-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
Datasets
This document describes the data used by the Linköping GraphQL Benchmark (LinGBM).
LinGBM is based on a scalable synthetic dataset that can be generated in an unlimited number of different sizes. Instead of designing a new dataset generator from scratch, LinGBM uses the dataset generator of the Berlin SPARQL Benchmark (BSBM). However, for LinGBM it was necessary to develop a slightly extended version of this dataset generator.
The generated data can be created in the form of an SQL database or an RDF graph. While the RDF versions can be written in several RDF serialization formats, the SQL-database versions are written as an SQL dump file that can be imported by a MySQL server.
In the remainder of this document we provide i) an Entity-Relationship diagram that models the scenario captured by the benchmark datasets, ii) the corresponding relational schema of the SQL-database version of the benchmark datasets, and iii) an overview of the average cardinalities of the relationships in the generated data. For more details regarding the datasets and the dataset generator we refer to the BSBM Dataset Specification.
The generated benchmark datasets capture a fictitious e-commerce scenario with products that have a type, a producer, and a number of different features. Moreover, for each product, there are offers by different vendors and reviews by different persons. Overall, the captured scenario consists of nine types of entities and eight types of relationships between such entities. The following Entity-Relationship diagram illustrates these entity types and relationship types.
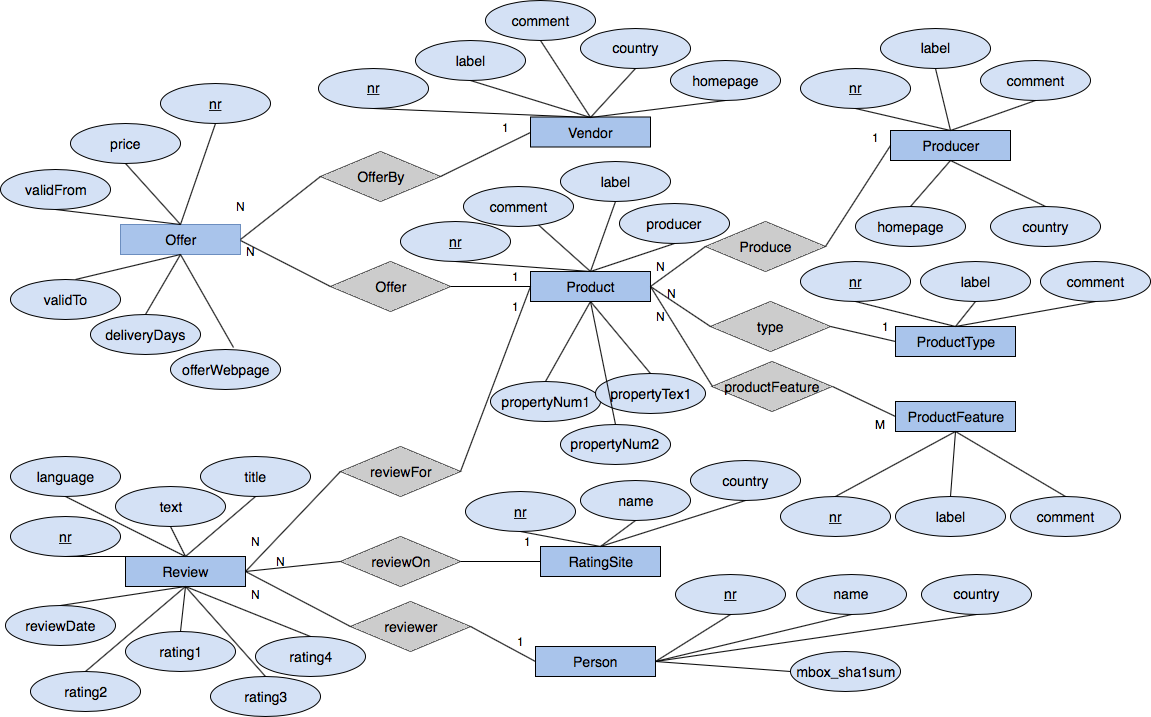
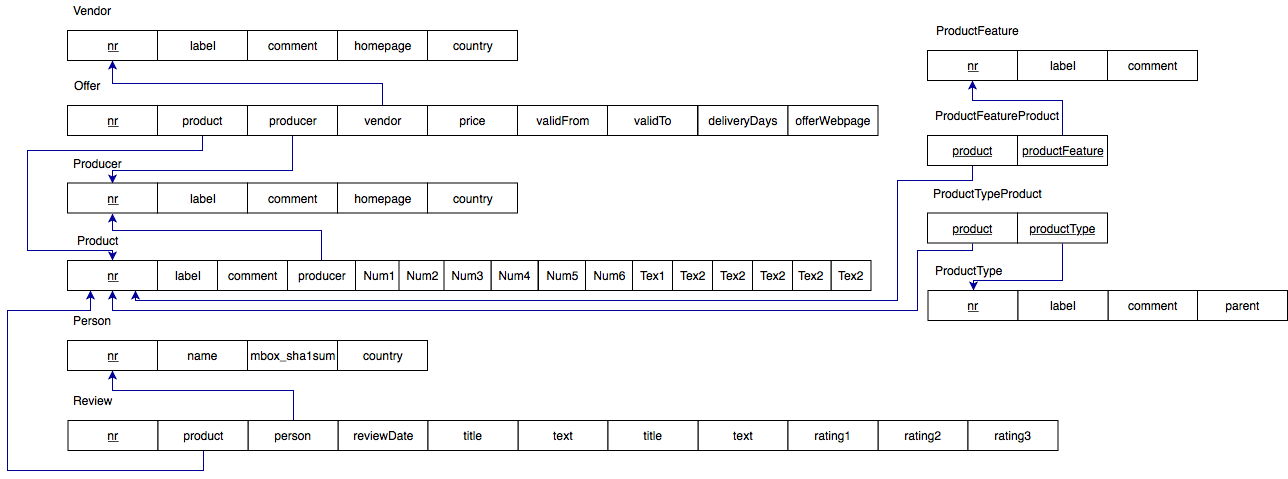
The relational schema of the SQL-database version of the benchmark datasets consists of the following 10 relations/tables (where the underlined attributes belong to the primary key of the corresponding relation).
