There is a snake in an n x n matrix grid and can move in four possible directions. Each cell in the grid is identified by the position: grid[i][j] = (i * n) + j.
The snake starts at cell 0 and follows a sequence of commands.
+ +You are given an integer n representing the size of the grid and an array of strings commands where each command[i] is either "UP", "RIGHT", "DOWN", and "LEFT". It's guaranteed that the snake will remain within the grid boundaries throughout its movement.
Return the position of the final cell where the snake ends up after executing commands.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: n = 2, commands = ["RIGHT","DOWN"]
+ +Output: 3
+ +Explanation:
+ +| 0 | +1 | +
| 2 | +3 | +
| 0 | +1 | +
| 2 | +3 | +
| 0 | +1 | +
| 2 | +3 | +
Example 2:
+ +Input: n = 3, commands = ["DOWN","RIGHT","UP"]
+ +Output: 1
+ +Explanation:
+ +| 0 | +1 | +2 | +
| 3 | +4 | +5 | +
| 6 | +7 | +8 | +
| 0 | +1 | +2 | +
| 3 | +4 | +5 | +
| 6 | +7 | +8 | +
| 0 | +1 | +2 | +
| 3 | +4 | +5 | +
| 6 | +7 | +8 | +
| 0 | +1 | +2 | +
| 3 | +4 | +5 | +
| 6 | +7 | +8 | +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
2 <= n <= 10
+ 1 <= commands.length <= 100
+ commandsconsists only of"UP","RIGHT","DOWN", and"LEFT".
+ - The input is generated such the snake will not move outside of the boundaries. +
现有一棵 无向 树,树中包含 n 个节点,按从 0 到 n - 1 标记。树的根节点是节点 0 。给你一个长度为 n - 1 的二维整数数组 edges,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示树中节点 ai 与节点 bi 之间存在一条边。
