` of the Create/Update operation. To learn how to do that, please take a look at the next section - how to make an operation wider or narrower.
+
+
+### How to make an operation wider or narrower
+
+If you want to make the contents of an operation take more / less space from the window, you can easily do that. You just need to change the class on the main `
` of that operation, what we call the "content class". Depending on the scope of your change (for one or all CRUDs) here's how you can do that:
+
+(A) for all CRUDs, by specifying the custom content class in your ```config/backpack/crud.php```:
+
+```php
+ // Here you may override the css-classes for the content section of the create view globally
+ // To override per view use $this->crud->setCreateContentClass('class-string')
+ 'create_content_class' => 'col-md-8 col-md-offset-2',
+
+ // Here you may override the css-classes for the content section of the edit view globally
+ // To override per view use $this->crud->setEditContentClass('class-string')
+ 'edit_content_class' => 'col-md-8 col-md-offset-2',
+
+ // Here you may override the css-classes for the content section of the revisions timeline view globally
+ // To override per view use $this->crud->setRevisionsTimelineContentClass('class-string')
+ 'revisions_timeline_content_class' => 'col-md-10 col-md-offset-1',
+
+ // Here you may override the css-class for the content section of the list view globally
+ // To override per view use $this->crud->setListContentClass('class-string')
+ 'list_content_class' => 'col-md-12',
+
+ // Here you may override the css-classes for the content section of the show view globally
+ // To override per view use $this->crud->setShowContentClass('class-string')
+ 'show_content_class' => 'col-md-8 col-md-offset-2',
+
+ // Here you may override the css-classes for the content section of the reorder view globally
+ // To override per view use $this->crud->setReorderContentClass('class-string')
+ 'reorder_content_class' => 'col-md-8 col-md-offset-2',
+```
+
+(B) for a single CRUD, by using:
+
+```php
+CRUD::setCreateContentClass('col-md-8 col-md-offset-2');
+CRUD::setUpdateContentClass('col-md-8 col-md-offset-2');
+CRUD::setListContentClass('col-md-8 col-md-offset-2');
+CRUD::setShowContentClass('col-md-8 col-md-offset-2');
+CRUD::setReorderContentClass('col-md-8 col-md-offset-2');
+CRUD::setRevisionsTimelineContentClass('col-md-8 col-md-offset-2');
+```
+
+
+
+## Miscellaneous
+
+
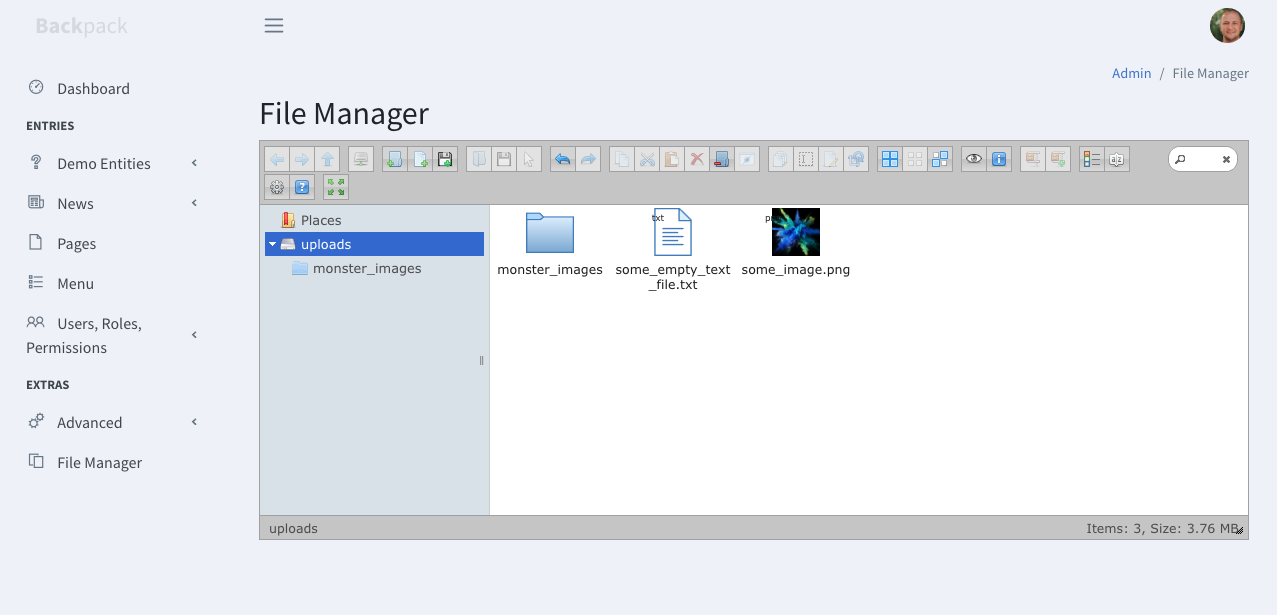
+### Use the Media Library (File Manager)
+
+The default Backpack installation doesn't come with a file management component. Because most projects don't need it. But we've created a first-party add-on that brings the power of [elFinder](http://elfinder.org/) to your Laravel projects. To install it, [follow the instructions on the add-ons page](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/FileManager). It's as easy as running:
+
+```bash
+# require the package
+composer require backpack/filemanager
+
+# then run the installation process
+php artisan backpack:filemanager:install
+```
+
+If you've chosen to install [backpack/filemanager](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/FileManager), you'll have elFinder integrated into:
+- TinyMCE (as "tinymce" field type)
+- CKEditor (as "ckeditor" field type)
+- CRUD (as "browse" and "browse_multiple" field types)
+- stand-alone, at the */admin/elfinder* route;
+
+For the integration, we use [barryvdh/laravel-elfinder](https://github.com/barryvdh/laravel-elfinder).
+
+
+
+
+### How to manually install Backpack
+
+If the automatic installation doesn't work for you and you need to manually install CRUD, here are all the commands it is running:
+
+1) In your terminal:
+
+``` bash
+composer require backpack/crud
+```
+
+2) Instead of running ```php artisan backpack:install``` you can run:
+```bash
+php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Backpack\CRUD\BackpackServiceProvider" --tag="minimum"
+php artisan migrate
+php artisan backpack:publish-middleware
+composer require --dev backpack/generators
+php artisan basset:install --no-check --no-interaction
+
+# then install ONE of the first-party themes:
+php artisan backpack:require:theme-tabler
+php artisan backpack:require:theme-coreuiv4
+php artisan backpack:require:theme-coreuiv2
+
+# then check assets can be correctly used
+php artisan basset:check
+```
+
+
+
+### Overwrite a Method on the CrudPanel Object
+
+Starting with Backpack v4, you can use a custom CrudPanel object instead of the one in the package. In your custom CrudPanel object, you can overwrite any method you want, but please note that this means that you're overwriting core components, and will be making it more difficult to upgrade to newer versions of Backpack.
+
+You can do this in any of your service providers (ex: ```app/Providers/AppServiceProvider.php```) to load your class instead of the one in the package:
+
+```php
+$this->app->extend('crud', function () {
+ return new \App\MyExtendedCrudPanel;
+});
+```
+
+Details and implementation [here](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/CRUD/pull/1990).
+
+
+
+
+### Error: Failed to Download Backpack PRO
+
+When trying to install Backpack\PRO (or any of our closed-source add-ons, really), you might run into the following error message:
+
+```bash
+Downloading backpack/pro (1.1.1)
+Failed to download backpack/pro from dist: The "https://backpackforlaravel.com/satis/download/dist/backpack/pro/backpack-pro-xxx-zip-zzz.zip" file could not be downloaded (HTTP/2 402 )
+```
+
+Or maybe:
+
+```bash
+Syncing backpack/pro (1.1.1) into cache
+Cloning failed using an ssh key for authentication, enter your GitHub credentials to access private repos
+Head to https://github.com/settings/tokens/new?scopes=repo&description=Composer+on+DESKTOP-BLABLA+2022-07-14+1559
+to retrieve a token.
+```
+
+What's happening there? That is a general Composer error - "file could not be downloaded". The error itself doesn't give too much information, but we can make an educated guess.
+
+**99% of the people who report this error have the same problem - they do not have access to that package version.** They bought updates until 1.0.13 (for example), so they DO NOT have access to the latest version (1.1.1 in this example). What you can do, in that case, is **lock the installation to the latest you have access to**, for example
+
+```bash
+composer require backpack/pro:"1.0.13"
+```
+
+Alternatively, you can purchase more access on the [Backpack website](https://backpackforlaravel.com/pricing). Or contact the team if there's a mistake.
+
+--
+
+How do you find out what's the last version you have access to?
+
+(1) **Whenever the error above happens, Backpack will send you an email**, with details and instructions. **Check your email**, it will also include the latest version you have access to.
+
+(2) [Your Tokens page](https://backpackforlaravel.com/user/tokens) will show more details. For each token you have, it will say when it stops giving you access to updates. If it doesn't say the last version directly, you can corroborate that last day with [the changelog](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects/CHANGELOG.md ), to determine what's the last version that _you_ have access to.
+
+--
+
+Why the ugly, general error? Because Composer doesn't allow vendors to customize the error, unfortunately. Backpack's server returns a better error message, but Composer doesn't show it.
+
+
+
+### Configuring the Temporary Directory
+
+The [dropzone field](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#dropzone-pro) and DropzoneOperation will upload the files to a temporary directory using AJAX. When an entry is saved, they move that file to the final directory. But if the user doesn't finish the saving process, the temp directory can still hold files that are not used anywhere.
+
+**Configure Temp Directory**
+
+To configure that temporary directory for ALL dropzone operations, call `php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Backpack\Pro\AddonServiceProvider" --tag="dropzone-config"` and then edit your `config/backpack/operations/dropzone.php` to fit your needs. Here are the most important values you'll find there:
+
+```php
+ 'temporary_disk' => 'local', // disk in config/filesystems.php that will be used
+ 'temporary_folder' => 'backpack/temp', // the directory inside the disk above
+ 'purge_temporary_files_older_than' => 72 // automatically delete files older than 72 hours
+```
+
+Alternatively, you can also configure the temp directory for the current CRUD only using:
+
+```php
+public function setupDropzoneOperation()
+{
+ CRUD::setOperationSetting('temporary_disk', 'public');
+ CRUD::setOperationSetting('temporary_folder', 'backpack/temp');
+ CRUD::setOperationSetting('purge_temporary_files_older_than', 72);
+}
+```
+
+**Delete Old Temp Files**
+
+Whenever new files are uploaded using the Dropzone operation, the operation deletes old files from the temp directory. But you can also run the `backpack:purge-temporary-files` command, to clean the temp directory.
+
+
+```bash
+php artisan backpack:purge-temporary-files --older-than=24 --disk=public --path="backpack/temp"
+```
+
+It accepts the following optional parameters:
+- `--older-than=24`: the number of hours after which temporary files are deleted.
+- `--disk=public`: the disk used by the temporary files.
+- `--path="backpack/temp"`: the folder inside the disk where files will be stored.
+
+
+You can use any strategy to run this command periodically - a cron job, a scheduled task or hooking into application termination hooks. Laravel provides a very easy way to setup your scheduled tasks. You can read more about it [here](https://laravel.com/docs/10.x/scheduling). For example, you can run the command every hour by adding the following line to your `app/Console/Kernel.php` in the `schedule()` method:
+```php
+// app/Console/Kernel.php
+$schedule->command('backpack:purge-temporary-files')->hourly();
+```
+
+After adding this, you need to setup a cron job that will process the Laravel scheduler. You can manually run it in development with `php artisan schedule:run`. For production, you can setup a cron job take care of it for you. You can read more about it [here](https://laravel.com/docs/10.x/scheduling#running-the-scheduler).
+
+
+### Enable database transactions for create and update
+
+In v6.6 we introduced the ability to enable database transactions for create and update operations. This is useful if you have a lot of relationships and you want to make sure that all of them are saved or none of them are saved.
+You can enable this feature globaly at `config/backpack/base.php` by enabling `useDatabaseTransactions`.
+
+> **Note:** This feature will be enable by default starting `v7`
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-clone.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-clone.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..23a24f5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-clone.md
@@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
+# Clone Operation
PRO
+
+--
+
+
+## About
+
+This CRUD operation allows your admins to duplicate one or more entries from the database.
+
+>**IMPORTANT:** The clone operation does NOT duplicate related entries. So n-n relationships will be unaffected. However, this also means that n-n relationships are ignored. So when you clone an entry, the new entry:
+>- will NOT have the same 1-1 relationships
+>- will have the same 1-n relationships
+>- will NOT have the same n-1 relationships
+>- will NOT have the same n-n relationships
+>
+>This might be somewhat counterintuitive for end users - though it should make perfect sense for us developers. This is why the Clone operation is NOT enabled by default.
+
+
+
+## Requirements
+
+This is a
PRO operation. It requires that you have [purchased access to `backpack/pro`](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects).
+
+
+## Clone a Single Item
+
+
+### How it Works
+
+Using AJAX, a POST request is performed towards ```/entity-name/{id}/clone```, which points to the ```clone()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+
+### How to Use
+
+To enable it, you need to ```use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\CloneOperation;``` on your EntityCrudController. For example:
+
+```php
+
+### How to Overwrite
+
+In case you need to change how this operation works, overwrite the ```clone()``` trait method in your EntityCrudController; make sure you give the method in the trait a different name, so that there are no conflicts:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\CloneOperation { clone as traitClone; }
+
+public function clone($id)
+{
+ CRUD::hasAccessOrFail('clone');
+ CRUD::setOperation('clone');
+
+ // whatever you want
+
+ // if you still want to call the old clone method
+ $this->traitClone($id);
+}
+```
+
+You can also overwrite the clone button by creating a file with the same name inside your ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/buttons/```. You can easily publish the clone button there to make changes using:
+
+```zsh
+php artisan backpack:button --from=clone
+```
+
+
+## Clone Multiple Items (Bulk Clone)
+
+In addition to the button for each entry, you can show checkboxes next to each element, and allow your admin to clone multiple entries at once.
+
+
+
+### How it Works
+
+Using AJAX, a POST request is performed towards ```/entity-name/bulk-clone```, which points to the ```bulkClone()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+**`NOTES:`**
+- The bulk checkbox is added inside the first column defined in the table. For that reason the first column should be visible on table to display the bulk actions checkbox next to it.
+- `Bulk Actions` also disable all click events for the first column, so make sure the first column **doesn't** contain an anchor tag (`
`), as it won't work.
+
+
+### How to Use
+
+To enable it, you need to ```use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\BulkCloneOperation;``` on your EntityCrudController.
+
+
+### How to Overwrite
+
+In case you need to change how this operation works, just create a ```bulkClone()``` method in your EntityCrudController:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\BulkCloneOperation { bulkClone as traitBulkClone; }
+
+public function bulkClone($id)
+{
+ // your custom code here
+ //
+ // then you can call the old bulk clone if you want
+ $this->traitBulkClone($id);
+}
+```
+
+You can also overwrite the bulk clone button by creating a file with the same name inside your ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/buttons/```. You can easily publish the clone button there to make changes using:
+
+```zsh
+php artisan backpack:button --from=bulk_clone
+```
+
+
+## Exempt attributes when cloning
+If you have attributes that should not be cloned (eg. a SKU with an unique constraint), you can overwrite the replicate method on your model:
+
+```php
+ public function replicate(array $except = null) {
+
+ return parent::replicate(['sku']);
+ }
+```
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-create.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-create.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..32b3bc8a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-create.md
@@ -0,0 +1,328 @@
+# Create Operation
+
+---
+
+
+## About
+
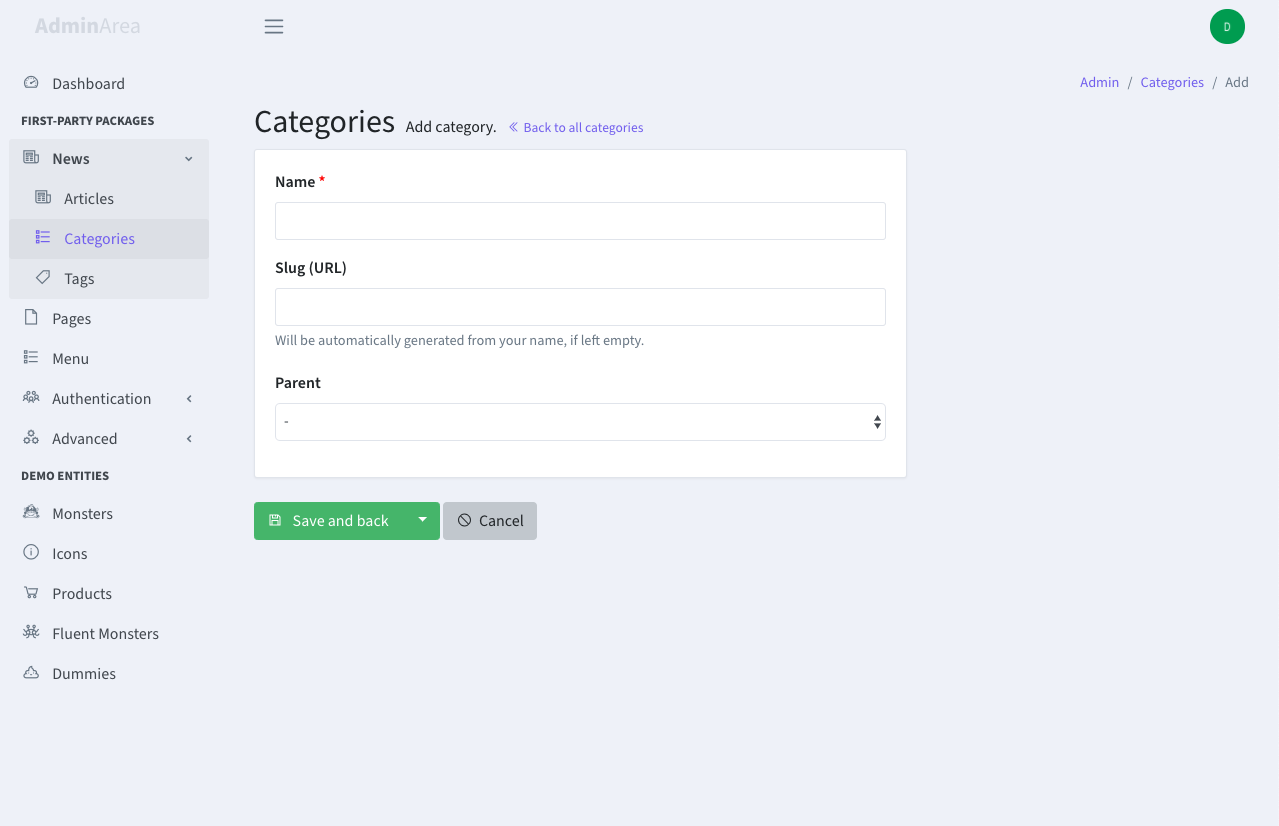
+This operation allows your admins to add new entries to a database table.
+
+
+
+
+## Requirements
+
+All editable attributes should be ```$fillable``` on your Model.
+
+
+## How to Use
+
+To use the Create operation, you must:
+
+**Step 0. Use the operation trait on your EntityCrudController**. This should be as simple as this:
+
+```php
+crud->setValidation(StoreRequest::class);
+ // $this->crud->addField($field_definition_array);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+**Step 1. Specify what field types** you'd like to show for each editable attribute, in your EntityCrudController's ```setupCreateOperation()``` method. You can do that using the [Fields API](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#fields-api). In short you can:
+
+```php
+protected function setupCreateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->addField($field_definition_array);
+}
+```
+
+**Step 2. Specify validation rules, in your the EntityCrudRequest file**. Then make sure that file is used for validation, by telling the CRUD to validate that request file in ```setupCreateOperation()```:
+```php
+$this->crud->setValidation(StoreRequest::class);
+```
+
+For more on how to manipulate fields, please read the [Fields documentation page](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields). For more on validation rules, check out [Laravel's validation docs](https://laravel.com/docs/master/validation#available-validation-rules).
+
+
+## How It Works
+
+CrudController is a RESTful controller, so the ```Create``` operation uses two routes:
+- GET to ```/entity-name/create``` - points to ```create()``` which shows the Add New Entry form (```create.blade.php```);
+- POST to ```/entity-name``` - points to ```store()``` which does the actual storing operation;
+
+The ```create()``` method will show all the fields you've defined for this operation using the [Fields API](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#fields-api), then upon Save the ```store()``` method will first check the validation from the FormRequest you've specified, then create the entry using the Eloquent model. Only attributes that are specified as fields, and are ```$fillable``` on the model will actually be stored in the database.
+
+
+## How to add custom sections(aka. Widgets)
+
+[Widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets) (aka cards, aka charts, aka graphs) provide a simple way to insert blade files into admin panel pages. You can use them to insert cards, charts, notices or custom content into pages. You can use the [default widget types](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#default-widget-types) or [create your own custom widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#creating-a-custom-widget-type).
+
+Backpack default template includes two [sections](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#requirements-1) where you can push widgets:
+
+* `before_content`
+* `after_content`
+
+To use widgets on create operation, define them inside `setupCreateOperation()` function.
+
+```php
+public function setupCreateOperation()
+{
+ // dynamic data to render in the following widget
+ $userCount = \App\Models\User::count();
+
+ //add div row using 'div' widget and make other widgets inside it to be in a row
+ Widget::add()->to('before_content')->type('div')->class('row')->content([
+
+ //widget made using fluent syntax
+ Widget::make()
+ ->type('progress')
+ ->class('card border-0 text-white bg-primary')
+ ->progressClass('progress-bar')
+ ->value($userCount)
+ ->description('Registered users.')
+ ->progress(100 * (int)$userCount / 1000)
+ ->hint(1000 - $userCount . ' more until next milestone.'),
+
+ //widget made using the array definition
+ Widget::make(
+ [
+ 'type' => 'card',
+ 'class' => 'card bg-dark text-white',
+ 'wrapper' => ['class' => 'col-sm-3 col-md-3'],
+ 'content' => [
+ 'header' => 'Example Widget',
+ 'body' => 'Widget placed at "before_content" secion in same row',
+ ]
+ ]
+ ),
+ ]);
+
+ //you can also add Script & CSS to your page using 'script' & 'style' widget
+ Widget::add()->type('script')->stack('after_scripts')->content('https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.12.0/jquery-ui.min.js');
+ Widget::add()->type('style')->stack('after_styles')->content('https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@shoelace-style/shoelace@2.0.0-beta.58/dist/themes/light.css');
+}
+```
+
+#### Output:
+* Using `before_content`:
+
+
+* Using `after_content`
+
+
+
+
+## Advanced Features and Techniques
+
+
+### Validation
+
+There are three ways you can define the [validation rules](https://laravel.com/docs/validation#available-validation-rules) for your fields:
+
+#### (A) Validating fields using FormRequests
+
+When you generate a CrudController, you'll notice a [Laravel FormRequest](https://laravel.com/docs/validation#form-request-validation) has also been generated, and that FormRequest is mentioned as the source of your validation rules:
+```php
+protected function setupCreateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->setValidation(StoreRequest::class);
+}
+```
+
+This works particularly well for bigger models, because you can mention a lot of rules, messages and attributes in your `FormRequest` and it will not increase the size of your `CrudController`.
+
+**Differences between the Create and Update validations?** Then create a separate request file for each operation and instruct your EntityCrudController to use those files:
+
+```php
+use App\Http\Requests\CreateTagRequest as StoreRequest;
+use App\Http\Requests\UpdateTagRequest as UpdateRequest;
+
+// ...
+
+public function setupCreateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->setValidation(CreateRequest::class);
+}
+
+public function setupUpdateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->setValidation(UpdateRequest::class);
+}
+```
+
+#### (B) Validating fields using a rules array
+
+For smaller models (with just a few validation rules), creating an entire FormRequest file to hold them might be overkill. If you prefer, you can pass an array of [validation rules](https://laravel.com/docs/validation#available-validation-rules) to the same `setValidation()` method (with an optional second parameter for the validation messages):
+
+```php
+protected function setupCreateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->setValidation([
+ 'name' => 'required|min:2',
+ ]);
+
+ // or maybe
+
+ $rules = ['name' => 'required|min:2'];
+ $messages = [
+ 'name.required' => 'You gotta give it a name, man.',
+ 'name.min' => 'You came up short. Try more than 2 characters.',
+ ];
+ $this->crud->setValidation($rules, $messages);
+}
+```
+
+This is more convenient for small and medium models. Plus, it's very easy to read.
+
+#### (C) Validating fields using field attributes
+
+Another good option for small & medium models is to define the [validation rules](https://laravel.com/docs/validation#available-validation-rules) directly on your fields:
+
+```php
+protected function setupCreateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->addField([
+ 'name' => 'content',
+ 'label' => 'Content',
+ 'type' => 'ckeditor',
+ 'placeholder' => 'Your textarea text here',
+ 'validationRules' => 'required|min:10',
+ 'validationMessages' => [
+ 'required' => 'You gotta write smth man.',
+ 'min' => 'More than 10 characters, bro. Wtf... You can do this!',
+ ]
+ ]);
+
+ // or using the fluent syntax
+
+ CRUD::field('email_address')->validationRules('required|email|unique:users.email_address');
+}
+```
+
+
+### Callbacks
+
+If you're coming from other CRUD systems (like GroceryCRUD) you might be looking for callbacks to run "before_insert", "before_update", "after_insert", "after_update". **There are no callbacks in Backpack**, because... they're not needed. There are plenty of other ways to do things before/after an entry is created.
+
+#### Use Events in your `setup()` method
+
+Laravel already triggers [multiple events](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent#events) in an entry's lifecycle. Those also include:
+- `creating` and `created`, which are triggered by the Create operation;
+- `saving` and `saved`, which are triggered by both the Create and the Update operations;
+
+So if you want to do something to a `Product` entry _before_ it's created, you can easily do that:
+```php
+public function setupCreateOperation()
+{
+
+ // ...
+
+ Product::creating(function($entry) {
+ $entry->author_id = backpack_user()->id;
+ });
+}
+```
+
+Take a closer look at [Eloquent events](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent#events) if you're not familiar with them, they're really _really_ powerful once you understand them. Please note that **these events will only get registered when the function gets called**, so if you define them in your `CrudController`, then:
+- they will NOT run when an entry is changed outside that CrudController;
+- if you want to expand the scope to cover both the `Create` and `Update` operations, you can easily do that, for example by using the `saving` and `saved` events, and moving the event-calling to your main `setup()` method;
+
+#### Use events in your field definition
+
+You can tell a field to do something to the entry when that field gets saved to the database. Rephrased, you can define standard [Eloquent events](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent#events) directly on fields. For example:
+
+```php
+// FLUENT syntax - use the convenience method "on" to define just ONE event
+CRUD::field('name')->on('saving', function ($entry) {
+ $entry->author_id = backpack_user()->id;
+});
+
+// FLUENT SYNTAX - you can define multiple events in one go
+CRUD::field('name')->events([
+ 'saving' => function ($entry) {
+ $entry->author_id = backpack_user()->id;
+ },
+ 'saved' => function ($entry) {
+ // TODO: upload some file
+ },
+]);
+
+// using the ARRAY SYNTAX, define an array of events and closures
+CRUD::addField([
+ 'name' => 'name',
+ 'events' => [
+ 'saving' => function ($entry) {
+ $entry->author_id = backpack_user()->id;
+ },
+ ],
+]);
+```
+
+> An important thing to notice when using model events in the fields is that those events will only be registered **in the same operations (create, update, etc)** where your fields are defined.
+> Take for example the `DeleteOperation`, which is ran when you delete an entry. If you define a field with a `deleting` event, that event will not be registered when you delete an entry, because the field is not defined in the `DeleteOperation`. If you want to use model events in the `DeleteOperation`, you can do that by using the `setupDeleteOperation()` method and defining the fields with the events there too, similar to how you do for create and update operations.
+
+#### Override the `store()` method
+
+The store code is inside a trait, so you can easily override it, if you want:
+
+```php
+crud->addField(['type' => 'hidden', 'name' => 'author_id']);
+ // $this->crud->removeField('password_confirmation');
+
+ // Note: By default Backpack ONLY saves the inputs that were added on page using Backpack fields.
+ // This is done by stripping the request of all inputs that do NOT match Backpack fields for this
+ // particular operation. This is an added security layer, to protect your database from malicious
+ // users who could theoretically add inputs using DeveloperTools or JavaScript. If you're not properly
+ // using $guarded or $fillable on your model, malicious inputs could get you into trouble.
+
+ // However, if you know you have proper $guarded or $fillable on your model, and you want to manipulate
+ // the request directly to add or remove request parameters, you can also do that.
+ // We have a config value you can set, either inside your operation in `config/backpack/crud.php` if
+ // you want it to apply to all CRUDs, or inside a particular CrudController:
+ // $this->crud->setOperationSetting('saveAllInputsExcept', ['_token', '_method', 'http_referrer', 'current_tab', 'save_action']);
+ // The above will make Backpack store all inputs EXCEPT for the ones it uses for various features.
+ // So you can manipulate the request and add any request variable you'd like.
+ // $this->crud->getRequest()->request->add(['author_id'=> backpack_user()->id]);
+ // $this->crud->getRequest()->request->remove('password_confirmation');
+
+ $response = $this->traitStore();
+ // do something after save
+ return $response;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+>But before you do that, ask yourself - **_is this something that should be done when an entry is added/updated/deleted from the application, too_**? Not just the admin panel? If so, a better place for it would be the Model. Remember your Model is a pure Eloquent Model, so the cleanest way might be to use [Eloquent Event Observers](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent#events) or [accessors and mutators](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent-mutators#accessors-and-mutators).
+
+
+### Translatable models and multi-language CRUDs
+
+For UX purposes, when creating multi-language entries, the Create form will only allow the admin to add an entry in one language, the default one. The admin can then edit that entry in all available languages, to translate it. Check out [this same section in the Update operation](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-update#translatable-models) for how to enable multi-language functionality.
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-delete.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-delete.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..36fe3c89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-delete.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+# Delete Operation
+
+--
+
+
+## About
+
+This CRUD operation allows your admins to remove one or more entries from the table.
+
+>In case your entity has SoftDeletes, it will perform a soft delete. The admin will _not_ know that his entry has been hard or soft deleted, since it will no longer show up in the ListEntries view.
+
+
+## Delete a Single Item
+
+
+### How it Works
+
+Using AJAX, a DELETE request is performed towards ```/entity-name/{id}```, which points to the ```destroy()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+
+### How to Use
+
+To enable it, you need to ```use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\DeleteOperation;``` on your EntityCrudController. For example:
+
+```php
+
+### How to Overwrite
+
+In case you need to change how this operation works, just create a ```destroy()``` method in your EntityCrudController:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\DeleteOperation { destroy as traitDestroy; }
+
+public function destroy($id)
+{
+ CRUD::hasAccessOrFail('delete');
+
+ return CRUD::delete($id);
+}
+```
+
+You can also overwrite the delete button by creating a file with the same name inside your ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/buttons/```. You can easily publish the delete button there to make changes using:
+
+```zsh
+php artisan backpack:button --from=delete
+```
+
+
+## Delete Multiple Items (Bulk Delete)
PRO
+
+In addition to the button for each entry,
PRO developers can show checkboxes next to each element, to allow their admin to delete multiple entries at once.
+
+
+
+### How it Works
+
+Using AJAX, a DELETE request is performed towards ```/entity-name/bulk-delete```, which points to the ```bulkDelete()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+**`NOTES:`**
+- The bulk checkbox is added inside the first column defined in the table. For that reason the first column should be visible on table to display the bulk actions checkbox next to it.
+- `Bulk Actions` also disable all click events for the first column, so make sure the first column **doesn't** contain an anchor tag (`
`), as it won't work.
+
+
+
+### How to Use
+
+You need to ```use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\BulkDeleteOperation;``` on your EntityCrudController.
+
+
+### How to Overwrite
+
+In case you need to change how this operation works, just create a ```bulkDelete()``` method in your EntityCrudController:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\BulkDeleteOperation { bulkDelete as traitBulkDelete; }
+
+public function bulkDelete()
+{
+ // your custom code here
+}
+```
+
+You can also overwrite the bulk delete button by creating a file with the same name inside your ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/buttons/```. You can easily publish the delete button there to make changes using:
+
+```zsh
+php artisan backpack:button --from=bulk_delete
+```
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-fetch.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-fetch.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2685f7b3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-fetch.md
@@ -0,0 +1,172 @@
+# Fetch Operation
PRO
+
+---
+
+
+## About
+
+This operation allows an EntityCrudController to respond to AJAX requests with entries in the database for _a different entity_, in a format that can be used by the ```relationship```, ```select2_from_ajax``` and ```select2_from_ajax_multiple``` fields.
+
+
+
+## Requirements
+
+This is a
PRO operation. It requires that you have [purchased access to `backpack/pro`](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects).
+
+
+## How to Use
+
+In order to enable this operation, in your CrudController you need to **use the ```FetchOperation``` trait and add a new method** that responds to the AJAX requests (following the naming convention ```fetchEntityName()```). For example, for a `Tag` model you'd do:
+
+```php
+ use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\FetchOperation;
+
+ protected function fetchTag()
+ {
+ return $this->fetch(\App\Models\Tag::class);
+ }
+```
+
+To customize the FetchOperation, pass an array to the ```fetch()``` call, rather than a class name. For example:
+
+```php
+fetch([
+ 'model' => \App\Models\Tag::class, // required
+ 'searchable_attributes' => ['name', 'description'],
+ 'paginate' => 10, // items to show per page
+ 'searchOperator' => 'LIKE',
+ 'query' => function($model) {
+ return $model->active();
+ } // to filter the results that are returned
+ ]);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+You can now point your AJAX select to this route, which will be ```backpack_url('your-main-entity/fetch/tag')``` .
+
+
+
+## How It Works
+
+Based on the fact that the ```fetchTag()``` method exists, the Fetch operation will create a ```/product/fetch/tag``` POST route, which points to ```fetchTag()```. Inside ```fetchTag()``` we call ```fetch()```, that responds with entries in the format ```select2``` needs.
+
+**Preventing FetchOperation from guessing the searchable attributes**
+
+If not specified `searchable_attributes` will be automatically inferred from model database columns. To prevent this behaviour you can setup an empty `searchable_attributes` array. For example:
+
+```php
+public function fetchUser() {
+ return $this->fetch([
+ 'model' => User::class,
+ 'query' => function($model) {
+ $search = request()->input('q') ?? false;
+ if ($search) {
+ return $model->whereRaw('CONCAT(`first_name`," ",`last_name`) LIKE "%' . $search . '%"');
+ }else{
+ return $model;
+ }
+ },
+ 'searchable_attributes' => []
+ ]);
+ }
+```
+
+
+## Using FetchOperation with `select2_ajax` filter
+
+The FetchOperation can also be used as the source URL for the `select2_ajax` filter. To do that, we need to:
+- change the `select2_ajax` filter method from `GET` (its default) to `POST` (what FetchOperation uses);
+- tell the filter what attribute we want to show to the user;
+
+```
+CRUD::addFilter([
+ 'name' => 'category_id',
+ 'type' => 'select2_ajax',
+ 'label' => 'Category',
+ 'placeholder' => 'Pick a category',
+ 'method' => 'POST', // mandatory change
+ // 'select_attribute' => 'name' // the attribute that will be shown to the user by default 'name'
+ // 'select_key' => 'id' // by default is ID, change it if your model uses some other key
+],
+backpack_url('product/fetch/category'), // the fetch route on the ProductCrudController
+function($value) { // if the filter is active
+ // CRUD::addClause('where', 'category_id', $value);
+});
+
+```
+
+
+
+## How to Overwrite
+
+In case you need to change how this operation works, it's best to take a look at the ```FetchOperation.php``` trait to understand how it works. It's a pretty simple operation. Most common ways to overwrite the Fetch operation are documented below:
+
+**Change the fetch database search operator**
+
+You can customize the search operator for `FetchOperation` just like you can in ListOperation. By default it's `LIKE`, but you can:
+- change the operator individually for each `fetchEntity` using `searchOperator => 'ILIKE'` in the fetch configuration;
+- change the operator for all FetchOperations inside that CrudPanel by doing:
+```php
+public function setupFetchOperationOperation() {
+ CRUD::setOperationSetting('searchOperator', 'ILIKE');
+ }
+```
+- change the operator globally in your project, by creating a config file in `config/backpack/operations/fetch.php` and add the following:
+```php
+ 'ILIKE',
+];
+```
+
+**Custom behaviour for one fetch method**
+
+To make a ```fetchCategory()``` method behave differently, you can copy-paste the logic inside the ```FetchOperation::fetch()``` and change it to do whatever you need. Instead of returning ```$this->fetch()``` you can return your own results, in this case fetch will only setup the ajax route for you.
+
+**Custom behaviour for multiple fetch methods inside a Controller**
+
+To make all calls to ```fetch()``` inside an EntityCrudController behave differently, you can easily overwrite the ```fetch()``` method in that controller:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\FetchOperation;
+
+public function fetch($arg)
+{
+ // your custom code here
+}
+```
+
+Then all ```$this->fetch()``` calls from that Controller will be using your custom code.
