diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards.md
index d6008e800a..4ba8e4d2a0 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ mapped_pages:
Dashboards are the best way to visualize and share insights from your {{es}} data.
-A **dashboard** is made of one or more **panels** that you can organize as you like. Each panel can display various types of content: *visualizations* such as charts, tables, metrics, and maps, *static annotations* like text or images, or even *specialized views* for Machine Learning or Observability data.
+A **dashboard** is made of one or more **panels** that you can organize as you like. Each panel can display various types of content: **visualizations** such as charts, tables, metrics, and maps, **static annotations** like text or images, or even **specialized views** for Machine Learning or Observability data.

diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/_tutorials.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/_tutorials.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 928a9d2442..0000000000
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/_tutorials.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
----
-mapped_pages:
- - https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/_tutorials.html
----
-
-# Tutorials [_tutorials]
-
-Learn more about building dashboards and creating visualizations with the following tutorials.
-
-These tutorials use [sample data](../overview/kibana-quickstart.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana) available in {{kib}} as a way to get started more easily, but you can apply and adapt these instructions to your own data as well.
-
-
-
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md
index e7c1e69f8a..366f2ba819 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md
@@ -10,31 +10,16 @@ mapped_pages:
There are three types of controls:
* [**Options list**](#create-and-add-options-list-and-range-slider-controls) — Adds a dropdown that allows to filter data by selecting one or more values.
-
- For example, if you are using the **[Logs] Web Traffic** dashboard from the sample web logs data, you can add an options list for the `machine.os.keyword` field that allows you to display only the logs generated from `osx` and `ios` operating systems.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_controlsOptionsList_8.7.0.png
- :alt: Options list control for the `machine.os.keyword` field with the `osx` and `ios` options selected
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ For example, if you are using the **[Logs] Web Traffic** dashboard from the sample web logs data, you can add an options list for the `machine.os.keyword` field that allows you to display only the logs generated from `osx` and `ios` operating systems.
+ 
* [**Range slider**](#create-and-add-options-list-and-range-slider-controls) — Adds a slider that allows to filter the data within a specified range of values. This type of control only works with numeric fields.
-
- For example, if you are using the **[Logs] Web Traffic** dashboard from the sample web logs data, you can add a range slider for the `hour_of_day` field that allows you to display only the log data from 9:00AM to 5:00PM.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_controlsRangeSlider_8.3.0.png
- :alt: Range slider control for the `hour_of_day` field with a range of `9` to `17` selected
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ For example, if you are using the **[Logs] Web Traffic** dashboard from the sample web logs data, you can add a range slider for the `hour_of_day` field that allows you to display only the log data from 9:00AM to 5:00PM.
+ 
* [**Time slider**](#add-time-slider-controls) — Adds a time range slider that allows to filter the data within a specified range of time, advance the time range backward and forward by a unit that you can define, and animate your change in data over the specified time range.
-
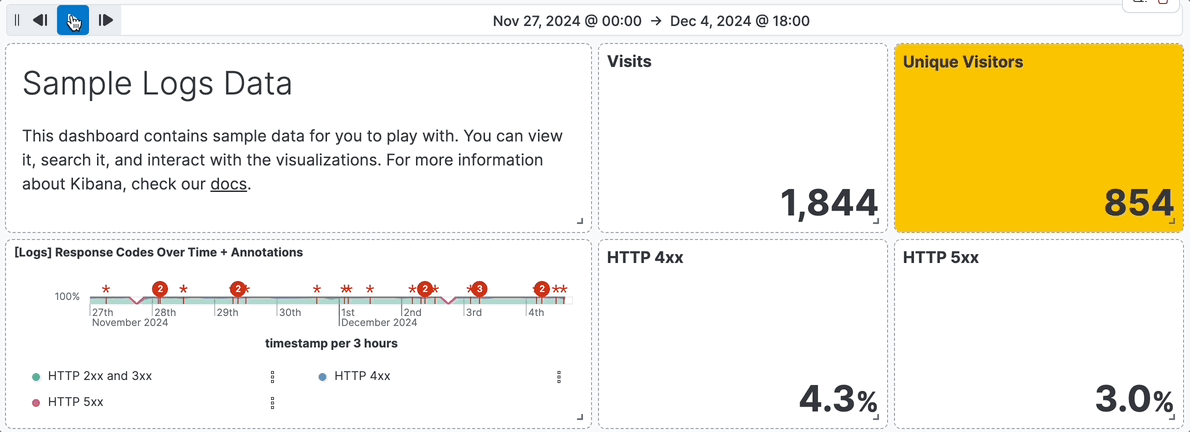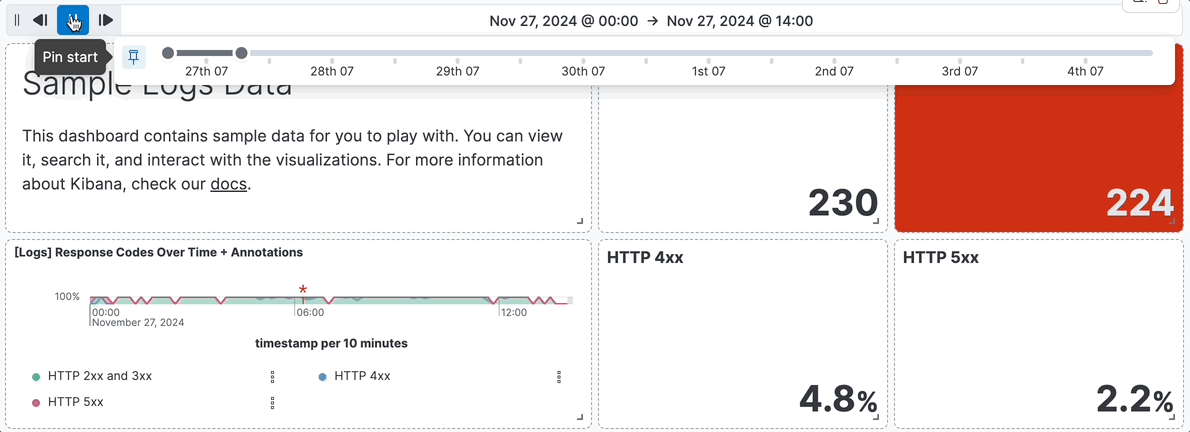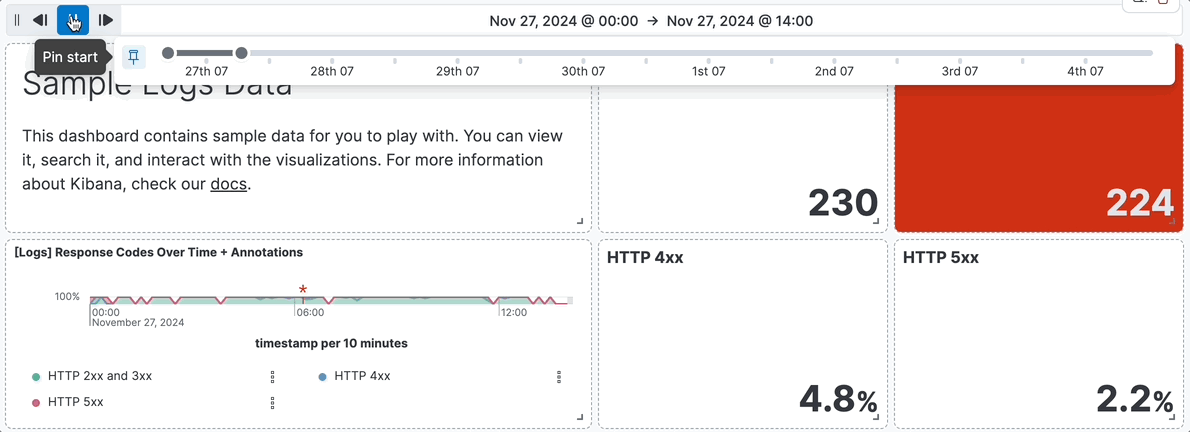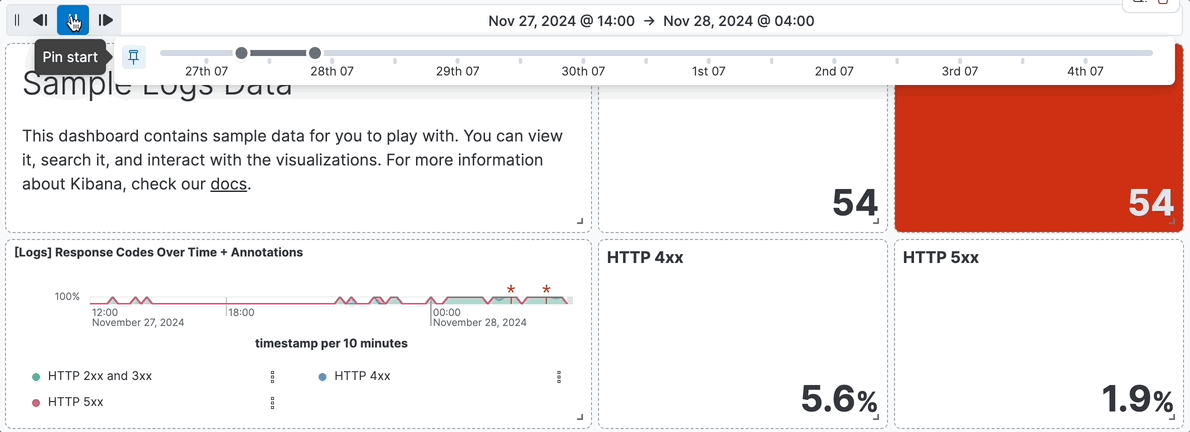
- For example, you are using the **[Logs] Web Traffic** dashboard from the sample web logs data, and the global time filter is **Last 7 days**. When you add the time slider, you can click the previous and next buttons to advance the time range backward or forward, and click the play button to watch how the data changes over the last 7 days.
-
- :::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt672f3aaadf9ea5a6/6750dd6c2452f972af0a88b4/dashboard_timeslidercontrol_8.17.0.gif
- :alt: Time slider control for the the Last 7 days
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ For example, you are using the **[Logs] Web Traffic** dashboard from the sample web logs data, and the global time filter is **Last 7 days**. When you add the time slider, you can click the previous and next buttons to advance the time range backward or forward, and click the play button to watch how the data changes over the last 7 days.
+ 
@@ -44,19 +29,14 @@ To add interactive Options list and Range slider controls, create the controls,
1. Open or create a new dashboard.
2. In **Edit** mode, select **Controls** > **Add control** in the dashboard toolbar.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard-add-control-8.15.0.png
- :alt: Controls button in the toolbar with the Add Control option selected
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ 
3. On the **Create control** flyout, from the **Data view** dropdown, select the data view that contains the field you want to use for the **Control**.
4. In the **Field** list, select the field you want to filter on.
5. Under **Control type**, select whether the control should be an **Options list** or a **Range slider**.
-
- ::::{tip}
- Range sliders are for Number type fields only.
- ::::
+ ::::{tip}
+ Range sliders are for Number type fields only.
+ ::::
6. Define how you want the control to appear:
@@ -75,9 +55,9 @@ To add interactive Options list and Range slider controls, create the controls,
* **Contains**: Show options that *contain* the entered value. This setting option is only available for *string* type fields. Results can take longer to show with this option.
* **Exact**: Show options that are a 100% match with the entered value.
- ::::{tip}
- The search is not case sensitive. For example, searching for `ios` would still retrieve `iOS` if that value exists.
- ::::
+ ::::{tip}
+ The search is not case sensitive. For example, searching for `ios` would still retrieve `iOS` if that value exists.
+ ::::
* **Ignore timeout for results** delays the display of the list of values to when it is fully loaded. This option is useful for large data sets, to avoid missing some available options in case they take longer to load and appear when using the control.
@@ -94,11 +74,7 @@ You can add one interactive time slider control to a dashboard.
1. Open or create a new dashboard.
2. In **Edit** mode, select **Controls** > **Add time slider control**.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard-add-time-slider-control-8.15.0.png
- :alt: Controls button in the toolbar with the Add a time slider option selected
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ 
3. The time slider control uses the time range from the global time filter. To change the time range in the time slider control, [change the global time filter](../query-filter/filtering.md).
4. Save the dashboard. The control can now be used.
@@ -109,11 +85,7 @@ You can add one interactive time slider control to a dashboard.
Several settings that apply to all controls of the same dashboard are available.
1. In **Edit** mode, select **Controls** > **Settings**.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard-controls-settings-8.15.0.png
- :alt: Controls button in the toolbar with the Settings option selected
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ 
2. On the **Control settings** flyout, configure the following settings:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/arrange-panels.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/arrange-panels.md
index 76c42b374c..1de792c08c 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/arrange-panels.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/arrange-panels.md
@@ -15,9 +15,9 @@ In the toolbar, click **Edit**, then use the following options:
* To resize, click the resize control, then drag to the new dimensions.
* To maximize to full screen, open the panel menu and click **Maximize**.
- ::::{tip}
- If you [share](sharing.md) a dashboard while viewing a full screen panel, the generated link will directly open the same panel in full screen mode.
- ::::
+ ::::{tip}
+ If you [share](sharing.md) a dashboard while viewing a full screen panel, the generated link will directly open the same panel in full screen mode.
+ ::::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/building.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/building.md
index 76e2944619..fa5d81ecc5 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/building.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/building.md
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/create-dashboards.html
---
-# Building [create-dashboards]
+# Building dashboards [create-dashboards]
{{kib}} offers many ways to build powerful dashboards that will help you visualize and keep track of the most important information contained in your {{es}} data.
@@ -16,9 +16,9 @@ $$$dashboard-minimum-requirements$$$
To create or edit dashboards, you first need to:
* have [data indexed into {{es}}](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/getting-started-index.html) and a [data view](../find-and-organize/data-views.md). A data view is a subset of your {{es}} data, and allows you to load just the right data when building a visualization or exploring it.
-
- ::::{tip}
- If you don’t have data at hand and still want to explore dashboards, you can import one of the [sample data sets](../../manage-data/ingest/sample-data.md) available.
- ::::
+
+ ::::{tip}
+ If you don’t have data at hand and still want to explore dashboards, you can import one of the [sample data sets](../../manage-data/ingest/sample-data.md) available.
+ ::::
* have sufficient permissions on the **Dashboard** feature. If that’s not the case, you might get a read-only indicator. A {{kib}} administrator can [grant you the required privileges](../../deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/kibana-privileges.md).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md
index 62925a2d97..74dd207c84 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md
@@ -46,10 +46,10 @@ To analyze the data with a custom time interval, create a bar chart that shows y
2. To zoom in on the data, click and drag your cursor across the bars.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_clickAndDragZoom_7.16.gif
- :alt: Cursor clicking and dragging across the bars to zoom in on the data
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_clickAndDragZoom_7.16.gif
+ :alt: Cursor clicking and dragging across the bars to zoom in on the data
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
3. In the layer pane, click **Count of records**.
@@ -81,10 +81,10 @@ To identify the 75th percentile of orders, add a reference line:
4. Click **Close**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_barChartCustomTimeInterval_8.3.png
- :alt: Orders per day
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_barChartCustomTimeInterval_8.3.png
+ :alt: Orders per day
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
5. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -109,20 +109,20 @@ To copy a function, you drag it to the **Add or drag-and-drop a field** area wit
1. Drag the **95th** field to **Add or drag-and-drop a field** for **Vertical axis**.
- :::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt8fb6969daa820faf/6700642c363a96bb08f48bee/drag-and-drop-a-field-8.16.0.gif
- :alt: Easily duplicate the items with drag and drop
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt8fb6969daa820faf/6700642c363a96bb08f48bee/drag-and-drop-a-field-8.16.0.gif
+ :alt: Easily duplicate the items with drag and drop
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
2. Click **95th [1]**, then enter `90` in the **Percentile** field.
3. In the **Name** field enter `90th`, then click **Close**.
4. To create the `50th` and `10th` percentiles, repeat the duplication steps.
5. Open the **Left Axis** menu, select **Custom** from the **Axis title** dropdown, then enter `Percentiles for product prices` in the **Axis title** field.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_lineChartMultipleDataSeries_7.16.png
- :alt: Percentiles for product prices chart
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_lineChartMultipleDataSeries_7.16.png
+ :alt: Percentiles for product prices chart
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
6. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -152,17 +152,17 @@ Add a layer to display the customer traffic:
2. In the **Series color** field, enter `#D36086`.
3. Click **Right** for the **Axis side**, then click **Close**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_advancedTutorial_numberOfCustomers_8.5.0.png
- :alt: Number of customers area chart in Lens
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_advancedTutorial_numberOfCustomers_8.5.0.png
+ :alt: Number of customers area chart in Lens
+ :::
4. From the **Available fields** list, drag **order_date** to the **Horizontal Axis** field in the second layer.
5. To change the position of the legend, open the **Legend** menu, then select the **Alignment** arrow that points up.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_mixedXYChart_7.16.png
- :alt: Layer visualization type menu
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_mixedXYChart_7.16.png
+ :alt: Layer visualization type menu
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
6. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -199,10 +199,10 @@ For each order category, create a filter:
6. Click **Close**.
7. Open the **Legend** menu, then select the **Alignment** arrow that points up.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_areaPercentageNumberOfOrdersByCategory_8.3.png
- :alt: Prices share by category
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_areaPercentageNumberOfOrdersByCategory_8.3.png
+ :alt: Prices share by category
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
8. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -235,10 +235,11 @@ Filter the results to display the data for only Saturday and Sunday:
4. Click **Close**.
5. Open the **Legend** menu, then click **Hide** next to **Display**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_areaChartCumulativeNumberOfSalesOnWeekend_7.16.png
- :alt: Area chart with cumulative sum of orders made on the weekend
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_areaChartCumulativeNumberOfSalesOnWeekend_7.16.png
+ :alt: Area chart with cumulative sum of orders made on the weekend
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
6. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -259,12 +260,13 @@ To create a week-over-week comparison, shift **Count of records [1]** by one wee
1. In the layer pane, click **Count of records [1]**.
2. Click **Advanced**, select **1 week ago** from the **Time shift** dropdown, then click **Close**.
- To use custom time shifts, enter the time value and increment, then press Enter. For example, enter **1w** to use the **1 week ago** time shift.
+ To use custom time shifts, enter the time value and increment, then press Enter. For example, enter **1w** to use the **1 week ago** time shift.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_time_shift.png
- :alt: Line chart with week-over-week sales comparison
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_time_shift.png
+ :alt: Line chart with week-over-week sales comparison
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
3. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -285,10 +287,11 @@ To compare time range changes as a percent, create a bar chart that compares the
6. From the **Value format** dropdown, select **Percent**, then enter `0` in the **Decimals** field.
7. Click **Close**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_percent_chage.png
- :alt: Bar chart with percent change in sales between the current time and the previous week
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_percent_chage.png
+ :alt: Bar chart with percent change in sales between the current time and the previous week
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
8. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -317,10 +320,11 @@ To split the metric, add columns for each continent using the **Columns** field:
1. From the **Available fields** list, drag **geoip.continent_name** to the **Split metrics by** field in the layer pane.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_table_over_time.png
- :alt: Date histogram table with groups for the customer count metric
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_table_over_time.png
+ :alt: Date histogram table with groups for the customer count metric
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
2. Click **Save and return**.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md
index b7fb8026f5..6b7419ee4c 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md
@@ -34,10 +34,10 @@ Open the visualization editor, then make sure the correct fields appear.
1. On the dashboard, click **Create visualization**.
2. Make sure the **{{kib}} Sample Data Logs** {{data-source}} appears.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_dataViewDropDown_8.4.0.png
- :alt: Data view dropdown
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_dataViewDropDown_8.4.0.png
+ :alt: Data view dropdown
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
To create the visualizations in this tutorial, you’ll use the following fields:
@@ -53,6 +53,7 @@ Click a field name to view more details, such as its top values and distribution
:::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt25c7a05e0f5daaa3/671966b9b1d3dd705a2ae650/tutorial-field-more-info.gif
:alt: Clicking a field name to view more details
:class: screenshot
+:width: 50%
:::
@@ -64,19 +65,19 @@ The only number function that you can use with **clientip** is **Unique count**,
1. Open the **Visualization type** dropdown, then select **Metric**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-visualization-type-dropdown-8.16.0.png
- :alt: Visualization type dropdown
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-visualization-type-dropdown-8.16.0.png
+ :alt: Visualization type dropdown
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
2. From the **Available fields** list, drag **clientip** to the workspace or layer pane.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-tutorial-unique-count-of-client-ip-8.16.0.png
- :alt: Metric visualization of the clientip field
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-tutorial-unique-count-of-client-ip-8.16.0.png
+ :alt: Metric visualization of the clientip field
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
- In the layer pane, **Unique count of clientip** appears because the editor automatically applies the **Unique count** function to the **clientip** field. **Unique count** is the only numeric function that works with IP addresses.
+ In the layer pane, **Unique count of clientip** appears because the editor automatically applies the **Unique count** function to the **clientip** field. **Unique count** is the only numeric function that works with IP addresses.