Vendor (nr, label, comment, homepage, country)
Offer (nr, product, producer, vendor, price, validFrom, validTo, deliveryDays, offerWebpage)
Producer (nr, label, comment, homepage, country)
Product (nr, label, comment, producer, propertyNum1, propertyNum2, propertyNum3, propertyNum4, propertyNum5, propertyNum6, propertyTex1, propertyTex2, propertyTex3, propertyTex4, propertyTex5, propertyTex6)
Person (nr, name, mbox_sha1sum, country)
Review (nr, product, producer, person, reviewDate, title, text, language, rating1, rating2, rating3, rating4, publisher)
ProductFeature (nr, label, comment)
ProductType (nr, label, comment, parent)
ProductTypeProduct (product, productType)
ProductFeatureProduct (product, productFeature)
The following diagram provides a visual illustration of the relational schema, including the referential integrity constraints (foreign keys) between the tables.
The following table provides an overview of the average cardinalities of the relationships in the generated data. For more details, refer to the rules for scaling and dataset population of the BSBM Dataset Specification.
| Relationship | cardinalities | note |
|---|---|---|
| Producer-Product | 1:N | One producer per product; on average 50 products per producer |
| Product-Review | 1:N | One product per review; on average 10 reviews per product (selection follows a normal distribution) |
| Product-Offer | 1:N | One product per offer; on average 20 offers per product (selection follows a normal distribution) |
| Person-Review | 1:N | One author per review; on average 20 reviews per person |
| Ratingsite-Review | 1:N | One rating site per review; on average 10,000 reviews per rating site |
| Vendors-Offers | 1:N | One vendor per offer; on average 2,000 offers per vendor |
| Product-ProductType | N:1 | one product type per product (leaves of the product type hierarchy only) |
| Product-ProductFeature | M:N | 10-20 features per product |