+
+In case you need to call the original ```fetch()``` method (from the trait) inside your custom ```fetch()``` method (inside the controller), you can do:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\FetchOperation { fetch as traitFetch; }
+
+public function fetch($arg)
+{
+ // your custom code here
+
+ // call the method in the trait
+ return $this->traitFetch();
+}
+```
+
+**Custom behaviour for all fetch calls, in all Controllers**
+
+If you want all your ```fetch()``` calls to behave differently, no matter what Controller they are in, you can:
+- duplicate the ```FetchOperation``` trait inside your application;
+- instead of using ```\Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\FetchOperation``` inside your controllers, use your custom operation trait;
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-inline-create.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-inline-create.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ad2447e5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-inline-create.md
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+# InlineCreate Operation
PRO
+
+---
+
+
+## About
+
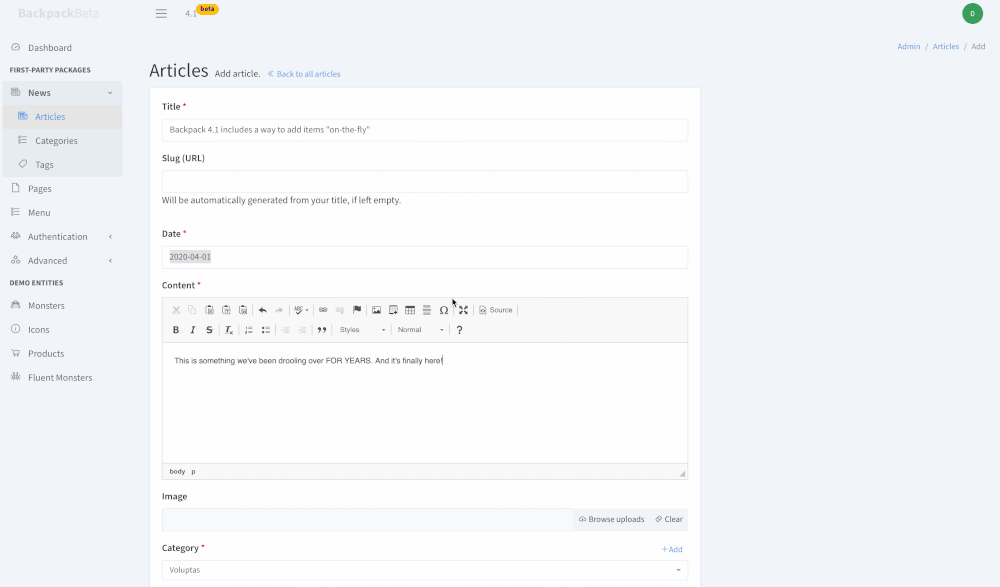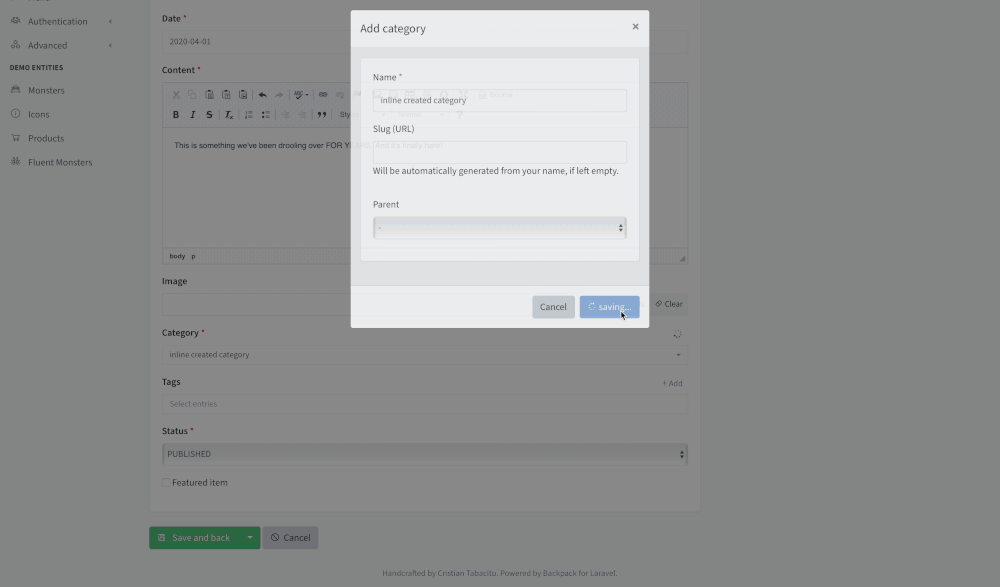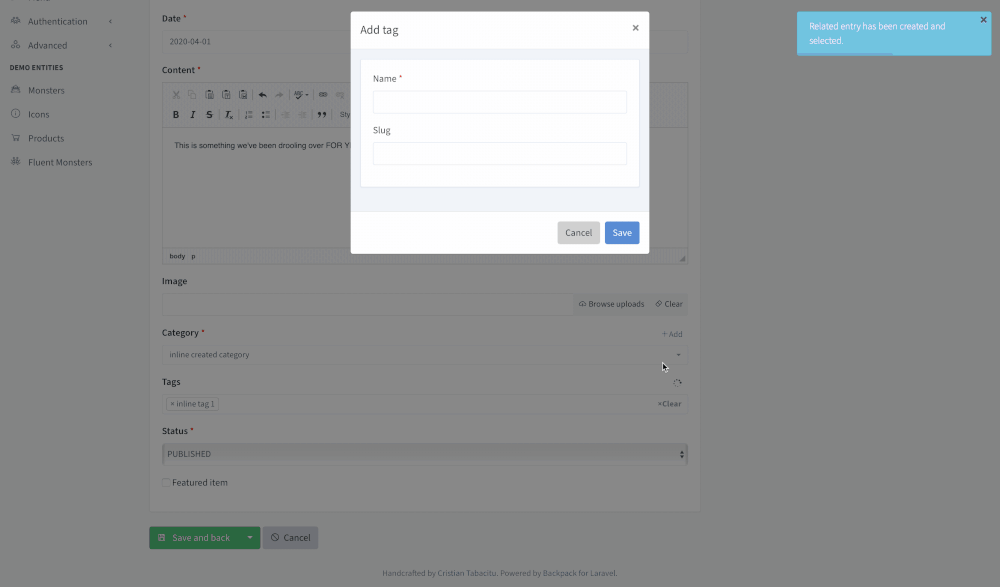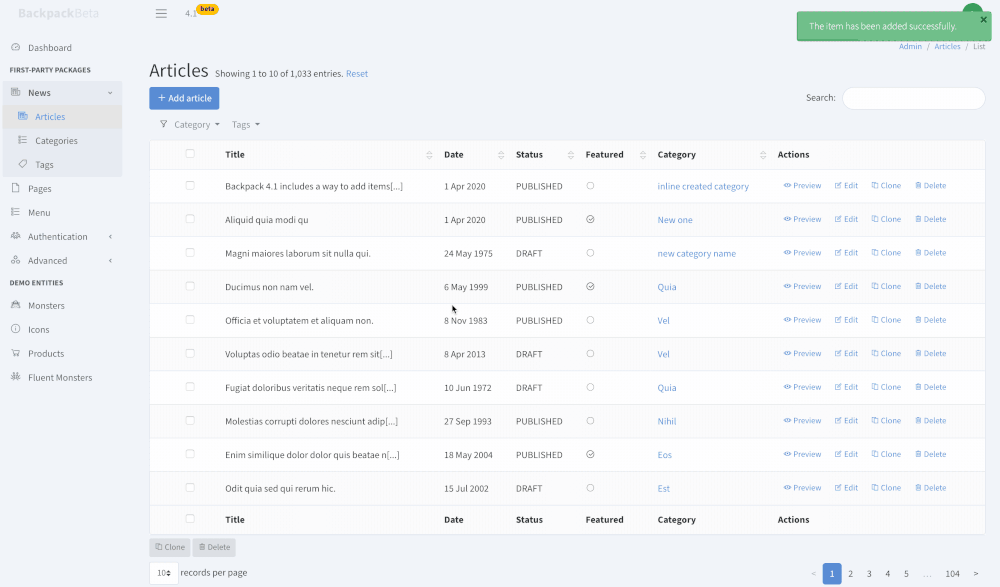
+This operation allows your admins to add new entries to a database table on-the-fly, from a modal.
+
+For example:
+- if you have an ```ArticleCrudController``` where your user can also select ```Categories```;
+- this operation adds the ability to create ```Categories``` right inside the ```ArticleCrudController```'s Create form;
+ - the admin needs to click an Add button
+ - a modal will show the form from ```CategoryCrudController```'s Create operation;
+
+
+
+
+
+## Requirements
+
+
+This is a
PRO operation. It requires that you have [purchased access to `backpack/pro`](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects).
+
+In addition, it needs:
+- a working Create operation;
+- correctly defined Eloquent relationships on both the primary Model, and the secondary Model;
+- a working Fetch operation to retrieve the secondary Model from the primary Model;
+- an understanding of what we call "_main_" and "_secondary_" in this case; using the same example as above, where you want to be able to add ```Categories``` in a modal, inside ```ArticleCrudController```'s create&update forms:
+ - the _main entity_ would be Article (big form);
+ - the _secondary entity_ would be Category (small form, in a modal);
+
+
+## How to Use
+
+> If your field name is comprised of multiple words (eg. `contact_number` or `contactNumber`) you will need to also define the `data_source` attribute for this field; keep in mind that by to generate a route, your field name will be parsed run through `Str::kebab()` - that means `_` (underscore) or `camelCase` will be converted to `-` (hyphens), so in `fetch` your route will be `contact-number` instead of the expected `contactNumber`. To fix this, you need to define: `data_source => backpack_url('monster/fetch/contact-number')` (replace with your strings)
+
+To use the Create operation, you must:
+
+**Step 1. Use the operation trait on your secondary entity's CrudController** (aka. the entity that will gain the ability to be created inline, in our example CategoryCrudController). Make sure you use `InlineCreateOperation` *after* `CreateOperation`:
+
+```php
+crud->setValidation(StoreRequest::class);
+ // $this->crud->addField($field_definition_array);
+ // }
+}
+```
+
+**Step 2. Use [the relationship field](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#relationship) inside the ```setupCreateOperation()``` or ```setupUpdateOperation()``` of the main entity** (where you'd like to be able to click a button and a modal shows up, in our example ArticleCrudController), and define ```inline_create``` on it:
+
+```php
+// for 1-n relationships (ex: category) - inside ArticleCrudController
+[
+ 'type' => "relationship",
+ 'name' => 'category', // the method on your model that defines the relationship
+ 'ajax' => true,
+ 'inline_create' => true, // assumes the URL will be "/admin/category/inline/create"
+]
+
+// for n-n relationships (ex: tags) - inside ArticleCrudController
+[
+ 'type' => "relationship",
+ 'name' => 'tags', // the method on your model that defines the relationship
+ 'ajax' => true,
+ 'inline_create' => [ 'entity' => 'tag' ] // specify the entity in singular
+ // that way the assumed URL will be "/admin/tag/inline/create"
+]
+
+// OPTIONALS - to customize behaviour
+[
+ 'type' => "relationship",
+ 'name' => 'tags', // the method on your model that defines the relationship
+ 'ajax' => true,
+ 'inline_create' => [ // specify the entity in singular
+ 'entity' => 'tag', // the entity in singular
+ // OPTIONALS
+ 'force_select' => true, // should the inline-created entry be immediately selected?
+ 'modal_class' => 'modal-dialog modal-xl', // use modal-sm, modal-lg to change width
+ 'modal_route' => route('tag-inline-create'), // InlineCreate::getInlineCreateModal()
+ 'create_route' => route('tag-inline-create-save'), // InlineCreate::storeInlineCreate()
+ 'add_button_label' => 'New tag', // configure the text for the `+ Add` inline button
+ 'include_main_form_fields' => ['field1', 'field2'], // pass certain fields from the main form to the modal, get them with: request('main_form_fields')
+ ]
+```
+
+
+**Step 3. OPTIONAL - You can create a ```setupInlineCreateOperation()``` method in the EntityCrudController**, to make the InlineCreateOperation different to the CreateOperation, for example have more/less fields, or different fields. Check out the [Fields API](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#fields-api) for a reference of all you can do with them.
+
+
+## How It Works
+
+The ```CreateInline``` operation uses two routes:
+- POST to ```/entity-name/inline/create/modal``` - ```getInlineCreateModal()``` which returns the contents of the Create form, according to how it's been defined by the CreateOperation (in ```setupCreateOperation()```, then overwritten by the InlineCreateOperation (in ```setupInlineCreateOperation()```);
+- POST to ```/entity-name/inline/create``` - points to ```storeInlineCreate()``` which does the actual saving in the database by calling the ```store()``` method from the CreateOperation;
+
+Since this operation is just a way to allow access to the Create operation from a modal, the ```getInlineCreateModal()``` method will show all the fields you've defined for this operation using the [Fields API](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#fields-api), then upon Save the ```store()``` method will first check the validation from the FormRequest you've specified, then create the entry using the Eloquent model. Only attributes that are specified as fields, and are ```$fillable``` on the model will actually be stored in the database.
+
+
+## Using Widgets with Inline Create
+
+When you have Widgets in your "related entry create form", for example a script widget with some javascript, you need to tell Backpack that you want to load that Widget inline too when the form is loaded in the modal. You can do that by adding the to the widget definition `inline()`:
+
+```diff
+- Widget::add()->type('script')->content('assets/my-javascript.js');
++ Widget::add()->type('script')->inline()->content('assets/my-javascript.js');
+```
+This will load the Widget in both instances, on the create form, and in the inline create form.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-list-entries.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-list-entries.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7b5b74a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-list-entries.md
@@ -0,0 +1,464 @@
+# List Operation
+
+---
+
+
+## About
+
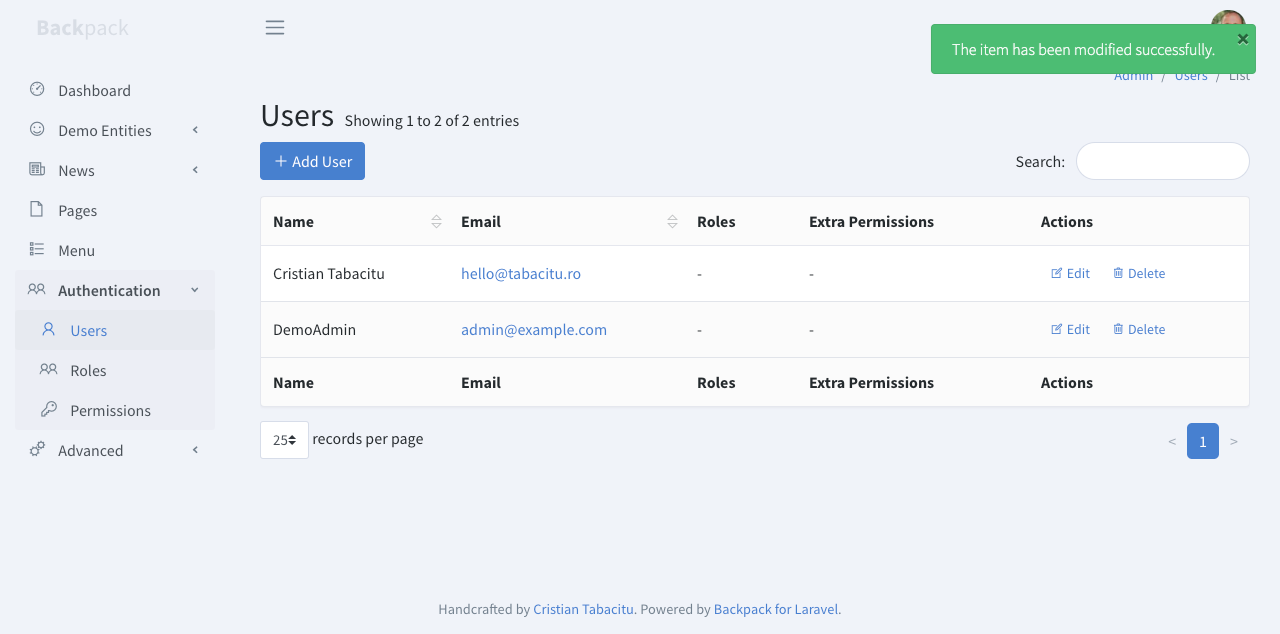
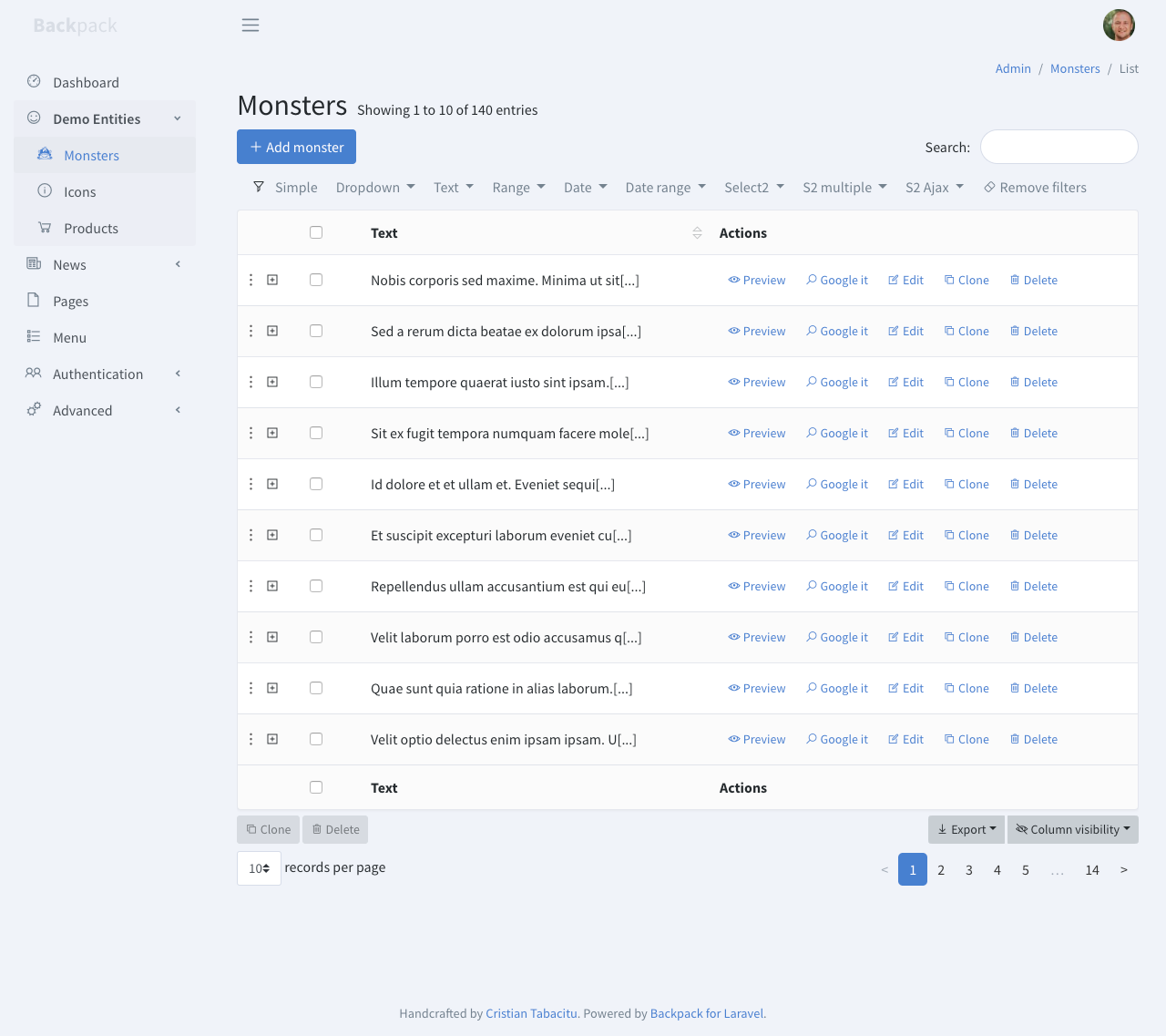
+This operation shows a table with all database entries. It's the first page the admin lands on (for an entity), and it's usually the gateway to all other operations, because it holds all the buttons.
+
+A simple List view might look like this:
+
+
+
+But a complex implementation of the ListEntries operation, using Columns, Filters, custom Buttons, custom Operations, responsive table, Details Row, Export Buttons will still look pretty good:
+
+
+
+You can easily customize [columns](#columns), [buttons](#buttons), [filters](#filters), [enable/disable additional features we've built](#other-features), or [overwrite the view and build your own features](#how-to-overwrite).
+
+
+## How It Works
+
+The main route leads to ```EntityCrudController::index()```, which shows the table view (```list.blade.php```. Inside that table view, we're using AJAX to fetch the entries and place them inside DataTables. That AJAX points to the same controller, ```EntityCrudController::search()```.
+
+Actions:
+- ```index()```
+- ```search()```
+
+For views, it uses:
+- ```list.blade.php```
+- ```columns/```
+- ```buttons/```
+
+
+## How to Use
+
+Use the operation trait on your controller:
+```php
+
+### Columns
+
+The List operation uses "columns" to determine how to show the attributes of an entry to the user. All column types must have their ```name```, ```label``` and ```type``` specified, but some could require some additional attributes.
+
+```php
+CRUD::column([
+ 'name' => 'name', // The db column name
+ 'label' => "Tag Name", // Table column heading
+ 'type' => 'Text'
+]);
+```
+
+Backpack has 22+ [column types](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns) you can use. Plus, you can easily [create your own type of column](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns##creating-a-custom-column-type). **Check out the [Columns](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns##creating-a-custom-column-type) documentation page** for a detailed look at column types, API and usage.
+
+
+### Buttons
+
+Buttons are used to trigger other operations. Some point to entirely new routes (```create```, ```update```, ```show```), others perform the operation on the current page using AJAX (```delete```).
+
+The List/Show operations have 3 places where buttons can be placed:
+ - ```top``` (where the Add button is)
+ - ```line``` (where the Edit and Delete buttons are)
+ - ```bottom``` (after the table)
+
+Backpack adds a few buttons by default:
+- ```add``` to the ```top``` stack;
+- ```edit``` and ```delete``` to the ```line``` stack;
+
+#### Merging line buttons into a dropdown
+
+**NOTE**: The `line` stack buttons can be converted into a dropdown to improve the available table space.
+
+
+This is done by setting the `lineButtonsAsDropdown` setting in list operation to `true`.
+
+a) For all CrudController (globally) in the `config/backpack/operations/list.php` file.
+
+b) For a specific CrudController, in its `setupListOperation()` define `CRUD::setOperationSetting('lineButtonsAsDropdown', true);`
+
+To learn more about buttons, **check out the [Buttons](/docs/{{version}}/crud-buttons) documentation page**.
+
+
+### Filters
PRO
+
+Filters show up right before the actual table, and provide a way for the admin to filter the results in the ListEntries table. To learn more about filters, **check out the [Filters](/docs/{{version}}/crud-filters) documentation page**. Please note that filters are a
PRO feature. Check out more differences in [FREE vs PRO](/docs/{{version}}/features-free-vs-paid#features).
+
+
+### Other Features
+
+
+#### Details Row
+
+The details row functionality allows you to present more information in the table view of a CRUD. When enabled, a "+" button will show up next to every row, which on click will expand a "details row" below it, showing additional information.
+
+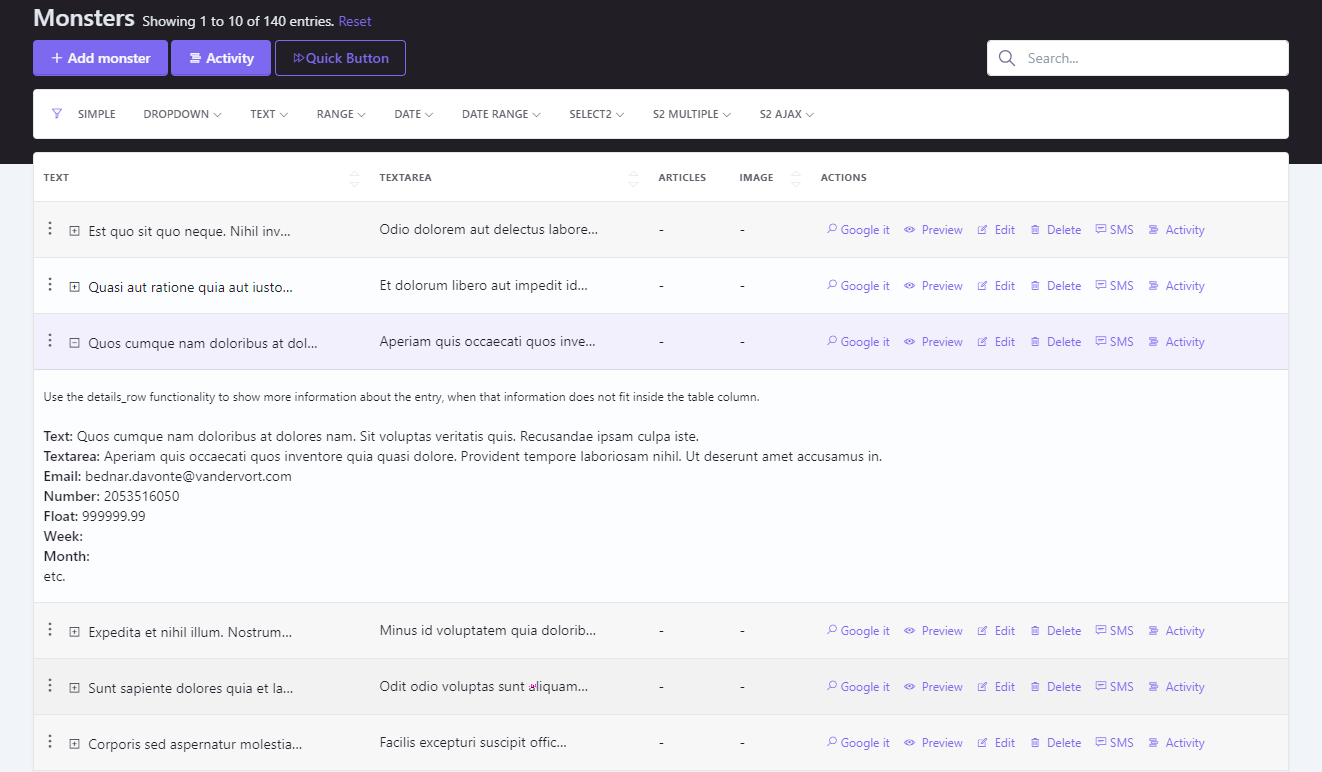
+
+On click, an AJAX request is sent to the `entity/{id}/details` route, which calls the `showDetailsRow()` method on your EntityCrudController. Everything returned by that method is then shown in the details row (usually a blade view).
+
+To use, inside your `EntityCrudController` you must first enable the functionality in your `setupListOperation` with: `CRUD::enableDetailsRow();`
+
+The `details_row` provided by Backpack display widgets from the `details_row` section by default. In your `setupListOperation` you can add widgets to the `details_row` section to display them in the details row. Inside those widgets you have access to `$entry` and `$crud` variables.
+
+```php
+public function setupListOperation()
+{
+ // ...
+ Widget::add()->to('details_row')->type('progress')->value(135)->description('Progress')->progress(50);
+ // ...
+}
+```
+
+Alternatively, if you don't want to use widgets and want to build your own details row, you can:
+1. Create a file in your resources folder, with the details row template for that entity. For example, `resources/views/admin/articles_details_row.blade.php`. You can use the `$entry` and `$crud` variables inside that view, to show information about the current entry.
+2. Tell Backpack what view to load with: `CRUD::setDetailsRowView('admin.articles_details_row')` in your `setupListOperation()` method.
+
+**NOTE:** Even when you don't `enableDetailsRow()`, Backpack register the necessary routes for it when using the ListOperation. If you are sure **you don't want to use details row** in that CrudController you can set `protected $setupDetailsRowRoute = false;` in your CrudController.
+
+##### Overwrite default details row functionality
+
+
+Backpack ships with a default details row template. If you want to use the same template across all your cruds you can overwrite it by creating a `resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/inc/details_row.blade.php` file. When doing `CRUD::enableDetailsRow()` this template will be used by default.
+
+You can also create a `showDetailsRow($id)` method in your CrudController to overwrite the default behaviour.
+
+
+#### Export Buttons
PRO
+
+Exporting the DataTable to PDF, CSV, XLS is as easy as typing ```CRUD::enableExportButtons();``` in your constructor.
+
+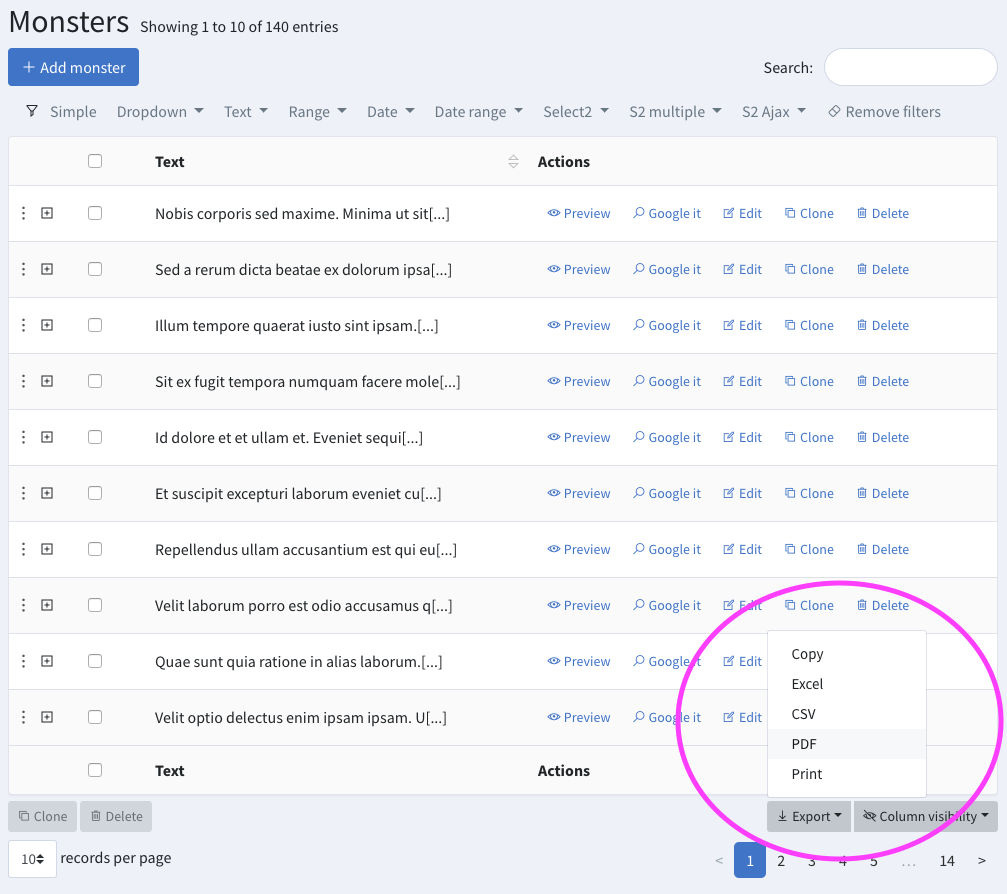
+
+**Please note that when clicked, the button will export**
+- **the _currently visible_ table columns** (except columns marked as ```visibleInExport => false```);
+- **the columns that are forced to export** (with ```visibleInExport => true``` or ```exportOnlyField => true```);
+
+**In the UI, the admin can use the "Visibility" button, and the "Items per page" dropdown to manipulate what is visible in the table - and consequently what will be exported.**
+
+**Export Buttons Rules**
+
+Available customization:
+```
+'visibleInExport' => true/false
+'visibleInTable' => true/false
+'exportOnlyField' => true
+```
+
+By default, the field will start visible in the table. Users can hide it toggling visibility. Will be exported if visible in the table.
+
+If you force `visibleInExport => true` you are saying that independent of field visibility in table it will **always** be exported.
+
+Contrary is `visibleInExport => false`, even if visible in table, field will not be exported as per developer instructions.
+
+Setting `visibleInTable => true` will force the field to stay in the table no matter what. User can't hide it. (By default all fields visible in the table will be exported. If you don't want to export this field use with combination with `visibleInExport => false`)
+
+Using `'visibleInTable' => false` will make the field start hidden in the table. But users can toggle it's visibility.
+
+If you want a field that is not on table, user can't show it, but will **ALWAYS** be exported use the `exportOnlyField => true`. If used will ignore any other custom visibility you defined.
+
+#### How to use different separator in DataTables (eg. semicolon instead of comma)
+
+
+
+If you want to change the separator in dataTable export to use semicolon (;) instead of comma (,) :
+
+**Step 1.** Copy vendor/backpack/crud/src/resources/views/crud/inc/export_buttons.blade.php to resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/inc/export_buttons.blade.php
+
+**Step 2.** Change it in your `dataTableConfiguration`:
+```php
+{
+ name: 'csvHtml5',
+ extend: 'csvHtml5',
+ fieldSeparator: ';',
+ exportOptions: {
+ columns: function ( idx, data, node ) {
+ var $column = crud.table.column( idx );
+ return ($column.visible() && $(node).attr('data-visible-in-export') != 'false') || $(node).attr('data-force-export') == 'true';
+ }
+ },
+ action: function(e, dt, button, config) {
+ crud.responsiveToggle(dt);
+ $.fn.DataTable.ext.buttons.csvHtml5.action.call(this, e, dt, button, config);
+ crud.responsiveToggle(dt);
+ }
+},
+
+```
+
+#### Custom Query
+
+
+
+
+By default, all entries are shown in the ListEntries table, before filtering. If you want to restrict the entries to a subset, you can use the methods below in your EntityCrudController's ```setupListOperation()``` method:
+
+```php
+// Change what entries are shown in the table view.
+// This changes all queries on the table view,
+// as opposed to filters, who only change it when that filter is applied.
+CRUD::addClause('active'); // apply a local scope
+CRUD::addClause('type', 'car'); // apply local dynamic scope
+CRUD::addClause('where', 'name', '=', 'car');
+CRUD::addClause('whereName', 'car');
+CRUD::addClause('whereHas', 'posts', function($query) {
+ $query->activePosts();
+ });
+CRUD::groupBy();
+CRUD::limit();
+CRUD::orderBy(); // please note it's generally a good idea to use crud->orderBy() inside "if (!CRUD::getRequest()->has('order')) {}"; that way, your custom order is applied ONLY IF the user hasn't forced another order (by clicking a column heading)
+
+// The above will change the used query, so the ListOperation will say
+// "Showing 140 entries, filtered from 1.000 entries". If you want to
+// that, and make it look like only those entries are in the databse,
+// you can change the baseQuery instead, by using:
+CRUD::addBaseClause('where', 'name', '=', 'car');
+```
+**NOTE:** The query constraints added in the `setup()` method operation _cannot_ be reset by `Reset Button`. They are permanent for that CRUD, for all operation.
+
+#### Custom Order
+
+
+
+By default, the List operation gets sorted by the primary key (usually `id`), descending. You can modify this behaviour by defining your own ordering:
+```php
+protected function setupListOperation()
+{
+ //change default order key
+ if (! $this->crud->getRequest()->has('order')){
+ $this->crud->orderBy('updated_at', 'desc');
+ }
+}
+```
+**NOTE**: We only apply the `orderBy` when the request don't have an `order` key.
+This is because we need to keep the ability to order in the Datatable Columns.
+If we didn't conditionally add the `orderBy`, it would become a __permanent order__ that can't be cleared by the Datatables `Reset` button and applied to every request.
+
+
+#### Responsive Table
+
+If your CRUD table has more columns than can fit inside the viewport (on mobile / tablet or smaller desktop screens), unimportant columns will start hiding and an expansion icon (three dots) will appear to the left of each row. We call this behaviour "_responsive table_", and consider this to be the best UX. By behaviour we consider the 1st column the most important, then 2nd, then 3rd, etc; the "actions" column is considered as important as the 1st column. You can of course [change the importance of columns](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns#define-which-columns-to-hide-in-responsive-table).
+
+If you do not like this, you can **toggle off the responsive behaviour for all CRUD tables** by changing this config value in your ```config/backpack/crud.php``` to ```false```:
+```php
+ // enable the datatables-responsive plugin, which hides columns if they don't fit?
+ // if not, a horizontal scrollbar will be shown instead
+ 'responsive_table' => true
+```
+
+To turn off the responsive table behaviour for _just one CRUD panel_, you can use ```CRUD::disableResponsiveTable()``` in your ```setupListOperation()``` method.
+
+
+#### Persistent Table
+
+By default, ListEntries will NOT remember your filtering, search and pagination when you leave the page. If you want ListEntries to do that, you can enable a ListEntries feature we call ```persistent_table```.
+
+**This will take the user back to the _filtered table_ after adding an item, previewing an item, creating an item or just browsing around**, preserving the table just like he/she left it - with the same filtering, pagination and search applied. It does so by saving the pagination, search and filtering for an arbitrary amount of time (by default: forever).
+
+To use ```persistent_table``` you can:
+- enable it for all CRUDs with the config option ```'persistent_table' => true``` in your ```config/backpack/crud.php```;
+- enable it inside a particular crud controller with ```CRUD::enablePersistentTable();```
+- disable it inside a particular crud controller with ```CRUD::disablePersistentTable();```
+
+> You can configure the persistent table duration in ``` config/backpack/crud.php ``` under `operations > list > persistentTableDuration`. False is forever. Set any amount of time you want in minutes. Note: you can configure it's expiring time on a per-crud basis using `CRUD::setOperationSetting('persistentTableDuration', 120); in your setupListOperation()` for 2 hours persistency. The default is `false` which means forever.
+
+
+#### Large Tables (millions of entries)
+
+By default, ListEntries uses a few features that are not appropriate for Eloquent models with millions (or billions) of records:
+- it shows the total number of entries (which can be a very slow query for big tables);
+- it paginates using 1/2/3 page buttons, instead of just previous & next;
+
+Starting with Backpack v5.4 we have an easy way to disable both of those, in order to make the ListOperation super-fast on big database tables. You just need to do:
+
+```php
+protected function setupListOperation()
+{
+ // ...
+ CRUD::setOperationSetting('showEntryCount', false);
+ // ...
