|
| 1 | +## Objective-C |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +React Native brownfield provides first-class support for Objective-C. |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +### Linking |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +The library is meant to work with [auto linking](https://github.com/react-native-community/cli/blob/master/docs/autolinking.md). In case you can't use this feature, please check out the following options: |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +<details> |
| 10 | +<summary>react-native link</summary> |
| 11 | +Run the following command in your terminal: |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +```bash |
| 14 | + react-native link @react-native-community/slider |
| 15 | +``` |
| 16 | +</details> |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +<details> |
| 19 | +Add the following line to your `Podfile`: |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +```ruby |
| 22 | + pod 'ReactNativeBrownfield', :path => '../node_modules/@callstack/react-native-brownfield/ios' |
| 23 | +``` |
| 24 | +</details> |
| 25 | + |
| 26 | +<details> |
| 27 | +<summary>Manually link the library on iOS</summary> |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +### `Open project.xcodeproj in Xcode` |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +Drag `ReactNativeBrownfield.xcodeproj` to your project on Xcode (usually under the Libraries group on Xcode): |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +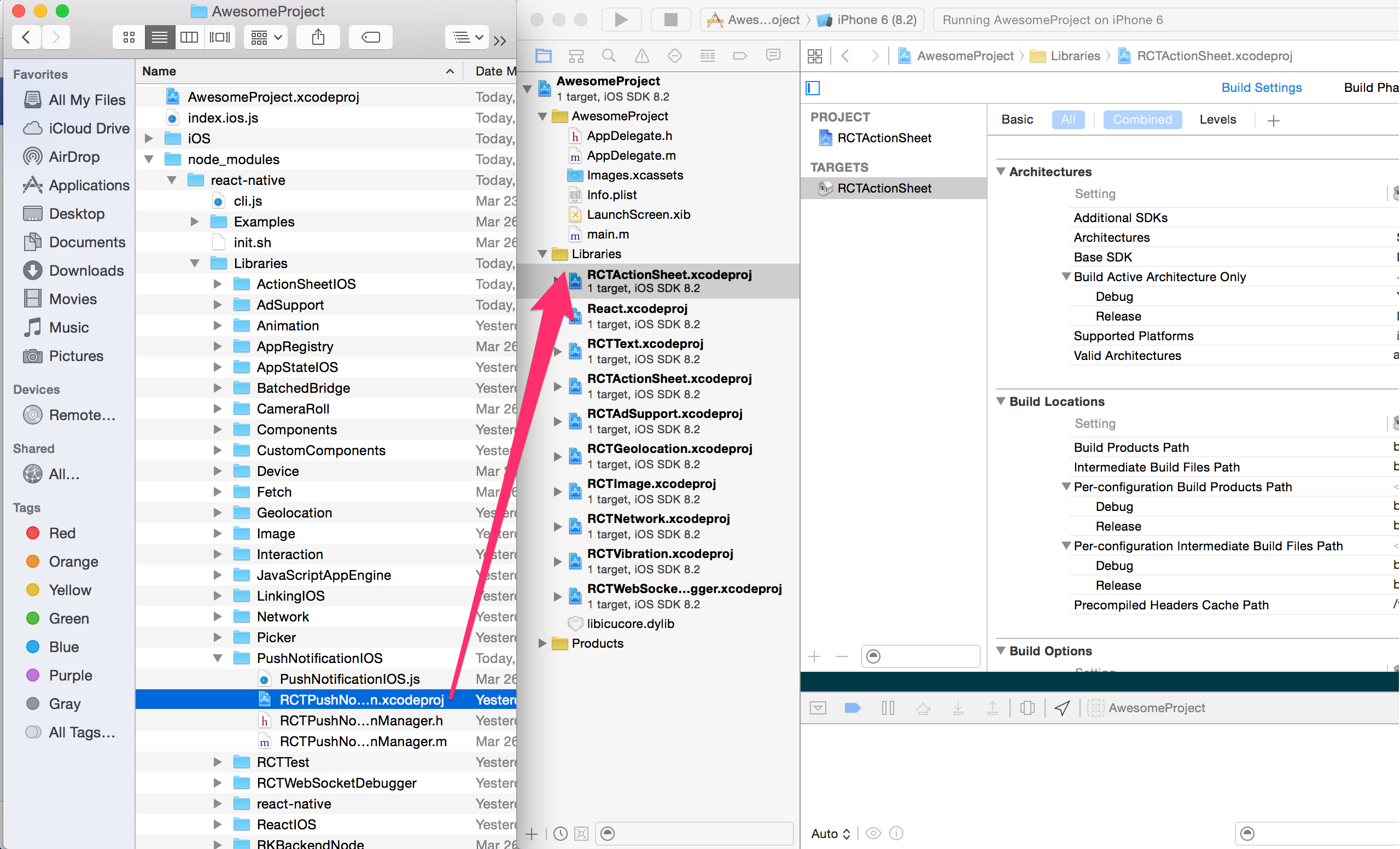 |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +### Link `libReactNativeBrownfield.a` binary with libraries |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +Click on your main project file (the one that represents the `.xcodeproj`) select `Build Phases` and drag the static library from the `Products` folder inside the Library you are importing to `Link Binary With Libraries` (or use the `+` sign and choose library from the list): |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | + |
| 40 | +</details> |
| 41 | + |
| 42 | +### API Reference |
| 43 | + |
| 44 | +#### ReactNativeBrownfield |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | +You can import the object from: |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | +```objc |
| 49 | + #import <ReactNativeBrownfield/ReactNativeBrownfield.h> |
| 50 | +``` |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +--- |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +**`shared` instance** |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +A singleton that keeps an instance of ReactNativeBrownfield object. |
| 57 | + |
| 58 | +```objc |
| 59 | + [ReactNativeBrownfield shared] |
| 60 | +``` |
| 61 | + |
| 62 | +--- |
| 63 | + |
| 64 | +**Properties:** |
| 65 | + |
| 66 | +| Property | Type | Default | Description | |
| 67 | +| -------------------- | --------- | -------------- | -------------------------------------------------- | |
| 68 | +| bridge | RCTBridge | nil | Launch options, typically passed from AppDelegate. | |
