|
1 | 1 | # optillm |
2 | 2 |
|
3 | | -optillm is an OpenAI API compatible optimizing inference proxy which implements several state-of-the-art techniques that can improve the accuracy and performance of LLMs, including [CePO](https://github.com/codelion/optillm?tab=readme-ov-file#the-cerebras-planning-and-optimization-cepo-method). The current focus is on implementing techniques that improve reasoning over coding, logical and mathematical queries. It is possible to beat the frontier models using these techniques across diverse tasks by doing additional compute at inference time. |
| 3 | +optillm is an OpenAI API compatible optimizing inference proxy which implements several state-of-the-art techniques that can improve the accuracy and performance of LLMs. The current focus is on implementing techniques that improve reasoning over coding, logical and mathematical queries. It is possible to beat the frontier models using these techniques across diverse tasks by doing additional compute at inference time. |
4 | 4 |
|
5 | 5 | [](https://huggingface.co/spaces/codelion/optillm) |
6 | 6 | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1SpuUb8d9xAoTh32M-9wJsB50AOH54EaH?usp=sharing) |
@@ -325,6 +325,15 @@ Authorization: Bearer your_secret_api_key |
325 | 325 |
|
326 | 326 | ## SOTA results on benchmarks with optillm |
327 | 327 |
|
| 328 | +### CePO on math and code benchmarks |
| 329 | + |
| 330 | +| Method | Math-L5 | MMLU-Pro (Math) | GPQA | CRUX | LiveCodeBench (pass@1) | Simple QA | |
| 331 | +| -------------------------: | :-----: | :-------------: | :--: | :--: | :--------------------: | :-------: | |
| 332 | +| Llama 3.1 70B | 41.6 | 72.9 | 41.7 | 64.2 | 24.5 | 14.7 | |
| 333 | +| Llama 3.3 70B | 51.0 | 78.6 | 49.1 | 72.6 | 27.1 | 20.9 | |
| 334 | +| Llama 3.1 405B | 49.8 | 79.2 | 50.7 | 73.0 | 31.8 | 13.5 | |
| 335 | +| CePO (using Llama 3.3 70B) | 69.6 | 84.8 | 55.5 | 80.1 | 31.9 | 22.6 | |
| 336 | + |
328 | 337 | ### coc-claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 on AIME 2024 pass@1 (Nov 2024) |
329 | 338 |
|
330 | 339 | | Model | Score | |
@@ -370,62 +379,6 @@ called patchflows. We saw huge performance gains across all the supported patchf |
370 | 379 |
|
371 | 380 | 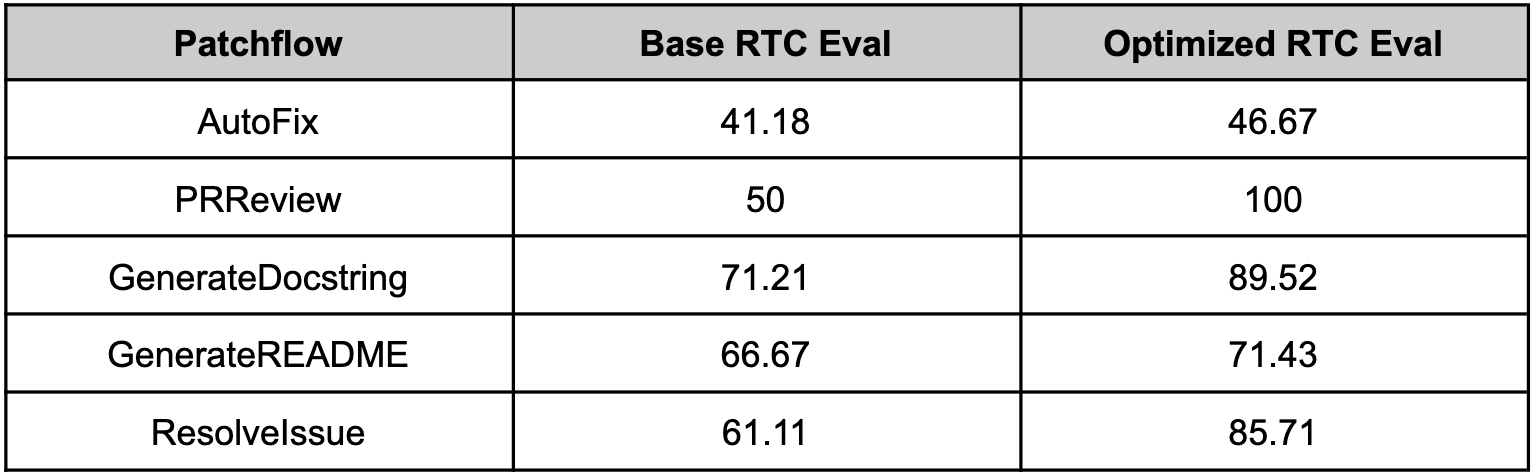 |
372 | 381 |
|
373 | | -## The Cerebras Planning and Optimization (CePO) Method |
374 | | - |
375 | | -CePO is an inference-time computation method designed to enhance the accuracy of large language models (LLMs) on tasks requiring reasoning and planning, such as solving math or coding problems. It integrates several advanced techniques, including Best of N, Chain of Thought (CoT), Self-Reflection, Self-Improvement, and Prompt Engineering. |
376 | | - |
377 | | -If you have any questions or want to contribute, please reach out to us on [cerebras.ai/discord](cerebras.ai/discord) |
378 | | - |
379 | | -### CePO Methodology |
380 | | - |
381 | | -In CePO, the Best of N technique is applied to `bestofn_n` solution candidates. Each solution is generated through the following four steps: |
382 | | - |
383 | | -**Step 1**: Plan Generation |
384 | | -The model generates a detailed, step-by-step plan to solve the problem, along with its confidence level for each step. |
385 | | - |
386 | | -**Step 2**: Initial Solution |
387 | | -Using the plan from Step 1, the model produces an initial solution. |
388 | | - |