+}
+```
+
+
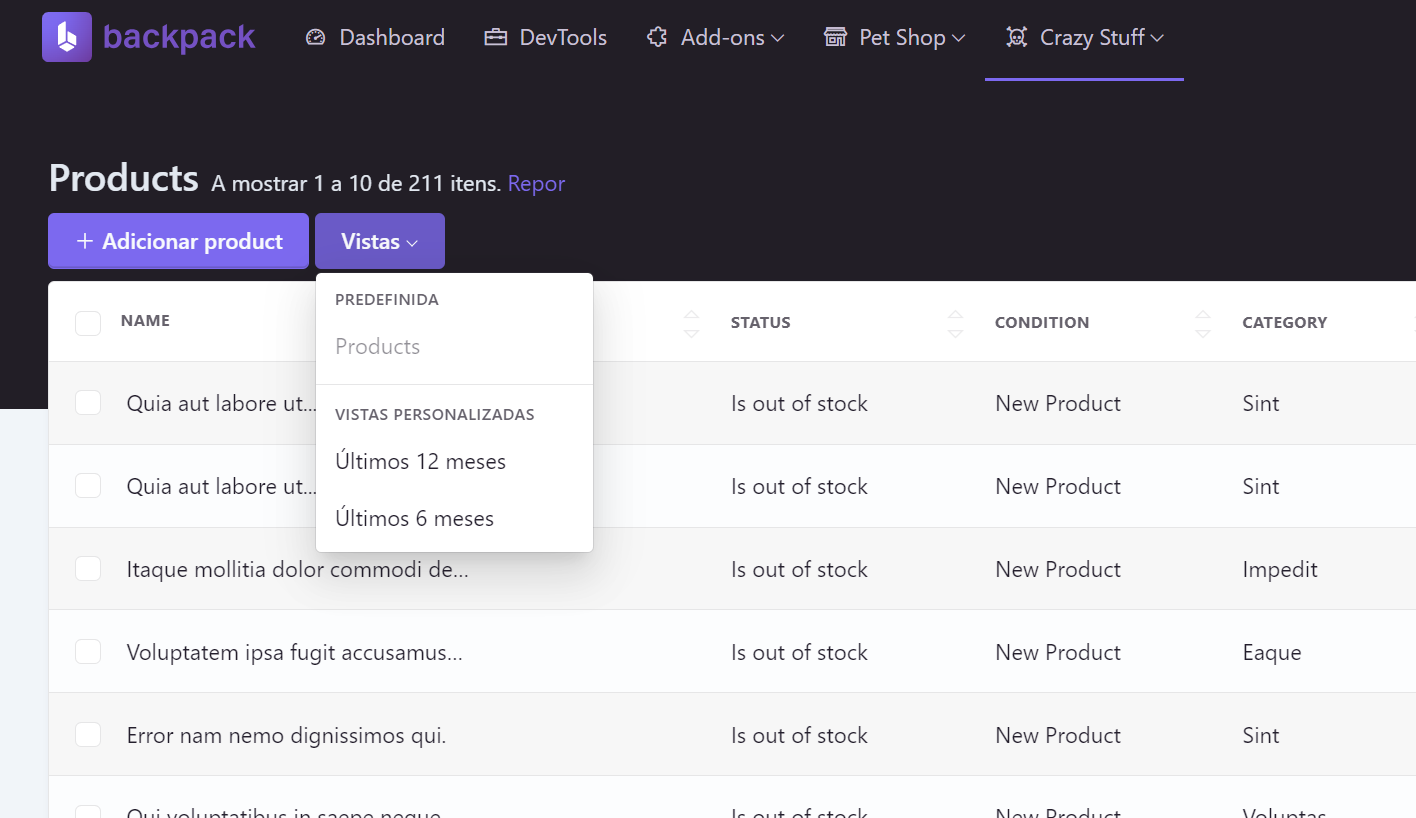
+#### Custom Views (for ListOperation)
PRO
+
+You might need different "views" or "pages" for your ListOperation, where each view has some filters/columns. For example:
+- default `Product` list view - show all products;
+- different `Best Sold Products` list view;
+- different `Products for accounting` list view
+
+The `CustomViews` operation helps you do exactly that - create alternative "views" for your ListOperation. Your admin will get a new dropdown right next to the "Add" button, to toggle between the different list views:
+
+
+
+
+To do that:
+
+1) **Use the `CustomViewOperation` trait in your CrudController**:
+
+```php
+class YourCrudController extends CrudController
+{
+ ...
+ use \Backpack\Pro\Http\Controllers\Operations\CustomViewOperation;
+```
+
+2) **Add `$this->runCustomViews()` at the end of your `setupListOperation()` method.** That will look for all the views you have defined. If you want to costumize the the title of your views, you can pass an array with the key being the name of the method and the value being the title of the view:
+
+```php
+public function setupListOperation()
+{
+ // ...
+
+ $this->runCustomViews();
+ // or
+ $this->runCustomViews([
+ 'setupLast12MonthsView' => __('Last 12 months'),
+ 'setupLast6MonthsView' => __('Last 6 months'),
+ ]);
+}
+```
+3) **Add the view logic you want to use in your CrudController.** This is meant to be run after all the the `setupListOperation()` columns, filters, buttons, etc. have been defined, so it should perform operations over the current state, like add or remove, columns, filters, buttons, etc, depending on your needs for that view.
+
+```php
+public function setupLast6MonthsView()
+{
+ // ...
+}
+
+public function setupLast12MonthsView()
+{
+ // ...
+}
+```
+
+**NOTE:** The `CustomView` will apply the query "on top" of the current `$crud->query`. If you would like to use a "fresh query" for your custom view you can use the `CRUD::setQuery()` method that will overwrite the previous set query.
+
+
+## How to add custom sections (aka. Widgets)
+
+[Widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets) (aka cards, aka charts, aka graphs) provide a simple way to insert blade files into admin panel pages. You can use them to insert cards, charts, notices or custom content into pages. You can use the [default widget types](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#default-widget-types) or [create your own custom widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#creating-a-custom-widget-type).
+
+Backpack's default template includes two [sections](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#requirements-1) where you can push widgets:
+
+* `before_content`
+* `after_content`
+
+To use widgets on list operation, define them inside `setupListOperation()` function.
+
+```php
+public function setupListOperation()
+{
+ // dynamic data to render in the following widget
+ $userCount = \App\Models\User::count();
+
+ //add div row using 'div' widget and make other widgets inside it to be in a row
+ Widget::add()->to('before_content')->type('div')->class('row')->content([
+
+ //widget made using fluent syntax
+ Widget::make()
+ ->type('progress')
+ ->class('card border-0 text-white bg-primary')
+ ->progressClass('progress-bar')
+ ->value($userCount)
+ ->description('Registered users.')
+ ->progress(100 * (int)$userCount / 1000)
+ ->hint(1000 - $userCount . ' more until next milestone.'),
+
+ //widget made using the array definition
+ Widget::make(
+ [
+ 'type' => 'card',
+ 'class' => 'card bg-dark text-white',
+ 'wrapper' => ['class' => 'col-sm-3 col-md-3'],
+ 'content' => [
+ 'header' => 'Example Widget',
+ 'body' => 'Widget placed at "before_content" secion in same row',
+ ]
+ ]
+ ),
+ ]);
+
+ //you can also add Script & CSS to your page using 'script' & 'style' widget
+ Widget::add()->type('script')->stack('after_scripts')->content('https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.12.0/jquery-ui.min.js');
+ Widget::add()->type('style')->stack('after_styles')->content('https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@shoelace-style/shoelace@2.0.0-beta.58/dist/themes/light.css');
+}
+```
+
+**Output:**
+* Using `before_content`:
+
+
+* Using `after_content`
+
+
+
+
+## How to Overwrite
+
+The main route leads to ```EntityCrudController::index()```, which loads ```list.blade.php```. Inside that table view, we're using AJAX to fetch the entries and place them inside a DataTables. The AJAX points to the same controller, ```EntityCrudController::search()```.
+
+
+### The View
+
+You can change how the ```list.blade.php``` file looks and works, by just placing a file with the same name in your ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/list.blade.php```. To quickly do that, run:
+
+```zsh
+php artisan backpack:publish crud/list
+```
+
+Keep in mind that by publishing this file, you won't be getting any updates we'll be pushing to it.
+
+
+### The Operation Logic
+
+Getting and showing the information is done inside the ```index()``` method. Take a look at the ```CrudController::index()``` method (your EntityCrudController is extending this CrudController) to see how it works.
+
+To overwrite it, just create an ```index()``` method in your ```EntityCrudController```.
+
+
+### The Search Logic
+
+An AJAX call is made to the ```search()``` method:
+- when entries are shown in the table;
+- when entries are filtered in the table;
+- when search is performed on the table;
+- when pagination is performed on the table;
+
+You can of course overwrite this ```search()``` method by just creating one with the same name in your ```EntityCrudController```. In addition, you can overwrite what a specific column is searching through (and how), by [using the searchLogic attribute](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns#custom-search-logic) on columns.
+
+
+
+## How to Debug
+
+Because the entries are fetched using AJAX requests, debugging the ListOperation can be a little difficult. Fortunately, we've thought of that.
+
+
+### Errors in AJAX requests
+
+If an error is thrown during the AJAX request, Backpack will show that error in a modal. Easy-peasy.
+
+
+### See query, models, views, exceptions in AJAX requests
+
+If you want to see or optimize database queries, you can do that using any Laravel tool that analyzes AJAX request. For example, here's how to analyze AJAX requests using the excellent [barryvdh/laravel-debugbar](https://github.com/barryvdh/laravel-debugbar). You just click the Folder icon to the right, and you select the latest request. Debugbar will then show you all info for that last AJAX request:
+
+
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-reorder.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-reorder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5cd6ac55
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-reorder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+# Reorder Operation
+
+---
+
+
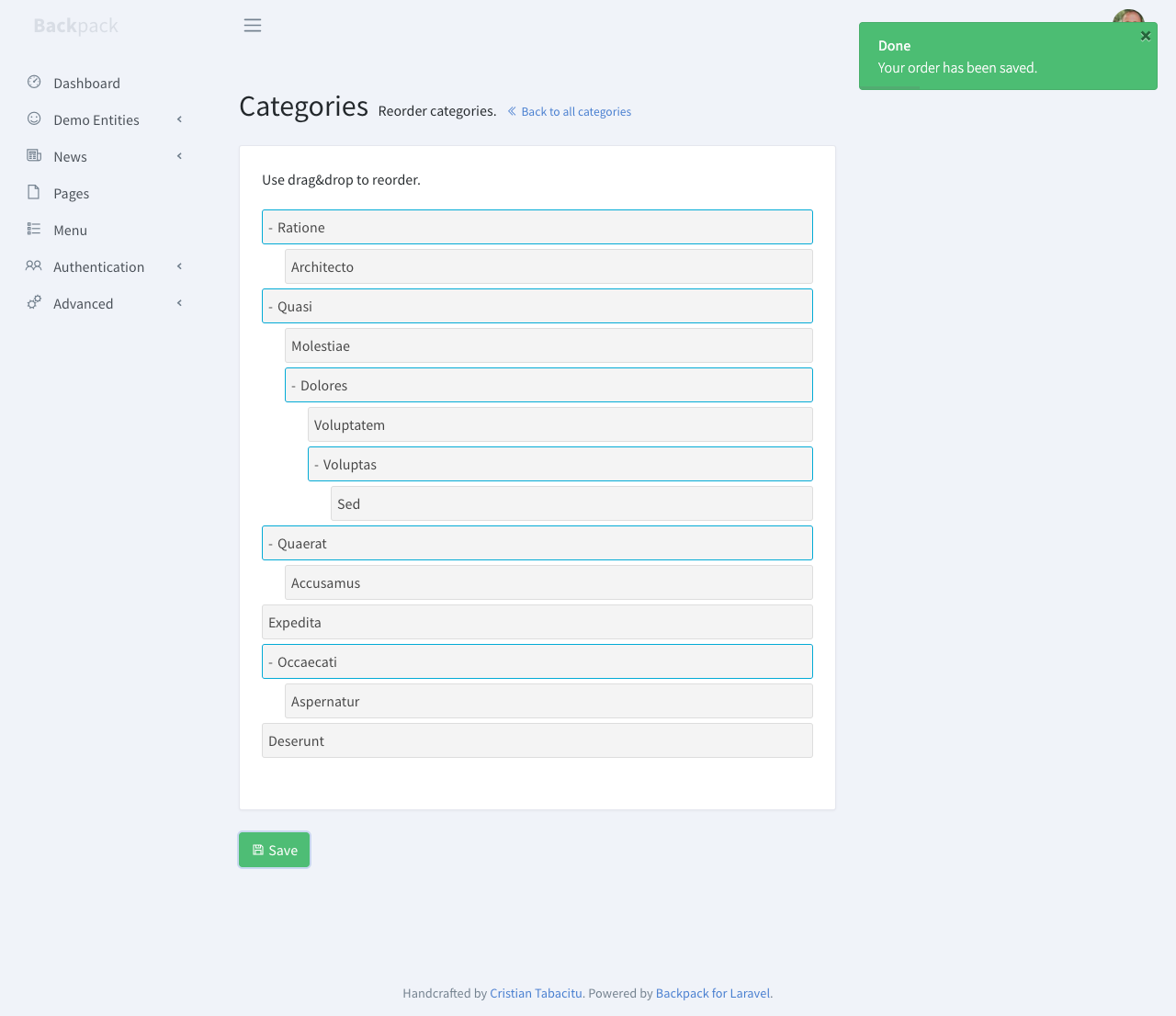
+## About
+
+This operation allows your admins to reorder & nest entries.
+
+
+
+
+## Requirements
+
+Your model should have the following integer fields, with a default value of 0: ```parent_id```, ```lft```, ```rgt```, ```depth```.
+
+Additionally, the `parent_id` field has to be nullable.
+
+
+## How to Use
+
+In order to enable this operation in your CrudController, you need to use the ```ReorderOperation``` trait, and have a ```setupReorderOperation()``` method that defines the ```label``` and ```max_level``` of allowed depth.
+
+```php
+
+## How It Works
+
+The ```/reorder``` route points to a ```reorder()``` method in your ```EntityCrudController```.
+
+
+## How to add custom sections(aka. Widgets)
+
+[Widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets) (aka cards, aka charts, aka graphs) provide a simple way to insert blade files into admin panel pages. You can use them to insert cards, charts, notices or custom content into pages. You can use the [default widget types](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#default-widget-types) or [create your own custom widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#creating-a-custom-widget-type).
+
+Backpack's default template includes two [sections](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#requirements-1) where you can push widgets:
+
+* `before_content`
+* `after_content`
+
+To use widgets on reorder operation, define them inside `setupReorderOperation()` function.
+
+```php
+public function setupReorderOperation()
+{
+ // dynamic data to render in the following widget
+ $userCount = \App\Models\User::count();
+
+ //add div row using 'div' widget and make other widgets inside it to be in a row
+ Widget::add()->to('before_content')->type('div')->class('row')->content([
+
+ //widget made using fluent syntax
+ Widget::make()
+ ->type('progress')
+ ->class('card border-0 text-white bg-primary')
+ ->progressClass('progress-bar')
+ ->value($userCount)
+ ->description('Registered users.')
+ ->progress(100 * (int)$userCount / 1000)
+ ->hint(1000 - $userCount . ' more until next milestone.'),
+
+ //widget made using the array definition
+ Widget::make(
+ [
+ 'type' => 'card',
+ 'class' => 'card bg-dark text-white',
+ 'wrapper' => ['class' => 'col-sm-3 col-md-3'],
+ 'content' => [
+ 'header' => 'Example Widget',
+ 'body' => 'Widget placed at "before_content" secion in same row',
+ ]
+ ]
+ ),
+ ]);
+
+ //you can also add Script & CSS to your page using 'script' & 'style' widget
+ Widget::add()->type('script')->stack('after_scripts')->content('https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.12.0/jquery-ui.min.js');
+ Widget::add()->type('style')->stack('after_styles')->content('https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@shoelace-style/shoelace@2.0.0-beta.58/dist/themes/light.css');
+}
+```
+
+#### Output:
+* Using `before_content`:
+
+
+* Using `after_content`
+
+
+
+
+## How to Overwrite
+
+In case you need to change how this operation works, take a look at the ```ReorderOperation.php``` trait to understand how it works. You can easily overwrite the ```reorder()``` or the ```saveReorder()``` methods:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\ReorderOperation { reorder as traitReorder; }
+
+public function reorder()
+{
+ // your custom code here
+
+ // call the method in the trait
+ return $this->traitReorder();
+}
+```
+
+You can also overwrite the reorder button by creating a file with the same name inside your ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/buttons/```. You can easily publish the reorder button there to make changes using:
+
+```zsh
+php artisan backpack:button --from=reorder
+```
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-revisions.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-revisions.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8f841408
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-revisions.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+# Revise Operation
+
+---
+
+
+## About
+
+Revise allows your admins to store, see and undo changes to entries on an Eloquent model.
+
+The operation provides you with a simple interface to work with [venturecraft/revisionable](https://github.com/VentureCraft/revisionable#implementation), which is a great package that stores all changes in a separate table. It can work as an audit trail, a backup system and an accountability system for the admins.
+
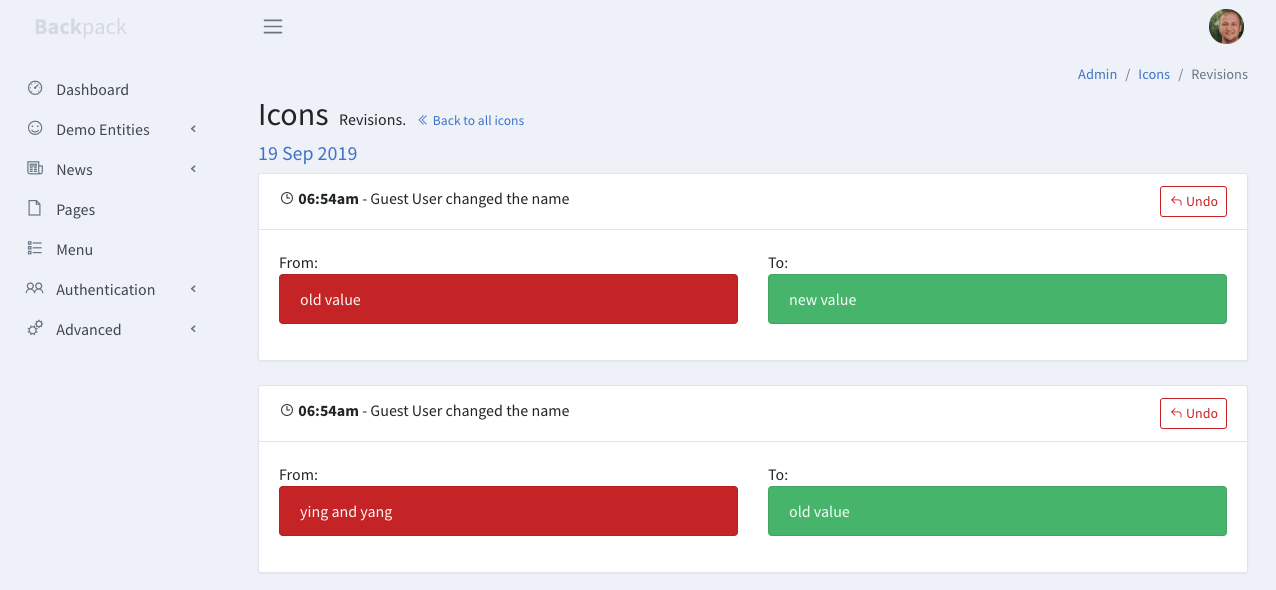
+When enabled, ```Revise``` will show another button in the table view, between _Edit_ and _Delete_. On click, that button opens another page which will allow an admin to see all changes and who made them:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## How to Use
+
+In order to enable this operation for a CrudController, you need to:
+
+**Step 1.** Install [the package](https://github.com/laravel-backpack/revise-operation) that provides this operation. This will also install venturecraft/revisionable if it's not already installed in your project.
+
+```bash
+composer require backpack/revise-operation
+```
+
+**Step 2.** Create the revisions table:
+
+```bash
+cp vendor/venturecraft/revisionable/src/migrations/2013_04_09_062329_create_revisions_table.php database/migrations/ && php artisan migrate
+```
+
+**Step 3.** Use [venturecraft/revisionable](https://github.com/VentureCraft/revisionable#implementation)'s trait on your model, and an ```identifiableName()``` method that returns an attribute on the model that the admin can use to distinguish between entries (ex: name, title, etc). If you are using another bootable trait be sure to override the boot method in your model.
+
+```php
+namespace App\Models;
+
+class Article extends Eloquent {
+ use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Models\Traits\CrudTrait, \Venturecraft\Revisionable\RevisionableTrait;
+
+ public function identifiableName()
+ {
+ return $this->name;
+ }
+
+ // If you are using another bootable trait
+ // be sure to override the boot method in your model
+ public static function boot()
+ {
+ parent::boot();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+**Step 4.** In your CrudController, use the operation trait:
+
+```php
+
+## About
+
+This CRUD operation allows your admins to preview an entry. When enabled, it will add a "Preview" button in the ListEntries view, that points to a show page. By default, it will show all attributes for that model:
+
+
+
+In case your entity is translatable, it will show a multi-language dropdown, just like Edit.
+
+
+## How it Works
+
+The ```/entity-name/{id}/show``` route points to the ```show()``` method in your EntityCrudController, which shows all columns that have been set up using [column types](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns), by showing a ```show.blade.php``` blade file.
+
+
+## How to Use
+
+To enable this operation, you need to use the ```ShowOperation``` trait on your CrudController:
+
+```php
+
+## How to Configure
+
+### setupShowOperation()
+
+You can manually define columns inside the ```setupShowOperation()``` method - thereby stopping the default "guessing" and "removing" of columns - you'll start from a blank slate and be in complete control of what columns are shown. For example:
+
+```php
+ // if you just want to show the same columns as inside ListOperation
+ protected function setupShowOperation()
+ {
+ $this->setupListOperation();
+ }
+```
+
+But you can also do both - let Backpack guess columns, and do stuff before or after that guessing, by calling the `autoSetupShowOperation()` method wherever you want inside your `setupShowOperation()`:
+
+```php
+ // show whatever you want
+ protected function setupShowOperation()
+ {
+ // MAYBE: do stuff before the autosetup
+
+ // automatically add the columns
+ $this->autoSetupShowOperation();
+
+ // MAYBE: do stuff after the autosetup
+
+ // for example, let's add some new columns
+ CRUD::column([
+ 'name' => 'my_custom_html',
+ 'label' => 'Custom HTML',
+ 'type' => 'custom_html',
+ 'value' => '
Something',
+ ]);
+ // in the following examples, please note that the table type is a PRO feature
+ CRUD::column([
+ 'name' => 'table',
+ 'label' => 'Table',
+ 'type' => 'table',
+ 'columns' => [
+ 'name' => 'Name',
+ 'desc' => 'Description',
+ 'price' => 'Price',
+ ]
+ ]);
+ CRUD::column([
+ 'name' => 'fake_table',
+ 'label' => 'Fake Table',
+ 'type' => 'table',
+ 'columns' => [
+ 'name' => 'Name',
+ 'desc' => 'Description',
+ 'price' => 'Price',
+ ],
+ ]);
+
+ // or maybe remove a column
+ CRUD::column('text')->remove();
+ }
+```
+### Tabs - display columns in tabs
+
+Adding the `tab` attribute to a column, will make the operation display the columns in tabs if `show.tabsEnabled` operation setting is not set to `false`.
+
+```php
+public function setupShowOperation()
+{
+ // using the array syntax
+ CRUD::column([
+ 'name' => 'name',
+ 'tab' => 'General',
+ ]);
+ // or using the fluent syntax
+ CRUD::column('description')->tab('Another tab');
+}
+```
+
+By default `horizontal` tabs are displayed. You can change them to `vertical` by adding in the setup function:
+`$this->crud->setOperationSetting('tabsType', 'vertical')`
+
+As like any other operation settings, those can be changed globaly for all CRUDs in the `config/backpack/operations/show.php` file.
+
+
+## How to add custom sections(aka. Widgets)
+
+[Widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets) (aka cards, aka charts, aka graphs) provide a simple way to insert blade files into admin panel pages. You can use them to insert cards, charts, notices or custom content into pages. You can use the [default widget types](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#default-widget-types) or [create your own custom widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#creating-a-custom-widget-type).
+
+Backpack's default template includes two [sections](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#requirements-1) where you can push widgets:
+
+* `before_content`
+* `after_content`
+
+To use widgets on show operation, define them inside `setupShowOperation()` function.
+
+```php
+public function setupShowOperation()
+{
+ // dynamic data to render in the following widget
+ $userCount = \App\Models\User::count();
+
+ //add div row using 'div' widget and make other widgets inside it to be in a row
+ Widget::add()->to('before_content')->type('div')->class('row')->content([
+
+ //widget made using fluent syntax
+ Widget::make()
+ ->type('progress')
+ ->class('card border-0 text-white bg-primary')
+ ->progressClass('progress-bar')
+ ->value($userCount)
+ ->description('Registered users.')
+ ->progress(100 * (int)$userCount / 1000)
+ ->hint(1000 - $userCount . ' more until next milestone.'),
+
+ //widget made using the array definition
+ Widget::make(
+ [
+ 'type' => 'card',
+ 'class' => 'card bg-dark text-white',
+ 'wrapper' => ['class' => 'col-sm-3 col-md-3'],
+ 'content' => [
+ 'header' => 'Example Widget',
+ 'body' => 'Widget placed at "before_content" secion in same row',
+ ]
+ ]
+ ),
+ ]);
+
+ //you can also add Script & CSS to your page using 'script' & 'style' widget
+ Widget::add()->type('script')->stack('after_scripts')->content('https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.12.0/jquery-ui.min.js');
+ Widget::add()->type('style')->stack('after_styles')->content('https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@shoelace-style/shoelace@2.0.0-beta.58/dist/themes/light.css');
+}
+```
+
+#### Output:
+* Using `before_content`:
+
+
+* Using `after_content`
+
+
+
+
+## How to Overwrite
+
+In case you need to modify the show logic in a meaningful way, you can create a ```show()``` method in your EntityCrudController. The route will then point to your method, instead of the one in the trait. For example:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\ShowOperation { show as traitShow; }
+
+public function show($id)
+{
+ // custom logic before
+ $content = $this->traitShow($id);
+ // custom logic after
+ return $content;
+}
+```
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-trash.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-trash.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e1b56b60
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-trash.md
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
+# Trash Operation
PRO
+
+--
+
+
+## About
+
+This CRUD operation allows your admins to soft delete, restore and permanently delete entries from the table. In other words, admins can send entries to the trash, recover them from trash or completely destroy them.
+
+
+## Requirements
+
+1. This is a
PRO operation. It requires that you have [purchased access to `backpack/pro`](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects).
+
+2. In addition, it needs that your Model uses Laravel's `SoftDeletes` trait. For that, you should:
+- generate a migration to add the `deleted_at` column to your table, eg. `php artisan make:migration add_soft_deletes_to_products --table=products`;
+- inside that file's `Schema::table()` closure, add `$table->softDeletes();`
+- run `php artisan migrate`
+- add `use SoftDeletes` on the corresponding model (and import that class namespace);
+
+
+## Trash a Single Item
PRO
+
+
+### How it Works
+- **Trash**:
+Using AJAX, a DELETE request is performed towards ```/entity-name/{id}/trash```, which points to the ```trash()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+- **Restore**:
+Using AJAX, a PUT request is performed towards ```/entity-name/{id}/restore```, which points to the ```restore()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+- **Destroy**:
+Using AJAX, a DELETE request is performed towards ```/entity-name/{id}/destroy```, which points to the ```destroy()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+
+### How to Use
+
+**Step 1.** If your EntityCrudController uses the `DeleteOperation`, remove it. `TrashOperation` is a complete alternative to `DeleteOperation`.
+
+**Step 2.** You need to ```use \Backpack\Pro\Http\Controllers\Operations\TrashOperation;``` inside your EntityCrudController. Ideally the TrashOperation should be the last one that gets used. For example:
+
+```php
+class ProductCrudController extends CrudController
+{
+ // ... other operations
+ use \Backpack\Pro\Http\Controllers\Operations\TrashOperation;
+}
+```
+This will make a Trash button and Trashed filter show up in the list view, and will enable the routes and functionality needed for the operation. If you're getting a "Trait not found" exception, make sure in the namespace you have typed `Backpack\Pro`, not `Backpack\PRO`.
+
+
+
+### How to configure
+
+You can easily disable the default trash filter:
+```php
+public function setupTrashOperation()
+{
+ CRUD::setOperationSetting('withTrashFilter', false);
+
+ // one of the things the filter does is preventing the update/access to trashed items.
+ // if you disable it and use Update/Show operations, you should manually disable the
+ // access to those operations or they will throw 404:
+ CRUD::setAccessCondition(['update', 'show'], function($entry) {
+ return ! $entry->trashed();
+ });
+}
+```
+
+Disabling the filter also will make the trashed items show in your List view. Note that, by default, the `Destroy` button is only shown in _trashed items_. If you want to allow your admins to _permanently delete_ without sending first to trash... you can achieve that by defining in your operation setup:
+
+```php
+// in the setupTrashOperation method
+CRUD::setOperationSetting('canDestroyNonTrashedItems', true);
+```
+
+
+### How to control access to operation actions
+
+When used, `TrashOperation` each action inside this operation (`trash`, `restore` and `destroy`) checks for access, before being performed. Likewise, `BulkTrashOperation` checks for access to `bulkTrash`, `bulkRestore` and `bulkDestroy`.
+
+That means you can revoke access to some operations, depending on user roles or anything else you want:
+```php
+// if user is not superadmin, don't allow permanently delete items
+public function setupTrashOperation()
+{
+ if(! backpack_user()->hasRole('superadmin')) {
+ CRUD::denyAccess('destroy');
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+### How to Override
+
+In case you need to change how this operation works, just create ```trash()```, ```restore()```,```destroy()``` methods in your EntityCrudController, and they will be used instead of the default ones. For example for `trash()`:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\Pro\Http\Controllers\Operations\TrashOperation { trash as traitTrash; }
+
+public function trash($id)
+{
+ CRUD::hasAccessOrFail('trash');
+
+ // your custom code here
+}
+```
+
+You can also override the buttons by creating a file with the same name inside your ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/buttons/```. You can easily publish the buttons there to make changes using:
+
+```zsh
+php artisan backpack:button --from=trash
+
+php artisan backpack:button --from=restore
+
+php artisan backpack:button --from=destroy
+```
+
+
+## BulkTrash (Trash Multiple Items)
PRO
+
+In addition to the button for each entry,
PRO developers can show checkboxes next to each element, to allow their admin to trash, restore & delete multiple entries at once.
+
+
+
+### How it Works
+
+- **BulkTrash**:
+Using AJAX, a DELETE request is performed towards ```/entity-name/{id}/bulk-trash```, which points to the ```bulkTrash()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+- **BulkRestore**:
+Using AJAX, a PUT request is performed towards ```/entity-name/{id}/bulk-restore```, which points to the ```bulkRestore()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+- **BulkDestroy**:
+Using AJAX, a DELETE request is performed towards ```/entity-name/{id}/bulk-destroy```, which points to the ```bulkDestroy()``` method in your EntityCrudController.
+
+
+### How to Use
+
+Assuming your Model already uses Larave's `SoftDeletes`, you just need to ```use \Backpack\Pro\Http\Controllers\Operations\BulkTrashOperation;``` on your EntityCrudController.
+
+
+### How to Override
+
+In case you need to change how this operation works, just create a ```bulkTrash()```, `bulkRestore()` or `bulkDestroy()` methods in your EntityCrudController:
+
+```php
+use \Backpack\Pro\Http\Controllers\Operations\BulkTrashOperation { bulkTrash as traitBulkTrash; }
+
+public function bulkTrash()
+{
+ CRUD::hasAccessOrFail('bulkTrash');
+
+ // your custom code here
+}
+```
+
+You can also override the buttons by creating a file with the same name inside your ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/buttons/```. You can easily publish the buttons there to make changes using:
+
+```zsh
+php artisan backpack:button --from=bulk_trash
+
+php artisan backpack:button --from=bulk_restore
+
+php artisan backpack:button --from=bulk_destroy
+```
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operation-update.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-update.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e6e7e92f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operation-update.md
@@ -0,0 +1,456 @@
+# Update Operation
+
+---
+
+
+## About
+
+This operation allows your admins to edit entries from the database.
+
+
+
+
+## Requirements
+
+All editable attributes should be ```$fillable``` on your Model.
+
+
+## How to Use
+
+**Step 0. Use the operation trait on your controller**:
+
+```php
+crud->setValidation(StoreRequest::class);
+ // $this->crud->addField()
+
+ // or just do everything you've done for the Create Operation
+ // $this->crud->setupCreateOperation();
+
+ // You can also do things depending on the current entry
+ // (the database item being edited or updated)
+ // if ($this->crud->getCurrentEntry()->smth == true) {}
+ }
+}
+```
+
+This will:
+- allow access to this operation;
+- make an Edit button appear in the ```line``` stack, next to each entry, in the List operation view;
+
+To use the Update operation, you must:
+
+**Step 1. Specify what field types** you'd like to show for each attribute, in your controller's ```setupUpdateOperation()``` method. You can do that using the [Fields API](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#fields-api). In short you can:
+
+```php
+// add a field only to the Update operation
+$this->crud->addField($field_definition_array);
+```
+
+**Step 2. Specify which FormRequest file to use for validation and authorization**, inside your ```setupUpdateOperation()``` method. You can pass the same FormRequest as you did for the Create operation if there are no differences. If you need separate validation for Create and Update [look here](#separate-validation).
+```php
+$this->crud->setValidation(StoreRequest::class);
+```
+
+For more on how to manipulate fields, please read the [Fields documentation page](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields). For more on validation rules, check out [Laravel's validation docs](https://laravel.com/docs/master/validation#available-validation-rules).
+
+**Step 3. (optional recommended) eager load relationships**. If you're displaying relationships in your fields, you might want to eager load them to avoid the N+1 problem. You can do that in the `setupUpdateOperation()` method:
+
+```php
+$this->crud->setOperationSetting('eagerLoadRelationships', true);
+```
+Note: You can enable this setting globally for all your cruds in the `config/backpack/operations/update.php` file.
+
+
+## How It Works
+
+CrudController is a RESTful controller, so the ```Update``` operation uses two routes:
+- GET to ```/entity-name/{id}/edit``` - points to ```edit()``` which shows the Edit form (```edit.blade.php```);
+- POST to ```/entity-name/{id}/edit``` - points to ```update()``` which uses Eloquent to update the entry in the database;
+
+The ```edit()``` method will show all the fields you've defined for this operation using the [Fields API](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#fields-api), then upon Save the ```update()``` method will first check the validation from the type-hinted FormRequest, then create the entry using the Eloquent model. Only attributes that have a field type added and are ```$fillable``` on the model will actually be updated in the database.
+
+
+## How to add custom sections(aka. Widgets)
+
+[Widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets) (aka cards, aka charts, aka graphs) provide a simple way to insert blade files into admin panel pages. You can use them to insert cards, charts, notices or custom content into pages. You can use the [default widget types](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#default-widget-types) or [create your own custom widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#creating-a-custom-widget-type).
+
+Backpack's default template includes two [sections](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets#requirements-1) where you can push widgets:
+
+* `before_content`
+* `after_content`
+
+To use widgets on update operation, define them inside `setupUpdateOperation()` function.
+
+```php
+public function setupUpdateOperation()
+{
+ // dynamic data to render in the following widget
+ $userCount = \App\Models\User::count();
+
+ //add div row using 'div' widget and make other widgets inside it to be in a row
+ Widget::add()->to('before_content')->type('div')->class('row')->content([
+
+ //widget made using fluent syntax
+ Widget::make()
+ ->type('progress')
+ ->class('card border-0 text-white bg-primary')
+ ->progressClass('progress-bar')
+ ->value($userCount)
+ ->description('Registered users.')
+ ->progress(100 * (int)$userCount / 1000)
+ ->hint(1000 - $userCount . ' more until next milestone.'),
+
+ //widget made using the array definition
+ Widget::make(
+ [
+ 'type' => 'card',
+ 'class' => 'card bg-dark text-white',
+ 'wrapper' => ['class' => 'col-sm-3 col-md-3'],
+ 'content' => [
+ 'header' => 'Example Widget',
+ 'body' => 'Widget placed at "before_content" secion in same row',
+ ]
+ ]
+ ),
+ ]);
+
+ //you can also add Script & CSS to your page using 'script' & 'style' widget
+ Widget::add()->type('script')->stack('after_scripts')->content('https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.12.0/jquery-ui.min.js');
+ Widget::add()->type('style')->stack('after_styles')->content('https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@shoelace-style/shoelace@2.0.0-beta.58/dist/themes/light.css');
+}
+```
+
+#### Output:
+* Using `before_content`:
+
+
+* Using `after_content`
+
+
+
+
+## Advanced Features and Techniques
+
+
+### Validation
+
+There are three ways you can define the [validation rules](https://laravel.com/docs/validation#available-validation-rules) for your fields:
+
+#### Validating fields using FormRequests
+
+When you generate a CrudController, you'll notice a [Laravel FormRequest](https://laravel.com/docs/validation#form-request-validation) has also been generated, and that FormRequest is mentioned as the source of your validation rules:
+```php
+protected function setupUpdateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->setValidation(StoreRequest::class);
+}
+```
+
+This works particularly well for bigger models, because you can mention a lot of rules, messages and attributes in your `FormRequest` and it will not increase the size of your `CrudController`.
