|
| 1 | +[Interfaces](/t/35928) allow (or deny) access to a resource outside of a snap's confinement. |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +Most users don't need to worry about interfaces. Snaps are designed for strong application isolation and safe interface connections are made automatically. |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +An interface is most commonly used to enable a snap to access sound playback or recording, your network, and your $HOME directory. But which interfaces a snap requires, and *provides*, is very much dependent on the type of snap and its own requirements. |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +See [Supported interfaces](/t/supported-interfaces/7744) for a comprehensive list of interfaces and what kind of access they permit. |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +<h2 id='heading--slots-plugs'>Plugs and slots</h2> |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +An interface provides a level of access to resources, such as audio playback, as defined by a *slot*. One or more snaps can access this resource by connecting a corresponding *plug* to the slot. |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +In other words, the slot is the provider of the resource while the plug is the consumer, and a slot can support multiple plug connections. |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +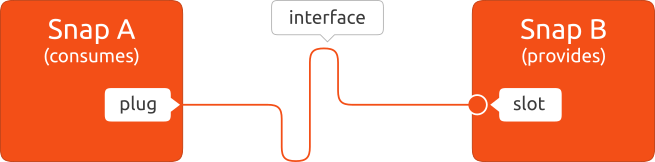 |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +In the output to `snap connections vlc` (see above), every interface used by VLC is listed in the first column. The *Plug* and *Slot* columns then describe how each interface is connected. |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +For instance, the `audio-playback` interface connects VLC's audio-playback plug to the system's audio-playback slot so you can hear the sound it produces. |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +<h2 id='heading--listing'>Listing interfaces</h2> |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +You can see which snaps are using an interface with the `interface` command: |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +```bash |
| 26 | +$ snap interface audio-playback |
| 27 | +name: audio-playback |
| 28 | +summary: allows audio playback via supporting services |
| 29 | +plugs: |
| 30 | + - chromium |
| 31 | + - vlc |
| 32 | + - zoom-client |
| 33 | +slots: |
| 34 | + - snapd |
| 35 | +``` |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +In the above output, you can see that Chromium, VLC and the Zoom snaps are connected to _snapd's_ audio-playback slot, which is synonymous with *Core* and *system*. |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | +To see all the interfaces being used by your system, run `snap interface`. To see all the interfaces available to your system, including those not currently being used, run `snap interface --all`. |
| 40 | + |
| 41 | +<h2 id='heading--snap-store'>Using a GUI</h2> |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +The Ubuntu Software/[Snap Store](https://snapcraft.io/snap-store) desktop application is installed by default on Ubuntu and can be used to list an application's interfaces and to connect and disconnect them. |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | +An application first needs to be installed as a snap: |
| 46 | + |
| 47 | +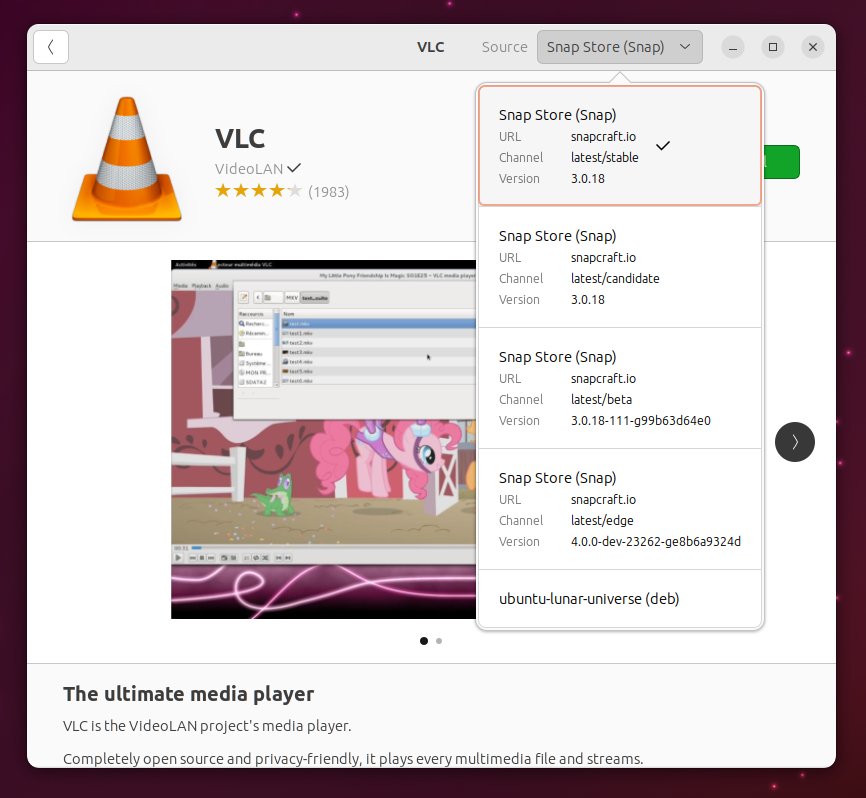 |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +To access the interface management functions, either search for an installed snap, or select it from the _Installed_ view. The interfaces for the selected application can then be viewed by selecting **Permissions**: |
| 50 | + |
| 51 | +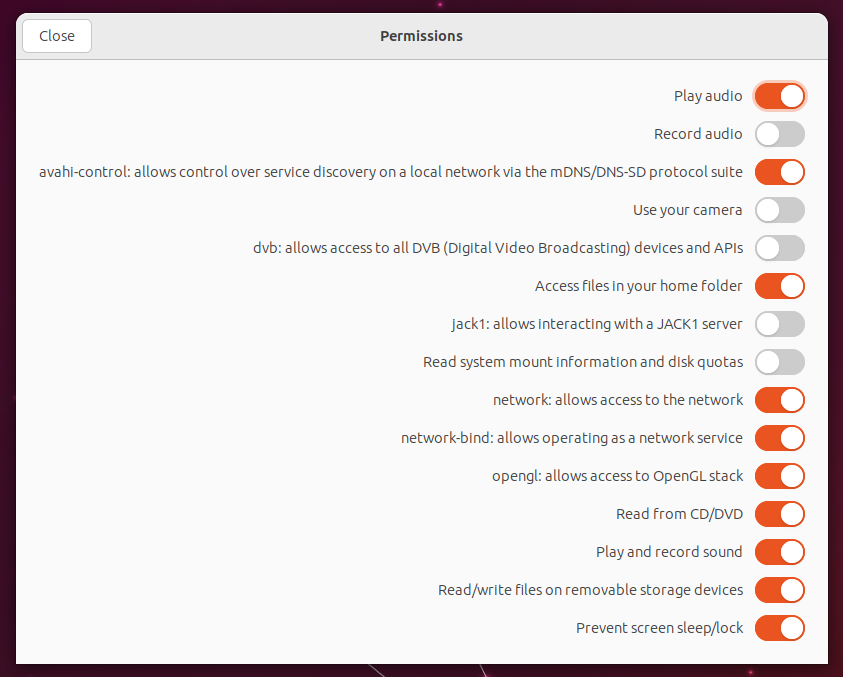 |
