diff --git a/.codespellrc b/.codespellrc
deleted file mode 100644
index a56ec23f4..000000000
--- a/.codespellrc
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
-[codespell]
-skip = .git,*.pdf,*.svg,*.csv,*.ipynb,*.drawio
-# Rever -- nobody knows
-# numer -- numerator variable
-ignore-words-list = rever,numer
diff --git a/.devcontainer/Dockerfile b/.devcontainer/Dockerfile
index 89a8ad868..776a32e99 100644
--- a/.devcontainer/Dockerfile
+++ b/.devcontainer/Dockerfile
@@ -8,6 +8,7 @@ RUN \
pip uninstall datajoint -y
USER root
-ENV DJ_HOST db
-ENV DJ_USER root
-ENV DJ_PASS password
+ENV DJ_HOST=db
+ENV DJ_USER=root
+ENV DJ_PASS=password
+ENV S3_ENDPOINT=minio:9000
diff --git a/.devcontainer/devcontainer.json b/.devcontainer/devcontainer.json
index 6ed3c52c4..51ca1e64c 100644
--- a/.devcontainer/devcontainer.json
+++ b/.devcontainer/devcontainer.json
@@ -1,56 +1,6 @@
-// For format details, see https://aka.ms/devcontainer.json. For config options, see the
-// README at: https://github.com/devcontainers/templates/tree/main/src/docker-existing-docker-compose
{
- "name": "Existing Docker Compose (Extend)",
- // Update the 'dockerComposeFile' list if you have more compose files or use different names.
- // The .devcontainer/docker-compose.yml file contains any overrides you need/want to make.
- "dockerComposeFile": [
- "../docker-compose.yaml",
- "docker-compose.yml"
- ],
- // The 'service' property is the name of the service for the container that VS Code should
- // use. Update this value and .devcontainer/docker-compose.yml to the real service name.
- "service": "app",
- // The optional 'workspaceFolder' property is the path VS Code should open by default when
- // connected. This is typically a file mount in .devcontainer/docker-compose.yml
- "workspaceFolder": "/workspaces/${localWorkspaceFolderBasename}",
- // Features to add to the dev container. More info: https://containers.dev/features.
- // "features": {},
- // Use 'forwardPorts' to make a list of ports inside the container available locally.
- "forwardPorts": [
- 80,
- 443,
- 3306,
- 8080,
- 9000
- ],
- "mounts": [
- "type=bind,source=${env:SSH_AUTH_SOCK},target=/ssh-agent"
- ],
- "containerEnv": {
- "SSH_AUTH_SOCK": "/ssh-agent"
- },
- // Uncomment the next line if you want start specific services in your Docker Compose config.
- // "runServices": [],
- // Uncomment the next line if you want to keep your containers running after VS Code shuts down.
- "shutdownAction": "stopCompose",
- "onCreateCommand": "python3 -m pip install -q -e .[dev]",
- "features": {
- "ghcr.io/devcontainers/features/git:1": {},
- "ghcr.io/devcontainers/features/docker-in-docker:2": {},
- "ghcr.io/devcontainers/features/github-cli:1": {},
- },
- // Configure tool-specific properties.
- "customizations": {
- "vscode": {
- "extensions": [
- "ms-python.python"
- ]
- }
- },
- "remoteEnv": {
- "LOCAL_WORKSPACE_FOLDER": "${localWorkspaceFolder}"
- }
- // Uncomment to connect as an existing user other than the container default. More info: https://aka.ms/dev-containers-non-root.
- // "remoteUser": "devcontainer"
+ "dockerComposeFile": ["../docker-compose.yaml", "docker-compose.yml"],
+ "service": "app",
+ "workspaceFolder": "/src",
+ "postCreateCommand": "curl -fsSL https://pixi.sh/install.sh | bash && echo 'export PATH=\"$HOME/.pixi/bin:$PATH\"' >> ~/.bashrc"
}
diff --git a/.devcontainer/docker-compose.yml b/.devcontainer/docker-compose.yml
index 5c22aaf14..c876f69f4 100644
--- a/.devcontainer/docker-compose.yml
+++ b/.devcontainer/docker-compose.yml
@@ -1,30 +1,14 @@
+# Devcontainer overrides for the app service from ../docker-compose.yaml
+# Inherits db and minio services automatically
services:
- # Update this to the name of the service you want to work with in your docker-compose.yml file
app:
- # Uncomment if you want to override the service's Dockerfile to one in the .devcontainer
- # folder. Note that the path of the Dockerfile and context is relative to the *primary*
- # docker-compose.yml file (the first in the devcontainer.json "dockerComposeFile"
- # array). The sample below assumes your primary file is in the root of your project.
container_name: datajoint-python-devcontainer
- image: datajoint/datajoint-python-devcontainer:${PY_VER:-3.11}-${DISTRO:-bookworm}
build:
- context: .
+ context: ..
dockerfile: .devcontainer/Dockerfile
args:
- PY_VER=${PY_VER:-3.11}
- DISTRO=${DISTRO:-bookworm}
-
- volumes:
- # Update this to wherever you want VS Code to mount the folder of your project
- - ..:/workspaces:cached
-
- # Uncomment the next four lines if you will use a ptrace-based debugger like C++, Go, and Rust.
- # cap_add:
- # - SYS_PTRACE
- # security_opt:
- # - seccomp:unconfined
-
user: root
-
- # Overrides default command so things don't shut down after the process ends.
+ # Keep container running for devcontainer
command: /bin/sh -c "while sleep 1000; do :; done"
diff --git a/.gitattributes b/.gitattributes
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..887a2c18f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.gitattributes
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+# SCM syntax highlighting & preventing 3-way merges
+pixi.lock merge=binary linguist-language=YAML linguist-generated=true
diff --git a/.github/pr_labeler.yaml b/.github/pr_labeler.yaml
index ab722839f..51ce9afee 100644
--- a/.github/pr_labeler.yaml
+++ b/.github/pr_labeler.yaml
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
# https://github.com/actions/labeler
breaking:
-- head-branch: ['breaking', 'BREAKING']
+- head-branch: ['breaking', 'BREAKING', 'pre/v2.0']
bug:
-- head-branch: ['fix', 'FIX', 'bug', 'BUG']
+- head-branch: ['fix', 'FIX', 'bug', 'BUG', 'pre/v2.0']
feature:
- head-branch: ['feat', 'FEAT']
documentation:
diff --git a/.github/workflows/label_prs.yaml b/.github/workflows/label_prs.yaml
index 9797a956f..8f3fcec95 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/label_prs.yaml
+++ b/.github/workflows/label_prs.yaml
@@ -14,5 +14,5 @@ jobs:
with:
repo-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
configuration-path: .github/pr_labeler.yaml
- sync-labels: true
+ sync-labels: false # Don't remove manually added labels
dot: true
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/lint.yaml b/.github/workflows/lint.yaml
index 62468a983..e7e6dc2ae 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/lint.yaml
+++ b/.github/workflows/lint.yaml
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ jobs:
extra_args: codespell --all-files
- uses: pre-commit/action@v3.0.1
with:
- extra_args: black --all-files
+ extra_args: ruff --all-files
- uses: pre-commit/action@v3.0.1
with:
- extra_args: flake8 --all-files
+ extra_args: ruff-format --all-files
diff --git a/.github/workflows/post_draft_release_published.yaml b/.github/workflows/post_draft_release_published.yaml
index 20160e62b..f9c3ee62d 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/post_draft_release_published.yaml
+++ b/.github/workflows/post_draft_release_published.yaml
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ jobs:
strategy:
matrix:
include:
- - py_ver: "3.9"
+ - py_ver: "3.10"
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
PY_VER: ${{matrix.py_ver}}
@@ -40,14 +40,14 @@ jobs:
- name: Update version.py
run: |
VERSION=$(echo "${{ github.event.release.name }}" | grep -oP '\d+\.\d+\.\d+')
- sed -i "s/^__version__ = .*/__version__ = \"$VERSION\"/" datajoint/version.py
- cat datajoint/version.py
+ sed -i "s/^__version__ = .*/__version__ = \"$VERSION\"/" src/datajoint/version.py
+ cat src/datajoint/version.py
# Commit the changes
BRANCH_NAME="update-version-$VERSION"
git switch -c $BRANCH_NAME
git config --global user.name "github-actions"
git config --global user.email "github-actions@github.com"
- git add datajoint/version.py
+ git add src/datajoint/version.py
git commit -m "Update version.py to $VERSION"
echo "BRANCH_NAME=$BRANCH_NAME" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Update README.md badge
diff --git a/.github/workflows/test.yaml b/.github/workflows/test.yaml
index 196ddec22..a4a91448f 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/test.yaml
+++ b/.github/workflows/test.yaml
@@ -1,42 +1,55 @@
name: Test
+
on:
push:
branches:
- - "**" # every branch
- - "!gh-pages" # exclude gh-pages branch
- - "!stage*" # exclude branches beginning with stage
+ - "**"
+ - "!gh-pages"
+ - "!stage*"
paths:
- - "datajoint"
- - "tests"
+ - "src/datajoint/**"
+ - "tests/**"
+ - "pyproject.toml"
+ - "pixi.lock"
+ - ".github/workflows/test.yaml"
pull_request:
branches:
- - "**" # every branch
- - "!gh-pages" # exclude gh-pages branch
- - "!stage*" # exclude branches beginning with stage
+ - "**"
+ - "!gh-pages"
+ - "!stage*"
paths:
- - "datajoint"
- - "tests"
+ - "src/datajoint/**"
+ - "tests/**"
+ - "pyproject.toml"
+ - "pixi.lock"
+ - ".github/workflows/test.yaml"
+
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
- strategy:
- matrix:
- py_ver: ["3.9", "3.10", "3.11", "3.12", "3.13"]
- mysql_ver: ["8.0"]
- include:
- - py_ver: "3.9"
- mysql_ver: "5.7"
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- - name: Set up Python ${{matrix.py_ver}}
- uses: actions/setup-python@v5
+
+ - name: Set up pixi
+ uses: prefix-dev/setup-pixi@v0.9.3
with:
- python-version: ${{matrix.py_ver}}
- - name: Integration test
- env:
- PY_VER: ${{matrix.py_ver}}
- MYSQL_VER: ${{matrix.mysql_ver}}
- # taking default variables set in docker-compose.yaml to sync with local test
- run: |
- export HOST_UID=$(id -u)
- docker compose --profile test up --quiet-pull --build --exit-code-from djtest djtest
+ cache: true
+ locked: false
+
+ - name: Run tests
+ run: pixi run -e test test-cov
+
+ # Unit tests run without containers (faster feedback)
+ unit-tests:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - uses: actions/checkout@v4
+
+ - name: Set up pixi
+ uses: prefix-dev/setup-pixi@v0.9.3
+ with:
+ cache: true
+ locked: false
+
+ - name: Run unit tests
+ run: pixi run -e test pytest tests/unit -v
diff --git a/.gitignore b/.gitignore
index f506fcb59..3c88c420c 100644
--- a/.gitignore
+++ b/.gitignore
@@ -185,3 +185,10 @@ cython_debug/
dj_local_conf.json
*.env
!.vscode/launch.json
+# pixi environments
+.pixi
+_content/
+
+# Local config
+.secrets/
+datajoint.json
diff --git a/.pre-commit-config.yaml b/.pre-commit-config.yaml
index 4a58e0483..218134d62 100644
--- a/.pre-commit-config.yaml
+++ b/.pre-commit-config.yaml
@@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
-# pip install datajoint[test]
# pre-commit install
# pre-commit run --all-files
# pre-commit autoupdate
-# SKIP=flake8 git commit -m "foo"
+# SKIP=ruff git commit -m "foo"
# See https://pre-commit.com for more information
# See https://pre-commit.com/hooks.html for more hooks
@@ -20,43 +19,40 @@ repos:
rev: v2.4.1
hooks:
- id: codespell
-- repo: https://github.com/pycqa/isort
- rev: 6.0.1 # Use the latest stable version
+ args: [--toml, pyproject.toml]
+- repo: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-pre-commit
+ rev: v0.8.4
hooks:
- - id: isort
- args:
- - --profile=black # Optional, makes isort compatible with Black
-- repo: https://github.com/psf/black
- rev: 25.1.0 # matching versions in pyproject.toml and github actions
- hooks:
- - id: black
- args: ["--check", "-v", "datajoint", "tests", "--diff"] # --required-version is conflicting with pre-commit
-- repo: https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8
- rev: 7.3.0
- hooks:
- # syntax tests
- - id: flake8
- args:
- - --select=E9,F63,F7,F82
- - --count
- - --show-source
- - --statistics
- files: datajoint # a lot of files in tests are not compliant
- # style tests
- - id: flake8
- args:
- - --ignore=E203,E722,W503
- - --count
- - --max-complexity=62
- - --max-line-length=127
- - --statistics
- - --per-file-ignores=datajoint/diagram.py:C901
- files: datajoint # a lot of files in tests are not compliant
+ # Run the linter
+ - id: ruff
+ args: [--fix]
+ files: ^(src/|tests/)
+ # Run the formatter
+ - id: ruff-format
+ files: ^(src/|tests/)
- repo: https://github.com/rhysd/actionlint
rev: v1.7.7
hooks:
# lint github actions workflow yaml
- id: actionlint
-
-## Suggest to add pytest hook that runs unit test | Prerequisite: split unit/integration test
-## https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/1211
+- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/mirrors-mypy
+ rev: v1.14.1
+ hooks:
+ - id: mypy
+ files: ^src/datajoint/
+ additional_dependencies:
+ - pydantic
+ - pydantic-settings
+ - types-PyMySQL
+ - types-tqdm
+ - pandas-stubs
+ - numpy
+- repo: local
+ hooks:
+ - id: unit-tests
+ name: unit tests
+ entry: pytest tests/unit/ -v --tb=short
+ language: system
+ pass_filenames: false
+ always_run: true
+ stages: [pre-commit]
diff --git a/DOCSTRING_STYLE.md b/DOCSTRING_STYLE.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..77b6dc90a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/DOCSTRING_STYLE.md
@@ -0,0 +1,499 @@
+# DataJoint Python Docstring Style Guide
+
+This document defines the canonical docstring format for datajoint-python.
+All public APIs must follow this NumPy-style format for consistency and
+automated documentation generation via mkdocstrings.
+
+## Quick Reference
+
+```python
+def function(param1, param2, *, keyword_only=None):
+ """
+ Short one-line summary (imperative mood, no period).
+
+ Extended description providing context and details. May span
+ multiple lines. Explain what the function does, not how.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ param1 : type
+ Description of param1.
+ param2 : type
+ Description of param2.
+ keyword_only : type, optional
+ Description. Default is None.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ type
+ Description of return value.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ ExceptionType
+ When and why this exception is raised.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> result = function("value", 42)
+ >>> print(result)
+ expected_output
+
+ See Also
+ --------
+ related_function : Brief description.
+
+ Notes
+ -----
+ Additional technical notes, algorithms, or implementation details.
+ """
+```
+
+---
+
+## Module Docstrings
+
+Every module must begin with a docstring explaining its purpose.
+
+```python
+"""
+Connection management for DataJoint.
+
+This module provides the Connection class that manages database connections,
+transaction handling, and query execution. It also provides the ``conn()``
+function for accessing a persistent shared connection.
+
+Key Components
+--------------
+Connection : class
+ Manages a single database connection with transaction support.
+conn : function
+ Returns a persistent connection object shared across modules.
+
+Example
+-------
+>>> import datajoint as dj
+>>> connection = dj.conn()
+>>> connection.query("SHOW DATABASES")
+"""
+```
+
+---
+
+## Class Docstrings
+
+```python
+class Table(QueryExpression):
+ """
+ Base class for all DataJoint tables.
+
+ Table implements data manipulation (insert, delete, update) and inherits
+ query functionality from QueryExpression. Concrete table classes must
+ define the ``definition`` property specifying the table structure.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ None
+ Tables are typically instantiated via schema decoration, not directly.
+
+ Attributes
+ ----------
+ definition : str
+ DataJoint table definition string (DDL).
+ primary_key : list of str
+ Names of primary key attributes.
+ heading : Heading
+ Table heading with attribute metadata.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ Define a table using the schema decorator:
+
+ >>> @schema
+ ... class Mouse(dj.Manual):
+ ... definition = '''
+ ... mouse_id : int
+ ... ---
+ ... dob : date
+ ... sex : enum("M", "F", "U")
+ ... '''
+
+ Insert data:
+
+ >>> Mouse.insert1({"mouse_id": 1, "dob": "2024-01-15", "sex": "M"})
+
+ See Also
+ --------
+ Manual : Table for manually entered data.
+ Computed : Table for computed results.
+ QueryExpression : Query operator base class.
+ """
+```
+
+---
+
+## Method Docstrings
+
+### Standard Method
+
+```python
+def insert(self, rows, *, replace=False, skip_duplicates=False, ignore_extra_fields=False):
+ """
+ Insert one or more rows into the table.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ rows : iterable
+ Rows to insert. Each row can be:
+ - dict: ``{"attr": value, ...}``
+ - numpy.void: Record array element
+ - sequence: Values in heading order
+ - QueryExpression: Results of a query
+ - pathlib.Path: Path to CSV file
+ replace : bool, optional
+ If True, replace existing rows with matching primary keys.
+ Default is False.
+ skip_duplicates : bool, optional
+ If True, silently skip rows that would cause duplicate key errors.
+ Default is False.
+ ignore_extra_fields : bool, optional
+ If True, ignore fields not in the table heading.
+ Default is False.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ None
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DuplicateError
+ When inserting a row with an existing primary key and neither
+ ``replace`` nor ``skip_duplicates`` is True.
+ DataJointError
+ When required attributes are missing or types are incompatible.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ Insert a single row:
+
+ >>> Mouse.insert1({"mouse_id": 1, "dob": "2024-01-15", "sex": "M"})
+
+ Insert multiple rows:
+
+ >>> Mouse.insert([
+ ... {"mouse_id": 2, "dob": "2024-02-01", "sex": "F"},
+ ... {"mouse_id": 3, "dob": "2024-02-15", "sex": "M"},
+ ... ])
+
+ Insert from a query:
+
+ >>> TargetTable.insert(SourceTable & "condition > 5")
+
+ See Also
+ --------
+ insert1 : Insert exactly one row.
+ """
+```
+
+### Method with Complex Return
+
+```python
+def fetch(self, *attrs, offset=None, limit=None, order_by=None, format=None, as_dict=False):
+ """
+ Retrieve data from the table.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ *attrs : str
+ Attribute names to fetch. If empty, fetches all attributes.
+ Use "KEY" to fetch primary key as dict.
+ offset : int, optional
+ Number of rows to skip. Default is None (no offset).
+ limit : int, optional
+ Maximum number of rows to return. Default is None (no limit).
+ order_by : str or list of str, optional
+ Attribute(s) to sort by. Use "KEY" for primary key order,
+ append " DESC" for descending. Default is None (unordered).
+ format : {"array", "frame"}, optional
+ Output format when fetching all attributes:
+ - "array": numpy structured array (default)
+ - "frame": pandas DataFrame
+ as_dict : bool, optional
+ If True, return list of dicts instead of structured array.
+ Default is False.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ numpy.ndarray or list of dict or pandas.DataFrame
+ Query results in the requested format:
+ - Single attribute: 1D array of values
+ - Multiple attributes: tuple of 1D arrays
+ - No attributes specified: structured array, DataFrame, or list of dicts
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ Fetch all data as structured array:
+
+ >>> data = Mouse.fetch()
+
+ Fetch specific attributes:
+
+ >>> ids, dobs = Mouse.fetch("mouse_id", "dob")
+
+ Fetch as list of dicts:
+
+ >>> rows = Mouse.fetch(as_dict=True)
+ >>> for row in rows:
+ ... print(row["mouse_id"])
+
+ Fetch with ordering and limit:
+
+ >>> recent = Mouse.fetch(order_by="dob DESC", limit=10)
+
+ See Also
+ --------
+ fetch1 : Fetch exactly one row.
+ head : Fetch first N rows ordered by key.
+ tail : Fetch last N rows ordered by key.
+ """
+```
+
+### Generator Method
+
+```python
+def make(self, key):
+ """
+ Compute and insert results for one key.
+
+ This method must be implemented by subclasses of Computed or Imported
+ tables. It is called by ``populate()`` for each key in ``key_source``
+ that is not yet in the table.
+
+ The method can be implemented in two ways:
+
+ **Simple mode** (regular method):
+ Fetch, compute, and insert within a single transaction.
+
+ **Tripartite mode** (generator method):
+ Split into ``make_fetch``, ``make_compute``, ``make_insert`` for
+ long-running computations with deferred transactions.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ key : dict
+ Primary key values identifying the entity to compute.
+
+ Yields
+ ------
+ tuple
+ In tripartite mode, yields fetched data and computed results.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ NotImplementedError
+ If neither ``make`` nor the tripartite methods are implemented.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ Simple implementation:
+
+ >>> class ProcessedData(dj.Computed):
+ ... definition = '''
+ ... -> RawData
+ ... ---
+ ... result : float
+ ... '''
+ ...
+ ... def make(self, key):
+ ... raw = (RawData & key).fetch1("data")
+ ... result = expensive_computation(raw)
+ ... self.insert1({**key, "result": result})
+
+ See Also
+ --------
+ populate : Execute make for all pending keys.
+ key_source : Query defining keys to populate.
+ """
+```
+
+---
+
+## Property Docstrings
+
+```python
+@property
+def primary_key(self):
+ """
+ list of str : Names of primary key attributes.
+
+ The primary key uniquely identifies each row in the table.
+ Derived from the table definition.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> Mouse.primary_key
+ ['mouse_id']
+ """
+ return self.heading.primary_key
+```
+
+---
+
+## Parameter Types
+
+Use these type annotations in docstrings:
+
+| Python Type | Docstring Format |
+|-------------|------------------|
+| `str` | `str` |
+| `int` | `int` |
+| `float` | `float` |
+| `bool` | `bool` |
+| `None` | `None` |
+| `list` | `list` or `list of str` |
+| `dict` | `dict` or `dict[str, int]` |
+| `tuple` | `tuple` or `tuple of (str, int)` |
+| Optional | `str or None` or `str, optional` |
+| Union | `str or int` |
+| Literal | `{"option1", "option2"}` |
+| Callable | `callable` |
+| Class | `ClassName` |
+| Any | `object` |
+
+---
+
+## Section Order
+
+Sections must appear in this order (include only relevant sections):
+
+1. **Short Summary** (required) - One line, imperative mood
+2. **Deprecation Warning** - If applicable
+3. **Extended Summary** - Additional context
+4. **Parameters** - Input arguments
+5. **Returns** / **Yields** - Output values
+6. **Raises** - Exceptions
+7. **Warns** - Warnings issued
+8. **See Also** - Related functions/classes
+9. **Notes** - Technical details
+10. **References** - Citations
+11. **Examples** (strongly encouraged) - Usage demonstrations
+
+---
+
+## Style Rules
+
+### Do
+
+- Use imperative mood: "Insert rows" not "Inserts rows"
+- Start with capital letter, no period at end of summary
+- Document all public methods
+- Include at least one example for public APIs
+- Use backticks for code: ``parameter``, ``ClassName``
+- Reference related items in See Also
+
+### Don't
+
+- Don't document private methods extensively (brief is fine)
+- Don't repeat the function signature in the description
+- Don't use "This function..." or "This method..."
+- Don't include implementation details in Parameters
+- Don't use first person ("I", "we")
+
+---
+
+## Examples Section Best Practices
+
+```python
+"""
+Examples
+--------
+Basic usage:
+
+>>> table.insert1({"id": 1, "value": 42})
+
+With options:
+
+>>> table.insert(rows, skip_duplicates=True)
+
+Error handling:
+
+>>> try:
+... table.insert1({"id": 1}) # duplicate
+... except dj.errors.DuplicateError:
+... print("Already exists")
+Already exists
+"""
+```
+
+---
+
+## Converting from Sphinx Style
+
+Replace Sphinx-style docstrings:
+
+```python
+# Before (Sphinx style)
+def method(self, param1, param2):
+ """
+ Brief description.
+
+ :param param1: Description of param1.
+ :type param1: str
+ :param param2: Description of param2.
+ :type param2: int
+ :returns: Description of return value.
+ :rtype: bool
+ :raises ValueError: When param1 is empty.
+ """
+
+# After (NumPy style)
+def method(self, param1, param2):
+ """
+ Brief description.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ param1 : str
+ Description of param1.
+ param2 : int
+ Description of param2.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ bool
+ Description of return value.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ ValueError
+ When param1 is empty.
+ """
+```
+
+---
+
+## Validation
+
+Docstrings are validated by:
+
+1. **mkdocstrings** - Parses for API documentation
+2. **ruff** - Linting (D100-D417 rules when enabled)
+3. **pytest --doctest-modules** - Executes examples
+
+Run locally:
+
+```bash
+# Build docs to check parsing
+mkdocs build --config-file docs/mkdocs.yaml
+
+# Check docstring examples
+pytest --doctest-modules src/datajoint/
+```
+
+---
+
+## References
+
+- [NumPy Docstring Guide](https://numpydoc.readthedocs.io/en/latest/format.html)
+- [mkdocstrings Python Handler](https://mkdocstrings.github.io/python/)
+- [PEP 257 - Docstring Conventions](https://peps.python.org/pep-0257/)
diff --git a/Dockerfile b/Dockerfile
index 0d727f6b4..780e1c540 100644
--- a/Dockerfile
+++ b/Dockerfile
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ RUN ${CONDA_BIN} install --no-pin -qq -y -n base -c conda-forge \
ENV PATH="$PATH:/home/mambauser/.local/bin"
COPY --chown=${HOST_UID:-1000}:mambauser ./pyproject.toml ./README.md ./LICENSE.txt /main/
-COPY --chown=${HOST_UID:-1000}:mambauser ./datajoint /main/datajoint
+COPY --chown=${HOST_UID:-1000}:mambauser ./src/datajoint /main/src/datajoint
VOLUME /src
WORKDIR /src
diff --git a/LICENSE b/LICENSE
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3f8b99424
--- /dev/null
+++ b/LICENSE
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+ Apache License
+ Version 2.0, January 2004
+ http://www.apache.org/licenses/
+
+ TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
+
+ 1. Definitions.
+
+ "License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
+ and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
+
+ "Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
+ the copyright owner that is granting the License.
+
+ "Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
+ other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
+ control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
+ "control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
+ direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
+ otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
+ outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
+
+ "You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
+ exercising permissions granted by this License.
+
+ "Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
+ including but not limited to software source code, documentation
+ source, and configuration files.
+
+ "Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
+ transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
+ not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
+ and conversions to other media types.
+
+ "Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
+ Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
+ copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
+ (an example is provided in the Appendix below).
+
+ "Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
+ form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
+ editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
+ represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
+ of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
+ separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
+ the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
+
+ "Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
+ the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
+ to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
+ submitted to the Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
+ or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
+ the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
+ means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
+ to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
+ communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
+ and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
+ Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
+ excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
+ designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
+
+ "Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
+ on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
+ subsequently incorporated within the Work.
+
+ 2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
+ this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
+ worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
+ copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
+ publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
+ Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
+
+ 3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
+ this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
+ worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
+ (except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
+ use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
+ where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
+ by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
+ Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
+ with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
+ institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
+ cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
+ or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
+ or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
+ granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
+ as of the date such litigation is filed.
+
+ 4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
+ Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
+ modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
+ meet the following conditions:
+
+ (a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
+ Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
+
+ (b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
+ stating that You changed the files; and
+
+ (c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
+ that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
+ attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
+ excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
+ the Derivative Works; and
+
+ (d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
+ distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
+ include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
+ within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
+ pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
+ of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
+ as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
+ documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
+ within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
+ wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
+ of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
+ do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
+ notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
+ or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
+ that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
+ as modifying the License.
+
+ You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
+ may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
+ for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
+ for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
+ reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
+ the conditions stated in this License.
+
+ 5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
+ any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
+ by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
+ this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
+ Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
+ the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
+ with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
+
+ 6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
+ names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
+ except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
+ origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
+
+ 7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
+ agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
+ Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+ WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
+ implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
+ of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
+ PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
+ appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
+ risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
+
+ 8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
+ whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
+ unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
+ negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
+ liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
+ incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
+ result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
+ Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
+ work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
+ other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
+ has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
+
+ 9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
+ the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
+ and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
+ or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
+ License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
+ on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
+ of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
+ defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
+ incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
+ of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
+
+ END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
+
+ Copyright 2014-2026 DataJoint Inc. and contributors
+
+ Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+ you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+ You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+ http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+ Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+ distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+ WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+ See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+ limitations under the License.
diff --git a/LICENSE.txt b/LICENSE.txt
deleted file mode 100644
index 90f4edaaa..000000000
--- a/LICENSE.txt
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,504 +0,0 @@
- GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
- Version 2.1, February 1999
-
- Copyright (C) 1991, 1999 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
- 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
- Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
- of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
-
-(This is the first released version of the Lesser GPL. It also counts
- as the successor of the GNU Library Public License, version 2, hence
- the version number 2.1.)
-
- Preamble
-
- The licenses for most software are designed to take away your
-freedom to share and change it. By contrast, the GNU General Public
-Licenses are intended to guarantee your freedom to share and change
-free software--to make sure the software is free for all its users.
-
- This license, the Lesser General Public License, applies to some
-specially designated software packages--typically libraries--of the
-Free Software Foundation and other authors who decide to use it. You
-can use it too, but we suggest you first think carefully about whether
-this license or the ordinary General Public License is the better
-strategy to use in any particular case, based on the explanations below.
-
- When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom of use,
-not price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that
-you have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge
-for this service if you wish); that you receive source code or can get
-it if you want it; that you can change the software and use pieces of
-it in new free programs; and that you are informed that you can do
-these things.
-
- To protect your rights, we need to make restrictions that forbid
-distributors to deny you these rights or to ask you to surrender these
-rights. These restrictions translate to certain responsibilities for
-you if you distribute copies of the library or if you modify it.
-
- For example, if you distribute copies of the library, whether gratis
-or for a fee, you must give the recipients all the rights that we gave
-you. You must make sure that they, too, receive or can get the source
-code. If you link other code with the library, you must provide
-complete object files to the recipients, so that they can relink them
-with the library after making changes to the library and recompiling
-it. And you must show them these terms so they know their rights.
-
- We protect your rights with a two-step method: (1) we copyright the
-library, and (2) we offer you this license, which gives you legal
-permission to copy, distribute and/or modify the library.
-
- To protect each distributor, we want to make it very clear that
-there is no warranty for the free library. Also, if the library is
-modified by someone else and passed on, the recipients should know
-that what they have is not the original version, so that the original
-author's reputation will not be affected by problems that might be
-introduced by others.
-
- Finally, software patents pose a constant threat to the existence of
-any free program. We wish to make sure that a company cannot
-effectively restrict the users of a free program by obtaining a
-restrictive license from a patent holder. Therefore, we insist that
-any patent license obtained for a version of the library must be
-consistent with the full freedom of use specified in this license.
-
- Most GNU software, including some libraries, is covered by the
-ordinary GNU General Public License. This license, the GNU Lesser
-General Public License, applies to certain designated libraries, and
-is quite different from the ordinary General Public License. We use
-this license for certain libraries in order to permit linking those
-libraries into non-free programs.
-
- When a program is linked with a library, whether statically or using
-a shared library, the combination of the two is legally speaking a
-combined work, a derivative of the original library. The ordinary
-General Public License therefore permits such linking only if the
-entire combination fits its criteria of freedom. The Lesser General
-Public License permits more lax criteria for linking other code with
-the library.
-
- We call this license the "Lesser" General Public License because it
-does Less to protect the user's freedom than the ordinary General
-Public License. It also provides other free software developers Less
-of an advantage over competing non-free programs. These disadvantages
-are the reason we use the ordinary General Public License for many
-libraries. However, the Lesser license provides advantages in certain
-special circumstances.
-
- For example, on rare occasions, there may be a special need to
-encourage the widest possible use of a certain library, so that it becomes
-a de-facto standard. To achieve this, non-free programs must be
-allowed to use the library. A more frequent case is that a free
-library does the same job as widely used non-free libraries. In this
-case, there is little to gain by limiting the free library to free
-software only, so we use the Lesser General Public License.
-
- In other cases, permission to use a particular library in non-free
-programs enables a greater number of people to use a large body of
-free software. For example, permission to use the GNU C Library in
-non-free programs enables many more people to use the whole GNU
-operating system, as well as its variant, the GNU/Linux operating
-system.
-
- Although the Lesser General Public License is Less protective of the
-users' freedom, it does ensure that the user of a program that is
-linked with the Library has the freedom and the wherewithal to run
-that program using a modified version of the Library.
-
- The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and
-modification follow. Pay close attention to the difference between a
-"work based on the library" and a "work that uses the library". The
-former contains code derived from the library, whereas the latter must
-be combined with the library in order to run.
-
- GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
- TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR COPYING, DISTRIBUTION AND MODIFICATION
-
- 0. This License Agreement applies to any software library or other
-program which contains a notice placed by the copyright holder or
-other authorized party saying it may be distributed under the terms of
-this Lesser General Public License (also called "this License").
-Each licensee is addressed as "you".
-
- A "library" means a collection of software functions and/or data
-prepared so as to be conveniently linked with application programs
-(which use some of those functions and data) to form executables.
-
- The "Library", below, refers to any such software library or work
-which has been distributed under these terms. A "work based on the
-Library" means either the Library or any derivative work under
-copyright law: that is to say, a work containing the Library or a
-portion of it, either verbatim or with modifications and/or translated
-straightforwardly into another language. (Hereinafter, translation is
-included without limitation in the term "modification".)
-
- "Source code" for a work means the preferred form of the work for
-making modifications to it. For a library, complete source code means
-all the source code for all modules it contains, plus any associated
-interface definition files, plus the scripts used to control compilation
-and installation of the library.
-
- Activities other than copying, distribution and modification are not
-covered by this License; they are outside its scope. The act of
-running a program using the Library is not restricted, and output from
-such a program is covered only if its contents constitute a work based
-on the Library (independent of the use of the Library in a tool for
-writing it). Whether that is true depends on what the Library does
-and what the program that uses the Library does.
-
- 1. You may copy and distribute verbatim copies of the Library's
-complete source code as you receive it, in any medium, provided that
-you conspicuously and appropriately publish on each copy an
-appropriate copyright notice and disclaimer of warranty; keep intact
-all the notices that refer to this License and to the absence of any
-warranty; and distribute a copy of this License along with the
-Library.
-
- You may charge a fee for the physical act of transferring a copy,
-and you may at your option offer warranty protection in exchange for a
-fee.
-
- 2. You may modify your copy or copies of the Library or any portion
-of it, thus forming a work based on the Library, and copy and
-distribute such modifications or work under the terms of Section 1
-above, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
-
- a) The modified work must itself be a software library.
-
- b) You must cause the files modified to carry prominent notices
- stating that you changed the files and the date of any change.
-
- c) You must cause the whole of the work to be licensed at no
- charge to all third parties under the terms of this License.
-
- d) If a facility in the modified Library refers to a function or a
- table of data to be supplied by an application program that uses
- the facility, other than as an argument passed when the facility
- is invoked, then you must make a good faith effort to ensure that,
- in the event an application does not supply such function or
- table, the facility still operates, and performs whatever part of
- its purpose remains meaningful.
-
- (For example, a function in a library to compute square roots has
- a purpose that is entirely well-defined independent of the
- application. Therefore, Subsection 2d requires that any
- application-supplied function or table used by this function must
- be optional: if the application does not supply it, the square
- root function must still compute square roots.)
-
-These requirements apply to the modified work as a whole. If
-identifiable sections of that work are not derived from the Library,
-and can be reasonably considered independent and separate works in
-themselves, then this License, and its terms, do not apply to those
-sections when you distribute them as separate works. But when you
-distribute the same sections as part of a whole which is a work based
-on the Library, the distribution of the whole must be on the terms of
-this License, whose permissions for other licensees extend to the
-entire whole, and thus to each and every part regardless of who wrote
-it.
-
-Thus, it is not the intent of this section to claim rights or contest
-your rights to work written entirely by you; rather, the intent is to
-exercise the right to control the distribution of derivative or
-collective works based on the Library.
-
-In addition, mere aggregation of another work not based on the Library
-with the Library (or with a work based on the Library) on a volume of
-a storage or distribution medium does not bring the other work under
-the scope of this License.
-
- 3. You may opt to apply the terms of the ordinary GNU General Public
-License instead of this License to a given copy of the Library. To do
-this, you must alter all the notices that refer to this License, so
-that they refer to the ordinary GNU General Public License, version 2,
-instead of to this License. (If a newer version than version 2 of the
-ordinary GNU General Public License has appeared, then you can specify
-that version instead if you wish.) Do not make any other change in
-these notices.
-
- Once this change is made in a given copy, it is irreversible for
-that copy, so the ordinary GNU General Public License applies to all
-subsequent copies and derivative works made from that copy.
-
- This option is useful when you wish to copy part of the code of
-the Library into a program that is not a library.
-
- 4. You may copy and distribute the Library (or a portion or
-derivative of it, under Section 2) in object code or executable form
-under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above provided that you accompany
-it with the complete corresponding machine-readable source code, which
-must be distributed under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above on a
-medium customarily used for software interchange.
-
- If distribution of object code is made by offering access to copy
-from a designated place, then offering equivalent access to copy the
-source code from the same place satisfies the requirement to
-distribute the source code, even though third parties are not
-compelled to copy the source along with the object code.
-
- 5. A program that contains no derivative of any portion of the
-Library, but is designed to work with the Library by being compiled or
-linked with it, is called a "work that uses the Library". Such a
-work, in isolation, is not a derivative work of the Library, and
-therefore falls outside the scope of this License.
-
- However, linking a "work that uses the Library" with the Library
-creates an executable that is a derivative of the Library (because it
-contains portions of the Library), rather than a "work that uses the
-library". The executable is therefore covered by this License.
-Section 6 states terms for distribution of such executables.
-
- When a "work that uses the Library" uses material from a header file
-that is part of the Library, the object code for the work may be a
-derivative work of the Library even though the source code is not.
-Whether this is true is especially significant if the work can be
-linked without the Library, or if the work is itself a library. The
-threshold for this to be true is not precisely defined by law.
-
- If such an object file uses only numerical parameters, data
-structure layouts and accessors, and small macros and small inline
-functions (ten lines or less in length), then the use of the object
-file is unrestricted, regardless of whether it is legally a derivative
-work. (Executables containing this object code plus portions of the
-Library will still fall under Section 6.)
-
- Otherwise, if the work is a derivative of the Library, you may
-distribute the object code for the work under the terms of Section 6.
-Any executables containing that work also fall under Section 6,
-whether or not they are linked directly with the Library itself.
-
- 6. As an exception to the Sections above, you may also combine or
-link a "work that uses the Library" with the Library to produce a
-work containing portions of the Library, and distribute that work
-under terms of your choice, provided that the terms permit
-modification of the work for the customer's own use and reverse
-engineering for debugging such modifications.
-
- You must give prominent notice with each copy of the work that the
-Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are covered by
-this License. You must supply a copy of this License. If the work
-during execution displays copyright notices, you must include the
-copyright notice for the Library among them, as well as a reference
-directing the user to the copy of this License. Also, you must do one
-of these things:
-
- a) Accompany the work with the complete corresponding
- machine-readable source code for the Library including whatever
- changes were used in the work (which must be distributed under
- Sections 1 and 2 above); and, if the work is an executable linked
- with the Library, with the complete machine-readable "work that
- uses the Library", as object code and/or source code, so that the
- user can modify the Library and then relink to produce a modified
- executable containing the modified Library. (It is understood
- that the user who changes the contents of definitions files in the
- Library will not necessarily be able to recompile the application
- to use the modified definitions.)
-
- b) Use a suitable shared library mechanism for linking with the
- Library. A suitable mechanism is one that (1) uses at run time a
- copy of the library already present on the user's computer system,
- rather than copying library functions into the executable, and (2)
- will operate properly with a modified version of the library, if
- the user installs one, as long as the modified version is
- interface-compatible with the version that the work was made with.
-
- c) Accompany the work with a written offer, valid for at
- least three years, to give the same user the materials
- specified in Subsection 6a, above, for a charge no more
- than the cost of performing this distribution.
-
- d) If distribution of the work is made by offering access to copy
- from a designated place, offer equivalent access to copy the above
- specified materials from the same place.
-
- e) Verify that the user has already received a copy of these
- materials or that you have already sent this user a copy.
-
- For an executable, the required form of the "work that uses the
-Library" must include any data and utility programs needed for
-reproducing the executable from it. However, as a special exception,
-the materials to be distributed need not include anything that is
-normally distributed (in either source or binary form) with the major
-components (compiler, kernel, and so on) of the operating system on
-which the executable runs, unless that component itself accompanies
-the executable.
-
- It may happen that this requirement contradicts the license
-restrictions of other proprietary libraries that do not normally
-accompany the operating system. Such a contradiction means you cannot
-use both them and the Library together in an executable that you
-distribute.
-
- 7. You may place library facilities that are a work based on the
-Library side-by-side in a single library together with other library
-facilities not covered by this License, and distribute such a combined
-library, provided that the separate distribution of the work based on
-the Library and of the other library facilities is otherwise
-permitted, and provided that you do these two things:
-
- a) Accompany the combined library with a copy of the same work
- based on the Library, uncombined with any other library
- facilities. This must be distributed under the terms of the
- Sections above.
-
- b) Give prominent notice with the combined library of the fact
- that part of it is a work based on the Library, and explaining
- where to find the accompanying uncombined form of the same work.
-
- 8. You may not copy, modify, sublicense, link with, or distribute
-the Library except as expressly provided under this License. Any
-attempt otherwise to copy, modify, sublicense, link with, or
-distribute the Library is void, and will automatically terminate your
-rights under this License. However, parties who have received copies,
-or rights, from you under this License will not have their licenses
-terminated so long as such parties remain in full compliance.
-
- 9. You are not required to accept this License, since you have not
-signed it. However, nothing else grants you permission to modify or
-distribute the Library or its derivative works. These actions are
-prohibited by law if you do not accept this License. Therefore, by
-modifying or distributing the Library (or any work based on the
-Library), you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so, and
-all its terms and conditions for copying, distributing or modifying
-the Library or works based on it.
-
- 10. Each time you redistribute the Library (or any work based on the
-Library), the recipient automatically receives a license from the
-original licensor to copy, distribute, link with or modify the Library
-subject to these terms and conditions. You may not impose any further
-restrictions on the recipients' exercise of the rights granted herein.
-You are not responsible for enforcing compliance by third parties with
-this License.
-
- 11. If, as a consequence of a court judgment or allegation of patent
-infringement or for any other reason (not limited to patent issues),
-conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
-otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
-excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot
-distribute so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this
-License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you
-may not distribute the Library at all. For example, if a patent
-license would not permit royalty-free redistribution of the Library by
-all those who receive copies directly or indirectly through you, then
-the only way you could satisfy both it and this License would be to
-refrain entirely from distribution of the Library.
-
-If any portion of this section is held invalid or unenforceable under any
-particular circumstance, the balance of the section is intended to apply,
-and the section as a whole is intended to apply in other circumstances.
-
-It is not the purpose of this section to induce you to infringe any
-patents or other property right claims or to contest validity of any
-such claims; this section has the sole purpose of protecting the
-integrity of the free software distribution system which is
-implemented by public license practices. Many people have made
-generous contributions to the wide range of software distributed
-through that system in reliance on consistent application of that
-system; it is up to the author/donor to decide if he or she is willing
-to distribute software through any other system and a licensee cannot
-impose that choice.
-
-This section is intended to make thoroughly clear what is believed to
-be a consequence of the rest of this License.
-
- 12. If the distribution and/or use of the Library is restricted in
-certain countries either by patents or by copyrighted interfaces, the
-original copyright holder who places the Library under this License may add
-an explicit geographical distribution limitation excluding those countries,
-so that distribution is permitted only in or among countries not thus
-excluded. In such case, this License incorporates the limitation as if
-written in the body of this License.
-
- 13. The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new
-versions of the Lesser General Public License from time to time.
-Such new versions will be similar in spirit to the present version,
-but may differ in detail to address new problems or concerns.
-
-Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the Library
-specifies a version number of this License which applies to it and
-"any later version", you have the option of following the terms and
-conditions either of that version or of any later version published by
-the Free Software Foundation. If the Library does not specify a
-license version number, you may choose any version ever published by
-the Free Software Foundation.
-
- 14. If you wish to incorporate parts of the Library into other free
-programs whose distribution conditions are incompatible with these,
-write to the author to ask for permission. For software which is
-copyrighted by the Free Software Foundation, write to the Free
-Software Foundation; we sometimes make exceptions for this. Our
-decision will be guided by the two goals of preserving the free status
-of all derivatives of our free software and of promoting the sharing
-and reuse of software generally.
-
- NO WARRANTY
-
- 15. BECAUSE THE LIBRARY IS LICENSED FREE OF CHARGE, THERE IS NO
-WARRANTY FOR THE LIBRARY, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW.
-EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR
-OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE LIBRARY "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY
-KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
-IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
-PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE
-LIBRARY IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE LIBRARY PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME
-THE COST OF ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
-
- 16. IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN
-WRITING WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MAY MODIFY
-AND/OR REDISTRIBUTE THE LIBRARY AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU
-FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR
-CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE
-LIBRARY (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEING
-RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD PARTIES OR A
-FAILURE OF THE LIBRARY TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER SOFTWARE), EVEN IF
-SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
-DAMAGES.
-
- END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
-
- How to Apply These Terms to Your New Libraries
-
- If you develop a new library, and you want it to be of the greatest
-possible use to the public, we recommend making it free software that
-everyone can redistribute and change. You can do so by permitting
-redistribution under these terms (or, alternatively, under the terms of the
-ordinary General Public License).
-
- To apply these terms, attach the following notices to the library. It is
-safest to attach them to the start of each source file to most effectively
-convey the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least the
-"copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
-
- {description}
- Copyright (C) {year} {fullname}
-
- This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
- modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
- License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
- version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
-
- This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
- Lesser General Public License for more details.
-
- You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
- License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
- Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301
- USA
-
-Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
-
-You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or your
-school, if any, to sign a "copyright disclaimer" for the library, if
-necessary. Here is a sample; alter the names:
-
- Yoyodyne, Inc., hereby disclaims all copyright interest in the
- library `Frob' (a library for tweaking knobs) written by James Random
- Hacker.
-
- {signature of Ty Coon}, 1 April 1990
- Ty Coon, President of Vice
-
-That's all there is to it!
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index e582c8ec5..40a1a2c7c 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,116 +1,69 @@
-# Welcome to DataJoint for Python!
+# DataJoint for Python
+
+DataJoint is a framework for scientific data pipelines that introduces the **Relational Workflow Model**—a paradigm where your database schema is an executable specification of your workflow.
+
+Traditional databases store data but don't understand how it was computed. DataJoint extends relational databases with native workflow semantics:
+
+- **Tables represent workflow steps** — Each table is a step in your pipeline where entities are created
+- **Foreign keys encode dependencies** — Parent tables must be populated before child tables
+- **Computations are declarative** — Define *what* to compute; DataJoint determines *when* and tracks *what's done*
+- **Results are immutable** — Computed results preserve full provenance and reproducibility
+
+### Object-Augmented Schemas
+
+Scientific data includes both structured metadata and large data objects (time series, images, movies, neural recordings, gene sequences). DataJoint solves this with **Object-Augmented Schemas (OAS)**—a unified architecture where relational tables and object storage are managed as one system with identical guarantees for integrity, transactions, and lifecycle.
+
+### DataJoint 2.0
+
+**DataJoint 2.0** solidifies these core concepts with a modernized API, improved type system, and enhanced object storage integration. Existing users can refer to the [Migration Guide](https://docs.datajoint.com/migration/) for upgrading from earlier versions.
+
+**Documentation:** https://docs.datajoint.com
-
-
| PyPI |
 -
-
-
-  -
-
|
-
-
- | Conda Forge |
+ Conda |
 -
-
-
-  -
-
-
- |
-
-
- | Since Release |
-
-
-  -
-
|
- | Test Status |
+ Tests |

|
-
-
- | Release Status |
-
-
-  -
-
-
- |
-
-
- | Doc Status |
-
-
-  -
-
-
- |
-
-
| Coverage |
-  +
+ 
|
-
- | Developer Chat |
-
-
-  -
-
-
- |
-
| License |
-
-  +
+
+
+  +
+
+
+ |
+ Citation |
+
+
+ 
|
-
- | Citation |
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
-
-  -
-
-
- |
-
-
-DataJoint for Python is a framework for scientific workflow management based on
-relational principles. DataJoint is built on the foundation of the relational data
-model and prescribes a consistent method for organizing, populating, computing, and
-querying data.
-
-DataJoint was initially developed in 2009 by Dimitri Yatsenko in Andreas Tolias' Lab at
-Baylor College of Medicine for the distributed processing and management of large
-volumes of data streaming from regular experiments. Starting in 2011, DataJoint has
-been available as an open-source project adopted by other labs and improved through
-contributions from several developers.
-Presently, the primary developer of DataJoint open-source software is the company
-DataJoint ().
-
## Data Pipeline Example
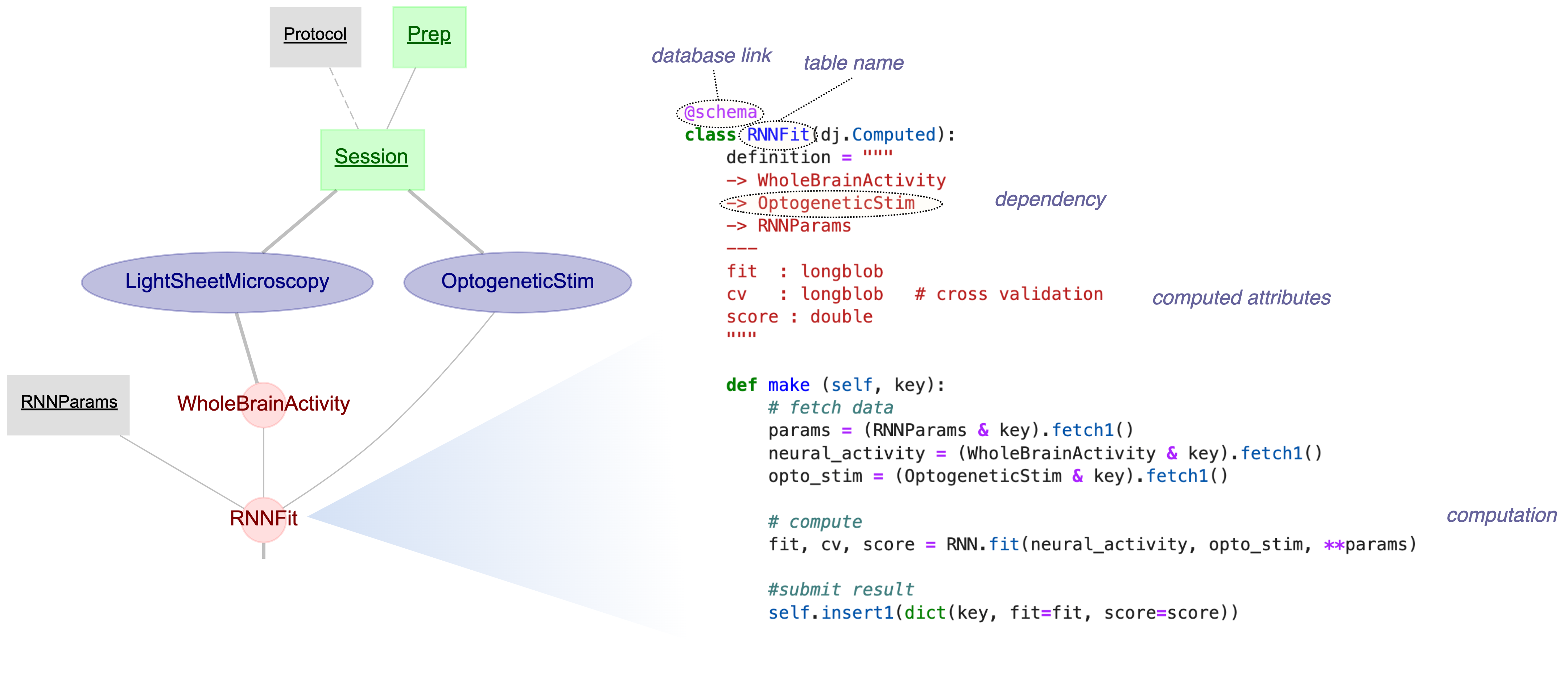
@@ -141,3 +94,129 @@ DataJoint ().
- [Contribution Guidelines](https://docs.datajoint.com/about/contribute/)
- [Developer Guide](https://docs.datajoint.com/core/datajoint-python/latest/develop/)
+
+## Developer Guide
+
+### Prerequisites
+
+- [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/) (Docker daemon must be running)
+- [pixi](https://pixi.sh) (recommended) or Python 3.10+
+
+### Quick Start with pixi (Recommended)
+
+[pixi](https://pixi.sh) manages all dependencies including Python, graphviz, and test tools:
+
+```bash
+# Clone the repo
+git clone https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python.git
+cd datajoint-python
+
+# Install dependencies and run tests (containers managed by testcontainers)
+pixi run test
+
+# Run with coverage
+pixi run test-cov
+
+# Run pre-commit hooks
+pixi run pre-commit run --all-files
+```
+
+### Running Tests
+
+Tests use [testcontainers](https://testcontainers.com/) to automatically manage MySQL and MinIO containers.
+**No manual `docker-compose up` required** - containers start when tests run and stop afterward.
+
+```bash
+# Run all tests (recommended)
+pixi run test
+
+# Run with coverage report
+pixi run test-cov
+
+# Run only unit tests (no containers needed)
+pixi run -e test pytest tests/unit/
+
+# Run specific test file
+pixi run -e test pytest tests/integration/test_blob.py -v
+```
+
+**macOS Docker Desktop users:** If tests fail to connect to Docker, set `DOCKER_HOST`:
+```bash
+export DOCKER_HOST=unix://$HOME/.docker/run/docker.sock
+```
+
+### Alternative: Using pip
+
+If you prefer pip over pixi:
+
+```bash
+pip install -e ".[test]"
+pytest tests/
+```
+
+### Alternative: External Containers
+
+For development/debugging, you may prefer persistent containers that survive test runs:
+
+```bash
+# Start containers manually
+docker compose up -d db minio
+
+# Run tests using external containers
+DJ_USE_EXTERNAL_CONTAINERS=1 pixi run test
+# Or with pip: DJ_USE_EXTERNAL_CONTAINERS=1 pytest tests/
+
+# Stop containers when done
+docker compose down
+```
+
+### Alternative: Full Docker
+
+Run tests entirely in Docker (no local Python needed):
+
+```bash
+docker compose --profile test up djtest --build
+```
+
+### Pre-commit Hooks
+
+Pre-commit hooks run automatically on `git commit` to check code quality.
+**All hooks must pass before committing.**
+
+```bash
+# Install hooks (first time only)
+pixi run pre-commit install
+# Or with pip: pip install pre-commit && pre-commit install
+
+# Run all checks manually
+pixi run pre-commit run --all-files
+
+# Run specific hook
+pixi run pre-commit run ruff --all-files
+```
+
+Hooks include:
+- **ruff**: Python linting and formatting
+- **codespell**: Spell checking
+- **YAML/JSON/TOML validation**
+- **Large file detection**
+
+### Before Submitting a PR
+
+1. **Run all tests**: `pixi run test`
+2. **Run pre-commit**: `pixi run pre-commit run --all-files`
+3. **Check coverage**: `pixi run test-cov`
+
+### Environment Variables
+
+For external container mode (`DJ_USE_EXTERNAL_CONTAINERS=1`):
+
+| Variable | Default | Description |
+|----------|---------|-------------|
+| `DJ_HOST` | `localhost` | MySQL hostname |
+| `DJ_PORT` | `3306` | MySQL port |
+| `DJ_USER` | `root` | MySQL username |
+| `DJ_PASS` | `password` | MySQL password |
+| `S3_ENDPOINT` | `localhost:9000` | MinIO endpoint |
+
+For Docker-based testing (devcontainer, djtest), set `DJ_HOST=db` and `S3_ENDPOINT=minio:9000`.
diff --git a/RELEASE_MEMO.md b/RELEASE_MEMO.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..25fdc6ca0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/RELEASE_MEMO.md
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
+# DataJoint 2.0 Release Memo
+
+## PyPI Release Process
+
+### Steps
+
+1. **Run "Manual Draft Release" workflow** on GitHub Actions
+2. **Edit the draft release**:
+ - Change release name to `Release 2.0.0`
+ - Change tag to `v2.0.0`
+3. **Publish the release**
+4. Automation will:
+ - Update `version.py` to `2.0.0`
+ - Build and publish to PyPI
+ - Create PR to merge version update back to master
+
+### Version Note
+
+The release drafter computes version from the previous tag (`v0.14.6`), so it would generate `0.14.7` or `0.15.0`. You must **manually edit** the release name to include `2.0.0`.
+
+The regex on line 42 of `post_draft_release_published.yaml` extracts version from the release name:
+```bash
+VERSION=$(echo "${{ github.event.release.name }}" | grep -oP '\d+\.\d+\.\d+')
+```
+
+---
+
+## Conda-Forge Release Process
+
+DataJoint has a [conda-forge feedstock](https://github.com/conda-forge/datajoint-feedstock).
+
+### How Conda-Forge Updates Work
+
+Conda-forge has **automated bots** that detect new PyPI releases and create PRs automatically:
+
+1. **You publish to PyPI** (via the GitHub release workflow)
+2. **regro-cf-autotick-bot** detects the new version within ~24 hours
+3. **Bot creates a PR** to the feedstock with updated version and hash
+4. **Maintainers review and merge** (you're listed as a maintainer)
+5. **Package builds automatically** for all platforms
+
+### Manual Update (if bot doesn't trigger)
+
+If the bot doesn't create a PR, manually update the feedstock:
+
+1. **Fork** [conda-forge/datajoint-feedstock](https://github.com/conda-forge/datajoint-feedstock)
+
+2. **Edit `recipe/meta.yaml`**:
+ ```yaml
+ {% set version = "2.0.0" %}
+
+ package:
+ name: datajoint
+ version: {{ version }}
+
+ source:
+ url: https://pypi.io/packages/source/d/datajoint/datajoint-{{ version }}.tar.gz
+ sha256:
+
+ build:
+ number: 0 # Reset to 0 for new version
+ ```
+
+3. **Get the SHA256 hash**:
+ ```bash
+ curl -sL https://pypi.org/pypi/datajoint/2.0.0/json | jq -r '.urls[] | select(.packagetype=="sdist") | .digests.sha256'
+ ```
+
+4. **Update license** (important for 2.0!):
+ ```yaml
+ about:
+ license: Apache-2.0 # Changed from LGPL-2.1-only
+ license_file: LICENSE
+ ```
+
+5. **Submit PR** to the feedstock
+
+### Action Items for 2.0 Release
+
+1. **First**: Publish to PyPI via GitHub release (name it "Release 2.0.0")
+2. **Wait**: ~24 hours for conda-forge bot to detect
+3. **Check**: [datajoint-feedstock PRs](https://github.com/conda-forge/datajoint-feedstock/pulls) for auto-PR
+4. **Review**: Ensure license changed from LGPL to Apache-2.0
+5. **Merge**: As maintainer, approve and merge the PR
+
+### Timeline
+
+| Step | When |
+|------|------|
+| PyPI release | Day 0 |
+| Bot detects & creates PR | Day 0-1 |
+| Review & merge PR | Day 1-2 |
+| Conda-forge package available | Day 1-2 |
+
+### Verification
+
+After release:
+```bash
+conda search datajoint -c conda-forge
+# Should show 2.0.0
+```
+
+---
+
+## Maintainers
+
+- @datajointbot
+- @dimitri-yatsenko
+- @drewyangdev
+- @guzman-raphael
+- @ttngu207
+
+## Links
+
+- [datajoint-feedstock on GitHub](https://github.com/conda-forge/datajoint-feedstock)
+- [datajoint on Anaconda.org](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/datajoint)
+- [datajoint on PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/datajoint/)
diff --git a/activate.sh b/activate.sh
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1632accc8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/activate.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
+#! /usr/bin/bash
+# This script registers dot plugins so that we can use graphviz
+# to write png images
+dot -c
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/datajoint/__init__.py b/datajoint/__init__.py
deleted file mode 100644
index a7c5e7b2f..000000000
--- a/datajoint/__init__.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-"""
-DataJoint for Python is a framework for building data pipelines using MySQL databases
-to represent pipeline structure and bulk storage systems for large objects.
-DataJoint is built on the foundation of the relational data model and prescribes a
-consistent method for organizing, populating, and querying data.
-
-The DataJoint data model is described in https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11104
-
-DataJoint is free software under the LGPL License. In addition, we request
-that any use of DataJoint leading to a publication be acknowledged in the publication.
-
-Please cite:
-
- - http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2015/11/14/031658
- - http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/031658
-"""
-
-__author__ = "DataJoint Contributors"
-__date__ = "November 7, 2020"
-__all__ = [
- "__author__",
- "__version__",
- "config",
- "conn",
- "Connection",
- "Schema",
- "schema",
- "VirtualModule",
- "create_virtual_module",
- "list_schemas",
- "Table",
- "FreeTable",
- "Manual",
- "Lookup",
- "Imported",
- "Computed",
- "Part",
- "Not",
- "AndList",
- "Top",
- "U",
- "Diagram",
- "Di",
- "ERD",
- "set_password",
- "kill",
- "MatCell",
- "MatStruct",
- "AttributeAdapter",
- "errors",
- "DataJointError",
- "key",
- "key_hash",
- "logger",
- "cli",
-]
-
-from . import errors
-from .admin import kill, set_password
-from .attribute_adapter import AttributeAdapter
-from .blob import MatCell, MatStruct
-from .cli import cli
-from .connection import Connection, conn
-from .diagram import Diagram
-from .errors import DataJointError
-from .expression import AndList, Not, Top, U
-from .fetch import key
-from .hash import key_hash
-from .logging import logger
-from .schemas import Schema, VirtualModule, list_schemas
-from .settings import config
-from .table import FreeTable, Table
-from .user_tables import Computed, Imported, Lookup, Manual, Part
-from .version import __version__
-
-ERD = Di = Diagram # Aliases for Diagram
-schema = Schema # Aliases for Schema
-create_virtual_module = VirtualModule # Aliases for VirtualModule
diff --git a/datajoint/admin.py b/datajoint/admin.py
deleted file mode 100644
index e1eb803ec..000000000
--- a/datajoint/admin.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,127 +0,0 @@
-import logging
-from getpass import getpass
-
-import pymysql
-from packaging import version
-
-from .connection import conn
-from .settings import config
-from .utils import user_choice
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-
-
-def set_password(new_password=None, connection=None, update_config=None):
- connection = conn() if connection is None else connection
- if new_password is None:
- new_password = getpass("New password: ")
- confirm_password = getpass("Confirm password: ")
- if new_password != confirm_password:
- logger.warning("Failed to confirm the password! Aborting password change.")
- return
-
- if version.parse(
- connection.query("select @@version;").fetchone()[0]
- ) >= version.parse("5.7"):
- # SET PASSWORD is deprecated as of MySQL 5.7 and removed in 8+
- connection.query("ALTER USER user() IDENTIFIED BY '%s';" % new_password)
- else:
- connection.query("SET PASSWORD = PASSWORD('%s')" % new_password)
- logger.info("Password updated.")
-
- if update_config or (
- update_config is None and user_choice("Update local setting?") == "yes"
- ):
- config["database.password"] = new_password
- config.save_local(verbose=True)
-
-
-def kill(restriction=None, connection=None, order_by=None):
- """
- view and kill database connections.
-
- :param restriction: restriction to be applied to processlist
- :param connection: a datajoint.Connection object. Default calls datajoint.conn()
- :param order_by: order by a single attribute or the list of attributes. defaults to 'id'.
-
- Restrictions are specified as strings and can involve any of the attributes of
- information_schema.processlist: ID, USER, HOST, DB, COMMAND, TIME, STATE, INFO.
-
- Examples:
- dj.kill('HOST LIKE "%compute%"') lists only connections from hosts containing "compute".
- dj.kill('TIME > 600') lists only connections in their current state for more than 10 minutes
- """
-
- if connection is None:
- connection = conn()
-
- if order_by is not None and not isinstance(order_by, str):
- order_by = ",".join(order_by)
-
- query = (
- "SELECT * FROM information_schema.processlist WHERE id <> CONNECTION_ID()"
- + ("" if restriction is None else " AND (%s)" % restriction)
- + (" ORDER BY %s" % (order_by or "id"))
- )
-
- while True:
- print(" ID USER HOST STATE TIME INFO")
- print("+--+ +----------+ +-----------+ +-----------+ +-----+")
- cur = (
- {k.lower(): v for k, v in elem.items()}
- for elem in connection.query(query, as_dict=True)
- )
- for process in cur:
- try:
- print(
- "{id:>4d} {user:<12s} {host:<12s} {state:<12s} {time:>7d} {info}".format(
- **process
- )
- )
- except TypeError:
- print(process)
- response = input('process to kill or "q" to quit > ')
- if response == "q":
- break
- if response:
- try:
- pid = int(response)
- except ValueError:
- pass # ignore non-numeric input
- else:
- try:
- connection.query("kill %d" % pid)
- except pymysql.err.InternalError:
- logger.warn("Process not found")
-
-
-def kill_quick(restriction=None, connection=None):
- """
- Kill database connections without prompting. Returns number of terminated connections.
-
- :param restriction: restriction to be applied to processlist
- :param connection: a datajoint.Connection object. Default calls datajoint.conn()
-
- Restrictions are specified as strings and can involve any of the attributes of
- information_schema.processlist: ID, USER, HOST, DB, COMMAND, TIME, STATE, INFO.
-
- Examples:
- dj.kill('HOST LIKE "%compute%"') terminates connections from hosts containing "compute".
- """
- if connection is None:
- connection = conn()
-
- query = (
- "SELECT * FROM information_schema.processlist WHERE id <> CONNECTION_ID()"
- + ("" if restriction is None else " AND (%s)" % restriction)
- )
-
- cur = (
- {k.lower(): v for k, v in elem.items()}
- for elem in connection.query(query, as_dict=True)
- )
- nkill = 0
- for process in cur:
- connection.query("kill %d" % process["id"])
- nkill += 1
- return nkill
diff --git a/datajoint/attribute_adapter.py b/datajoint/attribute_adapter.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 2a8e59a51..000000000
--- a/datajoint/attribute_adapter.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-import re
-
-from .errors import DataJointError, _support_adapted_types
-
-
-class AttributeAdapter:
- """
- Base class for adapter objects for user-defined attribute types.
- """
-
- @property
- def attribute_type(self):
- """
- :return: a supported DataJoint attribute type to use; e.g. "longblob", "blob@store"
- """
- raise NotImplementedError("Undefined attribute adapter")
-
- def get(self, value):
- """
- convert value retrieved from the the attribute in a table into the adapted type
-
- :param value: value from the database
-
- :return: object of the adapted type
- """
- raise NotImplementedError("Undefined attribute adapter")
-
- def put(self, obj):
- """
- convert an object of the adapted type into a value that DataJoint can store in a table attribute
-
- :param obj: an object of the adapted type
- :return: value to store in the database
- """
- raise NotImplementedError("Undefined attribute adapter")
-
-
-def get_adapter(context, adapter_name):
- """
- Extract the AttributeAdapter object by its name from the context and validate.
- """
- if not _support_adapted_types():
- raise DataJointError("Support for Adapted Attribute types is disabled.")
- adapter_name = adapter_name.lstrip("<").rstrip(">")
- try:
- adapter = context[adapter_name]
- except KeyError:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute adapter '{adapter_name}' is not defined.".format(
- adapter_name=adapter_name
- )
- )
- if not isinstance(adapter, AttributeAdapter):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute adapter '{adapter_name}' must be an instance of datajoint.AttributeAdapter".format(
- adapter_name=adapter_name
- )
- )
- if not isinstance(adapter.attribute_type, str) or not re.match(
- r"^\w", adapter.attribute_type
- ):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Invalid attribute type {type} in attribute adapter '{adapter_name}'".format(
- type=adapter.attribute_type, adapter_name=adapter_name
- )
- )
- return adapter
diff --git a/datajoint/autopopulate.py b/datajoint/autopopulate.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 226e64dda..000000000
--- a/datajoint/autopopulate.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,476 +0,0 @@
-"""This module defines class dj.AutoPopulate"""
-
-import contextlib
-import datetime
-import inspect
-import logging
-import multiprocessing as mp
-import random
-import signal
-import traceback
-
-import deepdiff
-from tqdm import tqdm
-
-from .errors import DataJointError, LostConnectionError
-from .expression import AndList, QueryExpression
-from .hash import key_hash
-
-# noinspection PyExceptionInherit,PyCallingNonCallable
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-
-
-# --- helper functions for multiprocessing --
-
-
-def _initialize_populate(table, jobs, populate_kwargs):
- """
- Initialize the process for multiprocessing.
- Saves the unpickled copy of the table to the current process and reconnects.
- """
- process = mp.current_process()
- process.table = table
- process.jobs = jobs
- process.populate_kwargs = populate_kwargs
- table.connection.connect() # reconnect
-
-
-def _call_populate1(key):
- """
- Call current process' table._populate1()
- :key - a dict specifying job to compute
- :return: key, error if error, otherwise None
- """
- process = mp.current_process()
- return process.table._populate1(key, process.jobs, **process.populate_kwargs)
-
-
-class AutoPopulate:
- """
- AutoPopulate is a mixin class that adds the method populate() to a Table class.
- Auto-populated tables must inherit from both Table and AutoPopulate,
- must define the property `key_source`, and must define the callback method `make`.
- """
-
- _key_source = None
- _allow_insert = False
-
- @property
- def key_source(self):
- """
- :return: the query expression that yields primary key values to be passed,
- sequentially, to the ``make`` method when populate() is called.
- The default value is the join of the parent tables references from the primary key.
- Subclasses may override they key_source to change the scope or the granularity
- of the make calls.
- """
-
- def _rename_attributes(table, props):
- return (
- table.proj(
- **{
- attr: ref
- for attr, ref in props["attr_map"].items()
- if attr != ref
- }
- )
- if props["aliased"]
- else table.proj()
- )
-
- if self._key_source is None:
- parents = self.target.parents(
- primary=True, as_objects=True, foreign_key_info=True
- )
- if not parents:
- raise DataJointError(
- "A table must have dependencies "
- "from its primary key for auto-populate to work"
- )
- self._key_source = _rename_attributes(*parents[0])
- for q in parents[1:]:
- self._key_source *= _rename_attributes(*q)
- return self._key_source
-
- def make(self, key):
- """
- This method must be implemented by derived classes to perform automated computation.
- The method must implement the following three steps:
-
- 1. Fetch data from tables above in the dependency hierarchy, restricted by the given key.
- 2. Compute secondary attributes based on the fetched data.
- 3. Insert the new tuple(s) into the current table.
-
- The method can be implemented either as:
- (a) Regular method: All three steps are performed in a single database transaction.
- The method must return None.
- (b) Generator method:
- The make method is split into three functions:
- - `make_fetch`: Fetches data from the parent tables.
- - `make_compute`: Computes secondary attributes based on the fetched data.
- - `make_insert`: Inserts the computed data into the current table.
-
- Then populate logic is executes as follows:
-
-
- fetched_data1 = self.make_fetch(key)
- computed_result = self.make_compute(key, *fetched_data1)
- begin transaction:
- fetched_data2 = self.make_fetch(key)
- if fetched_data1 != fetched_data2:
- cancel transaction
- else:
- self.make_insert(key, *computed_result)
- commit_transaction
-
-
- Importantly, the output of make_fetch is a tuple that serves as the input into `make_compute`.
- The output of `make_compute` is a tuple that serves as the input into `make_insert`.
-
- The functionality must be strictly divided between these three methods:
- - All database queries must be completed in `make_fetch`.
- - All computation must be completed in `make_compute`.
- - All database inserts must be completed in `make_insert`.
-
- DataJoint may programmatically enforce this separation in the future.
-
- :param key: The primary key value used to restrict the data fetching.
- :raises NotImplementedError: If the derived class does not implement the required methods.
- """
-
- if not (
- hasattr(self, "make_fetch")
- and hasattr(self, "make_insert")
- and hasattr(self, "make_compute")
- ):
- # user must implement `make`
- raise NotImplementedError(
- "Subclasses of AutoPopulate must implement the method `make` "
- "or (`make_fetch` + `make_compute` + `make_insert`)"
- )
-
- # User has implemented `_fetch`, `_compute`, and `_insert` methods instead
-
- # Step 1: Fetch data from parent tables
- fetched_data = self.make_fetch(key) # fetched_data is a tuple
- computed_result = yield fetched_data # passed as input into make_compute
-
- # Step 2: If computed result is not passed in, compute the result
- if computed_result is None:
- # this is only executed in the first invocation
- computed_result = self.make_compute(key, *fetched_data)
- yield computed_result # this is passed to the second invocation of make
-
- # Step 3: Insert the computed result into the current table.
- self.make_insert(key, *computed_result)
- yield
-
- @property
- def target(self):
- """
- :return: table to be populated.
- In the typical case, dj.AutoPopulate is mixed into a dj.Table class by
- inheritance and the target is self.
- """
- return self
-
- def _job_key(self, key):
- """
- :param key: they key returned for the job from the key source
- :return: the dict to use to generate the job reservation hash
- This method allows subclasses to control the job reservation granularity.
- """
- return key
-
- def _jobs_to_do(self, restrictions):
- """
- :return: the query yielding the keys to be computed (derived from self.key_source)
- """
- if self.restriction:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot call populate on a restricted table. "
- "Instead, pass conditions to populate() as arguments."
- )
- todo = self.key_source
-
- # key_source is a QueryExpression subclass -- trigger instantiation
- if inspect.isclass(todo) and issubclass(todo, QueryExpression):
- todo = todo()
-
- if not isinstance(todo, QueryExpression):
- raise DataJointError("Invalid key_source value")
-
- try:
- # check if target lacks any attributes from the primary key of key_source
- raise DataJointError(
- "The populate target lacks attribute %s "
- "from the primary key of key_source"
- % next(
- name
- for name in todo.heading.primary_key
- if name not in self.target.heading
- )
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass
- return (todo & AndList(restrictions)).proj()
-
- def populate(
- self,
- *restrictions,
- keys=None,
- suppress_errors=False,
- return_exception_objects=False,
- reserve_jobs=False,
- order="original",
- limit=None,
- max_calls=None,
- display_progress=False,
- processes=1,
- make_kwargs=None,
- ):
- """
- ``table.populate()`` calls ``table.make(key)`` for every primary key in
- ``self.key_source`` for which there is not already a tuple in table.
-
- :param restrictions: a list of restrictions each restrict
- (table.key_source - target.proj())
- :param keys: The list of keys (dicts) to send to self.make().
- If None (default), then use self.key_source to query they keys.
- :param suppress_errors: if True, do not terminate execution.
- :param return_exception_objects: return error objects instead of just error messages
- :param reserve_jobs: if True, reserve jobs to populate in asynchronous fashion
- :param order: "original"|"reverse"|"random" - the order of execution
- :param limit: if not None, check at most this many keys
- :param max_calls: if not None, populate at most this many keys
- :param display_progress: if True, report progress_bar
- :param processes: number of processes to use. Set to None to use all cores
- :param make_kwargs: Keyword arguments which do not affect the result of computation
- to be passed down to each ``make()`` call. Computation arguments should be
- specified within the pipeline e.g. using a `dj.Lookup` table.
- :type make_kwargs: dict, optional
- :return: a dict with two keys
- "success_count": the count of successful ``make()`` calls in this ``populate()`` call
- "error_list": the error list that is filled if `suppress_errors` is True
- """
- if self.connection.in_transaction:
- raise DataJointError("Populate cannot be called during a transaction.")
-
- valid_order = ["original", "reverse", "random"]
- if order not in valid_order:
- raise DataJointError(
- "The order argument must be one of %s" % str(valid_order)
- )
- jobs = (
- self.connection.schemas[self.target.database].jobs if reserve_jobs else None
- )
-
- if reserve_jobs:
- # Define a signal handler for SIGTERM
- def handler(signum, frame):
- logger.info("Populate terminated by SIGTERM")
- raise SystemExit("SIGTERM received")
-
- old_handler = signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, handler)
-
- if keys is None:
- keys = (self._jobs_to_do(restrictions) - self.target).fetch(
- "KEY", limit=limit
- )
-
- # exclude "error", "ignore" or "reserved" jobs
- if reserve_jobs:
- exclude_key_hashes = (
- jobs
- & {"table_name": self.target.table_name}
- & 'status in ("error", "ignore", "reserved")'
- ).fetch("key_hash")
- keys = [key for key in keys if key_hash(key) not in exclude_key_hashes]
-
- if order == "reverse":
- keys.reverse()
- elif order == "random":
- random.shuffle(keys)
-
- logger.debug("Found %d keys to populate" % len(keys))
-
- keys = keys[:max_calls]
- nkeys = len(keys)
-
- error_list = []
- success_list = []
-
- if nkeys:
- processes = min(_ for _ in (processes, nkeys, mp.cpu_count()) if _)
-
- populate_kwargs = dict(
- suppress_errors=suppress_errors,
- return_exception_objects=return_exception_objects,
- make_kwargs=make_kwargs,
- )
-
- if processes == 1:
- for key in (
- tqdm(keys, desc=self.__class__.__name__)
- if display_progress
- else keys
- ):
- status = self._populate1(key, jobs, **populate_kwargs)
- if status is True:
- success_list.append(1)
- elif isinstance(status, tuple):
- error_list.append(status)
- else:
- assert status is False
- else:
- # spawn multiple processes
- self.connection.close() # disconnect parent process from MySQL server
- del self.connection._conn.ctx # SSLContext is not pickleable
- with (
- mp.Pool(
- processes, _initialize_populate, (self, jobs, populate_kwargs)
- ) as pool,
- (
- tqdm(desc="Processes: ", total=nkeys)
- if display_progress
- else contextlib.nullcontext()
- ) as progress_bar,
- ):
- for status in pool.imap(_call_populate1, keys, chunksize=1):
- if status is True:
- success_list.append(1)
- elif isinstance(status, tuple):
- error_list.append(status)
- else:
- assert status is False
- if display_progress:
- progress_bar.update()
- self.connection.connect() # reconnect parent process to MySQL server
-
- # restore original signal handler:
- if reserve_jobs:
- signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, old_handler)
-
- return {
- "success_count": sum(success_list),
- "error_list": error_list,
- }
-
- def _populate1(
- self, key, jobs, suppress_errors, return_exception_objects, make_kwargs=None
- ):
- """
- populates table for one source key, calling self.make inside a transaction.
- :param jobs: the jobs table or None if not reserve_jobs
- :param key: dict specifying job to populate
- :param suppress_errors: bool if errors should be suppressed and returned
- :param return_exception_objects: if True, errors must be returned as objects
- :return: (key, error) when suppress_errors=True,
- True if successfully invoke one `make()` call, otherwise False
- """
- # use the legacy `_make_tuples` callback.
- make = self._make_tuples if hasattr(self, "_make_tuples") else self.make
-
- if jobs is not None and not jobs.reserve(
- self.target.table_name, self._job_key(key)
- ):
- return False
-
- # if make is a generator, it transaction can be delayed until the final stage
- is_generator = inspect.isgeneratorfunction(make)
- if not is_generator:
- self.connection.start_transaction()
-
- if key in self.target: # already populated
- if not is_generator:
- self.connection.cancel_transaction()
- if jobs is not None:
- jobs.complete(self.target.table_name, self._job_key(key))
- return False
-
- logger.debug(f"Making {key} -> {self.target.full_table_name}")
- self.__class__._allow_insert = True
-
- try:
- if not is_generator:
- make(dict(key), **(make_kwargs or {}))
- else:
- # tripartite make - transaction is delayed until the final stage
- gen = make(dict(key), **(make_kwargs or {}))
- fetched_data = next(gen)
- fetch_hash = deepdiff.DeepHash(
- fetched_data, ignore_iterable_order=False
- )[fetched_data]
- computed_result = next(gen) # perform the computation
- # fetch and insert inside a transaction
- self.connection.start_transaction()
- gen = make(dict(key), **(make_kwargs or {})) # restart make
- fetched_data = next(gen)
- if (
- fetch_hash
- != deepdiff.DeepHash(fetched_data, ignore_iterable_order=False)[
- fetched_data
- ]
- ): # raise error if fetched data has changed
- raise DataJointError(
- "Referential integrity failed! The `make_fetch` data has changed"
- )
- gen.send(computed_result) # insert
-
- except (KeyboardInterrupt, SystemExit, Exception) as error:
- try:
- self.connection.cancel_transaction()
- except LostConnectionError:
- pass
- error_message = "{exception}{msg}".format(
- exception=error.__class__.__name__,
- msg=": " + str(error) if str(error) else "",
- )
- logger.debug(
- f"Error making {key} -> {self.target.full_table_name} - {error_message}"
- )
- if jobs is not None:
- # show error name and error message (if any)
- jobs.error(
- self.target.table_name,
- self._job_key(key),
- error_message=error_message,
- error_stack=traceback.format_exc(),
- )
- if not suppress_errors or isinstance(error, SystemExit):
- raise
- else:
- logger.error(error)
- return key, error if return_exception_objects else error_message
- else:
- self.connection.commit_transaction()
- logger.debug(f"Success making {key} -> {self.target.full_table_name}")
- if jobs is not None:
- jobs.complete(self.target.table_name, self._job_key(key))
- return True
- finally:
- self.__class__._allow_insert = False
-
- def progress(self, *restrictions, display=False):
- """
- Report the progress of populating the table.
- :return: (remaining, total) -- numbers of tuples to be populated
- """
- todo = self._jobs_to_do(restrictions)
- total = len(todo)
- remaining = len(todo - self.target)
- if display:
- logger.info(
- "%-20s" % self.__class__.__name__
- + " Completed %d of %d (%2.1f%%) %s"
- % (
- total - remaining,
- total,
- 100 - 100 * remaining / (total + 1e-12),
- datetime.datetime.strftime(
- datetime.datetime.now(), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
- ),
- ),
- )
- return remaining, total
diff --git a/datajoint/cli.py b/datajoint/cli.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 3b7e72c25..000000000
--- a/datajoint/cli.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-import argparse
-from code import interact
-from collections import ChainMap
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-
-def cli(args: list = None):
- """
- Console interface for DataJoint Python
-
- :param args: List of arguments to be passed in, defaults to reading stdin
- :type args: list, optional
- """
- parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
- prog="datajoint",
- description="DataJoint console interface.",
- conflict_handler="resolve",
- )
- parser.add_argument(
- "-V", "--version", action="version", version=f"{dj.__name__} {dj.__version__}"
- )
- parser.add_argument(
- "-u",
- "--user",
- type=str,
- default=dj.config["database.user"],
- required=False,
- help="Datajoint username",
- )
- parser.add_argument(
- "-p",
- "--password",
- type=str,
- default=dj.config["database.password"],
- required=False,
- help="Datajoint password",
- )
- parser.add_argument(
- "-h",
- "--host",
- type=str,
- default=dj.config["database.host"],
- required=False,
- help="Datajoint host",
- )
- parser.add_argument(
- "-s",
- "--schemas",
- nargs="+",
- type=str,
- required=False,
- help="A list of virtual module mappings in `db:schema ...` format",
- )
- kwargs = vars(parser.parse_args(args))
- mods = {}
- if kwargs["user"]:
- dj.config["database.user"] = kwargs["user"]
- if kwargs["password"]:
- dj.config["database.password"] = kwargs["password"]
- if kwargs["host"]:
- dj.config["database.host"] = kwargs["host"]
- if kwargs["schemas"]:
- for vm in kwargs["schemas"]:
- d, m = vm.split(":")
- mods[m] = dj.create_virtual_module(m, d)
-
- banner = "dj repl\n"
- if mods:
- modstr = "\n".join(" - {}".format(m) for m in mods)
- banner += "\nschema modules:\n\n" + modstr + "\n"
- interact(banner, local=dict(ChainMap(mods, locals(), globals())))
-
- raise SystemExit
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- cli()
diff --git a/datajoint/condition.py b/datajoint/condition.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 96cfbb6ef..000000000
--- a/datajoint/condition.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,356 +0,0 @@
-"""methods for generating SQL WHERE clauses from datajoint restriction conditions"""
-
-import collections
-import datetime
-import decimal
-import inspect
-import json
-import re
-import uuid
-from dataclasses import dataclass
-from typing import List, Union
-
-import numpy
-import pandas
-
-from .errors import DataJointError
-
-JSON_PATTERN = re.compile(
- r"^(?P\w+)(\.(?P[\w.*\[\]]+))?(:(?P[\w(,\s)]+))?$"
-)
-
-
-def translate_attribute(key):
- match = JSON_PATTERN.match(key)
- if match is None:
- return match, key
- match = match.groupdict()
- if match["path"] is None:
- return match, match["attr"]
- else:
- return match, "json_value(`{}`, _utf8mb4'$.{}'{})".format(
- *[
- ((f" returning {v}" if k == "type" else v) if v else "")
- for k, v in match.items()
- ]
- )
-
-
-class PromiscuousOperand:
- """
- A container for an operand to ignore join compatibility
- """
-
- def __init__(self, operand):
- self.operand = operand
-
-
-class AndList(list):
- """
- A list of conditions to by applied to a query expression by logical conjunction: the
- conditions are AND-ed. All other collections (lists, sets, other entity sets, etc) are
- applied by logical disjunction (OR).
-
- Example:
- expr2 = expr & dj.AndList((cond1, cond2, cond3))
- is equivalent to
- expr2 = expr & cond1 & cond2 & cond3
- """
-
- def append(self, restriction):
- if isinstance(restriction, AndList):
- # extend to reduce nesting
- self.extend(restriction)
- else:
- super().append(restriction)
-
-
-@dataclass
-class Top:
- """
- A restriction to the top entities of a query.
- In SQL, this corresponds to ORDER BY ... LIMIT ... OFFSET
- """
-
- limit: Union[int, None] = 1
- order_by: Union[str, List[str]] = "KEY"
- offset: int = 0
-
- def __post_init__(self):
- self.order_by = self.order_by or ["KEY"]
- self.offset = self.offset or 0
-
- if self.limit is not None and not isinstance(self.limit, int):
- raise TypeError("Top limit must be an integer")
- if not isinstance(self.order_by, (str, collections.abc.Sequence)) or not all(
- isinstance(r, str) for r in self.order_by
- ):
- raise TypeError("Top order_by attributes must all be strings")
- if not isinstance(self.offset, int):
- raise TypeError("The offset argument must be an integer")
- if self.offset and self.limit is None:
- self.limit = 999999999999 # arbitrary large number to allow query
- if isinstance(self.order_by, str):
- self.order_by = [self.order_by]
-
-
-class Not:
- """invert restriction"""
-
- def __init__(self, restriction):
- self.restriction = restriction
-
-
-def assert_join_compatibility(expr1, expr2):
- """
- Determine if expressions expr1 and expr2 are join-compatible. To be join-compatible,
- the matching attributes in the two expressions must be in the primary key of one or the
- other expression.
- Raises an exception if not compatible.
-
- :param expr1: A QueryExpression object
- :param expr2: A QueryExpression object
- """
- from .expression import QueryExpression, U
-
- for rel in (expr1, expr2):
- if not isinstance(rel, (U, QueryExpression)):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Object %r is not a QueryExpression and cannot be joined." % rel
- )
- if not isinstance(expr1, U) and not isinstance(
- expr2, U
- ): # dj.U is always compatible
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot join query expressions on dependent attribute `%s`"
- % next(
- r
- for r in set(expr1.heading.secondary_attributes).intersection(
- expr2.heading.secondary_attributes
- )
- )
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # all ok
-
-
-def make_condition(query_expression, condition, columns):
- """
- Translate the input condition into the equivalent SQL condition (a string)
-
- :param query_expression: a dj.QueryExpression object to apply condition
- :param condition: any valid restriction object.
- :param columns: a set passed by reference to collect all column names used in the
- condition.
- :return: an SQL condition string or a boolean value.
- """
- from .expression import Aggregation, QueryExpression, U
-
- def prep_value(k, v):
- """prepare SQL condition"""
- key_match, k = translate_attribute(k)
- if key_match["path"] is None:
- k = f"`{k}`"
- if (
- query_expression.heading[key_match["attr"]].json
- and key_match["path"] is not None
- and isinstance(v, dict)
- ):
- return f"{k}='{json.dumps(v)}'"
- if v is None:
- return f"{k} IS NULL"
- if query_expression.heading[key_match["attr"]].uuid:
- if not isinstance(v, uuid.UUID):
- try:
- v = uuid.UUID(v)
- except (AttributeError, ValueError):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Badly formed UUID {v} in restriction by `{k}`".format(k=k, v=v)
- )
- return f"{k}=X'{v.bytes.hex()}'"
- if isinstance(
- v,
- (
- datetime.date,
- datetime.datetime,
- datetime.time,
- decimal.Decimal,
- list,
- ),
- ):
- return f'{k}="{v}"'
- if isinstance(v, str):
- v = v.replace("%", "%%").replace("\\", "\\\\")
- return f'{k}="{v}"'
- return f"{k}={v}"
-
- def combine_conditions(negate, conditions):
- return f"{'NOT ' if negate else ''} ({')AND('.join(conditions)})"
-
- negate = False
- while isinstance(condition, Not):
- negate = not negate
- condition = condition.restriction
-
- # restrict by string
- if isinstance(condition, str):
- columns.update(extract_column_names(condition))
- return combine_conditions(
- negate, conditions=[condition.strip().replace("%", "%%")]
- ) # escape %, see issue #376
-
- # restrict by AndList
- if isinstance(condition, AndList):
- # omit all conditions that evaluate to True
- items = [
- item
- for item in (
- make_condition(query_expression, cond, columns) for cond in condition
- )
- if item is not True
- ]
- if any(item is False for item in items):
- return negate # if any item is False, the whole thing is False
- if not items:
- return not negate # and empty AndList is True
- return combine_conditions(negate, conditions=items)
-
- # restriction by dj.U evaluates to True
- if isinstance(condition, U):
- return not negate
-
- # restrict by boolean
- if isinstance(condition, bool):
- return negate != condition
-
- # restrict by a mapping/dict -- convert to an AndList of string equality conditions
- if isinstance(condition, collections.abc.Mapping):
- common_attributes = set(c.split(".", 1)[0] for c in condition).intersection(
- query_expression.heading.names
- )
- if not common_attributes:
- return not negate # no matching attributes -> evaluates to True
- columns.update(common_attributes)
- return combine_conditions(
- negate,
- conditions=[
- prep_value(k, v)
- for k, v in condition.items()
- if k.split(".", 1)[0] in common_attributes # handle json indexing
- ],
- )
-
- # restrict by a numpy record -- convert to an AndList of string equality conditions
- if isinstance(condition, numpy.void):
- common_attributes = set(condition.dtype.fields).intersection(
- query_expression.heading.names
- )
- if not common_attributes:
- return not negate # no matching attributes -> evaluate to True
- columns.update(common_attributes)
- return combine_conditions(
- negate,
- conditions=[prep_value(k, condition[k]) for k in common_attributes],
- )
-
- # restrict by a QueryExpression subclass -- trigger instantiation and move on
- if inspect.isclass(condition) and issubclass(condition, QueryExpression):
- condition = condition()
-
- # restrict by another expression (aka semijoin and antijoin)
- check_compatibility = True
- if isinstance(condition, PromiscuousOperand):
- condition = condition.operand
- check_compatibility = False
-
- if isinstance(condition, QueryExpression):
- if check_compatibility:
- assert_join_compatibility(query_expression, condition)
- common_attributes = [
- q for q in condition.heading.names if q in query_expression.heading.names
- ]
- columns.update(common_attributes)
- if isinstance(condition, Aggregation):
- condition = condition.make_subquery()
- return (
- # without common attributes, any non-empty set matches everything
- (not negate if condition else negate)
- if not common_attributes
- else "({fields}) {not_}in ({subquery})".format(
- fields="`" + "`,`".join(common_attributes) + "`",
- not_="not " if negate else "",
- subquery=condition.make_sql(common_attributes),
- )
- )
-
- # restrict by pandas.DataFrames
- if isinstance(condition, pandas.DataFrame):
- condition = condition.to_records() # convert to numpy.recarray and move on
-
- # if iterable (but not a string, a QueryExpression, or an AndList), treat as an OrList
- try:
- or_list = [make_condition(query_expression, q, columns) for q in condition]
- except TypeError:
- raise DataJointError("Invalid restriction type %r" % condition)
- else:
- or_list = [
- item for item in or_list if item is not False
- ] # ignore False conditions
- if any(item is True for item in or_list): # if any item is True, entirely True
- return not negate
- return (
- f"{'NOT ' if negate else ''} ({' OR '.join(or_list)})"
- if or_list
- else negate
- )
-
-
-def extract_column_names(sql_expression):
- """
- extract all presumed column names from an sql expression such as the WHERE clause,
- for example.
-
- :param sql_expression: a string containing an SQL expression
- :return: set of extracted column names
- This may be MySQL-specific for now.
- """
- assert isinstance(sql_expression, str)
- result = set()
- s = sql_expression # for terseness
- # remove escaped quotes
- s = re.sub(r"(\\\")|(\\\')", "", s)
- # remove quoted text
- s = re.sub(r"'[^']*'", "", s)
- s = re.sub(r'"[^"]*"', "", s)
- # find all tokens in back quotes and remove them
- result.update(re.findall(r"`([a-z][a-z_0-9]*)`", s))
- s = re.sub(r"`[a-z][a-z_0-9]*`", "", s)
- # remove space before parentheses
- s = re.sub(r"\s*\(", "(", s)
- # remove tokens followed by ( since they must be functions
- s = re.sub(r"(\b[a-z][a-z_0-9]*)\(", "(", s)
- remaining_tokens = set(re.findall(r"\b[a-z][a-z_0-9]*\b", s))
- # update result removing reserved words
- result.update(
- remaining_tokens
- - {
- "is",
- "in",
- "between",
- "like",
- "and",
- "or",
- "null",
- "not",
- "interval",
- "second",
- "minute",
- "hour",
- "day",
- "month",
- "week",
- "year",
- }
- )
- return result
diff --git a/datajoint/connection.py b/datajoint/connection.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 21b1c97a4..000000000
--- a/datajoint/connection.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,404 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This module contains the Connection class that manages the connection to the database, and
-the ``conn`` function that provides access to a persistent connection in datajoint.
-"""
-
-import logging
-import pathlib
-import re
-import warnings
-from contextlib import contextmanager
-from getpass import getpass
-
-import pymysql as client
-
-from . import errors
-from .blob import pack, unpack
-from .dependencies import Dependencies
-from .hash import uuid_from_buffer
-from .settings import config
-from .version import __version__
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-query_log_max_length = 300
-
-
-cache_key = "query_cache" # the key to lookup the query_cache folder in dj.config
-
-
-def translate_query_error(client_error, query):
- """
- Take client error and original query and return the corresponding DataJoint exception.
-
- :param client_error: the exception raised by the client interface
- :param query: sql query with placeholders
- :return: an instance of the corresponding subclass of datajoint.errors.DataJointError
- """
- logger.debug("type: {}, args: {}".format(type(client_error), client_error.args))
-
- err, *args = client_error.args
-
- # Loss of connection errors
- if err in (0, "(0, '')"):
- return errors.LostConnectionError(
- "Server connection lost due to an interface error.", *args
- )
- if err == 2006:
- return errors.LostConnectionError("Connection timed out", *args)
- if err == 2013:
- return errors.LostConnectionError("Server connection lost", *args)
- # Access errors
- if err in (1044, 1142):
- return errors.AccessError("Insufficient privileges.", args[0], query)
- # Integrity errors
- if err == 1062:
- return errors.DuplicateError(*args)
- if err == 1217: # MySQL 8 error code
- return errors.IntegrityError(*args)
- if err == 1451:
- return errors.IntegrityError(*args)
- if err == 1452:
- return errors.IntegrityError(*args)
- # Syntax errors
- if err == 1064:
- return errors.QuerySyntaxError(args[0], query)
- # Existence errors
- if err == 1146:
- return errors.MissingTableError(args[0], query)
- if err == 1364:
- return errors.MissingAttributeError(*args)
- if err == 1054:
- return errors.UnknownAttributeError(*args)
- # all the other errors are re-raised in original form
- return client_error
-
-
-def conn(
- host=None, user=None, password=None, *, init_fun=None, reset=False, use_tls=None
-):
- """
- Returns a persistent connection object to be shared by multiple modules.
- If the connection is not yet established or reset=True, a new connection is set up.
- If connection information is not provided, it is taken from config which takes the
- information from dj_local_conf.json. If the password is not specified in that file
- datajoint prompts for the password.
-
- :param host: hostname
- :param user: mysql user
- :param password: mysql password
- :param init_fun: initialization function
- :param reset: whether the connection should be reset or not
- :param use_tls: TLS encryption option. Valid options are: True (required), False
- (required no TLS), None (TLS preferred, default), dict (Manually specify values per
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/connection-options.html#encrypted-connection-options).
- """
- if not hasattr(conn, "connection") or reset:
- host = host if host is not None else config["database.host"]
- user = user if user is not None else config["database.user"]
- password = password if password is not None else config["database.password"]
- if user is None:
- user = input("Please enter DataJoint username: ")
- if password is None:
- password = getpass(prompt="Please enter DataJoint password: ")
- init_fun = (
- init_fun if init_fun is not None else config["connection.init_function"]
- )
- use_tls = use_tls if use_tls is not None else config["database.use_tls"]
- conn.connection = Connection(host, user, password, None, init_fun, use_tls)
- return conn.connection
-
-
-class EmulatedCursor:
- """acts like a cursor"""
-
- def __init__(self, data):
- self._data = data
- self._iter = iter(self._data)
-
- def __iter__(self):
- return self
-
- def __next__(self):
- return next(self._iter)
-
- def fetchall(self):
- return self._data
-
- def fetchone(self):
- return next(self._iter)
-
- @property
- def rowcount(self):
- return len(self._data)
-
-
-class Connection:
- """
- A dj.Connection object manages a connection to a database server.
- It also catalogues modules, schemas, tables, and their dependencies (foreign keys).
-
- Most of the parameters below should be set in the local configuration file.
-
- :param host: host name, may include port number as hostname:port, in which case it overrides the value in port
- :param user: user name
- :param password: password
- :param port: port number
- :param init_fun: connection initialization function (SQL)
- :param use_tls: TLS encryption option
- """
-
- def __init__(self, host, user, password, port=None, init_fun=None, use_tls=None):
- if ":" in host:
- # the port in the hostname overrides the port argument
- host, port = host.split(":")
- port = int(port)
- elif port is None:
- port = config["database.port"]
- self.conn_info = dict(host=host, port=port, user=user, passwd=password)
- if use_tls is not False:
- self.conn_info["ssl"] = (
- use_tls if isinstance(use_tls, dict) else {"ssl": {}}
- )
- self.conn_info["ssl_input"] = use_tls
- self.init_fun = init_fun
- self._conn = None
- self._query_cache = None
- self.connect()
- if self.is_connected:
- logger.info(
- "DataJoint {version} connected to {user}@{host}:{port}".format(
- version=__version__, **self.conn_info
- )
- )
- self.connection_id = self.query("SELECT connection_id()").fetchone()[0]
- else:
- raise errors.LostConnectionError(
- "Connection failed {user}@{host}:{port}".format(**self.conn_info)
- )
- self._in_transaction = False
- self.schemas = dict()
- self.dependencies = Dependencies(self)
-
- def __eq__(self, other):
- return self.conn_info == other.conn_info
-
- def __repr__(self):
- connected = "connected" if self.is_connected else "disconnected"
- return "DataJoint connection ({connected}) {user}@{host}:{port}".format(
- connected=connected, **self.conn_info
- )
-
- def connect(self):
- """Connect to the database server."""
- with warnings.catch_warnings():
- warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", ".*deprecated.*")
- try:
- self._conn = client.connect(
- init_command=self.init_fun,
- sql_mode="NO_ZERO_DATE,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,"
- "STRICT_ALL_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY",
- charset=config["connection.charset"],
- **{
- k: v
- for k, v in self.conn_info.items()
- if k not in ["ssl_input"]
- },
- )
- except client.err.InternalError:
- self._conn = client.connect(
- init_command=self.init_fun,
- sql_mode="NO_ZERO_DATE,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,"
- "STRICT_ALL_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY",
- charset=config["connection.charset"],
- **{
- k: v
- for k, v in self.conn_info.items()
- if not (
- k == "ssl_input"
- or k == "ssl"
- and self.conn_info["ssl_input"] is None
- )
- },
- )
- self._conn.autocommit(True)
-
- def set_query_cache(self, query_cache=None):
- """
- When query_cache is not None, the connection switches into the query caching mode, which entails:
- 1. Only SELECT queries are allowed.
- 2. The results of queries are cached under the path indicated by dj.config['query_cache']
- 3. query_cache is a string that differentiates different cache states.
-
- :param query_cache: a string to initialize the hash for query results
- """
- self._query_cache = query_cache
-
- def purge_query_cache(self):
- """Purges all query cache."""
- if (
- isinstance(config.get(cache_key), str)
- and pathlib.Path(config[cache_key]).is_dir()
- ):
- for path in pathlib.Path(config[cache_key]).iterdir():
- if not path.is_dir():
- path.unlink()
-
- def close(self):
- self._conn.close()
-
- def register(self, schema):
- self.schemas[schema.database] = schema
- self.dependencies.clear()
-
- def ping(self):
- """Ping the connection or raises an exception if the connection is closed."""
- self._conn.ping(reconnect=False)
-
- @property
- def is_connected(self):
- """Return true if the object is connected to the database server."""
- try:
- self.ping()
- except:
- return False
- return True
-
- @staticmethod
- def _execute_query(cursor, query, args, suppress_warnings):
- try:
- with warnings.catch_warnings():
- if suppress_warnings:
- # suppress all warnings arising from underlying SQL library
- warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
- cursor.execute(query, args)
- except client.err.Error as err:
- raise translate_query_error(err, query)
-
- def query(
- self, query, args=(), *, as_dict=False, suppress_warnings=True, reconnect=None
- ):
- """
- Execute the specified query and return the tuple generator (cursor).
-
- :param query: SQL query
- :param args: additional arguments for the client.cursor
- :param as_dict: If as_dict is set to True, the returned cursor objects returns
- query results as dictionary.
- :param suppress_warnings: If True, suppress all warnings arising from underlying query library
- :param reconnect: when None, get from config, when True, attempt to reconnect if disconnected
- """
- # check cache first:
- use_query_cache = bool(self._query_cache)
- if use_query_cache and not re.match(r"\s*(SELECT|SHOW)", query):
- raise errors.DataJointError(
- "Only SELECT queries are allowed when query caching is on."
- )
- if use_query_cache:
- if not config[cache_key]:
- raise errors.DataJointError(
- f"Provide filepath dj.config['{cache_key}'] when using query caching."
- )
- hash_ = uuid_from_buffer(
- (str(self._query_cache) + re.sub(r"`\$\w+`", "", query)).encode()
- + pack(args)
- )
- cache_path = pathlib.Path(config[cache_key]) / str(hash_)
- try:
- buffer = cache_path.read_bytes()
- except FileNotFoundError:
- pass # proceed to query the database
- else:
- return EmulatedCursor(unpack(buffer))
-
- if reconnect is None:
- reconnect = config["database.reconnect"]
- logger.debug("Executing SQL:" + query[:query_log_max_length])
- cursor_class = client.cursors.DictCursor if as_dict else client.cursors.Cursor
- cursor = self._conn.cursor(cursor=cursor_class)
- try:
- self._execute_query(cursor, query, args, suppress_warnings)
- except errors.LostConnectionError:
- if not reconnect:
- raise
- logger.warning("Reconnecting to MySQL server.")
- self.connect()
- if self._in_transaction:
- self.cancel_transaction()
- raise errors.LostConnectionError(
- "Connection was lost during a transaction."
- )
- logger.debug("Re-executing")
- cursor = self._conn.cursor(cursor=cursor_class)
- self._execute_query(cursor, query, args, suppress_warnings)
-
- if use_query_cache:
- data = cursor.fetchall()
- cache_path.write_bytes(pack(data))
- return EmulatedCursor(data)
-
- return cursor
-
- def get_user(self):
- """
- :return: the user name and host name provided by the client to the server.
- """
- return self.query("SELECT user()").fetchone()[0]
-
- # ---------- transaction processing
- @property
- def in_transaction(self):
- """
- :return: True if there is an open transaction.
- """
- self._in_transaction = self._in_transaction and self.is_connected
- return self._in_transaction
-
- def start_transaction(self):
- """
- Starts a transaction error.
- """
- if self.in_transaction:
- raise errors.DataJointError("Nested connections are not supported.")
- self.query("START TRANSACTION WITH CONSISTENT SNAPSHOT")
- self._in_transaction = True
- logger.debug("Transaction started")
-
- def cancel_transaction(self):
- """
- Cancels the current transaction and rolls back all changes made during the transaction.
- """
- self.query("ROLLBACK")
- self._in_transaction = False
- logger.debug("Transaction cancelled. Rolling back ...")
-
- def commit_transaction(self):
- """
- Commit all changes made during the transaction and close it.
-
- """
- self.query("COMMIT")
- self._in_transaction = False
- logger.debug("Transaction committed and closed.")
-
- # -------- context manager for transactions
- @property
- @contextmanager
- def transaction(self):
- """
- Context manager for transactions. Opens an transaction and closes it after the with statement.
- If an error is caught during the transaction, the commits are automatically rolled back.
- All errors are raised again.
-
- Example:
- >>> import datajoint as dj
- >>> with dj.conn().transaction as conn:
- >>> # transaction is open here
- """
- try:
- self.start_transaction()
- yield self
- except:
- self.cancel_transaction()
- raise
- else:
- self.commit_transaction()
diff --git a/datajoint/declare.py b/datajoint/declare.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 304476798..000000000
--- a/datajoint/declare.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,591 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This module hosts functions to convert DataJoint table definitions into mysql table definitions, and to
-declare the corresponding mysql tables.
-"""
-
-import logging
-import re
-from hashlib import sha1
-
-import pyparsing as pp
-
-from .attribute_adapter import get_adapter
-from .condition import translate_attribute
-from .errors import FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH, DataJointError, _support_filepath_types
-from .settings import config
-
-UUID_DATA_TYPE = "binary(16)"
-MAX_TABLE_NAME_LENGTH = 64
-CONSTANT_LITERALS = {
- "CURRENT_TIMESTAMP",
- "NULL",
-} # SQL literals to be used without quotes (case insensitive)
-EXTERNAL_TABLE_ROOT = "~external"
-
-TYPE_PATTERN = {
- k: re.compile(v, re.I)
- for k, v in dict(
- INTEGER=r"((tiny|small|medium|big|)int|integer)(\s*\(.+\))?(\s+unsigned)?(\s+auto_increment)?|serial$",
- DECIMAL=r"(decimal|numeric)(\s*\(.+\))?(\s+unsigned)?$",
- FLOAT=r"(double|float|real)(\s*\(.+\))?(\s+unsigned)?$",
- STRING=r"(var)?char\s*\(.+\)$",
- JSON=r"json$",
- ENUM=r"enum\s*\(.+\)$",
- BOOL=r"bool(ean)?$", # aliased to tinyint(1)
- TEMPORAL=r"(date|datetime|time|timestamp|year)(\s*\(.+\))?$",
- INTERNAL_BLOB=r"(tiny|small|medium|long|)blob$",
- EXTERNAL_BLOB=r"blob@(?P[a-z][\-\w]*)$",
- INTERNAL_ATTACH=r"attach$",
- EXTERNAL_ATTACH=r"attach@(?P[a-z][\-\w]*)$",
- FILEPATH=r"filepath@(?P[a-z][\-\w]*)$",
- UUID=r"uuid$",
- ADAPTED=r"<.+>$",
- ).items()
-}
-
-# custom types are stored in attribute comment
-SPECIAL_TYPES = {
- "UUID",
- "INTERNAL_ATTACH",
- "EXTERNAL_ATTACH",
- "EXTERNAL_BLOB",
- "FILEPATH",
- "ADAPTED",
-}
-NATIVE_TYPES = set(TYPE_PATTERN) - SPECIAL_TYPES
-EXTERNAL_TYPES = {
- "EXTERNAL_ATTACH",
- "EXTERNAL_BLOB",
- "FILEPATH",
-} # data referenced by a UUID in external tables
-SERIALIZED_TYPES = {
- "EXTERNAL_ATTACH",
- "INTERNAL_ATTACH",
- "EXTERNAL_BLOB",
- "INTERNAL_BLOB",
-} # requires packing data
-
-assert set().union(SPECIAL_TYPES, EXTERNAL_TYPES, SERIALIZED_TYPES) <= set(TYPE_PATTERN)
-
-
-def match_type(attribute_type):
- try:
- return next(
- category
- for category, pattern in TYPE_PATTERN.items()
- if pattern.match(attribute_type)
- )
- except StopIteration:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Unsupported attribute type {type}".format(type=attribute_type)
- )
-
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-
-
-def build_foreign_key_parser_old():
- # old-style foreign key parser. Superseded by expression-based syntax. See issue #436
- # This will be deprecated in a future release.
- left = pp.Literal("(").suppress()
- right = pp.Literal(")").suppress()
- attribute_name = pp.Word(pp.srange("[a-z]"), pp.srange("[a-z0-9_]"))
- new_attrs = pp.Optional(
- left + pp.delimitedList(attribute_name) + right
- ).setResultsName("new_attrs")
- arrow = pp.Literal("->").suppress()
- lbracket = pp.Literal("[").suppress()
- rbracket = pp.Literal("]").suppress()
- option = pp.Word(pp.srange("[a-zA-Z]"))
- options = pp.Optional(
- lbracket + pp.delimitedList(option) + rbracket
- ).setResultsName("options")
- ref_table = pp.Word(pp.alphas, pp.alphanums + "._").setResultsName("ref_table")
- ref_attrs = pp.Optional(
- left + pp.delimitedList(attribute_name) + right
- ).setResultsName("ref_attrs")
- return new_attrs + arrow + options + ref_table + ref_attrs
-
-
-def build_foreign_key_parser():
- arrow = pp.Literal("->").suppress()
- lbracket = pp.Literal("[").suppress()
- rbracket = pp.Literal("]").suppress()
- option = pp.Word(pp.srange("[a-zA-Z]"))
- options = pp.Optional(
- lbracket + pp.delimitedList(option) + rbracket
- ).setResultsName("options")
- ref_table = pp.restOfLine.setResultsName("ref_table")
- return arrow + options + ref_table
-
-
-def build_attribute_parser():
- quoted = pp.QuotedString('"') ^ pp.QuotedString("'")
- colon = pp.Literal(":").suppress()
- attribute_name = pp.Word(pp.srange("[a-z]"), pp.srange("[a-z0-9_]")).setResultsName(
- "name"
- )
- data_type = (
- pp.Combine(pp.Word(pp.alphas) + pp.SkipTo("#", ignore=quoted))
- ^ pp.QuotedString("<", endQuoteChar=">", unquoteResults=False)
- ).setResultsName("type")
- default = pp.Literal("=").suppress() + pp.SkipTo(
- colon, ignore=quoted
- ).setResultsName("default")
- comment = pp.Literal("#").suppress() + pp.restOfLine.setResultsName("comment")
- return attribute_name + pp.Optional(default) + colon + data_type + comment
-
-
-foreign_key_parser_old = build_foreign_key_parser_old()
-foreign_key_parser = build_foreign_key_parser()
-attribute_parser = build_attribute_parser()
-
-
-def is_foreign_key(line):
- """
-
- :param line: a line from the table definition
- :return: true if the line appears to be a foreign key definition
- """
- arrow_position = line.find("->")
- return arrow_position >= 0 and not any(c in line[:arrow_position] for c in "\"#'")
-
-
-def compile_foreign_key(
- line, context, attributes, primary_key, attr_sql, foreign_key_sql, index_sql
-):
- """
- :param line: a line from a table definition
- :param context: namespace containing referenced objects
- :param attributes: list of attribute names already in the declaration -- to be updated by this function
- :param primary_key: None if the current foreign key is made from the dependent section. Otherwise it is the list
- of primary key attributes thus far -- to be updated by the function
- :param attr_sql: list of sql statements defining attributes -- to be updated by this function.
- :param foreign_key_sql: list of sql statements specifying foreign key constraints -- to be updated by this function.
- :param index_sql: list of INDEX declaration statements, duplicate or redundant indexes are ok.
- """
- # Parse and validate
- from .expression import QueryExpression
- from .table import Table
-
- try:
- result = foreign_key_parser.parseString(line)
- except pp.ParseException as err:
- raise DataJointError('Parsing error in line "%s". %s.' % (line, err))
-
- try:
- ref = eval(result.ref_table, context)
- except Exception:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Foreign key reference %s could not be resolved" % result.ref_table
- )
-
- options = [opt.upper() for opt in result.options]
- for opt in options: # check for invalid options
- if opt not in {"NULLABLE", "UNIQUE"}:
- raise DataJointError('Invalid foreign key option "{opt}"'.format(opt=opt))
- is_nullable = "NULLABLE" in options
- is_unique = "UNIQUE" in options
- if is_nullable and primary_key is not None:
- raise DataJointError(
- 'Primary dependencies cannot be nullable in line "{line}"'.format(line=line)
- )
-
- if isinstance(ref, type) and issubclass(ref, Table):
- ref = ref()
-
- # check that dependency is of a supported type
- if (
- not isinstance(ref, QueryExpression)
- or len(ref.restriction)
- or len(ref.support) != 1
- or not isinstance(ref.support[0], str)
- ):
- raise DataJointError(
- 'Dependency "%s" is not supported (yet). Use a base table or its projection.'
- % result.ref_table
- )
-
- # declare new foreign key attributes
- for attr in ref.primary_key:
- if attr not in attributes:
- attributes.append(attr)
- if primary_key is not None:
- primary_key.append(attr)
- attr_sql.append(
- ref.heading[attr].sql.replace("NOT NULL ", "", int(is_nullable))
- )
-
- # declare the foreign key
- foreign_key_sql.append(
- "FOREIGN KEY (`{fk}`) REFERENCES {ref} (`{pk}`) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT".format(
- fk="`,`".join(ref.primary_key),
- pk="`,`".join(ref.heading[name].original_name for name in ref.primary_key),
- ref=ref.support[0],
- )
- )
-
- # declare unique index
- if is_unique:
- index_sql.append(
- "UNIQUE INDEX ({attrs})".format(
- attrs=",".join("`%s`" % attr for attr in ref.primary_key)
- )
- )
-
-
-def prepare_declare(definition, context):
- # split definition into lines
- definition = re.split(r"\s*\n\s*", definition.strip())
- # check for optional table comment
- table_comment = (
- definition.pop(0)[1:].strip() if definition[0].startswith("#") else ""
- )
- if table_comment.startswith(":"):
- raise DataJointError('Table comment must not start with a colon ":"')
- in_key = True # parse primary keys
- primary_key = []
- attributes = []
- attribute_sql = []
- foreign_key_sql = []
- index_sql = []
- external_stores = []
-
- for line in definition:
- if not line or line.startswith("#"): # ignore additional comments
- pass
- elif line.startswith("---") or line.startswith("___"):
- in_key = False # start parsing dependent attributes
- elif is_foreign_key(line):
- compile_foreign_key(
- line,
- context,
- attributes,
- primary_key if in_key else None,
- attribute_sql,
- foreign_key_sql,
- index_sql,
- )
- elif re.match(r"^(unique\s+)?index\s*.*$", line, re.I): # index
- compile_index(line, index_sql)
- else:
- name, sql, store = compile_attribute(line, in_key, foreign_key_sql, context)
- if store:
- external_stores.append(store)
- if in_key and name not in primary_key:
- primary_key.append(name)
- if name not in attributes:
- attributes.append(name)
- attribute_sql.append(sql)
-
- return (
- table_comment,
- primary_key,
- attribute_sql,
- foreign_key_sql,
- index_sql,
- external_stores,
- )
-
-
-def declare(full_table_name, definition, context):
- """
- Parse declaration and generate the SQL CREATE TABLE code
-
- :param full_table_name: full name of the table
- :param definition: DataJoint table definition
- :param context: dictionary of objects that might be referred to in the table
- :return: SQL CREATE TABLE statement, list of external stores used
- """
- table_name = full_table_name.strip("`").split(".")[1]
- if len(table_name) > MAX_TABLE_NAME_LENGTH:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Table name `{name}` exceeds the max length of {max_length}".format(
- name=table_name, max_length=MAX_TABLE_NAME_LENGTH
- )
- )
-
- (
- table_comment,
- primary_key,
- attribute_sql,
- foreign_key_sql,
- index_sql,
- external_stores,
- ) = prepare_declare(definition, context)
-
- if config.get("add_hidden_timestamp", False):
- metadata_attr_sql = [
- "`_{full_table_name}_timestamp` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP"
- ]
- attribute_sql.extend(
- attr.format(
- full_table_name=sha1(
- full_table_name.replace("`", "").encode("utf-8")
- ).hexdigest()
- )
- for attr in metadata_attr_sql
- )
-
- if not primary_key:
- raise DataJointError("Table must have a primary key")
-
- return (
- "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS %s (\n" % full_table_name
- + ",\n".join(
- attribute_sql
- + ["PRIMARY KEY (`" + "`,`".join(primary_key) + "`)"]
- + foreign_key_sql
- + index_sql
- )
- + '\n) ENGINE=InnoDB, COMMENT "%s"' % table_comment
- ), external_stores
-
-
-def _make_attribute_alter(new, old, primary_key):
- """
- :param new: new attribute declarations
- :param old: old attribute declarations
- :param primary_key: primary key attributes
- :return: list of SQL ALTER commands
- """
- # parse attribute names
- name_regexp = re.compile(r"^`(?P\w+)`")
- original_regexp = re.compile(r'COMMENT "{\s*(?P\w+)\s*}')
- matched = ((name_regexp.match(d), original_regexp.search(d)) for d in new)
- new_names = dict((d.group("name"), n and n.group("name")) for d, n in matched)
- old_names = [name_regexp.search(d).group("name") for d in old]
-
- # verify that original names are only used once
- renamed = set()
- for v in new_names.values():
- if v:
- if v in renamed:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Alter attempted to rename attribute {%s} twice." % v
- )
- renamed.add(v)
-
- # verify that all renamed attributes existed in the old definition
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute {} does not exist in the original definition".format(
- next(attr for attr in renamed if attr not in old_names)
- )
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass
-
- # dropping attributes
- to_drop = [n for n in old_names if n not in renamed and n not in new_names]
- sql = ["DROP `%s`" % n for n in to_drop]
- old_names = [name for name in old_names if name not in to_drop]
-
- # add or change attributes in order
- prev = None
- for new_def, (new_name, old_name) in zip(new, new_names.items()):
- if new_name not in primary_key:
- after = None # if None, then must include the AFTER clause
- if prev:
- try:
- idx = old_names.index(old_name or new_name)
- except ValueError:
- after = prev[0]
- else:
- if idx >= 1 and old_names[idx - 1] != (prev[1] or prev[0]):
- after = prev[0]
- if new_def not in old or after:
- sql.append(
- "{command} {new_def} {after}".format(
- command=(
- "ADD"
- if (old_name or new_name) not in old_names
- else "MODIFY" if not old_name else "CHANGE `%s`" % old_name
- ),
- new_def=new_def,
- after="" if after is None else "AFTER `%s`" % after,
- )
- )
- prev = new_name, old_name
-
- return sql
-
-
-def alter(definition, old_definition, context):
- """
- :param definition: new table definition
- :param old_definition: current table definition
- :param context: the context in which to evaluate foreign key definitions
- :return: string SQL ALTER command, list of new stores used for external storage
- """
- (
- table_comment,
- primary_key,
- attribute_sql,
- foreign_key_sql,
- index_sql,
- external_stores,
- ) = prepare_declare(definition, context)
- (
- table_comment_,
- primary_key_,
- attribute_sql_,
- foreign_key_sql_,
- index_sql_,
- external_stores_,
- ) = prepare_declare(old_definition, context)
-
- # analyze differences between declarations
- sql = list()
- if primary_key != primary_key_:
- raise NotImplementedError("table.alter cannot alter the primary key (yet).")
- if foreign_key_sql != foreign_key_sql_:
- raise NotImplementedError("table.alter cannot alter foreign keys (yet).")
- if index_sql != index_sql_:
- raise NotImplementedError("table.alter cannot alter indexes (yet)")
- if attribute_sql != attribute_sql_:
- sql.extend(_make_attribute_alter(attribute_sql, attribute_sql_, primary_key))
- if table_comment != table_comment_:
- sql.append('COMMENT="%s"' % table_comment)
- return sql, [e for e in external_stores if e not in external_stores_]
-
-
-def compile_index(line, index_sql):
- def format_attribute(attr):
- match, attr = translate_attribute(attr)
- if match is None:
- return attr
- if match["path"] is None:
- return f"`{attr}`"
- return f"({attr})"
-
- match = re.match(r"(?Punique\s+)?index\s*\(\s*(?P.*)\)", line, re.I)
- if match is None:
- raise DataJointError(f'Table definition syntax error in line "{line}"')
- match = match.groupdict()
-
- attr_list = re.findall(r"(?:[^,(]|\([^)]*\))+", match["args"])
- index_sql.append(
- "{unique}index ({attrs})".format(
- unique="unique " if match["unique"] else "",
- attrs=",".join(format_attribute(a.strip()) for a in attr_list),
- )
- )
-
-
-def substitute_special_type(match, category, foreign_key_sql, context):
- """
- :param match: dict containing with keys "type" and "comment" -- will be modified in place
- :param category: attribute type category from TYPE_PATTERN
- :param foreign_key_sql: list of foreign key declarations to add to
- :param context: context for looking up user-defined attribute_type adapters
- """
- if category == "UUID":
- match["type"] = UUID_DATA_TYPE
- elif category == "INTERNAL_ATTACH":
- match["type"] = "LONGBLOB"
- elif category in EXTERNAL_TYPES:
- if category == "FILEPATH" and not _support_filepath_types():
- raise DataJointError(
- """
- The filepath data type is disabled until complete validation.
- To turn it on as experimental feature, set the environment variable
- {env} = TRUE or upgrade datajoint.
- """.format(
- env=FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH
- )
- )
- match["store"] = match["type"].split("@", 1)[1]
- match["type"] = UUID_DATA_TYPE
- foreign_key_sql.append(
- "FOREIGN KEY (`{name}`) REFERENCES `{{database}}`.`{external_table_root}_{store}` (`hash`) "
- "ON UPDATE RESTRICT ON DELETE RESTRICT".format(
- external_table_root=EXTERNAL_TABLE_ROOT, **match
- )
- )
- elif category == "ADAPTED":
- adapter = get_adapter(context, match["type"])
- match["type"] = adapter.attribute_type
- category = match_type(match["type"])
- if category in SPECIAL_TYPES:
- # recursive redefinition from user-defined datatypes.
- substitute_special_type(match, category, foreign_key_sql, context)
- else:
- assert False, "Unknown special type"
-
-
-def compile_attribute(line, in_key, foreign_key_sql, context):
- """
- Convert attribute definition from DataJoint format to SQL
-
- :param line: attribution line
- :param in_key: set to True if attribute is in primary key set
- :param foreign_key_sql: the list of foreign key declarations to add to
- :param context: context in which to look up user-defined attribute type adapterss
- :returns: (name, sql, is_external) -- attribute name and sql code for its declaration
- """
- try:
- match = attribute_parser.parseString(line + "#", parseAll=True)
- except pp.ParseException as err:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Declaration error in position {pos} in line:\n {line}\n{msg}".format(
- line=err.args[0], pos=err.args[1], msg=err.args[2]
- )
- )
- match["comment"] = match["comment"].rstrip("#")
- if "default" not in match:
- match["default"] = ""
- match = {k: v.strip() for k, v in match.items()}
- match["nullable"] = match["default"].lower() == "null"
-
- if match["nullable"]:
- if in_key:
- raise DataJointError(
- 'Primary key attributes cannot be nullable in line "%s"' % line
- )
- match["default"] = "DEFAULT NULL" # nullable attributes default to null
- else:
- if match["default"]:
- quote = (
- match["default"].split("(")[0].upper() not in CONSTANT_LITERALS
- and match["default"][0] not in "\"'"
- )
- match["default"] = (
- "NOT NULL DEFAULT " + ('"%s"' if quote else "%s") % match["default"]
- )
- else:
- match["default"] = "NOT NULL"
-
- match["comment"] = match["comment"].replace(
- '"', '\\"'
- ) # escape double quotes in comment
-
- if match["comment"].startswith(":"):
- raise DataJointError(
- 'An attribute comment must not start with a colon in comment "{comment}"'.format(
- **match
- )
- )
-
- category = match_type(match["type"])
- if category in SPECIAL_TYPES:
- match["comment"] = ":{type}:{comment}".format(
- **match
- ) # insert custom type into comment
- substitute_special_type(match, category, foreign_key_sql, context)
-
- if category in SERIALIZED_TYPES and match["default"] not in {
- "DEFAULT NULL",
- "NOT NULL",
- }:
- raise DataJointError(
- "The default value for a blob or attachment attributes can only be NULL in:\n{line}".format(
- line=line
- )
- )
-
- sql = (
- "`{name}` {type} {default}"
- + (' COMMENT "{comment}"' if match["comment"] else "")
- ).format(**match)
- return match["name"], sql, match.get("store")
diff --git a/datajoint/errors.py b/datajoint/errors.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 03555bf13..000000000
--- a/datajoint/errors.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,129 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Exception classes for the DataJoint library
-"""
-
-import os
-
-
-# --- Top Level ---
-class DataJointError(Exception):
- """
- Base class for errors specific to DataJoint internal operation.
- """
-
- def suggest(self, *args):
- """
- regenerate the exception with additional arguments
-
- :param args: addition arguments
- :return: a new exception of the same type with the additional arguments
- """
- return self.__class__(*(self.args + args))
-
-
-# --- Second Level ---
-class LostConnectionError(DataJointError):
- """
- Loss of server connection
- """
-
-
-class QueryError(DataJointError):
- """
- Errors arising from queries to the database
- """
-
-
-# --- Third Level: QueryErrors ---
-class QuerySyntaxError(QueryError):
- """
- Errors arising from incorrect query syntax
- """
-
-
-class AccessError(QueryError):
- """
- User access error: insufficient privileges.
- """
-
-
-class MissingTableError(DataJointError):
- """
- Query on a table that has not been declared
- """
-
-
-class DuplicateError(QueryError):
- """
- An integrity error caused by a duplicate entry into a unique key
- """
-
-
-class IntegrityError(QueryError):
- """
- An integrity error triggered by foreign key constraints
- """
-
-
-class UnknownAttributeError(QueryError):
- """
- User requests an attribute name not found in query heading
- """
-
-
-class MissingAttributeError(QueryError):
- """
- An error arising when a required attribute value is not provided in INSERT
- """
-
-
-class MissingExternalFile(DataJointError):
- """
- Error raised when an external file managed by DataJoint is no longer accessible
- """
-
-
-class BucketInaccessible(DataJointError):
- """
- Error raised when a S3 bucket is inaccessible
- """
-
-
-# environment variables to control availability of experimental features
-
-ADAPTED_TYPE_SWITCH = "DJ_SUPPORT_ADAPTED_TYPES"
-FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH = "DJ_SUPPORT_FILEPATH_MANAGEMENT"
-
-
-def _switch_adapted_types(on):
- """
- Enable (on=True) or disable (on=False) support for AttributeAdapter
- """
- if on:
- os.environ[ADAPTED_TYPE_SWITCH] = "TRUE"
- else:
- del os.environ[ADAPTED_TYPE_SWITCH]
-
-
-def _support_adapted_types():
- """
- check if support for AttributeAdapter is enabled
- """
- return os.getenv(ADAPTED_TYPE_SWITCH, "FALSE").upper() == "TRUE"
-
-
-def _switch_filepath_types(on):
- """
- Enable (on=True) or disable (on=False) support for AttributeAdapter
- """
- if on:
- os.environ[FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH] = "TRUE"
- else:
- del os.environ[FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH]
-
-
-def _support_filepath_types():
- """
- check if support for AttributeAdapter is enabled
- """
- return os.getenv(FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH, "FALSE").upper() == "TRUE"
diff --git a/datajoint/expression.py b/datajoint/expression.py
deleted file mode 100644
index dd90087b8..000000000
--- a/datajoint/expression.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,991 +0,0 @@
-import copy
-import inspect
-import logging
-import re
-from itertools import count
-
-from .condition import (
- AndList,
- Not,
- PromiscuousOperand,
- Top,
- assert_join_compatibility,
- extract_column_names,
- make_condition,
- translate_attribute,
-)
-from .declare import CONSTANT_LITERALS
-from .errors import DataJointError
-from .fetch import Fetch, Fetch1
-from .preview import preview, repr_html
-from .settings import config
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-
-
-class QueryExpression:
- """
- QueryExpression implements query operators to derive new entity set from its input.
- A QueryExpression object generates a SELECT statement in SQL.
- QueryExpression operators are restrict, join, proj, aggr, and union.
-
- A QueryExpression object has a support, a restriction (an AndList), and heading.
- Property `heading` (type dj.Heading) contains information about the attributes.
- It is loaded from the database and updated by proj.
-
- Property `support` is the list of table names or other QueryExpressions to be joined.
-
- The restriction is applied first without having access to the attributes generated by the projection.
- Then projection is applied by selecting modifying the heading attribute.
-
- Application of operators does not always lead to the creation of a subquery.
- A subquery is generated when:
- 1. A restriction is applied on any computed or renamed attributes
- 2. A projection is applied remapping remapped attributes
- 3. Subclasses: Join, Aggregation, and Union have additional specific rules.
- """
-
- _restriction = None
- _restriction_attributes = None
- _left = [] # list of booleans True for left joins, False for inner joins
- _original_heading = None # heading before projections
-
- # subclasses or instantiators must provide values
- _connection = None
- _heading = None
- _support = None
- _top = None
-
- # If the query will be using distinct
- _distinct = False
-
- @property
- def connection(self):
- """a dj.Connection object"""
- assert self._connection is not None
- return self._connection
-
- @property
- def support(self):
- """A list of table names or subqueries to from the FROM clause"""
- assert self._support is not None
- return self._support
-
- @property
- def heading(self):
- """a dj.Heading object, reflects the effects of the projection operator .proj"""
- return self._heading
-
- @property
- def original_heading(self):
- """a dj.Heading object reflecting the attributes before projection"""
- return self._original_heading or self.heading
-
- @property
- def restriction(self):
- """a AndList object of restrictions applied to input to produce the result"""
- if self._restriction is None:
- self._restriction = AndList()
- return self._restriction
-
- @property
- def restriction_attributes(self):
- """the set of attribute names invoked in the WHERE clause"""
- if self._restriction_attributes is None:
- self._restriction_attributes = set()
- return self._restriction_attributes
-
- @property
- def primary_key(self):
- return self.heading.primary_key
-
- _subquery_alias_count = count() # count for alias names used in the FROM clause
-
- def from_clause(self):
- support = (
- (
- "(" + src.make_sql() + ") as `$%x`" % next(self._subquery_alias_count)
- if isinstance(src, QueryExpression)
- else src
- )
- for src in self.support
- )
- clause = next(support)
- for s, left in zip(support, self._left):
- clause += " NATURAL{left} JOIN {clause}".format(
- left=" LEFT" if left else "", clause=s
- )
- return clause
-
- def where_clause(self):
- return (
- ""
- if not self.restriction
- else " WHERE (%s)" % ")AND(".join(str(s) for s in self.restriction)
- )
-
- def sorting_clauses(self):
- if not self._top:
- return ""
- clause = ", ".join(
- _wrap_attributes(
- _flatten_attribute_list(self.primary_key, self._top.order_by)
- )
- )
- if clause:
- clause = f" ORDER BY {clause}"
- if self._top.limit is not None:
- clause += f" LIMIT {self._top.limit}{f' OFFSET {self._top.offset}' if self._top.offset else ''}"
-
- return clause
-
- def make_sql(self, fields=None):
- """
- Make the SQL SELECT statement.