3. In the layer pane, click **Unique count of clientip**.
@@ -99,10 +100,10 @@ To visualize the **bytes** field over time:
3. To zoom in on the data, click and drag your cursor across the bars.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_end_to_end_3_1_1.gif
- :alt: Zoom in on the data
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_end_to_end_3_1_1.gif
+ :alt: Zoom in on the data
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
To emphasize the change in **Median of bytes** over time, change the visualization type to **Line** with one of the following options:
@@ -123,17 +124,19 @@ To save space on the dashboard, hide the axis labels.
1. Open the **Left axis** menu, then select **None** from the **Axis title** dropdown.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-line-chart-left-axis-8.16.0.png
- :alt: Left axis menu
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-line-chart-left-axis-8.16.0.png
+ :alt: Left axis menu
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
2. Open the **Bottom axis** menu, then select **None** from the **Axis title** dropdown.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-line-chart-bottom-axis-8.16.0.png
- :alt: Bottom axis menu
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-line-chart-bottom-axis-8.16.0.png
+ :alt: Bottom axis menu
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
3. Click **Save and return**
@@ -142,10 +145,11 @@ Since you removed the axis labels, add a panel title:
1. Hover over the panel and click . The **Settings** flyout appears.
2. In the **Title** field, enter `Median of bytes`, then click **Apply**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_lineChartMetricOverTime_8.4.0.png
- :alt: Line chart that displays metric data over time
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_lineChartMetricOverTime_8.4.0.png
+ :alt: Line chart that displays metric data over time
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
@@ -162,10 +166,11 @@ The **Top values** function ranks the unique values of a field by another functi
3. Drag **request.keyword** to the workspace.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-tutorial-top-values-of-field-8.16.0.png
- :alt: Vertical bar chart with top values of request.keyword by most unique visitors
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-tutorial-top-values-of-field-8.16.0.png
+ :alt: Vertical bar chart with top values of request.keyword by most unique visitors
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
When you drag a text or IP address field to the workspace, the editor adds the **Top values** function ranked by **Count of records** to show the most frequent values.
@@ -174,10 +179,11 @@ The chart labels are unable to display because the **request.keyword** field con
1. Open the **Visualization type** dropdown, then select **Table**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-table-with-request-keyword-and-client-ip-8.16.0.png
- :alt: Table with top values of request.keyword by most unique visitors
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-table-with-request-keyword-and-client-ip-8.16.0.png
+ :alt: Table with top values of request.keyword by most unique visitors
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
2. In the layer pane, click **Top 5 values of request.keyword**.
@@ -185,10 +191,11 @@ The chart labels are unable to display because the **request.keyword** field con
2. In the **Name** field, enter `Page URL`.
3. Click **Close**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_tableTopFieldValues_7.16.png
- :alt: Table that displays the top field values
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_tableTopFieldValues_7.16.png
+ :alt: Table that displays the top field values
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
3. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -221,10 +228,10 @@ Specify the file size ranges:
* **Ranges** — `10240` → `+∞`
* **Label** — `Above 10KB`
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_end_to_end_6_1.png
- :alt: Custom ranges configuration
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_end_to_end_6_1.png
+ :alt: Custom ranges configuration
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
4. From the **Value format** dropdown, select **Bytes (1024)**, then click **Close**.
@@ -232,10 +239,11 @@ To display the values as a percentage of the sum of all values, use the **Pie**
1. Open the **Visualization Type** dropdown, then select **Pie**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_pieChartCompareSubsetOfDocs_7.16.png
- :alt: Pie chart that compares a subset of documents to all documents
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_pieChartCompareSubsetOfDocs_7.16.png
+ :alt: Pie chart that compares a subset of documents to all documents
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
2. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -260,10 +268,11 @@ The distribution of a number can help you find patterns. For example, you can an
4. From the **Available fields** list, drag **hour_of_day** to **Horizontal axis** field in the layer pane.
5. In the layer pane, click **hour_of_day**, then slide the **Intervals granularity** slider until the horizontal axis displays hourly intervals.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_barChartDistributionOfNumberField_7.16.png
- :alt: Bar chart that displays the distribution of a number field
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_barChartDistributionOfNumberField_7.16.png
+ :alt: Bar chart that displays the distribution of a number field
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 60%
+ :::
6. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -307,10 +316,11 @@ Add the user geography grouping:
1. From the **Available fields** list, drag **geo.srcdest** to the workspace.
2. To change the **Group by** order, drag **Top 3 values of geo.srcdest** in the layer pane so that appears first.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_end_to_end_7_2.png
- :alt: Treemap visualization
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_end_to_end_7_2.png
+ :alt: Treemap visualization
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
Remove the documents that do not match the filter criteria:
@@ -318,10 +328,11 @@ Remove the documents that do not match the filter criteria:
1. In the layer pane, click **Top 3 values of geo.srcdest**.
2. Click **Advanced**, deselect **Group other values as "Other"**, then click **Close**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_treemapMultiLevelChart_7.16.png
- :alt: Treemap visualization
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_treemapMultiLevelChart_7.16.png
+ :alt: Treemap visualization
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
3. Click **Save and return**.
@@ -342,10 +353,10 @@ Decrease the size of the following panels, then move the panels to the first row
* **Sum of bytes from large requests**
* **Website traffic**
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_logsDashboard_8.4.0.png
- :alt: Logs dashboard
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_logsDashboard_8.4.0.png
+ :alt: Logs dashboard
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard.md
index 3d3f53a9b9..cf36dc56a9 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard.md
@@ -17,10 +17,7 @@ mapped_pages:
* **Add from library**. Select existing content that has already been configured and saved to the **Visualize Library**.
* [**Controls**](add-controls.md). Add controls to help filter the content of your dashboard.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-add_content_to_dashboard_8.15.0.png
- :alt: Options to add content to your dashboard
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ 
4. Organize your dashboard by [organizing the various panels](arrange-panels.md).
5. Define the main settings of your dashboard from the **Settings** menu located in the toolbar.
@@ -36,10 +33,6 @@ mapped_pages:
* **Sync tooltips across panels** — When you hover your cursor over a **Lens** chart, the tooltips on all other related dashboard charts automatically appear.
3. Click **Apply**.
-
- :::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt4a6e9807f1fac9f8/6750ee9cef6d5a250c229e50/dashboard-settings-8.17.0.gif
- :alt: Change and apply dashboard settings
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ 
6. Click **Save** to save the dashboard.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/drilldowns.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/drilldowns.md
index 3d47016a16..96d77d08cc 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/drilldowns.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/drilldowns.md
@@ -15,17 +15,7 @@ There are three types of drilldowns you can add to dashboards:
Third-party developers can create drilldowns. To learn how to code drilldowns, refer to [this example plugin](https://github.com/elastic/kibana/blob/master/x-pack/examples/ui_actions_enhanced_examples).
-
-![]() -
+[](https://videos.elastic.co/watch/UhGkdJGC32HRn3oS5ZYJL1?)
## Create dashboard drilldowns [dashboard-drilldowns]
@@ -77,11 +67,10 @@ Create a drilldown that opens the **Detailed logs** dashboard from the **[Logs]
3. Save the dashboard.
4. In the data table panel, hover over a value, click **+**, then select `View details`.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_drilldownOnPanel_8.3.png
- :alt: Drilldown on data table that navigates to another dashboard
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_drilldownOnPanel_8.3.png
+ :alt: Drilldown on data table that navigates to another dashboard
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -164,11 +153,10 @@ Create a drilldown that opens **Discover** from the [**Sample web logs**](../ove
5. Click **Create drilldown**.
6. Save the dashboard.
7. On the **[Logs] Bytes distribution** bar vertical stacked chart, click a bar, then select **View bytes distribution in Discover**.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_discoverDrilldown_8.3.png
- :alt: Drilldown on bar vertical stacked chart that navigates to Discover
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_discoverDrilldown_8.3.png
+ :alt: Drilldown on bar vertical stacked chart that navigates to Discover
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
index 9ce5ab47bc..9e9cc15476 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
@@ -17,5 +17,6 @@ To duplicate a managed dashboard, follow the instructions above or click the **M
:::{image} ../../images/kibana-managed-dashboard-popover-8.16.0.png
:alt: Managed badge dialog with Duplicate button
:class: screenshot
+:width: 50%
:::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/_import_dashboards.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/import-dashboards.md
similarity index 100%
rename from explore-analyze/dashboards/_import_dashboards.md
rename to explore-analyze/dashboards/import-dashboards.md
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md
index c658ac5050..5591feed7a 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/_manage_dashboards.html
---
-# Managing [_manage_dashboards]
+# Managing dashboards [_manage_dashboards]
## Browse dashboards [find-dashboards]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md
index 2973b5d326..9aef0533cc 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md
@@ -8,17 +8,13 @@ mapped_pages:
1. Open the **Dashboards** page in {{kib}}.
2. Locate the dashboard you want to edit.
- ::::{tip}
- When looking for a specific dashboard, you can filter them by tag or by creator, or search the list based on their name and description. Note that the creator information is only available for dashboards created on or after version 8.14.
- ::::
+ ::::{tip}
+ When looking for a specific dashboard, you can filter them by tag or by creator, or search the list based on their name and description. Note that the creator information is only available for dashboards created on or after version 8.14.
+ ::::
3. Click the dashboard **Title** you want to open.
4. Make sure that you are in **Edit** mode to be able to make changes to the dashboard. You can switch between **Edit** and **View** modes from the toolbar.
-
- :::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt619b284e92c2be27/6750f3a512a5eae780936fe3/switch-to-view-mode-8.17.0.gif
- :alt: Switch between Edit and View modes
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ 
5. Make the changes that you need to the dashboard:
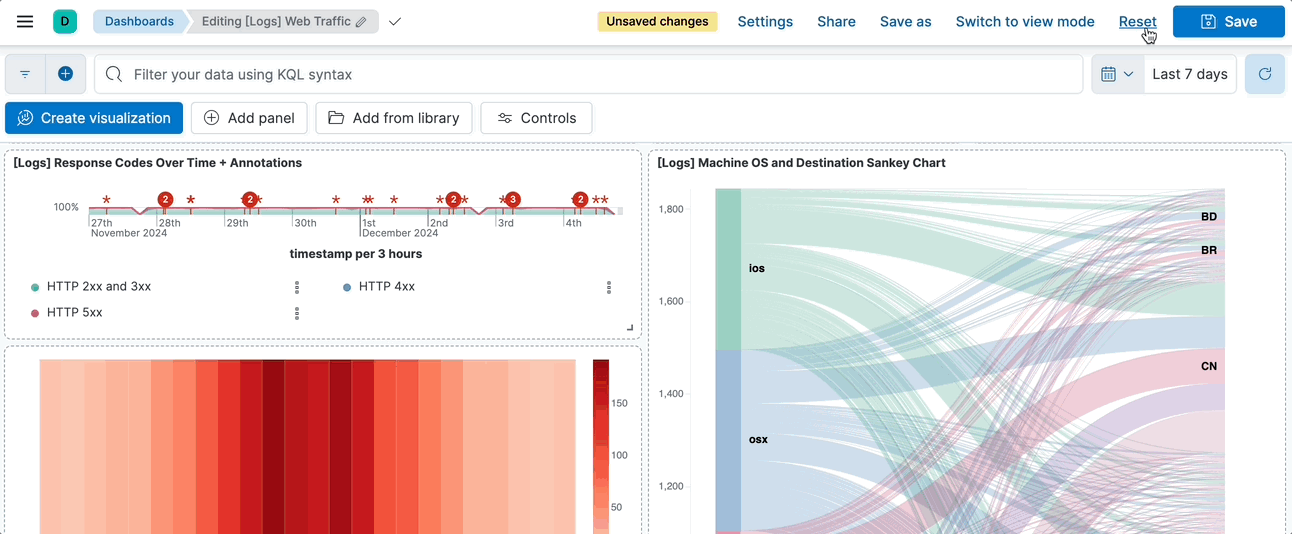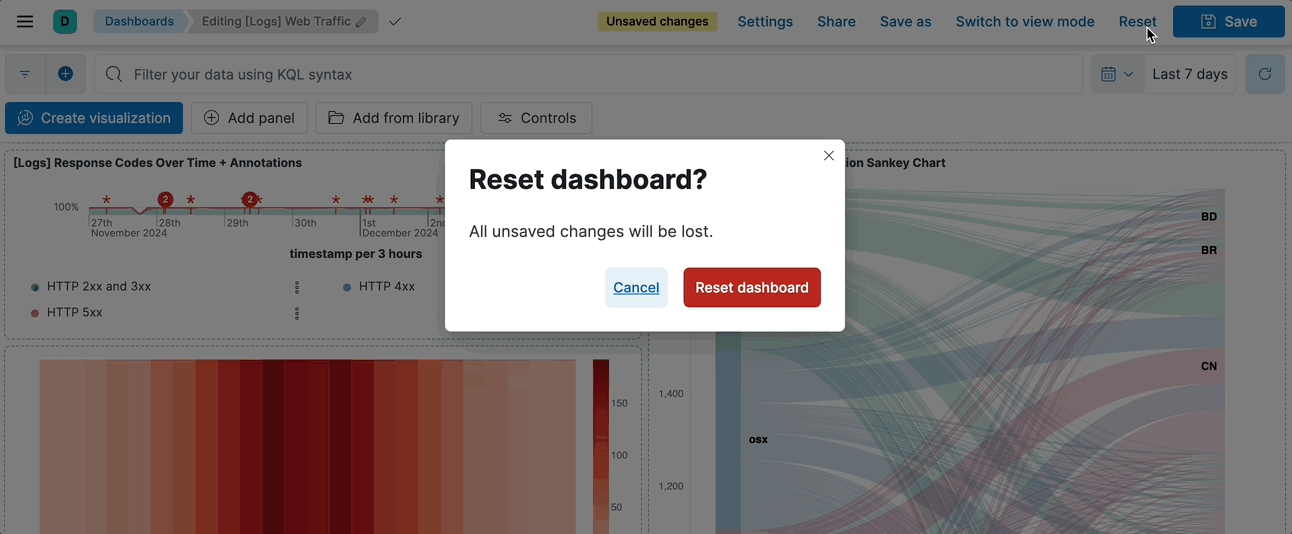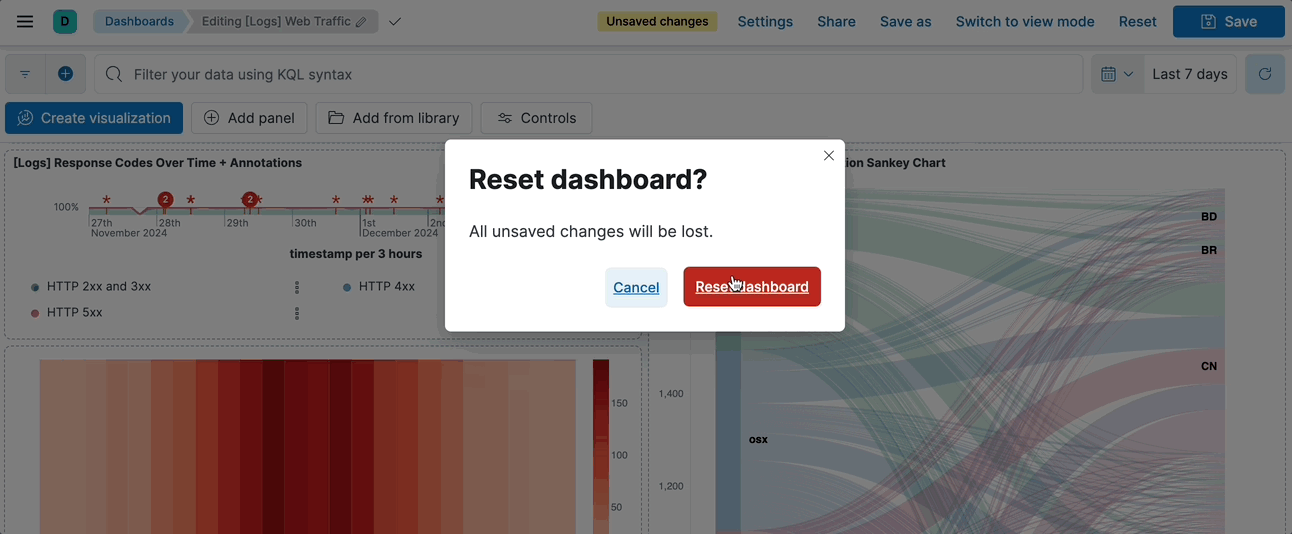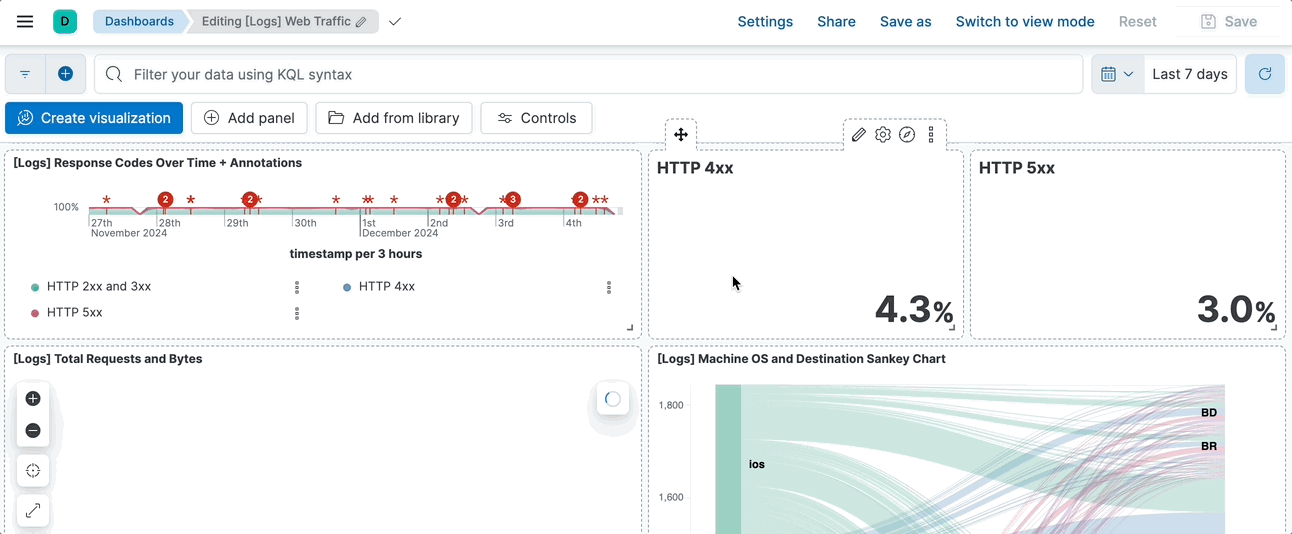
@@ -44,8 +40,4 @@ Once changes are saved, you can no longer revert them in one click, and instead