如果一个节点的所有子节点为根的 子树 包含的节点数相同,则认为该节点是一个 好节点。
+ +返回给定树中 好节点 的数量。
+ +子树 指的是一个节点以及它所有后代节点构成的一棵树。
+ ++ +
+ +
示例 1:
+ +输入:edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]]
+ +输出:7
+ +说明:
+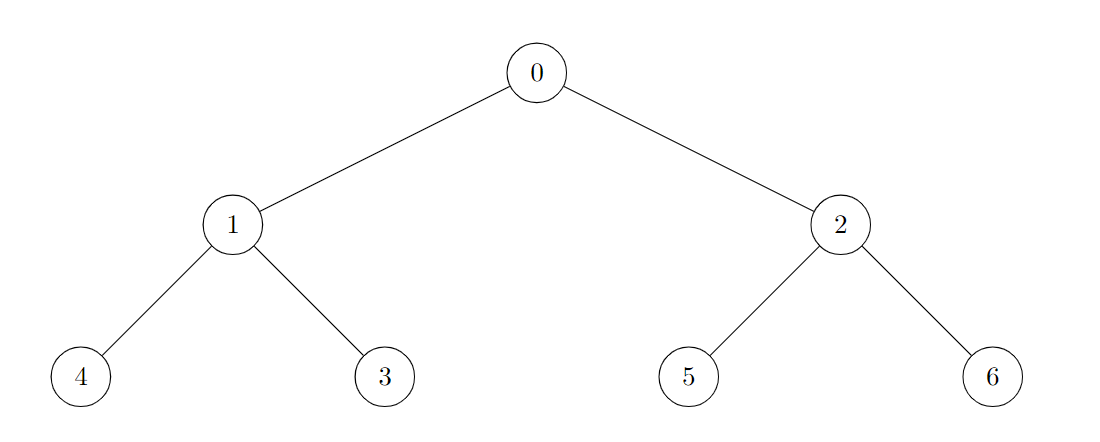 +
+树的所有节点都是好节点。
+示例 2:
+ +输入:edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[0,5],[1,6],[2,7],[3,8]]
+ +输出:6
+ +说明:
+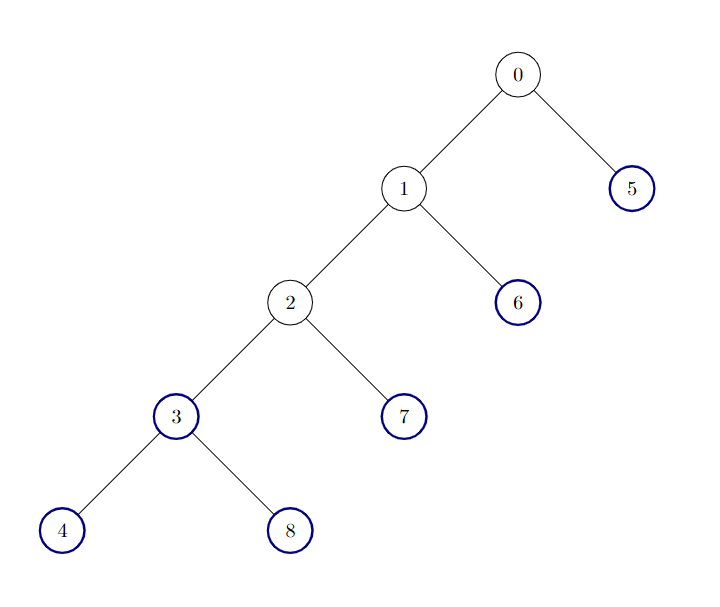 +
+树中有 6 个好节点。上图中已将这些节点着色。
+示例 3:
+ +输入:edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[0,5],[5,6],[6,7],[7,8],[0,9],[9,10],[9,12],[10,11]]
+ +输出:12
+ +解释:
+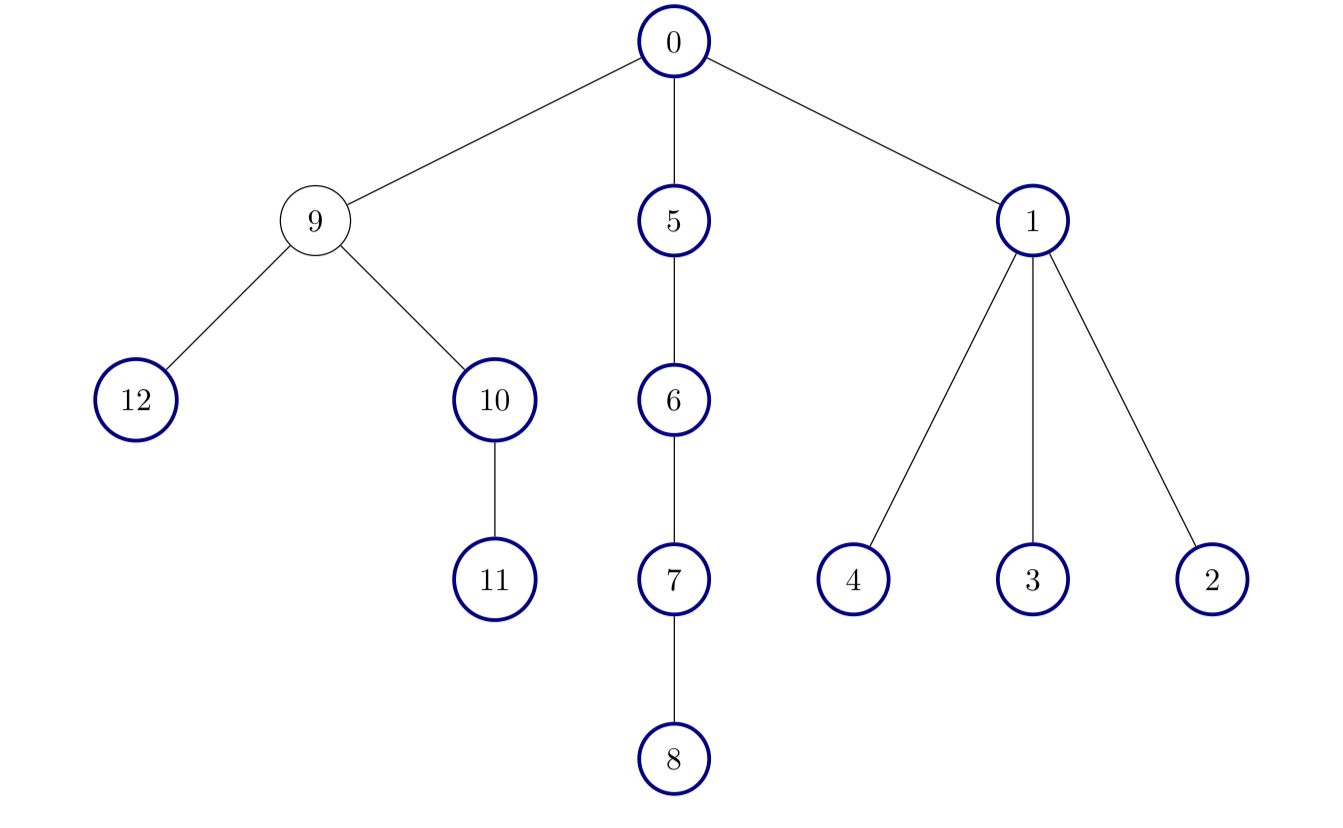 +
+除了节点 9 以外其他所有节点都是好节点。
++ +
提示:
+ +-
+
2 <= n <= 105
+ edges.length == n - 1
+ edges[i].length == 2
+ 0 <= ai, bi < n
+ - 输入确保
edges总表示一棵有效的树。
+
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
A node is good if all the subtrees rooted at its children have the same size.
+ +Return the number of good nodes in the given tree.
+ +A subtree of treeName is a tree consisting of a node in treeName and all of its descendants.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]]
+ +Output: 7
+ +Explanation:
+ +
+All of the nodes of the given tree are good.
+Example 2:
+ +Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[0,5],[1,6],[2,7],[3,8]]
+ +Output: 6
+ +Explanation:
+ +
+There are 6 good nodes in the given tree. They are colored in the image above.