389 | | -Steps 1 and 2 are repeated `planning_n` times to generate multiple solution proposals. |
390 | | -If the model exceeds the token budget during Step 1 or 2, the plan/solution is marked as incomplete, rejected, and regenerated. A maximum of `planning_m` attempts is made to generate `planning_n` valid proposals. |
391 | | - |
392 | | -**Step 3**: Plan Refinement |
393 | | -The model reviews all generated solution proposals and their associated plans, identifying inconsistencies. Based on this analysis, a refined, final step-by-step plan is constructed. |
394 | | - |
395 | | -**Step 4**: Final Solution |
396 | | -The model uses the refined plan from Step 3 to produce the final answer. |
397 | | - |
398 | | -### CePO Current Status |
399 | | - |
400 | | -This project is a work in progress, and the provided code is in an early experimental stage. While the proposed approach works well across the benchmarks we tested, further improvements can be achieved by task-specific customizations to prompts. |
401 | | - |
402 | | -### CePO Results |
403 | | - |
404 | | -#### Comparison of CePO with default settings and base model |
405 | | - |
406 | | -| Method | Math-L5 | MMLU-Pro (Math) | GPQA | CRUX | LiveCodeBench (pass@1) | Simple QA | |
407 | | -| -------------------------: | :-----: | :-------------: | :--: | :--: | :--------------------: | :-------: | |
408 | | -| Llama 3.1 70B | 41.6 | 72.9 | 41.7 | 64.2 | 24.5 | 14.7 | |
409 | | -| Llama 3.3 70B | 51.0 | 78.6 | 49.1 | 72.6 | 27.1 | 20.9 | |
410 | | -| Llama 3.1 405B | 49.8 | 79.2 | 50.7 | 73.0 | 31.8 | 13.5 | |
411 | | -| CePO (using Llama 3.3 70B) | 69.6 | 84.8 | 55.5 | 80.1 | 31.9 | 22.6 | |
412 | | - |
413 | | -#### CePO Ablation studies |
414 | | - |
415 | | -We conducted ablation studies to evaluate the impact of various hyperparameters in the CePO framework. Our results indicate that the chosen hyperparameter settings strike a good balance between computational cost and accuracy. |
416 | | - |
417 | | -Interestingly, the self-critique and quality improvement capabilities of existing off-the-shelf models do not always scale proportionally with increased inference compute. Addressing this limitation remains a key focus, and we plan to explore custom model fine-tuning as a potential solution in the future. |
418 | | - |
419 | | -| bestofn_n | planning_n | planning_m | bestofn_rating_type | Math-L5 | MMLU-Pro (Math) | GPQA | CRUX | Comments | |
420 | | -| :-------: | :--------: | :--------: | :-----------------: | :-----: | :-------------: | :---: | :---: | :------------- | |
421 | | -| 3 | 3 | 6 | absolute | 69.6 | 84.8 | 55.5 | 80.1 | Default config | |
422 | | -| 3 | 3 | 6 | pairwise | 67.7 | 83.5 | 55.6 | 79.8 | | |
423 | | -| 3 | 2 | 5 | absolute | 67.1 | 85.1 | 55.1 | 79.0 | | |
424 | | -| 3 | 5 | 8 | absolute | 69.4 | 84.3 | 55.6 | 81.1 | | |
425 | | -| 5 | 3 | 6 | absolute | 68.7 | 85.4 | 54.8 | 79.9 | | |
426 | | -| 7 | 3 | 6 | absolute | 69.6 | 82.8 | 54.7 | 78.4 | | |
427 | | -| 9 | 3 | 6 | absolute | 68.9 | 83.4 | 55.7 | 80.6 | | |
428 | | - |
429 | 382 | ## References |
430 | 383 |
|
431 | 384 | - [Chain of Code: Reasoning with a Language Model-Augmented Code Emulator](https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.04474) - [Inspired the implementation of coc plugin](https://github.com/codelion/optillm/blob/main/optillm/plugins/coc_plugin.py) |
|
0 commit comments