1. In the toolbar, click **Reset**.
2. On the **Reset dashboard?** window, click **Reset dashboard**.
-
- :::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blte0c08bede75b3874/6750f5566cdeea14b273b048/reset-dashboard-8.17.0.gif
- :alt: Reset dashboard to revert unsaved changes
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ 
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
index 7ce6059b9f..456de2e903 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/share-the-dashboard.html
---
-# Sharing [share-the-dashboard]
+# Sharing dashboards [share-the-dashboard]
To share a dashboard with a larger audience, click **Share** in the toolbar. For detailed information about the sharing options, refer to [Reporting](../report-and-share.md).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
index 48539c4001..30ab0916d5 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/_use_and_filter_dashboards.html
---
-# Using [_use_and_filter_dashboards]
+# Exploring dashboards [_use_and_filter_dashboards]
## Search and filter your dashboard data [search-or-filter-your-data]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md b/explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md
index 02e92127d5..d8045dadeb 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ Numeral formatting patterns are used in multiple places in {{kib}}, including:
* [Advanced settings](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/advanced-options.html)
* [Data view formatters](find-and-organize/data-views.md#field-formatters-numeric)
-* [**TSVB**](visualize/legacy-editors.md#tsvb-panel)
+* [**TSVB**](visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md)
* [**Canvas**](visualize/canvas.md)
The simplest pattern format is `0`, and the default {{kib}} pattern is `0,0.[000]`. The numeral pattern syntax expresses:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/toc.yml b/explore-analyze/toc.yml
index ad9940280c..041aa882c4 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/toc.yml
+++ b/explore-analyze/toc.yml
@@ -253,7 +253,7 @@ toc:
- file: dashboards/drilldowns.md
- file: dashboards/arrange-panels.md
- file: dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
- - file: dashboards/_import_dashboards.md
+ - file: dashboards/import-dashboards.md
- file: dashboards/managing.md
- file: dashboards/sharing.md
- file: dashboards/tutorials.md
@@ -263,8 +263,8 @@ toc:
- file: visualize.md
children:
- file: visualize/supported-chart-types.md
- - file: visualize/manage-panels.md
- file: visualize/visualize-library.md
+ - file: visualize/manage-panels.md
- file: visualize/lens.md
- file: visualize/esorql.md
- file: visualize/field-statistics.md
@@ -315,6 +315,10 @@ toc:
- file: visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
- file: visualize/graph/graph-troubleshooting.md
- file: visualize/legacy-editors.md
+ children:
+ - file: visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md
+ - file: visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md
+ - file: visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md
- file: find-and-organize.md
children:
- file: find-and-organize/data-views.md
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize.md b/explore-analyze/visualize.md
index 6775f0c799..7fc0ee2c15 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize.md
@@ -13,21 +13,26 @@ $$$panels-editors$$$
| **Content** | **Panel type** | **Description** |
| --- | --- | --- |
-| Visualizations | [Lens](visualize/lens.md) | The default editor for creating powerful [charts](visualize/supported-chart-types.md) in {{kib}} |
+| Visualizations | | |
+| [Lens](visualize/lens.md) | The default editor for creating powerful [charts](visualize/supported-chart-types.md) in {{kib}} |
| [ES|QL](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-kibana.md) | Create visualizations from ES|QL queries |
| [Maps](visualize/maps.md) | Create beautiful displays of your geographical data |
| [Field statistics](visualize/field-statistics.md) | Add a field statistics view of your data to your dashboards |
| [Custom visualizations](visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md) | Use Vega to create new types of visualizations |
-| Annotations and navigation | [Text](visualize/text-panels.md) | Add context to your dashboard with markdown-based **text** |
+| Annotations and navigation | | |
+| [Text](visualize/text-panels.md) | Add context to your dashboard with markdown-based **text** |
| [Image](visualize/image-panels.md) | Personalize your dashboard with custom images |
| [Links](visualize/link-panels.md) | Add links to other dashboards or to external websites |
-| Machine Learning and Analytics | [Anomaly swim lane](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-anomalies.md) | Display the results from machine learning anomaly detection jobs |
+| Machine Learning and Analytics | | |
+| [Anomaly swim lane](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-anomalies.md) | Display the results from machine learning anomaly detection jobs |
| [Anomaly chart](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-anomalies.md) | Display an anomaly chart from the **Anomaly Explorer** |
| [Single metric viewer](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-anomalies.md) | Display an anomaly chart from the **Single Metric Viewer** |
| [Change point detection](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-aiops.md#change-point-detection) | Display a chart to visualize change points in your data |
-| Observability | [SLO overview](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/observability/current/slo.md) | Visualize a selected SLO’s health, including name, current SLI value, target, and status |
+| Observability | | |
+| [SLO overview](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/observability/current/slo.md) | Visualize a selected SLO’s health, including name, current SLI value, target, and status |
| [SLO Alerts](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/observability/current/slo.md) | Visualize one or more SLO alerts, including status, rule name, duration, and reason. In addition, configure and update alerts, or create cases directly from the panel |
| [SLO Error Budget](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/observability/current/slo.md) | Visualize the consumption of your SLO’s error budget |
-| Legacy | [Log stream](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/observability.html#logs-app) (deprecated) | Display a table of live streaming logs |
-| [Aggregation based](visualize/legacy-editors.md#add-aggregation-based-visualization-panels) | While these panel types are still available, we recommend to use [Lens](visualize/lens.md) |
-| [TSVB](visualize/legacy-editors.md#tsvb-panel) |
+| Legacy | | |
+| [Log stream](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/observability.html#logs-app) (deprecated) | Display a table of live streaming logs |
+| [Aggregation based](visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md) | While these panel types are still available, we recommend to use [Lens](visualize/lens.md) |
+| [TSVB](visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md) |
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md
index 0d8051712e..cfbd3c0054 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md
@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ Choose the type of element you want to use, then use the preconfigured demo data
* **{{es}} SQL** — Access your data in {{es}} using [SQL syntax](../query-filter/languages/sql-spec.md).
* **{{es}} documents** — Access your data in {{es}} without using aggregations. To use, select a {{data-source}} and fields. Use **{{es}} documents** when you have low-volume datasets, and you want to view raw documents or to plot exact, non-aggregated values on a chart.
- * **Timelion** — Access your time series data using [**Timelion**](legacy-editors.md#timelion) queries. To use **Timelion** queries, you can enter a query using the [Lucene Query Syntax](../query-filter/languages/lucene-query-syntax.md).
+ * **Timelion** — Access your time series data using [**Timelion**](legacy-editors/timelion.md) queries. To use **Timelion** queries, you can enter a query using the [Lucene Query Syntax](../query-filter/languages/lucene-query-syntax.md).
Each element can display a different {{data-source}}, and pages and workpads often contain multiple {{data-sources}}.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md
index d0a392c11f..f22296e010 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md
@@ -30,10 +30,10 @@ To customize your workpad to look the way you want, add your own images.
1. Click the Elastic logo.
2. Drag the image file to the **Select or drag and drop an image** field.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-canvas_tutorialCustomImage_7.17.0.png
- :alt: The Analytics logo added to the workpad
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-canvas_tutorialCustomImage_7.17.0.png
+ :alt: The Analytics logo added to the workpad
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md
index 477519523d..07b7077b9c 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md
@@ -29,17 +29,17 @@ For example, to change the {{data-source}} for a set of charts:
1. Specify the variable options.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-specify_variable_syntax.png
- :alt: Variable syntax options
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-specify_variable_syntax.png
+ :alt: Variable syntax options
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
2. Copy the variable, then apply it to each element you want to update in the **Expression editor**.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-copy_variable_syntax.png
- :alt: Copied variable syntax pasted in the Expression editor
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-copy_variable_syntax.png
+ :alt: Copied variable syntax pasted in the Expression editor
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md
index f7b404d47e..4b2f63fe8d 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md
@@ -219,19 +219,19 @@ To generate the data, **Vega-Lite** uses the `source_0` and `data_0`. `source_0`
2. From the **View** dropdown, select **Vega debug**.
3. From the dropdown, select **source_0**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_4.png
- :alt: Table for data_0 with columns key
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_4.png
+ :alt: Table for data_0 with columns key
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
4. To compare to the visually encoded data, select **data_0** from the dropdown.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_5.png
- :alt: Table for data_0 where the key is NaN instead of a string
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_5.png
+ :alt: Table for data_0 where the key is NaN instead of a string
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
- **key** is unable to convert because the property is category (`Men's Clothing`, `Women's Clothing`, etc.) instead of a timestamp.
+ **key** is unable to convert because the property is category (`Men's Clothing`, `Women's Clothing`, etc.) instead of a timestamp.
@@ -257,10 +257,10 @@ In the **Vega-Lite** spec, add the `encoding` block:
1. Click **Inspect**, then select **Vega Debug** from the **View** dropdown.
2. From the dropdown, select **data_0**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_6.png
- :alt: Table for data_0 showing that the column time_buckets.buckets.key is undefined
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_6.png
+ :alt: Table for data_0 showing that the column time_buckets.buckets.key is undefined
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
**Vega-Lite** is unable to extract the `time_buckets.buckets` inner array.
@@ -283,10 +283,10 @@ In the **Vega-Lite** spec, add a `transform` block, then click **Update**:
1. Click **Inspect**, then select **Vega Debug** from the **View** dropdown.
2. From the dropdown, select **data_0**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_7.png
- :alt: Table showing data_0 with multiple pages of results
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_7.png
+ :alt: Table showing data_0 with multiple pages of results
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
Vega-Lite displays **undefined** values because there are duplicate names.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md
index ddf5945bac..f40d5f4a63 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md
@@ -20,9 +20,9 @@ You can then **Save** and add it to an existing or a new dashboard using the sav
1. From your dashboard, select **Add panel**.
2. Choose **ES|QL** under **Visualizations**. An ES|QL editor appears and lets you configure your query and its associated visualization. The **Suggestions** panel can help you find alternative ways to configure the visualization.
- ::::{tip}
- Check the [ES|QL reference](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-language.html) to get familiar with the syntax and optimize your query.
- ::::
+ ::::{tip}
+ Check the [ES|QL reference](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-language.html) to get familiar with the syntax and optimize your query.
+ ::::
3. When editing your query or its configuration, run the query to update the preview of the visualization.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/field-statistics.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/field-statistics.md
index 2513d13fd8..d5aeb101ad 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/field-statistics.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/field-statistics.md
@@ -10,9 +10,9 @@ mapped_pages:
1. From your dashboard, select **Add panel**.
2. Choose **Field statistics** under **Visualizations**. An ES|QL editor appears and lets you configure your query with the fields and information that you want to show.
- ::::{tip}
- Check the [ES|QL reference](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-language.html) to get familiar with the syntax and optimize your query.
- ::::
+ ::::{tip}
+ Check the [ES|QL reference](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-language.html) to get familiar with the syntax and optimize your query.
+ ::::
3. When editing your query or its configuration, run the query to update the preview of the visualization.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md
index a2fbdc92cc..a1ce03036f 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md
@@ -49,19 +49,20 @@ Use **Graph** to reveal the relationships in your data.
2. Select the data source that you want to explore.
- {{kib}} graphs the relationships between the top fields.
+ {{kib}} graphs the relationships between the top fields.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-url-connections.png
- :alt: URL connections
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-url-connections.png
+ :alt: URL connections
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
3. Add more fields, or click an existing field to edit, disable or deselect it.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-menu.png
- :alt: menu for editing, disabling, or removing a field from the graph
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-menu.png
+ :alt: menu for editing, disabling, or removing a field from the graph
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
4. Enter a query to discover relationships between terms in the selected fields.
@@ -69,10 +70,11 @@ Use **Graph** to reveal the relationships in your data.
5. To view more information about a relationship, click any connection or vertex.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-control-bar.png
- :alt: Graph toolbar
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-control-bar.png
+ :alt: Graph toolbar
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
6. Use the graph toolbar to display additional connections:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
index 07916cb671..fb126535ee 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
@@ -45,6 +45,7 @@ You can also use security to grant read only or all access to different roles. W
:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-graph-read-only-badge.png
:alt: Example of Graph's read only access indicator in Kibana's header
:class: screenshot
+:width: 50%
:::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md
index 5bdd55b85d..137b1170a9 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md
@@ -5,974 +5,10 @@ mapped_pages:
# Legacy editors [legacy-editors]
-## Aggregation-based [add-aggregation-based-visualization-panels]
+Legacy editors are still available but have been replaced by better alternatives. Consider using one of the [modern editors](../visualize.md) offered in Elastic such as **Lens**.
-Aggregation-based visualizations are the core {{kib}} panels, and are not optimized for a specific use case.
+The legacy editors are:
-With aggregation-based visualizations, you can:
-
-* Split charts up to three aggregation levels, which is more than **Lens** and **TSVB**
-* Create visualization with non-time series data
-* Use a [Discover session](../discover/save-open-search.md) as an input
-* Sort data tables and use the summary row and percentage column features
-* Assign colors to data series
-* Extend features with plugins
-
-Aggregation-based visualizations include the following limitations:
-
-* Limited styling options
-* Math is unsupported
-* Multiple indices is unsupported
-
-
-#### Types of aggregation-based visualizations [types-of-visualizations]
-
-{{kib}} supports the following types of aggregation-based visualizations.
-
-| | |
-| --- | --- |
-| **Area**: Displays data points, connected by a line, where the area between the line and axes are shaded.Use area charts to compare two or more categories over time, and display the magnitude of trends. |  |
-| **Data table**: Displays your aggregation results in a tabular format. Use data tables to display server configuration details, track counts, min,or max values for a specific field, and monitor the status of key services. |  |
-| **Gauge**: Displays your data along a scale that changes color according to where your data falls on the expected scale. Use the gauge to show how metricvalues relate to reference threshold values, or determine how a specified field is performing versus how it is expected to perform. |  |
-| **Goal**: Displays how your metric progresses toward a fixed goal. Use the goal to display an easy to read visual of the status of your goal progression. |  |
-| **Heat map**: Displays graphical representations of data where the individual values are represented by colors. Use heat maps when your data set includescategorical data. For example, use a heat map to see the flights of origin countries compared to destination countries using the sample flight data. |  |
-| **Horizontal Bar**: Displays bars side-by-side where each bar represents a category. Use bar charts to compare data across alarge number of categories, display data that includes categories with negative values, and easily identifythe categories that represent the highest and lowest values. {{kib}} also supports vertical bar charts. |  |
-| **Line**: Displays data points that are connected by a line. Use line charts to visualize a sequence of values, discovertrends over time, and forecast future values. |  |
-| **Metric**: Displays a single numeric value for an aggregation. Use the metric visualization when you have a numeric value that is powerful enough to tella story about your data. |  |
-| **Pie**: Displays slices that represent a data category, where the slice size is proportional to the quantity it represents.Use pie charts to show comparisons between multiple categories, illustrate the dominance of one category over others,and show percentage or proportional data. |  |
-| **Tag cloud**: Graphical representations of how frequently a word appears in the source text. Use tag clouds to easily produce a summary of large documents andcreate visual art for a specific topic. |  |
-
-
-#### Create an aggregation-based visualization panel [create-aggregation-based-panel]
-
-Choose the type of visualization you want to create, then use the editor to configure the options.
-
-1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**.
-
- 1. Select the visualization type you want to create.
- 2. Select the data source you want to visualize.
-
- ::::{note}
- There is no performance impact on the data source you select. For example, saved Discover sessions perform the same as {{data-sources}}.
- ::::
-
-2. Add the [aggregations](supported-chart-types.md#aggregation-reference) you want to visualize using the editor, then click **Update**.
-
- ::::{note}
- For the **Date Histogram** to use an **auto interval**, the date field must match the primary time field of the {{data-source}}.
- ::::
-
-3. To change the order, drag and drop the aggregations in the editor.
-
- 
-
-4. To customize the series colors, click the series in the legend, then select the color you want to use.
-
- 
-
-
-
-#### Try it: Create an aggregation-based bar chart [try-it-aggregation-based-panel]
-
-You collected data from your web server, and you want to visualize and analyze the data on a dashboard. To create a dashboard panel of the data, create a bar chart that displays the top five log traffic sources for every three hours.
-
-
-##### Add the data and create the dashboard [_add_the_data_and_create_the_dashboard]
-
-Add the sample web logs data that you’ll use to create the bar chart, then create the dashboard.
-
-1. [Install the web logs sample data set](../overview/kibana-quickstart.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana).
-2. Go to **Dashboards**.
-3. On the **Dashboards** page, click **Create dashboard**.
-
-
-##### Open and set up the aggregation-based bar chart [_open_and_set_up_the_aggregation_based_bar_chart]
-
-Open the **Aggregation based** editor and change the time range.
-
-1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**, select **Vertical bar**, then select **Kibana Sample Data Logs**.
-2. Make sure the [time filter](../query-filter/filtering.md) is **Last 7 days**.
-
-
-##### Create the bar chart [tutorial-configure-the-bar-chart]
-
-To create the bar chart, add a [bucket aggregation](supported-chart-types.md#bucket-aggregations), then add the terms sub-aggregation to display the top values.
-
-1. Add a **Buckets** aggregation.
-
- 1. Click **Add**, then select **X-axis**.
- 2. From the **Aggregation** dropdown, select **Date Histogram**.
- 3. Click **Update**.
-
- 
-
-2. To show the top five log traffic sources, add a sub-bucket aggregation.
-
- 1. Click **Add**, then select **Split series**.
-
- ::::{tip}
- Aggregation-based panels support a maximum of three **Split series**.
- ::::
-
- 2. From the **Sub aggregation** dropdown, select **Terms**.
- 3. From the **Field** dropdown, select **geo.src**.
- 4. Click **Update**.
-
- 
-
-
-
-#### Open and edit aggregation-based visualizations in Lens [edit-agg-based-visualizations-in-lens]
-
-When you open aggregation-based visualizations in **Lens**, all configuration options appear in the **Lens** visualization editor.
-
-You can open the following aggregation-based visualizations in **Lens**:
-
-* Area
-* Data table
-* Gauge
-* Goal
-* Heat map
-* Horizontal bar
-* Line
-* Metric
-* Pie
-* Vertical bar
-
-To get started, click **Edit visualization in Lens** in the toolbar.
-
-For more information, check out [Create visualizations with Lens](lens.md).
-
-
-##### Save and add the panel [save-the-aggregation-based-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-
-## TSVB [tsvb-panel]
-
-**TSVB** is a set of visualization types that you configure and display on dashboards.
-
-With **TSVB**, you can:
-
-* Combine an infinite number of [aggregations](supported-chart-types.md#aggregation-reference) to display your data.
-* Annotate time series data with timestamped events from an {{es}} index.
-* View the data in several types of visualizations, including charts, data tables, and markdown panels.
-* Display multiple [data views](../find-and-organize/data-views.md) in each visualization.
-* Use custom functions and some math on aggregations.
-* Customize the data with labels and colors.
-
-:::{image} ../../images/kibana-tsvb-screenshot.png
-:alt: TSVB overview
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-#### Open and set up TSVB [tsvb-data-view-mode]
-
-Open **TSVB**, then configure the required settings. You can create **TSVB** visualizations with only {{data-sources}}, or {{es}} index strings.
-
-When you use only {{data-sources}}, you are able to:
-
-* Create visualizations with runtime fields
-* Add URL drilldowns
-* Add interactive filters for time series visualizations
-* Improve performance
-
-::::{important}
-:name: tsvb-index-patterns-mode
-
-Creating **TSVB** visualizations with an {{es}} index string is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. By default, you create **TSVB** visualizations with only {{data-sources}}. To use an {{es}} index string, contact your administrator, or go to [Advanced Settings](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/advanced-options.html) and set `metrics:allowStringIndices` to `true`.
-::::
-
-
-1. On the dashboard, click **Select type**, then select **TSVB**.
-2. In **TSVB**, click **Panel options**, then specify the **Data** settings.
-3. Open the **Data view mode** options next to the **Data view** dropdown.
-4. Select **Use only {{kib}} {data-sources}**.
-5. From the **Data view** dropdown, select the {{data-source}}, then select the **Time field** and **Interval**.
-6. Select a **Drop last bucket** option.
-
- By default, **TSVB** drops the last bucket because the time filter intersects the time range of the last bucket. To view the partial data, select **No**.
-
-7. To view a filtered set of documents, enter [KQL filters](../query-filter/languages/kql.md) in the **Panel filter** field.
-
-
-#### Configure the series [tsvb-function-reference]
-
-Each **TSVB** visualization shares the same options to create a **Series**. Each series can be thought of as a separate {{es}} aggregation. The **Options** control the styling and {{es}} options, and are inherited from **Panel options**. When you have separate options for each series, you can compare different {{es}} indices, and view two time ranges from the same index.
-
-To configure the value of each series, select the function, then configure the function inputs. Only the last function is displayed.
-
-1. From the **Aggregation** dropdown, select the function for the series. **TSVB** provides you with shortcuts for some frequently-used functions:
-
- **Filter Ratio**
- : Returns a percent value by calculating a metric on two sets of documents. For example, calculate the error rate as a percentage of the overall events over time.
-
- **Counter Rate**
- : Used when dealing with monotonically increasing counters. Shortcut for **Max**, **Derivative**, and **Positive Only**.
-
- **Positive Only**
- : Removes any negative values from the results, which can be used as a post-processing step after a derivative.
-
- **Series Agg**
- : Applies a function to all of the **Group by** series to reduce the values to a single number. This function must always be the last metric in the series. For example, if the **Time Series** visualization shows 10 series, the sum **Series Agg** calculates the sum of all 10 bars and outputs a single Y value per X value. This is often confused with the overall sum function, which outputs a single Y value per unique series.
-
- **Math**
- : For each series, apply simple and advanced calculations. Only use **Math** for the last function in a series.
-
-2. To display each group separately, select one of the following options from the **Group by** dropdown:
-
- * **Filters** — Groups the data into the specified filters. To differentiate the groups, assign a color to each filter.
- * **Terms** — Displays the top values of the field. The color is only configurable in the **Time Series** chart. To configure, click **Options**, then select an option from the **Split color theme** dropdown.
-
-3. Click **Options**, then configure the inputs for the function. For example, to use a different field format, make a selection from the **Data formatter** dropdown.
-
-
-#### TSVB visualization options [configure-the-visualizations]
-
-The configuration options differ for each **TSVB** visualization.
-
-
-##### Time Series [tsvb-time-series]
-
-By default, the y-axis displays the full range of data, including zero. To automatically scale the y-axis from the minimum to maximum values of the data, click **Data > Options > Fill**, then enter `0` in the **Fill** field. You can add annotations to the x-axis based on timestamped documents in a separate {{es}} index.
-
-
-##### All chart types except Time Series [all-chart-types-except-time-series]
-
-The **Data timerange mode** dropdown in **Panel options** controls the timespan that **TSVB** uses to match documents. **Last value** is unable to match all documents, only the specific interval. **Entire timerange** matches all documents specified in the time filter.
-
-
-##### Metric, Top N, and Gauge [metric-topn-gauge]
-
-**Color rules** in **Panel options** contains conditional coloring based on the values.
-
-
-##### Top N and Table [topn-table]
-
-When you click a series, **TSVB** applies a filter based on the series name. To change this behavior, click **Panel options**, then specify a URL in the **Item URL** field, which opens a URL instead of applying a filter on click.