+
+**Do you need different Create and Update validations?** Then create a separate request file for each operation and instruct your EntityCrudController to use those files:
+
+```php
+use App\Http\Requests\CreateTagRequest as StoreRequest;
+use App\Http\Requests\UpdateTagRequest as UpdateRequest;
+
+// ...
+
+public function setupCreateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->setValidation(CreateRequest::class);
+}
+
+public function setupUpdateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->setValidation(UpdateRequest::class);
+}
+```
+
+#### Validating fields using a rules array
+
+For smaller models (with just a few validation rules), creating an entire FormRequest file to hold them might be overkill. If you prefer, you can pass an array of [validation rules](https://laravel.com/docs/validation#available-validation-rules) to the same `setValidation()` method (with an optional second parameter for the validation messages):
+
+```php
+protected function setupUpdateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->setValidation([
+ 'name' => 'required|min:2',
+ ]);
+
+ // or maybe
+ $rules = ['name' => 'required|min:2'];
+ $messages = [
+ 'name.required' => 'You gotta give it a name, man.',
+ 'name.min' => 'You came up short. Try more than 2 characters.',
+ ];
+ $this->crud->setValidation($rules, $messages);
+}
+```
+
+This is more convenient for small and medium models. Plus, it's very easy to read.
+
+#### Validating fields using field attributes
+
+Another good option for small & medium models is to define the [validation rules](https://laravel.com/docs/validation#available-validation-rules) directly on your fields:
+
+```php
+protected function setupUpdateOperation()
+{
+ $this->crud->addField([
+ 'name' => 'content',
+ 'label' => 'Content',
+ 'type' => 'ckeditor',
+ 'placeholder' => 'Your textarea text here',
+ 'validationRules' => 'required|min:10',
+ 'validationMessages' => [
+ 'required' => 'You gotta write smth man.',
+ 'min' => 'More than 10 characters, bro. Wtf... You can do this!',
+ ]
+ ]);
+ // CAREFUL! This MUST be called AFTER the fields are defined, NEVER BEFORE
+ $this->crud->setValidation();
+}
+```
+
+You must then call `setValidation()` without a parameter, and Backpack will go through all defined fields, get their `validationRules` and validate them. It is VERY IMPORTANT to call `setValidation()` _after_ you've defined the fields! Otherwise Backpack won't find any `validationRules`.
+
+
+### Callbacks
+
+Developers coming other CRUD systems (like GroceryCRUD) will be looking for callbacks to run "before_insert", "before_update", "after_insert", "after_update". **There are no callbacks in Backpack**, because... they're not needed. There are plenty of other ways to do things before/after an entry is updated.
+
+
+#### Use Events in your `setup()` method
+
+Laravel already triggers [multiple events](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent#events) in an entry's lifecycle. Those also include:
+- `updating` and `updated`, which are triggered by the Update operation;
+- `saving` and `saved`, which are triggered by both the Create and the Update operations;
+
+So if you want to do something to a `Product` entry _before_ it's updated, you can easily do that:
+```php
+public function setupUpdateOperation()
+{
+
+ // ...
+
+ Product::updating(function($entry) {
+ $entry->last_edited_by = backpack_user()->id;
+ });
+}
+```
+
+Take a closer look at [Eloquent events](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent#events) if you're not familiar with them, they're really _really_ powerful once you understand them. Please note that **these events will only get registered when the function gets called**, so if you define them in your `CrudController`, then:
+- they will NOT run when an entry is changed outside that CrudController;
+- if you want to expand the scope to cover both the `Create` and `Update` operations, you can easily do that, for example by using the `saving` and `saved` events, and moving the event-calling to your main `setup()` method;
+
+#### Use events in your field definition
+
+You can tell a field to do something to the entry when that field gets saved to the database. Rephrased, you can define standard [Eloquent events](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent#events) directly on fields. For example:
+
+```php
+// FLUENT syntax - use the convenience method "on" to define just ONE event
+CRUD::field('name')->on('updating', function ($entry) {
+ $entry->last_edited_by = backpack_user()->id;
+});
+
+// FLUENT SYNTAX - you can define multiple events in one go
+CRUD::field('name')->events([
+ 'updating' => function ($entry) {
+ $entry->last_edited_by = backpack_user()->id;
+ },
+ 'saved' => function ($entry) {
+ // TODO: upload some file
+ },
+]);
+
+// using the ARRAY SYNTAX, define an array of events and closures
+CRUD::addField([
+ 'name' => 'name',
+ 'events' => [
+ 'updating' => function ($entry) {
+ $entry->author_id = backpack_user()->id;
+ },
+ ],
+]);
+```
+
+#### Override the `update()` method
+
+The store code is inside a trait, so you can easily overwrite it:
+
+```php
+crud->addField(['type' => 'hidden', 'name' => 'author_id']);
+ // $this->crud->removeField('password_confirmation');
+
+ // Note: By default Backpack ONLY saves the inputs that were added on page using Backpack fields.
+ // This is done by stripping the request of all inputs that do NOT match Backpack fields for this
+ // particular operation. This is an added security layer, to protect your database from malicious
+ // users who could theoretically add inputs using DeveloperTools or JavaScript. If you're not properly
+ // using $guarded or $fillable on your model, malicious inputs could get you into trouble.
+
+ // However, if you know you have proper $guarded or $fillable on your model, and you want to manipulate
+ // the request directly to add or remove request parameters, you can also do that.
+ // We have a config value you can set, either inside your operation in `config/backpack/crud.php` if
+ // you want it to apply to all CRUDs, or inside a particular CrudController:
+ // $this->crud->setOperationSetting('saveAllInputsExcept', ['_token', '_method', 'http_referrer', 'current_tab', 'save_action']);
+ // The above will make Backpack store all inputs EXCEPT for the ones it uses for various features.
+ // So you can manipulate the request and add any request variable you'd like.
+ // $this->crud->getRequest()->request->add(['author_id'=> backpack_user()->id]);
+ // $this->crud->getRequest()->request->remove('password_confirmation');
+ // $this->crud->getRequest()->request->add(['author_id'=> backpack_user()->id]);
+ // $this->crud->getRequest()->request->remove('password_confirmation');
+
+ $response = $this->traitUpdate();
+ // do something after save
+ return $response;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+>But before you do that, ask yourself - **_is this something that should be done when an entry is added/updated/deleted from the application, too_**? Not just the admin admin? If so, a better place for it would be the Model. Remember your Model is a pure Eloquent Model, so the cleanest way might be to use [Eloquent Event Observers](https://laravel.com/docs/5.5/eloquent#events) or [accessors and mutators](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent-mutators#accessors-and-mutators).
+
+
+### Translatable models and multi-language CRUDs
+
+
+
+For localized apps, you can let your admins edit multi-lingual entries. Translations are stored using [spatie/laravel-translatable](https://github.com/spatie/laravel-translatable).
+
+In order to make one of your Models translatable (localization), you need to:
+0. Be running MySQL 5.7+ (or a PostgreSQL with JSON column support);
+1. [Install spatie/laravel-translatable](https://github.com/spatie/laravel-translatable#installation);
+2. In your database, make all translatable columns either JSON or TEXT.
+3. Use Backpack's ```HasTranslations``` trait on your model (instead of using spatie's ```HasTranslations```) and define what fields are translatable, inside the ```$translatable``` property. For example:
+
+```php
+ You DO NOT need to cast translatable string columns as array/json/object in the Eloquent model. From Eloquent's perspective they're strings. So:
+> - you _should NOT_ cast ```name```; it's a string in Eloquent, even though it's stored as JSON in the db by SpatieTranslatable;
+> - you _should_ cast ```extras``` to ```array```, if each translation stores an array of some sort;
+
+Change the languages available to translate to/from, in your crud config file (```config/backpack/crud.php```). By default there are quite a few enabled (English, French, German, Italian, Romanian).
+
+Additionally, if you have slugs (but only if you need translatable slugs), you'll need to use backpack's classes instead of the ones provided by `cviebrock/eloquent-sluggable`.
+Make sure you have `cviebrock/eloquent-sluggable` installed as well, if not, please do it with `composer require cviebrock/eloquent-sluggable`:
+
+```php
+ [
+ 'source' => 'slug_or_name',
+ ],
+ ];
+ }
+}
+```
+> If your slugs are not translatable, use the ```cviebrock/eloquent-sluggable``` traits. The Backpack's ```Sluggable``` trait saves your slug as a JSON object, regardless of the ```slug``` field being defined inside the ```$translatable``` property.
+
+
+### Delete button on Update operation
+
+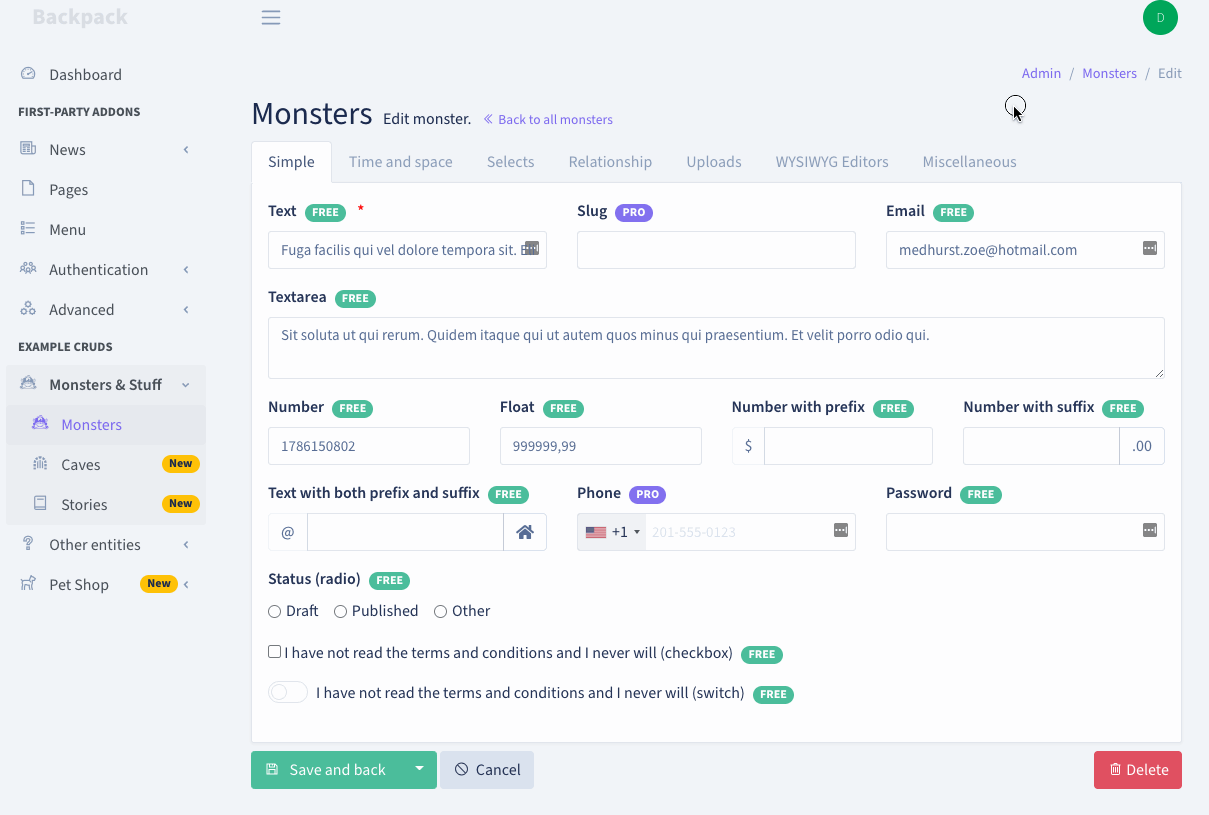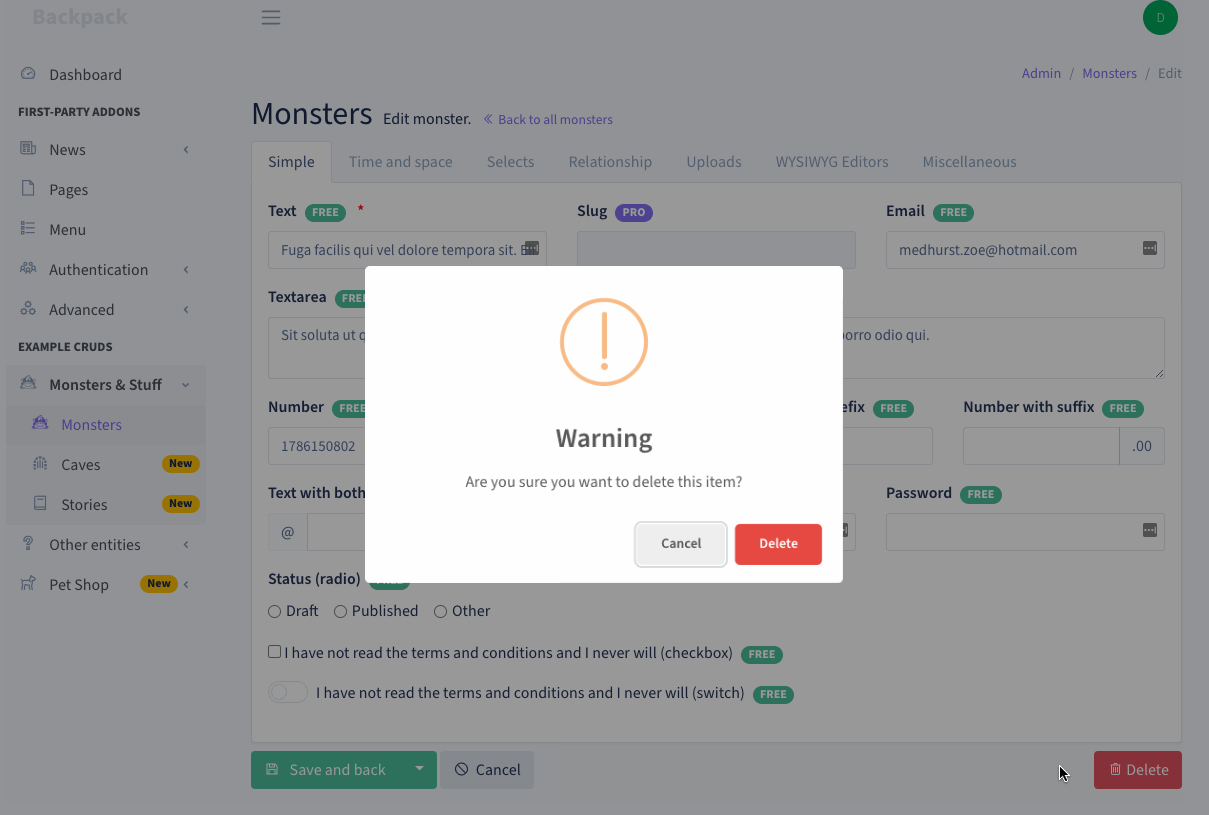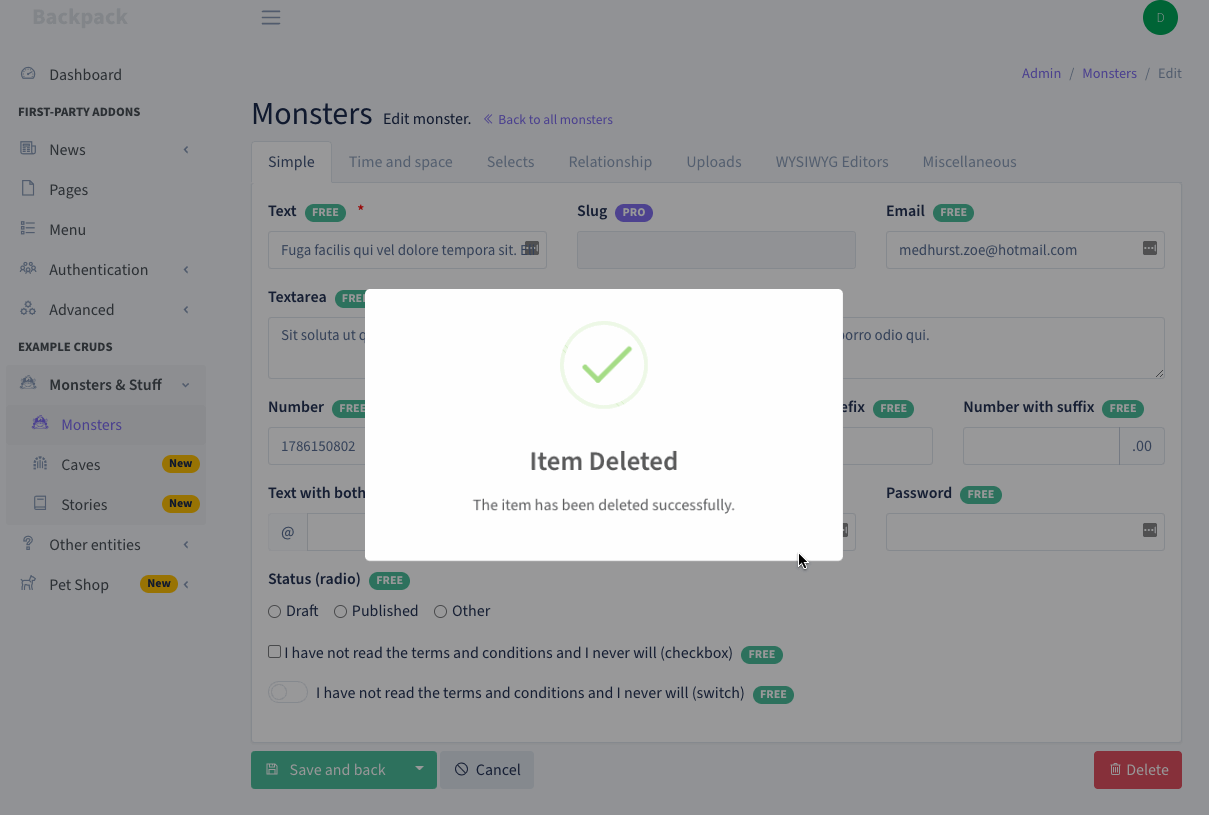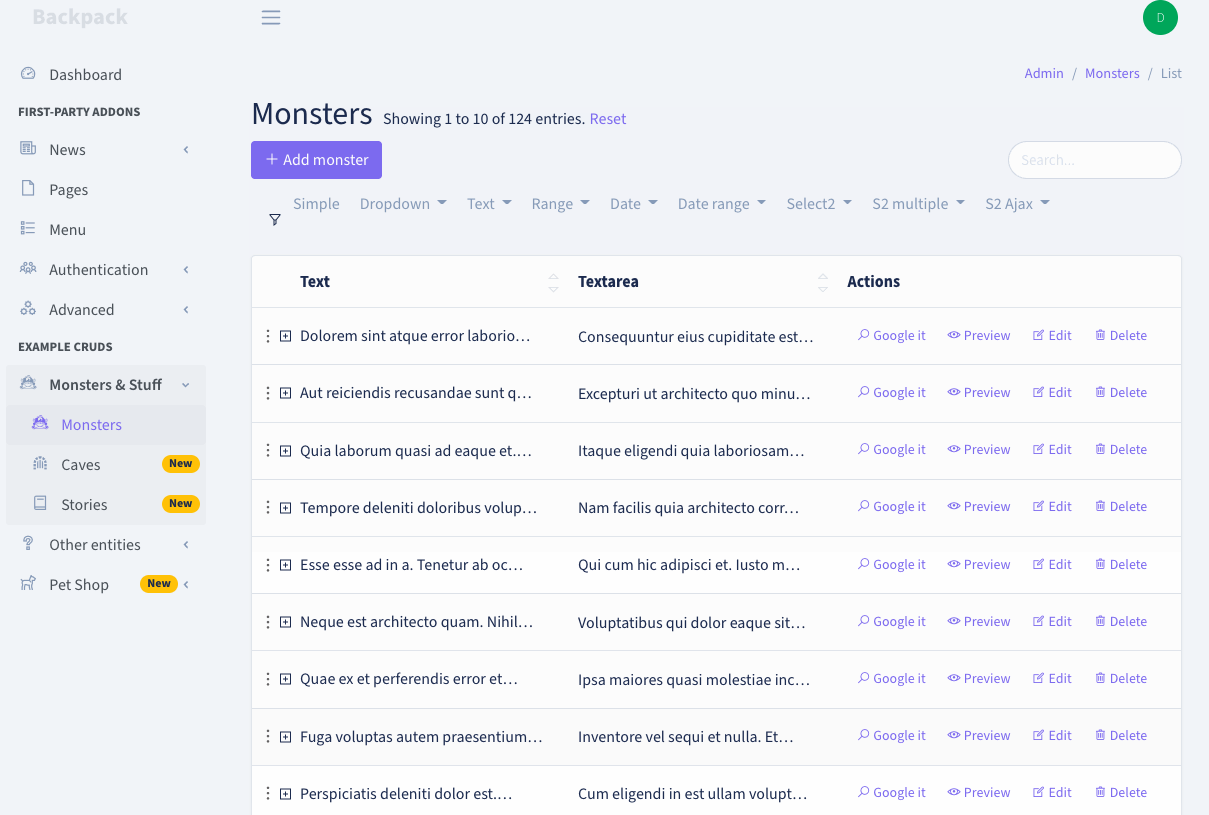
+
+If you want to display a **Delete** button right on the **Update** operation, you simply need to add a line to the `setupUpdateOperation()` method:
+
+```php
+ protected function setupUpdateOperation()
+ {
+ // your code...
+
+ $this->crud->setOperationSetting('showDeleteButton', true); // <--- add this!
+
+ // alternatively you can pass an URL to where user should be redirected after entry is deleted:
+ // $this->crud->setOperationSetting('showDeleteButton', 'https://someurl.com');
+ }
+```
+
+This will allow admins to remove entries right from the **Update Operation**, and it will redirect them back ot the **List Operation** afterwards.
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-operations.md b/7.x-dev/crud-operations.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..459b393c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-operations.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1150 @@
+# Operations
+
+---
+
+When creating a CRUD Panel, your ```EntityCrudController``` (where Entity = your model name) is extending ```CrudController```. **By default, no operations are enabled.** No routes are registered.
+
+To use an operation, you need to use the operation trait on your controller. For example, to enable the List operation:
+
+```php
+
+## Standard Operations
+
+No operations are enabled by default.
+
+But Backpack does provide the logic for the most common operations admins perform on Eloquent model. You just need to use it (and maybe configure it) in your controller.
+
+Operations provided by Backpack:
+- [List](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-list-entries) - allows the admin to see all entries for a model, with pagination, search
FREE and filters
PRO
+- [Create](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-create) - allows the admin to add a new entry;
FREE
+- [Update](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-update) - allows the admin to edit an existing entry;
FREE
+- [Show](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-show) - allows the admin to preview an entry;
FREE
+- [Delete](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-delete) - allows the admin to remove and entry;
FREE
+- [BulkDelete](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-delete) - allows the admin to remove multiple entries in one go;
PRO
+- [Clone](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-clone) - allows the admin to make a copy of a database entry;
PRO
+- [BulkClone](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-clone) - allows the admin to make a copy of multiple database entries in one go;
PRO
+- [Reorder](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-reorder) - allows the admin to reorder & nest all entries of a model, in a hierarchy tree;
FREE
+- [Revisions](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-revisions) - shows an audit log of all changes to an entry, and allows you to undo modifications;
FREE
+
+
+
+### Operation Actions
+
+Each Operation is actually _a trait_, which can be used on CrudControllers. This trait can contain one or more methods (or functions). Since Laravel calls each Controller method an _action_, that means each _Operation_ can have one or many _actions_. For example, we have the ```create``` operation and two actions: ```create()``` and ```store()```.
+
+```php
+trait CreateOperation
+{
+ public function create()
+ {
+ // ...
+ }
+
+ public function store()
+ {
+ // ...
+ }
+}
+```
+
+An action can do something with AJAX and return true/false, it can return a view, or whatever else you can do inside a controller method. Notice that it's a ```public``` method - which is a Laravel requirement, in order to point a route to it.
+
+You can check which action is currently being performed using the [standard Laravel Route API](https://laravel.com/api/8.x/Illuminate/Routing/Route.html):
+
+- ```\Route::getCurrentRoute()->getAction()``` or ```$this->crud->getRequest()->route()->getAction()```:
+```
+array:8 [▼
+ "middleware" => array:2 [▼
+ 0 => "web"
+ 1 => "admin"
+ ]
+ "as" => "crud.monster.index"
+ "uses" => "App\Http\Controllers\Admin\MonsterCrudController@index"
+ "operation" => "list"
+ "controller" => "App\Http\Controllers\Admin\MonsterCrudController@index"
+ "namespace" => "App\Http\Controllers\Admin"
+ "prefix" => "admin"
+ "where" => []
+]
+```
+- ```\Route::getCurrentRoute()->getActionName()``` or ```$this->crud->getRequest()->route()->getActionName()```:
+```
+App\Http\Controllers\Admin\MonsterCrudController@index
+```
+- ```\Route::getCurrentRoute()->getActionMethod()``` or ```$this->crud->getRequest()->route()->getActionMethod()```:
+```
+index
+```
+
+You can also use the shortcuts on the CrudPanel object:
+```php
+$this->crud->getActionMethod(); // returns the method on the controller that was called by the route; ex: create(), update(), edit() etc;
+$this->crud->actionIs('create'); // checks if the controller method given is the one called by the route
+```
+
+
+### Titles, Headings and Subheadings
+
+For standard CRUD operations, each _action_ that shows an interface uses some texts to show the user what page, operation or action he is currently performing:
+- **Title** - page title, shown in the browser's title bar;
+- **Heading** - biggest heading on page;
+- **Subheading** - short description of the current page, sits beside the heading;
+
+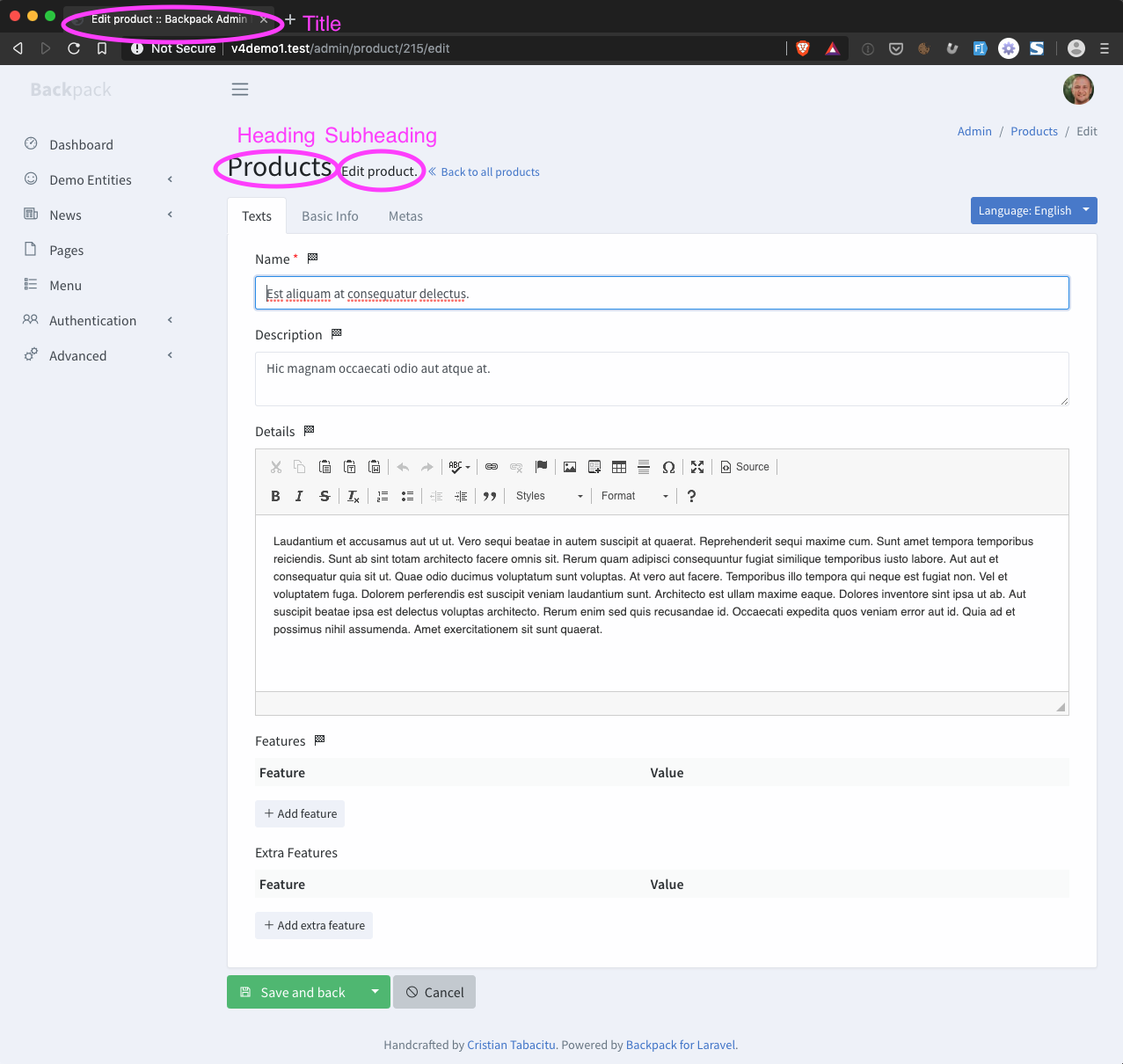
+
+You can get and set the above using:
+```php
+// Getters
+$this->crud->getTitle('create'); // get the Title for the create action
+$this->crud->getHeading('create'); // get the Heading for the create action
+$this->crud->getSubheading('create'); // get the Subheading for the create action
+
+// Setters
+$this->crud->setTitle('some string', 'create'); // set the Title for the create action
+$this->crud->setHeading('some string', 'create'); // set the Heading for the create action
+$this->crud->setSubheading('some string', 'create'); // set the Subheading for the create action
+```
+
+These methods are usually useful inside actions, not in ```setup()```. Since action methods are called _after_ ```setup()```, any call to these getters and setters in ```setup()``` would get overwritten by the call in the action.
+
+
+### Handling Access to Operations
+
+Admins are allowed to do an operation or not using a very simple system: ```$crud->settings['operation_name']['access']``` will either be ```true``` or ```false```. When you enable a stock Backpack operation by doing ```use SomeOperation;``` on your controller, all operations will run ```$this->crud->allowAccess('operation_name');```, which will toggle that variable to ```true```.
+
+You can easily add or remove elements to this access array in your ```setup()``` method, or your custom methods, using:
+```php
+$this->crud->allowAccess('operation_name');
+$this->crud->allowAccess(['list', 'update', 'delete']);
+$this->crud->denyAccess('operation');
+$this->crud->denyAccess(['update', 'create', 'delete']);
+
+// allow or deny access depending on the entry in the table
+$this->crud->operation('list', function() {
+ $this->crud->setAccessCondition(['update', 'delete'], function ($entry) {
+ return $entry->id===1 ? true : false;
+ });
+});
+
+$this->crud->hasAccess('operation_name'); // returns true/false
+$this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('create'); // throws 403 error
+$this->crud->hasAccessToAll(['create', 'update']); // returns true/false
+$this->crud->hasAccessToAny(['create', 'update']); // returns true/false
+```
+
+
+### Operation Routes
+
+Starting with Backpack 4.0, routes can be defined in the CrudController. Your ```routes/backpack/custom.php``` file will have calls like ```Route::crud('product', 'ProductCrudController');```. This ```Route::crud()``` is a macro that will go to that controller and run all the methods that look like ```setupXxxRoutes()```. That means each operation can have its own method to define the routes it needs. And they do - if you check out the code of any operation, you'll see every one of them has a ```setupOperationNameRoutes()``` method.
+
+If you want to add a new route to your controller, there are two ways to do it:
+1. Add a route in your ```routes/backpack/custom.php```;
+2. Add a method following the ```setupXxxRoutes()``` convention to your controller;
+
+Inside a ```setupOperationNameRoutes()```, you'll notice that's also where we define the operation name:
+
+```php
+ protected function setupShowRoutes($segment, $routeName, $controller)
+ {
+ Route::get($segment.'/{id}/show', [
+ 'as' => $routeName.'.show',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@show',
+ 'operation' => 'show',
+ ]);
+ }
+```
+
+
+### Getting an Operation Name
+
+Once an operation name has been set using that route, you can do ```$crud->getOperation()``` inside your views and do things according to this.
+
+
+
+## Creating a Custom Operation
+
+
+### Command-line Tool
+
+If you've installed ```backpack/generators```, you can do ```php artisan backpack:crud-operation {OperationName}``` to generate an empty operation trait, that you can edit and use on your CrudControllers. For example:
+
+```bash
+php artisan backpack:crud-operation Comment
+```
+
+Will generate ```app/Http/Controllers/Admin/Operations/CommentOperation``` with the following contents:
+
+```php
+ $routeName.'.comment',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@comment',
+ 'operation' => 'comment',
+ ]);
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Add the default settings, buttons, etc that this operation needs.
+ */
+ protected function setupCommentDefaults()
+ {
+ $this->crud->allowAccess('comment');
+
+ $this->crud->operation('comment', function () {
+ $this->crud->loadDefaultOperationSettingsFromConfig();
+ });
+
+ $this->crud->operation('list', function () {
+ // $this->crud->addButton('top', 'comment', 'view', 'crud::buttons.comment');
+ // $this->crud->addButton('line', 'comment', 'view', 'crud::buttons.comment');
+ });
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Show the view for performing the operation.
+ *
+ * @return Response
+ */
+ public function comment()
+ {
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('comment');
+
+ // prepare the fields you need to show
+ $this->data['crud'] = $this->crud;
+ $this->data['title'] = $this->crud->getTitle() ?? 'comment '.$this->crud->entity_name;
+
+ // load the view
+ return view("crud::operations.comment", $this->data);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+You'll notice the generated operation has:
+- a GET route (inside ```setupCommentRoutes()```);
+- a method that sets the defaults for this operation (```setupCommentDefaults()```);
+- a method to perform the operation, or show an interface (```comment()```);
+
+You can customize these to fit the operation you have in mind, then ```use \App\Http\Controllers\Admin\Operations\CommentOperation;``` inside the CrudControllers where you want the operation.
+
+
+### Contents of a Custom Operation
+
+Thanks to [Backpack's simple architecture](/docs/{{version}}/crud-basics#architecture), each CRUD panel uses a controller and a route, that are placed inside your project. That means you hold the keys to how this controller works.
+
+To add an operation to an ```EntityCrudController```, you can:
+- decide on your operation name; for example... "publish";
+- create a method that loads the routes inside your controller:
+```php
+ protected function setupPublishRoutes($segment, $routeName, $controller)
+ {
+ Route::get($segment.'/{id}/publish', [
+ 'as' => $routeName.'.publish',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@publish',
+ 'operation' => 'publish',
+ ]);
+ }
+```
+- create a method that performs the operation you want:
+```php
+ public function publish()
+ {
+ // do something
+ // return something
+ }
+```
+- [add a new button for this operation to the List view](/docs/{{version}}/crud-buttons#creating-a-custom-button), or enable access to it, inside a ```setupPublishDefaults()``` method:
+```php
+ protected function setupPublishDefaults()
+ {
+ $this->crud->allowAccess('publish');
+
+ $this->crud->operation('list', function () {
+ $this->crud->addButton('line', 'publish', 'view', 'buttons.publish', 'beginning');
+ });
+ }
+```
+
+Take a look at the examples below for a better picture and code examples.
+
+If you intend to reuse this operation across multiple controllers, you can group all the methods above in a trait, say ```PublishOperation.php``` and then just use that trait on the controllers where you need the operation:
+
+```php
+ $routeName.'.publish',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@publish',
+ 'operation' => 'publish',
+ ]);
+ }
+
+ protected function setupPublishDefaults()
+ {
+ $this->crud->allowAccess('publish');
+
+ $this->crud->operation('list', function () {
+ $this->crud->addButton('line', 'publish', 'view', 'buttons.publish', 'beginning');
+ });
+ }
+
+ public function publish()
+ {
+ // do something
+ // return something
+ }
+}
+```
+
+In the example above, you could just do ```use \App\Http\Controllers\Admin\Operations\PublishOperation;``` on any EntityCrudController, and your operation will be added - complete with routes, buttons, access, actions, everything.
+
+
+### Access to Custom Operations
+
+Since you're creating a new operation, in terms of restricting access you can:
+1. allow access to this new operation depending on access to a default operation (usually if the admin can ```update```, he's OK to perform custom operations);
+2. customize access to this particular operation, by just using a different key than the default ones; for example, you can allow access by using ```$this->crud->allowAccess('publish')``` in your ```setup()``` method, then check for access to that operation using ```$this->crud->hasAccess('publish')```;
+
+
+### Adding Settings to the CrudPanel object
+
+#### Using the Settings API
+
+Anything an operation does to configure itself, or process information, should be stored inside ```$this->crud->settings``` . It's an associative array, and you can add/change things using the Settings API:
+
+```php
+// for the operation that is currently being performed
+$this->crud->setOperationSetting('show_title', true);
+$this->crud->getOperationSetting('show_title');
+$this->crud->hasOperationSetting('show_title');
+
+// for a particular operation, pass the operation name as a last parameter
+$this->crud->setOperationSetting('show_title', true, 'create');
+$this->crud->getOperationSetting('show_title', 'create');
+$this->crud->hasOperationSetting('show_title', 'create');
+
+// alternatively, you could use the direct methods with no fallback to the current operation
+$this->crud->set('create.show_title', false);
+$this->crud->get('create.show_title');
+$this->crud->has('create.show_title');
+```
+
+#### Using the crud config file
+
+Additionally, operations can load default settings from the config file. You'll notice the ```config/backpack/crud.php``` file contains an array of operations, each with various settings. Those settings there are loaded by the operation as defaults, to allow users to change one setting in the config, and have that default changed across ALL of their CRUDs. If you take a look at the List operation you'll notice this:
+
+```php
+ /**
+ * Add the default settings, buttons, etc that this operation needs.