-
- :param fields: used to explicitly set the select attributes
- """
- return "SELECT {distinct}{fields} FROM {from_}{where}{sorting}".format(
- distinct="DISTINCT " if self._distinct else "",
- fields=self.heading.as_sql(fields or self.heading.names),
- from_=self.from_clause(),
- where=self.where_clause(),
- sorting=self.sorting_clauses(),
- )
-
- # --------- query operators -----------
- def make_subquery(self):
- """create a new SELECT statement where self is the FROM clause"""
- result = QueryExpression()
- result._connection = self.connection
- result._support = [self]
- result._heading = self.heading.make_subquery_heading()
- return result
-
- def restrict(self, restriction):
- """
- Produces a new expression with the new restriction applied.
- rel.restrict(restriction) is equivalent to rel & restriction.
- rel.restrict(Not(restriction)) is equivalent to rel - restriction
- The primary key of the result is unaffected.
- Successive restrictions are combined as logical AND: r & a & b is equivalent to r & AndList((a, b))
- Any QueryExpression, collection, or sequence other than an AndList are treated as OrLists
- (logical disjunction of conditions)
- Inverse restriction is accomplished by either using the subtraction operator or the Not class.
-
- The expressions in each row equivalent:
-
- rel & True rel
- rel & False the empty entity set
- rel & 'TRUE' rel
- rel & 'FALSE' the empty entity set
- rel - cond rel & Not(cond)
- rel - 'TRUE' rel & False
- rel - 'FALSE' rel
- rel & AndList((cond1,cond2)) rel & cond1 & cond2
- rel & AndList() rel
- rel & [cond1, cond2] rel & OrList((cond1, cond2))
- rel & [] rel & False
- rel & None rel & False
- rel & any_empty_entity_set rel & False
- rel - AndList((cond1,cond2)) rel & [Not(cond1), Not(cond2)]
- rel - [cond1, cond2] rel & Not(cond1) & Not(cond2)
- rel - AndList() rel & False
- rel - [] rel
- rel - None rel
- rel - any_empty_entity_set rel
-
- When arg is another QueryExpression, the restriction rel & arg restricts rel to elements that match at least
- one element in arg (hence arg is treated as an OrList).
- Conversely, rel - arg restricts rel to elements that do not match any elements in arg.
- Two elements match when their common attributes have equal values or when they have no common attributes.
- All shared attributes must be in the primary key of either rel or arg or both or an error will be raised.
-
- QueryExpression.restrict is the only access point that modifies restrictions. All other operators must
- ultimately call restrict()
-
- :param restriction: a sequence or an array (treated as OR list), another QueryExpression, an SQL condition
- string, or an AndList.
- """
- attributes = set()
- if isinstance(restriction, Top):
- result = (
- self.make_subquery()
- if self._top and not self._top.__eq__(restriction)
- else copy.copy(self)
- ) # make subquery to avoid overwriting existing Top
- result._top = restriction
- return result
- new_condition = make_condition(self, restriction, attributes)
- if new_condition is True:
- return self # restriction has no effect, return the same object
- # check that all attributes in condition are present in the query
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute `%s` is not found in query."
- % next(attr for attr in attributes if attr not in self.heading.names)
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # all ok
- # If the new condition uses any new attributes, a subquery is required.
- # However, Aggregation's HAVING statement works fine with aliased attributes.
- need_subquery = (
- isinstance(self, Union)
- or (not isinstance(self, Aggregation) and self.heading.new_attributes)
- or self._top
- )
- if need_subquery:
- result = self.make_subquery()
- else:
- result = copy.copy(self)
- result._restriction = AndList(
- self.restriction
- ) # copy to preserve the original
- result.restriction.append(new_condition)
- result.restriction_attributes.update(attributes)
- return result
-
- def restrict_in_place(self, restriction):
- self.__dict__.update(self.restrict(restriction).__dict__)
-
- def __and__(self, restriction):
- """
- Restriction operator e.g. ``q1 & q2``.
- :return: a restricted copy of the input argument
- See QueryExpression.restrict for more detail.
- """
- return self.restrict(restriction)
-
- def __xor__(self, restriction):
- """
- Permissive restriction operator ignoring compatibility check e.g. ``q1 ^ q2``.
- """
- if inspect.isclass(restriction) and issubclass(restriction, QueryExpression):
- restriction = restriction()
- if isinstance(restriction, Not):
- return self.restrict(Not(PromiscuousOperand(restriction.restriction)))
- return self.restrict(PromiscuousOperand(restriction))
-
- def __sub__(self, restriction):
- """
- Inverted restriction e.g. ``q1 - q2``.
- :return: a restricted copy of the input argument
- See QueryExpression.restrict for more detail.
- """
- return self.restrict(Not(restriction))
-
- def __neg__(self):
- """
- Convert between restriction and inverted restriction e.g. ``-q1``.
- :return: target restriction
- See QueryExpression.restrict for more detail.
- """
- if isinstance(self, Not):
- return self.restriction
- return Not(self)
-
- def __mul__(self, other):
- """
- join of query expressions `self` and `other` e.g. ``q1 * q2``.
- """
- return self.join(other)
-
- def __matmul__(self, other):
- """
- Permissive join of query expressions `self` and `other` ignoring compatibility check
- e.g. ``q1 @ q2``.
- """
- if inspect.isclass(other) and issubclass(other, QueryExpression):
- other = other() # instantiate
- return self.join(other, semantic_check=False)
-
- def join(self, other, semantic_check=True, left=False):
- """
- create the joined QueryExpression.
- a * b is short for A.join(B)
- a @ b is short for A.join(B, semantic_check=False)
- Additionally, left=True will retain the rows of self, effectively performing a left join.
- """
- # trigger subqueries if joining on renamed attributes
- if isinstance(other, U):
- return other * self
- if inspect.isclass(other) and issubclass(other, QueryExpression):
- other = other() # instantiate
- if not isinstance(other, QueryExpression):
- raise DataJointError("The argument of join must be a QueryExpression")
- if semantic_check:
- assert_join_compatibility(self, other)
- join_attributes = set(n for n in self.heading.names if n in other.heading.names)
- # needs subquery if self's FROM clause has common attributes with other's FROM clause
- need_subquery1 = need_subquery2 = bool(
- (set(self.original_heading.names) & set(other.original_heading.names))
- - join_attributes
- )
- # need subquery if any of the join attributes are derived
- need_subquery1 = (
- need_subquery1
- or isinstance(self, Aggregation)
- or any(n in self.heading.new_attributes for n in join_attributes)
- or isinstance(self, Union)
- )
- need_subquery2 = (
- need_subquery2
- or isinstance(other, Aggregation)
- or any(n in other.heading.new_attributes for n in join_attributes)
- or isinstance(self, Union)
- )
- if need_subquery1:
- self = self.make_subquery()
- if need_subquery2:
- other = other.make_subquery()
- result = QueryExpression()
- result._connection = self.connection
- result._support = self.support + other.support
- result._left = self._left + [left] + other._left
- result._heading = self.heading.join(other.heading)
- result._restriction = AndList(self.restriction)
- result._restriction.append(other.restriction)
- result._original_heading = self.original_heading.join(other.original_heading)
- assert len(result.support) == len(result._left) + 1
- return result
-
- def __add__(self, other):
- """union e.g. ``q1 + q2``."""
- return Union.create(self, other)
-
- def proj(self, *attributes, **named_attributes):
- """
- Projection operator.
-
- :param attributes: attributes to be included in the result. (The primary key is already included).
- :param named_attributes: new attributes computed or renamed from existing attributes.
- :return: the projected expression.
- Primary key attributes cannot be excluded but may be renamed.
- If the attribute list contains an Ellipsis ..., then all secondary attributes are included too
- Prefixing an attribute name with a dash '-attr' removes the attribute from the list if present.
- Keyword arguments can be used to rename attributes as in name='attr', duplicate them as in name='(attr)', or
- self.proj(...) or self.proj(Ellipsis) -- include all attributes (return self)
- self.proj() -- include only primary key
- self.proj('attr1', 'attr2') -- include primary key and attributes attr1 and attr2
- self.proj(..., '-attr1', '-attr2') -- include all attributes except attr1 and attr2
- self.proj(name1='attr1') -- include primary key and 'attr1' renamed as name1
- self.proj('attr1', dup='(attr1)') -- include primary key and attribute attr1 twice, with the duplicate 'dup'
- self.proj(k='abs(attr1)') adds the new attribute k with the value computed as an expression (SQL syntax)
- from other attributes available before the projection.
- Each attribute name can only be used once.
- """
- named_attributes = {
- k: translate_attribute(v)[1] for k, v in named_attributes.items()
- }
- # new attributes in parentheses are included again with the new name without removing original
- duplication_pattern = re.compile(
- rf'^\s*\(\s*(?!{"|".join(CONSTANT_LITERALS)})(?P[a-zA-Z_]\w*)\s*\)\s*$'
- )
- # attributes without parentheses renamed
- rename_pattern = re.compile(
- rf'^\s*(?!{"|".join(CONSTANT_LITERALS)})(?P[a-zA-Z_]\w*)\s*$'
- )
- replicate_map = {
- k: m.group("name")
- for k, m in (
- (k, duplication_pattern.match(v)) for k, v in named_attributes.items()
- )
- if m
- }
- rename_map = {
- k: m.group("name")
- for k, m in (
- (k, rename_pattern.match(v)) for k, v in named_attributes.items()
- )
- if m
- }
- compute_map = {
- k: v
- for k, v in named_attributes.items()
- if not duplication_pattern.match(v) and not rename_pattern.match(v)
- }
- attributes = set(attributes)
- # include primary key
- attributes.update((k for k in self.primary_key if k not in rename_map.values()))
- # include all secondary attributes with Ellipsis
- if Ellipsis in attributes:
- attributes.discard(Ellipsis)
- attributes.update(
- (
- a
- for a in self.heading.secondary_attributes
- if a not in attributes and a not in rename_map.values()
- )
- )
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "%s is not a valid data type for an attribute in .proj"
- % next(a for a in attributes if not isinstance(a, str))
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # normal case
- # remove excluded attributes, specified as `-attr'
- excluded = set(a for a in attributes if a.strip().startswith("-"))
- attributes.difference_update(excluded)
- excluded = set(a.lstrip("-").strip() for a in excluded)
- attributes.difference_update(excluded)
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot exclude primary key attribute %s",
- next(a for a in excluded if a in self.primary_key),
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # all ok
- # check that all attributes exist in heading
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute `%s` not found."
- % next(a for a in attributes if a not in self.heading.names)
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # all ok
-
- # check that all mentioned names are present in heading
- mentions = attributes.union(replicate_map.values()).union(rename_map.values())
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute '%s' not found."
- % next(a for a in mentions if not self.heading.names)
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # all ok
-
- # check that newly created attributes do not clash with any other selected attributes
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute `%s` already exists"
- % next(
- a
- for a in rename_map
- if a in attributes.union(compute_map).union(replicate_map)
- )
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # all ok
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute `%s` already exists"
- % next(
- a
- for a in compute_map
- if a in attributes.union(rename_map).union(replicate_map)
- )
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # all ok
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute `%s` already exists"
- % next(
- a
- for a in replicate_map
- if a in attributes.union(rename_map).union(compute_map)
- )
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # all ok
-
- # need a subquery if the projection remaps any remapped attributes
- used = set(q for v in compute_map.values() for q in extract_column_names(v))
- used.update(rename_map.values())
- used.update(replicate_map.values())
- used.intersection_update(self.heading.names)
- need_subquery = isinstance(self, Union) or any(
- self.heading[name].attribute_expression is not None for name in used
- )
- if not need_subquery and self.restriction:
- # need a subquery if the restriction applies to attributes that have been renamed
- need_subquery = any(
- name in self.restriction_attributes
- for name in self.heading.new_attributes
- )
-
- result = self.make_subquery() if need_subquery else copy.copy(self)
- result._original_heading = result.original_heading
- result._heading = result.heading.select(
- attributes,
- rename_map=dict(**rename_map, **replicate_map),
- compute_map=compute_map,
- )
- return result
-
- def aggr(self, group, *attributes, keep_all_rows=False, **named_attributes):
- """
- Aggregation of the type U('attr1','attr2').aggr(group, computation="QueryExpression")
- has the primary key ('attr1','attr2') and performs aggregation computations for all matching elements of `group`.
-
- :param group: The query expression to be aggregated.
- :param keep_all_rows: True=keep all the rows from self. False=keep only rows that match entries in group.
- :param named_attributes: computations of the form new_attribute="sql expression on attributes of group"
- :return: The derived query expression
- """
- if Ellipsis in attributes:
- # expand ellipsis to include only attributes from the left table
- attributes = set(attributes)
- attributes.discard(Ellipsis)
- attributes.update(self.heading.secondary_attributes)
- return Aggregation.create(self, group=group, keep_all_rows=keep_all_rows).proj(
- *attributes, **named_attributes
- )
-
- aggregate = aggr # alias for aggr
-
- # ---------- Fetch operators --------------------
- @property
- def fetch1(self):
- return Fetch1(self)
-
- @property
- def fetch(self):
- return Fetch(self)
-
- def head(self, limit=25, **fetch_kwargs):
- """
- shortcut to fetch the first few entries from query expression.
- Equivalent to fetch(order_by="KEY", limit=25)
-
- :param limit: number of entries
- :param fetch_kwargs: kwargs for fetch
- :return: query result
- """
- return self.fetch(order_by="KEY", limit=limit, **fetch_kwargs)
-
- def tail(self, limit=25, **fetch_kwargs):
- """
- shortcut to fetch the last few entries from query expression.
- Equivalent to fetch(order_by="KEY DESC", limit=25)[::-1]
-
- :param limit: number of entries
- :param fetch_kwargs: kwargs for fetch
- :return: query result
- """
- return self.fetch(order_by="KEY DESC", limit=limit, **fetch_kwargs)[::-1]
-
- def __len__(self):
- """:return: number of elements in the result set e.g. ``len(q1)``."""
- result = self.make_subquery() if self._top else copy.copy(self)
- return result.connection.query(
- "SELECT {select_} FROM {from_}{where}".format(
- select_=(
- "count(*)"
- if any(result._left)
- else "count(DISTINCT {fields})".format(
- fields=result.heading.as_sql(
- result.primary_key, include_aliases=False
- )
- )
- ),
- from_=result.from_clause(),
- where=result.where_clause(),
- )
- ).fetchone()[0]
-
- def __bool__(self):
- """
- :return: True if the result is not empty. Equivalent to len(self) > 0 but often
- faster e.g. ``bool(q1)``.
- """
- return bool(
- self.connection.query(
- "SELECT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM {from_}{where})".format(
- from_=self.from_clause(), where=self.where_clause()
- )
- ).fetchone()[0]
- )
-
- def __contains__(self, item):
- """
- returns True if the restriction in item matches any entries in self
- e.g. ``restriction in q1``.
-
- :param item: any restriction
- (item in query_expression) is equivalent to bool(query_expression & item) but may be
- executed more efficiently.
- """
- return bool(self & item) # May be optimized e.g. using an EXISTS query
-
- def __iter__(self):
- """
- returns an iterator-compatible QueryExpression object e.g. ``iter(q1)``.
-
- :param self: iterator-compatible QueryExpression object
- """
- self._iter_only_key = all(v.in_key for v in self.heading.attributes.values())
- self._iter_keys = self.fetch("KEY")
- return self
-
- def __next__(self):
- """
- returns the next record on an iterator-compatible QueryExpression object
- e.g. ``next(q1)``.
-
- :param self: A query expression
- :type self: :class:`QueryExpression`
- :rtype: dict
- """
- try:
- key = self._iter_keys.pop(0)
- except AttributeError:
- # self._iter_keys is missing because __iter__ has not been called.
- raise TypeError(
- "A QueryExpression object is not an iterator. "
- "Use iter(obj) to create an iterator."
- )
- except IndexError:
- raise StopIteration
- else:
- if self._iter_only_key:
- return key
- else:
- try:
- return (self & key).fetch1()
- except DataJointError:
- # The data may have been deleted since the moment the keys were fetched
- # -- move on to next entry.
- return next(self)
-
- def cursor(self, as_dict=False):
- """
- See expression.fetch() for input description.
- :return: query cursor
- """
- sql = self.make_sql()
- logger.debug(sql)
- return self.connection.query(sql, as_dict=as_dict)
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """
- returns the string representation of a QueryExpression object e.g. ``str(q1)``.
-
- :param self: A query expression
- :type self: :class:`QueryExpression`
- :rtype: str
- """
- return (
- super().__repr__()
- if config["loglevel"].lower() == "debug"
- else self.preview()
- )
-
- def preview(self, limit=None, width=None):
- """:return: a string of preview of the contents of the query."""
- return preview(self, limit, width)
-
- def _repr_html_(self):
- """:return: HTML to display table in Jupyter notebook."""
- return repr_html(self)
-
-
-class Aggregation(QueryExpression):
- """
- Aggregation.create(arg, group, comp1='calc1', ..., compn='calcn') yields an entity set
- with primary key from arg.
- The computed arguments comp1, ..., compn use aggregation calculations on the attributes of
- group or simple projections and calculations on the attributes of arg.
- Aggregation is used QueryExpression.aggr and U.aggr.
- Aggregation is a private class in DataJoint, not exposed to users.
- """
-
- _left_restrict = None # the pre-GROUP BY conditions for the WHERE clause
- _subquery_alias_count = count()
-
- @classmethod
- def create(cls, arg, group, keep_all_rows=False):
- if inspect.isclass(group) and issubclass(group, QueryExpression):
- group = group() # instantiate if a class
- assert isinstance(group, QueryExpression)
- if keep_all_rows and len(group.support) > 1 or group.heading.new_attributes:
- group = group.make_subquery() # subquery if left joining a join
- join = arg.join(group, left=keep_all_rows) # reuse the join logic
- result = cls()
- result._connection = join.connection
- result._heading = join.heading.set_primary_key(
- arg.primary_key
- ) # use left operand's primary key
- result._support = join.support
- result._left = join._left
- result._left_restrict = join.restriction # WHERE clause applied before GROUP BY
- result._grouping_attributes = result.primary_key
-
- return result
-
- def where_clause(self):
- return (
- ""
- if not self._left_restrict
- else " WHERE (%s)" % ")AND(".join(str(s) for s in self._left_restrict)
- )
-
- def make_sql(self, fields=None):
- fields = self.heading.as_sql(fields or self.heading.names)
- assert self._grouping_attributes or not self.restriction
- distinct = set(self.heading.names) == set(self.primary_key)
- return (
- "SELECT {distinct}{fields} FROM {from_}{where}{group_by}{sorting}".format(
- distinct="DISTINCT " if distinct else "",
- fields=fields,
- from_=self.from_clause(),
- where=self.where_clause(),
- group_by=(
- ""
- if not self.primary_key
- else (
- " GROUP BY `%s`" % "`,`".join(self._grouping_attributes)
- + (
- ""
- if not self.restriction
- else " HAVING (%s)" % ")AND(".join(self.restriction)
- )
- )
- ),
- sorting=self.sorting_clauses(),
- )
- )
-
- def __len__(self):
- return self.connection.query(
- "SELECT count(1) FROM ({subquery}) `${alias:x}`".format(
- subquery=self.make_sql(), alias=next(self._subquery_alias_count)
- )
- ).fetchone()[0]
-
- def __bool__(self):
- return bool(
- self.connection.query("SELECT EXISTS({sql})".format(sql=self.make_sql()))
- )
-
-
-class Union(QueryExpression):
- """
- Union is the private DataJoint class that implements the union operator.
- """
-
- __count = count()
-
- @classmethod
- def create(cls, arg1, arg2):
- if inspect.isclass(arg2) and issubclass(arg2, QueryExpression):
- arg2 = arg2() # instantiate if a class
- if not isinstance(arg2, QueryExpression):
- raise DataJointError(
- "A QueryExpression can only be unioned with another QueryExpression"
- )
- if arg1.connection != arg2.connection:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot operate on QueryExpressions originating from different connections."
- )
- if set(arg1.primary_key) != set(arg2.primary_key):
- raise DataJointError(
- "The operands of a union must share the same primary key."
- )
- if set(arg1.heading.secondary_attributes) & set(
- arg2.heading.secondary_attributes
- ):
- raise DataJointError(
- "The operands of a union must not share any secondary attributes."
- )
- result = cls()
- result._connection = arg1.connection
- result._heading = arg1.heading.join(arg2.heading)
- result._support = [arg1, arg2]
- return result
-
- def make_sql(self):
- arg1, arg2 = self._support
- if (
- not arg1.heading.secondary_attributes
- and not arg2.heading.secondary_attributes
- ):
- # no secondary attributes: use UNION DISTINCT
- fields = arg1.primary_key
- return "SELECT * FROM (({sql1}) UNION ({sql2})) as `_u{alias}{sorting}`".format(
- sql1=(
- arg1.make_sql()
- if isinstance(arg1, Union)
- else arg1.make_sql(fields)
- ),
- sql2=(
- arg2.make_sql()
- if isinstance(arg2, Union)
- else arg2.make_sql(fields)
- ),
- alias=next(self.__count),
- sorting=self.sorting_clauses(),
- )
- # with secondary attributes, use union of left join with antijoin
- fields = self.heading.names
- sql1 = arg1.join(arg2, left=True).make_sql(fields)
- sql2 = (
- (arg2 - arg1)
- .proj(..., **{k: "NULL" for k in arg1.heading.secondary_attributes})
- .make_sql(fields)
- )
- return "({sql1}) UNION ({sql2})".format(sql1=sql1, sql2=sql2)
-
- def from_clause(self):
- """The union does not use a FROM clause"""
- assert False
-
- def where_clause(self):
- """The union does not use a WHERE clause"""
- assert False
-
- def __len__(self):
- return self.connection.query(
- "SELECT count(1) FROM ({subquery}) `${alias:x}`".format(
- subquery=self.make_sql(),
- alias=next(QueryExpression._subquery_alias_count),
- )
- ).fetchone()[0]
-
- def __bool__(self):
- return bool(
- self.connection.query("SELECT EXISTS({sql})".format(sql=self.make_sql()))
- )
-
-
-class U:
- """
- dj.U objects are the universal sets representing all possible values of their attributes.
- dj.U objects cannot be queried on their own but are useful for forming some queries.
- dj.U('attr1', ..., 'attrn') represents the universal set with the primary key attributes attr1 ... attrn.
- The universal set is the set of all possible combinations of values of the attributes.
- Without any attributes, dj.U() represents the set with one element that has no attributes.
-
- Restriction:
-
- dj.U can be used to enumerate unique combinations of values of attributes from other expressions.
-
- The following expression yields all unique combinations of contrast and brightness found in the `stimulus` set:
-
- >>> dj.U('contrast', 'brightness') & stimulus
-
- Aggregation:
-
- In aggregation, dj.U is used for summary calculation over an entire set:
-
- The following expression yields one element with one attribute `s` containing the total number of elements in
- query expression `expr`:
-
- >>> dj.U().aggr(expr, n='count(*)')
-
- The following expressions both yield one element containing the number `n` of distinct values of attribute `attr` in
- query expression `expr`.
-
- >>> dj.U().aggr(expr, n='count(distinct attr)')
- >>> dj.U().aggr(dj.U('attr').aggr(expr), 'n=count(*)')
-
- The following expression yields one element and one attribute `s` containing the sum of values of attribute `attr`
- over entire result set of expression `expr`:
-
- >>> dj.U().aggr(expr, s='sum(attr)')
-
- The following expression yields the set of all unique combinations of attributes `attr1`, `attr2` and the number of
- their occurrences in the result set of query expression `expr`.
-
- >>> dj.U(attr1,attr2).aggr(expr, n='count(*)')
-
- Joins:
-
- If expression `expr` has attributes 'attr1' and 'attr2', then expr * dj.U('attr1','attr2') yields the same result
- as `expr` but `attr1` and `attr2` are promoted to the the primary key. This is useful for producing a join on
- non-primary key attributes.
- For example, if `attr` is in both expr1 and expr2 but not in their primary keys, then expr1 * expr2 will throw
- an error because in most cases, it does not make sense to join on non-primary key attributes and users must first
- rename `attr` in one of the operands. The expression dj.U('attr') * rel1 * rel2 overrides this constraint.
- """
-
- def __init__(self, *primary_key):
- self._primary_key = primary_key
-
- @property
- def primary_key(self):
- return self._primary_key
-
- def __and__(self, other):
- if inspect.isclass(other) and issubclass(other, QueryExpression):
- other = other() # instantiate if a class
- if not isinstance(other, QueryExpression):
- raise DataJointError("Set U can only be restricted with a QueryExpression.")
- result = copy.copy(other)
- result._distinct = True
- result._heading = result.heading.set_primary_key(self.primary_key)
- result = result.proj()
- return result
-
- def join(self, other, left=False):
- """
- Joining U with a query expression has the effect of promoting the attributes of U to
- the primary key of the other query expression.
-
- :param other: the other query expression to join with.
- :param left: ignored. dj.U always acts as if left=False
- :return: a copy of the other query expression with the primary key extended.
- """
- if inspect.isclass(other) and issubclass(other, QueryExpression):
- other = other() # instantiate if a class
- if not isinstance(other, QueryExpression):
- raise DataJointError("Set U can only be joined with a QueryExpression.")
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute `%s` not found"
- % next(k for k in self.primary_key if k not in other.heading.names)
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # all ok
- result = copy.copy(other)
- result._heading = result.heading.set_primary_key(
- other.primary_key
- + [k for k in self.primary_key if k not in other.primary_key]
- )
- return result
-
- def __mul__(self, other):
- """shorthand for join"""
- return self.join(other)
-
- def aggr(self, group, **named_attributes):
- """
- Aggregation of the type U('attr1','attr2').aggr(group, computation="QueryExpression")
- has the primary key ('attr1','attr2') and performs aggregation computations for all matching elements of `group`.
-
- :param group: The query expression to be aggregated.
- :param named_attributes: computations of the form new_attribute="sql expression on attributes of group"
- :return: The derived query expression
- """
- if named_attributes.get("keep_all_rows", False):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot set keep_all_rows=True when aggregating on a universal set."
- )
- return Aggregation.create(self, group=group, keep_all_rows=False).proj(
- **named_attributes
- )
-
- aggregate = aggr # alias for aggr
-
-
-def _flatten_attribute_list(primary_key, attrs):
- """
- :param primary_key: list of attributes in primary key
- :param attrs: list of attribute names, which may include "KEY", "KEY DESC" or "KEY ASC"
- :return: generator of attributes where "KEY" is replaced with its component attributes
- """
- for a in attrs:
- if re.match(r"^\s*KEY(\s+[aA][Ss][Cc])?\s*$", a):
- if primary_key:
- yield from primary_key
- elif re.match(r"^\s*KEY\s+[Dd][Ee][Ss][Cc]\s*$", a):
- if primary_key:
- yield from (q + " DESC" for q in primary_key)
- else:
- yield a
-
-
-def _wrap_attributes(attr):
- for entry in attr: # wrap attribute names in backquotes
- yield re.sub(r"\b((?!asc|desc)\w+)\b", r"`\1`", entry, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
diff --git a/datajoint/external.py b/datajoint/external.py
deleted file mode 100644
index b3de2ff5d..000000000
--- a/datajoint/external.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,515 +0,0 @@
-import logging
-from collections.abc import Mapping
-from pathlib import Path, PurePosixPath, PureWindowsPath
-
-from tqdm import tqdm
-
-from . import errors, s3
-from .declare import EXTERNAL_TABLE_ROOT
-from .errors import DataJointError, MissingExternalFile
-from .hash import uuid_from_buffer, uuid_from_file
-from .heading import Heading
-from .settings import config
-from .table import FreeTable, Table
-from .utils import safe_copy, safe_write
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-
-CACHE_SUBFOLDING = (
- 2,
- 2,
-) # (2, 2) means "0123456789abcd" will be saved as "01/23/0123456789abcd"
-SUPPORT_MIGRATED_BLOBS = True # support blobs migrated from datajoint 0.11.*
-
-
-def subfold(name, folds):
- """
- subfolding for external storage: e.g. subfold('aBCdefg', (2, 3)) --> ['ab','cde']
- """
- return (
- (name[: folds[0]].lower(),) + subfold(name[folds[0] :], folds[1:])
- if folds
- else ()
- )
-
-
-class ExternalTable(Table):
- """
- The table tracking externally stored objects.
- Declare as ExternalTable(connection, database)
- """
-
- def __init__(self, connection, store, database):
- self.store = store
- self.spec = config.get_store_spec(store)
- self._s3 = None
- self.database = database
- self._connection = connection
- self._heading = Heading(
- table_info=dict(
- conn=connection,
- database=database,
- table_name=self.table_name,
- context=None,
- )
- )
- self._support = [self.full_table_name]
- if not self.is_declared:
- self.declare()
- self._s3 = None
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "file" and not Path(self.spec["location"]).is_dir():
- raise FileNotFoundError(
- "Inaccessible local directory %s" % self.spec["location"]
- ) from None
-
- @property
- def definition(self):
- return """
- # external storage tracking
- hash : uuid # hash of contents (blob), of filename + contents (attach), or relative filepath (filepath)
- ---
- size :bigint unsigned # size of object in bytes
- attachment_name=null : varchar(255) # the filename of an attachment
- filepath=null : varchar(1000) # relative filepath or attachment filename
- contents_hash=null : uuid # used for the filepath datatype
- timestamp=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP :timestamp # automatic timestamp
- """
-
- @property
- def table_name(self):
- return f"{EXTERNAL_TABLE_ROOT}_{self.store}"
-
- @property
- def s3(self):
- if self._s3 is None:
- self._s3 = s3.Folder(**self.spec)
- return self._s3
-
- # - low-level operations - private
-
- def _make_external_filepath(self, relative_filepath):
- """resolve the complete external path based on the relative path"""
- # Strip root
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "s3":
- posix_path = PurePosixPath(PureWindowsPath(self.spec["location"]))
- location_path = (
- Path(*posix_path.parts[1:])
- if len(self.spec["location"]) > 0
- and any(case in posix_path.parts[0] for case in ("\\", ":"))
- else Path(posix_path)
- )
- return PurePosixPath(location_path, relative_filepath)
- # Preserve root
- elif self.spec["protocol"] == "file":
- return PurePosixPath(Path(self.spec["location"]), relative_filepath)
- else:
- assert False
-
- def _make_uuid_path(self, uuid, suffix=""):
- """create external path based on the uuid hash"""
- return self._make_external_filepath(
- PurePosixPath(
- self.database,
- "/".join(subfold(uuid.hex, self.spec["subfolding"])),
- uuid.hex,
- ).with_suffix(suffix)
- )
-
- def _upload_file(self, local_path, external_path, metadata=None):
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "s3":
- self.s3.fput(local_path, external_path, metadata)
- elif self.spec["protocol"] == "file":
- safe_copy(local_path, external_path, overwrite=True)
- else:
- assert False
-
- def _download_file(self, external_path, download_path):
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "s3":
- self.s3.fget(external_path, download_path)
- elif self.spec["protocol"] == "file":
- safe_copy(external_path, download_path)
- else:
- assert False
-
- def _upload_buffer(self, buffer, external_path):
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "s3":
- self.s3.put(external_path, buffer)
- elif self.spec["protocol"] == "file":
- safe_write(external_path, buffer)
- else:
- assert False
-
- def _download_buffer(self, external_path):
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "s3":
- return self.s3.get(external_path)
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "file":
- try:
- return Path(external_path).read_bytes()
- except FileNotFoundError:
- raise errors.MissingExternalFile(
- f"Missing external file {external_path}"
- ) from None
- assert False
-
- def _remove_external_file(self, external_path):
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "s3":
- self.s3.remove_object(external_path)
- elif self.spec["protocol"] == "file":
- try:
- Path(external_path).unlink()
- except FileNotFoundError:
- pass
-
- def exists(self, external_filepath):
- """
- :return: True if the external file is accessible
- """
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "s3":
- return self.s3.exists(external_filepath)
- if self.spec["protocol"] == "file":
- return Path(external_filepath).is_file()
- assert False
-
- # --- BLOBS ----
-
- def put(self, blob):
- """
- put a binary string (blob) in external store
- """
- uuid = uuid_from_buffer(blob)
- self._upload_buffer(blob, self._make_uuid_path(uuid))
- # insert tracking info
- self.connection.query(
- "INSERT INTO {tab} (hash, size) VALUES (%s, {size}) ON DUPLICATE KEY "
- "UPDATE timestamp=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP".format(
- tab=self.full_table_name, size=len(blob)
- ),
- args=(uuid.bytes,),
- )
- return uuid
-
- def get(self, uuid):
- """
- get an object from external store.
- """
- if uuid is None:
- return None
- # attempt to get object from cache
- blob = None
- cache_folder = config.get("cache", None)
- if cache_folder:
- try:
- cache_path = Path(cache_folder, *subfold(uuid.hex, CACHE_SUBFOLDING))
- cache_file = Path(cache_path, uuid.hex)
- blob = cache_file.read_bytes()
- except FileNotFoundError:
- pass # not cached
- # download blob from external store
- if blob is None:
- try:
- blob = self._download_buffer(self._make_uuid_path(uuid))
- except MissingExternalFile:
- if not SUPPORT_MIGRATED_BLOBS:
- raise
- # blobs migrated from datajoint 0.11 are stored at explicitly defined filepaths
- relative_filepath, contents_hash = (self & {"hash": uuid}).fetch1(
- "filepath", "contents_hash"
- )
- if relative_filepath is None:
- raise
- blob = self._download_buffer(
- self._make_external_filepath(relative_filepath)
- )
- if cache_folder:
- cache_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
- safe_write(cache_path / uuid.hex, blob)
- return blob
-
- # --- ATTACHMENTS ---
-
- def upload_attachment(self, local_path):
- attachment_name = Path(local_path).name
- uuid = uuid_from_file(local_path, init_string=attachment_name + "\0")
- external_path = self._make_uuid_path(uuid, "." + attachment_name)
- self._upload_file(local_path, external_path)
- # insert tracking info
- self.connection.query(
- """
- INSERT INTO {tab} (hash, size, attachment_name)
- VALUES (%s, {size}, "{attachment_name}")
- ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE timestamp=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP""".format(
- tab=self.full_table_name,
- size=Path(local_path).stat().st_size,
- attachment_name=attachment_name,
- ),
- args=[uuid.bytes],
- )
- return uuid
-
- def get_attachment_name(self, uuid):
- return (self & {"hash": uuid}).fetch1("attachment_name")
-
- def download_attachment(self, uuid, attachment_name, download_path):
- """save attachment from memory buffer into the save_path"""
- external_path = self._make_uuid_path(uuid, "." + attachment_name)
- self._download_file(external_path, download_path)
-
- # --- FILEPATH ---
-
- def upload_filepath(self, local_filepath):
- """
- Raise exception if an external entry already exists with a different contents checksum.
- Otherwise, copy (with overwrite) file to remote and
- If an external entry exists with the same checksum, then no copying should occur
- """
- local_filepath = Path(local_filepath)
- try:
- relative_filepath = str(
- local_filepath.relative_to(self.spec["stage"]).as_posix()
- )
- except ValueError:
- raise DataJointError(
- "The path {path} is not in stage {stage}".format(
- path=local_filepath.parent, **self.spec
- )
- )
- uuid = uuid_from_buffer(
- init_string=relative_filepath
- ) # hash relative path, not contents
- contents_hash = uuid_from_file(local_filepath)
-
- # check if the remote file already exists and verify that it matches
- check_hash = (self & {"hash": uuid}).fetch("contents_hash")
- if check_hash.size:
- # the tracking entry exists, check that it's the same file as before
- if contents_hash != check_hash[0]:
- raise DataJointError(
- f"A different version of '{relative_filepath}' has already been placed."
- )
- else:
- # upload the file and create its tracking entry
- self._upload_file(
- local_filepath,
- self._make_external_filepath(relative_filepath),
- metadata={"contents_hash": str(contents_hash)},
- )
- self.connection.query(
- "INSERT INTO {tab} (hash, size, filepath, contents_hash) VALUES (%s, {size}, '{filepath}', %s)".format(
- tab=self.full_table_name,
- size=Path(local_filepath).stat().st_size,
- filepath=relative_filepath,
- ),
- args=(uuid.bytes, contents_hash.bytes),
- )
- return uuid
-
- def download_filepath(self, filepath_hash):
- """
- sync a file from external store to the local stage
-
- :param filepath_hash: The hash (UUID) of the relative_path
- :return: hash (UUID) of the contents of the downloaded file or Nones
- """
-
- def _need_checksum(local_filepath, expected_size):
- limit = config.get("filepath_checksum_size_limit")
- actual_size = Path(local_filepath).stat().st_size
- if expected_size != actual_size:
- # this should never happen without outside interference
- raise DataJointError(
- f"'{local_filepath}' downloaded but size did not match."
- )
- return limit is None or actual_size < limit
-
- if filepath_hash is not None:
- relative_filepath, contents_hash, size = (
- self & {"hash": filepath_hash}
- ).fetch1("filepath", "contents_hash", "size")
- external_path = self._make_external_filepath(relative_filepath)
- local_filepath = Path(self.spec["stage"]).absolute() / relative_filepath
-
- file_exists = Path(local_filepath).is_file() and (
- not _need_checksum(local_filepath, size)
- or uuid_from_file(local_filepath) == contents_hash
- )
-
- if not file_exists:
- self._download_file(external_path, local_filepath)
- if (
- _need_checksum(local_filepath, size)
- and uuid_from_file(local_filepath) != contents_hash
- ):
- # this should never happen without outside interference
- raise DataJointError(
- f"'{local_filepath}' downloaded but did not pass checksum."
- )
- if not _need_checksum(local_filepath, size):
- logger.warning(
- f"Skipped checksum for file with hash: {contents_hash}, and path: {local_filepath}"
- )
- return str(local_filepath), contents_hash
-
- # --- UTILITIES ---
-
- @property
- def references(self):
- """
- :return: generator of referencing table names and their referencing columns
- """
- return (
- {k.lower(): v for k, v in elem.items()}
- for elem in self.connection.query(
- """
- SELECT concat('`', table_schema, '`.`', table_name, '`') as referencing_table, column_name
- FROM information_schema.key_column_usage
- WHERE referenced_table_name="{tab}" and referenced_table_schema="{db}"
- """.format(
- tab=self.table_name, db=self.database
- ),
- as_dict=True,
- )
- )
-
- def fetch_external_paths(self, **fetch_kwargs):
- """
- generate complete external filepaths from the query.
- Each element is a tuple: (uuid, path)
-
- :param fetch_kwargs: keyword arguments to pass to fetch
- """
- fetch_kwargs.update(as_dict=True)
- paths = []
- for item in self.fetch("hash", "attachment_name", "filepath", **fetch_kwargs):
- if item["attachment_name"]:
- # attachments
- path = self._make_uuid_path(item["hash"], "." + item["attachment_name"])
- elif item["filepath"]:
- # external filepaths
- path = self._make_external_filepath(item["filepath"])
- else:
- # blobs
- path = self._make_uuid_path(item["hash"])
- paths.append((item["hash"], path))
- return paths
-
- def unused(self):
- """
- query expression for unused hashes
-
- :return: self restricted to elements that are not in use by any tables in the schema
- """
- return self - [
- FreeTable(self.connection, ref["referencing_table"]).proj(
- hash=ref["column_name"]
- )
- for ref in self.references
- ]
-
- def used(self):
- """
- query expression for used hashes
-
- :return: self restricted to elements that in use by tables in the schema
- """
- return self & [
- FreeTable(self.connection, ref["referencing_table"]).proj(
- hash=ref["column_name"]
- )
- for ref in self.references
- ]
-
- def delete(
- self,
- *,
- delete_external_files=None,
- limit=None,
- display_progress=True,
- errors_as_string=True,
- ):
- """
-
- :param delete_external_files: True or False. If False, only the tracking info is removed from the external
- store table but the external files remain intact. If True, then the external files themselves are deleted too.
- :param errors_as_string: If True any errors returned when deleting from external files will be strings
- :param limit: (integer) limit the number of items to delete
- :param display_progress: if True, display progress as files are cleaned up
- :return: if deleting external files, returns errors
- """
- if delete_external_files not in (True, False):
- raise DataJointError(
- "The delete_external_files argument must be set to either "
- "True or False in delete()"
- )
-
- if not delete_external_files:
- self.unused().delete_quick()
- else:
- items = self.unused().fetch_external_paths(limit=limit)
- if display_progress:
- items = tqdm(items)
- # delete items one by one, close to transaction-safe
- error_list = []
- for uuid, external_path in items:
- row = (self & {"hash": uuid}).fetch()
- if row.size:
- try:
- (self & {"hash": uuid}).delete_quick()
- except Exception:
- pass # if delete failed, do not remove the external file
- else:
- try:
- self._remove_external_file(external_path)
- except Exception as error:
- # adding row back into table after failed delete
- self.insert1(row[0], skip_duplicates=True)
- error_list.append(
- (
- uuid,
- external_path,
- str(error) if errors_as_string else error,
- )
- )
- return error_list
-
-
-class ExternalMapping(Mapping):
- """
- The external manager contains all the tables for all external stores for a given schema
- :Example:
- e = ExternalMapping(schema)
- external_table = e[store]
- """
-
- def __init__(self, schema):
- self.schema = schema
- self._tables = {}
-
- def __repr__(self):
- return "External file tables for schema `{schema}`:\n ".format(
- schema=self.schema.database
- ) + "\n ".join(
- '"{store}" {protocol}:{location}'.format(store=k, **v.spec)
- for k, v in self.items()
- )
-
- def __getitem__(self, store):
- """
- Triggers the creation of an external table.
- Should only be used when ready to save or read from external storage.
-
- :param store: the name of the store
- :return: the ExternalTable object for the store
- """
- if store not in self._tables:
- self._tables[store] = ExternalTable(
- connection=self.schema.connection,
- store=store,
- database=self.schema.database,
- )
- return self._tables[store]
-
- def __len__(self):
- return len(self._tables)
-
- def __iter__(self):
- return iter(self._tables)
diff --git a/datajoint/fetch.py b/datajoint/fetch.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 1c9b811f1..000000000
--- a/datajoint/fetch.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,344 +0,0 @@
-import itertools
-import json
-import numbers
-import uuid
-from functools import partial
-from pathlib import Path
-
-import numpy as np
-import pandas
-
-from datajoint.condition import Top
-
-from . import blob, hash
-from .errors import DataJointError
-from .settings import config
-from .utils import safe_write
-
-
-class key:
- """
- object that allows requesting the primary key as an argument in expression.fetch()
- The string "KEY" can be used instead of the class key
- """
-
- pass
-
-
-def is_key(attr):
- return attr is key or attr == "KEY"
-
-
-def to_dicts(recarray):
- """convert record array to a dictionaries"""
- for rec in recarray:
- yield dict(zip(recarray.dtype.names, rec.tolist()))
-
-
-def _get(connection, attr, data, squeeze, download_path):
- """
- This function is called for every attribute
-
- :param connection: a dj.Connection object
- :param attr: attribute name from the table's heading
- :param data: literal value fetched from the table
- :param squeeze: if True squeeze blobs
- :param download_path: for fetches that download data, e.g. attachments
- :return: unpacked data
- """
- if data is None:
- return
- if attr.json:
- return json.loads(data)
-
- extern = (
- connection.schemas[attr.database].external[attr.store]
- if attr.is_external
- else None
- )
-
- # apply attribute adapter if present
- adapt = attr.adapter.get if attr.adapter else lambda x: x
-
- if attr.is_filepath:
- return adapt(extern.download_filepath(uuid.UUID(bytes=data))[0])
- if attr.is_attachment:
- # Steps:
- # 1. get the attachment filename
- # 2. check if the file already exists at download_path, verify checksum
- # 3. if exists and checksum passes then return the local filepath
- # 4. Otherwise, download the remote file and return the new filepath
- _uuid = uuid.UUID(bytes=data) if attr.is_external else None
- attachment_name = (
- extern.get_attachment_name(_uuid)
- if attr.is_external
- else data.split(b"\0", 1)[0].decode()
- )
- local_filepath = Path(download_path) / attachment_name
- if local_filepath.is_file():
- attachment_checksum = (
- _uuid if attr.is_external else hash.uuid_from_buffer(data)
- )
- if attachment_checksum == hash.uuid_from_file(
- local_filepath, init_string=attachment_name + "\0"
- ):
- return adapt(
- str(local_filepath)
- ) # checksum passed, no need to download again
- # generate the next available alias filename
- for n in itertools.count():
- f = local_filepath.parent / (
- local_filepath.stem + "_%04x" % n + local_filepath.suffix
- )
- if not f.is_file():
- local_filepath = f
- break
- if attachment_checksum == hash.uuid_from_file(
- f, init_string=attachment_name + "\0"
- ):
- return adapt(str(f)) # checksum passed, no need to download again
- # Save attachment
- if attr.is_external:
- extern.download_attachment(_uuid, attachment_name, local_filepath)
- else:
- # write from buffer
- safe_write(local_filepath, data.split(b"\0", 1)[1])
- return adapt(str(local_filepath)) # download file from remote store
-
- return adapt(
- uuid.UUID(bytes=data)
- if attr.uuid
- else (
- blob.unpack(
- extern.get(uuid.UUID(bytes=data)) if attr.is_external else data,
- squeeze=squeeze,
- )
- if attr.is_blob
- else data
- )
- )
-
-
-class Fetch:
- """
- A fetch object that handles retrieving elements from the table expression.
-
- :param expression: the QueryExpression object to fetch from.
- """
-
- def __init__(self, expression):
- self._expression = expression
-
- def __call__(
- self,
- *attrs,
- offset=None,
- limit=None,
- order_by=None,
- format=None,
- as_dict=None,
- squeeze=False,
- download_path=".",
- ):
- """
- Fetches the expression results from the database into an np.array or list of dictionaries and
- unpacks blob attributes.
-
- :param attrs: zero or more attributes to fetch. If not provided, the call will return all attributes of this
- table. If provided, returns tuples with an entry for each attribute.
- :param offset: the number of tuples to skip in the returned result
- :param limit: the maximum number of tuples to return
- :param order_by: a single attribute or the list of attributes to order the results. No ordering should be assumed
- if order_by=None. To reverse the order, add DESC to the attribute name or names: e.g. ("age DESC",
- "frequency") To order by primary key, use "KEY" or "KEY DESC"
- :param format: Effective when as_dict=None and when attrs is empty None: default from config['fetch_format'] or
- 'array' if not configured "array": use numpy.key_array "frame": output pandas.DataFrame. .
- :param as_dict: returns a list of dictionaries instead of a record array. Defaults to False for .fetch() and to
- True for .fetch('KEY')
- :param squeeze: if True, remove extra dimensions from arrays
- :param download_path: for fetches that download data, e.g. attachments
- :return: the contents of the table in the form of a structured numpy.array or a dict list
- """
- if offset or order_by or limit:
- self._expression = self._expression.restrict(
- Top(
- limit,
- order_by,
- offset,
- )
- )
-
- attrs_as_dict = as_dict and attrs
- if attrs_as_dict:
- # absorb KEY into attrs and prepare to return attributes as dict (issue #595)
- if any(is_key(k) for k in attrs):
- attrs = list(self._expression.primary_key) + [
- a for a in attrs if a not in self._expression.primary_key
- ]
- if as_dict is None:
- as_dict = bool(attrs) # default to True for "KEY" and False otherwise
- # format should not be specified with attrs or is_dict=True
- if format is not None and (as_dict or attrs):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot specify output format when as_dict=True or "
- "when attributes are selected to be fetched separately."
- )
- if format not in {None, "array", "frame"}:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Fetch output format must be in "
- '{{"array", "frame"}} but "{}" was given'.format(format)
- )
-
- if not (attrs or as_dict) and format is None:
- format = config["fetch_format"] # default to array
- if format not in {"array", "frame"}:
- raise DataJointError(
- 'Invalid entry "{}" in datajoint.config["fetch_format"]: '
- 'use "array" or "frame"'.format(format)
- )
-
- get = partial(
- _get,
- self._expression.connection,
- squeeze=squeeze,
- download_path=download_path,
- )
- if attrs: # a list of attributes provided
- attributes = [a for a in attrs if not is_key(a)]
- ret = self._expression.proj(*attributes)
- ret = ret.fetch(
- offset=offset,
- limit=limit,
- order_by=order_by,
- as_dict=False,
- squeeze=squeeze,
- download_path=download_path,
- format="array",
- )
- if attrs_as_dict:
- ret = [
- {k: v for k, v in zip(ret.dtype.names, x) if k in attrs}
- for x in ret
- ]
- else:
- return_values = [
- (
- list(
- (to_dicts if as_dict else lambda x: x)(
- ret[self._expression.primary_key]
- )
- )
- if is_key(attribute)
- else ret[attribute]
- )
- for attribute in attrs
- ]
- ret = return_values[0] if len(attrs) == 1 else return_values
- else: # fetch all attributes as a numpy.record_array or pandas.DataFrame
- cur = self._expression.cursor(as_dict=as_dict)
- heading = self._expression.heading
- if as_dict:
- ret = [
- dict((name, get(heading[name], d[name])) for name in heading.names)
- for d in cur
- ]
- else:
- ret = list(cur.fetchall())
- record_type = (
- heading.as_dtype
- if not ret
- else np.dtype(
- [
- (
- (
- name,
- type(value),
- ) # use the first element to determine blob type
- if heading[name].is_blob
- and isinstance(value, numbers.Number)
- else (name, heading.as_dtype[name])
- )
- for value, name in zip(ret[0], heading.as_dtype.names)
- ]
- )
- )
- try:
- ret = np.array(ret, dtype=record_type)
- except Exception as e:
- raise e
- for name in heading:
- # unpack blobs and externals
- ret[name] = list(map(partial(get, heading[name]), ret[name]))
- if format == "frame":
- ret = pandas.DataFrame(ret).set_index(heading.primary_key)
- return ret
-
-
-class Fetch1:
- """
- Fetch object for fetching the result of a query yielding one row.
-
- :param expression: a query expression to fetch from.
- """
-
- def __init__(self, expression):
- self._expression = expression
-
- def __call__(self, *attrs, squeeze=False, download_path="."):
- """
- Fetches the result of a query expression that yields one entry.
-
- If no attributes are specified, returns the result as a dict.
- If attributes are specified returns the corresponding results as a tuple.
-
- Examples:
- d = rel.fetch1() # as a dictionary
- a, b = rel.fetch1('a', 'b') # as a tuple
-
- :params *attrs: attributes to return when expanding into a tuple.
- If attrs is empty, the return result is a dict
- :param squeeze: When true, remove extra dimensions from arrays in attributes
- :param download_path: for fetches that download data, e.g. attachments
- :return: the one tuple in the table in the form of a dict
- """
- heading = self._expression.heading
-
- if not attrs: # fetch all attributes, return as ordered dict
- cur = self._expression.cursor(as_dict=True)
- ret = cur.fetchone()
- if not ret or cur.fetchone():
- raise DataJointError(
- "fetch1 requires exactly one tuple in the input set."
- )
- ret = dict(
- (
- name,
- _get(
- self._expression.connection,
- heading[name],
- ret[name],
- squeeze=squeeze,
- download_path=download_path,
- ),
- )
- for name in heading.names
- )
- else: # fetch some attributes, return as tuple
- attributes = [a for a in attrs if not is_key(a)]
- result = self._expression.proj(*attributes).fetch(
- squeeze=squeeze, download_path=download_path, format="array"
- )
- if len(result) != 1:
- raise DataJointError(
- "fetch1 should only return one tuple. %d tuples found" % len(result)
- )
- return_values = tuple(
- (
- next(to_dicts(result[self._expression.primary_key]))
- if is_key(attribute)
- else result[attribute][0]
- )
- for attribute in attrs
- )
- ret = return_values[0] if len(attrs) == 1 else return_values
- return ret
diff --git a/datajoint/hash.py b/datajoint/hash.py
deleted file mode 100644
index f58c65732..000000000
--- a/datajoint/hash.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-import hashlib
-import io
-import uuid
-from pathlib import Path
-
-
-def key_hash(mapping):
- """
- 32-byte hash of the mapping's key values sorted by the key name.
- This is often used to convert a long primary key value into a shorter hash.
- For example, the JobTable in datajoint.jobs uses this function to hash the primary key of autopopulated tables.
- """
- hashed = hashlib.md5()
- for k, v in sorted(mapping.items()):
- hashed.update(str(v).encode())
- return hashed.hexdigest()
-
-
-def uuid_from_stream(stream, *, init_string=""):
- """
- :return: 16-byte digest of stream data
- :stream: stream object or open file handle
- :init_string: string to initialize the checksum
- """
- hashed = hashlib.md5(init_string.encode())
- chunk = True
- chunk_size = 1 << 14
- while chunk:
- chunk = stream.read(chunk_size)
- hashed.update(chunk)
- return uuid.UUID(bytes=hashed.digest())
-
-
-def uuid_from_buffer(buffer=b"", *, init_string=""):
- return uuid_from_stream(io.BytesIO(buffer), init_string=init_string)
-
-
-def uuid_from_file(filepath, *, init_string=""):
- return uuid_from_stream(Path(filepath).open("rb"), init_string=init_string)
diff --git a/datajoint/heading.py b/datajoint/heading.py
deleted file mode 100644
index c81b5a61a..000000000
--- a/datajoint/heading.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,533 +0,0 @@
-import logging
-import re
-from collections import defaultdict, namedtuple
-from itertools import chain
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from .attribute_adapter import AttributeAdapter, get_adapter
-from .declare import (
- EXTERNAL_TYPES,
- NATIVE_TYPES,
- SPECIAL_TYPES,
- TYPE_PATTERN,
- UUID_DATA_TYPE,
-)
-from .errors import FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH, DataJointError, _support_filepath_types
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-
-default_attribute_properties = (
- dict( # these default values are set in computed attributes
- name=None,
- type="expression",
- in_key=False,
- nullable=False,
- default=None,
- comment="calculated attribute",
- autoincrement=False,
- numeric=None,
- string=None,
- uuid=False,
- json=None,
- is_blob=False,
- is_attachment=False,
- is_filepath=False,
- is_external=False,
- is_hidden=False,
- adapter=None,
- store=None,
- unsupported=False,
- attribute_expression=None,
- database=None,
- dtype=object,
- )
-)
-
-
-class Attribute(namedtuple("_Attribute", default_attribute_properties)):
- """
- Properties of a table column (attribute)
- """
-
- def todict(self):
- """Convert namedtuple to dict."""
- return dict((name, self[i]) for i, name in enumerate(self._fields))
-
- @property
- def sql_type(self):
- """:return: datatype (as string) in database. In most cases, it is the same as self.type"""
- return UUID_DATA_TYPE if self.uuid else self.type
-
- @property
- def sql_comment(self):
- """:return: full comment for the SQL declaration. Includes custom type specification"""
- return (":uuid:" if self.uuid else "") + self.comment
-
- @property
- def sql(self):
- """
- Convert primary key attribute tuple into its SQL CREATE TABLE clause.
- Default values are not reflected.
- This is used for declaring foreign keys in referencing tables
-
- :return: SQL code for attribute declaration
- """
- return '`{name}` {type} NOT NULL COMMENT "{comment}"'.format(
- name=self.name, type=self.sql_type, comment=self.sql_comment
- )
-
- @property
- def original_name(self):
- if self.attribute_expression is None:
- return self.name
- assert self.attribute_expression.startswith("`")
- return self.attribute_expression.strip("`")
-
-
-class Heading:
- """
- Local class for table headings.
- Heading contains the property attributes, which is an dict in which the keys are
- the attribute names and the values are Attributes.
- """
-
- def __init__(self, attribute_specs=None, table_info=None):
- """
-
- :param attribute_specs: a list of dicts with the same keys as Attribute
- :param table_info: a dict with information to load the heading from the database
- """
- self.indexes = None
- self.table_info = table_info
- self._table_status = None
- self._attributes = (
- None
- if attribute_specs is None
- else dict((q["name"], Attribute(**q)) for q in attribute_specs)
- )
-
- def __len__(self):
- return 0 if self.attributes is None else len(self.attributes)
-
- @property
- def table_status(self):
- if self.table_info is None:
- return None
- if self._table_status is None:
- self._init_from_database()
- return self._table_status
-
- @property
- def attributes(self):
- if self._attributes is None:
- self._init_from_database() # lazy loading from database
- return {k: v for k, v in self._attributes.items() if not v.is_hidden}
-
- @property
- def names(self):
- return [k for k in self.attributes]
-
- @property
- def primary_key(self):
- return [k for k, v in self.attributes.items() if v.in_key]
-
- @property
- def secondary_attributes(self):
- return [k for k, v in self.attributes.items() if not v.in_key]
-
- @property
- def blobs(self):
- return [k for k, v in self.attributes.items() if v.is_blob]
-
- @property
- def non_blobs(self):
- return [
- k
- for k, v in self.attributes.items()
- if not (v.is_blob or v.is_attachment or v.is_filepath or v.json)
- ]
-
- @property
- def new_attributes(self):
- return [
- k for k, v in self.attributes.items() if v.attribute_expression is not None
- ]
-
- def __getitem__(self, name):
- """shortcut to the attribute"""
- return self.attributes[name]
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """
- :return: heading representation in DataJoint declaration format but without foreign key expansion
- """
- in_key = True
- ret = ""
- if self._table_status is not None:
- ret += "# " + self.table_status["comment"] + "\n"
- for v in self.attributes.values():
- if in_key and not v.in_key:
- ret += "---\n"
- in_key = False
- ret += "%-20s : %-28s # %s\n" % (
- v.name if v.default is None else "%s=%s" % (v.name, v.default),
- "%s%s" % (v.type, "auto_increment" if v.autoincrement else ""),
- v.comment,
- )
- return ret
-
- @property
- def has_autoincrement(self):
- return any(e.autoincrement for e in self.attributes.values())
-
- @property
- def as_dtype(self):
- """
- represent the heading as a numpy dtype
- """
- return np.dtype(
- dict(names=self.names, formats=[v.dtype for v in self.attributes.values()])
- )
-
- def as_sql(self, fields, include_aliases=True):
- """
- represent heading as the SQL SELECT clause.
- """
- return ",".join(
- (
- "`%s`" % name
- if self.attributes[name].attribute_expression is None
- else self.attributes[name].attribute_expression
- + (" as `%s`" % name if include_aliases else "")
- )
- for name in fields
- )
-
- def __iter__(self):
- return iter(self.attributes)
-
- def _init_from_database(self):
- """initialize heading from an existing database table."""
- conn, database, table_name, context = (
- self.table_info[k] for k in ("conn", "database", "table_name", "context")
- )
- info = conn.query(
- 'SHOW TABLE STATUS FROM `{database}` WHERE name="{table_name}"'.format(
- table_name=table_name, database=database
- ),
- as_dict=True,
- ).fetchone()
- if info is None:
- if table_name == "~log":
- logger.warning("Could not create the ~log table")
- return
- raise DataJointError(
- "The table `{database}`.`{table_name}` is not defined.".format(
- table_name=table_name, database=database
- )
- )
- self._table_status = {k.lower(): v for k, v in info.items()}
- cur = conn.query(
- "SHOW FULL COLUMNS FROM `{table_name}` IN `{database}`".format(
- table_name=table_name, database=database
- ),
- as_dict=True,
- )
-
- attributes = cur.fetchall()
-
- rename_map = {
- "Field": "name",
- "Type": "type",
- "Null": "nullable",
- "Default": "default",
- "Key": "in_key",
- "Comment": "comment",
- }
-
- fields_to_drop = ("Privileges", "Collation")
-
- # rename and drop attributes
- attributes = [
- {
- rename_map[k] if k in rename_map else k: v
- for k, v in x.items()
- if k not in fields_to_drop
- }
- for x in attributes
- ]
- numeric_types = {
- ("float", False): np.float64,
- ("float", True): np.float64,
- ("double", False): np.float64,
- ("double", True): np.float64,
- ("tinyint", False): np.int64,
- ("tinyint", True): np.int64,
- ("smallint", False): np.int64,
- ("smallint", True): np.int64,
- ("mediumint", False): np.int64,
- ("mediumint", True): np.int64,
- ("int", False): np.int64,
- ("int", True): np.int64,
- ("bigint", False): np.int64,
- ("bigint", True): np.uint64,
- }
-
- sql_literals = ["CURRENT_TIMESTAMP"]
-
- # additional attribute properties
- for attr in attributes:
- attr.update(
- in_key=(attr["in_key"] == "PRI"),
- database=database,
- nullable=attr["nullable"] == "YES",
- autoincrement=bool(
- re.search(r"auto_increment", attr["Extra"], flags=re.I)
- ),
- numeric=any(
- TYPE_PATTERN[t].match(attr["type"])
- for t in ("DECIMAL", "INTEGER", "FLOAT")
- ),
- string=any(
- TYPE_PATTERN[t].match(attr["type"])
- for t in ("ENUM", "TEMPORAL", "STRING")
- ),
- is_blob=bool(TYPE_PATTERN["INTERNAL_BLOB"].match(attr["type"])),
- uuid=False,
- json=bool(TYPE_PATTERN["JSON"].match(attr["type"])),
- is_attachment=False,
- is_filepath=False,
- adapter=None,
- store=None,
- is_external=False,
- attribute_expression=None,
- is_hidden=attr["name"].startswith("_"),
- )
-
- if any(TYPE_PATTERN[t].match(attr["type"]) for t in ("INTEGER", "FLOAT")):
- attr["type"] = re.sub(
- r"\(\d+\)", "", attr["type"], count=1
- ) # strip size off integers and floats
- attr["unsupported"] = not any(
- (attr["is_blob"], attr["numeric"], attr["numeric"])
- )
- attr.pop("Extra")
-
- # process custom DataJoint types
- special = re.match(r":(?P[^:]+):(?P.*)", attr["comment"])
- if special:
- special = special.groupdict()
- attr.update(special)
- # process adapted attribute types
- if special and TYPE_PATTERN["ADAPTED"].match(attr["type"]):
- assert context is not None, "Declaration context is not set"
- adapter_name = special["type"]
- try:
- attr.update(adapter=get_adapter(context, adapter_name))
- except DataJointError:
- # if no adapter, then delay the error until the first invocation
- attr.update(adapter=AttributeAdapter())
- else:
- attr.update(type=attr["adapter"].attribute_type)
- if not any(r.match(attr["type"]) for r in TYPE_PATTERN.values()):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Invalid attribute type '{type}' in adapter object <{adapter_name}>.".format(
- adapter_name=adapter_name, **attr
- )
- )
- special = not any(
- TYPE_PATTERN[c].match(attr["type"]) for c in NATIVE_TYPES
- )
-
- if special:
- try:
- category = next(
- c for c in SPECIAL_TYPES if TYPE_PATTERN[c].match(attr["type"])
- )
- except StopIteration:
- if attr["type"].startswith("external"):
- url = (
- "https://docs.datajoint.io/python/admin/5-blob-config.html"
- "#migration-between-datajoint-v0-11-and-v0-12"
- )
- raise DataJointError(
- "Legacy datatype `{type}`. Migrate your external stores to "
- "datajoint 0.12: {url}".format(url=url, **attr)
- )
- raise DataJointError(
- "Unknown attribute type `{type}`".format(**attr)
- )
- if category == "FILEPATH" and not _support_filepath_types():
- raise DataJointError(
- """
- The filepath data type is disabled until complete validation.
- To turn it on as experimental feature, set the environment variable
- {env} = TRUE or upgrade datajoint.
- """.format(
- env=FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH
- )
- )
- attr.update(
- unsupported=False,
- is_attachment=category in ("INTERNAL_ATTACH", "EXTERNAL_ATTACH"),
- is_filepath=category == "FILEPATH",
- # INTERNAL_BLOB is not a custom type but is included for completeness
- is_blob=category in ("INTERNAL_BLOB", "EXTERNAL_BLOB"),
- uuid=category == "UUID",
- is_external=category in EXTERNAL_TYPES,
- store=(
- attr["type"].split("@")[1]
- if category in EXTERNAL_TYPES
- else None
- ),
- )
-
- if attr["in_key"] and any(
- (
- attr["is_blob"],
- attr["is_attachment"],
- attr["is_filepath"],
- attr["json"],
- )
- ):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Json, Blob, attachment, or filepath attributes are not allowed in the primary key"
- )
-
- if (
- attr["string"]
- and attr["default"] is not None
- and attr["default"] not in sql_literals
- ):
- attr["default"] = '"%s"' % attr["default"]
-
- if attr["nullable"]: # nullable fields always default to null
- attr["default"] = "null"
-
- # fill out dtype. All floats and non-nullable integers are turned into specific dtypes
- attr["dtype"] = object
- if attr["numeric"] and not attr["adapter"]:
- is_integer = TYPE_PATTERN["INTEGER"].match(attr["type"])
- is_float = TYPE_PATTERN["FLOAT"].match(attr["type"])
- if is_integer and not attr["nullable"] or is_float:
- is_unsigned = bool(re.match("sunsigned", attr["type"], flags=re.I))
- t = re.sub(r"\(.*\)", "", attr["type"]) # remove parentheses
- t = re.sub(r" unsigned$", "", t) # remove unsigned
- assert (t, is_unsigned) in numeric_types, (
- "dtype not found for type %s" % t
- )
- attr["dtype"] = numeric_types[(t, is_unsigned)]
-
- if attr["adapter"]:
- # restore adapted type name
- attr["type"] = adapter_name
-
- self._attributes = dict(((q["name"], Attribute(**q)) for q in attributes))
-
- # Read and tabulate secondary indexes
- keys = defaultdict(dict)
- for item in conn.query(
- "SHOW KEYS FROM `{db}`.`{tab}`".format(db=database, tab=table_name),
- as_dict=True,
- ):
- if item["Key_name"] != "PRIMARY":
- keys[item["Key_name"]][item["Seq_in_index"]] = dict(
- column=item["Column_name"]
- or f"({item['Expression']})".replace(r"\'", "'"),
- unique=(item["Non_unique"] == 0),
- nullable=item["Null"].lower() == "yes",
- )
- self.indexes = {
- tuple(item[k]["column"] for k in sorted(item.keys())): dict(
- unique=item[1]["unique"],
- nullable=any(v["nullable"] for v in item.values()),
- )
- for item in keys.values()
- }
-
- def select(self, select_list, rename_map=None, compute_map=None):
- """
- derive a new heading by selecting, renaming, or computing attributes.
- In relational algebra these operators are known as project, rename, and extend.
-
- :param select_list: the full list of existing attributes to include
- :param rename_map: dictionary of renamed attributes: keys=new names, values=old names
- :param compute_map: a direction of computed attributes
- This low-level method performs no error checking.
- """
- rename_map = rename_map or {}
- compute_map = compute_map or {}
- copy_attrs = list()
- for name in self.attributes:
- if name in select_list:
- copy_attrs.append(self.attributes[name].todict())
- copy_attrs.extend(
- (
- dict(
- self.attributes[old_name].todict(),
- name=new_name,
- attribute_expression="`%s`" % old_name,
- )
- for new_name, old_name in rename_map.items()
- if old_name == name
- )
- )
- compute_attrs = (
- dict(default_attribute_properties, name=new_name, attribute_expression=expr)
- for new_name, expr in compute_map.items()
- )
- return Heading(chain(copy_attrs, compute_attrs))
-
- def join(self, other):
- """
- Join two headings into a new one.
- It assumes that self and other are headings that share no common dependent attributes.
- """
- return Heading(
- [self.attributes[name].todict() for name in self.primary_key]
- + [
- other.attributes[name].todict()
- for name in other.primary_key
- if name not in self.primary_key
- ]
- + [
- self.attributes[name].todict()
- for name in self.secondary_attributes
- if name not in other.primary_key
- ]
- + [
- other.attributes[name].todict()
- for name in other.secondary_attributes
- if name not in self.primary_key
- ]
- )
-
- def set_primary_key(self, primary_key):
- """
- Create a new heading with the specified primary key.
- This low-level method performs no error checking.
- """
- return Heading(
- chain(
- (
- dict(self.attributes[name].todict(), in_key=True)
- for name in primary_key
- ),
- (
- dict(self.attributes[name].todict(), in_key=False)
- for name in self.names
- if name not in primary_key
- ),
- )
- )
-
- def make_subquery_heading(self):
- """
- Create a new heading with removed attribute sql_expressions.
- Used by subqueries, which resolve the sql_expressions.
- """
- return Heading(
- dict(v.todict(), attribute_expression=None)
- for v in self.attributes.values()
- )
diff --git a/datajoint/jobs.py b/datajoint/jobs.py
deleted file mode 100644
index d6b31e13e..000000000
--- a/datajoint/jobs.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
-import os
-import platform
-
-from .errors import DuplicateError
-from .hash import key_hash
-from .heading import Heading
-from .settings import config
-from .table import Table
-
-ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH = 2047
-TRUNCATION_APPENDIX = "...truncated"
-
-
-class JobTable(Table):
- """
- A base table with no definition. Allows reserving jobs
- """
-
- def __init__(self, conn, database):
- self.database = database
- self._connection = conn
- self._heading = Heading(
- table_info=dict(
- conn=conn, database=database, table_name=self.table_name, context=None
- )
- )
- self._support = [self.full_table_name]
-
- self._definition = """ # job reservation table for `{database}`
- table_name :varchar(255) # className of the table
- key_hash :char(32) # key hash
- ---
- status :enum('reserved','error','ignore') # if tuple is missing, the job is available
- key=null :blob # structure containing the key
- error_message="" :varchar({error_message_length}) # error message returned if failed
- error_stack=null :mediumblob # error stack if failed
- user="" :varchar(255) # database user
- host="" :varchar(255) # system hostname
- pid=0 :int unsigned # system process id
- connection_id = 0 : bigint unsigned # connection_id()
- timestamp=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP :timestamp # automatic timestamp
- """.format(
- database=database, error_message_length=ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH
- )
- if not self.is_declared:
- self.declare()
- self._user = self.connection.get_user()
-
- @property
- def definition(self):
- return self._definition
-
- @property
- def table_name(self):
- return "~jobs"
-
- def delete(self):
- """bypass interactive prompts and dependencies"""
- self.delete_quick()
-
- def drop(self):
- """bypass interactive prompts and dependencies"""
- self.drop_quick()
-
- def reserve(self, table_name, key):
- """
- Reserve a job for computation. When a job is reserved, the job table contains an entry for the
- job key, identified by its hash. When jobs are completed, the entry is removed.
-
- :param table_name: `database`.`table_name`
- :param key: the dict of the job's primary key
- :return: True if reserved job successfully. False = the jobs is already taken
- """
- job = dict(
- table_name=table_name,
- key_hash=key_hash(key),
- status="reserved",
- host=platform.node(),
- pid=os.getpid(),
- connection_id=self.connection.connection_id,
- key=key,
- user=self._user,
- )
- try:
- with config(enable_python_native_blobs=True):
- self.insert1(job, ignore_extra_fields=True)
- except DuplicateError:
- return False
- return True
-
- def ignore(self, table_name, key):
- """
- Set a job to be ignored for computation. When a job is ignored, the job table contains an entry for the
- job key, identified by its hash, with status "ignore".
-
- Args:
- table_name:
- Table name (str) - `database`.`table_name`
- key:
- The dict of the job's primary key
-
- Returns:
- True if ignore job successfully. False = the jobs is already taken
- """
- job = dict(
- table_name=table_name,
- key_hash=key_hash(key),
- status="ignore",
- host=platform.node(),
- pid=os.getpid(),
- connection_id=self.connection.connection_id,
- key=key,
- user=self._user,
- )
- try:
- with config(enable_python_native_blobs=True):
- self.insert1(job, ignore_extra_fields=True)
- except DuplicateError:
- return False
- return True
-
- def complete(self, table_name, key):
- """
- Log a completed job. When a job is completed, its reservation entry is deleted.
-
- :param table_name: `database`.`table_name`
- :param key: the dict of the job's primary key
- """
- job_key = dict(table_name=table_name, key_hash=key_hash(key))
- (self & job_key).delete_quick()
-
- def error(self, table_name, key, error_message, error_stack=None):
- """
- Log an error message. The job reservation is replaced with an error entry.
- if an error occurs, leave an entry describing the problem
-
- :param table_name: `database`.`table_name`
- :param key: the dict of the job's primary key
- :param error_message: string error message
- :param error_stack: stack trace
- """
- if len(error_message) > ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH:
- error_message = (
- error_message[: ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH - len(TRUNCATION_APPENDIX)]
- + TRUNCATION_APPENDIX
- )
- with config(enable_python_native_blobs=True):
- self.insert1(
- dict(
- table_name=table_name,
- key_hash=key_hash(key),
- status="error",
- host=platform.node(),
- pid=os.getpid(),
- connection_id=self.connection.connection_id,
- user=self._user,
- key=key,
- error_message=error_message,
- error_stack=error_stack,
- ),
- replace=True,
- ignore_extra_fields=True,
- )
diff --git a/datajoint/preview.py b/datajoint/preview.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 564c92a0a..000000000
--- a/datajoint/preview.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,153 +0,0 @@
-"""methods for generating previews of query expression results in python command line and Jupyter"""
-
-from .settings import config
-
-
-def preview(query_expression, limit, width):
- heading = query_expression.heading
- rel = query_expression.proj(*heading.non_blobs)
- if limit is None:
- limit = config["display.limit"]
- if width is None:
- width = config["display.width"]
- tuples = rel.fetch(limit=limit + 1, format="array")
- has_more = len(tuples) > limit
- tuples = tuples[:limit]
- columns = heading.names
- widths = {
- f: min(
- max(
- [len(f)] + [len(str(e)) for e in tuples[f]]
- if f in tuples.dtype.names
- else [len("=BLOB=")]
- )
- + 4,
- width,
- )
- for f in columns
- }
- templates = {f: "%%-%d.%ds" % (widths[f], widths[f]) for f in columns}
- return (
- " ".join(
- [templates[f] % ("*" + f if f in rel.primary_key else f) for f in columns]
- )
- + "\n"
- + " ".join(["+" + "-" * (widths[column] - 2) + "+" for column in columns])
- + "\n"
- + "\n".join(
- " ".join(
- templates[f] % (tup[f] if f in tup.dtype.names else "=BLOB=")
- for f in columns
- )
- for tup in tuples
- )
- + ("\n ...\n" if has_more else "\n")
- + (" (Total: %d)\n" % len(rel) if config["display.show_tuple_count"] else "")
- )
-
-
-def repr_html(query_expression):
- heading = query_expression.heading
- rel = query_expression.proj(*heading.non_blobs)
- info = heading.table_status
- tuples = rel.fetch(limit=config["display.limit"] + 1, format="array")
- has_more = len(tuples) > config["display.limit"]
- tuples = tuples[0 : config["display.limit"]]
-
- css = """
-
- """
- head_template = """"""
- return """
- {css}
- {title}
-
- """.format(
- css=css,
- title="" if info is None else "%s" % info["comment"],
- head="".join(
- head_template.format(
- column=c,
- comment=heading.attributes[c].comment,
- primary=(
- "primary" if c in query_expression.primary_key else "nonprimary"
- ),
- )
- for c in heading.names
- ),
- ellipsis=" ... " if has_more else "",
- body=" | ".join(
- [
- "\n".join(
- [
- "| %s | "
- % (tup[name] if name in tup.dtype.names else "=BLOB=")
- for name in heading.names
- ]
- )
- for tup in tuples
- ]
- ),
- count=(
- ("Total: %d
" % len(rel))
- if config["display.show_tuple_count"]
- else ""
- ),
- )
diff --git a/datajoint/s3.py b/datajoint/s3.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 98dc75708..000000000
--- a/datajoint/s3.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,123 +0,0 @@
-"""
-AWS S3 operations
-"""
-
-import logging
-import uuid
-from io import BytesIO
-from pathlib import Path
-
-import minio # https://docs.minio.io/docs/python-client-api-reference
-import urllib3
-
-from . import errors
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-
-
-class Folder:
- """
- A Folder instance manipulates a flat folder of objects within an S3-compatible object store
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- endpoint,
- bucket,
- access_key,
- secret_key,
- *,
- secure=False,
- proxy_server=None,
- **_,
- ):
- # from https://docs.min.io/docs/python-client-api-reference
- self.client = minio.Minio(
- endpoint,
- access_key=access_key,
- secret_key=secret_key,
- secure=secure,
- http_client=(
- urllib3.ProxyManager(
- proxy_server,
- timeout=urllib3.Timeout.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT,
- cert_reqs="CERT_REQUIRED",
- retries=urllib3.Retry(
- total=5,
- backoff_factor=0.2,
- status_forcelist=[500, 502, 503, 504],
- ),
- )
- if proxy_server
- else None
- ),
- )
- self.bucket = bucket
- if not self.client.bucket_exists(bucket):
- raise errors.BucketInaccessible("Inaccessible s3 bucket %s" % bucket)
-
- def put(self, name, buffer):
- logger.debug("put: {}:{}".format(self.bucket, name))
- return self.client.put_object(
- self.bucket, str(name), BytesIO(buffer), length=len(buffer)
- )
-
- def fput(self, local_file, name, metadata=None):
- logger.debug("fput: {} -> {}:{}".format(self.bucket, local_file, name))
- return self.client.fput_object(
- self.bucket, str(name), str(local_file), metadata=metadata
- )
-
- def get(self, name):
- logger.debug("get: {}:{}".format(self.bucket, name))
- try:
- with self.client.get_object(self.bucket, str(name)) as result:
- data = [d for d in result.stream()]
- return b"".join(data)
- except minio.error.S3Error as e:
- if e.code == "NoSuchKey":
- raise errors.MissingExternalFile("Missing s3 key %s" % name)
- else:
- raise e
-
- def fget(self, name, local_filepath):
- """get file from object name to local filepath"""
- logger.debug("fget: {}:{}".format(self.bucket, name))
- name = str(name)
- stat = self.client.stat_object(self.bucket, name)
- meta = {k.lower().lstrip("x-amz-meta"): v for k, v in stat.metadata.items()}
- data = self.client.get_object(self.bucket, name)
- local_filepath = Path(local_filepath)
- local_filepath.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
- with local_filepath.open("wb") as f:
- for d in data.stream(1 << 16):
- f.write(d)
- if "contents_hash" in meta:
- return uuid.UUID(meta["contents_hash"])
-
- def exists(self, name):
- logger.debug("exists: {}:{}".format(self.bucket, name))
- try:
- self.client.stat_object(self.bucket, str(name))
- except minio.error.S3Error as e:
- if e.code == "NoSuchKey":
- return False
- else:
- raise e
- return True
-
- def get_size(self, name):
- logger.debug("get_size: {}:{}".format(self.bucket, name))
- try:
- return self.client.stat_object(self.bucket, str(name)).size
- except minio.error.S3Error as e:
- if e.code == "NoSuchKey":
- raise errors.MissingExternalFile
- raise e
-
- def remove_object(self, name):
- logger.debug("remove_object: {}:{}".format(self.bucket, name))
- try:
- self.client.remove_object(self.bucket, str(name))
- except minio.error.MinioException:
- raise errors.DataJointError("Failed to delete %s from s3 storage" % name)
diff --git a/datajoint/schemas.py b/datajoint/schemas.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 8cb7a3668..000000000
--- a/datajoint/schemas.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,546 +0,0 @@
-import collections
-import inspect
-import itertools
-import logging
-import re
-import types
-import warnings
-
-from .connection import conn
-from .errors import AccessError, DataJointError
-from .external import ExternalMapping
-from .heading import Heading
-from .jobs import JobTable
-from .settings import config
-from .table import FreeTable, Log, lookup_class_name
-from .user_tables import Computed, Imported, Lookup, Manual, Part, _get_tier
-from .utils import to_camel_case, user_choice
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-
-
-def ordered_dir(class_):
- """
- List (most) attributes of the class including inherited ones, similar to `dir` built-in function,
- but respects order of attribute declaration as much as possible.
-
- :param class_: class to list members for
- :return: a list of attributes declared in class_ and its superclasses
- """
- attr_list = list()
- for c in reversed(class_.mro()):
- attr_list.extend(e for e in c.__dict__ if e not in attr_list)
- return attr_list
-
-
-class Schema:
- """
- A schema object is a decorator for UserTable classes that binds them to their database.
- It also specifies the namespace `context` in which other UserTable classes are defined.
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- schema_name=None,
- context=None,
- *,
- connection=None,
- create_schema=True,
- create_tables=True,
- add_objects=None,
- ):
- """
- Associate database schema `schema_name`. If the schema does not exist, attempt to
- create it on the server.
-
- If the schema_name is omitted, then schema.activate(..) must be called later
- to associate with the database.
-
- :param schema_name: the database schema to associate.
- :param context: dictionary for looking up foreign key references, leave None to use local context.
- :param connection: Connection object. Defaults to datajoint.conn().
- :param create_schema: When False, do not create the schema and raise an error if missing.
- :param create_tables: When False, do not create tables and raise errors when accessing missing tables.
- :param add_objects: a mapping with additional objects to make available to the context in which table classes
- are declared.
- """
- self._log = None
- self.connection = connection
- self.database = None
- self.context = context
- self.create_schema = create_schema
- self.create_tables = create_tables
- self._jobs = None
- self.external = ExternalMapping(self)
- self.add_objects = add_objects
- self.declare_list = []
- if schema_name:
- self.activate(schema_name)
-
- def is_activated(self):
- return self.database is not None
-
- def activate(
- self,
- schema_name=None,
- *,
- connection=None,
- create_schema=None,
- create_tables=None,
- add_objects=None,
- ):
- """
- Associate database schema `schema_name`. If the schema does not exist, attempt to
- create it on the server.
-
- :param schema_name: the database schema to associate.
- schema_name=None is used to assert that the schema has already been activated.
- :param connection: Connection object. Defaults to datajoint.conn().
- :param create_schema: If False, do not create the schema and raise an error if missing.
- :param create_tables: If False, do not create tables and raise errors when attempting
- to access missing tables.
- :param add_objects: a mapping with additional objects to make available to the context
- in which table classes are declared.
- """
- if schema_name is None:
- if self.exists:
- return
- raise DataJointError("Please provide a schema_name to activate the schema.")
- if self.database is not None and self.exists:
- if self.database == schema_name: # already activated
- return
- raise DataJointError(
- "The schema is already activated for schema {db}.".format(
- db=self.database
- )
- )
- if connection is not None:
- self.connection = connection
- if self.connection is None:
- self.connection = conn()
- self.database = schema_name
- if create_schema is not None:
- self.create_schema = create_schema
- if create_tables is not None:
- self.create_tables = create_tables
- if add_objects:
- self.add_objects = add_objects
- if not self.exists:
- if not self.create_schema or not self.database:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Database `{name}` has not yet been declared. "
- "Set argument create_schema=True to create it.".format(
- name=schema_name
- )
- )
- # create database
- logger.debug("Creating schema `{name}`.".format(name=schema_name))
- try:
- self.connection.query(
- "CREATE DATABASE `{name}`".format(name=schema_name)
- )
- except AccessError:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Schema `{name}` does not exist and could not be created. "
- "Check permissions.".format(name=schema_name)
- )
- else:
- self.log("created")
- self.connection.register(self)
-
- # decorate all tables already decorated
- for cls, context in self.declare_list:
- if self.add_objects:
- context = dict(context, **self.add_objects)
- self._decorate_master(cls, context)
-
- def _assert_exists(self, message=None):
- if not self.exists:
- raise DataJointError(
- message
- or "Schema `{db}` has not been created.".format(db=self.database)
- )
-
- def __call__(self, cls, *, context=None):
- """
- Binds the supplied class to a schema. This is intended to be used as a decorator.
-
- :param cls: class to decorate.
- :param context: supplied when called from spawn_missing_classes
- """
- context = context or self.context or inspect.currentframe().f_back.f_locals
- if issubclass(cls, Part):
- raise DataJointError(
- "The schema decorator should not be applied to Part tables."
- )
- if self.is_activated():
- self._decorate_master(cls, context)
- else:
- self.declare_list.append((cls, context))
- return cls
-
- def _decorate_master(self, cls, context):
- """
-
- :param cls: the master class to process
- :param context: the class' declaration context
- """
- self._decorate_table(
- cls, context=dict(context, self=cls, **{cls.__name__: cls})
- )
- # Process part tables
- for part in ordered_dir(cls):
- if part[0].isupper():
- part = getattr(cls, part)
- if inspect.isclass(part) and issubclass(part, Part):
- part._master = cls
- # allow addressing master by name or keyword 'master'
- self._decorate_table(
- part,
- context=dict(
- context, master=cls, self=part, **{cls.__name__: cls}
- ),
- )
-
- def _decorate_table(self, table_class, context, assert_declared=False):
- """
- assign schema properties to the table class and declare the table
- """
- table_class.database = self.database
- table_class._connection = self.connection
- table_class._heading = Heading(
- table_info=dict(
- conn=self.connection,
- database=self.database,
- table_name=table_class.table_name,
- context=context,
- )
- )
- table_class._support = [table_class.full_table_name]
- table_class.declaration_context = context
-
- # instantiate the class, declare the table if not already
- instance = table_class()
- is_declared = instance.is_declared
- if not is_declared and not assert_declared and self.create_tables:
- instance.declare(context)
- self.connection.dependencies.clear()
- is_declared = is_declared or instance.is_declared
-
- # add table definition to the doc string
- if isinstance(table_class.definition, str):
- table_class.__doc__ = (
- (table_class.__doc__ or "")
- + "\nTable definition:\n\n"
- + table_class.definition
- )
-
- # fill values in Lookup tables from their contents property
- if (
- isinstance(instance, Lookup)
- and hasattr(instance, "contents")
- and is_declared
- ):
- contents = list(instance.contents)
- if len(contents) > len(instance):
- if instance.heading.has_autoincrement:
- warnings.warn(
- (
- "Contents has changed but cannot be inserted because "
- "{table} has autoincrement."
- ).format(table=instance.__class__.__name__)
- )
- else:
- instance.insert(contents, skip_duplicates=True)
-
- @property
- def log(self):
- self._assert_exists()
- if self._log is None:
- self._log = Log(self.connection, self.database)
- return self._log
-
- def __repr__(self):
- return "Schema `{name}`\n".format(name=self.database)
-
- @property
- def size_on_disk(self):
- """
- :return: size of the entire schema in bytes
- """
- self._assert_exists()
- return int(
- self.connection.query(
- """
- SELECT SUM(data_length + index_length)
- FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema='{db}'
- """.format(
- db=self.database
- )
- ).fetchone()[0]
- )
-
- def spawn_missing_classes(self, context=None):
- """
- Creates the appropriate python user table classes from tables in the schema and places them
- in the context.
-
- :param context: alternative context to place the missing classes into, e.g. locals()
- """
- self._assert_exists()
- if context is None:
- if self.context is not None:
- context = self.context
- else:
- # if context is missing, use the calling namespace
- frame = inspect.currentframe().f_back
- context = frame.f_locals
- del frame
- tables = [
- row[0]
- for row in self.connection.query("SHOW TABLES in `%s`" % self.database)
- if lookup_class_name(
- "`{db}`.`{tab}`".format(db=self.database, tab=row[0]), context, 0
- )
- is None
- ]
- master_classes = (Lookup, Manual, Imported, Computed)
- part_tables = []
- for table_name in tables:
- class_name = to_camel_case(table_name)
- if class_name not in context:
- try:
- cls = next(
- cls
- for cls in master_classes
- if re.fullmatch(cls.tier_regexp, table_name)
- )
- except StopIteration:
- if re.fullmatch(Part.tier_regexp, table_name):
- part_tables.append(table_name)
- else:
- # declare and decorate master table classes
- context[class_name] = self(
- type(class_name, (cls,), dict()), context=context
- )
-
- # attach parts to masters
- for table_name in part_tables:
- groups = re.fullmatch(Part.tier_regexp, table_name).groupdict()
- class_name = to_camel_case(groups["part"])
- try:
- master_class = context[to_camel_case(groups["master"])]
- except KeyError:
- raise DataJointError(
- "The table %s does not follow DataJoint naming conventions"
- % table_name
- )
- part_class = type(class_name, (Part,), dict(definition=...))
- part_class._master = master_class
- self._decorate_table(part_class, context=context, assert_declared=True)
- setattr(master_class, class_name, part_class)
-
- def drop(self, force=False):
- """
- Drop the associated schema if it exists
- """
- if not self.exists:
- logger.info(
- "Schema named `{database}` does not exist. Doing nothing.".format(
- database=self.database
- )
- )
- elif (
- not config["safemode"]
- or force
- or user_choice(
- "Proceed to delete entire schema `%s`?" % self.database, default="no"
- )
- == "yes"
- ):
- logger.debug("Dropping `{database}`.".format(database=self.database))
- try:
- self.connection.query(
- "DROP DATABASE `{database}`".format(database=self.database)
- )
- logger.debug(
- "Schema `{database}` was dropped successfully.".format(
- database=self.database
- )
- )
- except AccessError:
- raise AccessError(
- "An attempt to drop schema `{database}` "
- "has failed. Check permissions.".format(database=self.database)
- )
-
- @property
- def exists(self):
- """
- :return: true if the associated schema exists on the server
- """
- if self.database is None:
- raise DataJointError("Schema must be activated first.")
- return bool(
- self.connection.query(
- "SELECT schema_name "
- "FROM information_schema.schemata "
- "WHERE schema_name = '{database}'".format(database=self.database)
- ).rowcount
- )
-
- @property
- def jobs(self):
- """
- schema.jobs provides a view of the job reservation table for the schema
-
- :return: jobs table
- """
- self._assert_exists()
- if self._jobs is None:
- self._jobs = JobTable(self.connection, self.database)
- return self._jobs
-
- @property
- def code(self):
- self._assert_exists()
- return self.save()
-
- def save(self, python_filename=None):
- """
- Generate the code for a module that recreates the schema.
- This method is in preparation for a future release and is not officially supported.
-
- :return: a string containing the body of a complete Python module defining this schema.
- """
- self.connection.dependencies.load()
- self._assert_exists()
- module_count = itertools.count()
- # add virtual modules for referenced modules with names vmod0, vmod1, ...
- module_lookup = collections.defaultdict(
- lambda: "vmod" + str(next(module_count))
- )
- db = self.database
-
- def make_class_definition(table):
- tier = _get_tier(table).__name__
- class_name = table.split(".")[1].strip("`")
- indent = ""
- if tier == "Part":
- class_name = class_name.split("__")[-1]
- indent += " "
- class_name = to_camel_case(class_name)
-
- def replace(s):
- d, tabs = s.group(1), s.group(2)
- return ("" if d == db else (module_lookup[d] + ".")) + ".".join(
- to_camel_case(tab) for tab in tabs.lstrip("__").split("__")
- )
-
- return ("" if tier == "Part" else "\n@schema\n") + (
- "{indent}class {class_name}(dj.{tier}):\n"
- '{indent} definition = """\n'
- '{indent} {defi}"""'
- ).format(
- class_name=class_name,
- indent=indent,
- tier=tier,
- defi=re.sub(
- r"`([^`]+)`.`([^`]+)`",
- replace,
- FreeTable(self.connection, table).describe(),
- ).replace("\n", "\n " + indent),
- )
-
- tables = self.connection.dependencies.topo_sort()
- body = "\n\n".join(make_class_definition(table) for table in tables)
- python_code = "\n\n".join(
- (
- '"""This module was auto-generated by datajoint from an existing schema"""',
- "import datajoint as dj\n\nschema = dj.Schema('{db}')".format(db=db),
- "\n".join(
- "{module} = dj.VirtualModule('{module}', '{schema_name}')".format(
- module=v, schema_name=k
- )
- for k, v in module_lookup.items()
- ),
- body,
- )
- )
- if python_filename is None:
- return python_code
- with open(python_filename, "wt") as f:
- f.write(python_code)
-
- def list_tables(self):
- """
- Return a list of all tables in the schema except tables with ~ in first character such
- as ~logs and ~job
-
- :return: A list of table names from the database schema.
- """
- self.connection.dependencies.load()
- return [
- t
- for d, t in (
- table_name.replace("`", "").split(".")
- for table_name in self.connection.dependencies.topo_sort()
- )
- if d == self.database
- ]
-
-
-class VirtualModule(types.ModuleType):
- """
- A virtual module imitates a Python module representing a DataJoint schema from table definitions in the database.
- It declares the schema objects and a class for each table.
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- module_name,
- schema_name,
- *,
- create_schema=False,
- create_tables=False,
- connection=None,
- add_objects=None,
- ):
- """
- Creates a python module with the given name from the name of a schema on the server and
- automatically adds classes to it corresponding to the tables in the schema.
-
- :param module_name: displayed module name
- :param schema_name: name of the database in mysql
- :param create_schema: if True, create the schema on the database server
- :param create_tables: if True, module.schema can be used as the decorator for declaring new
- :param connection: a dj.Connection object to pass into the schema
- :param add_objects: additional objects to add to the module
- :return: the python module containing classes from the schema object and the table classes
- """
- super(VirtualModule, self).__init__(name=module_name)
- _schema = Schema(
- schema_name,
- create_schema=create_schema,
- create_tables=create_tables,
- connection=connection,
- )
- if add_objects:
- self.__dict__.update(add_objects)
- self.__dict__["schema"] = _schema
- _schema.spawn_missing_classes(context=self.__dict__)
-
-
-def list_schemas(connection=None):
- """
- :param connection: a dj.Connection object
- :return: list of all accessible schemas on the server
- """
- return [
- r[0]
- for r in (connection or conn()).query(
- "SELECT schema_name "
- "FROM information_schema.schemata "
- 'WHERE schema_name <> "information_schema"'
- )
- ]
diff --git a/datajoint/settings.py b/datajoint/settings.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 30b206f99..000000000
--- a/datajoint/settings.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,303 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Settings for DataJoint
-"""
-
-import collections
-import json
-import logging
-import os
-import pprint
-from contextlib import contextmanager
-from enum import Enum
-
-from .errors import DataJointError
-
-LOCALCONFIG = "dj_local_conf.json"
-GLOBALCONFIG = ".datajoint_config.json"
-# subfolding for external storage in filesystem.
-# 2, 2 means that file abcdef is stored as /ab/cd/abcdef
-DEFAULT_SUBFOLDING = (2, 2)
-
-validators = collections.defaultdict(lambda: lambda value: True)
-validators["database.port"] = lambda a: isinstance(a, int)
-
-Role = Enum("Role", "manual lookup imported computed job")
-role_to_prefix = {
- Role.manual: "",
- Role.lookup: "#",
- Role.imported: "_",
- Role.computed: "__",
- Role.job: "~",
-}
-prefix_to_role = dict(zip(role_to_prefix.values(), role_to_prefix))
-
-default = dict(
- {
- "database.host": "localhost",
- "database.password": None,
- "database.user": None,
- "database.port": 3306,
- "database.reconnect": True,
- "connection.init_function": None,
- "connection.charset": "", # pymysql uses '' as default
- "loglevel": "INFO",
- "safemode": True,
- "fetch_format": "array",
- "display.limit": 12,
- "display.width": 14,
- "display.show_tuple_count": True,
- "database.use_tls": None,
- "enable_python_native_blobs": True, # python-native/dj0 encoding support
- "add_hidden_timestamp": False,
- # file size limit for when to disable checksums
- "filepath_checksum_size_limit": None,
- }
-)
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-log_levels = {
- "INFO": logging.INFO,
- "WARNING": logging.WARNING,
- "CRITICAL": logging.CRITICAL,
- "DEBUG": logging.DEBUG,
- "ERROR": logging.ERROR,
- None: logging.NOTSET,
-}
-
-
-class Config(collections.abc.MutableMapping):
- instance = None
-
- def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
- if not Config.instance:
- Config.instance = Config.__Config(*args, **kwargs)
- else:
- Config.instance._conf.update(dict(*args, **kwargs))
-
- def __getattr__(self, name):
- return getattr(self.instance, name)
-
- def __getitem__(self, item):
- return self.instance.__getitem__(item)
-
- def __setitem__(self, item, value):
- self.instance.__setitem__(item, value)
-
- def __str__(self):
- return pprint.pformat(self.instance._conf, indent=4)
-
- def __repr__(self):
- return self.__str__()
-
- def __delitem__(self, key):
- del self.instance._conf[key]
-
- def __iter__(self):
- return iter(self.instance._conf)
-
- def __len__(self):
- return len(self.instance._conf)
-
- def save(self, filename, verbose=False):
- """
- Saves the settings in JSON format to the given file path.
-
- :param filename: filename of the local JSON settings file.
- :param verbose: report having saved the settings file
- """
- with open(filename, "w") as fid:
- json.dump(self._conf, fid, indent=4)
- if verbose:
- logger.info("Saved settings in " + filename)
-
- def load(self, filename):
- """
- Updates the setting from config file in JSON format.
-
- :param filename: filename of the local JSON settings file. If None, the local config file is used.
- """
- if filename is None:
- filename = LOCALCONFIG
- with open(filename, "r") as fid:
- logger.info(f"DataJoint is configured from {os.path.abspath(filename)}")
- self._conf.update(json.load(fid))
-
- def save_local(self, verbose=False):
- """
- saves the settings in the local config file
- """
- self.save(LOCALCONFIG, verbose)
-
- def save_global(self, verbose=False):
- """
- saves the settings in the global config file
- """
- self.save(os.path.expanduser(os.path.join("~", GLOBALCONFIG)), verbose)
-
- def get_store_spec(self, store):
- """
- find configuration of external stores for blobs and attachments
- """
- try:
- spec = self["stores"][store]
- except KeyError:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Storage {store} is requested but not configured".format(store=store)
- )
-
- spec["subfolding"] = spec.get("subfolding", DEFAULT_SUBFOLDING)
- spec_keys = { # REQUIRED in uppercase and allowed in lowercase
- "file": ("PROTOCOL", "LOCATION", "subfolding", "stage"),
- "s3": (
- "PROTOCOL",
- "ENDPOINT",
- "BUCKET",
- "ACCESS_KEY",
- "SECRET_KEY",
- "LOCATION",
- "secure",
- "subfolding",
- "stage",
- "proxy_server",
- ),
- }
-
- try:
- spec_keys = spec_keys[spec.get("protocol", "").lower()]
- except KeyError:
- raise DataJointError(
- 'Missing or invalid protocol in dj.config["stores"]["{store}"]'.format(
- store=store
- )
- )
-
- # check that all required keys are present in spec
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- 'dj.config["stores"]["{store}"] is missing "{k}"'.format(
- store=store,
- k=next(
- k.lower()
- for k in spec_keys
- if k.isupper() and k.lower() not in spec
- ),
- )
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass
-
- # check that only allowed keys are present in spec
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- 'Invalid key "{k}" in dj.config["stores"]["{store}"]'.format(
- store=store,
- k=next(
- k
- for k in spec
- if k.upper() not in spec_keys and k.lower() not in spec_keys
- ),
- )
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # no invalid keys
-
- return spec
-
- @contextmanager
- def __call__(self, **kwargs):
- """
- The config object can also be used in a with statement to change the state of the configuration
- temporarily. kwargs to the context manager are the keys into config, where '.' is replaced by a
- double underscore '__'. The context manager yields the changed config object.
-
- Example:
- >>> import datajoint as dj
- >>> with dj.config(safemode=False, database__host="localhost") as cfg:
- >>> # do dangerous stuff here
- """
-
- try:
- backup = self.instance
- self.instance = Config.__Config(self.instance._conf)
- new = {k.replace("__", "."): v for k, v in kwargs.items()}
- self.instance._conf.update(new)
- yield self
- except:
- self.instance = backup
- raise
- else:
- self.instance = backup
-
- class __Config:
- """
- Stores datajoint settings. Behaves like a dictionary, but applies validator functions
- when certain keys are set.
-
- The default parameters are stored in datajoint.settings.default . If a local config file
- exists, the settings specified in this file override the default settings.
- """
-
- def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
- self._conf = dict(default)
- # use the free update to set keys
- self._conf.update(dict(*args, **kwargs))
-
- def __getitem__(self, key):
- return self._conf[key]
-
- def __setitem__(self, key, value):
- logger.debug("Setting {0:s} to {1:s}".format(str(key), str(value)))
- if validators[key](value):
- self._conf[key] = value
- else:
- raise DataJointError("Validator for {0:s} did not pass".format(key))
- valid_logging_levels = {"DEBUG", "INFO", "WARNING", "ERROR", "CRITICAL"}
- if key == "loglevel":
- if value not in valid_logging_levels:
- raise ValueError(
- f"'{value}' is not a valid logging value {tuple(valid_logging_levels)}"
- )
- logger.setLevel(value)
-
-
-# Load configuration from file
-config = Config()
-config_files = (
- os.path.expanduser(n) for n in (LOCALCONFIG, os.path.join("~", GLOBALCONFIG))
-)
-try:
- config.load(next(n for n in config_files if os.path.exists(n)))
-except StopIteration:
- logger.info("No config file was found.")
-
-# override login credentials with environment variables
-mapping = {
- k: v
- for k, v in zip(
- (
- "database.host",
- "database.user",
- "database.password",
- "external.aws_access_key_id",
- "external.aws_secret_access_key",
- "loglevel",
- ),
- map(
- os.getenv,
- (
- "DJ_HOST",
- "DJ_USER",
- "DJ_PASS",
- "DJ_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID",
- "DJ_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY",
- "DJ_LOG_LEVEL",
- ),
- ),
- )
- if v is not None
-}
-if mapping:
- logger.info(f"Overloaded settings {tuple(mapping)} from environment variables.")
- config.update(mapping)
-
-logger.setLevel(log_levels[config["loglevel"]])
diff --git a/datajoint/table.py b/datajoint/table.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 7e3e0c3a1..000000000
--- a/datajoint/table.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,1118 +0,0 @@
-import collections
-import csv
-import inspect
-import itertools
-import json
-import logging
-import platform
-import re
-import uuid
-from pathlib import Path
-from typing import Union
-
-import numpy as np
-import pandas
-
-from . import blob
-from .condition import make_condition
-from .declare import alter, declare
-from .errors import (
- AccessError,
- DataJointError,
- DuplicateError,
- IntegrityError,
- UnknownAttributeError,
-)
-from .expression import QueryExpression
-from .heading import Heading
-from .settings import config
-from .utils import get_master, is_camel_case, user_choice
-from .version import __version__ as version
-
-logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
-
-foreign_key_error_regexp = re.compile(
- r"[\w\s:]*\((?P`[^`]+`.`[^`]+`), "
- r"CONSTRAINT (?P`[^`]+`) "
- r"(FOREIGN KEY \((?P[^)]+)\) "
- r"REFERENCES (?P`[^`]+`(\.`[^`]+`)?) \((?P[^)]+)\)[\s\w]+\))?"
-)
-
-constraint_info_query = " ".join(
- """
- SELECT
- COLUMN_NAME as fk_attrs,
- CONCAT('`', REFERENCED_TABLE_SCHEMA, '`.`', REFERENCED_TABLE_NAME, '`') as parent,
- REFERENCED_COLUMN_NAME as pk_attrs
- FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.KEY_COLUMN_USAGE
- WHERE
- CONSTRAINT_NAME = %s AND TABLE_SCHEMA = %s AND TABLE_NAME = %s;
- """.split()
-)
-
-
-class _RenameMap(tuple):
- """for internal use"""
-
- pass
-
-
-class Table(QueryExpression):
- """
- Table is an abstract class that represents a table in the schema.
- It implements insert and delete methods and inherits query functionality.
- To make it a concrete class, override the abstract properties specifying the connection,
- table name, database, and definition.
- """
-
- _table_name = None # must be defined in subclass
- _log_ = None # placeholder for the Log table object
-
- # These properties must be set by the schema decorator (schemas.py) at class level
- # or by FreeTable at instance level
- database = None
- declaration_context = None
-
- @property
- def table_name(self):
- return self._table_name
-
- @property
- def class_name(self):
- return self.__class__.__name__
-
- @property
- def definition(self):
- raise NotImplementedError(
- "Subclasses of Table must implement the `definition` property"
- )
-
- def declare(self, context=None):
- """
- Declare the table in the schema based on self.definition.
-
- :param context: the context for foreign key resolution. If None, foreign keys are
- not allowed.
- """
- if self.connection.in_transaction:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot declare new tables inside a transaction, "
- "e.g. from inside a populate/make call"
- )
- # Enforce strict CamelCase #1150
- if not is_camel_case(self.class_name):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Table class name `{name}` is invalid. Please use CamelCase. ".format(
- name=self.class_name
- )
- + "Classes defining tables should be formatted in strict CamelCase."
- )
- sql, external_stores = declare(self.full_table_name, self.definition, context)
- sql = sql.format(database=self.database)
- try:
- # declare all external tables before declaring main table
- for store in external_stores:
- self.connection.schemas[self.database].external[store]
- self.connection.query(sql)
- except AccessError:
- # skip if no create privilege
- pass
- else:
- self._log("Declared " + self.full_table_name)
-
- def alter(self, prompt=True, context=None):
- """
- Alter the table definition from self.definition
- """
- if self.connection.in_transaction:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot update table declaration inside a transaction, "
- "e.g. from inside a populate/make call"
- )
- if context is None:
- frame = inspect.currentframe().f_back
- context = dict(frame.f_globals, **frame.f_locals)
- del frame
- old_definition = self.describe(context=context)
- sql, external_stores = alter(self.definition, old_definition, context)
- if not sql:
- if prompt:
- logger.warning("Nothing to alter.")
- else:
- sql = "ALTER TABLE {tab}\n\t".format(
- tab=self.full_table_name
- ) + ",\n\t".join(sql)
- if not prompt or user_choice(sql + "\n\nExecute?") == "yes":
- try:
- # declare all external tables before declaring main table
- for store in external_stores:
- self.connection.schemas[self.database].external[store]
- self.connection.query(sql)
- except AccessError:
- # skip if no create privilege
- pass
- else:
- # reset heading
- self.__class__._heading = Heading(
- table_info=self.heading.table_info
- )
- if prompt:
- logger.info("Table altered")
- self._log("Altered " + self.full_table_name)
-
- def from_clause(self):
- """
- :return: the FROM clause of SQL SELECT statements.
- """
- return self.full_table_name
-
- def get_select_fields(self, select_fields=None):
- """
- :return: the selected attributes from the SQL SELECT statement.
- """
- return (
- "*" if select_fields is None else self.heading.project(select_fields).as_sql
- )
-
- def parents(self, primary=None, as_objects=False, foreign_key_info=False):
- """
-
- :param primary: if None, then all parents are returned. If True, then only foreign keys composed of
- primary key attributes are considered. If False, return foreign keys including at least one
- secondary attribute.
- :param as_objects: if False, return table names. If True, return table objects.
- :param foreign_key_info: if True, each element in result also includes foreign key info.
- :return: list of parents as table names or table objects
- with (optional) foreign key information.
- """
- get_edge = self.connection.dependencies.parents
- nodes = [
- next(iter(get_edge(name).items())) if name.isdigit() else (name, props)
- for name, props in get_edge(self.full_table_name, primary).items()
- ]
- if as_objects:
- nodes = [(FreeTable(self.connection, name), props) for name, props in nodes]
- if not foreign_key_info:
- nodes = [name for name, props in nodes]
- return nodes
-
- def children(self, primary=None, as_objects=False, foreign_key_info=False):
- """
- :param primary: if None, then all children are returned. If True, then only foreign keys composed of
- primary key attributes are considered. If False, return foreign keys including at least one
- secondary attribute.
- :param as_objects: if False, return table names. If True, return table objects.
- :param foreign_key_info: if True, each element in result also includes foreign key info.
- :return: list of children as table names or table objects
- with (optional) foreign key information.
- """
- get_edge = self.connection.dependencies.children
- nodes = [
- next(iter(get_edge(name).items())) if name.isdigit() else (name, props)
- for name, props in get_edge(self.full_table_name, primary).items()
- ]
- if as_objects:
- nodes = [(FreeTable(self.connection, name), props) for name, props in nodes]
- if not foreign_key_info:
- nodes = [name for name, props in nodes]
- return nodes
-
- def descendants(self, as_objects=False):
- """
- :param as_objects: False - a list of table names; True - a list of table objects.
- :return: list of tables descendants in topological order.
- """
- return [
- FreeTable(self.connection, node) if as_objects else node
- for node in self.connection.dependencies.descendants(self.full_table_name)
- if not node.isdigit()
- ]
-
- def ancestors(self, as_objects=False):
- """
- :param as_objects: False - a list of table names; True - a list of table objects.
- :return: list of tables ancestors in topological order.
- """
- return [
- FreeTable(self.connection, node) if as_objects else node
- for node in self.connection.dependencies.ancestors(self.full_table_name)
- if not node.isdigit()
- ]
-
- def parts(self, as_objects=False):
- """
- return part tables either as entries in a dict with foreign key information or a list of objects
-
- :param as_objects: if False (default), the output is a dict describing the foreign keys. If True, return table objects.
- """
- self.connection.dependencies.load(force=False)
- nodes = [
- node
- for node in self.connection.dependencies.nodes
- if not node.isdigit() and node.startswith(self.full_table_name[:-1] + "__")
- ]
- return [FreeTable(self.connection, c) for c in nodes] if as_objects else nodes
-
- @property
- def is_declared(self):
- """
- :return: True is the table is declared in the schema.
- """
- return (
- self.connection.query(
- 'SHOW TABLES in `{database}` LIKE "{table_name}"'.format(
- database=self.database, table_name=self.table_name
- )
- ).rowcount
- > 0
- )
-
- @property
- def full_table_name(self):
- """
- :return: full table name in the schema
- """
- return r"`{0:s}`.`{1:s}`".format(self.database, self.table_name)
-
- @property
- def _log(self):
- if self._log_ is None:
- self._log_ = Log(
- self.connection,
- database=self.database,
- skip_logging=self.table_name.startswith("~"),
- )
- return self._log_
-
- @property
- def external(self):
- return self.connection.schemas[self.database].external
-
- def update1(self, row):
- """
- ``update1`` updates one existing entry in the table.
- Caution: In DataJoint the primary modes for data manipulation is to ``insert`` and
- ``delete`` entire records since referential integrity works on the level of records,
- not fields. Therefore, updates are reserved for corrective operations outside of main
- workflow. Use UPDATE methods sparingly with full awareness of potential violations of
- assumptions.
-
- :param row: a ``dict`` containing the primary key values and the attributes to update.
- Setting an attribute value to None will reset it to the default value (if any).
-
- The primary key attributes must always be provided.
-
- Examples:
-
- >>> table.update1({'id': 1, 'value': 3}) # update value in record with id=1
- >>> table.update1({'id': 1, 'value': None}) # reset value to default
- """
- # argument validations
- if not isinstance(row, collections.abc.Mapping):
- raise DataJointError("The argument of update1 must be dict-like.")
- if not set(row).issuperset(self.primary_key):
- raise DataJointError(
- "The argument of update1 must supply all primary key values."
- )
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute `%s` not found."
- % next(k for k in row if k not in self.heading.names)
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass # ok
- if len(self.restriction):
- raise DataJointError("Update cannot be applied to a restricted table.")
- key = {k: row[k] for k in self.primary_key}
- if len(self & key) != 1:
- raise DataJointError("Update can only be applied to one existing entry.")
- # UPDATE query
- row = [
- self.__make_placeholder(k, v)
- for k, v in row.items()
- if k not in self.primary_key
- ]
- query = "UPDATE {table} SET {assignments} WHERE {where}".format(
- table=self.full_table_name,
- assignments=",".join("`%s`=%s" % r[:2] for r in row),
- where=make_condition(self, key, set()),
- )
- self.connection.query(query, args=list(r[2] for r in row if r[2] is not None))
-
- def insert1(self, row, **kwargs):
- """
- Insert one data record into the table. For ``kwargs``, see ``insert()``.
-
- :param row: a numpy record, a dict-like object, or an ordered sequence to be inserted
- as one row.
- """
- self.insert((row,), **kwargs)
-
- def insert(
- self,
- rows,
- replace=False,
- skip_duplicates=False,
- ignore_extra_fields=False,
- allow_direct_insert=None,
- ):
- """
- Insert a collection of rows.
-
- :param rows: Either (a) an iterable where an element is a numpy record, a
- dict-like object, a pandas.DataFrame, a sequence, or a query expression with
- the same heading as self, or (b) a pathlib.Path object specifying a path
- relative to the current directory with a CSV file, the contents of which
- will be inserted.
- :param replace: If True, replaces the existing tuple.
- :param skip_duplicates: If True, silently skip duplicate inserts.
- :param ignore_extra_fields: If False, fields that are not in the heading raise error.
- :param allow_direct_insert: Only applies in auto-populated tables. If False (default),
- insert may only be called from inside the make callback.
-
- Example:
-
- >>> Table.insert([
- >>> dict(subject_id=7, species="mouse", date_of_birth="2014-09-01"),
- >>> dict(subject_id=8, species="mouse", date_of_birth="2014-09-02")])
- """
- if isinstance(rows, pandas.DataFrame):
- # drop 'extra' synthetic index for 1-field index case -
- # frames with more advanced indices should be prepared by user.
- rows = rows.reset_index(
- drop=len(rows.index.names) == 1 and not rows.index.names[0]
- ).to_records(index=False)
-
- if isinstance(rows, Path):
- with open(rows, newline="") as data_file:
- rows = list(csv.DictReader(data_file, delimiter=","))
-
- # prohibit direct inserts into auto-populated tables
- if not allow_direct_insert and not getattr(self, "_allow_insert", True):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Inserts into an auto-populated table can only be done inside "
- "its make method during a populate call."
- " To override, set keyword argument allow_direct_insert=True."
- )
-
- if inspect.isclass(rows) and issubclass(rows, QueryExpression):
- rows = rows() # instantiate if a class
- if isinstance(rows, QueryExpression):
- # insert from select
- if not ignore_extra_fields:
- try:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attribute %s not found. To ignore extra attributes in insert, "
- "set ignore_extra_fields=True."
- % next(
- name for name in rows.heading if name not in self.heading
- )
- )
- except StopIteration:
- pass
- fields = list(name for name in rows.heading if name in self.heading)
- query = "{command} INTO {table} ({fields}) {select}{duplicate}".format(
- command="REPLACE" if replace else "INSERT",
- fields="`" + "`,`".join(fields) + "`",
- table=self.full_table_name,
- select=rows.make_sql(fields),
- duplicate=(
- " ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE `{pk}`={table}.`{pk}`".format(
- table=self.full_table_name, pk=self.primary_key[0]
- )
- if skip_duplicates
- else ""
- ),
- )
- self.connection.query(query)
- return
-
- # collects the field list from first row (passed by reference)
- field_list = []
- rows = list(
- self.__make_row_to_insert(row, field_list, ignore_extra_fields)
- for row in rows
- )
- if rows:
- try:
- query = "{command} INTO {destination}(`{fields}`) VALUES {placeholders}{duplicate}".format(
- command="REPLACE" if replace else "INSERT",
- destination=self.from_clause(),
- fields="`,`".join(field_list),
- placeholders=",".join(
- "(" + ",".join(row["placeholders"]) + ")" for row in rows
- ),
- duplicate=(
- " ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE `{pk}`=`{pk}`".format(
- pk=self.primary_key[0]
- )
- if skip_duplicates
- else ""
- ),
- )
- self.connection.query(
- query,
- args=list(
- itertools.chain.from_iterable(
- (v for v in r["values"] if v is not None) for r in rows
- )
- ),
- )
- except UnknownAttributeError as err:
- raise err.suggest(
- "To ignore extra fields in insert, set ignore_extra_fields=True"
- )
- except DuplicateError as err:
- raise err.suggest(
- "To ignore duplicate entries in insert, set skip_duplicates=True"
- )
-
- def delete_quick(self, get_count=False):
- """
- Deletes the table without cascading and without user prompt.
- If this table has populated dependent tables, this will fail.
- """
- query = "DELETE FROM " + self.full_table_name + self.where_clause()
- self.connection.query(query)
- count = (
- self.connection.query("SELECT ROW_COUNT()").fetchone()[0]
- if get_count
- else None
- )
- self._log(query[:255])
- return count
-
- def delete(
- self,
- transaction: bool = True,
- safemode: Union[bool, None] = None,
- force_parts: bool = False,
- force_masters: bool = False,
- ) -> int:
- """
- Deletes the contents of the table and its dependent tables, recursively.
-
- Args:
- transaction: If `True`, use of the entire delete becomes an atomic transaction.
- This is the default and recommended behavior. Set to `False` if this delete is
- nested within another transaction.
- safemode: If `True`, prohibit nested transactions and prompt to confirm. Default
- is `dj.config['safemode']`.
- force_parts: Delete from parts even when not deleting from their masters.
- force_masters: If `True`, include part/master pairs in the cascade.
- Default is `False`.
-
- Returns:
- Number of deleted rows (excluding those from dependent tables).
-
- Raises:
- DataJointError: Delete exceeds maximum number of delete attempts.
- DataJointError: When deleting within an existing transaction.
- DataJointError: Deleting a part table before its master.
- """
- deleted = set()
- visited_masters = set()
-
- def cascade(table):
- """service function to perform cascading deletes recursively."""
- max_attempts = 50
- for _ in range(max_attempts):
- try:
- delete_count = table.delete_quick(get_count=True)
- except IntegrityError as error:
- match = foreign_key_error_regexp.match(error.args[0])
- if match is None:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cascading deletes failed because the error message is missing foreign key information."
- "Make sure you have REFERENCES privilege to all dependent tables."
- ) from None
- match = match.groupdict()
- # if schema name missing, use table
- if "`.`" not in match["child"]:
- match["child"] = "{}.{}".format(
- table.full_table_name.split(".")[0], match["child"]
- )
- if (
- match["pk_attrs"] is not None
- ): # fully matched, adjusting the keys
- match["fk_attrs"] = [
- k.strip("`") for k in match["fk_attrs"].split(",")
- ]
- match["pk_attrs"] = [
- k.strip("`") for k in match["pk_attrs"].split(",")
- ]
- else: # only partially matched, querying with constraint to determine keys
- match["fk_attrs"], match["parent"], match["pk_attrs"] = list(
- map(
- list,
- zip(
- *table.connection.query(
- constraint_info_query,
- args=(
- match["name"].strip("`"),
- *[
- _.strip("`")
- for _ in match["child"].split("`.`")
- ],
- ),
- ).fetchall()
- ),
- )
- )
- match["parent"] = match["parent"][0]
-
- # Restrict child by table if
- # 1. if table's restriction attributes are not in child's primary key
- # 2. if child renames any attributes
- # Otherwise restrict child by table's restriction.
- child = FreeTable(table.connection, match["child"])
- if (
- set(table.restriction_attributes) <= set(child.primary_key)
- and match["fk_attrs"] == match["pk_attrs"]
- ):
- child._restriction = table._restriction
- child._restriction_attributes = table.restriction_attributes
- elif match["fk_attrs"] != match["pk_attrs"]:
- child &= table.proj(
- **dict(zip(match["fk_attrs"], match["pk_attrs"]))
- )
- else:
- child &= table.proj()
-
- master_name = get_master(child.full_table_name)
- if (
- force_masters
- and master_name
- and master_name != table.full_table_name
- and master_name not in visited_masters
- ):
- master = FreeTable(table.connection, master_name)
- master._restriction_attributes = set()
- master._restriction = [
- make_condition( # &= may cause in target tables in subquery
- master,
- (master.proj() & child.proj()).fetch(),
- master._restriction_attributes,
- )
- ]
- visited_masters.add(master_name)
- cascade(master)
- else:
- cascade(child)
- else:
- deleted.add(table.full_table_name)
- logger.info(
- "Deleting {count} rows from {table}".format(
- count=delete_count, table=table.full_table_name
- )
- )
- break
- else:
- raise DataJointError("Exceeded maximum number of delete attempts.")
- return delete_count
-
- safemode = config["safemode"] if safemode is None else safemode
-
- # Start transaction
- if transaction:
- if not self.connection.in_transaction:
- self.connection.start_transaction()
- else:
- if not safemode:
- transaction = False
- else:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Delete cannot use a transaction within an ongoing transaction. "
- "Set transaction=False or safemode=False)."
- )
-
- # Cascading delete
- try:
- delete_count = cascade(self)
- except:
- if transaction:
- self.connection.cancel_transaction()
- raise
-
- if not force_parts:
- # Avoid deleting from child before master (See issue #151)
- for part in deleted:
- master = get_master(part)
- if master and master not in deleted:
- if transaction:
- self.connection.cancel_transaction()
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attempt to delete part table {part} before deleting from "
- "its master {master} first.".format(part=part, master=master)
- )
-
- # Confirm and commit
- if delete_count == 0:
- if safemode:
- logger.warning("Nothing to delete.")
- if transaction:
- self.connection.cancel_transaction()
- elif not transaction:
- logger.info("Delete completed")
- else:
- if not safemode or user_choice("Commit deletes?", default="no") == "yes":
- if transaction:
- self.connection.commit_transaction()
- if safemode:
- logger.info("Delete committed.")
- else:
- if transaction:
- self.connection.cancel_transaction()
- if safemode:
- logger.warning("Delete cancelled")
- return delete_count
-
- def drop_quick(self):
- """
- Drops the table without cascading to dependent tables and without user prompt.
- """
- if self.is_declared:
- query = "DROP TABLE %s" % self.full_table_name
- self.connection.query(query)
- logger.info("Dropped table %s" % self.full_table_name)
- self._log(query[:255])
- else:
- logger.info(
- "Nothing to drop: table %s is not declared" % self.full_table_name
- )
-
- def drop(self):
- """
- Drop the table and all tables that reference it, recursively.
- User is prompted for confirmation if config['safemode'] is set to True.
- """
- if self.restriction:
- raise DataJointError(
- "A table with an applied restriction cannot be dropped."
- " Call drop() on the unrestricted Table."
- )
- self.connection.dependencies.load()
- do_drop = True
- tables = [
- table
- for table in self.connection.dependencies.descendants(self.full_table_name)
- if not table.isdigit()
- ]
-
- # avoid dropping part tables without their masters: See issue #374
- for part in tables:
- master = get_master(part)
- if master and master not in tables:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Attempt to drop part table {part} before dropping "
- "its master. Drop {master} first.".format(part=part, master=master)
- )
-
- if config["safemode"]:
- for table in tables:
- logger.info(
- table + " (%d tuples)" % len(FreeTable(self.connection, table))
- )
- do_drop = user_choice("Proceed?", default="no") == "yes"
- if do_drop:
- for table in reversed(tables):
- FreeTable(self.connection, table).drop_quick()
- logger.info("Tables dropped. Restart kernel.")
-
- @property
- def size_on_disk(self):
- """
- :return: size of data and indices in bytes on the storage device
- """
- ret = self.connection.query(
- 'SHOW TABLE STATUS FROM `{database}` WHERE NAME="{table}"'.format(
- database=self.database, table=self.table_name
- ),
- as_dict=True,
- ).fetchone()
- return ret["Data_length"] + ret["Index_length"]
-
- def describe(self, context=None, printout=False):
- """
- :return: the definition string for the query using DataJoint DDL.
- """
- if context is None:
- frame = inspect.currentframe().f_back
- context = dict(frame.f_globals, **frame.f_locals)
- del frame
- if self.full_table_name not in self.connection.dependencies:
- self.connection.dependencies.load()
- parents = self.parents(foreign_key_info=True)
- in_key = True
- definition = (
- "# " + self.heading.table_status["comment"] + "\n"
- if self.heading.table_status["comment"]
- else ""
- )
- attributes_thus_far = set()
- attributes_declared = set()
- indexes = self.heading.indexes.copy()
- for attr in self.heading.attributes.values():
- if in_key and not attr.in_key:
- definition += "---\n"
- in_key = False
- attributes_thus_far.add(attr.name)
- do_include = True
- for parent_name, fk_props in parents:
- if attr.name in fk_props["attr_map"]:
- do_include = False
- if attributes_thus_far.issuperset(fk_props["attr_map"]):
- # foreign key properties
- try:
- index_props = indexes.pop(tuple(fk_props["attr_map"]))
- except KeyError:
- index_props = ""
- else:
- index_props = [k for k, v in index_props.items() if v]
- index_props = (
- " [{}]".format(", ".join(index_props))
- if index_props
- else ""
- )
-
- if not fk_props["aliased"]:
- # simple foreign key
- definition += "->{props} {class_name}\n".format(
- props=index_props,
- class_name=lookup_class_name(parent_name, context)
- or parent_name,
- )
- else:
- # projected foreign key
- definition += (
- "->{props} {class_name}.proj({proj_list})\n".format(
- props=index_props,
- class_name=lookup_class_name(parent_name, context)
- or parent_name,
- proj_list=",".join(
- '{}="{}"'.format(attr, ref)
- for attr, ref in fk_props["attr_map"].items()
- if ref != attr
- ),
- )
- )
- attributes_declared.update(fk_props["attr_map"])
- if do_include:
- attributes_declared.add(attr.name)
- definition += "%-20s : %-28s %s\n" % (
- (
- attr.name
- if attr.default is None
- else "%s=%s" % (attr.name, attr.default)
- ),
- "%s%s"
- % (attr.type, " auto_increment" if attr.autoincrement else ""),
- "# " + attr.comment if attr.comment else "",
- )
- # add remaining indexes
- for k, v in indexes.items():
- definition += "{unique}INDEX ({attrs})\n".format(
- unique="UNIQUE " if v["unique"] else "", attrs=", ".join(k)
- )
- if printout:
- logger.info("\n" + definition)
- return definition
-
- # --- private helper functions ----
- def __make_placeholder(self, name, value, ignore_extra_fields=False):
- """
- For a given attribute `name` with `value`, return its processed value or value placeholder
- as a string to be included in the query and the value, if any, to be submitted for
- processing by mysql API.
-
- :param name: name of attribute to be inserted
- :param value: value of attribute to be inserted
- """
- if ignore_extra_fields and name not in self.heading:
- return None
- attr = self.heading[name]
- if attr.adapter:
- value = attr.adapter.put(value)
- if value is None or (attr.numeric and (value == "" or np.isnan(float(value)))):
- # set default value
- placeholder, value = "DEFAULT", None
- else: # not NULL
- placeholder = "%s"
- if attr.uuid:
- if not isinstance(value, uuid.UUID):
- try:
- value = uuid.UUID(value)
- except (AttributeError, ValueError):
- raise DataJointError(
- "badly formed UUID value {v} for attribute `{n}`".format(
- v=value, n=name
- )
- )
- value = value.bytes
- elif attr.is_blob:
- value = blob.pack(value)
- value = (
- self.external[attr.store].put(value).bytes
- if attr.is_external
- else value
- )
- elif attr.is_attachment:
- attachment_path = Path(value)
- if attr.is_external:
- # value is hash of contents
- value = (
- self.external[attr.store]
- .upload_attachment(attachment_path)
- .bytes
- )
- else:
- # value is filename + contents
- value = (
- str.encode(attachment_path.name)
- + b"\0"
- + attachment_path.read_bytes()
- )
- elif attr.is_filepath:
- value = self.external[attr.store].upload_filepath(value).bytes
- elif attr.numeric:
- value = str(int(value) if isinstance(value, bool) else value)
- elif attr.json:
- value = json.dumps(value)
- return name, placeholder, value
-
- def __make_row_to_insert(self, row, field_list, ignore_extra_fields):
- """
- Helper function for insert and update
-
- :param row: A tuple to insert
- :return: a dict with fields 'names', 'placeholders', 'values'
- """
-
- def check_fields(fields):
- """
- Validates that all items in `fields` are valid attributes in the heading
-
- :param fields: field names of a tuple
- """
- if not field_list:
- if not ignore_extra_fields:
- for field in fields:
- if field not in self.heading:
- raise KeyError(
- "`{0:s}` is not in the table heading".format(field)
- )
- elif set(field_list) != set(fields).intersection(self.heading.names):
- raise DataJointError("Attempt to insert rows with different fields.")
-
- if isinstance(row, np.void): # np.array
- check_fields(row.dtype.fields)
- attributes = [
- self.__make_placeholder(name, row[name], ignore_extra_fields)
- for name in self.heading
- if name in row.dtype.fields
- ]
- elif isinstance(row, collections.abc.Mapping): # dict-based
- check_fields(row)
- attributes = [
- self.__make_placeholder(name, row[name], ignore_extra_fields)
- for name in self.heading
- if name in row
- ]
- else: # positional
- try:
- if len(row) != len(self.heading):
- raise DataJointError(
- "Invalid insert argument. Incorrect number of attributes: "
- "{given} given; {expected} expected".format(
- given=len(row), expected=len(self.heading)
- )
- )
- except TypeError:
- raise DataJointError("Datatype %s cannot be inserted" % type(row))
- else:
- attributes = [
- self.__make_placeholder(name, value, ignore_extra_fields)
- for name, value in zip(self.heading, row)
- ]
- if ignore_extra_fields:
- attributes = [a for a in attributes if a is not None]
-
- assert len(attributes), "Empty tuple"
- row_to_insert = dict(zip(("names", "placeholders", "values"), zip(*attributes)))
- if not field_list:
- # first row sets the composition of the field list
- field_list.extend(row_to_insert["names"])
- else:
- # reorder attributes in row_to_insert to match field_list
- order = list(row_to_insert["names"].index(field) for field in field_list)
- row_to_insert["names"] = list(row_to_insert["names"][i] for i in order)
- row_to_insert["placeholders"] = list(
- row_to_insert["placeholders"][i] for i in order
- )
- row_to_insert["values"] = list(row_to_insert["values"][i] for i in order)
- return row_to_insert
-
-
-def lookup_class_name(name, context, depth=3):
- """
- given a table name in the form `schema_name`.`table_name`, find its class in the context.
-
- :param name: `schema_name`.`table_name`
- :param context: dictionary representing the namespace
- :param depth: search depth into imported modules, helps avoid infinite recursion.
- :return: class name found in the context or None if not found
- """
- # breadth-first search
- nodes = [dict(context=context, context_name="", depth=depth)]
- while nodes:
- node = nodes.pop(0)
- for member_name, member in node["context"].items():
- # skip IPython's implicit variables
- if not member_name.startswith("_"):
- if inspect.isclass(member) and issubclass(member, Table):
- if member.full_table_name == name: # found it!
- return ".".join([node["context_name"], member_name]).lstrip(".")
- try: # look for part tables
- parts = member.__dict__
- except AttributeError:
- pass # not a UserTable -- cannot have part tables.
- else:
- for part in (
- getattr(member, p)
- for p in parts
- if p[0].isupper() and hasattr(member, p)
- ):
- if (
- inspect.isclass(part)
- and issubclass(part, Table)
- and part.full_table_name == name
- ):
- return ".".join(
- [node["context_name"], member_name, part.__name__]
- ).lstrip(".")
- elif (
- node["depth"] > 0
- and inspect.ismodule(member)
- and member.__name__ != "datajoint"
- ):
- try:
- nodes.append(
- dict(
- context=dict(inspect.getmembers(member)),
- context_name=node["context_name"] + "." + member_name,
- depth=node["depth"] - 1,
- )
- )
- except ImportError:
- pass # could not import, so do not attempt
- return None
-
-
-class FreeTable(Table):
- """
- A base table without a dedicated class. Each instance is associated with a table
- specified by full_table_name.