| 69 | +| entryFile | NSString | index | Path to JavaScript root. | |
| 70 | +| fallbackResource | NSString | nil | Path to bundle fallback resource. | |
| 71 | +| bundlePath | NSString | main.jsbundle | Path to bundle fallback resource. | |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | +--- |
| 74 | + |
| 75 | +**Methods:** |
| 76 | + |
| 77 | +`startReactNative` |
| 78 | + |
| 79 | +Starts React Native, produces an instance of a bridge. You can use it to initialize React Native in your app. |
| 80 | + |
| 81 | +Params: |
| 82 | + |
| 83 | +| Param | Required | Type | Description | |
| 84 | +| ----------------------- | -------- | ------------- | ----------------------------------------------------- | |
| 85 | +| onBundleLoaded | No | void(^)(void) | Callback invoked after JS bundle is fully loaded. | |
| 86 | +| launchOptions | No | NSDictionary | Launch options, typically passed from AppDelegate. | |
| 87 | + |
| 88 | +Examples: |
| 89 | + |
| 90 | +```objc |
| 91 | + [[ReactNativeBrownfield shared] startReactNative]; |
| 92 | +``` |
| 93 | + |
| 94 | +```objc |
| 95 | + [[ReactNativeBrownfield shared] startReactNative:^(void){ |
| 96 | + NSLog(@"React Native started"); |
| 97 | + }]; |
| 98 | +``` |
| 99 | +
|
| 100 | +```objc |
| 101 | + [[ReactNativeBrownfield shared] startReactNative:^(void){ |
| 102 | + NSLog(@"React Native started"); |
| 103 | + }, launchOptions]; |
| 104 | +``` |
| 105 | + |
| 106 | +--- |
| 107 | + |
| 108 | +#### ReactNativeViewController |
| 109 | + |
| 110 | +A view controller that's rendering `RCTRootView` within its bounds. It automatically uses an instance of a bridge created in `startReactNative` method. It works well with exposed JavaScript method. It's the simplest way to embed React Native into your navigation stack. |
| 111 | + |
| 112 | +You can import it from: |
| 113 | + |
| 114 | +```objc |
| 115 | + #import <ReactNativeBrownfield/ReactNativeViewController.h> |
| 116 | +``` |
| 117 | + |
| 118 | +--- |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | +**Constructors:** |
| 121 | + |
| 122 | +`initWithModuleName andInitialProperties` |
| 123 | + |
| 124 | +| Param | Required | Type | Description | |
| 125 | +| ------------------ | --------- | ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- | |
| 126 | +| moduleName | Yes | NSString | Name of React Native component registered to `AppRegistry`. | |
| 127 | +| initialProperties | No | NSString | Initial properties to be passed to React Native component. | |
| 128 | + |
| 129 | +Examples: |
| 130 | + |
| 131 | +```objc |
| 132 | + [[ReactNativeViewController alloc] initWithModuleName:@"ReactNative"] |
| 133 | +``` |
| 134 | +
|
| 135 | +```objc |
| 136 | + [[ReactNativeViewController alloc] initWithModuleName:@"ReactNative" andInitialProperties:@{@"score": 12}] |
| 137 | +``` |
| 138 | + |
| 139 | +--- |
| 140 | + |
| 141 | +### Linking |
| 142 | + |
| 143 | +You can find an example app [here](../example/objc). |
| 144 | + |
| 145 | + |
0 commit comments