|
1 | 1 | --- |
2 | | -mapped_pages: |
3 | | - - https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/semantic-search.html |
4 | | - - https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/serverless/current/elasticsearch-reference-semantic-search.html |
| 2 | +navigation_title: Semantic search |
| 3 | +description: An introduction to semantic search in Elasticsearch. |
5 | 4 | applies_to: |
6 | | - stack: |
7 | | - serverless: |
| 5 | + serverless: all |
| 6 | + stack: all |
8 | 7 | products: |
9 | 8 | - id: elasticsearch |
10 | | - - id: cloud-serverless |
11 | 9 | --- |
| 10 | +# Get started with semantic search |
12 | 11 |
|
13 | | -# Semantic search [semantic-search] |
| 12 | +_Semantic search_ is a type of AI-powered search that enables you to use natural language in your queries. |
| 13 | +It returns results that match the meaning of a query, as opposed to literal keyword matches. |
| 14 | +For example, if you want to search for workplace guidelines on a second income, you could search for "side hustle", which is not a term you're likely to see in a formal HR document. |
14 | 15 |
|
15 | | -:::{note} |
16 | | -This page focuses on the semantic search workflows available in {{es}}. For detailed information about lower-level vector search implementations, refer to [vector search](vector.md). |
| 16 | +Semantic search uses {{es}} [vector database](https://www.elastic.co/what-is/vector-database) and [vector search](https://www.elastic.co/what-is/vector-search) technology. |
| 17 | +Each _vector_ (or _vector embedding_) is an array of numbers that represent different characteristics of the text, such as sentiment, context, and syntactics. |
| 18 | +These numeric representations make vector comparisons very efficient. |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +In this quickstart guide, you'll create vectors for a small set of sample data, store them in {{es}}, then run a semantic query. |
| 21 | +By playing with a simple use case, you'll take the first steps toward understanding whether it's applicable to your own data. |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +## Prerequisites |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +- If you're using {{es-serverless}}, you must have a `developer` or `admin` predefined role or an equivalent custom role to add the sample data. |
| 26 | +- If you're using [{{ech}}](/deploy-manage/deploy/elastic-cloud/cloud-hosted.md) or [running {{es}} locally](/deploy-manage/deploy/self-managed/local-development-installation-quickstart.md), start {{es}} and {{kib}}. To add the sample data, log in with a user that has the `superuser` built-in role. |
| 27 | + |