-
- :param conn: a dj.Connection object
- :param full_table_name: in format `database`.`table_name`
- """
-
- def __init__(self, conn, full_table_name):
- self.database, self._table_name = (
- s.strip("`") for s in full_table_name.split(".")
- )
- self._connection = conn
- self._support = [full_table_name]
- self._heading = Heading(
- table_info=dict(
- conn=conn,
- database=self.database,
- table_name=self.table_name,
- context=None,
- )
- )
-
- def __repr__(self):
- return (
- "FreeTable(`%s`.`%s`)\n" % (self.database, self._table_name)
- + super().__repr__()
- )
-
-
-class Log(Table):
- """
- The log table for each schema.
- Instances are callable. Calls log the time and identifying information along with the event.
-
- :param skip_logging: if True, then log entry is skipped by default. See __call__
- """
-
- _table_name = "~log"
-
- def __init__(self, conn, database, skip_logging=False):
- self.database = database
- self.skip_logging = skip_logging
- self._connection = conn
- self._heading = Heading(
- table_info=dict(
- conn=conn, database=database, table_name=self.table_name, context=None
- )
- )
- self._support = [self.full_table_name]
-
- self._definition = """ # event logging table for `{database}`
- id :int unsigned auto_increment # event order id
- ---
- timestamp = CURRENT_TIMESTAMP : timestamp # event timestamp
- version :varchar(12) # datajoint version
- user :varchar(255) # user@host
- host="" :varchar(255) # system hostname
- event="" :varchar(255) # event message
- """.format(
- database=database
- )
-
- super().__init__()
-
- if not self.is_declared:
- self.declare()
- self.connection.dependencies.clear()
- self._user = self.connection.get_user()
-
- @property
- def definition(self):
- return self._definition
-
- def __call__(self, event, skip_logging=None):
- """
-
- :param event: string to write into the log table
- :param skip_logging: If True then do not log. If None, then use self.skip_logging
- """
- skip_logging = self.skip_logging if skip_logging is None else skip_logging
- if not skip_logging:
- try:
- self.insert1(
- dict(
- user=self._user,
- version=version + "py",
- host=platform.uname().node,
- event=event,
- ),
- skip_duplicates=True,
- ignore_extra_fields=True,
- )
- except DataJointError:
- logger.info("could not log event in table ~log")
-
- def delete(self):
- """
- bypass interactive prompts and cascading dependencies
-
- :return: number of deleted items
- """
- return self.delete_quick(get_count=True)
-
- def drop(self):
- """bypass interactive prompts and cascading dependencies"""
- self.drop_quick()
diff --git a/docker-compose.yaml b/docker-compose.yaml
index 40b211756..2c48ffd10 100644
--- a/docker-compose.yaml
+++ b/docker-compose.yaml
@@ -1,14 +1,24 @@
-# HOST_UID=$(id -u) PY_VER=3.11 DJ_VERSION=$(grep -oP '\d+\.\d+\.\d+' datajoint/version.py) docker compose --profile test up --build --exit-code-from djtest djtest
+# Development environment with MySQL and MinIO services
+#
+# NOTE: docker-compose is OPTIONAL for running tests.
+# Tests use testcontainers to automatically manage containers.
+# Just run: pytest tests/
+#
+# Use docker-compose for development/debugging when you want
+# persistent containers that survive test runs:
+# docker compose up -d db minio # Start services manually
+# pytest tests/ # Tests will use these containers
+#
+# Full Docker testing (CI):
+# docker compose --profile test up djtest --build
services:
db:
image: datajoint/mysql:${MYSQL_VER:-8.0}
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=${DJ_PASS:-password}
command: mysqld --default-authentication-plugin=mysql_native_password
- # ports:
- # - "3306:3306"
- # volumes:
- # - ./mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql
+ ports:
+ - "3306:3306"
healthcheck:
test: [ "CMD", "mysqladmin", "ping", "-h", "localhost" ]
timeout: 30s
@@ -19,18 +29,15 @@ services:
environment:
- MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=datajoint
- MINIO_SECRET_KEY=datajoint
- # ports:
- # - "9000:9000"
- # volumes:
- # - ./minio/config:/root/.minio
- # - ./minio/data:/data
+ ports:
+ - "9000:9000"
command: server --address ":9000" /data
healthcheck:
test:
- "CMD"
- "curl"
- "--fail"
- - "http://minio:9000/minio/health/live"
+ - "http://localhost:9000/minio/health/live"
timeout: 30s
retries: 5
interval: 15s
@@ -40,7 +47,7 @@ services:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
args:
- PY_VER: ${PY_VER:-3.9}
+ PY_VER: ${PY_VER:-3.10}
HOST_UID: ${HOST_UID:-1000}
depends_on:
db:
diff --git a/docs/mkdocs.yaml b/docs/mkdocs.yaml
index 4de4f58e1..db2ea16f9 100644
--- a/docs/mkdocs.yaml
+++ b/docs/mkdocs.yaml
@@ -1,82 +1,16 @@
# ---------------------- PROJECT SPECIFIC ---------------------------
-site_name: DataJoint Documentation
+site_name: DataJoint Python - Developer Documentation
+site_description: Developer documentation for DataJoint Python contributors
repo_url: https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python
repo_name: datajoint/datajoint-python
nav:
- - DataJoint Python: index.md
- - Quick Start Guide: quick-start.md
- - Concepts:
- - Principles: concepts/principles.md
- - Data Model: concepts/data-model.md
- - Data Pipelines: concepts/data-pipelines.md
- - Teamwork: concepts/teamwork.md
- - Terminology: concepts/terminology.md
- - System Administration:
- - Database Administration: sysadmin/database-admin.md
- - Bulk Storage Systems: sysadmin/bulk-storage.md
- - External Store: sysadmin/external-store.md
- - Client Configuration:
- - Install: client/install.md
- - Credentials: client/credentials.md
- - Settings: client/settings.md
- - File Stores: client/stores.md
- - Schema Design:
- - Schema Creation: design/schema.md
- - Table Definition:
- - Table Tiers: design/tables/tiers.md
- - Declaration Syntax: design/tables/declare.md
- - Primary Key: design/tables/primary.md
- - Attributes: design/tables/attributes.md
- - Lookup Tables: design/tables/lookup.md
- - Manual Tables: design/tables/manual.md
- - Blobs: design/tables/blobs.md
- - Attachments: design/tables/attach.md
- - Filepaths: design/tables/filepath.md
- - Custom Datatypes: design/tables/customtype.md
- - Dependencies: design/tables/dependencies.md
- - Indexes: design/tables/indexes.md
- - Master-Part Relationships: design/tables/master-part.md
- - Schema Diagrams: design/diagrams.md
- - Entity Normalization: design/normalization.md
- - Data Integrity: design/integrity.md
- - Schema Recall: design/recall.md
- - Schema Drop: design/drop.md
- - Schema Modification: design/alter.md
- - Data Manipulations:
- - manipulation/index.md
- - Insert: manipulation/insert.md
- - Delete: manipulation/delete.md
- - Update: manipulation/update.md
- - Transactions: manipulation/transactions.md
- - Data Queries:
- - Principles: query/principles.md
- - Example Schema: query/example-schema.md
- - Fetch: query/fetch.md
- - Iteration: query/iteration.md
- - Operators: query/operators.md
- - Restrict: query/restrict.md
- - Projection: query/project.md
- - Join: query/join.md
- - Aggregation: query/aggregation.md
- - Union: query/union.md
- - Universal Sets: query/universals.md
- - Query Caching: query/query-caching.md
- - Computations:
- - Make Method: compute/make.md
- - Populate: compute/populate.md
- - Key Source: compute/key-source.md
- - Distributed Computing: compute/distributed.md
- - Publish Data: publish-data.md
- - Internals:
- - SQL Transpilation: internal/transpilation.md
- - Tutorials:
- - JSON Datatype: tutorials/json.ipynb
- - FAQ: faq.md
- - Developer Guide: develop.md
- - Citation: citation.md
- - Changelog: changelog.md
- - API: api/ # defer to gen-files + literate-nav
+ - Home: index.md
+ - Contributing: develop.md
+ - Architecture:
+ - architecture/index.md
+ - SQL Transpilation: architecture/transpilation.md
+ - API Reference: api/ # defer to gen-files + literate-nav
# ---------------------------- STANDARD -----------------------------
@@ -93,7 +27,7 @@ theme:
favicon: assets/images/company-logo-blue.png
features:
- toc.integrate
- - content.code.annotate # Add codeblock annotations
+ - content.code.annotate
palette:
- media: "(prefers-color-scheme: light)"
scheme: datajoint
@@ -113,26 +47,18 @@ plugins:
handlers:
python:
paths:
- - "."
- - /main/
+ - "../src"
options:
- filters:
- - "!^_"
- docstring_style: sphinx # Replaces google default pending docstring updates
+ docstring_style: numpy
members_order: source
group_by_category: false
line_length: 88
+ show_source: false
- gen-files:
scripts:
- ./src/api/make_pages.py
- literate-nav:
nav_file: navigation.md
- - exclude-search:
- exclude:
- - "*/navigation.md"
- - "*/archive/*md"
- - mkdocs-jupyter:
- include: ["*.ipynb"]
- section-index
markdown_extensions:
- attr_list
@@ -154,41 +80,23 @@ markdown_extensions:
- name: mermaid
class: mermaid
format: !!python/name:pymdownx.superfences.fence_code_format
- - pymdownx.magiclink # Displays bare URLs as links
- - pymdownx.tasklist: # Renders check boxes in tasks lists
+ - pymdownx.magiclink
+ - pymdownx.tasklist:
custom_checkbox: true
- md_in_html
extra:
- generator: false # Disable watermark
+ generator: false
version:
provider: mike
social:
- icon: main/company-logo
link: https://www.datajoint.com
name: DataJoint
- - icon: fontawesome/brands/slack
- link: https://datajoint.slack.com
- name: Slack
- - icon: fontawesome/brands/linkedin
- link: https://www.linkedin.com/company/datajoint
- name: LinkedIn
- - icon: fontawesome/brands/twitter
- link: https://twitter.com/datajoint
- name: Twitter
- icon: fontawesome/brands/github
link: https://github.com/datajoint
name: GitHub
- - icon: fontawesome/brands/docker
- link: https://hub.docker.com/u/datajoint
- name: DockerHub
- - icon: fontawesome/brands/python
- link: https://pypi.org/user/datajointbot
- name: PyPI
- - icon: fontawesome/brands/stack-overflow
- link: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/datajoint
- name: StackOverflow
- - icon: fontawesome/brands/youtube
- link: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCdeCuFOTCXlVMRzh6Wk-lGg
- name: YouTube
+ - icon: fontawesome/brands/slack
+ link: https://datajoint.slack.com
+ name: Slack
extra_css:
- assets/stylesheets/extra.css
diff --git a/docs/src/api/make_pages.py b/docs/src/api/make_pages.py
index 3072cb46a..25dc29943 100644
--- a/docs/src/api/make_pages.py
+++ b/docs/src/api/make_pages.py
@@ -9,9 +9,7 @@
nav = mkdocs_gen_files.Nav()
for path in sorted(Path(package).glob("**/*.py")):
with mkdocs_gen_files.open(f"api/{path.with_suffix('')}.md", "w") as f:
- module_path = ".".join(
- [p for p in path.with_suffix("").parts if p != "__init__"]
- )
+ module_path = ".".join([p for p in path.with_suffix("").parts if p != "__init__"])
print(f"::: {module_path}", file=f)
nav[path.parts] = f"{path.with_suffix('')}.md"
diff --git a/docs/src/architecture/index.md b/docs/src/architecture/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..953fd7962
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/src/architecture/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+# Architecture
+
+Internal design documentation for DataJoint developers.
+
+## Query System
+
+- [SQL Transpilation](transpilation.md) — How DataJoint translates query expressions to SQL
+
+## Design Principles
+
+DataJoint's architecture follows several key principles:
+
+1. **Immutable Query Expressions** — Query expressions are immutable; operators create new objects
+2. **Lazy Evaluation** — Queries are not executed until data is fetched
+3. **Query Optimization** — Unnecessary attributes are projected out before execution
+4. **Semantic Matching** — Joins use lineage-based attribute matching
+
+## Module Overview
+
+| Module | Purpose |
+|--------|---------|
+| `expression.py` | QueryExpression base class and operators |
+| `table.py` | Table class with data manipulation |
+| `fetch.py` | Data retrieval implementation |
+| `declare.py` | Table definition parsing |
+| `heading.py` | Attribute and heading management |
+| `blob.py` | Blob serialization |
+| `codecs.py` | Type codec system |
+| `connection.py` | Database connection management |
+| `schemas.py` | Schema binding and activation |
+
+## Contributing
+
+See the [Contributing Guide](../develop.md) for development setup instructions.
diff --git a/docs/src/internal/transpilation.md b/docs/src/architecture/transpilation.md
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/src/internal/transpilation.md
rename to docs/src/architecture/transpilation.md
diff --git a/docs/src/changelog.md b/docs/src/changelog.md
deleted file mode 120000
index 699cc9e7b..000000000
--- a/docs/src/changelog.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
-../../CHANGELOG.md
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/src/citation.md b/docs/src/citation.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b5eb2d88b..000000000
--- a/docs/src/citation.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-# Citation
-
-If your work uses the DataJoint for Python, please cite the following manuscript and Research Resource Identifier (RRID):
-
-- Yatsenko D, Reimer J, Ecker AS, Walker EY, Sinz F, Berens P, Hoenselaar A, Cotton RJ, Siapas AS, Tolias AS. DataJoint: managing big scientific data using MATLAB or Python. bioRxiv. 2015 Jan 1:031658. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/031658
-
-- DataJoint for Python - [RRID:SCR_014543](https://scicrunch.org/resolver/SCR_014543) - Version `Enter datajoint-python version you are using here`
diff --git a/docs/src/client/credentials.md b/docs/src/client/credentials.md
deleted file mode 100644
index bac54a6cf..000000000
--- a/docs/src/client/credentials.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-# Credentials
-
-Configure the connection through DataJoint's `config` object:
-
-```python
-> import datajoint as dj
-DataJoint 0.4.9 (February 1, 2017)
-No configuration found. Use `dj.config` to configure and save the configuration.
-```
-
-You may now set the database credentials:
-
-```python
-dj.config['database.host'] = "alicelab.datajoint.io"
-dj.config['database.user'] = "alice"
-dj.config['database.password'] = "haha not my real password"
-```
-
-Skip setting the password to make DataJoint prompt to enter the password every time.
-
-You may save the configuration in the local work directory with
-`dj.config.save_local()` or for all your projects in `dj.config.save_global()`.
-Configuration changes should be made through the `dj.config` interface; the config file
-should not be modified directly by the user.
-
-You may leave the user or the password as `None`, in which case you will be prompted to
-enter them manually for every session.
-Setting the password as an empty string allows access without a password.
-
-Note that the system environment variables `DJ_HOST`, `DJ_USER`, and `DJ_PASS` will
-overwrite the settings in the config file.
-You can use them to set the connection credentials instead of config files.
-
-To change the password, the `dj.set_password` function will walk you through the
-process:
-
-```python
-dj.set_password()
-```
-
-After that, update the password in the configuration and save it as described above:
-
-```python
-dj.config['database.password'] = 'my#cool!new*psswrd'
-dj.config.save_local() # or dj.config.save_global()
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/client/install.md b/docs/src/client/install.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d9684f302..000000000
--- a/docs/src/client/install.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,209 +0,0 @@
-# Install and Connect
-
-DataJoint is implemented for Python 3.4+.
-You may install it from [PyPI](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/datajoint):
-
-```bash
-pip3 install datajoint
-```
-
-or upgrade
-
-```bash
-pip3 install --upgrade datajoint
-```
-
-## DataJoint Python Windows Install Guide
-
-This document outlines the steps necessary to install DataJoint on Windows for use in
-connecting to a remote server hosting a DataJoint database.
-Some limited discussion of installing MySQL is discussed in `MySQL for Windows`, but is
-not covered in-depth since this is an uncommon usage scenario and not strictly required
-to connect to DataJoint pipelines.
-
-### Quick steps
-
-Quick install steps for advanced users are as follows:
-
-- Install latest Python 3.x and ensure it is in `PATH` (3.6.3 current at time of writing)
- ```bash
- pip install datajoint
- ```
-
-For ERD drawing support:
-
-- Install Graphviz for Windows and ensure it is in `PATH` (64 bit builds currently
-tested; URL below.)
- ```bash
- pip install pydotplus matplotlib
- ```
-
-Detailed instructions follow.
-
-### Step 1: install Python
-
-Python for Windows is available from:
-
-https://www.python.org/downloads/windows
-
-The latest 64 bit 3.x version, currently 3.6.3, is available from the [Python site](https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.6.3/python-3.6.3-amd64.exe).
-
-From here run the installer to install Python.
-
-For a single-user machine, the regular installation process is sufficient - be sure to
-select the `Add Python to PATH` option:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-For a shared machine, run the installer as administrator (right-click, run as
-administrator) and select the advanced installation.
-Be sure to select options as follows:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-### Step 2: verify installation
-
-To verify the Python installation and make sure that your system is ready to install
-DataJoint, open a command window by entering `cmd` into the Windows search bar:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-From here `python` and the Python package manager `pip` can be verified by running
-`python -V` and `pip -V`, respectively:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-If you receive the error message that either `pip` or `python` is not a recognized
-command, please uninstall Python and ensure that the option to add Python to the `PATH`
-variable was properly configured.
-
-### Step 3: install DataJoint
-
-DataJoint (and other Python modules) can be easily installed using the `pip` Python
-package manager which is installed as a part of Python and was verified in the previous
-step.
-
-To install DataJoint simply run `pip install datajoint`:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-This will proceed to install DataJoint, along with several other required packages from
-the PIP repository.
-When finished, a summary of the activity should be presented:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-Note: You can find out more about the packages installed here and many other freely
-available open source packages via [pypi](https://pypi.python.org/pypi), the Python
-package index site.
-
-### (Optional) step 4: install packages for ERD support
-
-To draw diagrams of your DataJoint schema, the following additional steps should be
-followed.
-
-#### Install Graphviz
-
-DataJoint currently utilizes [Graphviz](http://graphviz.org) to generate the ERD
-visualizations.
-Although a Windows version of Graphviz is available from the main site, it is an older
-and out of date 32-bit version.
-The recommended pre-release builds of the 64 bit version are available here:
-
-https://ci.appveyor.com/project/ellson/graphviz-pl238
-
-More specifically, the build artifacts from the `Win64; Configuration: Release` are
-recommended, available
-[here](https://ci.appveyor.com/api/buildjobs/hlkclpfhf6gnakjq/artifacts/build%2FGraphviz-install.exe).
-
-This is a regular Windows installer executable, and will present a dialog when starting:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-It is important that an option to place Graphviz in the `PATH` be selected.
-
-For a personal installation:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-To install system wide:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-Once installed, Graphviz can be verified from a fresh command window as follows:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-If you receive the error message that the `dot` program is not a recognized command,
-please uninstall Graphviz and ensure that the
-option to add Python to the PATH variable was properly configured.
-
-Important: in some cases, running the `dot -c` command in a command prompt is required
-to properly initialize the Graphviz installation.
-
-#### Install PyDotPlus
-
-The PyDotPlus library links the Graphviz installation to DataJoint and is easily
-installed via `pip`:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-#### Install Matplotlib
-
-The Matplotlib library provides useful plotting utilities which are also used by
-DataJoint's `Diagram` drawing facility.
-The package is easily installed via `pip`:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-### (Optional) step 5: install Jupyter Notebook
-
-As described on the www.jupyter.org website:
-
-'''
-The Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows
-you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations,
-visualizations and narrative text.
-'''
-
-Although not a part of DataJoint, Jupyter Notebook can be a very useful tool for
-building and interacting with DataJoint pipelines.
-It is easily installed from `pip` as well:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-Once installed, Jupyter Notebook can be started via the `jupyter notebook` command,
-which should now be on your path:
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-By default Jupyter Notebook will start a local private web server session from the
-directory where it was started and start a web browser session connected to the session.
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-You now should be able to use the notebook viewer to navigate the filesystem and to
-create new project folders and interactive Jupyter/Python/DataJoint notebooks.
-
-### Git for Windows
-
-The [Git](https://git-scm.com/) version control system is not a part of DataJoint but
-is recommended for interacting with the broader Python/Git/GitHub sharing ecosystem.
-
-The Git for Windows installer is available from https://git-scm.com/download/win.
-
-{: style="align:left"}
-
-The default settings should be sufficient and correct in most cases.
-
-### MySQL for Windows
-
-For hosting pipelines locally, the MySQL server package is required.
-
-MySQL for windows can be installed via the installers available from the
-[MySQL website](https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/windows/).
-Please note that although DataJoint should be fully compatible with a Windows MySQL
-server installation, this mode of operation is not tested by the DataJoint team.
diff --git a/docs/src/client/settings.md b/docs/src/client/settings.md
deleted file mode 100644
index cb9a69fff..000000000
--- a/docs/src/client/settings.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
-# Configuration Settings
-
-If you are not using DataJoint on your own, or are setting up a DataJoint
-system for other users, some additional configuration options may be required
-to support [TLS](#tls-configuration) or
-[external storage](../sysadmin/external-store.md).
-
-## TLS Configuration
-
-Starting with v0.12, DataJoint will by default use TLS if it is available. TLS can be
-forced on or off with the boolean `dj.config['database.use_tls']`.
diff --git a/docs/src/compute/distributed.md b/docs/src/compute/distributed.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 68c31f093..000000000
--- a/docs/src/compute/distributed.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
-# Distributed Computing
-
-## Job reservations
-
-Running `populate` on the same table on multiple computers will causes them to attempt
-to compute the same data all at once.
-This will not corrupt the data since DataJoint will reject any duplication.
-One solution could be to cause the different computing nodes to populate the tables in
-random order.
-This would reduce some collisions but not completely prevent them.
-
-To allow efficient distributed computing, DataJoint provides a built-in job reservation
-process.
-When `dj.Computed` tables are auto-populated using job reservation, a record of each
-ongoing computation is kept in a schema-wide `jobs` table, which is used internally by
-DataJoint to coordinate the auto-population effort among multiple computing processes.
-
-Job reservations are activated by setting the keyword argument `reserve_jobs=True` in
-`populate` calls.
-
-With job management enabled, the `make` method of each table class will also consult
-the `jobs` table for reserved jobs as part of determining the next record to compute
-and will create an entry in the `jobs` table as part of the attempt to compute the
-resulting record for that key.
-If the operation is a success, the record is removed.
-In the event of failure, the job reservation entry is updated to indicate the details
-of failure.
-Using this simple mechanism, multiple processes can participate in the auto-population
-effort without duplicating computational effort, and any errors encountered during the
-course of the computation can be individually inspected to determine the cause of the
-issue.
-
-As part of DataJoint, the jobs table can be queried using native DataJoint syntax. For
-example, to list the jobs currently being run:
-
-```python
-In [1]: schema.jobs
-Out[1]:
-*table_name *key_hash status error_message user host pid connection_id timestamp key error_stack
-+------------+ +------------+ +----------+ +------------+ +------------+ +------------+ +-------+ +------------+ +------------+ +--------+ +------------+
-__job_results e4da3b7fbbce23 reserved datajoint@localhos localhost 15571 59 2017-09-04 14:
-(2 tuples)
-```
-
-The above output shows that a record for the `JobResults` table is currently reserved
-for computation, along with various related details of the reservation, such as the
-MySQL connection ID, client user and host, process ID on the remote system, timestamp,
-and the key for the record that the job is using for its computation.
-Since DataJoint table keys can be of varying types, the key is stored in a binary
-format to allow the table to store arbitrary types of record key data.
-The subsequent sections will discuss querying the jobs table for key data.
-
-As mentioned above, jobs encountering errors during computation will leave their record
-reservations in place, and update the reservation record with details of the error.
-
-For example, if a Python process is interrupted via the keyboard, a KeyboardError will
-be logged to the database as follows:
-
-```python
-In [2]: schema.jobs
-Out[2]:
-*table_name *key_hash status error_message user host pid connection_id timestamp key error_stack
-+------------+ +------------+ +--------+ +------------+ +------------+ +------------+ +-------+ +------------+ +------------+ +--------+ +------------+
-__job_results 3416a75f4cea91 error KeyboardInterr datajoint@localhos localhost 15571 59 2017-09-04 14:
-(1 tuples)
-```
-
-By leaving the job reservation record in place, the error can be inspected, and if
-necessary the corresponding `dj.Computed` update logic can be corrected.
-From there the jobs entry can be cleared, and the computation can then be resumed.
-In the meantime, the presence of the job reservation will prevent this particular
-record from being processed during subsequent auto-population calls.
-Inspecting the job record for failure details can proceed much like any other DataJoint
-query.
-
-For example, given the above table, errors can be inspected as follows:
-
-```python
-In [3]: (schema.jobs & 'status="error"' ).fetch(as_dict=True)
-Out[3]:
-[OrderedDict([('table_name', '__job_results'),
- ('key_hash', 'c81e728d9d4c2f636f067f89cc14862c'),
- ('status', 'error'),
- ('key', rec.array([(2,)],
- dtype=[('id', 'O')])),
- ('error_message', 'KeyboardInterrupt'),
- ('error_stack', None),
- ('user', 'datajoint@localhost'),
- ('host', 'localhost'),
- ('pid', 15571),
- ('connection_id', 59),
- ('timestamp', datetime.datetime(2017, 9, 4, 15, 3, 53))])]
-```
-
-This particular error occurred when processing the record with ID `2`, resulted from a
-`KeyboardInterrupt`, and has no additional
-error trace.
-
-After any system or code errors have been resolved, the table can simply be cleaned of
-errors and the computation rerun.
-
-For example:
-
-```python
-In [4]: (schema.jobs & 'status="error"' ).delete()
-```
-
-In some cases, it may be preferable to inspect the jobs table records using populate
-keys.
-Since job keys are hashed and stored as a blob in the jobs table to support the varying
-types of keys, we need to query using the key hash instead of simply using the raw key
-data.
-
-This can be done by using `dj.key_hash` to convert the key as follows:
-
-```python
-In [4]: jk = {'table_name': JobResults.table_name, 'key_hash' : dj.key_hash({'id': 2})}
-
-In [5]: schema.jobs & jk
-Out[5]:
-*table_name *key_hash status key error_message error_stac user host pid connection_id timestamp
-+------------+ +------------+ +--------+ +--------+ +------------+ +--------+ +------------+ +-------+ +--------+ +------------+ +------------+
-__job_results c81e728d9d4c2f error =BLOB= KeyboardInterr =BLOB= datajoint@localhost localhost 15571 59 2017-09-04 14:
-(Total: 1)
-
-In [6]: (schema.jobs & jk).delete()
-
-In [7]: schema.jobs & jk
-Out[7]:
-*table_name *key_hash status key error_message error_stac user host pid connection_id timestamp
-+------------+ +----------+ +--------+ +--------+ +------------+ +--------+ +------+ +------+ +-----+ +------------+ +-----------+
-
-(Total: 0)
-```
-
-## Managing connections
-
-The DataJoint method `dj.kill` allows for viewing and termination of database
-connections.
-Restrictive conditions can be used to identify specific connections.
-Restrictions are specified as strings and can involve any of the attributes of
-`information_schema.processlist`: `ID`, `USER`, `HOST`, `DB`, `COMMAND`, `TIME`,
-`STATE`, and `INFO`.
-
-Examples:
-
- `dj.kill('HOST LIKE "%compute%"')` lists only connections from hosts containing "compute".
- `dj.kill('TIME > 600')` lists only connections older than 10 minutes.
-
-A list of connections meeting the restriction conditions (if present) are presented to
-the user, along with the option to kill processes. By default, output is ordered by
-ascending connection ID. To change the output order of dj.kill(), an additional
-order_by argument can be provided.
-
-For example, to sort the output by hostname in descending order:
-
-```python
-In [3]: dj.kill(None, None, 'host desc')
-Out[3]:
- ID USER HOST STATE TIME INFO
-+--+ +----------+ +-----------+ +-----------+ +-----+
- 33 chris localhost:54840 1261 None
- 17 chris localhost:54587 3246 None
- 4 event_scheduler localhost Waiting on empty queue 187180 None
-process to kill or "q" to quit > q
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/compute/key-source.md b/docs/src/compute/key-source.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 76796ec0c..000000000
--- a/docs/src/compute/key-source.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,51 +0,0 @@
-# Key Source
-
-## Default key source
-
-**Key source** refers to the set of primary key values over which
-[autopopulate](./populate.md) iterates, calling the `make` method at each iteration.
-Each `key` from the key source is passed to the table's `make` call.
-By default, the key source for a table is the [join](../query/join.md) of its primary
-[dependencies](../design/tables/dependencies.md).
-
-For example, consider a schema with three tables.
-The `Stimulus` table contains one attribute `stimulus_type` with one of two values,
-"Visual" or "Auditory".
-The `Modality` table contains one attribute `modality` with one of three values, "EEG",
-"fMRI", and "PET".
-The `Protocol` table has primary dependencies on both the `Stimulus` and `Modality` tables.
-
-The key source for `Protocol` will then be all six combinations of `stimulus_type` and
-`modality` as shown in the figure below.
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-## Custom key source
-
-A custom key source can be configured by setting the `key_source` property within a
-table class, after the `definition` string.
-
-Any [query object](../query/fetch.md) can be used as the key source.
-In most cases the new key source will be some alteration of the default key source.
-Custom key sources often involve restriction to limit the key source to only relevant
-entities.
-Other designs may involve using only one of a table's primary dependencies.
-
-In the example below, the `EEG` table depends on the `Recording` table that lists all
-recording sessions.
-However, the `populate` method of `EEG` should only ingest recordings where the
-`recording_type` is `EEG`.
-Setting a custom key source prevents the `populate` call from iterating over recordings
-of the wrong type.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class EEG(dj.Imported):
-definition = """
--> Recording
----
-sample_rate : float
-eeg_data : longblob
-"""
-key_source = Recording & 'recording_type = "EEG"'
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/compute/make.md b/docs/src/compute/make.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1b5569b65..000000000
--- a/docs/src/compute/make.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,215 +0,0 @@
-# Transactions in Make
-
-Each call of the [make](../compute/make.md) method is enclosed in a transaction.
-DataJoint users do not need to explicitly manage transactions but must be aware of
-their use.
-
-Transactions produce two effects:
-
-First, the state of the database appears stable within the `make` call throughout the
-transaction:
-two executions of the same query will yield identical results within the same `make`
-call.
-
-Second, any changes to the database (inserts) produced by the `make` method will not
-become visible to other processes until the `make` call completes execution.
-If the `make` method raises an exception, all changes made so far will be discarded and
-will never become visible to other processes.
-
-Transactions are particularly important in maintaining
-[group integrity](../design/integrity.md#group-integrity) with
-[master-part relationships](../design/tables/master-part.md).
-The `make` call of a master table first inserts the master entity and then inserts all
-the matching part entities in the part tables.
-None of the entities become visible to other processes until the entire `make` call
-completes, at which point they all become visible.
-
-### Three-Part Make Pattern for Long Computations
-
-For long-running computations, DataJoint provides an advanced pattern called the
-**three-part make** that separates the `make` method into three distinct phases.
-This pattern is essential for maintaining database performance and data integrity
-during expensive computations.
-
-#### The Problem: Long Transactions
-
-Traditional `make` methods perform all operations within a single database transaction:
-
-```python
-def make(self, key):
- # All within one transaction
- data = (ParentTable & key).fetch1() # Fetch
- result = expensive_computation(data) # Compute (could take hours)
- self.insert1(dict(key, result=result)) # Insert
-```
-
-This approach has significant limitations:
-- **Database locks**: Long transactions hold locks on tables, blocking other operations
-- **Connection timeouts**: Database connections may timeout during long computations
-- **Memory pressure**: All fetched data must remain in memory throughout the computation
-- **Failure recovery**: If computation fails, the entire transaction is rolled back
-
-#### The Solution: Three-Part Make Pattern
-
-The three-part make pattern splits the `make` method into three distinct phases,
-allowing the expensive computation to occur outside of database transactions:
-
-```python
-def make_fetch(self, key):
- """Phase 1: Fetch all required data from parent tables"""
- fetched_data = ((ParentTable1 & key).fetch1(), (ParentTable2 & key).fetch1())
- return fetched_data # must be a sequence, eg tuple or list
-
-def make_compute(self, key, *fetched_data):
- """Phase 2: Perform expensive computation (outside transaction)"""
- computed_result = expensive_computation(*fetched_data)
- return computed_result # must be a sequence, eg tuple or list
-
-def make_insert(self, key, *computed_result):
- """Phase 3: Insert results into the current table"""
- self.insert1(dict(key, result=computed_result))
-```
-
-#### Execution Flow
-
-To achieve data intensity without long transactions, the three-part make pattern follows this sophisticated execution sequence:
-
-```python
-# Step 1: Fetch data outside transaction
-fetched_data1 = self.make_fetch(key)
-computed_result = self.make_compute(key, *fetched_data1)
-
-# Step 2: Begin transaction and verify data consistency
-begin transaction:
- fetched_data2 = self.make_fetch(key)
- if fetched_data1 != fetched_data2: # deep comparison
- cancel transaction # Data changed during computation
- else:
- self.make_insert(key, *computed_result)
- commit_transaction
-```
-
-#### Key Benefits
-
-1. **Reduced Database Lock Time**: Only the fetch and insert operations occur within transactions, minimizing lock duration
-2. **Connection Efficiency**: Database connections are only used briefly for data transfer
-3. **Memory Management**: Fetched data can be processed and released during computation
-4. **Fault Tolerance**: Computation failures don't affect database state
-5. **Scalability**: Multiple computations can run concurrently without database contention
-
-#### Referential Integrity Protection
-
-The pattern includes a critical safety mechanism: **referential integrity verification**.
-Before inserting results, the system:
-
-1. Re-fetches the source data within the transaction
-2. Compares it with the originally fetched data using deep hashing
-3. Only proceeds with insertion if the data hasn't changed
-
-This prevents the "phantom read" problem where source data changes during long computations,
-ensuring that results remain consistent with their inputs.
-
-#### Implementation Details
-
-The pattern is implemented using Python generators in the `AutoPopulate` class:
-
-```python
-def make(self, key):
- # Step 1: Fetch data from parent tables
- fetched_data = self.make_fetch(key)
- computed_result = yield fetched_data
-
- # Step 2: Compute if not provided
- if computed_result is None:
- computed_result = self.make_compute(key, *fetched_data)
- yield computed_result
-
- # Step 3: Insert the computed result
- self.make_insert(key, *computed_result)
- yield
-```
-Therefore, it is possible to override the `make` method to implement the three-part make pattern by using the `yield` statement to return the fetched data and computed result as above.
-
-#### Use Cases
-
-This pattern is particularly valuable for:
-
-- **Machine learning model training**: Hours-long training sessions
-- **Image processing pipelines**: Large-scale image analysis
-- **Statistical computations**: Complex statistical analyses
-- **Data transformations**: ETL processes with heavy computation
-- **Simulation runs**: Time-consuming simulations
-
-#### Example: Long-Running Image Analysis
-
-Here's an example of how to implement the three-part make pattern for a
-long-running image analysis task:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class ImageAnalysis(dj.Computed):
- definition = """
- # Complex image analysis results
- -> Image
- ---
- analysis_result : longblob
- processing_time : float
- """
-
- def make_fetch(self, key):
- """Fetch the image data needed for analysis"""
- image_data = (Image & key).fetch1('image')
- params = (Params & key).fetch1('params')
- return (image_data, params) # pack fetched_data
-
- def make_compute(self, key, image_data, params):
- """Perform expensive image analysis outside transaction"""
- import time
- start_time = time.time()
-
- # Expensive computation that could take hours
- result = complex_image_analysis(image_data, params)
- processing_time = time.time() - start_time
- return result, processing_time
-
- def make_insert(self, key, analysis_result, processing_time):
- """Insert the analysis results"""
- self.insert1(dict(key,
- analysis_result=analysis_result,
- processing_time=processing_time))
-```
-
-The exact same effect may be achieved by overriding the `make` method as a generator function using the `yield` statement to return the fetched data and computed result as above:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class ImageAnalysis(dj.Computed):
- definition = """
- # Complex image analysis results
- -> Image
- ---
- analysis_result : longblob
- processing_time : float
- """
-
- def make(self, key):
- image_data = (Image & key).fetch1('image')
- params = (Params & key).fetch1('params')
- computed_result = yield (image, params) # pack fetched_data
-
- if computed_result is None:
- # Expensive computation that could take hours
- import time
- start_time = time.time()
- result = complex_image_analysis(image_data, params)
- processing_time = time.time() - start_time
- computed_result = result, processing_time #pack
- yield computed_result
-
- result, processing_time = computed_result # unpack
- self.insert1(dict(key,
- analysis_result=result,
- processing_time=processing_time))
- yield # yield control back to the caller
-```
-We expect that most users will prefer to use the three-part implementation over the generator function implementation due to its conceptual complexity.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/src/compute/populate.md b/docs/src/compute/populate.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 45c863f17..000000000
--- a/docs/src/compute/populate.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,317 +0,0 @@
-# Auto-populate
-
-Auto-populated tables are used to define, execute, and coordinate computations in a
-DataJoint pipeline.
-
-Tables in the initial portions of the pipeline are populated from outside the pipeline.
-In subsequent steps, computations are performed automatically by the DataJoint pipeline
-in auto-populated tables.
-
-Computed tables belong to one of the two auto-populated
-[data tiers](../design/tables/tiers.md): `dj.Imported` and `dj.Computed`.
-DataJoint does not enforce the distinction between imported and computed tables: the
-difference is purely semantic, a convention for developers to follow.
-If populating a table requires access to external files such as raw storage that is not
-part of the database, the table is designated as **imported**.
-Otherwise it is **computed**.
-
-Auto-populated tables are defined and queried exactly as other tables.
-(See [Manual Tables](../design/tables/manual.md).)
-Their data definition follows the same [definition syntax](../design/tables/declare.md).
-
-## Make
-
-For auto-populated tables, data should never be entered using
-[insert](../manipulation/insert.md) directly.
-Instead these tables must define the callback method `make(self, key)`.
-The `insert` method then can only be called on `self` inside this callback method.
-
-Imagine that there is a table `test.Image` that contains 2D grayscale images in its
-`image` attribute.
-Let us define the computed table, `test.FilteredImage` that filters the image in some
-way and saves the result in its `filtered_image` attribute.
-
-The class will be defined as follows.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class FilteredImage(dj.Computed):
- definition = """
- # Filtered image
- -> Image
- ---
- filtered_image : longblob
- """
-
- def make(self, key):
- img = (test.Image & key).fetch1('image')
- key['filtered_image'] = myfilter(img)
- self.insert1(key)
-```
-
-The `make` method receives one argument: the dict `key` containing the primary key
-value of an element of [key source](key-source.md) to be worked on.
-
-The key represents the partially filled entity, usually already containing the
-[primary key](../design/tables/primary.md) attributes of the key source.
-
-The `make` callback does three things:
-
-1. [Fetches](../query/fetch.md) data from tables upstream in the pipeline using the
-`key` for [restriction](../query/restrict.md).
-2. Computes and adds any missing attributes to the fields already in `key`.
-3. Inserts the entire entity into `self`.
-
-A single `make` call may populate multiple entities when `key` does not specify the
-entire primary key of the populated table, when the definition adds new attributes to the primary key.
-This design is uncommon and not recommended.
-The standard practice for autopopulated tables is to have its primary key composed of
-foreign keys pointing to parent tables.
-
-### Three-Part Make Pattern for Long Computations
-
-For long-running computations, DataJoint provides an advanced pattern called the
-**three-part make** that separates the `make` method into three distinct phases.
-This pattern is essential for maintaining database performance and data integrity
-during expensive computations.
-
-#### The Problem: Long Transactions
-
-Traditional `make` methods perform all operations within a single database transaction:
-
-```python
-def make(self, key):
- # All within one transaction
- data = (ParentTable & key).fetch1() # Fetch
- result = expensive_computation(data) # Compute (could take hours)
- self.insert1(dict(key, result=result)) # Insert
-```
-
-This approach has significant limitations:
-- **Database locks**: Long transactions hold locks on tables, blocking other operations
-- **Connection timeouts**: Database connections may timeout during long computations
-- **Memory pressure**: All fetched data must remain in memory throughout the computation
-- **Failure recovery**: If computation fails, the entire transaction is rolled back
-
-#### The Solution: Three-Part Make Pattern
-
-The three-part make pattern splits the `make` method into three distinct phases,
-allowing the expensive computation to occur outside of database transactions:
-
-```python
-def make_fetch(self, key):
- """Phase 1: Fetch all required data from parent tables"""
- fetched_data = ((ParentTable & key).fetch1(),)
- return fetched_data # must be a sequence, eg tuple or list
-
-def make_compute(self, key, *fetched_data):
- """Phase 2: Perform expensive computation (outside transaction)"""
- computed_result = expensive_computation(*fetched_data)
- return computed_result # must be a sequence, eg tuple or list
-
-def make_insert(self, key, *computed_result):
- """Phase 3: Insert results into the current table"""
- self.insert1(dict(key, result=computed_result))
-```
-
-#### Execution Flow
-
-To achieve data intensity without long transactions, the three-part make pattern follows this sophisticated execution sequence:
-
-```python
-# Step 1: Fetch data outside transaction
-fetched_data1 = self.make_fetch(key)
-computed_result = self.make_compute(key, *fetched_data1)
-
-# Step 2: Begin transaction and verify data consistency
-begin transaction:
- fetched_data2 = self.make_fetch(key)
- if fetched_data1 != fetched_data2: # deep comparison
- cancel transaction # Data changed during computation
- else:
- self.make_insert(key, *computed_result)
- commit_transaction
-```
-
-#### Key Benefits
-
-1. **Reduced Database Lock Time**: Only the fetch and insert operations occur within transactions, minimizing lock duration
-2. **Connection Efficiency**: Database connections are only used briefly for data transfer
-3. **Memory Management**: Fetched data can be processed and released during computation
-4. **Fault Tolerance**: Computation failures don't affect database state
-5. **Scalability**: Multiple computations can run concurrently without database contention
-
-#### Referential Integrity Protection
-
-The pattern includes a critical safety mechanism: **referential integrity verification**.
-Before inserting results, the system:
-
-1. Re-fetches the source data within the transaction
-2. Compares it with the originally fetched data using deep hashing
-3. Only proceeds with insertion if the data hasn't changed
-
-This prevents the "phantom read" problem where source data changes during long computations,
-ensuring that results remain consistent with their inputs.
-
-#### Implementation Details
-
-The pattern is implemented using Python generators in the `AutoPopulate` class:
-
-```python
-def make(self, key):
- # Step 1: Fetch data from parent tables
- fetched_data = self.make_fetch(key)
- computed_result = yield fetched_data
-
- # Step 2: Compute if not provided
- if computed_result is None:
- computed_result = self.make_compute(key, *fetched_data)
- yield computed_result
-
- # Step 3: Insert the computed result
- self.make_insert(key, *computed_result)
- yield
-```
-Therefore, it is possible to override the `make` method to implement the three-part make pattern by using the `yield` statement to return the fetched data and computed result as above.
-
-#### Use Cases
-
-This pattern is particularly valuable for:
-
-- **Machine learning model training**: Hours-long training sessions
-- **Image processing pipelines**: Large-scale image analysis
-- **Statistical computations**: Complex statistical analyses
-- **Data transformations**: ETL processes with heavy computation
-- **Simulation runs**: Time-consuming simulations
-
-#### Example: Long-Running Image Analysis
-
-Here's an example of how to implement the three-part make pattern for a
-long-running image analysis task:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class ImageAnalysis(dj.Computed):
- definition = """
- # Complex image analysis results
- -> Image
- ---
- analysis_result : longblob
- processing_time : float
- """
-
- def make_fetch(self, key):
- """Fetch the image data needed for analysis"""
- return (Image & key).fetch1('image'),
-
- def make_compute(self, key, image_data):
- """Perform expensive image analysis outside transaction"""
- import time
- start_time = time.time()
-
- # Expensive computation that could take hours
- result = complex_image_analysis(image_data)
- processing_time = time.time() - start_time
- return result, processing_time
-
- def make_insert(self, key, analysis_result, processing_time):
- """Insert the analysis results"""
- self.insert1(dict(key,
- analysis_result=analysis_result,
- processing_time=processing_time))
-```
-
-The exact same effect may be achieved by overriding the `make` method as a generator function using the `yield` statement to return the fetched data and computed result as above:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class ImageAnalysis(dj.Computed):
- definition = """
- # Complex image analysis results
- -> Image
- ---
- analysis_result : longblob
- processing_time : float
- """
-
- def make(self, key):
- image_data = (Image & key).fetch1('image')
- computed_result = yield (image_data, ) # pack fetched_data
-
- if computed_result is None:
- # Expensive computation that could take hours
- import time
- start_time = time.time()
- result = complex_image_analysis(image_data)
- processing_time = time.time() - start_time
- computed_result = result, processing_time #pack
- yield computed_result
-
- result, processing_time = computed_result # unpack
- self.insert1(dict(key,
- analysis_result=result,
- processing_time=processing_time))
- yield # yield control back to the caller
-```
-We expect that most users will prefer to use the three-part implementation over the generator function implementation due to its conceptual complexity.
-
-## Populate
-
-The inherited `populate` method of `dj.Imported` and `dj.Computed` automatically calls
-`make` for every key for which the auto-populated table is missing data.
-
-The `FilteredImage` table can be populated as
-
-```python
-FilteredImage.populate()
-```
-
-The progress of long-running calls to `populate()` in datajoint-python can be
-visualized by adding the `display_progress=True` argument to the populate call.
-
-Note that it is not necessary to specify which data needs to be computed.
-DataJoint will call `make`, one-by-one, for every key in `Image` for which
-`FilteredImage` has not yet been computed.
-
-Chains of auto-populated tables form computational pipelines in DataJoint.
-
-## Populate options
-
-The `populate` method accepts a number of optional arguments that provide more features
-and allow greater control over the method's behavior.
-
-- `restrictions` - A list of restrictions, restricting as
-`(tab.key_source & AndList(restrictions)) - tab.proj()`.
- Here `target` is the table to be populated, usually `tab` itself.
-- `suppress_errors` - If `True`, encountering an error will cancel the current `make`
-call, log the error, and continue to the next `make` call.
- Error messages will be logged in the job reservation table (if `reserve_jobs` is
- `True`) and returned as a list.
- See also `return_exception_objects` and `reserve_jobs`.
- Defaults to `False`.
-- `return_exception_objects` - If `True`, error objects are returned instead of error
- messages.
- This applies only when `suppress_errors` is `True`.
- Defaults to `False`.
-- `reserve_jobs` - If `True`, reserves job to indicate to other distributed processes.
- The job reservation table may be access as `schema.jobs`.
- Errors are logged in the jobs table.
- Defaults to `False`.
-- `order` - The order of execution, either `"original"`, `"reverse"`, or `"random"`.
- Defaults to `"original"`.
-- `display_progress` - If `True`, displays a progress bar.
- Defaults to `False`.
-- `limit` - If not `None`, checks at most this number of keys.
- Defaults to `None`.
-- `max_calls` - If not `None`, populates at most this many keys.
- Defaults to `None`, which means no limit.
-
-## Progress
-
-The method `table.progress` reports how many `key_source` entries have been populated
-and how many remain.
-Two optional parameters allow more advanced use of the method.
-A parameter of restriction conditions can be provided, specifying which entities to
-consider.
-A Boolean parameter `display` (default is `True`) allows disabling the output, such
-that the numbers of remaining and total entities are returned but not printed.
diff --git a/docs/src/concepts/data-model.md b/docs/src/concepts/data-model.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 90460361a..000000000
--- a/docs/src/concepts/data-model.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,172 +0,0 @@
-# Data Model
-
-## What is a data model?
-
-A **data model** is a conceptual framework that defines how data is organized,
-represented, and transformed. It gives us the components for creating blueprints for the
-structure and operations of data management systems, ensuring consistency and efficiency
-in data handling.
-
-Data management systems are built to accommodate these models, allowing us to manage
-data according to the principles laid out by the model. If you’re studying data science
-or engineering, you’ve likely encountered different data models, each providing a unique
-approach to organizing and manipulating data.
-
-A data model is defined by considering the following key aspects:
-
-+ What are the fundamental elements used to structure the data?
-+ What operations are available for defining, creating, and manipulating the data?
-+ What mechanisms exist to enforce the structure and rules governing valid data interactions?
-
-## Types of data models
-
-Among the most familiar data models are those based on files and folders: data of any
-kind are lumped together into binary strings called **files**, files are collected into
-folders, and folders can be nested within other folders to create a folder hierarchy.
-
-Another family of data models are various **tabular models**.
-For example, items in CSV files are listed in rows, and the attributes of each item are
-stored in columns.
-Various **spreadsheet** models allow forming dependencies between cells and groups of
-cells, including complex calculations.
-
-The **object data model** is common in programming, where data are represented as
-objects in memory with properties and methods for transformations of such data.
-
-## Relational data model
-
-The **relational model** is a way of thinking about data as sets and operations on sets.
-Formalized almost a half-century ago ([Codd,
-1969](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=362384.362685)). The relational data model is
-one of the most powerful and precise ways to store and manage structured data. At its
-core, this model organizes all data into tables--representing mathematical
-relations---where each table consists of rows (representing mathematical tuples) and
-columns (often called attributes).
-
-### Core principles of the relational data model
-
-**Data representation:**
- Data are represented and manipulated in the form of relations.
- A relation is a set (i.e. an unordered collection) of entities of values for each of
- the respective named attributes of the relation.
- Base relations represent stored data while derived relations are formed from base
- relations through query expressions.
- A collection of base relations with their attributes, domain constraints, uniqueness
- constraints, and referential constraints is called a schema.
-
-**Domain constraints:**
- Each attribute (column) in a table is associated with a specific attribute domain (or
- datatype, a set of possible values), ensuring that the data entered is valid.
- Attribute domains may not include relations, which keeps the data model
- flat, i.e. free of nested structures.
-
-**Uniqueness constraints:**
- Entities within relations are addressed by values of their attributes.
- To identify and relate data elements, uniqueness constraints are imposed on subsets
- of attributes.
- Such subsets are then referred to as keys.
- One key in a relation is designated as the primary key used for referencing its elements.
-
-**Referential constraints:**
- Associations among data are established by means of referential constraints with the
- help of foreign keys.
- A referential constraint on relation A referencing relation B allows only those
- entities in A whose foreign key attributes match the key attributes of an entity in B.
-
-**Declarative queries:**
- Data queries are formulated through declarative, as opposed to imperative,
- specifications of sought results.
- This means that query expressions convey the logic for the result rather than the
- procedure for obtaining it.
- Formal languages for query expressions include relational algebra, relational
- calculus, and SQL.
-
-The relational model has many advantages over both hierarchical file systems and
-tabular models for maintaining data integrity and providing flexible access to
-interesting subsets of the data.
-
-Popular implementations of the relational data model rely on the Structured Query
-Language (SQL).
-SQL comprises distinct sublanguages for schema definition, data manipulation, and data
-queries.
-SQL thoroughly dominates in the space of relational databases and is often conflated
-with the relational data model in casual discourse.
-Various terminologies are used to describe related concepts from the relational data
-model.
-Similar to spreadsheets, relations are often visualized as tables with *attributes*
-corresponding to *columns* and *entities* corresponding to *rows*.
-In particular, SQL uses the terms *table*, *column*, and *row*.
-
-## The DataJoint Model
-
-DataJoint is a conceptual refinement of the relational data model offering a more
-expressive and rigorous framework for database programming ([Yatsenko et al.,
-2018](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11104)). The DataJoint model facilitates conceptual
-clarity, efficiency, workflow management, and precise and flexible data
-queries. By enforcing entity normalization,
-simplifying dependency declarations, offering a rich query algebra, and visualizing
-relationships through schema diagrams, DataJoint makes relational database programming
-more intuitive and robust for complex data pipelines.
-
-The model has emerged over a decade of continuous development of complex data
-pipelines for neuroscience experiments ([Yatsenko et al.,
-2015](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2015/11/14/031658)). DataJoint has allowed
-researchers with no prior knowledge of databases to collaborate effectively on common
-data pipelines sustaining data integrity and supporting flexible access. DataJoint is
-currently implemented as client libraries in MATLAB and Python. These libraries work by
-transpiling DataJoint queries into SQL before passing them on to conventional relational
-database systems that serve as the backend, in combination with bulk storage systems for
-storing large contiguous data objects.
-
-DataJoint comprises:
-
-+ a schema [definition](../design/tables/declare.md) language
-+ a data [manipulation](../manipulation/index.md) language
-+ a data [query](../query/principles.md) language
-+ a [diagramming](../design/diagrams.md) notation for visualizing relationships between
-modeled entities
-
-The key refinement of DataJoint over other relational data models and their
-implementations is DataJoint's support of
-[entity normalization](../design/normalization.md).
-
-### Core principles of the DataJoint model
-
-**Entity Normalization**
- DataJoint enforces entity normalization, ensuring that every entity set (table) is
- well-defined, with each element belonging to the same type, sharing the same
- attributes, and distinguished by the same primary key. This principle reduces
- redundancy and avoids data anomalies, similar to Boyce-Codd Normal Form, but with a
- more intuitive structure than traditional SQL.
-
-**Simplified Schema Definition and Dependency Management**
- DataJoint introduces a schema definition language that is more expressive and less
- error-prone than SQL. Dependencies are explicitly declared using arrow notation
- (->), making referential constraints easier to understand and visualize. The
- dependency structure is enforced as an acyclic directed graph, which simplifies
- workflows by preventing circular dependencies.
-
-**Integrated Query Operators producing a Relational Algebra**
- DataJoint introduces five query operators (restrict, join, project, aggregate, and
- union) with algebraic closure, allowing them to be combined seamlessly. These
- operators are designed to maintain operational entity normalization, ensuring query
- outputs remain valid entity sets.
-
-**Diagramming Notation for Conceptual Clarity**
- DataJoint’s schema diagrams simplify the representation of relationships between
- entity sets compared to ERM diagrams. Relationships are expressed as dependencies
- between entity sets, which are visualized using solid or dashed lines for primary
- and secondary dependencies, respectively.
-
-**Unified Logic for Binary Operators**
- DataJoint simplifies binary operations by requiring attributes involved in joins or
- comparisons to be homologous (i.e., sharing the same origin). This avoids the
- ambiguity and pitfalls of natural joins in SQL, ensuring more predictable query
- results.
-
-**Optimized Data Pipelines for Scientific Workflows**
- DataJoint treats the database as a data pipeline where each entity set defines a
- step in the workflow. This makes it ideal for scientific experiments and complex
- data processing, such as in neuroscience. Its MATLAB and Python libraries transpile
- DataJoint queries into SQL, bridging the gap between scientific programming and
- relational databases.
diff --git a/docs/src/concepts/data-pipelines.md b/docs/src/concepts/data-pipelines.md
deleted file mode 100644
index cf20b075b..000000000
--- a/docs/src/concepts/data-pipelines.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
-# Data Pipelines
-
-## What is a data pipeline?
-
-A scientific **data pipeline** is a collection of processes and systems for organizing
-the data, computations, and workflows used by a research group as they jointly perform
-complex sequences of data acquisition, processing, and analysis.
-
-A variety of tools can be used for supporting shared data pipelines:
-
-Data repositories
- Research teams set up a shared **data repository**.
- This minimal data management tool allows depositing and retrieving data and managing
- user access.
- For example, this may include a collection of files with standard naming conventions
- organized into folders and sub-folders.
- Or a data repository might reside on the cloud, for example in a collection of S3
- buckets.
- This image of data management -- where files are warehoused and retrieved from a
- hierarchically-organized system of folders -- is an approach that is likely familiar
- to most scientists.
-
-Database systems
- **Databases** are a form of data repository providing additional capabilities:
-
- 1. Defining, communicating, and enforcing structure in the stored data.
- 2. Maintaining data integrity: correct identification of data and consistent cross-references, dependencies, and groupings among the data.
- 3. Supporting queries that retrieve various cross-sections and transformation of the deposited data.
-
- Most scientists have some familiarity with these concepts, for example the notion of maintaining consistency between data and the metadata that describes it, or applying a filter to an Excel spreadsheet to retrieve specific subsets of information.
- However, usually the more advanced concepts involved in building and using relational databases fall under the specific expertise of data scientists.
-
-Data pipelines
- **Data pipeline** frameworks may include all the features of a database system along
- with additional functionality:
-
- 1. Integrating computations to perform analyses and manage intermediate results in a principled way.
- 2. Supporting distributed computations without conflict.
- 3. Defining, communicating, and enforcing **workflow**, making clear the sequence of steps that must be performed for data entry, acquisition, and processing.
-
- Again, the informal notion of an analysis "workflow" will be familiar to most scientists, along with the logistical difficulties associated with managing a workflow that is shared by multiple scientists within or across labs.
-
- Therefore, a full-featured data pipeline framework may also be described as a [scientific workflow system](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scientific_workflow_system).
-
-Major features of data management frameworks: data repositories, databases, and data pipelines.
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-## What is DataJoint?
-
-DataJoint is a free open-source framework for creating scientific data pipelines
-directly from MATLAB or Python (or any mixture of the two).
-The data are stored in a language-independent way that allows interoperability between
-MATLAB and Python, with additional languages in the works.
-DataJoint pipelines become the central tool in the operations of data-intensive labs or
-consortia as they organize participants with different roles and skills around a common
-framework.
-
-In DataJoint, a data pipeline is a sequence of steps (more generally, a directed
-acyclic graph) with integrated data storage at each step.
-The pipeline may have some nodes requiring manual data entry or import from external
-sources, some that read from raw data files, and some that perform computations on data
-stored in other database nodes.
-In a typical scenario, experimenters and acquisition instruments feed data into nodes
-at the head of the pipeline, while downstream nodes perform automated computations for
-data processing and analysis.
-
-For example, this is the pipeline for a simple mouse experiment involving calcium
-imaging in mice.
-
-{: style="width:250px; align:center"}
-
-In this example, the experimenter first enters information about a mouse, then enters
-information about each imaging session in that mouse, and then each scan performed in
-each imaging session.
-Next the automated portion of the pipeline takes over to import the raw imaging data,
-perform image alignment to compensate for motion, image segmentation to identify cells
-in the images, and extraction of calcium traces.
-Finally, the receptive field (RF) computation is performed by relating the calcium
-signals to the visual stimulus information.
-
-## How DataJoint works
-
-DataJoint enables data scientists to build and operate scientific data pipelines.
-
-Conceptual overview of DataJoint operation.
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-DataJoint provides a simple and powerful data model, which is detailed more formally in [Yatsenko D, Walker EY, Tolias AS (2018). DataJoint: A Simpler Relational Data Model.](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11104).
-Put most generally, a "data model" defines how to think about data and the operations
-that can be performed on them.
-DataJoint's model is a refinement of the relational data model: all nodes in the
-pipeline are simple tables storing data, tables are related by their shared attributes,
-and query operations can combine the contents of multiple tables.
-DataJoint enforces specific constraints on the relationships between tables that help
-maintain data integrity and enable flexible access.
-DataJoint uses a succinct data definition language, a powerful data query language, and
-expressive visualizations of the pipeline.
-A well-defined and principled approach to data organization and computation enables
-teams of scientists to work together efficiently.
-The data become immediately available to all participants with appropriate access privileges.
-Some of the "participants" may be computational agents that perform processing and
-analysis, and so DataJoint features a built-in distributed job management process to
-allow distributing analysis between any number of computers.
-
-From a practical point of view, the back-end data architecture may vary depending on
-project requirements.
-Typically, the data architecture includes a relational database server (e.g. MySQL) and
-a bulk data storage system (e.g. [AWS S3](https://aws.amazon.com/s3/) or a filesystem).
-However, users need not interact with the database directly, but via MATLAB or Python
-objects that are each associated with an individual table in the database.
-One of the main advantages of this approach is that DataJoint clearly separates the
-data model facing the user from the data architecture implementing data management and
-computing. DataJoint works well in combination with good code sharing (e.g. with
-[git](https://git-scm.com/)) and environment sharing (e.g. with
-[Docker](https://www.docker.com/)).
-
-DataJoint is designed for quick prototyping and continuous exploration as experimental
-designs change or evolve.
-New analysis methods can be added or removed at any time, and the structure of the
-workflow itself can change over time, for example as new data acquisition methods are
-developed.
-
-With DataJoint, data sharing and publishing is no longer a separate step at the end of
-the project.
-Instead data sharing is an inherent feature of the process: to share data with other
-collaborators or to publish the data to the world, one only needs to set the access
-privileges.
-
-## Real-life example
-
-The [Mesoscale Activity Project](https://www.simonsfoundation.org/funded-project/%20multi-regional-neuronal-dynamics-of-memory-guided-flexible-behavior/)
-(MAP) is a collaborative project between four neuroscience labs.
-MAP uses DataJoint for data acquisition, processing, analysis, interfaces, and external sharing.
-
-The DataJoint pipeline for the MAP project.
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-The pipeline is hosted in the cloud through [Amazon Web Services](https://aws.amazon.com/) (AWS).
-MAP data scientists at the Janelia Research Campus and Baylor College of Medicine
-defined the data pipeline.
-Experimental scientists enter manual data directly into the pipeline using the
-[Helium web interface](https://github.com/mattbdean/Helium).
-The raw data are preprocessed using the DataJoint client libraries in MATLAB and Python;
-the preprocessed data are ingested into the pipeline while the bulky and raw data are
-shared using [Globus](https://globus.org) transfer through the
-[PETREL](https://www.alcf.anl.gov/petrel) storage servers provided by the Argonne
-National Lab.
-Data are made immediately available for exploration and analysis to collaborating labs,
-and the analysis results are also immediately shared.
-Analysis data may be visualized through web interfaces.
-Intermediate results may be exported into the [NWB](https://nwb.org) format for sharing
-with external groups.
-
-## Summary of DataJoint features
-
-1. A free, open-source framework for scientific data pipelines and workflow management
-2. Data hosting in cloud or in-house
-3. MySQL, filesystems, S3, and Globus for data management
-4. Define, visualize, and query data pipelines from MATLAB or Python
-5. Enter and view data through GUIs
-6. Concurrent access by multiple users and computational agents
-7. Data integrity: identification, dependencies, groupings
-8. Automated distributed computation
diff --git a/docs/src/concepts/principles.md b/docs/src/concepts/principles.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2bf491590..000000000
--- a/docs/src/concepts/principles.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,136 +0,0 @@
-# Principles
-
-## Theoretical Foundations
-
-*DataJoint Core* implements a systematic framework for the joint management of
-structured scientific data and its associated computations.
-The framework builds on the theoretical foundations of the
-[Relational Model](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relational_model) and
-the [Entity-Relationship Model](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Entity%E2%80%93relationship_model),
-introducing a number of critical clarifications for the effective use of databases as
-scientific data pipelines.
-Notably, DataJoint introduces the concept of *computational dependencies* as a native
-first-class citizen of the data model.
-This integration of data structure and computation into a single model, defines a new
-class of *computational scientific databases*.
-
-This page defines the key principles of this model without attachment to a specific
-implementation while a more complete description of the model can be found in
-[Yatsenko et al, 2018](https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1807.11104).
-
-DataJoint developers are developing these principles into an
-[open standard](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_standard) to allow multiple
-alternative implementations.
-
-## Data Representation
-
-### Tables = Entity Sets
-
-DataJoint uses only one data structure in all its operations—the *entity set*.
-
-1. All data are represented in the form of *entity sets*, i.e. an ordered collection of
-*entities*.
-2. All entities of an entity set belong to the same well-defined entity class and have
-the same set of named attributes.
-3. Attributes in an entity set has a *data type* (or *domain*), representing the set of
-its valid values.
-4. Each entity in an entity set provides the *attribute values* for all of the
-attributes of its entity class.
-5. Each entity set has a *primary key*, *i.e.* a subset of attributes that, jointly,
-uniquely identify any entity in the set.
-
-These formal terms have more common (even if less precise) variants:
-
-| formal | common |
-|:-:|:--:|
-| entity set | *table* |
-| attribute | *column* |
-| attribute value | *field* |
-
-A collection of *stored tables* make up a *database*.
-*Derived tables* are formed through *query expressions*.
-
-### Table Definition
-
-DataJoint introduces a streamlined syntax for defining a stored table.
-
-Each line in the definition defines an attribute with its name, data type, an optional
-default value, and an optional comment in the format:
-
-```python
-name [=default] : type [# comment]
-```
-
-Primary attributes come first and are separated from the rest of the attributes with
-the divider `---`.
-
-For example, the following code defines the entity set for entities of class `Employee`:
-
-```python
-employee_id : int
----
-ssn = null : int # optional social security number
-date_of_birth : date
-gender : enum('male', 'female', 'other')
-home_address="" : varchar(1000)
-primary_phone="" : varchar(12)
-```
-
-### Data Tiers
-
-Stored tables are designated into one of four *tiers* indicating how their data
-originates.
-
-| table tier | data origin |
-| --- | --- |
-| lookup | contents are part of the table definition, defined *a priori* rather than entered externally. Typical stores general facts, parameters, options, *etc.* |
-| manual | contents are populated by external mechanisms such as manual entry through web apps or by data ingest scripts |
-| imported | contents are populated automatically by pipeline computations accessing data from upstream in the pipeline **and** from external data sources such as raw data stores.|
-| computed | contents are populated automatically by pipeline computations accessing data from upstream in the pipeline. |
-
-### Object Serialization
-
-### Data Normalization
-
-A collection of data is considered normalized when organized into a collection of
-entity sets, where each entity set represents a well-defined entity class with all its
-attributes applicable to each entity in the set and the same primary key identifying
-
-The normalization procedure often includes splitting data from one table into several
-tables, one for each proper entity set.
-
-### Databases and Schemas
-
-Stored tables are named and grouped into namespaces called *schemas*.
-A collection of schemas make up a *database*.
-A *database* has a globally unique address or name.
-A *schema* has a unique name within its database.
-Within a *connection* to a particular database, a stored table is identified as
-`schema.Table`.
-A schema typically groups tables that are logically related.
-
-## Dependencies
-
-Entity sets can form referential dependencies that express and
-
-### Diagramming
-
-## Data integrity
-
-### Entity integrity
-
-*Entity integrity* is the guarantee made by the data management process of the 1:1
-mapping between real-world entities and their digital representations.
-In practice, entity integrity is ensured when it is made clear
-
-### Referential integrity
-
-### Group integrity
-
-## Data manipulations
-
-## Data queries
-
-### Query Operators
-
-## Pipeline computations
diff --git a/docs/src/concepts/teamwork.md b/docs/src/concepts/teamwork.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a0a782dde..000000000
--- a/docs/src/concepts/teamwork.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-# Teamwork
-
-## Data management in a science project
-
-Science labs organize their projects as a sequence of activities of experiment design,
-data acquisition, and processing and analysis.
-
-{: style="width:510px; display:block; margin: 0 auto;"}
-
-Workflow and dataflow in a common findings-centered approach to data science in a science lab.
-
-Many labs lack a uniform data management strategy that would span longitudinally across
-the entire project lifecycle as well as laterally across different projects.
-
-Prior to publishing their findings, the research team may need to publish the data to
-support their findings.
-Without a data management system, this requires custom repackaging of the data to
-conform to the [FAIR principles](https://www.nature.com/articles/sdata201618) for
-scientific data management.
-
-## Data-centric project organization
-
-DataJoint is designed to support a data-centric approach to large science projects in
-which data are viewed as a principal output of the research project and are managed
-systematically throughout in a single framework through the entire process.
-
-This approach requires formulating a general data science plan and upfront investment
-for setting up resources and processes and training the teams.
-The team uses DataJoint to build data pipelines to support multiple projects.
-
-{: style="width:510px; display:block; margin: 0 auto;"}
-
-Workflow and dataflow in a data pipeline-centered approach.
-
-Data pipelines support project data across their entire lifecycle, including the
-following functions
-
-- experiment design
-- animal colony management
-- electronic lab book: manual data entry during experiments through graphical user interfaces.
-- acquisition from instrumentation in the course of experiments
-- ingest from raw acquired data
-- computations for data analysis
-- visualization of analysis results
-- export for sharing and publishing
-
-Through all these activities, all these data are made accessible to all authorized
-participants and distributed computations can be done in parallel without compromising
-data integrity.
-
-## Team roles
-
-The adoption of a uniform data management framework allows separation of roles and
-division of labor among team members, leading to greater efficiency and better scaling.
-
-{: style="width:510px; display:block; margin: 0 auto;"}
-
-Distinct responsibilities of data science and data engineering.
-
-### Scientists
-
-Design and conduct experiments, collecting data.
-They interact with the data pipeline through graphical user interfaces designed by
-others.
-They understand what analysis is used to test their hypotheses.
-
-### Data scientists
-
-Have the domain expertise and select and implement the processing and analysis
-methods for experimental data.
-Data scientists are in charge of defining and managing the data pipeline using
-DataJoint's data model, but they may not know the details of the underlying
-architecture.
-They interact with the pipeline using client programming interfaces directly from
-languages such as MATLAB and Python.
-
-The bulk of this manual is written for working data scientists, except for System
-Administration.
-
-### Data engineers
-
-Work with the data scientists to support the data pipeline.
-They rely on their understanding of the DataJoint data model to configure and
-administer the required IT resources such as database servers, data storage
-servers, networks, cloud instances, [Globus](https://globus.org) endpoints, etc.
-Data engineers can provide general solutions such as web hosting, data publishing,
-interfaces, exports and imports.
-
-The System Administration section of this tutorial contains materials helpful in
-accomplishing these tasks.
-
-DataJoint is designed to delineate a clean boundary between **data science** and **data
-engineering**.
-This allows data scientists to use the same uniform data model for data pipelines
-backed by a variety of information technologies.
-This delineation also enables economies of scale as a single data engineering team can
-support a wide spectrum of science projects.
diff --git a/docs/src/concepts/terminology.md b/docs/src/concepts/terminology.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0fdc41e96..000000000
--- a/docs/src/concepts/terminology.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,127 +0,0 @@
-
-
-# Terminology
-
-DataJoint introduces a principled data model, which is described in detail in
-[Yatsenko et al., 2018](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11104).
-This data model is a conceptual refinement of the Relational Data Model and also draws
-on the Entity-Relationship Model (ERM).
-
-The Relational Data Model was inspired by the concepts of relations in Set Theory.
-When the formal relational data model was formulated, it introduced additional
-terminology (e.g. *relation*, *attribute*, *tuple*, *domain*).
-Practical programming languages such as SQL do not precisely follow the relational data
-model and introduce other terms to approximate relational concepts (e.g. *table*,
-*column*, *row*, *datatype*).
-Subsequent data models (e.g. ERM) refined the relational data model and introduced
-their own terminology to describe analogous concepts (e.g. *entity set*,
-*relationship set*, *attribute set*).
-As a result, similar concepts may be described using different sets of terminologies,
-depending on the context and the speaker's background.
-
-For example, what is known as a **relation** in the formal relational model is called a
-**table** in SQL; the analogous concept in ERM and DataJoint is called an **entity
-set**.
-
-The DataJoint documentation follows the terminology defined in
-[Yatsenko et al, 2018](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11104), except *entity set* is
-replaced with the more colloquial *table* or *query result* in most cases.
-
-The table below summarizes the terms used for similar concepts across the related data
-models.
-
-Data model terminology
-| Relational | ERM | SQL | DataJoint (formal) | This manual |
-| -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
-| relation | entity set | table | entity set | table |
-| tuple | entity | row | entity | entity |
-| domain | value set | datatype | datatype | datatype |
-| attribute | attribute | column | attribute | attribute |
-| attribute value | attribute value | field value | attribute value | attribute value |
-| primary key | primary key | primary key | primary key | primary key |
-| foreign key | foreign key | foreign key | foreign key | foreign key |
-| schema | schema | schema or database | schema | schema |
-| relational expression | data query | `SELECT` statement | query expression | query expression |
-
-## DataJoint: databases, schemas, packages, and modules
-
-A **database** is collection of tables on the database server.
-DataJoint users do not interact with it directly.
-
-A **DataJoint schema** is
-
- - a database on the database server containing tables with data *and*
- - a collection of classes (in MATLAB or Python) associated with the database, one
- class for each table.
-
-In MATLAB, the collection of classes is organized as a **package**, i.e. a file folder
-starting with a `+`.
-
-In Python, the collection of classes is any set of classes decorated with the
-appropriate `schema` object.
-Very commonly classes for tables in one database are organized as a distinct Python
-module.
-Thus, typical DataJoint projects have one module per database.
-However, this organization is up to the user's discretion.
-
-## Base tables
-
-**Base tables** are tables stored in the database, and are often referred to simply as
-*tables* in DataJoint.
-Base tables are distinguished from **derived tables**, which result from relational
-[operators](../query/operators.md).
-
-## Relvars and relation values
-
-Early versions of the DataJoint documentation referred to the relation objects as
-[relvars](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relvar).
-This term emphasizes the fact that relational variables and expressions do not contain
-actual data but are rather symbolic representations of data to be retrieved from the
-database.
-The specific value of a relvar would then be referred to as the **relation value**.
-The value of a relvar can change with changes in the state of the database.
-
-The more recent iteration of the documentation has grown less pedantic and more often
-uses the term *table* instead.
-
-## Metadata
-
-The vocabulary of DataJoint does not include this term.
-
-In data science, the term **metadata** commonly means "data about the data" rather than
-the data themselves.
-For example, metadata could include data sizes, timestamps, data types, indexes,
-keywords.
-
-In contrast, neuroscientists often use the term to refer to conditions and annotations
-about experiments.
-This distinction arose when such information was stored separately from experimental
-recordings, such as in physical notebooks.
-Such "metadata" are used to search and to classify the data and are in fact an integral
-part of the *actual* data.
-
-In DataJoint, all data other than blobs can be used in searches and categorization.
-These fields may originate from manual annotations, preprocessing, or analyses just as
-easily as from recordings or behavioral performance.
-Since "metadata" in the neuroscience sense are not distinguished from any other data in
-a pipeline, DataJoint avoids the term entirely.
-Instead, DataJoint differentiates data into [data tiers](../design/tables/tiers.md).
-
-## Glossary
-
-We've taken careful consideration to use consistent terminology.
-
-
-
-| Term | Definition |
-| --- | --- |
-| DAG | directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a set of nodes and connected with a set of directed edges that form no cycles. This means that there is never a path back to a node after passing through it by following the directed edges. Formal workflow management systems represent workflows in the form of DAGs. |
-| data pipeline | A sequence of data transformation steps from data sources through multiple intermediate structures. More generally, a data pipeline is a directed acyclic graph. In DataJoint, each step is represented by a table in a relational database. |
-| DataJoint | a software framework for database programming directly from matlab and python. Thanks to its support of automated computational dependencies, DataJoint serves as a workflow management system. |
-| DataJoint Elements | software modules implementing portions of experiment workflows designed for ease of integration into diverse custom workflows. |
-| DataJoint pipeline | the data schemas and transformations underlying a DataJoint workflow. DataJoint allows defining code that specifies both the workflow and the data pipeline, and we have used the words "pipeline" and "workflow" almost interchangeably. |
-| DataJoint schema | a software module implementing a portion of an experiment workflow. Includes database table definitions, dependencies, and associated computations. |
-| foreign key | a field that is linked to another table's primary key. |
-| primary key | the subset of table attributes that uniquely identify each entity in the table. |
-| secondray attribute | any field in a table not in the primary key. |
-| workflow | a formal representation of the steps for executing an experiment from data collection to analysis. Also the software configured for performing these steps. A typical workflow is composed of tables with inter-dependencies and processes to compute and insert data into the tables. |
diff --git a/docs/src/design/alter.md b/docs/src/design/alter.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 70ed39341..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/alter.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
-# Altering Populated Pipelines
-
-Tables can be altered after they have been declared and populated. This is useful when
-you want to add new secondary attributes or change the data type of existing attributes.
-Users can use the `definition` property to update a table's attributes and then use
-`alter` to apply the changes in the database. Currently, `alter` does not support
-changes to primary key attributes.
-
-Let's say we have a table `Student` with the following attributes:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Student(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- student_id: int
- ---
- first_name: varchar(40)
- last_name: varchar(40)
- home_address: varchar(100)
- """
-```
-
-We can modify the table to include a new attribute `email`:
-
-```python
-Student.definition = """
-student_id: int
----
-first_name: varchar(40)
-last_name: varchar(40)
-home_address: varchar(100)
-email: varchar(100)
-"""
-Student.alter()
-```
-
-The `alter` method will update the table in the database to include the new attribute
-`email` added by the user in the table's `definition` property.
-
-Similarly, you can modify the data type or length of an existing attribute. For example,
-to alter the `home_address` attribute to have a length of 200 characters:
-
-```python
-Student.definition = """
-student_id: int
----
-first_name: varchar(40)
-last_name: varchar(40)
-home_address: varchar(200)
-email: varchar(100)
-"""
-Student.alter()
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/design/diagrams.md b/docs/src/design/diagrams.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 826f78926..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/diagrams.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,110 +0,0 @@
-# Diagrams
-
-Diagrams are a great way to visualize the pipeline and understand the flow
-of data. DataJoint diagrams are based on **entity relationship diagram** (ERD).
-Objects of type `dj.Diagram` allow visualizing portions of the data pipeline in
-graphical form.
-Tables are depicted as nodes and [dependencies](./tables/dependencies.md) as directed
-edges between them.
-The `draw` method plots the graph.
-
-## Diagram notation
-
-Consider the following diagram
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-DataJoint uses the following conventions:
-
-- Tables are indicated as nodes in the graph.
- The corresponding class name is indicated by each node.
-- [Data tiers](./tables/tiers.md) are indicated as colors and symbols:
- - Lookup=gray rectangle
- - Manual=green rectangle
- - Imported=blue oval
- - Computed=red circle
- - Part=black text
- The names of [part tables](./tables/master-part.md) are indicated in a smaller font.
-- [Dependencies](./tables/dependencies.md) are indicated as edges in the graph and
-always directed downward, forming a **directed acyclic graph**.
-- Foreign keys contained within the primary key are indicated as solid lines.
- This means that the referenced table becomes part of the primary key of the dependent table.
-- Foreign keys that are outside the primary key are indicated by dashed lines.
-- If the primary key of the dependent table has no other attributes besides the foreign
-key, the foreign key is a thick solid line, indicating a 1:{0,1} relationship.
-- Foreign keys made without renaming the foreign key attributes are in black whereas
-foreign keys that rename the attributes are indicated in red.
-
-## Diagramming an entire schema
-
-To plot the Diagram for an entire schema, an Diagram object can be initialized with the
-schema object (which is normally used to decorate table objects)
-
-```python
-import datajoint as dj
-schema = dj.Schema('my_database')
-dj.Diagram(schema).draw()
-```
-
-or alternatively an object that has the schema object as an attribute, such as the
-module defining a schema:
-
-```python
-import datajoint as dj
-import seq # import the sequence module defining the seq database
-dj.Diagram(seq).draw() # draw the Diagram
-```
-
-Note that calling the `.draw()` method is not necessary when working in a Jupyter
-notebook.
-You can simply let the object display itself, for example by entering `dj.Diagram(seq)`
-in a notebook cell.
-The Diagram will automatically render in the notebook by calling its `_repr_html_`
-method.
-A Diagram displayed without `.draw()` will be rendered as an SVG, and hovering the
-mouse over a table will reveal a compact version of the output of the `.describe()`
-method.
-
-### Initializing with a single table
-
-A `dj.Diagram` object can be initialized with a single table.
-
-```python
-dj.Diagram(seq.Genome).draw()
-```
-
-A single node makes a rather boring graph but ERDs can be added together or subtracted
-from each other using graph algebra.
-
-### Adding diagrams together
-
-However two graphs can be added, resulting in new graph containing the union of the
-sets of nodes from the two original graphs.
-The corresponding foreign keys will be automatically
-
-```python
-# plot the Diagram with tables Genome and Species from module seq.
-(dj.Diagram(seq.Genome) + dj.Diagram(seq.Species)).draw()
-```
-
-### Expanding diagrams upstream and downstream
-
-Adding a number to an Diagram object adds nodes downstream in the pipeline while
-subtracting a number from Diagram object adds nodes upstream in the pipeline.
-
-Examples:
-
-```python
-# Plot all the tables directly downstream from `seq.Genome`
-(dj.Diagram(seq.Genome)+1).draw()
-```
-
-```python
-# Plot all the tables directly upstream from `seq.Genome`
-(dj.Diagram(seq.Genome)-1).draw()
-```
-
-```python
-# Plot the local neighborhood of `seq.Genome`
-(dj.Diagram(seq.Genome)+1-1+1-1).draw()
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/design/drop.md b/docs/src/design/drop.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 35a9ac513..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/drop.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
-# Drop
-
-The `drop` method completely removes a table from the database, including its
-definition.
-It also removes all dependent tables, recursively.
-DataJoint will first display the tables being dropped and the number of entities in
-each before prompting the user for confirmation to proceed.
-
-The `drop` method is often used during initial design to allow altered table
-definitions to take effect.
-
-```python
-# drop the Person table from its schema
-Person.drop()
-```
-
-## Dropping part tables
-
-A [part table](../design/tables/master-part.md) is usually removed as a consequence of
-calling `drop` on its master table.
-To enforce this workflow, calling `drop` directly on a part table produces an error.
-In some cases, it may be necessary to override this behavior.
-To remove a part table without removing its master, use the argument `force=True`.
diff --git a/docs/src/design/integrity.md b/docs/src/design/integrity.md
deleted file mode 100644
index cb7122755..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/integrity.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,218 +0,0 @@
-# Data Integrity
-
-The term **data integrity** describes guarantees made by the data management process
-that prevent errors and corruption in data due to technical failures and human errors
-arising in the course of continuous use by multiple agents.
-DataJoint pipelines respect the following forms of data integrity: **entity
-integrity**, **referential integrity**, and **group integrity** as described in more
-detail below.
-
-## Entity integrity
-
-In a proper relational design, each table represents a collection of discrete
-real-world entities of some kind.
-**Entity integrity** is the guarantee made by the data management process that entities
-from the real world are reliably and uniquely represented in the database system.
-Entity integrity states that the data management process must prevent duplicate
-representations or misidentification of entities.
-DataJoint enforces entity integrity through the use of
-[primary keys](./tables/primary.md).
-
-Entity integrity breaks down when a process allows data pertaining to the same
-real-world entity to be entered into the database system multiple times.
-For example, a school database system may use unique ID numbers to distinguish students.
-Suppose the system automatically generates an ID number each time a student record is
-entered into the database without checking whether a record already exists for that
-student.
-Such a system violates entity integrity, because the same student may be assigned
-multiple ID numbers.
-The ID numbers succeed in uniquely identifying each student record but fail to do so
-for the actual students.
-
-Note that a database cannot guarantee or enforce entity integrity by itself.
-Entity integrity is a property of the entire data management process as a whole,
-including institutional practices and user actions in addition to database
-configurations.
-
-## Referential integrity
-
-**Referential integrity** is the guarantee made by the data management process that
-related data across the database remain present, correctly associated, and mutually
-consistent.
-Guaranteeing referential integrity means enforcing the constraint that no entity can
-exist in the database without all the other entities on which it depends.
-Referential integrity cannot exist without entity integrity: references to entity
-cannot be validated if the identity of the entity itself is not guaranteed.
-
-Referential integrity fails when a data management process allows new data to be
-entered that refers to other data missing from the database.
-For example, assume that each electrophysiology recording must refer to the mouse
-subject used during data collection.
-Perhaps an experimenter attempts to insert ephys data into the database that refers to
-a nonexistent mouse, due to a misspelling.
-A system guaranteeing referential integrity, such as DataJoint, will refuse the
-erroneous data.
-
-Enforcement of referential integrity does not stop with data ingest.
-[Deleting](../manipulation/delete.md) data in DataJoint also deletes any dependent
-downstream data.
-Such cascading deletions are necessary to maintain referential integrity.
-Consider the deletion of a mouse subject without the deletion of the experimental
-sessions involving that mouse.
-A database that allows such deletion will break referential integrity, as the
-experimental sessions for the removed mouse depend on missing data.
-Any data management process that allows data to be deleted with no consideration of
-dependent data cannot maintain referential integrity.
-
-[Updating](../manipulation/update.md) data already present in a database system also
-jeopardizes referential integrity.
-For this reason, the DataJoint workflow does not include updates to entities once they
-have been ingested into a pipeline.
-Allowing updates to upstream entities would break the referential integrity of any
-dependent data downstream.
-For example, permitting a user to change the name of a mouse subject would invalidate
-any experimental sessions that used that mouse, presuming the mouse name was part of
-the primary key.
-The proper way to change data in DataJoint is to delete the existing entities and to
-insert corrected ones, preserving referential integrity.
-
-## Group integrity
-
-**Group integrity** denotes the guarantee made by the data management process that
-entities composed of multiple parts always appear in their complete form.
-Group integrity in DataJoint is formalized through
-[master-part](./tables/master-part.md) relationships.
-The master-part relationship has important implications for dependencies, because a
-downstream entity depending on a master entity set may be considered to depend on the
-parts as well.
-
-## Relationships
-
-In DataJoint, the term **relationship** is used rather generally to describe the
-effects of particular configurations of [dependencies](./tables/dependencies.md)
-between multiple entity sets.
-It is often useful to classify relationships as one-to-one, many-to-one, one-to-many,
-and many-to-many.
-
-In a **one-to-one relationship**, each entity in a downstream table has exactly one
-corresponding entity in the upstream table.
-A dependency of an entity set containing the death dates of mice on an entity set
-describing the mice themselves would obviously be a one-to-one relationship, as in the
-example below.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Mouse(dj.Manual):
-definition = """
-mouse_name : varchar(64)
----
-mouse_dob : datetime
-"""
-
-@schema
-class MouseDeath(dj.Manual):
-definition = """
--> Mouse
----
-death_date : datetime
-"""
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-In a **one-to-many relationship**, multiple entities in a downstream table may depend
-on the same entity in the upstream table.
-The example below shows a table containing individual channel data from multi-channel
-recordings, representing a one-to-many relationship.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class EEGRecording(dj.Manual):
-definition = """
--> Session
-eeg_recording_id : int
----
-eeg_system : varchar(64)
-num_channels : int
-"""
-
-@schema
-class ChannelData(dj.Imported):
-definition = """
--> EEGRecording
-channel_idx : int
----
-channel_data : longblob
-"""
-```
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-In a **many-to-one relationship**, each entity in a table is associated with multiple
-entities from another table.
-Many-to-one relationships between two tables are usually established using a separate
-membership table.
-The example below includes a table of mouse subjects, a table of subject groups, and a
-membership [part table](./tables/master-part.md) listing the subjects in each group.
-A many-to-one relationship exists between the `Mouse` table and the `SubjectGroup`
-table, with is expressed through entities in `GroupMember`.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Mouse(dj.Manual):
-definition = """
-mouse_name : varchar(64)
----
-mouse_dob : datetime
-"""
-
-@schema
-class SubjectGroup(dj.Manual):
-definition = """
-group_number : int
----
-group_name : varchar(64)
-"""
-
-class GroupMember(dj.Part):
- definition = """
- -> master
- -> Mouse
- """
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-In a **many-to-many relationship**, multiple entities in one table may each relate to
-multiple entities in another upstream table.
-Many-to-many relationships between two tables are usually established using a separate
-association table.
-Each entity in the association table links one entity from each of the two upstream
-tables it depends on.
-The below example of a many-to-many relationship contains a table of recording
-modalities and a table of multimodal recording sessions.
-Entities in a third table represent the modes used for each session.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class RecordingModality(dj.Lookup):
-definition = """
-modality : varchar(64)
-"""
-
-@schema
-class MultimodalSession(dj.Manual):
-definition = """
--> Session
-modes : int
-"""
-class SessionMode(dj.Part):
- definition = """
- -> master
- -> RecordingModality
- """
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-The types of relationships between entity sets are expressed in the
-[Diagram](diagrams.md) of a schema.
diff --git a/docs/src/design/normalization.md b/docs/src/design/normalization.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 000028396..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/normalization.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
-# Entity Normalization
-
-DataJoint uses a uniform way of representing any data.
-It does so in the form of **entity sets**, unordered collections of entities of the
-same type.
-The term **entity normalization** describes the commitment to represent all data as
-well-formed entity sets.
-Entity normalization is a conceptual refinement of the
-[relational data model](../concepts/data-model.md) and is the central principle of the
-DataJoint model ([Yatsenko et al., 2018](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11104)).
-Entity normalization leads to clear and logical database designs and to easily
-comprehensible data queries.
-
-Entity sets are a type of **relation**
-(from the [relational data model](../concepts/data-model.md)) and are often visualized
-as **tables**.
-Hence the terms **relation**, **entity set**, and **table** can be used interchangeably
-when entity normalization is assumed.
-
-## Criteria of a well-formed entity set
-
-1. All elements of an entity set belong to the same well-defined and readily identified
-**entity type** from the model world.
-2. All attributes of an entity set are applicable directly to each of its elements,
-although some attribute values may be missing (set to null).
-3. All elements of an entity set must be distinguishable form each other by the same
-primary key.
-4. Primary key attribute values cannot be missing, i.e. set to null.
-5. All elements of an entity set participate in the same types of relationships with
-other entity sets.
-
-## Entity normalization in schema design
-
-Entity normalization applies to schema design in that the designer is responsible for
-the identification of the essential entity types in their model world and of the
-dependencies among the entity types.
-
-The term entity normalization may also apply to a procedure for refactoring a schema
-design that does not meet the above criteria into one that does.
-In some cases, this may require breaking up some entity sets into multiple entity sets,
-which may cause some entities to be represented across multiple entity sets.
-In other cases, this may require converting attributes into their own entity sets.
-Technically speaking, entity normalization entails compliance with the
-[Boyce-Codd normal form](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boyce%E2%80%93Codd_normal_form)
-while lacking the representational power for the applicability of more complex normal
-forms ([Kent, 1983](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=358054)).
-Adherence to entity normalization prevents redundancies in storage and data
-manipulation anomalies.
-The same criteria originally motivated the formulation of the classical relational
-normal forms.
-
-## Entity normalization in data queries
-
-Entity normalization applies to data queries as well.
-DataJoint's [query operators](../query/operators.md) are designed to preserve the
-entity normalization of their inputs.
-For example, the outputs of operators [restriction](../query/restrict.md),
-[proj](../query/project.md), and [aggr](../query/aggregation.md) retain the same entity
-type as the (first) input.
-The [join](../query/join.md) operator produces a new entity type comprising the pairing
-of the entity types of its inputs.
-[Universal sets](../query/universals.md) explicitly introduce virtual entity sets when
-necessary to accomplish a query.
-
-## Examples of poor normalization
-
-Design choices lacking entity normalization may lead to data inconsistencies or
-anomalies.
-Below are several examples of poorly normalized designs and their normalized
-alternatives.
-
-### Indirect attributes
-
-All attributes should apply to the entity itself.
-Avoid attributes that actually apply to one of the entity's other attributes.
-For example, consider the table `Author` with attributes `author_name`, `institution`,
-and `institution_address`.
-The attribute `institution_address` should really be held in a separate `Institution`
-table that `Author` depends on.
-
-### Repeated attributes
-
-Avoid tables with repeated attributes of the same category.
-A better solution is to create a separate table that depends on the first (often a
-[part table](../design/tables/master-part.md)), with multiple individual entities
-rather than repeated attributes.
-For example, consider the table `Protocol` that includes the attributes `equipment1`,
-`equipment2`, and `equipment3`.
-A better design would be to create a `ProtocolEquipment` table that links each entity
-in `Protocol` with multiple entities in `Equipment` through
-[dependencies](../design/tables/dependencies.md).
-
-### Attributes that do not apply to all entities
-
-All attributes should be relevant to every entity in a table.
-Attributes that apply only to a subset of entities in a table likely belong in a
-separate table containing only that subset of entities.
-For example, a table `Protocol` should include the attribute `stimulus` only if all
-experiment protocols include stimulation.
-If the not all entities in `Protocol` involve stimulation, then the `stimulus`
-attribute should be moved to a part table that has `Protocol` as its master.
-Only protocols using stimulation will have an entry in this part table.
-
-### Transient attributes
-
-Attributes should be relevant to all entities in a table at all times.
-Attributes that do not apply to all entities should be moved to another dependent table
-containing only the appropriate entities.
-This principle also applies to attributes that have not yet become meaningful for some
-entities or that will not remain meaningful indefinitely.
-For example, consider the table `Mouse` with attributes `birth_date` and `death_date`,
-where `death_date` is set to `NULL` for living mice.
-Since the `death_date` attribute is not meaningful for mice that are still living,
-the proper design would include a separate table `DeceasedMouse` that depends on
-`Mouse`.
-`DeceasedMouse` would only contain entities for dead mice, which improves integrity and
-averts the need for [updates](../manipulation/update.md).
diff --git a/docs/src/design/recall.md b/docs/src/design/recall.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 56226cabd..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/recall.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,207 +0,0 @@
-# Work with Existing Pipelines
-
-## Loading Classes
-
-This section describes how to work with database schemas without access to the
-original code that generated the schema. These situations often arise when the
-database is created by another user who has not shared the generating code yet
-or when the database schema is created from a programming language other than
-Python.
-
-```python
-import datajoint as dj
-```
-
-### Working with schemas and their modules
-
-Typically a DataJoint schema is created as a dedicated Python module. This
-module defines a schema object that is used to link classes declared in the
-module to tables in the database schema. As an example, examine the university
-module: [university.py](https://github.com/datajoint-company/db-programming-with-datajoint/blob/master/notebooks/university.py).
-
-You may then import the module to interact with its tables:
-
-```python
-import university as uni
-dj.Diagram(uni)
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-Note that dj.Diagram can extract the diagram from a schema object or from a
-Python module containing its schema object, lending further support to the
-convention of one-to-one correspondence between database schemas and Python
-modules in a DataJoint project:
-
-`dj.Diagram(uni)`
-
-is equivalent to
-
-`dj.Diagram(uni.schema)`
-
-```python
-# students without majors
-uni.Student - uni.StudentMajor
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-### Spawning missing classes
-
-Now imagine that you do not have access to `university.py` or you do not have
-its latest version. You can still connect to the database schema but you will
-not have classes declared to interact with it.
-
-So let's start over in this scenario.
-
-You may use the `dj.list_schemas` function (new in DataJoint 0.12.0) to
-list the names of database schemas available to you.
-
-```python
-import datajoint as dj
-dj.list_schemas()
-```
-
-```text
-*['dimitri_alter','dimitri_attach','dimitri_blob','dimitri_blobs',
-'dimitri_nphoton','dimitri_schema','dimitri_university','dimitri_uuid',
-'university']*
-```
-
-Just as with a new schema, we start by creating a schema object to connect to
-the chosen database schema:
-
-```python
-schema = dj.Schema('dimitri_university')
-```
-
-If the schema already exists, `dj.Schema` is initialized as usual and you may plot
-the schema diagram. But instead of seeing class names, you will see the raw
-table names as they appear in the database.
-
-```python
-# let's plot its diagram
-dj.Diagram(schema)
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-You may view the diagram but, at this point, there is no way to interact with
-these tables. A similar situation arises when another developer has added new
-tables to the schema but has not yet shared the updated module code with you.
-Then the diagram will show a mixture of class names and database table names.
-
-Now you may use the `spawn_missing_classes` method to spawn classes into
-the local namespace for any tables missing their classes:
-
-```python
-schema.spawn_missing_classes()
-dj.Diagram(schema)
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-Now you may interact with these tables as if they were declared right here in
-this namespace:
-
-```python
-# students without majors
-Student - StudentMajor
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-### Creating a virtual module
-
-Virtual modules provide a way to access the classes corresponding to tables in a
-DataJoint schema without having to create local files.
-
-`spawn_missing_classes` creates the new classes in the local namespace.
-However, it is often more convenient to import a schema with its Python module,
-equivalent to the Python command:
-
-```python
-import university as uni
-```
-
-We can mimic this import without having access to `university.py` using the
-`VirtualModule` class object:
-
-```python
-import datajoint as dj
-
-uni = dj.VirtualModule(module_name='university.py', schema_name='dimitri_university')
-```
-
-Now `uni` behaves as an imported module complete with the schema object and all
-the table classes.
-
-```python
-dj.Diagram(uni)
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-```python
-uni.Student - uni.StudentMajor
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-`dj.VirtualModule` takes required arguments
-
-- `module_name`: displayed module name.
-
-- `schema_name`: name of the database in MySQL.
-
-And `dj.VirtualModule` takes optional arguments.
-
-First, `create_schema=False` assures that an error is raised when the schema
-does not already exist. Set it to `True` if you want to create an empty schema.
-
-```python
-dj.VirtualModule('what', 'nonexistent')
-```
-
-Returns
-
-```python
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
-DataJointError Traceback (most recent call last)
-.
-.
-.
-DataJointError: Database named `nonexistent` was not defined. Set argument create_schema=True to create it.
-```
-
-The other optional argument, `create_tables=False` is passed to the schema
-object. It prevents the use of the schema object of the virtual module for
-creating new tables in the existing schema. This is a precautionary measure
-since virtual modules are often used for completed schemas. You may set this
-argument to `True` if you wish to add new tables to the existing schema. A
-more common approach in this scenario would be to create a new schema object and
-to use the `spawn_missing_classes` function to make the classes available.
-
-However, you if do decide to create new tables in an existing tables using the
-virtual module, you may do so by using the schema object from the module as the
-decorator for declaring new tables:
-
-```python
-uni = dj.VirtualModule('university.py', 'dimitri_university', create_tables=True)
-```
-
-```python
-@uni.schema
-class Example(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- -> uni.Student
- ---
- example : varchar(255)
- """
-```
-
-```python
-dj.Diagram(uni)
-```
-
-{: style="align:center"}
diff --git a/docs/src/design/schema.md b/docs/src/design/schema.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 94bf6cdcc..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/schema.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
-# Schema Creation
-
-## Schemas
-
-On the database server, related tables are grouped into a named collection called a **schema**.
-This grouping organizes the data and allows control of user access.
-A database server may contain multiple schemas each containing a subset of the tables.
-A single pipeline may comprise multiple schemas.
-Tables are defined within a schema, so a schema must be created before the creation of
-any tables.
-
-By convention, the `datajoint` package is imported as `dj`.
- The documentation refers to the package as `dj` throughout.
-
-Create a new schema using the `dj.Schema` class object:
-
-```python
-import datajoint as dj
-schema = dj.Schema('alice_experiment')
-```
-
-This statement creates the database schema `alice_experiment` on the server.
-
-The returned object `schema` will then serve as a decorator for DataJoint classes, as
-described in [table declaration syntax](./tables/declare.md).
-
-It is a common practice to have a separate Python module for each schema.
-Therefore, each such module has only one `dj.Schema` object defined and is usually
-named `schema`.
-
-The `dj.Schema` constructor can take a number of optional parameters after the schema
-name.
-
-- `context` - Dictionary for looking up foreign key references.
- Defaults to `None` to use local context.
-- `connection` - Specifies the DataJoint connection object.
- Defaults to `dj.conn()`.
-- `create_schema` - When `False`, the schema object will not create a schema on the
-database and will raise an error if one does not already exist.
- Defaults to `True`.
-- `create_tables` - When `False`, the schema object will not create tables on the
-database and will raise errors when accessing missing tables.
- Defaults to `True`.
-
-## Working with existing data
-
-See the chapter [recall](recall.md) for how to work with data in
-existing pipelines, including accessing a pipeline from one language when the pipeline
-was developed using another.
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/attach.md b/docs/src/design/tables/attach.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c4950ffdf..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/attach.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-# External Data
-
-## File Attachment Datatype
-
-### Configuration & Usage
-
-Corresponding to issue
-[#480](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/480),
-the `attach` attribute type allows users to `attach` files into DataJoint
-schemas as DataJoint-managed files. This is in contrast to traditional `blobs`
-which are encodings of programming language data structures such as arrays.
-
-The functionality is modeled after email attachments, where users `attach`
-a file along with a message and message recipients have access to a
-copy of that file upon retrieval of the message.
-
-For DataJoint `attach` attributes, DataJoint will copy the input
-file into a DataJoint store, hash the file contents, and track
-the input file name. Subsequent `fetch` operations will transfer a
-copy of the file to the local directory of the Python process and
-return a pointer to it's location for subsequent client usage. This
-allows arbitrary files to be `uploaded` or `attached` to a DataJoint
-schema for later use in processing. File integrity is preserved by
-checksum comparison against the attachment data and verifying the contents
-during retrieval.
-
-For example, given a `localattach` store:
-
-```python
-dj.config['stores'] = {
- 'localattach': {
- 'protocol': 'file',
- 'location': '/data/attach'
- }
-}
-```
-
-A `ScanAttachment` table can be created:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class ScanAttachment(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- -> Session
- ---
- scan_image: attach@localattach # attached image scans
- """
-```
-
-Files can be added using an insert pointing to the source file:
-
-```python
->>> ScanAttachment.insert1((0, '/input/image0.tif'))
-```
-
-And then retrieved to the current directory using `fetch`:
-
-```python
->>> s0 = (ScanAttachment & {'session_id': 0}).fetch1()
->>> s0
-{'session_id': 0, 'scan_image': './image0.tif'}
->>> fh = open(s0['scan_image'], 'rb')
->>> fh
-<_io.BufferedReader name='./image0.tif')
-```
-
-
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/attributes.md b/docs/src/design/tables/attributes.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0c2e7a8f9..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/attributes.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-# Datatypes
-
-DataJoint supports the following datatypes.
-To conserve database resources, use the smallest and most restrictive datatype
-sufficient for your data.
-This also ensures that only valid data are entered into the pipeline.
-
-## Most common datatypes
-
-- `tinyint`: an 8-bit integer number, ranging from -128 to 127.
-- `tinyint unsigned`: an 8-bit positive integer number, ranging from 0 to 255.
-- `smallint`: a 16-bit integer number, ranging from -32,768 to 32,767.
-- `smallint unsigned`: a 16-bit positive integer, ranging from 0 to 65,535.
-- `int`: a 32-bit integer number, ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
-- `int unsigned`: a 32-bit positive integer, ranging from 0 to 4,294,967,295.
-- `enum`: one of several explicitly enumerated values specified as strings.
- Use this datatype instead of text strings to avoid spelling variations and to save
- storage space.
- For example, the datatype for an anesthesia attribute could be
- `enum("urethane", "isoflurane", "fentanyl")`.
- Do not use enums in primary keys due to the difficulty of changing their definitions
- consistently in multiple tables.
-
-- `date`: date as `'YYYY-MM-DD'`.
-- `time`: time as `'HH:MM:SS'`.
-- `datetime`: Date and time to the second as `'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'`
-- `timestamp`: Date and time to the second as `'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'`.
- The default value may be set to `CURRENT_TIMESTAMP`.
- Unlike `datetime`, a `timestamp` value will be adjusted to the local time zone.
-
-- `char(N)`: a character string up to *N* characters (but always takes the entire *N*
-bytes to store).
-- `varchar(N)`: a text string of arbitrary length up to *N* characters that takes
-*M+1* or *M+2* bytes of storage, where *M* is the actual length of each stored string.
-- `float`: a single-precision floating-point number.
- Takes 4 bytes.
- Single precision is sufficient for many measurements.
-
-- `double`: a double-precision floating-point number.
- Takes 8 bytes.
- Because equality comparisons are error-prone, neither `float` nor `double` should be
- used in primary keys.
-- `decimal(N,F)`: a fixed-point number with *N* total decimal digits and *F*
-fractional digits.
- This datatype is well suited to represent numbers whose magnitude is well defined
- and does not warrant the use of floating-point representation or requires precise
- decimal representations (e.g. dollars and cents).
- Because of its well-defined precision, `decimal` values can be used in equality
- comparison and be included in primary keys.
-
-- `longblob`: arbitrary numeric array (e.g. matrix, image, structure), up to 4
-[GiB](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gibibyte) in size.
- Numeric arrays are compatible between MATLAB and Python (NumPy).
- The `longblob` and other `blob` datatypes can be configured to store data
- [externally](../../sysadmin/external-store.md) by using the `blob@store` syntax.
-
-## Less common (but supported) datatypes
-
-- `decimal(N,F) unsigned`: same as `decimal`, but limited to nonnegative values.
-- `mediumint` a 24-bit integer number, ranging from -8,388,608 to 8,388,607.
-- `mediumint unsigned`: a 24-bit positive integer, ranging from 0 to 16,777,216.
-- `mediumblob`: arbitrary numeric array, up to 16
-[MiB](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mibibyte)
-- `blob`: arbitrary numeric array, up to 64
-[KiB](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kibibyte)
-- `tinyblob`: arbitrary numeric array, up to 256 bytes (actually smaller due to header
-info).
-
-## Special DataJoint-only datatypes
-
-These types abstract certain kinds of non-database data to facilitate use
-together with DataJoint.
-
-- `attach`: a [file attachment](attach.md) similar to email attachments facillitating
-sending/receiving an opaque data file to/from a DataJoint pipeline.
-
-- `filepath@store`: a [filepath](filepath.md) used to link non-DataJoint managed files
-into a DataJoint pipeline.
-
-## Datatypes not (yet) supported
-
-- `binary`
-- `text`
-- `longtext`
-- `bit`
-
-For additional information about these datatypes, see
-http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/data-types.html
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/blobs.md b/docs/src/design/tables/blobs.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9f73d54d4..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/blobs.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
-# Blobs
-
-DataJoint provides functionality for serializing and deserializing complex data types
-into binary blobs for efficient storage and compatibility with MATLAB's mYm
-serialization. This includes support for:
-
-+ Basic Python data types (e.g., integers, floats, strings, dictionaries).
-+ NumPy arrays and scalars.
-+ Specialized data types like UUIDs, decimals, and datetime objects.
-
-## Serialization and Deserialization Process
-
-Serialization converts Python objects into a binary representation for efficient storage
-within the database. Deserialization converts the binary representation back into the
-original Python object.
-
-Blobs over 1 KiB are compressed using the zlib library to reduce storage requirements.
-
-## Supported Data Types
-
-DataJoint supports the following data types for serialization:
-
-+ Scalars: Integers, floats, booleans, strings.
-+ Collections: Lists, tuples, sets, dictionaries.
-+ NumPy: Arrays, structured arrays, and scalars.
-+ Custom Types: UUIDs, decimals, datetime objects, MATLAB cell and struct arrays.
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/customtype.md b/docs/src/design/tables/customtype.md
deleted file mode 100644
index aad194ff5..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/customtype.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-# Custom Types
-
-In modern scientific research, data pipelines often involve complex workflows that
-generate diverse data types. From high-dimensional imaging data to machine learning
-models, these data types frequently exceed the basic representations supported by
-traditional relational databases. For example:
-
-+ A lab working on neural connectivity might use graph objects to represent brain
- networks.
-+ Researchers processing raw imaging data might store custom objects for pre-processing
- configurations.
-+ Computational biologists might store fitted machine learning models or parameter
- objects for downstream predictions.
-
-To handle these diverse needs, DataJoint provides the `dj.AttributeAdapter` method. It
-enables researchers to store and retrieve complex, non-standard data types—like Python
-objects or data structures—in a relational database while maintaining the
-reproducibility, modularity, and query capabilities required for scientific workflows.
-
-## Uses in Scientific Research
-
-Imagine a neuroscience lab studying neural connectivity. Researchers might generate
-graphs (e.g., networkx.Graph) to represent connections between brain regions, where:
-
-+ Nodes are brain regions.
-+ Edges represent connections weighted by signal strength or another metric.
-
-Storing these graph objects in a database alongside other experimental data (e.g.,
-subject metadata, imaging parameters) ensures:
-
-1. Centralized Data Management: All experimental data and analysis results are stored
- together for easy access and querying.
-2. Reproducibility: The exact graph objects used in analysis can be retrieved later for
- validation or further exploration.
-3. Scalability: Graph data can be integrated into workflows for larger datasets or
- across experiments.
-
-However, since graphs are not natively supported by relational databases, here’s where
-`dj.AttributeAdapter` becomes essential. It allows researchers to define custom logic for
-serializing graphs (e.g., as edge lists) and deserializing them back into Python
-objects, bridging the gap between advanced data types and the database.
-
-### Example: Storing Graphs in DataJoint
-
-To store a networkx.Graph object in a DataJoint table, researchers can define a custom
-attribute type in a datajoint table class:
-
-```python
-import datajoint as dj
-
-class GraphAdapter(dj.AttributeAdapter):
-
- attribute_type = 'longblob' # this is how the attribute will be declared
-
- def put(self, obj):
- # convert the nx.Graph object into an edge list
- assert isinstance(obj, nx.Graph)
- return list(obj.edges)
-
- def get(self, value):
- # convert edge list back into an nx.Graph
- return nx.Graph(value)
-
-
-# instantiate for use as a datajoint type
-graph = GraphAdapter()
-
-
-# define a table with a graph attribute
-schema = dj.schema('test_graphs')
-
-
-@schema
-class Connectivity(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- conn_id : int
- ---
- conn_graph = null : # a networkx.Graph object
- """
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/declare.md b/docs/src/design/tables/declare.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d4fb070a2..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/declare.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,242 +0,0 @@
-# Declaration Syntax
-
-## Creating Tables
-
-### Classes represent tables
-
-To make it easy to work with tables in MATLAB and Python, DataJoint programs create a
-separate class for each table.
-Computer programmers refer to this concept as
-[object-relational mapping](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Object-relational_mapping).
-For example, the class `experiment.Subject` in the DataJoint client language may
-correspond to the table called `subject` on the database server.
-Users never need to see the database directly; they only interact with data in the
-database by creating and interacting with DataJoint classes.
-
-#### Data tiers
-
-The table class must inherit from one of the following superclasses to indicate its
-data tier: `dj.Lookup`, `dj.Manual`, `dj.Imported`, `dj.Computed`, or `dj.Part`.
-See [tiers](tiers.md) and [master-part](./master-part.md).
-
-### Defining a table
-
-To define a DataJoint table in Python:
-
-1. Define a class inheriting from the appropriate DataJoint class: `dj.Lookup`,
-`dj.Manual`, `dj.Imported` or `dj.Computed`.
-
-2. Decorate the class with the schema object (see [schema](../schema.md))
-
-3. Define the class property `definition` to define the table heading.
-
-For example, the following code defines the table `Person`:
-
-```python
-import datajoint as dj
-schema = dj.Schema('alice_experiment')
-
-@schema
-class Person(dj.Manual):
- definition = '''
- username : varchar(20) # unique user name
- ---
- first_name : varchar(30)
- last_name : varchar(30)
- '''
-```
-
-The `@schema` decorator uses the class name and the data tier to check whether an
-appropriate table exists on the database.
-If a table does not already exist, the decorator creates one on the database using the
-definition property.
-The decorator attaches the information about the table to the class, and then returns
-the class.
-
-The class will become usable after you define the `definition` property as described in
-[Table definition](#table-definition).
-
-#### DataJoint classes in Python
-
-DataJoint for Python is implemented through the use of classes providing access to the
-actual tables stored on the database.
-Since only a single table exists on the database for any class, interactions with all
-instances of the class are equivalent.
-As such, most methods can be called on the classes themselves rather than on an object,
-for convenience.
-Whether calling a DataJoint method on a class or on an instance, the result will only
-depend on or apply to the corresponding table.
-All of the basic functionality of DataJoint is built to operate on the classes
-themselves, even when called on an instance.
-For example, calling `Person.insert(...)` (on the class) and `Person.insert(...)` (on
-an instance) both have the identical effect of inserting data into the table on the
-database server.
-DataJoint does not prevent a user from working with instances, but the workflow is
-complete without the need for instantiation.
-It is up to the user whether to implement additional functionality as class methods or
-methods called on instances.
-
-### Valid class names
-
-Note that in both MATLAB and Python, the class names must follow the CamelCase compound
-word notation:
-
-- start with a capital letter and
-- contain only alphanumerical characters (no underscores).
-
-Examples of valid class names:
-
-`TwoPhotonScan`, `Scan2P`, `Ephys`, `MembraneVoltage`
-
-Invalid class names:
-
-`Two_photon_Scan`, `twoPhotonScan`, `2PhotonScan`, `membranePotential`, `membrane_potential`
-
-## Table Definition
-
-DataJoint models data as sets of **entities** with shared **attributes**, often
-visualized as tables with rows and columns.
-Each row represents a single entity and the values of all of its attributes.
-Each column represents a single attribute with a name and a datatype, applicable to
-entity in the table.
-Unlike rows in a spreadsheet, entities in DataJoint don't have names or numbers: they
-can only be identified by the values of their attributes.
-Defining a table means defining the names and datatypes of the attributes as well as
-the constraints to be applied to those attributes.
-Both MATLAB and Python use the same syntax define tables.
-
-For example, the following code in defines the table `User`, that contains users of the
-database:
-
-The table definition is contained in the `definition` property of the class.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class User(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- # database users
- username : varchar(20) # unique user name
- ---
- first_name : varchar(30)
- last_name : varchar(30)
- role : enum('admin', 'contributor', 'viewer')
- """
-```
-
-This defines the class `User` that creates the table in the database and provides all
-its data manipulation functionality.
-
-### Table creation on the database server
-
-Users do not need to do anything special to have a table created in the database.
-Tables are created at the time of class definition.
-In fact, table creation on the database is one of the jobs performed by the decorator
-`@schema` of the class.
-
-### Changing the definition of an existing table
-
-Once the table is created in the database, the definition string has no further effect.
-In other words, changing the definition string in the class of an existing table will
-not actually update the table definition.
-To change the table definition, one must first [drop](../drop.md) the existing table.
-This means that all the data will be lost, and the new definition will be applied to
-create the new empty table.
-
-Therefore, in the initial phases of designing a DataJoint pipeline, it is common to
-experiment with variations of the design before populating it with substantial amounts
-of data.
-
-It is possible to modify a table without dropping it.
-This topic is covered separately.
-
-### Reverse-engineering the table definition
-
-DataJoint objects provide the `describe` method, which displays the table definition
-used to define the table when it was created in the database.
-This definition may differ from the definition string of the class if the definition
-string has been edited after creation of the table.
-
-Examples
-
-```python
-s = lab.User.describe()
-```
-
-## Definition Syntax
-
-The table definition consists of one or more lines.
-Each line can be one of the following:
-
-- The optional first line starting with a `#` provides a description of the table's purpose.
- It may also be thought of as the table's long title.
-- A new attribute definition in any of the following forms (see
-[Attributes](./attributes.md) for valid datatypes):
- ``name : datatype``
- ``name : datatype # comment``
- ``name = default : datatype``
- ``name = default : datatype # comment``
-- The divider `---` (at least three hyphens) separating primary key attributes above
-from secondary attributes below.
-- A foreign key in the format `-> ReferencedTable`.
- (See [Dependencies](dependencies.md).)
-
-For example, the table for Persons may have the following definition:
-
-```python
-# Persons in the lab
-username : varchar(16) # username in the database
----
-full_name : varchar(255)
-start_date : date # date when joined the lab
-```
-
-This will define the table with attributes `username`, `full_name`, and `start_date`,
-in which `username` is the [primary key](primary.md).
-
-### Attribute names
-
-Attribute names must be in lowercase and must start with a letter.
-They can only contain alphanumerical characters and underscores.
-The attribute name cannot exceed 64 characters.
-
-Valid attribute names
- `first_name`, `two_photon_scan`, `scan_2p`, `two_photon_scan`
-
-Invalid attribute names
- `firstName`, `first name`, `2photon_scan`, `two-photon_scan`, `TwoPhotonScan`
-
-Ideally, attribute names should be unique across all tables that are likely to be used
-in queries together.
-For example, tables often have attributes representing the start times of sessions,
-recordings, etc.
-Such attributes must be uniquely named in each table, such as `session_start_time` or
-`recording_start_time`.
-
-### Default values
-
-Secondary attributes can be given default values.
-A default value will be used for an attribute if no other value is given at the time
-the entity is [inserted](../../manipulation/insert.md) into the table.
-Generally, default values are numerical values or character strings.
-Default values for dates must be given as strings as well, contained within quotes
-(with the exception of `CURRENT_TIMESTAMP`).
-Note that default values can only be used when inserting as a mapping.
-Primary key attributes cannot have default values (with the exceptions of
-`auto_increment` and `CURRENT_TIMESTAMP` attributes; see [primary-key](primary.md)).
-
-An attribute with a default value of `NULL` is called a **nullable attribute**.
-A nullable attribute can be thought of as applying to all entities in a table but
-having an optional *value* that may be absent in some entities.
-Nullable attributes should *not* be used to indicate that an attribute is inapplicable
-to some entities in a table (see [normalization](../normalization.md)).
-Nullable attributes should be used sparingly to indicate optional rather than
-inapplicable attributes that still apply to all entities in the table.
-`NULL` is a special literal value and does not need to be enclosed in quotes.
-
-Here are some examples of attributes with default values:
-
-```python
-failures = 0 : int
-due_date = "2020-05-31" : date
-additional_comments = NULL : varchar(256)
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/dependencies.md b/docs/src/design/tables/dependencies.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e06278ee8..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/dependencies.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,241 +0,0 @@
-# Dependencies
-
-## Understanding dependencies
-
-A schema contains collections of tables of related data.
-Accordingly, entities in one table often derive some of their meaning or context from
-entities in other tables.
-A **foreign key** defines a **dependency** of entities in one table on entities in
-another within a schema.
-In more complex designs, dependencies can even exist between entities in tables from
-different schemas.
-Dependencies play a functional role in DataJoint and do not simply label the structure
-of a pipeline.
-Dependencies provide entities in one table with access to data in another table and
-establish certain constraints on entities containing a foreign key.
-
-A DataJoint pipeline, including the dependency relationships established by foreign
-keys, can be visualized as a graph with nodes and edges.
-The diagram of such a graph is called the **entity relationship diagram** or
-[Diagram](../diagrams.md).
-The nodes of the graph are tables and the edges connecting them are foreign keys.
-The edges are directed and the overall graph is a **directed acyclic graph**, a graph
-with no loops.
-
-For example, the Diagram below is the pipeline for multipatching experiments
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-The graph defines the direction of the workflow.
-The tables at the top of the flow need to be populated first, followed by those tables
-one step below and so forth until the last table is populated at the bottom of the
-pipeline.
-The top of the pipeline tends to be dominated by lookup tables (gray stars) and manual
-tables (green squares).
-The middle has many imported tables (blue triangles), and the bottom has computed
-tables (red stars).
-
-## Defining a dependency
-
-Foreign keys are defined with arrows `->` in the [table definition](declare.md),
-pointing to another table.
-
-A foreign key may be defined as part of the [primary-key](primary.md).
-
-In the Diagram, foreign keys from the primary key are shown as solid lines.
-This means that the primary key of the referenced table becomes part of the primary key
-of the new table.
-A foreign key outside the primary key is indicated by dashed line in the ERD.
-
-For example, the following definition for the table `mp.Slice` has three foreign keys,
-including one within the primary key.
-
-```python
-# brain slice
--> mp.Subject
-slice_id : smallint # slice number within subject
----
--> mp.BrainRegion
--> mp.Plane
-slice_date : date # date of the slicing (not patching)
-thickness : smallint unsigned # slice thickness in microns
-experimenter : varchar(20) # person who performed this experiment
-```
-
-You can examine the resulting table heading with
-
-```python
-mp.BrainSlice.heading
-```
-
-The heading of `mp.Slice` may look something like
-
-```python
-subject_id : char(8) # experiment subject id
-slice_id : smallint # slice number within subject
----
-brain_region : varchar(12) # abbreviated name for brain region
-plane : varchar(12) # plane of section
-slice_date : date # date of the slicing (not patching)
-thickness : smallint unsigned # slice thickness in microns
-experimenter : varchar(20) # person who performed this experiment
-```
-
-This displayed heading reflects the actual attributes in the table.
-The foreign keys have been replaced by the primary key attributes of the referenced
-tables, including their data types and comments.
-
-## How dependencies work
-
-The foreign key `-> A` in the definition of table `B` has the following effects:
-
-1. The primary key attributes of `A` are made part of `B`'s definition.
-2. A referential constraint is created in `B` with reference to `A`.
-3. If one does not already exist, an index is created to speed up searches in `B` for
-matches to `A`.
- (The reverse search is already fast because it uses the primary key of `A`.)
-
-A referential constraint means that an entity in `B` cannot exist without a matching
-entity in `A`.
-**Matching** means attributes in `B` that correspond to the primary key of `A` must
-have the same values.
-An attempt to insert an entity into `B` that does not have a matching counterpart in
-`A` will fail.
-Conversely, deleting an entity from `A` that has matching entities in `B` will result
-in the deletion of those matching entities and so forth, recursively, downstream in the
-pipeline.
-
-When `B` references `A` with a foreign key, one can say that `B` **depends** on `A`.
-In DataJoint terms, `B` is the **dependent table** and `A` is the **referenced table**
-with respect to the foreign key from `B` to `A`.
-
-Note to those already familiar with the theory of relational databases: The usage of
-the words "depends" and "dependency" here should not be confused with the unrelated
-concept of *functional dependencies* that is used to define normal forms.
-
-## Referential integrity
-
-Dependencies enforce the desired property of databases known as
-**referential integrity**.
-Referential integrity is the guarantee made by the data management process that related
-data across the database remain present, correctly associated, and mutually consistent.
-Guaranteeing referential integrity means enforcing the constraint that no entity can
-exist in the database without all the other entities on which it depends.
-An entity in table `B` depends on an entity in table `A` when they belong to them or
-are computed from them.
-
-## Dependencies with renamed attributes
-
-In most cases, a dependency includes the primary key attributes of the referenced table
-as they appear in its table definition.
-Sometimes it can be helpful to choose a new name for a foreign key attribute that
-better fits the context of the dependent table.
-DataJoint provides the following [projection](../../query/project.md) syntax to rename
-the primary key attributes when they are included in the new table.
-
-The dependency
-
-```python
--> Table.project(new_attr='old_attr')
-```
-
-renames the primary key attribute `old_attr` of `Table` as `new_attr` before
-integrating it into the table definition.
-Any additional primary key attributes will retain their original names.
-For example, the table `Experiment` may depend on table `User` but rename the `user`
-attribute into `operator` as follows:
-
-```python
--> User.proj(operator='user')
-```
-
-In the above example, an entity in the dependent table depends on exactly one entity in
-the referenced table.
-Sometimes entities may depend on multiple entities from the same table.
-Such a design requires a way to distinguish between dependent attributes having the
-same name in the reference table.
-For example, a table for `Synapse` may reference the table `Cell` twice as
-`presynaptic` and `postsynaptic`.
-The table definition may appear as
-
-```python
-# synapse between two cells
--> Cell.proj(presynaptic='cell_id')
--> Cell.proj(postsynaptic='cell_id')
----
-connection_strength : double # (pA) peak synaptic current
-```
-
-If the primary key of `Cell` is (`animal_id`, `slice_id`, `cell_id`), then the primary
-key of `Synapse` resulting from the above definition will be (`animal_id`, `slice_id`,
-`presynaptic`, `postsynaptic`).
-Projection always returns all of the primary key attributes of a table, so `animal_id`
-and `slice_id` are included, with their original names.
-
-Note that the design of the `Synapse` table above imposes the constraint that the
-synapse can only be found between cells in the same animal and in the same slice.
-
-Allowing representation of synapses between cells from different slices requires the
-renamimg of `slice_id` as well:
-
-```python
-# synapse between two cells
--> Cell(presynaptic_slice='slice_id', presynaptic_cell='cell_id')
--> Cell(postsynaptic_slice='slice_id', postsynaptic_cell='cell_id')
----
-connection_strength : double # (pA) peak synaptic current
-```
-
-In this case, the primary key of `Synapse` will be (`animal_id`, `presynaptic_slice`,
-`presynaptic_cell`, `postsynaptic_slice`, `postsynaptic_cell`).
-This primary key still imposes the constraint that synapses can only form between cells
-within the same animal but now allows connecting cells across different slices.
-
-In the Diagram, renamed foreign keys are shown as red lines with an additional dot node
-in the middle to indicate that a renaming took place.
-
-## Foreign key options
-
-Note: Foreign key options are currently in development.
-
-Foreign keys allow the additional options `nullable` and `unique`, which can be
-inserted in square brackets following the arrow.
-
-For example, in the following table definition
-
-```python
-rig_id : char(4) # experimental rig
----
--> Person
-```
-
-each rig belongs to a person, but the table definition does not prevent one person
-owning multiple rigs.
-With the `unique` option, a person may only appear once in the entire table, which
-means that no one person can own more than one rig.
-
-```python
-rig_id : char(4) # experimental rig
----
--> [unique] Person
-```
-
-With the `nullable` option, a rig may not belong to anyone, in which case the foreign
-key attributes for `Person` are set to `NULL`:
-
-```python
-rig_id : char(4) # experimental rig
----
--> [nullable] Person
-```
-
-Finally with both `unique` and `nullable`, a rig may or may not be owned by anyone and
-each person may own up to one rig.
-
-```python
-rig_id : char(4) # experimental rig
----
--> [unique, nullable] Person
-```
-
-Foreign keys made from the primary key cannot be nullable but may be unique.
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/filepath.md b/docs/src/design/tables/filepath.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 05e9ca744..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/filepath.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
-# Filepath Datatype
-
-Note: Filepath Datatype is available as a preview feature in DataJoint Python v0.12.
-This means that the feature is required to be explicitly enabled. To do so, make sure
-to set the environment variable `FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH=TRUE` prior to use.
-
-## Configuration & Usage
-
-Corresponding to issue
-[#481](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/481),
-the `filepath` attribute type links DataJoint records to files already
-managed outside of DataJoint. This can aid in sharing data with
-other systems such as allowing an image viewer application to
-directly use files from a DataJoint pipeline, or to allow downstream
-tables to reference data which reside outside of DataJoint
-pipelines.
-
-To define a table using the `filepath` datatype, an existing DataJoint
-[store](../../sysadmin/external-store.md) should be created and then referenced in the
-new table definition. For example, given a simple store:
-
-```python
- dj.config['stores'] = {
- 'data': {
- 'protocol': 'file',
- 'location': '/data',
- 'stage': '/data'
- }
- }
-```
-
-we can define an `ScanImages` table as follows:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class ScanImages(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- -> Session
- image_id: int
- ---
- image_path: filepath@data
- """
-```
-
-This table can now be used for tracking paths within the `/data` local directory.
-For example:
-
-```python
->>> ScanImages.insert1((0, 0, '/data/images/image_0.tif'))
->>> (ScanImages() & {'session_id': 0}).fetch1(as_dict=True)
-{'session_id': 0, 'image_id': 0, 'image_path': '/data/images/image_0.tif'}
-```
-
-As can be seen from the example, unlike [blob](blobs.md) records, file
-paths are managed as path locations to the underlying file.
-
-## Integrity Notes
-
-Unlike other data in DataJoint, data in `filepath` records are
-deliberately intended for shared use outside of DataJoint. To help
-ensure integrity of `filepath` records, DataJoint will record a
-checksum of the file data on `insert`, and will verify this checksum
-on `fetch`. However, since the underlying file data may be shared
-with other applications, special care should be taken to ensure
-records stored in `filepath` attributes are not modified outside
-of the pipeline, or, if they are, that records in the pipeline are
-updated accordingly. A safe method of changing `filepath` data is
-as follows:
-
-1. Delete the `filepath` database record.
- This will ensure that any downstream records in the pipeline depending
- on the `filepath` record are purged from the database.
-2. Modify `filepath` data.
-3. Re-insert corresponding the `filepath` record.
- This will add the record back to DataJoint with an updated file checksum.
-4. Compute any downstream dependencies, if needed.
- This will ensure that downstream results dependent on the `filepath`
- record are updated to reflect the newer `filepath` contents.
-
-### Disable Fetch Verification
-
-Note: Skipping the checksum is not recommended as it ensures file integrity i.e.
-downloaded files are not corrupted. With S3 stores, most of the time to complete a
-`.fetch()` is from the file download itself as opposed to evaluating the checksum. This
-option will primarily benefit `filepath` usage connected to a local `file` store.
-
-To disable checksums you can set a threshold in bytes
-for when to stop evaluating checksums like in the example below:
-
-```python
-dj.config["filepath_checksum_size_limit"] = 5 * 1024**3 # Skip for all files greater than 5GiB
-```
-
-The default is `None` which means it will always verify checksums.
-
-
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/indexes.md b/docs/src/design/tables/indexes.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9d8148c36..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/indexes.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-# Indexes
-
-Table indexes are data structures that allow fast lookups by an indexed attribute or
-combination of attributes.
-
-In DataJoint, indexes are created by one of the three mechanisms:
-
-1. Primary key
-2. Foreign key
-3. Explicitly defined indexes
-
-The first two mechanisms are obligatory. Every table has a primary key, which serves as
-an unique index. Therefore, restrictions by a primary key are very fast. Foreign keys
-create additional indexes unless a suitable index already exists.
-
-## Indexes for single primary key tables
-
-Let’s say a mouse in the lab has a lab-specific ID but it also has a separate id issued
-by the animal facility.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Mouse(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- mouse_id : int # lab-specific ID
- ---
- tag_id : int # animal facility ID
- """
-```
-
-In this case, searching for a mouse by `mouse_id` is much faster than by `tag_id`
-because `mouse_id` is a primary key, and is therefore indexed.
-
-To make searches faster on fields other than the primary key or a foreign key, you can
-add a secondary index explicitly.
-
-Regular indexes are declared as `index(attr1, ..., attrN)` on a separate line anywhere in
-the table declaration (below the primary key divide).
-
-Indexes can be declared with unique constraint as `unique index (attr1, ..., attrN)`.
-
-Let’s redeclare the table with a unique index on `tag_id`.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Mouse(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- mouse_id : int # lab-specific ID
- ---
- tag_id : int # animal facility ID
- unique index (tag_id)
- """
-```
-Now, searches with `mouse_id` and `tag_id` are similarly fast.
-
-## Indexes for tables with multiple primary keys
-
-Let’s now imagine that rats in a lab are identified by the combination of `lab_name` and
-`rat_id` in a table `Rat`.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Rat(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- lab_name : char(16)
- rat_id : int unsigned # lab-specific ID
- ---
- date_of_birth = null : date
- """
-```
-Note that despite the fact that `rat_id` is in the index, searches by `rat_id` alone are not
-helped by the index because it is not first in the index. This is similar to searching for
-a word in a dictionary that orders words alphabetically. Searching by the first letters
-of a word is easy but searching by the last few letters of a word requires scanning the
-whole dictionary.
-
-In this table, the primary key is a unique index on the combination `(lab_name, rat_id)`.
-Therefore searches on these attributes or on `lab_name` alone are fast. But this index
-cannot help searches on `rat_id` alone. Similarly, searing by `date_of_birth` requires a
-full-table scan and is inefficient.
-
-To speed up searches by the `rat_id` and `date_of_birth`, we can explicit indexes to
-`Rat`:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Rat2(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- lab_name : char(16)
- rat_id : int unsigned # lab-specific ID
- ---
- date_of_birth = null : date
-
- index(rat_id)
- index(date_of_birth)
- """
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/lookup.md b/docs/src/design/tables/lookup.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 79b2c67ba..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/lookup.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
-# Lookup Tables
-
-Lookup tables contain basic facts that are not specific to an experiment and are fairly
-persistent.
-Their contents are typically small.
-In GUIs, lookup tables are often used for drop-down menus or radio buttons.
-In computed tables, they are often used to specify alternative methods for computations.
-Lookup tables are commonly populated from their `contents` property.
-In a [diagram](../diagrams.md) they are shown in gray.
-The decision of which tables are lookup tables and which are manual can be somewhat
-arbitrary.
-
-The table below is declared as a lookup table with its contents property provided to
-generate entities.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class User(dj.Lookup):
- definition = """
- # users in the lab
- username : varchar(20) # user in the lab
- ---
- first_name : varchar(20) # user first name
- last_name : varchar(20) # user last name
- """
- contents = [
- ['cajal', 'Santiago', 'Cajal'],
- ['hubel', 'David', 'Hubel'],
- ['wiesel', 'Torsten', 'Wiesel']
- ]
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/manual.md b/docs/src/design/tables/manual.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d97b6ce52..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/manual.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
-# Manual Tables
-
-Manual tables are populated during experiments through a variety of interfaces.
-Not all manual information is entered by typing.
-Automated software can enter it directly into the database.
-What makes a manual table manual is that it does not perform any computations within
-the DataJoint pipeline.
-
-The following code defines three manual tables `Animal`, `Session`, and `Scan`:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Animal(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- # information about animal
- animal_id : int # animal id assigned by the lab
- ---
- -> Species
- date_of_birth=null : date # YYYY-MM-DD optional
- sex='' : enum('M', 'F', '') # leave empty if unspecified
- """
-
-@schema
-class Session(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- # Experiment Session
- -> Animal
- session : smallint # session number for the animal
- ---
- session_date : date # YYYY-MM-DD
- -> User
- -> Anesthesia
- -> Rig
- """
-
-@schema
-class Scan(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- # Two-photon imaging scan
- -> Session
- scan : smallint # scan number within the session
- ---
- -> Lens
- laser_wavelength : decimal(5,1) # um
- laser_power : decimal(4,1) # mW
- """
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/master-part.md b/docs/src/design/tables/master-part.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 629bfb8ab..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/master-part.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
-# Master-Part Relationship
-
-Often an entity in one table is inseparably associated with a group of entities in
-another, forming a **master-part** relationship.
-The master-part relationship ensures that all parts of a complex representation appear
-together or not at all.
-This has become one of the most powerful data integrity principles in DataJoint.
-
-As an example, imagine segmenting an image to identify regions of interest.
-The resulting segmentation is inseparable from the ROIs that it produces.
-In this case, the two tables might be called `Segmentation` and `Segmentation.ROI`.
-
-In Python, the master-part relationship is expressed by making the part a nested class
-of the master.
-The part is subclassed from `dj.Part` and does not need the `@schema` decorator.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Segmentation(dj.Computed):
- definition = """ # image segmentation
- -> Image
- """
-
- class ROI(dj.Part):
- definition = """ # Region of interest resulting from segmentation
- -> Segmentation
- roi : smallint # roi number
- ---
- roi_pixels : longblob # indices of pixels
- roi_weights : longblob # weights of pixels
- """
-
- def make(self, key):
- image = (Image & key).fetch1('image')
- self.insert1(key)
- count = itertools.count()
- Segmentation.ROI.insert(
- dict(key, roi=next(count), roi_pixel=roi_pixels, roi_weights=roi_weights)
- for roi_pixels, roi_weights in mylib.segment(image))
-```
-
-## Populating
-
-Master-part relationships can form in any data tier, but DataJoint observes them more
-strictly for auto-populated tables.
-To populate both the master `Segmentation` and the part `Segmentation.ROI`, it is
-sufficient to call the `populate` method of the master:
-
-```python
-Segmentation.populate()
-```
-
-Note that the entities in the master and the matching entities in the part are inserted
-within a single `make` call of the master, which means that they are a processed inside
-a single transactions: either all are inserted and committed or the entire transaction
-is rolled back.
-This ensures that partial results never appear in the database.
-
-For example, imagine that a segmentation is performed, but an error occurs halfway
-through inserting the results.
-If this situation were allowed to persist, then it might appear that 20 ROIs were
-detected where 45 had actually been found.
-
-## Deleting
-
-To delete from a master-part pair, one should never delete from the part tables
-directly.
-The only valid method to delete from a part table is to delete the master.
-This has been an unenforced rule, but upcoming versions of DataJoint will prohibit
-direct deletes from the master table.
-DataJoint's [delete](../../manipulation/delete.md) operation is also enclosed in a
-transaction.
-
-Together, the rules of master-part relationships ensure a key aspect of data integrity:
-results of computations involving multiple components and steps appear in their
-entirety or not at all.
-
-## Multiple parts
-
-The master-part relationship cannot be chained or nested.
-DataJoint does not allow part tables of other part tables per se.
-However, it is common to have a master table with multiple part tables that depend on
-each other.
-For example:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class ArrayResponse(dj.Computed):
-definition = """
-array: int
-"""
-
-class ElectrodeResponse(dj.Part):
-definition = """
--> master
-electrode: int # electrode number on the probe
-"""
-
-class ChannelResponse(dj.Part):
-definition = """
--> ElectrodeResponse
-channel: int
----
-response: longblob # response of a channel
-"""
-```
-
-Conceptually, one or more channels belongs to an electrode, and one or more electrodes
-belong to an array.
-This example assumes that information about an array's response (which consists
-ultimately of the responses of multiple electrodes each consisting of multiple channel
-responses) including it's electrodes and channels are entered together.
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/primary.md b/docs/src/design/tables/primary.md
deleted file mode 100644
index fc4f5b8e0..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/primary.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,178 +0,0 @@
-# Primary Key
-
-## Primary keys in DataJoint
-
-Entities in tables are neither named nor numbered.
-DataJoint does not answer questions of the type "What is the 10th element of this table?"
-Instead, entities are distinguished by the values of their attributes.
-Furthermore, the entire entity is not required for identification.
-In each table, a subset of its attributes are designated to be the **primary key**.
-Attributes in the primary key alone are sufficient to differentiate any entity from any
-other within the table.
-
-Each table must have exactly one
-[primary key](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Primary_key): a subset of its attributes
-that uniquely identify each entity in the table.
-The database uses the primary key to prevent duplicate entries, to relate data across
-tables, and to accelerate data queries.
-The choice of the primary key will determine how you identify entities.
-Therefore, make the primary key **short**, **expressive**, and **persistent**.
-
-For example, mice in our lab are assigned unique IDs.
-The mouse ID number `animal_id` of type `smallint` can serve as the primary key for the
-table `Mice`.
-An experiment performed on a mouse may be identified in the table `Experiments` by two
-attributes: `animal_id` and `experiment_number`.
-
-DataJoint takes the concept of primary keys somewhat more seriously than other models
-and query languages.
-Even **table expressions**, i.e. those tables produced through operations on other
-tables, have a well-defined primary key.
-All operators on tables are designed in such a way that the results always have a
-well-defined primary key.
-
-In all representations of tables in DataJoint, the primary key attributes are always
-listed before other attributes and highlighted for emphasis (e.g. in a **bold** font or
-marked with an asterisk \*)
-
-## Defining a primary key
-
-In table declarations, the primary key attributes always come first and are separated
-from the other attributes with a line containing at least three hyphens.
-For example, the following is the definition of a table containing database users where
-`username` is the primary key.
-
-```python
-# database users
-username : varchar(20) # unique user name
----
-first_name : varchar(30)
-last_name : varchar(30)
-role : enum('admin', 'contributor', 'viewer')
-```
-
-## Entity integrity
-
-The primary key defines and enforces the desired property of databases known as
-[entity integrity](../integrity.md).
-**Entity integrity** ensures that there is a one-to-one and unambiguous mapping between
-real-world entities and their representations in the database system.
-The data management process must prevent any duplication or misidentification of
-entities.
-
-To enforce entity integrity, DataJoint implements several rules:
-
-- Every table must have a primary key.
-- Primary key attributes cannot have default values (with the exception of
-`auto_increment` and `CURRENT_TIMESTAMP`; see below).
-- Operators on tables are defined with respect to the primary key and preserve a
-primary key in their results.
-
-## Datatypes in primary keys
-
-All integer types, dates, timestamps, and short character strings make good primary key
-attributes.
-Character strings are somewhat less suitable because they can be long and because they
-may have invisible trailing spaces.
-Floating-point numbers should be avoided because rounding errors may lead to
-misidentification of entities.
-Enums are okay as long as they do not need to be modified after
-[dependencies](dependencies.md) are already created referencing the table.
-Finally, DataJoint does not support blob types in primary keys.
-
-The primary key may be composite, i.e. comprising several attributes.
-In DataJoint, hierarchical designs often produce tables whose primary keys comprise
-many attributes.
-
-## Choosing primary key attributes
-
-A primary key comprising real-world attributes is a good choice when such real-world
-attributes are already properly and permanently assigned.
-Whatever characteristics are used to uniquely identify the actual entities can be used
-to identify their representations in the database.
-
-If there are no attributes that could readily serve as a primary key, an artificial
-attribute may be created solely for the purpose of distinguishing entities.
-In such cases, the primary key created for management in the database must also be used
-to uniquely identify the entities themselves.
-If the primary key resides only in the database while entities remain indistinguishable
-in the real world, then the process cannot ensure entity integrity.
-When a primary key is created as part of data management rather than based on
-real-world attributes, an institutional process must ensure the uniqueness and
-permanence of such an identifier.
-
-For example, the U.S. government assigns every worker an identifying attribute, the
-social security number.
-However, the government must go to great lengths to ensure that this primary key is
-assigned exactly once, by checking against other less convenient candidate keys (i.e.
-the combination of name, parents' names, date of birth, place of birth, etc.).
-Just like the SSN, well managed primary keys tend to get institutionalized and find
-multiple uses.
-
-Your lab must maintain a system for uniquely identifying important entities.
-For example, experiment subjects and experiment protocols must have unique IDs.
-Use these as the primary keys in the corresponding tables in your DataJoint databases.
-
-### Using hashes as primary keys
-
-Some tables include too many attributes in their primary keys.
-For example, the stimulus condition in a psychophysics experiment may have a dozen
-parameters such that a change in any one of them makes a different valid stimulus
-condition.
-In such a case, all the attributes would need to be included in the primary key to
-ensure entity integrity.
-However, long primary keys make it difficult to reference individual entities.
-To be most useful, primary keys need to be relatively short.
-
-This problem is effectively solved through the use of a hash of all the identifying
-attributes as the primary key.
-For example, MD5 or SHA-1 hash algorithms can be used for this purpose.
-To keep their representations human-readable, they may be encoded in base-64 ASCII.
-For example, the 128-bit MD5 hash can be represented by 21 base-64 ASCII characters,
-but for many applications, taking the first 8 to 12 characters is sufficient to avoid
-collisions.
-
-### `auto_increment`
-
-Some entities are created by the very action of being entered into the database.
-The action of entering them into the database gives them their identity.
-It is impossible to duplicate them since entering the same thing twice still means
-creating two distinct entities.
-
-In such cases, the use of an auto-incremented primary key is warranted.
-These are declared by adding the word `auto_increment` after the data type in the
-declaration.
-The datatype must be an integer.
-Then the database will assign incrementing numbers at each insert.
-
-The example definition below defines an auto-incremented primary key
-
-```python
-# log entries
-entry_id : smallint auto_increment
----
-entry_text : varchar(4000)
-entry_time = CURRENT_TIMESTAMP : timestamp(3) # automatic timestamp with millisecond precision
-```
-
-DataJoint passes `auto_increment` behavior to the underlying MySQL and therefore it has
-the same limitation: it can only be used for tables with a single attribute in the
-primary key.
-
-If you need to auto-increment an attribute in a composite primary key, you will need to
-do so programmatically within a transaction to avoid collisions.
-
-For example, let’s say that you want to auto-increment `scan_idx` in a table called
-`Scan` whose primary key is `(animal_id, session, scan_idx)`.
-You must already have the values for `animal_id` and `session` in the dictionary `key`.
-Then you can do the following:
-
-```python
-U().aggr(Scan & key, next='max(scan_idx)+1')
-
-# or
-
-Session.aggr(Scan, next='max(scan_idx)+1') & key
-```
-
-Note that the first option uses a [universal set](../../query/universals.md).
diff --git a/docs/src/design/tables/tiers.md b/docs/src/design/tables/tiers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2cf1f9428..000000000
--- a/docs/src/design/tables/tiers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-# Data Tiers
-
-DataJoint assigns all tables to one of the following data tiers that differentiate how
-the data originate.
-
-## Table tiers
-
-| Tier | Superclass | Description |
-| -- | -- | -- |
-| Lookup | `dj.Lookup` | Small tables containing general facts and settings of the data pipeline; not specific to any experiment or dataset. |
-| Manual | `dj.Manual` | Data entered from outside the pipeline, either by hand or with external helper scripts. |
-| Imported | `dj.Imported` | Data ingested automatically inside the pipeline but requiring access to data outside the pipeline. |
-| Computed | `dj.Computed` | Data computed automatically entirely inside the pipeline. |
-
-Table data tiers indicate to database administrators how valuable the data are.
-Manual data are the most valuable, as re-entry may be tedious or impossible.
-Computed data are safe to delete, as the data can always be recomputed from within DataJoint.
-Imported data are safer than manual data but less safe than computed data because of
-dependency on external data sources.
-With these considerations, database administrators may opt not to back up computed
-data, for example, or to back up imported data less frequently than manual data.
-
-The data tier of a table is specified by the superclass of its class.
-For example, the User class in [definitions](declare.md) uses the `dj.Manual`
-superclass.
-Therefore, the corresponding User table on the database would be of the Manual tier.
-Furthermore, the classes for **imported** and **computed** tables have additional
-capabilities for automated processing as described in
-[Auto-populate](../../compute/populate.md).
-
-## Internal conventions for naming tables
-
-On the server side, DataJoint uses a naming scheme to generate a table name
-corresponding to a given class.
-The naming scheme includes prefixes specifying each table's data tier.
-
-First, the name of the class is converted from `CamelCase` to `snake_case`
-([separation by underscores](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Snake_case)).
-Then the name is prefixed according to the data tier.
-
-- `Manual` tables have no prefix.
-- `Lookup` tables are prefixed with `#`.
-- `Imported` tables are prefixed with `_`, a single underscore.
-- `Computed` tables are prefixed with `__`, two underscores.
-
-For example:
-
-The table for the class `StructuralScan` subclassing `dj.Manual` will be named
-`structural_scan`.
-
-The table for the class `SpatialFilter` subclassing `dj.Lookup` will be named
-`#spatial_filter`.
-
-Again, the internal table names including prefixes are used only on the server side.
-These are never visible to the user, and DataJoint users do not need to know these
-conventions
-However, database administrators may use these naming patterns to set backup policies
-or to restrict access based on data tiers.
-
-## Part tables
-
-[Part tables](master-part.md) do not have their own tier.
-Instead, they share the same tier as their master table.
-The prefix for part tables also differs from the other tiers.
-They are prefixed by the name of their master table, separated by two underscores.
-
-For example, the table for the class `Channel(dj.Part)` with the master
-`Ephys(dj.Imported)` will be named `_ephys__channel`.
diff --git a/docs/src/develop.md b/docs/src/develop.md
index bc636cc20..4643683b6 100644
--- a/docs/src/develop.md
+++ b/docs/src/develop.md
@@ -1,202 +1,101 @@
-# Developer Guide
+# Contributing Guide
-## Table of Contents
-
-- [Contribute to DataJoint Python Documentation](#contribute-to-datajoint-python-documentation)
-- [Setup Development Environment](#setup-development-environment)
- - [Prerequisites](#prerequisites)
- - [With Virtual Environment](#with-virtual-environment)
- - [With DevContainer](#with-devcontainer)
- - [Extra Efficiency, Optional But Recommended](#extra-efficiency-optional-but-recommended)
- - [Pre-commit Hooks](#pre-commit-hooks)
- - [Integration Tests](#integration-tests)
- - [VSCode](#vscode)
- - [Jupyter Extension](#jupyter-extension)
- - [Debugger](#debugger)
- - [MySQL CLI](#mysql-cli)
-
-## Contribute to DataJoint Python Documentation
-
-> Contributions to documentations are equivalently important to any code for the community, please help us to resolve any confusions in documentations.
-
-[Here](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/blob/master/docs/README.md) is the instructions for contributing documentations, or you can find the same instructions at `$PROJECT_DIR/docs/README.md` in the repository.
-
-[Back to top](#table-of-contents)
-
-## Setup Development Environment
-
-> We have [DevContainer](https://containers.dev/) ready for contributors to develop without setting up their environment. If you are familiar with DevContainer, Docker or Github Codespace, this is the recommended development environment for you.
-> If you have never used Docker, it might be easier for you to use a virtual environment through `conda/mamba/venv`, it is also very straightforward to set up.
-
-### Prerequisites
-
-- Clone datajoint-python repository
+## Quick Start
```bash
-# If you have your SSH key set up with GitHub, you can clone using SSH
-git clone git@github.com:datajoint/datajoint-python.git
-# Otherwise, you can clone using HTTPS
+# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python.git
-```
-- If you don't use DevContainer, then either install Anaconda/[Miniconda](https://www.anaconda.com/docs/getting-started/miniconda/install)/Mamba, or just use Python's built-in `venv` module without install anything else.
-
-### With Virtual Environment
+cd datajoint-python
-```bash
-# Check if you have Python 3.9 or higher, if not please upgrade
-python --version
-# Create a virtual environment with venv
+# Create virtual environment (Python 3.10+)
python -m venv .venv
-source .venv/bin/activate
-pip install -e .[dev]
+source .venv/bin/activate # On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate
-# Or create a virtual environment with conda
-conda create -n dj python=3.13 # any 3.9+ is fine
-conda activate dj
-pip install -e .[dev]
-```
+# Install with development dependencies
+pip install -e ".[dev]"
-[Back to top](#table-of-contents)
+# Install pre-commit hooks
+pre-commit install
-### With DevContainer
+# Run tests
+pytest tests
+```
-#### Launch Environment
+## Development Environment
-Here are some options that provide a great developer experience:
+### Local Setup
-- **Cloud-based IDE**: (*recommended*)
- - Launch using [GitHub Codespaces](https://github.com/features/codespaces) using the option `Create codespace on master` in the codebase repository on your fork.
- - Build time for a 2-Core codespace is **~6m**. This is done infrequently and cached for convenience.
- - Start time for a 2-Core codespace is **~2m**. This will pull the built codespace from cache when you need it.
- - *Tip*: GitHub auto names the codespace but you can rename the codespace so that it is easier to identify later.
-- **Local IDE (VSCode - Dev Containers)**:
- - Ensure you have [Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-Installing-Git)
- - Ensure you have [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/)
- - Ensure you have [VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/)
- - Install the [Dev Containers extension](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-vscode-remote.remote-containers)
- - `git clone` the codebase repository and open it in VSCode
- - Use the `Dev Containers extension` to `Reopen in Container` (More info in the `Getting started` included with the extension)
- - You will know your environment has finished loading once you see a terminal open related to `Running postStartCommand` with a final message: `Done. Press any key to close the terminal.`.
-- **Local IDE (Docker Compose)**:
- - Ensure you have [Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-Installing-Git)
- - Ensure you have [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/)
- - `git clone` the codebase repository and open it in VSCode
- - Issue the following command in the terminal to build and run the Docker container: `HOST_UID=$(id -u) PY_VER=3.11 DJ_VERSION=$(grep -oP '\d+\.\d+\.\d+' datajoint/version.py) docker compose --profile test run --rm -it djtest -- sh -c 'pip install -qe ".[dev]" && bash'`
- - Issue the following command in the terminal to stop the Docker compose stack: `docker compose --profile test down`
+Requirements:
-[Back to top](#table-of-contents)
+- Python 3.10 or higher
+- MySQL 8.0+ or Docker (for running tests)
-## Extra Efficiency, Optional But Recommended
+The `[dev]` extras install all development tools: pytest, pre-commit, black, ruff, and documentation builders.
-### Pre-commit Hooks
+### Using Docker for Database
-We recommend using [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/) to automatically run linters and formatters on your code before committing.
-To set up pre-commit, run the following command in your terminal:
+Tests require a MySQL database. Start one with Docker:
```bash
-pip install pre-commit
-pre-commit install
+docker compose up -d db
```
-You can manually run pre-commit on all files with the following command:
+Configure connection (or set environment variables):
```bash
-pre-commit run --all-files
+export DJ_HOST=localhost
+export DJ_USER=root
+export DJ_PASS=password
```
-This will run all the linters and formatters specified in the `.pre-commit-config.yaml` file. If all check passed, you can commit your code. Otherwise, you need to fix the failed checks and run the command again.
-> Pre-commit will automatically run the linters and formatters on all staged files before committing. However, if your code doesn't follow the linters and formatters, the commit will fail.
-> Some hooks will automatically fix your problem, and add the fixed files as git's `unstaged` files, you just need to add them(`git add .`) to git's `staged` files and commit again.
-> Some hooks will not automatically fix your problem, so you need to check the pre-commit failed log to fix them manually and include the update to your `staged` files and commit again.
+### Alternative: GitHub Codespaces
-If you really don't want to use pre-commit, or if you don't like it, you can uninstall it with the following command:
+For a pre-configured environment, use [GitHub Codespaces](https://github.com/features/codespaces):
-```bash
-pre-commit uninstall
-```
+1. Fork the repository
+2. Click "Create codespace on master"
+3. Wait for environment to build (~6 minutes first time, ~2 minutes from cache)
-But when you issue a pull request, the same linter and formatter check will run against your contribution, you are going to have the same failure as well. So without pre-commit, you need to **manually run these linters and formatters before committing your code**:
+## Code Quality
-- Syntax tests
+### Pre-commit Hooks
-The following will verify that there are no syntax errors.
+Pre-commit runs automatically on `git commit`. To run manually:
-```
-flake8 datajoint --count --select=E9,F63,F7,F82 --show-source --statistics
+```bash
+pre-commit run --all-files
```
-- Style tests
+Hooks include:
-The following will verify that there are no code styling errors.
+- **ruff** — Linting and import sorting
+- **black** — Code formatting
+- **mypy** — Type checking (optional)
-```
-flake8 --ignore=E203,E722,W503 datajoint --count --max-complexity=62 --max-line-length=127 --statistics
-```
-
-The following will ensure the codebase has been formatted with [black](https://black.readthedocs.io/en/stable/).
+### Running Tests
-```
-black datajoint --check -v --diff
-```
+```bash
+# Full test suite with coverage
+pytest -sv --cov=datajoint tests
-The following will ensure the test suite has been formatted with [black](https://black.readthedocs.io/en/stable/).
+# Single test file
+pytest tests/test_connection.py
+# Single test function
+pytest tests/test_connection.py::test_dj_conn -v
```
-black tests --check -v --diff
-```
-
-[Back to top](#table-of-contents)
-
-### Integration Tests
-
-The following will verify there are no regression errors by running our test suite of unit and integration tests.
-
-- Entire test suite:
- ```
- pytest -sv --cov-report term-missing --cov=datajoint tests
- ```
-
-- A single functional test:
- ```
- pytest -sv tests/test_connection.py::test_dj_conn
- ```
-- A single class test:
- ```
- pytest -sv tests/test_aggr_regressions.py::TestIssue558
- ```
-[Back to top](#table-of-contents)
+## Submitting Changes
-### VSCode
+1. Create a feature branch from `master`
+2. Make your changes
+3. Ensure tests pass and pre-commit is clean
+4. Submit a pull request
-#### Jupyter Extension
+PRs trigger CI checks automatically. All checks must pass before merge.
-Be sure to go through this documentation if you are new to [Running Jupyter Notebooks with VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/datascience/jupyter-notebooks#_create-or-open-a-jupyter-notebook).
+## Documentation
-#### Debugger
-
-[VSCode Debugger](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/debugging) is a powerful tool that can really accelerate fixes.
-
-Try it as follows:
-
-- Create a python script of your choice
-- `import datajoint` (This will use the current state of the source)
-- Add breakpoints by adding red dots next to line numbers
-- Select the `Run and Debug` tab
-- Start by clicking the button `Run and Debug`
-
-[Back to top](#table-of-contents)
-
-### MySQL CLI
-
-> Installation instruction is in [here](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql-shell/8.0/en/mysql-shell-install.html)
-
-It is often useful in development to connect to DataJoint's relational database backend directly using the MySQL CLI.
-
-Connect as follows to the database running within your developer environment:
-
-```
-mysql -hdb -uroot -ppassword
-```
+Docstrings use NumPy style. See [DOCSTRING_STYLE.md](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/blob/master/DOCSTRING_STYLE.md) for guidelines.
-[Back to top](#table-of-contents)
\ No newline at end of file
+User documentation is maintained at [docs.datajoint.com](https://docs.datajoint.com).
diff --git a/docs/src/faq.md b/docs/src/faq.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c4c82d014..000000000
--- a/docs/src/faq.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,192 +0,0 @@
-# Frequently Asked Questions
-
-## How do I use DataJoint with a GUI?
-
-It is common to enter data during experiments using a graphical user interface.
-
-1. The [DataJoint platform](https://works.datajoint.com) platform is a web-based,
- end-to-end platform to host and execute data pipelines.
-
-2. [DataJoint LabBook](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-labbook) is an open
-source project for data entry but is no longer actively maintained.
-
-## Does DataJoint support other programming languages?
-
-DataJoint [Python](https://docs.datajoint.com/core/datajoint-python/) is the most
-up-to-date version and all future development will focus on the Python API. The
-[Matlab](https://datajoint.com/docs/core/datajoint-matlab/) API was actively developed
-through 2023. Previous projects implemented some DataJoint features in
-[Julia](https://github.com/BrainCOGS/neuronex_workshop_2018/tree/julia/julia) and
-[Rust](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-core). DataJoint's data model and data
-representation are largely language independent, which means that any language with a
-DataJoint client can work with a data pipeline defined in any other language. DataJoint
-clients for other programming languages will be implemented based on demand. All
-languages must comply to the same data model and computation approach as defined in
-[DataJoint: a simpler relational data model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11104).
-
-## Can I use DataJoint with my current database?
-
-Researchers use many different tools to keep records, from simple formalized file
-hierarchies to complete software packages for colony management and standard file types
-like NWB. Existing projects have built interfaces with many such tools, such as
-[PyRAT](https://github.com/SFB1089/adamacs/blob/main/notebooks/03_pyrat_insert.ipynb).
-The only requirement for interface is that tool has an open API. Contact
-[support@datajoint.com](mailto:Support@DataJoint.com) with inquiries. The DataJoint
-team will consider development requests based on community demand.
-
-## Is DataJoint an ORM?
-
-Programmers are familiar with object-relational mappings (ORM) in various programming
-languages. Python in particular has several popular ORMs such as
-[SQLAlchemy](https://www.sqlalchemy.org/) and [Django ORM](https://tutorial.djangogirls.org/en/django_orm/).
-The purpose of ORMs is to allow representations and manipulations of objects from the
-host programming language as data in a relational database. ORMs allow making objects
-persistent between program executions by creating a bridge (i.e., mapping) between the
-object model used by the host language and the relational model allowed by the database.
-The result is always a compromise, usually toward the object model. ORMs usually forgo
-key concepts, features, and capabilities of the relational model for the sake of
-convenient programming constructs in the language.
-
-In contrast, DataJoint implements a data model that is a refinement of the relational
-data model without compromising its core principles of data representation and queries.
-DataJoint supports data integrity (entity integrity, referential integrity, and group
-integrity) and provides a fully capable relational query language. DataJoint remains
-absolutely data-centric, with the primary focus on the structure and integrity of the
-data pipeline. Other ORMs are more application-centric, primarily focusing on the
-application design while the database plays a secondary role supporting the application
-with object persistence and sharing.
-
-## What is the difference between DataJoint and Alyx?
-
-[Alyx](https://github.com/cortex-lab/alyx) is an experiment management database
-application developed in Kenneth Harris' lab at UCL.
-
-Alyx is an application with a fixed pipeline design with a nice graphical user
-interface. In contrast, DataJoint is a general-purpose library for designing and
-building data processing pipelines.
-
-Alyx is geared towards ease of data entry and tracking for a specific workflow
-(e.g. mouse colony information and some pre-specified experiments) and data types.
-DataJoint could be used as a more general purposes tool to design, implement, and
-execute processing on such workflows/pipelines from scratch, and DataJoint focuses on
-flexibility, data integrity, and ease of data analysis. The purposes are partly
-overlapping and complementary. The
-[International Brain Lab project](https://internationalbrainlab.com) is developing a
-bridge from Alyx to DataJoint, hosted as an
-[open-source project](https://github.com/datajoint-company/ibl-pipeline). It
-implements a DataJoint schema that replicates the major features of the Alyx
-application and a synchronization script from an existing Alyx database to its
-DataJoint counterpart.
-
-## Where is my data?
-
-New users often ask this question thinking of passive **data repositories** --
-collections of files and folders and a separate collection of metadata -- information
-about how the files were collected and what they contain.
-Let's address metadata first, since the answer there is easy: Everything goes in the
-database!
-Any information about the experiment that would normally be stored in a lab notebook,
-in an Excel spreadsheet, or in a Word document is entered into tables in the database.
-These tables can accommodate numbers, strings, dates, or numerical arrays.
-The entry of metadata can be manual, or it can be an automated part of data acquisition
-(in this case the acquisition software itself is modified to enter information directly
-into the database).
-
-Depending on their size and contents, raw data files can be stored in a number of ways.
-In the simplest and most common scenario, raw data continues to be stored in either a
-local filesystem or in the cloud as collections of files and folders.
-The paths to these files are entered in the database (again, either manually or by
-automated processes).
-This is the point at which the notion of a **data pipeline** begins.
-Below these "manual tables" that contain metadata and file paths are a series of tables
-that load raw data from these files, process it in some way, and insert derived or
-summarized data directly into the database.
-For example, in an imaging application, the very large raw `.TIFF` stacks would reside on
-the filesystem, but the extracted fluorescent trace timeseries for each cell in the
-image would be stored as a numerical array directly in the database.
-Or the raw video used for animal tracking might be stored in a standard video format on
-the filesystem, but the computed X/Y positions of the animal would be stored in the
-database.
-Storing these intermediate computations in the database makes them easily available for
-downstream analyses and queries.
-
-## Do I have to manually enter all my data into the database?
-
-No! While some of the data will be manually entered (the same way that it would be
-manually recorded in a lab notebook), the advantage of DataJoint is that standard
-downstream processing steps can be run automatically on all new data with a single
-command.
-This is where the notion of a **data pipeline** comes into play.
-When the workflow of cleaning and processing the data, extracting important features,
-and performing basic analyses is all implemented in a DataJoint pipeline, minimal
-effort is required to analyze newly-collected data.
-Depending on the size of the raw files and the complexity of analysis, useful results
-may be available in a matter of minutes or hours.
-Because these results are stored in the database, they can be made available to anyone
-who is given access credentials for additional downstream analyses.
-
-## Won't the database get too big if all my data are there?
-
-Typically, this is not a problem.
-If you find that your database is getting larger than a few dozen TB, DataJoint
-provides transparent solutions for storing very large chunks of data (larger than the 4
-GB that can be natively stored as a LONGBLOB in MySQL).
-However, in many scenarios even long time series or images can be stored directly in
-the database with little effect on performance.
-
-## Why not just process the data and save them back to a file?
-
-There are two main advantages to storing results in the database.
-The first is data integrity.
-Because the relationships between data are enforced by the structure of the database,
-DataJoint ensures that the metadata in the upstream nodes always correctly describes
-the computed results downstream in the pipeline.
-If a specific experimental session is deleted, for example, all the data extracted from
-that session are automatically removed as well, so there is no chance of "orphaned"
-data.
-Likewise, the database ensures that computations are atomic.
-This means that any computation performed on a dataset is performed in an all-or-none
-fashion.
-Either all of the data are processed and inserted, or none at all.
-This ensures that there are no incomplete data.
-Neither of these important features of data integrity can be guaranteed by a file
-system.
-
-The second advantage of storing intermediate results in a data pipeline is flexible
-access.
-Accessing arbitrarily complex subsets of the data can be achieved with DataJoint's
-flexible query language.
-When data are stored in files, collecting the desired data requires trawling through
-the file hierarchy, finding and loading the files of interest, and selecting the
-interesting parts of the data.
-
-This brings us to the final important question:
-
-## How do I get my data out?
-
-This is the fun part. See [queries](query/operators.md) for details of the DataJoint
-query language directly from Python.
-
-## Interfaces
-
-Multiple interfaces may be used to get the data into and out of the pipeline.
-
-Some labs use third-party GUI applications such as
-[HeidiSQL](https://www.heidisql.com/) and
-[Navicat](https://www.navicat.com/), for example. These applications allow entering
-and editing data in tables similarly to spreadsheets.
-
-The Helium Application (https://mattbdean.github.io/Helium/ and
-https://github.com/mattbdean/Helium) is web application for browsing DataJoint
-pipelines and entering new data.
-Matt Dean develops and maintains Helium under the direction of members of Karel
-Svoboda's lab at Janelia Research Campus and Vathes LLC.
-
-Data may also be imported or synchronized into a DataJoint pipeline from existing LIMS
-(laboratory information management systems).
-For example, the [International Brain Lab](https://internationalbrainlab.com)
-synchronizes data from an [Alyx database](https://github.com/cortex-lab/alyx).
-For implementation details, see https://github.com/int-brain-lab/IBL-pipeline.
-
-Other labs (e.g. Sinz Lab) have developed GUI interfaces using the Flask web framework
-in Python.
diff --git a/docs/src/images/StudentTable.png b/docs/src/images/StudentTable.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c8623f2ab..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/StudentTable.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/added-example-ERD.svg b/docs/src/images/added-example-ERD.svg
deleted file mode 100644
index 0884853f4..000000000
--- a/docs/src/images/added-example-ERD.svg
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,207 +0,0 @@
-
-
diff --git a/docs/src/images/data-engineering.png b/docs/src/images/data-engineering.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e038ac299..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/data-engineering.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/data-science-after.png b/docs/src/images/data-science-after.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e4f824cab..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/data-science-after.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/data-science-before.png b/docs/src/images/data-science-before.png
deleted file mode 100644
index eb8ee311d..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/data-science-before.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/diff-example1.png b/docs/src/images/diff-example1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2c8844b81..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/diff-example1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/diff-example2.png b/docs/src/images/diff-example2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index ab7465c7b..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/diff-example2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/diff-example3.png b/docs/src/images/diff-example3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b4f511fec..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/diff-example3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/dimitri-ERD.svg b/docs/src/images/dimitri-ERD.svg
deleted file mode 100644
index 590b30887..000000000
--- a/docs/src/images/dimitri-ERD.svg
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
-
-
diff --git a/docs/src/images/doc_1-1.png b/docs/src/images/doc_1-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 4f6f0fa0b..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/doc_1-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/doc_1-many.png b/docs/src/images/doc_1-many.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 32fbbf15b..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/doc_1-many.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/doc_many-1.png b/docs/src/images/doc_many-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 961a306dc..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/doc_many-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/doc_many-many.png b/docs/src/images/doc_many-many.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3aa484dd6..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/doc_many-many.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/how-it-works.png b/docs/src/images/how-it-works.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 10c611f3d..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/how-it-works.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-cmd-prompt.png b/docs/src/images/install-cmd-prompt.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 58c9fa964..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-cmd-prompt.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-datajoint-1.png b/docs/src/images/install-datajoint-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 7aa0a7133..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-datajoint-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-datajoint-2.png b/docs/src/images/install-datajoint-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 970e8c6d4..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-datajoint-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-git-1.png b/docs/src/images/install-git-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 7503dbb61..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-git-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-graphviz-1.png b/docs/src/images/install-graphviz-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index dc79e58f1..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-graphviz-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-graphviz-2a.png b/docs/src/images/install-graphviz-2a.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 394598db7..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-graphviz-2a.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-graphviz-2b.png b/docs/src/images/install-graphviz-2b.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 790f88d40..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-graphviz-2b.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-jupyter-1.png b/docs/src/images/install-jupyter-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 14d697942..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-jupyter-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-jupyter-2.png b/docs/src/images/install-jupyter-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 0d69e6667..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-jupyter-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-matplotlib.png b/docs/src/images/install-matplotlib.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d092376bb..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-matplotlib.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-pydotplus.png b/docs/src/images/install-pydotplus.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 4a0b33f91..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-pydotplus.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-python-advanced-1.png b/docs/src/images/install-python-advanced-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b07c70e94..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-python-advanced-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-python-advanced-2.png b/docs/src/images/install-python-advanced-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b10be09cc..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-python-advanced-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-python-simple.png b/docs/src/images/install-python-simple.png
deleted file mode 100644
index ec28cf8cc..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-python-simple.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-run-jupyter-1.png b/docs/src/images/install-run-jupyter-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index cd1e9cfb5..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-run-jupyter-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-run-jupyter-2.png b/docs/src/images/install-run-jupyter-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 7fcee8ee7..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-run-jupyter-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-verify-graphviz.png b/docs/src/images/install-verify-graphviz.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6468a98c3..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-verify-graphviz.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-verify-jupyter.png b/docs/src/images/install-verify-jupyter.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 73defac5d..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-verify-jupyter.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/install-verify-python.png b/docs/src/images/install-verify-python.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 54ad47290..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/install-verify-python.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/join-example1.png b/docs/src/images/join-example1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index a518896ef..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/join-example1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/join-example2.png b/docs/src/images/join-example2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c219a6a02..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/join-example2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/join-example3.png b/docs/src/images/join-example3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b2782469e..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/join-example3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/key_source_combination.png b/docs/src/images/key_source_combination.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3db45de37..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/key_source_combination.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/map-dataflow.png b/docs/src/images/map-dataflow.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5a3bb34ce..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/map-dataflow.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/matched_tuples1.png b/docs/src/images/matched_tuples1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c27593e14..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/matched_tuples1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/matched_tuples2.png b/docs/src/images/matched_tuples2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 673fa5865..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/matched_tuples2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/matched_tuples3.png b/docs/src/images/matched_tuples3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index f60e11b50..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/matched_tuples3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/mp-diagram.png b/docs/src/images/mp-diagram.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d834726fb..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/mp-diagram.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/op-restrict.png b/docs/src/images/op-restrict.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e686ac94a..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/op-restrict.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/outer-example1.png b/docs/src/images/outer-example1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 0a7c7552f..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/outer-example1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/pipeline-database.png b/docs/src/images/pipeline-database.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 035df17cb..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/pipeline-database.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/pipeline.png b/docs/src/images/pipeline.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 0d91f72e9..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/pipeline.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/python_collection.png b/docs/src/images/python_collection.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 76fd1d7b0..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/python_collection.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/queries_example_diagram.png b/docs/src/images/queries_example_diagram.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d6aae1377..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/queries_example_diagram.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/query_object_preview.png b/docs/src/images/query_object_preview.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 16cedc8fc..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/query_object_preview.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/restrict-example1.png b/docs/src/images/restrict-example1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 451e68c58..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/restrict-example1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/restrict-example2.png b/docs/src/images/restrict-example2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index aa9a4636b..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/restrict-example2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/restrict-example3.png b/docs/src/images/restrict-example3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e8de7f6ca..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/restrict-example3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/shapes_pipeline.svg b/docs/src/images/shapes_pipeline.svg
deleted file mode 100644
index 14572c4ce..000000000
--- a/docs/src/images/shapes_pipeline.svg
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-
diff --git a/docs/src/images/spawned-classes-ERD.svg b/docs/src/images/spawned-classes-ERD.svg
deleted file mode 100644
index 313841e81..000000000
--- a/docs/src/images/spawned-classes-ERD.svg
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,147 +0,0 @@
-
-
diff --git a/docs/src/images/union-example1.png b/docs/src/images/union-example1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e693e7170..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/union-example1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/union-example2.png b/docs/src/images/union-example2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 82cc5cc51..000000000
Binary files a/docs/src/images/union-example2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/src/images/virtual-module-ERD.svg b/docs/src/images/virtual-module-ERD.svg
deleted file mode 100644
index 28eb0c481..000000000
--- a/docs/src/images/virtual-module-ERD.svg
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,147 +0,0 @@
-
-
diff --git a/docs/src/index.md b/docs/src/index.md
index 6e3bf2a2d..63b318a1c 100644
--- a/docs/src/index.md
+++ b/docs/src/index.md
@@ -1,44 +1,44 @@
-# Welcome to DataJoint for Python!
+# DataJoint for Python
-DataJoint for Python is a framework for scientific workflow management based on
-relational principles. DataJoint is built on the foundation of the relational data
-model and prescribes a consistent method for organizing, populating, computing, and
-querying data.
+DataJoint is an open-source Python framework for building scientific data pipelines.
+It implements the **Relational Workflow Model**—a paradigm that extends relational
+databases with native support for computational workflows.
-DataJoint was initially developed in 2009 by Dimitri Yatsenko in Andreas Tolias' Lab at
-Baylor College of Medicine for the distributed processing and management of large
-volumes of data streaming from regular experiments. Starting in 2011, DataJoint has
-been available as an open-source project adopted by other labs and improved through
-contributions from several developers.
-Presently, the primary developer of DataJoint open-source software is the company [DataJoint](https://datajoint.com){:target="_blank"}.
+## Documentation
-## Data Pipeline Example
+**User documentation** is available at **[docs.datajoint.com](https://docs.datajoint.com)**, including:
-
+- Tutorials and getting started guides
+- Concepts and explanations
+- How-to guides
+- API reference
-[Yatsenko et al., bioRxiv 2021](https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.30.437358){:target="_blank"}
+## This Site
-## Getting Started
+This site contains **developer documentation** for contributors to the DataJoint codebase:
-- Install with Conda
+- [Contributing Guide](develop.md) — Development environment setup
+- [Architecture](architecture/index.md) — Internal design documentation
+- [API Reference](api/) — Auto-generated from source
- ```bash
- conda install -c conda-forge datajoint
- ```
+## Quick Links
-- Install with pip
+| Resource | Link |
+|----------|------|
+| User Documentation | [docs.datajoint.com](https://docs.datajoint.com) |
+| GitHub Repository | [github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python) |
+| PyPI Package | [pypi.org/project/datajoint](https://pypi.org/project/datajoint) |
+| Issue Tracker | [GitHub Issues](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues) |
+| Community | [DataJoint Slack](https://datajoint.slack.com) |
- ```bash
- pip install datajoint
- ```
+## Installation
-- [Quick Start Guide](./quick-start.md)
+```bash
+pip install datajoint
+```
-- [Interactive Tutorials](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-tutorials){:target="_blank"} on GitHub Codespaces
+## License
-- [DataJoint Elements](https://docs.datajoint.com/elements/) - Catalog of example pipelines for neuroscience experiments
+DataJoint is released under the [Apache 2.0 License](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/blob/master/LICENSE).
-- Contribute
- - [Development Environment](./develop)
-
- - [Guidelines](https://docs.datajoint.com/about/contribute/)
+Copyright 2024 DataJoint Inc. and contributors.
diff --git a/docs/src/manipulation/delete.md b/docs/src/manipulation/delete.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4e34c69ce..000000000
--- a/docs/src/manipulation/delete.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
-# Delete
-
-The `delete` method deletes entities from a table and all dependent entries in
-dependent tables.
-
-Delete is often used in conjunction with the [restriction](../query/restrict.md)
-operator to define the subset of entities to delete.
-Delete is performed as an atomic transaction so that partial deletes never occur.
-
-## Examples
-
-```python
-# delete all entries from tuning.VonMises
-tuning.VonMises.delete()
-
-# delete entries from tuning.VonMises for mouse 1010
-(tuning.VonMises & 'mouse=1010').delete()
-
-# delete entries from tuning.VonMises except mouse 1010
-(tuning.VonMises - 'mouse=1010').delete()
-```
-
-## Deleting from part tables
-
-Entities in a [part table](../design/tables/master-part.md) are usually removed as a
-consequence of deleting the master table.
-
-To enforce this workflow, calling `delete` directly on a part table produces an error.
-In some cases, it may be necessary to override this behavior.
-To remove entities from a part table without calling `delete` master, use the argument `force_parts=True`.
-To include the corresponding entries in the master table, use the argument `force_masters=True`.
diff --git a/docs/src/manipulation/index.md b/docs/src/manipulation/index.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 295195778..000000000
--- a/docs/src/manipulation/index.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
-# Data Manipulation
-
-Data **manipulation** operations change the state of the data stored in the database
-without modifying the structure of the stored data.
-These operations include [insert](insert.md), [delete](delete.md), and
-[update](update.md).
-
-Data manipulation operations in DataJoint respect the
-[integrity](../design/integrity.md) constraints.
diff --git a/docs/src/manipulation/insert.md b/docs/src/manipulation/insert.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c64e55f17..000000000
--- a/docs/src/manipulation/insert.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-# Insert
-
-The `insert` method of DataJoint table objects inserts entities into the table.
-
-In Python there is a separate method `insert1` to insert one entity at a time.
-The entity may have the form of a Python dictionary with key names matching the
-attribute names in the table.
-
-```python
-lab.Person.insert1(
- dict(username='alice',
- first_name='Alice',
- last_name='Cooper'))
-```
-
-The entity also may take the form of a sequence of values in the same order as the
-attributes in the table.
-
-```python
-lab.Person.insert1(['alice', 'Alice', 'Cooper'])
-```
-
-Additionally, the entity may be inserted as a
-[NumPy record array](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.record.html#numpy.record)
- or [Pandas DataFrame](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.DataFrame.html).
-
-The `insert` method accepts a sequence or a generator of multiple entities and is used
-to insert multiple entities at once.
-
-```python
-lab.Person.insert([
- ['alice', 'Alice', 'Cooper'],
- ['bob', 'Bob', 'Dylan'],
- ['carol', 'Carol', 'Douglas']])
-```
-
-Several optional parameters can be used with `insert`:
-
- `replace` If `True`, replaces the existing entity.
- (Default `False`.)
-
- `skip_duplicates` If `True`, silently skip duplicate inserts.
- (Default `False`.)
-
- `ignore_extra_fields` If `False`, fields that are not in the heading raise an error.
- (Default `False`.)
-
- `allow_direct_insert` If `True`, allows inserts outside of populate calls.
- Applies only in auto-populated tables.
- (Default `None`.)
-
-## Batched inserts
-
-Inserting a set of entities in a single `insert` differs from inserting the same set of
-entities one-by-one in a `for` loop in two ways:
-
-1. Network overhead is reduced.
- Network overhead can be tens of milliseconds per query.
- Inserting 1000 entities in a single `insert` call may save a few seconds over
- inserting them individually.
-2. The insert is performed as an all-or-nothing transaction.
- If even one insert fails because it violates any constraint, then none of the
- entities in the set are inserted.
-
-However, inserting too many entities in a single query may run against buffer size or
-packet size limits of the database server.
-Due to these limitations, performing inserts of very large numbers of entities should
-be broken up into moderately sized batches, such as a few hundred at a time.
-
-## Server-side inserts
-
-Data inserted into a table often come from other tables already present on the database server.
-In such cases, data can be [fetched](../query/fetch.md) from the first table and then
-inserted into another table, but this results in transfers back and forth between the
-database and the local system.
-Instead, data can be inserted from one table into another without transfers between the
-database and the local system using [queries](../query/principles.md).
-
-In the example below, a new schema has been created in preparation for phase two of a
-project.
-Experimental protocols from the first phase of the project will be reused in the second
-phase.
-Since the entities are already present on the database in the `Protocol` table of the
-`phase_one` schema, we can perform a server-side insert into `phase_two.Protocol`
-without fetching a local copy.
-
-```python
-# Server-side inserts are faster...
-phase_two.Protocol.insert(phase_one.Protocol)
-
-# ...than fetching before inserting
-protocols = phase_one.Protocol.fetch()
-phase_two.Protocol.insert(protocols)
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/manipulation/transactions.md b/docs/src/manipulation/transactions.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 58b9a3167..000000000
--- a/docs/src/manipulation/transactions.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-# Transactions
-
-In some cases, a sequence of several operations must be performed as a single
-operation:
-interrupting the sequence of such operations halfway would leave the data in an invalid
-state.
-While the sequence is in progress, other processes accessing the database will not see
-the partial results until the transaction is complete.
-The sequence may include [data queries](../query/principles.md) and
-[manipulations](index.md).
-
-In such cases, the sequence of operations may be enclosed in a transaction.
-
-Transactions are formed using the `transaction` property of the connection object.
-The connection object may be obtained from any table object.
-The `transaction` property can then be used as a context manager in Python's `with`
-statement.
-
-For example, the following code inserts matching entries for the master table `Session`
-and its part table `Session.Experimenter`.
-
-```python
-# get the connection object
-connection = Session.connection
-
-# insert Session and Session.Experimenter entries in a transaction
-with connection.transaction:
- key = {'subject_id': animal_id, 'session_time': session_time}
- Session.insert1({**key, 'brain_region':region, 'cortical_layer':layer})
- Session.Experimenter.insert1({**key, 'experimenter': username})
-```
-
-Here, to external observers, both inserts will take effect together upon exiting from
-the `with` block or will not have any effect at all.
-For example, if the second insert fails due to an error, the first insert will be
-rolled back.
diff --git a/docs/src/manipulation/update.md b/docs/src/manipulation/update.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7faa7cb87..000000000
--- a/docs/src/manipulation/update.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
-# Cautious Update
-
-In database programming, the **update** operation refers to modifying the values of
-individual attributes in an entity within a table without replacing the entire entity.
-Such an in-place update mechanism is not part of DataJoint's data manipulation model,
-because it circumvents data
-[dependency constraints](../design/integrity.md#referential-integrity).
-
-This is not to say that data cannot be changed once they are part of a pipeline.
-In DataJoint, data is changed by replacing entire entities rather than by updating the
-values of their attributes.
-The process of deleting existing entities and inserting new entities with corrected
-values ensures the [integrity](../design/integrity.md) of the data throughout the
-pipeline.
-
-This approach applies specifically to automated tables
-(see [Auto-populated tables](../compute/populate.md)).
-However, manual tables are often edited outside DataJoint through other interfaces.
-It is up to the user's discretion to allow updates in manual tables, and the user must
-be cognizant of the fact that updates will not trigger re-computation of dependent data.
-
-## Usage
-
-For some cases, it becomes necessary to deliberately correct existing values where a
-user has chosen to accept the above responsibility despite the caution.
-
-The `update1` method accomplishes this if the record already exists. Note that updates
-to primary key values are not allowed.
-
-The method should only be used to fix problems, and not as part of a regular workflow.
-When updating an entry, make sure that any information stored in dependent tables that
-depends on the update values is properly updated as well.
-
-## Examples
-
-```python
-# with record as a dict specifying the primary and
-# secondary attribute values
-table.update1(record)
-
-# update value in record with id as primary key
-table.update1({'id': 1, 'value': 3})
-
-# reset value to default with id as primary key
-table.update1({'id': 1, 'value': None})
-# or
-table.update1({'id': 1})
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/publish-data.md b/docs/src/publish-data.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3ec2d7211..000000000
--- a/docs/src/publish-data.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-# Publishing Data
-
-DataJoint is a framework for building data pipelines that support rigorous flow of
-structured data between experimenters, data scientists, and computing agents *during*
-data acquisition and processing within a centralized project.
-Publishing final datasets for the outside world may require additional steps and
-conversion.
-
-## Provide access to a DataJoint server
-
-One approach for publishing data is to grant public access to an existing pipeline.
-Then public users will be able to query the data pipelines using DataJoint's query
-language and output interfaces just like any other users of the pipeline.
-For security, this may require synchronizing the data onto a separate read-only public
-server.
-
-## Containerizing as a DataJoint pipeline
-
-Containerization platforms such as [Docker](https://www.docker.com/) allow convenient
-distribution of environments including database services and data.
-It is convenient to publish DataJoint pipelines as a docker container that deploys the
-populated DataJoint pipeline.
-One example of publishing a DataJoint pipeline as a docker container is
-> Sinz, F., Ecker, A.S., Fahey, P., Walker, E., Cobos, E., Froudarakis, E., Yatsenko, D., Pitkow, Z., Reimer, J. and Tolias, A., 2018. Stimulus domain transfer in recurrent models for large scale cortical population prediction on video. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (pp. 7198-7209). https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2018/10/25/452672
-
-The code and the data can be found at [https://github.com/sinzlab/Sinz2018_NIPS](https://github.com/sinzlab/Sinz2018_NIPS).
-
-## Exporting into a collection of files
-
-Another option for publishing and archiving data is to export the data from the
-DataJoint pipeline into a collection of files.
-DataJoint provides features for exporting and importing sections of the pipeline.
-Several ongoing projects are implementing the capability to export from DataJoint
-pipelines into [Neurodata Without Borders](https://www.nwb.org/) files.
diff --git a/docs/src/query/aggregation.md b/docs/src/query/aggregation.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e47fd0b33..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/aggregation.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
-# Aggr
-
-**Aggregation**, performed with the `aggr` operator, is a special form of `proj` with
-the additional feature of allowing aggregation calculations on another table.
-It has the form `tab.aggr(other, ...)` where `other` is another table.
-Without the argument `other`, `aggr` and `proj` are exactly equivalent.
-Aggregation allows adding calculated attributes to each entity in `tab` based on
-aggregation functions over attributes in the
-[matching](./operators.md#matching-entities) entities of `other`.
-
-Aggregation functions include `count`, `sum`, `min`, `max`, `avg`, `std`, `variance`,
-and others.
-Aggregation functions can only be used in the definitions of new attributes within the
-`aggr` operator.
-
-As with `proj`, the output of `aggr` has the same entity class, the same primary key,
-and the same number of elements as `tab`.
-Primary key attributes are always included in the output and may be renamed, just like
-in `proj`.
-
-## Examples
-
-```python
-# Number of students in each course section
-Section.aggr(Enroll, n="count(*)")
-
-# Average grade in each course
-Course.aggr(Grade * LetterGrade, avg_grade="avg(points)")
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/query/example-schema.md b/docs/src/query/example-schema.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 063e36574..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/example-schema.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
-# Example Schema
-
-The example schema below contains data for a university enrollment system.
-Information about students, departments, courses, etc. are organized in multiple tables.
-
-Warning:
- Empty primary keys, such as in the `CurrentTerm` table, are not yet supported by
- DataJoint.
- This feature will become available in a future release.
- See [Issue #113](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/113) for more
- information.
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Student (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
-student_id : int unsigned # university ID
----
-first_name : varchar(40)
-last_name : varchar(40)
-sex : enum('F', 'M', 'U')
-date_of_birth : date
-home_address : varchar(200) # street address
-home_city : varchar(30)
-home_state : char(2) # two-letter abbreviation
-home_zipcode : char(10)
-home_phone : varchar(14)
-"""
-
-@schema
-class Department (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
-dept : char(6) # abbreviated department name, e.g. BIOL
----
-dept_name : varchar(200) # full department name
-dept_address : varchar(200) # mailing address
-dept_phone : varchar(14)
-"""
-
-@schema
-class StudentMajor (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
--> Student
----
--> Department
-declare_date : date # when student declared her major
-"""
-
-@schema
-class Course (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
--> Department
-course : int unsigned # course number, e.g. 1010
----
-course_name : varchar(200) # e.g. "Cell Biology"
-credits : decimal(3,1) # number of credits earned by completing the course
-"""
-
-@schema
-class Term (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
-term_year : year
-term : enum('Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall')
-"""
-
-@schema
-class Section (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
--> Course
--> Term
-section : char(1)
----
-room : varchar(12) # building and room code
-"""
-
-@schema
-class CurrentTerm (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
----
--> Term
-"""
-
-@schema
-class Enroll (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
--> Section
--> Student
-"""
-
-@schema
-class LetterGrade (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
-grade : char(2)
----
-points : decimal(3,2)
-"""
-
-@schema
-class Grade (dj.Manual):
-definition = """
--> Enroll
----
--> LetterGrade
-"""
-```
-
-## Example schema diagram
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-Example schema for a university database.
-Tables contain data on students, departments, courses, etc.
diff --git a/docs/src/query/fetch.md b/docs/src/query/fetch.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 105d70084..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/fetch.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
-# Fetch
-
-Data queries in DataJoint comprise two distinct steps:
-
-1. Construct the `query` object to represent the required data using tables and
-[operators](operators.md).
-2. Fetch the data from `query` into the workspace of the host language -- described in
-this section.
-
-Note that entities returned by `fetch` methods are not guaranteed to be sorted in any
-particular order unless specifically requested.
-Furthermore, the order is not guaranteed to be the same in any two queries, and the
-contents of two identical queries may change between two sequential invocations unless
-they are wrapped in a transaction.
-Therefore, if you wish to fetch matching pairs of attributes, do so in one `fetch` call.
-
-The examples below are based on the [example schema](example-schema.md) for this part
-of the documentation.
-
-## Entire table
-
-The following statement retrieves the entire table as a NumPy
-[recarray](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.recarray.html).
-
-```python
-data = query.fetch()
-```
-
-To retrieve the data as a list of `dict`:
-
-```python
-data = query.fetch(as_dict=True)
-```
-
-In some cases, the amount of data returned by fetch can be quite large; in these cases
-it can be useful to use the `size_on_disk` attribute to determine if running a bare
-fetch would be wise.
-Please note that it is only currently possible to query the size of entire tables
-stored directly in the database at this time.
-
-## As separate variables
-
-```python
-name, img = query.fetch1('name', 'image') # when query has exactly one entity
-name, img = query.fetch('name', 'image') # [name, ...] [image, ...]
-```
-
-## Primary key values
-
-```python
-keydict = tab.fetch1("KEY") # single key dict when tab has exactly one entity
-keylist = tab.fetch("KEY") # list of key dictionaries [{}, ...]
-```
-
-`KEY` can also used when returning attribute values as separate variables, such that
-one of the returned variables contains the entire primary keys.
-
-## Sorting and limiting the results
-
-To sort the result, use the `order_by` keyword argument.
-
-```python
-# ascending order:
-data = query.fetch(order_by='name')
-# descending order:
-data = query.fetch(order_by='name desc')
-# by name first, year second:
-data = query.fetch(order_by=('name desc', 'year'))
-# sort by the primary key:
-data = query.fetch(order_by='KEY')
-# sort by name but for same names order by primary key:
-data = query.fetch(order_by=('name', 'KEY desc'))
-```
-
-The `order_by` argument can be a string specifying the attribute to sort by. By default
-the sort is in ascending order. Use `'attr desc'` to sort in descending order by
-attribute `attr`. The value can also be a sequence of strings, in which case, the sort
-performed on all the attributes jointly in the order specified.
-
-The special attribute name `'KEY'` represents the primary key attributes in order that
-they appear in the index. Otherwise, this name can be used as any other argument.
-
-If an attribute happens to be a SQL reserved word, it needs to be enclosed in
-backquotes. For example:
-
-```python
-data = query.fetch(order_by='`select` desc')
-```
-
-The `order_by` value is eventually passed to the `ORDER BY`
-[clause](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/order-by-optimization.html).
-
-Similarly, the `limit` and `offset` arguments can be used to limit the result to a
-subset of entities.
-
-For example, one could do the following:
-
-```python
-data = query.fetch(order_by='name', limit=10, offset=5)
-```
-
-Note that an `offset` cannot be used without specifying a `limit` as well.
-
-## Usage with Pandas
-
-The [pandas library](http://pandas.pydata.org/) is a popular library for data analysis
-in Python which can easily be used with DataJoint query results.
-Since the records returned by `fetch()` are contained within a `numpy.recarray`, they
-can be easily converted to `pandas.DataFrame` objects by passing them into the
-`pandas.DataFrame` constructor.
-For example:
-
-```python
-import pandas as pd
-frame = pd.DataFrame(tab.fetch())
-```
-
-Calling `fetch()` with the argument `format="frame"` returns results as
-`pandas.DataFrame` objects indexed by the table's primary key attributes.
-
-```python
-frame = tab.fetch(format="frame")
-```
-
-Returning results as a `DataFrame` is not possible when fetching a particular subset of
-attributes or when `as_dict` is set to `True`.
diff --git a/docs/src/query/iteration.md b/docs/src/query/iteration.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 60d95f107..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/iteration.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-# Iteration
-
-The DataJoint model primarily handles data as sets, in the form of tables. However, it
-can sometimes be useful to access or to perform actions such as visualization upon
-individual entities sequentially. In DataJoint this is accomplished through iteration.
-
-In the simple example below, iteration is used to display the names and values of the
-attributes of each entity in the simple table or table expression.
-
-```python
-for entity in table:
- print(entity)
-```
-
-This example illustrates the function of the iterator: DataJoint iterates through the
-whole table expression, returning the entire entity during each step. In this case,
-each entity will be returned as a `dict` containing all attributes.
-
-At the start of the above loop, DataJoint internally fetches only the primary keys of
-the entities. Since only the primary keys are needed to distinguish between entities,
-DataJoint can then iterate over the list of primary keys to execute the loop. At each
-step of the loop, DataJoint uses a single primary key to fetch an entire entity for use
-in the iteration, such that `print(entity)` will print all attributes of each entity.
-By first fetching only the primary keys and then fetching each entity individually,
-DataJoint saves memory at the cost of network overhead. This can be particularly useful
-for tables containing large amounts of data in secondary attributes.
-
-The memory savings of the above syntax may not be worth the additional network overhead
-in all cases, such as for tables with little data stored as secondary attributes. In
-the example below, DataJoint fetches all of the attributes of each entity in a single
-call and then iterates over the list of entities stored in memory.
-
-```python
-for entity in table.fetch(as_dict=True):
- print(entity)
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/query/join.md b/docs/src/query/join.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d0ab0eae0..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/join.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
-# Join
-
-## Join operator `*`
-
-The Join operator `A * B` combines the matching information in `A` and `B`.
-The result contains all matching combinations of entities from both arguments.
-
-### Principles of joins
-
-1. The operands `A` and `B` must be **join-compatible**.
-2. The primary key of the result is the union of the primary keys of the operands.
-
-### Examples of joins
-
-Example 1 : When the operands have no common attributes, the result is the cross
-product -- all combinations of entities.
-
-{: style="width:464px; align:center"}
-
-Example 2 : When the operands have common attributes, only entities with matching
-values are kept.
-
-{: style="width:689px; align:center"}
-
-Example 3 : Joining on secondary attribute.
-
-{: style="width:689px; align:center"}
-
-### Properties of join
-
-1. When `A` and `B` have the same attributes, the join `A * B` becomes equivalent to
-the set intersection `A` ∩ `B`.
- Hence, DataJoint does not need a separate intersection operator.
-
-2. Commutativity: `A * B` is equivalent to `B * A`.
-
-3. Associativity: `(A * B) * C` is equivalent to `A * (B * C)`.
diff --git a/docs/src/query/operators.md b/docs/src/query/operators.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ee3549f35..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/operators.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,395 +0,0 @@
-# Operators
-
-[Data queries](principles.md) have the form of expressions using operators to derive
-the desired table.
-The expressions themselves do not contain any data.
-They represent the desired data symbolically.
-
-Once a query is formed, the [fetch](fetch.md) methods are used to bring the data into
-the local workspace.
-Since the expressions are only symbolic representations, repeated `fetch` calls may
-yield different results as the state of the database is modified.
-
-DataJoint implements a complete algebra of operators on tables:
-
-| operator | notation | meaning |
-|------------------------------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [join](#join) | A * B | All matching information from A and B |
-| [restriction](#restriction) | A & cond | The subset of entities from A that meet the condition |
-| [restriction](#restriction) | A - cond | The subset of entities from A that do not meet the condition |
-| [proj](#proj) | A.proj(...) | Selects and renames attributes from A or computes new attributes |
-| [aggr](#aggr) | A.aggr(B, ...) | Same as projection with computations based on matching information in B |
-| [union](#union) | A + B | All unique entities from both A and B |
-| [universal set](#universal-set)\*| dj.U() | All unique entities from both A and B |
-| [top](#top)\*| dj.Top() | The top rows of A
-
-\*While not technically query operators, it is useful to discuss Universal Set and Top in the
-same context.
-
-## Principles of relational algebra
-
-DataJoint's algebra improves upon the classical relational algebra and upon other query
-languages to simplify and enhance the construction and interpretation of precise and
-efficient data queries.
-
-1. **Entity integrity**: Data are represented and manipulated in the form of tables
-representing [well-formed entity sets](../design/integrity.md).
- This applies to the inputs and outputs of query operators.
- The output of a query operator is an entity set with a well-defined entity type, a
- primary key, unique attribute names, etc.
-2. **Algebraic closure**: All operators operate on entity sets and yield entity sets.
- Thus query expressions may be used as operands in other expressions or may be
- assigned to variables to be used in other expressions.
-3. **Attributes are identified by names**: All attributes have explicit names.
- This includes results of queries.
- Operators use attribute names to determine how to perform the operation.
- The order of the attributes is not significant.
-
-## Matching entities
-
-Binary operators in DataJoint are based on the concept of **matching entities**; this
-phrase will be used throughout the documentation.
-
- Two entities **match** when they have no common attributes or when their common
- attributes contain the same values.
-
-Here **common attributes** are those that have the same names in both entities.
-It is usually assumed that the common attributes are of compatible datatypes to allow
-equality comparisons.
-
-Another way to phrase the same definition is
-
- Two entities match when they have no common attributes whose values differ.
-
-It may be conceptually convenient to imagine that all tables always have an additional
-invisible attribute, `omega` whose domain comprises only one value, 1.
-Then the definition of matching entities is simplified:
-
- Two entities match when their common attributes contain the same values.
-
-Matching entities can be **merged** into a single entity without any conflicts of
-attribute names and values.
-
-### Examples
-
-This is a matching pair of entities:
-
-{: style="width:366px"}
-
-and so is this one:
-
-{: style="width:366px"}
-
-but these entities do *not* match:
-
-{: style="width:366px"}
-
-## Join compatibility
-
-All binary operators with other tables as their two operands require that the operands
-be **join-compatible**, which means that:
-
-1. All common attributes in both operands (attributes with the same name) must be part
-of either the primary key or a foreign key.
-2. All common attributes in the two relations must be of a compatible datatype for
-equality comparisons.
-
-## Restriction
-
-The restriction operator `A & cond` selects the subset of entities from `A` that meet
-the condition `cond`. The exclusion operator `A - cond` selects the complement of
-restriction, i.e. the subset of entities from `A` that do not meet the condition
-`cond`. This means that the restriction and exclusion operators are complementary.
-The same query could be constructed using either `A & cond` or `A - Not(cond)`.
-
-
-{: style="height:200px"}
-
-
-The condition `cond` may be one of the following:
-
-=== "Python"
-
- - another table
- - a mapping, e.g. `dict`
- - an expression in a character string
- - a collection of conditions as a `list`, `tuple`, or Pandas `DataFrame`
- - a Boolean expression (`True` or `False`)
- - an `AndList`
- - a `Not` object
- - a query expression
-
-??? Warning "Permissive Operators"
-
- To circumvent compatibility checks, DataJoint offers permissive operators for
- Restriction (`^`) and Join (`@`). Use with Caution.
-
-## Proj
-
-The `proj` operator represents **projection** and is used to select attributes
-(columns) from a table, to rename them, or to create new calculated attributes.
-
-1. A simple projection *selects a subset of attributes* of the original
-table, which may not include the [primary key](../concepts/glossary#primary-key).
-
-2. A more complex projection *renames an attribute* in another table. This could be
-useful when one table should be referenced multiple times in another. A user table,
-could contain all personnel. A project table references one person for the lead and
-another the coordinator, both referencing the common personnel pool.
-
-3. Projection can also perform calculations (as available in
-[MySQL](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/functions.html)) on a single attribute.
-
-## Aggr
-
-**Aggregation** is a special form of `proj` with the added feature of allowing
- aggregation calculations on another table. It has the form `table.aggr
- (other, ...)` where `other` is another table. Aggregation allows adding calculated
- attributes to each entity in `table` based on aggregation functions over attributes
- in the matching entities of `other`.
-
-Aggregation functions include `count`, `sum`, `min`, `max`, `avg`, `std`, `variance`,
-and others.
-
-## Union
-
-The result of the union operator `A + B` contains all the entities from both operands.
-
-[Entity normalization](../design/normalization) requires that `A` and `B` are of the same type,
-with with the same [primary key](../concepts/glossary#primary-key), using homologous
-attributes. Without secondary attributes, the result is the simple set union. With
-secondary attributes, they must have the same names and datatypes. The two operands
-must also be **disjoint**, without any duplicate primary key values across both inputs.
-These requirements prevent ambiguity of attribute values and preserve entity identity.
-
-??? Note "Principles of union"
-
- 1. As in all operators, the order of the attributes in the operands is not
- significant.
-
- 2. Operands `A` and `B` must have the same primary key attributes. Otherwise, an
- error will be raised.
-
- 3. Operands `A` and `B` may not have any common non-key attributes. Otherwise, an
- error will be raised.
-
- 4. The result `A + B` will have the same primary key as `A` and `B`.
-
- 5. The result `A + B` will have all the non-key attributes from both `A` and `B`.
-
- 6. For entities that are found in both `A` and `B` (based on the primary key), the
- secondary attributes will be filled from the corresponding entities in `A` and
- `B`.
-
- 7. For entities that are only found in either `A` or `B`, the other operand's
- secondary attributes will filled with null values.
-
-For union, order does not matter.
-
-
-{: style="height:200px"}
-
-
-{: style="height:200px"}
-
-
-??? Note "Properties of union"
-
- 1. Commutative: `A + B` is equivalent to `B + A`.
- 2. Associative: `(A + B) + C` is equivalent to `A + (B + C)`.
-
-## Universal Set
-
-All of the above operators are designed to preserve their input type. Some queries may
-require creating a new entity type not already represented by existing tables. This
-means that the new type must be defined as part of the query.
-
-Universal sets fulfill this role using `dj.U` notation. They denote the set of all
-possible entities with given attributes of any possible datatype. Attributes of
-universal sets are allowed to be matched to any namesake attributes, even those that do
-not come from the same initial source.
-
-Universal sets should be used sparingly when no suitable base tables already exist. In
-some cases, defining a new base table can make queries clearer and more semantically
-constrained.
-
-The examples below will use the table definitions in [table tiers](../reproduce/table-tiers).
-
-
-
-## Top
-
-Similar to the universal set operator, the top operator uses `dj.Top` notation. It is used to
-restrict a query by the given `limit`, `order_by`, and `offset` parameters:
-
-```python
-Session & dj.Top(limit=10, order_by='session_date')
-```
-
-The result of this expression returns the first 10 rows of `Session` and sorts them
-by their `session_date` in ascending order.
-
-### `order_by`
-
-| Example | Description |
-|-------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| `order_by="session_date DESC"` | Sort by `session_date` in *descending* order |
-| `order_by="KEY"` | Sort by the primary key |
-| `order_by="KEY DESC"` | Sort by the primary key in *descending* order |
-| `order_by=["subject_id", "session_date"]` | Sort by `subject_id`, then sort matching `subject_id`s by their `session_date` |
-
-The default values for `dj.Top` parameters are `limit=1`, `order_by="KEY"`, and `offset=0`.
-
-## Restriction
-
-`&` and `-` operators permit restriction.
-
-### By a mapping
-
-For a [Session table](../reproduce/table-tiers#manual-tables), that has the attribute
-`session_date`, we can restrict to sessions from January 1st, 2022:
-
-```python
-Session & {'session_date': "2022-01-01"}
-```
-
-If there were any typos (e.g., using `sess_date` instead of `session_date`), our query
-will return all of the entities of `Session`.
-
-### By a string
-
-Conditions may include arithmetic operations, functions, range tests, etc. Restriction
-of table `A` by a string containing an attribute not found in table `A` produces an
-error.
-
-```python
-Session & 'user = "Alice"' # (1)
-Session & 'session_date >= "2022-01-01"' # (2)
-```
-
-1. All the sessions performed by Alice
-2. All of the sessions on or after January 1st, 2022
-
-### By a collection
-
-When `cond` is a collection of conditions, the conditions are applied by logical
-disjunction (logical OR). Restricting a table by a collection will return all entities
-that meet *any* of the conditions in the collection.
-
-For example, if we restrict the `Session` table by a collection containing two
-conditions, one for user and one for date, the query will return any sessions with a
-matching user *or* date.
-
-A collection can be a list, a tuple, or a Pandas `DataFrame`.
-
-``` python
-cond_list = ['user = "Alice"', 'session_date = "2022-01-01"'] # (1)
-cond_tuple = ('user = "Alice"', 'session_date = "2022-01-01"') # (2)
-import pandas as pd
-cond_frame = pd.DataFrame(data={'user': ['Alice'], 'session_date': ['2022-01-01']}) # (3)
-
-Session() & ['user = "Alice"', 'session_date = "2022-01-01"']
-```
-
-1. A list
-2. A tuple
-3. A data frame
-
-`dj.AndList` represents logical conjunction(logical AND). Restricting a table by an
-`AndList` will return all entities that meet *all* of the conditions in the list. `A &
-dj.AndList([c1, c2, c3])` is equivalent to `A & c1 & c2 & c3`.
-
-```python
-Student() & dj.AndList(['user = "Alice"', 'session_date = "2022-01-01"'])
-```
-
-The above will show all the sessions that Alice conducted on the given day.
-
-### By a `Not` object
-
-The special function `dj.Not` represents logical negation, such that `A & dj.Not
-(cond)` is equivalent to `A - cond`.
-
-### By a query
-
-Restriction by a query object is a generalization of restriction by a table. The example
-below creates a query object corresponding to all the users named Alice. The `Session`
-table is then restricted by the query object, returning all the sessions performed by
-Alice.
-
-``` python
-query = User & 'user = "Alice"'
-Session & query
-```
-
-## Proj
-
-Renaming an attribute in python can be done via keyword arguments:
-
-```python
-table.proj(new_attr='old_attr')
-```
-
-This can be done in the context of a table definition:
-
-```python
-@schema
-class Session(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- # Experiment Session
- -> Animal
- session : smallint # session number for the animal
- ---
- session_datetime : datetime # YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
- session_start_time : float # seconds relative to session_datetime
- session_end_time : float # seconds relative to session_datetime
- -> User.proj(experimenter='username')
- -> User.proj(supervisor='username')
- """
-```
-
-Or to rename multiple values in a table with the following syntax:
-`Table.proj(*existing_attributes,*renamed_attributes)`
-
-```python
-Session.proj('session','session_date',start='session_start_time',end='session_end_time')
-```
-
-Projection can also be used to to compute new attributes from existing ones.
-
-```python
-Session.proj(duration='session_end_time-session_start_time') & 'duration > 10'
-```
-
-## Aggr
-
-For more complicated calculations, we can use aggregation.
-
-``` python
-Subject.aggr(Session,n="count(*)") # (1)
-Subject.aggr(Session,average_start="avg(session_start_time)") # (2)
-```
-
-1. Number of sessions per subject.
-2. Average `session_start_time` for each subject
-
-
-
-## Universal set
-
-Universal sets offer the complete list of combinations of attributes.
-
-``` python
-# All home cities of students
-dj.U('laser_wavelength', 'laser_power') & Scan # (1)
-dj.U('laser_wavelength', 'laser_power').aggr(Scan, n="count(*)") # (2)
-dj.U().aggr(Session, n="max(session)") # (3)
-```
-
-1. All combinations of wavelength and power.
-2. Total number of scans for each combination.
-3. Largest session number.
-
-`dj.U()`, as shown in the last example above, is often useful for integer IDs.
-For an example of this process, see the source code for
-[Element Array Electrophysiology's `insert_new_params`](https://docs.datajoint.com/elements/element-array-ephys/latest/api/element_array_ephys/ephys_acute/#element_array_ephys.ephys_acute.ClusteringParamSet.insert_new_params).
diff --git a/docs/src/query/principles.md b/docs/src/query/principles.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9b9fd284d..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/principles.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-# Query Principles
-
-**Data queries** retrieve data from the database.
-A data query is performed with the help of a **query object**, which is a symbolic
-representation of the query that does not in itself contain any actual data.
-The simplest query object is an instance of a **table class**, representing the
-contents of an entire table.
-
-For example, if `experiment.Session` is a DataJoint table class, you can create a query
-object to retrieve its entire contents as follows:
-
-```python
-query = experiment.Session()
-```
-
-More generally, a query object may be formed as a **query expression** constructed by
-applying [operators](operators.md) to other query objects.
-
-For example, the following query retrieves information about all experiments and scans
-for mouse 102 (excluding experiments with no scans):
-
-```python
-query = experiment.Session * experiment.Scan & 'animal_id = 102'
-```
-
-Note that for brevity, query operators can be applied directly to class objects rather
-than instance objects so that `experiment.Session` may be used in place of
-`experiment.Session()`.
-
-You can preview the contents of the query in Python, Jupyter Notebook, or MATLAB by
-simply displaying the object.
-In the image below, the object `query` is first defined as a restriction of the table
-`EEG` by values of the attribute `eeg_sample_rate` greater than 1000 Hz.
-Displaying the object gives a preview of the entities that will be returned by `query`.
-Note that this preview only lists a few of the entities that will be returned.
-Also, the preview does not contain any data for attributes of datatype `blob`.
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-Defining a query object and previewing the entities returned by the query.
-
-Once the desired query object is formed, the query can be executed using its
-[fetch](fetch.md) methods.
-To **fetch** means to transfer the data represented by the query object from the
-database server into the workspace of the host language.
-
-```python
-s = query.fetch()
-```
-
-Here fetching from the `query` object produces the NumPy record array `s` of the
-queried data.
-
-## Checking for returned entities
-
-The preview of the query object shown above displayed only a few of the entities
-returned by the query but also displayed the total number of entities that would be
-returned.
-It can be useful to know the number of entities returned by a query, or even whether a
-query will return any entities at all, without having to fetch all the data themselves.
-
-The `bool` function applied to a query object evaluates to `True` if the query returns
-any entities and to `False` if the query result is empty.
-
-The `len` function applied to a query object determines the number of entities returned
-by the query.
-
-```python
-# number of sessions since the start of 2018.
-n = len(Session & 'session_date >= "2018-01-01"')
-```
-
-## Normalization in queries
-
-Query objects adhere to entity [entity normalization](../design/normalization.md) just
-like the stored tables do.
-The result of a query is a well-defined entity set with an readily identifiable entity
-class and designated primary attributes that jointly distinguish any two entities from
-each other.
-The query [operators](operators.md) are designed to keep the result normalized even in
-complex query expressions.
diff --git a/docs/src/query/project.md b/docs/src/query/project.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 99e5749c7..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/project.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-# Proj
-
-The `proj` operator represents **projection** and is used to select attributes
-(columns) from a table, to rename them, or to create new calculated attributes.
-
-## Simple projection
-
-The simple projection selects a subset of attributes of the original table.
-However, the primary key attributes are always included.
-
-Using the [example schema](example-schema.md), let table `department` have attributes
-**dept**, *dept_name*, *dept_address*, and *dept_phone*.
-The primary key attribute is in bold.
-
-Then `department.proj()` will have attribute **dept**.
-
-`department.proj('dept')` will have attribute **dept**.
-
-`department.proj('dept_name', 'dept_phone')` will have attributes **dept**,
-*dept_name*, and *dept_phone*.
-
-## Renaming
-
-In addition to selecting attributes, `proj` can rename them.
-Any attribute can be renamed, including primary key attributes.
-
-This is done using keyword arguments:
-`tab.proj(new_attr='old_attr')`
-
-For example, let table `tab` have attributes **mouse**, **session**, *session_date*,
-*stimulus*, and *behavior*.
-The primary key attributes are in bold.
-
-Then
-
-```python
-tab.proj(animal='mouse', 'stimulus')
-```
-
-will have attributes **animal**, **session**, and *stimulus*.
-
-Renaming is often used to control the outcome of a [join](join.md).
-For example, let `tab` have attributes **slice**, and **cell**.
-Then `tab * tab` will simply yield `tab`.
-However,
-
-```python
-tab * tab.proj(other='cell')
-```
-
-yields all ordered pairs of all cells in each slice.
-
-## Calculations
-
-In addition to selecting or renaming attributes, `proj` can compute new attributes from
-existing ones.
-
-For example, let `tab` have attributes `mouse`, `scan`, `surface_z`, and `scan_z`.
-To obtain the new attribute `depth` computed as `scan_z - surface_z` and then to
-restrict to `depth > 500`:
-
-```python
-tab.proj(depth='scan_z-surface_z') & 'depth > 500'
-```
-
-Calculations are passed to SQL and are not parsed by DataJoint.
-For available functions, you may refer to the
-[MySQL documentation](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/functions.html).
diff --git a/docs/src/query/query-caching.md b/docs/src/query/query-caching.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 124381b63..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/query-caching.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
-# Query Caching
-
-Query caching allows avoiding repeated queries to the database by caching the results
-locally for faster retrieval.
-
-To enable queries, set the query cache local path in `dj.config`, create the directory,
-and activate the query caching.
-
-```python
-# set the query cache path
-dj.config['query_cache'] = os.path.expanduser('~/dj_query_cache')
-
-# access the active connection object for the tables
-conn = dj.conn() # if queries co-located with tables
-conn = module.schema.connection # if schema co-located with tables
-conn = module.table.connection # most flexible
-
-# activate query caching for a namespace called 'main'
-conn.set_query_cache(query_cache='main')
-```
-
-The `query_cache` argument is an arbitrary string serving to differentiate cache
-states; setting a new value will effectively start a new cache, triggering retrieval of
-new values once.
-
-To turn off query caching, use the following:
-
-```python
-conn.set_query_cache(query_cache=None)
-# or
-conn.set_query_cache()
-```
-
-While query caching is enabled, any insert or delete calls and any transactions are
-disabled and will raise an error. This ensures that stale data are not used for
-updating the database in violation of data integrity.
-
-To clear and remove the query cache, use the following:
-
-```python
-conn.purge_query_cache()
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/query/restrict.md b/docs/src/query/restrict.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f8b61e641..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/restrict.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,205 +0,0 @@
-# Restriction
-
-## Restriction operators `&` and `-`
-
-The restriction operator `A & cond` selects the subset of entities from `A` that meet
-the condition `cond`.
-The exclusion operator `A - cond` selects the complement of restriction, i.e. the
-subset of entities from `A` that do not meet the condition `cond`.
-
-Restriction and exclusion.
-
-{: style="width:400px; align:center"}
-
-The condition `cond` may be one of the following:
-
-+ another table
-+ a mapping, e.g. `dict`
-+ an expression in a character string
-+ a collection of conditions as a `list`, `tuple`, or Pandas `DataFrame`
-+ a Boolean expression (`True` or `False`)
-+ an `AndList`
-+ a `Not` object
-+ a query expression
-
-As the restriction and exclusion operators are complementary, queries can be
-constructed using both operators that will return the same results.
-For example, the queries `A & cond` and `A - Not(cond)` will return the same entities.
-
-## Restriction by a table
-
-When restricting table `A` with another table, written `A & B`, the two tables must be
-**join-compatible** (see `join-compatible` in [Operators](./operators.md)).
-The result will contain all entities from `A` for which there exist a matching entity
-in `B`.
-Exclusion of table `A` with table `B`, or `A - B`, will contain all entities from `A`
-for which there are no matching entities in `B`.
-
-Restriction by another table.
-
-{: style="width:546px; align:center"}
-
-Exclusion by another table.
-
-{: style="width:539px; align:center"}
-
-### Restriction by a table with no common attributes
-
-Restriction of table `A` with another table `B` having none of the same attributes as
-`A` will simply return all entities in `A`, unless `B` is empty as described below.
-Exclusion of table `A` with `B` having no common attributes will return no entities,
-unless `B` is empty as described below.
-
-Restriction by a table having no common attributes.
-
-{: style="width:571px; align:center"}
-
-Exclusion by a table having no common attributes.
-
-{: style="width:571px; align:center"}
-
-### Restriction by an empty table
-
-Restriction of table `A` with an empty table will return no entities regardless of
-whether there are any matching attributes.
-Exclusion of table `A` with an empty table will return all entities in `A`.
-
-Restriction by an empty table.
-
-{: style="width:563px; align:center"}
-
-Exclusion by an empty table.
-
-{: style="width:571px; align:center"}
-
-## Restriction by a mapping
-
-A key-value mapping may be used as an operand in restriction.
-For each key that is an attribute in `A`, the paired value is treated as part of an
-equality condition.
-Any key-value pairs without corresponding attributes in `A` are ignored.
-
-Restriction by an empty mapping or by a mapping with no keys matching the attributes in
-`A` will return all the entities in `A`.
-Exclusion by an empty mapping or by a mapping with no matches will return no entities.
-
-For example, let's say that table `Session` has the attribute `session_date` of
-[datatype](../design/tables/attributes.md) `datetime`.
-You are interested in sessions from January 1st, 2018, so you write the following
-restriction query using a mapping.
-
-```python
-Session & {'session_date': "2018-01-01"}
-```
-
-Our mapping contains a typo omitting the final `e` from `session_date`, so no keys in
-our mapping will match any attribute in `Session`.
-As such, our query will return all of the entities of `Session`.
-
-## Restriction by a string
-
-Restriction can be performed when `cond` is an explicit condition on attribute values,
-expressed as a string.
-Such conditions may include arithmetic operations, functions, range tests, etc.
-Restriction of table `A` by a string containing an attribute not found in table `A`
-produces an error.
-
-```python
-# All the sessions performed by Alice
-Session & 'user = "Alice"'
-
-# All the experiments at least one minute long
-Experiment & 'duration >= 60'
-```
-
-## Restriction by a collection
-
-A collection can be a list, a tuple, or a Pandas `DataFrame`.
-
-```python
-# a list:
-cond_list = ['first_name = "Aaron"', 'last_name = "Aaronson"']
-
-# a tuple:
-cond_tuple = ('first_name = "Aaron"', 'last_name = "Aaronson"')
-
-# a dataframe:
-import pandas as pd
-cond_frame = pd.DataFrame(
- data={'first_name': ['Aaron'], 'last_name': ['Aaronson']})
-```
-
-When `cond` is a collection of conditions, the conditions are applied by logical
-disjunction (logical OR).
-Thus, restriction of table `A` by a collection will return all entities in `A` that
-meet *any* of the conditions in the collection.
-For example, if you restrict the `Student` table by a collection containing two
-conditions, one for a first and one for a last name, your query will return any
-students with a matching first name *or* a matching last name.
-
-```python
-Student() & ['first_name = "Aaron"', 'last_name = "Aaronson"']
-```
-
-Restriction by a collection, returning all entities matching any condition in the collection.
-
-{: style="align:center"}
-
-Restriction by an empty collection returns no entities.
-Exclusion of table `A` by an empty collection returns all the entities of `A`.
-
-## Restriction by a Boolean expression
-
-`A & True` and `A - False` are equivalent to `A`.
-
-`A & False` and `A - True` are empty.
-
-## Restriction by an `AndList`
-
-The special function `dj.AndList` represents logical conjunction (logical AND).
-Restriction of table `A` by an `AndList` will return all entities in `A` that meet
-*all* of the conditions in the list.
-`A & dj.AndList([c1, c2, c3])` is equivalent to `A & c1 & c2 & c3`.
-Usually, it is more convenient to simply write out all of the conditions, as
-`A & c1 & c2 & c3`.
-However, when a list of conditions has already been generated, the list can simply be
-passed as the argument to `dj.AndList`.
-
-Restriction of table `A` by an empty `AndList`, as in `A & dj.AndList([])`, will return
-all of the entities in `A`.
-Exclusion by an empty `AndList` will return no entities.
-
-## Restriction by a `Not` object
-
-The special function `dj.Not` represents logical negation, such that `A & dj.Not(cond)`
-is equivalent to `A - cond`.
-
-## Restriction by a query
-
-Restriction by a query object is a generalization of restriction by a table (which is
-also a query object), because DataJoint queries always produce well-defined entity
-sets, as described in [entity normalization](../design/normalization.md).
-As such, restriction by queries follows the same behavior as restriction by tables
-described above.
-
-The example below creates a query object corresponding to all the sessions performed by
-the user Alice.
-The `Experiment` table is then restricted by the query object, returning all the
-experiments that are part of sessions performed by Alice.
-
-```python
-query = Session & 'user = "Alice"'
-Experiment & query
-```
-
-## Restriction by `dj.Top`
-
-Restriction by `dj.Top` returns the number of entities specified by the `limit`
-argument. These entities can be returned in the order specified by the `order_by`
-argument. And finally, the `offset` argument can be used to offset the returned entities
-which is useful for pagination in web applications.
-
-```python
-# Return the first 10 sessions in descending order of session date
-Session & dj.Top(limit=10, order_by='session_date DESC')
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/query/union.md b/docs/src/query/union.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 71f0fa687..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/union.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
-# Union
-
-The union operator is not yet implemented -- this page serves as the specification for
-the upcoming implementation.
-Union is rarely needed in practice.
-
-## Union operator `+`
-
-The result of the union operator `A + B` contains all the entities from both operands.
-[Entity normalization](../design/normalization.md) requires that the operands in a
-union both belong to the same entity type with the same primary key using homologous
-attributes.
-In the absence of any secondary attributes, the result of a union is the simple set union.
-
-When secondary attributes are present, they must have the same names and datatypes in
-both operands.
-The two operands must also be **disjoint**, without any duplicate primary key values
-across both inputs.
-These requirements prevent ambiguity of attribute values and preserve entity identity.
-
-## Principles of union
-
-1. As in all operators, the order of the attributes in the operands is not significant.
-2. Operands `A` and `B` must have the same primary key attributes.
- Otherwise, an error will be raised.
-3. Operands `A` and `B` may not have any common non-key attributes.
- Otherwise, an error will be raised.
-4. The result `A + B` will have the same primary key as `A` and `B`.
-5. The result `A + B` will have all the non-key attributes from both `A` and `B`.
-6. For entities that are found in both `A` and `B` (based on the primary key), the
-secondary attributes will be filled from the corresponding entities in `A` and `B`.
-7. For entities that are only found in either `A` or `B`, the other operand's secondary
-attributes will filled with null values.
-
-## Examples of union
-
-Example 1 : Note that the order of the attributes does not matter.
-
-{: style="width:404px; align:center"}
-
-Example 2 : Non-key attributes are combined from both tables and filled with NULLs when missing.
-
-{: style="width:539px; align:center"}
-
-## Properties of union
-
-1. Commutative: `A + B` is equivalent to `B + A`.
-2. Associative: `(A + B) + C` is equivalent to `A + (B + C)`.
diff --git a/docs/src/query/universals.md b/docs/src/query/universals.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a9f12dd96..000000000
--- a/docs/src/query/universals.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-# Universal Sets
-
-All [query operators](operators.md) are designed to preserve the entity types of their
-inputs.
-However, some queries require creating a new entity type that is not represented by any
-stored tables.
-This means that a new entity type must be explicitly defined as part of the query.
-Universal sets fulfill this role.
-
-**Universal sets** are used in DataJoint to define virtual tables with arbitrary
-primary key structures for use in query expressions.
-A universal set, defined using class `dj.U`, denotes the set of all possible entities
-with given attributes of any possible datatype.
-Universal sets allow query expressions using virtual tables when no suitable base table exists.
-Attributes of universal sets are allowed to be matched to any namesake attributes, even
-those that do not come from the same initial source.
-
-For example, you may like to query the university database for the complete list of
-students' home cities, along with the number of students from each city.
-The [schema](example-schema.md) for the university database does not have a table for
-cities and states.
-A virtual table can fill the role of the nonexistent base table, allowing queries that
-would not be possible otherwise.
-
-```python
-# All home cities of students
-dj.U('home_city', 'home_state') & Student
-
-# Total number of students from each city
-dj.U('home_city', 'home_state').aggr(Student, n="count(*)")
-
-# Total number of students from each state
-U('home_state').aggr(Student, n="count(*)")
-
-# Total number of students in the database
-U().aggr(Student, n="count(*)")
-```
-
-The result of aggregation on a universal set is restricted to the entities with matches
-in the aggregated table, such as `Student` in the example above.
-In other words, `X.aggr(A, ...)` is interpreted as `(X & A).aggr(A, ...)` for universal
-set `X`.
-All attributes of a universal set are considered primary.
-
-Universal sets should be used sparingly when no suitable base tables already exist.
-In some cases, defining a new base table can make queries clearer and more semantically constrained.
diff --git a/docs/src/quick-start.md b/docs/src/quick-start.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a7f255658..000000000
--- a/docs/src/quick-start.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,469 +0,0 @@
-# Quick Start Guide
-
-## Tutorials
-
-The easiest way to get started is through the [DataJoint
-Tutorials](https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-tutorials). These tutorials are
-configured to run using [GitHub Codespaces](https://github.com/features/codespaces)
-where the full environment including the database is already set up.
-
-Advanced users can install DataJoint locally. Please see the installation instructions below.
-
-## Installation
-
-First, please [install Python](https://www.python.org/downloads/) version
-3.8 or later.
-
-Next, please install DataJoint via one of the following:
-
-=== "conda"
-
- Pre-Requisites
- - Ensure you have [conda](https://conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/user-guide/install/index.html#regular-installation)
- installed.
-
- To add the `conda-forge` channel:
-
- ```bash
- conda config --add channels conda-forge
- ```
-
- To install:
-
- ```bash
- conda install -c conda-forge datajoint
- ```
-
-=== "pip + :fontawesome-brands-windows:"
-
- Pre-Requisites
- - Ensure you have [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/installation/) installed.
- - Install [graphviz](https://graphviz.org/download/#windows) pre-requisite for
- diagram visualization.
-
- To install:
-
- ```bash
- pip install datajoint
- ```
-
-=== "pip + :fontawesome-brands-apple:"
-
- Pre-Requisites
- - Ensure you have [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/installation/) installed.
- - Install [graphviz](https://graphviz.org/download/#mac) pre-requisite for
- diagram visualization.
-
- To install:
-
- ```bash
- pip install datajoint
- ```
-
-=== "pip + :fontawesome-brands-linux:"
-
- Pre-Requisites
- - Ensure you have [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/installation/) installed.
- - Install [graphviz](https://graphviz.org/download/#linux) pre-requisite for
- diagram visualization.
-
- To install:
-
- ```bash
- pip install datajoint
- ```
-
-## Connection
-
-=== "environment variables"
-
- Before using `datajoint`, set the following environment variables like so:
-
- ```bash linenums="1"
- DJ_HOST={host_address}
- DJ_USER={user}
- DJ_PASS={password}
- ```
-
-=== "memory"
-
- To set connection settings within Python, perform:
-
- ```python linenums="1"
- import datajoint as dj
-
- dj.config["database.host"] = "{host_address}"
- dj.config["database.user"] = "{user}"
- dj.config["database.password"] = "{password}"
- ```
-
- These configuration settings can be saved either locally or system-wide using one
- of the following commands:
- ```python
- dj.config.save_local()
- dj.config.save_global()
- ```
-
-=== "file"
-
- Before using `datajoint`, create a file named `dj_local_conf.json` in the current
- directory like so:
-
- ```json linenums="1"
- {
- "database.host": "{host_address}",
- "database.user": "{user}",
- "database.password": "{password}"
- }
- ```
-
- These settings will be loaded whenever a Python instance is launched from this
- directory. To configure settings globally, save a similar file as
- `.datajoint_config.json` in your home directory. A local config, if present, will
- take precedent over global settings.
-
-## Data Pipeline Definition
-
-Let's definite a simple data pipeline.
-
-```python linenums="1"
-import datajoint as dj
-schema = dj.Schema(f"{dj.config['database.user']}_shapes") # This statement creates the database schema `{username}_shapes` on the server.
-
-@schema # The `@schema` decorator for DataJoint classes creates the table on the server.
-class Rectangle(dj.Manual):
- definition = """ # The table is defined by the the `definition` property.
- shape_id: int
- ---
- shape_height: float
- shape_width: float
- """
-
-@schema
-class Area(dj.Computed):
- definition = """
- -> Rectangle
- ---
- shape_area: float
- """
- def make(self, key):
- rectangle = (Rectangle & key).fetch1()
- Area.insert1(
- dict(
- shape_id=rectangle["shape_id"],
- shape_area=rectangle["shape_height"] * rectangle["shape_width"],
- )
- )
-```
-
-It is a common practice to have a separate Python module for each schema. Therefore,
-each such module has only one `dj.Schema` object defined and is usually named
-`schema`.
-
-The `dj.Schema` constructor can take a number of optional parameters
-after the schema name.
-
-- `context` - Dictionary for looking up foreign key references.
- Defaults to `None` to use local context.
-- `connection` - Specifies the DataJoint connection object. Defaults
- to `dj.conn()`.
-- `create_schema` - When `False`, the schema object will not create a
- schema on the database and will raise an error if one does not
- already exist. Defaults to `True`.
-- `create_tables` - When `False`, the schema object will not create
- tables on the database and will raise errors when accessing missing
- tables. Defaults to `True`.
-
-The `@schema` decorator uses the class name and the data tier to check whether an
-appropriate table exists on the database. If a table does not already exist, the
-decorator creates one on the database using the definition property. The decorator
-attaches the information about the table to the class, and then returns the class.
-
-## Diagram
-
-### Display
-
-The diagram displays the relationship of the data model in the data pipeline.
-
-This can be done for an entire schema:
-
-```python
-import datajoint as dj
-schema = dj.Schema('my_database')
-dj.Diagram(schema)
-```
-
-
-
-Or for individual or sets of tables:
-```python
-dj.Diagram(schema.Rectangle)
-dj.Diagram(schema.Rectangle) + dj.Diagram(schema.Area)
-```
-
-What if I don't see the diagram?
-
-Some Python interfaces may require additional `draw` method.
-
-```python
-dj.Diagram(schema).draw()
-```
-
-Calling the `.draw()` method is not necessary when working in a Jupyter notebook by
-entering `dj.Diagram(schema)` in a notebook cell. The Diagram will automatically
-render in the notebook by calling its `_repr_html_` method. A Diagram displayed
-without `.draw()` will be rendered as an SVG, and hovering the mouse over a table
-will reveal a compact version of the output of the `.describe()` method.
-
-For more information about diagrams, see [this article](../design/diagrams).
-
-### Customize
-
-Adding or subtracting a number to a diagram object adds nodes downstream or upstream,
-respectively, in the pipeline.
-
-```python
-(dj.Diagram(schema.Rectangle)+1).draw() # Plot all the tables directly downstream from `schema.Rectangle`
-```
-
-```python
-(dj.Diagram('my_schema')-1+1).draw() # Plot all tables directly downstream of those directly upstream of this schema.
-```
-
-### Save
-
-The diagram can be saved as either `png` or `svg`.
-
-```python
-dj.Diagram(schema).save(filename='my-diagram', format='png')
-```
-
-## Insert data
-
-Data entry is as easy as providing the appropriate data structure to a permitted
-[table](./design/tables/tiers.md).
-
-Let's add data for a rectangle:
-
-```python
-Rectangle.insert1(dict(shape_id=1, shape_height=2, shape_width=4))
-```
-
-Given the following [table definition](./design/tables/declare.md), we can insert data
-as tuples, dicts, pandas dataframes, or pathlib `Path` relative paths to local CSV
-files.
-
-```python
-mouse_id: int # unique mouse id
----
-dob: date # mouse date of birth
-sex: enum('M', 'F', 'U') # sex of mouse - Male, Female, or Unknown
-```
-
-=== "Tuple"
-
- ```python
- mouse.insert1( (0, '2017-03-01', 'M') ) # Single entry
- data = [
- (1, '2016-11-19', 'M'),
- (2, '2016-11-20', 'U'),
- (5, '2016-12-25', 'F')
- ]
- mouse.insert(data) # Multi-entry
- ```
-
-=== "Dict"
-
- ```python
- mouse.insert1( dict(mouse_id=0, dob='2017-03-01', sex='M') ) # Single entry
- data = [
- {'mouse_id':1, 'dob':'2016-11-19', 'sex':'M'},
- {'mouse_id':2, 'dob':'2016-11-20', 'sex':'U'},
- {'mouse_id':5, 'dob':'2016-12-25', 'sex':'F'}
- ]
- mouse.insert(data) # Multi-entry
- ```
-
-=== "Pandas"
-
- ```python
- import pandas as pd
- data = pd.DataFrame(
- [[1, "2016-11-19", "M"], [2, "2016-11-20", "U"], [5, "2016-12-25", "F"]],
- columns=["mouse_id", "dob", "sex"],
- )
- mouse.insert(data)
- ```
-
-=== "CSV"
-
- Given the following CSV in the current working directory as `mice.csv`
-
- ```console
- mouse_id,dob,sex
- 1,2016-11-19,M
- 2,2016-11-20,U
- 5,2016-12-25,F
- ```
-
- We can import as follows:
-
- ```python
- from pathlib import Path
- mouse.insert(Path('./mice.csv'))
- ```
-
-## Run computation
-
-Let's start the computations on our entity: `Area`.
-
-```python
-Area.populate(display_progress=True)
-```
-
-The `make` method populates automated tables from inserted data. Read more in the
-full article [here](./compute/make.md)
-
-## Query
-
-Let's inspect the results.
-
-```python
-Area & "shape_area >= 8"
-```
-
-| shaped_id | shape_area |
-| --- | --- |
-| 1 | 8.0 |
-
-## Fetch
-
-Data queries in DataJoint comprise two distinct steps:
-
-1. Construct the `query` object to represent the required data using
- tables and [operators](../query/operators).
-2. Fetch the data from `query` into the workspace of the host language.
-
-Note that entities returned by `fetch` methods are not guaranteed to be sorted in any
-particular order unless specifically requested. Furthermore, the order is not
-guaranteed to be the same in any two queries, and the contents of two identical queries
-may change between two sequential invocations unless they are wrapped in a transaction.
-Therefore, if you wish to fetch matching pairs of attributes, do so in one `fetch`
-call.
-
-```python
-data = query.fetch()
-```
-
-### Entire table
-
-A `fetch` command can either retrieve table data as a NumPy
-[recarray](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.recarray.html)
-or a as a list of `dict`
-
-```python
-data = query.fetch() # NumPy recarray
-data = query.fetch(as_dict=True) # List of `dict`
-```
-
-In some cases, the amount of data returned by fetch can be quite large; it can be
-useful to use the `size_on_disk` attribute to determine if running a bare fetch
-would be wise. Please note that it is only currently possible to query the size of
-entire tables stored directly in the database at this time.
-
-### Separate variables
-
-```python
-name, img = query.fetch1('mouse_id', 'dob') # when query has exactly one entity
-name, img = query.fetch('mouse_id', 'dob') # [mouse_id, ...] [dob, ...]
-```
-
-### Primary key values
-
-```python
-keydict = tab.fetch1("KEY") # single key dict when tab has exactly one entity
-keylist = tab.fetch("KEY") # list of key dictionaries [{}, ...]
-```
-
-`KEY` can also used when returning attribute values as separate
-variables, such that one of the returned variables contains the entire
-primary keys.
-
-### Sorting results
-
-To sort the result, use the `order_by` keyword argument.
-
-```python
-data = query.fetch(order_by='mouse_id') # ascending order
-data = query.fetch(order_by='mouse_id desc') # descending order
-data = query.fetch(order_by=('mouse_id', 'dob')) # by ID first, dob second
-data = query.fetch(order_by='KEY') # sort by the primary key
-```
-
-The `order_by` argument can be a string specifying the attribute to sort by. By default
-the sort is in ascending order. Use `'attr desc'` to sort in descending order by
-attribute `attr`. The value can also be a sequence of strings, in which case, the sort
-performed on all the attributes jointly in the order specified.
-
-The special attribute named `'KEY'` represents the primary key attributes in order that
-they appear in the index. Otherwise, this name can be used as any other argument.
-
-If an attribute happens to be a SQL reserved word, it needs to be enclosed in
-backquotes. For example:
-
-```python
-data = query.fetch(order_by='`select` desc')
-```
-
-The `order_by` value is eventually passed to the `ORDER BY`
-[clause](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/order-by-optimization.html).
-
-### Limiting results
-
-Similar to sorting, the `limit` and `offset` arguments can be used to limit the result
-to a subset of entities.
-
-```python
-data = query.fetch(order_by='mouse_id', limit=10, offset=5)
-```
-
-Note that an `offset` cannot be used without specifying a `limit` as
-well.
-
-### Usage with Pandas
-
-The `pandas` [library](http://pandas.pydata.org/) is a popular library for data analysis
-in Python which can easily be used with DataJoint query results. Since the records
-returned by `fetch()` are contained within a `numpy.recarray`, they can be easily
-converted to `pandas.DataFrame` objects by passing them into the `pandas.DataFrame`
-constructor. For example:
-
-```python
-import pandas as pd
-frame = pd.DataFrame(tab.fetch())
-```
-
-Calling `fetch()` with the argument `format="frame"` returns results as
-`pandas.DataFrame` objects indexed by the table's primary key attributes.
-
-```python
-frame = tab.fetch(format="frame")
-```
-
-Returning results as a `DataFrame` is not possible when fetching a particular subset of
-attributes or when `as_dict` is set to `True`.
-
-## Drop
-
-The `drop` method completely removes a table from the database, including its
-definition. It also removes all dependent tables, recursively. DataJoint will first
-display the tables being dropped and the number of entities in each before prompting
-the user for confirmation to proceed.
-
-The `drop` method is often used during initial design to allow altered
-table definitions to take effect.
-
-```python
-# drop the Person table from its schema
-Person.drop()
-```
diff --git a/docs/src/sysadmin/bulk-storage.md b/docs/src/sysadmin/bulk-storage.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 12af44791..000000000
--- a/docs/src/sysadmin/bulk-storage.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-# Bulk Storage Systems
-
-## Why External Bulk Storage?
-
-DataJoint supports the storage of large data objects associated with
-relational records externally from the MySQL Database itself. This is
-significant and useful for a number of reasons.
-
-### Cost
-
-One reason is that the high-performance storage commonly used in database systems is
-more expensive than typical commodity storage. Therefore, storing the smaller identifying
-information typically used in queries on fast, relational database storage and storing
-the larger bulk data used for analysis or processing on lower cost commodity storage
-enables large savings in storage expense.
-
-### Flexibility
-
-Storing bulk data separately also facilitates more flexibility in
-usage, since the bulk data can managed using separate maintenance
-processes than those in the relational storage.
-
-For example, larger relational databases may require many hours to be
-restored in the event of system failures. If the relational portion of
-the data is stored separately, with the larger bulk data stored on
-another storage system, this downtime can be reduced to a matter of
-minutes. Similarly, due to the lower cost of bulk commodity storage,
-more emphasis can be put into redundancy of this data and backups to
-help protect the non-relational data.
-
-### Performance
-
-Storing the non-relational bulk data separately can have system
-performance impacts by removing data transfer, disk I/O, and memory
-load from the database server and shifting these to the bulk storage
-system. Additionally, DataJoint supports caching of bulk data records
-which can allow for faster processing of records which already have
-been retrieved in previous queries.
-
-### Data Sharing
-
-DataJoint provides pluggable support for different external bulk storage backends,
-allowing data sharing by publishing bulk data to S3-Protocol compatible data shares both
-in the cloud and on locally managed systems and other common tools for data sharing,
-such as Globus, etc.
-
-## Bulk Storage Scenarios
-
-Typical bulk storage considerations relate to the cost of the storage
-backend per unit of storage, the amount of data which will be stored,
-the desired focus of the shared data (system performance, data
-flexibility, data sharing), and data access. Some common scenarios are
-given in the following table:
-
-| Scenario | Storage Solution | System Requirements | Notes |
-| -- | -- | -- | -- |
-| Local Object Cache | Local External Storage | Local Hard Drive | Used to Speed Access to other Storage |
-| LAN Object Cache | Network External Storage | Local Network Share | Used to Speed Access to other storage, reduce Cloud/Network Costs/Overhead |
-| Local Object Store | Local/Network External Storage | Local/Network Storage | Used to store objects externally from the database |
-| Local S3-Compatible Store | Local S3-Compatible Server | Network S3-Server | Used to host S3-Compatible services locally (e.g. minio) for internal use or to lower cloud costs |
-| Cloud S3-Compatible Storage | Cloud Provider | Internet Connectivity | Used to reduce/remove requirement for external storage management, data sharing |
-| Globus Storage | Globus Endpoint | Local/Local Network Storage, Internet Connectivity | Used for institutional data transfer or publishing. |
-
-## Bulk Storage Considerations
-
-Although external bulk storage provides a variety of advantages for
-storage cost and data sharing, it also uses slightly different data
-input/retrieval semantics and as such has different performance
-characteristics.
-
-### Performance Characteristics
-
-In the direct database connection scenario, entire result sets are
-either added or retrieved from the database in a single stream
-action. In the case of external storage, individual record components
-are retrieved in a set of sequential actions per record, each one
-subject to the network round trip to the given storage medium. As
-such, tables using many small records may be ill suited to external
-storage usage in the absence of a caching mechanism. While some of
-these impacts may be addressed by code changes in a future release of
-DataJoint, to some extent, the impact is directly related from needing
-to coordinate the activities of the database data stream with the
-external storage system, and so cannot be avoided.
-
-### Network Traffic
-
-Some of the external storage solutions mentioned above incur cost both
-at a data volume and transfer bandwidth level. The number of users
-querying the database, data access, and use of caches should be
-considered in these cases to reduce this cost if applicable.
-
-### Data Coherency
-
-When storing all data directly in the relational data store, it is
-relatively easy to ensure that all data in the database is consistent
-in the event of system issues such as crash recoveries, since MySQL’s
-relational storage engine manages this for you. When using external
-storage however, it is important to ensure that any data recoveries of
-the database system are paired with a matching point-in-time of the
-external storage system. While DataJoint does use hashing to help
-facilitate a guarantee that external files are uniquely named
-throughout their lifecycle, the pairing of a given relational dataset
-against a given filesystem state is loosely coupled, and so an
-incorrect pairing could result in processing failures or other issues.
diff --git a/docs/src/sysadmin/database-admin.md b/docs/src/sysadmin/database-admin.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 352a3af11..000000000
--- a/docs/src/sysadmin/database-admin.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,364 +0,0 @@
-# Database Administration
-
-## Hosting
-
-Let’s say a person, a lab, or a multi-lab consortium decide to use DataJoint as their
-data pipeline platform.
-What IT resources and support will be required?
-
-DataJoint uses a MySQL-compatible database server such as MySQL, MariaDB, Percona
-Server, or Amazon Aurora to store the structured data used for all relational
-operations.
-Large blocks of data associated with these records such as multidimensional numeric
-arrays (signals, images, scans, movies, etc) can be stored within the database or
-stored in additionally configured [bulk storage](../client/stores.md).
-
-The first decisions you need to make are where this server will be hosted and how it
-will be administered.
-The server may be hosted on your personal computer, on a dedicated machine in your lab,
-or in a cloud-based database service.
-
-### Cloud hosting
-
-Increasingly, many teams make use of cloud-hosted database services, which allow great
-flexibility and easy administration of the database server.
-A cloud hosting option will be provided through https://works.datajoint.com.
-DataJoint Works simplifies the setup for labs that wish to host their data pipelines in
-the cloud and allows sharing pipelines between multiple groups and locations.
-Being an open-source solution, other cloud services such as Amazon RDS can also be used
-in this role, albeit with less DataJoint-centric customization.
-
-### Self hosting
-
-In the most basic configuration, the relational database management system (database
-server) is installed on an individual user's personal computer.
-To support a group of users, a specialized machine can be configured as a dedicated
-database server.
-This server can be accessed by multiple DataJoint clients to query the data and perform
-computations.
-
-For larger groups and multi-site collaborations with heavy workloads, the database
-server cluster may be configured in the cloud or on premises.
-The following section provides some basic guidelines for these configurations here and
-in the subsequent sections of the documentation.
-
-### General server / hardware support requirements
-
-The following table lists some likely scenarios for DataJoint database server
-deployments and some reasonable estimates of the required computer hardware.
-The required IT/systems support needed to ensure smooth operations in the absence of
-local database expertise is also listed.
-
-#### IT infrastructures
-
-| Usage Scenario | DataJoint Database Computer | Required IT Support |
-| -- | -- | -- |
-| Single User | Personal Laptop or Workstation | Self-Supported or Ad-Hoc General IT Support |
-| Small Group (e.g. 2-10 Users) | Workstation or Small Server | Ad-Hoc General or Experienced IT Support |
-| Medium Group (e.g. 10-30 Users) | Small to Medium Server | Ad-Hoc/Part Time Experienced or Specialized IT Support |
-| Large Group/Department (e.g. 30-50+ Users) | Medium/Large Server or Multi-Server Replication | Part Time/Dedicated Experienced or Specialized IT Support |
-| Multi-Location Collaboration (30+ users, Geographically Distributed) | Large Server, Advanced Replication | Dedicated Specialized IT Support |
-
-## Configuration
-
-### Hardware considerations
-
-As in any computer system, CPU, RAM memory, disk storage, and network speed are
-important components of performance.
-The relational database component of DataJoint is no exception to this rule.
-This section discusses the various factors relating to selecting a server for your
-DataJoint pipelines.
-
-#### CPU
-
-CPU speed and parallelism (number of cores/threads) will impact the speed of queries
-and the number of simultaneous queries which can be efficiently supported by the system.
-It is a good rule of thumb to have enough cores to support the number of active users
-and background tasks you expect to have running during a typical 'busy' day of usage.
-For example, a team of 10 people might want to have 8 cores to support a few active
-queries and background tasks.
-
-#### RAM
-
-The amount of RAM will impact the amount of DataJoint data kept in memory, allowing for
-faster querying of data since the data can be searched and returned to the user without
-needing to access the slower disk drives.
-It is a good idea to get enough memory to fully store the more important and frequently
-accessed portions of your dataset with room to spare, especially if in-database blob
-storage is used instead of external [bulk storage](bulk-storage.md).
-
-#### Disk
-
-The disk storage for a DataJoint database server should have fast random access,
-ideally with flash-based storage to eliminate the rotational delay of mechanical hard
-drives.
-
-#### Networking
-
-When network connections are used, network speed and latency are important to ensure
-that large query results can be quickly transferred across the network and that delays
-due to data entry/query round-trip have minimal impact on the runtime of the program.
-
-#### General recommendations
-
-DataJoint datasets can consist of many thousands or even millions of records.
-Generally speaking one would want to make sure that the relational database system has
-sufficient CPU speed and parallelism to support a typical number of concurrent users
-and to execute searches quickly.
-The system should have enough RAM to store the primary key values of commonly used
-tables and operating system caches.
-Disk storage should be fast enough to support quick loading of and searching through
-the data.
-Lastly, network bandwidth must be sufficient to support transferring user records
-quickly.
-
-### Large-scale installations
-
-Database replication may be beneficial if system downtime or precise database
-responsiveness is a concern
-Replication can allow for easier coordination of maintenance activities, faster
-recovery in the event of system problems, and distribution of the database workload
-across server machines to increase throughput and responsiveness.
-
-#### Multi-master replication
-
-Multi-master replication configurations allow for all replicas to be used in a read/
-write fashion, with the workload being distributed among all machines.
-However, multi-master replication is also more complicated, requiring front-end
-machines to distribute the workload, similar performance characteristics on all
-replicas to prevent bottlenecks, and redundant network connections to ensure the
-replicated machines are always in sync.
-
-### Recommendations
-
-It is usually best to go with the simplest solution which can suit the requirements of
-the installation, adjusting workloads where possible and adding complexity only as
-needs dictate.
-
-Resource requirements of course depend on the data collection and processing needs of
-the given pipeline, but there are general size guidelines that can inform any system
-configuration decisions.
-A reasonably powerful workstation or small server should support the needs of a small
-group (2-10 users).
-A medium or large server should support the needs of a larger user community (10-30
-users).
-A replicated or distributed setup of 2 or more medium or large servers may be required
-in larger cases.
-These requirements can be reduced through the use of external or cloud storage, which
-is discussed in the subsequent section.
-
-| Usage Scenario | DataJoint Database Computer | Hardware Recommendation |
-| -- | -- | -- |
-| Single User | Personal Laptop or Workstation | 4 Cores, 8-16GB or more of RAM, SSD or better storage |
-| Small Group (e.g. 2-10 Users) | Workstation or Small Server | 8 or more Cores, 16GB or more of RAM, SSD or better storage |
-| Medium Group (e.g. 10-30 Users) | Small to Medium Server | 8-16 or more Cores, 32GB or more of RAM, SSD/RAID or better storage |
-| Large Group/Department (e.g. 30-50+ Users) | Medium/Large Server or Multi-Server Replication | 16-32 or more Cores, 64GB or more of RAM, SSD Raid storage, multiple machines |
-| Multi-Location Collaboration (30+ users, Geographically Distributed) | Large Server, Advanced Replication | 16-32 or more Cores, 64GB or more of RAM, SSD Raid storage, multiple machines; potentially multiple machines in multiple locations |
-
-### Docker
-
-A Docker image is available for a MySQL server configured to work with DataJoint: https://github.com/datajoint/mysql-docker.
-
-## User Management
-
-Create user accounts on the MySQL server. For example, if your
-username is alice, the SQL code for this step is:
-
-```mysql
-CREATE USER 'alice'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'alices-secret-password';
-```
-
-Existing users can be listed using the following SQL:
-
-```mysql
-SELECT user, host from mysql.user;
-```
-
-Teams that use DataJoint typically divide their data into schemas
-grouped together by common prefixes. For example, a lab may have a
-collection of schemas that begin with `common_`. Some common
-processing may be organized into several schemas that begin with
-`pipeline_`. Typically each user has all privileges to schemas that
-begin with their username.
-
-For example, alice may have privileges to select and insert data from
-the common schemas (but not create new tables), and have all
-privileges to the pipeline schemas.
-
-Then the SQL code to grant her privileges might look like:
-
-```mysql
-GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON `common\_%`.* TO 'alice'@'%';
-GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `pipeline\_%`.* TO 'alice'@'%';
-GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `alice\_%`.* TO 'alice'@'%';
-```
-
-To note, the ```ALL PRIVILEGES``` option allows the user to create
-and remove databases without administrator intervention.
-
-Once created, a user's privileges can be listed using the ```SHOW GRANTS```
-statement.
-
-```mysql
-SHOW GRANTS FOR 'alice'@'%';
-```
-
-### Grouping with Wildcards
-
-Depending on the complexity of your installation, using additional
-wildcards to group access rules together might make managing user
-access rules simpler. For example, the following equivalent
-convention:
-
-```mysql
-GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `user_alice\_%`.* TO 'alice'@'%';
-```
-
-Could then facilitate using a rule like:
-
-```mysql
-GRANT SELECT ON `user\_%\_%`.* TO 'bob'@'%';
-```
-
-to enable `bob` to query all other users tables using the
-`user_username_database` convention without needing to explicitly
-give him access to `alice\_%`, `charlie\_%`, and so on.
-
-This convention can be further expanded to create notions of groups
-and protected schemas for background processing, etc. For example:
-
-```mysql
-GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `group\_shared\_%`.* TO 'alice'@'%';
-GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `group\_shared\_%`.* TO 'bob'@'%';
-
-GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `group\_wonderland\_%`.* TO 'alice'@'%';
-GRANT SELECT ON `group\_wonderland\_%`.* TO 'alice'@'%';
-```
-
-could allow both bob an alice to read/write into the
-```group\_shared``` databases, but in the case of the
-```group\_wonderland``` databases, read write access is restricted
-to alice.
-
-## Backups and Recovery
-
-Backing up your DataJoint installation is critical to ensuring that your work is safe
-and can be continued in the event of system failures, and several mechanisms are
-available to use.
-
-Much like your live installation, your backup will consist of two portions:
-
-- Backup of the Relational Data
-- Backup of optional external bulk storage
-
-This section primarily deals with backup of the relational data since most of the
-optional bulk storage options use "regular" flat-files for storage and can be backed up
-via any "normal" disk backup regime.
-
-There are many options to backup MySQL; subsequent sections discuss a few options.
-
-### Cloud hosted backups
-
-In the case of cloud-hosted options, many cloud vendors provide automated backup of
-your data, and some facility for downloading such backups externally.
-Due to the wide variety of cloud-specific options, discussion of these options falls
-outside of the scope of this documentation.
-However, since the cloud server is also a MySQL server, other options listed here may
-work for your situation.
-
-### Disk-based backup
-
-The simplest option for many cases is to perform a disk-level backup of your MySQL
-installation using standard disk backup tools.
-It should be noted that all database activity should be stopped for the duration of the
-backup to prevent errors with the backed up data.
-This can be done in one of two ways:
-
-- Stopping the MySQL server program
-- Using database locks
-
-These methods are required since MySQL data operations can be ongoing in the background
-even when no user activity is ongoing.
-To use a database lock to perform a backup, the following commands can be used as the
-MySQL administrator:
-
-```mysql
-FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK;
-UNLOCK TABLES;
-```
-
-The backup should be performed between the issuing of these two commands, ensuring the
-database data is consistent on disk when it is backed up.
-
-### MySQLDump
-
-Disk based backups may not be feasible for every installation, or a database may
-require constant activity such that stopping it for backups is not feasible.
-In such cases, the simplest option is
-[MySQLDump](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql-backup-excerpt/8.0/en/using-mysqldump.html),
- a command line tool that prints the contents of your database contents in SQL form.
-
-This tool is generally acceptable for most cases and is especially well suited for
-smaller installations due to its simplicity and ease of use.
-
-For larger installations, the lower speed of MySQLDump can be a limitation, since it
-has to convert the database contents to and from SQL rather than dealing with the
-database files directly.
-Additionally, since backups are performed within a transaction, the backup will be
-valid up to the time the backup began rather than to its completion, which can make
-ensuring that the latest data are fully backed up more difficult as the time it takes
-to run a backup grows.
-
-### Percona XTraBackup
-
-The Percona `xtrabackup` tool provides near-realtime backup capability of a MySQL
-installation, with extended support for replicated databases, and is a good tool for
-backing up larger databases.
-
-However, this tool requires local disk access as well as reasonably fast backup media,
-since it builds an ongoing transaction log in real time to ensure that backups are
-valid up to the point of their completion.
-This strategy fails if it cannot keep up with the write speed of the database.
-Further, the backups it generates are in binary format and include incomplete database
-transactions, which require careful attention to detail when restoring.
-
-As such, this solution is recommended only for advanced use cases or larger databases
-where limitations of the other solutions may apply.
-
-### Locking and DDL issues
-
-One important thing to note is that at the time of writing, MySQL's transactional
-system is not `data definition language` aware, meaning that changes to table
-structures occurring during some backup schemes can result in corrupted backup copies.
-If schema changes will be occurring during your backup window, it is a good idea to
-ensure that appropriate locking mechanisms are used to prevent these changes during
-critical steps of the backup process.
-
-However, on busy installations which cannot be stopped, the use of locks in many backup
-utilities may cause issues if your programs expect to write data to the database during
-the backup window.
-
-In such cases it might make sense to review the given backup tools for locking related
-options or to use other mechanisms such as replicas or alternate backup tools to
-prevent interaction of the database.
-
-### Replication and snapshots for backup
-
-Larger databases consisting of many Terabytes of data may take many hours or even days
-to backup and restore, and so downtime resulting from system failure can create major
-impacts to ongoing work.
-
-While not backup tools per-se, use of MySQL replication and disk snapshots
-can be useful to assist in reducing the downtime resulting from a full database outage.
-
-Replicas can be configured so that one copy of the data is immediately online in the
-event of server crash.
-When a server fails in this case, users and programs simply restart and point to the
-new server before resuming work.
-
-Replicas can also reduce the system load generated by regular backup procedures, since
-they can be backed up instead of the main server.
-Additionally they can allow more flexibility in a given backup scheme, such as allowing
-for disk snapshots on a busy system that would not otherwise be able to be stopped.
-A replica copy can be stopped temporarily and then resumed while a disk snapshot or
-other backup operation occurs.
diff --git a/docs/src/sysadmin/external-store.md b/docs/src/sysadmin/external-store.md
deleted file mode 100644
index aac61fe24..000000000
--- a/docs/src/sysadmin/external-store.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,293 +0,0 @@
-# External Store
-
-DataJoint organizes most of its data in a relational database.
-Relational databases excel at representing relationships between entities and storing
-structured data.
-However, relational databases are not particularly well-suited for storing large
-continuous chunks of data such as images, signals, and movies.
-An attribute of type `longblob` can contain an object up to 4 GiB in size (after
-compression) but storing many such large objects may hamper the performance of queries
-on the entire table.
-A good rule of thumb is that objects over 10 MiB in size should not be put in the
-relational database.
-In addition, storing data in cloud-hosted relational databases (e.g. AWS RDS) may be
-more expensive than in cloud-hosted simple storage systems (e.g. AWS S3).
-
-DataJoint allows the use of `external` storage to store large data objects within its
-relational framework but outside of the main database.
-
-Defining an externally-stored attribute is used using the notation `blob@storename`
-(see also: [definition syntax](../design/tables/declare.md)) and works the same way as
-a `longblob` attribute from the users perspective. However, its data are stored in an
-external storage system rather than in the relational database.
-
-Various systems can play the role of external storage, including a shared file system
-accessible to all team members with access to these objects or a cloud storage
-solutions such as AWS S3.
-
-For example, the following table stores motion-aligned two-photon movies.
-
-```python
-# Motion aligned movies
--> twophoton.Scan
----
-aligned_movie : blob@external # motion-aligned movie in 'external' store
-```
-
-All [insert](../manipulation/insert.md) and [fetch](../query/fetch.md) operations work
-identically for `external` attributes as they do for `blob` attributes, with the same
-serialization protocol.
-Similar to `blobs`, `external` attributes cannot be used in restriction conditions.
-
-Multiple external storage configurations may be used simultaneously with the
-`@storename` portion of the attribute definition determining the storage location.
-
-```python
-# Motion aligned movies
--> twophoton.Scan
----
-aligned_movie : blob@external-raw # motion-aligned movie in 'external-raw' store
-```
-
-## Principles of operation
-
-External storage is organized to emulate individual attribute values in the relational
-database.
-DataJoint organizes external storage to preserve the same data integrity principles as
-in relational storage.
-
-1. The external storage locations are specified in the DataJoint connection
-configuration with one specification for each store.
-
- ```python
- dj.config['stores'] = {
- 'external': dict( # 'regular' external storage for this pipeline
- protocol='s3',
- endpoint='s3.amazonaws.com:9000',
- bucket = 'testbucket',
- location = 'datajoint-projects/lab1',
- access_key='1234567',
- secret_key='foaf1234'),
- 'external-raw': dict( # 'raw' storage for this pipeline
- protocol='file',
- location='/net/djblobs/myschema')
- }
- # external object cache - see fetch operation below for details.
- dj.config['cache'] = '/net/djcache'
- ```
-
-2. Each schema corresponds to a dedicated folder at the storage location with the same
-name as the database schema.
-
-3. Stored objects are identified by the [SHA-256](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SHA-2)
-hashes (in web-safe base-64 ASCII) of their serialized contents.
- This scheme allows for the same object—used multiple times in the same schema—to be
- stored only once.
-
-4. In the `external-raw` storage, the objects are saved as files with the hash as the
-filename.
-
-5. In the `external` storage, external files are stored in a directory layout
-corresponding to the hash of the filename. By default, this corresponds to the first 2
-characters of the hash, followed by the second 2 characters of the hash, followed by
-the actual file.
-
-6. Each database schema has an auxiliary table named `~external_` for each
-configured external store.
-
- It is automatically created the first time external storage is used.
- The primary key of `~external_` is the hash of the data (for blobs and
- attachments) or of the relative paths to the files for filepath-based storage.
- Other attributes are the `count` of references by tables in the schema, the `size`
- of the object in bytes, and the `timestamp` of the last event (creation, update, or
- deletion).
-
- Below are sample entries in `~external_`.
-
- | HASH | size | filepath | contents_hash | timestamp |
- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
- | 1GEqtEU6JYEOLS4sZHeHDxWQ3JJfLlH VZio1ga25vd2 | 1039536788 | NULL | NULL | 2017-06-07 23:14:01 |
-
- The fields `filepath` and `contents_hash` relate to the
- [filepath](../design/tables/filepath.md) datatype, which will be discussed
- separately.
-
-7. Attributes of type `@` are declared as renamed
-[foreign keys](../design/tables/dependencies.md) referencing the
-`~external_` table (but are not shown as such to the user).
-
-8. The [insert](../manipulation/insert.md) operation encodes and hashes the blob data.
-If an external object is not present in storage for the same hash, the object is saved
-and if the save operation is successful, corresponding entities in table
-`~external_` for that store are created.
-
-9. The [delete](../manipulation/delete.md) operation first deletes the foreign key
-reference in the target table. The external table entry and actual external object is
-not actually deleted at this time (`soft-delete`).
-
-10. The [fetch](../query/fetch.md) operation uses the hash values to find the data.
- In order to prevent excessive network overhead, a special external store named
- `cache` can be configured.
- If the `cache` is enabled, the `fetch` operation need not access
- `~external_` directly.
- Instead `fetch` will retrieve the cached object without downloading directly from
- the `real` external store.
-
-11. Cleanup is performed regularly when the database is in light use or off-line.
-
-12. DataJoint never removes objects from the local `cache` folder.
- The `cache` folder may just be periodically emptied entirely or based on file
- access date.
- If dedicated `cache` folders are maintained for each schema, then a special
- procedure will be provided to remove all objects that are no longer listed in
- `~external_`.
-
-Data removal from external storage is separated from the delete operations to ensure
-that data are not lost in race conditions between inserts and deletes of the same
-objects, especially in cases of transactional processing or in processes that are
-likely to get terminated.
-The cleanup steps are performed in a separate process when the risks of race conditions
-are minimal.
-The process performing the cleanups must be isolated to prevent interruptions resulting
-in loss of data integrity.
-
-## Configuration
-
-The following steps must be performed to enable external storage:
-
-1. Assign external location settings for each storage as shown in the
-[Step 1](#principles-of-operation) example above. Use `dj.config` for configuration.
-
- - `protocol` [`s3`, `file`] Specifies whether `s3` or `file` external storage is
- desired.
- - `endpoint` [`s3`] Specifies the remote endpoint to the external data for all
- schemas as well as the target port.
- - `bucket` [`s3`] Specifies the appropriate `s3` bucket organization.
- - `location` [`s3`, `file`] Specifies the subdirectory within the root or bucket of
- store to preserve data. External objects are thus stored remotely with the following
- path structure:
- `////
".join(
+ [
+ "\n".join(["| %s | " % get_html_display_value(tup, name, idx) for name in heading.names])
+ for idx, tup in enumerate(tuples)
+ ]
+ ),
+ count=(("Total: %d
" % len(rel)) if config["display.show_tuple_count"] else ""),
+ )
diff --git a/src/datajoint/schemas.py b/src/datajoint/schemas.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..399ab1b9f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/datajoint/schemas.py
@@ -0,0 +1,909 @@
+"""
+Schema management for DataJoint.
+
+This module provides the Schema class for binding Python table classes to
+database schemas, and utilities for schema introspection and management.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+import collections
+import inspect
+import itertools
+import logging
+import re
+import types
+import warnings
+from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Any
+
+from .connection import conn
+from .errors import AccessError, DataJointError
+
+if TYPE_CHECKING:
+ from .connection import Connection
+from .heading import Heading
+from .jobs import Job
+from .settings import config
+from .table import FreeTable, lookup_class_name
+from .user_tables import Computed, Imported, Lookup, Manual, Part, _get_tier
+from .utils import to_camel_case, user_choice
+
+logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
+
+
+def ordered_dir(class_: type) -> list[str]:
+ """
+ List class attributes respecting declaration order.
+
+ Similar to the ``dir()`` built-in, but preserves attribute declaration
+ order as much as possible.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ class_ : type
+ Class to list members for.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ list[str]
+ Attributes declared in class_ and its superclasses.
+ """
+ attr_list = list()
+ for c in reversed(class_.mro()):
+ attr_list.extend(e for e in c.__dict__ if e not in attr_list)
+ return attr_list
+
+
+class Schema:
+ """
+ Decorator that binds table classes to a database schema.
+
+ Schema objects associate Python table classes with database schemas and
+ provide the namespace context for foreign key resolution.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ schema_name : str, optional
+ Database schema name. If omitted, call ``activate()`` later.
+ context : dict, optional
+ Namespace for foreign key lookup. None uses caller's context.
+ connection : Connection, optional
+ Database connection. Defaults to ``dj.conn()``.
+ create_schema : bool, optional
+ If False, raise error if schema doesn't exist. Default True.
+ create_tables : bool, optional
+ If False, raise error when accessing missing tables. Default True.
+ add_objects : dict, optional
+ Additional objects for the declaration context.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> schema = dj.Schema('my_schema')
+ >>> @schema
+ ... class Session(dj.Manual):
+ ... definition = '''
+ ... session_id : int
+ ... '''
+ """
+
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ schema_name: str | None = None,
+ context: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
+ *,
+ connection: Connection | None = None,
+ create_schema: bool = True,
+ create_tables: bool = True,
+ add_objects: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
+ ) -> None:
+ """
+ Initialize the schema object.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ schema_name : str, optional
+ Database schema name. If omitted, call ``activate()`` later.
+ context : dict, optional
+ Namespace for foreign key lookup. None uses caller's context.
+ connection : Connection, optional
+ Database connection. Defaults to ``dj.conn()``.
+ create_schema : bool, optional
+ If False, raise error if schema doesn't exist. Default True.
+ create_tables : bool, optional
+ If False, raise error when accessing missing tables. Default True.
+ add_objects : dict, optional
+ Additional objects for the declaration context.
+ """
+ self.connection = connection
+ self.database = None
+ self.context = context
+ self.create_schema = create_schema
+ self.create_tables = create_tables
+ self.add_objects = add_objects
+ self.declare_list = []
+ if schema_name:
+ self.activate(schema_name)
+
+ def is_activated(self) -> bool:
+ """Check if the schema has been activated."""
+ return self.database is not None
+
+ def activate(
+ self,
+ schema_name: str | None = None,
+ *,
+ connection: Connection | None = None,
+ create_schema: bool | None = None,
+ create_tables: bool | None = None,
+ add_objects: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
+ ) -> None:
+ """
+ Associate with a database schema.
+
+ If the schema does not exist, attempts to create it on the server.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ schema_name : str, optional
+ Database schema name. None asserts schema is already activated.
+ connection : Connection, optional
+ Database connection. Defaults to ``dj.conn()``.
+ create_schema : bool, optional
+ If False, raise error if schema doesn't exist.
+ create_tables : bool, optional
+ If False, raise error when accessing missing tables.
+ add_objects : dict, optional
+ Additional objects for the declaration context.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DataJointError
+ If schema_name is None and schema not yet activated, or if
+ schema already activated for a different database.
+ """
+ if schema_name is None:
+ if self.exists:
+ return
+ raise DataJointError("Please provide a schema_name to activate the schema.")
+ if self.database is not None and self.exists:
+ if self.database == schema_name: # already activated
+ return
+ raise DataJointError("The schema is already activated for schema {db}.".format(db=self.database))
+ if connection is not None:
+ self.connection = connection
+ if self.connection is None:
+ self.connection = conn()
+ self.database = schema_name
+ if create_schema is not None:
+ self.create_schema = create_schema
+ if create_tables is not None:
+ self.create_tables = create_tables
+ if add_objects:
+ self.add_objects = add_objects
+ if not self.exists:
+ if not self.create_schema or not self.database:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Database `{name}` has not yet been declared. Set argument create_schema=True to create it.".format(
+ name=schema_name
+ )
+ )
+ # create database
+ logger.debug("Creating schema `{name}`.".format(name=schema_name))
+ try:
+ self.connection.query("CREATE DATABASE `{name}`".format(name=schema_name))
+ except AccessError:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Schema `{name}` does not exist and could not be created. Check permissions.".format(name=schema_name)
+ )
+ self.connection.register(self)
+
+ # decorate all tables already decorated
+ for cls, context in self.declare_list:
+ if self.add_objects:
+ context = dict(context, **self.add_objects)
+ self._decorate_master(cls, context)
+
+ def _assert_exists(self, message=None):
+ if not self.exists:
+ raise DataJointError(message or "Schema `{db}` has not been created.".format(db=self.database))
+
+ def __call__(self, cls: type, *, context: dict[str, Any] | None = None) -> type:
+ """
+ Bind a table class to this schema. Used as a decorator.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ cls : type
+ Table class to decorate.
+ context : dict, optional
+ Declaration context. Supplied by spawn_missing_classes.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ type
+ The decorated class.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DataJointError
+ If applied to a Part table (use on master only).
+ """
+ context = context or self.context or inspect.currentframe().f_back.f_locals
+ if issubclass(cls, Part):
+ raise DataJointError("The schema decorator should not be applied to Part tables.")
+ if self.is_activated():
+ self._decorate_master(cls, context)
+ else:
+ self.declare_list.append((cls, context))
+ return cls
+
+ def _decorate_master(self, cls: type, context: dict[str, Any]) -> None:
+ """
+ Process a master table class and its part tables.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ cls : type
+ Master table class to process.
+ context : dict
+ Declaration context for foreign key resolution.
+ """
+ self._decorate_table(cls, context=dict(context, self=cls, **{cls.__name__: cls}))
+ # Process part tables
+ for part in ordered_dir(cls):
+ if part[0].isupper():
+ part = getattr(cls, part)
+ if inspect.isclass(part) and issubclass(part, Part):
+ part._master = cls
+ # allow addressing master by name or keyword 'master'
+ self._decorate_table(
+ part,
+ context=dict(context, master=cls, self=part, **{cls.__name__: cls}),
+ )
+
+ def _decorate_table(self, table_class: type, context: dict[str, Any], assert_declared: bool = False) -> None:
+ """
+ Assign schema properties to the table class and declare the table.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ table_class : type
+ Table class to decorate.
+ context : dict
+ Declaration context for foreign key resolution.
+ assert_declared : bool, optional
+ If True, assert table is already declared. Default False.
+ """
+ table_class.database = self.database
+ table_class._connection = self.connection
+ table_class._heading = Heading(
+ table_info=dict(
+ conn=self.connection,
+ database=self.database,
+ table_name=table_class.table_name,
+ context=context,
+ )
+ )
+ table_class._support = [table_class.full_table_name]
+ table_class.declaration_context = context
+
+ # instantiate the class, declare the table if not already
+ instance = table_class()
+ is_declared = instance.is_declared
+ if not is_declared and not assert_declared and self.create_tables:
+ instance.declare(context)
+ self.connection.dependencies.clear()
+ is_declared = is_declared or instance.is_declared
+
+ # add table definition to the doc string
+ if isinstance(table_class.definition, str):
+ table_class.__doc__ = (table_class.__doc__ or "") + "\nTable definition:\n\n" + table_class.definition
+
+ # fill values in Lookup tables from their contents property
+ if isinstance(instance, Lookup) and hasattr(instance, "contents") and is_declared:
+ contents = list(instance.contents)
+ if len(contents) > len(instance):
+ if instance.heading.has_autoincrement:
+ warnings.warn(
+ ("Contents has changed but cannot be inserted because {table} has autoincrement.").format(
+ table=instance.__class__.__name__
+ )
+ )
+ else:
+ instance.insert(contents, skip_duplicates=True)
+
+ def __repr__(self):
+ return "Schema `{name}`\n".format(name=self.database)
+
+ @property
+ def size_on_disk(self) -> int:
+ """
+ Return the total size of all tables in the schema.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ int
+ Size in bytes (data + indices).
+ """
+ self._assert_exists()
+ return int(
+ self.connection.query(
+ """
+ SELECT SUM(data_length + index_length)
+ FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema='{db}'
+ """.format(db=self.database)
+ ).fetchone()[0]
+ )
+
+ def spawn_missing_classes(self, context: dict[str, Any] | None = None) -> None:
+ """
+ Create Python table classes for tables without existing classes.
+
+ Introspects the database schema and creates appropriate Python classes
+ (Lookup, Manual, Imported, Computed, Part) for tables that don't have
+ corresponding classes in the context.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ context : dict, optional
+ Namespace to place created classes into. Defaults to caller's
+ local namespace.
+ """
+ self._assert_exists()
+ if context is None:
+ if self.context is not None:
+ context = self.context
+ else:
+ # if context is missing, use the calling namespace
+ frame = inspect.currentframe().f_back
+ context = frame.f_locals
+ del frame
+ tables = [
+ row[0]
+ for row in self.connection.query("SHOW TABLES in `%s`" % self.database)
+ if lookup_class_name("`{db}`.`{tab}`".format(db=self.database, tab=row[0]), context, 0) is None
+ ]
+ master_classes = (Lookup, Manual, Imported, Computed)
+ part_tables = []
+ for table_name in tables:
+ class_name = to_camel_case(table_name)
+ if class_name not in context:
+ try:
+ cls = next(cls for cls in master_classes if re.fullmatch(cls.tier_regexp, table_name))
+ except StopIteration:
+ if re.fullmatch(Part.tier_regexp, table_name):
+ part_tables.append(table_name)
+ else:
+ # declare and decorate master table classes
+ context[class_name] = self(type(class_name, (cls,), dict()), context=context)
+
+ # attach parts to masters
+ for table_name in part_tables:
+ groups = re.fullmatch(Part.tier_regexp, table_name).groupdict()
+ class_name = to_camel_case(groups["part"])
+ try:
+ master_class = context[to_camel_case(groups["master"])]
+ except KeyError:
+ raise DataJointError("The table %s does not follow DataJoint naming conventions" % table_name)
+ part_class = type(class_name, (Part,), dict(definition=...))
+ part_class._master = master_class
+ self._decorate_table(part_class, context=context, assert_declared=True)
+ setattr(master_class, class_name, part_class)
+
+ def drop(self, prompt: bool | None = None) -> None:
+ """
+ Drop the associated schema and all its tables.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ prompt : bool, optional
+ If True, show confirmation prompt before dropping.
+ If False, drop without confirmation.
+ If None (default), use ``dj.config['safemode']`` setting.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ AccessError
+ If insufficient permissions to drop the schema.
+ """
+ prompt = config["safemode"] if prompt is None else prompt
+
+ if not self.exists:
+ logger.info("Schema named `{database}` does not exist. Doing nothing.".format(database=self.database))
+ elif not prompt or user_choice("Proceed to delete entire schema `%s`?" % self.database, default="no") == "yes":
+ logger.debug("Dropping `{database}`.".format(database=self.database))
+ try:
+ self.connection.query("DROP DATABASE `{database}`".format(database=self.database))
+ logger.debug("Schema `{database}` was dropped successfully.".format(database=self.database))
+ except AccessError:
+ raise AccessError(
+ "An attempt to drop schema `{database}` has failed. Check permissions.".format(database=self.database)
+ )
+
+ @property
+ def exists(self) -> bool:
+ """
+ Check if the associated schema exists on the server.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ bool
+ True if the schema exists.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DataJointError
+ If schema has not been activated.
+ """
+ if self.database is None:
+ raise DataJointError("Schema must be activated first.")
+ return bool(
+ self.connection.query(
+ "SELECT schema_name FROM information_schema.schemata WHERE schema_name = '{database}'".format(
+ database=self.database
+ )
+ ).rowcount
+ )
+
+ @property
+ def lineage_table_exists(self) -> bool:
+ """
+ Check if the ~lineage table exists in this schema.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ bool
+ True if the lineage table exists.
+ """
+ from .lineage import lineage_table_exists
+
+ self._assert_exists()
+ return lineage_table_exists(self.connection, self.database)
+
+ @property
+ def lineage(self) -> dict[str, str]:
+ """
+ Get all lineages for tables in this schema.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ dict[str, str]
+ Mapping of ``'schema.table.attribute'`` to its lineage origin.
+ """
+ from .lineage import get_schema_lineages
+
+ self._assert_exists()
+ return get_schema_lineages(self.connection, self.database)
+
+ def rebuild_lineage(self) -> None:
+ """
+ Rebuild the ~lineage table for all tables in this schema.
+
+ Recomputes lineage for all attributes by querying FK relationships
+ from the information_schema. Use to restore lineage for schemas that
+ predate the lineage system or after corruption.
+
+ Notes
+ -----
+ After rebuilding, restart the Python kernel and reimport to pick up
+ the new lineage information.
+
+ Upstream schemas (referenced via cross-schema foreign keys) must
+ have their lineage rebuilt first.
+ """
+ from .lineage import rebuild_schema_lineage
+
+ self._assert_exists()
+ rebuild_schema_lineage(self.connection, self.database)
+
+ @property
+ def jobs(self) -> list[Job]:
+ """
+ Return Job objects for auto-populated tables with job tables.
+
+ Only returns Job objects when both the target table and its
+ ``~~table_name`` job table exist in the database. Job tables are
+ created lazily on first access to ``table.jobs`` or
+ ``populate(reserve_jobs=True)``.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ list[Job]
+ Job objects for existing job tables.
+ """
+ self._assert_exists()
+ jobs_list = []
+
+ # Get all existing job tables (~~prefix)
+ # Note: %% escapes the % in pymysql
+ result = self.connection.query(f"SHOW TABLES IN `{self.database}` LIKE '~~%%'").fetchall()
+ existing_job_tables = {row[0] for row in result}
+
+ # Iterate over auto-populated tables and check if their job table exists
+ for table_name in self.list_tables():
+ table = FreeTable(self.connection, f"`{self.database}`.`{table_name}`")
+ tier = _get_tier(table.full_table_name)
+ if tier in (Computed, Imported):
+ # Compute expected job table name: ~~base_name
+ base_name = table_name.lstrip("_")
+ job_table_name = f"~~{base_name}"
+ if job_table_name in existing_job_tables:
+ jobs_list.append(Job(table))
+
+ return jobs_list
+
+ @property
+ def code(self):
+ self._assert_exists()
+ return self.save()
+
+ def save(self, python_filename: str | None = None) -> str:
+ """
+ Generate Python code that recreates this schema.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ python_filename : str, optional
+ If provided, write the code to this file.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ str
+ Python module source code defining this schema.
+
+ Notes
+ -----
+ This method is in preparation for a future release and is not
+ officially supported.
+ """
+ self.connection.dependencies.load()
+ self._assert_exists()
+ module_count = itertools.count()
+ # add virtual modules for referenced modules with names vmod0, vmod1, ...
+ module_lookup = collections.defaultdict(lambda: "vmod" + str(next(module_count)))
+ db = self.database
+
+ def make_class_definition(table):
+ tier = _get_tier(table).__name__
+ class_name = table.split(".")[1].strip("`")
+ indent = ""
+ if tier == "Part":
+ class_name = class_name.split("__")[-1]
+ indent += " "
+ class_name = to_camel_case(class_name)
+
+ def replace(s):
+ d, tabs = s.group(1), s.group(2)
+ return ("" if d == db else (module_lookup[d] + ".")) + ".".join(
+ to_camel_case(tab) for tab in tabs.lstrip("__").split("__")
+ )
+
+ return ("" if tier == "Part" else "\n@schema\n") + (
+ '{indent}class {class_name}(dj.{tier}):\n{indent} definition = """\n{indent} {defi}"""'
+ ).format(
+ class_name=class_name,
+ indent=indent,
+ tier=tier,
+ defi=re.sub(
+ r"`([^`]+)`.`([^`]+)`",
+ replace,
+ FreeTable(self.connection, table).describe(),
+ ).replace("\n", "\n " + indent),
+ )
+
+ tables = self.connection.dependencies.topo_sort()
+ body = "\n\n".join(make_class_definition(table) for table in tables)
+ python_code = "\n\n".join(
+ (
+ '"""This module was auto-generated by datajoint from an existing schema"""',
+ "import datajoint as dj\n\nschema = dj.Schema('{db}')".format(db=db),
+ "\n".join(
+ "{module} = dj.VirtualModule('{module}', '{schema_name}')".format(module=v, schema_name=k)
+ for k, v in module_lookup.items()
+ ),
+ body,
+ )
+ )
+ if python_filename is None:
+ return python_code
+ with open(python_filename, "wt") as f:
+ f.write(python_code)
+
+ def list_tables(self) -> list[str]:
+ """
+ Return all user tables in the schema.
+
+ Excludes hidden tables (starting with ``~``) such as ``~lineage``
+ and job tables (``~~``).
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ list[str]
+ Table names in topological order.
+ """
+ self.connection.dependencies.load()
+ return [
+ t
+ for d, t in (table_name.replace("`", "").split(".") for table_name in self.connection.dependencies.topo_sort())
+ if d == self.database
+ ]
+
+ def _find_table_name(self, name: str) -> str | None:
+ """
+ Find the actual SQL table name for a given base name.
+
+ Handles tier prefixes: Manual (none), Lookup (#), Imported (_), Computed (__).
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ name : str
+ Base table name without tier prefix.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ str or None
+ The actual SQL table name, or None if not found.
+ """
+ tables = self.list_tables()
+ # Check exact match first
+ if name in tables:
+ return name
+ # Check with tier prefixes
+ for prefix in ("", "#", "_", "__"):
+ candidate = f"{prefix}{name}"
+ if candidate in tables:
+ return candidate
+ return None
+
+ def get_table(self, name: str) -> FreeTable:
+ """
+ Get a table instance by name.
+
+ Returns a FreeTable instance for the given table name. This is useful
+ for accessing tables when you don't have the Python class available.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ name : str
+ Table name (e.g., 'experiment', 'session__trial' for parts).
+ Can be snake_case (SQL name) or CamelCase (class name).
+ Tier prefixes are optional and will be auto-detected.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ FreeTable
+ A FreeTable instance for the table.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DataJointError
+ If the table does not exist.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> schema = dj.Schema('my_schema')
+ >>> experiment = schema.get_table('experiment')
+ >>> experiment.fetch()
+ """
+ self._assert_exists()
+ # Convert CamelCase to snake_case if needed
+ if name[0].isupper():
+ name = re.sub(r"(? FreeTable:
+ """
+ Get a table instance by name using bracket notation.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ name : str
+ Table name (snake_case or CamelCase).
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ FreeTable
+ A FreeTable instance for the table.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> schema = dj.Schema('my_schema')
+ >>> schema['Experiment'].fetch()
+ >>> schema['session'].fetch()
+ """
+ return self.get_table(name)
+
+ def __iter__(self):
+ """
+ Iterate over all tables in the schema.
+
+ Yields FreeTable instances for each table in topological order.
+
+ Yields
+ ------
+ FreeTable
+ Table instances in dependency order.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> for table in schema:
+ ... print(table.full_table_name, len(table))
+ """
+ self._assert_exists()
+ for table_name in self.list_tables():
+ yield self.get_table(table_name)
+
+ def __contains__(self, name: str) -> bool:
+ """
+ Check if a table exists in the schema.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ name : str
+ Table name (snake_case or CamelCase).
+ Tier prefixes are optional and will be auto-detected.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ bool
+ True if the table exists.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> 'Experiment' in schema
+ True
+ """
+ if name[0].isupper():
+ name = re.sub(r"(?>> lab = dj.VirtualModule('lab', 'my_lab_schema')
+ >>> lab.Subject.fetch()
+ """
+
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ module_name: str,
+ schema_name: str,
+ *,
+ create_schema: bool = False,
+ create_tables: bool = False,
+ connection: Connection | None = None,
+ add_objects: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
+ ) -> None:
+ """
+ Initialize the virtual module.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ module_name : str
+ Display name for the module.
+ schema_name : str
+ Database schema name.
+ create_schema : bool, optional
+ If True, create the schema if it doesn't exist. Default False.
+ create_tables : bool, optional
+ If True, allow declaring new tables. Default False.
+ connection : Connection, optional
+ Database connection. Defaults to ``dj.conn()``.
+ add_objects : dict, optional
+ Additional objects to add to the module namespace.
+ """
+ super(VirtualModule, self).__init__(name=module_name)
+ _schema = Schema(
+ schema_name,
+ create_schema=create_schema,
+ create_tables=create_tables,
+ connection=connection,
+ )
+ if add_objects:
+ self.__dict__.update(add_objects)
+ self.__dict__["schema"] = _schema
+ _schema.spawn_missing_classes(context=self.__dict__)
+
+
+def list_schemas(connection: Connection | None = None) -> list[str]:
+ """
+ List all accessible schemas on the server.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ connection : Connection, optional
+ Database connection. Defaults to ``dj.conn()``.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ list[str]
+ Names of all accessible schemas.
+ """
+ return [
+ r[0]
+ for r in (connection or conn()).query(
+ 'SELECT schema_name FROM information_schema.schemata WHERE schema_name <> "information_schema"'
+ )
+ ]
+
+
+def virtual_schema(
+ schema_name: str,
+ *,
+ connection: Connection | None = None,
+ create_schema: bool = False,
+ create_tables: bool = False,
+ add_objects: dict[str, Any] | None = None,
+) -> VirtualModule:
+ """
+ Create a virtual module for an existing database schema.
+
+ This is the recommended way to access database schemas when you don't have
+ the Python source code that defined them. Returns a module-like object with
+ table classes as attributes.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ schema_name : str
+ Database schema name.
+ connection : Connection, optional
+ Database connection. Defaults to ``dj.conn()``.
+ create_schema : bool, optional
+ If True, create the schema if it doesn't exist. Default False.
+ create_tables : bool, optional
+ If True, allow declaring new tables. Default False.
+ add_objects : dict, optional
+ Additional objects to add to the module namespace.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ VirtualModule
+ A module-like object with table classes as attributes.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> lab = dj.virtual_schema('my_lab')
+ >>> lab.Subject.fetch()
+ >>> lab.Session & 'subject_id="M001"'
+
+ See Also
+ --------
+ Schema : For defining new schemas with Python classes.
+ VirtualModule : The underlying class (prefer virtual_schema function).
+ """
+ return VirtualModule(
+ schema_name,
+ schema_name,
+ connection=connection,
+ create_schema=create_schema,
+ create_tables=create_tables,
+ add_objects=add_objects,
+ )
diff --git a/src/datajoint/settings.py b/src/datajoint/settings.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5812f2257
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/datajoint/settings.py
@@ -0,0 +1,976 @@
+"""
+DataJoint configuration system using pydantic-settings.
+
+This module provides strongly-typed configuration with automatic loading
+from environment variables, secrets directories, and JSON config files.
+
+Configuration sources (in priority order):
+
+1. Environment variables (``DJ_*``)
+2. Secrets directories (``.secrets/`` in project, ``/run/secrets/datajoint/``)
+3. Project config file (``datajoint.json``, searched recursively up to ``.git/.hg``)
+
+Examples
+--------
+>>> import datajoint as dj
+>>> dj.config.database.host
+'localhost'
+>>> with dj.config.override(safemode=False):
+... # dangerous operations here
+... pass
+
+Project structure::
+
+ myproject/
+ ├── .git/
+ ├── datajoint.json # Project config (commit this)
+ ├── .secrets/ # Local secrets (gitignore this)
+ │ ├── database.password
+ │ └── aws.secret_access_key
+ └── src/
+ └── analysis.py # Config found via parent search
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+import json
+import logging
+import os
+import warnings
+from contextlib import contextmanager
+from copy import deepcopy
+from enum import Enum
+from pathlib import Path
+from typing import Any, Iterator, Literal
+
+from pydantic import Field, SecretStr, field_validator
+from pydantic_settings import BaseSettings, SettingsConfigDict
+
+from .errors import DataJointError
+
+CONFIG_FILENAME = "datajoint.json"
+SECRETS_DIRNAME = ".secrets"
+SYSTEM_SECRETS_DIR = Path("/run/secrets/datajoint")
+DEFAULT_SUBFOLDING = (2, 2)
+
+# Mapping of config keys to environment variables
+# Environment variables take precedence over config file values
+ENV_VAR_MAPPING = {
+ "database.host": "DJ_HOST",
+ "database.user": "DJ_USER",
+ "database.password": "DJ_PASS",
+ "database.port": "DJ_PORT",
+ "external.aws_access_key_id": "DJ_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID",
+ "external.aws_secret_access_key": "DJ_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY",
+ "loglevel": "DJ_LOG_LEVEL",
+}
+
+Role = Enum("Role", "manual lookup imported computed job")
+role_to_prefix = {
+ Role.manual: "",
+ Role.lookup: "#",
+ Role.imported: "_",
+ Role.computed: "__",
+ Role.job: "~",
+}
+prefix_to_role = dict(zip(role_to_prefix.values(), role_to_prefix))
+
+logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
+
+
+def find_config_file(start: Path | None = None) -> Path | None:
+ """
+ Search for datajoint.json in current and parent directories.
+
+ Searches upward from ``start`` until finding the config file or hitting
+ a project boundary (``.git``, ``.hg``) or filesystem root.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ start : Path, optional
+ Directory to start search from. Defaults to current working directory.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ Path or None
+ Path to config file if found, None otherwise.
+ """
+ current = (start or Path.cwd()).resolve()
+
+ while True:
+ config_path = current / CONFIG_FILENAME
+ if config_path.is_file():
+ return config_path
+
+ # Stop at project/repo root
+ if (current / ".git").exists() or (current / ".hg").exists():
+ return None
+
+ # Stop at filesystem root
+ if current == current.parent:
+ return None
+
+ current = current.parent
+
+
+def find_secrets_dir(config_path: Path | None = None) -> Path | None:
+ """
+ Find the secrets directory.
+
+ Priority:
+
+ 1. ``.secrets/`` in same directory as datajoint.json (project secrets)
+ 2. ``/run/secrets/datajoint/`` (Docker/Kubernetes secrets)
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ config_path : Path, optional
+ Path to datajoint.json if found.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ Path or None
+ Path to secrets directory if found, None otherwise.
+ """
+ # Check project secrets directory (next to config file)
+ if config_path is not None:
+ project_secrets = config_path.parent / SECRETS_DIRNAME
+ if project_secrets.is_dir():
+ return project_secrets
+
+ # Check system secrets directory (Docker/Kubernetes)
+ if SYSTEM_SECRETS_DIR.is_dir():
+ return SYSTEM_SECRETS_DIR
+
+ return None
+
+
+def read_secret_file(secrets_dir: Path | None, name: str) -> str | None:
+ """
+ Read a secret value from a file in the secrets directory.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ secrets_dir : Path or None
+ Path to secrets directory.
+ name : str
+ Name of the secret file (e.g., ``'database.password'``).
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ str or None
+ Secret value as string, or None if not found.
+ """
+ if secrets_dir is None:
+ return None
+
+ secret_path = secrets_dir / name
+ if secret_path.is_file():
+ return secret_path.read_text().strip()
+
+ return None
+
+
+class DatabaseSettings(BaseSettings):
+ """Database connection settings."""
+
+ model_config = SettingsConfigDict(
+ env_prefix="DJ_",
+ case_sensitive=False,
+ extra="forbid",
+ validate_assignment=True,
+ )
+
+ host: str = Field(default="localhost", validation_alias="DJ_HOST")
+ user: str | None = Field(default=None, validation_alias="DJ_USER")
+ password: SecretStr | None = Field(default=None, validation_alias="DJ_PASS")
+ port: int = Field(default=3306, validation_alias="DJ_PORT")
+ reconnect: bool = True
+ use_tls: bool | None = None
+
+
+class ConnectionSettings(BaseSettings):
+ """Connection behavior settings."""
+
+ model_config = SettingsConfigDict(extra="forbid", validate_assignment=True)
+
+ init_function: str | None = None
+ charset: str = "" # pymysql uses '' as default
+
+
+class DisplaySettings(BaseSettings):
+ """Display and preview settings."""
+
+ model_config = SettingsConfigDict(extra="forbid", validate_assignment=True)
+
+ limit: int = 12
+ width: int = 14
+ show_tuple_count: bool = True
+
+
+class ExternalSettings(BaseSettings):
+ """External storage credentials."""
+
+ model_config = SettingsConfigDict(
+ env_prefix="DJ_",
+ case_sensitive=False,
+ extra="forbid",
+ validate_assignment=True,
+ )
+
+ aws_access_key_id: str | None = Field(default=None, validation_alias="DJ_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID")
+ aws_secret_access_key: SecretStr | None = Field(default=None, validation_alias="DJ_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY")
+
+
+class JobsSettings(BaseSettings):
+ """Job queue configuration for AutoPopulate 2.0."""
+
+ model_config = SettingsConfigDict(
+ env_prefix="DJ_JOBS_",
+ case_sensitive=False,
+ extra="forbid",
+ validate_assignment=True,
+ )
+
+ auto_refresh: bool = Field(default=True, description="Auto-refresh jobs queue on populate")
+ keep_completed: bool = Field(default=False, description="Keep success records in jobs table")
+ stale_timeout: int = Field(default=3600, ge=0, description="Seconds before pending job is checked for staleness")
+ default_priority: int = Field(default=5, ge=0, le=255, description="Default priority for new jobs (lower = more urgent)")
+ version_method: Literal["git", "none"] | None = Field(
+ default=None, description="Method to obtain version: 'git' (commit hash), 'none' (empty), or None (disabled)"
+ )
+ allow_new_pk_fields_in_computed_tables: bool = Field(
+ default=False,
+ description="Allow native (non-FK) primary key fields in Computed/Imported tables. "
+ "When True, bypasses the FK-only PK validation. Job granularity will be degraded for such tables.",
+ )
+ add_job_metadata: bool = Field(
+ default=False,
+ description="Add hidden job metadata attributes (_job_start_time, _job_duration, _job_version) "
+ "to Computed and Imported tables during declaration. Tables created without this setting "
+ "will not receive metadata updates during populate.",
+ )
+
+
+class ObjectStorageSettings(BaseSettings):
+ """Object storage configuration for the object type."""
+
+ model_config = SettingsConfigDict(
+ env_prefix="DJ_OBJECT_STORAGE_",
+ case_sensitive=False,
+ extra="forbid",
+ validate_assignment=True,
+ )
+
+ # Required settings
+ project_name: str | None = Field(default=None, description="Unique project identifier")
+ protocol: str | None = Field(default=None, description="Storage protocol: file, s3, gcs, azure")
+ location: str | None = Field(default=None, description="Base path or bucket prefix")
+
+ # Cloud storage settings
+ bucket: str | None = Field(default=None, description="Bucket name (S3, GCS)")
+ container: str | None = Field(default=None, description="Container name (Azure)")
+ endpoint: str | None = Field(default=None, description="S3 endpoint URL")
+ access_key: str | None = Field(default=None, description="Access key")
+ secret_key: SecretStr | None = Field(default=None, description="Secret key")
+ secure: bool = Field(default=True, description="Use HTTPS")
+
+ # Optional settings
+ default_store: str | None = Field(default=None, description="Default store name when not specified")
+ partition_pattern: str | None = Field(default=None, description="Path pattern with {attribute} placeholders")
+ token_length: int = Field(default=8, ge=4, le=16, description="Random suffix length for filenames")
+
+ # Named stores configuration (object_storage.stores..*)
+ stores: dict[str, dict[str, Any]] = Field(default_factory=dict, description="Named object stores")
+
+
+class Config(BaseSettings):
+ """
+ Main DataJoint configuration.
+
+ Settings are loaded from (in priority order):
+
+ 1. Environment variables (``DJ_*``)
+ 2. Secrets directory (``.secrets/`` or ``/run/secrets/datajoint/``)
+ 3. Config file (``datajoint.json``, searched in parent directories)
+ 4. Default values
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ Access settings via attributes:
+
+ >>> config.database.host
+ >>> config.safemode
+
+ Override temporarily with context manager:
+
+ >>> with config.override(safemode=False):
+ ... pass
+ """
+
+ model_config = SettingsConfigDict(
+ env_prefix="DJ_",
+ case_sensitive=False,
+ extra="forbid",
+ validate_assignment=True,
+ )
+
+ # Nested settings groups
+ database: DatabaseSettings = Field(default_factory=DatabaseSettings)
+ connection: ConnectionSettings = Field(default_factory=ConnectionSettings)
+ display: DisplaySettings = Field(default_factory=DisplaySettings)
+ external: ExternalSettings = Field(default_factory=ExternalSettings)
+ jobs: JobsSettings = Field(default_factory=JobsSettings)
+ object_storage: ObjectStorageSettings = Field(default_factory=ObjectStorageSettings)
+
+ # Top-level settings
+ loglevel: Literal["DEBUG", "INFO", "WARNING", "ERROR", "CRITICAL"] = Field(default="INFO", validation_alias="DJ_LOG_LEVEL")
+ safemode: bool = True
+ enable_python_native_blobs: bool = True
+ filepath_checksum_size_limit: int | None = None
+
+ # External stores configuration
+ stores: dict[str, dict[str, Any]] = Field(default_factory=dict)
+
+ # Cache paths
+ cache: Path | None = None
+ query_cache: Path | None = None
+
+ # Download path for attachments and filepaths
+ download_path: str = "."
+
+ # Internal: track where config was loaded from
+ _config_path: Path | None = None
+ _secrets_dir: Path | None = None
+
+ @field_validator("loglevel", mode="after")
+ @classmethod
+ def set_logger_level(cls, v: str) -> str:
+ """Update logger level when loglevel changes."""
+ logger.setLevel(v)
+ return v
+
+ @field_validator("cache", "query_cache", mode="before")
+ @classmethod
+ def convert_path(cls, v: Any) -> Path | None:
+ """Convert string paths to Path objects."""
+ if v is None:
+ return None
+ return Path(v) if not isinstance(v, Path) else v
+
+ def get_store_spec(self, store: str) -> dict[str, Any]:
+ """
+ Get configuration for an external store.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ store : str
+ Name of the store to retrieve.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ dict[str, Any]
+ Store configuration dict with validated fields.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DataJointError
+ If store is not configured or has invalid config.
+ """
+ if store not in self.stores:
+ raise DataJointError(f"Storage '{store}' is requested but not configured")
+
+ spec = dict(self.stores[store])
+ spec.setdefault("subfolding", DEFAULT_SUBFOLDING)
+
+ # Validate protocol
+ protocol = spec.get("protocol", "").lower()
+ supported_protocols = ("file", "s3", "gcs", "azure")
+ if protocol not in supported_protocols:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ f'Missing or invalid protocol in config.stores["{store}"]. '
+ f"Supported protocols: {', '.join(supported_protocols)}"
+ )
+
+ # Define required and allowed keys by protocol
+ required_keys: dict[str, tuple[str, ...]] = {
+ "file": ("protocol", "location"),
+ "s3": ("protocol", "endpoint", "bucket", "access_key", "secret_key", "location"),
+ "gcs": ("protocol", "bucket", "location"),
+ "azure": ("protocol", "container", "location"),
+ }
+ allowed_keys: dict[str, tuple[str, ...]] = {
+ "file": ("protocol", "location", "subfolding", "stage"),
+ "s3": (
+ "protocol",
+ "endpoint",
+ "bucket",
+ "access_key",
+ "secret_key",
+ "location",
+ "secure",
+ "subfolding",
+ "stage",
+ "proxy_server",
+ ),
+ "gcs": (
+ "protocol",
+ "bucket",
+ "location",
+ "token",
+ "project",
+ "subfolding",
+ "stage",
+ ),
+ "azure": (
+ "protocol",
+ "container",
+ "location",
+ "account_name",
+ "account_key",
+ "connection_string",
+ "subfolding",
+ "stage",
+ ),
+ }
+
+ # Check required keys
+ missing = [k for k in required_keys[protocol] if k not in spec]
+ if missing:
+ raise DataJointError(f'config.stores["{store}"] is missing: {", ".join(missing)}')
+
+ # Check for invalid keys
+ invalid = [k for k in spec if k not in allowed_keys[protocol]]
+ if invalid:
+ raise DataJointError(f'Invalid key(s) in config.stores["{store}"]: {", ".join(invalid)}')
+
+ return spec
+
+ def get_object_storage_spec(self) -> dict[str, Any]:
+ """
+ Get validated object storage configuration.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ dict[str, Any]
+ Object storage configuration dict.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DataJointError
+ If object storage is not configured or has invalid config.
+ """
+ os_settings = self.object_storage
+
+ # Check if object storage is configured
+ if not os_settings.protocol:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Object storage is not configured. Set object_storage.protocol in datajoint.json "
+ "or DJ_OBJECT_STORAGE_PROTOCOL environment variable."
+ )
+
+ if not os_settings.project_name:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Object storage project_name is required. Set object_storage.project_name in datajoint.json "
+ "or DJ_OBJECT_STORAGE_PROJECT_NAME environment variable."
+ )
+
+ protocol = os_settings.protocol.lower()
+ supported_protocols = ("file", "s3", "gcs", "azure")
+ if protocol not in supported_protocols:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ f"Invalid object_storage.protocol: {protocol}. Supported protocols: {', '.join(supported_protocols)}"
+ )
+
+ # Build spec dict
+ spec = {
+ "project_name": os_settings.project_name,
+ "protocol": protocol,
+ "location": os_settings.location or "",
+ "partition_pattern": os_settings.partition_pattern,
+ "token_length": os_settings.token_length,
+ }
+
+ # Add protocol-specific settings
+ if protocol == "s3":
+ if not os_settings.endpoint or not os_settings.bucket:
+ raise DataJointError("object_storage.endpoint and object_storage.bucket are required for S3")
+ if not os_settings.access_key or not os_settings.secret_key:
+ raise DataJointError("object_storage.access_key and object_storage.secret_key are required for S3")
+ spec.update(
+ {
+ "endpoint": os_settings.endpoint,
+ "bucket": os_settings.bucket,
+ "access_key": os_settings.access_key,
+ "secret_key": os_settings.secret_key.get_secret_value() if os_settings.secret_key else None,
+ "secure": os_settings.secure,
+ }
+ )
+ elif protocol == "gcs":
+ if not os_settings.bucket:
+ raise DataJointError("object_storage.bucket is required for GCS")
+ spec["bucket"] = os_settings.bucket
+ elif protocol == "azure":
+ if not os_settings.container:
+ raise DataJointError("object_storage.container is required for Azure")
+ spec["container"] = os_settings.container
+
+ return spec
+
+ def get_object_store_spec(self, store_name: str | None = None) -> dict[str, Any]:
+ """
+ Get validated configuration for a specific object store.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ store_name : str, optional
+ Name of the store. None for default store.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ dict[str, Any]
+ Object store configuration dict.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DataJointError
+ If store is not configured or has invalid config.
+ """
+ if store_name is None:
+ # Return default store spec
+ return self.get_object_storage_spec()
+
+ os_settings = self.object_storage
+
+ # Check if named store exists
+ if store_name not in os_settings.stores:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ f"Object store '{store_name}' is not configured. "
+ f"Add object_storage.stores.{store_name}.* settings to datajoint.json"
+ )
+
+ store_config = os_settings.stores[store_name]
+ protocol = store_config.get("protocol", "").lower()
+
+ supported_protocols = ("file", "s3", "gcs", "azure")
+ if protocol not in supported_protocols:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ f"Invalid protocol for store '{store_name}': {protocol}. Supported protocols: {', '.join(supported_protocols)}"
+ )
+
+ # Use project_name from default config if not specified in store
+ project_name = store_config.get("project_name") or os_settings.project_name
+ if not project_name:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ f"project_name is required for object store '{store_name}'. "
+ "Set object_storage.project_name or object_storage.stores.{store_name}.project_name"
+ )
+
+ # Build spec dict
+ spec = {
+ "project_name": project_name,
+ "protocol": protocol,
+ "location": store_config.get("location", ""),
+ "partition_pattern": store_config.get("partition_pattern") or os_settings.partition_pattern,
+ "token_length": store_config.get("token_length") or os_settings.token_length,
+ "store_name": store_name,
+ }
+
+ # Add protocol-specific settings
+ if protocol == "s3":
+ endpoint = store_config.get("endpoint")
+ bucket = store_config.get("bucket")
+ if not endpoint or not bucket:
+ raise DataJointError(f"endpoint and bucket are required for S3 store '{store_name}'")
+ spec.update(
+ {
+ "endpoint": endpoint,
+ "bucket": bucket,
+ "access_key": store_config.get("access_key"),
+ "secret_key": store_config.get("secret_key"),
+ "secure": store_config.get("secure", True),
+ }
+ )
+ elif protocol == "gcs":
+ bucket = store_config.get("bucket")
+ if not bucket:
+ raise DataJointError(f"bucket is required for GCS store '{store_name}'")
+ spec["bucket"] = bucket
+ elif protocol == "azure":
+ container = store_config.get("container")
+ if not container:
+ raise DataJointError(f"container is required for Azure store '{store_name}'")
+ spec["container"] = container
+
+ return spec
+
+ def load(self, filename: str | Path) -> None:
+ """
+ Load settings from a JSON file.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ filename : str or Path
+ Path to load configuration from.
+ """
+ filepath = Path(filename)
+ if not filepath.exists():
+ raise FileNotFoundError(f"Config file not found: {filepath}")
+
+ logger.info(f"Loading configuration from {filepath.absolute()}")
+
+ with open(filepath) as f:
+ data = json.load(f)
+
+ self._update_from_flat_dict(data)
+ self._config_path = filepath
+
+ def _update_from_flat_dict(self, data: dict[str, Any]) -> None:
+ """
+ Update settings from a dict (flat dot-notation or nested).
+
+ Environment variables take precedence over config file values.
+ If an env var is set for a setting, the file value is skipped.
+ """
+ for key, value in data.items():
+ # Handle nested dicts by recursively updating
+ if isinstance(value, dict) and hasattr(self, key):
+ group_obj = getattr(self, key)
+ for nested_key, nested_value in value.items():
+ if hasattr(group_obj, nested_key):
+ # Check if env var is set for this nested key
+ full_key = f"{key}.{nested_key}"
+ env_var = ENV_VAR_MAPPING.get(full_key)
+ if env_var and os.environ.get(env_var):
+ logger.debug(f"Skipping {full_key} from file (env var {env_var} takes precedence)")
+ continue
+ setattr(group_obj, nested_key, nested_value)
+ continue
+
+ # Handle flat dot-notation keys
+ parts = key.split(".")
+ if len(parts) == 1:
+ if hasattr(self, key) and not key.startswith("_"):
+ # Check if env var is set for this key
+ env_var = ENV_VAR_MAPPING.get(key)
+ if env_var and os.environ.get(env_var):
+ logger.debug(f"Skipping {key} from file (env var {env_var} takes precedence)")
+ continue
+ setattr(self, key, value)
+ elif len(parts) == 2:
+ group, attr = parts
+ if hasattr(self, group):
+ group_obj = getattr(self, group)
+ if hasattr(group_obj, attr):
+ # Check if env var is set for this key
+ env_var = ENV_VAR_MAPPING.get(key)
+ if env_var and os.environ.get(env_var):
+ logger.debug(f"Skipping {key} from file (env var {env_var} takes precedence)")
+ continue
+ setattr(group_obj, attr, value)
+ elif len(parts) == 4:
+ # Handle object_storage.stores.. pattern
+ group, subgroup, store_name, attr = parts
+ if group == "object_storage" and subgroup == "stores":
+ if store_name not in self.object_storage.stores:
+ self.object_storage.stores[store_name] = {}
+ self.object_storage.stores[store_name][attr] = value
+
+ def _load_secrets(self, secrets_dir: Path) -> None:
+ """Load secrets from a secrets directory."""
+ self._secrets_dir = secrets_dir
+
+ # Map of secret file names to config paths
+ secret_mappings = {
+ "database.password": ("database", "password"),
+ "database.user": ("database", "user"),
+ "aws.access_key_id": ("external", "aws_access_key_id"),
+ "aws.secret_access_key": ("external", "aws_secret_access_key"),
+ }
+
+ for secret_name, (group, attr) in secret_mappings.items():
+ value = read_secret_file(secrets_dir, secret_name)
+ if value is not None:
+ group_obj = getattr(self, group)
+ # Only set if not already set by env var
+ if getattr(group_obj, attr) is None:
+ setattr(group_obj, attr, value)
+ logger.debug(f"Loaded secret '{secret_name}' from {secrets_dir}")
+
+ @contextmanager
+ def override(self, **kwargs: Any) -> Iterator["Config"]:
+ """
+ Temporarily override configuration values.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ **kwargs : Any
+ Settings to override. Use double underscore for nested settings
+ (e.g., ``database__host="localhost"``).
+
+ Yields
+ ------
+ Config
+ The config instance with overridden values.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> with config.override(safemode=False, database__host="test"):
+ ... # config.safemode is False here
+ ... pass
+ >>> # config.safemode is restored
+ """
+ # Store original values
+ backup = {}
+
+ # Convert double underscore to nested access
+ converted = {}
+ for key, value in kwargs.items():
+ if "__" in key:
+ parts = key.split("__")
+ converted[tuple(parts)] = value
+ else:
+ converted[(key,)] = value
+
+ try:
+ # Save originals and apply overrides
+ for key_parts, value in converted.items():
+ if len(key_parts) == 1:
+ key = key_parts[0]
+ if hasattr(self, key):
+ backup[key_parts] = deepcopy(getattr(self, key))
+ setattr(self, key, value)
+ elif len(key_parts) == 2:
+ group, attr = key_parts
+ if hasattr(self, group):
+ group_obj = getattr(self, group)
+ if hasattr(group_obj, attr):
+ backup[key_parts] = deepcopy(getattr(group_obj, attr))
+ setattr(group_obj, attr, value)
+
+ yield self
+
+ finally:
+ # Restore original values
+ for key_parts, original in backup.items():
+ if len(key_parts) == 1:
+ setattr(self, key_parts[0], original)
+ elif len(key_parts) == 2:
+ group, attr = key_parts
+ setattr(getattr(self, group), attr, original)
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def save_template(
+ path: str | Path = "datajoint.json",
+ minimal: bool = True,
+ create_secrets_dir: bool = True,
+ ) -> Path:
+ """
+ Create a template datajoint.json configuration file.
+
+ Credentials should NOT be stored in datajoint.json. Instead, use either:
+
+ - Environment variables (``DJ_USER``, ``DJ_PASS``, ``DJ_HOST``, etc.)
+ - The ``.secrets/`` directory (created alongside datajoint.json)
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ path : str or Path, optional
+ Where to save the template. Default ``'datajoint.json'``.
+ minimal : bool, optional
+ If True (default), create minimal template with just database settings.
+ If False, create full template with all available settings.
+ create_secrets_dir : bool, optional
+ If True (default), also create a ``.secrets/`` directory with
+ template files for credentials.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ Path
+ Absolute path to the created config file.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ FileExistsError
+ If config file already exists (won't overwrite).
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> import datajoint as dj
+ >>> dj.config.save_template() # Creates minimal template + .secrets/
+ >>> dj.config.save_template("full-config.json", minimal=False)
+ """
+ filepath = Path(path)
+ if filepath.exists():
+ raise FileExistsError(f"File already exists: {filepath}. Remove it first or choose a different path.")
+
+ if minimal:
+ template = {
+ "database": {
+ "host": "localhost",
+ "port": 3306,
+ },
+ }
+ else:
+ template = {
+ "database": {
+ "host": "localhost",
+ "port": 3306,
+ "reconnect": True,
+ "use_tls": None,
+ },
+ "connection": {
+ "init_function": None,
+ "charset": "",
+ },
+ "display": {
+ "limit": 12,
+ "width": 14,
+ "show_tuple_count": True,
+ },
+ "object_storage": {
+ "project_name": None,
+ "protocol": None,
+ "location": None,
+ "bucket": None,
+ "endpoint": None,
+ "secure": True,
+ "partition_pattern": None,
+ "token_length": 8,
+ },
+ "stores": {},
+ "loglevel": "INFO",
+ "safemode": True,
+ "enable_python_native_blobs": True,
+ "cache": None,
+ "query_cache": None,
+ "download_path": ".",
+ }
+
+ with open(filepath, "w") as f:
+ json.dump(template, f, indent=2)
+ f.write("\n")
+
+ logger.info(f"Created template configuration at {filepath.absolute()}")
+
+ # Create .secrets/ directory with template files
+ if create_secrets_dir:
+ secrets_dir = filepath.parent / SECRETS_DIRNAME
+ secrets_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
+
+ # Create placeholder secret files
+ secret_templates = {
+ "database.user": "your_username",
+ "database.password": "your_password",
+ }
+ for secret_name, placeholder in secret_templates.items():
+ secret_file = secrets_dir / secret_name
+ if not secret_file.exists():
+ secret_file.write_text(placeholder)
+
+ # Create .gitignore to prevent committing secrets
+ gitignore_path = secrets_dir / ".gitignore"
+ if not gitignore_path.exists():
+ gitignore_path.write_text("# Never commit secrets\n*\n!.gitignore\n")
+
+ logger.info(
+ f"Created {SECRETS_DIRNAME}/ directory with credential templates. "
+ f"Edit the files in {secrets_dir.absolute()}/ to set your credentials."
+ )
+
+ return filepath.absolute()
+
+ # Dict-like access for convenience
+ def __getitem__(self, key: str) -> Any:
+ """Get setting by dot-notation key (e.g., 'database.host')."""
+ parts = key.split(".")
+ obj: Any = self
+ for part in parts:
+ if hasattr(obj, part):
+ obj = getattr(obj, part)
+ elif isinstance(obj, dict):
+ obj = obj[part]
+ else:
+ raise KeyError(f"Setting '{key}' not found")
+ # Unwrap SecretStr for compatibility
+ if isinstance(obj, SecretStr):
+ return obj.get_secret_value()
+ return obj
+
+ def __setitem__(self, key: str, value: Any) -> None:
+ """Set setting by dot-notation key (e.g., 'database.host')."""
+ parts = key.split(".")
+ if len(parts) == 1:
+ if hasattr(self, key):
+ setattr(self, key, value)
+ else:
+ raise KeyError(f"Setting '{key}' not found")
+ else:
+ obj: Any = self
+ for part in parts[:-1]:
+ obj = getattr(obj, part)
+ setattr(obj, parts[-1], value)
+
+ def __delitem__(self, key: str) -> None:
+ """Reset setting to default by dot-notation key."""
+ # Get the default value from the model fields (access from class, not instance)
+ parts = key.split(".")
+ if len(parts) == 1:
+ field_info = type(self).model_fields.get(key)
+ if field_info is not None:
+ default = field_info.default
+ if default is not None:
+ setattr(self, key, default)
+ elif field_info.default_factory is not None:
+ setattr(self, key, field_info.default_factory())
+ else:
+ setattr(self, key, None)
+ else:
+ raise KeyError(f"Setting '{key}' not found")
+ else:
+ # For nested settings, reset to None or empty
+ obj: Any = self
+ for part in parts[:-1]:
+ obj = getattr(obj, part)
+ setattr(obj, parts[-1], None)
+
+ def get(self, key: str, default: Any = None) -> Any:
+ """Get setting with optional default value."""
+ try:
+ return self[key]
+ except KeyError:
+ return default
+
+
+def _create_config() -> Config:
+ """Create and initialize the global config instance."""
+ cfg = Config()
+
+ # Find config file (recursive parent search)
+ config_path = find_config_file()
+
+ if config_path is not None:
+ try:
+ cfg.load(config_path)
+ except Exception as e:
+ warnings.warn(f"Failed to load config from {config_path}: {e}")
+ else:
+ warnings.warn(
+ f"No {CONFIG_FILENAME} found. Using defaults and environment variables. "
+ f"Run `dj.config.save_template()` to create a template configuration.",
+ stacklevel=2,
+ )
+
+ # Find and load secrets
+ secrets_dir = find_secrets_dir(config_path)
+ if secrets_dir is not None:
+ cfg._load_secrets(secrets_dir)
+
+ # Set initial log level
+ logger.setLevel(cfg.loglevel)
+
+ return cfg
+
+
+# Global config instance
+config = _create_config()
diff --git a/src/datajoint/staged_insert.py b/src/datajoint/staged_insert.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..8f9c94d2c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/datajoint/staged_insert.py
@@ -0,0 +1,312 @@
+"""
+Staged insert context manager for direct object storage writes.
+
+This module provides the StagedInsert class which allows writing directly
+to object storage before finalizing the database insert.
+"""
+
+import json
+import mimetypes
+from contextlib import contextmanager
+from datetime import datetime, timezone
+from typing import IO, Any
+
+import fsspec
+
+from .errors import DataJointError
+from .settings import config
+from .storage import StorageBackend, build_object_path
+
+
+class StagedInsert:
+ """
+ Context manager for staged insert operations.
+
+ Allows direct writes to object storage before finalizing the database insert.
+ Used for large objects like Zarr arrays where copying from local storage
+ is inefficient.
+
+ Usage:
+ with table.staged_insert1 as staged:
+ staged.rec['subject_id'] = 123
+ staged.rec['session_id'] = 45
+
+ # Create object storage directly
+ z = zarr.open(staged.store('raw_data', '.zarr'), mode='w', shape=(1000, 1000))
+ z[:] = data
+
+ # Assign to record
+ staged.rec['raw_data'] = z
+
+ # On successful exit: metadata computed, record inserted
+ # On exception: storage cleaned up, no record inserted
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self, table):
+ """
+ Initialize a staged insert.
+
+ Args:
+ table: The Table instance to insert into
+ """
+ self._table = table
+ self._rec: dict[str, Any] = {}
+ self._staged_objects: dict[str, dict] = {} # field -> {path, ext, token}
+ self._backend: StorageBackend | None = None
+
+ @property
+ def rec(self) -> dict[str, Any]:
+ """Record dict for setting attribute values."""
+ return self._rec
+
+ @property
+ def fs(self) -> fsspec.AbstractFileSystem:
+ """Return fsspec filesystem for advanced operations."""
+ self._ensure_backend()
+ return self._backend.fs
+
+ def _ensure_backend(self):
+ """Ensure storage backend is initialized."""
+ if self._backend is None:
+ try:
+ spec = config.get_object_storage_spec()
+ self._backend = StorageBackend(spec)
+ except DataJointError:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Object storage is not configured. Set object_storage settings in datajoint.json "
+ "or DJ_OBJECT_STORAGE_* environment variables."
+ )
+
+ def _get_storage_path(self, field: str, ext: str = "") -> str:
+ """
+ Get or create the storage path for a field.
+
+ Args:
+ field: Name of the object attribute
+ ext: Optional extension (e.g., ".zarr")
+
+ Returns:
+ Full storage path
+ """
+ self._ensure_backend()
+
+ if field in self._staged_objects:
+ return self._staged_objects[field]["full_path"]
+
+ # Validate field is an object attribute
+ if field not in self._table.heading:
+ raise DataJointError(f"Attribute '{field}' not found in table heading")
+
+ attr = self._table.heading[field]
+ # Check if this is an object Codec (has codec with "object" as name)
+ if not (attr.codec and attr.codec.name == "object"):
+ raise DataJointError(f"Attribute '{field}' is not an type")
+
+ # Extract primary key from rec
+ primary_key = {k: self._rec[k] for k in self._table.primary_key if k in self._rec}
+ if len(primary_key) != len(self._table.primary_key):
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Primary key values must be set in staged.rec before calling store() or open(). "
+ f"Missing: {set(self._table.primary_key) - set(primary_key)}"
+ )
+
+ # Get storage spec
+ spec = config.get_object_storage_spec()
+ partition_pattern = spec.get("partition_pattern")
+ token_length = spec.get("token_length", 8)
+
+ # Build storage path (relative - StorageBackend will add location prefix)
+ relative_path, token = build_object_path(
+ schema=self._table.database,
+ table=self._table.class_name,
+ field=field,
+ primary_key=primary_key,
+ ext=ext if ext else None,
+ partition_pattern=partition_pattern,
+ token_length=token_length,
+ )
+
+ # Store staged object info (all paths are relative, backend adds location)
+ self._staged_objects[field] = {
+ "relative_path": relative_path,
+ "ext": ext if ext else None,
+ "token": token,
+ }
+
+ return relative_path
+
+ def store(self, field: str, ext: str = "") -> fsspec.FSMap:
+ """
+ Get an FSMap store for direct writes to an object field.
+
+ Args:
+ field: Name of the object attribute
+ ext: Optional extension (e.g., ".zarr", ".hdf5")
+
+ Returns:
+ fsspec.FSMap suitable for Zarr/xarray
+ """
+ path = self._get_storage_path(field, ext)
+ return self._backend.get_fsmap(path)
+
+ def open(self, field: str, ext: str = "", mode: str = "wb") -> IO:
+ """
+ Open a file for direct writes to an object field.
+
+ Args:
+ field: Name of the object attribute
+ ext: Optional extension (e.g., ".bin", ".dat")
+ mode: File mode (default: "wb")
+
+ Returns:
+ File-like object for writing
+ """
+ path = self._get_storage_path(field, ext)
+ return self._backend.open(path, mode)
+
+ def _compute_metadata(self, field: str) -> dict:
+ """
+ Compute metadata for a staged object after writing is complete.
+
+ Args:
+ field: Name of the object attribute
+
+ Returns:
+ JSON-serializable metadata dict
+ """
+ info = self._staged_objects[field]
+ relative_path = info["relative_path"]
+ ext = info["ext"]
+
+ # Check if it's a directory (multiple files) or single file
+ # _full_path adds the location prefix
+ full_remote_path = self._backend._full_path(relative_path)
+
+ try:
+ is_dir = self._backend.fs.isdir(full_remote_path)
+ except Exception:
+ is_dir = False
+
+ if is_dir:
+ # Calculate total size and file count
+ total_size = 0
+ item_count = 0
+ files = []
+
+ for root, dirs, filenames in self._backend.fs.walk(full_remote_path):
+ for filename in filenames:
+ file_path = f"{root}/{filename}"
+ try:
+ file_size = self._backend.fs.size(file_path)
+ rel_path = file_path[len(full_remote_path) :].lstrip("/")
+ files.append({"path": rel_path, "size": file_size})
+ total_size += file_size
+ item_count += 1
+ except Exception:
+ pass
+
+ # Create manifest
+ manifest = {
+ "files": files,
+ "total_size": total_size,
+ "item_count": item_count,
+ "created": datetime.now(timezone.utc).isoformat(),
+ }
+
+ # Write manifest alongside folder
+ manifest_path = f"{relative_path}.manifest.json"
+ self._backend.put_buffer(json.dumps(manifest, indent=2).encode(), manifest_path)
+
+ metadata = {
+ "path": relative_path,
+ "size": total_size,
+ "hash": None,
+ "ext": ext,
+ "is_dir": True,
+ "timestamp": datetime.now(timezone.utc).isoformat(),
+ "item_count": item_count,
+ }
+ else:
+ # Single file
+ try:
+ size = self._backend.size(relative_path)
+ except Exception:
+ size = 0
+
+ metadata = {
+ "path": relative_path,
+ "size": size,
+ "hash": None,
+ "ext": ext,
+ "is_dir": False,
+ "timestamp": datetime.now(timezone.utc).isoformat(),
+ }
+
+ # Add mime_type for files
+ if ext:
+ mime_type, _ = mimetypes.guess_type(f"file{ext}")
+ if mime_type:
+ metadata["mime_type"] = mime_type
+
+ return metadata
+
+ def _finalize(self):
+ """
+ Finalize the staged insert by computing metadata and inserting the record.
+ """
+ # Process each staged object
+ for field in list(self._staged_objects.keys()):
+ metadata = self._compute_metadata(field)
+ # Store metadata dict in the record (ObjectType.encode handles it)
+ self._rec[field] = metadata
+
+ # Insert the record
+ self._table.insert1(self._rec)
+
+ def _cleanup(self):
+ """
+ Clean up staged objects on failure.
+ """
+ if self._backend is None:
+ return
+
+ for field, info in self._staged_objects.items():
+ relative_path = info["relative_path"]
+ try:
+ # Check if it's a directory
+ full_remote_path = self._backend._full_path(relative_path)
+ if self._backend.fs.exists(full_remote_path):
+ if self._backend.fs.isdir(full_remote_path):
+ self._backend.remove_folder(relative_path)
+ else:
+ self._backend.remove(relative_path)
+ except Exception:
+ pass # Best effort cleanup
+
+
+@contextmanager
+def staged_insert1(table):
+ """
+ Context manager for staged insert operations.
+
+ Args:
+ table: The Table instance to insert into
+
+ Yields:
+ StagedInsert instance for setting record values and getting storage handles
+
+ Example:
+ with staged_insert1(Recording) as staged:
+ staged.rec['subject_id'] = 123
+ staged.rec['session_id'] = 45
+ z = zarr.open(staged.store('raw_data', '.zarr'), mode='w')
+ z[:] = data
+ staged.rec['raw_data'] = z
+ """
+ staged = StagedInsert(table)
+ try:
+ yield staged
+ staged._finalize()
+ except Exception:
+ staged._cleanup()
+ raise
diff --git a/src/datajoint/storage.py b/src/datajoint/storage.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..846228137
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/datajoint/storage.py
@@ -0,0 +1,1016 @@
+"""
+Storage backend abstraction using fsspec for unified file operations.
+
+This module provides a unified interface for storage operations across different
+backends (local filesystem, S3, GCS, Azure, etc.) using the fsspec library.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+import json
+import logging
+import secrets
+import urllib.parse
+from datetime import datetime, timezone
+from pathlib import Path, PurePosixPath
+from typing import Any
+
+import fsspec
+
+from . import errors
+
+logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
+
+# Characters safe for use in filenames and URLs
+TOKEN_ALPHABET = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789-_"
+
+# Supported URL protocols
+URL_PROTOCOLS = ("file://", "s3://", "gs://", "gcs://", "az://", "abfs://", "http://", "https://")
+
+
+def is_url(path: str) -> bool:
+ """
+ Check if a path is a URL.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ path : str
+ Path string to check.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ bool
+ True if path starts with a supported URL protocol.
+ """
+ return path.lower().startswith(URL_PROTOCOLS)
+
+
+def normalize_to_url(path: str) -> str:
+ """
+ Normalize a path to URL form.
+
+ Converts local filesystem paths to file:// URLs. URLs are returned unchanged.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ path : str
+ Path string (local path or URL).
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ str
+ URL form of the path.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> normalize_to_url("/data/file.dat")
+ 'file:///data/file.dat'
+ >>> normalize_to_url("s3://bucket/key")
+ 's3://bucket/key'
+ >>> normalize_to_url("file:///already/url")
+ 'file:///already/url'
+ """
+ if is_url(path):
+ return path
+ # Convert local path to file:// URL
+ # Ensure absolute path and proper format
+ abs_path = str(Path(path).resolve())
+ # Handle Windows paths (C:\...) vs Unix paths (/...)
+ if abs_path.startswith("/"):
+ return f"file://{abs_path}"
+ else:
+ # Windows: file:///C:/path
+ return f"file:///{abs_path.replace(chr(92), '/')}"
+
+
+def parse_url(url: str) -> tuple[str, str]:
+ """
+ Parse a URL into protocol and path.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ url : str
+ URL (e.g., ``'s3://bucket/path/file.dat'`` or ``'file:///path/to/file'``).
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ tuple[str, str]
+ ``(protocol, path)`` where protocol is fsspec-compatible.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DataJointError
+ If URL protocol is not supported.
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> parse_url("s3://bucket/key/file.dat")
+ ('s3', 'bucket/key/file.dat')
+ >>> parse_url("file:///data/file.dat")
+ ('file', '/data/file.dat')
+ """
+ url_lower = url.lower()
+
+ # Map URL schemes to fsspec protocols
+ protocol_map = {
+ "file://": "file",
+ "s3://": "s3",
+ "gs://": "gcs",
+ "gcs://": "gcs",
+ "az://": "abfs",
+ "abfs://": "abfs",
+ "http://": "http",
+ "https://": "https",
+ }
+
+ for prefix, protocol in protocol_map.items():
+ if url_lower.startswith(prefix):
+ path = url[len(prefix) :]
+ return protocol, path
+
+ raise errors.DataJointError(f"Unsupported URL protocol: {url}")
+
+
+def generate_token(length: int = 8) -> str:
+ """
+ Generate a random token for filename collision avoidance.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ length : int, optional
+ Token length, clamped to 4-16 characters. Default 8.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ str
+ Random URL-safe string.
+ """
+ length = max(4, min(16, length))
+ return "".join(secrets.choice(TOKEN_ALPHABET) for _ in range(length))
+
+
+def encode_pk_value(value: Any) -> str:
+ """
+ Encode a primary key value for use in storage paths.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ value : any
+ Primary key value (int, str, date, datetime, etc.).
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ str
+ Path-safe string representation.
+ """
+ if isinstance(value, (int, float)):
+ return str(value)
+ if isinstance(value, datetime):
+ # Use ISO format with safe separators
+ return value.strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H-%M-%S")
+ if hasattr(value, "isoformat"):
+ # Handle date objects
+ return value.isoformat()
+
+ # String handling
+ s = str(value)
+ # Check if path-safe (no special characters)
+ unsafe_chars = '/\\:*?"<>|'
+ if any(c in s for c in unsafe_chars) or len(s) > 100:
+ # URL-encode unsafe strings or truncate long ones
+ if len(s) > 100:
+ # Truncate and add hash suffix for uniqueness
+ import hashlib
+
+ hash_suffix = hashlib.md5(s.encode()).hexdigest()[:8]
+ s = s[:50] + "_" + hash_suffix
+ return urllib.parse.quote(s, safe="")
+ return s
+
+
+def build_object_path(
+ schema: str,
+ table: str,
+ field: str,
+ primary_key: dict[str, Any],
+ ext: str | None,
+ partition_pattern: str | None = None,
+ token_length: int = 8,
+) -> tuple[str, str]:
+ """
+ Build the storage path for an object attribute.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ schema : str
+ Schema name.
+ table : str
+ Table name.
+ field : str
+ Field/attribute name.
+ primary_key : dict[str, Any]
+ Dict of primary key attribute names to values.
+ ext : str or None
+ File extension (e.g., ``".dat"``).
+ partition_pattern : str, optional
+ Partition pattern with ``{attr}`` placeholders.
+ token_length : int, optional
+ Length of random token suffix. Default 8.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ tuple[str, str]
+ ``(relative_path, token)``.
+ """
+ token = generate_token(token_length)
+
+ # Build filename: field_token.ext
+ filename = f"{field}_{token}"
+ if ext:
+ if not ext.startswith("."):
+ ext = "." + ext
+ filename += ext
+
+ # Build primary key path components
+ pk_parts = []
+ partition_attrs = set()
+
+ # Extract partition attributes if pattern specified
+ if partition_pattern:
+ import re
+
+ partition_attrs = set(re.findall(r"\{(\w+)\}", partition_pattern))
+
+ # Build partition prefix (attributes specified in partition pattern)
+ partition_parts = []
+ for attr in partition_attrs:
+ if attr in primary_key:
+ partition_parts.append(f"{attr}={encode_pk_value(primary_key[attr])}")
+
+ # Build remaining PK path (attributes not in partition)
+ for attr, value in primary_key.items():
+ if attr not in partition_attrs:
+ pk_parts.append(f"{attr}={encode_pk_value(value)}")
+
+ # Construct full path
+ # Pattern: {partition_attrs}/{schema}/{table}/objects/{remaining_pk}/{filename}
+ parts = []
+ if partition_parts:
+ parts.extend(partition_parts)
+ parts.append(schema)
+ parts.append(table)
+ parts.append("objects")
+ if pk_parts:
+ parts.extend(pk_parts)
+ parts.append(filename)
+
+ return "/".join(parts), token
+
+
+class StorageBackend:
+ """
+ Unified storage backend using fsspec.
+
+ Provides a consistent interface for file operations across different storage
+ backends including local filesystem and cloud object storage (S3, GCS, Azure).
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ spec : dict[str, Any]
+ Storage configuration dictionary. See ``__init__`` for details.
+
+ Attributes
+ ----------
+ spec : dict
+ Storage configuration dictionary.
+ protocol : str
+ Storage protocol (``'file'``, ``'s3'``, ``'gcs'``, ``'azure'``).
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self, spec: dict[str, Any]) -> None:
+ """
+ Initialize storage backend from configuration spec.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ spec : dict[str, Any]
+ Storage configuration dictionary containing:
+
+ - ``protocol``: Storage protocol (``'file'``, ``'s3'``, ``'gcs'``, ``'azure'``)
+ - ``location``: Base path or bucket prefix
+ - ``bucket``: Bucket name (for cloud storage)
+ - ``endpoint``: Endpoint URL (for S3-compatible storage)
+ - ``access_key``: Access key (for cloud storage)
+ - ``secret_key``: Secret key (for cloud storage)
+ - ``secure``: Use HTTPS (default True for cloud)
+ """
+ self.spec = spec
+ self.protocol = spec.get("protocol", "file")
+ self._fs = None
+ self._validate_spec()
+
+ def _validate_spec(self):
+ """Validate configuration spec for the protocol."""
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ location = self.spec.get("location")
+ if location and not Path(location).is_dir():
+ raise FileNotFoundError(f"Inaccessible local directory {location}")
+ elif self.protocol == "s3":
+ required = ["endpoint", "bucket", "access_key", "secret_key"]
+ missing = [k for k in required if not self.spec.get(k)]
+ if missing:
+ raise errors.DataJointError(f"Missing S3 configuration: {', '.join(missing)}")
+
+ @property
+ def fs(self) -> fsspec.AbstractFileSystem:
+ """Get or create the fsspec filesystem instance."""
+ if self._fs is None:
+ self._fs = self._create_filesystem()
+ return self._fs
+
+ def _create_filesystem(self) -> fsspec.AbstractFileSystem:
+ """Create fsspec filesystem based on protocol."""
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ return fsspec.filesystem("file", auto_mkdir=True)
+
+ elif self.protocol == "s3":
+ # Build S3 configuration
+ endpoint = self.spec["endpoint"]
+ # Determine if endpoint includes protocol
+ if not endpoint.startswith(("http://", "https://")):
+ secure = self.spec.get("secure", False)
+ endpoint_url = f"{'https' if secure else 'http'}://{endpoint}"
+ else:
+ endpoint_url = endpoint
+
+ return fsspec.filesystem(
+ "s3",
+ key=self.spec["access_key"],
+ secret=self.spec["secret_key"],
+ client_kwargs={"endpoint_url": endpoint_url},
+ )
+
+ elif self.protocol == "gcs":
+ return fsspec.filesystem(
+ "gcs",
+ token=self.spec.get("token"),
+ project=self.spec.get("project"),
+ )
+
+ elif self.protocol == "azure":
+ return fsspec.filesystem(
+ "abfs",
+ account_name=self.spec.get("account_name"),
+ account_key=self.spec.get("account_key"),
+ connection_string=self.spec.get("connection_string"),
+ )
+
+ else:
+ raise errors.DataJointError(f"Unsupported storage protocol: {self.protocol}")
+
+ def _full_path(self, path: str | PurePosixPath) -> str:
+ """
+ Construct full path including location/bucket prefix.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Relative path within the storage location.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ str
+ Full path suitable for fsspec operations.
+ """
+ path = str(path)
+ if self.protocol == "s3":
+ bucket = self.spec["bucket"]
+ location = self.spec.get("location", "")
+ if location:
+ return f"{bucket}/{location}/{path}"
+ return f"{bucket}/{path}"
+ elif self.protocol in ("gcs", "azure"):
+ bucket = self.spec.get("bucket") or self.spec.get("container")
+ location = self.spec.get("location", "")
+ if location:
+ return f"{bucket}/{location}/{path}"
+ return f"{bucket}/{path}"
+ else:
+ # Local filesystem - prepend location if specified
+ location = self.spec.get("location", "")
+ if location:
+ return str(Path(location) / path)
+ return path
+
+ def get_url(self, path: str | PurePosixPath) -> str:
+ """
+ Get the full URL for a path in storage.
+
+ Returns a consistent URL representation for any storage backend,
+ including file:// URLs for local filesystem.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Relative path within the storage location.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ str
+ Full URL (e.g., 's3://bucket/path' or 'file:///data/path').
+
+ Examples
+ --------
+ >>> backend = StorageBackend({"protocol": "file", "location": "/data"})
+ >>> backend.get_url("schema/table/file.dat")
+ 'file:///data/schema/table/file.dat'
+
+ >>> backend = StorageBackend({"protocol": "s3", "bucket": "mybucket", ...})
+ >>> backend.get_url("schema/table/file.dat")
+ 's3://mybucket/schema/table/file.dat'
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(path)
+
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ # Ensure absolute path for file:// URL
+ abs_path = str(Path(full_path).resolve())
+ if abs_path.startswith("/"):
+ return f"file://{abs_path}"
+ else:
+ # Windows path
+ return f"file:///{abs_path.replace(chr(92), '/')}"
+ elif self.protocol == "s3":
+ return f"s3://{full_path}"
+ elif self.protocol == "gcs":
+ return f"gs://{full_path}"
+ elif self.protocol == "azure":
+ return f"az://{full_path}"
+ else:
+ # Fallback: use protocol prefix
+ return f"{self.protocol}://{full_path}"
+
+ def put_file(self, local_path: str | Path, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath, metadata: dict | None = None) -> None:
+ """
+ Upload a file from local filesystem to storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ local_path : str or Path
+ Path to local file.
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Destination path in storage.
+ metadata : dict, optional
+ Metadata to attach to the file (cloud storage only).
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+ logger.debug(f"put_file: {local_path} -> {self.protocol}:{full_path}")
+
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ # For local filesystem, use safe copy with atomic rename
+ from .utils import safe_copy
+
+ Path(full_path).parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+ safe_copy(local_path, full_path, overwrite=True)
+ else:
+ # For cloud storage, use fsspec put
+ self.fs.put_file(str(local_path), full_path)
+
+ def get_file(self, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath, local_path: str | Path) -> None:
+ """
+ Download a file from storage to local filesystem.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Path in storage.
+ local_path : str or Path
+ Destination path on local filesystem.
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+ logger.debug(f"get_file: {self.protocol}:{full_path} -> {local_path}")
+
+ local_path = Path(local_path)
+ local_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ from .utils import safe_copy
+
+ safe_copy(full_path, local_path)
+ else:
+ self.fs.get_file(full_path, str(local_path))
+
+ def put_buffer(self, buffer: bytes, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath) -> None:
+ """
+ Write bytes to storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ buffer : bytes
+ Bytes to write.
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Destination path in storage.
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+ logger.debug(f"put_buffer: {len(buffer)} bytes -> {self.protocol}:{full_path}")
+
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ from .utils import safe_write
+
+ Path(full_path).parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+ safe_write(full_path, buffer)
+ else:
+ self.fs.pipe_file(full_path, buffer)
+
+ def get_buffer(self, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath) -> bytes:
+ """
+ Read bytes from storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Path in storage.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ bytes
+ File contents.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ MissingExternalFile
+ If the file does not exist.
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+ logger.debug(f"get_buffer: {self.protocol}:{full_path}")
+
+ try:
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ return Path(full_path).read_bytes()
+ else:
+ return self.fs.cat_file(full_path)
+ except FileNotFoundError:
+ raise errors.MissingExternalFile(f"Missing external file {full_path}") from None
+
+ def exists(self, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath) -> bool:
+ """
+ Check if a file exists in storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Path in storage.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ bool
+ True if file exists.
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+ logger.debug(f"exists: {self.protocol}:{full_path}")
+
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ return Path(full_path).is_file()
+ else:
+ return self.fs.exists(full_path)
+
+ def remove(self, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath) -> None:
+ """
+ Remove a file from storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Path in storage.
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+ logger.debug(f"remove: {self.protocol}:{full_path}")
+
+ try:
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ Path(full_path).unlink(missing_ok=True)
+ else:
+ self.fs.rm(full_path)
+ except FileNotFoundError:
+ pass # Already gone
+
+ def size(self, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath) -> int:
+ """
+ Get file size in bytes.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Path in storage.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ int
+ File size in bytes.
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ return Path(full_path).stat().st_size
+ else:
+ return self.fs.size(full_path)
+
+ def open(self, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath, mode: str = "rb"):
+ """
+ Open a file in storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Path in storage.
+ mode : str, optional
+ File mode (``'rb'``, ``'wb'``, etc.). Default ``'rb'``.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ file-like
+ File-like object for reading or writing.
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+
+ # For write modes on local filesystem, ensure parent directory exists
+ if self.protocol == "file" and "w" in mode:
+ Path(full_path).parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+
+ return self.fs.open(full_path, mode)
+
+ def put_folder(self, local_path: str | Path, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath) -> dict:
+ """
+ Upload a folder to storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ local_path : str or Path
+ Path to local folder.
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Destination path in storage.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ dict
+ Manifest with keys ``'files'``, ``'total_size'``, ``'item_count'``,
+ ``'created'``.
+ """
+ local_path = Path(local_path)
+ if not local_path.is_dir():
+ raise errors.DataJointError(f"Not a directory: {local_path}")
+
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+ logger.debug(f"put_folder: {local_path} -> {self.protocol}:{full_path}")
+
+ # Collect file info for manifest
+ files = []
+ total_size = 0
+
+ # Use os.walk for Python 3.10 compatibility (Path.walk() requires 3.12+)
+ import os
+
+ for root, dirs, filenames in os.walk(local_path):
+ root_path = Path(root)
+ for filename in filenames:
+ file_path = root_path / filename
+ rel_path = file_path.relative_to(local_path).as_posix()
+ file_size = file_path.stat().st_size
+ files.append({"path": rel_path, "size": file_size})
+ total_size += file_size
+
+ # Upload folder contents
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ import shutil
+
+ dest = Path(full_path)
+ dest.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+ for item in local_path.iterdir():
+ if item.is_file():
+ shutil.copy2(item, dest / item.name)
+ else:
+ shutil.copytree(item, dest / item.name, dirs_exist_ok=True)
+ else:
+ self.fs.put(str(local_path), full_path, recursive=True)
+
+ # Build manifest
+ manifest = {
+ "files": files,
+ "total_size": total_size,
+ "item_count": len(files),
+ "created": datetime.now(timezone.utc).isoformat(),
+ }
+
+ # Write manifest alongside folder
+ manifest_path = f"{remote_path}.manifest.json"
+ self.put_buffer(json.dumps(manifest, indent=2).encode(), manifest_path)
+
+ return manifest
+
+ def remove_folder(self, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath) -> None:
+ """
+ Remove a folder and its manifest from storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Path to folder in storage.
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+ logger.debug(f"remove_folder: {self.protocol}:{full_path}")
+
+ try:
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ import shutil
+
+ shutil.rmtree(full_path, ignore_errors=True)
+ else:
+ self.fs.rm(full_path, recursive=True)
+ except FileNotFoundError:
+ pass
+
+ # Also remove manifest
+ manifest_path = f"{remote_path}.manifest.json"
+ self.remove(manifest_path)
+
+ def get_fsmap(self, remote_path: str | PurePosixPath) -> fsspec.FSMap:
+ """
+ Get an FSMap for a path (useful for Zarr/xarray).
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ remote_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Path in storage.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ fsspec.FSMap
+ Mapping interface for the storage path.
+ """
+ full_path = self._full_path(remote_path)
+ return fsspec.FSMap(full_path, self.fs)
+
+ def copy_from_url(self, source_url: str, dest_path: str | PurePosixPath) -> int:
+ """
+ Copy a file from a remote URL to managed storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ source_url : str
+ Remote URL (``s3://``, ``gs://``, ``http://``, etc.).
+ dest_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Destination path in managed storage.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ int
+ Size of copied file in bytes.
+ """
+ protocol, source_path = parse_url(source_url)
+ full_dest = self._full_path(dest_path)
+
+ logger.debug(f"copy_from_url: {protocol}://{source_path} -> {self.protocol}:{full_dest}")
+
+ # Get source filesystem
+ source_fs = fsspec.filesystem(protocol)
+
+ # Check if source is a directory
+ if source_fs.isdir(source_path):
+ return self._copy_folder_from_url(source_fs, source_path, dest_path)
+
+ # Copy single file
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ # Download to local destination
+ Path(full_dest).parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+ source_fs.get_file(source_path, full_dest)
+ return Path(full_dest).stat().st_size
+ else:
+ # Remote-to-remote copy via streaming
+ with source_fs.open(source_path, "rb") as src:
+ content = src.read()
+ self.fs.pipe_file(full_dest, content)
+ return len(content)
+
+ def _copy_folder_from_url(
+ self, source_fs: fsspec.AbstractFileSystem, source_path: str, dest_path: str | PurePosixPath
+ ) -> dict:
+ """
+ Copy a folder from a remote URL to managed storage.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ source_fs : fsspec.AbstractFileSystem
+ Source filesystem.
+ source_path : str
+ Path in source filesystem.
+ dest_path : str or PurePosixPath
+ Destination path in managed storage.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ dict
+ Manifest with keys ``'files'``, ``'total_size'``, ``'item_count'``,
+ ``'created'``.
+ """
+ full_dest = self._full_path(dest_path)
+ logger.debug(f"copy_folder_from_url: {source_path} -> {self.protocol}:{full_dest}")
+
+ # Collect file info for manifest
+ files = []
+ total_size = 0
+
+ # Walk source directory
+ for root, dirs, filenames in source_fs.walk(source_path):
+ for filename in filenames:
+ src_file = f"{root}/{filename}" if root != source_path else f"{source_path}/{filename}"
+ rel_path = src_file[len(source_path) :].lstrip("/")
+ file_size = source_fs.size(src_file)
+ files.append({"path": rel_path, "size": file_size})
+ total_size += file_size
+
+ # Copy file
+ dest_file = f"{full_dest}/{rel_path}"
+ if self.protocol == "file":
+ Path(dest_file).parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+ source_fs.get_file(src_file, dest_file)
+ else:
+ with source_fs.open(src_file, "rb") as src:
+ content = src.read()
+ self.fs.pipe_file(dest_file, content)
+
+ # Build manifest
+ manifest = {
+ "files": files,
+ "total_size": total_size,
+ "item_count": len(files),
+ "created": datetime.now(timezone.utc).isoformat(),
+ }
+
+ # Write manifest alongside folder
+ manifest_path = f"{dest_path}.manifest.json"
+ self.put_buffer(json.dumps(manifest, indent=2).encode(), manifest_path)
+
+ return manifest
+
+ def source_is_directory(self, source: str) -> bool:
+ """
+ Check if a source path (local or remote URL) is a directory.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ source : str
+ Local path or remote URL.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ bool
+ True if source is a directory.
+ """
+ if is_url(source):
+ protocol, path = parse_url(source)
+ source_fs = fsspec.filesystem(protocol)
+ return source_fs.isdir(path)
+ else:
+ return Path(source).is_dir()
+
+ def source_exists(self, source: str) -> bool:
+ """
+ Check if a source path (local or remote URL) exists.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ source : str
+ Local path or remote URL.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ bool
+ True if source exists.
+ """
+ if is_url(source):
+ protocol, path = parse_url(source)
+ source_fs = fsspec.filesystem(protocol)
+ return source_fs.exists(path)
+ else:
+ return Path(source).exists()
+
+ def get_source_size(self, source: str) -> int | None:
+ """
+ Get the size of a source file (local or remote URL).
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ source : str
+ Local path or remote URL.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ int or None
+ Size in bytes, or None if directory or cannot determine.
+ """
+ try:
+ if is_url(source):
+ protocol, path = parse_url(source)
+ source_fs = fsspec.filesystem(protocol)
+ if source_fs.isdir(path):
+ return None
+ return source_fs.size(path)
+ else:
+ p = Path(source)
+ if p.is_dir():
+ return None
+ return p.stat().st_size
+ except Exception:
+ return None
+
+
+STORE_METADATA_FILENAME = "datajoint_store.json"
+
+
+def get_storage_backend(spec: dict[str, Any]) -> StorageBackend:
+ """
+ Factory function to create a storage backend from configuration.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ spec : dict[str, Any]
+ Storage configuration dictionary.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ StorageBackend
+ Configured storage backend instance.
+ """
+ return StorageBackend(spec)
+
+
+def verify_or_create_store_metadata(backend: StorageBackend, spec: dict[str, Any]) -> dict:
+ """
+ Verify or create the store metadata file at the storage root.
+
+ On first use, creates the ``datajoint_store.json`` file with project info.
+ On subsequent uses, verifies the ``project_name`` matches.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ backend : StorageBackend
+ Storage backend instance.
+ spec : dict[str, Any]
+ Object storage configuration spec.
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ dict
+ Store metadata dictionary.
+
+ Raises
+ ------
+ DataJointError
+ If ``project_name`` mismatch detected.
+ """
+ from .version import __version__ as dj_version
+
+ project_name = spec.get("project_name")
+ location = spec.get("location", "")
+
+ # Metadata file path at storage root
+ metadata_path = f"{location}/{STORE_METADATA_FILENAME}" if location else STORE_METADATA_FILENAME
+
+ try:
+ # Try to read existing metadata
+ if backend.exists(metadata_path):
+ metadata_content = backend.get_buffer(metadata_path)
+ metadata = json.loads(metadata_content)
+
+ # Verify project_name matches
+ store_project = metadata.get("project_name")
+ if store_project and store_project != project_name:
+ raise errors.DataJointError(
+ f"Object store project name mismatch.\n"
+ f' Client configured: "{project_name}"\n'
+ f' Store metadata: "{store_project}"\n'
+ f"Ensure all clients use the same object_storage.project_name setting."
+ )
+
+ return metadata
+ else:
+ # Create new metadata
+ metadata = {
+ "project_name": project_name,
+ "created": datetime.now(timezone.utc).isoformat(),
+ "format_version": "1.0",
+ "datajoint_version": dj_version,
+ }
+
+ # Optional database info - not enforced, just informational
+ # These would need to be passed in from the connection context
+ # For now, omit them
+
+ backend.put_buffer(json.dumps(metadata, indent=2).encode(), metadata_path)
+ return metadata
+
+ except errors.DataJointError:
+ raise
+ except Exception as e:
+ # Log warning but don't fail - metadata is informational
+ logger.warning(f"Could not verify/create store metadata: {e}")
+ return {"project_name": project_name}
diff --git a/src/datajoint/table.py b/src/datajoint/table.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0040943c5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/datajoint/table.py
@@ -0,0 +1,1368 @@
+import collections
+import csv
+import inspect
+import itertools
+import json
+import logging
+import re
+import uuid
+import warnings
+from dataclasses import dataclass, field
+from pathlib import Path
+
+import numpy as np
+import pandas
+
+from .condition import make_condition
+from .declare import alter, declare
+from .errors import (
+ AccessError,
+ DataJointError,
+ DuplicateError,
+ IntegrityError,
+ UnknownAttributeError,
+)
+from .expression import QueryExpression
+from .heading import Heading
+from .settings import config
+from .staged_insert import staged_insert1 as _staged_insert1
+from .utils import get_master, is_camel_case, user_choice
+
+logger = logging.getLogger(__name__.split(".")[0])
+
+foreign_key_error_regexp = re.compile(
+ r"[\w\s:]*\((?P`[^`]+`.`[^`]+`), "
+ r"CONSTRAINT (?P`[^`]+`) "
+ r"(FOREIGN KEY \((?P[^)]+)\) "
+ r"REFERENCES (?P`[^`]+`(\.`[^`]+`)?) \((?P[^)]+)\)[\s\w]+\))?"
+)
+
+constraint_info_query = " ".join(
+ """
+ SELECT
+ COLUMN_NAME as fk_attrs,
+ CONCAT('`', REFERENCED_TABLE_SCHEMA, '`.`', REFERENCED_TABLE_NAME, '`') as parent,
+ REFERENCED_COLUMN_NAME as pk_attrs
+ FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.KEY_COLUMN_USAGE
+ WHERE
+ CONSTRAINT_NAME = %s AND TABLE_SCHEMA = %s AND TABLE_NAME = %s;
+ """.split()
+)
+
+
+class _RenameMap(tuple):
+ """for internal use"""
+
+ pass
+
+
+@dataclass
+class ValidationResult:
+ """
+ Result of table.validate() call.
+
+ Attributes:
+ is_valid: True if all rows passed validation
+ errors: List of (row_index, field_name, error_message) tuples
+ rows_checked: Number of rows that were validated
+ """
+
+ is_valid: bool
+ errors: list = field(default_factory=list) # list of (row_index, field_name | None, message)
+ rows_checked: int = 0
+
+ def __bool__(self) -> bool:
+ """Allow using ValidationResult in boolean context."""
+ return self.is_valid
+
+ def raise_if_invalid(self):
+ """Raise DataJointError if validation failed."""
+ if not self.is_valid:
+ raise DataJointError(self.summary())
+
+ def summary(self) -> str:
+ """Return formatted error summary."""
+ if self.is_valid:
+ return f"Validation passed: {self.rows_checked} rows checked"
+ lines = [f"Validation failed: {len(self.errors)} error(s) in {self.rows_checked} rows"]
+ for row_idx, field_name, message in self.errors[:10]: # Show first 10 errors
+ field_str = f" in field '{field_name}'" if field_name else ""
+ lines.append(f" Row {row_idx}{field_str}: {message}")
+ if len(self.errors) > 10:
+ lines.append(f" ... and {len(self.errors) - 10} more errors")
+ return "\n".join(lines)
+
+
+class Table(QueryExpression):
+ """
+ Table is an abstract class that represents a table in the schema.
+ It implements insert and delete methods and inherits query functionality.
+ To make it a concrete class, override the abstract properties specifying the connection,
+ table name, database, and definition.
+ """
+
+ _table_name = None # must be defined in subclass
+
+ # These properties must be set by the schema decorator (schemas.py) at class level
+ # or by FreeTable at instance level
+ database = None
+ declaration_context = None
+
+ @property
+ def table_name(self):
+ # For UserTable subclasses, table_name is computed by the metaclass.
+ # Delegate to the class's table_name if _table_name is not set.
+ if self._table_name is None:
+ return type(self).table_name
+ return self._table_name
+
+ @property
+ def class_name(self):
+ return self.__class__.__name__
+
+ # Base tier class names that should not raise errors when heading is None
+ _base_tier_classes = frozenset({"Table", "UserTable", "Lookup", "Manual", "Imported", "Computed", "Part"})
+
+ @property
+ def heading(self):
+ """
+ Return the table's heading, or raise a helpful error if not configured.
+
+ Overrides QueryExpression.heading to provide a clear error message
+ when the table is not properly associated with an activated schema.
+ For base tier classes (Lookup, Manual, etc.), returns None to support
+ introspection (e.g., help()).
+ """
+ if self._heading is None:
+ # Don't raise error for base tier classes - they're used for introspection
+ if self.__class__.__name__ in self._base_tier_classes:
+ return None
+ raise DataJointError(
+ f"Table `{self.__class__.__name__}` is not properly configured. "
+ "Ensure the schema is activated before using the table. "
+ "Example: schema.activate('database_name') or schema = dj.Schema('database_name')"
+ )
+ return self._heading
+
+ @property
+ def definition(self):
+ raise NotImplementedError("Subclasses of Table must implement the `definition` property")
+
+ def declare(self, context=None):
+ """
+ Declare the table in the schema based on self.definition.
+
+ :param context: the context for foreign key resolution. If None, foreign keys are
+ not allowed.
+ """
+ if self.connection.in_transaction:
+ raise DataJointError("Cannot declare new tables inside a transaction, e.g. from inside a populate/make call")
+ # Enforce strict CamelCase #1150
+ if not is_camel_case(self.class_name):
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Table class name `{name}` is invalid. Please use CamelCase. ".format(name=self.class_name)
+ + "Classes defining tables should be formatted in strict CamelCase."
+ )
+ sql, _external_stores, primary_key, fk_attribute_map = declare(self.full_table_name, self.definition, context)
+
+ # Call declaration hook for validation (subclasses like AutoPopulate can override)
+ self._declare_check(primary_key, fk_attribute_map)
+
+ sql = sql.format(database=self.database)
+ try:
+ self.connection.query(sql)
+ except AccessError:
+ # Only suppress if table already exists (idempotent declaration)
+ # Otherwise raise - user needs to know about permission issues
+ if self.is_declared:
+ return
+ raise AccessError(
+ f"Cannot declare table {self.full_table_name}. "
+ f"Check that you have CREATE privilege on schema `{self.database}` "
+ f"and REFERENCES privilege on any referenced parent tables."
+ ) from None
+
+ # Populate lineage table for this table's attributes
+ self._populate_lineage(primary_key, fk_attribute_map)
+
+ def _declare_check(self, primary_key, fk_attribute_map):
+ """
+ Hook for declaration-time validation. Subclasses can override.
+
+ Called before the table is created in the database. Override this method
+ to add validation logic (e.g., AutoPopulate validates FK-only primary keys).
+
+ :param primary_key: list of primary key attribute names
+ :param fk_attribute_map: dict mapping child_attr -> (parent_table, parent_attr)
+ """
+ pass # Default: no validation
+
+ def _populate_lineage(self, primary_key, fk_attribute_map):
+ """
+ Populate the ~lineage table with lineage information for this table's attributes.
+
+ Lineage is stored for:
+ - All FK attributes (traced to their origin)
+ - Native primary key attributes (lineage = self)
+
+ :param primary_key: list of primary key attribute names
+ :param fk_attribute_map: dict mapping child_attr -> (parent_table, parent_attr)
+ """
+ from .lineage import (
+ ensure_lineage_table,
+ get_lineage,
+ delete_table_lineages,
+ insert_lineages,
+ )
+
+ # Ensure the ~lineage table exists
+ ensure_lineage_table(self.connection, self.database)
+
+ # Delete any existing lineage entries for this table (for idempotent re-declaration)
+ delete_table_lineages(self.connection, self.database, self.table_name)
+
+ entries = []
+
+ # FK attributes: copy lineage from parent (whether in PK or not)
+ for attr, (parent_table, parent_attr) in fk_attribute_map.items():
+ # Parse parent table name: `schema`.`table` -> (schema, table)
+ parent_clean = parent_table.replace("`", "")
+ if "." in parent_clean:
+ parent_db, parent_tbl = parent_clean.split(".", 1)
+ else:
+ parent_db = self.database
+ parent_tbl = parent_clean
+
+ # Get parent's lineage for this attribute
+ parent_lineage = get_lineage(self.connection, parent_db, parent_tbl, parent_attr)
+ if parent_lineage:
+ # Copy parent's lineage
+ entries.append((self.table_name, attr, parent_lineage))
+ else:
+ # Parent doesn't have lineage entry - use parent as origin
+ # This can happen for legacy/external schemas without lineage tracking
+ lineage = f"{parent_db}.{parent_tbl}.{parent_attr}"
+ entries.append((self.table_name, attr, lineage))
+ logger.warning(
+ f"Lineage for `{parent_db}`.`{parent_tbl}`.`{parent_attr}` not found "
+ f"(parent schema's ~lineage table may be missing or incomplete). "
+ f"Using it as origin. Once the parent schema's lineage is rebuilt, "
+ f"run schema.rebuild_lineage() on this schema to correct the lineage."
+ )
+
+ # Native PK attributes (in PK but not FK): this table is the origin
+ for attr in primary_key:
+ if attr not in fk_attribute_map:
+ lineage = f"{self.database}.{self.table_name}.{attr}"
+ entries.append((self.table_name, attr, lineage))
+
+ if entries:
+ insert_lineages(self.connection, self.database, entries)
+
+ def alter(self, prompt=True, context=None):
+ """
+ Alter the table definition from self.definition
+ """
+ if self.connection.in_transaction:
+ raise DataJointError("Cannot update table declaration inside a transaction, e.g. from inside a populate/make call")
+ if context is None:
+ frame = inspect.currentframe().f_back
+ context = dict(frame.f_globals, **frame.f_locals)
+ del frame
+ old_definition = self.describe(context=context)
+ sql, _external_stores = alter(self.definition, old_definition, context)
+ if not sql:
+ if prompt:
+ logger.warning("Nothing to alter.")
+ else:
+ sql = "ALTER TABLE {tab}\n\t".format(tab=self.full_table_name) + ",\n\t".join(sql)
+ if not prompt or user_choice(sql + "\n\nExecute?") == "yes":
+ try:
+ self.connection.query(sql)
+ except AccessError:
+ # skip if no create privilege
+ pass
+ else:
+ # reset heading
+ self.__class__._heading = Heading(table_info=self.heading.table_info)
+ if prompt:
+ logger.info("Table altered")
+
+ def from_clause(self):
+ """
+ :return: the FROM clause of SQL SELECT statements.
+ """
+ return self.full_table_name
+
+ def get_select_fields(self, select_fields=None):
+ """
+ :return: the selected attributes from the SQL SELECT statement.
+ """
+ return "*" if select_fields is None else self.heading.project(select_fields).as_sql
+
+ def parents(self, primary=None, as_objects=False, foreign_key_info=False):
+ """
+
+ :param primary: if None, then all parents are returned. If True, then only foreign keys composed of
+ primary key attributes are considered. If False, return foreign keys including at least one
+ secondary attribute.
+ :param as_objects: if False, return table names. If True, return table objects.
+ :param foreign_key_info: if True, each element in result also includes foreign key info.
+ :return: list of parents as table names or table objects
+ with (optional) foreign key information.
+ """
+ get_edge = self.connection.dependencies.parents
+ nodes = [
+ next(iter(get_edge(name).items())) if name.isdigit() else (name, props)
+ for name, props in get_edge(self.full_table_name, primary).items()
+ ]
+ if as_objects:
+ nodes = [(FreeTable(self.connection, name), props) for name, props in nodes]
+ if not foreign_key_info:
+ nodes = [name for name, props in nodes]
+ return nodes
+
+ def children(self, primary=None, as_objects=False, foreign_key_info=False):
+ """
+ :param primary: if None, then all children are returned. If True, then only foreign keys composed of
+ primary key attributes are considered. If False, return foreign keys including at least one
+ secondary attribute.
+ :param as_objects: if False, return table names. If True, return table objects.
+ :param foreign_key_info: if True, each element in result also includes foreign key info.
+ :return: list of children as table names or table objects
+ with (optional) foreign key information.
+ """
+ get_edge = self.connection.dependencies.children
+ nodes = [
+ next(iter(get_edge(name).items())) if name.isdigit() else (name, props)
+ for name, props in get_edge(self.full_table_name, primary).items()
+ ]
+ if as_objects:
+ nodes = [(FreeTable(self.connection, name), props) for name, props in nodes]
+ if not foreign_key_info:
+ nodes = [name for name, props in nodes]
+ return nodes
+
+ def descendants(self, as_objects=False):
+ """
+ :param as_objects: False - a list of table names; True - a list of table objects.
+ :return: list of tables descendants in topological order.
+ """
+ return [
+ FreeTable(self.connection, node) if as_objects else node
+ for node in self.connection.dependencies.descendants(self.full_table_name)
+ if not node.isdigit()
+ ]
+
+ def ancestors(self, as_objects=False):
+ """
+ :param as_objects: False - a list of table names; True - a list of table objects.
+ :return: list of tables ancestors in topological order.
+ """
+ return [
+ FreeTable(self.connection, node) if as_objects else node
+ for node in self.connection.dependencies.ancestors(self.full_table_name)
+ if not node.isdigit()
+ ]
+
+ def parts(self, as_objects=False):
+ """
+ return part tables either as entries in a dict with foreign key information or a list of objects
+
+ :param as_objects: if False (default), the output is a dict describing the foreign keys. If True, return table objects.
+ """
+ self.connection.dependencies.load(force=False)
+ nodes = [
+ node
+ for node in self.connection.dependencies.nodes
+ if not node.isdigit() and node.startswith(self.full_table_name[:-1] + "__")
+ ]
+ return [FreeTable(self.connection, c) for c in nodes] if as_objects else nodes
+
+ @property
+ def is_declared(self):
+ """
+ :return: True is the table is declared in the schema.
+ """
+ return (
+ self.connection.query(
+ 'SHOW TABLES in `{database}` LIKE "{table_name}"'.format(database=self.database, table_name=self.table_name)
+ ).rowcount
+ > 0
+ )
+
+ @property
+ def full_table_name(self):
+ """
+ :return: full table name in the schema
+ """
+ if self.database is None or self.table_name is None:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ f"Class {self.__class__.__name__} is not associated with a schema. "
+ "Apply a schema decorator or use schema() to bind it."
+ )
+ return r"`{0:s}`.`{1:s}`".format(self.database, self.table_name)
+
+ def update1(self, row):
+ """
+ ``update1`` updates one existing entry in the table.
+ Caution: In DataJoint the primary modes for data manipulation is to ``insert`` and
+ ``delete`` entire records since referential integrity works on the level of records,
+ not fields. Therefore, updates are reserved for corrective operations outside of main
+ workflow. Use UPDATE methods sparingly with full awareness of potential violations of
+ assumptions.
+
+ :param row: a ``dict`` containing the primary key values and the attributes to update.
+ Setting an attribute value to None will reset it to the default value (if any).
+
+ The primary key attributes must always be provided.
+
+ Examples:
+
+ >>> table.update1({'id': 1, 'value': 3}) # update value in record with id=1
+ >>> table.update1({'id': 1, 'value': None}) # reset value to default
+ """
+ # argument validations
+ if not isinstance(row, collections.abc.Mapping):
+ raise DataJointError("The argument of update1 must be dict-like.")
+ if not set(row).issuperset(self.primary_key):
+ raise DataJointError("The argument of update1 must supply all primary key values.")
+ try:
+ raise DataJointError("Attribute `%s` not found." % next(k for k in row if k not in self.heading.names))
+ except StopIteration:
+ pass # ok
+ if len(self.restriction):
+ raise DataJointError("Update cannot be applied to a restricted table.")
+ key = {k: row[k] for k in self.primary_key}
+ if len(self & key) != 1:
+ raise DataJointError("Update can only be applied to one existing entry.")
+ # UPDATE query
+ row = [self.__make_placeholder(k, v) for k, v in row.items() if k not in self.primary_key]
+ query = "UPDATE {table} SET {assignments} WHERE {where}".format(
+ table=self.full_table_name,
+ assignments=",".join("`%s`=%s" % r[:2] for r in row),
+ where=make_condition(self, key, set()),
+ )
+ self.connection.query(query, args=list(r[2] for r in row if r[2] is not None))
+
+ def validate(self, rows, *, ignore_extra_fields=False) -> ValidationResult:
+ """
+ Validate rows without inserting them.
+
+ :param rows: Same format as insert() - iterable of dicts, tuples, numpy records,
+ or a pandas DataFrame.
+ :param ignore_extra_fields: If True, ignore fields not in the table heading.
+ :return: ValidationResult with is_valid, errors list, and rows_checked count.
+
+ Validates:
+ - Field existence (all fields must be in table heading)
+ - Row format (correct number of attributes for positional inserts)
+ - Codec validation (type checking via codec.validate())
+ - NULL constraints (non-nullable fields must have values)
+ - Primary key completeness (all PK fields must be present)
+ - UUID format and JSON serializability
+
+ Cannot validate (database-enforced):
+ - Foreign key constraints
+ - Unique constraints (other than PK)
+ - Custom MySQL constraints
+
+ Example::
+
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ if result:
+ table.insert(rows)
+ else:
+ print(result.summary())
+ """
+ errors = []
+
+ # Convert DataFrame to records
+ if isinstance(rows, pandas.DataFrame):
+ rows = rows.reset_index(drop=len(rows.index.names) == 1 and not rows.index.names[0]).to_records(index=False)
+
+ # Convert Path (CSV) to list of dicts
+ if isinstance(rows, Path):
+ with open(rows, newline="") as data_file:
+ rows = list(csv.DictReader(data_file, delimiter=","))
+
+ rows = list(rows) # Materialize iterator
+ row_count = len(rows)
+
+ for row_idx, row in enumerate(rows):
+ # Validate row format and fields
+ row_dict = None
+ try:
+ if isinstance(row, np.void): # numpy record
+ fields = list(row.dtype.fields.keys())
+ row_dict = {name: row[name] for name in fields}
+ elif isinstance(row, collections.abc.Mapping):
+ fields = list(row.keys())
+ row_dict = dict(row)
+ else: # positional tuple/list
+ if len(row) != len(self.heading):
+ errors.append(
+ (
+ row_idx,
+ None,
+ f"Incorrect number of attributes: {len(row)} given, {len(self.heading)} expected",
+ )
+ )
+ continue
+ fields = list(self.heading.names)
+ row_dict = dict(zip(fields, row))
+ except TypeError:
+ errors.append((row_idx, None, f"Invalid row type: {type(row).__name__}"))
+ continue
+
+ # Check for unknown fields
+ if not ignore_extra_fields:
+ for field_name in fields:
+ if field_name not in self.heading:
+ errors.append((row_idx, field_name, f"Field '{field_name}' not in table heading"))
+
+ # Validate each field value
+ for name in self.heading.names:
+ if name not in row_dict:
+ # Check if field is required (non-nullable, no default, not autoincrement)
+ attr = self.heading[name]
+ if not attr.nullable and attr.default is None and not attr.autoincrement:
+ errors.append((row_idx, name, f"Required field '{name}' is missing"))
+ continue
+
+ value = row_dict[name]
+ attr = self.heading[name]
+
+ # Skip validation for None values on nullable columns
+ if value is None:
+ if not attr.nullable and attr.default is None:
+ errors.append((row_idx, name, f"NULL value not allowed for non-nullable field '{name}'"))
+ continue
+
+ # Codec validation
+ if attr.codec:
+ try:
+ attr.codec.validate(value)
+ except (TypeError, ValueError) as e:
+ errors.append((row_idx, name, f"Codec validation failed: {e}"))
+ continue
+
+ # UUID validation
+ if attr.uuid and not isinstance(value, uuid.UUID):
+ try:
+ uuid.UUID(value)
+ except (AttributeError, ValueError):
+ errors.append((row_idx, name, f"Invalid UUID format: {value}"))
+ continue
+
+ # JSON serialization check
+ if attr.json:
+ try:
+ json.dumps(value)
+ except (TypeError, ValueError) as e:
+ errors.append((row_idx, name, f"Value not JSON serializable: {e}"))
+ continue
+
+ # Numeric NaN check
+ if attr.numeric and value != "" and not isinstance(value, (bool, np.bool_)):
+ try:
+ if np.isnan(float(value)):
+ # NaN is allowed - will be converted to NULL
+ pass
+ except (TypeError, ValueError):
+ # Not a number that can be checked for NaN - let it pass
+ pass
+
+ # Check primary key completeness
+ for pk_field in self.primary_key:
+ if pk_field not in row_dict or row_dict[pk_field] is None:
+ pk_attr = self.heading[pk_field]
+ if not pk_attr.autoincrement:
+ errors.append((row_idx, pk_field, f"Primary key field '{pk_field}' is missing or NULL"))
+
+ return ValidationResult(is_valid=len(errors) == 0, errors=errors, rows_checked=row_count)
+
+ def insert1(self, row, **kwargs):
+ """
+ Insert one data record into the table. For ``kwargs``, see ``insert()``.
+
+ :param row: a numpy record, a dict-like object, or an ordered sequence to be inserted
+ as one row.
+ """
+ self.insert((row,), **kwargs)
+
+ @property
+ def staged_insert1(self):
+ """
+ Context manager for staged insert with direct object storage writes.
+
+ Use this for large objects like Zarr arrays where copying from local storage
+ is inefficient. Allows writing directly to the destination storage before
+ finalizing the database insert.
+
+ Example:
+ with table.staged_insert1 as staged:
+ staged.rec['subject_id'] = 123
+ staged.rec['session_id'] = 45
+
+ # Create object storage directly
+ z = zarr.open(staged.store('raw_data', '.zarr'), mode='w', shape=(1000, 1000))
+ z[:] = data
+
+ # Assign to record
+ staged.rec['raw_data'] = z
+
+ # On successful exit: metadata computed, record inserted
+ # On exception: storage cleaned up, no record inserted
+
+ Yields:
+ StagedInsert: Context for setting record values and getting storage handles
+ """
+ return _staged_insert1(self)
+
+ def insert(
+ self,
+ rows,
+ replace=False,
+ skip_duplicates=False,
+ ignore_extra_fields=False,
+ allow_direct_insert=None,
+ chunk_size=None,
+ ):
+ """
+ Insert a collection of rows.
+
+ :param rows: Either (a) an iterable where an element is a numpy record, a
+ dict-like object, a pandas.DataFrame, a polars.DataFrame, a pyarrow.Table,
+ a sequence, or a query expression with the same heading as self, or
+ (b) a pathlib.Path object specifying a path relative to the current
+ directory with a CSV file, the contents of which will be inserted.
+ :param replace: If True, replaces the existing tuple.
+ :param skip_duplicates: If True, silently skip duplicate inserts.
+ :param ignore_extra_fields: If False, fields that are not in the heading raise error.
+ :param allow_direct_insert: Only applies in auto-populated tables. If False (default),
+ insert may only be called from inside the make callback.
+ :param chunk_size: If set, insert rows in batches of this size. Useful for very
+ large inserts to avoid memory issues. Each chunk is a separate transaction.
+
+ Example:
+
+ >>> Table.insert([
+ >>> dict(subject_id=7, species="mouse", date_of_birth="2014-09-01"),
+ >>> dict(subject_id=8, species="mouse", date_of_birth="2014-09-02")])
+
+ # Large insert with chunking
+ >>> Table.insert(large_dataset, chunk_size=10000)
+ """
+ if isinstance(rows, pandas.DataFrame):
+ # drop 'extra' synthetic index for 1-field index case -
+ # frames with more advanced indices should be prepared by user.
+ rows = rows.reset_index(drop=len(rows.index.names) == 1 and not rows.index.names[0]).to_records(index=False)
+
+ # Polars DataFrame -> list of dicts (soft dependency, check by type name)
+ if type(rows).__module__.startswith("polars") and type(rows).__name__ == "DataFrame":
+ rows = rows.to_dicts()
+
+ # PyArrow Table -> list of dicts (soft dependency, check by type name)
+ if type(rows).__module__.startswith("pyarrow") and type(rows).__name__ == "Table":
+ rows = rows.to_pylist()
+
+ if isinstance(rows, Path):
+ with open(rows, newline="") as data_file:
+ rows = list(csv.DictReader(data_file, delimiter=","))
+
+ # prohibit direct inserts into auto-populated tables
+ if not allow_direct_insert and not getattr(self, "_allow_insert", True):
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Inserts into an auto-populated table can only be done inside "
+ "its make method during a populate call."
+ " To override, set keyword argument allow_direct_insert=True."
+ )
+
+ if inspect.isclass(rows) and issubclass(rows, QueryExpression):
+ rows = rows() # instantiate if a class
+ if isinstance(rows, QueryExpression):
+ # insert from select - chunk_size not applicable
+ if chunk_size is not None:
+ raise DataJointError("chunk_size is not supported for QueryExpression inserts")
+ if not ignore_extra_fields:
+ try:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Attribute %s not found. To ignore extra attributes in insert, "
+ "set ignore_extra_fields=True." % next(name for name in rows.heading if name not in self.heading)
+ )
+ except StopIteration:
+ pass
+ fields = list(name for name in rows.heading if name in self.heading)
+ query = "{command} INTO {table} ({fields}) {select}{duplicate}".format(
+ command="REPLACE" if replace else "INSERT",
+ fields="`" + "`,`".join(fields) + "`",
+ table=self.full_table_name,
+ select=rows.make_sql(fields),
+ duplicate=(
+ " ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE `{pk}`={table}.`{pk}`".format(table=self.full_table_name, pk=self.primary_key[0])
+ if skip_duplicates
+ else ""
+ ),
+ )
+ self.connection.query(query)
+ return
+
+ # Chunked insert mode
+ if chunk_size is not None:
+ rows_iter = iter(rows)
+ while True:
+ chunk = list(itertools.islice(rows_iter, chunk_size))
+ if not chunk:
+ break
+ self._insert_rows(chunk, replace, skip_duplicates, ignore_extra_fields)
+ return
+
+ # Single batch insert (original behavior)
+ self._insert_rows(rows, replace, skip_duplicates, ignore_extra_fields)
+
+ def _insert_rows(self, rows, replace, skip_duplicates, ignore_extra_fields):
+ """
+ Internal helper to insert a batch of rows.
+
+ :param rows: Iterable of rows to insert
+ :param replace: If True, use REPLACE instead of INSERT
+ :param skip_duplicates: If True, use ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE
+ :param ignore_extra_fields: If True, ignore unknown fields
+ """
+ # collects the field list from first row (passed by reference)
+ field_list = []
+ rows = list(self.__make_row_to_insert(row, field_list, ignore_extra_fields) for row in rows)
+ if rows:
+ try:
+ # Handle empty field_list (all-defaults insert)
+ fields_clause = f"(`{'`,`'.join(field_list)}`)" if field_list else "()"
+ query = "{command} INTO {destination}{fields} VALUES {placeholders}{duplicate}".format(
+ command="REPLACE" if replace else "INSERT",
+ destination=self.from_clause(),
+ fields=fields_clause,
+ placeholders=",".join("(" + ",".join(row["placeholders"]) + ")" for row in rows),
+ duplicate=(
+ " ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE `{pk}`=`{pk}`".format(pk=self.primary_key[0]) if skip_duplicates else ""
+ ),
+ )
+ self.connection.query(
+ query,
+ args=list(itertools.chain.from_iterable((v for v in r["values"] if v is not None) for r in rows)),
+ )
+ except UnknownAttributeError as err:
+ raise err.suggest("To ignore extra fields in insert, set ignore_extra_fields=True")
+ except DuplicateError as err:
+ raise err.suggest("To ignore duplicate entries in insert, set skip_duplicates=True")
+
+ def insert_dataframe(self, df, index_as_pk=None, **insert_kwargs):
+ """
+ Insert DataFrame with explicit index handling.
+
+ This method provides symmetry with to_pandas(): data fetched with to_pandas()
+ (which sets primary key as index) can be modified and re-inserted using
+ insert_dataframe() without manual index manipulation.
+
+ :param df: pandas DataFrame to insert
+ :param index_as_pk: How to handle DataFrame index:
+ - None (default): Auto-detect. Use index as primary key if index names
+ match primary_key columns. Drop if unnamed RangeIndex.
+ - True: Treat index as primary key columns. Raises if index names don't
+ match table primary key.
+ - False: Ignore index entirely (drop it).
+ :param **insert_kwargs: Passed to insert() - replace, skip_duplicates,
+ ignore_extra_fields, allow_direct_insert, chunk_size
+
+ Example::
+
+ # Round-trip with to_pandas()
+ df = table.to_pandas() # PK becomes index
+ df['value'] = df['value'] * 2 # Modify data
+ table.insert_dataframe(df) # Auto-detects index as PK
+
+ # Explicit control
+ table.insert_dataframe(df, index_as_pk=True) # Use index
+ table.insert_dataframe(df, index_as_pk=False) # Ignore index
+ """
+ if not isinstance(df, pandas.DataFrame):
+ raise DataJointError("insert_dataframe requires a pandas DataFrame")
+
+ # Auto-detect if index should be used as PK
+ if index_as_pk is None:
+ index_as_pk = self._should_index_be_pk(df)
+
+ # Validate index if using as PK
+ if index_as_pk:
+ self._validate_index_columns(df)
+
+ # Prepare rows
+ if index_as_pk:
+ rows = df.reset_index(drop=False).to_records(index=False)
+ else:
+ rows = df.reset_index(drop=True).to_records(index=False)
+
+ self.insert(rows, **insert_kwargs)
+
+ def _should_index_be_pk(self, df) -> bool:
+ """
+ Auto-detect if DataFrame index should map to primary key.
+
+ Returns True if:
+ - Index has named columns that exactly match the table's primary key
+ Returns False if:
+ - Index is unnamed RangeIndex (synthetic index)
+ - Index names don't match primary key
+ """
+ # RangeIndex with no name -> False (synthetic index)
+ if df.index.names == [None]:
+ return False
+ # Check if index names match PK columns
+ index_names = set(n for n in df.index.names if n is not None)
+ return index_names == set(self.primary_key)
+
+ def _validate_index_columns(self, df):
+ """Validate that index columns match the table's primary key."""
+ index_names = [n for n in df.index.names if n is not None]
+ if set(index_names) != set(self.primary_key):
+ raise DataJointError(
+ f"DataFrame index columns {index_names} do not match "
+ f"table primary key {list(self.primary_key)}. "
+ f"Use index_as_pk=False to ignore index, or reset_index() first."
+ )
+
+ def delete_quick(self, get_count=False):
+ """
+ Deletes the table without cascading and without user prompt.
+ If this table has populated dependent tables, this will fail.
+ """
+ query = "DELETE FROM " + self.full_table_name + self.where_clause()
+ self.connection.query(query)
+ count = self.connection.query("SELECT ROW_COUNT()").fetchone()[0] if get_count else None
+ return count
+
+ def delete(
+ self,
+ transaction: bool = True,
+ prompt: bool | None = None,
+ part_integrity: str = "enforce",
+ ) -> int:
+ """
+ Deletes the contents of the table and its dependent tables, recursively.
+
+ Args:
+ transaction: If `True`, use of the entire delete becomes an atomic transaction.
+ This is the default and recommended behavior. Set to `False` if this delete is
+ nested within another transaction.
+ prompt: If `True`, show what will be deleted and ask for confirmation.
+ If `False`, delete without confirmation. Default is `dj.config['safemode']`.
+ part_integrity: Policy for master-part integrity. One of:
+ - ``"enforce"`` (default): Error if parts would be deleted without masters.
+ - ``"ignore"``: Allow deleting parts without masters (breaks integrity).
+ - ``"cascade"``: Also delete masters when parts are deleted (maintains integrity).
+
+ Returns:
+ Number of deleted rows (excluding those from dependent tables).
+
+ Raises:
+ DataJointError: Delete exceeds maximum number of delete attempts.
+ DataJointError: When deleting within an existing transaction.
+ DataJointError: Deleting a part table before its master (when part_integrity="enforce").
+ ValueError: Invalid part_integrity value.
+ """
+ if part_integrity not in ("enforce", "ignore", "cascade"):
+ raise ValueError(f"part_integrity must be 'enforce', 'ignore', or 'cascade', got {part_integrity!r}")
+ deleted = set()
+ visited_masters = set()
+
+ def cascade(table):
+ """service function to perform cascading deletes recursively."""
+ max_attempts = 50
+ for _ in range(max_attempts):
+ try:
+ delete_count = table.delete_quick(get_count=True)
+ except IntegrityError as error:
+ match = foreign_key_error_regexp.match(error.args[0])
+ if match is None:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Cascading deletes failed because the error message is missing foreign key information."
+ "Make sure you have REFERENCES privilege to all dependent tables."
+ ) from None
+ match = match.groupdict()
+ # if schema name missing, use table
+ if "`.`" not in match["child"]:
+ match["child"] = "{}.{}".format(table.full_table_name.split(".")[0], match["child"])
+ if match["pk_attrs"] is not None: # fully matched, adjusting the keys
+ match["fk_attrs"] = [k.strip("`") for k in match["fk_attrs"].split(",")]
+ match["pk_attrs"] = [k.strip("`") for k in match["pk_attrs"].split(",")]
+ else: # only partially matched, querying with constraint to determine keys
+ match["fk_attrs"], match["parent"], match["pk_attrs"] = list(
+ map(
+ list,
+ zip(
+ *table.connection.query(
+ constraint_info_query,
+ args=(
+ match["name"].strip("`"),
+ *[_.strip("`") for _ in match["child"].split("`.`")],
+ ),
+ ).fetchall()
+ ),
+ )
+ )
+ match["parent"] = match["parent"][0]
+
+ # Restrict child by table if
+ # 1. if table's restriction attributes are not in child's primary key
+ # 2. if child renames any attributes
+ # Otherwise restrict child by table's restriction.
+ child = FreeTable(table.connection, match["child"])
+ if set(table.restriction_attributes) <= set(child.primary_key) and match["fk_attrs"] == match["pk_attrs"]:
+ child._restriction = table._restriction
+ child._restriction_attributes = table.restriction_attributes
+ elif match["fk_attrs"] != match["pk_attrs"]:
+ child &= table.proj(**dict(zip(match["fk_attrs"], match["pk_attrs"])))
+ else:
+ child &= table.proj()
+
+ master_name = get_master(child.full_table_name)
+ if (
+ part_integrity == "cascade"
+ and master_name
+ and master_name != table.full_table_name
+ and master_name not in visited_masters
+ ):
+ master = FreeTable(table.connection, master_name)
+ master._restriction_attributes = set()
+ master._restriction = [
+ make_condition( # &= may cause in target tables in subquery
+ master,
+ (master.proj() & child.proj()).to_arrays(),
+ master._restriction_attributes,
+ )
+ ]
+ visited_masters.add(master_name)
+ cascade(master)
+ else:
+ cascade(child)
+ else:
+ deleted.add(table.full_table_name)
+ logger.info("Deleting {count} rows from {table}".format(count=delete_count, table=table.full_table_name))
+ break
+ else:
+ raise DataJointError("Exceeded maximum number of delete attempts.")
+ return delete_count
+
+ prompt = config["safemode"] if prompt is None else prompt
+
+ # Start transaction
+ if transaction:
+ if not self.connection.in_transaction:
+ self.connection.start_transaction()
+ else:
+ if not prompt:
+ transaction = False
+ else:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Delete cannot use a transaction within an ongoing transaction. Set transaction=False or prompt=False."
+ )
+
+ # Cascading delete
+ try:
+ delete_count = cascade(self)
+ except:
+ if transaction:
+ self.connection.cancel_transaction()
+ raise
+
+ if part_integrity == "enforce":
+ # Avoid deleting from part before master (See issue #151)
+ for part in deleted:
+ master = get_master(part)
+ if master and master not in deleted:
+ if transaction:
+ self.connection.cancel_transaction()
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Attempt to delete part table {part} before deleting from its master {master} first. "
+ "Use part_integrity='ignore' to allow, or part_integrity='cascade' to also delete master.".format(
+ part=part, master=master
+ )
+ )
+
+ # Confirm and commit
+ if delete_count == 0:
+ if prompt:
+ logger.warning("Nothing to delete.")
+ if transaction:
+ self.connection.cancel_transaction()
+ elif not transaction:
+ logger.info("Delete completed")
+ else:
+ if not prompt or user_choice("Commit deletes?", default="no") == "yes":
+ if transaction:
+ self.connection.commit_transaction()
+ if prompt:
+ logger.info("Delete committed.")
+ else:
+ if transaction:
+ self.connection.cancel_transaction()
+ if prompt:
+ logger.warning("Delete cancelled")
+ delete_count = 0 # Reset count when delete is cancelled
+ return delete_count
+
+ def drop_quick(self):
+ """
+ Drops the table without cascading to dependent tables and without user prompt.
+ """
+ if self.is_declared:
+ # Clean up lineage entries for this table
+ from .lineage import delete_table_lineages
+
+ delete_table_lineages(self.connection, self.database, self.table_name)
+
+ query = "DROP TABLE %s" % self.full_table_name
+ self.connection.query(query)
+ logger.info("Dropped table %s" % self.full_table_name)
+ else:
+ logger.info("Nothing to drop: table %s is not declared" % self.full_table_name)
+
+ def drop(self, prompt: bool | None = None):
+ """
+ Drop the table and all tables that reference it, recursively.
+
+ Args:
+ prompt: If `True`, show what will be dropped and ask for confirmation.
+ If `False`, drop without confirmation. Default is `dj.config['safemode']`.
+ """
+ if self.restriction:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "A table with an applied restriction cannot be dropped. Call drop() on the unrestricted Table."
+ )
+ prompt = config["safemode"] if prompt is None else prompt
+
+ self.connection.dependencies.load()
+ do_drop = True
+ tables = [table for table in self.connection.dependencies.descendants(self.full_table_name) if not table.isdigit()]
+
+ # avoid dropping part tables without their masters: See issue #374
+ for part in tables:
+ master = get_master(part)
+ if master and master not in tables:
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Attempt to drop part table {part} before dropping its master. Drop {master} first.".format(
+ part=part, master=master
+ )
+ )
+
+ if prompt:
+ for table in tables:
+ logger.info(table + " (%d tuples)" % len(FreeTable(self.connection, table)))
+ do_drop = user_choice("Proceed?", default="no") == "yes"
+ if do_drop:
+ for table in reversed(tables):
+ FreeTable(self.connection, table).drop_quick()
+ logger.info("Tables dropped. Restart kernel.")
+
+ @property
+ def size_on_disk(self):
+ """
+ :return: size of data and indices in bytes on the storage device
+ """
+ ret = self.connection.query(
+ 'SHOW TABLE STATUS FROM `{database}` WHERE NAME="{table}"'.format(database=self.database, table=self.table_name),
+ as_dict=True,
+ ).fetchone()
+ return ret["Data_length"] + ret["Index_length"]
+
+ def describe(self, context=None, printout=False):
+ """
+ :return: the definition string for the query using DataJoint DDL.
+ """
+ if context is None:
+ frame = inspect.currentframe().f_back
+ context = dict(frame.f_globals, **frame.f_locals)
+ del frame
+ if self.full_table_name not in self.connection.dependencies:
+ self.connection.dependencies.load()
+ parents = self.parents(foreign_key_info=True)
+ in_key = True
+ definition = "# " + self.heading.table_status["comment"] + "\n" if self.heading.table_status["comment"] else ""
+ attributes_thus_far = set()
+ attributes_declared = set()
+ indexes = self.heading.indexes.copy()
+ for attr in self.heading.attributes.values():
+ if in_key and not attr.in_key:
+ definition += "---\n"
+ in_key = False
+ attributes_thus_far.add(attr.name)
+ do_include = True
+ for parent_name, fk_props in parents:
+ if attr.name in fk_props["attr_map"]:
+ do_include = False
+ if attributes_thus_far.issuperset(fk_props["attr_map"]):
+ # foreign key properties
+ try:
+ index_props = indexes.pop(tuple(fk_props["attr_map"]))
+ except KeyError:
+ index_props = ""
+ else:
+ index_props = [k for k, v in index_props.items() if v]
+ index_props = " [{}]".format(", ".join(index_props)) if index_props else ""
+
+ if not fk_props["aliased"]:
+ # simple foreign key
+ definition += "->{props} {class_name}\n".format(
+ props=index_props,
+ class_name=lookup_class_name(parent_name, context) or parent_name,
+ )
+ else:
+ # projected foreign key
+ definition += "->{props} {class_name}.proj({proj_list})\n".format(
+ props=index_props,
+ class_name=lookup_class_name(parent_name, context) or parent_name,
+ proj_list=",".join(
+ '{}="{}"'.format(attr, ref) for attr, ref in fk_props["attr_map"].items() if ref != attr
+ ),
+ )
+ attributes_declared.update(fk_props["attr_map"])
+ if do_include:
+ attributes_declared.add(attr.name)
+ # Use original_type (core type alias) if available, otherwise use type
+ display_type = attr.original_type or attr.type
+ definition += "%-20s : %-28s %s\n" % (
+ (attr.name if attr.default is None else "%s=%s" % (attr.name, attr.default)),
+ "%s%s" % (display_type, " auto_increment" if attr.autoincrement else ""),
+ "# " + attr.comment if attr.comment else "",
+ )
+ # add remaining indexes
+ for k, v in indexes.items():
+ definition += "{unique}INDEX ({attrs})\n".format(unique="UNIQUE " if v["unique"] else "", attrs=", ".join(k))
+ if printout:
+ logger.info("\n" + definition)
+ return definition
+
+ # --- private helper functions ----
+ def __make_placeholder(self, name, value, ignore_extra_fields=False, row=None):
+ """
+ For a given attribute `name` with `value`, return its processed value or value placeholder
+ as a string to be included in the query and the value, if any, to be submitted for
+ processing by mysql API.
+
+ In the simplified type system:
+ - Codecs handle all custom encoding via type chains
+ - UUID values are converted to bytes
+ - JSON values are serialized
+ - Blob values pass through as bytes
+ - Numeric values are stringified
+
+ :param name: name of attribute to be inserted
+ :param value: value of attribute to be inserted
+ :param ignore_extra_fields: if True, return None for unknown fields
+ :param row: the full row dict (unused in simplified model)
+ """
+ if ignore_extra_fields and name not in self.heading:
+ return None
+ attr = self.heading[name]
+
+ # Apply adapter encoding with type chain support
+ if attr.codec:
+ from .codecs import resolve_dtype
+
+ # Skip validation and encoding for None values (nullable columns)
+ if value is None:
+ return name, "DEFAULT", None
+
+ attr.codec.validate(value)
+
+ # Resolve full type chain
+ _, type_chain, resolved_store = resolve_dtype(f"<{attr.codec.name}>", store_name=attr.store)
+
+ # Apply encoders from outermost to innermost
+ for attr_type in type_chain:
+ # Pass store_name to encoders that support it (check via introspection)
+ import inspect
+
+ sig = inspect.signature(attr_type.encode)
+ if "store_name" in sig.parameters:
+ value = attr_type.encode(value, key=None, store_name=resolved_store)
+ else:
+ value = attr_type.encode(value, key=None)
+
+ # Handle NULL values
+ if value is None or (attr.numeric and (value == "" or np.isnan(float(value)))):
+ placeholder, value = "DEFAULT", None
+ else:
+ placeholder = "%s"
+ # UUID - convert to bytes
+ if attr.uuid:
+ if not isinstance(value, uuid.UUID):
+ try:
+ value = uuid.UUID(value)
+ except (AttributeError, ValueError):
+ raise DataJointError(f"badly formed UUID value {value} for attribute `{name}`")
+ value = value.bytes
+ # JSON - serialize to string
+ elif attr.json:
+ value = json.dumps(value)
+ # Numeric - convert to string
+ elif attr.numeric:
+ value = str(int(value) if isinstance(value, (bool, np.bool_)) else value)
+ # Blob - pass through as bytes (use for automatic serialization)
+
+ return name, placeholder, value
+
+ def __make_row_to_insert(self, row, field_list, ignore_extra_fields):
+ """
+ Helper function for insert and update
+
+ :param row: A tuple to insert
+ :return: a dict with fields 'names', 'placeholders', 'values'
+ """
+
+ def check_fields(fields):
+ """
+ Validates that all items in `fields` are valid attributes in the heading
+
+ :param fields: field names of a tuple
+ """
+ if not field_list:
+ if not ignore_extra_fields:
+ for field in fields:
+ if field not in self.heading:
+ raise KeyError("`{0:s}` is not in the table heading".format(field))
+ elif set(field_list) != set(fields).intersection(self.heading.names):
+ raise DataJointError("Attempt to insert rows with different fields.")
+
+ # Convert row to dict for object attribute processing
+ row_dict = None
+ if isinstance(row, np.void): # np.array
+ check_fields(row.dtype.fields)
+ row_dict = {name: row[name] for name in row.dtype.fields}
+ attributes = [
+ self.__make_placeholder(name, row[name], ignore_extra_fields, row=row_dict)
+ for name in self.heading
+ if name in row.dtype.fields
+ ]
+ elif isinstance(row, collections.abc.Mapping): # dict-based
+ check_fields(row)
+ row_dict = dict(row)
+ attributes = [
+ self.__make_placeholder(name, row[name], ignore_extra_fields, row=row_dict)
+ for name in self.heading
+ if name in row
+ ]
+ else: # positional
+ warnings.warn(
+ "Positional inserts (tuples/lists) are deprecated and will be removed in a future version. "
+ "Use dict with explicit field names instead: table.insert1({'field': value, ...})",
+ DeprecationWarning,
+ stacklevel=4, # Point to user's insert()/insert1() call
+ )
+ try:
+ if len(row) != len(self.heading):
+ raise DataJointError(
+ "Invalid insert argument. Incorrect number of attributes: {given} given; {expected} expected".format(
+ given=len(row), expected=len(self.heading)
+ )
+ )
+ except TypeError:
+ raise DataJointError("Datatype %s cannot be inserted" % type(row))
+ else:
+ row_dict = dict(zip(self.heading.names, row))
+ attributes = [
+ self.__make_placeholder(name, value, ignore_extra_fields, row=row_dict)
+ for name, value in zip(self.heading, row)
+ ]
+ if ignore_extra_fields:
+ attributes = [a for a in attributes if a is not None]
+
+ if not attributes:
+ # Check if empty insert is allowed (all attributes have defaults)
+ required_attrs = [
+ attr.name
+ for attr in self.heading.attributes.values()
+ if not (attr.autoincrement or attr.nullable or attr.default is not None)
+ ]
+ if required_attrs:
+ raise DataJointError(f"Cannot insert empty row. The following attributes require values: {required_attrs}")
+ # All attributes have defaults - allow empty insert
+ row_to_insert = {"names": (), "placeholders": (), "values": ()}
+ else:
+ row_to_insert = dict(zip(("names", "placeholders", "values"), zip(*attributes)))
+ if not field_list:
+ # first row sets the composition of the field list
+ field_list.extend(row_to_insert["names"])
+ else:
+ # reorder attributes in row_to_insert to match field_list
+ order = list(row_to_insert["names"].index(field) for field in field_list)
+ row_to_insert["names"] = list(row_to_insert["names"][i] for i in order)
+ row_to_insert["placeholders"] = list(row_to_insert["placeholders"][i] for i in order)
+ row_to_insert["values"] = list(row_to_insert["values"][i] for i in order)
+ return row_to_insert
+
+
+def lookup_class_name(name, context, depth=3):
+ """
+ given a table name in the form `schema_name`.`table_name`, find its class in the context.
+
+ :param name: `schema_name`.`table_name`
+ :param context: dictionary representing the namespace
+ :param depth: search depth into imported modules, helps avoid infinite recursion.
+ :return: class name found in the context or None if not found
+ """
+ # breadth-first search
+ nodes = [dict(context=context, context_name="", depth=depth)]
+ while nodes:
+ node = nodes.pop(0)
+ for member_name, member in node["context"].items():
+ # skip IPython's implicit variables
+ if not member_name.startswith("_"):
+ if inspect.isclass(member) and issubclass(member, Table):
+ if member.full_table_name == name: # found it!
+ return ".".join([node["context_name"], member_name]).lstrip(".")
+ try: # look for part tables
+ parts = member.__dict__
+ except AttributeError:
+ pass # not a UserTable -- cannot have part tables.
+ else:
+ for part in (getattr(member, p) for p in parts if p[0].isupper() and hasattr(member, p)):
+ if inspect.isclass(part) and issubclass(part, Table) and part.full_table_name == name:
+ return ".".join([node["context_name"], member_name, part.__name__]).lstrip(".")
+ elif node["depth"] > 0 and inspect.ismodule(member) and member.__name__ != "datajoint":
+ try:
+ nodes.append(
+ dict(
+ context=dict(inspect.getmembers(member)),
+ context_name=node["context_name"] + "." + member_name,
+ depth=node["depth"] - 1,
+ )
+ )
+ except (ImportError, TypeError):
+ pass # could not inspect module members, skip
+ return None
+
+
+class FreeTable(Table):
+ """
+ A base table without a dedicated class. Each instance is associated with a table
+ specified by full_table_name.
+
+ :param conn: a dj.Connection object
+ :param full_table_name: in format `database`.`table_name`
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self, conn, full_table_name):
+ self.database, self._table_name = (s.strip("`") for s in full_table_name.split("."))
+ self._connection = conn
+ self._support = [full_table_name]
+ self._heading = Heading(
+ table_info=dict(
+ conn=conn,
+ database=self.database,
+ table_name=self.table_name,
+ context=None,
+ )
+ )
+
+ def __repr__(self):
+ return "FreeTable(`%s`.`%s`)\n" % (self.database, self._table_name) + super().__repr__()
diff --git a/src/datajoint/types.py b/src/datajoint/types.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..72cefee3c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/datajoint/types.py
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+"""
+Type definitions for DataJoint.
+
+This module defines type aliases used throughout the DataJoint codebase
+to improve code clarity and enable better static type checking.
+
+Python 3.10+ is required.
+"""
+
+from __future__ import annotations
+
+from typing import Any, TypeAlias
+
+# Primary key types
+PrimaryKey: TypeAlias = dict[str, Any]
+"""A dictionary mapping attribute names to values that uniquely identify an entity."""
+
+PrimaryKeyList: TypeAlias = list[dict[str, Any]]
+"""A list of primary key dictionaries."""
+
+# Row/record types
+Row: TypeAlias = dict[str, Any]
+"""A single row/record as a dictionary mapping attribute names to values."""
+
+RowList: TypeAlias = list[dict[str, Any]]
+"""A list of rows/records."""
+
+# Attribute types
+AttributeName: TypeAlias = str
+"""Name of a table attribute/column."""
+
+AttributeNames: TypeAlias = list[str]
+"""List of attribute/column names."""
+
+# Table and schema names
+TableName: TypeAlias = str
+"""Simple table name (e.g., 'session')."""
+
+FullTableName: TypeAlias = str
+"""Fully qualified table name (e.g., '`schema`.`table`')."""
+
+SchemaName: TypeAlias = str
+"""Database schema name."""
+
+# Foreign key mapping
+ForeignKeyMap: TypeAlias = dict[str, tuple[str, str]]
+"""Mapping of child_attr -> (parent_table, parent_attr) for foreign keys."""
+
+# Restriction types
+Restriction: TypeAlias = str | dict[str, Any] | bool | "QueryExpression" | list | None
+"""Valid restriction types for query operations."""
+
+# Fetch result types
+FetchResult: TypeAlias = list[dict[str, Any]]
+"""Result of a fetch operation as list of dictionaries."""
+
+
+# For avoiding circular imports
+if False: # TYPE_CHECKING equivalent that's always False
+ from .expression import QueryExpression
diff --git a/datajoint/user_tables.py b/src/datajoint/user_tables.py
similarity index 57%
rename from datajoint/user_tables.py
rename to src/datajoint/user_tables.py
index 9c2e79d34..942179685 100644
--- a/datajoint/user_tables.py
+++ b/src/datajoint/user_tables.py
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
from .autopopulate import AutoPopulate
from .errors import DataJointError
from .table import Table
-from .utils import ClassProperty, from_camel_case
+from .utils import from_camel_case
_base_regexp = r"[a-z][a-z0-9]*(_[a-z][a-z0-9]*)*"
@@ -25,7 +25,13 @@
"proj",
"aggr",
"join",
- "fetch",
+ "extend",
+ "to_dicts",
+ "to_pandas",
+ "to_polars",
+ "to_arrow",
+ "to_arrays",
+ "keys",
"fetch1",
"head",
"tail",
@@ -36,27 +42,26 @@
"children",
"insert",
"insert1",
+ "insert_dataframe",
"update1",
+ "validate",
"drop",
"drop_quick",
"delete",
"delete_quick",
+ "staged_insert1",
}
class TableMeta(type):
"""
TableMeta subclasses allow applying some instance methods and properties directly
- at class level. For example, this allows Table.fetch() instead of Table().fetch().
+ at class level. For example, this allows Table.to_dicts() instead of Table().to_dicts().
"""
def __getattribute__(cls, name):
# trigger instantiation for supported class attrs
- return (
- cls().__getattribute__(name)
- if name in supported_class_attrs
- else super().__getattribute__(name)
- )
+ return cls().__getattribute__(name) if name in supported_class_attrs else super().__getattribute__(name)
def __and__(cls, arg):
return cls() & arg
@@ -82,6 +87,26 @@ def __add__(cls, arg):
def __iter__(cls):
return iter(cls())
+ # Class properties - defined on metaclass to work at class level
+ @property
+ def connection(cls):
+ """The database connection for this table."""
+ return cls._connection
+
+ @property
+ def table_name(cls):
+ """The table name formatted for MySQL."""
+ if cls._prefix is None:
+ raise AttributeError("Class prefix is not defined!")
+ return cls._prefix + from_camel_case(cls.__name__)
+
+ @property
+ def full_table_name(cls):
+ """The fully qualified table name (`database`.`table`)."""
+ if cls.database is None:
+ return None
+ return r"`{0:s}`.`{1:s}`".format(cls.database, cls.table_name)
+
class UserTable(Table, metaclass=TableMeta):
"""
@@ -103,33 +128,7 @@ def definition(self):
"""
:return: a string containing the table definition using the DataJoint DDL.
"""
- raise NotImplementedError(
- 'Subclasses of Table must implement the property "definition"'
- )
-
- @ClassProperty
- def connection(cls):
- return cls._connection
-
- @ClassProperty
- def table_name(cls):
- """
- :return: the table name of the table formatted for mysql.
- """
- if cls._prefix is None:
- raise AttributeError("Class prefix is not defined!")
- return cls._prefix + from_camel_case(cls.__name__)
-
- @ClassProperty
- def full_table_name(cls):
- if cls not in {Manual, Imported, Lookup, Computed, Part, UserTable}:
- # for derived classes only
- if cls.database is None:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Class %s is not properly declared (schema decorator not applied?)"
- % cls.__name__
- )
- return r"`{0:s}`.`{1:s}`".format(cls.database, cls.table_name)
+ raise NotImplementedError('Subclasses of Table must implement the property "definition"')
class Manual(UserTable):
@@ -149,9 +148,7 @@ class Lookup(UserTable):
"""
_prefix = "#"
- tier_regexp = (
- r"(?P" + _prefix + _base_regexp.replace("TIER", "lookup") + ")"
- )
+ tier_regexp = r"(?P" + _prefix + _base_regexp.replace("TIER", "lookup") + ")"
class Imported(UserTable, AutoPopulate):
@@ -174,7 +171,28 @@ class Computed(UserTable, AutoPopulate):
tier_regexp = r"(?P" + _prefix + _base_regexp + ")"
-class Part(UserTable):
+class PartMeta(TableMeta):
+ """Metaclass for Part tables with overridden class properties."""
+
+ @property
+ def table_name(cls):
+ """The table name for a Part is derived from its master table."""
+ return None if cls.master is None else cls.master.table_name + "__" + from_camel_case(cls.__name__)
+
+ @property
+ def full_table_name(cls):
+ """The fully qualified table name (`database`.`table`)."""
+ if cls.database is None or cls.table_name is None:
+ return None
+ return r"`{0:s}`.`{1:s}`".format(cls.database, cls.table_name)
+
+ @property
+ def master(cls):
+ """The master table for this Part table."""
+ return cls._master
+
+
+class Part(UserTable, metaclass=PartMeta):
"""
Inherit from this class if the table's values are details of an entry in another table
and if this table is populated by the other table. For example, the entries inheriting from
@@ -195,51 +213,48 @@ class Part(UserTable):
+ ")"
)
- @ClassProperty
- def connection(cls):
- return cls._connection
-
- @ClassProperty
- def full_table_name(cls):
- return (
- None
- if cls.database is None or cls.table_name is None
- else r"`{0:s}`.`{1:s}`".format(cls.database, cls.table_name)
- )
-
- @ClassProperty
- def master(cls):
- return cls._master
-
- @ClassProperty
- def table_name(cls):
- return (
- None
- if cls.master is None
- else cls.master.table_name + "__" + from_camel_case(cls.__name__)
- )
-
- def delete(self, force=False):
+ def delete(self, part_integrity: str = "enforce", **kwargs):
"""
- unless force is True, prohibits direct deletes from parts.
+ Delete from a Part table.
+
+ Args:
+ part_integrity: Policy for master-part integrity. One of:
+ - ``"enforce"`` (default): Error - delete from master instead.
+ - ``"ignore"``: Allow direct deletion (breaks master-part integrity).
+ - ``"cascade"``: Delete parts AND cascade up to delete master.
+ **kwargs: Additional arguments passed to Table.delete()
+ (transaction, prompt)
+
+ Raises:
+ DataJointError: If part_integrity="enforce" (direct Part deletes prohibited)
"""
- if force:
- super().delete(force_parts=True)
- else:
+ if part_integrity == "enforce":
raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot delete from a Part directly. Delete from master instead"
+ "Cannot delete from a Part directly. Delete from master instead, "
+ "or use part_integrity='ignore' to break integrity, "
+ "or part_integrity='cascade' to also delete master."
)
+ super().delete(part_integrity=part_integrity, **kwargs)
- def drop(self, force=False):
+ def drop(self, part_integrity: str = "enforce"):
"""
- unless force is True, prohibits direct deletes from parts.
+ Drop a Part table.
+
+ Args:
+ part_integrity: Policy for master-part integrity. One of:
+ - ``"enforce"`` (default): Error - drop master instead.
+ - ``"ignore"``: Allow direct drop (breaks master-part structure).
+ Note: ``"cascade"`` is not supported for drop (too destructive).
+
+ Raises:
+ DataJointError: If part_integrity="enforce" (direct Part drops prohibited)
"""
- if force:
+ if part_integrity == "ignore":
super().drop()
+ elif part_integrity == "enforce":
+ raise DataJointError("Cannot drop a Part directly. Drop master instead, or use part_integrity='ignore' to force.")
else:
- raise DataJointError(
- "Cannot drop a Part directly. Delete from master instead"
- )
+ raise ValueError(f"part_integrity for drop must be 'enforce' or 'ignore', got {part_integrity!r}")
def alter(self, prompt=True, context=None):
# without context, use declaration context which maps master keyword to master table
@@ -263,10 +278,6 @@ def _get_tier(table_name):
return _AliasNode
else:
try:
- return next(
- tier
- for tier in user_table_classes
- if re.fullmatch(tier.tier_regexp, table_name.split("`")[-2])
- )
+ return next(tier for tier in user_table_classes if re.fullmatch(tier.tier_regexp, table_name.split("`")[-2]))
except StopIteration:
return None
diff --git a/datajoint/utils.py b/src/datajoint/utils.py
similarity index 91%
rename from datajoint/utils.py
rename to src/datajoint/utils.py
index c34536685..e8303a993 100644
--- a/datajoint/utils.py
+++ b/src/datajoint/utils.py
@@ -7,14 +7,6 @@
from .errors import DataJointError
-class ClassProperty:
- def __init__(self, f):
- self.f = f
-
- def __get__(self, obj, owner):
- return self.f(owner)
-
-
def user_choice(prompt, choices=("yes", "no"), default=None):
"""
Prompts the user for confirmation. The default value, if any, is capitalized.
@@ -25,9 +17,7 @@ def user_choice(prompt, choices=("yes", "no"), default=None):
:return: the user's choice
"""
assert default is None or default in choices
- choice_list = ", ".join(
- (choice.title() if choice == default else choice for choice in choices)
- )
+ choice_list = ", ".join((choice.title() if choice == default else choice for choice in choices))
response = None
while response not in choices:
response = input(prompt + " [" + choice_list + "]: ")
@@ -97,9 +87,7 @@ def convert(match):
return ("_" if match.groups()[0] else "") + match.group(0).lower()
if not is_camel_case(s):
- raise DataJointError(
- "ClassName must be alphanumeric in CamelCase, begin with a capital letter"
- )
+ raise DataJointError("ClassName must be alphanumeric in CamelCase, begin with a capital letter")
return re.sub(r"(\B[A-Z])|(\b[A-Z])", convert, s)
diff --git a/datajoint/version.py b/src/datajoint/version.py
similarity index 64%
rename from datajoint/version.py
rename to src/datajoint/version.py
index 5fb608cef..31f651ea6 100644
--- a/datajoint/version.py
+++ b/src/datajoint/version.py
@@ -1,6 +1,4 @@
# version bump auto managed by Github Actions:
# label_prs.yaml(prep), release.yaml(bump), post_release.yaml(edit)
# manually set this version will be eventually overwritten by the above actions
-__version__ = "0.14.6"
-
-assert len(__version__) <= 10 # The log table limits version to the 10 characters
+__version__ = "2.0.0a16"
diff --git a/tests/conftest.py b/tests/conftest.py
index 88d55e32f..6d03dece7 100644
--- a/tests/conftest.py
+++ b/tests/conftest.py
@@ -1,136 +1,297 @@
-import json
+"""
+Pytest configuration for DataJoint tests.
+
+Tests are organized by their dependencies:
+- Unit tests: No external dependencies, run with `pytest -m "not requires_mysql"`
+- Integration tests: Require MySQL/MinIO, marked with @pytest.mark.requires_mysql
+
+Containers are automatically started via testcontainers when needed.
+Just run: pytest tests/
+
+To use external containers instead (e.g., docker-compose), set:
+ DJ_USE_EXTERNAL_CONTAINERS=1
+ DJ_HOST=localhost DJ_PORT=3306 S3_ENDPOINT=localhost:9000 pytest
+
+To run only unit tests (no Docker required):
+ pytest -m "not requires_mysql"
+"""
+
+import logging
import os
-import shutil
-from os import environ, remove
-from pathlib import Path
+from os import remove
from typing import Dict, List
import certifi
-import minio
-import networkx as nx
import pytest
import urllib3
-from packaging import version
import datajoint as dj
-from datajoint import errors
-from datajoint.errors import (
- ADAPTED_TYPE_SWITCH,
- FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH,
- DataJointError,
-)
-
-from . import schema, schema_adapted, schema_advanced, schema_external, schema_simple
+from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
+
+from . import schema, schema_advanced, schema_external, schema_object, schema_simple
from . import schema_uuid as schema_uuid_module
+from . import schema_type_aliases as schema_type_aliases_module
+
+logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
+
+
+# =============================================================================
+# Pytest Hooks
+# =============================================================================
+
+
+def pytest_collection_modifyitems(config, items):
+ """Auto-mark integration tests based on their fixtures."""
+ # Tests that use these fixtures require MySQL
+ mysql_fixtures = {
+ "connection_root",
+ "connection_root_bare",
+ "connection_test",
+ "schema_any",
+ "schema_any_fresh",
+ "schema_simp",
+ "schema_adv",
+ "schema_ext",
+ "schema_uuid",
+ "schema_type_aliases",
+ "schema_obj",
+ "db_creds_root",
+ "db_creds_test",
+ }
+ # Tests that use these fixtures require MinIO
+ minio_fixtures = {
+ "minio_client",
+ "s3fs_client",
+ "s3_creds",
+ "stores_config",
+ "mock_stores",
+ }
+ for item in items:
+ # Get all fixtures this test uses (directly or indirectly)
+ try:
+ fixturenames = set(item.fixturenames)
+ except AttributeError:
+ continue
-@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def prefix():
- return os.environ.get("DJ_TEST_DB_PREFIX", "djtest")
+ # Auto-add marks based on fixture usage
+ if fixturenames & mysql_fixtures:
+ item.add_marker(pytest.mark.requires_mysql)
+ if fixturenames & minio_fixtures:
+ item.add_marker(pytest.mark.requires_minio)
-@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def monkeysession():
- with pytest.MonkeyPatch.context() as mp:
- yield mp
+# =============================================================================
+# Container Fixtures - Auto-start MySQL and MinIO via testcontainers
+# =============================================================================
+# Check if we should use external containers (for CI or manual docker-compose)
+USE_EXTERNAL_CONTAINERS = os.environ.get("DJ_USE_EXTERNAL_CONTAINERS", "").lower() in ("1", "true", "yes")
-@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
-def monkeymodule():
- with pytest.MonkeyPatch.context() as mp:
- yield mp
+@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
+def mysql_container():
+ """Start MySQL container for the test session (or use external)."""
+ if USE_EXTERNAL_CONTAINERS:
+ # Use external container - return None, credentials come from env
+ logger.info("Using external MySQL container")
+ yield None
+ return
-@pytest.fixture
-def enable_adapted_types(monkeypatch):
- monkeypatch.setenv(ADAPTED_TYPE_SWITCH, "TRUE")
- yield
- monkeypatch.delenv(ADAPTED_TYPE_SWITCH, raising=True)
+ from testcontainers.mysql import MySqlContainer
+ container = MySqlContainer(
+ image="mysql:8.0",
+ username="root",
+ password="password",
+ dbname="test",
+ )
+ container.start()
-@pytest.fixture
-def enable_filepath_feature(monkeypatch):
- monkeypatch.setenv(FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH, "TRUE")
- yield
- monkeypatch.delenv(FILEPATH_FEATURE_SWITCH, raising=True)
+ host = container.get_container_host_ip()
+ port = container.get_exposed_port(3306)
+ logger.info(f"MySQL container started at {host}:{port}")
+ yield container
-@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def db_creds_test() -> Dict:
- return dict(
- host=os.getenv("DJ_TEST_HOST", "db"),
- user=os.getenv("DJ_TEST_USER", "datajoint"),
- password=os.getenv("DJ_TEST_PASSWORD", "datajoint"),
- )
+ container.stop()
+ logger.info("MySQL container stopped")
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def db_creds_root() -> Dict:
- return dict(
- host=os.getenv("DJ_HOST", "db"),
- user=os.getenv("DJ_USER", "root"),
- password=os.getenv("DJ_PASS", "password"),
+def minio_container():
+ """Start MinIO container for the test session (or use external)."""
+ if USE_EXTERNAL_CONTAINERS:
+ # Use external container - return None, credentials come from env
+ logger.info("Using external MinIO container")
+ yield None
+ return
+
+ from testcontainers.minio import MinioContainer
+
+ container = MinioContainer(
+ image="minio/minio:latest",
+ access_key="datajoint",
+ secret_key="datajoint",
)
+ container.start()
+
+ host = container.get_container_host_ip()
+ port = container.get_exposed_port(9000)
+ logger.info(f"MinIO container started at {host}:{port}")
+
+ yield container
+
+ container.stop()
+ logger.info("MinIO container stopped")
+
+
+# =============================================================================
+# Credential Fixtures - Derived from containers or environment
+# =============================================================================
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def connection_root_bare(db_creds_root):
- connection = dj.Connection(**db_creds_root)
- yield connection
+def prefix():
+ return os.environ.get("DJ_TEST_DB_PREFIX", "djtest")
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def connection_root(connection_root_bare, prefix):
- """Root user database connection."""
- dj.config["safemode"] = False
- conn_root = connection_root_bare
- # Create MySQL users
- if version.parse(
- conn_root.query("select @@version;").fetchone()[0]
- ) >= version.parse("8.0.0"):
- # create user if necessary on mysql8
- conn_root.query(
- """
- CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'datajoint'@'%%'
- IDENTIFIED BY 'datajoint';
- """
+def db_creds_root(mysql_container) -> Dict:
+ """Root database credentials from container or environment."""
+ if mysql_container is not None:
+ # From testcontainer
+ host = mysql_container.get_container_host_ip()
+ port = mysql_container.get_exposed_port(3306)
+ return dict(
+ host=f"{host}:{port}",
+ user="root",
+ password="password",
)
- conn_root.query(
- """
- CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'djview'@'%%'
- IDENTIFIED BY 'djview';
- """
+ else:
+ # From environment (external container)
+ host = os.environ.get("DJ_HOST", "localhost")
+ port = os.environ.get("DJ_PORT", "3306")
+ return dict(
+ host=f"{host}:{port}" if port else host,
+ user=os.environ.get("DJ_USER", "root"),
+ password=os.environ.get("DJ_PASS", "password"),
)
- conn_root.query(
- """
- CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'djssl'@'%%'
- IDENTIFIED BY 'djssl'
- REQUIRE SSL;
- """
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
+def db_creds_test(mysql_container) -> Dict:
+ """Test user database credentials from container or environment."""
+ if mysql_container is not None:
+ # From testcontainer
+ host = mysql_container.get_container_host_ip()
+ port = mysql_container.get_exposed_port(3306)
+ return dict(
+ host=f"{host}:{port}",
+ user="datajoint",
+ password="datajoint",
)
- conn_root.query("GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `djtest%%`.* TO 'datajoint'@'%%';")
- conn_root.query("GRANT SELECT ON `djtest%%`.* TO 'djview'@'%%';")
- conn_root.query("GRANT SELECT ON `djtest%%`.* TO 'djssl'@'%%';")
else:
- # grant permissions. For MySQL 5.7 this also automatically creates user
- # if not exists
- conn_root.query(
- """
- GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `djtest%%`.* TO 'datajoint'@'%%'
- IDENTIFIED BY 'datajoint';
- """
+ # From environment (external container)
+ host = os.environ.get("DJ_HOST", "localhost")
+ port = os.environ.get("DJ_PORT", "3306")
+ return dict(
+ host=f"{host}:{port}" if port else host,
+ user=os.environ.get("DJ_TEST_USER", "datajoint"),
+ password=os.environ.get("DJ_TEST_PASSWORD", "datajoint"),
)
- conn_root.query(
- "GRANT SELECT ON `djtest%%`.* TO 'djview'@'%%' IDENTIFIED BY 'djview';"
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
+def s3_creds(minio_container) -> Dict:
+ """S3/MinIO credentials from container or environment."""
+ if minio_container is not None:
+ # From testcontainer
+ host = minio_container.get_container_host_ip()
+ port = minio_container.get_exposed_port(9000)
+ return dict(
+ endpoint=f"{host}:{port}",
+ access_key="datajoint",
+ secret_key="datajoint",
+ bucket="datajoint.test",
)
- conn_root.query(
- """
- GRANT SELECT ON `djtest%%`.* TO 'djssl'@'%%'
- IDENTIFIED BY 'djssl'
- REQUIRE SSL;
- """
+ else:
+ # From environment (external container)
+ return dict(
+ endpoint=os.environ.get("S3_ENDPOINT", "localhost:9000"),
+ access_key=os.environ.get("S3_ACCESS_KEY", "datajoint"),
+ secret_key=os.environ.get("S3_SECRET_KEY", "datajoint"),
+ bucket=os.environ.get("S3_BUCKET", "datajoint.test"),
)
+
+# =============================================================================
+# DataJoint Configuration
+# =============================================================================
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
+def configure_datajoint(db_creds_root):
+ """Configure DataJoint to use test database.
+
+ This fixture is NOT autouse - it only runs when a test requests
+ a fixture that depends on it (e.g., connection_root_bare).
+ """
+ # Parse host:port from credentials
+ host_port = db_creds_root["host"]
+ if ":" in host_port:
+ host, port = host_port.rsplit(":", 1)
+ else:
+ host, port = host_port, "3306"
+
+ dj.config["database.host"] = host
+ dj.config["database.port"] = int(port)
+ dj.config["safemode"] = False
+
+ logger.info(f"Configured DataJoint to use MySQL at {host}:{port}")
+
+
+# =============================================================================
+# Connection Fixtures
+# =============================================================================
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
+def connection_root_bare(db_creds_root, configure_datajoint):
+ """Bare root connection without user setup."""
+ connection = dj.Connection(**db_creds_root)
+ yield connection
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
+def connection_root(connection_root_bare, prefix):
+ """Root database connection with test users created."""
+ conn_root = connection_root_bare
+
+ # Create MySQL users (MySQL 8.0+ syntax - we only support 8.0+)
+ conn_root.query(
+ """
+ CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'datajoint'@'%%'
+ IDENTIFIED BY 'datajoint';
+ """
+ )
+ conn_root.query(
+ """
+ CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'djview'@'%%'
+ IDENTIFIED BY 'djview';
+ """
+ )
+ conn_root.query(
+ """
+ CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'djssl'@'%%'
+ IDENTIFIED BY 'djssl'
+ REQUIRE SSL;
+ """
+ )
+ conn_root.query("GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `djtest%%`.* TO 'datajoint'@'%%';")
+ conn_root.query("GRANT SELECT ON `djtest%%`.* TO 'djview'@'%%';")
+ conn_root.query("GRANT SELECT ON `djtest%%`.* TO 'djssl'@'%%';")
+
yield conn_root
# Teardown
@@ -142,7 +303,6 @@ def connection_root(connection_root_bare, prefix):
if os.path.exists("dj_local_conf.json"):
remove("dj_local_conf.json")
- # Remove created users
conn_root.query("DROP USER IF EXISTS `datajoint`")
conn_root.query("DROP USER IF EXISTS `djview`")
conn_root.query("DROP USER IF EXISTS `djssl`")
@@ -155,33 +315,19 @@ def connection_test(connection_root, prefix, db_creds_test):
database = f"{prefix}%%"
permission = "ALL PRIVILEGES"
- # Create MySQL users
- if version.parse(
- connection_root.query("select @@version;").fetchone()[0]
- ) >= version.parse("8.0.0"):
- # create user if necessary on mysql8
- connection_root.query(
- f"""
- CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS '{db_creds_test["user"]}'@'%%'
- IDENTIFIED BY '{db_creds_test["password"]}';
- """
- )
- connection_root.query(
- f"""
- GRANT {permission} ON `{database}`.*
- TO '{db_creds_test["user"]}'@'%%';
- """
- )
- else:
- # grant permissions. For MySQL 5.7 this also automatically creates user
- # if not exists
- connection_root.query(
- f"""
- GRANT {permission} ON `{database}`.*
- TO '{db_creds_test["user"]}'@'%%'
- IDENTIFIED BY '{db_creds_test["password"]}';
- """
- )
+ # MySQL 8.0+ syntax
+ connection_root.query(
+ f"""
+ CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS '{db_creds_test["user"]}'@'%%'
+ IDENTIFIED BY '{db_creds_test["password"]}';
+ """
+ )
+ connection_root.query(
+ f"""
+ GRANT {permission} ON `{database}`.*
+ TO '{db_creds_test["user"]}'@'%%';
+ """
+ )
connection = dj.Connection(**db_creds_test)
yield connection
@@ -189,50 +335,63 @@ def connection_test(connection_root, prefix, db_creds_test):
connection.close()
-@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def s3_creds() -> Dict:
- return dict(
- endpoint=os.environ.get("S3_ENDPOINT", "minio:9000"),
- access_key=os.environ.get("S3_ACCESS_KEY", "datajoint"),
- secret_key=os.environ.get("S3_SECRET_KEY", "datajoint"),
- bucket=os.environ.get("S3_BUCKET", "datajoint.test"),
- )
+# =============================================================================
+# S3/MinIO Fixtures
+# =============================================================================
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def stores_config(s3_creds, tmpdir_factory):
- stores_config = {
- "raw": dict(protocol="file", location=tmpdir_factory.mktemp("raw")),
+ """Configure object storage stores for tests."""
+ return {
+ "raw": dict(protocol="file", location=str(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("raw"))),
"repo": dict(
- stage=tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo"),
+ stage=str(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo")),
protocol="file",
- location=tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo"),
+ location=str(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo")),
),
"repo-s3": dict(
- s3_creds,
protocol="s3",
+ endpoint=s3_creds["endpoint"],
+ access_key=s3_creds["access_key"],
+ secret_key=s3_creds["secret_key"],
+ bucket=s3_creds.get("bucket", "datajoint-test"),
location="dj/repo",
- stage=tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo-s3"),
- ),
- "local": dict(
- protocol="file", location=tmpdir_factory.mktemp("local"), subfolding=(1, 1)
+ stage=str(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo-s3")),
+ secure=False, # MinIO runs without SSL in tests
),
+ "local": dict(protocol="file", location=str(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("local"))),
"share": dict(
- s3_creds, protocol="s3", location="dj/store/repo", subfolding=(2, 4)
+ protocol="s3",
+ endpoint=s3_creds["endpoint"],
+ access_key=s3_creds["access_key"],
+ secret_key=s3_creds["secret_key"],
+ bucket=s3_creds.get("bucket", "datajoint-test"),
+ location="dj/store/repo",
+ secure=False, # MinIO runs without SSL in tests
),
}
- return stores_config
@pytest.fixture
def mock_stores(stores_config):
- og_stores_config = dj.config.get("stores")
- dj.config["stores"] = stores_config
+ """Configure object storage stores for tests using new object_storage system."""
+ # Save original configuration
+ og_project_name = dj.config.object_storage.project_name
+ og_stores = dict(dj.config.object_storage.stores)
+
+ # Set test configuration
+ dj.config.object_storage.project_name = "djtest"
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores.clear()
+ for name, config in stores_config.items():
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores[name] = config
+
yield
- if og_stores_config is None:
- del dj.config["stores"]
- else:
- dj.config["stores"] = og_stores_config
+
+ # Restore original configuration
+ dj.config.object_storage.project_name = og_project_name
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores.clear()
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores.update(og_stores)
@pytest.fixture
@@ -246,16 +405,111 @@ def mock_cache(tmpdir_factory):
dj.config["cache"] = og_cache
-@pytest.fixture
-def schema_any(connection_test, prefix):
- schema_any = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_test1", schema.LOCALS_ANY, connection=connection_test
+@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
+def http_client():
+ client = urllib3.PoolManager(
+ timeout=30,
+ cert_reqs="CERT_REQUIRED",
+ ca_certs=certifi.where(),
+ retries=urllib3.Retry(total=3, backoff_factor=0.2, status_forcelist=[500, 502, 503, 504]),
)
- assert schema.LOCALS_ANY, "LOCALS_ANY is empty"
+ yield client
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
+def s3fs_client(s3_creds):
+ """Initialize s3fs filesystem for MinIO."""
+ import s3fs
+
+ return s3fs.S3FileSystem(
+ endpoint_url=f"http://{s3_creds['endpoint']}",
+ key=s3_creds["access_key"],
+ secret=s3_creds["secret_key"],
+ )
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
+def minio_client(s3_creds, s3fs_client, teardown=False):
+ """S3 filesystem with test bucket created (legacy name for compatibility)."""
+ bucket = s3_creds["bucket"]
+
+ # Create bucket if it doesn't exist
+ try:
+ s3fs_client.mkdir(bucket)
+ except Exception:
+ # Bucket may already exist
+ pass
+
+ yield s3fs_client
+
+ if not teardown:
+ return
+ # Clean up objects and bucket
try:
- schema_any.jobs.delete()
- except DataJointError:
+ files = s3fs_client.ls(bucket, detail=False)
+ for f in files:
+ s3fs_client.rm(f)
+ s3fs_client.rmdir(bucket)
+ except Exception:
pass
+
+
+# =============================================================================
+# Cleanup Fixtures
+# =============================================================================
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def clean_autopopulate(experiment, trial, ephys):
+ """Cleanup fixture for autopopulate tests."""
+ yield
+ ephys.delete()
+ trial.delete()
+ experiment.delete()
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def clean_jobs(schema_any):
+ """Cleanup fixture for jobs tests."""
+ # schema.jobs returns a list of Job objects for existing job tables
+ for job in schema_any.jobs:
+ try:
+ job.delete()
+ except DataJointError:
+ pass
+ yield
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def clean_test_tables(test, test_extra, test_no_extra):
+ """Cleanup fixture for relation tests."""
+ if not test:
+ test.insert(test.contents, skip_duplicates=True)
+ yield
+ test.delete()
+ test.insert(test.contents, skip_duplicates=True)
+ test_extra.delete()
+ test_no_extra.delete()
+
+
+# =============================================================================
+# Schema Fixtures
+# =============================================================================
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
+def schema_any(connection_test, prefix):
+ schema_any = dj.Schema(prefix + "_test1", schema.LOCALS_ANY, connection=connection_test)
+ assert schema.LOCALS_ANY, "LOCALS_ANY is empty"
+ # Clean up any existing job tables (schema.jobs returns a list)
+ for job in schema_any.jobs:
+ try:
+ job.delete()
+ except DataJointError:
+ pass
+ # Allow native PK fields for legacy test tables (Experiment, Trial)
+ original_value = dj.config.jobs.allow_new_pk_fields_in_computed_tables
+ dj.config.jobs.allow_new_pk_fields_in_computed_tables = True
schema_any(schema.TTest)
schema_any(schema.TTest2)
schema_any(schema.TTest3)
@@ -294,11 +548,81 @@ def schema_any(connection_test, prefix):
schema_any(schema.SessionDateA)
schema_any(schema.Stimulus)
schema_any(schema.Longblob)
+ # Restore original config value after all tables are declared
+ dj.config.jobs.allow_new_pk_fields_in_computed_tables = original_value
yield schema_any
- try:
- schema_any.jobs.delete()
- except DataJointError:
- pass
+ # Clean up job tables before dropping schema (if schema still exists)
+ if schema_any.exists:
+ for job in schema_any.jobs:
+ try:
+ job.delete()
+ except DataJointError:
+ pass
+ schema_any.drop()
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def schema_any_fresh(connection_test, prefix):
+ """Function-scoped schema_any for tests that need fresh schema state."""
+ schema_any = dj.Schema(prefix + "_test1_fresh", schema.LOCALS_ANY, connection=connection_test)
+ assert schema.LOCALS_ANY, "LOCALS_ANY is empty"
+ # Clean up any existing job tables
+ for job in schema_any.jobs:
+ try:
+ job.delete()
+ except DataJointError:
+ pass
+ # Allow native PK fields for legacy test tables (Experiment, Trial)
+ original_value = dj.config.jobs.allow_new_pk_fields_in_computed_tables
+ dj.config.jobs.allow_new_pk_fields_in_computed_tables = True
+ schema_any(schema.TTest)
+ schema_any(schema.TTest2)
+ schema_any(schema.TTest3)
+ schema_any(schema.NullableNumbers)
+ schema_any(schema.TTestExtra)
+ schema_any(schema.TTestNoExtra)
+ schema_any(schema.Auto)
+ schema_any(schema.User)
+ schema_any(schema.Subject)
+ schema_any(schema.Language)
+ schema_any(schema.Experiment)
+ schema_any(schema.Trial)
+ schema_any(schema.Ephys)
+ schema_any(schema.Image)
+ schema_any(schema.UberTrash)
+ schema_any(schema.UnterTrash)
+ schema_any(schema.SimpleSource)
+ schema_any(schema.SigIntTable)
+ schema_any(schema.SigTermTable)
+ schema_any(schema.DjExceptionName)
+ schema_any(schema.ErrorClass)
+ schema_any(schema.DecimalPrimaryKey)
+ schema_any(schema.IndexRich)
+ schema_any(schema.ThingA)
+ schema_any(schema.ThingB)
+ schema_any(schema.ThingC)
+ schema_any(schema.ThingD)
+ schema_any(schema.ThingE)
+ schema_any(schema.Parent)
+ schema_any(schema.Child)
+ schema_any(schema.ComplexParent)
+ schema_any(schema.ComplexChild)
+ schema_any(schema.SubjectA)
+ schema_any(schema.SessionA)
+ schema_any(schema.SessionStatusA)
+ schema_any(schema.SessionDateA)
+ schema_any(schema.Stimulus)
+ schema_any(schema.Longblob)
+ # Restore original config value after all tables are declared
+ dj.config.jobs.allow_new_pk_fields_in_computed_tables = original_value
+ yield schema_any
+ # Clean up job tables before dropping schema (if schema still exists)
+ if schema_any.exists:
+ for job in schema_any.jobs:
+ try:
+ job.delete()
+ except DataJointError:
+ pass
schema_any.drop()
@@ -310,7 +634,6 @@ def thing_tables(schema_any):
d = schema.ThingD()
e = schema.ThingE()
- # clear previous contents if any.
c.delete_quick()
b.delete_quick()
a.delete_quick()
@@ -322,11 +645,9 @@ def thing_tables(schema_any):
yield a, b, c, d, e
-@pytest.fixture
+@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def schema_simp(connection_test, prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_relational", schema_simple.LOCALS_SIMPLE, connection=connection_test
- )
+ schema = dj.Schema(prefix + "_relational", schema_simple.LOCALS_SIMPLE, connection=connection_test)
schema(schema_simple.SelectPK)
schema(schema_simple.KeyPK)
schema(schema_simple.IJ)
@@ -352,7 +673,7 @@ def schema_simp(connection_test, prefix):
schema.drop()
-@pytest.fixture
+@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def schema_adv(connection_test, prefix):
schema = dj.Schema(
prefix + "_advanced",
@@ -373,9 +694,7 @@ def schema_adv(connection_test, prefix):
@pytest.fixture
-def schema_ext(
- connection_test, enable_filepath_feature, mock_stores, mock_cache, prefix
-):
+def schema_ext(connection_test, mock_stores, mock_cache, prefix):
schema = dj.Schema(
prefix + "_extern",
context=schema_external.LOCALS_EXTERNAL,
@@ -393,7 +712,7 @@ def schema_ext(
schema.drop()
-@pytest.fixture
+@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def schema_uuid(connection_test, prefix):
schema = dj.Schema(
prefix + "_test1",
@@ -407,56 +726,24 @@ def schema_uuid(connection_test, prefix):
schema.drop()
-@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def http_client():
- # Initialize httpClient with relevant timeout.
- client = urllib3.PoolManager(
- timeout=30,
- cert_reqs="CERT_REQUIRED",
- ca_certs=certifi.where(),
- retries=urllib3.Retry(
- total=3, backoff_factor=0.2, status_forcelist=[500, 502, 503, 504]
- ),
- )
- yield client
-
-
-@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def minio_client_bare(s3_creds):
- """Initialize MinIO with an endpoint and access/secret keys."""
- client = minio.Minio(
- endpoint=s3_creds["endpoint"],
- access_key=s3_creds["access_key"],
- secret_key=s3_creds["secret_key"],
- secure=False,
+@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
+def schema_type_aliases(connection_test, prefix):
+ """Schema for testing numeric type aliases."""
+ schema = dj.Schema(
+ prefix + "_type_aliases",
+ context=schema_type_aliases_module.LOCALS_TYPE_ALIASES,
+ connection=connection_test,
)
- return client
-
-
-@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
-def minio_client(s3_creds, minio_client_bare, teardown=False):
- """Initialize a MinIO client and create buckets for testing session."""
- # Setup MinIO bucket
- aws_region = "us-east-1"
- try:
- minio_client_bare.make_bucket(s3_creds["bucket"], location=aws_region)
- except minio.error.S3Error as e:
- if e.code != "BucketAlreadyOwnedByYou":
- raise e
+ schema(schema_type_aliases_module.TypeAliasTable)
+ schema(schema_type_aliases_module.TypeAliasPrimaryKey)
+ schema(schema_type_aliases_module.TypeAliasNullable)
+ yield schema
+ schema.drop()
- yield minio_client_bare
- if not teardown:
- return
- # Teardown S3
- objs = list(minio_client_bare.list_objects(s3_creds["bucket"], recursive=True))
- objs = [
- minio_client_bare.remove_object(
- s3_creds["bucket"], o.object_name.encode("utf-8")
- )
- for o in objs
- ]
- minio_client_bare.remove_bucket(s3_creds["bucket"])
+# =============================================================================
+# Table Fixtures
+# =============================================================================
@pytest.fixture
@@ -530,3 +817,71 @@ def channel(schema_any):
@pytest.fixture
def trash(schema_any):
return schema.UberTrash()
+
+
+# =============================================================================
+# Object Storage Fixtures
+# =============================================================================
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def object_storage_config(tmpdir_factory):
+ """Create object storage configuration for testing."""
+ location = str(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("object_storage"))
+ return {
+ "project_name": "test_project",
+ "protocol": "file",
+ "location": location,
+ "token_length": 8,
+ }
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def mock_object_storage(object_storage_config):
+ """Mock object storage configuration in datajoint config."""
+ # Save original values
+ original = {
+ "project_name": dj.config.object_storage.project_name,
+ "protocol": dj.config.object_storage.protocol,
+ "location": dj.config.object_storage.location,
+ "token_length": dj.config.object_storage.token_length,
+ "stores": dict(dj.config.object_storage.stores),
+ }
+
+ # Set test values
+ dj.config.object_storage.project_name = object_storage_config["project_name"]
+ dj.config.object_storage.protocol = object_storage_config["protocol"]
+ dj.config.object_storage.location = object_storage_config["location"]
+ dj.config.object_storage.token_length = object_storage_config.get("token_length", 8)
+
+ # Configure 'local' store using same location
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores["local"] = {
+ "protocol": "file",
+ "location": object_storage_config["location"],
+ }
+
+ yield object_storage_config
+
+ # Restore original values
+ dj.config.object_storage.project_name = original["project_name"]
+ dj.config.object_storage.protocol = original["protocol"]
+ dj.config.object_storage.location = original["location"]
+ dj.config.object_storage.token_length = original["token_length"]
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores.clear()
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores.update(original["stores"])
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def schema_obj(connection_test, prefix, mock_object_storage):
+ """Schema for object type tests."""
+ schema = dj.Schema(
+ prefix + "_object",
+ context=schema_object.LOCALS_OBJECT,
+ connection=connection_test,
+ )
+ schema(schema_object.ObjectFile)
+ schema(schema_object.ObjectFolder)
+ schema(schema_object.ObjectMultiple)
+ schema(schema_object.ObjectWithOther)
+ yield schema
+ schema.drop()
diff --git a/tests/integration/__init__.py b/tests/integration/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e69de29bb
diff --git a/tests/data/Course.csv b/tests/integration/data/Course.csv
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/data/Course.csv
rename to tests/integration/data/Course.csv
diff --git a/tests/data/CurrentTerm.csv b/tests/integration/data/CurrentTerm.csv
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/data/CurrentTerm.csv
rename to tests/integration/data/CurrentTerm.csv
diff --git a/tests/data/Department.csv b/tests/integration/data/Department.csv
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/data/Department.csv
rename to tests/integration/data/Department.csv
diff --git a/tests/data/Enroll.csv b/tests/integration/data/Enroll.csv
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/data/Enroll.csv
rename to tests/integration/data/Enroll.csv
diff --git a/tests/data/Grade.csv b/tests/integration/data/Grade.csv
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/data/Grade.csv
rename to tests/integration/data/Grade.csv
diff --git a/tests/data/Section.csv b/tests/integration/data/Section.csv
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/data/Section.csv
rename to tests/integration/data/Section.csv
diff --git a/tests/data/Student.csv b/tests/integration/data/Student.csv
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/data/Student.csv
rename to tests/integration/data/Student.csv
diff --git a/tests/data/StudentMajor.csv b/tests/integration/data/StudentMajor.csv
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/data/StudentMajor.csv
rename to tests/integration/data/StudentMajor.csv
diff --git a/tests/data/Term.csv b/tests/integration/data/Term.csv
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/data/Term.csv
rename to tests/integration/data/Term.csv
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_aggr_regressions.py b/tests/integration/test_aggr_regressions.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..cf4f920b0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_aggr_regressions.py
@@ -0,0 +1,249 @@
+"""
+Regression tests for issues 386, 449, 484, and 558 — all related to processing complex aggregations and projections.
+"""
+
+import pytest
+
+import datajoint as dj
+
+from tests.schema_aggr_regress import LOCALS_AGGR_REGRESS, A, B, Q, R, S, X
+from tests.schema_uuid import Item, Topic
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
+def schema_aggr_reg(connection_test, prefix):
+ schema = dj.Schema(
+ prefix + "_aggr_regress",
+ context=LOCALS_AGGR_REGRESS,
+ connection=connection_test,
+ )
+ schema(R)
+ schema(Q)
+ schema(S)
+ yield schema
+ schema.drop()
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
+def schema_aggr_reg_with_abx(connection_test, prefix):
+ schema = dj.Schema(
+ prefix + "_aggr_regress_with_abx",
+ context=LOCALS_AGGR_REGRESS,
+ connection=connection_test,
+ )
+ schema(R)
+ schema(Q)
+ schema(S)
+ schema(A)
+ schema(B)
+ schema(X)
+ yield schema
+ schema.drop()
+
+
+def test_issue386(schema_aggr_reg):
+ """
+ --------------- ISSUE 386 -------------------
+ Issue 386 resulted from the loss of aggregated attributes when the aggregation was used as the restrictor
+ Q & (R.aggr(S, n='count(*)') & 'n=2')
+ Error: Unknown column 'n' in HAVING
+ """
+ result = R.aggr(S, n="count(*)") & "n=10"
+ result = Q & result
+ result.to_dicts()
+
+
+def test_issue449(schema_aggr_reg):
+ """
+ ---------------- ISSUE 449 ------------------
+ Issue 449 arises from incorrect group by attributes after joining with a dj.U()
+ Note: dj.U() * table pattern is no longer supported in 2.0, use dj.U() & table instead
+ """
+ result = dj.U("n") & R.aggr(S, n="max(s)")
+ result.to_dicts()
+
+
+def test_issue484(schema_aggr_reg):
+ """
+ ---------------- ISSUE 484 -----------------
+ Issue 484
+ """
+ q = dj.U().aggr(S, n="max(s)")
+ q.to_arrays("n")
+ q.fetch1("n")
+ q = dj.U().aggr(S, n="avg(s)")
+ result = dj.U().aggr(q, m="max(n)")
+ result.to_dicts()
+
+
+def test_union_join(schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
+ """
+ This test fails if it runs after TestIssue558.
+
+ https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/930
+ """
+ A.insert(zip([100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600]))
+ B.insert([(100, 11), (200, 22), (300, 33), (400, 44)])
+ q1 = B & "id < 300"
+ q2 = B & "id > 300"
+
+ expected_data = [
+ {"id": 0, "id2": 5},
+ {"id": 1, "id2": 6},
+ {"id": 2, "id2": 7},
+ {"id": 3, "id2": 8},
+ {"id": 4, "id2": 9},
+ {"id": 100, "id2": 11},
+ {"id": 200, "id2": 22},
+ {"id": 400, "id2": 44},
+ ]
+
+ assert ((q1 + q2) * A).to_dicts() == expected_data
+
+
+class TestIssue558:
+ """
+ --------------- ISSUE 558 ------------------
+ Issue 558 resulted from the fact that DataJoint saves subqueries and often combines a restriction followed
+ by a projection into a single SELECT statement, which in several unusual cases produces unexpected results.
+ """
+
+ def test_issue558_part1(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
+ q = (A - B).proj(id2="3")
+ assert len(A - B) == len(q)
+
+ def test_issue558_part2(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
+ d = dict(id=3, id2=5)
+ assert len(X & d) == len((X & d).proj(id2="3"))
+
+
+def test_left_join_invalid_raises_error(schema_uuid):
+ """Left join requires A → B. Topic ↛ Item, so this should raise an error."""
+ from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
+
+ # Clean up from previous tests
+ Item().delete_quick()
+ Topic().delete_quick()
+
+ Topic().add("jeff")
+ Item.populate()
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ Topic.join(Item, left=True)
+ assert "left operand to determine" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+
+
+def test_left_join_valid(schema_uuid):
+ """Left join where A → B: Item → Topic (topic_id is in Item)."""
+ # Clean up from previous tests
+ Item().delete_quick()
+ Topic().delete_quick()
+
+ Topic().add("jeff")
+ Item.populate()
+ Topic().add("jeff2") # Topic without Items
+ # Item.join(Topic, left=True) is valid because Item → Topic
+ q = Item.join(Topic, left=True)
+ qf = q.to_arrays()
+ assert len(q) == len(qf)
+ # All Items should have matching Topics since they were populated from Topics
+ assert len(q) == len(Item())
+
+
+def test_extend_valid(schema_uuid):
+ """extend() is an alias for join(left=True) when A → B."""
+ # Clean up from previous tests
+ Item().delete_quick()
+ Topic().delete_quick()
+
+ Topic().add("alice")
+ Item.populate()
+ # Item → Topic (topic_id is in Item), so extend is valid
+ q_extend = Item.extend(Topic)
+ q_left_join = Item.join(Topic, left=True)
+ # Should produce identical results
+ assert len(q_extend) == len(q_left_join)
+ assert set(q_extend.heading.names) == set(q_left_join.heading.names)
+ assert q_extend.primary_key == q_left_join.primary_key
+
+
+def test_extend_invalid_raises_error(schema_uuid):
+ """extend() requires A → B. Topic ↛ Item, so this should raise an error."""
+ from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
+
+ # Clean up from previous tests
+ Item().delete_quick()
+ Topic().delete_quick()
+
+ Topic().add("bob")
+ Item.populate()
+ # Topic ↛ Item (item_id not in Topic), so extend should fail
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ Topic.extend(Item)
+ assert "left operand to determine" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+
+
+class TestBoolMethod:
+ """
+ Tests for __bool__ method on Aggregation and Union (issue #1234).
+
+ bool(query) should return True if query has rows, False if empty.
+ """
+
+ def test_aggregation_bool_with_results(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
+ """Aggregation with results should be truthy."""
+ A.insert([(1,), (2,), (3,)])
+ B.insert([(1, 10), (1, 20), (2, 30)])
+ aggr = A.aggr(B, count="count(id2)")
+ assert bool(aggr) is True
+ assert len(aggr) > 0
+
+ def test_aggregation_bool_empty(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
+ """Aggregation with no results should be falsy."""
+ A.insert([(1,), (2,), (3,)])
+ B.insert([(1, 10), (1, 20), (2, 30)])
+ # Restrict to non-existent entry
+ aggr = (A & "id=999").aggr(B, count="count(id2)")
+ assert bool(aggr) is False
+ assert len(aggr) == 0
+
+ def test_aggregation_bool_matches_len(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
+ """bool(aggr) should equal len(aggr) > 0."""
+ A.insert([(10,), (20,)])
+ B.insert([(10, 100)])
+ # With results
+ aggr_has = A.aggr(B, count="count(id2)")
+ assert bool(aggr_has) == (len(aggr_has) > 0)
+ # Without results
+ aggr_empty = (A & "id=999").aggr(B, count="count(id2)")
+ assert bool(aggr_empty) == (len(aggr_empty) > 0)
+
+ def test_union_bool_with_results(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
+ """Union with results should be truthy."""
+ A.insert([(100,), (200,)])
+ B.insert([(100, 1), (200, 2)])
+ q1 = B & "id=100"
+ q2 = B & "id=200"
+ union = q1 + q2
+ assert bool(union) is True
+ assert len(union) > 0
+
+ def test_union_bool_empty(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
+ """Union with no results should be falsy."""
+ A.insert([(100,), (200,)])
+ B.insert([(100, 1), (200, 2)])
+ q1 = B & "id=999"
+ q2 = B & "id=998"
+ union = q1 + q2
+ assert bool(union) is False
+ assert len(union) == 0
+
+ def test_union_bool_matches_len(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
+ """bool(union) should equal len(union) > 0."""
+ A.insert([(100,), (200,)])
+ B.insert([(100, 1)])
+ # With results
+ union_has = (B & "id=100") + (B & "id=100")
+ assert bool(union_has) == (len(union_has) > 0)
+ # Without results
+ union_empty = (B & "id=999") + (B & "id=998")
+ assert bool(union_empty) == (len(union_empty) > 0)
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_alter.py b/tests/integration/test_alter.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..fbf074332
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_alter.py
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+import re
+
+import pytest
+
+
+from tests import schema as schema_any_module
+from tests.schema_alter import LOCALS_ALTER, Experiment, Parent
+
+COMBINED_CONTEXT = {
+ **schema_any_module.LOCALS_ANY,
+ **LOCALS_ALTER,
+}
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def schema_alter(connection_test, schema_any_fresh):
+ # Overwrite Experiment and Parent nodes using fresh schema
+ schema_any_fresh(Experiment, context=LOCALS_ALTER)
+ schema_any_fresh(Parent, context=LOCALS_ALTER)
+ yield schema_any_fresh
+ schema_any_fresh.drop()
+
+
+class TestAlter:
+ def verify_alter(self, schema_alter, table, attribute_sql):
+ definition_original = schema_alter.connection.query(f"SHOW CREATE TABLE {table.full_table_name}").fetchone()[1]
+ table.definition = table.definition_new
+ table.alter(prompt=False)
+ definition_new = schema_alter.connection.query(f"SHOW CREATE TABLE {table.full_table_name}").fetchone()[1]
+ assert re.sub(f"{attribute_sql},\n ", "", definition_new) == definition_original
+
+ def test_alter(self, schema_alter):
+ original = schema_alter.connection.query("SHOW CREATE TABLE " + Experiment.full_table_name).fetchone()[1]
+ Experiment.definition = Experiment.definition1
+ Experiment.alter(prompt=False, context=COMBINED_CONTEXT)
+ altered = schema_alter.connection.query("SHOW CREATE TABLE " + Experiment.full_table_name).fetchone()[1]
+ assert original != altered
+ Experiment.definition = Experiment.original_definition
+ Experiment().alter(prompt=False, context=COMBINED_CONTEXT)
+ restored = schema_alter.connection.query("SHOW CREATE TABLE " + Experiment.full_table_name).fetchone()[1]
+ assert altered != restored
+ assert original == restored
+
+ def test_alter_part(self, schema_alter):
+ """
+ https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/936
+ """
+ # Regex includes optional COMMENT for type annotations
+ self.verify_alter(schema_alter, table=Parent.Child, attribute_sql=r"`child_id` .* DEFAULT NULL[^,]*")
+ self.verify_alter(
+ schema_alter,
+ table=Parent.Grandchild,
+ attribute_sql=r"`grandchild_id` .* DEFAULT NULL[^,]*",
+ )
diff --git a/tests/test_attach.py b/tests/integration/test_attach.py
similarity index 56%
rename from tests/test_attach.py
rename to tests/integration/test_attach.py
index 362db6933..f7ad953fe 100644
--- a/tests/test_attach.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_attach.py
@@ -1,13 +1,14 @@
import os
from pathlib import Path
-import pytest
-from .schema_external import Attach
+from tests.schema_external import Attach
def test_attach_attributes(schema_ext, minio_client, tmpdir_factory):
"""Test saving files in attachments"""
+ import datajoint as dj
+
# create a mock file
table = Attach()
source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
@@ -23,29 +24,32 @@ def test_attach_attributes(schema_ext, minio_client, tmpdir_factory):
table.insert1(dict(attach=i, img=attach1, txt=attach2))
download_folder = Path(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("download"))
- keys, path1, path2 = table.fetch(
- "KEY", "img", "txt", download_path=download_folder, order_by="KEY"
- )
+ keys = table.keys(order_by="KEY")
+
+ with dj.config.override(download_path=str(download_folder)):
+ path1, path2 = table.to_arrays("img", "txt", order_by="KEY")
- # verify that different attachment are renamed if their filenames collide
- assert path1[0] != path2[0]
- assert path1[0] != path1[1]
- assert Path(path1[0]).parent == download_folder
- with Path(path1[-1]).open("rb") as f:
- check1 = f.read()
- with Path(path2[-1]).open("rb") as f:
- check2 = f.read()
- assert data1 == check1
- assert data2 == check2
+ # verify that different attachment are renamed if their filenames collide
+ assert path1[0] != path2[0]
+ assert path1[0] != path1[1]
+ assert Path(path1[0]).parent == download_folder
+ with Path(path1[-1]).open("rb") as f:
+ check1 = f.read()
+ with Path(path2[-1]).open("rb") as f:
+ check2 = f.read()
+ assert data1 == check1
+ assert data2 == check2
- # verify that existing files are not duplicated if their filename matches issue #592
- p1, p2 = (Attach & keys[0]).fetch1("img", "txt", download_path=download_folder)
- assert p1 == path1[0]
- assert p2 == path2[0]
+ # verify that existing files are not duplicated if their filename matches issue #592
+ p1, p2 = (Attach & keys[0]).fetch1("img", "txt")
+ assert p1 == path1[0]
+ assert p2 == path2[0]
def test_return_string(schema_ext, minio_client, tmpdir_factory):
"""Test returning string on fetch"""
+ import datajoint as dj
+
# create a mock file
table = Attach()
source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
@@ -61,8 +65,7 @@ def test_return_string(schema_ext, minio_client, tmpdir_factory):
table.insert1(dict(attach=2, img=attach1, txt=attach2))
download_folder = Path(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("download"))
- keys, path1, path2 = table.fetch(
- "KEY", "img", "txt", download_path=download_folder, order_by="KEY"
- )
+ with dj.config.override(download_path=str(download_folder)):
+ path1, path2 = table.to_arrays("img", "txt", order_by="KEY")
assert isinstance(path1[0], str)
diff --git a/tests/test_autopopulate.py b/tests/integration/test_autopopulate.py
similarity index 62%
rename from tests/test_autopopulate.py
rename to tests/integration/test_autopopulate.py
index 899d90d9e..6afa6d10b 100644
--- a/tests/test_autopopulate.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_autopopulate.py
@@ -1,13 +1,11 @@
-import pymysql
+import platform
import pytest
import datajoint as dj
from datajoint import DataJointError
-from . import schema
-
-def test_populate(trial, subject, experiment, ephys, channel):
+def test_populate(clean_autopopulate, trial, subject, experiment, ephys, channel):
# test simple populate
assert subject, "root tables are empty"
assert not experiment, "table already filled?"
@@ -16,7 +14,7 @@ def test_populate(trial, subject, experiment, ephys, channel):
# test restricted populate
assert not trial, "table already filled?"
- restriction = subject.proj(animal="subject_id").fetch("KEY")[0]
+ restriction = subject.proj(animal="subject_id").keys()[0]
d = trial.connection.dependencies
d.load()
trial.populate(restriction)
@@ -33,7 +31,7 @@ def test_populate(trial, subject, experiment, ephys, channel):
assert channel
-def test_populate_with_success_count(subject, experiment, trial):
+def test_populate_with_success_count(clean_autopopulate, subject, experiment, trial):
# test simple populate
assert subject, "root tables are empty"
assert not experiment, "table already filled?"
@@ -43,7 +41,7 @@ def test_populate_with_success_count(subject, experiment, trial):
# test restricted populate
assert not trial, "table already filled?"
- restriction = subject.proj(animal="subject_id").fetch("KEY")[0]
+ restriction = subject.proj(animal="subject_id").keys()[0]
d = trial.connection.dependencies
d.load()
ret = trial.populate(restriction, suppress_errors=True)
@@ -51,61 +49,70 @@ def test_populate_with_success_count(subject, experiment, trial):
assert len(trial.key_source & trial) == success_count
-def test_populate_key_list(subject, experiment, trial):
- # test simple populate
+def test_populate_max_calls(clean_autopopulate, subject, experiment, trial):
+ # test populate with max_calls limit
assert subject, "root tables are empty"
assert not experiment, "table already filled?"
- keys = experiment.key_source.fetch("KEY", order_by="KEY")
n = 3
- assert len(keys) > n
- keys = keys[:n]
- ret = experiment.populate(keys=keys)
+ total_keys = len(experiment.key_source)
+ assert total_keys > n
+ ret = experiment.populate(max_calls=n)
assert n == ret["success_count"]
-def test_populate_exclude_error_and_ignore_jobs(schema_any, subject, experiment):
- # test simple populate
+def test_populate_exclude_error_and_ignore_jobs(clean_autopopulate, subject, experiment):
+ # test that error and ignore jobs are excluded from populate
assert subject, "root tables are empty"
assert not experiment, "table already filled?"
- keys = experiment.key_source.fetch("KEY", limit=2)
+ # Refresh jobs to create pending entries
+ experiment.jobs.refresh()
+
+ keys = experiment.jobs.pending.keys(limit=2)
for idx, key in enumerate(keys):
if idx == 0:
- schema_any.jobs.ignore(experiment.table_name, key)
+ experiment.jobs.ignore(key)
else:
- schema_any.jobs.error(experiment.table_name, key, "")
+ # Create an error job by first reserving then setting error
+ experiment.jobs.reserve(key)
+ experiment.jobs.error(key, "test error")
- experiment.populate(reserve_jobs=True)
+ # Populate should skip error and ignore jobs
+ experiment.populate(reserve_jobs=True, refresh=False)
assert len(experiment.key_source & experiment) == len(experiment.key_source) - 2
-def test_allow_direct_insert(subject, experiment):
+def test_allow_direct_insert(clean_autopopulate, subject, experiment):
assert subject, "root tables are empty"
- key = subject.fetch("KEY", limit=1)[0]
+ key = subject.keys(limit=1)[0]
key["experiment_id"] = 1000
key["experiment_date"] = "2018-10-30"
experiment.insert1(key, allow_direct_insert=True)
+@pytest.mark.skipif(
+ platform.system() == "Darwin",
+ reason="multiprocessing with spawn method (macOS default) cannot pickle thread locks",
+)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("processes", [None, 2])
-def test_multi_processing(subject, experiment, processes):
+def test_multi_processing(clean_autopopulate, subject, experiment, processes):
assert subject, "root tables are empty"
assert not experiment, "table already filled?"
- experiment.populate(processes=None)
+ experiment.populate(processes=processes)
assert len(experiment) == len(subject) * experiment.fake_experiments_per_subject
-def test_allow_insert(subject, experiment):
+def test_allow_insert(clean_autopopulate, subject, experiment):
assert subject, "root tables are empty"
- key = subject.fetch("KEY")[0]
+ key = subject.keys()[0]
key["experiment_id"] = 1001
key["experiment_date"] = "2018-10-30"
with pytest.raises(DataJointError):
experiment.insert1(key)
-def test_load_dependencies(prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(f"{prefix}_load_dependencies_populate")
+def test_load_dependencies(prefix, connection_test):
+ schema = dj.Schema(f"{prefix}_load_dependencies_populate", connection=connection_test)
@schema
class ImageSource(dj.Lookup):
@@ -119,7 +126,7 @@ class Image(dj.Imported):
definition = """
-> ImageSource
---
- image_data: longblob
+ image_data:
"""
def make(self, key):
@@ -132,7 +139,7 @@ class Crop(dj.Computed):
definition = """
-> Image
---
- crop_image: longblob
+ crop_image:
"""
def make(self, key):
diff --git a/tests/test_blob.py b/tests/integration/test_blob.py
similarity index 90%
rename from tests/test_blob.py
rename to tests/integration/test_blob.py
index 7c790db75..d2d047aab 100644
--- a/tests/test_blob.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_blob.py
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
import datajoint as dj
from datajoint.blob import pack, unpack
-from .schema import Longblob
+from tests.schema import Longblob
@pytest.fixture
@@ -61,27 +61,19 @@ def test_pack():
x = -255
y = unpack(pack(x))
- assert (
- x == y and isinstance(y, int) and not isinstance(y, np.ndarray)
- ), "Scalar int did not match"
+ assert x == y and isinstance(y, int) and not isinstance(y, np.ndarray), "Scalar int did not match"
x = -25523987234234287910987234987098245697129798713407812347
y = unpack(pack(x))
- assert (
- x == y and isinstance(y, int) and not isinstance(y, np.ndarray)
- ), "Unbounded int did not match"
+ assert x == y and isinstance(y, int) and not isinstance(y, np.ndarray), "Unbounded int did not match"
x = 7.0
y = unpack(pack(x))
- assert (
- x == y and isinstance(y, float) and not isinstance(y, np.ndarray)
- ), "Scalar float did not match"
+ assert x == y and isinstance(y, float) and not isinstance(y, np.ndarray), "Scalar float did not match"
x = 7j
y = unpack(pack(x))
- assert (
- x == y and isinstance(y, complex) and not isinstance(y, np.ndarray)
- ), "Complex scalar did not match"
+ assert x == y and isinstance(y, complex) and not isinstance(y, np.ndarray), "Complex scalar did not match"
x = True
assert unpack(pack(x)) is True, "Scalar bool did not match"
@@ -98,9 +90,7 @@ def test_pack():
}
y = unpack(pack(x))
assert x == y, "Dict do not match!"
- assert not isinstance(
- ["range"][0], np.ndarray
- ), "Scalar int was coerced into array."
+ assert not isinstance(["range"][0], np.ndarray), "Scalar int was coerced into array."
x = uuid.uuid4()
assert x == unpack(pack(x)), "UUID did not match"
@@ -142,9 +132,7 @@ def test_pack():
assert x == unpack(pack(x)), "String object did not pack/unpack correctly"
x = np.array(["yes"])
- assert x == unpack(
- pack(x)
- ), "Numpy string array object did not pack/unpack correctly"
+ assert x == unpack(pack(x)), "Numpy string array object did not pack/unpack correctly"
x = np.datetime64("1998").astype("datetime64[us]")
assert x == unpack(pack(x))
@@ -202,7 +190,7 @@ def test_insert_longblob_32bit(schema_any, enable_feature_32bit_dims):
"0023000000410200000001000000070000000400000000000000640064006400640064006400640025"
"00000041020000000100000008000000040000000000000053007400610067006500200031003000')"
)
- dj.conn().query(query_32_blob).fetchall()
+ schema_any.connection.query(query_32_blob).fetchall()
fetched = (Longblob & "id=1").fetch1()
expected = {
"id": 1,
diff --git a/tests/test_blob_matlab.py b/tests/integration/test_blob_matlab.py
similarity index 72%
rename from tests/test_blob_matlab.py
rename to tests/integration/test_blob_matlab.py
index 081841fb4..b7b05a0cb 100644
--- a/tests/test_blob_matlab.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_blob_matlab.py
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ class Blob(dj.Manual):
id : int
-----
comment : varchar(255)
- blob : longblob
+ blob :
"""
@@ -36,17 +36,15 @@ def insert_blobs(schema):
schema.connection.query(
"""
INSERT INTO {table_name} (`id`, `comment`, `blob`) VALUES
- (1,'simple string',0x6D596D00410200000000000000010000000000000010000000000000000400000000000000630068006100720061006300740065007200200073007400720069006E006700),
- (2,'1D vector',0x6D596D0041020000000000000001000000000000000C000000000000000600000000000000000000000000F03F00000000000030400000000000003F4000000000000047400000000000804E4000000000000053400000000000C056400000000000805A400000000000405E4000000000000061400000000000E062400000000000C06440),
- (3,'string array',0x6D596D00430200000000000000010000000000000002000000000000002F0000000000000041020000000000000001000000000000000700000000000000040000000000000073007400720069006E00670031002F0000000000000041020000000000000001000000000000000700000000000000040000000000000073007400720069006E0067003200),
- (4,'struct array',0x6D596D005302000000000000000100000000000000020000000000000002000000610062002900000000000000410200000000000000010000000000000001000000000000000600000000000000000000000000F03F9000000000000000530200000000000000010000000000000001000000000000000100000063006900000000000000410200000000000000030000000000000003000000000000000600000000000000000000000000204000000000000008400000000000001040000000000000F03F0000000000001440000000000000224000000000000018400000000000001C40000000000000004029000000000000004102000000000000000100000000000000010000000000000006000000000000000000000000000040100100000000000053020000000000000001000000000000000100000000000000010000004300E9000000000000004102000000000000000500000000000000050000000000000006000000000000000000000000003140000000000000374000000000000010400000000000002440000000000000264000000000000038400000000000001440000000000000184000000000000028400000000000003240000000000000F03F0000000000001C400000000000002A400000000000003340000000000000394000000000000020400000000000002C400000000000003440000000000000354000000000000000400000000000002E400000000000003040000000000000364000000000000008400000000000002240),
- (5,'3D double array',0x6D596D004103000000000000000200000000000000030000000000000004000000000000000600000000000000000000000000F03F000000000000004000000000000008400000000000001040000000000000144000000000000018400000000000001C40000000000000204000000000000022400000000000002440000000000000264000000000000028400000000000002A400000000000002C400000000000002E40000000000000304000000000000031400000000000003240000000000000334000000000000034400000000000003540000000000000364000000000000037400000000000003840),
- (6,'3D uint8 array',0x6D596D0041030000000000000002000000000000000300000000000000040000000000000009000000000000000102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F101112131415161718),
- (7,'3D complex array',0x6D596D0041030000000000000002000000000000000300000000000000040000000000000006000000010000000000000000C0724000000000000028C000000000000038C0000000000000000000000000000038C0000000000000000000000000000052C00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000052C00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000052C00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000AA4C58E87AB62B400000000000000000AA4C58E87AB62BC0000000000000008000000000000052400000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000080000000000000008000000000000052C000000000000000800000000000000080000000000000008000000000000000800000000000000080
+ (1,'simple string',0x6D596D00410200000000000000010000000000000010000000000000000400000000000000630068006100720061006300740065007200200073007400720069006E006700), # noqa: E501
+ (2,'1D vector',0x6D596D0041020000000000000001000000000000000C000000000000000600000000000000000000000000F03F00000000000030400000000000003F4000000000000047400000000000804E4000000000000053400000000000C056400000000000805A400000000000405E4000000000000061400000000000E062400000000000C06440), # noqa: E501
+ (3,'string array',0x6D596D00430200000000000000010000000000000002000000000000002F0000000000000041020000000000000001000000000000000700000000000000040000000000000073007400720069006E00670031002F0000000000000041020000000000000001000000000000000700000000000000040000000000000073007400720069006E0067003200), # noqa: E501
+ (4,'struct array',0x6D596D005302000000000000000100000000000000020000000000000002000000610062002900000000000000410200000000000000010000000000000001000000000000000600000000000000000000000000F03F9000000000000000530200000000000000010000000000000001000000000000000100000063006900000000000000410200000000000000030000000000000003000000000000000600000000000000000000000000204000000000000008400000000000001040000000000000F03F0000000000001440000000000000224000000000000018400000000000001C40000000000000004029000000000000004102000000000000000100000000000000010000000000000006000000000000000000000000000040100100000000000053020000000000000001000000000000000100000000000000010000004300E9000000000000004102000000000000000500000000000000050000000000000006000000000000000000000000003140000000000000374000000000000010400000000000002440000000000000264000000000000038400000000000001440000000000000184000000000000028400000000000003240000000000000F03F0000000000001C400000000000002A400000000000003340000000000000394000000000000020400000000000002C400000000000003440000000000000354000000000000000400000000000002E400000000000003040000000000000364000000000000008400000000000002240), # noqa: E501
+ (5,'3D double array',0x6D596D004103000000000000000200000000000000030000000000000004000000000000000600000000000000000000000000F03F000000000000004000000000000008400000000000001040000000000000144000000000000018400000000000001C40000000000000204000000000000022400000000000002440000000000000264000000000000028400000000000002A400000000000002C400000000000002E40000000000000304000000000000031400000000000003240000000000000334000000000000034400000000000003540000000000000364000000000000037400000000000003840), # noqa: E501
+ (6,'3D uint8 array',0x6D596D0041030000000000000002000000000000000300000000000000040000000000000009000000000000000102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F101112131415161718), # noqa: E501
+ (7,'3D complex array',0x6D596D0041030000000000000002000000000000000300000000000000040000000000000006000000010000000000000000C0724000000000000028C000000000000038C0000000000000000000000000000038C0000000000000000000000000000052C00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000052C00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000052C00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000AA4C58E87AB62B400000000000000000AA4C58E87AB62BC0000000000000008000000000000052400000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000080000000000000008000000000000052C000000000000000800000000000000080000000000000008000000000000000800000000000000080 # noqa: E501
);
- """.format(
- table_name=Blob.full_table_name
- )
+ """.format(table_name=Blob.full_table_name)
)
@@ -70,7 +68,7 @@ def test_complex_matlab_blobs(schema_blob_pop):
"""
test correct de-serialization of various blob types
"""
- blobs = Blob().fetch("blob", order_by="KEY")
+ blobs = Blob().to_arrays("blob", order_by="KEY")
blob = blobs[0] # 'simple string' 'character string'
assert blob[0] == "character string"
@@ -84,9 +82,7 @@ def test_complex_matlab_blobs(schema_blob_pop):
assert_array_equal(blob, np.array([["string1", "string2"]]))
assert_array_equal(blob, unpack(pack(blob)))
- blob = blobs[
- 3
- ] # 'struct array' struct('a', {1,2}, 'b', {struct('c', magic(3)), struct('C', magic(5))})
+ blob = blobs[3] # 'struct array' struct('a', {1,2}, 'b', {struct('c', magic(3)), struct('C', magic(5))})
assert isinstance(blob, dj.MatStruct)
assert tuple(blob.dtype.names) == ("a", "b")
assert_array_equal(blob.a[0, 0], np.array([[1.0]]))
@@ -117,17 +113,13 @@ def test_complex_matlab_squeeze(schema_blob_pop):
"""
test correct de-serialization of various blob types
"""
- blob = (Blob & "id=1").fetch1(
- "blob", squeeze=True
- ) # 'simple string' 'character string'
+ blob = (Blob & "id=1").fetch1("blob", squeeze=True) # 'simple string' 'character string'
assert blob == "character string"
blob = (Blob & "id=2").fetch1("blob", squeeze=True) # '1D vector' 1:15:180
assert_array_equal(blob, np.r_[1:180:15])
- blob = (Blob & "id=3").fetch1(
- "blob", squeeze=True
- ) # 'string array' {'string1' 'string2'}
+ blob = (Blob & "id=3").fetch1("blob", squeeze=True) # 'string array' {'string1' 'string2'}
assert isinstance(blob, dj.MatCell)
assert_array_equal(blob, np.array(["string1", "string2"]))
@@ -148,9 +140,7 @@ def test_complex_matlab_squeeze(schema_blob_pop):
assert isinstance(blob[1].b, dj.MatStruct)
assert tuple(blob[1].b.C.item().shape) == (5, 5)
- blob = (Blob & "id=5").fetch1(
- "blob", squeeze=True
- ) # '3D double array' reshape(1:24, [2,3,4])
+ blob = (Blob & "id=5").fetch1("blob", squeeze=True) # '3D double array' reshape(1:24, [2,3,4])
assert np.array_equal(blob, np.r_[1:25].reshape((2, 3, 4), order="F"))
assert blob.dtype == "float64"
@@ -170,3 +160,71 @@ def test_iter(schema_blob_pop):
from_iter = {d["id"]: d for d in Blob()}
assert len(from_iter) == len(Blob())
assert from_iter[1]["blob"] == "character string"
+
+
+def test_cell_array_with_nested_arrays():
+ """
+ Test unpacking MATLAB cell arrays containing arrays of different sizes.
+ Regression test for issue #1098.
+ """
+ # Create a cell array with nested arrays of different sizes (ragged)
+ cell = np.empty(2, dtype=object)
+ cell[0] = np.array([1, 2, 3])
+ cell[1] = np.array([4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
+ cell = cell.reshape((1, 2)).view(dj.MatCell)
+
+ # Pack and unpack
+ packed = pack(cell)
+ unpacked = unpack(packed)
+
+ # Should preserve structure
+ assert isinstance(unpacked, dj.MatCell)
+ assert unpacked.shape == (1, 2)
+ assert_array_equal(unpacked[0, 0], np.array([1, 2, 3]))
+ assert_array_equal(unpacked[0, 1], np.array([4, 5, 6, 7, 8]))
+
+
+def test_cell_array_with_empty_elements():
+ """
+ Test unpacking MATLAB cell arrays containing empty arrays.
+ Regression test for issue #1056.
+ """
+ # Create a cell array with empty elements: {[], [], []}
+ cell = np.empty(3, dtype=object)
+ cell[0] = np.array([])
+ cell[1] = np.array([])
+ cell[2] = np.array([])
+ cell = cell.reshape((3, 1)).view(dj.MatCell)
+
+ # Pack and unpack
+ packed = pack(cell)
+ unpacked = unpack(packed)
+
+ # Should preserve structure
+ assert isinstance(unpacked, dj.MatCell)
+ assert unpacked.shape == (3, 1)
+ for i in range(3):
+ assert unpacked[i, 0].size == 0
+
+
+def test_cell_array_mixed_empty_nonempty():
+ """
+ Test unpacking MATLAB cell arrays with mixed empty and non-empty elements.
+ """
+ # Create a cell array: {[1,2], [], [3,4,5]}
+ cell = np.empty(3, dtype=object)
+ cell[0] = np.array([1, 2])
+ cell[1] = np.array([])
+ cell[2] = np.array([3, 4, 5])
+ cell = cell.reshape((3, 1)).view(dj.MatCell)
+
+ # Pack and unpack
+ packed = pack(cell)
+ unpacked = unpack(packed)
+
+ # Should preserve structure
+ assert isinstance(unpacked, dj.MatCell)
+ assert unpacked.shape == (3, 1)
+ assert_array_equal(unpacked[0, 0], np.array([1, 2]))
+ assert unpacked[1, 0].size == 0
+ assert_array_equal(unpacked[2, 0], np.array([3, 4, 5]))
diff --git a/tests/test_cascading_delete.py b/tests/integration/test_cascading_delete.py
similarity index 75%
rename from tests/test_cascading_delete.py
rename to tests/integration/test_cascading_delete.py
index 71216fcb2..28f175bea 100644
--- a/tests/test_cascading_delete.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_cascading_delete.py
@@ -2,12 +2,23 @@
import datajoint as dj
-from .schema import ComplexChild, ComplexParent
-from .schema_simple import A, B, D, E, G, L, Profile, Website
+from tests.schema import ComplexChild, ComplexParent
+from tests.schema_simple import A, B, D, E, G, L, Profile, Website
@pytest.fixture
def schema_simp_pop(schema_simp):
+ # Clean up tables first to ensure fresh state with module-scoped schema
+ # Delete in reverse dependency order
+ Profile().delete()
+ Website().delete()
+ G().delete()
+ E().delete()
+ D().delete()
+ B().delete()
+ L().delete()
+ A().delete()
+
A().insert(A.contents, skip_duplicates=True)
L().insert(L.contents, skip_duplicates=True)
B().populate()
@@ -19,9 +30,7 @@ def schema_simp_pop(schema_simp):
def test_delete_tree(schema_simp_pop):
assert not dj.config["safemode"], "safemode must be off for testing"
- assert (
- L() and A() and B() and B.C() and D() and E() and E.F()
- ), "schema is not populated"
+ assert L() and A() and B() and B.C() and D() and E() and E.F(), "schema is not populated"
A().delete()
assert not A() or B() or B.C() or D() or E() or E.F(), "incomplete delete"
@@ -29,19 +38,15 @@ def test_delete_tree(schema_simp_pop):
def test_stepwise_delete(schema_simp_pop):
assert not dj.config["safemode"], "safemode must be off for testing"
assert L() and A() and B() and B.C(), "schema population failed"
- B.C().delete(force=True)
+ B.C().delete(part_integrity="ignore")
assert not B.C(), "failed to delete child tables"
B().delete()
- assert (
- not B()
- ), "failed to delete from the parent table following child table deletion"
+ assert not B(), "failed to delete from the parent table following child table deletion"
def test_delete_tree_restricted(schema_simp_pop):
assert not dj.config["safemode"], "safemode must be off for testing"
- assert (
- L() and A() and B() and B.C() and D() and E() and E.F()
- ), "schema is not populated"
+ assert L() and A() and B() and B.C() and D() and E() and E.F(), "schema is not populated"
cond = "cond_in_a"
rel = A() & cond
rest = dict(
@@ -53,9 +58,7 @@ def test_delete_tree_restricted(schema_simp_pop):
F=len(E.F() - rel),
)
rel.delete()
- assert not (
- rel or B() & rel or B.C() & rel or D() & rel or E() & rel or (E.F() & rel)
- ), "incomplete delete"
+ assert not (rel or B() & rel or B.C() & rel or D() & rel or E() & rel or (E.F() & rel)), "incomplete delete"
assert len(A()) == rest["A"], "invalid delete restriction"
assert len(B()) == rest["B"], "invalid delete restriction"
assert len(B.C()) == rest["C"], "invalid delete restriction"
@@ -66,9 +69,7 @@ def test_delete_tree_restricted(schema_simp_pop):
def test_delete_lookup(schema_simp_pop):
assert not dj.config["safemode"], "safemode must be off for testing"
- assert bool(
- L() and A() and B() and B.C() and D() and E() and E.F()
- ), "schema is not populated"
+ assert bool(L() and A() and B() and B.C() and D() and E() and E.F()), "schema is not populated"
L().delete()
assert not bool(L() or D() or E() or E.F()), "incomplete delete"
A().delete() # delete all is necessary because delete L deletes from subtables.
@@ -76,9 +77,7 @@ def test_delete_lookup(schema_simp_pop):
def test_delete_lookup_restricted(schema_simp_pop):
assert not dj.config["safemode"], "safemode must be off for testing"
- assert (
- L() and A() and B() and B.C() and D() and E() and E.F()
- ), "schema is not populated"
+ assert L() and A() and B() and B.C() and D() and E() and E.F(), "schema is not populated"
rel = L() & "cond_in_l"
original_count = len(L())
deleted_count = len(rel)
@@ -96,10 +95,7 @@ def test_delete_complex_keys(schema_any):
child_key_count = 1
restriction = dict(
{"parent_id_{}".format(i + 1): i for i in range(parent_key_count)},
- **{
- "child_id_{}".format(i + 1): (i + parent_key_count)
- for i in range(child_key_count)
- },
+ **{"child_id_{}".format(i + 1): (i + parent_key_count) for i in range(child_key_count)},
)
assert len(ComplexParent & restriction) == 1, "Parent record missing"
assert len(ComplexChild & restriction) == 1, "Child record missing"
@@ -117,19 +113,19 @@ def test_delete_parts_error(schema_simp_pop):
"""test issue #151"""
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
Profile().populate_random()
- Website().delete(force_masters=False)
+ Website().delete(part_integrity="enforce")
def test_delete_parts(schema_simp_pop):
"""test issue #151"""
Profile().populate_random()
- Website().delete(force_masters=True)
+ Website().delete(part_integrity="cascade")
def test_delete_parts_complex(schema_simp_pop):
"""test issue #151 with complex master/part. PR #1158."""
prev_len = len(G())
- (A() & "id_a=1").delete(force_masters=True)
+ (A() & "id_a=1").delete(part_integrity="cascade")
assert prev_len - len(G()) == 16, "Failed to delete parts"
diff --git a/tests/test_cli.py b/tests/integration/test_cli.py
similarity index 71%
rename from tests/test_cli.py
rename to tests/integration/test_cli.py
index be0faf64d..35230ea4e 100644
--- a/tests/test_cli.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_cli.py
@@ -2,7 +2,6 @@
Collection of test cases to test the dj cli
"""
-import json
import subprocess
import pytest
@@ -13,7 +12,7 @@
def test_cli_version(capsys):
with pytest.raises(SystemExit) as pytest_wrapped_e:
dj.cli(args=["-V"])
- assert pytest_wrapped_e.type == SystemExit
+ assert pytest_wrapped_e.type is SystemExit
assert pytest_wrapped_e.value.code == 0
captured_output = capsys.readouterr().out
@@ -23,7 +22,7 @@ def test_cli_version(capsys):
def test_cli_help(capsys):
with pytest.raises(SystemExit) as pytest_wrapped_e:
dj.cli(args=["--help"])
- assert pytest_wrapped_e.type == SystemExit
+ assert pytest_wrapped_e.type is SystemExit
assert pytest_wrapped_e.value.code == 0
captured_output = capsys.readouterr().out
@@ -44,13 +43,14 @@ def test_cli_config():
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()
cleaned = stdout.strip(" >\t\n\r")
- for key in ("database.user", "database.password", "database.host"):
+ # Config now uses pydantic format: Config(database=DatabaseSettings(host=..., user=..., ...))
+ for key in ("host=", "user=", "password="):
assert key in cleaned, f"Key {key} not found in config from stdout: {cleaned}"
def test_cli_args():
process = subprocess.Popen(
- ["dj", "-utest_user", "-ptest_pass", "-htest_host"],
+ ["dj", "-u", "test_user", "-p", "test_pass", "--host", "test_host"],
stdin=subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
@@ -63,12 +63,12 @@ def test_cli_args():
process.stdin.flush()
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()
- assert "test_user" == stdout[5:14]
- assert "test_pass" == stdout[21:30]
- assert "test_host" == stdout[37:46]
+ assert "test_user" in stdout
+ assert "test_pass" in stdout
+ assert "test_host" in stdout
-def test_cli_schemas(prefix, connection_root):
+def test_cli_schemas(prefix, connection_root, db_creds_root):
schema = dj.Schema(prefix + "_cli", locals(), connection=connection_root)
@schema
@@ -79,8 +79,19 @@ class IJ(dj.Lookup):
"""
contents = list(dict(i=i, j=j + 2) for i in range(3) for j in range(3))
+ # Pass credentials via CLI args to avoid prompting for username
process = subprocess.Popen(
- ["dj", "-s", "djtest_cli:test_schema"],
+ [
+ "dj",
+ "-u",
+ db_creds_root["user"],
+ "-p",
+ db_creds_root["password"],
+ "--host",
+ db_creds_root["host"],
+ "-s",
+ f"{prefix}_cli:test_schema",
+ ],
stdin=subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
@@ -89,7 +100,7 @@ class IJ(dj.Lookup):
process.stdin.write("test_schema.__dict__['__name__']\n")
process.stdin.write("test_schema.__dict__['schema']\n")
- process.stdin.write("test_schema.IJ.fetch(as_dict=True)\n")
+ process.stdin.write("test_schema.IJ.to_dicts()\n")
process.stdin.flush()
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()
@@ -108,6 +119,6 @@ class IJ(dj.Lookup):
cleaned = stdout.strip(" >\t\n\r")
for key in (
"test_schema",
- "Schema `djtest_cli`",
+ f"Schema `{prefix}_cli`",
):
- assert key in cleaned, f"Key {key} not found in config from stdout: {cleaned}"
+ assert key in cleaned, f"Key {key} not found in stdout: {cleaned}"
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_codec_chaining.py b/tests/integration/test_codec_chaining.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..defbd428f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_codec_chaining.py
@@ -0,0 +1,368 @@
+"""
+Tests for codec chaining (composition).
+
+This tests the → → json composition pattern
+and similar codec chains.
+"""
+
+from datajoint.codecs import (
+ Codec,
+ _codec_registry,
+ resolve_dtype,
+)
+
+
+class TestCodecChainResolution:
+ """Tests for resolving codec chains."""
+
+ def setup_method(self):
+ """Clear test codecs from registry before each test."""
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def teardown_method(self):
+ """Clean up test codecs after each test."""
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def test_single_codec_chain(self):
+ """Test resolving a single-codec chain."""
+
+ class TestSingle(Codec):
+ name = "test_single"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "varchar(100)"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return str(value)
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "varchar(100)"
+ assert len(chain) == 1
+ assert chain[0].name == "test_single"
+ assert store is None
+
+ def test_two_codec_chain(self):
+ """Test resolving a two-codec chain."""
+
+ class TestInner(Codec):
+ name = "test_inner"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "bytes"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ class TestOuter(Codec):
+ name = "test_outer"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "bytes"
+ assert len(chain) == 2
+ assert chain[0].name == "test_outer"
+ assert chain[1].name == "test_inner"
+
+ def test_three_codec_chain(self):
+ """Test resolving a three-codec chain."""
+
+ class TestBase(Codec):
+ name = "test_base"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "json"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ class TestMiddle(Codec):
+ name = "test_middle"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ class TestTop(Codec):
+ name = "test_top"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "json"
+ assert len(chain) == 3
+ assert chain[0].name == "test_top"
+ assert chain[1].name == "test_middle"
+ assert chain[2].name == "test_base"
+
+
+class TestCodecChainEncodeDecode:
+ """Tests for encode/decode through codec chains."""
+
+ def setup_method(self):
+ """Clear test codecs from registry before each test."""
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def teardown_method(self):
+ """Clean up test codecs after each test."""
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def test_encode_order(self):
+ """Test that encode is applied outer → inner."""
+ encode_order = []
+
+ class TestInnerEnc(Codec):
+ name = "test_inner_enc"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "bytes"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ encode_order.append("inner")
+ return value + b"_inner"
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ class TestOuterEnc(Codec):
+ name = "test_outer_enc"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ encode_order.append("outer")
+ return value + b"_outer"
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ _, chain, _ = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ # Apply encode in order: outer first, then inner
+ value = b"start"
+ for codec in chain:
+ value = codec.encode(value)
+
+ assert encode_order == ["outer", "inner"]
+ assert value == b"start_outer_inner"
+
+ def test_decode_order(self):
+ """Test that decode is applied inner → outer (reverse of encode)."""
+ decode_order = []
+
+ class TestInnerDec(Codec):
+ name = "test_inner_dec"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "bytes"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ decode_order.append("inner")
+ return stored.replace(b"_inner", b"")
+
+ class TestOuterDec(Codec):
+ name = "test_outer_dec"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ decode_order.append("outer")
+ return stored.replace(b"_outer", b"")
+
+ _, chain, _ = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ # Apply decode in reverse order: inner first, then outer
+ value = b"start_outer_inner"
+ for codec in reversed(chain):
+ value = codec.decode(value)
+
+ assert decode_order == ["inner", "outer"]
+ assert value == b"start"
+
+ def test_roundtrip(self):
+ """Test encode/decode roundtrip through a codec chain."""
+
+ class TestInnerRt(Codec):
+ name = "test_inner_rt"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "bytes"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ # Compress (just add prefix for testing)
+ return b"COMPRESSED:" + value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ # Decompress
+ return stored.replace(b"COMPRESSED:", b"")
+
+ class TestOuterRt(Codec):
+ name = "test_outer_rt"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ # Serialize (just encode string for testing)
+ return str(value).encode("utf-8")
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ # Deserialize
+ return stored.decode("utf-8")
+
+ _, chain, _ = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ # Original value
+ original = "test data"
+
+ # Encode: outer → inner
+ encoded = original
+ for codec in chain:
+ encoded = codec.encode(encoded)
+
+ assert encoded == b"COMPRESSED:test data"
+
+ # Decode: inner → outer (reversed)
+ decoded = encoded
+ for codec in reversed(chain):
+ decoded = codec.decode(decoded)
+
+ assert decoded == original
+
+
+class TestBuiltinCodecChains:
+ """Tests for built-in codec chains."""
+
+ def test_blob_internal_resolves_to_bytes(self):
+ """Test that (internal) → bytes."""
+ final_dtype, chain, _ = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "bytes"
+ assert len(chain) == 1
+ assert chain[0].name == "blob"
+
+ def test_blob_external_resolves_to_json(self):
+ """Test that → → json."""
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "json"
+ assert len(chain) == 2
+ assert chain[0].name == "blob"
+ assert chain[1].name == "hash"
+ assert store == "store"
+
+ def test_attach_internal_resolves_to_bytes(self):
+ """Test that (internal) → bytes."""
+ final_dtype, chain, _ = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "bytes"
+ assert len(chain) == 1
+ assert chain[0].name == "attach"
+
+ def test_attach_external_resolves_to_json(self):
+ """Test that → → json."""
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "json"
+ assert len(chain) == 2
+ assert chain[0].name == "attach"
+ assert chain[1].name == "hash"
+ assert store == "store"
+
+ def test_hash_external_resolves_to_json(self):
+ """Test that → json (external only)."""
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "json"
+ assert len(chain) == 1
+ assert chain[0].name == "hash"
+ assert store == "store"
+
+ def test_object_external_resolves_to_json(self):
+ """Test that → json (external only)."""
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "json"
+ assert len(chain) == 1
+ assert chain[0].name == "object"
+ assert store == "store"
+
+ def test_filepath_external_resolves_to_json(self):
+ """Test that → json (external only)."""
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "json"
+ assert len(chain) == 1
+ assert chain[0].name == "filepath"
+ assert store == "store"
+
+
+class TestStoreNameParsing:
+ """Tests for store name parsing in codec specs."""
+
+ def test_codec_with_store(self):
+ """Test parsing codec with store name."""
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "json"
+ assert store == "mystore"
+
+ def test_codec_without_store(self):
+ """Test parsing codec without store name."""
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert store is None
+
+ def test_filepath_with_store(self):
+ """Test parsing filepath with store name."""
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+
+ assert final_dtype == "json"
+ assert store == "s3store"
diff --git a/tests/test_adapted_attributes.py b/tests/integration/test_codecs.py
similarity index 61%
rename from tests/test_adapted_attributes.py
rename to tests/integration/test_codecs.py
index ffd137795..6d160e5b5 100644
--- a/tests/test_adapted_attributes.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_codecs.py
@@ -1,5 +1,9 @@
-import os
-import tempfile
+"""
+Tests for custom codecs.
+
+These tests verify the Codec system for custom data types.
+"""
+
from itertools import zip_longest
import networkx as nx
@@ -7,66 +11,51 @@
import datajoint as dj
-from . import schema_adapted
-from .schema_adapted import Connectivity, Layout
+from tests import schema_codecs
+from tests.schema_codecs import Connectivity, Layout
@pytest.fixture
def schema_name(prefix):
- return prefix + "_test_custom_datatype"
-
-
-@pytest.fixture
-def adapted_graph_instance():
- yield schema_adapted.GraphAdapter()
+ return prefix + "_test_codecs"
@pytest.fixture
-def schema_ad(
+def schema_codec(
connection_test,
- adapted_graph_instance,
- enable_adapted_types,
- enable_filepath_feature,
s3_creds,
tmpdir,
schema_name,
):
- dj.config["stores"] = {
- "repo-s3": dict(
- s3_creds, protocol="s3", location="adapted/repo", stage=str(tmpdir)
- )
- }
- context = {
- **schema_adapted.LOCALS_ADAPTED,
- "graph": adapted_graph_instance,
- "layout_to_filepath": schema_adapted.LayoutToFilepath(),
- }
+ dj.config["stores"] = {"repo-s3": dict(s3_creds, protocol="s3", location="codecs/repo", stage=str(tmpdir))}
+ # Codecs are auto-registered via __init_subclass__ in schema_codecs
+ context = {**schema_codecs.LOCALS_CODECS}
schema = dj.schema(schema_name, context=context, connection=connection_test)
- schema(schema_adapted.Connectivity)
- schema(schema_adapted.Layout)
+ schema(schema_codecs.Connectivity)
+ schema(schema_codecs.Layout)
yield schema
schema.drop()
@pytest.fixture
-def local_schema(schema_ad, schema_name):
+def local_schema(schema_codec, schema_name):
"""Fixture for testing spawned classes"""
- local_schema = dj.Schema(schema_name)
+ local_schema = dj.Schema(schema_name, connection=schema_codec.connection)
local_schema.spawn_missing_classes()
yield local_schema
- local_schema.drop()
+ # Don't drop - schema_codec fixture handles cleanup
@pytest.fixture
-def schema_virtual_module(schema_ad, adapted_graph_instance, schema_name):
+def schema_virtual_module(schema_codec, schema_name):
"""Fixture for testing virtual modules"""
- schema_virtual_module = dj.VirtualModule(
- "virtual_module", schema_name, add_objects={"graph": adapted_graph_instance}
- )
+ # Codecs are registered globally, no need to add_objects
+ schema_virtual_module = dj.VirtualModule("virtual_module", schema_name, connection=schema_codec.connection)
return schema_virtual_module
-def test_adapted_type(schema_ad):
+def test_codec_graph(schema_codec):
+ """Test basic codec encode/decode with graph type."""
c = Connectivity()
graphs = [
nx.lollipop_graph(4, 2),
@@ -75,7 +64,7 @@ def test_adapted_type(schema_ad):
nx.cycle_graph(5),
]
c.insert((i, g) for i, g in enumerate(graphs))
- returned_graphs = c.fetch("conn_graph", order_by="connid")
+ returned_graphs = c.to_arrays("conn_graph", order_by="connid")
for g1, g2 in zip(graphs, returned_graphs):
assert isinstance(g2, nx.Graph)
assert len(g1.edges) == len(g2.edges)
@@ -83,8 +72,8 @@ def test_adapted_type(schema_ad):
c.delete()
-def test_adapted_filepath_type(schema_ad, minio_client):
- """https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/684"""
+def test_codec_chained(schema_codec, minio_client):
+ """Test codec chaining (layout -> blob)."""
c = Connectivity()
c.delete()
c.insert1((0, nx.lollipop_graph(4, 2)))
@@ -100,7 +89,8 @@ def test_adapted_filepath_type(schema_ad, minio_client):
c.delete()
-def test_adapted_spawned(local_schema, enable_adapted_types):
+def test_codec_spawned(local_schema):
+ """Test codecs work with spawned classes."""
c = Connectivity() # a spawned class
graphs = [
nx.lollipop_graph(4, 2),
@@ -109,7 +99,7 @@ def test_adapted_spawned(local_schema, enable_adapted_types):
nx.cycle_graph(5),
]
c.insert((i, g) for i, g in enumerate(graphs))
- returned_graphs = c.fetch("conn_graph", order_by="connid")
+ returned_graphs = c.to_arrays("conn_graph", order_by="connid")
for g1, g2 in zip(graphs, returned_graphs):
assert isinstance(g2, nx.Graph)
assert len(g1.edges) == len(g2.edges)
@@ -117,7 +107,8 @@ def test_adapted_spawned(local_schema, enable_adapted_types):
c.delete()
-def test_adapted_virtual(schema_virtual_module):
+def test_codec_virtual_module(schema_virtual_module):
+ """Test codecs work with virtual modules."""
c = schema_virtual_module.Connectivity()
graphs = [
nx.lollipop_graph(4, 2),
@@ -127,7 +118,7 @@ def test_adapted_virtual(schema_virtual_module):
]
c.insert((i, g) for i, g in enumerate(graphs))
c.insert1({"connid": 100}) # test work with NULLs
- returned_graphs = c.fetch("conn_graph", order_by="connid")
+ returned_graphs = c.to_arrays("conn_graph", order_by="connid")
for g1, g2 in zip_longest(graphs, returned_graphs):
if g1 is None:
assert g2 is None
diff --git a/tests/test_connection.py b/tests/integration/test_connection.py
similarity index 65%
rename from tests/test_connection.py
rename to tests/integration/test_connection.py
index db301d9af..ff3940587 100644
--- a/tests/test_connection.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_connection.py
@@ -46,6 +46,36 @@ def test_dj_connection_class(connection_test):
assert connection_test.is_connected
+def test_connection_context_manager(db_creds_test):
+ """
+ Connection should support context manager protocol for automatic cleanup.
+ """
+ # Test basic context manager usage
+ with dj.Connection(**db_creds_test) as conn:
+ assert conn.is_connected
+ # Verify we can use the connection
+ result = conn.query("SELECT 1").fetchone()
+ assert result[0] == 1
+
+ # Connection should be closed after exiting context
+ assert not conn.is_connected
+
+
+def test_connection_context_manager_exception(db_creds_test):
+ """
+ Connection should close even when exception is raised inside context.
+ """
+ conn = None
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError):
+ with dj.Connection(**db_creds_test) as conn:
+ assert conn.is_connected
+ raise ValueError("Test exception")
+
+ # Connection should still be closed after exception
+ assert conn is not None
+ assert not conn.is_connected
+
+
def test_persistent_dj_conn(db_creds_root):
"""
conn() method should provide persistent connection across calls.
@@ -88,13 +118,9 @@ def test_transaction_rollback(schema_tx, connection_test):
raise DataJointError("Testing rollback")
except DataJointError:
pass
- assert (
- len(Subjects()) == 1
- ), "Length is not 1. Expected because rollback should have happened."
+ assert len(Subjects()) == 1, "Length is not 1. Expected because rollback should have happened."
- assert (
- len(Subjects & "subject_id = 2") == 0
- ), "Length is not 0. Expected because rollback should have happened."
+ assert len(Subjects & "subject_id = 2") == 0, "Length is not 0. Expected because rollback should have happened."
def test_cancel(schema_tx, connection_test):
@@ -108,9 +134,5 @@ def test_cancel(schema_tx, connection_test):
connection_test.start_transaction()
Subjects.insert1(tmp[1])
connection_test.cancel_transaction()
- assert (
- len(Subjects()) == 1
- ), "Length is not 1. Expected because rollback should have happened."
- assert (
- len(Subjects & "subject_id = 2") == 0
- ), "Length is not 0. Expected because rollback should have happened."
+ assert len(Subjects()) == 1, "Length is not 1. Expected because rollback should have happened."
+ assert len(Subjects & "subject_id = 2") == 0, "Length is not 0. Expected because rollback should have happened."
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_content_storage.py b/tests/integration/test_content_storage.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e6d0f14cc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_content_storage.py
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
+"""
+Tests for content-addressed storage (content_registry.py).
+"""
+
+import hashlib
+from unittest.mock import MagicMock, patch
+
+import pytest
+
+from datajoint.content_registry import (
+ build_content_path,
+ compute_content_hash,
+ content_exists,
+ delete_content,
+ get_content,
+ get_content_size,
+ put_content,
+)
+from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
+
+
+class TestComputeContentHash:
+ """Tests for compute_content_hash function."""
+
+ def test_computes_sha256(self):
+ """Test that SHA256 hash is computed correctly."""
+ data = b"Hello, World!"
+ result = compute_content_hash(data)
+
+ # Verify against known SHA256 hash
+ expected = hashlib.sha256(data).hexdigest()
+ assert result == expected
+ assert len(result) == 64 # SHA256 produces 64 hex chars
+
+ def test_empty_bytes(self):
+ """Test hashing empty bytes."""
+ result = compute_content_hash(b"")
+ expected = hashlib.sha256(b"").hexdigest()
+ assert result == expected
+
+ def test_different_content_different_hash(self):
+ """Test that different content produces different hashes."""
+ hash1 = compute_content_hash(b"content1")
+ hash2 = compute_content_hash(b"content2")
+ assert hash1 != hash2
+
+ def test_same_content_same_hash(self):
+ """Test that same content produces same hash."""
+ data = b"identical content"
+ hash1 = compute_content_hash(data)
+ hash2 = compute_content_hash(data)
+ assert hash1 == hash2
+
+
+class TestBuildContentPath:
+ """Tests for build_content_path function."""
+
+ def test_builds_hierarchical_path(self):
+ """Test that path is built with proper hierarchy."""
+ # Example hash: abcdef...
+ test_hash = "abcdef0123456789" * 4 # 64 chars
+ result = build_content_path(test_hash)
+
+ # Path should be _content/{hash[:2]}/{hash[2:4]}/{hash}
+ assert result == f"_content/ab/cd/{test_hash}"
+
+ def test_rejects_invalid_hash_length(self):
+ """Test that invalid hash length raises error."""
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError, match="Invalid content hash length"):
+ build_content_path("tooshort")
+
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError, match="Invalid content hash length"):
+ build_content_path("a" * 65) # Too long
+
+ def test_real_hash_path(self):
+ """Test path building with a real computed hash."""
+ data = b"test content"
+ content_hash = compute_content_hash(data)
+ path = build_content_path(content_hash)
+
+ # Verify structure
+ parts = path.split("/")
+ assert parts[0] == "_content"
+ assert len(parts[1]) == 2
+ assert len(parts[2]) == 2
+ assert len(parts[3]) == 64
+ assert parts[1] == content_hash[:2]
+ assert parts[2] == content_hash[2:4]
+ assert parts[3] == content_hash
+
+
+class TestPutContent:
+ """Tests for put_content function."""
+
+ @patch("datajoint.content_registry.get_store_backend")
+ def test_stores_new_content(self, mock_get_backend):
+ """Test storing new content."""
+ mock_backend = MagicMock()
+ mock_backend.exists.return_value = False
+ mock_get_backend.return_value = mock_backend
+
+ data = b"new content"
+ result = put_content(data, store_name="test_store")
+
+ # Verify return value
+ assert "hash" in result
+ assert result["hash"] == compute_content_hash(data)
+ assert result["store"] == "test_store"
+ assert result["size"] == len(data)
+
+ # Verify backend was called
+ mock_backend.put_buffer.assert_called_once()
+
+ @patch("datajoint.content_registry.get_store_backend")
+ def test_deduplicates_existing_content(self, mock_get_backend):
+ """Test that existing content is not re-uploaded."""
+ mock_backend = MagicMock()
+ mock_backend.exists.return_value = True # Content already exists
+ mock_get_backend.return_value = mock_backend
+
+ data = b"existing content"
+ result = put_content(data, store_name="test_store")
+
+ # Verify return value is still correct
+ assert result["hash"] == compute_content_hash(data)
+ assert result["size"] == len(data)
+
+ # Verify put_buffer was NOT called (deduplication)
+ mock_backend.put_buffer.assert_not_called()
+
+
+class TestGetContent:
+ """Tests for get_content function."""
+
+ @patch("datajoint.content_registry.get_store_backend")
+ def test_retrieves_content(self, mock_get_backend):
+ """Test retrieving content by hash."""
+ data = b"stored content"
+ content_hash = compute_content_hash(data)
+
+ mock_backend = MagicMock()
+ mock_backend.get_buffer.return_value = data
+ mock_get_backend.return_value = mock_backend
+
+ result = get_content(content_hash, store_name="test_store")
+
+ assert result == data
+
+ @patch("datajoint.content_registry.get_store_backend")
+ def test_verifies_hash(self, mock_get_backend):
+ """Test that hash is verified on retrieval."""
+ data = b"original content"
+ content_hash = compute_content_hash(data)
+
+ # Return corrupted data
+ mock_backend = MagicMock()
+ mock_backend.get_buffer.return_value = b"corrupted content"
+ mock_get_backend.return_value = mock_backend
+
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError, match="Content hash mismatch"):
+ get_content(content_hash, store_name="test_store")
+
+
+class TestContentExists:
+ """Tests for content_exists function."""
+
+ @patch("datajoint.content_registry.get_store_backend")
+ def test_returns_true_when_exists(self, mock_get_backend):
+ """Test that True is returned when content exists."""
+ mock_backend = MagicMock()
+ mock_backend.exists.return_value = True
+ mock_get_backend.return_value = mock_backend
+
+ content_hash = "a" * 64
+ assert content_exists(content_hash, store_name="test_store") is True
+
+ @patch("datajoint.content_registry.get_store_backend")
+ def test_returns_false_when_not_exists(self, mock_get_backend):
+ """Test that False is returned when content doesn't exist."""
+ mock_backend = MagicMock()
+ mock_backend.exists.return_value = False
+ mock_get_backend.return_value = mock_backend
+
+ content_hash = "a" * 64
+ assert content_exists(content_hash, store_name="test_store") is False
+
+
+class TestDeleteContent:
+ """Tests for delete_content function."""
+
+ @patch("datajoint.content_registry.get_store_backend")
+ def test_deletes_existing_content(self, mock_get_backend):
+ """Test deleting existing content."""
+ mock_backend = MagicMock()
+ mock_backend.exists.return_value = True
+ mock_get_backend.return_value = mock_backend
+
+ content_hash = "a" * 64
+ result = delete_content(content_hash, store_name="test_store")
+
+ assert result is True
+ mock_backend.remove.assert_called_once()
+
+ @patch("datajoint.content_registry.get_store_backend")
+ def test_returns_false_for_nonexistent(self, mock_get_backend):
+ """Test that False is returned when content doesn't exist."""
+ mock_backend = MagicMock()
+ mock_backend.exists.return_value = False
+ mock_get_backend.return_value = mock_backend
+
+ content_hash = "a" * 64
+ result = delete_content(content_hash, store_name="test_store")
+
+ assert result is False
+ mock_backend.remove.assert_not_called()
+
+
+class TestGetContentSize:
+ """Tests for get_content_size function."""
+
+ @patch("datajoint.content_registry.get_store_backend")
+ def test_returns_size(self, mock_get_backend):
+ """Test getting content size."""
+ mock_backend = MagicMock()
+ mock_backend.size.return_value = 1024
+ mock_get_backend.return_value = mock_backend
+
+ content_hash = "a" * 64
+ result = get_content_size(content_hash, store_name="test_store")
+
+ assert result == 1024
diff --git a/tests/test_declare.py b/tests/integration/test_declare.py
similarity index 70%
rename from tests/test_declare.py
rename to tests/integration/test_declare.py
index 828021939..3097a9457 100644
--- a/tests/test_declare.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_declare.py
@@ -4,27 +4,21 @@
import datajoint as dj
from datajoint.declare import declare
-from datajoint.settings import config
-from .schema import *
-
-
-@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
-def enable_add_hidden_timestamp():
- orig_config_val = config.get("add_hidden_timestamp")
- config["add_hidden_timestamp"] = True
- yield
- if orig_config_val is not None:
- config["add_hidden_timestamp"] = orig_config_val
-
-
-@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
-def disable_add_hidden_timestamp():
- orig_config_val = config.get("add_hidden_timestamp")
- config["add_hidden_timestamp"] = False
- yield
- if orig_config_val is not None:
- config["add_hidden_timestamp"] = orig_config_val
+from tests.schema import (
+ Auto,
+ Ephys,
+ Experiment,
+ IndexRich,
+ Subject,
+ TTest,
+ TTest2,
+ ThingA, # noqa: F401 - needed in globals for foreign key resolution
+ ThingB, # noqa: F401 - needed in globals for foreign key resolution
+ ThingC,
+ Trial,
+ User,
+)
def test_schema_decorator(schema_any):
@@ -77,7 +71,7 @@ def test_part(schema_any):
"""
Lookup and part with the same name. See issue #365
"""
- local_schema = dj.Schema(schema_any.database)
+ local_schema = dj.Schema(schema_any.database, connection=schema_any.connection)
@local_schema
class Type(dj.Lookup):
@@ -101,10 +95,9 @@ class Type(dj.Part):
def test_attributes(schema_any):
"""
- Test autoincrement declaration
+ Test attribute declarations
"""
auto = Auto()
- auto.fill()
subject = Subject()
experiment = Experiment()
trial = Trial()
@@ -112,7 +105,7 @@ def test_attributes(schema_any):
channel = Ephys.Channel()
assert auto.heading.names == ["id", "name"]
- assert auto.heading.attributes["id"].autoincrement
+ assert auto.heading.attributes["id"].numeric
# test attribute declarations
assert subject.heading.names == [
@@ -178,48 +171,30 @@ def test_dependencies(schema_any):
assert set(experiment.parents(primary=False)) == {user.full_table_name}
assert experiment.full_table_name in user.children(primary=False)
assert set(experiment.parents(primary=False)) == {user.full_table_name}
- assert set(
- s.full_table_name for s in experiment.parents(primary=False, as_objects=True)
- ) == {user.full_table_name}
+ assert set(s.full_table_name for s in experiment.parents(primary=False, as_objects=True)) == {user.full_table_name}
assert experiment.full_table_name in subject.descendants()
- assert experiment.full_table_name in {
- s.full_table_name for s in subject.descendants(as_objects=True)
- }
+ assert experiment.full_table_name in {s.full_table_name for s in subject.descendants(as_objects=True)}
assert subject.full_table_name in experiment.ancestors()
- assert subject.full_table_name in {
- s.full_table_name for s in experiment.ancestors(as_objects=True)
- }
+ assert subject.full_table_name in {s.full_table_name for s in experiment.ancestors(as_objects=True)}
assert trial.full_table_name in experiment.descendants()
- assert trial.full_table_name in {
- s.full_table_name for s in experiment.descendants(as_objects=True)
- }
+ assert trial.full_table_name in {s.full_table_name for s in experiment.descendants(as_objects=True)}
assert experiment.full_table_name in trial.ancestors()
- assert experiment.full_table_name in {
- s.full_table_name for s in trial.ancestors(as_objects=True)
- }
+ assert experiment.full_table_name in {s.full_table_name for s in trial.ancestors(as_objects=True)}
assert set(trial.children(primary=True)) == {
ephys.full_table_name,
trial.Condition.full_table_name,
}
assert set(trial.parts()) == {trial.Condition.full_table_name}
- assert set(s.full_table_name for s in trial.parts(as_objects=True)) == {
- trial.Condition.full_table_name
- }
+ assert set(s.full_table_name for s in trial.parts(as_objects=True)) == {trial.Condition.full_table_name}
assert set(ephys.parents(primary=True)) == {trial.full_table_name}
- assert set(
- s.full_table_name for s in ephys.parents(primary=True, as_objects=True)
- ) == {trial.full_table_name}
+ assert set(s.full_table_name for s in ephys.parents(primary=True, as_objects=True)) == {trial.full_table_name}
assert set(ephys.children(primary=True)) == {channel.full_table_name}
- assert set(
- s.full_table_name for s in ephys.children(primary=True, as_objects=True)
- ) == {channel.full_table_name}
+ assert set(s.full_table_name for s in ephys.children(primary=True, as_objects=True)) == {channel.full_table_name}
assert set(channel.parents(primary=True)) == {ephys.full_table_name}
- assert set(
- s.full_table_name for s in channel.parents(primary=True, as_objects=True)
- ) == {ephys.full_table_name}
+ assert set(s.full_table_name for s in channel.parents(primary=True, as_objects=True)) == {ephys.full_table_name}
def test_descendants_only_contain_part_table(schema_any):
@@ -268,7 +243,7 @@ class BadName(dj.Manual):
schema_any(BadName)
-def test_bad_fk_rename(schema_any):
+def test_bad_fk_rename(schema_any_fresh):
"""issue #381"""
class A(dj.Manual):
@@ -281,9 +256,9 @@ class B(dj.Manual):
b -> A # invalid, the new syntax is (b) -> A
"""
- schema_any(A)
+ schema_any_fresh(A)
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- schema_any(B)
+ schema_any_fresh(B)
def test_primary_nullable_foreign_key(schema_any):
@@ -313,7 +288,7 @@ class Q(dj.Manual):
definition = """
experiment : int
---
- description : text
+ description : completely_invalid_type_xyz
"""
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
@@ -388,42 +363,5 @@ class Table_With_Underscores(dj.Manual):
"""
schema_any(TableNoUnderscores)
- with pytest.raises(
- dj.DataJointError, match="must be alphanumeric in CamelCase"
- ) as e:
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="must be alphanumeric in CamelCase"):
schema_any(Table_With_Underscores)
-
-
-def test_add_hidden_timestamp_default_value():
- config_val = config.get("add_hidden_timestamp")
- assert (
- config_val is not None and not config_val
- ), "Default value for add_hidden_timestamp is not False"
-
-
-def test_add_hidden_timestamp_enabled(enable_add_hidden_timestamp, schema_any):
- assert config["add_hidden_timestamp"], "add_hidden_timestamp is not enabled"
- msg = f"{Experiment().heading._attributes=}"
- assert any(
- a.name.endswith("_timestamp") for a in Experiment().heading._attributes.values()
- ), msg
- assert any(
- a.name.startswith("_") for a in Experiment().heading._attributes.values()
- ), msg
- assert any(a.is_hidden for a in Experiment().heading._attributes.values()), msg
- assert not any(a.is_hidden for a in Experiment().heading.attributes.values()), msg
-
-
-def test_add_hidden_timestamp_disabled(disable_add_hidden_timestamp, schema_any):
- assert not config[
- "add_hidden_timestamp"
- ], "expected add_hidden_timestamp to be False"
- msg = f"{Experiment().heading._attributes=}"
- assert not any(
- a.name.endswith("_timestamp") for a in Experiment().heading._attributes.values()
- ), msg
- assert not any(
- a.name.startswith("_") for a in Experiment().heading._attributes.values()
- ), msg
- assert not any(a.is_hidden for a in Experiment().heading._attributes.values()), msg
- assert not any(a.is_hidden for a in Experiment().heading.attributes.values()), msg
diff --git a/tests/test_dependencies.py b/tests/integration/test_dependencies.py
similarity index 96%
rename from tests/test_dependencies.py
rename to tests/integration/test_dependencies.py
index 3be4a21dc..7d9c5dd6e 100644
--- a/tests/test_dependencies.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_dependencies.py
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ def test_nullable_dependency(thing_tables):
c.insert1(dict(a=3, b1=1, b2=1))
c.insert1(dict(a=4, b1=1, b2=2))
- assert len(c) == len(c.fetch()) == 5
+ assert len(c) == len(c.to_arrays()) == 5
def test_topo_sort():
diff --git a/tests/test_erd.py b/tests/integration/test_erd.py
similarity index 80%
rename from tests/test_erd.py
rename to tests/integration/test_erd.py
index e2344cf8a..1fbad394b 100644
--- a/tests/test_erd.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_erd.py
@@ -1,7 +1,6 @@
import datajoint as dj
-from .schema_advanced import *
-from .schema_simple import LOCALS_SIMPLE, A, B, D, E, G, L, OutfitLaunch
+from tests.schema_simple import LOCALS_SIMPLE, A, B, D, E, G, L
def test_decorator(schema_simp):
@@ -20,9 +19,7 @@ def test_dependencies(schema_simp):
assert set(A().children()) == set([B.full_table_name, D.full_table_name])
assert set(D().parents(primary=True)) == set([A.full_table_name])
assert set(D().parents(primary=False)) == set([L.full_table_name])
- assert set(deps.descendants(L.full_table_name)).issubset(
- cls.full_table_name for cls in (L, D, E, E.F, E.G, E.H, E.M, G)
- )
+ assert set(deps.descendants(L.full_table_name)).issubset(cls.full_table_name for cls in (L, D, E, E.F, E.G, E.H, E.M, G))
def test_erd(schema_simp):
@@ -39,14 +36,10 @@ def test_erd_algebra(schema_simp):
erd3 = erd1 * erd2
erd4 = (erd0 + E).add_parts() - B - E
assert erd0.nodes_to_show == set(cls.full_table_name for cls in [B])
- assert erd1.nodes_to_show == set(
- cls.full_table_name for cls in (B, B.C, E, E.F, E.G, E.H, E.M, G)
- )
+ assert erd1.nodes_to_show == set(cls.full_table_name for cls in (B, B.C, E, E.F, E.G, E.H, E.M, G))
assert erd2.nodes_to_show == set(cls.full_table_name for cls in (A, B, D, E, L))
assert erd3.nodes_to_show == set(cls.full_table_name for cls in (B, E))
- assert erd4.nodes_to_show == set(
- cls.full_table_name for cls in (B.C, E.F, E.G, E.H, E.M)
- )
+ assert erd4.nodes_to_show == set(cls.full_table_name for cls in (B.C, E.F, E.G, E.H, E.M))
def test_repr_svg(schema_adv):
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_fetch.py b/tests/integration/test_fetch.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..8cde34deb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_fetch.py
@@ -0,0 +1,399 @@
+"""Tests for the modern fetch API: to_dicts, to_pandas, to_arrays, keys, fetch1"""
+
+import decimal
+import itertools
+import os
+import shutil
+from operator import itemgetter
+
+import numpy as np
+import pandas
+import pytest
+
+import datajoint as dj
+
+from tests import schema
+
+
+def test_getattribute(subject):
+ """Testing fetch with attributes using new API"""
+ list1 = sorted(subject.proj().to_dicts(), key=itemgetter("subject_id"))
+ list2 = sorted(subject.keys(), key=itemgetter("subject_id"))
+ for l1, l2 in zip(list1, list2):
+ assert l1 == l2, "Primary key is not returned correctly"
+
+ tmp = subject.to_arrays(order_by="subject_id")
+
+ subject_notes, real_id = subject.to_arrays("subject_notes", "real_id")
+
+ np.testing.assert_array_equal(sorted(subject_notes), sorted(tmp["subject_notes"]))
+ np.testing.assert_array_equal(sorted(real_id), sorted(tmp["real_id"]))
+
+
+def test_getattribute_for_fetch1(subject):
+ """Testing Fetch1.__call__ with attributes"""
+ assert (subject & "subject_id=10").fetch1("subject_id") == 10
+ assert (subject & "subject_id=10").fetch1("subject_id", "species") == (
+ 10,
+ "monkey",
+ )
+
+
+def test_order_by(lang, languages):
+ """Tests order_by sorting order"""
+ for ord_name, ord_lang in itertools.product(*2 * [["ASC", "DESC"]]):
+ cur = lang.to_arrays(order_by=("name " + ord_name, "language " + ord_lang))
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=ord_lang == "DESC")
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=ord_name == "DESC")
+ for c, l in zip(cur, languages): # noqa: E741
+ assert np.all(cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)), "Sorting order is different"
+
+
+def test_order_by_default(lang, languages):
+ """Tests order_by sorting order with defaults"""
+ cur = lang.to_arrays(order_by=("language", "name DESC"))
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
+ for c, l in zip(cur, languages): # noqa: E741
+ assert np.all([cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)]), "Sorting order is different"
+
+
+def test_limit(lang):
+ """Test the limit kwarg"""
+ limit = 4
+ cur = lang.to_arrays(limit=limit)
+ assert len(cur) == limit, "Length is not correct"
+
+
+def test_order_by_limit(lang, languages):
+ """Test the combination of order by and limit kwargs"""
+ cur = lang.to_arrays(limit=4, order_by=["language", "name DESC"])
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
+ assert len(cur) == 4, "Length is not correct"
+ for c, l in list(zip(cur, languages))[:4]: # noqa: E741
+ assert np.all([cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)]), "Sorting order is different"
+
+
+def test_head_tail(schema_any):
+ """Test head() and tail() convenience methods"""
+ query = schema.User * schema.Language
+ n = 5
+ # head and tail now return list of dicts
+ head_result = query.head(n)
+ assert isinstance(head_result, list)
+ assert len(head_result) == n
+ assert all(isinstance(row, dict) for row in head_result)
+
+ n = 4
+ tail_result = query.tail(n)
+ assert isinstance(tail_result, list)
+ assert len(tail_result) == n
+ assert all(isinstance(row, dict) for row in tail_result)
+
+
+def test_limit_offset(lang, languages):
+ """Test the limit and offset kwargs together"""
+ cur = lang.to_arrays(offset=2, limit=4, order_by=["language", "name DESC"])
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
+ assert len(cur) == 4, "Length is not correct"
+ for c, l in list(zip(cur, languages[2:6])): # noqa: E741
+ assert np.all([cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)]), "Sorting order is different"
+
+
+def test_iter(lang, languages):
+ """Test iterator - now lazy streaming"""
+ languages_copy = languages.copy()
+ languages_copy.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
+ languages_copy.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
+
+ # Iteration now yields dicts directly
+ result = list(lang.to_dicts(order_by=["language", "name DESC"]))
+ for row, (tname, tlang) in list(zip(result, languages_copy)):
+ assert row["name"] == tname and row["language"] == tlang, "Values are not the same"
+
+
+def test_keys(lang, languages):
+ """test key fetch"""
+ languages_copy = languages.copy()
+ languages_copy.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
+ languages_copy.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
+
+ # Use to_arrays for attribute fetch
+ cur = lang.to_arrays("name", "language", order_by=("language", "name DESC"))
+ # Use keys() for primary key fetch
+ cur2 = list(lang.keys(order_by=["language", "name DESC"]))
+
+ for c, c2 in zip(zip(*cur), cur2):
+ assert c == tuple(c2.values()), "Values are not the same"
+
+
+def test_fetch1_step1(lang, languages):
+ assert (
+ lang.contents
+ == languages
+ == [
+ ("Fabian", "English"),
+ ("Edgar", "English"),
+ ("Dimitri", "English"),
+ ("Dimitri", "Ukrainian"),
+ ("Fabian", "German"),
+ ("Edgar", "Japanese"),
+ ]
+ ), "Unexpected contents in Language table"
+ key = {"name": "Edgar", "language": "Japanese"}
+ true = languages[-1]
+ dat = (lang & key).fetch1()
+ for k, (ke, c) in zip(true, dat.items()):
+ assert k == c == (lang & key).fetch1(ke), "Values are not the same"
+
+
+def test_misspelled_attribute(schema_any):
+ """Test that misspelled attributes raise error"""
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
+ (schema.Language & 'lang = "ENGLISH"').to_dicts()
+
+
+def test_to_dicts(lang):
+ """Test to_dicts returns list of dictionaries"""
+ d = lang.to_dicts()
+ for dd in d:
+ assert isinstance(dd, dict)
+
+
+def test_offset(lang, languages):
+ """Tests offset"""
+ cur = lang.to_arrays(limit=4, offset=1, order_by=["language", "name DESC"])
+
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
+ languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
+ assert len(cur) == 4, "Length is not correct"
+ for c, l in list(zip(cur, languages[1:]))[:4]: # noqa: E741
+ assert np.all([cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)]), "Sorting order is different"
+
+
+def test_len(lang):
+ """Tests __len__"""
+ assert len(lang.to_arrays()) == len(lang), "__len__ is not behaving properly"
+
+
+def test_fetch1_step2(lang):
+ """Tests whether fetch1 raises error for multiple rows"""
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
+ lang.fetch1()
+
+
+def test_fetch1_step3(lang):
+ """Tests whether fetch1 raises error for multiple rows with attribute"""
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
+ lang.fetch1("name")
+
+
+def test_decimal(schema_any):
+ """Tests that decimal fields are correctly fetched and used in restrictions, see issue #334"""
+ rel = schema.DecimalPrimaryKey()
+ assert len(rel.to_arrays()), "Table DecimalPrimaryKey contents are empty"
+ rel.insert1([decimal.Decimal("3.1415926")])
+ keys = rel.to_arrays()
+ assert len(keys) > 0
+ assert len(rel & keys[0]) == 1
+ keys = rel.keys()
+ assert len(keys) >= 2
+ assert len(rel & keys[1]) == 1
+
+
+def test_nullable_numbers(schema_any):
+ """test mixture of values and nulls in numeric attributes"""
+ table = schema.NullableNumbers()
+ table.insert(
+ (
+ (
+ k,
+ np.random.randn(),
+ np.random.randint(-1000, 1000),
+ np.random.randn(),
+ )
+ for k in range(10)
+ )
+ )
+ table.insert1((100, None, None, None))
+ f, d, i = table.to_arrays("fvalue", "dvalue", "ivalue")
+ # Check for None in integer column
+ assert None in i
+ # Check for None or nan in float columns (None may be returned for nullable fields)
+ assert any(v is None or (isinstance(v, float) and np.isnan(v)) for v in d)
+ assert any(v is None or (isinstance(v, float) and np.isnan(v)) for v in f)
+
+
+def test_to_pandas(subject):
+ """Test to_pandas returns DataFrame with primary key as index"""
+ df = subject.to_pandas(order_by="subject_id")
+ assert isinstance(df, pandas.DataFrame)
+ assert df.index.names == subject.primary_key
+
+
+def test_to_polars(subject):
+ """Test to_polars returns polars DataFrame"""
+ polars = pytest.importorskip("polars")
+ df = subject.to_polars()
+ assert isinstance(df, polars.DataFrame)
+
+
+def test_to_arrow(subject):
+ """Test to_arrow returns PyArrow Table"""
+ pyarrow = pytest.importorskip("pyarrow")
+ table = subject.to_arrow()
+ assert isinstance(table, pyarrow.Table)
+
+
+def test_same_secondary_attribute(schema_any):
+ children = (schema.Child * schema.Parent().proj()).to_arrays()["name"]
+ assert len(children) == 1
+ assert children[0] == "Dan"
+
+
+def test_query_caching(schema_any):
+ """Test query caching with to_arrays"""
+ # initialize cache directory
+ os.makedirs(os.path.expanduser("~/dj_query_cache"), exist_ok=True)
+
+ with dj.config.override(query_cache=os.path.expanduser("~/dj_query_cache")):
+ conn = schema.TTest3.connection
+ # insert sample data and load cache
+ schema.TTest3.insert([dict(key=100 + i, value=200 + i) for i in range(2)])
+ conn.set_query_cache(query_cache="main")
+ cached_res = schema.TTest3().to_arrays()
+ # attempt to insert while caching enabled
+ try:
+ schema.TTest3.insert([dict(key=200 + i, value=400 + i) for i in range(2)])
+ assert False, "Insert allowed while query caching enabled"
+ except dj.DataJointError:
+ conn.set_query_cache()
+ # insert new data
+ schema.TTest3.insert([dict(key=600 + i, value=800 + i) for i in range(2)])
+ # re-enable cache to access old results
+ conn.set_query_cache(query_cache="main")
+ previous_cache = schema.TTest3().to_arrays()
+ # verify properly cached and how to refresh results
+ assert all([c == p for c, p in zip(cached_res, previous_cache)])
+ conn.set_query_cache()
+ uncached_res = schema.TTest3().to_arrays()
+ assert len(uncached_res) > len(cached_res)
+ # purge query cache
+ conn.purge_query_cache()
+
+ # reset cache directory state
+ shutil.rmtree(os.path.expanduser("~/dj_query_cache"), ignore_errors=True)
+
+
+def test_fetch_group_by(schema_any):
+ """
+ https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/914
+ """
+ assert schema.Parent().keys(order_by="name") == [{"parent_id": 1}]
+
+
+def test_dj_u_distinct(schema_any):
+ """
+ Test developed to see if removing DISTINCT from the select statement
+ generation breaks the dj.U universal set implementation
+ """
+
+ # Contents to be inserted
+ contents = [(1, 2, 3), (2, 2, 3), (3, 3, 2), (4, 5, 5)]
+ schema.Stimulus.insert(contents)
+
+ # Query the whole table
+ test_query = schema.Stimulus()
+
+ # Use dj.U to create a list of unique contrast and brightness combinations
+ result = dj.U("contrast", "brightness") & test_query
+ expected_result = [
+ {"contrast": 2, "brightness": 3},
+ {"contrast": 3, "brightness": 2},
+ {"contrast": 5, "brightness": 5},
+ ]
+
+ fetched_result = result.to_dicts(order_by=("contrast", "brightness"))
+ schema.Stimulus.delete_quick()
+ assert fetched_result == expected_result
+
+
+def test_backslash(schema_any):
+ """
+ https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/999
+ """
+ expected = "She\\Hulk"
+ schema.Parent.insert([(2, expected)])
+ q = schema.Parent & dict(name=expected)
+ assert q.fetch1("name") == expected
+ q.delete()
+
+
+def test_lazy_iteration(lang, languages):
+ """Test that iteration is lazy (uses generator)"""
+ # The new iteration is a generator
+ iter_obj = iter(lang)
+ # Should be a generator
+ import types
+
+ assert isinstance(iter_obj, types.GeneratorType)
+
+ # Each item should be a dict
+ first = next(iter_obj)
+ assert isinstance(first, dict)
+ assert "name" in first and "language" in first
+
+
+def test_to_arrays_include_key(lang, languages):
+ """Test to_arrays with include_key=True returns keys as list of dicts"""
+ # Fetch with include_key=True
+ keys, names, langs = lang.to_arrays("name", "language", include_key=True, order_by="KEY")
+
+ # keys should be a list of dicts with primary key columns
+ assert isinstance(keys, list)
+ assert all(isinstance(k, dict) for k in keys)
+ assert all(set(k.keys()) == {"name", "language"} for k in keys)
+
+ # names and langs should be numpy arrays
+ assert isinstance(names, np.ndarray)
+ assert isinstance(langs, np.ndarray)
+
+ # Length should match
+ assert len(keys) == len(names) == len(langs) == len(languages)
+
+ # Keys should match the data
+ for key, name, language in zip(keys, names, langs):
+ assert key["name"] == name
+ assert key["language"] == language
+
+ # Keys should be usable for restrictions
+ first_key = keys[0]
+ restricted = lang & first_key
+ assert len(restricted) == 1
+ assert restricted.fetch1("name") == first_key["name"]
+
+
+def test_to_arrays_include_key_single_attr(subject):
+ """Test to_arrays include_key with single attribute"""
+ keys, species = subject.to_arrays("species", include_key=True)
+
+ assert isinstance(keys, list)
+ assert isinstance(species, np.ndarray)
+ assert len(keys) == len(species)
+
+ # Verify keys have only primary key columns
+ assert all("subject_id" in k for k in keys)
+
+
+def test_to_arrays_without_include_key(lang):
+ """Test that to_arrays without include_key doesn't return keys"""
+ result = lang.to_arrays("name", "language")
+
+ # Should return tuple of arrays, not (keys, ...)