+ */
+ protected function setupListDefaults()
+ {
+ $this->crud->allowAccess('list');
+
+ $this->crud->operation('list', function () {
+ $this->crud->loadDefaultOperationSettingsFromConfig();
+ });
+ }
+```
+
+You can do the same in custom operations. Because this call happens in setupListDefaults(), inside an operation closure, the settings will only be added when that operation is being performed.
+
+
+
+### Adding Methods to the CrudPanel Object
+
+You can add static methods to this ```$this->crud``` (which is a CrudPanel object) object with ```$this->crud->macro()```, because the object is [macroable](https://unnikked.ga/understanding-the-laravel-macroable-trait-dab051f09172). So you can do:
+
+```php
+class MonsterCrudController extends CrudController
+{
+ public function setup()
+ {
+ $this->crud->macro('doStuff', function($something) {
+ echo '
'; var_dump($something); echo '
';
+ dd($this);
+ });
+ $this->crud->macro('getColumnsInTheFormatIWant', function() {
+ $columns = $this->columns();
+ // ... do something to $columns;
+ return $columns;
+ });
+
+ // bla-bla-bla the actual setup code
+ }
+ public function sendEmail()
+ {
+ // ...
+ $this->crud->doStuff();
+ dd($this->crud->getColumnsInTheFormatIWant());
+ // ...
+ }
+ public function markPending()
+ {
+ // ...
+ $this->crud->doStuff();
+ dd($this->crud->getColumnsInTheFormatIWant());
+ // ...
+ }
+}
+```
+
+So if you define a custom operation that needs some static methods added to the ```CrudPanel``` object, you can add them. The best place to register your macros in a custom operation would probably be inside your ```setupXxxDefaults()``` method, inside an operation closure. That way, the static methods you add are only added when that operation is being performed. For example:
+
+```php
+protected function setupPrintDefaults()
+{
+ $this->crud->allowAccess('print');
+
+ $this->crud->operation('print', function() {
+ $this->crud->macro('getColumnsInTheFormatIWant', function() {
+ $columns = $this->columns();
+ // ... do something to $columns;
+ return $columns;
+ });
+ });
+}
+```
+
+With the example above, you'll be able to use ```$this->crud->getColumnsInTheFormatIWant()``` inside your operation actions.
+
+
+### Using a feature from another operation
+
+Anything an operation does to configure itself, or process information, is stored on the ```$this->crud->settings``` property. Operation features (ex: fields, columns, buttons, filters, etc) are created in such a way that all they do is add an entry in settings, for an operation, and manipulate it. That means there is nothing stopping you from using a feature from one operation in a different operation.
+
+If you create a Print operation, and want to use the ```columns``` feature that List and Show use, you can just go ahead and do ```$this->crud->addColumn()``` calls inside your operation. You'll notice the columns are stored inside ```$this->crud->settings['print.columns']```, so they're completely different from the ones in the List or Show operation. You'll need to actually do something with the columns you added, inside your operation methods or views - of course.
+
+
+
+### Examples
+
+
+#### Creating a New Operation With No Interface
+
+Let's say we have a ```UserCrudController``` and we want to create a simple ```Clone``` operation, which would create another entry with the same info. So very similar to ```Delete```. What we need to do is:
+
+1. Create a route for this operation - as we've learned above we can do that in a ```setupXxxRoutes()``` method:
+
+```php
+ protected function setupCloneRoutes($segment, $routeName, $controller)
+ {
+ Route::post($segment.'/{id}/clone', [
+ 'as' => $routeName.'.clone',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@clone',
+ 'operation' => 'clone',
+ ]);
+ }
+```
+
+2. Add the method inside ```UserCrudController```:
+
+```php
+public function clone($id)
+{
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('create');
+ $this->crud->setOperation('Clone');
+
+ $clonedEntry = $this->crud->model->findOrFail($id)->replicate();
+
+ return (string) $clonedEntry->push();
+}
+```
+
+3. Create a button for this method. Since our operation is similar to "Delete", lets start from that one and customize what we need. The button should clone the entry using an AJAX call. No need to load another page for an operation this simple. We'll create a ```resources\views\vendor\backpack\crud\buttons\clone.blade.php``` file:
+
+```php
+@if ($crud->hasAccess('create'))
+
Clone
+@endif
+
+{{-- Button Javascript --}}
+{{-- - used right away in AJAX operations (ex: List) --}}
+{{-- - pushed to the end of the page, after jQuery is loaded, for non-AJAX operations (ex: Show) --}}
+@push('after_scripts') @if (request()->ajax()) @endpush @endif
+
+@if (!request()->ajax()) @endpush @endif
+```
+
+4. We can now actually add this button to our ```UserCrudController::setupCloneOperation()``` method, or our ```setupCloneDefaults()``` method:
+
+```php
+protected function setupCloneDefaults() {
+ $this->crud->allowAccess('clone');
+
+ $this->crud->operation(['list', 'show'], function () {
+ $this->crud->addButtonFromView('line', 'clone', 'clone', 'beginning');
+ });
+}
+```
+
+>Of course, **if you plan to re-use this operation on another EntityCrudController**, it's a good idea to isolate the method inside a trait, then use that trait on each EntityCrudController where you want the operation to work.
+
+
+#### Creating a New Operation With An Interface
+
+Let's say we have a ```UserCrudController``` and we want to create a simple ```Moderate``` operation, where we show a form where the admin can add his observations and what not. In this respect, it should be similar to ```Update``` - the button should lead to a separate form, then that form will probably have a Save button. So when creating the methods, we should look at ```CrudController::edit()``` and ```CrudController::updateCrud()``` for working examples.
+
+What we need to do is:
+
+1. Create routes for this operation - we can do that using the ```setupOperationNameRoutes()``` convention inside a ```UserCrudController```:
+
+```php
+ protected function setupModerateRoutes($segment, $routeName, $controller)
+ {
+ Route::get($segment.'/{id}/moderate', [
+ 'as' => $routeName.'.getModerate',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@getModerateForm',
+ 'operation' => 'moderate',
+ ]);
+ Route::post($segment.'/{id}/moderate', [
+ 'as' => $routeName.'.postModerate',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@postModerateForm',
+ 'operation' => 'moderate',
+ ]);
+ }
+```
+
+2. Add the methods inside ```UserCrudController```:
+
+```php
+public function getModerateForm($id)
+{
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('update');
+ $this->crud->setOperation('Moderate');
+
+ // get the info for that entry
+ $this->data['entry'] = $this->crud->getEntry($id);
+ $this->data['crud'] = $this->crud;
+ $this->data['title'] = 'Moderate '.$this->crud->entity_name;
+
+ return view('vendor.backpack.crud.moderate', $this->data);
+}
+
+public function postModerateForm(Request $request = null)
+{
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('update');
+
+ // TODO: do whatever logic you need here
+ // ...
+ // You can use
+ // - $this->crud
+ // - $this->crud->getEntry($id)
+ // - $request
+ // ...
+
+ // show a success message
+ \Alert::success('Moderation saved for this entry.')->flash();
+
+ return \Redirect::to($this->crud->route);
+}
+```
+
+3. Create the ```/resources/views/vendor/backpack/crud/moderate.php``` blade file, which shows the moderate form and what not. Best to start from the ```edit.blade.php``` file and customize:
+
+```html
+@extends(backpack_view('layouts.top_left'))
+
+@php
+ $defaultBreadcrumbs = [
+ trans('backpack::crud.admin') => backpack_url('dashboard'),
+ $crud->entity_name_plural => url($crud->route),
+ 'Moderate' => false,
+ ];
+
+ // if breadcrumbs aren't defined in the CrudController, use the default breadcrumbs
+ $breadcrumbs = $breadcrumbs ?? $defaultBreadcrumbs;
+@endphp
+
+@section('header')
+
+@endsection
+
+@section('content')
+
+
+
+
+
+ Something in the card body
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+@endsection
+
+```
+
+4. Create a button for this operation. Since our operation is similar to "Update", lets start from that one and customize what we need. The button should just take the admin to the route that shows the Moderate form. Nothing fancy. We'll create a ```resources\views\vendor\backpack\crud\buttons\moderate.blade.php``` file:
+
+```php
+@if ($crud->hasAccess('moderate'))
+
Moderate
+@endif
+```
+
+4. We can now actually add this button to our ```UserCrudController::setup()```, to register that button inside the List operation:
+
+```php
+$this->crud->operation('list', function() {
+ $this->crud->addButtonFromView('line', 'moderate', 'moderate', 'beginning');
+});
+```
+
+Or better yet, we can do this inside a ```setupModerateDefaults()``` method, which gets called automatically by CrudController when the ```moderate``` operation is being performed (thanks to the operation name set on the routes):
+
+```php
+protected function setupModerateDefaults()
+{
+ $this->crud->allowAccess('moderate');
+
+ $this->crud->operation('list', function() {
+ $this->crud->addButtonFromView('line', 'moderate', 'moderate', 'beginning');
+ });
+}
+```
+
+>Of course, **if you plan to re-use this operation on another EntityCrudController**, it's a good idea to isolate the method inside a trait, then use that trait on each EntityCrudController where you want the operation to be enabled.
+
+```php
+ $routeName.'.getModerate',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@getModerateForm',
+ 'operation' => 'moderate',
+ ]);
+ Route::post($segment.'/{id}/moderate', [
+ 'as' => $routeName.'.postModerate',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@postModerateForm',
+ 'operation' => 'moderate',
+ ]);
+ }
+
+ protected function setupmoderateDefaults()
+ {
+ $this->crud->allowAccess('moderate');
+
+ $this->crud->operation('list', function() {
+ $this->crud->addButtonFromView('line', 'moderate', 'moderate', 'beginning');
+ });
+ }
+
+ public function getModerateForm($id)
+ {
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('update');
+ $this->crud->setOperation('Moderate');
+
+ // get the info for that entry
+ $this->data['entry'] = $this->crud->getEntry($id);
+ $this->data['crud'] = $this->crud;
+ $this->data['title'] = 'Moderate '.$this->crud->entity_name;
+
+ return view('vendor.backpack.crud.moderate', $this->data);
+ }
+
+ public function postModerateForm(Request $request = null)
+ {
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('update');
+
+ // TODO: do whatever logic you need here
+ // ...
+ // You can use
+ // - $this->crud
+ // - $this->crud->getEntry($id)
+ // - $request
+ // ...
+
+ // show a success message
+ \Alert::success('Moderation saved for this entry.')->flash();
+
+ return \Redirect::to($this->crud->route);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+#### Creating a New Operation With a Bulk Action (No Interface)
+
+Say we want to create a ```BulkClone``` operation, with a button which clones multiple entries at the same time. So very similar to our ```BulkDelete```. What we need to do is:
+
+1. Create a new button:
+
+```html
+@if ($crud->hasAccess('bulkClone') && $crud->get('list.bulkActions'))
+
Clone
+@endif
+
+@push('after_scripts')
+
+@endpush
+```
+
+2. Create a method in your EntityCrudController (or in a trait, if you want to re-use it for multiple CRUDs):
+
+```php
+ public function bulkClone()
+ {
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('create');
+
+ $entries = $this->crud->getRequest()->input('entries');
+ $clonedEntries = [];
+
+ foreach ($entries as $key => $id) {
+ if ($entry = $this->crud->model->find($id)) {
+ $clonedEntries[] = $entry->replicate()->push();
+ }
+ }
+
+ return $clonedEntries;
+ }
+```
+
+3. Add a route to point to this new method:
+
+```php
+protected function setupBulkCloneRoutes($segment, $routeName, $controller)
+{
+ Route::post($segment.'/bulk-clone', [
+ 'as' => $routeName.'.bulkClone',
+ 'uses' => $controller.'@bulkClone',
+ 'operation' => 'bulkClone',
+ ]);
+}
+```
+
+4. Setup the default features we need for the operation to work:
+
+```php
+protected function setupBulkCloneDefaults()
+{
+ $this->crud->allowAccess('bulkClone');
+
+ $this->crud->operation('list', function () {
+ $this->crud->enableBulkActions();
+ $this->crud->addButton('bottom', 'bulk_clone', 'view', 'bulk_clone', 'beginning');
+ });
+}
+```
+
+
+Now there's a Clone button on our List bottom stack, that works as expected for multiple entries.
+
+The button makes one call for all entries, and only triggers one notification. If you would rather make a call for each entry, you can use something like below:
+
+```html
+@if ($crud->hasAccess('create') && $crud->bulk_actions)
+
Clone
+@endif
+
+@push('after_scripts')
+
+@endpush
+```
+
+
+
+#### Creating a New Operation With a Form
+
+Say we want to create a ```Comment``` operation. Click the Comment button on an entry, and it brings up a form with a textarea. Submit the form and you're back to the list view. Let's get started. What we need to do is:
+
+**Step 0.** Install ```backpack/generators``` if you haven't yet. [https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/Generators](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/Generators). We have built a set of commands to help you create a new form operation easy peasy. You can use it like this:
+
+```bash
+php artisan backpack:crud-operation Comment # will create a form for the entries in your list view, with the id in the URL
+
+php artisan backpack:crud-operation Comment --no-id # will create a form, without the id in the URL (generators v4.0.4+)
+```
+
+
+**Step 1.** Back to our goal, lets generate the operation trait, by running `php artisan backpack:crud-form-operation Comment`. This will create a new trait, `CommentOperation` that should look very similar to this:
+
+```php
+formRoutes(
+ operationName: 'comment',
+ routesHaveIdSegment: true,
+ segment: $segment,
+ routeName: $routeName,
+ controller: $controller
+ );
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Add the default settings, buttons, etc that this operation needs.
+ */
+ protected function setupCommentDefaults(): void
+ {
+ $this->formDefaults(
+ operationName: 'comment',
+ buttonStack: 'line', // alternatives: top, bottom
+ // buttonMeta: [
+ // 'icon' => 'la la-home',
+ // 'label' => 'Comment',
+ // 'wrapper' => [
+ // 'target' => '_blank',
+ // ],
+ // ],
+ );
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Method to handle the GET request and display the View with a Backpack form
+ *
+ * @param int $id
+ * @return \Illuminate\Contracts\View\View
+ */
+ public function getCommentForm(int $id)
+ {
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('comment');
+
+ return $this->formView($id);
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Method to handle the POST request and perform the operation
+ *
+ * @param int $id
+ * @return array|\Illuminate\Http\RedirectResponse
+ */
+ public function postCommentForm(int $id)
+ {
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('comment');
+
+ return $this->formAction(id: $id, formLogic: function ($inputs, $entry) {
+ // You logic goes here...
+ // dd('got to ' . __METHOD__, $inputs, $entry);
+
+ // show a success message
+ \Alert::success('Something was done!')->flash();
+ });
+ }
+}
+
+```
+> Notes : Please Keep in mind, when you set the **buttonStack** to *top* or *bottom*, don't forget to set the **routesHaveIdSegment** to *false*, otherwise it won't show your form.
+
+**Step 2.** Now let's use this operation trait on our CrudController. For example in our UserCrudController we'd have to do this next to all other operations:
+```php
+ use \App\Http\Controllers\Admin\Operations\CommentOperation;
+```
+
+**Step 3.** Now let's add the fields. We have a decision to make... who adds the fields? Does it make more sense for:
+- **(a)** the developer to add the fields, because they vary from CrudController to CrudController;
+- **(b)** the operation itself to add the fields, because the fields never change when you add the operation to multiple CrudControllers;
+
+If **(a)** made more sense, we'd just create a new function in our CrudController, called `setupCommentOperation()`, and define the fields there.
+
+In case **(b)** makes more sense, we will define the fields at the operation itself in `setupCommentDefaults()`.
+
+```php
+// a) whenever we use this operation, we want to always setup the same fields
+
+// inside `ComentOperation.php`
+public function setupCommentDefaults(): void
+{
+ // ...
+
+ $this->crud->operation('comment', function () {
+ $this->crud->field('message')->type('textarea');
+ });
+}
+
+// b) when the operation can accept different fields for each crud controller, eg: UserCrudController may have some fields, while in PostCrudController we may have others
+
+// inside `UserCrudController.php`
+public function setupCommentOperation(): void
+{
+ $this->crud->field('message')->type('textarea');
+}
+
+// inside `PostCrudController.php`
+public function setupCommentOperation(): void
+{
+ $this->crud->field('message')->type('textarea');
+ $this->crud->field('rating')->type('number');
+
+ // if you want to add a FormRequest to validate the fields you do it here.
+ // later when you handle the form submission, the request will be automatically validated
+ $this->crud->setValidation(CommentRequest::class); // this file is not automatically created. You have to create it yourself.
+}
+
+```
+
+**Step 4.** Let's actually add the comment to the database. Inside the `CommentOperation` trait, if we go to `postCommentForm()` well see we have a placeholder for our logic there:
+
+```php
+ public function postCommentForm(int $id)
+ {
+ $this->crud->hasAccessOrFail('comment');
+
+ return $this->formAction(id: $id, formLogic: function ($inputs, $entry) {
+ // You logic goes here...
+
+ // You can validate the inputs using the Laravel Validator, eg:
+ // $valid = Validator::make($inputs, ['message' => 'required'])->validated();
+
+ // alternatively if you set a FormRequest in the setupCommentOperation() method,
+ // the request will be validated here already
+
+ // and then save it to database
+ // $entry->comments()->create($valid);
+
+ // show a success message
+ \Alert::success('Something was done!')->flash();
+ });
+ }
+```
+
+That's it. This all you needed to do to achieve a working operation with a Backpack form, that looks a lot like this:
+
+
+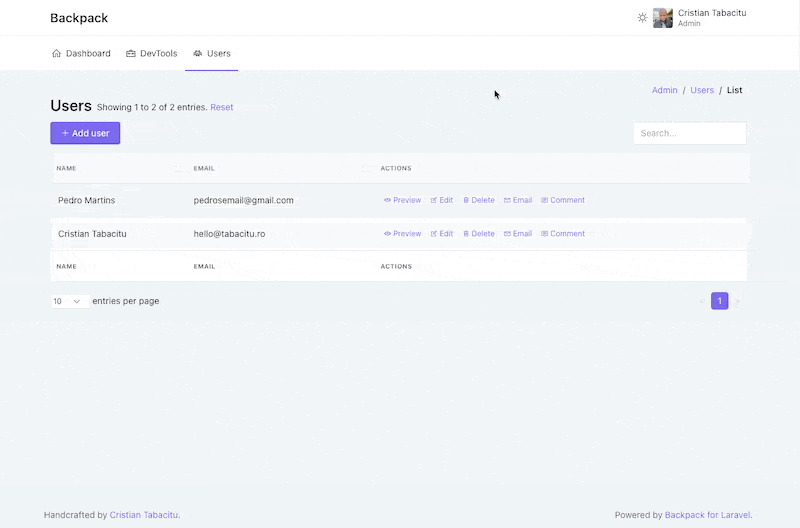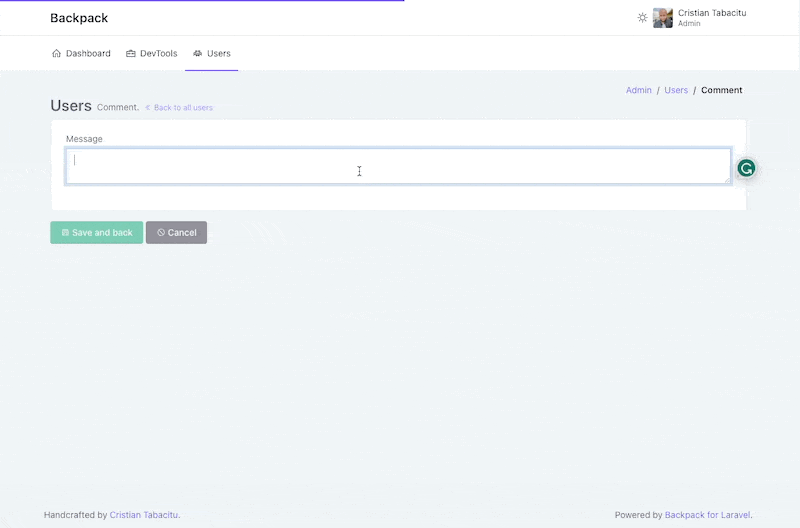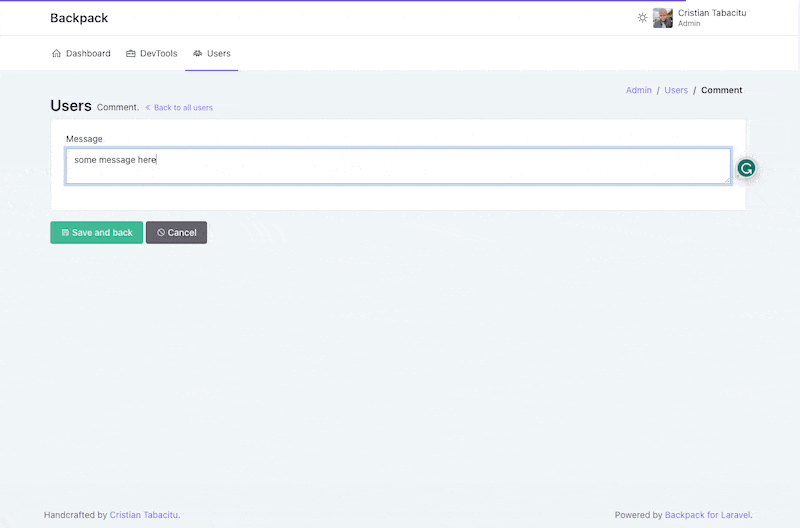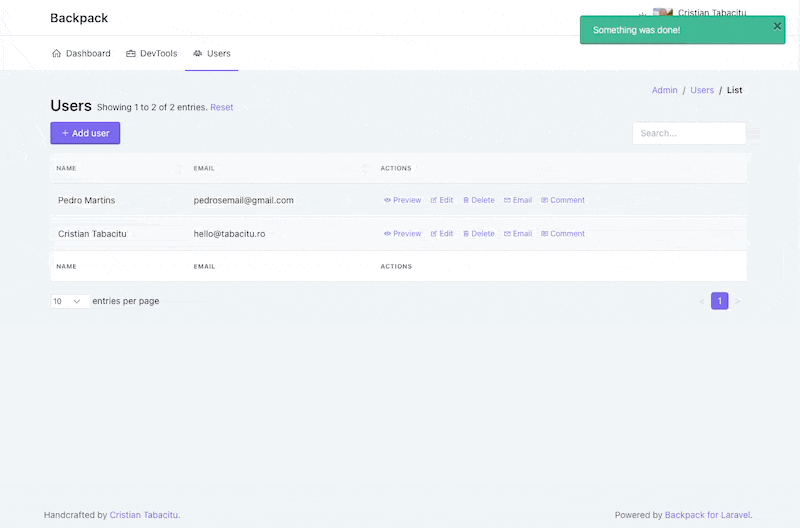
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-save-actions.md b/7.x-dev/crud-save-actions.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4fb61c85
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-save-actions.md
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
+# Save Actions
+
+---
+
+
+## About
+
+`Create` and `Update` forms end in a Save button with a drop menu. Every option in that dropdown is a SaveAction - they determine where the user is redirected after the saving is complete.
+
+
+## Default Save Actions
+
+There are four save actions registered by Backpack by default. They are:
+ - ```save_and_back``` (Save your entity and go back to previous URL)
+ - ```save_and_edit``` (Save and edit the current entry)
+ - ```save_and_new``` (Save and go to create new entity page)
+ - ```save_and_preview``` (Save and go to show the current entity)
+
+
+## Save Actions API
+
+Inside your CrudController, inside your ```setupCreateOperation()``` or ```setupUpdateOperation()``` methods, you can change what save buttons are shown for each operation by using the methods below:
+
+#### addSaveAction(array $saveAction)
+
+Adds a new SaveAction to the "Save" button/dropdown.
+
+```php
+CRUD::addSaveAction([
+ 'name' => 'save_action_one',
+ 'redirect' => function($crud, $request, $itemId) {
+ return $crud->route;
+ }, // what's the redirect URL, where the user will be taken after saving?
+
+ // OPTIONAL:
+ 'button_text' => 'Custom save message', // override text appearing on the button
+ // You can also provide translatable texts, for example:
+ // 'button_text' => trans('backpack::crud.save_action_one'),
+ 'visible' => function($crud) {
+ return true;
+ }, // customize when this save action is visible for the current operation
+ 'referrer_url' => function($crud, $request, $itemId) {
+ return $crud->route;
+ }, // override http_referrer_url
+ 'order' => 1, // change the order save actions are in
+]);
+```
+
+#### addSaveActions(array $saveActions)
+
+The same principle of `addSaveAction([])` but for adding multiple actions with only one crud call.
+
+```php
+CRUD::addSaveActions([
+ [
+ 'name' => 'save_action_one',
+ 'visible' => function($crud) {
+ return true;
+ },
+ 'redirect' => function($crud, $request, $itemId) {
+ return $crud->route;
+ },
+ ],
+ [
+ 'name' => 'save_action_two',
+ 'visible' => function($crud) {
+ return true;
+ },
+ 'redirect' => function($crud, $request, $itemId) {
+ return $crud->route;
+ },
+ ],
+]);
+```
+
+#### replaceSaveActions(array $saveActions)
+
+This allows you to replace the current save actions with the ones provided in an array.
+
+```php
+CRUD::replaceSaveActions(
+ [
+ 'name' => 'save_action_one',
+ 'visible' => function($crud) {
+ return true;
+ },
+ 'redirect' => function($crud, $request, $itemId) {
+ return $crud->route;
+ },
+ ],
+);
+```
+
+
+#### removeSaveAction(string $saveAction)
+
+This allows you to remove a specific save action from the save actions array. Provide the name of the save action that you would like to remove.
+```php
+CRUD::removeSaveAction('save_action_one');
+```
+
+#### removeSaveActions(array $saveActions)
+
+The same principle as `removeSaveAction()` but to remove multiple actions at same time. You should provide an array with save action names.
+```php
+CRUD::removeSaveActions(['save_action_one','save_action_two']);
+```
+
+#### orderSaveAction(string $saveAction, int $wantedOrder)
+
+You can specify a certain order for a certain save action.
+
+```php
+CRUD::orderSaveAction('save_action_one', 1);
+```
+
+We will setup the save action in the desired order and try to re-order the other save actions accordingly. If you want more granular control over all save actions order, you can define ```order``` when creating the save action, or use ```orderSaveActions()```
+
+#### orderSaveActions(array $saveActions)
+
+Allows you to reorder multiple save actions at same time. You can use it by either specifying only the names of the save actions, in the order you want, or by specifying their order number too:
+
+```php
+// make save actions show up in this order
+CRUD::orderSaveActions(['save_action_one','save_action_two']);
+// or
+CRUD::orderSaveActions(['save_action_one' => 3,'save_action_two' => 2]);
+```
+
+#### setSaveActions(array $saveActions)
+
+Alias for ```replaceSaveActions(array $saveActions)```.
+
+## Action change notification
+
+By default, a change of the save action is shown to the user with a notification. If you want to disable the notification
+you can configure this in the setup of you CRUD controller:
+
+```php
+CRUD::setOperationSetting('showSaveActionChange', false);
+```
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-tutorial.md b/7.x-dev/crud-tutorial.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dca4eccd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-tutorial.md
@@ -0,0 +1,356 @@
+# CRUD Crash Course
+
+---
+
+What's the simplest entity you can think of? It will probably be something like ```Tag```, which only holds an ```id``` and a ```name```. Let's create this new entity in the database, the model for it, then create a CRUD Panel to let admins manage entries for this entity.
+
+We assume:
+- you've [installed Backpack](/docs/{{version}}/installation);
+- you don't already have a ```Tag``` model in your project;
+
+
+## Generate Files
+
+In order to build a CRUD, we need an Eloquent model. So let's create a migration and model, using [Jeffrey Way's Generators](https://github.com/laracasts/Laravel-5-Generators-Extended):
+
+```zsh
+# install a 3rd party tool to generate migrations from the command line
+composer require --dev laracasts/generators
+
+# generate a migration and run it
+php artisan make:migration:schema create_tags_table --schema="name:string:unique"
+php artisan migrate
+```
+
+> **Note:** If you have a lot of database tables to generate, we heavily recommend **our paid addon - [Backpack DevTools](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools).** It's a GUI that helps you generate Migrations, Models (complete with relationships) and CRUDs from the browser. It does cost extra, but it's well worth the price if you use Backpack regularly or your models are not dead-simple.
+
+Now that we have the ```tags``` table in the database, let's generate the actual files we'll be using:
+
+```zsh
+php artisan backpack:crud tag #use singular, not plural
+```
+
+The code above will have generated:
+- a migration (```database/migrations/yyyy_mm_dd_xyz_create_tags_table.php```);
+- a database table (```tags``` with just two columns: ```id``` and ```name```);
+- a model (```app/Models/Tag.php```);
+- a controller (```app/Http/Controllers/Admin/TagCrudController.php```);
+- a request (```app/Http/Requests/TagCrudRequest.php```);
+- a resource route, as a line inside ```routes/backpack/custom.php```;
+- a new menu item in ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/ui/inc/menu_items.blade.php```;
+
+**Next up:** we'll need to go through the generated files, and customize for our needs.
+
+
+## Customize Generated Files
+
+We'll skip the migration and database table, since there's nothing there specific to Backpack, nothing to customize, and we've already run the migration.
+
+
+### The Model
+
+Let's take a look at the generated model:
+
+```php
+
+### The Controller
+
+Let's take a look at ```app/Http/Controllers/Admin/TagCrudController.php```. It should look something like this:
+
+```php
+setupCreateOperation();
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+What we should notice inside this TagCrudController is that:
+- ```TagCrudController extends CrudController```;
+- ```TagCrudController``` has a ```setup()``` method, where we must define the basics of our CRUD panel; everything we write here is applied on ALL operations;
+- All operations are enabled by using that operation's trait on the controller;
+- Each operation is set up inside a ```setupXxxOperation()``` method;
+
+#### Operation Setup Methods
+
+The best way to configure operations is to define each operation inside its ```setupXxxOperation()``` method, like the generated file above does. Over there the `setupXxxOperation()` methods:
+- add a simple ```text``` column for our ```name``` attribute for the List operation (the table view);
+- add a simple ```text``` field for our ```name``` attribute to the Create and Update forms;
+
+#### Operation Setup Closures
+
+An alternative to defining operations inside ```setupXxxOperation()``` methods is to do everything inside the ```setup()``` method. However, as we've mentioned before, everything you run in your ```setup()``` method is run for ALL operations. So you can easily end up bloating your operation with unnecessary operations. If you don't like having a method to configure each operation, and want to define everything in ```setup()```, you should do so inside an ```operation()``` closure. Whatever's inside that closure will only be run for that operation. For example, everything we've done above would look like this if done inside operation closures:
+
+```php
+ public function setup()
+ {
+ CRUD::setModel('App\Models\Tag');
+ CRUD::setRoute(config('backpack.base.route_prefix') . '/tag');
+ CRUD::setEntityNameStrings('tag', 'tags');
+
+ CRUD::operation('list', function() {
+ CRUD::column('name');
+ });
+
+ CRUD::operation(['create', 'update'], function() {
+ CRUD::addValidation(TagCrudRequest::class);
+ CRUD::field('name');
+ });
+ }
+
+
+}
+```
+
+#### Other Calls
+
+Here, inside your ```setup()``` or ```setupXxxOperation``` methods, you can also do a lot of other things, like adding buttons, adding filters, customizing your query, etc. For a full list of the things you can do inside ```setup()``` check out our [cheat sheet](/docs/{{version}}/crud-cheat-sheet).
+
+Next, let's continue to another generated file.
+
+
+### The Request
+
+Backpack can also generate a [standard FormRequest file](https://laravel.com/docs/master/validation#form-request-validation), that you can use for validation of the Create and Update forms. There is nothing Backpack-specific in here, but let's take a look at the generated ```app/Http/Requests/TagRequest.php``` file:
+
+```php
+check();
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Get the validation rules that apply to the request.
+ *
+ * @return array
+ */
+ public function rules()
+ {
+ return [
+ // 'name' => 'required|min:5|max:255'
+ ];
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Get the validation attributes that apply to the request.
+ *
+ * @return array
+ */
+ public function attributes()
+ {
+ return [
+ //
+ ];
+ }
+
+ /**
+ * Get the validation messages that apply to the request.
+ *
+ * @return array
+ */
+ public function messages()
+ {
+ return [
+ //
+ ];
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+This file is a 100% pure FormRequest file - all Laravel, nothing particular to Backpack. In generated FormRequest files, no validation rules are imposed by default - unless you've generated requests using [Backpack DevTools](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools), which does its best to populate the validation rules from the database schema - just saying, it will save you time here too 😉. But we do want ```name``` to be ```required``` and ```unique```, so let's do that, using the [standard Laravel validation rules](https://laravel.com/docs/master/validation#available-validation-rules):
+
+```diff
+ /**
+ * Get the validation rules that apply to the request.
+ *
+ * @return array
+ */
+ public function rules()
+ {
+ return [
+- // 'name' => 'required|min:5|max:255'
++ 'name' => 'required|min:5|max:255|unique:tags,name'
+ ];
+ }
+```
+
+> If your validation needs to be different between the Create and Update operations, [you can easily do that too](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-create#separate-requests-for-create-and-update), by specifying different FormRequest files for each operation.
+
+
+### The Route
+
+We have already generated our CRUD route, and we don't need to do anything about it, but let's check our ```routes/backpack/custom.php```. It should look like this:
+
+```php
+ config('backpack.base.route_prefix', 'admin'),
+ 'middleware' => ['web', config('backpack.base.middleware_key', 'admin')],
+ 'namespace' => 'App\Http\Controllers\Admin',
+], function () { // custom admin routes
+ // CRUD resources and other admin routes
+ Route::crud('tag', 'TagCrudController');
+}); // this should be the absolute last line of this file
+```
+
+Here, we can see that our routes have been placed:
+- under a prefix that we can change in ```config/backpack/base.php```;
+- under a middleware we can change in ```config/backpack/base.php```;
+- inside the ```App\Http\Controllers\Admin``` namespace, because that's where our custom CrudControllers will be generated;
+
+**It's generally a good idea to have the all admin routes in this separate file.** If you edit this file in the future, make sure you leave the last line intact, so that other routes can be automatically generated inside this file. And of course, add your routes inside this route group, so that:
+- you have a single prefix for your admin routes (ex: ```admin/tag```, ```admin/product```, ```admin/dashboard```);
+- all your admin panel functionality is protected by the same middleware;
+- all your admin panel controllers live in one place (```App\Http\Controllers\Admin```);
+
+
+### The Menu Item
+
+We've previously generated a menu item in the ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/ui/inc/menu_items.blade.php``` file. That is using our menu item Blade components. The "active" state of the menu is done with JavaScript, based on the ```href``` attribute.
+
+This is the bit that has been generated for you:
+
+```php
+
+```
+
+You can of course change anything here, if you want. For example, change `la la-question` to `la la-tag`.
+
+
+## The result
+
+You are now ready to go to ```your-app-name.domain/admin/tag``` and see your fully functional admin panel for ```Tags```.
+
+**Congratulations, you should now have a good understanding of how Backpack\CRUD works!** This is a very very basic example, but the process will be identical for Models with 50+ attributes, complicated logic, etc.
+
+If you do have complex models, we _heavily_ recommend you go purchase [Backpack DevTools](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools) right now. It's the official paid GUI for generating all of the above. And while you're at it, you can [purchase a Backpack license](https://backpackforlaravel.com/pricing) too 😉
diff --git a/7.x-dev/crud-uploaders.md b/7.x-dev/crud-uploaders.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2b49ef32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/crud-uploaders.md
@@ -0,0 +1,212 @@
+# Uploaders
+
+---
+
+
+## About
+
+Uploading and managing files is a common task in Admin Panels. Starting with Backpack v6, you can fully setup your upload fields in your field definition, using purpose-built classes we call Uploaders. No more need to create mutators, manual validation of input or custom code to handle the files - though you can still do that, if you want.
+
+
+## How it works
+
+When adding an upload field (`upload`, `upload_multiple`, `image` or `dropzone`) to your operation, tell Backpack that you want to use the appropriate Uploader, by using `withFiles()`:
+
+```php
+CRUD::field('avatar')->type('upload')->withFiles();
+```
+
+That's it. Backpack will now handle the upload, storage and deletion of the files for you. By default it will use `public` disk, and will delete the files when the entry is deleted(*).
+
+> **IMPORTANT**:
+> - Make sure you've linked the `storage` folder to your `public` folder. You can do that by running `php artisan storage:link` in your terminal.
+> - (*) If you want your files to be deleted when the entry is deleted, please [Configure File Deletion](#deleting-files-when-entry-is-deleted)
+
+
+
+## Configuring the Uploaders
+
+The `withFiles()` method accepts an array of options that you can use to customize the upload.
+
+```php
+CRUD::field('avatar')
+ ->type('upload')
+ ->withFiles([
+ 'disk' => 'public', // the disk where file will be stored
+ 'path' => 'uploads', // the path inside the disk where file will be stored
+]);
+```
+**Note**: If you've defined `disk` or `prefix` on the field, you no longer need to define `disk` or `path` within `withFiles()` - it will pick those up. Make sure you are not defining both.
+
+
+**Configuration options:**
+
+- **`disk`** - default: **`public`**
+The disk where the file will be stored. You can use any disk defined in your `config/filesystems.php` file.
+- **`path`** - default: **`/`**
+The path inside the disk where the file will be stored. It maps to `prefix` in field definition.