| 52 | + |
| 53 | +Each interface can now be connected or disconnected by selecting the toggle switch to the right of its description, and you may be prompted for your password. |
| 54 | + |
| 55 | +--> |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +<h2 id='heading--listing'>Snap connections</h2> |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +On the terminal, the _snap_ command provides more granular control over interface connections and which interfaces are operational on your system. |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +The `snap connections` command lists which interfaces are connected and being used, while adding `--all` additionally shows interfaces with unconnected slots or plugs (shown in the output as a `-`): |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | +```bash |
| 64 | +$ snap connections --all |
| 65 | +Interface Plug Slot Notes |
| 66 | +adb-support scrcpy:adb-support :adb-support - |
| 67 | +alsa ffmpeg:alsa :alsa manual |
| 68 | +appstream-metadata snap-store:appstream-metadata :appstream-metadata - |
| 69 | +iaudio-playback ardour:audio-playback :audio-playback - |
| 70 | +dbus - cameractrls:dbus-daemon - |
| 71 | +[...] |
| 72 | +``` |
| 73 | + |
| 74 | +To see which interfaces a snap is using, and which interfaces it could use but isn't, type `snap connections <snapname>`: |
| 75 | + |
| 76 | +```bash |
| 77 | +$ snap connections vlc |
| 78 | +Interface Plug Slot Notes |
| 79 | +audio-playback vlc:audio-playback :audio-playback - |
| 80 | +audio-record vlc:audio-record - - |
| 81 | +camera vlc:camera - - |
| 82 | +desktop vlc:desktop :desktop - |
| 83 | +home vlc:home :home - |
| 84 | +(...) |
| 85 | +``` |
| 86 | + |
| 87 | +In the above output, the [`camera`](/t/the-home-interface/7838) interface is not connected because its slot is empty. This means VLC cannot access any connected cameras. |
| 88 | + |
| 89 | +VLC can access the user's _/home_ directory because the [`home`](/t/the-home-interface/7838) interface is connected to the system `$HOME` directory (denoted by the `:home` slot name). |
| 90 | + |
| 91 | +To see all connected interfaces on your system, use the _snap connections_ command without a snap name: |
| 92 | + |
| 93 | +```bash |
| 94 | +$ snap connections |
| 95 | +Interface Plug Slot Notes |
| 96 | +adb-support scrcpy:adb-support :adb-support - |
| 97 | +alsa ffmpeg:alsa :alsa manual |
| 98 | +alsa telegram-desktop:alsa :alsa manual |
| 99 | +audio-playback ardour:audio-playback :audio-playback - |
| 100 | +audio-playback chromium:audio-playback :audio-playback - |
| 101 | +(...) |
| 102 | +``` |
| 103 | + |
| 104 | +Adding `--all` to the _snap connections_ command will list all interfaces, including those without a connection: |
| 105 | + |
| 106 | +```bash |
| 107 | +$ snap connections --all |
| 108 | +Interface Plug Slot Notes |
| 109 | +adb-support scrcpy:adb-support :adb-support - |
| 110 | +alsa entropypianotuner:alsa - - |
| 111 | +alsa ffmpeg:alsa :alsa manual |
| 112 | +alsa guvcview:alsa - - |
| 113 | +(...) |
| 114 | +``` |
| 115 | + |
| 116 | +<h3 id='heading--auto-connections'>Auto-connections</h3> |
| 117 | + |
| 118 | +Many interfaces are automatically connected when a snap is installed, and this ability is a property of either the interface itself, or the snap. |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | +Automatically connecting interfaces include the [network](/t/the-network-interface/7880), [audio-playback](/t/the-audio-playback-interface/13089) and [opengl](/t/the-opengl-interface/7894) interfaces. This _auto-connection_ ability is carefully reviewed for each interface, where permissiveness, security and privacy implications, and the expectations of the user, are all considered. |
