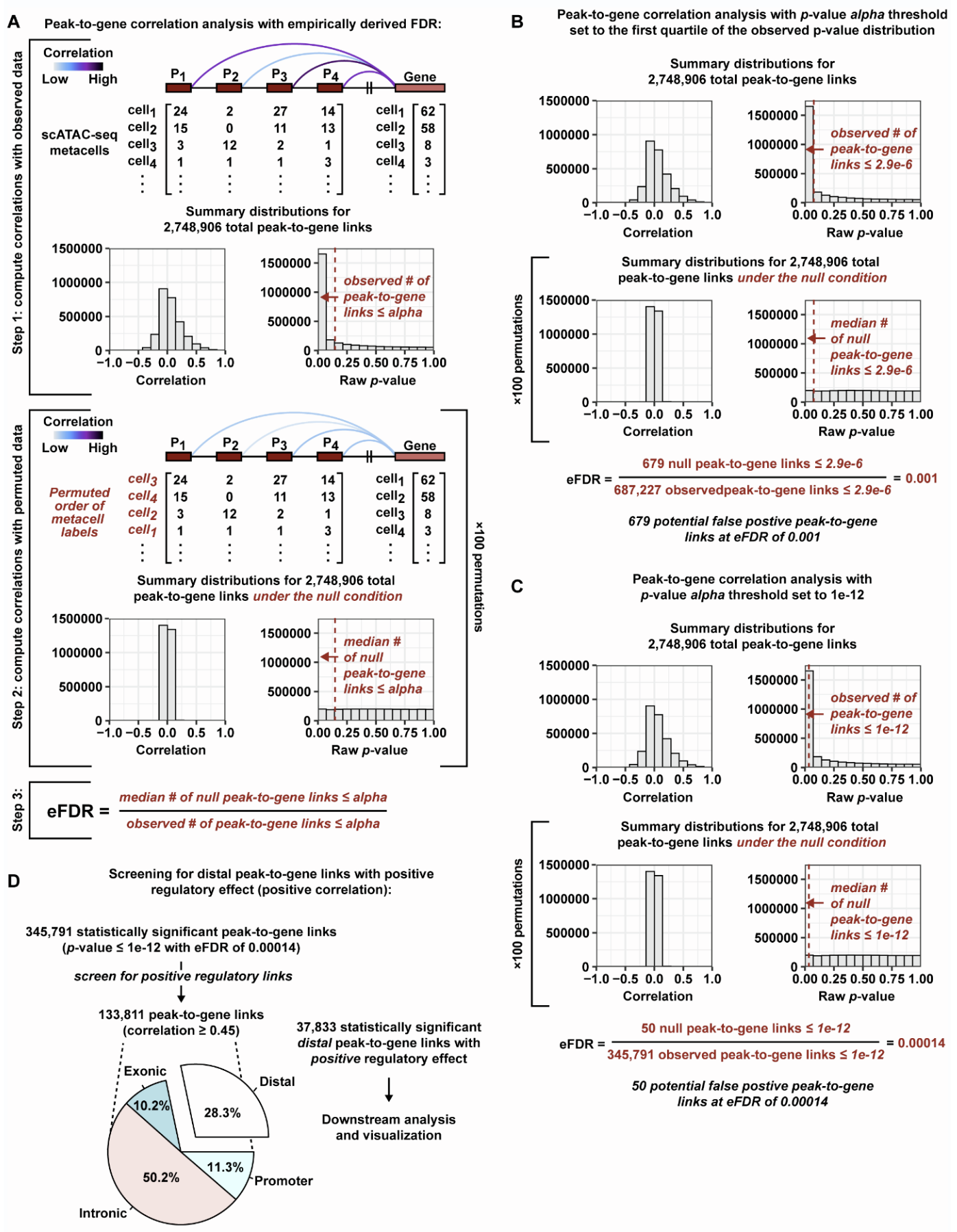
Adapted from Regner et al., A multi-omic single-cell landscape of human gynecologic malignancies, Molecular Cell (2021), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.10.013
A) Schematic illustrating the peak-to-gene correlation analysis. Step 1: the peak count
information from scATAC-seq cells is aggregated into metacells via a KNN algorithm before
computing the correlation between every peak and every gene located up to 250kb away. The
distribution of correlation values and raw p-values are visualized in histograms and the number
of observed peak-to-gene link tests <= alpha is recorded. Step 2: the peak-to-gene correlations
are re-computed for a permuted null version of the dataset where the scATAC-seq metacell
labels are shuffled, breaking the link or any potential correlation between peaks and genes. The
process is repeated for a total of 100 permutations. For each permutation, the number of null
peak-to-gene link tests <= alpha is recorded. As an example, the distribution of null correlation
values and null raw p-values are visualized in histograms for one permutation run. Step 3: The
median number of null peak-to-gene link tests <= alpha across 100 permutations is divided by
the number of observed peak-to-gene link tests <= alpha to arrive at an empirically derived FDR
(eFDR).
B) The peak-to-gene correlation analysis, as described in A, but using an alpha threshold equal
to the first quartile in the distribution of raw p-values.
C) The peak-to-gene correlation analysis, as described in A, but using an alpha threshold equal
to 1e-12.
D) Flow chart demonstrating the screening procedure used to identify distal peak-to-gene links
with positive regulatory effects. The pie chart depicts the proportion of positive regulatory peak-
to-gene links that are distal peak-to-gene relationships.
How to implement using ArchR?
The authors developed this approach by making only a slight modification the source code of
addPeak2GeneLinksto create a new functionaddPermPeak2GeneLinks. Before computing the correlations, the ATAC aggregate/metacell labels are randomly shuffled withsample()while the corresponding RNA aggregate/metacell labels are left unmodified. This effectively breaks the link between peak accessibility and gene expression offering a robust set of null peak-to-gene associations:Code from https://github.com/RegnerM2015/scENDO_scOVAR_2020/blob/main/PeaktoGeneLink_Analysis/Full_Cohort/Archr_Peak_Null_Permute.R#L222-L241
Limitations
There are some limitations associated with this approach. First, this approach is computationally expensive as you would have to run the
addPermPeak2GeneLinksn times to generate n permutations. Secondly, it may be difficult to implement this framework into the current ArchR suite of tools. We are open to suggestions and new ideas for making this approach accessible to the community!Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions