-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 100
Capturing AFP network traffic
You can use a nice program called CocoaPacketAnalyzer in order to capture AFP network traffic.
Download and extract the program from the above link.
Start it.
Press “Capturing”.
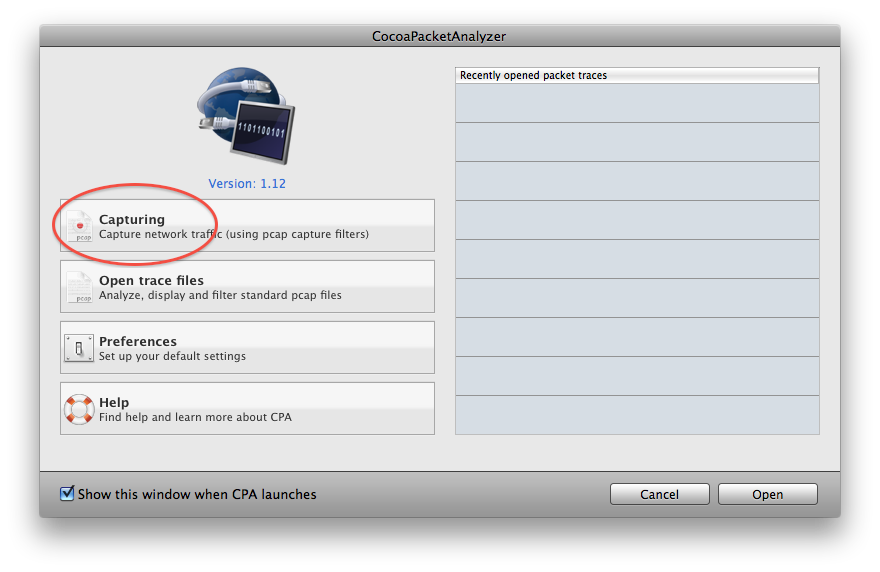
In the dialog window that opens, choose the active network interface. The first time, you may be asked to scan for interfaces.
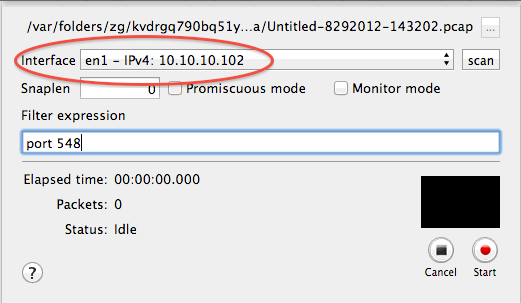
Enter “port 548” as the filter expression.
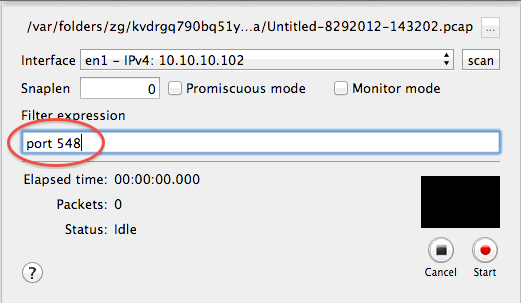
When ready to do the actual trace, press “start.” When done with the trace, press “stop.” Minimize activities on the AFP volume and perform only necessary actions.
Finally, choose “Save” from the “File” menu to save the trace to a file.
Editor's note: Use the application that you download from the above link, rather than the one available in the App Store. The latter can only analyze pcap logs, and not capture them.
Another useful thing only available in Terminal with tcpdump is using a ringbuffer:
# tcpdump -s 0 -w afp.pcap -C 10 -W 2 port 548This limits the captured data to two capture files (-W 2) with a size of 10 MB each (-C 10). This way for large amount of AFP traffic, only the last 10-20 MB will be saved and available for analysis.
Author
Ralph Böhme
Published on
August 29, 2012
Resources
- Getting Started
- FAQ
- Troubleshooting
- Connect to AFP Server
- Webmin Module
- Benchmarks
- Interoperability with Samba
OS Specific Guides
- Installing Netatalk on Alpine Linux
- Installing Netatalk on Debian Linux
- Installing Netatalk on Fedora Linux
- Installing Netatalk on FreeBSD
- Installing Netatalk on macOS
- Installing Netatalk on NetBSD
- Installing Netatalk on OmniOS
- Installing Netatalk on OpenBSD
- Installing Netatalk on OpenIndiana
- Installing Netatalk on openSUSE
- Installing Netatalk on Solaris
- Installing Netatalk on Ubuntu
Tech Notes
- Kerberos
- Special Files and Folders
- Spotlight
- MySQL CNID Backend
- Slow AFP read performance
- Limiting Time Machine volumes
- Netatalk and ZFS nbmand property
Retro AFP
Development