diff --git a/content/en/overview/quick_start/overview.md b/content/en/overview/quick_start/overview.md
index 05f2a5a..679b7ef 100644
--- a/content/en/overview/quick_start/overview.md
+++ b/content/en/overview/quick_start/overview.md
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ When building applications with large models, a common problem is: **How can AI
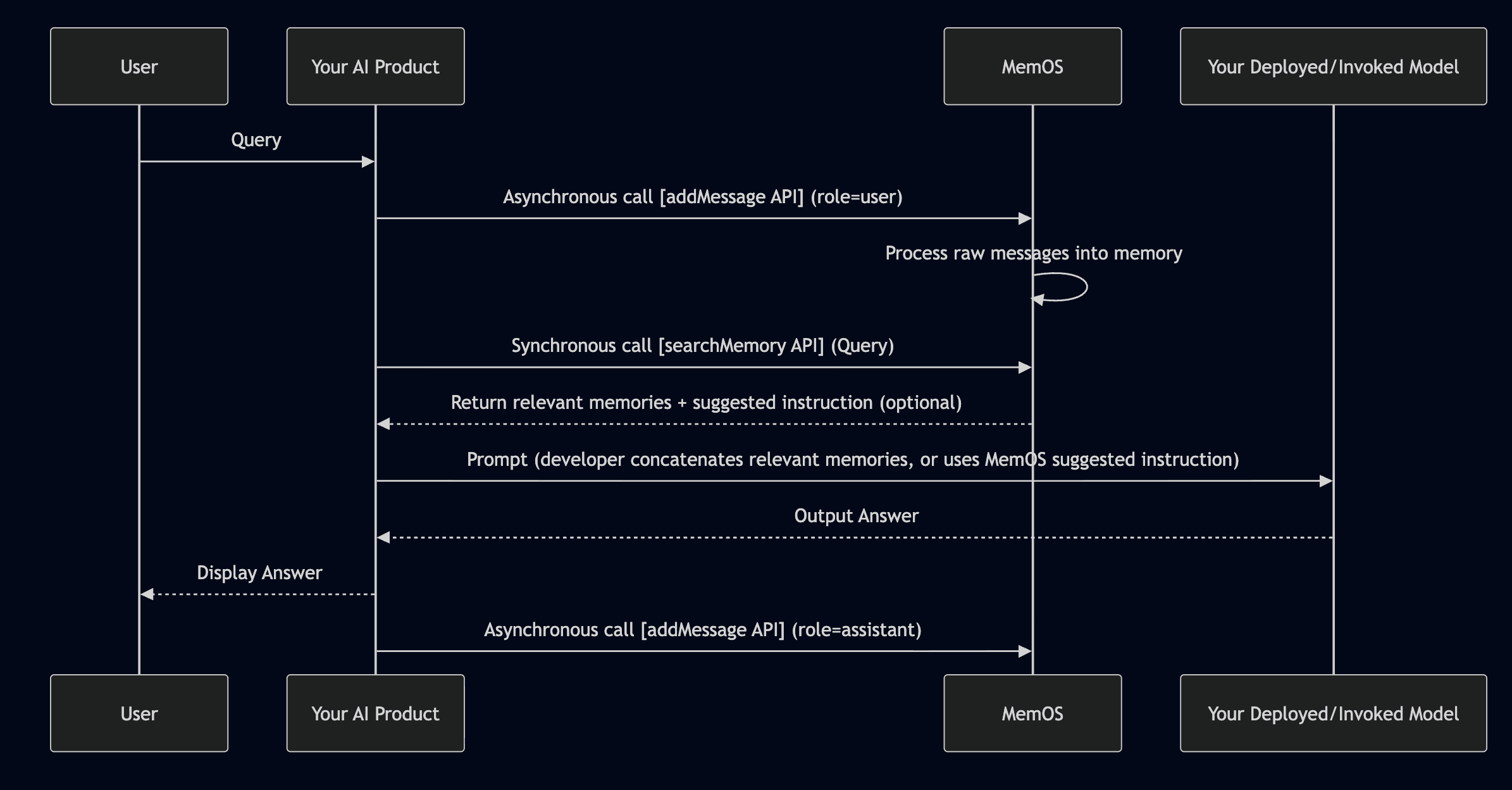
MemOS provides two core APIs to help you achieve this:
- `addMessage` — Submit raw conversations to us, we automatically process and store them as memory
-- `searchMemory` — Recall relevant memories and optional suggested instructions in subsequent conversations, making AI responses more aligned with user needs
+- `searchMemory` — Recall factual memories and preference memories in subsequent conversations, so that the AI's responses are more aligned with the user's needs
@@ -50,17 +50,16 @@ import os
import requests
import json
+# Replace with your MemOS API Key
os.environ["MEMOS_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
os.environ["MEMOS_BASE_URL"] = "https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1"
data = {
"messages": [
- {"role": "user", "content": "I want to travel during summer vacation, can you recommend something?"},
- {"role": "assistant", "content": "Sure! Are you traveling alone or with family/friends?"},
- {"role": "user", "content": "Of course I’m bringing my kid, our family always travels together."},
- {"role": "assistant", "content": "Got it, so you’re traveling with your children as a family, right?"},
- {"role": "user", "content": "Yes, with both kids and elderly, we usually travel as a whole family."},
- {"role": "assistant", "content": "Understood, I’ll recommend destinations suitable for family trips."}
+ {"role": "user", "content": "I’ve planned to travel to Guangzhou this summer. What chain hotels are available for accommodation?"},
+ {"role": "assistant", "content": "You can consider options like 7 Days Inn, All Seasons, Hilton, etc."},
+ {"role": "user", "content": "I’ll choose 7 Days Inn."},
+ {"role": "assistant", "content": "Alright, feel free to ask me if you have any other questions."}
],
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"conversation_id": "0610"
@@ -83,17 +82,9 @@ print(res.json())
::note
**Conversation B: occurred on 2025-09-28**
-In a new conversation, when the user asks AI to recommend a National Day trip plan, MemOS automatically recalls relevant memories for AI reference, enabling more personalized recommendations.
+When the user asks in a new session for National Day travel and hotel recommendations, MemOS automatically recalls factual (where they’ve been) and preference memories (hotel choices) to help the AI give more personalized suggestions.
::
-> MemOS supports returning **`related memories (matches)`**, **`stitched instructions (instruction)` (coming soon)**, and **`full instructions (full_instruction)` (coming soon)** simultaneously. In practice, you only need to choose one based on your business needs.
-
-> - **Need full control** → use **matches**, only returns memory items, developers manually stitch them into instructions;
-> - **Want to save stitching work, but still need to add business rules** → use **instruction**, system has combined memories and user query into semi-finished instructions, developers can further refine them;
-> - **Pursue one-click direct use** → use **full_instruction**, system has generated complete terminal instructions ready to be sent to the model.
-
-> **Why this design**: Most memory systems stop at “recalling facts”, but facts ≠ executable Prompts. MemOS’s unique instruction completion chain saves you from complex stitching and fine-tuning, directly converting memories into model-readable and executable prompts.