+ +Example 3:
+ +Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[0,5],[5,6],[6,7],[7,8],[0,9],[9,10],[9,12],[10,11]]
+ +Output: 12
+ +Explanation:
+ +
+All nodes except node 9 are good.
++
Constraints:
+ +-
+
2 <= n <= 105
+ edges.length == n - 1
+ edges[i].length == 2
+ 0 <= ai, bi < n
+ - The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
+
给你一个长度为 n 的 正 整数数组 nums 。
如果两个 非负 整数数组 (arr1, arr2) 满足以下条件,我们称它们是 单调 数组对:
-
+
- 两个数组的长度都是
n。
+ arr1是单调 非递减 的,换句话说arr1[0] <= arr1[1] <= ... <= arr1[n - 1]。
+ arr2是单调 非递增 的,换句话说arr2[0] >= arr2[1] >= ... >= arr2[n - 1]。
+ - 对于所有的
0 <= i <= n - 1都有arr1[i] + arr2[i] == nums[i]。
+
请你返回所有 单调 数组对的数目。
+ +由于答案可能很大,请你将它对 109 + 7 取余 后返回。
+ +
示例 1:
+ +输入:nums = [2,3,2]
+ +输出:4
+ +解释:
+ +单调数组对包括:
+ +-
+
([0, 1, 1], [2, 2, 1])
+ ([0, 1, 2], [2, 2, 0])
+ ([0, 2, 2], [2, 1, 0])
+ ([1, 2, 2], [1, 1, 0])
+
示例 2:
+ +输入:nums = [5,5,5,5]
+ +输出:126
++ +
提示:
+ +-
+
1 <= n == nums.length <= 2000
+ 1 <= nums[i] <= 50
+
You are given an array of positive integers nums of length n.
We call a pair of non-negative integer arrays (arr1, arr2) monotonic if:
-
+
- The lengths of both arrays are
n.
+ arr1is monotonically non-decreasing, in other words,arr1[0] <= arr1[1] <= ... <= arr1[n - 1].
+ arr2is monotonically non-increasing, in other words,arr2[0] >= arr2[1] >= ... >= arr2[n - 1].
+ arr1[i] + arr2[i] == nums[i]for all0 <= i <= n - 1.
+
Return the count of monotonic pairs.
+ +Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [2,3,2]
+ +Output: 4
+ +Explanation:
+ +The good pairs are:
+ +-
+
([0, 1, 1], [2, 2, 1])
+ ([0, 1, 2], [2, 2, 0])
+ ([0, 2, 2], [2, 1, 0])
+ ([1, 2, 2], [1, 1, 0])
+
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [5,5,5,5]
+ +Output: 126
++
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= n == nums.length <= 2000
+ 1 <= nums[i] <= 50
+
给你一个长度为 n 的 正 整数数组 nums 。
如果两个 非负 整数数组 (arr1, arr2) 满足以下条件,我们称它们是 单调 数组对:
-
+
- 两个数组的长度都是
n。
+ arr1是单调 非递减 的,换句话说arr1[0] <= arr1[1] <= ... <= arr1[n - 1]。
+ arr2是单调 非递增 的,换句话说arr2[0] >= arr2[1] >= ... >= arr2[n - 1]。
+ - 对于所有的
0 <= i <= n - 1都有arr1[i] + arr2[i] == nums[i]。
+
请你返回所有 单调 数组对的数目。
+ +由于答案可能很大,请你将它对 109 + 7 取余 后返回。
+ +
示例 1:
+ +输入:nums = [2,3,2]
+ +输出:4
+ +解释:
+ +单调数组对包括:
+ +-
+
([0, 1, 1], [2, 2, 1])
+ ([0, 1, 2], [2, 2, 0])
+ ([0, 2, 2], [2, 1, 0])
+ ([1, 2, 2], [1, 1, 0])
+
示例 2:
+ +输入:nums = [5,5,5,5]
+ +输出:126
++ +
提示:
+ +-
+
1 <= n == nums.length <= 2000
+ 1 <= nums[i] <= 1000
+
You are given an array of positive integers nums of length n.
We call a pair of non-negative integer arrays (arr1, arr2) monotonic if:
-
+
- The lengths of both arrays are
n.
+ arr1is monotonically non-decreasing, in other words,arr1[0] <= arr1[1] <= ... <= arr1[n - 1].
+ arr2is monotonically non-increasing, in other words,arr2[0] >= arr2[1] >= ... >= arr2[n - 1].
+ arr1[i] + arr2[i] == nums[i]for all0 <= i <= n - 1.
+
Return the count of monotonic pairs.
+ +Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [2,3,2]
+ +Output: 4
+ +Explanation:
+ +The good pairs are:
+ +-
+
([0, 1, 1], [2, 2, 1])
+ ([0, 1, 2], [2, 2, 0])
+ ([0, 2, 2], [2, 1, 0])
+ ([1, 2, 2], [1, 1, 0])
+
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [5,5,5,5]
+ +Output: 126
++
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= n == nums.length <= 2000
+ 1 <= nums[i] <= 1000
+