+ assert isinstance(result, tuple)
+ assert len(result) == 2
+ names, langs = result
+ assert isinstance(names, np.ndarray)
+ assert isinstance(langs, np.ndarray)
diff --git a/tests/test_fetch_same.py b/tests/integration/test_fetch_same.py
similarity index 85%
rename from tests/test_fetch_same.py
rename to tests/integration/test_fetch_same.py
index 0c136b097..05c971836 100644
--- a/tests/test_fetch_same.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_fetch_same.py
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ class ProjData(dj.Manual):
---
resp : float
sim : float
- big : longblob
+ big :
blah : varchar(10)
"""
@@ -47,23 +47,23 @@ def schema_fetch_same(connection_test, prefix):
def test_object_conversion_one(schema_fetch_same):
- new = ProjData().proj(sub="resp").fetch("sub")
+ new = ProjData().proj(sub="resp").to_arrays("sub")
assert new.dtype == np.float64
def test_object_conversion_two(schema_fetch_same):
- [sub, add] = ProjData().proj(sub="resp", add="sim").fetch("sub", "add")
+ [sub, add] = ProjData().proj(sub="resp", add="sim").to_arrays("sub", "add")
assert sub.dtype == np.float64
assert add.dtype == np.float64
def test_object_conversion_all(schema_fetch_same):
- new = ProjData().proj(sub="resp", add="sim").fetch()
+ new = ProjData().proj(sub="resp", add="sim").to_arrays()
assert new["sub"].dtype == np.float64
assert new["add"].dtype == np.float64
def test_object_no_convert(schema_fetch_same):
- new = ProjData().fetch()
+ new = ProjData().to_arrays()
assert new["big"].dtype == "object"
assert new["blah"].dtype == "object"
diff --git a/tests/test_foreign_keys.py b/tests/integration/test_foreign_keys.py
similarity index 80%
rename from tests/test_foreign_keys.py
rename to tests/integration/test_foreign_keys.py
index b271c6c1f..014340898 100644
--- a/tests/test_foreign_keys.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_foreign_keys.py
@@ -1,6 +1,12 @@
from datajoint.declare import declare
-from .schema_advanced import *
+from tests.schema_advanced import (
+ Cell, # noqa: F401 - needed in globals for foreign key resolution
+ GlobalSynapse,
+ LocalSynapse,
+ Parent,
+ Person,
+)
def test_aliased_fk(schema_adv):
@@ -16,7 +22,7 @@ def test_aliased_fk(schema_adv):
link = person.proj(parent_name="full_name", parent="person_id")
parents = person * parent * link
parents &= dict(full_name="May K. Hall")
- assert set(parents.fetch("parent_name")) == {"Hanna R. Walters", "Russel S. James"}
+ assert set(parents.to_arrays("parent_name")) == {"Hanna R. Walters", "Russel S. James"}
delete_count = person.delete()
assert delete_count == 16
@@ -25,9 +31,7 @@ def test_describe(schema_adv):
"""real_definition should match original definition"""
for rel in (LocalSynapse, GlobalSynapse):
describe = rel.describe()
- s1 = declare(rel.full_table_name, rel.definition, schema_adv.context)[0].split(
- "\n"
- )
+ s1 = declare(rel.full_table_name, rel.definition, schema_adv.context)[0].split("\n")
s2 = declare(rel.full_table_name, describe, globals())[0].split("\n")
for c1, c2 in zip(s1, s2):
assert c1 == c2
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_gc.py b/tests/integration/test_gc.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e0c5fafca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_gc.py
@@ -0,0 +1,341 @@
+"""
+Tests for garbage collection (gc.py).
+"""
+
+from unittest.mock import MagicMock, patch
+
+import pytest
+
+from datajoint import gc
+from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
+
+
+class TestUsesContentStorage:
+ """Tests for _uses_content_storage helper function."""
+
+ def test_returns_false_for_no_adapter(self):
+ """Test that False is returned when attribute has no codec."""
+ attr = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec = None
+
+ assert gc._uses_content_storage(attr) is False
+
+ def test_returns_true_for_hash_type(self):
+ """Test that True is returned for type."""
+ attr = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec.name = "hash"
+ attr.store = "mystore"
+
+ assert gc._uses_content_storage(attr) is True
+
+ def test_returns_true_for_blob_external(self):
+ """Test that True is returned for type (external)."""
+ attr = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec.name = "blob"
+ attr.store = "mystore"
+
+ assert gc._uses_content_storage(attr) is True
+
+ def test_returns_true_for_attach_external(self):
+ """Test that True is returned for type (external)."""
+ attr = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec.name = "attach"
+ attr.store = "mystore"
+
+ assert gc._uses_content_storage(attr) is True
+
+ def test_returns_false_for_blob_internal(self):
+ """Test that False is returned for internal storage."""
+ attr = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec.name = "blob"
+ attr.store = None
+
+ assert gc._uses_content_storage(attr) is False
+
+
+class TestExtractContentRefs:
+ """Tests for _extract_content_refs helper function."""
+
+ def test_returns_empty_for_none(self):
+ """Test that empty list is returned for None value."""
+ assert gc._extract_content_refs(None) == []
+
+ def test_parses_json_string(self):
+ """Test parsing JSON string with hash."""
+ value = '{"hash": "abc123", "store": "mystore"}'
+ refs = gc._extract_content_refs(value)
+
+ assert len(refs) == 1
+ assert refs[0] == ("abc123", "mystore")
+
+ def test_parses_dict_directly(self):
+ """Test parsing dict with hash."""
+ value = {"hash": "def456", "store": None}
+ refs = gc._extract_content_refs(value)
+
+ assert len(refs) == 1
+ assert refs[0] == ("def456", None)
+
+ def test_returns_empty_for_invalid_json(self):
+ """Test that empty list is returned for invalid JSON."""
+ assert gc._extract_content_refs("not json") == []
+
+ def test_returns_empty_for_dict_without_hash(self):
+ """Test that empty list is returned for dict without hash key."""
+ assert gc._extract_content_refs({"other": "data"}) == []
+
+
+class TestUsesObjectStorage:
+ """Tests for _uses_object_storage helper function."""
+
+ def test_returns_false_for_no_adapter(self):
+ """Test that False is returned when attribute has no codec."""
+ attr = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec = None
+
+ assert gc._uses_object_storage(attr) is False
+
+ def test_returns_true_for_object_type(self):
+ """Test that True is returned for type."""
+ attr = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec.name = "object"
+
+ assert gc._uses_object_storage(attr) is True
+
+ def test_returns_false_for_other_types(self):
+ """Test that False is returned for non-object types."""
+ attr = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec = MagicMock()
+ attr.codec.name = "blob"
+
+ assert gc._uses_object_storage(attr) is False
+
+
+class TestExtractObjectRefs:
+ """Tests for _extract_object_refs helper function."""
+
+ def test_returns_empty_for_none(self):
+ """Test that empty list is returned for None value."""
+ assert gc._extract_object_refs(None) == []
+
+ def test_parses_json_string(self):
+ """Test parsing JSON string with path."""
+ value = '{"path": "schema/table/objects/pk/field_abc123", "store": "mystore"}'
+ refs = gc._extract_object_refs(value)
+
+ assert len(refs) == 1
+ assert refs[0] == ("schema/table/objects/pk/field_abc123", "mystore")
+
+ def test_parses_dict_directly(self):
+ """Test parsing dict with path."""
+ value = {"path": "test/path", "store": None}
+ refs = gc._extract_object_refs(value)
+
+ assert len(refs) == 1
+ assert refs[0] == ("test/path", None)
+
+ def test_returns_empty_for_dict_without_path(self):
+ """Test that empty list is returned for dict without path key."""
+ assert gc._extract_object_refs({"other": "data"}) == []
+
+
+class TestScan:
+ """Tests for scan function."""
+
+ def test_requires_at_least_one_schema(self):
+ """Test that at least one schema is required."""
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError, match="At least one schema must be provided"):
+ gc.scan()
+
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.scan_object_references")
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.list_stored_objects")
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.scan_references")
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.list_stored_content")
+ def test_returns_stats(self, mock_list_content, mock_scan_refs, mock_list_objects, mock_scan_objects):
+ """Test that scan returns proper statistics."""
+ # Mock content-addressed storage
+ mock_scan_refs.return_value = {"hash1", "hash2"}
+ mock_list_content.return_value = {
+ "hash1": 100,
+ "hash3": 200, # orphaned
+ }
+
+ # Mock path-addressed storage
+ mock_scan_objects.return_value = {"path/to/obj1"}
+ mock_list_objects.return_value = {
+ "path/to/obj1": 500,
+ "path/to/obj2": 300, # orphaned
+ }
+
+ mock_schema = MagicMock()
+ stats = gc.scan(mock_schema, store_name="test_store")
+
+ # Content stats
+ assert stats["content_referenced"] == 2
+ assert stats["content_stored"] == 2
+ assert stats["content_orphaned"] == 1
+ assert "hash3" in stats["orphaned_hashes"]
+
+ # Object stats
+ assert stats["object_referenced"] == 1
+ assert stats["object_stored"] == 2
+ assert stats["object_orphaned"] == 1
+ assert "path/to/obj2" in stats["orphaned_paths"]
+
+ # Combined totals
+ assert stats["referenced"] == 3
+ assert stats["stored"] == 4
+ assert stats["orphaned"] == 2
+ assert stats["orphaned_bytes"] == 500 # 200 content + 300 object
+
+
+class TestCollect:
+ """Tests for collect function."""
+
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.scan")
+ def test_dry_run_does_not_delete(self, mock_scan):
+ """Test that dry_run=True doesn't delete anything."""
+ mock_scan.return_value = {
+ "referenced": 1,
+ "stored": 2,
+ "orphaned": 1,
+ "orphaned_bytes": 100,
+ "orphaned_hashes": ["orphan_hash"],
+ "orphaned_paths": [],
+ "content_orphaned": 1,
+ "object_orphaned": 0,
+ }
+
+ mock_schema = MagicMock()
+ stats = gc.collect(mock_schema, store_name="test_store", dry_run=True)
+
+ assert stats["deleted"] == 0
+ assert stats["bytes_freed"] == 0
+ assert stats["dry_run"] is True
+
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.delete_content")
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.list_stored_content")
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.scan")
+ def test_deletes_orphaned_content(self, mock_scan, mock_list_stored, mock_delete):
+ """Test that orphaned content is deleted when dry_run=False."""
+ mock_scan.return_value = {
+ "referenced": 1,
+ "stored": 2,
+ "orphaned": 1,
+ "orphaned_bytes": 100,
+ "orphaned_hashes": ["orphan_hash"],
+ "orphaned_paths": [],
+ "content_orphaned": 1,
+ "object_orphaned": 0,
+ }
+ mock_list_stored.return_value = {"orphan_hash": 100}
+ mock_delete.return_value = True
+
+ mock_schema = MagicMock()
+ stats = gc.collect(mock_schema, store_name="test_store", dry_run=False)
+
+ assert stats["deleted"] == 1
+ assert stats["content_deleted"] == 1
+ assert stats["bytes_freed"] == 100
+ assert stats["dry_run"] is False
+ mock_delete.assert_called_once_with("orphan_hash", "test_store")
+
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.delete_object")
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.list_stored_objects")
+ @patch("datajoint.gc.scan")
+ def test_deletes_orphaned_objects(self, mock_scan, mock_list_objects, mock_delete):
+ """Test that orphaned objects are deleted when dry_run=False."""
+ mock_scan.return_value = {
+ "referenced": 1,
+ "stored": 2,
+ "orphaned": 1,
+ "orphaned_bytes": 500,
+ "orphaned_hashes": [],
+ "orphaned_paths": ["path/to/orphan"],
+ "content_orphaned": 0,
+ "object_orphaned": 1,
+ }
+ mock_list_objects.return_value = {"path/to/orphan": 500}
+ mock_delete.return_value = True
+
+ mock_schema = MagicMock()
+ stats = gc.collect(mock_schema, store_name="test_store", dry_run=False)
+
+ assert stats["deleted"] == 1
+ assert stats["object_deleted"] == 1
+ assert stats["bytes_freed"] == 500
+ assert stats["dry_run"] is False
+ mock_delete.assert_called_once_with("path/to/orphan", "test_store")
+
+
+class TestFormatStats:
+ """Tests for format_stats function."""
+
+ def test_formats_scan_stats(self):
+ """Test formatting scan statistics."""
+ stats = {
+ "referenced": 10,
+ "stored": 15,
+ "orphaned": 5,
+ "orphaned_bytes": 1024 * 1024, # 1 MB
+ "content_referenced": 6,
+ "content_stored": 8,
+ "content_orphaned": 2,
+ "content_orphaned_bytes": 512 * 1024,
+ "object_referenced": 4,
+ "object_stored": 7,
+ "object_orphaned": 3,
+ "object_orphaned_bytes": 512 * 1024,
+ }
+
+ result = gc.format_stats(stats)
+
+ assert "Referenced in database: 10" in result
+ assert "Stored in backend: 15" in result
+ assert "Orphaned (unreferenced): 5" in result
+ assert "1.00 MB" in result
+ # Check for detailed sections
+ assert "Content-Addressed Storage" in result
+ assert "Path-Addressed Storage" in result
+
+ def test_formats_collect_stats_dry_run(self):
+ """Test formatting collect statistics with dry_run."""
+ stats = {
+ "referenced": 10,
+ "stored": 15,
+ "orphaned": 5,
+ "deleted": 0,
+ "bytes_freed": 0,
+ "dry_run": True,
+ }
+
+ result = gc.format_stats(stats)
+
+ assert "DRY RUN" in result
+
+ def test_formats_collect_stats_actual(self):
+ """Test formatting collect statistics after actual deletion."""
+ stats = {
+ "referenced": 10,
+ "stored": 15,
+ "orphaned": 5,
+ "deleted": 3,
+ "content_deleted": 2,
+ "object_deleted": 1,
+ "bytes_freed": 2 * 1024 * 1024, # 2 MB
+ "errors": 2,
+ "dry_run": False,
+ }
+
+ result = gc.format_stats(stats)
+
+ assert "Deleted: 3" in result
+ assert "Content: 2" in result
+ assert "Objects: 1" in result
+ assert "2.00 MB" in result
+ assert "Errors: 2" in result
diff --git a/tests/test_groupby.py b/tests/integration/test_groupby.py
similarity index 93%
rename from tests/test_groupby.py
rename to tests/integration/test_groupby.py
index 109972760..8e13f5b64 100644
--- a/tests/test_groupby.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_groupby.py
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-from .schema_simple import A, D
+from tests.schema_simple import A, D
def test_aggr_with_proj(schema_simp):
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_hidden_job_metadata.py b/tests/integration/test_hidden_job_metadata.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c86f32d9d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_hidden_job_metadata.py
@@ -0,0 +1,273 @@
+"""Tests for hidden job metadata in computed tables."""
+
+import time
+
+import pytest
+
+import datajoint as dj
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def schema_job_metadata(connection_test, prefix):
+ """Create a schema with job metadata enabled."""
+ # Enable job metadata for this test
+ original_setting = dj.config.jobs.add_job_metadata
+ dj.config.jobs.add_job_metadata = True
+
+ schema = dj.Schema(prefix + "_job_metadata", connection=connection_test)
+
+ class Source(dj.Lookup):
+ definition = """
+ source_id : uint8
+ ---
+ value : float32
+ """
+ contents = [(1, 1.0), (2, 2.0), (3, 3.0)]
+
+ class ComputedWithMetadata(dj.Computed):
+ definition = """
+ -> Source
+ ---
+ result : float32
+ """
+
+ def make(self, key):
+ time.sleep(0.01) # Small delay to ensure non-zero duration
+ source = (Source & key).fetch1()
+ self.insert1({**key, "result": source["value"] * 2})
+
+ class ImportedWithMetadata(dj.Imported):
+ definition = """
+ -> Source
+ ---
+ imported_value : float32
+ """
+
+ def make(self, key):
+ source = (Source & key).fetch1()
+ self.insert1({**key, "imported_value": source["value"] + 10})
+
+ class ManualTable(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ manual_id : uint8
+ ---
+ data : float32
+ """
+
+ class ComputedWithPart(dj.Computed):
+ definition = """
+ -> Source
+ ---
+ total : float32
+ """
+
+ class Detail(dj.Part):
+ definition = """
+ -> master
+ detail_idx : uint8
+ ---
+ detail_value : float32
+ """
+
+ def make(self, key):
+ source = (Source & key).fetch1()
+ self.insert1({**key, "total": source["value"] * 3})
+ self.Detail.insert1({**key, "detail_idx": 0, "detail_value": source["value"]})
+
+ context = {
+ "Source": Source,
+ "ComputedWithMetadata": ComputedWithMetadata,
+ "ImportedWithMetadata": ImportedWithMetadata,
+ "ManualTable": ManualTable,
+ "ComputedWithPart": ComputedWithPart,
+ }
+
+ schema(Source, context=context)
+ schema(ComputedWithMetadata, context=context)
+ schema(ImportedWithMetadata, context=context)
+ schema(ManualTable, context=context)
+ schema(ComputedWithPart, context=context)
+
+ yield {
+ "schema": schema,
+ "Source": Source,
+ "ComputedWithMetadata": ComputedWithMetadata,
+ "ImportedWithMetadata": ImportedWithMetadata,
+ "ManualTable": ManualTable,
+ "ComputedWithPart": ComputedWithPart,
+ }
+
+ # Cleanup
+ schema.drop()
+ dj.config.jobs.add_job_metadata = original_setting
+
+
+class TestHiddenJobMetadataDeclaration:
+ """Test that hidden job metadata columns are added during declaration."""
+
+ def test_computed_table_has_hidden_metadata(self, schema_job_metadata):
+ """Computed tables should have hidden job metadata columns."""
+ table = schema_job_metadata["ComputedWithMetadata"]
+ # Force heading to load from database
+ _ = table.heading.attributes
+ # Check _attributes (includes hidden)
+ all_attrs = table.heading._attributes
+ assert all_attrs is not None, "heading._attributes should not be None after loading"
+ assert "_job_start_time" in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_duration" in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_version" in all_attrs
+ # Check that they're hidden
+ assert all_attrs["_job_start_time"].is_hidden
+ assert all_attrs["_job_duration"].is_hidden
+ assert all_attrs["_job_version"].is_hidden
+
+ def test_imported_table_has_hidden_metadata(self, schema_job_metadata):
+ """Imported tables should have hidden job metadata columns."""
+ table = schema_job_metadata["ImportedWithMetadata"]
+ _ = table.heading.attributes # Force load
+ all_attrs = table.heading._attributes
+ assert "_job_start_time" in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_duration" in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_version" in all_attrs
+
+ def test_manual_table_no_hidden_metadata(self, schema_job_metadata):
+ """Manual tables should NOT have hidden job metadata columns."""
+ table = schema_job_metadata["ManualTable"]
+ _ = table.heading.attributes # Force load
+ all_attrs = table.heading._attributes
+ assert "_job_start_time" not in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_duration" not in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_version" not in all_attrs
+
+ def test_lookup_table_no_hidden_metadata(self, schema_job_metadata):
+ """Lookup tables should NOT have hidden job metadata columns."""
+ table = schema_job_metadata["Source"]
+ _ = table.heading.attributes # Force load
+ all_attrs = table.heading._attributes
+ assert "_job_start_time" not in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_duration" not in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_version" not in all_attrs
+
+ def test_part_table_no_hidden_metadata(self, schema_job_metadata):
+ """Part tables should NOT have hidden job metadata columns."""
+ master = schema_job_metadata["ComputedWithPart"]
+ part = master.Detail
+ _ = part.heading.attributes # Force load
+ all_attrs = part.heading._attributes
+ assert "_job_start_time" not in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_duration" not in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_version" not in all_attrs
+
+
+class TestHiddenJobMetadataPopulation:
+ """Test that job metadata is populated during make()."""
+
+ def test_metadata_populated_after_make(self, schema_job_metadata):
+ """Job metadata should be populated after make() completes."""
+ table = schema_job_metadata["ComputedWithMetadata"]
+ table.populate()
+
+ # Fetch hidden attributes using raw SQL since fetch() filters them
+ conn = table.connection
+ result = conn.query(f"SELECT _job_start_time, _job_duration, _job_version FROM {table.full_table_name}").fetchall()
+ assert len(result) == 3
+
+ for row in result:
+ start_time, duration, version = row
+ assert start_time is not None
+ assert duration is not None
+ assert duration >= 0
+ # Version may be empty string if git not available
+ assert version is not None
+
+ def test_metadata_not_in_default_fetch(self, schema_job_metadata):
+ """Hidden metadata should not appear in default fetch()."""
+ table = schema_job_metadata["ComputedWithMetadata"]
+ table.populate()
+
+ result = table.to_dicts()
+ for row in result:
+ assert "_job_start_time" not in row
+ assert "_job_duration" not in row
+ assert "_job_version" not in row
+
+ def test_hidden_attrs_not_in_heading_names(self, schema_job_metadata):
+ """Hidden attributes should not appear in heading.names."""
+ table = schema_job_metadata["ComputedWithMetadata"]
+ _ = table.heading.attributes # Force load
+ names = table.heading.names
+ assert "_job_start_time" not in names
+ assert "_job_duration" not in names
+ assert "_job_version" not in names
+
+
+class TestHiddenAttributesExcludedFromJoins:
+ """Test that hidden attributes are excluded from join operations."""
+
+ def test_hidden_attrs_excluded_from_join(self, schema_job_metadata):
+ """Hidden attributes should not participate in join matching."""
+ computed = schema_job_metadata["ComputedWithMetadata"]
+ imported = schema_job_metadata["ImportedWithMetadata"]
+
+ # Populate both tables
+ computed.populate()
+ imported.populate()
+
+ # Both have _job_start_time, _job_duration, _job_version
+ # But these should NOT be used for joining
+ joined = computed * imported
+ # Should join on source_id only
+ assert len(joined) == 3
+
+ # The result heading should not have hidden attributes
+ assert "_job_start_time" not in joined.heading.names
+ assert "_job_duration" not in joined.heading.names
+
+
+class TestConfigDisabled:
+ """Test behavior when add_job_metadata is disabled."""
+
+ def test_no_metadata_when_disabled(self, connection_test, prefix):
+ """Tables should not have metadata columns when config is disabled."""
+ # Ensure disabled
+ original_setting = dj.config.jobs.add_job_metadata
+ dj.config.jobs.add_job_metadata = False
+
+ schema = dj.Schema(prefix + "_no_metadata", connection=connection_test)
+
+ class Source(dj.Lookup):
+ definition = """
+ source_id : uint8
+ """
+ contents = [(1,), (2,)]
+
+ class ComputedNoMetadata(dj.Computed):
+ definition = """
+ -> Source
+ ---
+ result : float32
+ """
+
+ def make(self, key):
+ self.insert1({**key, "result": 1.0})
+
+ context = {"Source": Source, "ComputedNoMetadata": ComputedNoMetadata}
+ schema(Source, context=context)
+ schema(ComputedNoMetadata, context=context)
+
+ try:
+ # Force heading to load from database
+ _ = ComputedNoMetadata.heading.attributes
+ # Check no hidden metadata columns
+ all_attrs = ComputedNoMetadata.heading._attributes
+ assert all_attrs is not None
+ assert "_job_start_time" not in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_duration" not in all_attrs
+ assert "_job_version" not in all_attrs
+
+ # Populate should still work
+ ComputedNoMetadata.populate()
+ assert len(ComputedNoMetadata()) == 2
+ finally:
+ schema.drop()
+ dj.config.jobs.add_job_metadata = original_setting
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_insert.py b/tests/integration/test_insert.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..de22e5565
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_insert.py
@@ -0,0 +1,509 @@
+"""Tests for insert API improvements: validate(), chunk_size, insert_dataframe(), deprecation warnings."""
+
+import warnings
+
+import numpy as np
+import pandas
+import pytest
+
+import datajoint as dj
+
+
+class SimpleTable(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ id : int32
+ ---
+ value : varchar(100)
+ score=null : float64
+ """
+
+
+class AutoIncrementTable(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ # auto_increment requires native int type
+ id : int auto_increment
+ ---
+ value : varchar(100)
+ """
+
+
+@pytest.fixture
+def schema_insert(connection_test, prefix):
+ schema = dj.Schema(
+ prefix + "_insert_test",
+ context=dict(SimpleTable=SimpleTable, AutoIncrementTable=AutoIncrementTable),
+ connection=connection_test,
+ )
+ schema(SimpleTable)
+ schema(AutoIncrementTable)
+ yield schema
+ schema.drop()
+
+
+class TestValidate:
+ """Tests for the validate() method."""
+
+ def test_validate_valid_rows(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that valid rows pass validation."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [
+ {"id": 1, "value": "one", "score": 1.0},
+ {"id": 2, "value": "two", "score": 2.0},
+ ]
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ assert result.is_valid
+ assert len(result.errors) == 0
+ assert result.rows_checked == 2
+ assert bool(result) is True
+
+ def test_validate_missing_required_field(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that missing required fields are detected."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"value": "one"}] # Missing 'id' which is PK
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ assert not result.is_valid
+ assert len(result.errors) > 0
+ assert "id" in result.errors[0][2] # Error message mentions 'id'
+
+ def test_validate_unknown_field(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that unknown fields are detected."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"id": 1, "value": "one", "unknown_field": "test"}]
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ assert not result.is_valid
+ assert any("unknown_field" in err[2] for err in result.errors)
+
+ def test_validate_ignore_extra_fields(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that ignore_extra_fields works."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"id": 1, "value": "one", "unknown_field": "test"}]
+ result = table.validate(rows, ignore_extra_fields=True)
+ assert result.is_valid
+
+ def test_validate_wrong_tuple_length(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that wrong tuple length is detected."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [(1, "one")] # Missing score
+ with warnings.catch_warnings():
+ warnings.simplefilter("ignore", DeprecationWarning)
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ assert not result.is_valid
+ assert "Incorrect number of attributes" in result.errors[0][2]
+
+ def test_validate_nullable_field(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that nullable fields can be omitted."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"id": 1, "value": "one"}] # score is nullable, can be omitted
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ assert result.is_valid
+
+ def test_validate_result_summary(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that summary() produces readable output."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"id": 1, "value": "one"}]
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ summary = result.summary()
+ assert "Validation passed" in summary
+
+ rows = [{"value": "one"}] # Missing id
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ summary = result.summary()
+ assert "Validation failed" in summary
+
+ def test_validate_raise_if_invalid(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that raise_if_invalid() raises for invalid rows."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"value": "one"}] # Missing id
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
+ result.raise_if_invalid()
+
+ def test_validate_dataframe(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test validating a DataFrame."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = pandas.DataFrame({"id": [1, 2], "value": ["one", "two"], "score": [1.0, 2.0]})
+ result = table.validate(df)
+ assert result.is_valid
+
+ def test_validate_autoincrement_pk(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that autoincrement PK doesn't require value."""
+ table = AutoIncrementTable()
+ rows = [{"value": "one"}] # id is auto_increment, can be omitted
+ result = table.validate(rows)
+ assert result.is_valid
+
+
+class TestChunkedInsert:
+ """Tests for chunk_size parameter in insert()."""
+
+ def test_chunked_insert(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test inserting with chunk_size."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"id": i, "value": f"val{i}", "score": float(i)} for i in range(100)]
+ table.insert(rows, chunk_size=10)
+ assert len(table) == 100
+
+ def test_chunked_insert_single_chunk(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test chunked insert where data fits in one chunk."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"id": i, "value": f"val{i}"} for i in range(5)]
+ table.insert(rows, chunk_size=100) # chunk_size larger than data
+ assert len(table) == 5
+
+ def test_chunked_insert_exact_chunks(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test chunked insert where data divides evenly."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"id": i, "value": f"val{i}"} for i in range(20)]
+ table.insert(rows, chunk_size=5) # 4 chunks of 5
+ assert len(table) == 20
+
+ def test_chunked_insert_with_skip_duplicates(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test chunked insert with skip_duplicates."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ rows = [{"id": i, "value": f"val{i}"} for i in range(10)]
+ table.insert(rows)
+ # Insert again with duplicates
+ more_rows = [{"id": i, "value": f"val{i}"} for i in range(15)]
+ table.insert(more_rows, chunk_size=5, skip_duplicates=True)
+ assert len(table) == 15
+
+ def test_chunked_insert_query_expression_error(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that chunk_size raises error for QueryExpression inserts."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="chunk_size is not supported"):
+ table.insert(table.proj(), chunk_size=10)
+
+
+class TestInsertDataFrame:
+ """Tests for insert_dataframe() method."""
+
+ def test_insert_dataframe_basic(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test basic DataFrame insert."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = pandas.DataFrame({"id": [1, 2, 3], "value": ["a", "b", "c"], "score": [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]})
+ table.insert_dataframe(df)
+ assert len(table) == 3
+
+ def test_insert_dataframe_index_as_pk_auto(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test auto-detection of index as PK."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ # Create DataFrame with PK as index
+ df = pandas.DataFrame({"value": ["a", "b"], "score": [1.0, 2.0]})
+ df.index = pandas.Index([1, 2], name="id")
+ table.insert_dataframe(df) # Auto-detects index as PK
+ assert len(table) == 2
+ assert set(table.to_arrays("id")) == {1, 2}
+
+ def test_insert_dataframe_index_as_pk_true(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test explicit index_as_pk=True."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = pandas.DataFrame({"value": ["a", "b"], "score": [1.0, 2.0]})
+ df.index = pandas.Index([1, 2], name="id")
+ table.insert_dataframe(df, index_as_pk=True)
+ assert len(table) == 2
+
+ def test_insert_dataframe_index_as_pk_false(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test explicit index_as_pk=False."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = pandas.DataFrame({"id": [1, 2], "value": ["a", "b"], "score": [1.0, 2.0]})
+ df = df.set_index("id") # Set id as index
+ # With index_as_pk=False, index is dropped and we need id as column
+ df = df.reset_index() # Put id back as column
+ table.insert_dataframe(df, index_as_pk=False)
+ assert len(table) == 2
+
+ def test_insert_dataframe_rangeindex_dropped(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that RangeIndex is automatically dropped."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = pandas.DataFrame({"id": [1, 2], "value": ["a", "b"], "score": [1.0, 2.0]})
+ # df has default RangeIndex which should be dropped
+ table.insert_dataframe(df)
+ assert len(table) == 2
+
+ def test_insert_dataframe_index_mismatch_error(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test error when index doesn't match PK."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = pandas.DataFrame({"value": ["a", "b"], "score": [1.0, 2.0]})
+ df.index = pandas.Index([1, 2], name="wrong_name")
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="do not match"):
+ table.insert_dataframe(df, index_as_pk=True)
+
+ def test_insert_dataframe_not_dataframe_error(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test error when not a DataFrame."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="requires a pandas DataFrame"):
+ table.insert_dataframe([{"id": 1, "value": "a"}])
+
+ def test_insert_dataframe_roundtrip(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test roundtrip: to_pandas() -> modify -> insert_dataframe()."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ # Insert initial data
+ table.insert([{"id": i, "value": f"val{i}", "score": float(i)} for i in range(3)])
+
+ # Fetch as DataFrame
+ df = table.to_pandas()
+
+ # Clear table and re-insert
+ with dj.config.override(safemode=False):
+ table.delete()
+
+ table.insert_dataframe(df)
+ assert len(table) == 3
+
+ def test_insert_dataframe_with_chunk_size(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test insert_dataframe with chunk_size."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = pandas.DataFrame({"id": range(100), "value": [f"v{i}" for i in range(100)], "score": np.arange(100.0)})
+ table.insert_dataframe(df, chunk_size=25)
+ assert len(table) == 100
+
+
+try:
+ import polars
+
+ HAS_POLARS = True
+except ImportError:
+ HAS_POLARS = False
+
+try:
+ import pyarrow
+
+ HAS_PYARROW = True
+except ImportError:
+ HAS_PYARROW = False
+
+
+@pytest.mark.skipif(not HAS_POLARS, reason="polars not installed")
+class TestPolarsInsert:
+ """Tests for Polars DataFrame insert support."""
+
+ def test_insert_polars_basic(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test inserting a Polars DataFrame."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = polars.DataFrame({"id": [1, 2, 3], "value": ["a", "b", "c"], "score": [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]})
+ table.insert(df)
+ assert len(table) == 3
+ assert set(table.to_arrays("id")) == {1, 2, 3}
+
+ def test_insert_polars_with_options(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test Polars insert with skip_duplicates and chunk_size."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = polars.DataFrame({"id": [1, 2], "value": ["a", "b"], "score": [1.0, 2.0]})
+ table.insert(df)
+
+ # Insert more with duplicates
+ df2 = polars.DataFrame({"id": [2, 3, 4], "value": ["b", "c", "d"], "score": [2.0, 3.0, 4.0]})
+ table.insert(df2, skip_duplicates=True)
+ assert len(table) == 4
+
+ def test_insert_polars_chunk_size(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test Polars insert with chunk_size."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ df = polars.DataFrame(
+ {"id": list(range(50)), "value": [f"v{i}" for i in range(50)], "score": [float(i) for i in range(50)]}
+ )
+ table.insert(df, chunk_size=10)
+ assert len(table) == 50
+
+ def test_insert_polars_roundtrip(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test roundtrip: to_polars() -> insert()."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ table.insert([{"id": i, "value": f"val{i}", "score": float(i)} for i in range(3)])
+
+ # Fetch as Polars
+ df = table.to_polars()
+ assert isinstance(df, polars.DataFrame)
+
+ # Clear and re-insert
+ with dj.config.override(safemode=False):
+ table.delete()
+
+ table.insert(df)
+ assert len(table) == 3
+
+
+@pytest.mark.skipif(not HAS_PYARROW, reason="pyarrow not installed")
+class TestArrowInsert:
+ """Tests for PyArrow Table insert support."""
+
+ def test_insert_arrow_basic(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test inserting a PyArrow Table."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ arrow_table = pyarrow.table({"id": [1, 2, 3], "value": ["a", "b", "c"], "score": [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]})
+ table.insert(arrow_table)
+ assert len(table) == 3
+ assert set(table.to_arrays("id")) == {1, 2, 3}
+
+ def test_insert_arrow_with_options(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test Arrow insert with skip_duplicates."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ arrow_table = pyarrow.table({"id": [1, 2], "value": ["a", "b"], "score": [1.0, 2.0]})
+ table.insert(arrow_table)
+
+ # Insert more with duplicates
+ arrow_table2 = pyarrow.table({"id": [2, 3, 4], "value": ["b", "c", "d"], "score": [2.0, 3.0, 4.0]})
+ table.insert(arrow_table2, skip_duplicates=True)
+ assert len(table) == 4
+
+ def test_insert_arrow_chunk_size(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test Arrow insert with chunk_size."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ arrow_table = pyarrow.table(
+ {"id": list(range(50)), "value": [f"v{i}" for i in range(50)], "score": [float(i) for i in range(50)]}
+ )
+ table.insert(arrow_table, chunk_size=10)
+ assert len(table) == 50
+
+ def test_insert_arrow_roundtrip(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test roundtrip: to_arrow() -> insert()."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ table.insert([{"id": i, "value": f"val{i}", "score": float(i)} for i in range(3)])
+
+ # Fetch as Arrow
+ arrow_table = table.to_arrow()
+ assert isinstance(arrow_table, pyarrow.Table)
+
+ # Clear and re-insert
+ with dj.config.override(safemode=False):
+ table.delete()
+
+ table.insert(arrow_table)
+ assert len(table) == 3
+
+
+class TestDeprecationWarning:
+ """Tests for positional insert deprecation warning."""
+
+ def test_positional_insert_warning(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that positional inserts emit deprecation warning."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ with pytest.warns(DeprecationWarning, match="Positional inserts"):
+ table.insert1((1, "value1", 1.0))
+
+ def test_positional_insert_multiple_warning(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that positional inserts in insert() emit warning."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ with pytest.warns(DeprecationWarning, match="Positional inserts"):
+ table.insert([(2, "value2", 2.0)])
+
+ def test_dict_insert_no_warning(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that dict inserts don't emit warning."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ with warnings.catch_warnings():
+ warnings.simplefilter("error", DeprecationWarning)
+ # Should not raise DeprecationWarning
+ table.insert1({"id": 3, "value": "value3", "score": 3.0})
+
+ def test_numpy_record_no_warning(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that numpy record inserts don't emit warning."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+ # Create numpy record
+ dtype = [("id", int), ("value", "U100"), ("score", float)]
+ record = np.array([(4, "value4", 4.0)], dtype=dtype)[0]
+ with warnings.catch_warnings():
+ warnings.simplefilter("error", DeprecationWarning)
+ # Should not raise DeprecationWarning
+ table.insert1(record)
+
+
+class TestValidationResult:
+ """Tests for ValidationResult class."""
+
+ def test_validation_result_bool(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test ValidationResult boolean behavior."""
+ valid = dj.ValidationResult(is_valid=True, errors=[], rows_checked=1)
+ invalid = dj.ValidationResult(is_valid=False, errors=[(0, "field", "error")], rows_checked=1)
+ assert bool(valid) is True
+ assert bool(invalid) is False
+
+ def test_validation_result_summary_valid(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test ValidationResult summary for valid result."""
+ result = dj.ValidationResult(is_valid=True, errors=[], rows_checked=5)
+ assert "Validation passed" in result.summary()
+ assert "5 rows checked" in result.summary()
+
+ def test_validation_result_summary_invalid(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test ValidationResult summary for invalid result."""
+ errors = [(0, "field1", "error1"), (1, "field2", "error2")]
+ result = dj.ValidationResult(is_valid=False, errors=errors, rows_checked=2)
+ summary = result.summary()
+ assert "Validation failed" in summary
+ assert "2 error(s)" in summary
+ assert "Row 0" in summary
+ assert "Row 1" in summary
+
+ def test_validation_result_summary_truncated(self, schema_insert):
+ """Test that summary truncates long error lists."""
+ errors = [(i, f"field{i}", f"error{i}") for i in range(20)]
+ result = dj.ValidationResult(is_valid=False, errors=errors, rows_checked=20)
+ summary = result.summary()
+ assert "and 10 more errors" in summary
+
+
+class AllDefaultsTable(dj.Manual):
+ """Table where all attributes have defaults."""
+
+ definition = """
+ id : int auto_increment
+ ---
+ timestamp=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP : datetime
+ notes=null : varchar(200)
+ """
+
+
+class TestEmptyInsert:
+ """Tests for inserting empty dicts (GitHub issue #1280)."""
+
+ @pytest.fixture
+ def schema_empty_insert(self, connection_test, prefix):
+ schema = dj.Schema(
+ prefix + "_empty_insert_test",
+ context=dict(AllDefaultsTable=AllDefaultsTable, SimpleTable=SimpleTable),
+ connection=connection_test,
+ )
+ schema(AllDefaultsTable)
+ schema(SimpleTable)
+ yield schema
+ schema.drop()
+
+ def test_empty_insert_all_defaults(self, schema_empty_insert):
+ """Test that empty insert succeeds when all attributes have defaults."""
+ table = AllDefaultsTable()
+ assert len(table) == 0
+
+ # Insert empty dict - should use all defaults
+ table.insert1({})
+ assert len(table) == 1
+
+ # Check that values were populated with defaults
+ row = table.fetch1()
+ assert row["id"] == 1 # auto_increment starts at 1
+ assert row["timestamp"] is not None # CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
+ assert row["notes"] is None # nullable defaults to NULL
+
+ def test_empty_insert_multiple(self, schema_empty_insert):
+ """Test inserting multiple empty dicts."""
+ table = AllDefaultsTable()
+
+ # Insert multiple empty dicts
+ table.insert([{}, {}, {}])
+ assert len(table) == 3
+
+ # Each should have unique auto_increment id
+ ids = set(table.to_arrays("id"))
+ assert ids == {1, 2, 3}
+
+ def test_empty_insert_required_fields_error(self, schema_empty_insert):
+ """Test that empty insert raises clear error when fields are required."""
+ table = SimpleTable()
+
+ # SimpleTable has required fields (id, value)
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ table.insert1({})
+
+ error_msg = str(exc_info.value)
+ assert "Cannot insert empty row" in error_msg
+ assert "require values" in error_msg
+ # Should list the required attributes
+ assert "id" in error_msg
+ assert "value" in error_msg
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_jobs.py b/tests/integration/test_jobs.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..bc00cf0f8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_jobs.py
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+"""Tests for per-table Job management (AutoPopulate 2.0)."""
+
+import random
+import string
+
+import datajoint as dj
+from datajoint.jobs import ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH, TRUNCATION_APPENDIX
+
+from tests import schema
+
+
+def test_reserve_job(clean_jobs, subject, experiment):
+ """Test job reservation, completion, and error workflows."""
+ assert subject
+
+ # Refresh jobs to create pending entries
+ experiment.jobs.refresh()
+ pending_count = len(experiment.jobs.pending)
+ assert pending_count > 0, "no pending jobs created"
+
+ # Reserve all pending jobs
+ keys = experiment.jobs.pending.keys()
+ for key in keys:
+ assert experiment.jobs.reserve(key), "failed to reserve a job"
+
+ # Try to reserve already-reserved jobs - should fail
+ for key in keys:
+ assert not experiment.jobs.reserve(key), "failed to respect reservation"
+
+ # Complete jobs
+ for key in keys:
+ experiment.jobs.complete(key)
+
+ # Check jobs are completed (or deleted if keep_completed=False)
+ if dj.config.jobs.keep_completed:
+ assert len(experiment.jobs.completed) == len(keys)
+ else:
+ assert len(experiment.jobs) == 0, "failed to free jobs"
+
+ # Refresh again to create new pending jobs
+ experiment.jobs.refresh()
+ keys = experiment.jobs.pending.keys()
+
+ # Reserve and mark as error
+ for key in keys:
+ experiment.jobs.reserve(key)
+ experiment.jobs.error(key, "error message")
+
+ # Try to reserve error jobs - should fail
+ for key in keys:
+ assert not experiment.jobs.reserve(key), "failed to ignore error jobs"
+
+ # Clear error jobs
+ experiment.jobs.errors.delete()
+ assert len(experiment.jobs) == 0, "failed to clear error jobs"
+
+
+def test_job_status_filters(clean_jobs, subject, experiment):
+ """Test job status filter properties."""
+ # Refresh to create pending jobs
+ experiment.jobs.refresh()
+
+ # All should be pending
+ total = len(experiment.jobs)
+ assert total > 0
+ assert len(experiment.jobs.pending) == total
+ assert len(experiment.jobs.reserved) == 0
+ assert len(experiment.jobs.errors) == 0
+
+ # Reserve some jobs
+ keys = experiment.jobs.pending.keys(limit=2)
+ for key in keys:
+ experiment.jobs.reserve(key)
+
+ assert len(experiment.jobs.reserved) == 2
+
+ # Mark one as error
+ experiment.jobs.error(keys[0], "test error")
+ assert len(experiment.jobs.errors) == 1
+
+
+def test_sigint(clean_jobs, schema_any):
+ """Test that KeyboardInterrupt is recorded as error."""
+ sig_int_table = schema.SigIntTable()
+ try:
+ sig_int_table.populate(reserve_jobs=True)
+ except KeyboardInterrupt:
+ pass
+
+ assert len(sig_int_table.jobs.errors) > 0, "SigInt job error not recorded"
+ status, error_message = sig_int_table.jobs.errors.fetch1("status", "error_message")
+ assert status == "error"
+ assert "KeyboardInterrupt" in error_message
+
+
+def test_sigterm(clean_jobs, schema_any):
+ """Test that SystemExit is recorded as error."""
+ sig_term_table = schema.SigTermTable()
+ try:
+ sig_term_table.populate(reserve_jobs=True)
+ except SystemExit:
+ pass
+
+ assert len(sig_term_table.jobs.errors) > 0, "SigTerm job error not recorded"
+ status, error_message = sig_term_table.jobs.errors.fetch1("status", "error_message")
+ assert status == "error"
+ assert "SIGTERM" in error_message or "SystemExit" in error_message
+
+
+def test_suppress_dj_errors(clean_jobs, schema_any):
+ """Test that DataJoint errors are suppressible without native py blobs."""
+ error_class = schema.ErrorClass()
+ with dj.config.override(enable_python_native_blobs=False):
+ error_class.populate(reserve_jobs=True, suppress_errors=True)
+ assert len(schema.DjExceptionName()) == len(error_class.jobs.errors) > 0
+
+
+def test_long_error_message(clean_jobs, subject, experiment):
+ """Test that long error messages are truncated."""
+ # Create long and short error messages
+ long_error_message = "".join(random.choice(string.ascii_letters) for _ in range(ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH + 100))
+ short_error_message = "".join(random.choice(string.ascii_letters) for _ in range(ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH // 2))
+
+ # Refresh to create pending jobs
+ experiment.jobs.refresh()
+ key = experiment.jobs.pending.keys(limit=1)[0]
+
+ # Test long error message truncation
+ experiment.jobs.reserve(key)
+ experiment.jobs.error(key, long_error_message)
+ error_message = experiment.jobs.errors.fetch1("error_message")
+ assert len(error_message) == ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH, "error message is longer than max allowed"
+ assert error_message.endswith(TRUNCATION_APPENDIX), "appropriate ending missing for truncated error message"
+ experiment.jobs.delete()
+
+ # Refresh and test short error message (not truncated)
+ experiment.jobs.refresh()
+ key = experiment.jobs.pending.keys(limit=1)[0]
+ experiment.jobs.reserve(key)
+ experiment.jobs.error(key, short_error_message)
+ error_message = experiment.jobs.errors.fetch1("error_message")
+ assert error_message == short_error_message, "error messages do not agree"
+ assert not error_message.endswith(TRUNCATION_APPENDIX), "error message should not be truncated"
+
+
+def test_long_error_stack(clean_jobs, subject, experiment):
+ """Test that long error stacks are stored correctly."""
+ # Create long error stack
+ STACK_SIZE = 89942 # Does not fit into small blob (should be 64k, but found to be higher)
+ long_error_stack = "".join(random.choice(string.ascii_letters) for _ in range(STACK_SIZE))
+
+ # Refresh to create pending jobs
+ experiment.jobs.refresh()
+ key = experiment.jobs.pending.keys(limit=1)[0]
+
+ # Test long error stack
+ experiment.jobs.reserve(key)
+ experiment.jobs.error(key, "error message", long_error_stack)
+ error_stack = experiment.jobs.errors.fetch1("error_stack")
+ assert error_stack == long_error_stack, "error stacks do not agree"
diff --git a/tests/test_json.py b/tests/integration/test_json.py
similarity index 70%
rename from tests/test_json.py
rename to tests/integration/test_json.py
index 0a819b99e..40c8074de 100644
--- a/tests/test_json.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_json.py
@@ -7,8 +7,18 @@
import datajoint as dj
from datajoint.declare import declare
-if Version(dj.conn().query("select @@version;").fetchone()[0]) < Version("8.0.0"):
- pytest.skip("These tests require MySQL >= v8.0.0", allow_module_level=True)
+
+def mysql_version_check(connection):
+ """Check if MySQL version is >= 8.0.0"""
+ version_str = connection.query("select @@version;").fetchone()[0]
+ if Version(version_str) < Version("8.0.0"):
+ pytest.skip("These tests require MySQL >= v8.0.0")
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="module", autouse=True)
+def check_mysql_version(connection_root):
+ """Automatically check MySQL version for all tests in this module"""
+ mysql_version_check(connection_root)
class Team(dj.Lookup):
@@ -67,9 +77,7 @@ class Team(dj.Lookup):
@pytest.fixture
def schema_json(connection_test, prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_json", context=dict(Team=Team), connection=connection_test
- )
+ schema = dj.Schema(prefix + "_json", context=dict(Team=Team), connection=connection_test)
schema(Team)
yield schema
schema.drop()
@@ -131,13 +139,10 @@ def test_restrict(schema_json):
assert (Team & {"car.safety_inspected": "false"}).fetch1("name") == "business"
- assert (Team & {"car.safety_inspected:unsigned": False}).fetch1(
- "name"
- ) == "business"
+ assert (Team & {"car.safety_inspected:unsigned": False}).fetch1("name") == "business"
- assert (Team & {"car.headlights[0].hyper_white": None}).fetch(
- "name", order_by="name", as_dict=True
- ) == [
+ # to_dicts returns all columns, use proj to select only name
+ assert (Team & {"car.headlights[0].hyper_white": None}).proj("name").to_dicts(order_by="name") == [
{"name": "engineering"},
{"name": "marketing"},
] # if entire record missing, JSON key is missing, or value set to JSON null
@@ -146,79 +151,62 @@ def test_restrict(schema_json):
assert (Team & {"car.tire_pressure": [34, 30, 27, 32]}).fetch1("name") == "business"
- assert (
- Team & {"car.headlights[1]": {"side": "right", "hyper_white": True}}
- ).fetch1("name") == "business"
+ assert (Team & {"car.headlights[1]": {"side": "right", "hyper_white": True}}).fetch1("name") == "business"
# sql operators
- assert (Team & "`car`->>'$.name' LIKE '%ching%'").fetch1(
- "name"
- ) == "business", "Missing substring"
+ assert (Team & "`car`->>'$.name' LIKE '%ching%'").fetch1("name") == "business", "Missing substring"
assert (Team & "`car`->>'$.length' > 30").fetch1("name") == "business", "<= 30"
- assert (
- Team & "JSON_VALUE(`car`, '$.safety_inspected' RETURNING UNSIGNED) = 0"
- ).fetch1("name") == "business", "Has `safety_inspected` set to `true`"
+ assert (Team & "JSON_VALUE(`car`, '$.safety_inspected' RETURNING UNSIGNED) = 0").fetch1(
+ "name"
+ ) == "business", "Has `safety_inspected` set to `true`"
assert (Team & "`car`->>'$.headlights[0].hyper_white' = 'null'").fetch1(
"name"
) == "engineering", "Has 1st `headlight` with `hyper_white` not set to `null`"
- assert (Team & "`car`->>'$.inspected' IS NOT NULL").fetch1(
- "name"
- ) == "engineering", "Missing `inspected` key"
+ assert (Team & "`car`->>'$.inspected' IS NOT NULL").fetch1("name") == "engineering", "Missing `inspected` key"
assert (Team & "`car`->>'$.tire_pressure' = '[34, 30, 27, 32]'").fetch1(
"name"
) == "business", "`tire_pressure` array did not match"
- assert (
- Team
- & """`car`->>'$.headlights[1]' = '{"side": "right", "hyper_white": true}'"""
- ).fetch1("name") == "business", "2nd `headlight` object did not match"
+ assert (Team & """`car`->>'$.headlights[1]' = '{"side": "right", "hyper_white": true}'""").fetch1(
+ "name"
+ ) == "business", "2nd `headlight` object did not match"
def test_proj(schema_json):
# proj necessary since we need to rename indexed value into a proper attribute name
- assert Team.proj(car_length="car.length").fetch(
- as_dict=True, order_by="car_length"
- ) == [
+ assert Team.proj(car_length="car.length").to_dicts(order_by="car_length") == [
{"name": "marketing", "car_length": None},
{"name": "business", "car_length": "100"},
{"name": "engineering", "car_length": "20.5"},
]
- assert Team.proj(car_length="car.length:decimal(4, 1)").fetch(
- as_dict=True, order_by="car_length"
- ) == [
+ assert Team.proj(car_length="car.length:decimal(4, 1)").to_dicts(order_by="car_length") == [
{"name": "marketing", "car_length": None},
{"name": "engineering", "car_length": 20.5},
{"name": "business", "car_length": 100.0},
]
- assert Team.proj(
- car_width="JSON_VALUE(`car`, '$.length' RETURNING float) - 15"
- ).fetch(as_dict=True, order_by="car_width") == [
+ assert Team.proj(car_width="JSON_VALUE(`car`, '$.length' RETURNING float) - 15").to_dicts(order_by="car_width") == [
{"name": "marketing", "car_width": None},
{"name": "engineering", "car_width": 5.5},
{"name": "business", "car_width": 85.0},
]
- assert (
- (Team & {"name": "engineering"}).proj(car_tire_pressure="car.tire_pressure")
- ).fetch1("car_tire_pressure") == "[32, 31, 33, 34]"
+ assert ((Team & {"name": "engineering"}).proj(car_tire_pressure="car.tire_pressure")).fetch1(
+ "car_tire_pressure"
+ ) == "[32, 31, 33, 34]"
assert np.array_equal(
- Team.proj(car_inspected="car.inspected").fetch(
- "car_inspected", order_by="name"
- ),
+ Team.proj(car_inspected="car.inspected").to_arrays("car_inspected", order_by="name"),
np.array([None, "true", None]),
)
assert np.array_equal(
- Team.proj(car_inspected="car.inspected:unsigned").fetch(
- "car_inspected", order_by="name"
- ),
+ Team.proj(car_inspected="car.inspected:unsigned").to_arrays("car_inspected", order_by="name"),
np.array([None, 1, None]),
)
diff --git a/tests/test_nan.py b/tests/integration/test_nan.py
similarity index 58%
rename from tests/test_nan.py
rename to tests/integration/test_nan.py
index 25e4e332b..17ec988b4 100644
--- a/tests/test_nan.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_nan.py
@@ -14,9 +14,7 @@ class NanTest(dj.Manual):
@pytest.fixture
def schema_nan(connection_test, prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_nantest", context=dict(NanTest=NanTest), connection=connection_test
- )
+ schema = dj.Schema(prefix + "_nantest", context=dict(NanTest=NanTest), connection=connection_test)
schema(NanTest)
yield schema
schema.drop()
@@ -30,7 +28,7 @@ def arr_a():
@pytest.fixture
def schema_nan_pop(schema_nan, arr_a):
rel = NanTest()
- with dj.config(safemode=False):
+ with dj.config.override(safemode=False):
rel.delete()
rel.insert(((i, value) for i, value in enumerate(arr_a)))
return schema_nan
@@ -38,15 +36,15 @@ def schema_nan_pop(schema_nan, arr_a):
def test_insert_nan(schema_nan_pop, arr_a):
"""Test fetching of null values"""
- b = NanTest().fetch("value", order_by="id")
- assert (np.isnan(arr_a) == np.isnan(b)).all(), "incorrect handling of Nans"
+ b = NanTest().to_arrays("value", order_by="id")
+ # Convert None to np.nan for comparison
+ b_float = np.array([np.nan if v is None else v for v in b], dtype=float)
+ assert (np.isnan(arr_a) == np.isnan(b_float)).all(), "incorrect handling of Nans"
assert np.allclose(
- arr_a[np.logical_not(np.isnan(arr_a))], b[np.logical_not(np.isnan(b))]
+ arr_a[np.logical_not(np.isnan(arr_a))], b_float[np.logical_not(np.isnan(b_float))]
), "incorrect storage of floats"
def test_nulls_do_not_affect_primary_keys(schema_nan_pop, arr_a):
"""Test against a case that previously caused a bug when skipping existing entries."""
- NanTest().insert(
- ((i, value) for i, value in enumerate(arr_a)), skip_duplicates=True
- )
+ NanTest().insert(((i, value) for i, value in enumerate(arr_a)), skip_duplicates=True)
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_object.py b/tests/integration/test_object.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d4d42a461
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_object.py
@@ -0,0 +1,761 @@
+"""
+Tests for the object column type.
+
+Tests cover:
+- Storage path generation
+- Insert with file, folder, and stream
+- Fetch returning ObjectRef
+- ObjectRef methods (read, open, download, listdir, walk, verify)
+- Staged insert
+- Error cases
+"""
+
+import io
+import json
+import os
+from pathlib import Path
+
+import pytest
+
+import datajoint as dj
+from datajoint.objectref import ObjectRef
+from datajoint.storage import build_object_path, generate_token, encode_pk_value
+
+from tests.schema_object import ObjectFile, ObjectFolder, ObjectMultiple, ObjectWithOther
+
+
+class TestStoragePathGeneration:
+ """Tests for storage path generation utilities."""
+
+ def test_generate_token_default_length(self):
+ """Test token generation with default length."""
+ token = generate_token()
+ assert len(token) == 8
+ # All characters should be URL-safe
+ safe_chars = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789-_"
+ assert all(c in safe_chars for c in token)
+
+ def test_generate_token_custom_length(self):
+ """Test token generation with custom length."""
+ token = generate_token(12)
+ assert len(token) == 12
+
+ def test_generate_token_minimum_length(self):
+ """Test token generation respects minimum length."""
+ token = generate_token(2) # Below minimum
+ assert len(token) == 4 # Should be clamped to minimum
+
+ def test_generate_token_maximum_length(self):
+ """Test token generation respects maximum length."""
+ token = generate_token(20) # Above maximum
+ assert len(token) == 16 # Should be clamped to maximum
+
+ def test_generate_token_uniqueness(self):
+ """Test that generated tokens are unique."""
+ tokens = [generate_token() for _ in range(100)]
+ assert len(set(tokens)) == 100
+
+ def test_encode_pk_value_integer(self):
+ """Test encoding integer primary key values."""
+ assert encode_pk_value(123) == "123"
+ assert encode_pk_value(0) == "0"
+ assert encode_pk_value(-5) == "-5"
+
+ def test_encode_pk_value_string(self):
+ """Test encoding string primary key values."""
+ assert encode_pk_value("simple") == "simple"
+ assert encode_pk_value("test_value") == "test_value"
+
+ def test_encode_pk_value_unsafe_chars(self):
+ """Test encoding strings with unsafe characters."""
+ # Slash should be URL-encoded
+ result = encode_pk_value("path/to/file")
+ assert "/" not in result or result == "path%2Fto%2Ffile"
+
+ def test_build_object_path_basic(self):
+ """Test basic object path building."""
+ path, token = build_object_path(
+ schema="myschema",
+ table="MyTable",
+ field="data_file",
+ primary_key={"id": 123},
+ ext=".dat",
+ )
+ assert "myschema" in path
+ assert "MyTable" in path
+ assert "objects" in path
+ assert "id=123" in path
+ assert "data_file_" in path
+ assert path.endswith(".dat")
+ assert len(token) == 8
+
+ def test_build_object_path_no_extension(self):
+ """Test object path building without extension."""
+ path, token = build_object_path(
+ schema="myschema",
+ table="MyTable",
+ field="data_folder",
+ primary_key={"id": 456},
+ ext=None,
+ )
+ assert not path.endswith(".")
+ assert "data_folder_" in path
+
+ def test_build_object_path_multiple_pk(self):
+ """Test object path with multiple primary key attributes."""
+ path, token = build_object_path(
+ schema="myschema",
+ table="MyTable",
+ field="raw_data",
+ primary_key={"subject_id": 1, "session_id": 2},
+ ext=".zarr",
+ )
+ assert "subject_id=1" in path
+ assert "session_id=2" in path
+
+ def test_build_object_path_with_partition(self):
+ """Test object path with partition pattern."""
+ path, token = build_object_path(
+ schema="myschema",
+ table="MyTable",
+ field="data",
+ primary_key={"subject_id": 1, "session_id": 2},
+ ext=".dat",
+ partition_pattern="{subject_id}",
+ )
+ # subject_id should be at the beginning due to partition
+ assert path.startswith("subject_id=1")
+
+
+class TestObjectRef:
+ """Tests for ObjectRef class."""
+
+ def test_from_json_string(self):
+ """Test creating ObjectRef from JSON string."""
+ json_str = json.dumps(
+ {
+ "path": "schema/Table/objects/id=1/data_abc123.dat",
+ "size": 1024,
+ "hash": None,
+ "ext": ".dat",
+ "is_dir": False,
+ "timestamp": "2025-01-15T10:30:00+00:00",
+ }
+ )
+ obj = ObjectRef.from_json(json_str)
+ assert obj.path == "schema/Table/objects/id=1/data_abc123.dat"
+ assert obj.size == 1024
+ assert obj.hash is None
+ assert obj.ext == ".dat"
+ assert obj.is_dir is False
+
+ def test_from_json_dict(self):
+ """Test creating ObjectRef from dict."""
+ data = {
+ "path": "schema/Table/objects/id=1/data_abc123.zarr",
+ "size": 5678,
+ "hash": None,
+ "ext": ".zarr",
+ "is_dir": True,
+ "timestamp": "2025-01-15T10:30:00+00:00",
+ "item_count": 42,
+ }
+ obj = ObjectRef.from_json(data)
+ assert obj.path == "schema/Table/objects/id=1/data_abc123.zarr"
+ assert obj.size == 5678
+ assert obj.is_dir is True
+ assert obj.item_count == 42
+
+ def test_from_json_zarr_style(self):
+ """Test creating ObjectRef from Zarr-style JSON with null size."""
+ data = {
+ "path": "schema/Recording/objects/id=1/neural_data_abc123.zarr",
+ "size": None,
+ "hash": None,
+ "ext": ".zarr",
+ "is_dir": True,
+ "timestamp": "2025-01-15T10:30:00+00:00",
+ }
+ obj = ObjectRef.from_json(data)
+ assert obj.path == "schema/Recording/objects/id=1/neural_data_abc123.zarr"
+ assert obj.size is None
+ assert obj.hash is None
+ assert obj.ext == ".zarr"
+ assert obj.is_dir is True
+ assert obj.item_count is None
+
+ def test_to_json(self):
+ """Test converting ObjectRef to JSON dict."""
+ from datetime import datetime, timezone
+
+ obj = ObjectRef(
+ path="schema/Table/objects/id=1/data.dat",
+ size=1024,
+ hash=None,
+ ext=".dat",
+ is_dir=False,
+ timestamp=datetime(2025, 1, 15, 10, 30, tzinfo=timezone.utc),
+ )
+ data = obj.to_json()
+ assert data["path"] == "schema/Table/objects/id=1/data.dat"
+ assert data["size"] == 1024
+ assert data["is_dir"] is False
+
+ def test_repr_file(self):
+ """Test string representation for file."""
+ from datetime import datetime, timezone
+
+ obj = ObjectRef(
+ path="test/path.dat",
+ size=1024,
+ hash=None,
+ ext=".dat",
+ is_dir=False,
+ timestamp=datetime.now(timezone.utc),
+ )
+ assert "file" in repr(obj)
+ assert "test/path.dat" in repr(obj)
+
+ def test_repr_folder(self):
+ """Test string representation for folder."""
+ from datetime import datetime, timezone
+
+ obj = ObjectRef(
+ path="test/folder.zarr",
+ size=5678,
+ hash=None,
+ ext=".zarr",
+ is_dir=True,
+ timestamp=datetime.now(timezone.utc),
+ )
+ assert "folder" in repr(obj)
+
+ def test_str(self):
+ """Test str() returns path."""
+ from datetime import datetime, timezone
+
+ obj = ObjectRef(
+ path="my/path/to/data.dat",
+ size=100,
+ hash=None,
+ ext=".dat",
+ is_dir=False,
+ timestamp=datetime.now(timezone.utc),
+ )
+ assert str(obj) == "my/path/to/data.dat"
+
+
+class TestObjectInsertFile:
+ """Tests for inserting files with object type."""
+
+ def test_insert_file(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test inserting a file."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ # Create a test file
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "test_data.dat")
+ data = os.urandom(1024)
+ with test_file.open("wb") as f:
+ f.write(data)
+
+ # Insert the file
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 1, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ # Verify record was inserted
+ assert len(table) == 1
+
+ # Cleanup
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_insert_file_with_extension(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test that file extension is preserved."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "data.csv")
+ test_file.write_text("a,b,c\n1,2,3\n")
+
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 2, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ # Fetch and check extension in metadata
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+ assert obj.ext == ".csv"
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_insert_file_nonexistent(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage):
+ """Test that inserting nonexistent file raises error."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="not found"):
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 3, "data_file": "/nonexistent/path/file.dat"})
+
+
+class TestObjectInsertFolder:
+ """Tests for inserting folders with object type."""
+
+ def test_insert_folder(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test inserting a folder."""
+ table = ObjectFolder()
+
+ # Create a test folder with files
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ data_folder = Path(source_folder, "data_folder")
+ data_folder.mkdir()
+
+ # Add some files
+ (data_folder / "file1.txt").write_text("content1")
+ (data_folder / "file2.txt").write_text("content2")
+ subdir = data_folder / "subdir"
+ subdir.mkdir()
+ (subdir / "file3.txt").write_text("content3")
+
+ # Insert the folder
+ table.insert1({"folder_id": 1, "data_folder": str(data_folder)})
+
+ assert len(table) == 1
+
+ # Fetch and verify
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_folder"]
+ assert obj.is_dir is True
+ assert obj.item_count == 3 # 3 files
+
+ table.delete()
+
+
+class TestObjectInsertStream:
+ """Tests for inserting from streams with object type."""
+
+ def test_insert_stream(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage):
+ """Test inserting from a stream."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ # Create a BytesIO stream
+ data = b"This is test data from a stream"
+ stream = io.BytesIO(data)
+
+ # Insert with extension and stream tuple
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 10, "data_file": (".txt", stream)})
+
+ assert len(table) == 1
+
+ # Fetch and verify extension
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+ assert obj.ext == ".txt"
+ assert obj.size == len(data)
+
+ table.delete()
+
+
+class TestObjectFetch:
+ """Tests for fetching object type attributes."""
+
+ def test_fetch_returns_objectref(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test that fetch returns ObjectRef."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "test.dat")
+ test_file.write_bytes(os.urandom(512))
+
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 20, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+
+ assert isinstance(obj, ObjectRef)
+ assert obj.size == 512
+ assert obj.is_dir is False
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_fetch_metadata_no_io(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test that accessing metadata does not perform I/O."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "test.dat")
+ test_file.write_bytes(os.urandom(256))
+
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 21, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+
+ # These should all work without I/O
+ assert obj.path is not None
+ assert obj.size == 256
+ assert obj.ext == ".dat"
+ assert obj.is_dir is False
+ assert obj.timestamp is not None
+
+ table.delete()
+
+
+class TestObjectRefOperations:
+ """Tests for ObjectRef file operations."""
+
+ def test_read_file(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test reading file content via ObjectRef."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "readable.dat")
+ original_data = os.urandom(128)
+ test_file.write_bytes(original_data)
+
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 30, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+
+ # Read content
+ content = obj.read()
+ assert content == original_data
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_open_file(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test opening file via ObjectRef."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "openable.txt")
+ test_file.write_text("Hello, World!")
+
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 31, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+
+ # Open and read
+ with obj.open(mode="rb") as f:
+ content = f.read()
+ assert content == b"Hello, World!"
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_download_file(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test downloading file via ObjectRef."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "downloadable.dat")
+ original_data = os.urandom(256)
+ test_file.write_bytes(original_data)
+
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 32, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+
+ # Download to new location
+ download_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("download")
+ local_path = obj.download(download_folder)
+
+ assert Path(local_path).exists()
+ assert Path(local_path).read_bytes() == original_data
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_exists(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test exists() method."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "exists.dat")
+ test_file.write_bytes(b"data")
+
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 33, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+
+ assert obj.exists() is True
+
+ table.delete()
+
+
+class TestObjectRefFolderOperations:
+ """Tests for ObjectRef folder operations."""
+
+ def test_listdir(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test listing folder contents."""
+ table = ObjectFolder()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ data_folder = Path(source_folder, "listable")
+ data_folder.mkdir()
+ (data_folder / "a.txt").write_text("a")
+ (data_folder / "b.txt").write_text("b")
+ (data_folder / "c.txt").write_text("c")
+
+ table.insert1({"folder_id": 40, "data_folder": str(data_folder)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_folder"]
+
+ contents = obj.listdir()
+ assert len(contents) == 3
+ assert "a.txt" in contents
+ assert "b.txt" in contents
+ assert "c.txt" in contents
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_walk(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test walking folder tree."""
+ table = ObjectFolder()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ data_folder = Path(source_folder, "walkable")
+ data_folder.mkdir()
+ (data_folder / "root.txt").write_text("root")
+ subdir = data_folder / "subdir"
+ subdir.mkdir()
+ (subdir / "nested.txt").write_text("nested")
+
+ table.insert1({"folder_id": 41, "data_folder": str(data_folder)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_folder"]
+
+ # Collect walk results
+ walk_results = list(obj.walk())
+ assert len(walk_results) >= 1
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_open_subpath(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test opening file within folder using subpath."""
+ table = ObjectFolder()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ data_folder = Path(source_folder, "subpathable")
+ data_folder.mkdir()
+ (data_folder / "inner.txt").write_text("inner content")
+
+ table.insert1({"folder_id": 42, "data_folder": str(data_folder)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_folder"]
+
+ with obj.open("inner.txt", mode="rb") as f:
+ content = f.read()
+ assert content == b"inner content"
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_read_on_folder_raises(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test that read() on folder raises error."""
+ table = ObjectFolder()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ data_folder = Path(source_folder, "folder")
+ data_folder.mkdir()
+ (data_folder / "file.txt").write_text("content")
+
+ table.insert1({"folder_id": 43, "data_folder": str(data_folder)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_folder"]
+
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="Cannot read"):
+ obj.read()
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_listdir_on_file_raises(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test that listdir() on file raises error."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "file.dat")
+ test_file.write_bytes(b"data")
+
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 44, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="Cannot listdir"):
+ obj.listdir()
+
+ table.delete()
+
+
+class TestObjectMultiple:
+ """Tests for tables with multiple object attributes."""
+
+ def test_multiple_objects(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test inserting multiple object attributes."""
+ table = ObjectMultiple()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ raw_file = Path(source_folder, "raw.dat")
+ raw_file.write_bytes(os.urandom(100))
+ processed_file = Path(source_folder, "processed.dat")
+ processed_file.write_bytes(os.urandom(200))
+
+ table.insert1(
+ {
+ "record_id": 1,
+ "raw_data": str(raw_file),
+ "processed": str(processed_file),
+ }
+ )
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ raw_obj = record["raw_data"]
+ processed_obj = record["processed"]
+
+ assert raw_obj.size == 100
+ assert processed_obj.size == 200
+ assert raw_obj.path != processed_obj.path
+
+ table.delete()
+
+
+class TestObjectWithOtherAttributes:
+ """Tests for object type mixed with other attributes."""
+
+ def test_object_with_other(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test table with object and other attribute types."""
+ table = ObjectWithOther()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "data.bin")
+ test_file.write_bytes(os.urandom(64))
+
+ table.insert1(
+ {
+ "subject_id": 1,
+ "session_id": 1,
+ "name": "Test Session",
+ "data_file": str(test_file),
+ "notes": "Some notes here",
+ }
+ )
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ assert record["name"] == "Test Session"
+ assert record["notes"] == "Some notes here"
+ assert isinstance(record["data_file"], ObjectRef)
+ assert record["data_file"].size == 64
+
+ table.delete()
+
+
+class TestObjectVerify:
+ """Tests for ObjectRef verification."""
+
+ def test_verify_file(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage, tmpdir_factory):
+ """Test verifying file integrity."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ source_folder = tmpdir_factory.mktemp("source")
+ test_file = Path(source_folder, "verifiable.dat")
+ test_file.write_bytes(os.urandom(128))
+
+ table.insert1({"file_id": 50, "data_file": str(test_file)})
+
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+
+ # Should not raise
+ assert obj.verify() is True
+
+ table.delete()
+
+
+class TestStagedInsert:
+ """Tests for staged insert operations."""
+
+ def test_staged_insert_basic(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage):
+ """Test basic staged insert."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ with table.staged_insert1 as staged:
+ staged.rec["file_id"] = 60
+
+ # Write directly to storage
+ with staged.open("data_file", ".dat") as f:
+ f.write(b"staged data content")
+
+ # No need to assign - metadata computed on exit
+
+ # Verify record was inserted
+ assert len(table) == 1
+ record = table.fetch1()
+ obj = record["data_file"]
+ assert obj.ext == ".dat"
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_staged_insert_exception_cleanup(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage):
+ """Test that staged insert cleans up on exception."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ try:
+ with table.staged_insert1 as staged:
+ staged.rec["file_id"] = 61
+
+ with staged.open("data_file", ".dat") as f:
+ f.write(b"will be cleaned up")
+
+ raise ValueError("Simulated error")
+ except ValueError:
+ pass
+
+ # No record should be inserted
+ assert len(table) == 0
+
+ def test_staged_insert_store_method(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage):
+ """Test staged insert store() method returns FSMap."""
+ import fsspec
+
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ with table.staged_insert1 as staged:
+ staged.rec["file_id"] = 62
+
+ store = staged.store("data_file", ".zarr")
+ assert isinstance(store, fsspec.FSMap)
+
+ # Write some data
+ store["test_key"] = b"test_value"
+
+ assert len(table) == 1
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_staged_insert_fs_property(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage):
+ """Test staged insert fs property returns filesystem."""
+ import fsspec
+
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ with table.staged_insert1 as staged:
+ staged.rec["file_id"] = 63
+
+ fs = staged.fs
+ assert isinstance(fs, fsspec.AbstractFileSystem)
+
+ # Just open and write to test fs works
+ with staged.open("data_file", ".txt") as f:
+ f.write(b"test")
+
+ table.delete()
+
+ def test_staged_insert_missing_pk_raises(self, schema_obj, mock_object_storage):
+ """Test that staged insert raises if PK not set before store()."""
+ table = ObjectFile()
+
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="Primary key"):
+ with table.staged_insert1 as staged:
+ # Don't set primary key
+ staged.store("data_file", ".dat")
diff --git a/tests/test_privileges.py b/tests/integration/test_privileges.py
similarity index 69%
rename from tests/test_privileges.py
rename to tests/integration/test_privileges.py
index 2bf67a386..0939823a0 100644
--- a/tests/test_privileges.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_privileges.py
@@ -1,10 +1,8 @@
-import os
-
import pytest
import datajoint as dj
-from . import schema, schema_privileges
+from tests import schema, schema_privileges
namespace = locals()
@@ -79,42 +77,36 @@ class TestUnprivileged:
def test_fail_create_schema(self, connection_djview):
"""creating a schema with no CREATE privilege"""
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- return dj.Schema(
- "forbidden_schema", namespace, connection=connection_djview
- )
+ return dj.Schema("forbidden_schema", namespace, connection=connection_djview)
def test_insert_failure(self, connection_djview, schema_any):
- unprivileged = dj.Schema(
- schema_any.database, namespace, connection=connection_djview
- )
+ unprivileged = dj.Schema(schema_any.database, namespace, connection=connection_djview)
unprivileged.spawn_missing_classes()
- assert issubclass(Language, dj.Lookup) and len(Language()) == len(
+ UnprivilegedLanguage = namespace["Language"]
+ assert issubclass(UnprivilegedLanguage, dj.Lookup) and len(UnprivilegedLanguage()) == len(
schema.Language()
), "failed to spawn missing classes"
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- Language().insert1(("Socrates", "Greek"))
+ UnprivilegedLanguage().insert1(("Socrates", "Greek"))
def test_failure_to_create_table(self, connection_djview, schema_any):
- unprivileged = dj.Schema(
- schema_any.database, namespace, connection=connection_djview
- )
-
- @unprivileged
- class Try(dj.Manual):
- definition = """ # should not matter really
- id : int
- ---
- value : float
- """
+ """Table declaration should raise AccessError when user lacks CREATE privilege."""
+ unprivileged = dj.Schema(schema_any.database, namespace, connection=connection_djview)
- with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- Try().insert1((1, 1.5))
+ # Should raise AccessError at declaration time, not silently fail
+ with pytest.raises(dj.errors.AccessError):
+
+ @unprivileged
+ class Try(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """ # should not matter really
+ id : int
+ ---
+ value : float
+ """
class TestSubset:
def test_populate_activate(self, connection_djsubset, schema_priv, prefix):
- schema_priv.activate(
- f"{prefix}_schema_privileges", create_schema=True, create_tables=False
- )
+ schema_priv.activate(f"{prefix}_schema_privileges", create_schema=True, create_tables=False)
schema_privileges.Child.populate()
assert schema_privileges.Child.progress(display=False)[0] == 0
diff --git a/tests/test_reconnection.py b/tests/integration/test_reconnection.py
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/test_reconnection.py
rename to tests/integration/test_reconnection.py
diff --git a/tests/test_relation.py b/tests/integration/test_relation.py
similarity index 84%
rename from tests/test_relation.py
rename to tests/integration/test_relation.py
index 565e1eafa..ea7d79d54 100644
--- a/tests/test_relation.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_relation.py
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
import datajoint as dj
from datajoint.table import Table
-from . import schema
+from tests import schema
def test_contents(user, subject):
@@ -19,13 +19,13 @@ def test_contents(user, subject):
# test contents
assert user
assert len(user) == len(user.contents)
- u = user.fetch(order_by=["username"])
+ u = user.to_arrays(order_by=["username"])
assert list(u["username"]) == sorted([s[0] for s in user.contents])
# test prepare
assert subject
assert len(subject) == len(subject.contents)
- u = subject.fetch(order_by=["subject_id"])
+ u = subject.to_arrays(order_by=["subject_id"])
assert list(u["subject_id"]) == sorted([s[0] for s in subject.contents])
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ def test_wrong_insert_type(user):
user.insert1(3)
-def test_insert_select(subject, test, test2):
+def test_insert_select(clean_test_tables, subject, test, test2):
test2.delete()
test2.insert(test)
assert len(test2) == len(test)
@@ -98,19 +98,19 @@ def test_insert_select(subject, test, test2):
assert len(subject) == 2 * original_length
-def test_insert_pandas_roundtrip(test, test2):
+def test_insert_pandas_roundtrip(clean_test_tables, test, test2):
"""ensure fetched frames can be inserted"""
test2.delete()
n = len(test)
assert n > 0
- df = test.fetch(format="frame")
+ df = test.to_pandas()
assert isinstance(df, pandas.DataFrame)
assert len(df) == n
test2.insert(df)
assert len(test2) == n
-def test_insert_pandas_userframe(test, test2):
+def test_insert_pandas_userframe(clean_test_tables, test, test2):
"""
ensure simple user-created frames (1 field, non-custom index)
can be inserted without extra index adjustment
@@ -118,50 +118,50 @@ def test_insert_pandas_userframe(test, test2):
test2.delete()
n = len(test)
assert n > 0
- df = pandas.DataFrame(test.fetch())
+ df = pandas.DataFrame(test.to_arrays())
assert isinstance(df, pandas.DataFrame)
assert len(df) == n
test2.insert(df)
assert len(test2) == n
-def test_insert_select_ignore_extra_fields0(test, test_extra):
+def test_insert_select_ignore_extra_fields0(clean_test_tables, test, test_extra):
"""need ignore extra fields for insert select"""
- test_extra.insert1((test.fetch("key").max() + 1, 0, 0))
+ test_extra.insert1((test.to_arrays("key").max() + 1, 0, 0))
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
test.insert(test_extra)
-def test_insert_select_ignore_extra_fields1(test, test_extra):
+def test_insert_select_ignore_extra_fields1(clean_test_tables, test, test_extra):
"""make sure extra fields works in insert select"""
test_extra.delete()
- keyno = test.fetch("key").max() + 1
+ keyno = test.to_arrays("key").max() + 1
test_extra.insert1((keyno, 0, 0))
test.insert(test_extra, ignore_extra_fields=True)
- assert keyno in test.fetch("key")
+ assert keyno in test.to_arrays("key")
-def test_insert_select_ignore_extra_fields2(test_no_extra, test):
+def test_insert_select_ignore_extra_fields2(clean_test_tables, test_no_extra, test):
"""make sure insert select still works when ignoring extra fields when there are none"""
test_no_extra.delete()
test_no_extra.insert(test, ignore_extra_fields=True)
-def test_insert_select_ignore_extra_fields3(test, test_no_extra, test_extra):
+def test_insert_select_ignore_extra_fields3(clean_test_tables, test, test_no_extra, test_extra):
"""make sure insert select works for from query result"""
# Recreate table state from previous tests
- keyno = test.fetch("key").max() + 1
+ keyno = test.to_arrays("key").max() + 1
test_extra.insert1((keyno, 0, 0))
test.insert(test_extra, ignore_extra_fields=True)
- assert len(test_extra.fetch("key")), "test_extra is empty"
+ assert len(test_extra.to_arrays("key")), "test_extra is empty"
test_no_extra.delete()
- assert len(test_extra.fetch("key")), "test_extra is empty"
- keystr = str(test_extra.fetch("key").max())
+ assert len(test_extra.to_arrays("key")), "test_extra is empty"
+ keystr = str(test_extra.to_arrays("key").max())
test_no_extra.insert((test_extra & "`key`=" + keystr), ignore_extra_fields=True)
-def test_skip_duplicates(test_no_extra, test):
+def test_skip_duplicates(clean_test_tables, test_no_extra, test):
"""test that skip_duplicates works when inserting from another table"""
test_no_extra.delete()
test_no_extra.insert(test, ignore_extra_fields=True, skip_duplicates=True)
@@ -182,9 +182,7 @@ def test_replace(subject):
skip_duplicates=True,
)
assert date != str((subject & key).fetch1("date_of_birth")), "inappropriate replace"
- subject.insert1(
- dict(key, real_id=7, date_of_birth=date, subject_notes=""), replace=True
- )
+ subject.insert1(dict(key, real_id=7, date_of_birth=date, subject_notes=""), replace=True)
assert date == str((subject & key).fetch1("date_of_birth")), "replace failed"
@@ -248,7 +246,7 @@ def test_blob_insert(img):
"""Tests inserting and retrieving blobs."""
X = np.random.randn(20, 10)
img.insert1((1, X))
- Y = img.fetch()[0]["img"]
+ Y = img.to_arrays()[0]["img"]
assert np.all(X == Y), "Inserted and retrieved image are not identical"
@@ -258,7 +256,7 @@ def test_drop(trash):
with patch.object(dj.utils, "input", create=True, return_value="yes"):
trash.drop()
try:
- trash.fetch()
+ trash.to_arrays()
raise Exception("Fetched after table dropped.")
except dj.DataJointError:
pass
@@ -277,9 +275,7 @@ def relation_selector(attr):
tiers = [dj.Imported, dj.Manual, dj.Lookup, dj.Computed]
for name, rel in getmembers(schema, relation_selector):
- assert re.match(
- rel.tier_regexp, rel.table_name
- ), "Regular expression does not match for {name}".format(name=name)
+ assert re.match(rel.tier_regexp, rel.table_name), "Regular expression does not match for {name}".format(name=name)
for tier in tiers:
assert issubclass(rel, tier) or not re.match(
tier.tier_regexp, rel.table_name
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_relation_u.py b/tests/integration/test_relation_u.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f3f7a6cbb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_relation_u.py
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+from pytest import raises
+
+import datajoint as dj
+
+from tests.schema import Language, TTest
+from tests.schema_simple import ArgmaxTest
+
+
+def test_restriction(lang, languages, trial):
+ """Test dj.U restriction semantics."""
+ language_set = {s[1] for s in languages}
+ rel = dj.U("language") & lang
+ assert list(rel.heading.names) == ["language"]
+ assert len(rel) == len(language_set)
+ assert set(rel.to_arrays("language")) == language_set
+ # dj.U & table promotes attributes to PK
+ assert list((dj.U("start_time") & trial).primary_key) == ["start_time"]
+
+
+def test_invalid_restriction(schema_any):
+ with raises(dj.DataJointError):
+ dj.U("color") & dict(color="red")
+
+
+def test_ineffective_restriction(lang):
+ rel = lang & dj.U("language")
+ assert rel.make_sql() == lang.make_sql()
+
+
+def test_join_with_u_removed(experiment):
+ """Test that table * dj.U(...) raises an error (removed in 2.0)."""
+ with raises(dj.DataJointError):
+ experiment * dj.U("experiment_date")
+
+ with raises(dj.DataJointError):
+ dj.U("experiment_date") * experiment
+
+
+def test_invalid_join(schema_any):
+ """Test that dj.U * non-QueryExpression raises an error."""
+ with raises(dj.DataJointError):
+ dj.U("language") * dict(language="English")
+
+
+def test_repr_without_attrs(schema_any):
+ """test dj.U() display"""
+ query = dj.U().aggr(Language, n="count(*)")
+ repr(query)
+
+
+def test_aggregations(schema_any):
+ lang = Language()
+ # test total aggregation on expression object
+ n1 = dj.U().aggr(lang, n="count(*)").fetch1("n")
+ assert n1 == len(lang.to_arrays())
+ # test total aggregation on expression class
+ n2 = dj.U().aggr(Language, n="count(*)").fetch1("n")
+ assert n1 == n2
+ rel = dj.U("language").aggr(Language, number_of_speakers="count(*)")
+ assert len(rel) == len(set(lang[1] for lang in Language.contents))
+ assert (rel & 'language="English"').fetch1("number_of_speakers") == 3
+
+
+def test_argmax(schema_any):
+ """Test argmax pattern using aggregation and restriction."""
+ rel = TTest()
+ # Get the maximum value using aggregation
+ max_val = dj.U().aggr(rel, mx="max(value)").fetch1("mx")
+ # Get tuples with that value
+ mx = rel & f"value={max_val}"
+ assert mx.to_arrays("value")[0] == max(rel.to_arrays("value"))
+
+
+def test_aggr(schema_any, schema_simp):
+ """Test aggregation with dj.U - the old * pattern is removed."""
+ rel = ArgmaxTest()
+ # The old pattern using dj.U("val") * rel is no longer supported
+ # Use aggregation directly instead
+ agg = dj.U("secondary_key").aggr(rel, min_val="min(val)")
+ # Verify aggregation works
+ assert len(agg) > 0
diff --git a/tests/test_relational_operand.py b/tests/integration/test_relational_operand.py
similarity index 61%
rename from tests/test_relational_operand.py
rename to tests/integration/test_relational_operand.py
index 2dbea672e..eea53288e 100644
--- a/tests/test_relational_operand.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_relational_operand.py
@@ -9,8 +9,24 @@
import datajoint as dj
from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
-from .schema import *
-from .schema_simple import *
+from tests.schema import Child, Ephys, Experiment, Parent, SessionA, SessionDateA, SessionStatusA, SubjectA, TTest3, Trial
+from tests.schema_simple import (
+ F,
+ IJ,
+ JI,
+ L,
+ A,
+ B,
+ D,
+ E,
+ DataA,
+ DataB,
+ KeyPK,
+ OutfitLaunch,
+ ReservedWord,
+ SelectPK,
+ TTestUpdate,
+)
@pytest.fixture
@@ -61,17 +77,13 @@ def test_rename(schema_simp_pop):
# test renaming
x = B().proj(i="id_a") & "i in (1,2,3,4)"
lenx = len(x)
- assert len(x) == len(
- B() & "id_a in (1,2,3,4)"
- ), "incorrect restriction of renamed attributes"
+ assert len(x) == len(B() & "id_a in (1,2,3,4)"), "incorrect restriction of renamed attributes"
assert len(x & "id_b in (1,2)") == len(
B() & "id_b in (1,2) and id_a in (1,2,3,4)"
), "incorrect restriction of renamed restriction"
assert len(x) == lenx, "restriction modified original"
y = x.proj(j="i")
- assert len(y) == len(
- B() & "id_a in (1,2,3,4)"
- ), "incorrect projection of restriction"
+ assert len(y) == len(B() & "id_a in (1,2,3,4)"), "incorrect projection of restriction"
z = y & "j in (3, 4, 5, 6)"
assert len(z) == len(B() & "id_a in (3,4)"), "incorrect nested subqueries"
@@ -92,24 +104,16 @@ def test_join(schema_simp_pop):
y = L()
rel = x * y
assert len(rel) == len(x) * len(y), "incorrect join"
- assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(
- rel.heading.names
- ), "incorrect join heading"
- assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(
- rel.primary_key
- ), "incorrect join primary_key"
+ assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(rel.heading.names), "incorrect join heading"
+ assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(rel.primary_key), "incorrect join primary_key"
# Test cartesian product of restricted relations
x = A() & "cond_in_a=1"
y = L() & "cond_in_l=1"
rel = x * y
assert len(rel) == len(x) * len(y), "incorrect join"
- assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(
- rel.heading.names
- ), "incorrect join heading"
- assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(
- rel.primary_key
- ), "incorrect join primary_key"
+ assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(rel.heading.names), "incorrect join heading"
+ assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(rel.primary_key), "incorrect join primary_key"
# Test join with common attributes
cond = A() & "cond_in_a=1"
@@ -118,36 +122,22 @@ def test_join(schema_simp_pop):
rel = x * y
assert len(rel) >= len(x) and len(rel) >= len(y), "incorrect join"
assert not rel - cond, "incorrect join, restriction, or antijoin"
- assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(
- rel.heading.names
- ), "incorrect join heading"
- assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(
- rel.primary_key
- ), "incorrect join primary_key"
+ assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(rel.heading.names), "incorrect join heading"
+ assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(rel.primary_key), "incorrect join primary_key"
# test renamed join
- x = B().proj(
- i="id_a"
- ) # rename the common attribute to achieve full cartesian product
+ x = B().proj(i="id_a") # rename the common attribute to achieve full cartesian product
y = D()
rel = x * y
assert len(rel) == len(x) * len(y), "incorrect join"
- assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(
- rel.heading.names
- ), "incorrect join heading"
- assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(
- rel.primary_key
- ), "incorrect join primary_key"
+ assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(rel.heading.names), "incorrect join heading"
+ assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(rel.primary_key), "incorrect join primary_key"
x = B().proj(a="id_a")
y = D()
rel = x * y
assert len(rel) == len(x) * len(y), "incorrect join"
- assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(
- rel.heading.names
- ), "incorrect join heading"
- assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(
- rel.primary_key
- ), "incorrect join primary_key"
+ assert set(x.heading.names).union(y.heading.names) == set(rel.heading.names), "incorrect join heading"
+ assert set(x.primary_key).union(y.primary_key) == set(rel.primary_key), "incorrect join primary_key"
# test pairing
# Approach 1: join then restrict
@@ -175,7 +165,7 @@ def test_issue_376(schema_any_pop):
def test_issue_463(schema_simp_pop):
- assert ((A & B) * B).fetch().size == len(A * B)
+ assert ((A & B) * B).to_arrays().size == len(A * B)
def test_project(schema_simp_pop):
@@ -187,53 +177,45 @@ def test_project(schema_simp_pop):
# projection after restriction
cond = L() & "cond_in_l"
assert len(D() & cond) + len(D() - cond) == len(D()), "failed semijoin or antijoin"
- assert len((D() & cond).proj()) == len((D() & cond)), (
- "projection failed: altered its argument" "s cardinality"
- )
+ assert len((D() & cond).proj()) == len((D() & cond)), "projection failed: altered its arguments cardinality"
-def test_rename_non_dj_attribute(
- connection_test, schema_simp_pop, schema_any_pop, prefix
-):
+def test_rename_non_dj_attribute(connection_test, schema_simp_pop, schema_any_pop, prefix):
schema = prefix + "_test1"
- connection_test.query(
- f"CREATE TABLE {schema}.test_table (oldID int PRIMARY KEY)"
- ).fetchall()
- mySchema = dj.VirtualModule(schema, schema)
+ connection_test.query(f"CREATE TABLE {schema}.test_table (oldID int PRIMARY KEY)").fetchall()
+ mySchema = dj.VirtualModule(schema, schema, connection=connection_test)
assert (
- "oldID"
- not in mySchema.TestTable.proj(new_name="oldID").heading.attributes.keys()
+ "oldID" not in mySchema.TestTable.proj(new_name="oldID").heading.attributes.keys()
), "Failed to rename attribute correctly"
connection_test.query(f"DROP TABLE {schema}.test_table")
def test_union(schema_simp_pop):
- x = set(zip(*IJ.fetch("i", "j")))
- y = set(zip(*JI.fetch("i", "j")))
- assert (
- len(x) > 0 and len(y) > 0 and len(IJ() * JI()) < len(x)
- ) # ensure the IJ and JI are non-trivial
- z = set(zip(*(IJ + JI).fetch("i", "j"))) # union
+ x = set(zip(*IJ.to_arrays("i", "j")))
+ y = set(zip(*JI.to_arrays("i", "j")))
+ # IJ and JI have attributes i,j from different origins, so use semantic_check=False
+ assert len(x) > 0 and len(y) > 0 and len(IJ().join(JI(), semantic_check=False)) < len(x)
+ z = set(zip(*(IJ + JI).to_arrays("i", "j"))) # union
assert x.union(y) == z
assert len(IJ + JI) == len(z)
-def test_outer_union_fail(schema_simp_pop):
+def test_outer_union_fail_1(schema_simp_pop):
"""Union of two tables with different primary keys raises an error."""
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
A() + B()
-def test_outer_union_fail(schema_any_pop):
+def test_outer_union_fail_2(schema_any_pop):
"""Union of two tables with different primary keys raises an error."""
t = Trial + Ephys
- t.fetch()
+ t.to_arrays()
assert set(t.heading.names) == set(Trial.heading.names) | set(Ephys.heading.names)
len(t)
def test_preview(schema_simp_pop):
- with dj.config(display__limit=7):
+ with dj.config.override(display__limit=7):
x = A().proj(a="id_a")
s = x.preview()
assert len(s.split("\n")) == len(x) + 2
@@ -242,25 +224,21 @@ def test_preview(schema_simp_pop):
def test_heading_repr(schema_simp_pop):
x = A * D
s = repr(x.heading)
- assert len(
- list(
- 1
- for g in s.split("\n")
- if g.strip() and not g.strip().startswith(("-", "#"))
- )
- ) == len(x.heading.attributes)
+ assert len(list(1 for g in s.split("\n") if g.strip() and not g.strip().startswith(("-", "#")))) == len(
+ x.heading.attributes
+ )
def test_aggregate(schema_simp_pop):
- x = B().aggregate(B.C())
+ # With exclude_nonmatching=True, only rows with matches are kept (INNER JOIN)
+ x = B().aggregate(B.C(), exclude_nonmatching=True)
assert len(x) == len(B() & B.C())
- x = B().aggregate(B.C(), keep_all_rows=True)
+ # Default behavior now keeps all rows (LEFT JOIN)
+ x = B().aggregate(B.C())
assert len(x) == len(B()) # test LEFT join
- assert len((x & "id_b=0").fetch()) == len(
- B() & "id_b=0"
- ) # test restricted aggregation
+ assert len((x & "id_b=0").to_arrays()) == len(B() & "id_b=0") # test restricted aggregation
x = B().aggregate(
B.C(),
@@ -268,37 +246,32 @@ def test_aggregate(schema_simp_pop):
count="count(id_c)",
mean="avg(value)",
max="max(value)",
- keep_all_rows=True,
)
assert len(x) == len(B())
y = x & "mean>0" # restricted aggregation
assert len(y) > 0
- assert all(y.fetch("mean") > 0)
- for n, count, mean, max_, key in zip(*x.fetch("n", "count", "mean", "max", dj.key)):
+ assert all(y.to_arrays("mean") > 0)
+ for n, count, mean, max_, key in zip(*x.to_arrays("n", "count", "mean", "max"), x.keys()):
assert n == count, "aggregation failed (count)"
- values = (B.C() & key).fetch("value")
+ values = (B.C() & key).to_arrays("value")
assert bool(len(values)) == bool(n), "aggregation failed (restriction)"
if n:
- assert np.isclose(
- mean, values.mean(), rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-5
- ), "aggregation failed (mean)"
- assert np.isclose(
- max_, values.max(), rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-5
- ), "aggregation failed (max)"
+ assert np.isclose(mean, values.mean(), rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-5), "aggregation failed (mean)"
+ assert np.isclose(max_, values.max(), rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-5), "aggregation failed (max)"
def test_aggr(schema_simp_pop):
- x = B.aggr(B.C)
+ # With exclude_nonmatching=True, only rows with matches are kept (INNER JOIN)
+ x = B.aggr(B.C, exclude_nonmatching=True)
l1 = len(x)
l2 = len(B & B.C)
assert l1 == l2
- x = B().aggr(B.C(), keep_all_rows=True)
+ # Default behavior now keeps all rows (LEFT JOIN)
+ x = B().aggr(B.C())
assert len(x) == len(B()) # test LEFT join
- assert len((x & "id_b=0").fetch()) == len(
- B() & "id_b=0"
- ) # test restricted aggregation
+ assert len((x & "id_b=0").to_arrays()) == len(B() & "id_b=0") # test restricted aggregation
x = B().aggr(
B.C(),
@@ -306,23 +279,18 @@ def test_aggr(schema_simp_pop):
count="count(id_c)",
mean="avg(value)",
max="max(value)",
- keep_all_rows=True,
)
assert len(x) == len(B())
y = x & "mean>0" # restricted aggregation
assert len(y) > 0
- assert all(y.fetch("mean") > 0)
- for n, count, mean, max_, key in zip(*x.fetch("n", "count", "mean", "max", dj.key)):
+ assert all(y.to_arrays("mean") > 0)
+ for n, count, mean, max_, key in zip(*x.to_arrays("n", "count", "mean", "max"), x.keys()):
assert n == count, "aggregation failed (count)"
- values = (B.C() & key).fetch("value")
+ values = (B.C() & key).to_arrays("value")
assert bool(len(values)) == bool(n), "aggregation failed (restriction)"
if n:
- assert np.isclose(
- mean, values.mean(), rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-5
- ), "aggregation failed (mean)"
- assert np.isclose(
- max_, values.max(), rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-5
- ), "aggregation failed (max)"
+ assert np.isclose(mean, values.mean(), rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-5), "aggregation failed (mean)"
+ assert np.isclose(max_, values.max(), rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-5), "aggregation failed (max)"
def test_semijoin(schema_simp_pop):
@@ -331,21 +299,22 @@ def test_semijoin(schema_simp_pop):
"""
x = IJ()
y = JI()
- n = len(x & y.fetch(as_dict=True))
- m = len(x - y.fetch(as_dict=True))
+ # IJ and JI have i,j from different origins - use semantic_check=False
+ n = len(x & y.to_dicts())
+ m = len(x - y.to_dicts())
assert n > 0 and m > 0
assert len(x) == m + n
- assert len(x & y.fetch()) == n
- assert len(x - y.fetch()) == m
- semi = x & y
- anti = x - y
+ assert len(x & y.to_arrays()) == n
+ assert len(x - y.to_arrays()) == m
+ semi = x.restrict(y, semantic_check=False)
+ anti = x.restrict(dj.Not(y), semantic_check=False)
assert len(semi) == n
assert len(anti) == m
def test_pandas_fetch_and_restriction(schema_simp_pop):
q = L & "cond_in_l = 0"
- df = q.fetch(format="frame") # pandas dataframe
+ df = q.to_pandas() # pandas dataframe
assert isinstance(df, pandas.DataFrame)
assert len(E & q) == len(E & df)
@@ -383,19 +352,14 @@ def test_restrictions_by_lists(schema_simp_pop):
assert len(x - set()) == lenx, "incorrect restriction by an empty set"
assert len(x & {}) == lenx, "incorrect restriction by a tuple with no attributes"
assert len(x - {}) == 0, "incorrect restriction by a tuple with no attributes"
- assert (
- len(x & {"foo": 0}) == lenx
- ), "incorrect restriction by a tuple with no matching attributes"
- assert (
- len(x - {"foo": 0}) == 0
- ), "incorrect restriction by a tuple with no matching attributes"
- assert len(x & y) == len(x & y.fetch()), "incorrect restriction by a list"
- assert len(x - y) == len(x - y.fetch()), "incorrect restriction by a list"
+ assert len(x & {"foo": 0}) == lenx, "incorrect restriction by a tuple with no matching attributes"
+ assert len(x - {"foo": 0}) == 0, "incorrect restriction by a tuple with no matching attributes"
+ assert len(x & y) == len(x & y.to_arrays()), "incorrect restriction by a list"
+ assert len(x - y) == len(x - y.to_arrays()), "incorrect restriction by a list"
w = A()
assert len(w) > 0, "incorrect test setup: w is empty"
assert (
- bool(set(w.heading.names) & set(y.heading.names))
- != "incorrect test setup: w and y should have no common attributes"
+ bool(set(w.heading.names) & set(y.heading.names)) != "incorrect test setup: w and y should have no common attributes"
)
assert len(w) == len(w & y), "incorrect restriction without common attributes"
assert len(w - y) == 0, "incorrect restriction without common attributes"
@@ -403,7 +367,7 @@ def test_restrictions_by_lists(schema_simp_pop):
def test_datetime(schema_any_pop):
"""Test date retrieval"""
- date = Experiment().fetch("experiment_date")[0]
+ date = Experiment().to_arrays("experiment_date")[0]
e1 = Experiment() & dict(experiment_date=str(date))
e2 = Experiment() & dict(experiment_date=date)
assert len(e1) == len(e2) > 0, "Two date restriction do not yield the same result"
@@ -423,28 +387,26 @@ def test_date(schema_simp_pop):
assert (F & "id=2").fetch1("date") == new_value
F.update1(dict((F & "id=2").fetch1("KEY"), date=None))
- assert (F & "id=2").fetch1("date") == None
+ assert (F & "id=2").fetch1("date") is None
def test_join_project(schema_simp_pop):
"""Test join of projected relations with matching non-primary key"""
- q = DataA.proj() * DataB.proj()
- assert (
- len(q) == len(DataA()) == len(DataB())
- ), "Join of projected relations does not work"
+ # DataA and DataB have 'idx' from different origins, so use semantic_check=False
+ q = DataA.proj().join(DataB.proj(), semantic_check=False)
+ assert len(q) == len(DataA()) == len(DataB()), "Join of projected relations does not work"
def test_ellipsis(schema_any_pop):
- r = Experiment.proj(..., "- data_path").head(1, as_dict=True)
+ # head() now returns list of dicts by default
+ r = Experiment.proj(..., "- data_path").head(1)
assert set(Experiment.heading).difference(r[0]) == {"data_path"}
def test_update_single_key(schema_simp_pop):
"""Test that only one row can be updated"""
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- TTestUpdate.update1(
- dict(TTestUpdate.fetch1("KEY"), string_attr="my new string")
- )
+ TTestUpdate.update1(dict(TTestUpdate.fetch1("KEY"), string_attr="my new string"))
def test_update_no_primary(schema_simp_pop):
@@ -462,9 +424,7 @@ def test_update_missing_attribute(schema_simp_pop):
def test_update_string_attribute(schema_simp_pop):
"""Test replacing a string value"""
rel = TTestUpdate() & dict(primary_key=0)
- s = "".join(
- random.choice(string.ascii_uppercase + string.digits) for _ in range(10)
- )
+ s = "".join(random.choice(string.ascii_uppercase + string.digits) for _ in range(10))
TTestUpdate.update1(dict(rel.fetch1("KEY"), string_attr=s))
assert s == rel.fetch1("string_attr"), "Updated string does not match"
@@ -476,7 +436,8 @@ def test_update_numeric_attribute(schema_simp_pop):
TTestUpdate.update1(dict(rel.fetch1("KEY"), num_attr=s))
assert s == rel.fetch1("num_attr"), "Updated integer does not match"
TTestUpdate.update1(dict(rel.fetch1("KEY"), num_attr=None))
- assert np.isnan(rel.fetch1("num_attr")), "Numeric value is not NaN"
+ # NULL values are returned as None
+ assert rel.fetch1("num_attr") is None, "Numeric value is not None/NULL"
def test_update_blob_attribute(schema_simp_pop):
@@ -490,9 +451,7 @@ def test_update_blob_attribute(schema_simp_pop):
def test_reserved_words(schema_simp_pop):
"""Test the user of SQL reserved words as attributes"""
rel = ReservedWord()
- rel.insert1(
- {"key": 1, "in": "ouch", "from": "bummer", "int": 3, "select": "major pain"}
- )
+ rel.insert1({"key": 1, "in": "ouch", "from": "bummer", "int": 3, "select": "major pain"})
assert (rel & {"key": 1, "in": "ouch", "from": "bummer"}).fetch1("int") == 3
assert (rel.proj("int", double="from") & {"double": "bummer"}).fetch1("int") == 3
(rel & {"key": 1}).delete()
@@ -501,23 +460,21 @@ def test_reserved_words(schema_simp_pop):
def test_reserved_words2(schema_simp_pop):
"""Test the user of SQL reserved words as attributes"""
rel = ReservedWord()
- rel.insert1(
- {"key": 1, "in": "ouch", "from": "bummer", "int": 3, "select": "major pain"}
- )
+ rel.insert1({"key": 1, "in": "ouch", "from": "bummer", "int": 3, "select": "major pain"})
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- (rel & "key=1").fetch(
- "in"
- ) # error because reserved word `key` is not in backquotes. See issue #249
+ (rel & "key=1").to_arrays("in") # error because reserved word `key` is not in backquotes. See issue #249
def test_permissive_join_basic(schema_any_pop):
- """Verify join compatibility check is skipped for join"""
- Child @ Parent
+ """Verify join compatibility check can be skipped with semantic_check=False"""
+ # The @ operator has been removed in 2.0, use .join(semantic_check=False) instead
+ Child().join(Parent(), semantic_check=False)
def test_permissive_restriction_basic(schema_any_pop):
- """Verify join compatibility check is skipped for restriction"""
- Child ^ Parent
+ """Verify restriction compatibility check can be skipped with semantic_check=False"""
+ # The ^ operator has been removed in 2.0, use .restrict(semantic_check=False) instead
+ Child().restrict(Parent(), semantic_check=False)
def test_complex_date_restriction(schema_simp_pop):
@@ -560,9 +517,7 @@ def test_joins_with_aggregation(schema_any_pop):
SessionA * SessionStatusA & 'status="trained_1a" or status="trained_1b"',
date_trained="min(date(session_start_time))",
)
- session_dates = (
- SessionDateA * (subj_query & 'date_trained<"2020-12-21"')
- ) & "session_date result[1]["id_l"] > result[2]["id_l"]
+ assert [r["id_l"] for r in result] == [29, 28, 27]
+
+ def test_top_merge_identical_order(self, schema_simp_pop):
+ """Test that Tops with identical order_by are merged."""
+ # Both Tops specify same ordering - should merge
+ query = L() & dj.Top(10, "id_l desc") & dj.Top(5, "id_l desc")
+ result = query.to_dicts()
+ # Merged limit is min(10, 5) = 5
+ assert len(result) == 5
+ assert [r["id_l"] for r in result] == [29, 28, 27, 26, 25]
+
+ def test_top_merge_offsets_add(self, schema_simp_pop):
+ """Test that offsets are added when merging Tops."""
+ # First Top: offset 2, second Top: offset 3, inherited order
+ query = L() & dj.Top(10, "id_l desc", offset=2) & dj.Top(3, order_by=None, offset=3)
+ result = query.to_dicts()
+ # Total offset = 2 + 3 = 5, so starts at 6th element (id_l=24)
+ assert len(result) == 3
+ assert [r["id_l"] for r in result] == [24, 23, 22]
+
+ def test_preview_respects_order(self, schema_simp_pop):
+ """Test that preview (to_arrays with limit) respects Top ordering (issue #1242)."""
+ # Apply descending order with no limit (None = unlimited)
+ query = L() & dj.Top(None, order_by="id_l desc")
+ # Preview should respect the ordering (single attr returns array directly)
+ id_l = query.to_arrays("id_l", limit=5)
+ assert list(id_l) == [29, 28, 27, 26, 25]
+
+ def test_top_different_order_subquery(self, schema_simp_pop):
+ """Test that different orderings create subquery."""
+ # First Top: descending, second Top: ascending - cannot merge
+ query = L() & dj.Top(10, "id_l desc") & dj.Top(3, "id_l asc")
+ result = query.to_dicts()
+ # Second Top reorders the result of first Top
+ # First Top gives ids 29-20, second Top takes lowest 3 of those
+ assert len(result) == 3
+ assert [r["id_l"] for r in result] == [20, 21, 22]
diff --git a/tests/test_schema.py b/tests/integration/test_schema.py
similarity index 75%
rename from tests/test_schema.py
rename to tests/integration/test_schema.py
index fb3cfa752..8cf231bf5 100644
--- a/tests/test_schema.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_schema.py
@@ -6,12 +6,8 @@
import datajoint as dj
-from . import schema
-
-
-class Ephys(dj.Imported):
- definition = """ # This is already declare in ./schema.py
- """
+from tests import schema
+from tests.schema import Ephys
def relation_selector(attr):
@@ -52,14 +48,12 @@ def schema_empty_module(schema_any, schema_empty):
@pytest.fixture
def schema_empty(connection_test, schema_any, prefix):
context = {**schema.LOCALS_ANY, "Ephys": Ephys}
- schema_empty = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_test1", context=context, connection=connection_test
- )
+ schema_empty = dj.Schema(prefix + "_test1", context=context, connection=connection_test)
schema_empty(Ephys)
# load the rest of the classes
schema_empty.spawn_missing_classes(context=context)
yield schema_empty
- schema_empty.drop()
+ # Don't drop the schema since schema_any still needs it
def test_schema_size_on_disk(schema_any):
@@ -72,8 +66,10 @@ def test_schema_list(schema_any):
assert schema_any.database in schemas
-def test_drop_unauthorized():
- info_schema = dj.schema("information_schema")
+@pytest.mark.requires_mysql
+def test_drop_unauthorized(connection_test):
+ """Test that dropping information_schema raises AccessError."""
+ info_schema = dj.schema("information_schema", connection=connection_test)
with pytest.raises(dj.errors.AccessError):
info_schema.drop()
@@ -93,18 +89,12 @@ def test_namespace_population(schema_empty_module):
setattr(schema_empty_module, k, v)
for name, rel in getmembers(schema, relation_selector):
- assert hasattr(
- schema_empty_module, name
- ), "{name} not found in schema_empty".format(name=name)
- assert (
- rel.__base__ is getattr(schema_empty_module, name).__base__
- ), "Wrong tier for {name}".format(name=name)
+ assert hasattr(schema_empty_module, name), "{name} not found in schema_empty".format(name=name)
+ assert rel.__base__ is getattr(schema_empty_module, name).__base__, "Wrong tier for {name}".format(name=name)
for name_part in dir(rel):
if name_part[0].isupper() and part_selector(getattr(rel, name_part)):
- assert (
- getattr(rel, name_part).__base__ is dj.Part
- ), "Wrong tier for {name}".format(name=name_part)
+ assert getattr(rel, name_part).__base__ is dj.Part, "Wrong tier for {name}".format(name=name_part)
def test_undecorated_table():
@@ -120,6 +110,32 @@ class UndecoratedClass(dj.Manual):
print(a.full_table_name)
+def test_non_activated_schema_heading_error():
+ """
+ Tables from non-activated schemas should raise informative errors.
+ Regression test for issue #1039.
+ """
+ # Create schema without activating (no database name)
+ schema = dj.Schema()
+
+ @schema
+ class TableA(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ id : int
+ ---
+ value : float
+ """
+
+ # Accessing heading should raise a helpful error
+ instance = TableA()
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="not properly configured"):
+ _ = instance.heading
+
+ # Operations that use heading should also raise helpful errors
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="not properly configured"):
+ _ = instance.primary_key # Uses heading.primary_key
+
+
def test_reject_decorated_part(schema_any):
"""
Decorating a dj.Part table should raise an informative exception.
@@ -141,15 +157,11 @@ def test_unauthorized_database(db_creds_test):
an attempt to create a database to which user has no privileges should raise an informative exception.
"""
with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- dj.Schema(
- "unauthorized_schema", connection=dj.conn(reset=True, **db_creds_test)
- )
+ dj.Schema("unauthorized_schema", connection=dj.conn(reset=True, **db_creds_test))
def test_drop_database(db_creds_test, prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_drop_test", connection=dj.conn(reset=True, **db_creds_test)
- )
+ schema = dj.Schema(prefix + "_drop_test", connection=dj.conn(reset=True, **db_creds_test))
assert schema.exists
schema.drop()
assert not schema.exists
@@ -242,7 +254,7 @@ class Subject(dj.Manual):
name: varchar(32)
"""
- Schema_A = dj.VirtualModule("Schema_A", "Schema_A")
+ Schema_A = dj.VirtualModule("Schema_A", "Schema_A") # noqa: F841
schema2 = dj.Schema("schema_b")
diff --git a/tests/test_schema_keywords.py b/tests/integration/test_schema_keywords.py
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/test_schema_keywords.py
rename to tests/integration/test_schema_keywords.py
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_semantic_matching.py b/tests/integration/test_semantic_matching.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d8dff27fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_semantic_matching.py
@@ -0,0 +1,342 @@
+"""
+Tests for semantic matching in joins.
+
+These tests verify the lineage-based semantic matching system
+that prevents incorrect joins on attributes with the same name
+but different origins.
+"""
+
+import pytest
+
+import datajoint as dj
+from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
+
+
+# Schema definitions for semantic matching tests
+LOCALS_SEMANTIC = {}
+
+
+class Student(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ student_id : int
+ ---
+ name : varchar(100)
+ """
+
+
+class Course(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ course_id : int
+ ---
+ title : varchar(100)
+ """
+
+
+class Enrollment(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ -> Student
+ -> Course
+ ---
+ grade : varchar(2)
+ """
+
+
+class Session(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ session_id : int
+ ---
+ date : date
+ """
+
+
+class Trial(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ -> Session
+ trial_num : int
+ ---
+ stimulus : varchar(100)
+ """
+
+
+class Response(dj.Computed):
+ definition = """
+ -> Trial
+ ---
+ response_time : float
+ """
+
+
+# Tables with generic 'id' attribute for collision testing
+class TableWithId1(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ id : int
+ ---
+ value1 : int
+ """
+
+
+class TableWithId2(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ id : int
+ ---
+ value2 : int
+ """
+
+
+# Register all classes in LOCALS_SEMANTIC
+for cls in [
+ Student,
+ Course,
+ Enrollment,
+ Session,
+ Trial,
+ Response,
+ TableWithId1,
+ TableWithId2,
+]:
+ LOCALS_SEMANTIC[cls.__name__] = cls
+
+
+@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
+def schema_semantic(connection_test, prefix):
+ """Schema for semantic matching tests."""
+ schema = dj.Schema(
+ prefix + "_semantic",
+ context=LOCALS_SEMANTIC,
+ connection=connection_test,
+ )
+ # Declare tables
+ schema(Student)
+ schema(Course)
+ schema(Enrollment)
+ schema(Session)
+ schema(Trial)
+ # Skip Response for now - it's a computed table
+ schema(TableWithId1)
+ schema(TableWithId2)
+
+ yield schema
+ schema.drop()
+
+
+class TestLineageComputation:
+ """Tests for lineage computation from dependency graph."""
+
+ def test_native_primary_key_has_lineage(self, schema_semantic):
+ """Native primary key attributes should have lineage pointing to their table."""
+ student = Student()
+ lineage = student.heading["student_id"].lineage
+ assert lineage is not None
+ assert "student_id" in lineage
+ # The lineage should include schema and table name
+ assert "student" in lineage.lower()
+
+ def test_inherited_attribute_traces_to_origin(self, schema_semantic):
+ """FK-inherited attributes should trace lineage to the original table."""
+ enrollment = Enrollment()
+ # student_id is inherited from Student
+ student_lineage = enrollment.heading["student_id"].lineage
+ assert student_lineage is not None
+ assert "student" in student_lineage.lower()
+
+ # course_id is inherited from Course
+ course_lineage = enrollment.heading["course_id"].lineage
+ assert course_lineage is not None
+ assert "course" in course_lineage.lower()
+
+ def test_secondary_attribute_no_lineage(self, schema_semantic):
+ """Native secondary attributes should have no lineage."""
+ student = Student()
+ name_lineage = student.heading["name"].lineage
+ assert name_lineage is None
+
+ def test_multi_hop_inheritance(self, schema_semantic):
+ """Lineage should trace through multiple FK hops."""
+ trial = Trial()
+ # session_id in Trial is inherited from Session
+ session_lineage = trial.heading["session_id"].lineage
+ assert session_lineage is not None
+ assert "session" in session_lineage.lower()
+
+
+class TestJoinCompatibility:
+ """Tests for join compatibility checking."""
+
+ def test_join_on_shared_lineage_works(self, schema_semantic):
+ """Joining tables with shared lineage should work."""
+ student = Student()
+ enrollment = Enrollment()
+
+ # This should work - student_id has same lineage in both
+ result = student * enrollment
+ assert "student_id" in result.heading.names
+
+ def test_join_different_lineage_default_fails(self, schema_semantic):
+ """By default (semantic_check=True), non-homologous namesakes cause an error."""
+ table1 = TableWithId1()
+ table2 = TableWithId2()
+
+ # Default is semantic_check=True, this should fail
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ table1 * table2
+
+ assert "lineage" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+ assert "id" in str(exc_info.value)
+
+ def test_join_different_lineage_semantic_check_false_works(self, schema_semantic):
+ """With semantic_check=False, no lineage checking - natural join proceeds."""
+ table1 = TableWithId1()
+ table2 = TableWithId2()
+
+ # With semantic_check=False, no error even with different lineages
+ result = table1.join(table2, semantic_check=False)
+ assert "id" in result.heading.names
+
+
+class TestRestrictCompatibility:
+ """Tests for restriction compatibility checking."""
+
+ def test_restrict_shared_lineage_works(self, schema_semantic):
+ """Restricting with shared lineage should work."""
+ student = Student()
+ enrollment = Enrollment()
+
+ # This should work - student_id has same lineage
+ result = student & enrollment
+ assert "student_id" in result.heading.names
+
+ def test_restrict_different_lineage_default_fails(self, schema_semantic):
+ """By default (semantic_check=True), non-homologous namesakes cause an error."""
+ table1 = TableWithId1()
+ table2 = TableWithId2()
+
+ # Default is semantic_check=True, this should fail
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ table1 & table2
+
+ assert "lineage" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+
+ def test_restrict_different_lineage_semantic_check_false_works(self, schema_semantic):
+ """With semantic_check=False, no lineage checking - restriction proceeds."""
+ table1 = TableWithId1()
+ table2 = TableWithId2()
+
+ # With semantic_check=False, no error even with different lineages
+ result = table1.restrict(table2, semantic_check=False)
+ assert "id" in result.heading.names
+
+
+class TestProjectionLineage:
+ """Tests for lineage preservation in projections."""
+
+ def test_projection_preserves_lineage(self, schema_semantic):
+ """Projected attributes should preserve their lineage."""
+ enrollment = Enrollment()
+
+ projected = enrollment.proj("grade")
+ # Primary key attributes should still have lineage
+ assert projected.heading["student_id"].lineage is not None
+
+ def test_renamed_attribute_preserves_lineage(self, schema_semantic):
+ """Renamed attributes should preserve their original lineage."""
+ student = Student()
+
+ renamed = student.proj(sid="student_id")
+ # The renamed attribute should have the same lineage as original
+ original_lineage = student.heading["student_id"].lineage
+ renamed_lineage = renamed.heading["sid"].lineage
+ assert renamed_lineage == original_lineage
+
+ def test_computed_attribute_no_lineage(self, schema_semantic):
+ """Computed attributes should have no lineage."""
+ student = Student()
+
+ computed = student.proj(doubled="student_id * 2")
+ # Computed attributes have no lineage
+ assert computed.heading["doubled"].lineage is None
+
+
+class TestRemovedOperators:
+ """Tests for removed operators."""
+
+ def test_matmul_operator_removed(self, schema_semantic):
+ """The @ operator should raise an error."""
+ student = Student()
+ course = Course()
+
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ student @ course
+
+ assert "@" in str(exc_info.value) or "matmul" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+ assert "removed" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+
+ def test_xor_operator_removed(self, schema_semantic):
+ """The ^ operator should raise an error."""
+ student = Student()
+ course = Course()
+
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ student ^ course
+
+ assert "^" in str(exc_info.value) or "removed" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+
+
+class TestUniversalSetOperators:
+ """Tests for dj.U operations."""
+
+ def test_u_mul_raises_error(self, schema_semantic):
+ """dj.U * table should raise an error."""
+ student = Student()
+
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ dj.U("student_id") * student
+
+ assert "no longer supported" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+
+ def test_table_mul_u_raises_error(self, schema_semantic):
+ """table * dj.U should raise an error."""
+ student = Student()
+
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ student * dj.U("student_id")
+
+ assert "no longer supported" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+
+ def test_u_sub_raises_error(self, schema_semantic):
+ """dj.U - table should raise an error (infinite set)."""
+ student = Student()
+
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError) as exc_info:
+ dj.U("student_id") - student
+
+ assert "infinite" in str(exc_info.value).lower()
+
+ def test_u_and_works(self, schema_semantic):
+ """dj.U & table should work for restriction."""
+ student = Student()
+ student.insert([{"student_id": 1, "name": "Alice"}, {"student_id": 2, "name": "Bob"}])
+
+ result = dj.U("student_id") & student
+ assert len(result) == 2
+
+
+class TestRebuildLineageUtility:
+ """Tests for the lineage rebuild utility."""
+
+ def test_rebuild_lineage_method_exists(self):
+ """The rebuild_lineage method should exist on Schema."""
+ assert hasattr(dj.Schema, "rebuild_lineage")
+
+ def test_rebuild_lineage_populates_table(self, schema_semantic):
+ """schema.rebuild_lineage() should populate the ~lineage table."""
+ from datajoint.lineage import get_table_lineages
+
+ # Run rebuild using Schema method
+ schema_semantic.rebuild_lineage()
+
+ # Check that ~lineage table was created
+ assert schema_semantic.lineage_table_exists
+
+ # Check that lineages were populated for Student table
+ lineages = get_table_lineages(schema_semantic.connection, schema_semantic.database, "student")
+ assert "student_id" in lineages
diff --git a/tests/test_tls.py b/tests/integration/test_tls.py
similarity index 66%
rename from tests/test_tls.py
rename to tests/integration/test_tls.py
index 6c2effc43..e46825227 100644
--- a/tests/test_tls.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_tls.py
@@ -5,20 +5,12 @@
def test_secure_connection(db_creds_test, connection_test):
- result = (
- dj.conn(reset=True, **db_creds_test)
- .query("SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Ssl_cipher';")
- .fetchone()[1]
- )
+ result = dj.conn(reset=True, **db_creds_test).query("SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Ssl_cipher';").fetchone()[1]
assert len(result) > 0
def test_insecure_connection(db_creds_test, connection_test):
- result = (
- dj.conn(use_tls=False, reset=True, **db_creds_test)
- .query("SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Ssl_cipher';")
- .fetchone()[1]
- )
+ result = dj.conn(use_tls=False, reset=True, **db_creds_test).query("SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Ssl_cipher';").fetchone()[1]
assert result == ""
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_type_aliases.py b/tests/integration/test_type_aliases.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..9aae0a8a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_type_aliases.py
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
+"""
+Tests for numeric type aliases (float32, float64, int8, int16, int32, int64, etc.)
+"""
+
+import pytest
+
+from datajoint.declare import CORE_TYPE_SQL, SPECIAL_TYPES, match_type
+
+from tests.schema_type_aliases import TypeAliasTable, TypeAliasPrimaryKey, TypeAliasNullable
+
+
+class TestTypeAliasPatterns:
+ """Test that type alias patterns are correctly defined and matched."""
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "alias,expected_category",
+ [
+ ("float32", "FLOAT32"),
+ ("float64", "FLOAT64"),
+ ("int64", "INT64"),
+ ("uint64", "UINT64"),
+ ("int32", "INT32"),
+ ("uint32", "UINT32"),
+ ("int16", "INT16"),
+ ("uint16", "UINT16"),
+ ("int8", "INT8"),
+ ("uint8", "UINT8"),
+ ("bool", "BOOL"),
+ ],
+ )
+ def test_type_alias_pattern_matching(self, alias, expected_category):
+ """Test that type aliases are matched to correct categories."""
+ category = match_type(alias)
+ assert category == expected_category
+ assert category in SPECIAL_TYPES
+ assert category.lower() in CORE_TYPE_SQL # CORE_TYPE_SQL uses lowercase keys
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "alias,expected_mysql_type",
+ [
+ ("float32", "float"),
+ ("float64", "double"),
+ ("int64", "bigint"),
+ ("uint64", "bigint unsigned"),
+ ("int32", "int"),
+ ("uint32", "int unsigned"),
+ ("int16", "smallint"),
+ ("uint16", "smallint unsigned"),
+ ("int8", "tinyint"),
+ ("uint8", "tinyint unsigned"),
+ ("bool", "tinyint"),
+ ],
+ )
+ def test_type_alias_mysql_mapping(self, alias, expected_mysql_type):
+ """Test that type aliases map to correct MySQL types."""
+ category = match_type(alias)
+ mysql_type = CORE_TYPE_SQL[category.lower()] # CORE_TYPE_SQL uses lowercase keys
+ assert mysql_type == expected_mysql_type
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "native_type,expected_category",
+ [
+ ("int", "INTEGER"),
+ ("bigint", "INTEGER"),
+ ("smallint", "INTEGER"),
+ ("tinyint", "INTEGER"),
+ ("float", "FLOAT"),
+ ("double", "FLOAT"),
+ ],
+ )
+ def test_native_types_still_work(self, native_type, expected_category):
+ """Test that native MySQL types still match correctly."""
+ category = match_type(native_type)
+ assert category == expected_category
+
+
+class TestTypeAliasTableCreation:
+ """Test table creation with type aliases."""
+
+ def test_create_table_with_all_aliases(self, schema_type_aliases):
+ """Test that tables with all type aliases can be created."""
+ assert TypeAliasTable().full_table_name is not None
+
+ def test_create_table_with_alias_primary_key(self, schema_type_aliases):
+ """Test that tables with type aliases in primary key can be created."""
+ assert TypeAliasPrimaryKey().full_table_name is not None
+
+ def test_create_table_with_nullable_aliases(self, schema_type_aliases):
+ """Test that tables with nullable type alias columns can be created."""
+ assert TypeAliasNullable().full_table_name is not None
+
+
+class TestTypeAliasHeading:
+ """Test that headings correctly preserve type alias information."""
+
+ def test_heading_preserves_type_aliases(self, schema_type_aliases):
+ """Test that heading shows original type aliases."""
+ heading = TypeAliasTable().heading
+ heading_str = repr(heading)
+
+ # Check that type aliases appear in the heading representation
+ assert "float32" in heading_str
+ assert "float64" in heading_str
+ assert "int64" in heading_str
+ assert "uint64" in heading_str
+ assert "int32" in heading_str
+ assert "uint32" in heading_str
+ assert "int16" in heading_str
+ assert "uint16" in heading_str
+ assert "int8" in heading_str
+ assert "uint8" in heading_str
+ assert "bool" in heading_str
+
+
+class TestTypeAliasInsertFetch:
+ """Test inserting and fetching data with type aliases."""
+
+ def test_insert_and_fetch(self, schema_type_aliases):
+ """Test inserting and fetching values with type aliases."""
+ table = TypeAliasTable()
+ table.delete()
+
+ test_data = dict(
+ id=1,
+ val_float32=3.14,
+ val_float64=2.718281828,
+ val_int64=9223372036854775807, # max int64
+ val_uint64=18446744073709551615, # max uint64
+ val_int32=2147483647, # max int32
+ val_uint32=4294967295, # max uint32
+ val_int16=32767, # max int16
+ val_uint16=65535, # max uint16
+ val_int8=127, # max int8
+ val_uint8=255, # max uint8
+ val_bool=1, # boolean true
+ )
+
+ table.insert1(test_data)
+ fetched = table.fetch1()
+
+ assert fetched["id"] == test_data["id"]
+ assert abs(fetched["val_float32"] - test_data["val_float32"]) < 0.001
+ assert abs(fetched["val_float64"] - test_data["val_float64"]) < 1e-9
+ assert fetched["val_int64"] == test_data["val_int64"]
+ assert fetched["val_uint64"] == test_data["val_uint64"]
+ assert fetched["val_int32"] == test_data["val_int32"]
+ assert fetched["val_uint32"] == test_data["val_uint32"]
+ assert fetched["val_int16"] == test_data["val_int16"]
+ assert fetched["val_uint16"] == test_data["val_uint16"]
+ assert fetched["val_int8"] == test_data["val_int8"]
+ assert fetched["val_uint8"] == test_data["val_uint8"]
+ assert fetched["val_bool"] == test_data["val_bool"]
+
+ def test_insert_primary_key_with_aliases(self, schema_type_aliases):
+ """Test using type aliases in primary key."""
+ table = TypeAliasPrimaryKey()
+ table.delete()
+
+ table.insert1(dict(pk_int32=100, pk_uint16=200, value="test"))
+ fetched = (table & dict(pk_int32=100, pk_uint16=200)).fetch1()
+
+ assert fetched["pk_int32"] == 100
+ assert fetched["pk_uint16"] == 200
+ assert fetched["value"] == "test"
+
+ def test_nullable_type_aliases(self, schema_type_aliases):
+ """Test nullable columns with type aliases."""