-
-
-##### Markdown [tsvb-markdown]
-
-The **Markdown** visualization supports Markdown with Handlebar (mustache) syntax to insert dynamic data, and supports custom CSS.
-
-
-#### Open and edit TSVB visualizations in Lens [edit-visualizations-in-lens]
-
-When you open **TSVB** visualizations in **Lens**, all configuration options and annotations appear in the **Lens** visualization editor.
-
-You can open the following **TSVB** visualizations in **Lens**:
-
-* Time Series
-* Metric
-* Top N
-* Gauge
-* Table
-
-To get started, click **Edit visualization in Lens** in the toolbar.
-
-For more information, check out [Create visualizations with Lens](lens.md).
-
-
-#### View the visualization data requests [view-data-and-requests-tsvb]
-
-View the requests that collect the visualization data.
-
-1. In the toolbar, click **Inspect**.
-2. From the **Request** dropdown, select the series you want to view.
-
-
-#### Save and add the panel [save-the-tsvb-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-
-#### Frequently asked questions [tsvb-faq]
-
-For answers to frequently asked **TSVB** question, review the following.
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I create dashboard drilldowns for Top N and Table visualizations?**
-:name: how-do-i-create-dashboard-drilldowns
-
-You can create dashboard drilldowns that include the specified time range for **Top N** and **Table** visualizations.
-
-1. Open the dashboard that you want to link to, then copy the URL.
-2. Open the dashboard with the **Top N** and **Table** visualization panel, then click **Edit** in the toolbar.
-3. Open the **Top N** or **Table** panel menu, then select **Edit visualization**.
-4. Click **Panel options**.
-5. In the **Item URL** field, enter the URL.
-
- For example `dashboards#/view/f193ca90-c9f4-11eb-b038-dd3270053a27`.
-
-6. Click **Save and return**.
-7. In the toolbar, click **Save as**, then make sure **Store time with dashboard** is deselected.
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I base drilldown URLs on my data?**
-:name: how-do-i-base-drilldowns-on-data
-
-You can build drilldown URLs dynamically with your visualization data.
-
-Do this by adding the `{{key}}` placeholder to your URL
-
-For example `https://example.org/{{key}}`
-
-This instructs TSVB to substitute the value from your visualization wherever it sees `{{key}}`.
-
-If your data contain reserved or invalid URL characters such as "#" or "&", you should apply a transform to URL-encode the key like this `{{encodeURIComponent key}}`. If you are dynamically constructing a drilldown to another location in Kibana (for example, clicking a table row takes to you a value-scoped Discover session), you will likely want to Rison-encode your key as it may contain invalid Rison characters. ([Rison](https://github.com/Nanonid/rison#rison---compact-data-in-uris) is the serialization format many parts of Kibana use to store information in their URL.)
-
-For example: `discover#/view/0ac50180-82d9-11ec-9f4a-55de56b00cc0?_a=(filters:!((query:(match_phrase:(foo.keyword:{{rison key}})))))`
-
-If both conditions apply, you can cover all cases by applying both transforms: `{{encodeURIComponent (rison key)}}`.
-
-Technical note: TSVB uses [Handlebars](https://handlebarsjs.com/) to perform these interpolations. `rison` and `encodeURIComponent` are custom Handlebars helpers provided by Kibana.
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **Why is my TSVB visualization missing data?**
-:name: why-is-my-tsvb-visualiztion-missing-data
-
-It depends, but most often there are two causes:
-
-* For **Time series** visualizations with a derivative function, the time interval can be too small. Derivatives require sequential values.
-* For all other **TSVB** visualizations, the cause is probably the **Data timerange mode**, which is controlled by **Panel options > Data timerange mode > Entire time range**. By default, **TSVB** displays the last whole bucket. For example, if the time filter is set to **Last 24 hours**, and the current time is 9:41, **TSVB** displays only the last 10 minutes — from 9:30 to 9:40.
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I calculate the difference between two data series?**
-:name: how-do-i-calculate-the-difference-between-two-data-series
-
-Performing math across data series is unsupported in **TSVB**. To calculate the difference between two data series, use [**Timelion**](#timelion) or [**Vega**](custom-visualizations-with-vega.md).
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I compare the current versus previous month?**
-:name: how-do-i-compare-the-current-versus-previous-month
-
-**TSVB** can display two series with time offsets, but it can’t perform math across series. To add a time offset:
-
-1. Click **Clone Series**, then choose a color for the new series.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-tsvb_clone_series.png
- :alt: Clone Series action
- :class: screenshot
- :::
-
-2. Click **Options**, then enter the offset value in the **Offset series time by** field.
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I calculate a month over month change?**
-:name: how-do-i-calculate-a-month-over-month-change
-
-The ability to calculate a month over month change is not fully supported in **TSVB**, but there is a special case that is supported *if* the time filter is set to 3 months or more *and* the **Interval** is `1m`. Use the **Derivative** to get the absolute monthly change. To convert to a percent, add the **Math** function with the `params.current / (params.current - params.derivative)` formula, then select **Percent** from the **Data Formatter** dropdown.
-
-For other types of month over month calculations, use [**Timelion**](#timelion) or [**Vega**](custom-visualizations-with-vega.md).
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I calculate the duration between the start and end of an event?**
-:name: calculate-duration-start-end
-
-Calculating the duration between the start and end of an event is unsupported in **TSVB** because **TSVB** requires correlation between different time periods. **TSVB** requires that the duration is pre-calculated.
-
-::::
-
-
-
-## Timelion [timelion]
-
-To use **Timelion**, you define a graph by chaining functions together, using the **Timelion**-specific syntax. The syntax enables some features that classical point series charts don’t offer, such as pulling data from different indices or data sources into one graph.
-
-**Timelion** is driven by a simple expression language that you use to:
-
-* Retrieve time series data from one or more indices
-* Perform math across two or more time series
-* Visualize the results
-
-
-
-
-#### Timelion expressions [_timelion_expressions]
-
-Timelion functions always start with a dot, followed by the function name, followed by parentheses containing all the parameters to the function.
-
-The `.es` (or `.elasticsearch` if you are a fan of typing long words) function gathers data from {{es}} and draws it over time. By default the .es function will just count the number of documents, resulting in a graph showing the amount of documents over time.
-
-
-#### Function parameters [_function_parameters]
-
-Functions can have multiple parameters, and so does the `.es` function. Each parameter has a name, that you can use inside the parentheses to set its value. The parameters also have an order, which is shown by the autocompletion or the documentation (using the Docs button in the top menu).
-
-If you don’t specify the parameter name, timelion assigns the values to the parameters in the order, they are listed in the documentation.
-
-The fist parameter of the .es function is the parameter q (for query), which is a Query String used to filter the data for this series. You can also explicitly reference this parameter by its name, and I would always recommend doing so as soon as you are passing more than one parameter to the function. The following two expressions are thus equivalent:
-
-Multiple parameters are separated by a comma. The .es function has another parameter called index, that can be used to specify a {{data-source}} for this series, so the query won’t be executed against all indexes (or whatever you changed the setting to).
-
-If the value of your parameter contains spaces or commas you have to put the value in single or double quotes. You can omit these quotes otherwise.
-
-
-##### .yaxis() function [customize-data-series-y-axis]
-
-{{kib}} supports many y-axis scales and ranges for your data series.
-
-The `.yaxis()` function supports the following parameters:
-
-* **yaxis** — The numbered y-axis to plot the series on. For example, use `.yaxis(2)` to display a second y-axis.
-* **min** — The minimum value for the y-axis range.
-* **max** — The maximum value for the y-axis range.
-* **position** — The location of the units. Values include `left` or `right`.
-* **label** — The label for the axis.
-* **color** — The color of the axis label.
-* **units** — The function to use for formatting the y-axis labels. Values include `bits`, `bits/s`, `bytes`, `bytes/s`, `currency(:ISO 4217 currency code)`, `percent`, and `custom(:prefix:suffix)`.
-* **tickDecimals** — The tick decimal precision.
-
-Example:
-
-```text
-.es(index= kibana_sample_data_logs,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:bytes')
- .label('Average Bytes for request')
- .title('Memory consumption over time in bytes').yaxis(1,units=bytes,position=left), <1>
-.es(index= kibana_sample_data_logs,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric=avg:machine.ram)
- .label('Average Machine RAM amount').yaxis(2,units=bytes,position=right) <2>
-```
-
-1. `.yaxis(1,units=bytes,position=left)` — Specifies the first y-axis for the first data series, and changes the units on the left.
-2. `.yaxis(2,units=bytes,position=left)` — Specifies the second y-axis for the second data series, and changes the units on the right.
-
-
-
-### Tutorial: Create visualizations with Timelion [_tutorial_create_visualizations_with_timelion]
-
-You collected data from your operating system using Metricbeat, and you want to visualize and analyze the data on a dashboard. To create panels of the data, use **Timelion** to create a time series visualization,
-
-
-#### Add the data and create the dashboard [_add_the_data_and_create_the_dashboard_2]
-
-Set up Metricbeat, then create the dashboard.
-
-1. To set up Metricbeat, go to [Metricbeat quick start: installation and configuration](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/current/metricbeat-installation-configuration.html)
-2. Go to **Dashboards**.
-3. On the **Dashboards** page, click **Create dashboard**.
-
-
-#### Open and set up Timelion [_open_and_set_up_timelion]
-
-Open **Timelion** and change the time range.
-
-1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**, then select **Timelion**.
-2. Make sure the [time filter](../query-filter/filtering.md) is **Last 7 days**.
-
-
-#### Create a time series visualization [timelion-tutorial-create-time-series-visualizations]
-
-To compare the real-time percentage of CPU time spent in user space to the results offset by one hour, create a time series visualization.
-
-
-##### Define the functions [define-the-functions]
-
-To track the real-time percentage of CPU, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
-```
-
-
-##### Compare the data [compare-the-data]
-
-To compare two data sets, add another series, and offset the data back by one hour, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct'),
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
-```
-
-
-##### Add label names [add-label-names]
-
-To easily distinguish between the two data sets, add label names, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('last hour'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('current hour')
-```
-
-
-##### Add a title [add-a-title]
-
-To make is easier for unfamiliar users to understand the purpose of the visualization, add a title, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('last hour'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('current hour')
- .title('CPU usage over time')
-```
-
-
-##### Change the appearance of the chart lines [change-the-chart-type]
-
-To differentiate between the current hour and the last hour, change the appearance of the chart lines, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('last hour')
- .lines(fill=1,width=0.5),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('current hour')
- .title('CPU usage over time')
-```
-
-
-##### Change the line colors [change-the-line-colors]
-
-**Timelion** supports standard color names, hexadecimal values, or a color schema for grouped data.
-
-To make the first data series stand out, change the line colors, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('last hour')
- .lines(fill=1,width=0.5)
- .color(gray),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('current hour')
- .title('CPU usage over time')
- .color(#1E90FF)
-```
-
-
-##### Adjust the legend [make-adjustments-to-the-legend]
-
-Move the legend to the north west position with two columns, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('last hour')
- .lines(fill=1,width=0.5)
- .color(gray),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('current hour')
- .title('CPU usage over time')
- .color(#1E90FF)
- .legend(columns=2, position=nw)
-```
-
-:::{image} ../../images/kibana-timelion-customize04.png
-:alt: Final time series visualization
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-
-
-##### Save and add the panel [save-the-timelion-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-
-### Visualize the inbound and outbound network traffic [timelion-tutorial-create-visualizations-with-mathematical-functions]
-
-To create a visualization for inbound and outbound network traffic, use mathematical functions.
-
-
-#### Define the functions [mathematical-functions-define-functions]
-
-To start tracking the inbound and outbound network traffic, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
-```
-
-
-#### Plot the rate of change [mathematical-functions-plot-change]
-
-To easily monitor the inbound traffic, plots the change in values over time, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
- .derivative()
-```
-
-Add a similar calculation for outbound traffic, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
- .derivative(),
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .multiply(-1) <1>
-```
-
-1. `.multiply(-1)` converts the outbound network traffic to a negative value since the outbound network traffic is leaving your machine. `.multiply()` multiplies the data series by a number, the result of a data series, or a list of data series.
-
-
-
-#### Change the data metric [mathematical-functions-convert-data]
-
-To make the data easier to analyze, change the data metric from `bytes` to `megabytes`, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .divide(1048576),
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .multiply(-1)
- .divide(1048576) <1>
-```
-
-1. `.divide()` accepts the same input as `.multiply()`, then divides the data series by the defined divisor.
-
-
-
-#### Customize and format the visualization [mathematical-functions-add-labels]
-
-Customize and format the visualization using the following functions, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .divide(1048576)
- .lines(fill=2, width=1)
- .color(green)
- .label("Inbound traffic")
- .title("Network traffic (MB/s)"),
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .multiply(-1)
- .divide(1048576)
- .lines(fill=2, width=1)
- .color(blue)
- .label("Outbound traffic")
- .legend(columns=2, position=nw)
-```
-
-:::{image} ../../images/kibana-timelion-math05.png
-:alt: Final visualization that displays inbound and outbound network traffic
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-
-
-##### Save and add the panel [save-the-network-timelion-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-
-#### Detect outliers and discover patterns over time [timelion-tutorial-create-visualizations-withconditional-logic-and-tracking-trends]
-
-To easily detect outliers and discover patterns over time, modify the time series data with conditional logic and create a trend with a moving average.
-
-With **Timelion** conditional logic, you can use the following operator values to compare your data:
-
-`eq`
-: equal
-
-`ne`
-: not equal
-
-`lt`
-: less than
-
-`lte`
-: less than or equal to
-
-`gt`
-: greater than
-
-`gte`
-: greater than or equal to
-
-
-##### Define the functions [conditional-define-functions]
-
-To chart the maximum value of `system.memory.actual.used.bytes`, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
-```
-
-
-##### Track used memory [conditional-track-memory]
-
-To track the amount of memory used, create two thresholds, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt, <1>
- 11300000000, <2>
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('warning')
- .color('#FFCC11'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,
- 11375000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('severe')
- .color('red')
-```
-
-1. `if()` compares each point to a number. When the condition is `true`, adjust the styling. When the condition is `false`, use the default styling.
-2. **Timelion** conditional logic for the *greater than* operator. In this example, the warning threshold is 11.3GB (`11300000000`), and the severe threshold is 11.375GB (`11375000000`). If the threshold values are too high or low for your machine, adjust the values.
-
-
-
-##### Determine the trend [conditional-determine-trend]
-
-To determine the trend, create a new data series, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,11300000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('warning')
- .color('#FFCC11'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,11375000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null).
- label('severe')
- .color('red'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .mvavg(10) <1>
-```
-
-1. `mvavg()` calculates the moving average over a specified period of time. In this example, `.mvavg(10)` creates a moving average with a window of 10 data points.
-
-
-
-##### Customize and format the visualization [conditional-format-visualization]
-
-Customize and format the visualization using the following functions, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .label('max memory')
- .title('Memory consumption over time'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,
- 11300000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('warning')
- .color('#FFCC11')
- .lines(width=5),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,
- 11375000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('severe')
- .color('red')
- .lines(width=5),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .mvavg(10)
- .label('mvavg')
- .lines(width=2)
- .color(#5E5E5E)
- .legend(columns=4, position=nw)
-```
-
-:::{image} ../../images/kibana-timelion-conditional04.png
-:alt: Final visualization that displays outliers and patterns over time
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-
-
-##### Save and add the panel [save-the-outlier-timelion-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-For more information about **Timelion** conditions, refer to [I have but one .condition()](https://www.elastic.co/blog/timeseries-if-then-else-with-timelion).
+- [Aggregation-based](legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md)
+- [TSVB](legacy-editors/tsvb.md)
+- [Timelion](legacy-editors/timelion.md)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d5a9573488
--- /dev/null
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md
@@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
+# Aggregation-based [add-aggregation-based-visualization-panels]
+
+Aggregation-based visualizations are the core {{kib}} panels, and are not optimized for a specific use case.
+
+With aggregation-based visualizations, you can:
+
+* Split charts up to three aggregation levels, which is more than **Lens** and **TSVB**
+* Create visualization with non-time series data
+* Use a [Discover session](../../discover/save-open-search.md) as an input
+* Sort data tables and use the summary row and percentage column features
+* Assign colors to data series
+* Extend features with plugins
+
+Aggregation-based visualizations include the following limitations:
+
+* Limited styling options
+* Math is unsupported
+* Multiple indices is unsupported
+
+
+## Types of aggregation-based visualizations [types-of-visualizations]
+
+{{kib}} supports the following types of aggregation-based visualizations.
+
+| | |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Area**: Displays data points, connected by a line, where the area between the line and axes are shaded.Use area charts to compare two or more categories over time, and display the magnitude of trends. |  |
+| **Data table**: Displays your aggregation results in a tabular format. Use data tables to display server configuration details, track counts, min,or max values for a specific field, and monitor the status of key services. |  |
+| **Gauge**: Displays your data along a scale that changes color according to where your data falls on the expected scale. Use the gauge to show how metricvalues relate to reference threshold values, or determine how a specified field is performing versus how it is expected to perform. |  |
+| **Goal**: Displays how your metric progresses toward a fixed goal. Use the goal to display an easy to read visual of the status of your goal progression. |  |
+| **Heat map**: Displays graphical representations of data where the individual values are represented by colors. Use heat maps when your data set includescategorical data. For example, use a heat map to see the flights of origin countries compared to destination countries using the sample flight data. |  |
+| **Horizontal Bar**: Displays bars side-by-side where each bar represents a category. Use bar charts to compare data across alarge number of categories, display data that includes categories with negative values, and easily identifythe categories that represent the highest and lowest values. {{kib}} also supports vertical bar charts. |  |
+| **Line**: Displays data points that are connected by a line. Use line charts to visualize a sequence of values, discovertrends over time, and forecast future values. |  |
+| **Metric**: Displays a single numeric value for an aggregation. Use the metric visualization when you have a numeric value that is powerful enough to tella story about your data. |  |
+| **Pie**: Displays slices that represent a data category, where the slice size is proportional to the quantity it represents.Use pie charts to show comparisons between multiple categories, illustrate the dominance of one category over others,and show percentage or proportional data. |  |
+| **Tag cloud**: Graphical representations of how frequently a word appears in the source text. Use tag clouds to easily produce a summary of large documents andcreate visual art for a specific topic. |  |
+
+
+## Create an aggregation-based visualization panel [create-aggregation-based-panel]
+
+Choose the type of visualization you want to create, then use the editor to configure the options.
+
+1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**.
+
+ 1. Select the visualization type you want to create.
+ 2. Select the data source you want to visualize.
+
+ ::::{note}
+ There is no performance impact on the data source you select. For example, saved Discover sessions perform the same as {{data-sources}}.
+ ::::
+
+2. Add the [aggregations](../supported-chart-types.md#aggregation-reference) you want to visualize using the editor, then click **Update**.
+
+ ::::{note}
+ For the **Date Histogram** to use an **auto interval**, the date field must match the primary time field of the {{data-source}}.
+ ::::
+
+3. To change the order, drag and drop the aggregations in the editor.
+
+ 
+
+4. To customize the series colors, click the series in the legend, then select the color you want to use.
+
+ 
+
+
+
+## Try it: Create an aggregation-based bar chart [try-it-aggregation-based-panel]
+
+You collected data from your web server, and you want to visualize and analyze the data on a dashboard. To create a dashboard panel of the data, create a bar chart that displays the top five log traffic sources for every three hours.
+
+
+### Add the data and create the dashboard [_add_the_data_and_create_the_dashboard]
+
+Add the sample web logs data that you’ll use to create the bar chart, then create the dashboard.
+
+1. [Install the web logs sample data set](../../overview/kibana-quickstart.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana).
+2. Go to **Dashboards**.
+3. On the **Dashboards** page, click **Create dashboard**.
+
+
+### Open and set up the aggregation-based bar chart [_open_and_set_up_the_aggregation_based_bar_chart]
+
+Open the **Aggregation based** editor and change the time range.
+
+1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**, select **Vertical bar**, then select **Kibana Sample Data Logs**.
+2. Make sure the [time filter](../../query-filter/filtering.md) is **Last 7 days**.
+
+
+### Create the bar chart [tutorial-configure-the-bar-chart]
+
+To create the bar chart, add a [bucket aggregation](../supported-chart-types.md#bucket-aggregations), then add the terms sub-aggregation to display the top values.
+
+1. Add a **Buckets** aggregation.
+
+ 1. Click **Add**, then select **X-axis**.
+ 2. From the **Aggregation** dropdown, select **Date Histogram**.
+ 3. Click **Update**.
+
+ 
+
+2. To show the top five log traffic sources, add a sub-bucket aggregation.
+
+ 1. Click **Add**, then select **Split series**.
+
+ ::::{tip}
+ Aggregation-based panels support a maximum of three **Split series**.
+ ::::
+
+ 2. From the **Sub aggregation** dropdown, select **Terms**.
+ 3. From the **Field** dropdown, select **geo.src**.