+- **`deleteWhenEntryIsDeleted`** - default: **`true`** (**NEED ADDITIONAL CONFIGURATION**!! See: [Configure File Deletion](#deleting-files-when-entry-is-deleted))
+The files will be deleted when the entry is deleted. Please take into consideration that `soft deleted models` don't delete the files.
+- **`temporaryUrl`** - default: **`false`**
+Some cloud disks like `s3` support the usage of temporary urls for display. Set this option to true if you want to use them.
+- **`temporaryUrlExpirationTime`** - default: **`1`**
+When `temporaryUrl` is set to `true`, this configures the amount of time in minutes the temporary url will be valid for.
+- **`uploader`** - default: **null**
+This allows you to overwrite or set the uploader class for this field. You can use any class that implements `UploaderInterface`.
+- **`fileNamer`** - default: **null**
+It accepts a `FileNameGeneratorInterface` instance or a closure. As the name implies, this will be used to generate the file name. Read more about in the [Naming uploaded files](#upload-name-files) section.
+
+
+### Handling uploads in relationship fields
+
+**IMPORTANT**: Please make sure you are **NOT** casting the uploaders attributes in your model. If you need a casted attribute to work with the values somewhere else, please create a different attribute that copies the uploader attribute value and manually cast it how you need it.
+
+Some relationships require additional configuration to properly work with the Uploaders, here are some examples:
+
+- **`BelongsToMany`**
+
+In this relationships, you should add the upload fields to the `withPivot()` method and create a Pivot model where Uploaders register their events. [Laravel Docs - Pivot Models](https://laravel.com/docs/10.x/eloquent-relationships#defining-custom-intermediate-table-models)
+
+Take for example an `Article` model has a `BelongsToMany` relationship defined with `Categories` model:
+
+```php
+// Article model
+public function categories() {
+ $this->belongsToMany(Category::class);
+}
+```
+
+To use an Uploader in this relation, you should create the `ArticleCategory` pivot model, and tell Laravel to use it.
+
+```php
+use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\Pivot;
+
+class ArticleCategory extends Pivot
+{
+
+}
+
+
+// and in your article/category models, update the relationship to:
+public function categories() {
+ $this->belongsToMany(Category::class)->withPivot('picture')->using(ArticleCategory::class); //assuming picture is the pivot field where you store the uploaded file path.
+}
+```
+
+- **`MorphToMany`**
+
+Everything like the previous `belongsToMany`, but the pivot model needs to extend `MorphPivot`.
+
+```php
+use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\MorphPivot;
+
+class ArticleCategory extends MorphPivot
+{
+
+}
+
+
+//in your model
+public function categories() {
+ $this->morphToMany(Category::class)->withPivot('picture')->using(ArticleCategory::class); //assuming picture is the pivot field where you store the uploaded file path.
+}
+```
+
+
+### Naming files when using Uploaders
+
+Backpack provides a naming strategy for uploaded files that works well for most scenarios:
+- For `upload`, `upload_multiple` and `dropzone` fields, the file name will be the original file name slugged and with a random 4 character string appended to it, to avoid name collisions. Eg: `my file.pdf` becomes `my-file-aY5x.pdf`.
+- For `image` it will generate a unique name for the file, and will keep the original extension. Eg: `my file.jpg` becomes `5f4a5b6c7d8e9f0a1b2c3d4e5f6a7b8c.jpg`.
+
+You can customize the naming strategy by creating a class that implements `FileNameGeneratorInterface` and pass it to the upload configuration (the default used by Backpack).
+
+```php
+CRUD::field('avatar')->type('upload')->withFiles([
+ 'fileNamer' => \Backpack\CRUD\app\Library\Uploaders\Support\FileNameGenerator::class,
+]);
+
+// alternativelly you can pass a closure:
+->withFiles([
+ 'fileNamer' => function($file, $uploader) { return 'the_file_name.png'; },
+])
+```
+
+### Subfields in Uploaders
+
+You can also use uploaders in subfields. The configuration is the same as for regular fields, just use the same `withFiles` key and pass it `true` if no further configuration is required.
+
+```php
+// subfields array
+[
+ [
+ 'name' => 'avatar',
+ 'type' => 'upload',
+ 'withFiles' => true
+ ],
+ [
+ 'name' => 'attachments',
+ 'type' => 'upload_multiple',
+ 'withFiles' => [
+ 'path' => 'attachments',
+ ],
+ ],
+]
+```
+
+
+### Configure uploaded files to be automatically deteled
+
+To automatically delete the uploaded files when the entry is deleted _in the admin panel_, we need to setup the upload fields in the `DeleteOperation` too:
+
+```php
+protected function setupDeleteOperation()
+{
+ CRUD::field('photo')->type('upload')->withFiles();
+
+ // Alternatively, if you are not doing much more than defining fields in your create operation:
+ // $this->setupCreateOperation();
+}
+```
+
+Alternatively, you can manually delete the file in your Model, using the `deleted` Eloquent model event. That would ensure the file gets deleted _even if_ the entry was deleted from outside the admin panel.
+
+```php
+class SomeModel extends Model
+{
+ protected static function booted()
+ {
+ static::deleted(function ($model) {
+ // delete the file
+ Storage::disk('my_disk')->delete($model->photo);
+ });
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+### Configuring uploaders in custom fields
+
+When using uploads in custom fields, you need to tell Backpack what Uploader to use for that custom field type.
+
+Imagine that you created a custom upload field starting from backpack `upload` field type with: `php artisan backpack:field custom_upload --from=upload`.
+
+You can tell Backpack what Uploader to use in 2 ways:
+
+- In the custom field defininiton inside the uploader configuration:
+```php
+CRUD::field('custom_upload')->withFiles([
+ 'uploader' => \Backpack\CRUD\app\Library\Uploaders\SingleFile::class,
+]);
+```
+- Or you can add it globally for that field type by adding in your Service Provider `boot()` method:
+```php
+app('UploadersRepository')->addUploaderClasses(['custom_upload' => \Backpack\CRUD\app\Library\Uploaders\SingleFile::class], 'withFiles');
+```
+
+
+### Uploaders for Spatie MediaLibrary
+
+The 3rd party package [`spatie/laravel-medialibrary`](https://spatie.be/docs/laravel-medialibrary/) gives you the power to easily associate files with Eloquent models. The package is incredibly popular, time-tested and well maintained.
+
+To have Backpack upload and retrieve files using this package, we've created special Uploaders. Then it will be as easy as doing `CRUD::field('avatar')->type('image')->withMedia();`. For more information and installation instructions please see the docs on Github for [`backpack/medialibrary-uploaders`](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/medialibrary-uploaders).
diff --git a/7.x-dev/custom-validation-rules.md b/7.x-dev/custom-validation-rules.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..86cfd6b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/custom-validation-rules.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+# Custom Validation Rules
+
+---
+
+
+## About
+
+Some Backpack fields are more difficult to validate using standard Laravel validation rules. So we've created a few custom validation rules, that will make validation them dead-simple.
+
+
+## `ValidUpload` for `upload` field type
+
+The `ValidUpload` rule is used to validate the `upload` field type. Using the custom rule helps developer avoid to setting different validation rules for different operations, (create/update).
+
+```php
+// for the field
+CRUD::field('avatar')->type('upload');
+
+// you can write the validation rule as
+
+use Backpack\CRUD\app\Library\Validation\Rules\ValidUpload;
+
+'avatar' => ValidUpload::field('required')->file('mimes:jpg,png|max:2048'),
+```
+
+The `::field()` constructor accepts the rules for the field, while `->file()` accepts the specific rules for files sent in field. The validation rule handles the `sometimes` case for you.
+
+
+## `ValidUploadMultiple` for `upload_multiple` field type
+
+You can use this validation rule to handle validation for your `upload_multiple` field - both for the Create and the Update operation in one go:
+- use the `::field()` constructor to define the rules for the field;
+- use the `->file()` method for rules specific to the files sent in field;
+
+```php
+// for the field
+CRUD::field('attachments')->type('upload_multiple');
+
+// you can write the validation rule as
+
+use Backpack\CRUD\app\Library\Validation\Rules\ValidUploadMultiple;
+
+'attachments' => ValidUploadMultiple::field(['min:2', 'max:5'])->file('mimes:pdf|max:10000'),
+
+```
+
+
+## `ValidDropzone` for `dropzone` field type
+
+You can use this validation rule to handle validation for your `dropzone` field - both for the Create and the Update operation in one go:
+- use the `::field()` constructor to define the rules for the field;
+- use the `->file()` method for rules specific to the files sent in field;
+
+```php
+// for the field
+CRUD::field('photos')->type('dropzone');
+
+// you can write the validation rule as
+
+use Backpack\Pro\Uploads\Validation\ValidDropzone;
+
+'attachments' => ValidDropzone::field('min:2|max:5')->file('file|mimes:jpg,png,gif|max:10000'),
+
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/7.x-dev/demo.md b/7.x-dev/demo.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..72394941
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/demo.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+# Demo
+
+---
+
+We've put together a working Laravel app (backend-only). This should make it easier to:
+- see how it looks & feels;
+- see how it works;
+- change stuff in code, to see how easy it is to customize Backpack;
+
+In this [Demo repository](https://github.com/laravel-backpack/demo), we've:
+- installed Laravel 11;
+- installed Backpack\CRUD;
FREE
+- installed Backpack\PRO;
PRO
+- installed Backpack\Editable-Columns;
PREMIUM
+- created a few demo models and admin panels for them, using dozens of field types, column types, filters, etc - to show off most of Backpack CRUD + PRO features;
+- installed a few Backpack extensions: PermissionManager, PageManager, LogManager, BackupManager, Settings, MenuCRUD, NewsCRUD;
+
+
+>**Don't use this demo to start your real projects.** Please use [the recommended installation procedure](/docs/{{version}}/installation). You don't want all the bogus entities we've created. You don't want all the packages we've used. And you _definitely_ don't want the default admin user. Start from scratch!
+
+
+## Demo Preview
+
+
+
+If you just want to take a look at the Backpack interface and click around, you don't have to install anything. **Take a look at [demo.backpackforlaravel.com](https://demo.backpackforlaravel.com/admin) - we've installed for you.** The online demo is wiped and reinstalled every hour, on the hour.
+
+
+## Demo Installation
+
+If you _do_ want to install the Demo and play around, it's easy to do so. But because the demo uses [Backpack/PRO](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects) and [Backpack/Editable-Columns](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/editable-columns), you need to [purchase "Everything" first](https://backpackforlaravel.com/pricing), or those addons individually. If you don't like it, we'll happily give you a refund.
+
+1) In your ```Projects``` or ```www``` directory, wherever you host your apps:
+
+```zsh
+git clone https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/demo.git backpack-demo
+```
+
+2) Set your database information in your ```.env``` file (use ```.env.example``` as an example);
+
+3) Authenticate and install the requirements:
+``` zsh
+cd backpack-demo
+
+# Tell Composer how to connet to the private Backpack repo.
+# You'll need to replace these with your real token and password:
+composer config http-basic.backpackforlaravel.com [your-token-username] [your-token-password]
+
+# Install all dependencies
+composer install
+```
+
+4) Populate the database:
+```zsh
+php artisan key:generate
+php artisan migrate
+php artisan db:seed --class="Backpack\Settings\database\seeds\SettingsTableSeeder"
+php artisan db:seed
+```
+
+5) Cache the CSS and JS assets using Basset:
+```zsh
+php artisan storage:link
+php artisan basset:cache
+```
+
+
+## Demo Usage
+
+Once everything's installed, and your database has been set up:
+
+- Your admin panel is available at `{APP_URL}`/admin
+- Login with email ```admin@example.com```, password ```admin```
+- You can register a different account, to check out the process and see your Gravatar inside the admin panel.
+- By default, registration is open only in your local environment. Check out ```config/backpack/base.php``` to change this and other preferences.
+- Check out the Monsters admin panel - it features over 50 field types.
+- Devs love Backpack not just for its standard functionality, but also for how easy it is to code your own, or customize every little bit of it. Our recommendation:
+ - Go through the [CRUD Tutorial](/docs/{{version}}/crud-tutorial) to understand it;
+ - Create a new CRUD panel for an entity, using the faster procedure outlined at the end of that page; say... ```car```;
+
+
+>**vhost configurations**
+>
+>Depending on your vhost configuration you might need to access the application via a different url, for example if you're using ```artisan serve``` you can access it on http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin - if you're using Laravel Valet, then it may look like http://backpack-demo.test/admin - you will need to access the url which matches your systems configuration. If you do not understand how to configure your virtual hosts, we suggest [watching Laracasts Episode #1](https://laracasts.com/series/laravel-from-scratch/episodes/1) to quickly get started.
diff --git a/7.x-dev/faq.md b/7.x-dev/faq.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2ae09bd4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/faq.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+# Frequently Asked Questions
+
+---
+
+
+
+## Licensing
+
+
+### Do I need a license to test Backpack?
+
+You don't need a license code AT ALL. Go ahead and install Backpack CRUD on your machine - it's free and open-source, released under the MIT License.
+
+You only need to pay if you want the extra features provided by our premium add-ons (e.g. [Backpack PRO](https://backpackforlaravel.com/pricing) and [Backpack DevTools](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools)). That's it.
+
+
+
+### Do I need a license to put a PRO project on a testing domain?
+
+No:
+- when you purchase [Backpack PRO for Unlimited Projects](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects), you can use it on any number of domains, subdomains and IPs (that's why it's called unlimited);
+- when you purchase [Backpack PRO for One Project](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-one-project), you get the right to use it on one MAIN domain, but also on as many staging/test/beta domains or subdomains as you need; if someone from our team contacts you, then you can explain, it's perfectly reasonable to have test instances - we know how it goes;
+
+
+
+### Can I use Backpack to create an open-source project?
+
+Yes you can! Use [Backpack CRUD v6](https://github.com/laravel-backpack/crud), which is free and open-source, released under the MIT License.
+
+
+
+### Can I use Backpack PRO in an open-source project?
+
+In short - no, you cannot. Please use [Backpack CRUD v6](https://github.com/laravel-backpack/crud) instead, which is free and open-source, released under the MIT License.
+
+Backpack PRO is a closed-source add-on, which requires payment in order to receive an access token. If you did include `backpack/pro` as a dependency in your open-source software, then your software would no longer be open-source. Everybody who installed your project/package would need to pay for Backpack PRO to get access to it.
+
+
+
+### Can I get Backpack PRO for free to use in a non-commercial project?
+
+No - we're no longer giving away free licenses. But we _have_ released Backpack CRUD v5 and v6 under the MIT License, which means it's free and open-source. It has fewer features, but you can do absolutely do anything you want with it.
+
+
+## Installation
+
+
+
+### How do I update Backpack to the latest non-breaking version?
+
+Run **`composer update`** on your project to update the dependencies given your version constrains in `composer.json`. If you want to update a specific package, you can run **`composer update backpack/crud`** for example to only update `backpack/crud` and it's dependencies.
+
+If you have your assets cached you can run `php artisan basset:clear` to clear the cache too. You can manually rebuild the asset cache if necessary with `php artisan basset:cache`. We do recommend you keep basset disabled on localhost while developing.
+
+Some packages may require you to run additional commands to update the database schema or publish new assets. Please refer to the package documentation or upgrade guide for more information.
+
+
+### How do I uninstall Backpack from my project?
+
+You can remove Backpack from your project pretty easily, if you decide to stop using it. You just have to do the opposite of the installation process:
+
+```bash
+# delete the files Backpack has placed inside your application
+rm -rf app/Http/Middleware/CheckIfAdmin.php
+rm -rf config/backpack
+rm -rf config/gravatar.php
+rm -rf resources/views/vendor/backpack
+rm -rf routes/backpack
+
+# delete any CrudControllers you've created, so MAYBE:
+rm -rf app/Http/Controllers/Admin
+
+# delete any Requests you've created for your CrudControllers.
+# MAKE SURE YOU DON'T NEED ANYTHING IN THIS DIRECTORY ANYMORE.
+# You might have OTHER requests that are not Backpack-related.
+rm -rf app/Http/Requests
+
+# (MUST) remove other Backpack packages that you are using, like PRO, Editable Columns, DevTools etc:
+composer remove --dev backpack/devtools
+composer remove backpack/pro
+composer remove backpack/editable-columns
+
+etc...
+
+# After everything related to Backpack is deleted, just need to delete the crud!
+composer remove backpack/crud
+
+```
+
+That's it! If you've decided NOT to use Backpack, we'd be super grateful if you could
send us an email telling us WHY you decided not to use Backpack, or why it didn't fit your project. It might help us take Backpack in a different direction, a direction where you might want to use it again. Thank you 🙏
+
+
+
+### Errors when installing paid add-ons
+
+When installing our [paid add-ons](https://backpackforlaravel.com/addons):
+- Composer will add our private repository (`repo.backpackforlaravel.com`) to your `composer.json` file;
+- Composer will try to download the `dist` version of the package from there;
+ - if successful, you're good;
+ - if the `dist` version fails to download, Composer will throw an error (with an HTTP code like 402); then Composer will try to download the `source` version of the package straight from our Github repo; that will 100% fail, because you do NOT have access to our private Github repo; to rephrase, you don't have access to the `source`, only to the `dist` version;
+
+Unfortunately, we cannot customize the errors that Composer throws, so the error text might be confusing. Please take a look at the HTTP error code shown in the error to understand what happened:
+- 400 Error - Bad Request - user and password do not match; please check your auth credentials;
+- 401 Error - Unauthorized - no token username or password; please check your auth credentials;
+- 402 Error - Payment Required - you are trying to download a version newer than you have access to; our system will send you an email with clear instructions on what to do to require the latest version you have access to; you can also check the latest version you have access to in your Backpack account, and require that version specifically; alternatively, please purchase the same product again to gain access to more updates, then it will work again;
+- 404 Error - Not Found - the package that you are trying to download does not exist;
+- 429 Error - Too Many Requests - our server has received too many requests from your IP address; please wait one minute and try again;
+
+If you still can't figure it out, please [open a new discussion in our Community Forum](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/community-forum/discussions/categories/q-a-help). Please make sure to:
+- mention the steps you have followed to get there (e.g. `composer require backpack/pro`, `php artisan backpack:require:pro` etc.);
+- include a screenshot of the console output, so we can understand what happened;
+- cross out any personal data (e.g. token username or password);
diff --git a/7.x-dev/features-free-vs-paid.md b/7.x-dev/features-free-vs-paid.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..997825e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/features-free-vs-paid.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+# Features (Free vs Paid)
+
+---
+
+Our software is open-core. That means there are features that you can use for free, and features you can only access by purchasing. Our goal with this split was to have:
+- a simplified version, that includes what most admin panels absolutely need, in `backpack\crud`;
FREE
+- a plug-and-play add-on, that adds features for more complex use cases, in `backpack\pro`;
PRO
+- add-ons to help in corner cases (both FREE and PAID);
+
+You do not _need to_ purchase anything from us. But we hope that:
+- if you're making money from your project, as soon as you need _one_ paid feature, you can justify its cost, to save the time it takes to build that yourself;
+- if you're _not_ making money from your project yet, as the project grows and starts making a profit, you'll _want to_ purchase, to get access to paid features and support its maintenance;
+
+
+## Features
+
+Everywhere in our docs, you'll see the
PRO label if it needs the `backpack\pro` add-on. Everything else is free, as part of `backpack\crud`. Here's a comparison table of all features, so you can easily understand what will be a good fit for you:
+
+
+
+
+ |
+ Backpack\CRUD |
+ Backpack\CRUD +
Backpack\PRO |
+
+
+
+
+ | Admin UI |
+ |
+ |
+
+
+ | - Alerts |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Authentication |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Custom Pages |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Breadcrumbs |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - HTML Components |
+ 180+ components |
+ 180+ components |
+
+
+ | - Widgets |
+ 9 widgets |
+ 9 widgets + chart |
+
+
+ | CRUD Panels |
+ |
+ |
+
+
+ | - List Operation |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Columns |
+ 28 columns types |
+
+ 28 free +
+ 29 pro columns
+ |
+
+
+ | - Buttons |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Search |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Filters |
+ - |
+ 10+ filter types |
+
+
+ | - Export Buttons |
+ - |
+ PRO |
+
+
+ | - Details Row |
+ - |
+ PRO |
+
+
+ | - Create & Update Operations |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Fields |
+ 28 field types |
+
+ 28 free +
+ 29 pro fields
+ |
+
+
+ | - Validation |
+ 3 ways |
+ 3 ways |
+
+
+ | - Multiple fields per line |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Split fields into tabs |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Translatable Models |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Save Actions |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Show Operation |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Columns |
+ 28 column types |
+
+ 28 free +
+ 29 pro columns
+ |
+
+
+ | - Delete Operation |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Reorder Operation |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - Revise Operation |
+ FREE |
+ FREE |
+
+
+ | - BulkDelete Operation |
+ - |
+ PRO |
+
+
+ | - Clone Operation |
+ - |
+ PRO |
+
+
+ | - BulkClone Operation |
+ - |
+ PRO |
+
+
+ | - Fetch Operation |
+ - |
+ PRO |
+
+
+ | - InlineCreate Operation |
+ - |
+ PRO |
+
+
+
+
+
+Both `backpack/crud` and `backpack/pro` will keep receiving active attention, maintenance and care from us, for many years going forward - this is our job. If you have suggestions, please [tell us](https://github.com/laravel-backpack/ideas).
+
+
+## Add-ons
+
+In addition to our main packages (`backpack\crud` and `backpack\pro`), whose features we've detailed above, we've also developed a series of single-purpose Backpack add-ons. Most developers won't need these, but those who do will be grateful that we took the time:
+ - some free: `backpack\permissionmanager`, `backpack\settings`, `backpack\pagemanager`, `backpack\newscrud`, `backpack\menucrud`, `backpack\filemanager`, `backpack\logmanager`, `backpack\backupmanager`, `backpack\revise-operation` etc.
FREE
+ - some paid: `backpack\devtools`, `backpack\figma-template`
PAID EXTRA
+
+We also encourage our community to build third-party add-ons (we've made it [super easy](/docs/{{version}}/add-ons-tutorial-using-the-addon-skeleton)). Our plan is to create more and more add-ons, as we discover more recurring problems, that we can solve for Laravel freelancers and development teams.
+
+For more information, see:
+- [our add-ons page](https://backpackforlaravel.com/addons) for more add-ons (including third-party add-ons);
+- [our pricing page](https://backpackforlaravel.com/pricing) for the first-party add-ons that we think are _so good_, that they're worth paying for;
diff --git a/7.x-dev/generating-code.md b/7.x-dev/generating-code.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a73cc55c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/generating-code.md
@@ -0,0 +1,222 @@
+# Generating Code
+
+---
+
+Backpack also provides ways to quickly write code inside your admin panels, for you to customize to your needs. There are two officials tools, both will help you publish, override or generate files, that you can customize to your liking:
+- [Backpack Generators](https://github.com/laravel-backpack/generators/) (FREE) - a command-line interface that has already been installed in your project;
+- [Backpack DevTools](/products/devtools) (PAID) - a web interface that helps do all of the above and more, from a browser;
+
+
+## Command-Line Interface (CLI) -
FREE
+
+If you've installed Backpack, you already have access to Backpack's command line interface. You can run `php artisan backpack` to get a quick list of everything you can do using our CLI. Here's that same list, a bit more organized:
+
+
+#### Generate Full CRUDs
+
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:build |
+ Create CRUDs for all Models that do not already have one. |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:crud |
+ Create a CRUD interface: Controller, Model, Request |
+
+
+
+
+#### Generate CRUD files
+
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:crud-controller |
+ Generate a Backpack CRUD controller. |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:crud-model |
+ Generate a Backpack CRUD model |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:crud-request |
+ Generate a Backpack CRUD request |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:crud-operation |
+ Generate a custom Backpack CRUD operation trait |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:crud-form-operation |
+ Generate a custom Backpack CRUD operation trait with Backpack Form |
+
+
+
+
+#### Generate CRUD operation components
+
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:button |
+ Generate a custom Backpack button |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:column |
+ Generate a custom Backpack column |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:field |
+ Generate a custom Backpack field |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:filter |
+ Generate a custom Backpack filter |
+
+
+
+
+#### Generate general admin panel files (non-CRUD)
+
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:page |
+ Generate a Backpack Page |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:page-controller |
+ Generate a Backpack PageController |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:chart |
+ Create a ChartController and route |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:chart-controller |
+ Generate a Backpack ChartController |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:widget |
+ Generate a Backpack widget |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:add-custom-route |
+ Add code to the routes/backpack/custom.php file |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:add-sidebar-content |
+ Add code to the Backpack sidebar_content file |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:publish |
+ Publishes a view to make changes to it, for your project |
+ |
+
+
+
+#### Installation & Debugging
+
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:install |
+ Install Backpack requirements on dev, publish CSS and JS assets and create uploads directory. |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:require:pro |
+ Require Backpack PRO |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:require:devtools |
+ Require Backpack DevTools on dev |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:require:editablecolumns |
+ Require Backpack Editable Columns |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:publish-middleware |
+ Publish the CheckIfAdmin middleware |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:fix |
+ Fix known Backpack issues. |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:user |
+ Create a new user |
+
+
+ php artisan backpack:version |
+ Show the version of PHP and Backpack packages. |
+
+
+
+
+## Web Interface (DevTools) -
PREMIUM
+
+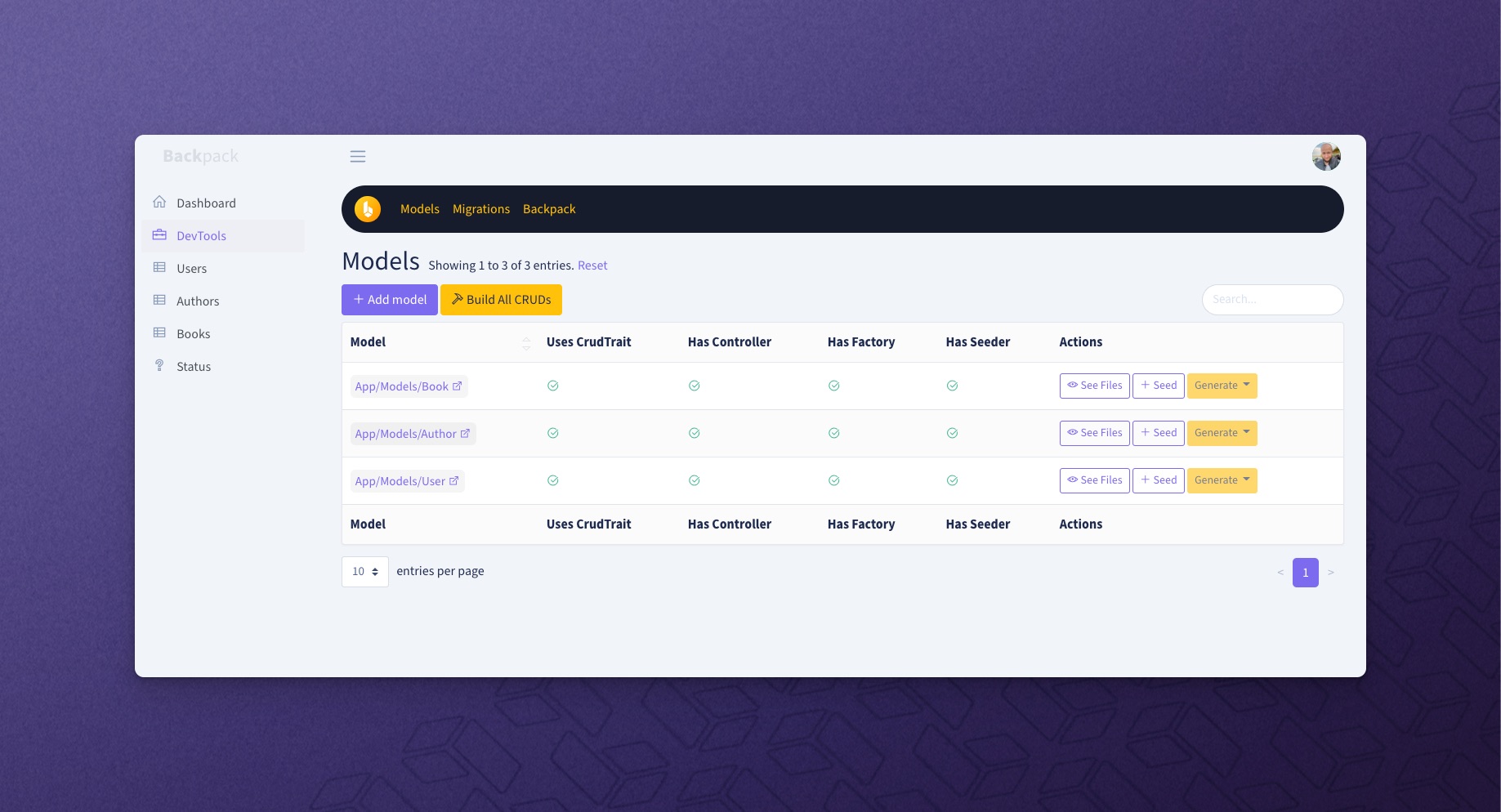
+
+For the people who want to step up their code-generation game, we've created [Backpack DevTools](/products/devtools). It empowers devs to do most of the things our CLI does, but:
+- in a more intuitive and easy-to-use environment (web browser);
+- in a more complete and correct way (eg. fills in validation rules, relationships etc.);
+- can also do things that the CLI can't (eg. generate Seeders, Factories);
+
+Here are a few things DevTools makes easy, and how:
+
+
+#### Generate Migration & Model
+
+As opposed to the CLI who can only generate an _empty_ model, DevTools can create near-perfect Eloquent Models, that include fillable and relationships. Just fill in one web form:
+
+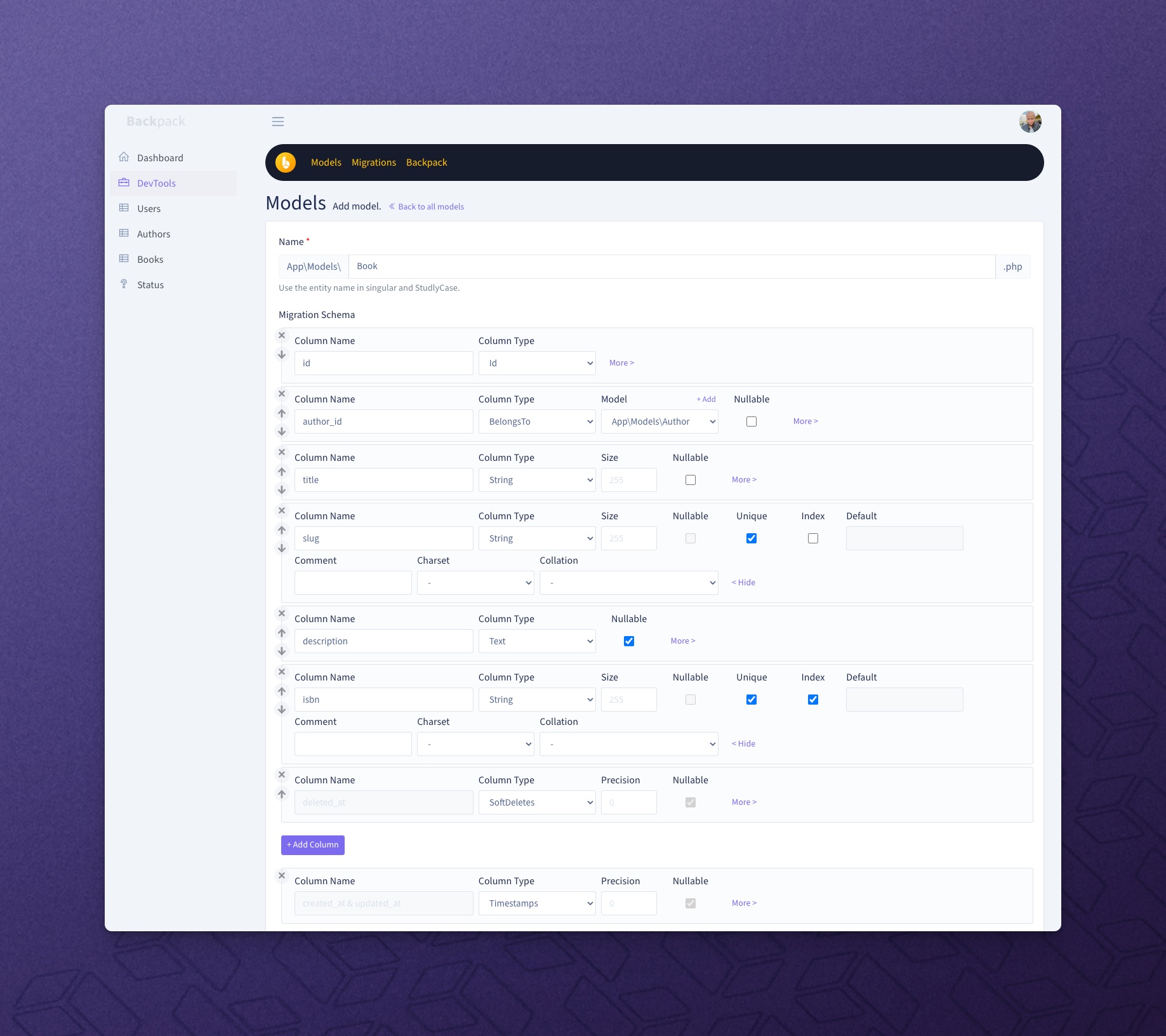
+
+While the code might not be perfect for complex models (will need a double-check and possibly customizations), it _will_ generate working code, and it _will_ save you the bulk of your work.
+
+
+#### Generate Factory & Seeder
+
+This is something the CLI doesn't offer at all.
+
+When generating a Model, you can also choose to generate a Factory and a Seeder for it. While the generated code isn't 100% perfect for complex models, it's a great starting point - and super-easy to customize after it's generated.
+
+One other benefit of having Factories and Seeders generated is that you'll then be able to Seed your tables (aka. add dummy entries) right from your admin panel, inside DevTools:
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Generate CRUDs
+
+The functionality here isn't much different from the CLI. DevTools will allow you to create standard CRUDs for your Eloquent models, from the comfort of your web browser. Hell, it will even show you a list of Models, to see which ones have CRUDs and which ones do not.
+
+
+
+*Note:* DevTools will _not_ allow you too choose operations, columns, fields etc for those CRUDs. The CRUDs that are generated are standard, just like the ones provided by our CLI. You can then customize operations, columns, fields etc in code, directly.
+
+
+
+#### Generate CRUD Operations
+
+While the CLI allows you to create blank operations, DevTools takes that to a whole different level. It allows you to quickly create fully-working Operations, where you just need to customize the logic. Using various combinations, DevTools allows you to create up to 16 types of operations
+
+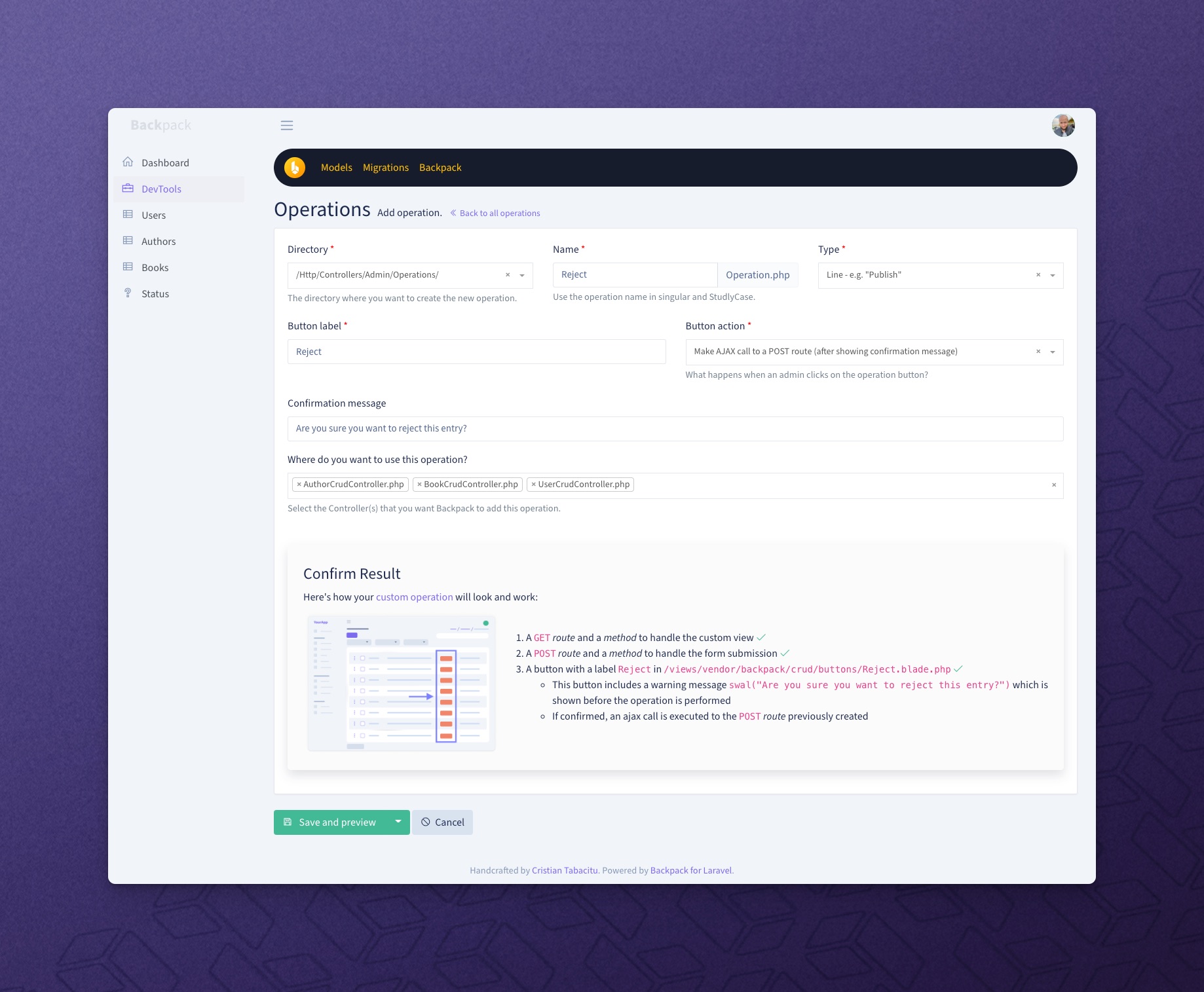
+
+
+#### Generate or Publish Operations Files
+
+Just like the CLI, DevTools will help generate custom buttons, columns, fields or filters... or alternatively... publish the _existing_ blade files, to customize them to your liking.