+ table = TypeAliasNullable()
+ table.delete()
+
+ # Insert with NULL values
+ table.insert1(dict(id=1, nullable_float32=None, nullable_int64=None))
+ fetched = table.fetch1()
+
+ assert fetched["id"] == 1
+ assert fetched["nullable_float32"] is None
+ assert fetched["nullable_int64"] is None
+
+ # Insert with actual values
+ table.insert1(dict(id=2, nullable_float32=1.5, nullable_int64=999))
+ fetched = (table & dict(id=2)).fetch1()
+
+ assert fetched["nullable_float32"] == 1.5
+ assert fetched["nullable_int64"] == 999
diff --git a/tests/test_university.py b/tests/integration/test_university.py
similarity index 70%
rename from tests/test_university.py
rename to tests/integration/test_university.py
index 24f01dd4c..d30b9f3e0 100644
--- a/tests/test_university.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_university.py
@@ -6,13 +6,24 @@
import datajoint as dj
from datajoint import DataJointError
-from . import schema_university
-from .schema_university import *
+from tests import schema_university
+from tests.schema_university import (
+ Student,
+ Department,
+ StudentMajor,
+ Course,
+ Term,
+ Section,
+ CurrentTerm,
+ Enroll,
+ LetterGrade,
+ Grade,
+)
def _hash4(table):
"""Hash of table contents"""
- data = table.fetch(order_by="KEY", as_dict=True)
+ data = table.to_dicts(order_by="KEY")
blob = dj.blob.pack(data, compress=False)
return hashlib.md5(blob).digest().hex()[:4]
@@ -37,9 +48,7 @@ def schema_uni_inactive():
@pytest.fixture
def schema_uni(db_creds_test, schema_uni_inactive, connection_test, prefix):
# Deferred activation
- schema_uni_inactive.activate(
- prefix + "_university", connection=dj.conn(**db_creds_test)
- )
+ schema_uni_inactive.activate(prefix + "_university", connection=dj.conn(**db_creds_test))
# --------------- Fill University -------------------
test_data_dir = Path(__file__).parent / "data"
for table in (
@@ -62,9 +71,7 @@ def schema_uni(db_creds_test, schema_uni_inactive, connection_test, prefix):
def test_activate_unauthorized(schema_uni_inactive, db_creds_test, connection_test):
with pytest.raises(DataJointError):
- schema_uni_inactive.activate(
- "unauthorized", connection=dj.conn(**db_creds_test)
- )
+ schema_uni_inactive.activate("unauthorized", connection=dj.conn(**db_creds_test))
def test_fill(schema_uni):
@@ -84,25 +91,17 @@ def test_restrict(schema_uni):
"""
utahns1 = Student & {"home_state": "UT"}
utahns2 = Student & 'home_state="UT"'
- assert len(utahns1) == len(utahns2.fetch("KEY")) == 7
+ assert len(utahns1) == len(utahns2.keys()) == 7
# male nonutahns
- sex1, state1 = ((Student & 'sex="M"') - {"home_state": "UT"}).fetch(
- "sex", "home_state", order_by="student_id"
- )
- sex2, state2 = ((Student & 'sex="M"') - {"home_state": "UT"}).fetch(
- "sex", "home_state", order_by="student_id"
- )
+ sex1, state1 = ((Student & 'sex="M"') - {"home_state": "UT"}).to_arrays("sex", "home_state", order_by="student_id")
+ sex2, state2 = ((Student & 'sex="M"') - {"home_state": "UT"}).to_arrays("sex", "home_state", order_by="student_id")
assert len(set(state1)) == len(set(state2)) == 44
assert set(sex1).pop() == set(sex2).pop() == "M"
# students from OK, NM, TX
- s1 = (Student & [{"home_state": s} for s in ("OK", "NM", "TX")]).fetch(
- "KEY", order_by="student_id"
- )
- s2 = (Student & 'home_state in ("OK", "NM", "TX")').fetch(
- "KEY", order_by="student_id"
- )
+ s1 = (Student & [{"home_state": s} for s in ("OK", "NM", "TX")]).keys(order_by="student_id")
+ s2 = (Student & 'home_state in ("OK", "NM", "TX")').keys(order_by="student_id")
assert len(s1) == 11
assert s1 == s2
@@ -139,34 +138,30 @@ def test_union(schema_uni):
def test_aggr(schema_uni):
- avg_grade_per_course = Course.aggr(
- Grade * LetterGrade, avg_grade="round(avg(points), 2)"
- )
+ # Default: keeps all courses (some may have NULL avg_grade if no grades)
+ avg_grade_per_course = Course.aggr(Grade * LetterGrade, avg_grade="round(avg(points), 2)")
assert len(avg_grade_per_course) == 45
- # GPA
+ # GPA - use exclude_nonmatching=True to only include students with grades
student_gpa = Student.aggr(
- Course * Grade * LetterGrade, gpa="round(sum(points*credits)/sum(credits), 2)"
+ Course * Grade * LetterGrade,
+ gpa="round(sum(points*credits)/sum(credits), 2)",
+ exclude_nonmatching=True,
)
- gpa = student_gpa.fetch("gpa")
- assert len(gpa) == 261
+ gpa = student_gpa.to_arrays("gpa")
+ assert len(gpa) == 261 # only students with grades
assert 2 < gpa.mean() < 3
# Sections in biology department with zero students in them
- section = (Section & {"dept": "BIOL"}).aggr(
- Enroll, n="count(student_id)", keep_all_rows=True
- ) & "n=0"
- assert len(set(section.fetch("dept"))) == 1
+ # aggr now keeps all rows by default (like proj), so sections with 0 enrollments are included
+ section = (Section & {"dept": "BIOL"}).aggr(Enroll, n="count(student_id)") & "n=0"
+ assert len(set(section.to_arrays("dept"))) == 1
assert len(section) == 17
assert bool(section)
# Test correct use of ellipses in a similar query
- section = (Section & {"dept": "BIOL"}).aggr(
- Grade, ..., n="count(student_id)", keep_all_rows=True
- ) & "n>1"
- assert not any(
- name in section.heading.names for name in Grade.heading.secondary_attributes
- )
- assert len(set(section.fetch("dept"))) == 1
+ section = (Section & {"dept": "BIOL"}).aggr(Grade, ..., n="count(student_id)") & "n>1"
+ assert not any(name in section.heading.names for name in Grade.heading.secondary_attributes)
+ assert len(set(section.to_arrays("dept"))) == 1
assert len(section) == 168
assert bool(section)
diff --git a/tests/test_update1.py b/tests/integration/test_update1.py
similarity index 55%
rename from tests/test_update1.py
rename to tests/integration/test_update1.py
index ff53466d4..ef6255bcc 100644
--- a/tests/test_update1.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_update1.py
@@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
import os
-import tempfile
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
@@ -15,44 +14,50 @@ class Thing(dj.Manual):
---
number=0 : int
frac : float
- picture = null : attach@update_store
- params = null : longblob
- img_file = null: filepath@update_repo
+ picture = null :
+ params = null :
+ img_file = null:
timestamp = CURRENT_TIMESTAMP : datetime
"""
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def mock_stores_update(tmpdir_factory):
- og_stores_config = dj.config.get("stores")
- if "stores" not in dj.config:
- dj.config["stores"] = {}
- dj.config["stores"]["update_store"] = dict(
- protocol="file", location=tmpdir_factory.mktemp("store")
+ """Configure object storage stores for update tests."""
+ og_project_name = dj.config.object_storage.project_name
+ og_stores = dict(dj.config.object_storage.stores)
+
+ # Configure stores
+ dj.config.object_storage.project_name = "djtest"
+ store_location = str(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("store"))
+ repo_stage = str(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo_stage"))
+ repo_location = str(tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo_loc"))
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores["update_store"] = dict(
+ protocol="file",
+ location=store_location,
)
- dj.config["stores"]["update_repo"] = dict(
- stage=tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo_stage"),
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores["update_repo"] = dict(
+ stage=repo_stage,
protocol="file",
- location=tmpdir_factory.mktemp("repo_loc"),
+ location=repo_location,
)
- yield
- if og_stores_config is None:
- del dj.config["stores"]
- else:
- dj.config["stores"] = og_stores_config
+ yield {"update_store": {"location": store_location}, "update_repo": {"stage": repo_stage, "location": repo_location}}
+
+ # Restore original
+ dj.config.object_storage.project_name = og_project_name
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores.clear()
+ dj.config.object_storage.stores.update(og_stores)
@pytest.fixture
def schema_update1(connection_test, prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_update1", context=dict(Thing=Thing), connection=connection_test
- )
+ schema = dj.Schema(prefix + "_update1", context=dict(Thing=Thing), connection=connection_test)
schema(Thing)
yield schema
schema.drop()
-def test_update1(tmpdir, enable_filepath_feature, schema_update1, mock_stores_update):
+def test_update1(tmpdir, schema_update1, mock_stores_update):
"""Test normal updates"""
# CHECK 1 -- initial insert
key = dict(thing=1)
@@ -70,21 +75,23 @@ def test_update1(tmpdir, enable_filepath_feature, schema_update1, mock_stores_up
attach_file.unlink()
assert not attach_file.is_file()
- # filepath
- stage_path = dj.config["stores"]["update_repo"]["stage"]
+ # filepath - note: stores a reference, doesn't move the file
+ store_location = mock_stores_update["update_repo"]["location"]
relpath, filename = "one/two/three", "picture.dat"
- managed_file = Path(stage_path, relpath, filename)
+ managed_file = Path(store_location, relpath, filename)
managed_file.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
original_file_data = os.urandom(3000)
with managed_file.open("wb") as f:
f.write(original_file_data)
- Thing.update1(dict(key, img_file=managed_file))
- managed_file.unlink()
- assert not managed_file.is_file()
+ # Insert the relative path within the store
+ Thing.update1(dict(key, img_file=f"{relpath}/{filename}"))
- check2 = Thing.fetch1(download_path=tmpdir)
+ with dj.config.override(download_path=str(tmpdir)):
+ check2 = Thing.fetch1()
buffer2 = Path(check2["picture"]).read_bytes() # read attachment
- final_file_data = managed_file.read_bytes() # read filepath
+ # For filepath, fetch returns ObjectRef - read the file through it
+ filepath_ref = check2["img_file"]
+ final_file_data = filepath_ref.read() if filepath_ref else managed_file.read_bytes()
# CHECK 3 -- reset to default values using None
Thing.update1(
@@ -99,9 +106,7 @@ def test_update1(tmpdir, enable_filepath_feature, schema_update1, mock_stores_up
)
check3 = Thing.fetch1()
- assert (
- check1["number"] == 0 and check1["picture"] is None and check1["params"] is None
- )
+ assert check1["number"] == 0 and check1["picture"] is None and check1["params"] is None
assert (
check2["number"] == 3
@@ -124,23 +129,19 @@ def test_update1(tmpdir, enable_filepath_feature, schema_update1, mock_stores_up
assert original_file_data == final_file_data
-def test_update1_nonexistent(
- enable_filepath_feature, schema_update1, mock_stores_update
-):
+def test_update1_nonexistent(schema_update1, mock_stores_update):
with pytest.raises(DataJointError):
# updating a non-existent entry
Thing.update1(dict(thing=100, frac=0.5))
-def test_update1_noprimary(enable_filepath_feature, schema_update1, mock_stores_update):
+def test_update1_noprimary(schema_update1, mock_stores_update):
with pytest.raises(DataJointError):
# missing primary key
Thing.update1(dict(number=None))
-def test_update1_misspelled_attribute(
- enable_filepath_feature, schema_update1, mock_stores_update
-):
+def test_update1_misspelled_attribute(schema_update1, mock_stores_update):
key = dict(thing=17)
Thing.insert1(dict(key, frac=1.5))
with pytest.raises(DataJointError):
diff --git a/tests/test_utils.py b/tests/integration/test_utils.py
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/test_utils.py
rename to tests/integration/test_utils.py
diff --git a/tests/test_uuid.py b/tests/integration/test_uuid.py
similarity index 95%
rename from tests/test_uuid.py
rename to tests/integration/test_uuid.py
index 4392e4769..14095df7e 100644
--- a/tests/test_uuid.py
+++ b/tests/integration/test_uuid.py
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
from datajoint import DataJointError
-from .schema_uuid import Basic, Item, Topic
+from tests.schema_uuid import Basic, Item, Topic
def test_uuid(schema_uuid):
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ def test_invalid_uuid_restrict1(schema_uuid):
k, m = (Basic & {"item": u}).fetch1("KEY", "number")
-def test_invalid_uuid_restrict1(schema_uuid):
+def test_invalid_uuid_restrict2(schema_uuid):
"""test that only UUID objects are accepted when inserting UUID fields"""
u = "abc"
with pytest.raises(DataJointError):
diff --git a/tests/integration/test_virtual_module.py b/tests/integration/test_virtual_module.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a8e953273
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/integration/test_virtual_module.py
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+"""Tests for virtual schema infrastructure."""
+
+import pytest
+
+import datajoint as dj
+from datajoint.table import FreeTable
+from datajoint.user_tables import UserTable
+
+
+class TestVirtualModule:
+ """Tests for VirtualModule class."""
+
+ def test_virtual_module_creates_table_classes(self, schema_any, connection_test):
+ """VirtualModule creates table classes from database schema."""
+ module = dj.VirtualModule("module", schema_any.database, connection=connection_test)
+ assert issubclass(module.Experiment, UserTable)
+
+ def test_virtual_module_has_schema_attribute(self, schema_any, connection_test):
+ """VirtualModule has schema attribute."""
+ module = dj.VirtualModule("module", schema_any.database, connection=connection_test)
+ assert hasattr(module, "schema")
+ assert module.schema.database == schema_any.database
+
+
+class TestVirtualSchema:
+ """Tests for dj.virtual_schema() function."""
+
+ def test_virtual_schema_creates_module(self, schema_any, connection_test):
+ """virtual_schema creates a VirtualModule."""
+ lab = dj.virtual_schema(schema_any.database, connection=connection_test)
+ assert isinstance(lab, dj.VirtualModule)
+
+ def test_virtual_schema_has_table_classes(self, schema_any, connection_test):
+ """virtual_schema module has table classes as attributes."""
+ lab = dj.virtual_schema(schema_any.database, connection=connection_test)
+ assert issubclass(lab.Experiment, UserTable)
+
+ def test_virtual_schema_tables_are_queryable(self, schema_any, connection_test):
+ """Tables from virtual_schema can be queried."""
+ lab = dj.virtual_schema(schema_any.database, connection=connection_test)
+ # Should not raise
+ lab.Experiment().to_dicts()
+
+
+class TestSchemaGetTable:
+ """Tests for Schema.get_table() method."""
+
+ def test_get_table_by_snake_case(self, schema_any):
+ """get_table works with snake_case table names."""
+ table = schema_any.get_table("experiment")
+ assert isinstance(table, FreeTable)
+ assert "experiment" in table.full_table_name
+
+ def test_get_table_by_camel_case(self, schema_any):
+ """get_table works with CamelCase table names."""
+ table = schema_any.get_table("Experiment")
+ assert isinstance(table, FreeTable)
+ assert "experiment" in table.full_table_name
+
+ def test_get_table_nonexistent_raises(self, schema_any):
+ """get_table raises DataJointError for nonexistent tables."""
+ with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError, match="does not exist"):
+ schema_any.get_table("NonexistentTable")
+
+
+class TestSchemaGetItem:
+ """Tests for Schema.__getitem__() method."""
+
+ def test_getitem_by_name(self, schema_any):
+ """Schema['TableName'] returns table instance."""
+ table = schema_any["Experiment"]
+ assert isinstance(table, FreeTable)
+
+ def test_getitem_is_queryable(self, schema_any):
+ """Table from __getitem__ can be queried."""
+ table = schema_any["Experiment"]
+ # Should not raise
+ table.to_dicts()
+
+
+class TestSchemaIteration:
+ """Tests for Schema.__iter__() method."""
+
+ def test_iter_yields_tables(self, schema_any):
+ """Iterating over schema yields FreeTable instances."""
+ tables = list(schema_any)
+ assert len(tables) > 0
+ assert all(isinstance(t, FreeTable) for t in tables)
+
+ def test_iter_in_dependency_order(self, schema_any):
+ """Iteration order respects dependencies."""
+ table_names = [t.table_name for t in schema_any]
+ # Tables should be in topological order
+ assert len(table_names) == len(set(table_names)) # no duplicates
+
+
+class TestSchemaContains:
+ """Tests for Schema.__contains__() method."""
+
+ def test_contains_existing_table(self, schema_any):
+ """'TableName' in schema returns True for existing tables."""
+ assert "Experiment" in schema_any
+ assert "experiment" in schema_any
+
+ def test_contains_nonexistent_table(self, schema_any):
+ """'TableName' in schema returns False for nonexistent tables."""
+ assert "NonexistentTable" not in schema_any
diff --git a/tests/schema.py b/tests/schema.py
index 2b7977465..4035e1211 100644
--- a/tests/schema.py
+++ b/tests/schema.py
@@ -16,24 +16,24 @@ class TTest(dj.Lookup):
"""
definition = """
- key : int # key
+ key : int32 # key
---
- value : int # value
+ value : int32 # value
"""
contents = [(k, 2 * k) for k in range(10)]
class TTest2(dj.Manual):
definition = """
- key : int # key
+ key : int32 # key
---
- value : int # value
+ value : int32 # value
"""
class TTest3(dj.Manual):
definition = """
- key : int
+ key : int32
---
value : varchar(300)
"""
@@ -41,11 +41,11 @@ class TTest3(dj.Manual):
class NullableNumbers(dj.Manual):
definition = """
- key : int
+ key : int32
---
- fvalue = null : float
- dvalue = null : double
- ivalue = null : int
+ fvalue = null : float32
+ dvalue = null : float64
+ ivalue = null : int32
"""
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ class TTestExtra(dj.Manual):
clone of Test but with an extra field
"""
- definition = TTest.definition + "\nextra : int # extra int\n"
+ definition = TTest.definition + "\nextra : int32 # extra int\n"
class TTestNoExtra(dj.Manual):
@@ -67,14 +67,11 @@ class TTestNoExtra(dj.Manual):
class Auto(dj.Lookup):
definition = """
- id :int auto_increment
+ id : uint8
---
name :varchar(12)
"""
-
- def fill(self):
- if not self:
- self.insert([dict(name="Godel"), dict(name="Escher"), dict(name="Bach")])
+ contents = [(1, "Godel"), (2, "Escher"), (3, "Bach")]
class User(dj.Lookup):
@@ -94,7 +91,7 @@ class User(dj.Lookup):
class Subject(dj.Lookup):
definition = """ # Basic information about animal subjects used in experiments
- subject_id :int # unique subject id
+ subject_id :int32 # unique subject id
---
real_id :varchar(40) # real-world name. Omit if the same as subject_id
species = "mouse" :enum('mouse', 'monkey', 'human')
@@ -131,13 +128,13 @@ class Language(dj.Lookup):
class Experiment(dj.Imported):
definition = """ # information about experiments
-> Subject
- experiment_id :smallint # experiment number for this subject
+ experiment_id :int16 # experiment number for this subject
---
experiment_date :date # date when experiment was started
-> [nullable] User
data_path="" :varchar(255) # file path to recorded data
notes="" :varchar(2048) # e.g. purpose of experiment
- entry_time=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP :timestamp # automatic timestamp
+ entry_time=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP :datetime # automatic timestamp
"""
fake_experiments_per_subject = 5
@@ -148,15 +145,13 @@ def make(self, key):
"""
from datetime import date, timedelta
- users = [None, None] + list(User().fetch()["username"])
+ users = [None, None] + list(User().to_arrays()["username"])
random.seed("Amazing Seed4")
self.insert(
dict(
key,
experiment_id=experiment_id,
- experiment_date=(
- date.today() - timedelta(random.expovariate(1 / 30))
- ).isoformat(),
+ experiment_date=(date.today() - timedelta(random.expovariate(1 / 30))).isoformat(),
username=random.choice(users),
)
for experiment_id in range(self.fake_experiments_per_subject)
@@ -166,17 +161,17 @@ def make(self, key):
class Trial(dj.Imported):
definition = """ # a trial within an experiment
-> Experiment.proj(animal='subject_id')
- trial_id :smallint # trial number
+ trial_id :int16 # trial number
---
- start_time :double # (s)
+ start_time :float64 # (s)
"""
class Condition(dj.Part):
definition = """ # trial conditions
-> Trial
- cond_idx : smallint # condition number
+ cond_idx : int16 # condition number
----
- orientation : float # degrees
+ orientation : float32 # degrees
"""
def make(self, key):
@@ -186,27 +181,24 @@ def make(self, key):
for trial_id in range(10):
key["trial_id"] = trial_id
self.insert1(dict(key, start_time=random.random() * 1e9))
- trial.insert(
- dict(key, cond_idx=cond_idx, orientation=random.random() * 360)
- for cond_idx in range(30)
- )
+ trial.insert(dict(key, cond_idx=cond_idx, orientation=random.random() * 360) for cond_idx in range(30))
class Ephys(dj.Imported):
definition = """ # some kind of electrophysiological recording
-> Trial
----
- sampling_frequency :double # (Hz)
+ sampling_frequency :float64 # (Hz)
duration :decimal(7,3) # (s)
"""
class Channel(dj.Part):
definition = """ # subtable containing individual channels
-> master
- channel :tinyint unsigned # channel number within Ephys
+ channel :uint8 # channel number within Ephys
----
- voltage : longblob
- current = null : longblob # optional current to test null handling
+ voltage :
+ current = null : # optional current to test null handling
"""
def _make_tuples(self, key):
@@ -214,9 +206,7 @@ def _make_tuples(self, key):
populate with random data
"""
random.seed(str(key))
- row = dict(
- key, sampling_frequency=6000, duration=np.minimum(2, random.expovariate(1))
- )
+ row = dict(key, sampling_frequency=6000, duration=np.minimum(2, random.expovariate(1)))
self.insert1(row)
number_samples = int(row["duration"] * row["sampling_frequency"] + 0.5)
sub = self.Channel()
@@ -233,15 +223,15 @@ def _make_tuples(self, key):
class Image(dj.Manual):
definition = """
# table for testing blob inserts
- id : int # image identifier
+ id : int32 # image identifier
---
- img : longblob # image
+ img : # image
"""
class UberTrash(dj.Lookup):
definition = """
- id : int
+ id : int32
---
"""
contents = [(1,)]
@@ -250,7 +240,7 @@ class UberTrash(dj.Lookup):
class UnterTrash(dj.Lookup):
definition = """
-> UberTrash
- my_id : int
+ my_id : int32
---
"""
contents = [(1, 1), (1, 2)]
@@ -258,7 +248,7 @@ class UnterTrash(dj.Lookup):
class SimpleSource(dj.Lookup):
definition = """
- id : int # id
+ id : int32 # id
"""
contents = [(x,) for x in range(10)]
@@ -318,7 +308,7 @@ class IndexRich(dj.Manual):
---
-> [unique, nullable] User.proj(first="username")
first_date : date
- value : int
+ value : int32
index (first_date, value)
"""
@@ -326,16 +316,16 @@ class IndexRich(dj.Manual):
# Schema for issue 656
class ThingA(dj.Manual):
definition = """
- a: int
+ a: int32
"""
class ThingB(dj.Manual):
definition = """
- b1: int
- b2: int
+ b1: int32
+ b2: int32
---
- b3: int
+ b3: int32
"""
@@ -350,7 +340,7 @@ class ThingC(dj.Manual):
# Additional tables for #1159
class ThingD(dj.Manual):
definition = """
- d: int
+ d: int32
---
-> ThingC
"""
@@ -364,7 +354,7 @@ class ThingE(dj.Manual):
class Parent(dj.Lookup):
definition = """
- parent_id: int
+ parent_id: int32
---
name: varchar(30)
"""
@@ -374,7 +364,7 @@ class Parent(dj.Lookup):
class Child(dj.Lookup):
definition = """
-> Parent
- child_id: int
+ child_id: int32
---
name: varchar(30)
"""
@@ -383,14 +373,12 @@ class Child(dj.Lookup):
# Related to issue #886 (8), #883 (5)
class ComplexParent(dj.Lookup):
- definition = "\n".join(["parent_id_{}: int".format(i + 1) for i in range(8)])
+ definition = "\n".join(["parent_id_{}: int32".format(i + 1) for i in range(8)])
contents = [tuple(i for i in range(8))]
class ComplexChild(dj.Lookup):
- definition = "\n".join(
- ["-> ComplexParent"] + ["child_id_{}: int".format(i + 1) for i in range(1)]
- )
+ definition = "\n".join(["-> ComplexParent"] + ["child_id_{}: int32".format(i + 1) for i in range(1)])
contents = [tuple(i for i in range(9))]
@@ -452,18 +440,18 @@ class SessionDateA(dj.Lookup):
class Stimulus(dj.Lookup):
definition = """
- id: int
+ id: int32
---
- contrast: int
- brightness: int
+ contrast: int32
+ brightness: int32
"""
class Longblob(dj.Manual):
definition = """
- id: int
+ id: int32
---
- data: longblob
+ data:
"""
diff --git a/tests/schema_adapted.py b/tests/schema_adapted.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 06e28c3d1..000000000
--- a/tests/schema_adapted.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
-import inspect
-import json
-import tempfile
-from pathlib import Path
-
-import networkx as nx
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-
-class GraphAdapter(dj.AttributeAdapter):
- attribute_type = "longblob" # this is how the attribute will be declared
-
- @staticmethod
- def get(obj):
- # convert edge list into a graph
- return nx.Graph(obj)
-
- @staticmethod
- def put(obj):
- # convert graph object into an edge list
- assert isinstance(obj, nx.Graph)
- return list(obj.edges)
-
-
-class LayoutToFilepath(dj.AttributeAdapter):
- """
- An adapted data type that saves a graph layout into fixed filepath
- """
-
- attribute_type = "filepath@repo-s3"
-
- @staticmethod
- def get(path):
- with open(path, "r") as f:
- return json.load(f)
-
- @staticmethod
- def put(layout):
- path = Path(dj.config["stores"]["repo-s3"]["stage"], "layout.json")
- with open(str(path), "w") as f:
- json.dump(layout, f)
- return path
-
-
-class Connectivity(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- connid : int
- ---
- conn_graph = null :
- """
-
-
-class Layout(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- # stores graph layout
- -> Connectivity
- ---
- layout:
- """
-
-
-LOCALS_ADAPTED = {k: v for k, v in locals().items() if inspect.isclass(v)}
-__all__ = list(LOCALS_ADAPTED)
diff --git a/tests/schema_alter.py b/tests/schema_alter.py
index b86f6c7ec..936d9cc12 100644
--- a/tests/schema_alter.py
+++ b/tests/schema_alter.py
@@ -6,30 +6,30 @@
class Experiment(dj.Imported):
original_definition = """ # information about experiments
-> Subject
- experiment_id :smallint # experiment number for this subject
+ experiment_id :int16 # experiment number for this subject
---
experiment_date :date # date when experiment was started
-> [nullable] User
data_path="" :varchar(255) # file path to recorded data
notes="" :varchar(2048) # e.g. purpose of experiment
- entry_time=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP :timestamp # automatic timestamp
+ entry_time=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP :datetime # automatic timestamp
"""
definition1 = """ # Experiment
-> Subject
- experiment_id :smallint # experiment number for this subject
+ experiment_id :int16 # experiment number for this subject
---
- data_path : int # some number
- extra=null : longblob # just testing
+ data_path : int32 # some number
+ extra=null : # just testing
-> [nullable] User
subject_notes=null :varchar(2048) # {notes} e.g. purpose of experiment
- entry_time=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP :timestamp # automatic timestamp
+ entry_time=CURRENT_TIMESTAMP :datetime # automatic timestamp
"""
class Parent(dj.Manual):
definition = """
- parent_id: int
+ parent_id: int32
"""
class Child(dj.Part):
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ class Child(dj.Part):
definition_new = """
-> master
---
- child_id=null: int
+ child_id=null: int32
"""
class Grandchild(dj.Part):
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ class Grandchild(dj.Part):
definition_new = """
-> master.Child
---
- grandchild_id=null: int
+ grandchild_id=null: int32
"""
diff --git a/tests/schema_codecs.py b/tests/schema_codecs.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6a8d478d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/schema_codecs.py
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+import inspect
+
+import networkx as nx
+
+import datajoint as dj
+
+
+class GraphCodec(dj.Codec):
+ """Custom codec for storing NetworkX graphs as edge lists."""
+
+ name = "graph"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ """Chain to blob for serialization."""
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, obj, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ """Convert graph object into an edge list."""
+ assert isinstance(obj, nx.Graph)
+ return list(obj.edges)
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ """Convert edge list into a graph."""
+ return nx.Graph(stored)
+
+
+class LayoutCodec(dj.Codec):
+ """Custom codec that saves a graph layout as serialized blob."""
+
+ name = "layout"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ """Chain to blob for serialization."""
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, layout, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ """Serialize layout dict."""
+ return layout # blob handles serialization
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ """Deserialize layout dict."""
+ return stored # blob handles deserialization
+
+
+class Connectivity(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ connid : int
+ ---
+ conn_graph = null :
+ """
+
+
+class Layout(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ # stores graph layout
+ -> Connectivity
+ ---
+ layout:
+ """
+
+
+LOCALS_CODECS = {k: v for k, v in locals().items() if inspect.isclass(v)}
+__all__ = list(LOCALS_CODECS)
diff --git a/tests/schema_external.py b/tests/schema_external.py
index a9e86964f..ae1803f5e 100644
--- a/tests/schema_external.py
+++ b/tests/schema_external.py
@@ -3,7 +3,6 @@
"""
import inspect
-import tempfile
import numpy as np
@@ -14,7 +13,7 @@ class Simple(dj.Manual):
definition = """
simple : int
---
- item : blob@local
+ item :
"""
@@ -22,7 +21,7 @@ class SimpleRemote(dj.Manual):
definition = """
simple : int
---
- item : blob@share
+ item :
"""
@@ -37,7 +36,7 @@ class Dimension(dj.Lookup):
definition = """
dim : int
---
- dimensions : blob
+ dimensions :
"""
contents = ([0, [100, 50]], [1, [3, 4, 8, 6]])
@@ -48,8 +47,8 @@ class Image(dj.Computed):
-> Seed
-> Dimension
----
- img : blob@share # objects are stored as specified by dj.config['stores']['share']
- neg : blob@local # objects are stored as specified by dj.config['stores']['local']
+ img : # objects are stored as specified by dj.config['stores']['share']
+ neg : # objects are stored as specified by dj.config['stores']['local']
"""
def make(self, key):
@@ -63,8 +62,8 @@ class Attach(dj.Manual):
# table for storing attachments
attach : int
----
- img : attach@share # attachments are stored as specified by: dj.config['stores']['raw']
- txt : attach # attachments are stored directly in the database
+ img : # attachments are stored as specified by: dj.config['stores']['share']
+ txt : # attachments are stored directly in the database
"""
@@ -73,7 +72,7 @@ class Filepath(dj.Manual):
# table for file management
fnum : int # test comment containing :
---
- img : filepath@repo # managed files
+ img : # managed files
"""
@@ -82,7 +81,7 @@ class FilepathS3(dj.Manual):
# table for file management
fnum : int
---
- img : filepath@repo-s3 # managed files
+ img : # managed files
"""
diff --git a/tests/schema_object.py b/tests/schema_object.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ef1d957dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/schema_object.py
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+"""
+Schema definitions for object type tests.
+"""
+
+import datajoint as dj
+
+LOCALS_OBJECT = locals()
+
+
+class ObjectFile(dj.Manual):
+ """Table for testing object type with files."""
+
+ definition = """
+ file_id : int
+ ---
+ data_file : # stored file
+ """
+
+
+class ObjectFolder(dj.Manual):
+ """Table for testing object type with folders."""
+
+ definition = """
+ folder_id : int
+ ---
+ data_folder : # stored folder
+ """
+
+
+class ObjectMultiple(dj.Manual):
+ """Table for testing multiple object attributes."""
+
+ definition = """
+ record_id : int
+ ---
+ raw_data : # raw data file
+ processed : # processed data file
+ """
+
+
+class ObjectWithOther(dj.Manual):
+ """Table for testing object type with other attributes."""
+
+ definition = """
+ subject_id : int
+ session_id : int
+ ---
+ name : varchar(100)
+ data_file :
+ notes : varchar(255)
+ """
diff --git a/tests/schema_simple.py b/tests/schema_simple.py
index 5e5137db5..f0e768d1f 100644
--- a/tests/schema_simple.py
+++ b/tests/schema_simple.py
@@ -83,10 +83,7 @@ def make(self, key):
sigma = random.lognormvariate(0, 4)
n = random.randint(0, 10)
self.insert1(dict(key, mu=mu, sigma=sigma, n=n))
- sub.insert(
- dict(key, id_c=j, value=random.normalvariate(mu, sigma))
- for j in range(n)
- )
+ sub.insert(dict(key, id_c=j, value=random.normalvariate(mu, sigma)) for j in range(n))
class L(dj.Lookup):
@@ -109,7 +106,7 @@ class D(dj.Computed):
def _make_tuples(self, key):
# make reference to a random tuple from L
random.seed(str(key))
- lookup = list(L().fetch("KEY"))
+ lookup = list(L().keys())
self.insert(dict(key, id_d=i, **random.choice(lookup)) for i in range(4))
@@ -144,26 +141,22 @@ class H(dj.Part):
"""
class M(dj.Part):
- definition = """ # test force_masters revisit
+ definition = """ # test part_integrity cascade
-> E
- id_m :int
+ id_m : uint16
---
-> E.H
"""
def make(self, key):
random.seed(str(key))
- l_contents = list(L().fetch("KEY"))
+ l_contents = list(L().keys())
part_f, part_g, part_h, part_m = E.F(), E.G(), E.H(), E.M()
- bc_references = list((B.C() & key).fetch("KEY"))
+ bc_references = list((B.C() & key).keys())
random.shuffle(bc_references)
self.insert1(dict(key, **random.choice(l_contents)))
- part_f.insert(
- dict(key, id_f=i, **ref)
- for i, ref in enumerate(bc_references)
- if random.getrandbits(1)
- )
+ part_f.insert(dict(key, id_f=i, **ref) for i, ref in enumerate(bc_references) if random.getrandbits(1))
g_inserts = [dict(key, id_g=i, **ref) for i, ref in enumerate(l_contents)]
part_g.insert(g_inserts)
h_inserts = [dict(key, id_h=i) for i in range(4)]
@@ -248,9 +241,7 @@ def populate_random(self, n=10):
with self.connection.transaction:
self.insert1(profile, ignore_extra_fields=True)
for url in profile["website"]:
- self.Website().insert1(
- dict(ssn=profile["ssn"], url_hash=Website().insert1_url(url))
- )
+ self.Website().insert1(dict(ssn=profile["ssn"], url_hash=Website().insert1_url(url)))
class TTestUpdate(dj.Lookup):
@@ -259,7 +250,7 @@ class TTestUpdate(dj.Lookup):
---
string_attr : varchar(255)
num_attr=null : float
- blob_attr : longblob
+ blob_attr :
"""
contents = [
diff --git a/tests/schema_type_aliases.py b/tests/schema_type_aliases.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..eb586de5d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/schema_type_aliases.py
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+"""
+Schema for testing numeric type aliases.
+"""
+
+import inspect
+
+import datajoint as dj
+
+
+class TypeAliasTable(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ # Table with all numeric type aliases
+ id : int
+ ---
+ val_float32 : float32 # 32-bit float
+ val_float64 : float64 # 64-bit float
+ val_int64 : int64 # 64-bit signed integer
+ val_uint64 : uint64 # 64-bit unsigned integer
+ val_int32 : int32 # 32-bit signed integer
+ val_uint32 : uint32 # 32-bit unsigned integer
+ val_int16 : int16 # 16-bit signed integer
+ val_uint16 : uint16 # 16-bit unsigned integer
+ val_int8 : int8 # 8-bit signed integer
+ val_uint8 : uint8 # 8-bit unsigned integer
+ val_bool : bool # boolean value
+ """
+
+
+class TypeAliasPrimaryKey(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ # Table with type alias in primary key
+ pk_int32 : int32
+ pk_uint16 : uint16
+ ---
+ value : varchar(100)
+ """
+
+
+class TypeAliasNullable(dj.Manual):
+ definition = """
+ # Table with nullable type alias columns
+ id : int
+ ---
+ nullable_float32 = null : float32
+ nullable_int64 = null : int64
+ """
+
+
+LOCALS_TYPE_ALIASES = {k: v for k, v in locals().items() if inspect.isclass(v)}
+__all__ = list(LOCALS_TYPE_ALIASES)
diff --git a/tests/schema_uuid.py b/tests/schema_uuid.py
index 4e295bc86..75b9cd373 100644
--- a/tests/schema_uuid.py
+++ b/tests/schema_uuid.py
@@ -24,9 +24,7 @@ class Topic(dj.Manual):
def add(self, topic):
"""add a new topic with a its UUID"""
- self.insert1(
- dict(topic_id=uuid.uuid5(top_level_namespace_id, topic), topic=topic)
- )
+ self.insert1(dict(topic_id=uuid.uuid5(top_level_namespace_id, topic), topic=topic))
class Item(dj.Computed):
@@ -41,9 +39,7 @@ class Item(dj.Computed):
def make(self, key):
for word in ("Habenula", "Hippocampus", "Hypothalamus", "Hypophysis"):
- self.insert1(
- dict(key, word=word, item_id=uuid.uuid5(key["topic_id"], word))
- )
+ self.insert1(dict(key, word=word, item_id=uuid.uuid5(key["topic_id"], word)))
LOCALS_UUID = {k: v for k, v in locals().items() if inspect.isclass(v)}
diff --git a/tests/test_admin.py b/tests/test_admin.py
deleted file mode 100644
index b7fa15a33..000000000
--- a/tests/test_admin.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,152 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Collection of test cases to test admin module.
-"""
-
-import os
-
-import pymysql
-import pytest
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-
-@pytest.fixture()
-def user_alice(db_creds_root) -> dict:
- # set up - reset config, log in as root, and create a new user alice
- # reset dj.config manually because its state may be changed by these tests
- if os.path.exists(dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG):
- os.remove(dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG)
- dj.config["database.password"] = os.getenv("DJ_PASS")
- root_conn = dj.conn(**db_creds_root, reset=True)
- new_credentials = dict(
- host=db_creds_root["host"],
- user="alice",
- password="oldpass",
- )
- root_conn.query(f"DROP USER IF EXISTS '{new_credentials['user']}'@'%%';")
- root_conn.query(
- f"CREATE USER '{new_credentials['user']}'@'%%' "
- f"IDENTIFIED BY '{new_credentials['password']}';"
- )
-
- # test the connection
- dj.Connection(**new_credentials)
-
- # return alice's credentials
- yield new_credentials
-
- # tear down - delete the user and the local config file
- root_conn.query(f"DROP USER '{new_credentials['user']}'@'%%';")
- if os.path.exists(dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG):
- os.remove(dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG)
-
-
-def test_set_password_prompt_match(monkeypatch, user_alice: dict):
- """
- Should be able to change the password using user prompt
- """
- # reset the connection to use alice's credentials
- dj.conn(**user_alice, reset=True)
-
- # prompts: new password / confirm password
- password_resp = iter(["newpass", "newpass"])
- # NOTE: because getpass.getpass is imported in datajoint.admin and used as
- # getpass in that module, we need to patch datajoint.admin.getpass
- # instead of getpass.getpass
- monkeypatch.setattr("datajoint.admin.getpass", lambda _: next(password_resp))
-
- # respond no to prompt to update local config
- monkeypatch.setattr("builtins.input", lambda _: "no")
-
- # reset password of user of current connection (alice)
- dj.set_password()
-
- # should not be able to connect with old credentials
- with pytest.raises(pymysql.err.OperationalError):
- dj.Connection(**user_alice)
-
- # should be able to connect with new credentials
- dj.Connection(host=user_alice["host"], user=user_alice["user"], password="newpass")
-
- # check that local config is not updated
- assert dj.config["database.password"] == os.getenv("DJ_PASS")
- assert not os.path.exists(dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG)
-
-
-def test_set_password_prompt_mismatch(monkeypatch, user_alice: dict):
- """
- Should not be able to change the password when passwords do not match
- """
- # reset the connection to use alice's credentials
- dj.conn(**user_alice, reset=True)
-
- # prompts: new password / confirm password
- password_resp = iter(["newpass", "wrong"])
- # NOTE: because getpass.getpass is imported in datajoint.admin and used as
- # getpass in that module, we need to patch datajoint.admin.getpass
- # instead of getpass.getpass
- monkeypatch.setattr("datajoint.admin.getpass", lambda _: next(password_resp))
-
- # reset password of user of current connection (alice)
- # should be nop
- dj.set_password()
-
- # should be able to connect with old credentials
- dj.Connection(**user_alice)
-
-
-def test_set_password_args(user_alice: dict):
- """
- Should be able to change the password with an argument
- """
- # reset the connection to use alice's credentials
- dj.conn(**user_alice, reset=True)
-
- # reset password of user of current connection (alice)
- dj.set_password(new_password="newpass", update_config=False)
-
- # should be able to connect with new credentials
- dj.Connection(host=user_alice["host"], user=user_alice["user"], password="newpass")
-
-
-def test_set_password_update_config(monkeypatch, user_alice: dict):
- """
- Should be able to change the password and update local config
- """
- # reset the connection to use alice's credentials
- dj.conn(**user_alice, reset=True)
-
- # respond yes to prompt to update local config
- monkeypatch.setattr("builtins.input", lambda _: "yes")
-
- # reset password of user of current connection (alice)
- dj.set_password(new_password="newpass")
-
- # should be able to connect with new credentials
- dj.Connection(host=user_alice["host"], user=user_alice["user"], password="newpass")
-
- # check that local config is updated
- # NOTE: the global config state is changed unless dj modules are reloaded
- # NOTE: this test is a bit unrealistic because the config user does not match
- # the user whose password is being updated, so the config credentials
- # will be invalid after update...
- assert dj.config["database.password"] == "newpass"
- assert os.path.exists(dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG)
-
-
-def test_set_password_conn(user_alice: dict):
- """
- Should be able to change the password using a given connection
- """
- # create a connection with alice's credentials
- conn_alice = dj.Connection(**user_alice)
-
- # reset password of user of alice's connection (alice) and do not update config
- dj.set_password(new_password="newpass", connection=conn_alice, update_config=False)
-
- # should be able to connect with new credentials
- dj.Connection(host=user_alice["host"], user=user_alice["user"], password="newpass")
-
- # check that local config is not updated
- assert dj.config["database.password"] == os.getenv("DJ_PASS")
- assert not os.path.exists(dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG)
diff --git a/tests/test_aggr_regressions.py b/tests/test_aggr_regressions.py
deleted file mode 100644
index ea740cd39..000000000
--- a/tests/test_aggr_regressions.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,130 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Regression tests for issues 386, 449, 484, and 558 — all related to processing complex aggregations and projections.
-"""
-
-import uuid
-
-import pytest
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-from .schema_aggr_regress import LOCALS_AGGR_REGRESS, A, B, Q, R, S, X
-from .schema_uuid import Item, Topic, top_level_namespace_id
-
-
-@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
-def schema_aggr_reg(connection_test, prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_aggr_regress",
- context=LOCALS_AGGR_REGRESS,
- connection=connection_test,
- )
- schema(R)
- schema(Q)
- schema(S)
- yield schema
- schema.drop()
-
-
-@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
-def schema_aggr_reg_with_abx(connection_test, prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_aggr_regress_with_abx",
- context=LOCALS_AGGR_REGRESS,
- connection=connection_test,
- )
- schema(R)
- schema(Q)
- schema(S)
- schema(A)
- schema(B)
- schema(X)
- yield schema
- schema.drop()
-
-
-def test_issue386(schema_aggr_reg):
- """
- --------------- ISSUE 386 -------------------
- Issue 386 resulted from the loss of aggregated attributes when the aggregation was used as the restrictor
- Q & (R.aggr(S, n='count(*)') & 'n=2')
- Error: Unknown column 'n' in HAVING
- """
- result = R.aggr(S, n="count(*)") & "n=10"
- result = Q & result
- result.fetch()
-
-
-def test_issue449(schema_aggr_reg):
- """
- ---------------- ISSUE 449 ------------------
- Issue 449 arises from incorrect group by attributes after joining with a dj.U()
- """
- result = dj.U("n") * R.aggr(S, n="max(s)")
- result.fetch()
-
-
-def test_issue484(schema_aggr_reg):
- """
- ---------------- ISSUE 484 -----------------
- Issue 484
- """
- q = dj.U().aggr(S, n="max(s)")
- n = q.fetch("n")
- n = q.fetch1("n")
- q = dj.U().aggr(S, n="avg(s)")
- result = dj.U().aggr(q, m="max(n)")
- result.fetch()
-
-
-def test_union_join(schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
- """
- This test fails if it runs after TestIssue558.
-
- https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/930
- """
- A.insert(zip([100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600]))
- B.insert([(100, 11), (200, 22), (300, 33), (400, 44)])
- q1 = B & "id < 300"
- q2 = B & "id > 300"
-
- expected_data = [
- {"id": 0, "id2": 5},
- {"id": 1, "id2": 6},
- {"id": 2, "id2": 7},
- {"id": 3, "id2": 8},
- {"id": 4, "id2": 9},
- {"id": 100, "id2": 11},
- {"id": 200, "id2": 22},
- {"id": 400, "id2": 44},
- ]
-
- assert ((q1 + q2) * A).fetch(as_dict=True) == expected_data
-
-
-class TestIssue558:
- """
- --------------- ISSUE 558 ------------------
- Issue 558 resulted from the fact that DataJoint saves subqueries and often combines a restriction followed
- by a projection into a single SELECT statement, which in several unusual cases produces unexpected results.
- """
-
- def test_issue558_part1(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
- q = (A - B).proj(id2="3")
- assert len(A - B) == len(q)
-
- def test_issue558_part2(self, schema_aggr_reg_with_abx):
- d = dict(id=3, id2=5)
- assert len(X & d) == len((X & d).proj(id2="3"))
-
-
-def test_left_join_len(schema_uuid):
- Topic().add("jeff")
- Item.populate()
- Topic().add("jeff2")
- Topic().add("jeff3")
- q = Topic.join(
- Item - dict(topic_id=uuid.uuid5(top_level_namespace_id, "jeff")), left=True
- )
- qf = q.fetch()
- assert len(q) == len(qf)
diff --git a/tests/test_alter.py b/tests/test_alter.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 375d31d55..000000000
--- a/tests/test_alter.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-import re
-
-import pytest
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-from . import schema as schema_any_module
-from .schema_alter import LOCALS_ALTER, Experiment, Parent
-
-COMBINED_CONTEXT = {
- **schema_any_module.LOCALS_ANY,
- **LOCALS_ALTER,
-}
-
-
-@pytest.fixture
-def schema_alter(connection_test, schema_any):
- # Overwrite Experiment and Parent nodes
- schema_any(Experiment, context=LOCALS_ALTER)
- schema_any(Parent, context=LOCALS_ALTER)
- yield schema_any
- schema_any.drop()
-
-
-class TestAlter:
- def verify_alter(self, schema_alter, table, attribute_sql):
- definition_original = schema_alter.connection.query(
- f"SHOW CREATE TABLE {table.full_table_name}"
- ).fetchone()[1]
- table.definition = table.definition_new
- table.alter(prompt=False)
- definition_new = schema_alter.connection.query(
- f"SHOW CREATE TABLE {table.full_table_name}"
- ).fetchone()[1]
- assert (
- re.sub(f"{attribute_sql},\n ", "", definition_new) == definition_original
- )
-
- def test_alter(self, schema_alter):
- original = schema_alter.connection.query(
- "SHOW CREATE TABLE " + Experiment.full_table_name
- ).fetchone()[1]
- Experiment.definition = Experiment.definition1
- Experiment.alter(prompt=False, context=COMBINED_CONTEXT)
- altered = schema_alter.connection.query(
- "SHOW CREATE TABLE " + Experiment.full_table_name
- ).fetchone()[1]
- assert original != altered
- Experiment.definition = Experiment.original_definition
- Experiment().alter(prompt=False, context=COMBINED_CONTEXT)
- restored = schema_alter.connection.query(
- "SHOW CREATE TABLE " + Experiment.full_table_name
- ).fetchone()[1]
- assert altered != restored
- assert original == restored
-
- def test_alter_part(self, schema_alter):
- """
- https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/936
- """
- self.verify_alter(
- schema_alter, table=Parent.Child, attribute_sql="`child_id` .* DEFAULT NULL"
- )
- self.verify_alter(
- schema_alter,
- table=Parent.Grandchild,
- attribute_sql="`grandchild_id` .* DEFAULT NULL",
- )
diff --git a/tests/test_bypass_serialization.py b/tests/test_bypass_serialization.py
deleted file mode 100644
index da7f0b0e3..000000000
--- a/tests/test_bypass_serialization.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-import pytest
-from numpy.testing import assert_array_equal
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-test_blob = np.array([1, 2, 3])
-
-
-class Input(dj.Lookup):
- definition = """
- id: int
- ---
- data: blob
- """
- contents = [(0, test_blob)]
-
-
-class Output(dj.Manual):
- definition = """
- id: int
- ---
- data: blob
- """
-
-
-@pytest.fixture
-def schema_in(connection_test, prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_test_bypass_serialization_in",
- context=dict(Input=Input),
- connection=connection_test,
- )
- schema(Input)
- yield schema
- schema.drop()
-
-
-@pytest.fixture
-def schema_out(connection_test, prefix):
- schema = dj.Schema(
- prefix + "_test_blob_bypass_serialization_out",
- context=dict(Output=Output),
- connection=connection_test,
- )
- schema(Output)
- yield schema
- schema.drop()
-
-
-def test_bypass_serialization(schema_in, schema_out):
- dj.blob.bypass_serialization = True
- contents = Input.fetch(as_dict=True)
- assert isinstance(contents[0]["data"], bytes)
- Output.insert(contents)
- dj.blob.bypass_serialization = False
- assert_array_equal(Input.fetch1("data"), Output.fetch1("data"))
diff --git a/tests/test_external.py b/tests/test_external.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 10021c0aa..000000000
--- a/tests/test_external.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,134 +0,0 @@
-import os
-
-import numpy as np
-from numpy.testing import assert_array_equal
-
-import datajoint as dj
-from datajoint.blob import pack, unpack
-from datajoint.external import ExternalTable
-
-from .schema_external import Simple, SimpleRemote
-
-
-def test_external_put(schema_ext, mock_stores, mock_cache):
- """
- external storage put and get and remove
- """
- ext = ExternalTable(
- schema_ext.connection, store="raw", database=schema_ext.database
- )
- initial_length = len(ext)
- input_ = np.random.randn(3, 7, 8)
- count = 7
- extra = 3
- for i in range(count):
- hash1 = ext.put(pack(input_))
- for i in range(extra):
- hash2 = ext.put(pack(np.random.randn(4, 3, 2)))
-
- fetched_hashes = ext.fetch("hash")
- assert all(hash in fetched_hashes for hash in (hash1, hash2))
- assert len(ext) == initial_length + 1 + extra
-
- output_ = unpack(ext.get(hash1))
- assert_array_equal(input_, output_)
-
-
-class TestLeadingSlash:
- def test_s3_leading_slash(self, schema_ext, mock_stores, mock_cache, minio_client):
- """
- s3 external storage configured with leading slash
- """
- self._leading_slash(schema_ext, index=100, store="share")
-
- def test_file_leading_slash(
- self, schema_ext, mock_stores, mock_cache, minio_client
- ):
- """
- File external storage configured with leading slash
- """
- self._leading_slash(schema_ext, index=200, store="local")
-
- def _leading_slash(self, schema_ext, index, store):
- oldConfig = dj.config["stores"][store]["location"]
- value = np.array([1, 2, 3])
-
- id = index
- dj.config["stores"][store]["location"] = "leading/slash/test"
- SimpleRemote.insert([{"simple": id, "item": value}])
- assert np.array_equal(
- value, (SimpleRemote & "simple={}".format(id)).fetch1("item")
- )
-
- id = index + 1
- dj.config["stores"][store]["location"] = "/leading/slash/test"
- SimpleRemote.insert([{"simple": id, "item": value}])
- assert np.array_equal(
- value, (SimpleRemote & "simple={}".format(id)).fetch1("item")
- )
-
- id = index + 2
- dj.config["stores"][store]["location"] = "leading\\slash\\test"
- SimpleRemote.insert([{"simple": id, "item": value}])
- assert np.array_equal(
- value, (SimpleRemote & "simple={}".format(id)).fetch1("item")
- )
-
- id = index + 3
- dj.config["stores"][store]["location"] = "f:\\leading\\slash\\test"
- SimpleRemote.insert([{"simple": id, "item": value}])
- assert np.array_equal(
- value, (SimpleRemote & "simple={}".format(id)).fetch1("item")
- )
-
- id = index + 4
- dj.config["stores"][store]["location"] = "f:\\leading/slash\\test"
- SimpleRemote.insert([{"simple": id, "item": value}])
- assert np.array_equal(
- value, (SimpleRemote & "simple={}".format(id)).fetch1("item")
- )
-
- id = index + 5
- dj.config["stores"][store]["location"] = "/"
- SimpleRemote.insert([{"simple": id, "item": value}])
- assert np.array_equal(
- value, (SimpleRemote & "simple={}".format(id)).fetch1("item")
- )
-
- id = index + 6
- dj.config["stores"][store]["location"] = "C:\\"
- SimpleRemote.insert([{"simple": id, "item": value}])
- assert np.array_equal(
- value, (SimpleRemote & "simple={}".format(id)).fetch1("item")
- )
-
- id = index + 7
- dj.config["stores"][store]["location"] = ""
- SimpleRemote.insert([{"simple": id, "item": value}])
- assert np.array_equal(
- value, (SimpleRemote & "simple={}".format(id)).fetch1("item")
- )
-
- dj.config["stores"][store]["location"] = oldConfig
-
-
-def test_remove_fail(schema_ext, mock_stores, mock_cache, minio_client):
- """
- https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/953
- """
- assert dj.config["stores"]["local"]["location"]
-
- data = dict(simple=2, item=[1, 2, 3])
- Simple.insert1(data)
- path1 = dj.config["stores"]["local"]["location"] + "/djtest_extern/4/c/"
- currentMode = int(oct(os.stat(path1).st_mode), 8)
- os.chmod(path1, 0o40555)
- (Simple & "simple=2").delete()
- listOfErrors = schema_ext.external["local"].delete(delete_external_files=True)
-
- assert (
- len(schema_ext.external["local"] & dict(hash=listOfErrors[0][0])) == 1
- ), "unexpected number of rows in external table"
- # ---------------------CLEAN UP--------------------
- os.chmod(path1, currentMode)
- listOfErrors = schema_ext.external["local"].delete(delete_external_files=True)
diff --git a/tests/test_external_class.py b/tests/test_external_class.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 84597e52f..000000000
--- a/tests/test_external_class.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
-from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-from . import schema_external
-
-
-def test_heading(schema_ext, mock_stores):
- heading = schema_external.Simple().heading
- assert "item" in heading
- assert heading["item"].is_external
-
-
-def test_insert_and_fetch(schema_ext, mock_stores, mock_cache):
- original_list = [1, 3, 8]
- schema_external.Simple().insert1(dict(simple=1, item=original_list))
- # test fetch
- q = (schema_external.Simple() & {"simple": 1}).fetch("item")[0]
- assert list(q) == original_list
- # test fetch1 as a tuple
- q = (schema_external.Simple() & {"simple": 1}).fetch1("item")
- assert list(q) == original_list
- # test fetch1 as a dict
- q = (schema_external.Simple() & {"simple": 1}).fetch1()
- assert list(q["item"]) == original_list
- # test without cache
- previous_cache = dj.config["cache"]
- dj.config["cache"] = None
- q = (schema_external.Simple() & {"simple": 1}).fetch1()
- assert list(q["item"]) == original_list
- # test with cache
- dj.config["cache"] = previous_cache
- q = (schema_external.Simple() & {"simple": 1}).fetch1()
- assert list(q["item"]) == original_list
-
-
-def test_populate(schema_ext, mock_stores):
- image = schema_external.Image()
- image.populate()
- remaining, total = image.progress()
- assert (
- total == len(schema_external.Dimension() * schema_external.Seed())
- and remaining == 0
- )
- for img, neg, dimensions in zip(
- *(image * schema_external.Dimension()).fetch("img", "neg", "dimensions")
- ):
- assert list(img.shape) == list(dimensions)
- assert_almost_equal(img, -neg)
- image.delete()
- for external_table in image.external.values():
- external_table.delete(display_progress=False, delete_external_files=True)
diff --git a/tests/test_fetch.py b/tests/test_fetch.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 7df767028..000000000
--- a/tests/test_fetch.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,374 +0,0 @@
-import decimal
-import io
-import itertools
-import logging
-import os
-import warnings
-from operator import itemgetter
-from typing import List
-
-import numpy as np
-import pandas
-import pytest
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-from . import schema
-
-
-def test_getattribute(subject):
- """Testing Fetch.__call__ with attributes"""
- list1 = sorted(subject.proj().fetch(as_dict=True), key=itemgetter("subject_id"))
- list2 = sorted(subject.fetch(dj.key), key=itemgetter("subject_id"))
- for l1, l2 in zip(list1, list2):
- assert l1 == l2, "Primary key is not returned correctly"
-
- tmp = subject.fetch(order_by="subject_id")
-
- subject_notes, key, real_id = subject.fetch("subject_notes", dj.key, "real_id")
-
- np.testing.assert_array_equal(sorted(subject_notes), sorted(tmp["subject_notes"]))
- np.testing.assert_array_equal(sorted(real_id), sorted(tmp["real_id"]))
- list1 = sorted(key, key=itemgetter("subject_id"))
- for l1, l2 in zip(list1, list2):
- assert l1 == l2, "Primary key is not returned correctly"
-
-
-def test_getattribute_for_fetch1(subject):
- """Testing Fetch1.__call__ with attributes"""
- assert (subject & "subject_id=10").fetch1("subject_id") == 10
- assert (subject & "subject_id=10").fetch1("subject_id", "species") == (
- 10,
- "monkey",
- )
-
-
-def test_order_by(lang, languages):
- """Tests order_by sorting order"""
- for ord_name, ord_lang in itertools.product(*2 * [["ASC", "DESC"]]):
- cur = lang.fetch(order_by=("name " + ord_name, "language " + ord_lang))
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=ord_lang == "DESC")
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=ord_name == "DESC")
- for c, l in zip(cur, languages):
- assert np.all(
- cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)
- ), "Sorting order is different"
-
-
-def test_order_by_default(lang, languages):
- """Tests order_by sorting order with defaults"""
- cur = lang.fetch(order_by=("language", "name DESC"))
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
- for c, l in zip(cur, languages):
- assert np.all([cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)]), "Sorting order is different"
-
-
-def test_limit(lang):
- """Test the limit kwarg"""
- limit = 4
- cur = lang.fetch(limit=limit)
- assert len(cur) == limit, "Length is not correct"
-
-
-def test_order_by_limit(lang, languages):
- """Test the combination of order by and limit kwargs"""
- cur = lang.fetch(limit=4, order_by=["language", "name DESC"])
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
- assert len(cur) == 4, "Length is not correct"
- for c, l in list(zip(cur, languages))[:4]:
- assert np.all([cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)]), "Sorting order is different"
-
-
-def test_head_tail(schema_any):
- query = schema.User * schema.Language
- n = 5
- frame = query.head(n, format="frame")
- assert isinstance(frame, pandas.DataFrame)
- array = query.head(n, format="array")
- assert array.size == n
- assert len(frame) == n
- assert query.primary_key == frame.index.names
-
- n = 4
- frame = query.tail(n, format="frame")
- array = query.tail(n, format="array")
- assert array.size == n
- assert len(frame) == n
- assert query.primary_key == frame.index.names
-
-
-def test_limit_offset(lang, languages):
- """Test the limit and offset kwargs together"""
- cur = lang.fetch(offset=2, limit=4, order_by=["language", "name DESC"])
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
- assert len(cur) == 4, "Length is not correct"
- for c, l in list(zip(cur, languages[2:6])):
- assert np.all([cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)]), "Sorting order is different"
-
-
-def test_iter(lang, languages):
- """Test iterator"""
- cur = lang.fetch(order_by=["language", "name DESC"])
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
- for (name, lang_val), (tname, tlang) in list(zip(cur, languages)):
- assert name == tname and lang_val == tlang, "Values are not the same"
- # now as dict
- cur = lang.fetch(as_dict=True, order_by=("language", "name DESC"))
- for row, (tname, tlang) in list(zip(cur, languages)):
- assert (
- row["name"] == tname and row["language"] == tlang
- ), "Values are not the same"
-
-
-def test_keys(lang, languages):
- """test key fetch"""
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
-
- lang = schema.Language()
- cur = lang.fetch("name", "language", order_by=("language", "name DESC"))
- cur2 = list(lang.fetch("KEY", order_by=["language", "name DESC"]))
-
- for c, c2 in zip(zip(*cur), cur2):
- assert c == tuple(c2.values()), "Values are not the same"
-
-
-def test_attributes_as_dict(subject):
- """
- Issue #595
- """
- attrs = ("species", "date_of_birth")
- result = subject.fetch(*attrs, as_dict=True)
- assert bool(result) and len(result) == len(subject)
- assert set(result[0]) == set(attrs)
-
-
-def test_fetch1_step1(lang, languages):
- assert (
- lang.contents
- == languages
- == [
- ("Fabian", "English"),
- ("Edgar", "English"),
- ("Dimitri", "English"),
- ("Dimitri", "Ukrainian"),
- ("Fabian", "German"),
- ("Edgar", "Japanese"),
- ]
- ), "Unexpected contents in Language table"
- key = {"name": "Edgar", "language": "Japanese"}
- true = languages[-1]
- dat = (lang & key).fetch1()
- for k, (ke, c) in zip(true, dat.items()):
- assert k == c == (lang & key).fetch1(ke), "Values are not the same"
-
-
-def test_misspelled_attribute(schema_any):
- with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- f = (schema.Language & 'lang = "ENGLISH"').fetch()
-
-
-def test_repr(subject):
- """Test string representation of fetch, returning table preview"""
- repr = subject.fetch.__repr__()
- n = len(repr.strip().split("\n"))
- limit = dj.config["display.limit"]
- # 3 lines are used for headers (2) and summary statement (1)
- assert n - 3 <= limit
-
-
-def test_fetch_none(lang):
- """Test preparing attributes for getitem"""
- with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- lang.fetch(None)
-
-
-def test_asdict(lang):
- """Test returns as dictionaries"""
- d = lang.fetch(as_dict=True)
- for dd in d:
- assert isinstance(dd, dict)
-
-
-def test_offset(lang, languages):
- """Tests offset"""
- cur = lang.fetch(limit=4, offset=1, order_by=["language", "name DESC"])
-
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
- languages.sort(key=itemgetter(1), reverse=False)
- assert len(cur) == 4, "Length is not correct"
- for c, l in list(zip(cur, languages[1:]))[:4]:
- assert np.all([cc == ll for cc, ll in zip(c, l)]), "Sorting order is different"
-
-
-def test_len(lang):
- """Tests __len__"""
- assert len(lang.fetch()) == len(lang), "__len__ is not behaving properly"
-
-
-def test_fetch1_step2(lang):
- """Tests whether fetch1 raises error"""
- with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- lang.fetch1()
-
-
-def test_fetch1_step3(lang):
- """Tests whether fetch1 raises error"""
- with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- lang.fetch1("name")
-
-
-def test_decimal(schema_any):
- """Tests that decimal fields are correctly fetched and used in restrictions, see issue #334"""
- rel = schema.DecimalPrimaryKey()
- assert len(rel.fetch()), "Table DecimalPrimaryKey contents are empty"
- rel.insert1([decimal.Decimal("3.1415926")])
- keys = rel.fetch()
- assert len(keys) > 0
- assert len(rel & keys[0]) == 1
- keys = rel.fetch(dj.key)
- assert len(keys) >= 2
- assert len(rel & keys[1]) == 1
-
-
-def test_nullable_numbers(schema_any):
- """test mixture of values and nulls in numeric attributes"""
- table = schema.NullableNumbers()
- table.insert(
- (
- (
- k,
- np.random.randn(),
- np.random.randint(-1000, 1000),
- np.random.randn(),
- )
- for k in range(10)
- )
- )
- table.insert1((100, None, None, None))
- f, d, i = table.fetch("fvalue", "dvalue", "ivalue")
- assert None in i
- assert any(np.isnan(d))
- assert any(np.isnan(f))
-
-
-def test_fetch_format(subject):
- """test fetch_format='frame'"""
- with dj.config(fetch_format="frame"):
- # test if lists are both dicts
- list1 = sorted(subject.proj().fetch(as_dict=True), key=itemgetter("subject_id"))
- list2 = sorted(subject.fetch(dj.key), key=itemgetter("subject_id"))
- for l1, l2 in zip(list1, list2):
- assert l1 == l2, "Primary key is not returned correctly"
-
- # tests if pandas dataframe
- tmp = subject.fetch(order_by="subject_id")
- assert isinstance(tmp, pandas.DataFrame)
- tmp = tmp.to_records()
-
- subject_notes, key, real_id = subject.fetch("subject_notes", dj.key, "real_id")
-
- np.testing.assert_array_equal(
- sorted(subject_notes), sorted(tmp["subject_notes"])
- )
- np.testing.assert_array_equal(sorted(real_id), sorted(tmp["real_id"]))
- list1 = sorted(key, key=itemgetter("subject_id"))
- for l1, l2 in zip(list1, list2):
- assert l1 == l2, "Primary key is not returned correctly"
-
-
-def test_key_fetch1(subject):
- """test KEY fetch1 - issue #976"""
- with dj.config(fetch_format="array"):
- k1 = (subject & "subject_id=10").fetch1("KEY")
- with dj.config(fetch_format="frame"):
- k2 = (subject & "subject_id=10").fetch1("KEY")
- assert k1 == k2
-
-
-def test_same_secondary_attribute(schema_any):
- children = (schema.Child * schema.Parent().proj()).fetch()["name"]
- assert len(children) == 1
- assert children[0] == "Dan"
-
-
-def test_query_caching(schema_any):
- # initialize cache directory
- os.mkdir(os.path.expanduser("~/dj_query_cache"))
-
- with dj.config(query_cache=os.path.expanduser("~/dj_query_cache")):
- conn = schema.TTest3.connection
- # insert sample data and load cache
- schema.TTest3.insert([dict(key=100 + i, value=200 + i) for i in range(2)])
- conn.set_query_cache(query_cache="main")
- cached_res = schema.TTest3().fetch()
- # attempt to insert while caching enabled
- try:
- schema.TTest3.insert([dict(key=200 + i, value=400 + i) for i in range(2)])
- assert False, "Insert allowed while query caching enabled"
- except dj.DataJointError:
- conn.set_query_cache()
- # insert new data
- schema.TTest3.insert([dict(key=600 + i, value=800 + i) for i in range(2)])
- # re-enable cache to access old results
- conn.set_query_cache(query_cache="main")
- previous_cache = schema.TTest3().fetch()
- # verify properly cached and how to refresh results
- assert all([c == p for c, p in zip(cached_res, previous_cache)])
- conn.set_query_cache()
- uncached_res = schema.TTest3().fetch()
- assert len(uncached_res) > len(cached_res)
- # purge query cache
- conn.purge_query_cache()
-
- # reset cache directory state (will fail if purge was unsuccessful)
- os.rmdir(os.path.expanduser("~/dj_query_cache"))
-
-
-def test_fetch_group_by(schema_any):
- """
- https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/914
- """
-
- assert schema.Parent().fetch("KEY", order_by="name") == [{"parent_id": 1}]
-
-
-def test_dj_u_distinct(schema_any):
- """
- Test developed to see if removing DISTINCT from the select statement
- generation breaks the dj.U universal set implementation
- """
-
- # Contents to be inserted
- contents = [(1, 2, 3), (2, 2, 3), (3, 3, 2), (4, 5, 5)]
- schema.Stimulus.insert(contents)
-
- # Query the whole table
- test_query = schema.Stimulus()
-
- # Use dj.U to create a list of unique contrast and brightness combinations
- result = dj.U("contrast", "brightness") & test_query
- expected_result = [
- {"contrast": 2, "brightness": 3},
- {"contrast": 3, "brightness": 2},
- {"contrast": 5, "brightness": 5},
- ]
-
- fetched_result = result.fetch(as_dict=True, order_by=("contrast", "brightness"))
- schema.Stimulus.delete_quick()
- assert fetched_result == expected_result
-
-
-def test_backslash(schema_any):
- """
- https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/999
- """
- expected = "She\\Hulk"
- schema.Parent.insert([(2, expected)])
- q = schema.Parent & dict(name=expected)
- assert q.fetch1("name") == expected
- q.delete()
diff --git a/tests/test_filepath.py b/tests/test_filepath.py
deleted file mode 100644
index cc3db2cc2..000000000
--- a/tests/test_filepath.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,268 +0,0 @@
-import io
-import logging
-import os
-import random
-from pathlib import Path
-
-import pytest
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-from .schema_external import Filepath, FilepathS3
-
-
-def test_path_match(schema_ext, enable_filepath_feature, minio_client, store="repo"):
- """test file path matches and empty file"""
- ext = schema_ext.external[store]
- stage_path = dj.config["stores"][store]["stage"]
-
- # create a mock file
- relpath = "path/to/films"
- managed_file = Path(stage_path, relpath, "vid.mov")
- managed_file.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
- open(str(managed_file), "a").close()
-
- # put the file
- uuid = ext.upload_filepath(str(managed_file))
-
- # remove
- managed_file.unlink()
- assert not managed_file.exists()
-
- # check filepath
- assert (ext & {"hash": uuid}).fetch1("filepath") == str(
- managed_file.relative_to(stage_path).as_posix()
- )
-
- # # Download the file and check its contents.
- restored_path, checksum = ext.download_filepath(uuid)
- assert restored_path == str(managed_file)
- assert checksum == dj.hash.uuid_from_file(str(managed_file))
-
- # cleanup
- ext.delete(delete_external_files=True)
-
-
-@pytest.mark.parametrize("store", ("repo", "repo-s3"))
-def test_filepath(enable_filepath_feature, schema_ext, store):
- """test file management"""
- ext = schema_ext.external[store]
- stage_path = dj.config["stores"][store]["stage"]
- filename = "picture.dat"
-
- # create a mock file
- relpath = "one/two/three"
- managed_file = Path(stage_path, relpath, filename)
- managed_file.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
- data = os.urandom(3000)
- with managed_file.open("wb") as f:
- f.write(data)
-
- # put the same file twice to ensure storing once
- uuid1 = ext.upload_filepath(str(managed_file))
- # no duplication should arise if file is the same
- uuid2 = ext.upload_filepath(str(managed_file))
- assert uuid1 == uuid2
-
- # remove to ensure downloading
- managed_file.unlink()
- assert not managed_file.exists()
-
- # Download the file and check its contents. Repeat causes no download from remote
- for _ in 1, 2:
- restored_path, checksum = ext.download_filepath(uuid1)
- assert restored_path == str(managed_file)
- assert checksum == dj.hash.uuid_from_file(str(managed_file))
-
- # verify same data
- with managed_file.open("rb") as f:
- synced_data = f.read()
- assert data == synced_data
-
- # cleanup
- ext.delete(delete_external_files=True)
- assert not ext.exists(ext._make_external_filepath(str(Path(relpath, filename))))
-
-
-@pytest.mark.parametrize("store", ("repo", "repo-s3"))
-def test_duplicate_upload(schema_ext, store):
- ext = schema_ext.external[store]
- stage_path = dj.config["stores"][store]["stage"]
- relpath = "one/two/three"
- managed_file = Path(stage_path, relpath, "plot.dat")
- managed_file.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
- with managed_file.open("wb") as f:
- f.write(os.urandom(300))
- ext.upload_filepath(str(managed_file))
- ext.upload_filepath(str(managed_file)) # this is fine because the file is the same
-
-
-@pytest.mark.parametrize("store", ("repo", "repo-s3"))
-def test_duplicate_error(schema_ext, store):
- """syncing duplicate non-matching file should fail"""
- ext = schema_ext.external[store]
- stage_path = dj.config["stores"][store]["stage"]
- relpath = "one/two/three"
- managed_file = Path(stage_path, relpath, "thesis.dat")
- managed_file.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
- with managed_file.open("wb") as f:
- f.write(os.urandom(300))
- ext.upload_filepath(str(managed_file))
- with managed_file.open("wb") as f:
- f.write(os.urandom(300))
- # this should raise exception because the file has changed
- with pytest.raises(dj.DataJointError):
- ext.upload_filepath(str(managed_file))
-
-
-class TestFilepath:
- def _test_filepath_class(
- self, table=Filepath(), store="repo", verify_checksum=True
- ):
- if not verify_checksum:
- dj.config["filepath_checksum_size_limit"] = 0
- stage_path = dj.config["stores"][store]["stage"]
- # create a mock file
- relative_path = "one/two/three"
- managed_file = Path(stage_path, relative_path, "attachment.dat")
- managed_file.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
- data = os.urandom(3000)
- with managed_file.open("wb") as f:
- f.write(data)
- with managed_file.open("rb") as f:
- contents = f.read()
- assert data == contents
-
- # upload file into shared repo
- table.insert1((1, str(managed_file)))
-
- # remove file locally
- managed_file.unlink()
- assert not managed_file.is_file()
-
- # fetch file from remote
- filepath = (table & {"fnum": 1}).fetch1("img")
- assert filepath == str(managed_file)
-
- # verify original contents
- with managed_file.open("rb") as f:
- contents = f.read()
- assert data == contents
-
- # delete from table
- table.delete()
- assert table.external[store]
-
- # delete from external table
- table.external[store].delete(delete_external_files=True)
- dj.config["filepath_checksum_size_limit"] = None
-
- @pytest.mark.parametrize(
- "table, store, n_repeats",
- (
- (Filepath(), "repo", 2),
- (FilepathS3(), "repo-s3", 2),
- ),
- )
- def test_filepath_class(
- self,
- schema_ext,
- table,
- store,
- n_repeats,
- minio_client,
- enable_filepath_feature,
- verify_checksum=True,
- ):
- for _ in range(n_repeats):
- self._test_filepath_class(table, store, verify_checksum)
-
- def test_filepath_class_no_checksum(self, schema_ext, enable_filepath_feature):
- logger = logging.getLogger("datajoint")
- log_capture = io.StringIO()
- stream_handler = logging.StreamHandler(log_capture)
- log_format = logging.Formatter(
- "[%(asctime)s][%(funcName)s][%(levelname)s]: %(message)s"
- )
- stream_handler.setFormatter(log_format)
- stream_handler.set_name("test_limit_warning")
- logger.addHandler(stream_handler)
- self._test_filepath_class(table=Filepath(), store="repo", verify_checksum=False)
- log_contents = log_capture.getvalue()
- log_capture.close()
- for handler in logger.handlers: # Clean up handler
- if handler.name == "test_limit_warning":
- logger.removeHandler(handler)
- assert "Skipped checksum for file with hash:" in log_contents
-
-
-@pytest.mark.parametrize(
- "table, store",
- (
- (Filepath(), "repo"),
- (FilepathS3(), "repo-s3"),
- ),
-)
-def test_filepath_cleanup(table, store, schema_ext, enable_filepath_feature):
- """test deletion of filepath entries from external table"""
- stage_path = dj.config["stores"][store]["stage"]
- n = 20
- contents = os.urandom(345)
- for i in range(n):
- relative_path = Path(*random.sample(("one", "two", "three", "four"), k=3))
- managed_file = Path(stage_path, relative_path, "file.dat")
- managed_file.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
- with managed_file.open("wb") as f:
- f.write(contents) # same in all files
- table.insert1((i, str(managed_file)))
- assert len(table) == n
-
- ext = schema_ext.external[store]
-
- assert len(table) == n
- assert 0 < len(ext) < n
-
- (table & "fnum in (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)").delete()
- m = n - len(table) # number deleted
- assert m == 6
-
- ext.delete(delete_external_files=True) # delete unused entries
- assert 0 < len(ext) <= n - m
-
-
-def test_delete_without_files(
- schema_ext,
- enable_filepath_feature,
- store="repo",
-):
- """test deletion of filepath entries from external table without removing files"""
- # do not delete unused entries
- schema_ext.external[store].delete(delete_external_files=False)
-
-
-def test_return_string(
- schema_ext, enable_filepath_feature, table=Filepath(), store="repo"
-):
- """test returning string on fetch"""
- stage_path = dj.config["stores"][store]["stage"]
- # create a mock file
- relative_path = "this/is/a/test"
- managed_file = Path(stage_path, relative_path, "string.dat")
- managed_file.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
- data = os.urandom(3000)
- with managed_file.open("wb") as f:
- f.write(data)
- with managed_file.open("rb") as f:
- contents = f.read()
- assert data == contents
-
- # upload file into shared repo
- table.insert1((138, str(managed_file)))
-
- # remove file locally
- managed_file.unlink()
- assert not managed_file.is_file()
-
- # fetch file from remote
- filepath = (table & {"fnum": 138}).fetch1("img")
- assert isinstance(filepath, str)
diff --git a/tests/test_jobs.py b/tests/test_jobs.py
deleted file mode 100644
index dc363076d..000000000
--- a/tests/test_jobs.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,149 +0,0 @@
-import random
-import string
-
-import pytest
-
-import datajoint as dj
-from datajoint.jobs import ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH, TRUNCATION_APPENDIX
-
-from . import schema
-
-
-def test_reserve_job(subject, schema_any):
- assert subject
- table_name = "fake_table"
-
- # reserve jobs
- for key in subject.fetch("KEY"):
- assert schema_any.jobs.reserve(table_name, key), "failed to reserve a job"
-
- # refuse jobs
- for key in subject.fetch("KEY"):
- assert not schema_any.jobs.reserve(
- table_name, key
- ), "failed to respect reservation"
-
- # complete jobs
- for key in subject.fetch("KEY"):
- schema_any.jobs.complete(table_name, key)
- assert not schema_any.jobs, "failed to free jobs"
-
- # reserve jobs again
- for key in subject.fetch("KEY"):
- assert schema_any.jobs.reserve(table_name, key), "failed to reserve new jobs"
-
- # finish with error
- for key in subject.fetch("KEY"):
- schema_any.jobs.error(table_name, key, "error message")
-
- # refuse jobs with errors
- for key in subject.fetch("KEY"):
- assert not schema_any.jobs.reserve(
- table_name, key
- ), "failed to ignore error jobs"
-
- # clear error jobs
- (schema_any.jobs & dict(status="error")).delete()
- assert not schema_any.jobs, "failed to clear error jobs"
-
-
-def test_restrictions(schema_any):
- jobs = schema_any.jobs
- jobs.delete()
- jobs.reserve("a", {"key": "a1"})
- jobs.reserve("a", {"key": "a2"})
- jobs.reserve("b", {"key": "b1"})
- jobs.error("a", {"key": "a2"}, "error")
- jobs.error("b", {"key": "b1"}, "error")
-
- assert len(jobs & {"table_name": "a"}) == 2
- assert len(jobs & {"status": "error"}) == 2
- assert len(jobs & {"table_name": "a", "status": "error"}) == 1
- jobs.delete()
-
-
-def test_sigint(schema_any):
- try:
- schema.SigIntTable().populate(reserve_jobs=True)
- except KeyboardInterrupt:
- pass
-
- assert len(schema_any.jobs.fetch()), "SigInt jobs table is empty"
- status, error_message = schema_any.jobs.fetch1("status", "error_message")
- assert status == "error"
- assert error_message == "KeyboardInterrupt"
-
-
-def test_sigterm(schema_any):
- try:
- schema.SigTermTable().populate(reserve_jobs=True)
- except SystemExit:
- pass
-
- assert len(schema_any.jobs.fetch()), "SigTerm jobs table is empty"
- status, error_message = schema_any.jobs.fetch1("status", "error_message")
- assert status == "error"
- assert error_message == "SystemExit: SIGTERM received"
-
-
-def test_suppress_dj_errors(schema_any):
- """test_suppress_dj_errors: dj errors suppressible w/o native py blobs"""
- with dj.config(enable_python_native_blobs=False):
- schema.ErrorClass.populate(reserve_jobs=True, suppress_errors=True)
- assert len(schema.DjExceptionName()) == len(schema_any.jobs) > 0
-
-
-def test_long_error_message(subject, schema_any):
- # create long error message
- long_error_message = "".join(
- random.choice(string.ascii_letters) for _ in range(ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH + 100)
- )
- short_error_message = "".join(
- random.choice(string.ascii_letters) for _ in range(ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH // 2)
- )
- assert subject
- table_name = "fake_table"
-
- key = subject.fetch("KEY", limit=1)[0]
-
- # test long error message
- schema_any.jobs.reserve(table_name, key)
- schema_any.jobs.error(table_name, key, long_error_message)
- error_message = schema_any.jobs.fetch1("error_message")
- assert (
- len(error_message) == ERROR_MESSAGE_LENGTH
- ), "error message is longer than max allowed"
- assert error_message.endswith(
- TRUNCATION_APPENDIX
- ), "appropriate ending missing for truncated error message"
- schema_any.jobs.delete()
-
- # test long error message
- schema_any.jobs.reserve(table_name, key)
- schema_any.jobs.error(table_name, key, short_error_message)
- error_message = schema_any.jobs.fetch1("error_message")
- assert error_message == short_error_message, "error messages do not agree"
- assert not error_message.endswith(
- TRUNCATION_APPENDIX
- ), "error message should not be truncated"
- schema_any.jobs.delete()
-
-
-def test_long_error_stack(subject, schema_any):
- # create long error stack
- STACK_SIZE = (
- 89942 # Does not fit into small blob (should be 64k, but found to be higher)
- )
- long_error_stack = "".join(
- random.choice(string.ascii_letters) for _ in range(STACK_SIZE)
- )
- assert subject
- table_name = "fake_table"
-
- key = subject.fetch("KEY", limit=1)[0]
-
- # test long error stack
- schema_any.jobs.reserve(table_name, key)
- schema_any.jobs.error(table_name, key, "error message", long_error_stack)
- error_stack = schema_any.jobs.fetch1("error_stack")
- assert error_stack == long_error_stack, "error stacks do not agree"
diff --git a/tests/test_log.py b/tests/test_log.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4b6e64613..000000000
--- a/tests/test_log.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
-def test_log(schema_any):
- ts, events = (schema_any.log & 'event like "Declared%%"').fetch(
- "timestamp", "event"
- )
- assert len(ts) >= 2
diff --git a/tests/test_relation_u.py b/tests/test_relation_u.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 59cee0249..000000000
--- a/tests/test_relation_u.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-import pytest
-from pytest import raises
-
-import datajoint as dj
-
-from .schema import *
-from .schema_simple import *
-
-
-def test_restriction(lang, languages, trial):
- language_set = {s[1] for s in languages}
- rel = dj.U("language") & lang
- assert list(rel.heading.names) == ["language"]
- assert len(rel) == len(language_set)
- assert set(rel.fetch("language")) == language_set
- # Test for issue #342
- rel = trial * dj.U("start_time")
- assert list(rel.primary_key) == trial.primary_key + ["start_time"]
- assert list(rel.primary_key) == list((rel & "trial_id>3").primary_key)
- assert list((dj.U("start_time") & trial).primary_key) == ["start_time"]
-
-
-def test_invalid_restriction(schema_any):
- with raises(dj.DataJointError):
- result = dj.U("color") & dict(color="red")
-
-
-def test_ineffective_restriction(lang):
- rel = lang & dj.U("language")
- assert rel.make_sql() == lang.make_sql()
-
-
-def test_join(experiment):
- rel = experiment * dj.U("experiment_date")
- assert experiment.primary_key == ["subject_id", "experiment_id"]
- assert rel.primary_key == experiment.primary_key + ["experiment_date"]
-
- rel = dj.U("experiment_date") * experiment
- assert experiment.primary_key == ["subject_id", "experiment_id"]
- assert rel.primary_key == experiment.primary_key + ["experiment_date"]
-
-
-def test_invalid_join(schema_any):
- with raises(dj.DataJointError):
- rel = dj.U("language") * dict(language="English")
-
-
-def test_repr_without_attrs(schema_any):
- """test dj.U() display"""
- query = dj.U().aggr(Language, n="count(*)")
- repr(query)
-
-
-def test_aggregations(schema_any):
- lang = Language()
- # test total aggregation on expression object
- n1 = dj.U().aggr(lang, n="count(*)").fetch1("n")
- assert n1 == len(lang.fetch())
- # test total aggregation on expression class
- n2 = dj.U().aggr(Language, n="count(*)").fetch1("n")
- assert n1 == n2
- rel = dj.U("language").aggr(Language, number_of_speakers="count(*)")
- assert len(rel) == len(set(l[1] for l in Language.contents))
- assert (rel & 'language="English"').fetch1("number_of_speakers") == 3
-
-
-def test_argmax(schema_any):
- rel = TTest()
- # get the tuples corresponding to the maximum value
- mx = (rel * dj.U().aggr(rel, mx="max(value)")) & "mx=value"
- assert mx.fetch("value")[0] == max(rel.fetch("value"))
-
-
-def test_aggr(schema_any, schema_simp):
- rel = ArgmaxTest()
- amax1 = (dj.U("val") * rel) & dj.U("secondary_key").aggr(rel, val="min(val)")
- amax2 = (dj.U("val") * rel) * dj.U("secondary_key").aggr(rel, val="min(val)")
- assert (
- len(amax1) == len(amax2) == rel.n
- ), "Aggregated argmax with join and restriction does not yield the same length."
diff --git a/tests/test_s3.py b/tests/test_s3.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 970310ca8..000000000
--- a/tests/test_s3.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
-import pytest
-from minio import Minio
-
-from datajoint.blob import pack
-from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
-from datajoint.hash import uuid_from_buffer
-
-from .schema_external import SimpleRemote
-
-
-def test_connection(http_client, minio_client, s3_creds):
- assert minio_client.bucket_exists(s3_creds["bucket"])
-
-
-def test_connection_secure(minio_client, s3_creds):
- assert minio_client.bucket_exists(s3_creds["bucket"])
-
-
-def test_remove_object_exception(schema_ext, s3_creds):
- # https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-python/issues/952
-
- # Insert some test data and remove it so that the external table is populated
- test = [1, [1, 2, 3]]
- SimpleRemote.insert1(test)
- SimpleRemote.delete()
-
- # Save the old external table minio client
- old_client = schema_ext.external["share"].s3.client
-
- # Apply our new minio client which has a user that does not exist
- schema_ext.external["share"].s3.client = Minio(
- s3_creds["endpoint"],
- access_key="jeffjeff",
- secret_key="jeffjeff",
- secure=False,
- )
-
- # This method returns a list of errors
- error_list = schema_ext.external["share"].delete(
- delete_external_files=True, errors_as_string=False
- )
-
- # Teardown
- schema_ext.external["share"].s3.client = old_client
- schema_ext.external["share"].delete(delete_external_files=True)
-
- with pytest.raises(DataJointError):
- # Raise the error we want if the error matches the expected uuid
- if str(error_list[0][0]) == str(uuid_from_buffer(pack(test[1]))):
- raise error_list[0][2]
diff --git a/tests/test_settings.py b/tests/test_settings.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4eb8be539..000000000
--- a/tests/test_settings.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
-import os
-import pprint
-import random
-import string
-
-import pytest
-
-import datajoint as dj
-from datajoint import DataJointError, settings
-
-__author__ = "Fabian Sinz"
-
-
-def test_load_save():
- """Testing load and save"""
- dj.config.save("tmp.json")
- conf = settings.Config()
- conf.load("tmp.json")
- assert conf == dj.config
- os.remove("tmp.json")
-
-
-def test_singleton():
- """Testing singleton property"""
- dj.config.save("tmp.json")
- conf = settings.Config()
- conf.load("tmp.json")
- conf["dummy.val"] = 2
-
- assert conf == dj.config
- os.remove("tmp.json")
-
-
-def test_singleton2():
- """Testing singleton property"""
- conf = settings.Config()
- conf["dummy.val"] = 2
- _ = settings.Config() # a new instance should not delete dummy.val
- assert conf["dummy.val"] == 2
-
-
-def test_validator():
- """Testing validator"""
- with pytest.raises(DataJointError):
- dj.config["database.port"] = "harbor"
-
-
-def test_del():
- """Testing del"""
- dj.config["peter"] = 2
- assert "peter" in dj.config
- del dj.config["peter"]
- assert "peter" not in dj.config
-
-
-def test_len():
- """Testing len"""
- len(dj.config) == len(dj.config._conf)
-
-
-def test_str():
- """Testing str"""
- str(dj.config) == pprint.pformat(dj.config._conf, indent=4)
-
-
-def test_repr():
- """Testing repr"""
- repr(dj.config) == pprint.pformat(dj.config._conf, indent=4)
-
-
-def test_save():
- """Testing save of config"""
- tmpfile = "".join(
- random.choice(string.ascii_uppercase + string.digits) for _ in range(20)
- )
- moved = False
- if os.path.isfile(settings.LOCALCONFIG):
- os.rename(settings.LOCALCONFIG, tmpfile)
- moved = True
- dj.config.save_local()
- assert os.path.isfile(settings.LOCALCONFIG)
- if moved:
- os.rename(tmpfile, settings.LOCALCONFIG)
-
-
-def test_load_save():
- """Testing load and save of config"""
- filename_old = dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG
- filename = (
- "".join(
- random.choice(string.ascii_uppercase + string.digits) for _ in range(50)
- )
- + ".json"
- )
- dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG = filename
- dj.config.save_local()
- dj.config.load(filename=filename)
- dj.settings.LOCALCONFIG = filename_old
- os.remove(filename)
-
-
-def test_contextmanager():
- """Testing context manager"""
- dj.config["arbitrary.stuff"] = 7
- with dj.config(arbitrary__stuff=10):
- assert dj.config["arbitrary.stuff"] == 10
- assert dj.config["arbitrary.stuff"] == 7
diff --git a/tests/test_virtual_module.py b/tests/test_virtual_module.py
deleted file mode 100644
index bd8a0c754..000000000
--- a/tests/test_virtual_module.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
-import datajoint as dj
-from datajoint.user_tables import UserTable
-
-
-def test_virtual_module(schema_any, connection_test):
- module = dj.VirtualModule("module", schema_any.database, connection=connection_test)
- assert issubclass(module.Experiment, UserTable)
diff --git a/tests/unit/__init__.py b/tests/unit/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e69de29bb
diff --git a/tests/unit/test_codecs.py b/tests/unit/test_codecs.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ada626748
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/test_codecs.py
@@ -0,0 +1,429 @@
+"""
+Tests for the Codec system.
+"""
+
+import pytest
+
+import datajoint as dj
+from datajoint.codecs import (
+ Codec,
+ _codec_registry,
+ get_codec,
+ is_codec_registered,
+ list_codecs,
+ resolve_dtype,
+ unregister_codec,
+)
+from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
+
+
+class TestCodecRegistry:
+ """Tests for the codec registry functionality."""
+
+ def setup_method(self):
+ """Clear any test codecs from registry before each test."""
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def teardown_method(self):
+ """Clean up test codecs after each test."""
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def test_register_codec_auto(self):
+ """Test auto-registration via __init_subclass__."""
+
+ class TestCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_decorator"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "bytes"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ assert is_codec_registered("test_decorator")
+ assert get_codec("test_decorator").name == "test_decorator"
+
+ def test_register_codec_skip(self):
+ """Test skipping registration with register=False."""
+
+ class TestCodec(Codec, register=False):
+ name = "test_skip"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "varchar(255)"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return str(value)
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ assert not is_codec_registered("test_skip")
+
+ def test_register_codec_idempotent(self):
+ """Test that defining the same codec class twice is idempotent."""
+
+ class TestCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_idempotent"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "int32"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ # Redefine the same name should not raise (same class)
+ assert is_codec_registered("test_idempotent")
+
+ def test_register_duplicate_name_different_class(self):
+ """Test that registering different classes with same name raises error."""
+
+ class TestCodec1(Codec):
+ name = "test_duplicate"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "int32"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError, match="already registered"):
+
+ class TestCodec2(Codec):
+ name = "test_duplicate"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "varchar(100)"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return str(value)
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ def test_unregister_codec(self):
+ """Test unregistering a codec."""
+
+ class TestCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_unregister"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "int32"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ assert is_codec_registered("test_unregister")
+ unregister_codec("test_unregister")
+ assert not is_codec_registered("test_unregister")
+
+ def test_get_codec_not_found(self):
+ """Test that getting an unregistered codec raises error."""
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError, match="Unknown codec"):
+ get_codec("nonexistent_codec")
+
+ def test_list_codecs(self):
+ """Test listing registered codecs."""
+
+ class TestCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_list"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "int32"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ codecs = list_codecs()
+ assert "test_list" in codecs
+ assert codecs == sorted(codecs) # Should be sorted
+
+ def test_get_codec_strips_brackets(self):
+ """Test that get_codec accepts names with or without angle brackets."""
+
+ class TestCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_brackets"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "int32"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ assert get_codec("test_brackets") is get_codec("")
+
+
+class TestCodecValidation:
+ """Tests for the validate method."""
+
+ def setup_method(self):
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def teardown_method(self):
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def test_validate_called_default(self):
+ """Test that default validate accepts any value."""
+
+ class TestCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_validate_default"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "bytes"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ t = get_codec("test_validate_default")
+ # Default validate should not raise for any value
+ t.validate(None)
+ t.validate(42)
+ t.validate("string")
+ t.validate([1, 2, 3])
+
+ def test_validate_custom(self):
+ """Test custom validation logic."""
+
+ class PositiveIntCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_positive_int"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "int32"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ def validate(self, value):
+ if not isinstance(value, int):
+ raise TypeError(f"Expected int, got {type(value).__name__}")
+ if value < 0:
+ raise ValueError("Value must be positive")
+
+ t = get_codec("test_positive_int")
+ t.validate(42) # Should pass
+
+ with pytest.raises(TypeError):
+ t.validate("not an int")
+
+ with pytest.raises(ValueError):
+ t.validate(-1)
+
+
+class TestCodecChaining:
+ """Tests for codec chaining (dtype referencing another codec)."""
+
+ def setup_method(self):
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def teardown_method(self):
+ for name in list(_codec_registry.keys()):
+ if name.startswith("test_"):
+ del _codec_registry[name]
+
+ def test_resolve_native_dtype(self):
+ """Test resolving a native dtype."""
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("bytes")
+ assert final_dtype == "bytes"
+ assert chain == []
+ assert store is None
+
+ def test_resolve_custom_dtype(self):
+ """Test resolving a custom dtype."""
+
+ class TestCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_resolve"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "varchar(100)"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+ assert final_dtype == "varchar(100)"
+ assert len(chain) == 1
+ assert chain[0].name == "test_resolve"
+ assert store is None
+
+ def test_resolve_chained_dtype(self):
+ """Test resolving a chained dtype."""
+
+ class InnerCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_inner"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return "bytes"
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ class OuterCodec(Codec):
+ name = "test_outer"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ final_dtype, chain, store = resolve_dtype("")
+ assert final_dtype == "bytes"
+ assert len(chain) == 2
+ assert chain[0].name == "test_outer"
+ assert chain[1].name == "test_inner"
+ assert store is None
+
+ def test_circular_reference_detection(self):
+ """Test that circular codec references are detected."""
+
+ class CodecA(Codec):
+ name = "test_circular_a"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ class CodecB(Codec):
+ name = "test_circular_b"
+
+ def get_dtype(self, is_external: bool) -> str:
+ return ""
+
+ def encode(self, value, *, key=None, store_name=None):
+ return value
+
+ def decode(self, stored, *, key=None):
+ return stored
+
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError, match="Circular codec reference"):
+ resolve_dtype("")
+
+
+class TestExportsAndAPI:
+ """Test that the public API is properly exported."""
+
+ def test_exports_from_datajoint(self):
+ """Test that Codec and helpers are exported from datajoint."""
+ assert hasattr(dj, "Codec")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "get_codec")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "list_codecs")
+
+
+class TestBlobCodec:
+ """Tests for the built-in BlobCodec."""
+
+ def test_blob_is_registered(self):
+ """Test that blob is automatically registered."""
+ assert is_codec_registered("blob")
+
+ def test_blob_properties(self):
+ """Test BlobCodec properties."""
+ blob_codec = get_codec("blob")
+ assert blob_codec.name == "blob"
+ assert blob_codec.get_dtype(is_external=False) == "bytes"
+ assert blob_codec.get_dtype(is_external=True) == ""
+
+ def test_blob_encode_decode_roundtrip(self):
+ """Test that encode/decode is a proper roundtrip."""
+ import numpy as np
+
+ blob_codec = get_codec("blob")
+
+ # Test with various data types
+ test_data = [
+ {"key": "value", "number": 42},
+ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
+ np.array([1.0, 2.0, 3.0]),
+ "simple string",
+ (1, 2, 3),
+ None,
+ ]
+
+ for original in test_data:
+ encoded = blob_codec.encode(original)
+ assert isinstance(encoded, bytes)
+ decoded = blob_codec.decode(encoded)
+ if isinstance(original, np.ndarray):
+ np.testing.assert_array_equal(decoded, original)
+ else:
+ assert decoded == original
+
+ def test_blob_encode_produces_valid_blob_format(self):
+ """Test that encoded data has valid blob protocol header."""
+ blob_codec = get_codec("blob")
+ encoded = blob_codec.encode({"test": "data"})
+
+ # Should start with compression prefix or protocol header
+ valid_prefixes = (b"ZL123\0", b"mYm\0", b"dj0\0")
+ assert any(encoded.startswith(p) for p in valid_prefixes)
+
+ def test_blob_in_list_codecs(self):
+ """Test that blob appears in list_codecs."""
+ codecs = list_codecs()
+ assert "blob" in codecs
+
+ def test_blob_handles_serialization(self):
+ """Test that BlobCodec handles serialization internally.
+
+ With the new design:
+ - Plain bytes columns store/return raw bytes (no serialization)
+ - handles pack/unpack in encode/decode
+ """
+ blob_codec = get_codec("blob")
+
+ # BlobCodec.encode() should produce packed bytes
+ data = {"key": "value"}
+ encoded = blob_codec.encode(data)
+ assert isinstance(encoded, bytes)
+
+ # BlobCodec.decode() should unpack back to original
+ decoded = blob_codec.decode(encoded)
+ assert decoded == data
diff --git a/tests/unit/test_condition.py b/tests/unit/test_condition.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3200e34c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/test_condition.py
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+"""Unit tests for condition.py - Top class and merge logic."""
+
+import pytest
+from datajoint.condition import Top
+
+
+class TestTopMerge:
+ """Tests for Top.merge() method."""
+
+ def test_merge_inherits_order(self):
+ """When other.order_by is None, ordering is inherited."""
+ top1 = Top(limit=10, order_by="score desc")
+ top2 = Top(limit=5, order_by=None)
+ merged = top1.merge(top2)
+ assert merged.order_by == ["score desc"]
+ assert merged.limit == 5
+ assert merged.offset == 0
+
+ def test_merge_limits_take_min(self):
+ """Merged limit is minimum of both."""
+ top1 = Top(limit=10, order_by="id")
+ top2 = Top(limit=3, order_by=None)
+ merged = top1.merge(top2)
+ assert merged.limit == 3
+
+ # Reverse order
+ top1 = Top(limit=3, order_by="id")
+ top2 = Top(limit=10, order_by=None)
+ merged = top1.merge(top2)
+ assert merged.limit == 3
+
+ def test_merge_none_limit_preserved(self):
+ """None limit (unlimited) is handled correctly."""
+ top1 = Top(limit=None, order_by="id")
+ top2 = Top(limit=5, order_by=None)
+ merged = top1.merge(top2)
+ assert merged.limit == 5
+
+ top1 = Top(limit=5, order_by="id")
+ top2 = Top(limit=None, order_by=None)
+ merged = top1.merge(top2)
+ assert merged.limit == 5
+
+ top1 = Top(limit=None, order_by="id")
+ top2 = Top(limit=None, order_by=None)
+ merged = top1.merge(top2)
+ assert merged.limit is None
+
+ def test_merge_offsets_add(self):
+ """Offsets are added together."""
+ top1 = Top(limit=10, order_by="id", offset=5)
+ top2 = Top(limit=3, order_by=None, offset=2)
+ merged = top1.merge(top2)
+ assert merged.offset == 7
+
+ def test_merge_preserves_existing_order(self):
+ """Merged Top preserves first Top's ordering."""
+ top1 = Top(limit=10, order_by=["col1 desc", "col2 asc"])
+ top2 = Top(limit=5, order_by=None)
+ merged = top1.merge(top2)
+ assert merged.order_by == ["col1 desc", "col2 asc"]
+
+
+class TestTopValidation:
+ """Tests for Top validation."""
+
+ def test_order_by_none_allowed(self):
+ """order_by=None is valid (means inherit)."""
+ top = Top(limit=5, order_by=None)
+ assert top.order_by is None
+
+ def test_order_by_string_converted_to_list(self):
+ """Single string order_by is converted to list."""
+ top = Top(order_by="id desc")
+ assert top.order_by == ["id desc"]
+
+ def test_order_by_list_preserved(self):
+ """List order_by is preserved."""
+ top = Top(order_by=["col1", "col2 desc"])
+ assert top.order_by == ["col1", "col2 desc"]
+
+ def test_invalid_limit_type_raises(self):
+ """Non-integer limit raises TypeError."""
+ with pytest.raises(TypeError):
+ Top(limit="5")
+
+ def test_invalid_order_by_type_raises(self):
+ """Non-string order_by raises TypeError."""
+ with pytest.raises(TypeError):
+ Top(order_by=123)
+
+ def test_invalid_offset_type_raises(self):
+ """Non-integer offset raises TypeError."""
+ with pytest.raises(TypeError):
+ Top(offset="1")
diff --git a/tests/test_hash.py b/tests/unit/test_hash.py
similarity index 100%
rename from tests/test_hash.py
rename to tests/unit/test_hash.py
diff --git a/tests/unit/test_lazy_imports.py b/tests/unit/test_lazy_imports.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..7c1dc4c9e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/test_lazy_imports.py
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+"""
+Tests for lazy import behavior.
+
+These tests verify that heavy dependencies (networkx, matplotlib, click)
+are not loaded until their associated features are accessed.
+"""
+
+import sys
+
+
+def test_lazy_diagram_import():
+ """Diagram module should not be loaded until dj.Diagram is accessed."""
+ # Remove datajoint from sys.modules to get fresh import
+ modules_to_remove = [key for key in sys.modules if key.startswith("datajoint")]
+ for mod in modules_to_remove:
+ del sys.modules[mod]
+
+ # Import datajoint
+ import datajoint as dj
+
+ # Diagram module should not be loaded yet
+ assert "datajoint.diagram" not in sys.modules, "diagram module loaded eagerly"
+
+ # Access Diagram - should trigger lazy load
+ Diagram = dj.Diagram
+ assert "datajoint.diagram" in sys.modules, "diagram module not loaded after access"
+ assert Diagram.__name__ == "Diagram"
+
+
+def test_lazy_admin_import():
+ """Admin module should not be loaded until dj.kill is accessed."""
+ # Remove datajoint from sys.modules to get fresh import
+ modules_to_remove = [key for key in sys.modules if key.startswith("datajoint")]
+ for mod in modules_to_remove:
+ del sys.modules[mod]
+
+ # Import datajoint
+ import datajoint as dj
+
+ # Admin module should not be loaded yet
+ assert "datajoint.admin" not in sys.modules, "admin module loaded eagerly"
+
+ # Access kill - should trigger lazy load
+ kill = dj.kill
+ assert "datajoint.admin" in sys.modules, "admin module not loaded after access"
+ assert callable(kill)
+
+
+def test_lazy_cli_import():
+ """CLI module should not be loaded until dj.cli is accessed."""
+ # Remove datajoint from sys.modules to get fresh import
+ modules_to_remove = [key for key in sys.modules if key.startswith("datajoint")]
+ for mod in modules_to_remove:
+ del sys.modules[mod]
+
+ # Import datajoint
+ import datajoint as dj
+
+ # CLI module should not be loaded yet
+ assert "datajoint.cli" not in sys.modules, "cli module loaded eagerly"
+
+ # Access cli - should trigger lazy load and return the function
+ cli_func = dj.cli
+ assert "datajoint.cli" in sys.modules, "cli module not loaded after access"
+ assert callable(cli_func), "dj.cli should be callable (the cli function)"
+
+
+def test_diagram_module_access():
+ """dj.diagram should return the diagram module for accessing module-level attrs."""
+ # Remove datajoint from sys.modules to get fresh import
+ modules_to_remove = [key for key in sys.modules if key.startswith("datajoint")]
+ for mod in modules_to_remove:
+ del sys.modules[mod]
+
+ import datajoint as dj
+
+ # Access dj.diagram should return the module
+ diagram_module = dj.diagram
+ assert hasattr(diagram_module, "diagram_active"), "diagram module should have diagram_active"
+ assert hasattr(diagram_module, "Diagram"), "diagram module should have Diagram class"
+
+
+def test_diagram_aliases():
+ """Di and ERD should be aliases for Diagram."""
+ # Remove datajoint from sys.modules to get fresh import
+ modules_to_remove = [key for key in sys.modules if key.startswith("datajoint")]
+ for mod in modules_to_remove:
+ del sys.modules[mod]
+
+ import datajoint as dj
+
+ # All aliases should resolve to the same class
+ assert dj.Diagram is dj.Di
+ assert dj.Diagram is dj.ERD
+
+
+def test_core_imports_available():
+ """Core functionality should be available immediately after import."""
+ # Remove datajoint from sys.modules to get fresh import
+ modules_to_remove = [key for key in sys.modules if key.startswith("datajoint")]
+ for mod in modules_to_remove:
+ del sys.modules[mod]
+
+ import datajoint as dj
+
+ # Core classes should be available without triggering lazy loads
+ assert hasattr(dj, "Schema")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "Table")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "Manual")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "Lookup")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "Computed")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "Imported")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "Part")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "Connection")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "config")
+ assert hasattr(dj, "errors")
+
+ # Heavy modules should still not be loaded
+ assert "datajoint.diagram" not in sys.modules
+ assert "datajoint.admin" not in sys.modules
+ assert "datajoint.cli" not in sys.modules
diff --git a/tests/unit/test_pk_rules.py b/tests/unit/test_pk_rules.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2c554091b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/test_pk_rules.py
@@ -0,0 +1,207 @@
+"""
+Unit tests for primary key determination rules.
+
+These tests verify the functional dependency logic used to determine
+primary keys in join operations.
+"""
+
+from datajoint.heading import Heading
+
+
+def make_heading(pk_attrs, secondary_attrs=None):
+ """Helper to create a Heading with specified PK and secondary attributes."""
+ secondary_attrs = secondary_attrs or []
+ attrs = []
+ for name in pk_attrs:
+ attrs.append(
+ {
+ "name": name,
+ "type": "int",
+ "original_type": None,
+ "in_key": True,
+ "nullable": False,
+ "default": None,
+ "comment": "",
+ "autoincrement": False,
+ "numeric": True,
+ "string": False,
+ "uuid": False,
+ "json": False,
+ "is_blob": False,
+ "is_hidden": False,
+ "codec": None,
+ "store": None,
+ "unsupported": False,
+ "attribute_expression": None,
+ "dtype": object,
+ "lineage": None,
+ }
+ )
+ for name in secondary_attrs:
+ attrs.append(
+ {
+ "name": name,
+ "type": "int",
+ "original_type": None,
+ "in_key": False,
+ "nullable": True,
+ "default": None,
+ "comment": "",
+ "autoincrement": False,
+ "numeric": True,
+ "string": False,
+ "uuid": False,
+ "json": False,
+ "is_blob": False,
+ "is_hidden": False,
+ "codec": None,
+ "store": None,
+ "unsupported": False,
+ "attribute_expression": None,
+ "dtype": object,
+ "lineage": None,
+ }
+ )
+ return Heading(attrs)
+
+
+class TestDetermines:
+ """Tests for Heading.determines() method."""
+
+ def test_a_determines_b_when_b_pk_subset_of_a(self):
+ """A → B when all of B's PK is in A."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"], ["z"])
+ b = make_heading(["x"])
+ assert a.determines(b)
+
+ def test_a_determines_b_when_b_pk_in_a_secondary(self):
+ """A → B when B's PK attrs are in A's secondary."""
+ a = make_heading(["x"], ["y", "z"])
+ b = make_heading(["y"])
+ assert a.determines(b)
+
+ def test_a_not_determines_b_when_attr_missing(self):
+ """A ↛ B when B has PK attr not in A at all."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"])
+ b = make_heading(["x", "z"])
+ assert not a.determines(b)
+
+ def test_both_determine_each_other(self):
+ """Both A → B and B → A can be true (bijection-like)."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"], ["z"])
+ b = make_heading(["y", "z"], ["x"])
+ assert a.determines(b)
+ assert b.determines(a)
+
+ def test_neither_determines(self):
+ """Neither direction when each has attrs not in the other."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"])
+ b = make_heading(["y", "z"])
+ assert not a.determines(b)
+ assert not b.determines(a)
+
+ def test_empty_pk_always_determined(self):
+ """Empty PK is always determined by any heading."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"])
+ b = make_heading([])
+ assert a.determines(b)
+
+ def test_session_trial_example(self):
+ """Classic FK example: Trial → Session (session_id in Trial's PK)."""
+ session = make_heading(["session_id"], ["date"])
+ trial = make_heading(["session_id", "trial_num"], ["stimulus"])
+ # Session → Trial? No (trial_num not in Session)
+ assert not session.determines(trial)
+ # Trial → Session? Yes (session_id in Trial)
+ assert trial.determines(session)
+
+
+class TestJoinPrimaryKey:
+ """Tests for Heading.join() primary key determination."""
+
+ def test_join_a_determines_b(self):
+ """When A → B, result PK = PK(A)."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"], ["z"])
+ b = make_heading(["x"])
+ result = a.join(b)
+ assert result.primary_key == ["x", "y"]
+
+ def test_join_b_determines_a(self):
+ """When B → A (not A → B), result PK = PK(B), B's attrs first."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"])
+ b = make_heading(["x", "z"], ["y"])
+ # A → B? No (z not in A)
+ # B → A? Yes (y is secondary in B)
+ result = a.join(b)
+ assert result.primary_key == ["x", "z"]
+ # B's attributes should come first
+ assert result.names[0] == "x"
+ assert result.names[1] == "z"
+
+ def test_join_both_determine(self):
+ """When both A → B and B → A, prefer A (left operand)."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"], ["z"])
+ b = make_heading(["y", "z"], ["x"])
+ result = a.join(b)
+ assert result.primary_key == ["x", "y"]
+
+ def test_join_neither_determines(self):
+ """When neither determines, result PK = union."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"])
+ b = make_heading(["y", "z"])
+ result = a.join(b)
+ # PK should be union: {x, y, z}
+ assert set(result.primary_key) == {"x", "y", "z"}
+ # A's PK first, then B's new PK attrs
+ assert result.primary_key == ["x", "y", "z"]
+
+ def test_join_preserves_secondary_attrs(self):
+ """Secondary attributes should be preserved in join."""
+ a = make_heading(["x"], ["a"])
+ b = make_heading(["x"], ["b"])
+ result = a.join(b)
+ assert "a" in result.secondary_attributes
+ assert "b" in result.secondary_attributes
+
+ def test_join_session_trial(self):
+ """Session * Trial should have Trial's PK."""
+ session = make_heading(["session_id"], ["date"])
+ trial = make_heading(["session_id", "trial_num"], ["stimulus"])
+ result = session.join(trial)
+ # B → A, so PK = PK(B) = {session_id, trial_num}
+ assert set(result.primary_key) == {"session_id", "trial_num"}
+
+ def test_join_nullable_pk_forces_union(self):
+ """nullable_pk=True should force union PK."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"], ["z"])
+ b = make_heading(["x"])
+ # Normally A → B, so PK = PK(A)
+ normal_result = a.join(b)
+ assert normal_result.primary_key == ["x", "y"]
+ # With nullable_pk=True, force union
+ nullable_result = a.join(b, nullable_pk=True)
+ assert nullable_result.primary_key == ["x", "y"] # Still same since B's PK is subset
+
+
+class TestJoinAttributeOrdering:
+ """Tests for attribute ordering in join results."""
+
+ def test_a_determines_b_ordering(self):
+ """When A → B, A's attributes come first."""
+ a = make_heading(["x"], ["a"])
+ b = make_heading(["x"], ["b"])
+ result = a.join(b)
+ names = result.names
+ assert names.index("x") < names.index("a")
+ assert names.index("a") < names.index("b")
+
+ def test_b_determines_a_ordering(self):
+ """When B → A, B's attributes come first."""
+ a = make_heading(["x", "y"])
+ b = make_heading(["x", "z"], ["y"])
+ result = a.join(b)
+ names = result.names
+ # B's attrs first: x, z, then A's non-overlapping attrs
+ assert names.index("x") < names.index("z")
+ # y should be secondary (demoted from A's PK)
+ assert "y" in result.secondary_attributes
diff --git a/tests/unit/test_settings.py b/tests/unit/test_settings.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..66d817f0c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/test_settings.py
@@ -0,0 +1,468 @@
+"""Tests for DataJoint settings module."""
+
+from pathlib import Path
+
+import pytest
+from pydantic import SecretStr, ValidationError
+
+import datajoint as dj
+from datajoint import settings
+from datajoint.errors import DataJointError
+from datajoint.settings import (
+ CONFIG_FILENAME,
+ SECRETS_DIRNAME,
+ find_config_file,
+ find_secrets_dir,
+ read_secret_file,
+)
+
+
+class TestConfigFileSearch:
+ """Test recursive config file search."""
+
+ def test_find_in_current_directory(self, tmp_path):
+ """Config file in current directory is found."""
+ config_file = tmp_path / CONFIG_FILENAME
+ config_file.write_text("{}")
+
+ found = find_config_file(tmp_path)
+ assert found == config_file
+
+ def test_find_in_parent_directory(self, tmp_path):
+ """Config file in parent directory is found."""
+ subdir = tmp_path / "src" / "pipeline"
+ subdir.mkdir(parents=True)
+ config_file = tmp_path / CONFIG_FILENAME
+ config_file.write_text("{}")
+
+ found = find_config_file(subdir)
+ assert found == config_file
+
+ def test_stop_at_git_boundary(self, tmp_path):
+ """Search stops at .git directory."""
+ (tmp_path / ".git").mkdir()
+ subdir = tmp_path / "src"
+ subdir.mkdir()
+ # No config file - should return None, not search above .git
+
+ found = find_config_file(subdir)
+ assert found is None
+
+ def test_stop_at_hg_boundary(self, tmp_path):
+ """Search stops at .hg directory."""
+ (tmp_path / ".hg").mkdir()
+ subdir = tmp_path / "src"
+ subdir.mkdir()
+
+ found = find_config_file(subdir)
+ assert found is None
+
+ def test_config_found_before_git(self, tmp_path):
+ """Config file found before reaching .git boundary."""
+ (tmp_path / ".git").mkdir()
+ config_file = tmp_path / CONFIG_FILENAME
+ config_file.write_text("{}")
+ subdir = tmp_path / "src"
+ subdir.mkdir()
+
+ found = find_config_file(subdir)
+ assert found == config_file
+
+ def test_returns_none_when_not_found(self, tmp_path):
+ """Returns None when no config file exists."""
+ (tmp_path / ".git").mkdir() # Create boundary
+ subdir = tmp_path / "src"
+ subdir.mkdir()
+
+ found = find_config_file(subdir)
+ assert found is None
+
+
+class TestSecretsDirectory:
+ """Test secrets directory detection and loading."""
+
+ def test_find_secrets_next_to_config(self, tmp_path):
+ """Finds .secrets/ directory next to config file."""
+ config_file = tmp_path / CONFIG_FILENAME
+ config_file.write_text("{}")
+ secrets_dir = tmp_path / SECRETS_DIRNAME
+ secrets_dir.mkdir()
+
+ found = find_secrets_dir(config_file)
+ assert found == secrets_dir
+
+ def test_no_secrets_dir_returns_none(self, tmp_path):
+ """Returns None when no secrets directory exists."""
+ config_file = tmp_path / CONFIG_FILENAME
+ config_file.write_text("{}")
+
+ found = find_secrets_dir(config_file)
+ # May return system secrets dir if it exists, otherwise None
+ if found is not None:
+ assert found == settings.SYSTEM_SECRETS_DIR
+
+ def test_read_secret_file(self, tmp_path):
+ """Reads secret value from file."""
+ (tmp_path / "database.password").write_text("my_secret\n")
+
+ value = read_secret_file(tmp_path, "database.password")
+ assert value == "my_secret" # Strips whitespace
+
+ def test_read_missing_secret_returns_none(self, tmp_path):
+ """Returns None for missing secret file."""
+ value = read_secret_file(tmp_path, "nonexistent")
+ assert value is None
+
+ def test_read_secret_from_none_dir(self):
+ """Returns None when secrets_dir is None."""
+ value = read_secret_file(None, "database.password")
+ assert value is None
+
+
+class TestSecretStr:
+ """Test SecretStr handling for sensitive fields."""
+
+ def test_password_is_secret_str(self):
+ """Password field uses SecretStr type."""
+ dj.config.database.password = "test_password"
+ assert isinstance(dj.config.database.password, SecretStr)
+ dj.config.database.password = None
+
+ def test_secret_str_masked_in_repr(self):
+ """SecretStr values are masked in repr."""
+ dj.config.database.password = "super_secret"
+ repr_str = repr(dj.config.database.password)
+ assert "super_secret" not in repr_str
+ assert "**" in repr_str
+ dj.config.database.password = None
+
+ def test_dict_access_unwraps_secret(self):
+ """Dict-style access returns plain string for secrets."""
+ dj.config.database.password = "unwrapped_secret"
+ value = dj.config["database.password"]
+ assert value == "unwrapped_secret"
+ assert isinstance(value, str)
+ assert not isinstance(value, SecretStr)
+ dj.config.database.password = None
+
+ def test_aws_secret_key_is_secret_str(self):
+ """AWS secret key uses SecretStr type."""
+ dj.config.external.aws_secret_access_key = "aws_secret"
+ assert isinstance(dj.config.external.aws_secret_access_key, SecretStr)
+ dj.config.external.aws_secret_access_key = None
+
+
+class TestSettingsAccess:
+ """Test accessing settings via different methods."""
+
+ def test_attribute_access(self):
+ """Test accessing settings via attributes."""
+ # Host can be localhost or db (docker), just verify it's a string
+ assert isinstance(dj.config.database.host, str)
+ assert len(dj.config.database.host) > 0
+ # Port may be 3306 (default) or a random port (testcontainers)
+ assert isinstance(dj.config.database.port, int)
+ assert 1 <= dj.config.database.port <= 65535
+ # safemode may be modified by conftest fixtures
+ assert isinstance(dj.config.safemode, bool)
+
+ def test_dict_style_access(self):
+ """Test accessing settings via dict-style notation."""
+ # Host can be localhost or db (docker), just verify it's a string
+ assert isinstance(dj.config["database.host"], str)
+ assert len(dj.config["database.host"]) > 0
+ # Port may be 3306 (default) or a random port (testcontainers)
+ assert isinstance(dj.config["database.port"], int)
+ assert 1 <= dj.config["database.port"] <= 65535
+ # safemode may be modified by conftest fixtures
+ assert isinstance(dj.config["safemode"], bool)
+
+ def test_get_with_default(self):
+ """Test get() method with default values."""
+ # Host can be localhost or db (docker), just verify it exists
+ assert dj.config.get("database.host") is not None
+ assert dj.config.get("nonexistent.key", "default") == "default"
+ assert dj.config.get("nonexistent.key") is None
+
+
+class TestSettingsModification:
+ """Test modifying settings."""
+
+ def test_attribute_assignment(self):
+ """Test setting values via attribute assignment."""
+ original = dj.config.database.host
+ try:
+ dj.config.database.host = "testhost"
+ assert dj.config.database.host == "testhost"
+ finally:
+ dj.config.database.host = original
+
+ def test_dict_style_assignment(self):
+ """Test setting values via dict-style notation."""
+ original = dj.config["database.host"]
+ try:
+ dj.config["database.host"] = "testhost2"
+ assert dj.config["database.host"] == "testhost2"
+ finally:
+ dj.config["database.host"] = original
+
+
+class TestTypeValidation:
+ """Test pydantic type validation."""
+
+ def test_port_must_be_integer(self):
+ """Test that port must be an integer."""
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError):
+ dj.config.database.port = "not_an_integer"
+
+ def test_loglevel_validation(self):
+ """Test that loglevel must be a valid level."""
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError):
+ dj.config.loglevel = "INVALID_LEVEL"
+
+ def test_fetch_format_validation(self):
+ """Test that fetch_format must be array or frame."""
+ with pytest.raises(ValidationError):
+ dj.config.fetch_format = "invalid"
+
+
+class TestContextManager:
+ """Test the override context manager."""
+
+ def test_override_simple_value(self):
+ """Test overriding a simple value."""
+ original = dj.config.safemode
+ with dj.config.override(safemode=False):
+ assert dj.config.safemode is False
+ assert dj.config.safemode == original
+
+ def test_override_nested_value(self):
+ """Test overriding nested values with double underscore."""
+ original = dj.config.database.host
+ with dj.config.override(database__host="override_host"):
+ assert dj.config.database.host == "override_host"
+ assert dj.config.database.host == original
+
+ def test_override_restores_on_exception(self):
+ """Test that override restores values even when exception occurs."""
+ original = dj.config.safemode
+ try:
+ with dj.config.override(safemode=False):
+ assert dj.config.safemode is False
+ raise ValueError("test exception")
+ except ValueError:
+ pass
+ assert dj.config.safemode == original
+
+
+class TestLoad:
+ """Test loading configuration."""
+
+ def test_load_config_file(self, tmp_path, monkeypatch):
+ """Test loading configuration from file.
+
+ Note: Environment variables take precedence over config file values.
+ We need to clear DJ_HOST to test file loading.
+ """
+ filename = tmp_path / "test_config.json"
+ filename.write_text('{"database": {"host": "loaded_host"}}')
+ original_host = dj.config.database.host
+
+ # Clear env var so file value takes effect
+ monkeypatch.delenv("DJ_HOST", raising=False)
+
+ try:
+ dj.config.load(filename)
+ assert dj.config.database.host == "loaded_host"
+ finally:
+ dj.config.database.host = original_host
+
+ def test_env_var_overrides_config_file(self, tmp_path, monkeypatch):
+ """Test that environment variables take precedence over config file.
+
+ When DJ_HOST is set, loading a config file should NOT override the value.
+ The env var value should be preserved.
+ """
+ filename = tmp_path / "test_config.json"
+ filename.write_text('{"database": {"host": "file_host"}}')
+ original_host = dj.config.database.host
+
+ # Set env var - it should take precedence over file
+ monkeypatch.setenv("DJ_HOST", "env_host")
+ # Reset config to pick up new env var
+ dj.config.database.host = "env_host"
+
+ try:
+ dj.config.load(filename)
+ # File value should be skipped because DJ_HOST is set
+ # The env var value should be preserved
+ assert dj.config.database.host == "env_host"
+ finally:
+ dj.config.database.host = original_host
+
+ def test_load_nonexistent_file(self):
+ """Test loading nonexistent file raises FileNotFoundError."""
+ with pytest.raises(FileNotFoundError):
+ dj.config.load("/nonexistent/path/config.json")
+
+
+class TestStoreSpec:
+ """Test external store configuration."""
+
+ def test_get_store_spec_not_configured(self):
+ """Test getting unconfigured store raises error."""
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError, match="not configured"):
+ dj.config.get_store_spec("nonexistent_store")
+
+ def test_get_store_spec_file_protocol(self):
+ """Test file protocol store spec validation."""
+ original_stores = dj.config.stores.copy()
+ try:
+ dj.config.stores["test_file"] = {
+ "protocol": "file",
+ "location": "/tmp/test",
+ }
+ spec = dj.config.get_store_spec("test_file")
+ assert spec["protocol"] == "file"
+ assert spec["location"] == "/tmp/test"
+ assert spec["subfolding"] == settings.DEFAULT_SUBFOLDING
+ finally:
+ dj.config.stores = original_stores
+
+ def test_get_store_spec_missing_required(self):
+ """Test missing required keys raises error."""
+ original_stores = dj.config.stores.copy()
+ try:
+ dj.config.stores["bad_store"] = {
+ "protocol": "file",
+ # missing location
+ }
+ with pytest.raises(DataJointError, match="missing"):
+ dj.config.get_store_spec("bad_store")
+ finally:
+ dj.config.stores = original_stores
+
+
+class TestDisplaySettings:
+ """Test display-related settings."""
+
+ def test_display_limit(self):
+ """Test display limit setting."""
+ original = dj.config.display.limit
+ try:
+ dj.config.display.limit = 50
+ assert dj.config.display.limit == 50
+ finally:
+ dj.config.display.limit = original
+
+
+class TestCachePaths:
+ """Test cache path settings."""
+
+ def test_cache_path_string(self):
+ """Test setting cache path as string."""
+ original = dj.config.cache
+ try:
+ dj.config.cache = "/tmp/cache"
+ assert dj.config.cache == Path("/tmp/cache")
+ finally:
+ dj.config.cache = original
+
+ def test_cache_path_none(self):
+ """Test cache path can be None."""
+ original = dj.config.cache
+ try:
+ dj.config.cache = None
+ assert dj.config.cache is None
+ finally:
+ dj.config.cache = original
+
+
+class TestSaveTemplate:
+ """Test save_template method for creating configuration templates."""
+
+ def test_save_minimal_template(self, tmp_path):
+ """Test creating a minimal template."""
+ config_path = tmp_path / "datajoint.json"
+ result = dj.config.save_template(config_path, minimal=True, create_secrets_dir=False)
+
+ assert result == config_path.absolute()
+ assert config_path.exists()
+
+ import json
+
+ with open(config_path) as f:
+ content = json.load(f)
+
+ assert "database" in content
+ assert content["database"]["host"] == "localhost"
+ assert content["database"]["port"] == 3306
+ # Minimal template should not have credentials
+ assert "password" not in content["database"]
+ assert "user" not in content["database"]
+
+ def test_save_full_template(self, tmp_path):
+ """Test creating a full template."""
+ config_path = tmp_path / "datajoint.json"
+ result = dj.config.save_template(config_path, minimal=False, create_secrets_dir=False)
+
+ assert result == config_path.absolute()
+ assert config_path.exists()
+
+ import json
+
+ with open(config_path) as f:
+ content = json.load(f)
+
+ # Full template should have all settings groups
+ assert "database" in content
+ assert "connection" in content
+ assert "display" in content
+ assert "object_storage" in content
+ assert "stores" in content
+ assert "loglevel" in content
+ assert "safemode" in content
+ # But still no credentials
+ assert "password" not in content["database"]
+ assert "user" not in content["database"]
+
+ def test_save_template_creates_secrets_dir(self, tmp_path):
+ """Test that save_template creates .secrets/ directory."""
+ config_path = tmp_path / "datajoint.json"
+ dj.config.save_template(config_path, create_secrets_dir=True)
+
+ secrets_dir = tmp_path / SECRETS_DIRNAME
+ assert secrets_dir.exists()
+ assert secrets_dir.is_dir()
+
+ # Check placeholder files created
+ assert (secrets_dir / "database.user").exists()
+ assert (secrets_dir / "database.password").exists()
+
+ # Check .gitignore created
+ gitignore = secrets_dir / ".gitignore"
+ assert gitignore.exists()
+ assert "*" in gitignore.read_text()
+
+ def test_save_template_refuses_overwrite(self, tmp_path):
+ """Test that save_template won't overwrite existing file."""
+ config_path = tmp_path / "datajoint.json"
+ config_path.write_text("{}")
+
+ with pytest.raises(FileExistsError, match="already exists"):
+ dj.config.save_template(config_path)
+
+ def test_save_template_secrets_dir_idempotent(self, tmp_path):
+ """Test that creating secrets dir doesn't overwrite existing secrets."""
+ config_path = tmp_path / "datajoint.json"
+ secrets_dir = tmp_path / SECRETS_DIRNAME
+ secrets_dir.mkdir()
+
+ # Pre-populate a secret
+ password_file = secrets_dir / "database.password"
+ password_file.write_text("existing_password")
+
+ dj.config.save_template(config_path, create_secrets_dir=True)
+
+ # Original password should be preserved
+ assert password_file.read_text() == "existing_password"
diff --git a/tests/unit/test_storage_urls.py b/tests/unit/test_storage_urls.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..649d695b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/unit/test_storage_urls.py
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+"""Unit tests for storage URL functions."""
+
+import pytest
+
+from datajoint.storage import (
+ URL_PROTOCOLS,
+ is_url,
+ normalize_to_url,
+ parse_url,
+)
+
+
+class TestURLProtocols:
+ """Test URL protocol constants."""
+
+ def test_url_protocols_includes_file(self):
+ """URL_PROTOCOLS should include file://."""
+ assert "file://" in URL_PROTOCOLS
+
+ def test_url_protocols_includes_s3(self):
+ """URL_PROTOCOLS should include s3://."""
+ assert "s3://" in URL_PROTOCOLS
+
+ def test_url_protocols_includes_cloud_providers(self):
+ """URL_PROTOCOLS should include major cloud providers."""
+ assert "gs://" in URL_PROTOCOLS
+ assert "az://" in URL_PROTOCOLS
+
+
+class TestIsUrl:
+ """Test is_url function."""
+
+ def test_s3_url(self):
+ assert is_url("s3://bucket/key")
+
+ def test_gs_url(self):
+ assert is_url("gs://bucket/key")
+
+ def test_file_url(self):
+ assert is_url("file:///path/to/file")
+
+ def test_http_url(self):
+ assert is_url("http://example.com/file")
+
+ def test_https_url(self):
+ assert is_url("https://example.com/file")
+
+ def test_local_path_not_url(self):
+ assert not is_url("/path/to/file")
+
+ def test_relative_path_not_url(self):
+ assert not is_url("relative/path/file.dat")
+
+ def test_case_insensitive(self):
+ assert is_url("S3://bucket/key")
+ assert is_url("FILE:///path")
+
+
+class TestNormalizeToUrl:
+ """Test normalize_to_url function."""
+
+ def test_local_path_to_file_url(self):
+ url = normalize_to_url("/data/file.dat")
+ assert url.startswith("file://")
+ assert "data/file.dat" in url
+
+ def test_s3_url_unchanged(self):
+ url = "s3://bucket/key/file.dat"
+ assert normalize_to_url(url) == url
+
+ def test_file_url_unchanged(self):
+ url = "file:///data/file.dat"
+ assert normalize_to_url(url) == url
+
+ def test_relative_path_becomes_absolute(self):
+ url = normalize_to_url("relative/path.dat")
+ assert url.startswith("file://")
+ # Should be absolute (contain full path)
+ assert "/" in url[7:] # After "file://"
+
+
+class TestParseUrl:
+ """Test parse_url function."""
+
+ def test_parse_s3(self):
+ protocol, path = parse_url("s3://bucket/key/file.dat")
+ assert protocol == "s3"
+ assert path == "bucket/key/file.dat"
+
+ def test_parse_gs(self):
+ protocol, path = parse_url("gs://bucket/key")
+ assert protocol == "gcs"
+ assert path == "bucket/key"
+
+ def test_parse_gcs(self):
+ protocol, path = parse_url("gcs://bucket/key")
+ assert protocol == "gcs"
+ assert path == "bucket/key"
+
+ def test_parse_file(self):
+ protocol, path = parse_url("file:///data/file.dat")
+ assert protocol == "file"
+ assert path == "/data/file.dat"
+
+ def test_parse_http(self):
+ protocol, path = parse_url("http://example.com/file")
+ assert protocol == "http"
+ assert path == "example.com/file"
+
+ def test_parse_https(self):
+ protocol, path = parse_url("https://example.com/file")
+ assert protocol == "https"
+ assert path == "example.com/file"
+
+ def test_unsupported_protocol_raises(self):
+ with pytest.raises(Exception, match="Unsupported URL protocol"):
+ parse_url("ftp://example.com/file")
+
+ def test_local_path_raises(self):
+ with pytest.raises(Exception, match="Unsupported URL protocol"):
+ parse_url("/local/path")
 -
-  -
-
 -
-  -
-
-
-  -
-
 -
-
-
-  +
+
+
+  +
+
+
+ 
 -
-
-
-  -
-  -
-
 -
-  -
-
-
-  -
-
 -
-
-
-  +
+
+
+  +
+
+
+ 
 -
-
-
-