-
```python
import os
import requests
@@ -103,16 +94,12 @@ os.environ["MEMOS_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
os.environ["MEMOS_BASE_URL"] = "https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1"
data = {
- "user_id": "memos_user_123",
- "conversation_id": "0928",
- "query": "Where to go for National Day travel?",
- "memory_limit_number": 6 # Optional, default is 6 if not provided
-
- # ==== Coming Soon ====
- # The following parameters will be supported in future versions, please do not pass them now
- # "return_matches": True,
- # "return_instruction": True,
- # "return_full_instruction": True
+ "user_id": "memos_user_123",
+ "conversation_id": "0928",
+ "query": "I want to travel during the National Day holiday. Please recommend a city I haven’t been to and a hotel brand I haven’t stayed at.",
+ "memory_limit_number": 6, # Fact memory limit — if not provided, default is 6
+ "include_preference":True, # Return preference memories — if not provided, defaults to enabled
+ "preference_limit_number":6 # Preference memory limit — if not provided, default is 6
}
headers = {
@@ -123,35 +110,34 @@ url = f"{os.environ['MEMOS_BASE_URL']}/search/memory"
res = requests.post(url=url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
-# Mode 1: Related Memories (matches)
print(f"result: {res.json()}")
-# Example output(simplified here for easier understanding, for reference only):
-# [
-# {
-# "memory_key": "Travel Habit",
-# "memory_value": "Travel with whole family (including kids and elderly)",
-# "confidence": 0.97,
-# "update_time": "2025-06-10T10:00:00Z"
-# }
-# ]
-
-# Mode 2 (coming soon): Stitched Instruction (semi-finished, structured, easy for further processing)
-# print("Instruction:", results["data"]["instruction"])
-# Example output:
-# Task: Answer user’s “Where to go for National Day travel?”
-# Audience: Family trip (including kids and elderly)
-# Requirements:
-# - Explicitly consider the needs of children and elderly in the response
-# - Destination suggestions must align with “family-friendly”
-# Notes: If key information is missing (departure, budget, duration), add clarification strategies via business logic
-
-# Mode 3 (coming soon): Full Instruction (terminal form, can be directly sent to model)
-# print("Full Instruction:", results["data"]["full_instruction"])
-# Example output:
-# You are a travel consultant.
-# The user always travels with their whole family (including kids and elderly).
-# Directly answer “Where to go for National Day travel?” and prioritize family-friendly destinations.
-# If information is insufficient, first ask clarification questions before giving suggestions.
+
+# Example output (simplified for easier understanding, for reference only)
+
+# Preference Memory
+# preference_detail_list [
+# {
+# "preference_type": "implicit_preference",
+# "preference": "Preference for budget-friendly accommodations.",
+# "reasoning": "The user's choice of 7 Days Inn over other options like Hilton suggests a potential preference for more budget-friendly accommodations. 7 Days Inn is known for being an economical option compared to Hilton, which is a higher-end hotel chain. This choice indicates that the user might prioritize cost-effectiveness in their accommodation decisions.",
+# "conversation_id": "0610"
+# }
+# ]
+
+# Fact Memory
+# memory_detail_list [
+# {
+# "memory_key": "Summer travel plans to Guangzhou",
+# "memory_value": "The user has planned to travel to Guangzhou during the summer of 2024 and has chosen to stay at 7 Days Inn for accommodation.",
+# "conversation_id": "0610",
+# "tags": [
+# "travel",
+# "Guangzhou",
+# "accommodation",
+# "hotel choice"
+# ]
+# }
+# ]
```
## 2. Option Two: Open-source Framework
@@ -170,13 +156,13 @@ Here we will explain in detail **how a message entering the system is processed
::note
**Deep Understanding**
-MemOS’s memory mechanism can be understood as a complete “workflow”:
-You submit raw messages → Processed into memory → Scheduling mechanism arranges invocation and storage based on task and context, and dynamically adjusts memory forms → Relevant memories are recalled when needed and injected as context or instructions → Lifecycle management ensures evolution and updates.
+MemOS’s memory mechanism works like a complete “workflow”:
+You send a message → the system processes it into memory → the scheduler decides when to store or use it based on context and tasks, and can adjust its form → related memories are recalled when needed → meanwhile, lifecycle management keeps them evolving and updated.
::
- [Memory Production](/overview/quick_start/mem_production)
- [Memory Scheduling](/overview/quick_start/mem_schedule)
-- [Memory Recall & Instruction Completion](/overview/quick_start/mem_recall)
+- [Memory Recall](/overview/quick_start/mem_recall)
- [Memory Lifecycle Management](/overview/quick_start/mem_lifecycle)
### 3.2 Practice with MemOS