| 28 | +To learn about role-based access control, check out [](/deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/user-roles.md). |
| 29 | + |
| 30 | +## Create a vector database |
| 31 | + |
| 32 | +When you create vectors (or _vectorize_ your data), you convert complex and nuanced documents into multidimensional numerical representations. |
| 33 | +You can choose from many different vector embedding models. Some are extremely hardware efficient and can be run with less computational power. Others have a greater understanding of the context, can answer questions, and lead a threaded conversation. |
| 34 | +The examples in this guide use the default Learned Sparse Encoder ([ELSER](/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-elser.md)) model, which provides great relevance across domains without the need for additional fine tuning. |
| 35 | + |
| 36 | +The way that you store vectors has a significant impact on the performance and accuracy of search results. |
| 37 | +They must be stored in specialized data structures designed to ensure efficient similarity search and speedy vector distance calculations. |
| 38 | +This guide uses the [semantic text field type](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/mapping-reference/semantic-text.md), which provides sensible defaults and automation. |
| 39 | + |
| 40 | +:::::{stepper} |
| 41 | +::::{step} Create an index |
| 42 | +An index is a collection of documents uniquely identified by a name or an alias. |
| 43 | +You can follow the guided index workflow: |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | +- If you're using {{es-serverless}}, {{ech}}, or running {{es}} locally: |
| 46 | + 1. Go to the **Index Management** page using the navigation menu or the [global search field](/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md). |
| 47 | + 2. Select **Create index**, select **Semantic Search**, and follow the guided workflow. |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +When you complete the workflow, you will have sample data and can skip to the steps related to exploring and searching it. |
| 50 | +Alternatively, run the following API request in [Console](/explore-analyze/query-filter/tools/console.md): |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +```console |
| 53 | +PUT /semantic-index |
| 54 | +``` |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +:::{tip} |
| 57 | +For an introduction to the concept of indices, check out [](/manage-data/data-store/index-basics.md). |
17 | 58 | ::: |
| 59 | +:::: |
| 60 | +::::{step} Create a semantic_text field mapping |
| 61 | +Each index has mappings that define how data is stored and indexed, like a schema in a relational database. |
| 62 | +The following example creates a mapping for a single field ("content"): |