+ 4. Click **Update**.
+ 
+
+
+
+## Open and edit aggregation-based visualizations in Lens [edit-agg-based-visualizations-in-lens]
+
+When you open aggregation-based visualizations in **Lens**, all configuration options appear in the **Lens** visualization editor.
+
+You can open the following aggregation-based visualizations in **Lens**:
+
+* Area
+* Data table
+* Gauge
+* Goal
+* Heat map
+* Horizontal bar
+* Line
+* Metric
+* Pie
+* Vertical bar
+
+To get started, click **Edit visualization in Lens** in the toolbar.
+
+For more information, check out [Create visualizations with Lens](../lens.md).
+
+
+### Save and add the panel [save-the-aggregation-based-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f65c40dd35
--- /dev/null
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md
@@ -0,0 +1,553 @@
+# Timelion [timelion]
+
+To use **Timelion**, you define a graph by chaining functions together, using the **Timelion**-specific syntax. The syntax enables some features that classical point series charts don’t offer, such as pulling data from different indices or data sources into one graph.
+
+**Timelion** is driven by a simple expression language that you use to:
+
+* Retrieve time series data from one or more indices
+* Perform math across two or more time series
+* Visualize the results
+
+
+
+
+## Timelion expressions [_timelion_expressions]
+
+Timelion functions always start with a dot, followed by the function name, followed by parentheses containing all the parameters to the function.
+
+The `.es` (or `.elasticsearch` if you are a fan of typing long words) function gathers data from {{es}} and draws it over time. By default the .es function will just count the number of documents, resulting in a graph showing the amount of documents over time.
+
+
+## Function parameters [_function_parameters]
+
+Functions can have multiple parameters, and so does the `.es` function. Each parameter has a name, that you can use inside the parentheses to set its value. The parameters also have an order, which is shown by the autocompletion or the documentation (using the Docs button in the top menu).
+
+If you don’t specify the parameter name, timelion assigns the values to the parameters in the order, they are listed in the documentation.
+
+The fist parameter of the .es function is the parameter q (for query), which is a Query String used to filter the data for this series. You can also explicitly reference this parameter by its name, and I would always recommend doing so as soon as you are passing more than one parameter to the function. The following two expressions are thus equivalent:
+
+Multiple parameters are separated by a comma. The .es function has another parameter called index, that can be used to specify a {{data-source}} for this series, so the query won’t be executed against all indexes (or whatever you changed the setting to).
+
+If the value of your parameter contains spaces or commas you have to put the value in single or double quotes. You can omit these quotes otherwise.
+
+
+### .yaxis() function [customize-data-series-y-axis]
+
+{{kib}} supports many y-axis scales and ranges for your data series.
+
+The `.yaxis()` function supports the following parameters:
+
+* **yaxis** — The numbered y-axis to plot the series on. For example, use `.yaxis(2)` to display a second y-axis.
+* **min** — The minimum value for the y-axis range.
+* **max** — The maximum value for the y-axis range.
+* **position** — The location of the units. Values include `left` or `right`.
+* **label** — The label for the axis.
+* **color** — The color of the axis label.
+* **units** — The function to use for formatting the y-axis labels. Values include `bits`, `bits/s`, `bytes`, `bytes/s`, `currency(:ISO 4217 currency code)`, `percent`, and `custom(:prefix:suffix)`.
+* **tickDecimals** — The tick decimal precision.
+
+Example:
+
+```text
+.es(index= kibana_sample_data_logs,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:bytes')
+ .label('Average Bytes for request')
+ .title('Memory consumption over time in bytes').yaxis(1,units=bytes,position=left), <1>
+.es(index= kibana_sample_data_logs,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric=avg:machine.ram)
+ .label('Average Machine RAM amount').yaxis(2,units=bytes,position=right) <2>
+```
+
+1. `.yaxis(1,units=bytes,position=left)` — Specifies the first y-axis for the first data series, and changes the units on the left.
+2. `.yaxis(2,units=bytes,position=left)` — Specifies the second y-axis for the second data series, and changes the units on the right.
+
+
+
+## Tutorial: Create visualizations with Timelion [_tutorial_create_visualizations_with_timelion]
+
+You collected data from your operating system using Metricbeat, and you want to visualize and analyze the data on a dashboard. To create panels of the data, use **Timelion** to create a time series visualization,
+
+
+## Add the data and create the dashboard [_add_the_data_and_create_the_dashboard_2]
+
+Set up Metricbeat, then create the dashboard.
+
+1. To set up Metricbeat, go to [Metricbeat quick start: installation and configuration](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/current/metricbeat-installation-configuration.html)
+2. Go to **Dashboards**.
+3. On the **Dashboards** page, click **Create dashboard**.
+
+
+## Open and set up Timelion [_open_and_set_up_timelion]
+
+Open **Timelion** and change the time range.
+
+1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**, then select **Timelion**.
+2. Make sure the [time filter](../../query-filter/filtering.md) is **Last 7 days**.
+
+
+## Create a time series visualization [timelion-tutorial-create-time-series-visualizations]
+
+To compare the real-time percentage of CPU time spent in user space to the results offset by one hour, create a time series visualization.
+
+
+### Define the functions [define-the-functions]
+
+To track the real-time percentage of CPU, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+```
+
+
+### Compare the data [compare-the-data]
+
+To compare two data sets, add another series, and offset the data back by one hour, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct'),
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+```
+
+
+### Add label names [add-label-names]
+
+To easily distinguish between the two data sets, add label names, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('last hour'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('current hour')
+```
+
+
+### Add a title [add-a-title]
+
+To make is easier for unfamiliar users to understand the purpose of the visualization, add a title, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('last hour'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('current hour')
+ .title('CPU usage over time')
+```
+
+
+### Change the appearance of the chart lines [change-the-chart-type]
+
+To differentiate between the current hour and the last hour, change the appearance of the chart lines, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('last hour')
+ .lines(fill=1,width=0.5),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('current hour')
+ .title('CPU usage over time')
+```
+
+
+### Change the line colors [change-the-line-colors]
+
+**Timelion** supports standard color names, hexadecimal values, or a color schema for grouped data.
+
+To make the first data series stand out, change the line colors, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('last hour')
+ .lines(fill=1,width=0.5)
+ .color(gray),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('current hour')
+ .title('CPU usage over time')
+ .color(#1E90FF)
+```
+
+
+### Adjust the legend [make-adjustments-to-the-legend]
+
+Move the legend to the north west position with two columns, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('last hour')
+ .lines(fill=1,width=0.5)
+ .color(gray),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('current hour')
+ .title('CPU usage over time')
+ .color(#1E90FF)
+ .legend(columns=2, position=nw)
+```
+
+:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-timelion-customize04.png
+:alt: Final time series visualization
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+
+
+### Save and add the panel [save-the-timelion-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
+
+## Visualize the inbound and outbound network traffic [timelion-tutorial-create-visualizations-with-mathematical-functions]
+
+To create a visualization for inbound and outbound network traffic, use mathematical functions.
+
+
+## Define the functions [mathematical-functions-define-functions]
+
+To start tracking the inbound and outbound network traffic, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+```
+
+
+## Plot the rate of change [mathematical-functions-plot-change]
+
+To easily monitor the inbound traffic, plots the change in values over time, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+```
+
+Add a similar calculation for outbound traffic, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+ .derivative(),
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .multiply(-1) <1>
+```
+
+1. `.multiply(-1)` converts the outbound network traffic to a negative value since the outbound network traffic is leaving your machine. `.multiply()` multiplies the data series by a number, the result of a data series, or a list of data series.
+
+
+
+## Change the data metric [mathematical-functions-convert-data]
+
+To make the data easier to analyze, change the data metric from `bytes` to `megabytes`, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .divide(1048576),
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .multiply(-1)
+ .divide(1048576) <1>
+```
+
+1. `.divide()` accepts the same input as `.multiply()`, then divides the data series by the defined divisor.
+
+
+
+## Customize and format the visualization [mathematical-functions-add-labels]
+
+Customize and format the visualization using the following functions, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .divide(1048576)
+ .lines(fill=2, width=1)
+ .color(green)
+ .label("Inbound traffic")
+ .title("Network traffic (MB/s)"),
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .multiply(-1)
+ .divide(1048576)
+ .lines(fill=2, width=1)
+ .color(blue)
+ .label("Outbound traffic")
+ .legend(columns=2, position=nw)
+```
+
+:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-timelion-math05.png
+:alt: Final visualization that displays inbound and outbound network traffic
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+
+
+### Save and add the panel [save-the-network-timelion-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
+
+## Detect outliers and discover patterns over time [timelion-tutorial-create-visualizations-withconditional-logic-and-tracking-trends]
+
+To easily detect outliers and discover patterns over time, modify the time series data with conditional logic and create a trend with a moving average.
+
+With **Timelion** conditional logic, you can use the following operator values to compare your data:
+
+`eq`
+: equal
+
+`ne`
+: not equal
+
+`lt`
+: less than
+
+`lte`
+: less than or equal to
+
+`gt`
+: greater than
+
+`gte`
+: greater than or equal to
+
+
+### Define the functions [conditional-define-functions]
+
+To chart the maximum value of `system.memory.actual.used.bytes`, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+```
+
+
+### Track used memory [conditional-track-memory]
+
+To track the amount of memory used, create two thresholds, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt, <1>
+ 11300000000, <2>
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('warning')
+ .color('#FFCC11'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,
+ 11375000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('severe')
+ .color('red')
+```
+
+1. `if()` compares each point to a number. When the condition is `true`, adjust the styling. When the condition is `false`, use the default styling.
+2. **Timelion** conditional logic for the *greater than* operator. In this example, the warning threshold is 11.3GB (`11300000000`), and the severe threshold is 11.375GB (`11375000000`). If the threshold values are too high or low for your machine, adjust the values.
+
+
+
+### Determine the trend [conditional-determine-trend]
+
+To determine the trend, create a new data series, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,11300000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('warning')
+ .color('#FFCC11'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,11375000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null).
+ label('severe')
+ .color('red'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .mvavg(10) <1>
+```
+
+1. `mvavg()` calculates the moving average over a specified period of time. In this example, `.mvavg(10)` creates a moving average with a window of 10 data points.
+
+
+
+### Customize and format the visualization [conditional-format-visualization]
+
+Customize and format the visualization using the following functions, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .label('max memory')
+ .title('Memory consumption over time'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,
+ 11300000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('warning')
+ .color('#FFCC11')
+ .lines(width=5),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,
+ 11375000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('severe')
+ .color('red')
+ .lines(width=5),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .mvavg(10)
+ .label('mvavg')
+ .lines(width=2)
+ .color(#5E5E5E)
+ .legend(columns=4, position=nw)
+```
+
+:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-timelion-conditional04.png
+:alt: Final visualization that displays outliers and patterns over time
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+
+
+### Save and add the panel [save-the-outlier-timelion-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
+For more information about **Timelion** conditions, refer to [I have but one .condition()](https://www.elastic.co/blog/timeseries-if-then-else-with-timelion).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3813988427
--- /dev/null
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md
@@ -0,0 +1,257 @@
+# TSVB [tsvb-panel]
+
+**TSVB** is a set of visualization types that you configure and display on dashboards.
+
+With **TSVB**, you can:
+
+* Combine an infinite number of [aggregations](../supported-chart-types.md#aggregation-reference) to display your data.
+* Annotate time series data with timestamped events from an {{es}} index.
+* View the data in several types of visualizations, including charts, data tables, and markdown panels.
+* Display multiple [data views](../../find-and-organize/data-views.md) in each visualization.
+* Use custom functions and some math on aggregations.
+* Customize the data with labels and colors.
+
+:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-tsvb-screenshot.png
+:alt: TSVB overview
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+## Open and set up TSVB [tsvb-data-view-mode]
+
+Open **TSVB**, then configure the required settings. You can create **TSVB** visualizations with only {{data-sources}}, or {{es}} index strings.
+
+When you use only {{data-sources}}, you are able to:
+
+* Create visualizations with runtime fields
+* Add URL drilldowns
+* Add interactive filters for time series visualizations
+* Improve performance
+
+::::{important}
+:name: tsvb-index-patterns-mode
+
+Creating **TSVB** visualizations with an {{es}} index string is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. By default, you create **TSVB** visualizations with only {{data-sources}}. To use an {{es}} index string, contact your administrator, or go to [Advanced Settings](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/advanced-options.html) and set `metrics:allowStringIndices` to `true`.
+::::
+
+
+1. On the dashboard, click **Select type**, then select **TSVB**.
+2. In **TSVB**, click **Panel options**, then specify the **Data** settings.
+3. Open the **Data view mode** options next to the **Data view** dropdown.
+4. Select **Use only {{kib}} {data-sources}**.
+5. From the **Data view** dropdown, select the {{data-source}}, then select the **Time field** and **Interval**.
+6. Select a **Drop last bucket** option.
+
+ By default, **TSVB** drops the last bucket because the time filter intersects the time range of the last bucket. To view the partial data, select **No**.
+
+7. To view a filtered set of documents, enter [KQL filters](../../query-filter/languages/kql.md) in the **Panel filter** field.
+
+
+## Configure the series [tsvb-function-reference]
+
+Each **TSVB** visualization shares the same options to create a **Series**. Each series can be thought of as a separate {{es}} aggregation. The **Options** control the styling and {{es}} options, and are inherited from **Panel options**. When you have separate options for each series, you can compare different {{es}} indices, and view two time ranges from the same index.
+
+To configure the value of each series, select the function, then configure the function inputs. Only the last function is displayed.
+
+1. From the **Aggregation** dropdown, select the function for the series. **TSVB** provides you with shortcuts for some frequently-used functions:
+
+ **Filter Ratio**
+ : Returns a percent value by calculating a metric on two sets of documents. For example, calculate the error rate as a percentage of the overall events over time.
+
+ **Counter Rate**
+ : Used when dealing with monotonically increasing counters. Shortcut for **Max**, **Derivative**, and **Positive Only**.
+
+ **Positive Only**
+ : Removes any negative values from the results, which can be used as a post-processing step after a derivative.
+
+ **Series Agg**
+ : Applies a function to all of the **Group by** series to reduce the values to a single number. This function must always be the last metric in the series. For example, if the **Time Series** visualization shows 10 series, the sum **Series Agg** calculates the sum of all 10 bars and outputs a single Y value per X value. This is often confused with the overall sum function, which outputs a single Y value per unique series.
+
+ **Math**
+ : For each series, apply simple and advanced calculations. Only use **Math** for the last function in a series.
+
+2. To display each group separately, select one of the following options from the **Group by** dropdown:
+
+ * **Filters** — Groups the data into the specified filters. To differentiate the groups, assign a color to each filter.
+ * **Terms** — Displays the top values of the field. The color is only configurable in the **Time Series** chart. To configure, click **Options**, then select an option from the **Split color theme** dropdown.
+
+3. Click **Options**, then configure the inputs for the function. For example, to use a different field format, make a selection from the **Data formatter** dropdown.
+
+
+## TSVB visualization options [configure-the-visualizations]
+
+The configuration options differ for each **TSVB** visualization.
+
+
+### Time Series [tsvb-time-series]
+
+By default, the y-axis displays the full range of data, including zero. To automatically scale the y-axis from the minimum to maximum values of the data, click **Data > Options > Fill**, then enter `0` in the **Fill** field. You can add annotations to the x-axis based on timestamped documents in a separate {{es}} index.
+
+
+### All chart types except Time Series [all-chart-types-except-time-series]
+
+The **Data timerange mode** dropdown in **Panel options** controls the timespan that **TSVB** uses to match documents. **Last value** is unable to match all documents, only the specific interval. **Entire timerange** matches all documents specified in the time filter.
+
+
+### Metric, Top N, and Gauge [metric-topn-gauge]
+
+**Color rules** in **Panel options** contains conditional coloring based on the values.
+
+
+### Top N and Table [topn-table]
+
+When you click a series, **TSVB** applies a filter based on the series name. To change this behavior, click **Panel options**, then specify a URL in the **Item URL** field, which opens a URL instead of applying a filter on click.
+
+
+### Markdown [tsvb-markdown]
+
+The **Markdown** visualization supports Markdown with Handlebar (mustache) syntax to insert dynamic data, and supports custom CSS.
+
+
+## Open and edit TSVB visualizations in Lens [edit-visualizations-in-lens]
+
+When you open **TSVB** visualizations in **Lens**, all configuration options and annotations appear in the **Lens** visualization editor.
+
+You can open the following **TSVB** visualizations in **Lens**:
+
+* Time Series
+* Metric
+* Top N
+* Gauge
+* Table
+
+To get started, click **Edit visualization in Lens** in the toolbar.
+
+For more information, check out [Create visualizations with Lens](../lens.md).
+
+
+## View the visualization data requests [view-data-and-requests-tsvb]
+
+View the requests that collect the visualization data.
+
+1. In the toolbar, click **Inspect**.
+2. From the **Request** dropdown, select the series you want to view.
+
+
+## Save and add the panel [save-the-tsvb-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
+
+## Frequently asked questions [tsvb-faq]
+
+For answers to frequently asked **TSVB** question, review the following.
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I create dashboard drilldowns for Top N and Table visualizations?
+:name: how-do-i-create-dashboard-drilldowns
+
+You can create dashboard drilldowns that include the specified time range for **Top N** and **Table** visualizations.
+
+1. Open the dashboard that you want to link to, then copy the URL.
+2. Open the dashboard with the **Top N** and **Table** visualization panel, then click **Edit** in the toolbar.
+3. Open the **Top N** or **Table** panel menu, then select **Edit visualization**.
+4. Click **Panel options**.
+5. In the **Item URL** field, enter the URL.
+
+ For example `dashboards#/view/f193ca90-c9f4-11eb-b038-dd3270053a27`.
+
+6. Click **Save and return**.
+7. In the toolbar, click **Save as**, then make sure **Store time with dashboard** is deselected.
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I base drilldown URLs on my data?
+:name: how-do-i-base-drilldowns-on-data
+
+You can build drilldown URLs dynamically with your visualization data.
+
+Do this by adding the `{{key}}` placeholder to your URL
+
+For example `https://example.org/{{key}}`
+
+This instructs TSVB to substitute the value from your visualization wherever it sees `{{key}}`.
+
+If your data contain reserved or invalid URL characters such as "#" or "&", you should apply a transform to URL-encode the key like this `{{encodeURIComponent key}}`. If you are dynamically constructing a drilldown to another location in Kibana (for example, clicking a table row takes to you a value-scoped Discover session), you will likely want to Rison-encode your key as it may contain invalid Rison characters. ([Rison](https://github.com/Nanonid/rison#rison---compact-data-in-uris) is the serialization format many parts of Kibana use to store information in their URL.)
+
+For example: `discover#/view/0ac50180-82d9-11ec-9f4a-55de56b00cc0?_a=(filters:!((query:(match_phrase:(foo.keyword:{{rison key}})))))`
+
+If both conditions apply, you can cover all cases by applying both transforms: `{{encodeURIComponent (rison key)}}`.
+
+Technical note: TSVB uses [Handlebars](https://handlebarsjs.com/) to perform these interpolations. `rison` and `encodeURIComponent` are custom Handlebars helpers provided by Kibana.
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} Why is my TSVB visualization missing data?
+:name: why-is-my-tsvb-visualiztion-missing-data
+
+It depends, but most often there are two causes:
+
+* For **Time series** visualizations with a derivative function, the time interval can be too small. Derivatives require sequential values.
+* For all other **TSVB** visualizations, the cause is probably the **Data timerange mode**, which is controlled by **Panel options > Data timerange mode > Entire time range**. By default, **TSVB** displays the last whole bucket. For example, if the time filter is set to **Last 24 hours**, and the current time is 9:41, **TSVB** displays only the last 10 minutes — from 9:30 to 9:40.
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I calculate the difference between two data series?
+:name: how-do-i-calculate-the-difference-between-two-data-series
+
+Performing math across data series is unsupported in **TSVB**. To calculate the difference between two data series, use [**Timelion**](timelion.md) or [**Vega**](../custom-visualizations-with-vega.md).
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I compare the current versus previous month?
+:name: how-do-i-compare-the-current-versus-previous-month
+
+**TSVB** can display two series with time offsets, but it can’t perform math across series. To add a time offset:
+
+1. Click **Clone Series**, then choose a color for the new series.
+
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-tsvb_clone_series.png
+ :alt: Clone Series action
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
+
+2. Click **Options**, then enter the offset value in the **Offset series time by** field.
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I calculate a month over month change?
+:name: how-do-i-calculate-a-month-over-month-change
+
+The ability to calculate a month over month change is not fully supported in **TSVB**, but there is a special case that is supported *if* the time filter is set to 3 months or more *and* the **Interval** is `1m`. Use the **Derivative** to get the absolute monthly change. To convert to a percent, add the **Math** function with the `params.current / (params.current - params.derivative)` formula, then select **Percent** from the **Data Formatter** dropdown.
+
+For other types of month over month calculations, use [**Timelion**](timelion.md) or [**Vega**](../custom-visualizations-with-vega.md).