| 121 | + |
| 122 | +A snap's developer can also request that an interface is connected automatically through a [manual review process](/t/permission-requests/12822). As above, these requests are carefully considered and reviewed before being granted or denied. |
| 123 | + |
| 124 | +Interfaces not connected automatically require the user to make a manual connection (see below), such as the [camera](/t/the-camera-interface/7776), [removable-media](/t/the-removable-media-interface/7910) and [audio-record](/t/the-audio-record-interface/13090) interfaces. Manual connections enable the user to have a complete control over what kind of access they allow. |
| 125 | + |
| 126 | +If a snap is installed prior to an interface being granted auto-connect permission, and permission is subsequently granted and the snap updated, when the installed snap updates, the interface will be auto-connected. |
| 127 | + |
| 128 | +For more technical details on how interface auto-connections are processed, see [The interface auto-connection mechanism](/t/the-interface-auto-connection-mechanism/20179). |
| 129 | + |
| 130 | +> ⓘ See the _Auto-connect_ column in the [Supported interfaces](/t/supported-interfaces/7744) table for which interfaces are connected automatically. |
| 131 | +
|
| 132 | +<h3 id='heading--manual-connections'>Manual connections</h3> |
| 133 | + |
| 134 | +When you need to connect an interface manually, such as when you want to grant a snap access to [audio-record](/t/the-audio-record-interface/13090) for audio input, use the `snap connect` command: |
| 135 | + |
| 136 | +```bash |
| 137 | +snap connect <snap>:<plug interface> |
| 138 | +``` |
| 139 | + |
| 140 | +With no further arguments, the plug will connect to the system via the snap daemon, _snapd_. |
| 141 | + |
| 142 | +For example, to connect VLC's _audio-record_ plug to the system's _audio-record_, you'd enter the following: |
| 143 | + |
| 144 | +```bash |
| 145 | +sudo snap connect vlc:audio-record |
| 146 | +``` |
| 147 | + |
| 148 | +To connect an interface to a slot provided by another snap, provide this as an additional argument: |
| 149 | + |
| 150 | +```bash |
| 151 | +snap connect <snap>:<plug interface> <snap>:<slot interface> |
| 152 | +``` |
| 153 | + |
| 154 | +A slot and a plug can only be connected if they have the same interface name. |
| 155 | + |
| 156 | +Add the `--no-wait` option to _snap connect_ or _snap disconnect_ to run the process in the background and return immediately to the command prompt. |
| 157 | + |
| 158 | +[note type="positive"] |
| 159 | +A successful connection grants any necessary permissions that may be required by the interface to function. |
| 160 | +[/note] |
| 161 | + |
| 162 | +<h2 id='heading--disconnect'>Disconnect interfaces</h2> |
| 163 | + |
| 164 | + |
| 165 | +To disconnect an interface, use `snap disconnect`: |
| 166 | + |
| 167 | +```bash |
| 168 | +snap disconnect <snap>:<plug interface> |
| 169 | +``` |
| 170 | + |
| 171 | +Following our previous example, you would disconnect *vlc:audio-record* with the following command: |
| 172 | + |
| 173 | +```bash |
| 174 | +sudo snap disconnect vlc:audio-record |
| 175 | +``` |
| 176 | + |
| 177 | +<h3 id='heading--forget'>Forget manual disconnections</h3> |
| 178 | + |
| 179 | +When an automatic connection ([see above](#heading--auto-connections)) is manually disconnected, its disconnected state is retained after a [snap refresh](/t/managing-updates/7022). This state is even stored **after a snap has been removed**, including removal with the `--purge` option. |
| 180 | + |
| 181 | +The `--forget` flag can be added to the disconnect command to reset this behaviour, and consequently, re-enable the automatic re-connection after a snap refresh. |
0 commit comments