| 63 | + |
| 64 | +```console |
| 65 | +PUT /semantic-index/_mapping |
| 66 | +{ |
| 67 | + "properties": { |
| 68 | + "content": { |
| 69 | + "type": "semantic_text" |
| 70 | + } |
| 71 | + } |
| 72 | +} |
| 73 | +``` |
| 74 | + |
| 75 | +When you use `semantic_text` fields, the type of vector is determined by the vector embedding model. |
| 76 | +In this case, the default ELSER model will be used to create sparse vectors. |
| 77 | + |
| 78 | +For a deeper dive, check out [Mapping embeddings to Elasticsearch field types: semantic_text, dense_vector, sparse_vector](https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/mapping-embeddings-to-elasticsearch-field-types). |
| 79 | +:::: |
| 80 | + |
| 81 | +::::{step} Add documents |
18 | 82 |
|
19 | | -{{es}} provides various semantic search capabilities using [natural language processing (NLP)](/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp.md) and [vector search](vector.md). |
| 83 | +You can use the Elasticsearch bulk API to ingest an array of documents: |
20 | 84 |
|
21 | | -To understand the infrastructure that powers semantic search and other NLP tasks, including managed services and inference endpoints, see the [Elastic Inference overview](../../explore-analyze/elastic-inference.md) page. |
| 85 | +```console |
| 86 | +POST /_bulk?pretty |
| 87 | +{ "index": { "_index": "semantic-index" } } |
| 88 | +{"content":"Yellowstone National Park is one of the largest national parks in the United States. It ranges from the Wyoming to Montana and Idaho, and contains an area of 2,219,791 acress across three different states. Its most famous for hosting the geyser Old Faithful and is centered on the Yellowstone Caldera, the largest super volcano on the American continent. Yellowstone is host to hundreds of species of animal, many of which are endangered or threatened. Most notably, it contains free-ranging herds of bison and elk, alongside bears, cougars and wolves. The national park receives over 4.5 million visitors annually and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site."} |
| 89 | +{ "index": { "_index": "semantic-index" } } |
| 90 | +{"content":"Yosemite National Park is a United States National Park, covering over 750,000 acres of land in California. A UNESCO World Heritage Site, the park is best known for its granite cliffs, waterfalls and giant sequoia trees. Yosemite hosts over four million visitors in most years, with a peak of five million visitors in 2016. The park is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including mule deer, black bears, and the endangered Sierra Nevada bighorn sheep. The park has 1,200 square miles of wilderness, and is a popular destination for rock climbers, with over 3,000 feet of vertical granite to climb. Its most famous and cliff is the El Capitan, a 3,000 feet monolith along its tallest face."} |