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I calculate the duration between the start and end of an event?
+:name: calculate-duration-start-end
+
+Calculating the duration between the start and end of an event is unsupported in **TSVB** because **TSVB** requires correlation between different time periods. **TSVB** requires that the duration is pre-calculated.
+
+::::
+
+
+
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md
index c5003774ba..c6c8906ba3 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md
@@ -63,10 +63,8 @@ Change the fields list to display a different {{data-source}}, different time ra
* If the fields list is empty, change the [time filter](../query-filter/filtering.md).
* To add fields, open the {{data-source}} dropdown, then select **Add a field to this {{data-source}}**.
-
- 
-
- For more information about adding fields to {{data-sources}} and examples, refer to [Explore your data with runtime fields](../find-and-organize/data-views.md#runtime-fields).
+ 
+ For more information about adding fields to {{data-sources}} and examples, refer to [Explore your data with runtime fields](../find-and-organize/data-views.md#runtime-fields).
@@ -118,10 +116,10 @@ To use a keyboard instead of a mouse, use the **Lens** fully accessible and cont
1. Select the field in the fields list or layer pane. Most fields have an inner and outer select state. The inner state opens a panel with detailed information or options. The outer state allows you to drag the field. Tab through the fields until you get the outer state on the field.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_drag_drop_2.png
- :alt: Lens drag and drop focus state
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_drag_drop_2.png
+ :alt: Lens drag and drop focus state
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
2. Complete the following actions:
@@ -130,10 +128,10 @@ To use a keyboard instead of a mouse, use the **Lens** fully accessible and cont
* To reorder the fields on the layer pane, use the Up and Down arrows.
* To duplicate an action, use the Left and Right arrows, then select the **Drop a field or click to add** field you want to use.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_drag_drop_3.gif
- :alt: Using drag and drop to reorder
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_drag_drop_3.gif
+ :alt: Using drag and drop to reorder
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
3. To confirm the action, press Space bar. To cancel, press Esc.
@@ -453,7 +451,7 @@ To save the panel to the dashboard:
For answers to common **Lens** questions, review the following.
-::::{dropdown} **When should I normalize the data by unit or use a custom interval?**
+::::{dropdown} When should I normalize the data by unit or use a custom interval?
:name: when-should-i-normalize-the-data-by-unit-or-use-a-custom-interval
* **Normalize by unit** — Calculates the average for the interval. When you normalize the data by unit, the data appears less granular, but **Lens** is able to calculate the data faster.
@@ -474,7 +472,7 @@ To create a custom interval:
::::
-::::{dropdown} **What data is categorized as Other?**
+::::{dropdown} What data is categorized as Other?
:name: what-is-the-other-category
The **Other** category contains all of the documents that do not match the specified criteria or filters. Use **Other** when you want to compare a value, or multiple values, to a whole.
@@ -486,7 +484,7 @@ To disable **Group other values as "Other"**, click a field in the layer pane, c
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I add documents without a field?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I add documents without a field?
:name: how-can-i-include-documents-without-the-field-in-the-operation
By default, **Lens** retrieves only the documents from the fields. For bucket aggregations, such as **Top values**, you can add documents that do not contain the fields, which is helpful when you want to make a comparison to the whole documentation set.
@@ -497,7 +495,7 @@ By default, **Lens** retrieves only the documents from the fields. For bucket ag
::::
-::::{dropdown} **When do I use runtime fields vs. formula?**
+::::{dropdown} When do I use runtime fields vs. formula?
:name: when-do-i-use-runtime-fields-vs-formula
Use runtime fields to format, concatenate, and extract document-level fields. Runtime fields work across all of {{kib}} and are best used for smaller computations without compromising performance.
@@ -507,7 +505,7 @@ Use formulas to compare multiple {{es}} aggregations that can be filtered or shi
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Can I add more than one y-axis scale?**
+::::{dropdown} Can I add more than one y-axis scale?
:name: is-it-possible-to-have-more-than-one-Y-axis-scale
For each y-axis, you can select **Left** and **Right**, and configure a different scale.
@@ -515,7 +513,7 @@ For each y-axis, you can select **Left** and **Right**, and configure a differen
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Why is my value the incorrect color when I use value-based coloring?**
+::::{dropdown} Why is my value the incorrect color when I use value-based coloring?
:name: why-is-my-value-with-the-right-color-using-value-based-coloring
Here’s a short list of few different aspects to check:
@@ -532,7 +530,7 @@ Here’s a short list of few different aspects to check:
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I sort by multiple columns?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I sort by multiple columns?
:name: can-i-sort-by-multiple-columns
Multiple column sorting is unsupported, but is supported in **Discover**. For information on how to sort multiple columns in **Discover**, refer to [Explore the fields in your data](../discover/discover-get-started.md#explore-fields-in-your-data).
@@ -540,7 +538,7 @@ Multiple column sorting is unsupported, but is supported in **Discover**. For in
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Why is my field missing from the fields list?**
+::::{dropdown} Why is my field missing from the fields list?
:name: why-my-field-is-missing-from-the-fields-list
The following field types do not appear in the **Available fields** list:
@@ -555,7 +553,7 @@ Verify if the field appears in the **Empty fields** list. **Lens** uses heuristi
::::
-::::{dropdown} **What do I do with gaps in time series visualizations?**
+::::{dropdown} What do I do with gaps in time series visualizations?
:name: how-to-handle-gaps-in-time-series-visualizations
When you create **Area** and **Line** charts with sparse time series data, open **Visual options** in the editor toolbar, then select a **Missing values** option.
@@ -563,7 +561,7 @@ When you create **Area** and **Line** charts with sparse time series data, open
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Can I statically define the y-axis scale?**
+::::{dropdown} Can I statically define the y-axis scale?
:name: is-it-possible-to-change-the-scale-of-Y-axis
You can set the scale, or *bounds*, for area, bar, and line charts. You can configure the bounds for all functions, except **Percentile**. Logarithmic scales are unsupported.
@@ -573,7 +571,7 @@ To configure the bounds, use the menus in the editor toolbar. Bar and area chart
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Is it possible to display icons in data tables?**
+::::{dropdown} Is it possible to display icons in data tables?
:name: is-it-possible-to-show-icons-in-datatable
You can display icons with [field formatters](../find-and-organize/data-views.md) in data tables.
@@ -581,7 +579,7 @@ You can display icons with [field formatters](../find-and-organize/data-views.md
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I inspect {{es}} queries in visualizations?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I inspect {{es}} queries in visualizations?
:name: is-it-possible-to-inspect-the-elasticsearch-queries-in-Lens
You can inspect the requests sent by the visualization to {{es}} using the Inspector. It can be accessed within the editor or in the dashboard.
@@ -589,7 +587,7 @@ You can inspect the requests sent by the visualization to {{es}} using the Inspe
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I isolate a single series in a chart?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I isolate a single series in a chart?
:name: how-to-isolate-a-single-series-in-a-chart
For area, line, and bar charts, press Shift, then click the series in the legend. All other series are automatically deselected.
@@ -597,7 +595,7 @@ For area, line, and bar charts, press Shift, then click the series in the legend
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I visualize saved Discover sessions?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I visualize saved Discover sessions?
:name: is-it-possible-to-use-saved-serches-in-lens
Visualizing saved Discover sessions is unsupported.
@@ -605,7 +603,7 @@ Visualizing saved Discover sessions is unsupported.
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I change the number of suggestions?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I change the number of suggestions?
:name: is-it-possible-to-decrease-or-increase-the-number-of-suggestions
Configuring the **Suggestions** is unsupported.
@@ -613,15 +611,15 @@ Configuring the **Suggestions** is unsupported.
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Is it possible to have pagination in a data table?**
+::::{dropdown} Is it possible to have pagination in a data table?
:name: is-it-possible-to-have-pagination-for-datatable
-Pagination in a data table is unsupported. To use pagination in data tables, create an [aggregation-based data table](legacy-editors.md#types-of-visualizations).
+Pagination in a data table is unsupported. To use pagination in data tables, create an [aggregation-based data table](legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md#types-of-visualizations).
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I change the color for a single data point?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I change the color for a single data point?
:name: is-it-possible-to-select-color-for-specific-bar-or-point
Specifying the color for a single data point, such as a single bar or line, is unsupported.
@@ -629,7 +627,7 @@ Specifying the color for a single data point, such as a single bar or line, is u
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How does dynamic coloring work for the metric visualization?**
+::::{dropdown} How does dynamic coloring work for the metric visualization?
:name: dynamic-metric-coloring
In the color palette editor, if you select **Value type: Number** the colors are applied based on the **Primary metric** value.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md
index fb4c6ac02b..e894ecaa61 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md
@@ -51,10 +51,10 @@ To edit links panels:
1. Hover over the panel and click  to edit the link. The **Edit links panel** flyout appears.
2. Click  next to the link.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-edit-links-panel.png
- :alt: A screenshot displaying the Edit icon next to the link
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-edit-links-panel.png
+ :alt: A screenshot displaying the Edit icon next to the link
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
3. Edit the link as needed and then click **Update link**.
4. Click **Save**.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md
index 2d0f51e3e4..6854eb74d7 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md
@@ -4,11 +4,77 @@ mapped_urls:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/serverless/current/maps.html
---
-# Maps
+# Maps [maps]
% What needs to be done: Align serverless/stateful
% Use migrated content from existing pages that map to this page:
% - [ ] ./raw-migrated-files/kibana/kibana/maps.md
-% - [ ] ./raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md
\ No newline at end of file
+% - [ ] ./raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md
+
+
+Create beautiful maps from your geographical data. With **Maps**, you can:
+
+* Build maps with multiple layers and indices.
+* Animate spatial temporal data.
+* Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles.
+* Embed your map in dashboards.
+* Symbolize features using data values.
+* Focus on only the data that’s important to you.
+
+On Elastic Cloud Serverless, Maps is only available for Security projects [](../../solutions/security/elastic-security-serverless.md).
+
+
+## Build maps with multiple layers and indices [_build_maps_with_multiple_layers_and_indices]
+
+Use multiple layers and indices to show all your data in a single map. Show how data sits relative to physical features like weather patterns, human-made features like international borders, and business-specific features like sales regions. Plot individual documents or use aggregations to plot any data set, no matter how large.
+
+:::{image} ../../images/kibana-sample_data_ecommerce.png
+:alt: sample data ecommerce
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+To learn about specific types of layers, check out [Heat map layer](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/heatmap-layer.md), [Tile layer](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/tile-layer.md), and [Vector layer](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-layer.md).
+
+
+## Animate spatial temporal data [_animate_spatial_temporal_data]
+
+Data comes to life with animation. Hard to detect patterns in static data pop out with movement. Use time slider to animate your data and gain deeper insights.
+
+This animated map uses the time slider to show Portland buses over a period of 15 minutes. The routes come alive as the bus locations update with time.
+
+:::{image} ../../images/kibana-timeslider.gif
+:alt: timeslider
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+To create this type of map, check out [Track, visualize, and alert assets in real time](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md).
+
+## Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles [_upload_geojson_files_and_shapefiles]
+
+Use **Maps** to drag and drop your GeoJSON and shapefile data into Elasticsearch, and then use them as layers in your map.
+
+
+## Embed your map in dashboards [_embed_your_map_in_dashboards]
+
+Viewing data from different angles provides better insights. Dimensions that are obscured in one visualization might be illuminated in another. Add your map to a [Dashboard](../../explore-analyze/dashboards.md) and view your geospatial data alongside bar charts, pie charts, tag clouds, and more.
+
+This choropleth map shows the density of non-emergency service requests in San Diego by council district. The map is embedded in a dashboard, so users can better understand when services are requested and gain insight into the top requested services.
+
+:::{image} ../../images/kibana-embed_in_dashboard.jpeg
+:alt: embed in dashboard
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+## Symbolize features using data values [_symbolize_features_using_data_values]
+
+Customize each layer to highlight meaningful dimensions in your data. For example, use dark colors to symbolize areas with more web log traffic, and lighter colors to symbolize areas with less traffic.
+
+
+## Focus on only the data that’s important to you [_focus_on_only_the_data_thats_important_to_you]
+
+Search across the layers in your map to focus on just the data you want. Combine free text search with field-based search using the [{{kib}} Query Language](../../explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/kql.md). Set the time filter to restrict layers by time. Draw a polygon on the map or use the shape from features to create spatial filters. Filter individual layers to compares facets.
+
+Check out [Search geographic data](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search.md).
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md
index 168d82a385..135e52949f 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md
@@ -565,10 +565,10 @@ Add a layer that uses attributes in the data to set the style and orientation of
4. Set **Border width** to 0.
5. Change **Symbol orientation** to use **By value** and the `trimet.bearing` field.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-top_hits_layer_style.png
- :alt: top hits layer style
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-top_hits_layer_style.png
+ :alt: top hits layer style
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
7. Click **Keep changes**.
8. Open the [time filter](../../query-filter/filtering.md), and set **Refresh every** to 10 seconds, and click **Start**.
@@ -738,10 +738,10 @@ With the alert configured and running, in a few minutes your `trimet_alerts` ind
* Enable the **Label** option with the `vehicleId` field
* Add the `vehicleId`, `boundaryId`, `detectionTime`, and `vehicleTime` fields to the tooltip configuration to allow viewing alert details on the map.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-vehicle_alerts.png
- :alt: vehicle alerts
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-vehicle_alerts.png
+ :alt: vehicle alerts
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
Congratulations! You have completed the tutorial and have the recipe for tracking assets. You can now try replicating this same analysis with your own data.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md
index 69c4dd872e..ec8c2b1201 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md
@@ -30,12 +30,12 @@ The data represents two real airports, two fictitious flight routes, and fictiti
1. [Create a new map](maps-getting-started.md#maps-create).
2. Zoom in on the New England area in the northeast United States.
- You’re adding flight paths to this area, and this sets up the map for a good view of the data.
+ You’re adding flight paths to this area, and this sets up the map for a good view of the data.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_new_england_map.png
- :alt: fu gs new england map
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_new_england_map.png
+ :alt: fu gs new england map
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -58,12 +58,12 @@ For each GeoJSON file you downloaded, complete the following steps:
7. Click **Keep changes**.
8. Once you’ve added all of the sample files, [save your map](maps-getting-started.md#maps-save).
- At this point, you could consider the map complete, but there are a few additions and tweaks that you can make to tell a better story with your data.
+ At this point, you could consider the map complete, but there are a few additions and tweaks that you can make to tell a better story with your data.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_flight_paths.png
- :alt: fu gs flight paths
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_flight_paths.png
+ :alt: fu gs flight paths
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -87,12 +87,12 @@ Looking at the `Lightning detected` layer, it’s clear where lightning has stru
6. When you’re finished modifying settings, click **Keep changes**.
- With your new lightning heat map layer, your map should look like this:
+ With your new lightning heat map layer, your map should look like this:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_lightning_intensity.png
- :alt: fu gs lightning intensity
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_lightning_intensity.png
+ :alt: fu gs lightning intensity
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md
index 8617d56c74..72f6f8655e 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md
@@ -481,9 +481,9 @@ If you cannot connect to Elastic Maps Service from the {{kib}} server or browser
1. Pull the {{hosted-ems}} Docker image.
- ::::{warning}
- Version 9.0.0-beta1 of {{hosted-ems}} has not yet been released. No Docker image is currently available for this version.
- ::::
+ ::::{warning}
+ Version 9.0.0-beta1 of {{hosted-ems}} has not yet been released. No Docker image is currently available for this version.
+ ::::
```bash
@@ -516,10 +516,10 @@ If you cannot connect to Elastic Maps Service from the {{kib}} server or browser
Once {{hosted-ems}} is running, follow instructions from the webpage at `localhost:8080` to define a configuration file and optionally download a more detailed basemaps database.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-elastic-maps-server-instructions.png
- :alt: Set-up instructions
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-elastic-maps-server-instructions.png
+ :alt: Set-up instructions
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md
index 4fa4130643..db4ec8bb93 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md
@@ -68,12 +68,12 @@ The first layer you’ll add is a choropleth layer to shade world countries by w
8. Click **Keep changes**.
- Your map now looks like this:
+ Your map now looks like this:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_add_cloropeth_layer.png
- :alt: Map showing the Total Requests by Destination layer
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_add_cloropeth_layer.png
+ :alt: Map showing the Total Requests by Destination layer
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -100,12 +100,12 @@ This layer displays web log documents as points. The layer is only visible when
7. In **Layer style**, set **Fill color** to **#2200FF**.
8. Click **Keep changes**.
- Your map will look like this from zoom level 9 to 24:
+ Your map will look like this from zoom level 9 to 24:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_add_es_document_layer.png
- :alt: Map showing what zoom level looks like a level 9
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_add_es_document_layer.png
+ :alt: Map showing what zoom level looks like a level 9
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -135,12 +135,12 @@ You’ll create a layer for [aggregated data](../../aggregations.md) and make it
7. Click **Keep changes** button.
- Your map will look like this between zoom levels 0 and 9:
+ Your map will look like this between zoom levels 0 and 9:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-sample_data_web_logs.png
- :alt: Map showing what zoom level 3 looks like
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-sample_data_web_logs.png
+ :alt: Map showing what zoom level 3 looks like
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -158,10 +158,10 @@ View your geospatial data alongside a heat map and pie chart, and then filter th
1. Click **Add from library** to open a list of panels that you can add to the dashboard.
2. Add **[Logs] Unique Destination Heatmap** and **[Logs] Bytes distribution** to the dashboard.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_dashboard_with_map.png
- :alt: Map in a dashboard with 2 other panels
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_dashboard_with_map.png
+ :alt: Map in a dashboard with 2 other panels
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
3. To filter for documents with unusually high byte values, click and drag in the **Bytes distribution** chart.
4. Remove the filter by clicking **x** next to its name in the filter bar.
@@ -170,17 +170,17 @@ View your geospatial data alongside a heat map and pie chart, and then filter th
1. Open a tooltip by clicking anywhere in the United States vector.
2. To show only documents where **geo.src** is **US**, click the filter icon in the row for **ISO 3066-1 alpha-2**.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_tooltip_filter.png
- :alt: Tooltip on map
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_tooltip_filter.png
+ :alt: Tooltip on map
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
- Your filtered map should look similar to this:
+ Your filtered map should look similar to this:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_map_filtered.png
- :alt: Map showing filtered data
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_map_filtered.png
+ :alt: Map showing filtered data
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md
index 37298b5c40..5860301916 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md
@@ -63,9 +63,9 @@ $$$aggregation-reference$$$
| Function | **Lens** | **TSVB** |
| --- | --- | --- |
| Counter rate | ✓ | ✓ |
-| [Filter ratio](legacy-editors.md#tsvb-function-reference) | Use [formula](lens.md#lens-formulas) | ✓ |
-| [Positive only](legacy-editors.md#tsvb-function-reference) | | ✓ |
-| [Series agg](legacy-editors.md#tsvb-function-reference) | Use [formula](lens.md#lens-formulas) | ✓ |
+| [Filter ratio](legacy-editors/tsvb.md#tsvb-function-reference) | Use [formula](lens.md#lens-formulas) | ✓ |
+| [Positive only](legacy-editors/tsvb.md#tsvb-function-reference) | | ✓ |
+| [Series agg](legacy-editors/tsvb.md#tsvb-function-reference) | Use [formula](lens.md#lens-formulas) | ✓ |
| Static value | ✓ | ✓ |
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md
index c2bfd74b71..57d0bd74d4 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md
@@ -5,8 +5,6 @@ mapped_pages:
# Visualize Library [visualize-library]
-This content applies to: [](../../solutions/search.md) [](../../solutions/observability.md) [](../../solutions/security/elastic-security-serverless.md)
-
The **Visualize Library** is a space where you can save visualization panels that you may want to use across multiple dashboards. The **Visualize Library** consists of two pages:
* **Visualizations**
@@ -15,7 +13,7 @@ The **Visualize Library** is a space where you can save visualization panels tha
## Visualizations [visualize-library-visualizations]
-By default the **Visualizations** page opens first. Here you can create new visualizations, or select from a list of previously created visualizations. To learn more, refer to [save to the Visualize Library](../../explore-analyze/index.md#elasticsearch-explore-your-data-visualizations-save-to-the-visualize-library).
+By default the **Visualizations** page opens first. Here you can create new visualizations, or select from a list of previously created visualizations. To learn more, refer to [save to the Visualize Library](../../explore-analyze/visualize/manage-panels.md).
## Annotation groups [visualize-library-annotation-groups]
diff --git a/images/kibana-dashboard_add_content_to_dashboard_8.15.0.png b/images/kibana-dashboard_add_content_to_dashboard_8.15.0.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8a8b9b9d5d
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/kibana-dashboard_add_content_to_dashboard_8.15.0.png differ
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md b/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3b1c20cd6e..0000000000
--- a/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-# {{maps-app}} [maps]
-
-This content applies to: [](../../../solutions/security/elastic-security-serverless.md)
-
-In **{{project-settings}} → {{maps-app}}** you can:
-
-* Build maps with multiple layers and indices.
-* Animate spatial temporal data.
-* Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles.