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Generate Custom Page
+
+Just like the CLI, DevTools will also help you generate completely custom admin panel pages, that DO NOT have CRUDs. This is very useful to generate pages for your Dashboards and other types of pages that do not depend on CRUD. Keep in mind you can copy-paste any HTML from https://backstrap.net into the views and it'll look identical.
+
+
+
+
+
+---
+
+
+Needless to say, we highlighy recommend purchasing [Backpack DevTools](/products/devtools). It saved us so many hours in development time, we can't even count. It's not a magic bullet - it's NOT a no-code solution. But it will help you generate so much code, and keep you working on the important bits, the actual logic.
diff --git a/7.x-dev/getting-started-advanced-features.md b/7.x-dev/getting-started-advanced-features.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f1c3ff57
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/getting-started-advanced-features.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+# 3. Advanced Features
+
+---
+
+**Duration:** 5 minutes
+
+Here are some other cool things Backpack makes easy for you. We recommend going through them one by one, just browsing. You might not need the feature _right now_, but when _you do_, you'll know where to find it.
+
+---
+
+
+## Other Operations
+- [Show](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-show) Operation - helps admins preview an entry
FREE
+- [Reorder](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-reorder) Operation - helps reorder and nest entries (hierarchy tree)
FREE
+- [Revise](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-revisions) Operation - helps record all changes to an entry and undo them
FREE
+- [Clone](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-clone) Operation - helps make a copy of an entry
PRO
+- [BulkDelete](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-delete) Operation - helps delete multiple items in one go
PRO
+- [BulkClone](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-clone) Operation - helps clone multiple items in one go
PRO
+
+---
+
+
+## Other Features
+- **Create & Update**
+ - [Manage files on disk](/docs/{{version}}/crud-how-to#use-the-media-library-file-manager) (media library)
FREE
+ - [Fake fields](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#optional-fake-field-attributes-stores-fake-attributes-as-json-in)
FREE
+ - Translatable models and [multi-language CRUDs](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-update#translatable-models)
FREE
+ - [Tabs in create/update forms](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#split-fields-into-tabs)
FREE
+
+--
+
+- **ListEntries**
+ - you can add a "+" button next to each entry to allow an admin to easily preview some quick information that was too big to fit inside a column - we call this [details row](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-list-entries#details-row)
PRO
+ - export all visible items in the table by adding [export buttons](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-list-entries#export-buttons)
PRO
+ - [custom search logic](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns#custom-search-logic) for the columns in a list view
FREE
+
+
+Additionally, here are a few more ways you can customize your CRUDs:
+- [Custom Views for each CRUD](/docs/{{version}}/crud-how-to#customize-views-for-each-crud-panel)
+- [Custom Content Class for each CRUD](/docs/{{version}}/crud-how-to#resize-the-content-wrapper-for-an-operation)
+- [Custom CSS or JS](/docs/{{version}}/crud-how-to#customize-css-and-js-for-default-crud-operations) for each CRUD Operation
+
+**That's it!** We told you we're done with long lessons. Hopefully, some of the above has peaked your interest and you've clicked through to see what Backpack can do. In the [next lesson](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-license-and-support) we'll go through a few other Backpack packages that cover some recurring use cases.
+
+
+
+
+ Next →
+
diff --git a/7.x-dev/getting-started-basics.md b/7.x-dev/getting-started-basics.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3f2e947f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/getting-started-basics.md
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+# 1. Basics
+
+---
+
+**Duration:** 5 minutes
+
+> **Are you already comfortable with Laravel?** In order to understand this series and make use of Backpack, you'll need to have a decent understanding of the Laravel framework. If you don't, please [watch this excellent intro series on Laracasts](https://laracasts.com/series/laravel-8-from-scratch) and familiarize yourself with Laravel first.
+
+
+
+## What is Backpack?
+A software package that helps Laravel professionals build administration panels - secure areas where administrators login and create, read, update, and delete application information. It is *not* a CMS, it is more a framework that lets you *build your own* CMS. You can install it in your existing project or in a totally new project.
+
+It's designed to be flexible enough to allow you to **build admin panels for everything from simple presentation websites to CRMs, ERPs, eCommerce, eLearning, etc**. We can vouch for that, because we have built all that stuff using Backpack already.
+
+
+## What's a CRUD?
+
+A **CRUD** is what we call a section of your admin panel that lets the admin _Create, Read, Update, or Delete_ entries of a certain entity (or Model). So you can have a CRUD for Products, a CRUD for Articles, a CRUD for Categories, or whatever else you might want to create, read, update, or delete.
+
+For the purpose of this series, we'll show examples on the ```Tag``` entity. This is how a Tag CRUD might look like:
+
+
+
+But Backpack is prepared for feature-packed CRUDs - since it's a good tool for very complex projects too. This is how a CRUD that uses all of Backpack's features might look like:
+
+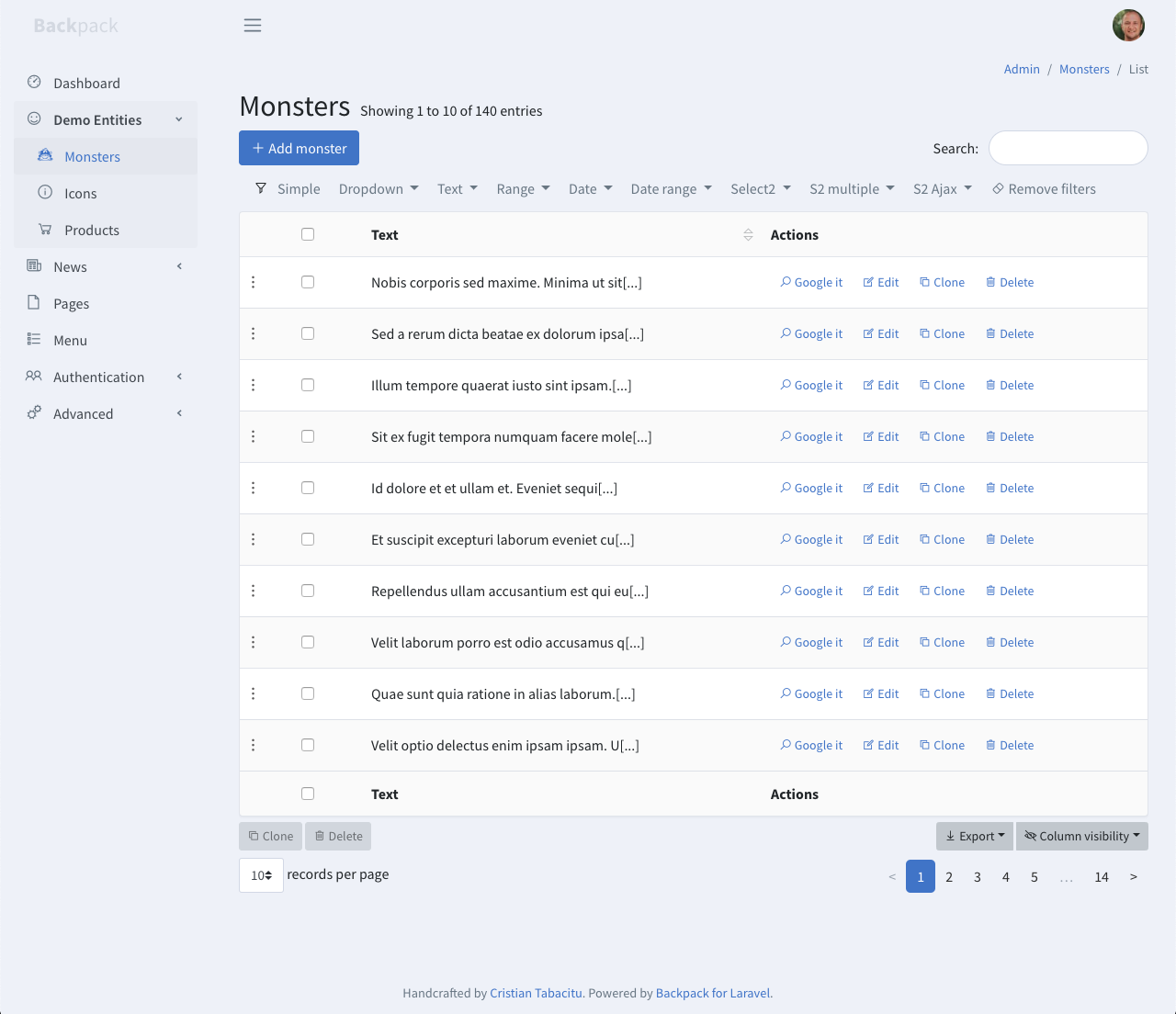
+
+However, you will _almost never_ use all of Backpack's features in one CRUD. But if you do, it will still look good, and it will be intuitive to use.
+
+
+## Main Features
+
+
+### Front-End Design
+
+New Backpack installs come with an HTML theme installed - you choose which theme. All themes use Bootstrap, and have many HTML blocks ready for you to use. When you're building a custom page in your admin panel, it's easy to just copy-paste the HTML from the the theme's demo or from its documentation. And the page will look good, without you having to design anything. Currently, we have three first-party themes:
+- [Tabler](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/theme-tabler)
+- [CoreUI v4](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/theme-coreuiv4)
+- [CoreUI v2](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/theme-tabler) (which still provides IE support)
+
+You can also create your own custom theme. In fact, we've built our theming system in such a way that if you buy a Bootstrap-based HTML template from Envato / GetBootstrap / WrapBootstrap, it should take you no more than 5 hours to create a Backpack theme that uses that HTML template.
+
+All themes also install Noty for triggering JS notification bubbles, and SweetAlerts. So you can easily use these across your admin panel. You can [trigger notification bubbles in PHP](/docs/{{version}}/base-about#triggering-notification-bubbles-in-php) or [trigger notification bubbles in JavaScript](/docs/{{version}}/base-about#triggering-notification-bubbles-in-javascript).
+
+
+### Authentication
+
+Backpack comes with an authentication system that's separate from Laravel's. This way, you can have different login screens for users and admins, if you need to. If not, you can choose to use only one authentication - either Laravel's or Backpack's.
+
+
+
+After you [install Backpack](/docs/{{version}}/installation) (don't do it now), you'll be able to log into your admin panel at ```http://yourapp/admin```. You can change the URL prefix from ```admin``` to something else in your ```config/backpack/base.php``` file, along with a bunch of other configuration options. [Click here](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/CRUD/blob/master/src/config/backpack/base.php) to browse the configuration file and see what it can do for you.
+
+
+
+### CRUDs
+
+This is where it gets interesting. As soon as you [install Backpack](/docs/{{version}}/installation) in your project, you can create **CRUDs** for your admins to easily manipulate database entries. Let's browse through a simple example of creating a CRUD administration panel for a Tag entity.
+
+You can generate everything a CRUD needs using one of the methods below:
+
+---
+
+**Option A)
PRO - using our GUI, [Backpack DevTools](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools)**
+
+Just install DevTools, fill in a web form with the columns for your entity, and it'll generate all the needed files. It's that simple. Check out [the images here](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools) to see how it works. It's especially useful for more complex entities. It is a paid tool though, so if you are not yet ready to purchase, let's explore the free option too.
+
+**Option B)
FREE - using the command-line interface**
+
+You can use anything you want to generate the Migration and Model, so in this case we're going to use [laracasts/generators](https://github.com/laracasts/Laravel-5-Generators-Extended):
+
+```zsh
+# STEP 0. install a 3d party tool to generate migrations
+composer require --dev laracasts/generators
+
+# STEP 1. create a migration
+php artisan make:migration:schema create_tags_table --model=0 --schema="name:string:unique,slug:string:unique"
+php artisan migrate
+
+# STEP 2. create a CRUD for it
+php artisan backpack:crud tag #use singular, not plural
+```
+
+---
+
+In both cases, what we're getting is a simple CRUD panel, which you should now be able to see in the Sidebar.
+
+For a simple entry like this, the generated CRUD panel will even work "as is", with no need for customisations. But don't expect this for more complex entities. They will usually have specific requirements and need customization. That's where Backpack shines - modifying anything in the CRUD panel is easy and intuitive, once you understand how it works.
+
+The methods above will generate:
+- a **migration** file
+- a **model** (```app\Models\Tag.php```)
+- a **request** file, for form validation (```app\Http\Requests\TagCrudRequest.php```)
+- a **controller** file, where you can customize how the CRUD panel looks and feels (```app\Http\Controllers\Admin\TagCrudController.php```)
+- a **route**, as a line inside ```routes/backpack/custom.php```
+
+It will also add:
+- a route inside ```routes/backpack/custom.php```, pointing to that controller
+- a menu item inside ```resources/views/vendor/backpack/ui/inc/menu_items.blade.php```
+
+You might have noticed that **no views** are generated. That's because in most cases you _don't need_ custom views with Backpack. All your custom code is in the controller, model, or request, so the default views are loaded from the package. If you do, however, need to customize a view, it is [really easy](/docs/{{version}}/crud-how-to#customize-views-for-each-crud-panel).
+
+Also, we won't be covering the **migration**, **model**, and **request** files here, as they are in no way custom. The only thing you need to make sure is that the Model is properly configured (database table, relationships, ```$fillable``` or ```$guarded``` properties, etc.) and that it uses our ```CrudTrait```. What we _will_ be covering is ```TagCrudController``` - which is where most of your logic will reside. Here's a copy of a simple one that you might use to achieve the above:
+
+```php
+type('text');
+ CRUD::field('slug')->type('text')->label('URL Segment (slug)');
+ }
+
+ public function setupUpdateOperation()
+ {
+ $this->setupCreateOperation();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+You should notice:
+- It uses basic inheritance (```TagCrudController extends CrudController```); so if you want to modify a behaviour (save, update, reorder, etc.), you can easily do that by overwriting the corresponding method in your ```TagCrudController```
+- All operations are enabled by using that operation's trait on the controller
+- The ```setup()``` method defines the basics of the CRUD panel
+- Each operation is set up inside a ```setupXxxOperation()``` method
+
+**That's it!** If you want to learn more, please [read the next lesson](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-crud-operations) of this series.
+
+
+
+
+ Next →
+
diff --git a/7.x-dev/getting-started-crud-operations.md b/7.x-dev/getting-started-crud-operations.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0c79813c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/getting-started-crud-operations.md
@@ -0,0 +1,268 @@
+# 2. CRUD Operations
+
+---
+
+**Duration:** 10 minutes
+
+Let's bring back the example from our first lesson. The Tags CRUD:
+
+
+
+With its ```TagCrudController```:
+
+```php
+type('text')->label('URL Segment (slug)');
+ }
+
+ public function setupUpdateOperation()
+ {
+ $this->setupCreateOperation();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+In the example above, we've enabled the most common operations:
+- **Create** - using a create form (aka "*add form*")
+- **List** - using AJAX DataTables (aka "*list view*", aka "*table view*")
+- **Update** - using an update form (aka "*edit form*")
+- **Delete** - using a *button* in the *list view*
+- **Show** - using a *button* in the *list view*
+
+These are the basic operations an admin can execute on an Eloquent model, thanks to Backpack. We do have additional operations (Reorder, Revisions, Clone, BulkDelete, and BulkClone), and you can easily _create a custom operation_, but let's not get ahead of ourselves. **Let's go through the most important features of the operations you'll be using _all the time_: List, Create, and Update**.
+
+
+## Create and Update Operations
+
+
+
+
+### Fields
+
+Inside your Controller's ```setupCreateOperation()``` or ```setupUpdateOperation()``` method, you'll be able to define which fields you want the admin to see, when creating/updating entries. In the example above, we only have two fields, both using the ```text``` field type. So that's what's shown to the admin. When the admin presses _Save_, assuming your model has those two attributes as ```$fillable```, Backpack will save the entry and take you back to the List view. Keep in mind we're using a _pure_ Eloquent model. So of course, inside the model you could use accessors, mutators, events, etc.
+
+
+But often, you won't just need text inputs. You'll need datepickers, upload buttons, 1-n relationships, n-n relationships, textareas, etc. For each field, you only need to define it properly in the Controller. Here are the most often used methods to manipulate fields:
+
+```php
+CRUD::field('price');
+CRUD::field('price')->prefix('$'); // set the "prefix" attribute to "$"
+CRUD::field('price')->remove(); // delete a field from the form
+CRUD::field('price')->after('name'); // move a field after a different field
+
+// you can of course chain these calls:
+CRUD::field('price')->label('Product price')->prefix('$')->after('name');
+
+// you can also add multiple attributes in one go, by creating
+// a field using an array, instead of just its name (a string);
+// we call this the array syntax:
+CRUD::field([
+ 'name' => 'price',
+ 'type' => 'number',
+ 'label' => 'Product price',
+ 'prefix' => '$',
+]);
+```
+
+A typical *field definition* will need at least three things:
+- ```name``` - the attribute (column in the database), which will also become the name of the input
+- ```type``` - the kind of field we want to use (text, number, select2, etc.)
+- ```label``` - the human-readable label for the input (will be generated from ```name``` if not given)
+
+
+You can use [one of the 44+ field types we've provided](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#default-field-types), or easily [create a custom field type](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#creating-a-custom-field-type) if you have a specific need that we haven't covered yet, or even [overwrite how a field type works](#overwriting-default-field-types). Take a few minutes and [browse the 44+ field types](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields#default-field-types) to understand how the definition array differs from one to another and how many use cases you have already covered.
+
+Let's take another example, slightly more complicated than the ```text``` fields we used above. Something you'll encounter all the time are relationship fields. So let's say the ```Tag``` model has an **n-n relationship** with an Article model:
+
+```php
+ public function articles()
+ {
+ return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Article', 'article_tag');
+ }
+```
+
+We could use the code below to add a ```select2_multiple``` field to the Tag update forms:
+
+```php
+CRUD::field([
+ 'type' => 'select2_multiple',
+ 'name' => 'articles', // the relationship name in your Model
+ 'entity' => 'articles', // the relationship name in your Model
+ 'attribute' => 'title', // attribute on Article that is shown to admin
+ 'pivot' => true, // on create&update, do you need to add/delete pivot table entries?
+]);
+```
+
+**Notes:**
+- If we call this inside ```setupUpdateOperation()```, then it will only be added on that operation
+- Because we haven't specified a ```label```, Backpack will take the "_articles_" name and turn it into a label, "_Articles_"
+
+If we had an Articles CRUD, and the reverse relationship defined on the ```Article``` model too, then we could also add a ```select2_multiple``` field in the Article CRUD to allow the admin to choose which tags apply to each article. This actually makes more sense than the above:
+
+```php
+CRUD::field([
+ 'label' => "Tags",
+ 'type' => 'select2_multiple',
+ 'name' => 'tags', // the method that defines the relationship in your Model
+ 'entity' => 'tags', // the method that defines the relationship in your Model
+ 'attribute' => 'name', // foreign key attribute that is shown to user
+ 'pivot' => true, // on create&update, do you need to add/delete pivot table entries?
+]);
+```
+
+
+### Callbacks
+
+Developers coming from other CRUD systems will be looking for callbacks to run ```before_insert```, ```before_update```, ```after_insert```, and ```after_update```. **There are no callbacks in Backpack**.
+
+Remember that Backpack is using Eloquent models. That means you can do X when Y is happening, by using the [model events](https://laravel.com/docs/10.x/eloquent#events). For example, in your MonsterCrudController you can do:
+
+```php
+public function setup() {
+ // this will get run for all operations that trigger the "deleting" model event
+ // by default, that's the Delete operation
+ Monster::deleting(function ($entry) {
+ // TODO: delete that entry's files from the disk
+ });
+
+ // this will get run on all operations that trigger the "saving" model event
+ // by default, that's the Create and Update operations
+ Monster::saving(function ($entry) {
+ // TODO: change one value to another or something
+ });
+}
+```
+
+Alternatively, if you need to change how an operation does something, then that's simple too. The ```store()``` and ```update()``` code is inside a trait, so you can easily override that method and call it inside your new method. For example, here's how we can do things before/after an item is saved in the Create operation:
+
+```php
+traitStore();
+ // do something after save
+ return $response;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+>But before you do that, ask yourself - **_is this something that should be done when an entry is added/updated/deleted from the application too_**? Not just from the admin panel? If so, a better place for it would be the Model. Remember your Model is a pure Eloquent Model, so the cleanest way might be to use [Eloquent Event Observers](https://laravel.com/docs/6.0/eloquent#events) or [accessors and mutators](https://laravel.com/docs/master/eloquent-mutators#accessors-and-mutators).
+
+
+## List Operation
+
+List shows the admin a table with all entries. On the front-end, the information is pulled using AJAX calls, and shown using DataTables. It's the most feature-packed operation in Backpack, but right now we're just going through the most important features you need to know about: columns, filters, and buttons.
+
+You should configure the List operation inside the ```setupListOperation()``` method.
+
+
+### Columns
+
+Columns help you specify *which* attributes are shown in the table and *in which order*. Their syntax is almost identical to fields. In fact, you'll find each Backpack field has a corresponding column, with the same name and syntax:
+
+```php
+CRUD::column($column_definition_array); // add a single column, at the end of the table
+CRUD::column('price')->type('number');
+CRUD::column('price')->type('number')->prefix('$');
+CRUD::column('price')->after('name'); // move column after another column
+CRUD::column('price')->remove(); // move column after another column
+
+// bulk actions
+CRUD::addColumns([$column_definition_array_1, $column_definition_array_2]); // add multiple columns, at the end of the table
+CRUD::setColumns([$column_definition_array_1, $column_definition_array_2]); // make these the only columns in the table
+CRUD::removeColumns(['column_name_1', 'column_name_2']); // remove an array of columns from the table
+CRUD::setColumnsDetails(['column_1', 'column_2'], ['attribute' => 'value']);
+```
+
+You can use one of the [44+ column types](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns#default-column-types) to show information to the user in the table, or easily [create a custom column type](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns#creating-a-custom-column-type) if you have a specific need. Here's an example of using the methods above:
+
+```php
+CRUD::column([
+ 'name' => 'published_at',
+ 'type' => 'date',
+ 'label' => 'Publish_date',
+]);
+
+// PRO TIP: to quickly add a text column, just pass the name string instead of an array
+CRUD::column('text'); // adds a text column, at the end of the stack
+```
+
+
+### Filters
+
+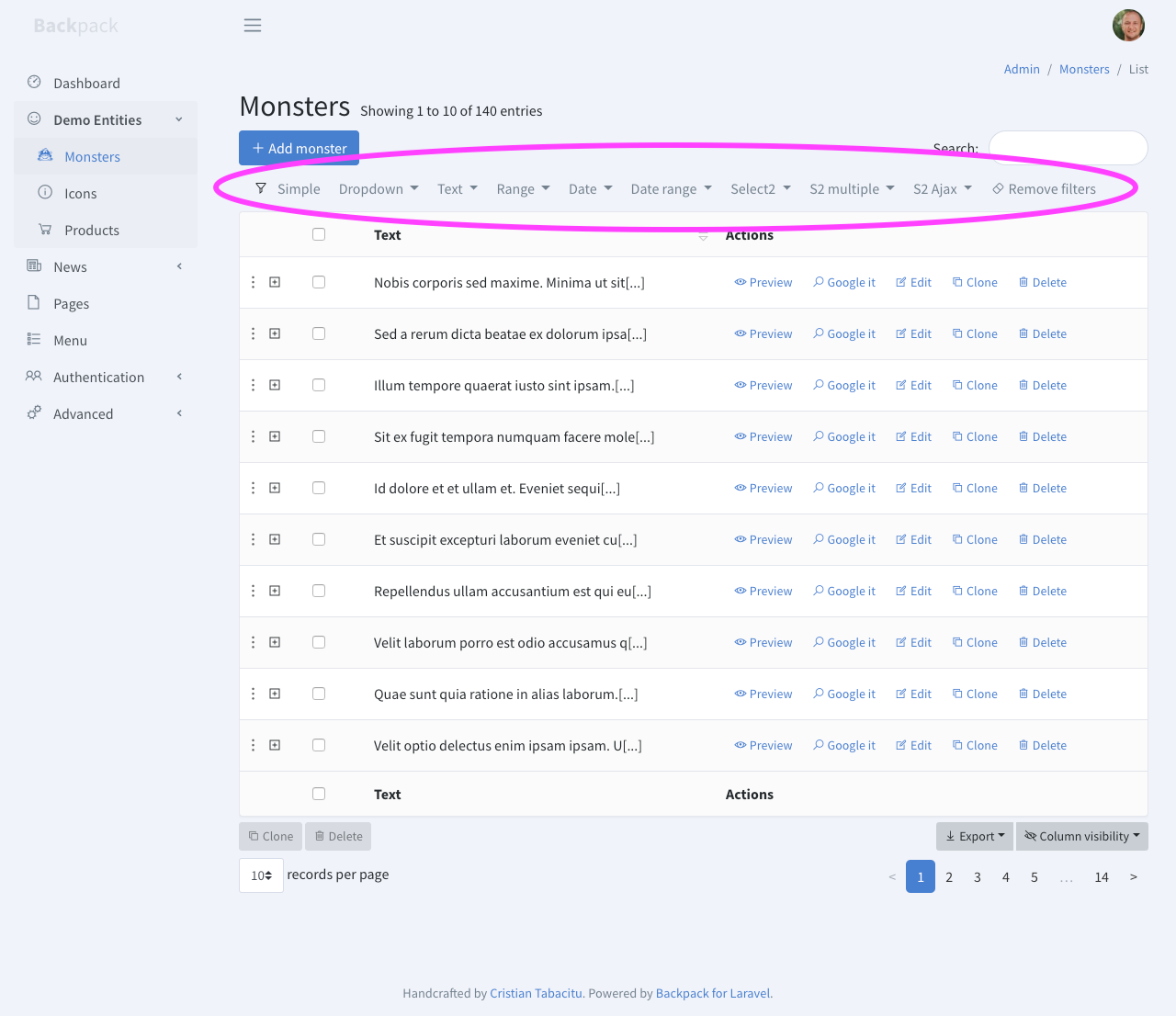
+
+Filters provide an easy way for the admin to _filter_ the List table. The syntax is very similar to Fields and Columns and you can use one of the [existing 8 filter types](/docs/{{version}}/crud-filters) or easily [create a custom filter](/docs/{{version}}/crud-filters#creating-custom-filters). Note that this is a PRO feature.
+
+```php
+CRUD::addFilter($options, $values, $filter_logic);
+CRUD::removeFilter($name);
+CRUD::removeAllFilters();
+```
+
+For more on filters, check out the [filters documentation page](/docs/{{version}}/crud-filters).
+
+
+### Buttons
+
+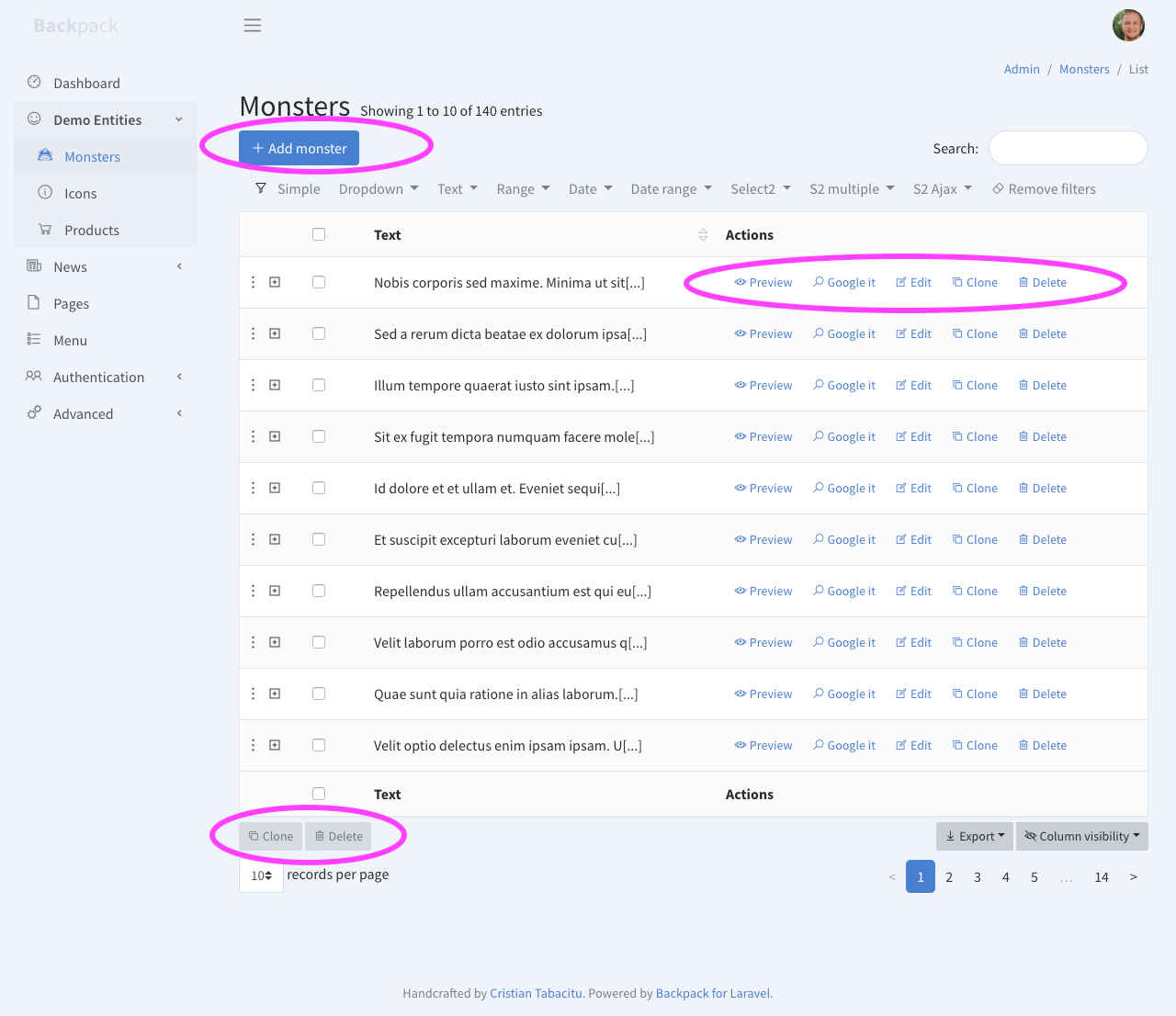
+
+If you want to add a custom button to an entry, you can do that. If you want to remove a button, you can also do that. Check out the [buttons documentation](/docs/{{version}}/crud-buttons).
+
+```php
+// positions: 'beginning' and 'end'
+// stacks: 'line', 'top', 'bottom'
+// types: view, model_function
+CRUD::addButton($stack, $name, $type, $content, $position);
+CRUD::removeButton($name);
+CRUD::removeButtonFromStack($name, $stack);
+```
+
+**That's it!** Thanks for sticking with us this long. This has been the most important and longest lesson. You can go ahead and [install Backpack](/docs/{{version}}/installation) now as you've already gone through the most important features. Or [read the next lesson](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-advanced-features) about advanced features.
+
+
+
+
+ Next →
+
diff --git a/7.x-dev/getting-started-license-and-support.md b/7.x-dev/getting-started-license-and-support.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fed5a439
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/getting-started-license-and-support.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+# 4. Add-ons, License, and Support
+
+---
+
+**Duration:** 3 minutes
+
+
+## Add-ons
+
+In addition to our core package (CRUD), we have quite a few packages you can install or download that deal with common use cases. Some have been developed by our core team, some by our wonderful community. For example, we have plug&play interfaces to manage [site-wide settings](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/Settings), [the default Laravel users table](https://github.com/eduardoarandah/UserManager), [users, groups & permissions](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/PermissionManager), [content for custom pages, using page templates](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/PageManager), [news articles, categories and tags](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/NewsCRUD), etc.
+
+Take a look at:
+- [all official add-ons](/docs/{{version}}/add-ons-official)
+- [all community add-ons](/docs/{{version}}/add-ons-community)
+
+
+## License
+
+
+Backpack is open-core. The features you'll find in our docs are split into two packages:
+
+- [Backpack\CRUD](https://github.com/laravel-backpack/crud) is the core, released under the [MIT License](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/CRUD/blob/master/LICENSE.md) (free, open-source)
FREE
+- [Backpack\PRO](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects) is a Backpack add-on, released under our [EULA](https://backpackforlaravel.com/eula) (paid, closed-source)
PRO
+
+Backpack\CRUD is perfect if you're building a simple admin panel - it's packed with features! It's also perfect if you're building an open-source project, the permissive license allows you to do whatever you want.
+
+When your admin panel grows and your needs become more complex, you can purchase our [Backpack\PRO](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects) add-on, which adds A LOT of features for complex use cases (see [list here](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects)). Our documentation includes instructions on how to use both Backpack\CRUD and Backpack\PRO, with all the PRO features clearly labeled
PRO
+
+
+
+## Support
+
+We offer free support for all our packages. If you report a bug, we will do our best to fix it in a timely manner. We publish a new patch version weekly, launch new features every month and major versions yearly. But please note that support does _not_ mean we can help with debugging, implementation issues specific to your project, brainstorming on solutions for your project, jumping on Zoom/Meet calls etc. We'd love to, but we just cannot do that, with thousands of developers using Backpack and such a small price. But. We do have good documentation and have been blessed with a **great community**, where people help each other out. If Backpack becomes your tool of choice, I highly recommend you join our gang. Help others with your experience, report bugs, create cool stuff and even influence the direction of Backpack. Use:
+
+- **[StackOverflow tag](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/backpack-for-laravel) for help requests**. If you need help creating something using Backpack, post your question on StackOverflow using the ```backpack-for-laravel``` tag. We've been blessed with a great community that is happy to help. Who doesn't like getting StackOverflow points?
+- **[Community Forum Issues](https://github.com/laravel-backpack/community-forum) for bugs**. Found a bug? Great! Please search for it on GitHub first - someone might have already found it. If not, open an issue, we're happy to make Backpack better.
+- **[Community Forum Discussions](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/community-forum/discussions) for showing off your work, asking for opinions on implementation, sharing tips, packages, etc.**
+
+Thank you for sticking with us for so long. This is the last Backpack lesson in this series. **Now you have absolutely no excuse - time to start your first Backpack project!** But first, here are a few more links, if you are still not sure whether you are ready:
+
+- [Go through the demo](/docs/{{version}}/demo) and play around
+- Read this [CRUD Crash Course](/docs/{{version}}/crud-tutorial) and do the steps yourself
+- Take a look at the [CrudController API Cheat Sheet](/docs/{{version}}/crud-cheat-sheet)
+
+
+
+
+ CRUD Crash Course
+
+
+ Demo
+
+
+ Cheat Sheet
+
diff --git a/7.x-dev/getting-started-videos.md b/7.x-dev/getting-started-videos.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ae0f8de0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/getting-started-videos.md
@@ -0,0 +1,187 @@
+# Getting Started Videos
+
+---
+
+**Total Duration:** 59 minutes
+
+
+
+
1. Intro
+
+Let's get to know Mauro Martinez, one of the Backpack maintainers and your teacher for this series.
+
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [Laravel](https://laravel.com)
+- ["Laravel from Scratch" series on Laracasts](http://laravelfromscratch.com/)
+- [Backpack's docs repo on Github](https://github.com/laravel-backpack/docs)
+
+----
+
+
+
2. Installation and Setup
+
+Let's set up a Laravel project and follow the Backpack installation.
+
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [Laravel docs - create project](https://laravel.com/docs/master/installation#your-first-laravel-project)
+- [Backpack docs - installation](/docs/{{version}}/installation)
+
+
+----
+
+
+
3. Look and Feel - Introduction to Backpack Themes
+A quick intro to Backpack themes - how to customize the look and feel of your admin panel, or use a Bootstrap theme of your choice.
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [About Themes](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-themes)
+- [Demo](https://demo.backpackforlaravel.com/admin)
+
+
+----
+
+
+
4. Dashboard
+Let's place some content on the admin dashboard using Backpack widgets - it's super easy.
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [Widgets](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets)
+- [Customize dashboard](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/base-how-to#customize-the-dashboard)
+
+
+----
+
+
+
5. CRUDs - Intro to Operations
+Operations are a very important part of Backpack - they allow you to do things like [Create](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-create), Read ([List](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-list-entries) and [Show](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-show)), [Update](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-update), and [Delete](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-delete). Let's understand how they work.
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [Set up CRUD - basic guide](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-crud-operations)
+- [Operations - in depth](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operations)
+
+
+----
+
+
+
6. DevTools - Generating CRUDs
+
+Go from an idea to a full CRUD in seconds! Quickly build an admin panel for your Eloquent models using a web interface to generate migrations, models, and CRUDs.
+
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [DevTools - about](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/generating-code#web-interface-devtools-premium)
+- [DevTools - installation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools)
+
+----
+
+
+
7. List Operation
+
+Let's take a deeper dive into the List operation and one important feature it is using - Backpack columns.