| 91 | +{ "index": { "_index": "semantic-index" } } |
| 92 | +{"content":"Rocky Mountain National Park is one of the most popular national parks in the United States. It receives over 4.5 million visitors annually, and is known for its mountainous terrain, including Longs Peak, which is the highest peak in the park. The park is home to a variety of wildlife, including elk, mule deer, moose, and bighorn sheep. The park is also home to a variety of ecosystems, including montane, subalpine, and alpine tundra. The park is a popular destination for hiking, camping, and wildlife viewing, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site."} |
| 93 | +``` |
22 | 94 |
|
23 | | -Learn more about use cases for AI-powered search in the [overview](ai-search/ai-search.md) page. |
| 95 | +The bulk ingestion might take longer than the default request timeout. |
| 96 | +If it times out, wait for the ELSER model to load (typically 1-5 minutes) then retry it. |
| 97 | +You can check the model state by going to the **{{models-app}}** page from the navigation menu or the [global search field](/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md). |
24 | 98 |
|
25 | | -## Overview of semantic search workflows [semantic-search-workflows-overview] |
| 99 | +First, the content is divided into smaller, manageable chunks to ensure that meaningful segments can be more effectively processed and searched. |
| 100 | +Each chunk of text is then transformed into a sparse vector by using the ELSER model's text expansion techniques. |
26 | 101 |
|
27 | | -You have several options for using NLP models for semantic search in the {{stack}}: |
| 102 | +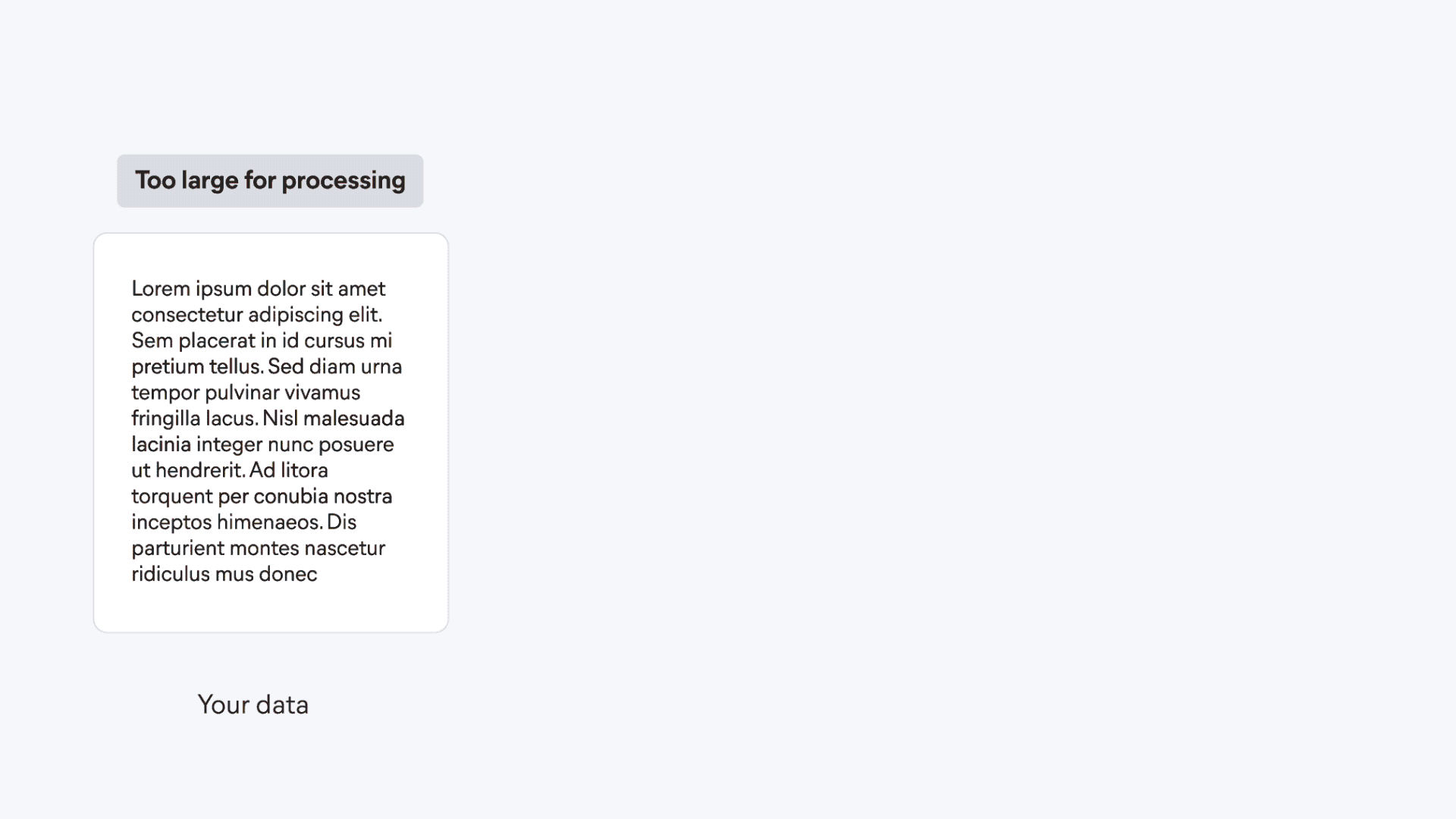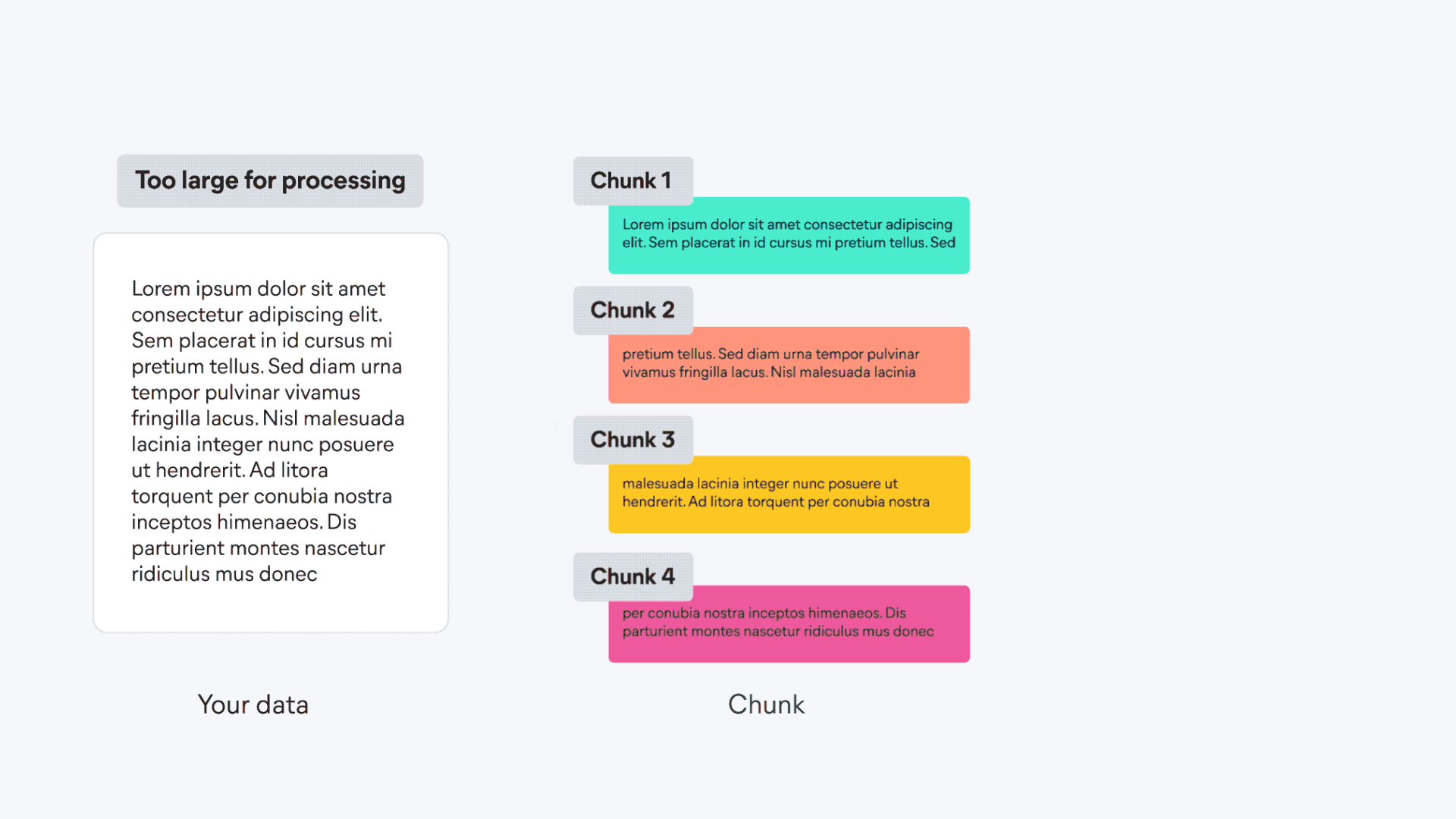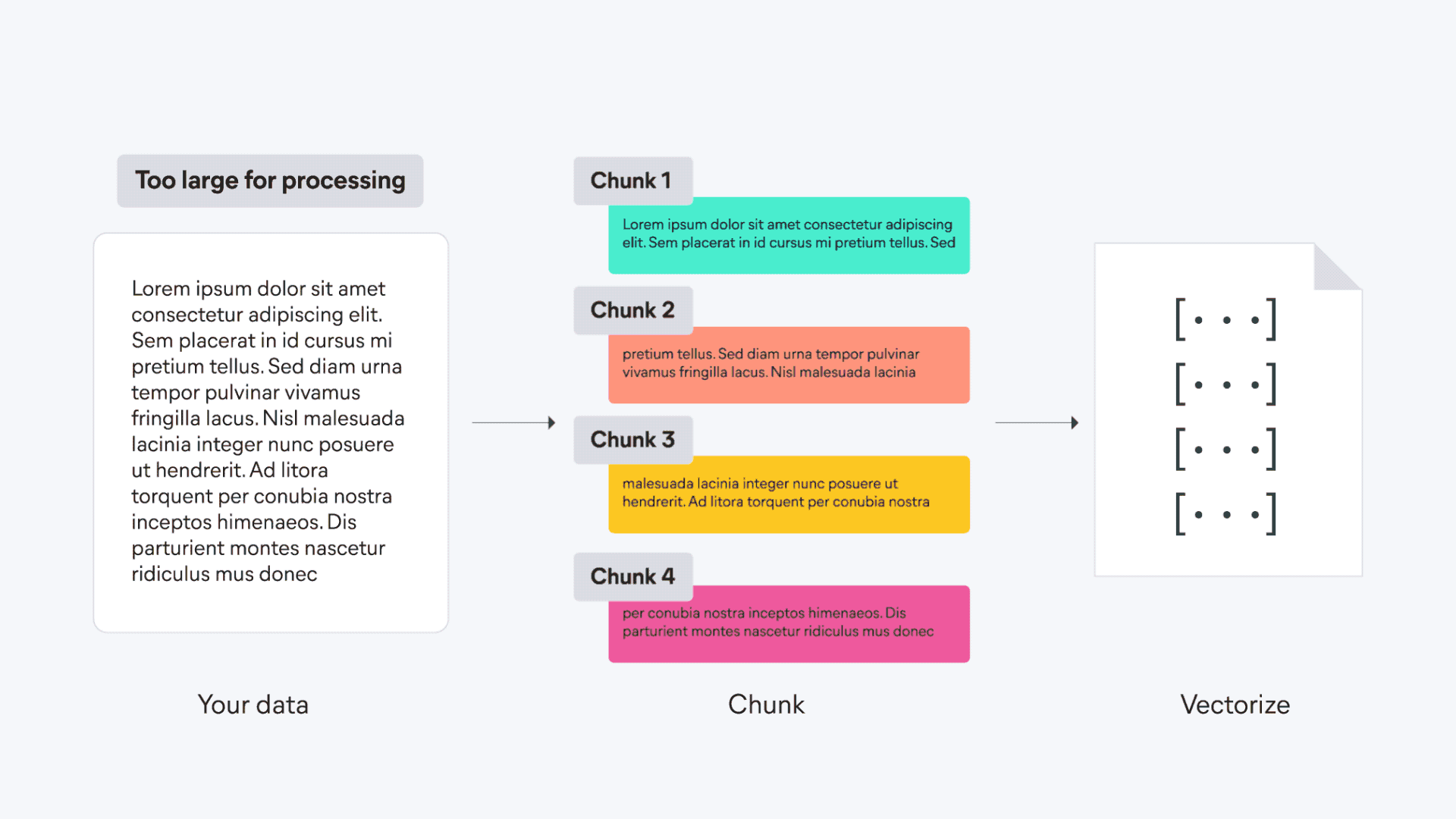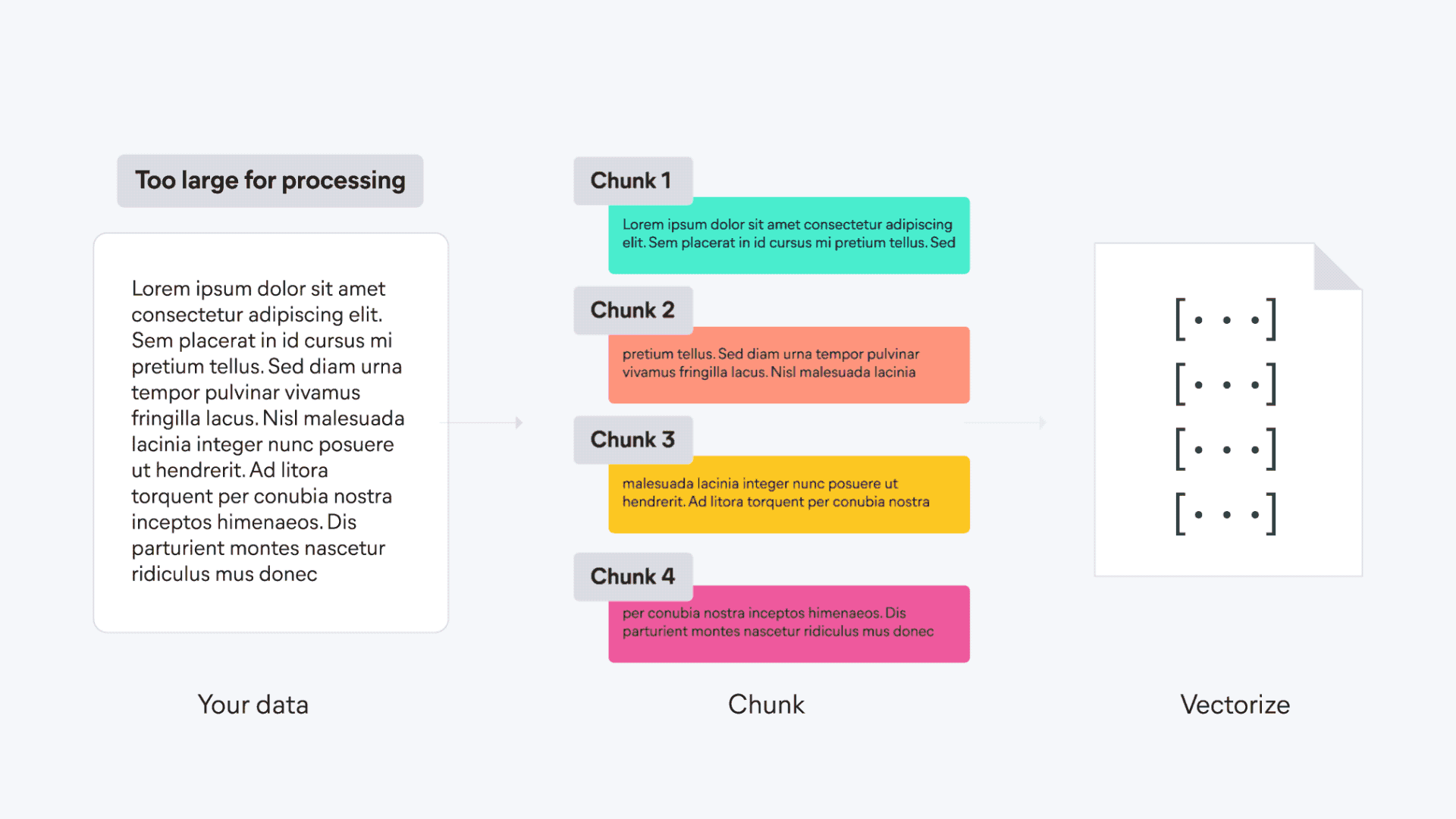 |
| 103 | + |
| 104 | +The vectors are stored in {{es}} and are ready to be used for semantic search. |
| 105 | +:::: |
| 106 | +::::{step} Explore the data |
28 | 107 |
|
29 | | -* [Option 1](#_semantic_text_workflow): Use the `semantic_text` workflow (recommended) |
30 | | -* [Option 2](#_infer_api_workflow): Use the {{infer}} API workflow |
31 | | -* [Option 3](#_model_deployment_workflow): Deploy models directly in {{es}} |
| 108 | +To familiarize yourself with this data set, open [Discover](/explore-analyze/discover.md) from the navigation menu or the global search field. |
32 | 109 |
|
33 | | -This diagram summarizes the relative complexity of each workflow: |
| 110 | +In **Discover**, you can click the expand icon {icon}`expand` to show details about documents in the table: |