-* Embed your map in dashboards.
-* Focus on only the data that’s important to you.
-
-
-## Build maps with multiple layers and indices [maps-build-maps-with-multiple-layers-and-indices]
-
-Use multiple layers and indices to show all your data in a single map. Show how data sits relative to physical features like weather patterns, human-made features like international borders, and business-specific features like sales regions. Plot individual documents or use aggregations to plot any data set, no matter how large.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/serverless-sample_data_ecommerce_map.png
-:alt: A world map with country and revenue layers
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-Go to **{{project-settings}} → {{maps-app}}** and click **Add layer**. To learn about specific types of layers, check out [Heat map layer](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/heatmap-layer.md), [Tile layer](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/tile-layer.md), and [Vector layer](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-layer.md).
-
-
-## Animate spatial temporal data [maps-animate-spatial-temporal-data]
-
-Data comes to life with animation. Hard to detect patterns in static data pop out with movement. Use time slider to animate your data and gain deeper insights.
-
-This animated map uses the time slider to show Portland buses over a period of 15 minutes. The routes come alive as the bus locations update with time.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/serverless-timeslider_map.gif
-:alt: An animated city map of Portland with changing bus locations
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-To create this type of map, check out [Track, visualize, and alert assets in real time](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md).
-
-
-## Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles [maps-upload-geojson-files-and-shapefiles]
-
-Use **{{maps-app}}** to drag and drop your GeoJSON and shapefile data and then use them as layers in your map. Check out [Import geospatial data](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/import-geospatial-data.md).
-
-
-## Embed your map in dashboards [maps-embed-your-map-in-dashboards]
-
-Viewing data from different angles provides better insights. Dimensions that are obscured in one visualization might be illuminated in another. Add your map to a [Dashboard](../../../explore-analyze/dashboards.md) and view your geospatial data alongside bar charts, pie charts, tag clouds, and more.
-
-This choropleth map shows the density of non-emergency service requests in San Diego by council district. The map is embedded in a dashboard, so users can better understand when services are requested and gain insight into the top requested services.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/serverless-embed_dashboard_map.jpeg
-:alt: A dashboard with a map
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-For a detailed example, check out [Build a map to compare metrics by country or region](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md).
-
-
-## Focus on only the data that’s important to you [maps-focus-on-only-the-data-thats-important-to-you]
-
-Search across the layers in your map to focus on just the data you want. Combine free text search with field-based search using the {{kib}} Query Language (KQL) Set the time filter to restrict layers by time. Draw a polygon on the map or use the shape from features to create spatial filters. Filter individual layers to compares facets.
-
-Check out [Search geographic data](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search.md).
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/kibana/kibana/maps.md b/raw-migrated-files/kibana/kibana/maps.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 797488c84c..0000000000
--- a/raw-migrated-files/kibana/kibana/maps.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-# Maps [maps]
-
-Create beautiful maps from your geographical data. With **Maps**, you can:
-
-* Build maps with multiple layers and indices.
-* Animate spatial temporal data.
-* Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles.
-* Embed your map in dashboards.
-* Symbolize features using data values.
-* Focus on only the data that’s important to you.
-
-
-## Build maps with multiple layers and indices [_build_maps_with_multiple_layers_and_indices]
-
-Use multiple layers and indices to show all your data in a single map. Show how data sits relative to physical features like weather patterns, human-made features like international borders, and business-specific features like sales regions. Plot individual documents or use aggregations to plot any data set, no matter how large.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-sample_data_ecommerce.png
-:alt: sample data ecommerce
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-## Animate spatial temporal data [_animate_spatial_temporal_data]
-
-Data comes to life with animation. Hard to detect patterns in static data pop out with movement. Use time slider to animate your data and gain deeper insights.
-
-This animated map uses the time slider to show Portland buses over a period of 15 minutes. The routes come alive as the bus locations update with time.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-timeslider.gif
-:alt: timeslider
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-## Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles [_upload_geojson_files_and_shapefiles]
-
-Use **Maps** to drag and drop your GeoJSON and shapefile data into Elasticsearch, and then use them as layers in your map.
-
-
-## Embed your map in dashboards [_embed_your_map_in_dashboards]
-
-Viewing data from different angles provides better insights. Dimensions that are obscured in one visualization might be illuminated in another. Add your map to a dashboard and view your geospatial data alongside bar charts, pie charts, tag clouds, and more.
-
-This choropleth map shows the density of non-emergency service requests in San Diego by council district. The map is embedded in a dashboard, so users can better understand when services are requested and gain insight into the top requested services.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-embed_in_dashboard.jpeg
-:alt: embed in dashboard
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-## Symbolize features using data values [_symbolize_features_using_data_values]
-
-Customize each layer to highlight meaningful dimensions in your data. For example, use dark colors to symbolize areas with more web log traffic, and lighter colors to symbolize areas with less traffic.
-
-
-## Focus on only the data that’s important to you [_focus_on_only_the_data_thats_important_to_you]
-
-Search across the layers in your map to focus on just the data you want. Combine free text search with field-based search using the [{{kib}} Query Language](../../../explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/kql.md). Set the time filter to restrict layers by time. Draw a polygon on the map or use the shape from features to create spatial filters. Filter individual layers to compares facets.
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/toc.yml b/raw-migrated-files/toc.yml
index 200c9814b1..aec7104527 100644
--- a/raw-migrated-files/toc.yml
+++ b/raw-migrated-files/toc.yml
@@ -306,7 +306,6 @@ toc:
- file: docs-content/serverless/ingest-wiz-data.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/intro.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/maintenance-windows.md
- - file: docs-content/serverless/maps.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/monitor-k8s-otel-edot.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/observability-add-logs-service-name.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/observability-aggregationOptions.md
@@ -690,7 +689,6 @@ toc:
- file: kibana/kibana/managing-data-views.md
- file: kibana/kibana/managing-saved-objects.md
- file: kibana/kibana/managing-tags.md
- - file: kibana/kibana/maps.md
- file: kibana/kibana/osquery.md
- file: kibana/kibana/playground.md
- file: kibana/kibana/reporting-getting-started.md
-
+[](https://videos.elastic.co/watch/UhGkdJGC32HRn3oS5ZYJL1?)
## Create dashboard drilldowns [dashboard-drilldowns]
@@ -77,11 +67,10 @@ Create a drilldown that opens the **Detailed logs** dashboard from the **[Logs]
3. Save the dashboard.
4. In the data table panel, hover over a value, click **+**, then select `View details`.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_drilldownOnPanel_8.3.png
- :alt: Drilldown on data table that navigates to another dashboard
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_drilldownOnPanel_8.3.png
+ :alt: Drilldown on data table that navigates to another dashboard
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -164,11 +153,10 @@ Create a drilldown that opens **Discover** from the [**Sample web logs**](../ove
5. Click **Create drilldown**.
6. Save the dashboard.
7. On the **[Logs] Bytes distribution** bar vertical stacked chart, click a bar, then select **View bytes distribution in Discover**.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_discoverDrilldown_8.3.png
- :alt: Drilldown on bar vertical stacked chart that navigates to Discover
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-dashboard_discoverDrilldown_8.3.png
+ :alt: Drilldown on bar vertical stacked chart that navigates to Discover
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
index 9ce5ab47bc..9e9cc15476 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
@@ -17,5 +17,6 @@ To duplicate a managed dashboard, follow the instructions above or click the **M
:::{image} ../../images/kibana-managed-dashboard-popover-8.16.0.png
:alt: Managed badge dialog with Duplicate button
:class: screenshot
+:width: 50%
:::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/_import_dashboards.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/import-dashboards.md
similarity index 100%
rename from explore-analyze/dashboards/_import_dashboards.md
rename to explore-analyze/dashboards/import-dashboards.md
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md
index c658ac5050..5591feed7a 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/_manage_dashboards.html
---
-# Managing [_manage_dashboards]
+# Managing dashboards [_manage_dashboards]
## Browse dashboards [find-dashboards]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md
index 2973b5d326..9aef0533cc 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md
@@ -8,17 +8,13 @@ mapped_pages:
1. Open the **Dashboards** page in {{kib}}.
2. Locate the dashboard you want to edit.
- ::::{tip}
- When looking for a specific dashboard, you can filter them by tag or by creator, or search the list based on their name and description. Note that the creator information is only available for dashboards created on or after version 8.14.
- ::::
+ ::::{tip}
+ When looking for a specific dashboard, you can filter them by tag or by creator, or search the list based on their name and description. Note that the creator information is only available for dashboards created on or after version 8.14.
+ ::::
3. Click the dashboard **Title** you want to open.
4. Make sure that you are in **Edit** mode to be able to make changes to the dashboard. You can switch between **Edit** and **View** modes from the toolbar.
-
- :::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt619b284e92c2be27/6750f3a512a5eae780936fe3/switch-to-view-mode-8.17.0.gif
- :alt: Switch between Edit and View modes
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ 
5. Make the changes that you need to the dashboard:
@@ -44,8 +40,4 @@ Once changes are saved, you can no longer revert them in one click, and instead
1. In the toolbar, click **Reset**.
2. On the **Reset dashboard?** window, click **Reset dashboard**.
-
- :::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blte0c08bede75b3874/6750f5566cdeea14b273b048/reset-dashboard-8.17.0.gif
- :alt: Reset dashboard to revert unsaved changes
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ 
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
index 7ce6059b9f..456de2e903 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/share-the-dashboard.html
---
-# Sharing [share-the-dashboard]
+# Sharing dashboards [share-the-dashboard]
To share a dashboard with a larger audience, click **Share** in the toolbar. For detailed information about the sharing options, refer to [Reporting](../report-and-share.md).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
index 48539c4001..30ab0916d5 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/_use_and_filter_dashboards.html
---
-# Using [_use_and_filter_dashboards]
+# Exploring dashboards [_use_and_filter_dashboards]
## Search and filter your dashboard data [search-or-filter-your-data]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md b/explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md
index 02e92127d5..d8045dadeb 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ Numeral formatting patterns are used in multiple places in {{kib}}, including:
* [Advanced settings](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/advanced-options.html)
* [Data view formatters](find-and-organize/data-views.md#field-formatters-numeric)
-* [**TSVB**](visualize/legacy-editors.md#tsvb-panel)
+* [**TSVB**](visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md)
* [**Canvas**](visualize/canvas.md)
The simplest pattern format is `0`, and the default {{kib}} pattern is `0,0.[000]`. The numeral pattern syntax expresses:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/toc.yml b/explore-analyze/toc.yml
index ad9940280c..041aa882c4 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/toc.yml
+++ b/explore-analyze/toc.yml
@@ -253,7 +253,7 @@ toc:
- file: dashboards/drilldowns.md
- file: dashboards/arrange-panels.md
- file: dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
- - file: dashboards/_import_dashboards.md
+ - file: dashboards/import-dashboards.md
- file: dashboards/managing.md
- file: dashboards/sharing.md
- file: dashboards/tutorials.md
@@ -263,8 +263,8 @@ toc:
- file: visualize.md
children:
- file: visualize/supported-chart-types.md
- - file: visualize/manage-panels.md
- file: visualize/visualize-library.md
+ - file: visualize/manage-panels.md
- file: visualize/lens.md
- file: visualize/esorql.md
- file: visualize/field-statistics.md
@@ -315,6 +315,10 @@ toc:
- file: visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
- file: visualize/graph/graph-troubleshooting.md
- file: visualize/legacy-editors.md
+ children:
+ - file: visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md
+ - file: visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md
+ - file: visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md
- file: find-and-organize.md
children:
- file: find-and-organize/data-views.md
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize.md b/explore-analyze/visualize.md
index 6775f0c799..7fc0ee2c15 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize.md
@@ -13,21 +13,26 @@ $$$panels-editors$$$
| **Content** | **Panel type** | **Description** |
| --- | --- | --- |
-| Visualizations | [Lens](visualize/lens.md) | The default editor for creating powerful [charts](visualize/supported-chart-types.md) in {{kib}} |
+| Visualizations | | |
+| [Lens](visualize/lens.md) | The default editor for creating powerful [charts](visualize/supported-chart-types.md) in {{kib}} |
| [ES|QL](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-kibana.md) | Create visualizations from ES|QL queries |
| [Maps](visualize/maps.md) | Create beautiful displays of your geographical data |
| [Field statistics](visualize/field-statistics.md) | Add a field statistics view of your data to your dashboards |
| [Custom visualizations](visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md) | Use Vega to create new types of visualizations |
-| Annotations and navigation | [Text](visualize/text-panels.md) | Add context to your dashboard with markdown-based **text** |
+| Annotations and navigation | | |
+| [Text](visualize/text-panels.md) | Add context to your dashboard with markdown-based **text** |
| [Image](visualize/image-panels.md) | Personalize your dashboard with custom images |
| [Links](visualize/link-panels.md) | Add links to other dashboards or to external websites |
-| Machine Learning and Analytics | [Anomaly swim lane](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-anomalies.md) | Display the results from machine learning anomaly detection jobs |
+| Machine Learning and Analytics | | |
+| [Anomaly swim lane](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-anomalies.md) | Display the results from machine learning anomaly detection jobs |
| [Anomaly chart](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-anomalies.md) | Display an anomaly chart from the **Anomaly Explorer** |
| [Single metric viewer](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-anomalies.md) | Display an anomaly chart from the **Single Metric Viewer** |
| [Change point detection](machine-learning/machine-learning-in-kibana/xpack-ml-aiops.md#change-point-detection) | Display a chart to visualize change points in your data |
-| Observability | [SLO overview](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/observability/current/slo.md) | Visualize a selected SLO’s health, including name, current SLI value, target, and status |
+| Observability | | |
+| [SLO overview](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/observability/current/slo.md) | Visualize a selected SLO’s health, including name, current SLI value, target, and status |
| [SLO Alerts](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/observability/current/slo.md) | Visualize one or more SLO alerts, including status, rule name, duration, and reason. In addition, configure and update alerts, or create cases directly from the panel |
| [SLO Error Budget](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/observability/current/slo.md) | Visualize the consumption of your SLO’s error budget |
-| Legacy | [Log stream](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/observability.html#logs-app) (deprecated) | Display a table of live streaming logs |
-| [Aggregation based](visualize/legacy-editors.md#add-aggregation-based-visualization-panels) | While these panel types are still available, we recommend to use [Lens](visualize/lens.md) |
-| [TSVB](visualize/legacy-editors.md#tsvb-panel) |
+| Legacy | | |
+| [Log stream](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/observability.html#logs-app) (deprecated) | Display a table of live streaming logs |
+| [Aggregation based](visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md) | While these panel types are still available, we recommend to use [Lens](visualize/lens.md) |
+| [TSVB](visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md) |
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md
index 0d8051712e..cfbd3c0054 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md
@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ Choose the type of element you want to use, then use the preconfigured demo data
* **{{es}} SQL** — Access your data in {{es}} using [SQL syntax](../query-filter/languages/sql-spec.md).
* **{{es}} documents** — Access your data in {{es}} without using aggregations. To use, select a {{data-source}} and fields. Use **{{es}} documents** when you have low-volume datasets, and you want to view raw documents or to plot exact, non-aggregated values on a chart.
- * **Timelion** — Access your time series data using [**Timelion**](legacy-editors.md#timelion) queries. To use **Timelion** queries, you can enter a query using the [Lucene Query Syntax](../query-filter/languages/lucene-query-syntax.md).
+ * **Timelion** — Access your time series data using [**Timelion**](legacy-editors/timelion.md) queries. To use **Timelion** queries, you can enter a query using the [Lucene Query Syntax](../query-filter/languages/lucene-query-syntax.md).
Each element can display a different {{data-source}}, and pages and workpads often contain multiple {{data-sources}}.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md
index d0a392c11f..f22296e010 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md
@@ -30,10 +30,10 @@ To customize your workpad to look the way you want, add your own images.
1. Click the Elastic logo.
2. Drag the image file to the **Select or drag and drop an image** field.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-canvas_tutorialCustomImage_7.17.0.png
- :alt: The Analytics logo added to the workpad
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-canvas_tutorialCustomImage_7.17.0.png
+ :alt: The Analytics logo added to the workpad
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md
index 477519523d..07b7077b9c 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md
@@ -29,17 +29,17 @@ For example, to change the {{data-source}} for a set of charts:
1. Specify the variable options.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-specify_variable_syntax.png
- :alt: Variable syntax options
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-specify_variable_syntax.png
+ :alt: Variable syntax options
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
2. Copy the variable, then apply it to each element you want to update in the **Expression editor**.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-copy_variable_syntax.png
- :alt: Copied variable syntax pasted in the Expression editor
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-copy_variable_syntax.png
+ :alt: Copied variable syntax pasted in the Expression editor
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md
index f7b404d47e..4b2f63fe8d 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md
@@ -219,19 +219,19 @@ To generate the data, **Vega-Lite** uses the `source_0` and `data_0`. `source_0`
2. From the **View** dropdown, select **Vega debug**.
3. From the dropdown, select **source_0**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_4.png
- :alt: Table for data_0 with columns key
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_4.png
+ :alt: Table for data_0 with columns key
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
4. To compare to the visually encoded data, select **data_0** from the dropdown.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_5.png
- :alt: Table for data_0 where the key is NaN instead of a string
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_5.png
+ :alt: Table for data_0 where the key is NaN instead of a string
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
- **key** is unable to convert because the property is category (`Men's Clothing`, `Women's Clothing`, etc.) instead of a timestamp.
+ **key** is unable to convert because the property is category (`Men's Clothing`, `Women's Clothing`, etc.) instead of a timestamp.
@@ -257,10 +257,10 @@ In the **Vega-Lite** spec, add the `encoding` block:
1. Click **Inspect**, then select **Vega Debug** from the **View** dropdown.
2. From the dropdown, select **data_0**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_6.png
- :alt: Table for data_0 showing that the column time_buckets.buckets.key is undefined
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_6.png
+ :alt: Table for data_0 showing that the column time_buckets.buckets.key is undefined
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
**Vega-Lite** is unable to extract the `time_buckets.buckets` inner array.
@@ -283,10 +283,10 @@ In the **Vega-Lite** spec, add a `transform` block, then click **Update**:
1. Click **Inspect**, then select **Vega Debug** from the **View** dropdown.
2. From the dropdown, select **data_0**.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_7.png
- :alt: Table showing data_0 with multiple pages of results
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-vega_lite_tutorial_7.png
+ :alt: Table showing data_0 with multiple pages of results
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
Vega-Lite displays **undefined** values because there are duplicate names.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md
index ddf5945bac..f40d5f4a63 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md
@@ -20,9 +20,9 @@ You can then **Save** and add it to an existing or a new dashboard using the sav
1. From your dashboard, select **Add panel**.
2. Choose **ES|QL** under **Visualizations**. An ES|QL editor appears and lets you configure your query and its associated visualization. The **Suggestions** panel can help you find alternative ways to configure the visualization.
- ::::{tip}
- Check the [ES|QL reference](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-language.html) to get familiar with the syntax and optimize your query.
- ::::
+ ::::{tip}
+ Check the [ES|QL reference](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-language.html) to get familiar with the syntax and optimize your query.
+ ::::
3. When editing your query or its configuration, run the query to update the preview of the visualization.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/field-statistics.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/field-statistics.md
index 2513d13fd8..d5aeb101ad 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/field-statistics.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/field-statistics.md
@@ -10,9 +10,9 @@ mapped_pages:
1. From your dashboard, select **Add panel**.
2. Choose **Field statistics** under **Visualizations**. An ES|QL editor appears and lets you configure your query with the fields and information that you want to show.
- ::::{tip}
- Check the [ES|QL reference](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-language.html) to get familiar with the syntax and optimize your query.
- ::::
+ ::::{tip}
+ Check the [ES|QL reference](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/esql-language.html) to get familiar with the syntax and optimize your query.
+ ::::
3. When editing your query or its configuration, run the query to update the preview of the visualization.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md
index a2fbdc92cc..a1ce03036f 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md
@@ -49,19 +49,20 @@ Use **Graph** to reveal the relationships in your data.
2. Select the data source that you want to explore.
- {{kib}} graphs the relationships between the top fields.
+ {{kib}} graphs the relationships between the top fields.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-url-connections.png
- :alt: URL connections
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-url-connections.png
+ :alt: URL connections
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
3. Add more fields, or click an existing field to edit, disable or deselect it.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-menu.png
- :alt: menu for editing, disabling, or removing a field from the graph
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-menu.png
+ :alt: menu for editing, disabling, or removing a field from the graph
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
4. Enter a query to discover relationships between terms in the selected fields.
@@ -69,10 +70,11 @@ Use **Graph** to reveal the relationships in your data.