+
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [List operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-list-entries)
+- [50+ Columns](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns)
+
+----
+
+
+
8. Create and Update Operations
+
+Now let's do a deeper dive into Backpack forms - particularly the ones in the Create and Update operations, which use Backpack fields, another important feature.
+
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [Create Operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-create)
+- [Update Operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-update)
+- [50+ Fields](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields)
+
+----
+
+
+
9. Show and Delete Operations
+Let's also address some easy operations - the Show and Delete operations. You'll see they are very similar to the ones above.
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [Delete operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-delete)
+- [Show operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-show)
+- [50+ Columns](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns)
+
+----
+
+
+
10. Reorder and BulkClone Operations
+Here are two other operation you will most likely need - they will help you reorder or duplicate entries.
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [Reorder Operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-reorder)
+- [Clone Operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-clone)
+- [Available Operations](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/{{version}}/crud-operations#standard-operations)
+
+
+----
+
+
+
11. Custom Operations using DevTools
+
+This video shows you how to create custom operations, using our premium add-on DevTools.
+
+
+
+
+Mentioned in this video:
+- [DevTools](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools)
+
+----
+
+
+Thank you for dedicating those 59 minutes to learning Backpack. **You should now be able to build your first admin panel.** But first, here are a few more links, if you are still not sure whether you are ready:
+
+- [Go through the demo](/docs/{{version}}/demo) and play around, browse the features (pay special attention to the Monsters CRUD)
+- Read this [CRUD Crash Course](/docs/{{version}}/crud-tutorial) and do the steps yourself
+- Take a look at the [CrudController API Cheat Sheet](/docs/{{version}}/crud-cheat-sheet)
+- Read our [Getting Started Text Course](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-basics)
+- Purchase and install [Backpack DevTools](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools) which will generate the minimum stuff for you
+
+
+
diff --git a/7.x-dev/index.md b/7.x-dev/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cb6360d6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+#### About
+
+- [Introduction](/docs/{{version}}/introduction)
+- [Demo](/docs/{{version}}/demo)
+- [Installation](/docs/{{version}}/installation)
+- [Features (Free vs Paid)](/docs/{{version}}/features-free-vs-paid)
+- [Release Notes](/docs/{{version}}/release-notes)
+- [Upgrade Guide](/docs/{{version}}/upgrade-guide)
+- [FAQ](/docs/{{version}}/faq)
+
+#### Getting Started
+- [Video Course](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-videos)
+- [Text Course](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-basics)
+ - [1. Basics](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-basics)
+ - [2. CRUD Operations](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-crud-operations)
+ - [3. Advanced Features](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-advanced-features)
+ - [4. Add-ons, License & Support](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-license-and-support)
+- [Tutorials](/docs/{{version}}/tutorials)
+
+#### Admin UI
+
+- [About](/docs/{{version}}/base-about)
+- [Alerts](/docs/{{version}}/base-alerts)
+- [Breadcrumbs](/docs/{{version}}/base-breadcrumbs)
+- [Themes](/docs/{{version}}/base-themes)
+- [Widgets](/docs/{{version}}/base-widgets)
+- [Components](/docs/{{version}}/base-components)
+- [FAQs](/docs/{{version}}/base-how-to)
+
+#### CRUD Panels
+
+- [Basics](/docs/{{version}}/crud-basics)
+- [Crash Course](/docs/{{version}}/crud-tutorial)
+- [Operations](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operations)
+ + [List](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-list-entries)
+ + [Columns](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns)
+ + [Buttons](/docs/{{version}}/crud-buttons)
+ + [Filters](/docs/{{version}}/crud-filters)
+ + [Create](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-create) & [Update](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-update)
+ + [Fields](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields)
+ + [Save Actions](/docs/{{version}}/crud-save-actions)
+ + [Uploaders](/docs/{{version}}/crud-uploaders)
+ + [CrudField JS Library](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fields-javascript-api)
+ + [Delete](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-delete)
+ + [Show](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-show)
+ + [Columns](/docs/{{version}}/crud-columns)
+- [Additional Operations](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operations)
+ + [Clone](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-clone)
+ + [Reorder](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-reorder)
+ + [Revise](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-revisions)
+ + [Fetch](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-fetch)
+ + [InlineCreate](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-inline-create)
+ + [Trash](/docs/{{version}}/crud-operation-trash)
+- [API](/docs/{{version}}/crud-cheat-sheet)
+ + [Cheat Sheet](/docs/{{version}}/crud-cheat-sheet)
+ + [Crud API](/docs/{{version}}/crud-api)
+ + [Fluent API](/docs/{{version}}/crud-fluent-syntax)
+- [Generating Code](/docs/{{version}}/generating-code)
+- [FAQ](/docs/{{version}}/crud-how-to)
+
+#### Add-ons
+
+- [Official Add-ons](/docs/{{version}}/add-ons-official)
+- [Community Add-ons](https://backpackforlaravel.com/addons)
+- [How to Create an Add-on](/docs/{{version}}/add-ons-tutorial-using-the-addon-skeleton)
+- [How to Create a Theme](/docs/{{version}}/add-ons-tutorial-how-to-create-a-theme)
diff --git a/7.x-dev/install-optionals.md b/7.x-dev/install-optionals.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e297b5fb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/install-optionals.md
@@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
+# Install Optional Packages
+
+---
+
+Each Backpack package has its own installation instructions in its readme file. We duplicate them here for easy access.
+
+Everything else is optional. Your project might use them or it might not. Only do each of the following steps if you need the functionality that package provides.
+
+
+## BackupManager
+
+[>> See screenshots and installation](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/BackupManager)
+
+1) In your terminal
+
+```bash
+# Install the package
+composer require backpack/backupmanager
+
+# Publish the config file and lang files:
+php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Backpack\BackupManager\BackupManagerServiceProvider"
+
+# [optional] Add a menu item for it in resources/views/vendor/backpack/ui/inc/menu_items.blade.php:
+php artisan backpack:add-menu-content "
"
+```
+
+2) Add a new "disk" to config/filesystems.php:
+
+```php
+// used for Backpack/BackupManager
+'backups' => [
+ 'driver' => 'local',
+ 'root' => storage_path('backups'), // that's where your backups are stored by default: storage/backups
+],
+```
+This is where you choose a different driver if you want your backups to be stored somewhere else (S3, Dropbox, Google Drive, Box, etc).
+
+3) [optional] Modify your backup options in config/backup.php
+
+4) [optional] Instruct Laravel to run the backups automatically in your console kernel:
+
+```php
+// app/Console/Kernel.php
+
+protected function schedule(Schedule $schedule)
+{
+ $schedule->command('backup:clean')->daily()->at('04:00');
+ $schedule->command('backup:run')->daily()->at('05:00');
+}
+```
+
+5) [optional] If you need to change the path to the mysql_dump command, you can do that in your config/database.php file. For MAMP on Mac OS, add these to your mysql connection:
+```php
+'dump' => [
+ 'dump_binary_path' => '/Applications/MAMP/Library/bin/', // only the path, so without `mysqldump` or `pg_dump`
+ 'use_single_transaction',
+ 'timeout' => 60 * 5, // 5 minute timeout
+]
+```
+
+
+## LogManager
+
+[>> See screenshots and installation](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/logmanager)
+
+
+1) Install via composer:
+
+```bash
+composer require backpack/logmanager
+```
+
+2) Add a "storage" filesystem disk in config/filesystems.php:
+
+```php
+// used for Backpack/LogManager
+'storage' => [
+ 'driver' => 'local',
+ 'root' => storage_path(),
+],
+```
+
+3) Configure Laravel to create a new log file for every day, in your .ENV file, if it's not already. Otherwise there will only be one file at all times.
+
+```
+APP_LOG=daily
+```
+
+or directly in your config/app.php file:
+```php
+'log' => env('APP_LOG', 'daily'),
+```
+
+4) [optional] Add a menu item for it in resources/views/vendor/backpack/ui/inc/menu_items.blade.php:
+
+```bash
+php artisan backpack:add-menu-content "
"
+```
+
+## Settings
+
+An interface for the administrator to easily change application settings. Uses Laravel Backpack.
+
+[>> See screenshots and installation](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/settings)
+
+Installation:
+
+```bash
+# install the package
+composer require backpack/settings
+
+# run the migration
+php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Backpack\Settings\SettingsServiceProvider"
+php artisan migrate
+
+# [optional] add a menu item for it in resources/views/vendor/backpack/ui/inc/menu_items.blade.php:
+php artisan backpack:add-menu-content "
"
+
+# [optional] insert some example dummy data to the database
+php artisan db:seed --class="Backpack\Settings\database\seeds\SettingsTableSeeder"
+```
+
+
+## PageManager
+
+An admin panel where you, as a developer, can define templates with different fields, and the admin can choose between those templates to create/edit pages with content.
+
+[>> See screenshots and installation](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/pagemanager)
+
+
+## PermissionManager
+
+An admin panel for user authentication on Laravel 5, using Backpack\CRUD. Add, edit, delete users, roles and permission.
+
+[>> See screenshots and installation](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/PermissionManager)
+
+
+## MenuCrud
+
+An admin panel for menu items on Laravel 5, using Backpack\CRUD. Add, edit, reorder, nest, rename menu items and link them to Backpack\PageManager pages, external link or custom internal link.
+
+[>> GitHub](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/MenuCRUD)
+
+
+## NewsCrud
+
+Since NewsCRUD does not provide any extra functionality other than Backpack\CRUD, it is not a package. It's just a tutorial to show you how this can be achieved. In the future, CRUD examples like this one will be easily installed from the command line, from a central repository. Until then, you will need to manually create the files.
+
+[>> GitHub](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/NewsCRUD)
+
+
+
+## FileManager
+
+Backpack admin interface for files and folders, using [barryvdh/laravel-elfinder](https://github.com/barryvdh/laravel-elfinder).
+
+[>> See screenshots and installation](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/FileManager)
+
+Installation:
+
+```bash
+composer require backpack/filemanager
+```
+
+```bash
+php artisan backpack:filemanager:install
+```
diff --git a/7.x-dev/installation.md b/7.x-dev/installation.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8fc6859d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/installation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+# Installation
+
+---
+
+
+## Requirements
+
+If you can run Laravel 10 or 11, you can install Backpack. Backpack does _not_ have additional requirements.
+
+For the following process, we assume:
+
+- you have a [working installation of Laravel](https://laravel.com/docs/11.x#installation) (an existing project is fine, you don't need a *fresh* Laravel install);
+
+- you have configured your .ENV file with your database and mail information;
+
+- you can run the ```composer``` command from any directory (you have ```composer``` registered as a global command); if you need to run ```php composer.phar``` or reference another directory, please remember to adapt the commands below to your configuration;
+
+
+## Installation
+
+
+### Install using Composer
+
+Go to your Laravel project's directory, then in your terminal, run:
+
+``` bash
+composer require backpack/crud
+php artisan backpack:install
+```
+
+Follow the prompts - in the end, the installer will also tell you your admin panel's URL, where you should go and login.
+
+> **NOTE:** When the installer asks you if you would like to create an admin user, Backpack assumes that you are using the default user structure with `name, email and password` fields. If that's not the case, please reply **NO** to that question and manually create your admin user.
+
+> **NOTE:** The installation command is interactive - it will ask you questions. You can bypass the questions by adding the `--no-interaction` argument to the install command.
+
+### Configure
+
+In most cases, it's a good idea to look at the configuration files and make the admin panel your own:
+- You should change the config values in ```config/backpack/base.php``` to make the admin panel your own.
+- You can also change ```config/backpack/ui.php``` to change the UI; Backpack is white label, so you can change configs to make it your own: project name, logo, developer name etc.
+- By default all users are considered admins; If that's not what you want in your application (you have both users and admins), please:
+ - Change ```app/Http/Middleware/CheckIfAdmin.php```, particularly ```checkIfUserIsAdmin($user)```, to make sure you only allow admins to access the admin panel;
+ - Change ```app/Providers/RouteServiceProvider::HOME```, which will send logged in (but not admin) users to `/home`, to something that works for your app;
+- If your User model has been moved from the default ```App\Models\User.php```, please change ```config/backpack/base.php``` to use the correct user model under the ```user_model_fqn``` config key;
+
+### Create your Eloquent Models
+
+Backpack assumes you already have your Eloquent Models properly set up. If you don't, **consider using something to quickly generate Migrations & Models**. You can use anything you want, but here are the options we recommend:
+
+- a) Generate from a **web interface** - [Backpack Devtools](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools) - premium product, paid separately. A simple GUI to quickly generate Migrations, Models, Factories, Seeders and CRUDs, right from your browser. Works well for entities of all sizes.
+
+- b) Generate from the **command-line** - [Laracasts Generators](https://github.com/laracasts/Laravel-5-Generators-Extended) - free & open-source. Adds a new artisan command so that you can do `php artisan make:migration:schema create_users_table --schema="username:string, email:string:unique"`. Works well for smaller entities.
+
+- c) Generate from a **YAML file** - [LaravelShift's Blueprint](https://blueprint.laravelshift.com/) - free & open-source. Enables you to create a `draft.yml` file in your repo, where you can specify the column using their custom YAML syntax. Works well for small & medium entities.
+
+### Create your CRUDs
+
+For each Eloquent model you want to have an admin panel, run:
+
+```bash
+php artisan backpack:crud {model} # use the model name, in singular
+```
+
+Alternatively, you can generate CRUDs for all Eloquent models, by running:
+
+```bash
+php artisan backpack:build
+```
+
+Then go through each CRUD file (Controller, Request, Route Item, Menu Item) and customize as you fit. If you don't know what those are, and how you can customize them... please go through our [Getting Started](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/5.x/introduction#how-to-start) section, it's important. At the very least, read our [Crash Course](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/5.x/crud-tutorial).
+
+
+### Install Add-ons
+
+In case you want to add extra functionality that's already been built, check out [the installation steps for the add-ons we've developed](/docs/{{version}}/install-optionals).
+
+
+## Frequently Asked Questions
+
+- **Error: The process X exceeded the timeout of 60 seconds.** It might mean GitHub or Packagist is unavailable at the moment. This usually doesn't last for more than a few minutes, so you can run ```php artisan backpack:install --timeout=600``` to increase the timeout to 10 minutes. If this doesn't work either, take a look behind the scenes with ```php artisan backpack:install --timeout=600 --debug```;
+
+- **Error: SQLSTATE[42000]: Syntax error or access violation: 1071 Specified key was too long**. Your MySQL version might be a bit old. Please [apply this quick fix](https://laravel-news.com/laravel-5-4-key-too-long-error), then run ```php artisan migrate:fresh```.
+
+- **Any other installation error?** If you can't install Backpack because of a different error, you can [try the manual installation process](/docs/{{version}}/crud-how-to#how-to-manually-install-backpack), which you can tweak to your needs.
diff --git a/7.x-dev/introduction.md b/7.x-dev/introduction.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..02ca3170
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/introduction.md
@@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
+# Introduction
+
+---
+
+Backpack is a collection of Laravel packages that help you **build custom administration panels**, for anything from presentation websites to complex web applications. You can install them on top of existing Laravel installations _or_ fresh projects.
+
+In a nutshell:
+
+- UI - Backpack will provide you with a _visual interface_ for the admin panel (the HTML, the CSS, the JS), authentication functionality & global bubble notifications; you can choose from one of the 3 themes we have developed (powered by Tabler, CoreUI v4 or CoreUI v2), a third-party theme or create your own theme; the enormous advantage of using a Bootstrap-based HTML theme is that when you need custom pages, you already have the HTML blocks for the UI, you don't have to design them yourself;
+- CRUDs - Backpack will also help you build _sections where your admins can manipulate entries for Eloquent models_; we call them _CRUD Panels_ after the most basic operations: Create, Read, Update & Delete; after [understanding Backpack](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-basics), you'll be able to create a CRUD panel in a few minutes per model:
+
+
+
+If you already have your Eloquent models, generating Backpack CRUDs is as simple as:
+```bash
+# -------------------------------
+# For one specific Eloquent Model
+# -------------------------------
+# Create a Model, Request, Controller, Route and sidebar item, so
+# that one Eloquent model you specify has an admin panel.
+
+php artisan backpack:crud tag # use singular, not plural (like the Model name)
+
+# -----------------------
+# For all Eloquent Models
+# -----------------------
+# Create a Model, Request, Controller, Route and sidebar item for
+# all Eloquent models that don't already have one.
+
+php artisan backpack:build
+```
+
+If you have NOT created your Eloquent models yet, you can use whatever you want for that. We recommend:
+- FREE - [`laravel-shift/blueprint`](https://github.com/laravel-shift/blueprint) as the best **YAML-based tool** for this;
+- PAID - [`backpack/devtools`](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/devtools) as the best **web interface** for this; it makes it dead simple to create Eloquent models, from the comfort of your web browser;
+
+---
+
+
+## How to Start
+
+We heavily recommend you spend a little time to understand Backpack, and only afterwards install and use it. Fortunately, it's super simple to get started. Using any of the options below will get you to a point where you can use Backpack in your projects:
+- **[Video Course](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-videos)** - 59 minutes
+- **[Text Course](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-basics)** - 20 minutes
+
+
+
+
Video Course
+
Text Course
+
+---
+
+
+## Need to Know
+
+
+### Requirements
+
+ - Laravel 10.x or 11.x
+ - MySQL / PostgreSQL / SQLite / SQL Server
+
+
+### How does it look?
+
+**Take a look at our [live demo](https://demo.backpackforlaravel.com/admin/login).** If you've purchased ["Everything"](https://backpackforlaravel.com/pricing) you can even [install the demo](/docs/{{version}}/demo) and fiddle with the code. Otherwise, you can just start a new Laravel project, [install Backpack\CRUD](/docs/{{version}}/installation) on top, and [follow our text course](/docs/{{version}}/getting-started-basics) to create a few CRUDs.
+
+
+### Security
+
+Backpack has never had a critical vulnerability/hack. But there _have_ been important security updates for dependencies (including Laravel). Please [register using Github](/auth/github) or [subscribe to our twice-a-year newsletter](https://backpackforlaravel.com/newsletter), so we can reach you in case your admin panel becomes vulnerable in any way.
+
+
+### Maintenance
+
+Backpack v6 is the current version and is actively maintained by the Backpack team, with the help of a wonderful community of Backpack veterans. [See all contributors](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/CRUD/graphs/contributors).
+
+
+### License
+
+Backpack is open-core:
+- **Backpack CRUD is free & open-source, licensed under the [MIT License](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/CRUD/blob/main/LICENSE.md)**; it is perfect if you're building a simple admin panel - it's packed with features! it's also perfect if you're building an open-source project, the permissive license allows you to do whatever you want;
+- **Backpack PRO is a paid, closed-source add-on, licensed under our [EULA](https://backpackforlaravel.com/eula)**; [PRO](https://backpackforlaravel.com/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects) adds additional functionality to CRUD, that will be useful when your admin panel grows (see our [FREE vs PRO comparison](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/6.x/features-free-vs-paid));
+- Of the other add-ons we've created, some are FREE and some are PAID; please see [our add-ons list](https://backpackforlaravel.test/docs/6.x/add-ons-official) for more info;
+
+[Our documentation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs) covers both CRUD and PRO, with all the PRO features clearly labeled
PRO.
+
+
+
+### Versioning, Updates and Upgrades
+
+Starting with the previous version, all our packages follow [semantic versioning](https://semver.org/). Here's what `major.minor.patch` (e.g. `7.0.1`) means for us:
+- `major` - breaking changes, major new features, complete rewrites; released **once a year**, in February; it adds features that were previously impossible and upgrades our dependencies; upgrading is done by following our clear and detailed upgrade guides;
+- `minor` - new features, released in backwards-compatible ways; **every few months**; update takes seconds;
+- `patch` - bug fixes & small non-breaking changes; historically **every week**; update takes seconds;
+
+When we release a new Backpack\CRUD version, all paid add-ons receive support for it the same day.
+
+When you buy a premium Backpack add-on, you get access to not only _updates_, but also _upgrades_ (for 12 months), that means that **any time you buy a Backpack add-on, it is very likely that you're not only buying the _current_ version** (`v7` at the moment), **but also the upgrade to the _next version_** (`v8` for example).
+
+
+### Add-ons
+
+Backpack's core is open-source and free (Backpack\CRUD).
FREE
+
+The reason we've been able to build and maintain Backpack since 2016 is that Laravel professionals have supported us, by buying our paid products. As of 2022, these are all Backpack add-ons, which we highly recommend:
+- [Backpack PRO](/products/pro-for-unlimited-projects) - a crazy amount of added features;
PAID
+- [Backpack DevTools](/products/devtools) - a developer UI for generating migrations, models and CRUDs;
PAID
+- [Backpack FigmaTemplate](/products/figma-template) - quickly create designs and mockups, using Backpack's design;
PAID
+- [Backpack EditableColumns](/products/editable-columns) - let your admins do quick edits, right in the table view;
PAID
+
+
+In addition to our open-source core and our closed-source add-ons, there are a few other add-ons you might want to take a look at, that treat common use cases. Some have been developed by our core team, some by our wonderful community. You can just install interfaces to manage [site-wide settings](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/Settings), [the default Laravel users table](https://github.com/eduardoarandah/UserManager), [users, groups & permissions](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/PermissionManager), [content for custom pages, using page templates](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/PageManager), [news articles, categories and tags](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/NewsCRUD), etc.
FREE
+
+For more information, please see [our add-ons page](/addons).
diff --git a/7.x-dev/release-notes.md b/7.x-dev/release-notes.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3df11af9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/release-notes.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+# Release Notes
+
+---
+
+**Planned launch date:** Dec 4th, 2024
+
+For the past 2 years, we've done our very best to make all changes to Backpack in a backwards-compatible way. To not push a new version, because we know it's a pain in the bee's hind to upgrade stuff. But... it's time for a new release. Have no fear though, we've made this super easy for you.
+
+Backpack v7 is a maintenance release. Yes, it does have a few breaking changes, but they will not impact 99.9% of projects. But that doesn't mean you shouldn't follow the upgrade guide! Please do - read it from top to bottom and make sure none of the changes impact you.
+
+Here are the BIG things Backpack v7 brings to the table and why you should upgrade from [Backpack v6](/docs/6.x) to v7. But first... we should give credit where credit is due. **Big BIG thanks to**:
+- **[Pedro Martins](https://github.com/pxpm)** for x;
+- **[Jorge Castro](https://github.com/jcastroa87)** for y;
+- **[Karan Datwani](https://github.com/karandatwani92)** for z;
+- **[Cristian Tabacitu](https://github.com/tabacitu)** for t;
+- **our paying customers**, who have made all of this possible by supporting our work 🙏
+
+Together, our team has put in an incredible amount of work to make v7 what it is - more than XXX commits, across YYY months, all while still maintaining, bug fixing and improving v6. Again, big thanks to everybody who has helped made this happen 🙏
+
+
+## Added
+
+### CRUD Lifecycle Hooks
+
+// TODO
+
+### Two-Factor Authentication
+
+// TODO
+
+### Re-Usable Filters
+
+// just like your air purifier
+// TODO
+
+### Browser Tests
+
+// TODO
+
+
+
+## Changed
+
+### Uploaders
+
+// TODO
+
+### Moved TinyMCE and CKEditor fields & columns
+
+// TODO
+
+### Basset
+
+// TODO
+
+### Parent Theme
+
+// TODO
+
+
+## Removed
+
+- Support for Laravel 10?! 👀
+- Support for PHP lower than 8.2?
+
+---
+
+If you like what you see, please help us out - share what you like on social media or tell a friend. To get all of the features above (and a lot more), please [follow the upgrade guide](/docs/{{version}}/upgrade-guide).
diff --git a/7.x-dev/theme-tabler.md b/7.x-dev/theme-tabler.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f3e9dcab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/theme-tabler.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+# Theme Tabler
+
+
+### About
+
+For more information about installation and/or configuration steps, see [backpack/theme-tabler](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/theme-tabler) on Github.
+
+
+## Components
+
+
+### Menu Dropdown Column
+
+In addition to regular menu components provided by Backpack [Menu Dropdown and Menu Dropdown Item](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/base-components#menu-dropdown-and-menu-dropdown-item), Tabler theme provides this new component which is used to create side by side menus on horizontal layouts.
+
+#### Requirements
+- Require `Backpack/CRUD:6.6.4` or higher
+- Require `Backpack/theme-tabler:1.2.1` or higher
+
+#### Usage
+In your parent dropdown item, enable the feature by setting `:withColumns="true"` and then use `x-theme-tabler::menu-dropdown-column` component to wrap each set of menu items. See the example below:
+
+```html
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+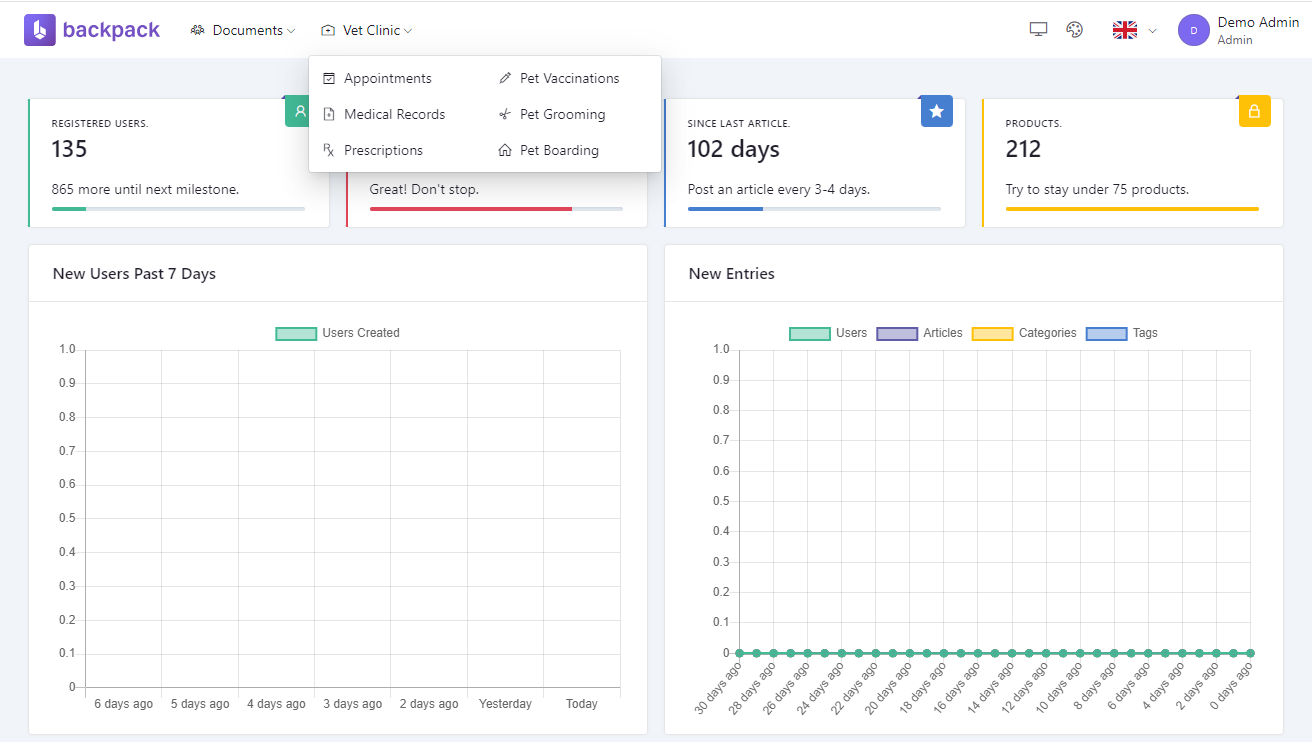
diff --git a/7.x-dev/themes/theme-tabler.md b/7.x-dev/themes/theme-tabler.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..943e68ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/themes/theme-tabler.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+# Theme Tabler
+
+
+### About
+
+For more information about installation and/or configuration steps, see [`backpack/theme-tabler`](https://github.com/Laravel-Backpack/theme-tabler) on Github.
+
+
+## Components
+
+
+### View Components
+
+`MenuDropdownMenu` - In addition to regular menu components provided by backpack [Menu Dropdown and Menu Dropdown Item](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/base-components#menu-dropdown-and-menu-dropdown-item), Tabler theme provides a new component `Menu Dropdown Menu` which is used to create side by side menus on horizontal layouts.
+> Backpack/CRUD `v6.6.4` or higher.
+> Backpack/theme-tabler `v1.2.1` or higher
+
+
+
+```html
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
diff --git a/7.x-dev/tutorials.md b/7.x-dev/tutorials.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0b144afc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/tutorials.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+# Tutorials for the admin UI
+
+---
+
+
+## Tutorials
+- [How to create an AJAX Operation with Quick Button.](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-create-an-ajax-operation-with-quick-button)
+- [Edit Laravel Translations from Your Admin Panel.](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-addon-edit-laravel-translations-from-your-admin-panel)
+- [Language switcher UI for your Laravel App](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/language-switcher-ui-for-your-laravel-app)
+- [Set a larger layout for your large set of menu items.](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-in-v6-a-larger-layout-for-your-large-set-of-menu-items)
+- [Setup Calendar view on your Laravel projects](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-in-v6-setup-calendar-view-on-your-laravel-projects)
+- [How to setup multiple views on List operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-in-v6-how-to-setup-multiple-views-on-list-operation)
+- [How to access CRUD fields via javascript to manipulate Form](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-access-crud-fields-via-javascript-to-manipulate-form)
+- [How to configure User Access Control and Permissions in 10 minutes](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/guide-on-access-control-for-your-admin-panel)
+- [Granular User Access, using Custom Closures](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-in-v6-granular-user-access-using-custom-closures)
+- [Excel Imports for Backpack!](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/cheers-to-lewis-and-excel-imports-for-backpack)
+- [How to Build an Image Slider CRUD - Backpack Basics](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-build-an-image-slider-crud-backpack-basics)
+- [How I created a custom “webcam” field for Backpack.](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-i-created-a-custom-webcam-field-for-backpack)
+- [How to create a Trash/Deleted section in Backpack CRUD](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-create-a-trash-deleted-section-in-backpack-crud)
+- [How to build a theme-picker for Backpack admin panel.](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-build-a-theme-picker-for-backpack-admin-panel)
+- [How to make custom JavaScript work with Backpack's List Operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-make-custom-javascript-work-with-backpack-s-list-operation)
+- [Easy Column Links using linkTo()](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/easy-column-links-using-linkto)
+- [CSS Hooks - Easy CSS Customization for Your Backpack CRUD Panels](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/css-hooks-easy-css-customization-for-your-backpack-crud-panels)
+- [How to use Spatie Media Library in Backpack](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-in-v6-how-to-use-spatie-media-library-in-backpack)
+- [How to change layout for panel & auth views](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-in-v6-how-to-change-layout-for-panel-auth-views)
+- [How to enable dark-mode on Backpack.](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-in-v6-how-to-enable-dark-mode-on-backpack)
+- [How to create your own custom theme to Backpack v6](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-in-v6-how-to-create-your-own-custom-theme-to-backpack-v6)
+- [How to change themes in Backpack v6](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-in-v6-how-to-change-themes-in-backpack-v6)
+- [How to add custom sections to CRUD tables and forms](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-add-custom-sections-to-crud-tables-and-forms)
+- [How to create a custom operation that uses Backpack fields](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-create-a-custom-operation-that-uses-backpack-fields)
+- [How to create a Backpack add-on with a custom Operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-create-a-backpack-add-on-with-a-custom-operation)
+- [How to use a custom operation inside PermissionManager](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-use-a-custom-operation-inside-permissionmanager)
+- [How to create a custom operation with a form](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-create-a-custom-operation-with-a-form)
+- [Editable Columns](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/new-addon-editable-columns)
+- [How to create a Print operation](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-create-a-print-operation)
+- [How to Add Impersonate Functionality to Your Backpack v4 Admin Panel](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/how-to-add-impersonate-functionality-to-your-admin-panel)
+- [Nested resources in Backpack CRUD](https://backpackforlaravel.com/articles/tutorials/nested-resources-in-backpack-crud)
+
+
+
+## Submit Your Tutorial
+
+We are always excited to see new contributions from our community. If you have created a tutorial that you think would benefit others, we'd love to hear about it!
+
+To submit your tutorial:
+
+1. Make sure your tutorial is well-documented and easy to follow.
+2. It includes clear, practical examples and relevant code snippets.
+3. Include screenshots or video to the tutorial if applicable for better understanding.
+4. Send your tutorial to hello@backpackforlaravel.com with the subject line "Tutorial Submission".
+
+We will review your submission and get back to you as soon as possible. Thank you for helping us build a robust resource for the Backpack for Laravel community!
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/7.x-dev/upgrade-guide.md b/7.x-dev/upgrade-guide.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..00ee27a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/7.x-dev/upgrade-guide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+# Upgrade Guide
+
+---
+
+This will guide you to upgrade from Backpack v6 to v7. The steps are color-coded by the probability that you will need it for your application:
High,
Medium and
Low. **At the very least, please read what's in bold**.
+
+
+## Requirements
+
+Please make sure your project respects the requirements below, before you start the upgrade process. You can check with ```php artisan backpack:version```:
+
+- PHP 8.1+
+- Laravel 11.x
+- Backpack\CRUD 6.x
+- 5-10 minutes (for most projects)
+
+**If you're running Backpack version 3.x-5.x, please follow ALL other upgrade guides first, to incrementally get to use Backpack v6**. Test that your app works well with each version, after each upgrade. Only _afterwards_ can you follow this guide, to upgrade from v5 to v6. Previous upgrade guides:
+- [upgrade from 5.x to 6.x](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/6.x/upgrade-guide);
+- [upgrade from 4.1 to 5.x](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/5.x/upgrade-guide);
+- [upgrade from 4.0 to 4.1](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/4.1/upgrade-guide);
+- [upgrade from 3.6 to 4.0](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/4.0/upgrade-guide);
+- [upgrade from 3.5 to 3.6](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/3.6/upgrade-guide);
+- [upgrade from 3.4 to 3.5](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/3.5/upgrade-guide);
+- [upgrade from 3.3 to 3.4](https://backpackforlaravel.com/docs/3.4/upgrade-guide);
+
+
+## Upgrade Steps
+
+
Step 0. **[Upgrade to Laravel 11](https://laravel.com/docs/11.x/upgrade) if you don't use it yet, then test to confirm your app is working fine.**
+
+
+### Composer
+
+
Step 1. Update your ```composer.json``` file to require:
+
+```
+ "backpack/crud": "v7-dev",
+```
+
+
Step 2. Bump the version of any first-party Backpack add-ons you have installed (eg. `backpack/pro`, `backpack/editable-columns` etc.) to the versions that support Backpack v6. For 3rd-party add-ons, please check each add-on's Github page. Here's a quick list of 1st party packages and versions:
+
+```js
+ "backpack/crud": "v7-dev",
+ "backpack/pro": "v3-dev",
+ "backpack/filemanager": "^3.0",
+ "backpack/theme-coreuiv2": "^1.0",
+ "backpack/theme-coreuiv4": "^1.0",
+ "backpack/theme-tabler": "^1.0",
+ "backpack/logmanager": "^5.0",
+ "backpack/settings": "^3.1",
+ "backpack/newscrud": "^5.0",
+ "backpack/permissionmanager": "^7.0",
+ "backpack/pagemanager": "^3.2",
+ "backpack/menucrud": "^4.0",
+ "backpack/backupmanager": "^5.0",
+ "backpack/editable-columns": "^3.0",
+ "backpack/revise-operation": "^2.0",
+ "backpack/medialibrary-uploaders": "^1.0",
+ "backpack/devtools": "^2.0",
+```
+
+
Step 3. Let's get the latest Backpack and install it. If you get any conflicts with **Backpack 1st party add-ons**, most of the time you just need to move one version up, eg: from `backpack/menucrud: ^3.0` to `backpack/menucrud: ^4.0`. See the step above again. Please run:
+
+```bash
+composer update
+
+# before calling the next command make sure you have no pending migrations with `php artisan migrate:status`
+# and that your webserver is running and accessible in the URL you defined in .env `APP_URL`.
+php artisan backpack:upgrade
+```
+
+// TODO: actually create an upgrade command that does only the things we need from the `install` command.
+
+
+### Models
+
+No changes needed.
+
+
+### Form Requests
+
+No changes needed.
+
+
+### Routes
+
+No changes needed.
+
+
+### Config
+
+No changes needed.
+
+
+### CrudControllers
+
+No changes needed.
+
+
+### CSS & JS Assets
+
+No changes needed.
+
+
+### Views
+
+No changes needed.
+
+
+### Security
+
+No changes needed.
+
+
+### Cache
+
+
Step xx. Clear your app's cache:
+```
+php artisan config:clear
+php artisan cache:clear
+php artisan view:clear
+```
+
+If the table view still looks wonky (search bar out of place, big + instead of ellipsis), then do a hard-reload in your browser (Cmd+Shift+R or Ctrl+Shift+F5) to purge the browser cache too.
+
+---
+
+
Step yy. If your pages are slow to load, that's because Basset caching the assets as you load the pages, so your first pageload will be quite slow. If you find that annoying, run `php artisan basset:cache` to cache all CSS and JS assets. Alternatively, if you want Basset NOT to run because you're making changes to CSS and JS files, you can add `BASSET_DEV_MODE=true` to your `.ENV` file.
+
+---
+
+
+### Upgrade Add-ons
+
+For any addons you might have upgraded, please double-check if they have an upgrade guide. For example:
+- Xx package has the upgrade guide here;
+- Yy package has the upgrade guide here;
+
+---
+
+**You're done! Good job.** Thank you for taking the time to upgrade. Now you can:
+- thoroughly test your application and your admin panel;
+- start using the [new features in Backpack v7](/docs/{{version}}/release-notes);