34 | 111 |
|
35 | | -:::{image} /solutions/images/elasticsearch-reference-semantic-options.svg |
36 | | -:alt: Overview of semantic search workflows in {{es}} |
| 112 | +:::{image} /solutions/images/serverless-discover-semantic.png |
| 113 | +:screenshot: |
| 114 | +:alt: Discover table view with document expanded |
37 | 115 | ::: |
38 | 116 |
|
39 | | -## Choose a semantic search workflow [using-nlp-models] |
| 117 | +For more tips, check out [](/explore-analyze/discover/discover-get-started.md). |
| 118 | +:::: |
| 119 | +::::: |
40 | 120 |
|
41 | | -### Option 1: `semantic_text` [_semantic_text_workflow] |
| 121 | +## Test semantic search |
42 | 122 |
|
43 | | -The simplest way to use NLP models in the {{stack}} is through the [`semantic_text` workflow](semantic-search/semantic-search-semantic-text.md). We recommend using this approach because it abstracts away a lot of manual work. All you need to do is create an index mapping to start ingesting, embedding, and querying data. There is no need to define model-related settings and parameters, or to create {{infer}} ingest pipelines. For guidance on the available query types for `semantic_text`, see [Querying `semantic_text` fields](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/mapping-reference/semantic-text.md#querying-semantic-text-fields). |
| 123 | +When you run a semantic search, the text in your query must be turned into vectors that use the same embedding model as your vector database. |
| 124 | +This step is performed automatically when you use `semantic_text` fields. |
| 125 | +You therefore only need to pick a query language and a method for comparing the vectors. |
44 | 126 |
|
45 | | -To learn more about supported services, refer to [](/explore-analyze/elastic-inference/inference-api.md) and the [{{infer}} API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/group/endpoint-inference) documentation. For an end-to-end tutorial, refer to [Semantic search with `semantic_text`](semantic-search/semantic-search-semantic-text.md). |
| 127 | +:::::{stepper} |
| 128 | +::::{step} Choose a query language |
46 | 129 |
|
47 | | -### Option 2: Inference API [_infer_api_workflow] |
| 130 | +{{es}} provides a variety of query languages for interacting with your data. |
| 131 | +For an overview of their features and use cases, check out [](/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages.md). |
| 132 | +The [Elasticsearch Query Language](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/esql.md) (ES|QL) is designed to be easy to read and write. |
| 133 | +It enables you to query your data directly in **Discover**, so it's a good one to start with. |
48 | 134 |
|
49 | | -The {{infer}} API workflow is more complex but offers greater control over the {{infer}} endpoint configuration. You need to create an {{infer}} endpoint, provide various model-related settings and parameters, and define an index mapping. Optionally you can also set up an {{infer}} ingest pipeline for automatic embedding during data ingestion, or alternatively, you can manually call the {{infer}} API. |
| 135 | +Go to **Discover** and select **Try ES|QL** from the application menu bar. |
| 136 | +:::: |
| 137 | +::::{step} Choose a vector comparison method |
| 138 | +You can search data that is stored in `semantic_text` fields by using a specific subset of queries, including `knn`, `match`, `semantic`, and `sparse_vector`. |
| 139 | +For the definitive list of supported queries, refer to [Semantic text field type](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/mapping-reference/semantic-text.md). |
50 | 140 |
|
51 | | -For an end-to-end tutorial, refer to [Semantic search with the {{infer}} API](semantic-search/semantic-search-inference.md). |
| 141 | +In ES|QL, you can perform semantic searches on `semantic_text` field types using the same match syntax as full-text search. |
| 142 | +For example: |
52 | 143 |
|
53 | | -### Option 3: Manual model deployment [_model_deployment_workflow] |
| 144 | +```esql |
| 145 | +FROM semantic-index <1> |
| 146 | +| WHERE content: "what's the biggest park?" <2> |
| 147 | +| LIMIT 10 <3> |
| 148 | +``` |
54 | 149 |
|
55 | | -You can also deploy NLP in {{es}} manually, without using an {{infer}} endpoint. This is the most complex and labor intensive workflow for performing semantic search in the {{stack}}. You need to select an NLP model from the [list of supported dense and sparse vector models](../../explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-model-ref.md#ml-nlp-model-ref-text-embedding), deploy it using the Eland client, create an index mapping, and set up a suitable ingest pipeline to start ingesting and querying data. |
| 150 | +1. The FROM source command returns a table of data from the specified index. |
| 151 | +2. A simplified syntax for the MATCH search function, this command performs a semantic query on the specified field. Think of some queries that are relevant to the documents you explored, such as finding the biggest park or the best for rappelling. |
| 152 | +3. The LIMIT processing command defines the maximum number of rows to return. |
56 | 153 |
|
57 | | -For an end-to-end tutorial, refer to [Semantic search with a model deployed in {{es}}](vector/dense-versus-sparse-ingest-pipelines.md). |
| 154 | +When you click **▶Run**, the results appear in a table. |
| 155 | +Each row in the table represents a document. |
58 | 156 |
|
59 | | -::::{tip} |
60 | | -Refer to [vector queries and field types](vector.md#vector-queries-and-field-types) for a quick reference overview. |
| 157 | +To learn more about these commands, refer to [ES|QL syntax reference](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/esql/esql-syntax-reference.md) and [](/solutions/search/esql-for-search.md). |
61 | 158 | :::: |
| 159 | +::::{step} Analyze the results |
| 160 | + |
| 161 | +To have a better understanding of how well each document matches your query, add commands to include the relevance score and sort the results based on that value. |
| 162 | +For example: |
| 163 | + |
| 164 | +```esql |
| 165 | +FROM semantic-index METADATA _score <1> |
| 166 | + | WHERE content: "best spot for rappelling" |
| 167 | + | KEEP content, _score <2> |
| 168 | + | SORT _score DESC <3> |
| 169 | + | LIMIT 10 |
| 170 | +``` |
| 171 | + |
| 172 | +1. The `METADATA` clause provides access to the query relevance score, which is a [metadata field](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/esql/esql-metadata-fields.md). |
| 173 | +2. The KEEP processing command affects the columns and their order in the results table. |
| 174 | +3. The results are sorted in descending order based on the `_score`. |
| 175 | + |
| 176 | +:::{tip} |
| 177 | +Click the **ES|QL help** button to open the in-product reference documentation for all commands and functions or to get recommended queries. For more tips, check out [Using ES|QL in Discover](/explore-analyze/discover/try-esql.md). |
| 178 | +::: |
| 179 | + |
| 180 | +In this example, the first row in the table is the document related to Rocky Mountain National Park, which had the highest relevance score for the query: |
62 | 181 |
|
63 | | -## Learn more [semantic-search-read-more] |
| 182 | +:::{image} /solutions/images/serverless-discover-semantic-esql.png |
| 183 | +:screenshot: |
| 184 | +:alt: Run an ES|QL semantic query in Discover |
| 185 | +::: |
| 186 | + |
| 187 | +Optionally, try out the same search as an API request in **Console**: |
| 188 | + |
| 189 | +```console |
| 190 | +POST /_query?format=txt |
| 191 | +{ |
| 192 | + "query": """ |
| 193 | + FROM semantic-index METADATA _score |
| 194 | + | WHERE content: "best spot for rappelling" |
| 195 | + | KEEP content, _score |
| 196 | + | SORT _score DESC |
| 197 | + | LIMIT 10 |
| 198 | + """ |
| 199 | +} |
| 200 | +``` |
| 201 | + |
| 202 | +When you finish your tests and no longer need the sample data set, delete the index: |
| 203 | + |
| 204 | +```console |
| 205 | +DELETE /semantic-index |
| 206 | +``` |
| 207 | + |
| 208 | +:::: |
| 209 | +::::: |
64 | 210 |
|
65 | | -### Interactive examples |
| 211 | +## Next steps |
66 | 212 |
|
67 | | -- The [`elasticsearch-labs`](https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch-labs) repo contains a number of interactive semantic search examples in the form of executable Python notebooks, using the {{es}} Python client |
68 | | -- [Semantic search with ELSER using the model deployment workflow](https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch-labs/blob/main/notebooks/search/03-ELSER.ipynb) |
69 | | -- [Semantic search with `semantic_text`](https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch-labs/blob/main/notebooks/search/09-semantic-text.ipynb) |
| 213 | +Thanks for taking the time to try out semantic search. |
| 214 | +For a deeper dive, go to [](/solutions/search/semantic-search.md). |
70 | 215 |
|
71 | | -### Blogs |
| 216 | +If you want to extend this example, try an index with more fields. |
| 217 | +For example, if you have both a `text` field and a `semantic_text` field, you can combine the strengths of traditional keyword search and advanced semantic search. |
| 218 | +A [hybrid search](/solutions/search/hybrid-semantic-text.md) provides comprehensive search capabilities to find relevant information based on both the raw text and its underlying meaning. |
72 | 219 |
|
73 | | -- [{{es}} new semantic_text mapping: Simplifying semantic search](https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/semantic-search-simplified-semantic-text) |
74 | | -- [GA information for `semantic_text`](https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/semantic-text-ga) |
75 | | -- [Introducing ELSER: Elastic's AI model for semantic search](https://www.elastic.co/blog/may-2023-launch-sparse-encoder-ai-model) |
76 | | -- [How to get the best of lexical and AI-powered search with Elastic's vector database](https://www.elastic.co/blog/lexical-ai-powered-search-elastic-vector-database) |
77 | | -- Information retrieval blog series: |
78 | | - - [Part 1: Steps to improve search relevance](https://www.elastic.co/blog/improving-information-retrieval-elastic-stack-search-relevance) |
79 | | - - [Part 2: Benchmarking passage retrieval](https://www.elastic.co/blog/improving-information-retrieval-elastic-stack-benchmarking-passage-retrieval) |
80 | | - - [Part 3: Introducing Elastic Learned Sparse Encoder, our new retrieval model](https://www.elastic.co/blog/may-2023-launch-information-retrieval-elasticsearch-ai-model) |
81 | | - - [Part 4: Hybrid retrieval](https://www.elastic.co/blog/improving-information-retrieval-elastic-stack-hybrid) |
| 220 | +To learn about more options, such as vector and keyword search, go to [](/solutions/search/search-approaches.md). |
| 221 | +For a summary of the AI-powered search use cases, go to [](/solutions/search/ai-search/ai-search.md). |
0 commit comments