5. To view more information about a relationship, click any connection or vertex.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-control-bar.png
- :alt: Graph toolbar
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-graph-control-bar.png
+ :alt: Graph toolbar
+ :class: screenshot
+ :width: 50%
+ :::
6. Use the graph toolbar to display additional connections:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
index 07916cb671..fb126535ee 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
@@ -45,6 +45,7 @@ You can also use security to grant read only or all access to different roles. W
:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-graph-read-only-badge.png
:alt: Example of Graph's read only access indicator in Kibana's header
:class: screenshot
+:width: 50%
:::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md
index 5bdd55b85d..137b1170a9 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md
@@ -5,974 +5,10 @@ mapped_pages:
# Legacy editors [legacy-editors]
-## Aggregation-based [add-aggregation-based-visualization-panels]
+Legacy editors are still available but have been replaced by better alternatives. Consider using one of the [modern editors](../visualize.md) offered in Elastic such as **Lens**.
-Aggregation-based visualizations are the core {{kib}} panels, and are not optimized for a specific use case.
+The legacy editors are:
-With aggregation-based visualizations, you can:
-
-* Split charts up to three aggregation levels, which is more than **Lens** and **TSVB**
-* Create visualization with non-time series data
-* Use a [Discover session](../discover/save-open-search.md) as an input
-* Sort data tables and use the summary row and percentage column features
-* Assign colors to data series
-* Extend features with plugins
-
-Aggregation-based visualizations include the following limitations:
-
-* Limited styling options
-* Math is unsupported
-* Multiple indices is unsupported
-
-
-#### Types of aggregation-based visualizations [types-of-visualizations]
-
-{{kib}} supports the following types of aggregation-based visualizations.
-
-| | |
-| --- | --- |
-| **Area**: Displays data points, connected by a line, where the area between the line and axes are shaded.Use area charts to compare two or more categories over time, and display the magnitude of trends. |  |
-| **Data table**: Displays your aggregation results in a tabular format. Use data tables to display server configuration details, track counts, min,or max values for a specific field, and monitor the status of key services. |  |
-| **Gauge**: Displays your data along a scale that changes color according to where your data falls on the expected scale. Use the gauge to show how metricvalues relate to reference threshold values, or determine how a specified field is performing versus how it is expected to perform. |  |
-| **Goal**: Displays how your metric progresses toward a fixed goal. Use the goal to display an easy to read visual of the status of your goal progression. |  |
-| **Heat map**: Displays graphical representations of data where the individual values are represented by colors. Use heat maps when your data set includescategorical data. For example, use a heat map to see the flights of origin countries compared to destination countries using the sample flight data. |  |
-| **Horizontal Bar**: Displays bars side-by-side where each bar represents a category. Use bar charts to compare data across alarge number of categories, display data that includes categories with negative values, and easily identifythe categories that represent the highest and lowest values. {{kib}} also supports vertical bar charts. |  |
-| **Line**: Displays data points that are connected by a line. Use line charts to visualize a sequence of values, discovertrends over time, and forecast future values. |  |
-| **Metric**: Displays a single numeric value for an aggregation. Use the metric visualization when you have a numeric value that is powerful enough to tella story about your data. |  |
-| **Pie**: Displays slices that represent a data category, where the slice size is proportional to the quantity it represents.Use pie charts to show comparisons between multiple categories, illustrate the dominance of one category over others,and show percentage or proportional data. |  |
-| **Tag cloud**: Graphical representations of how frequently a word appears in the source text. Use tag clouds to easily produce a summary of large documents andcreate visual art for a specific topic. |  |
-
-
-#### Create an aggregation-based visualization panel [create-aggregation-based-panel]
-
-Choose the type of visualization you want to create, then use the editor to configure the options.
-
-1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**.
-
- 1. Select the visualization type you want to create.
- 2. Select the data source you want to visualize.
-
- ::::{note}
- There is no performance impact on the data source you select. For example, saved Discover sessions perform the same as {{data-sources}}.
- ::::
-
-2. Add the [aggregations](supported-chart-types.md#aggregation-reference) you want to visualize using the editor, then click **Update**.
-
- ::::{note}
- For the **Date Histogram** to use an **auto interval**, the date field must match the primary time field of the {{data-source}}.
- ::::
-
-3. To change the order, drag and drop the aggregations in the editor.
-
- 
-
-4. To customize the series colors, click the series in the legend, then select the color you want to use.
-
- 
-
-
-
-#### Try it: Create an aggregation-based bar chart [try-it-aggregation-based-panel]
-
-You collected data from your web server, and you want to visualize and analyze the data on a dashboard. To create a dashboard panel of the data, create a bar chart that displays the top five log traffic sources for every three hours.
-
-
-##### Add the data and create the dashboard [_add_the_data_and_create_the_dashboard]
-
-Add the sample web logs data that you’ll use to create the bar chart, then create the dashboard.
-
-1. [Install the web logs sample data set](../overview/kibana-quickstart.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana).
-2. Go to **Dashboards**.
-3. On the **Dashboards** page, click **Create dashboard**.
-
-
-##### Open and set up the aggregation-based bar chart [_open_and_set_up_the_aggregation_based_bar_chart]
-
-Open the **Aggregation based** editor and change the time range.
-
-1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**, select **Vertical bar**, then select **Kibana Sample Data Logs**.
-2. Make sure the [time filter](../query-filter/filtering.md) is **Last 7 days**.
-
-
-##### Create the bar chart [tutorial-configure-the-bar-chart]
-
-To create the bar chart, add a [bucket aggregation](supported-chart-types.md#bucket-aggregations), then add the terms sub-aggregation to display the top values.
-
-1. Add a **Buckets** aggregation.
-
- 1. Click **Add**, then select **X-axis**.
- 2. From the **Aggregation** dropdown, select **Date Histogram**.
- 3. Click **Update**.
-
- 
-
-2. To show the top five log traffic sources, add a sub-bucket aggregation.
-
- 1. Click **Add**, then select **Split series**.
-
- ::::{tip}
- Aggregation-based panels support a maximum of three **Split series**.
- ::::
-
- 2. From the **Sub aggregation** dropdown, select **Terms**.
- 3. From the **Field** dropdown, select **geo.src**.
- 4. Click **Update**.
-
- 
-
-
-
-#### Open and edit aggregation-based visualizations in Lens [edit-agg-based-visualizations-in-lens]
-
-When you open aggregation-based visualizations in **Lens**, all configuration options appear in the **Lens** visualization editor.
-
-You can open the following aggregation-based visualizations in **Lens**:
-
-* Area
-* Data table
-* Gauge
-* Goal
-* Heat map
-* Horizontal bar
-* Line
-* Metric
-* Pie
-* Vertical bar
-
-To get started, click **Edit visualization in Lens** in the toolbar.
-
-For more information, check out [Create visualizations with Lens](lens.md).
-
-
-##### Save and add the panel [save-the-aggregation-based-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-
-## TSVB [tsvb-panel]
-
-**TSVB** is a set of visualization types that you configure and display on dashboards.
-
-With **TSVB**, you can:
-
-* Combine an infinite number of [aggregations](supported-chart-types.md#aggregation-reference) to display your data.
-* Annotate time series data with timestamped events from an {{es}} index.
-* View the data in several types of visualizations, including charts, data tables, and markdown panels.
-* Display multiple [data views](../find-and-organize/data-views.md) in each visualization.
-* Use custom functions and some math on aggregations.
-* Customize the data with labels and colors.
-
-:::{image} ../../images/kibana-tsvb-screenshot.png
-:alt: TSVB overview
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-#### Open and set up TSVB [tsvb-data-view-mode]
-
-Open **TSVB**, then configure the required settings. You can create **TSVB** visualizations with only {{data-sources}}, or {{es}} index strings.
-
-When you use only {{data-sources}}, you are able to:
-
-* Create visualizations with runtime fields
-* Add URL drilldowns
-* Add interactive filters for time series visualizations
-* Improve performance
-
-::::{important}
-:name: tsvb-index-patterns-mode
-
-Creating **TSVB** visualizations with an {{es}} index string is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. By default, you create **TSVB** visualizations with only {{data-sources}}. To use an {{es}} index string, contact your administrator, or go to [Advanced Settings](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/advanced-options.html) and set `metrics:allowStringIndices` to `true`.
-::::
-
-
-1. On the dashboard, click **Select type**, then select **TSVB**.
-2. In **TSVB**, click **Panel options**, then specify the **Data** settings.
-3. Open the **Data view mode** options next to the **Data view** dropdown.
-4. Select **Use only {{kib}} {data-sources}**.
-5. From the **Data view** dropdown, select the {{data-source}}, then select the **Time field** and **Interval**.
-6. Select a **Drop last bucket** option.
-
- By default, **TSVB** drops the last bucket because the time filter intersects the time range of the last bucket. To view the partial data, select **No**.
-
-7. To view a filtered set of documents, enter [KQL filters](../query-filter/languages/kql.md) in the **Panel filter** field.
-
-
-#### Configure the series [tsvb-function-reference]
-
-Each **TSVB** visualization shares the same options to create a **Series**. Each series can be thought of as a separate {{es}} aggregation. The **Options** control the styling and {{es}} options, and are inherited from **Panel options**. When you have separate options for each series, you can compare different {{es}} indices, and view two time ranges from the same index.
-
-To configure the value of each series, select the function, then configure the function inputs. Only the last function is displayed.
-
-1. From the **Aggregation** dropdown, select the function for the series. **TSVB** provides you with shortcuts for some frequently-used functions:
-
- **Filter Ratio**
- : Returns a percent value by calculating a metric on two sets of documents. For example, calculate the error rate as a percentage of the overall events over time.
-
- **Counter Rate**
- : Used when dealing with monotonically increasing counters. Shortcut for **Max**, **Derivative**, and **Positive Only**.
-
- **Positive Only**
- : Removes any negative values from the results, which can be used as a post-processing step after a derivative.
-
- **Series Agg**
- : Applies a function to all of the **Group by** series to reduce the values to a single number. This function must always be the last metric in the series. For example, if the **Time Series** visualization shows 10 series, the sum **Series Agg** calculates the sum of all 10 bars and outputs a single Y value per X value. This is often confused with the overall sum function, which outputs a single Y value per unique series.
-
- **Math**
- : For each series, apply simple and advanced calculations. Only use **Math** for the last function in a series.
-
-2. To display each group separately, select one of the following options from the **Group by** dropdown:
-
- * **Filters** — Groups the data into the specified filters. To differentiate the groups, assign a color to each filter.
- * **Terms** — Displays the top values of the field. The color is only configurable in the **Time Series** chart. To configure, click **Options**, then select an option from the **Split color theme** dropdown.
-
-3. Click **Options**, then configure the inputs for the function. For example, to use a different field format, make a selection from the **Data formatter** dropdown.
-
-
-#### TSVB visualization options [configure-the-visualizations]
-
-The configuration options differ for each **TSVB** visualization.
-
-
-##### Time Series [tsvb-time-series]
-
-By default, the y-axis displays the full range of data, including zero. To automatically scale the y-axis from the minimum to maximum values of the data, click **Data > Options > Fill**, then enter `0` in the **Fill** field. You can add annotations to the x-axis based on timestamped documents in a separate {{es}} index.
-
-
-##### All chart types except Time Series [all-chart-types-except-time-series]
-
-The **Data timerange mode** dropdown in **Panel options** controls the timespan that **TSVB** uses to match documents. **Last value** is unable to match all documents, only the specific interval. **Entire timerange** matches all documents specified in the time filter.
-
-
-##### Metric, Top N, and Gauge [metric-topn-gauge]
-
-**Color rules** in **Panel options** contains conditional coloring based on the values.
-
-
-##### Top N and Table [topn-table]
-
-When you click a series, **TSVB** applies a filter based on the series name. To change this behavior, click **Panel options**, then specify a URL in the **Item URL** field, which opens a URL instead of applying a filter on click.
-
-
-##### Markdown [tsvb-markdown]
-
-The **Markdown** visualization supports Markdown with Handlebar (mustache) syntax to insert dynamic data, and supports custom CSS.
-
-
-#### Open and edit TSVB visualizations in Lens [edit-visualizations-in-lens]
-
-When you open **TSVB** visualizations in **Lens**, all configuration options and annotations appear in the **Lens** visualization editor.
-
-You can open the following **TSVB** visualizations in **Lens**:
-
-* Time Series
-* Metric
-* Top N
-* Gauge
-* Table
-
-To get started, click **Edit visualization in Lens** in the toolbar.
-
-For more information, check out [Create visualizations with Lens](lens.md).
-
-
-#### View the visualization data requests [view-data-and-requests-tsvb]
-
-View the requests that collect the visualization data.
-
-1. In the toolbar, click **Inspect**.
-2. From the **Request** dropdown, select the series you want to view.
-
-
-#### Save and add the panel [save-the-tsvb-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-
-#### Frequently asked questions [tsvb-faq]
-
-For answers to frequently asked **TSVB** question, review the following.
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I create dashboard drilldowns for Top N and Table visualizations?**
-:name: how-do-i-create-dashboard-drilldowns
-
-You can create dashboard drilldowns that include the specified time range for **Top N** and **Table** visualizations.
-
-1. Open the dashboard that you want to link to, then copy the URL.
-2. Open the dashboard with the **Top N** and **Table** visualization panel, then click **Edit** in the toolbar.
-3. Open the **Top N** or **Table** panel menu, then select **Edit visualization**.
-4. Click **Panel options**.
-5. In the **Item URL** field, enter the URL.
-
- For example `dashboards#/view/f193ca90-c9f4-11eb-b038-dd3270053a27`.
-
-6. Click **Save and return**.
-7. In the toolbar, click **Save as**, then make sure **Store time with dashboard** is deselected.
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I base drilldown URLs on my data?**
-:name: how-do-i-base-drilldowns-on-data
-
-You can build drilldown URLs dynamically with your visualization data.
-
-Do this by adding the `{{key}}` placeholder to your URL
-
-For example `https://example.org/{{key}}`
-
-This instructs TSVB to substitute the value from your visualization wherever it sees `{{key}}`.
-
-If your data contain reserved or invalid URL characters such as "#" or "&", you should apply a transform to URL-encode the key like this `{{encodeURIComponent key}}`. If you are dynamically constructing a drilldown to another location in Kibana (for example, clicking a table row takes to you a value-scoped Discover session), you will likely want to Rison-encode your key as it may contain invalid Rison characters. ([Rison](https://github.com/Nanonid/rison#rison---compact-data-in-uris) is the serialization format many parts of Kibana use to store information in their URL.)
-
-For example: `discover#/view/0ac50180-82d9-11ec-9f4a-55de56b00cc0?_a=(filters:!((query:(match_phrase:(foo.keyword:{{rison key}})))))`
-
-If both conditions apply, you can cover all cases by applying both transforms: `{{encodeURIComponent (rison key)}}`.
-
-Technical note: TSVB uses [Handlebars](https://handlebarsjs.com/) to perform these interpolations. `rison` and `encodeURIComponent` are custom Handlebars helpers provided by Kibana.
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **Why is my TSVB visualization missing data?**
-:name: why-is-my-tsvb-visualiztion-missing-data
-
-It depends, but most often there are two causes:
-
-* For **Time series** visualizations with a derivative function, the time interval can be too small. Derivatives require sequential values.
-* For all other **TSVB** visualizations, the cause is probably the **Data timerange mode**, which is controlled by **Panel options > Data timerange mode > Entire time range**. By default, **TSVB** displays the last whole bucket. For example, if the time filter is set to **Last 24 hours**, and the current time is 9:41, **TSVB** displays only the last 10 minutes — from 9:30 to 9:40.
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I calculate the difference between two data series?**
-:name: how-do-i-calculate-the-difference-between-two-data-series
-
-Performing math across data series is unsupported in **TSVB**. To calculate the difference between two data series, use [**Timelion**](#timelion) or [**Vega**](custom-visualizations-with-vega.md).
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I compare the current versus previous month?**
-:name: how-do-i-compare-the-current-versus-previous-month
-
-**TSVB** can display two series with time offsets, but it can’t perform math across series. To add a time offset:
-
-1. Click **Clone Series**, then choose a color for the new series.
-
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-tsvb_clone_series.png
- :alt: Clone Series action
- :class: screenshot
- :::
-
-2. Click **Options**, then enter the offset value in the **Offset series time by** field.
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I calculate a month over month change?**
-:name: how-do-i-calculate-a-month-over-month-change
-
-The ability to calculate a month over month change is not fully supported in **TSVB**, but there is a special case that is supported *if* the time filter is set to 3 months or more *and* the **Interval** is `1m`. Use the **Derivative** to get the absolute monthly change. To convert to a percent, add the **Math** function with the `params.current / (params.current - params.derivative)` formula, then select **Percent** from the **Data Formatter** dropdown.
-
-For other types of month over month calculations, use [**Timelion**](#timelion) or [**Vega**](custom-visualizations-with-vega.md).
-
-::::
-
-
-::::{dropdown} **How do I calculate the duration between the start and end of an event?**
-:name: calculate-duration-start-end
-
-Calculating the duration between the start and end of an event is unsupported in **TSVB** because **TSVB** requires correlation between different time periods. **TSVB** requires that the duration is pre-calculated.
-
-::::
-
-
-
-## Timelion [timelion]
-
-To use **Timelion**, you define a graph by chaining functions together, using the **Timelion**-specific syntax. The syntax enables some features that classical point series charts don’t offer, such as pulling data from different indices or data sources into one graph.
-
-**Timelion** is driven by a simple expression language that you use to:
-
-* Retrieve time series data from one or more indices
-* Perform math across two or more time series
-* Visualize the results
-
-
-
-
-#### Timelion expressions [_timelion_expressions]
-
-Timelion functions always start with a dot, followed by the function name, followed by parentheses containing all the parameters to the function.
-
-The `.es` (or `.elasticsearch` if you are a fan of typing long words) function gathers data from {{es}} and draws it over time. By default the .es function will just count the number of documents, resulting in a graph showing the amount of documents over time.
-
-
-#### Function parameters [_function_parameters]
-
-Functions can have multiple parameters, and so does the `.es` function. Each parameter has a name, that you can use inside the parentheses to set its value. The parameters also have an order, which is shown by the autocompletion or the documentation (using the Docs button in the top menu).
-
-If you don’t specify the parameter name, timelion assigns the values to the parameters in the order, they are listed in the documentation.
-
-The fist parameter of the .es function is the parameter q (for query), which is a Query String used to filter the data for this series. You can also explicitly reference this parameter by its name, and I would always recommend doing so as soon as you are passing more than one parameter to the function. The following two expressions are thus equivalent:
-
-Multiple parameters are separated by a comma. The .es function has another parameter called index, that can be used to specify a {{data-source}} for this series, so the query won’t be executed against all indexes (or whatever you changed the setting to).
-
-If the value of your parameter contains spaces or commas you have to put the value in single or double quotes. You can omit these quotes otherwise.
-
-
-##### .yaxis() function [customize-data-series-y-axis]
-
-{{kib}} supports many y-axis scales and ranges for your data series.
-
-The `.yaxis()` function supports the following parameters:
-
-* **yaxis** — The numbered y-axis to plot the series on. For example, use `.yaxis(2)` to display a second y-axis.
-* **min** — The minimum value for the y-axis range.
-* **max** — The maximum value for the y-axis range.
-* **position** — The location of the units. Values include `left` or `right`.
-* **label** — The label for the axis.
-* **color** — The color of the axis label.
-* **units** — The function to use for formatting the y-axis labels. Values include `bits`, `bits/s`, `bytes`, `bytes/s`, `currency(:ISO 4217 currency code)`, `percent`, and `custom(:prefix:suffix)`.
-* **tickDecimals** — The tick decimal precision.
-
-Example:
-
-```text
-.es(index= kibana_sample_data_logs,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:bytes')
- .label('Average Bytes for request')
- .title('Memory consumption over time in bytes').yaxis(1,units=bytes,position=left), <1>
-.es(index= kibana_sample_data_logs,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric=avg:machine.ram)
- .label('Average Machine RAM amount').yaxis(2,units=bytes,position=right) <2>
-```
-
-1. `.yaxis(1,units=bytes,position=left)` — Specifies the first y-axis for the first data series, and changes the units on the left.
-2. `.yaxis(2,units=bytes,position=left)` — Specifies the second y-axis for the second data series, and changes the units on the right.
-
-
-
-### Tutorial: Create visualizations with Timelion [_tutorial_create_visualizations_with_timelion]
-
-You collected data from your operating system using Metricbeat, and you want to visualize and analyze the data on a dashboard. To create panels of the data, use **Timelion** to create a time series visualization,
-
-
-#### Add the data and create the dashboard [_add_the_data_and_create_the_dashboard_2]
-
-Set up Metricbeat, then create the dashboard.
-
-1. To set up Metricbeat, go to [Metricbeat quick start: installation and configuration](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/current/metricbeat-installation-configuration.html)
-2. Go to **Dashboards**.
-3. On the **Dashboards** page, click **Create dashboard**.
-
-
-#### Open and set up Timelion [_open_and_set_up_timelion]
-
-Open **Timelion** and change the time range.
-
-1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**, then select **Timelion**.
-2. Make sure the [time filter](../query-filter/filtering.md) is **Last 7 days**.
-
-
-#### Create a time series visualization [timelion-tutorial-create-time-series-visualizations]
-
-To compare the real-time percentage of CPU time spent in user space to the results offset by one hour, create a time series visualization.
-
-
-##### Define the functions [define-the-functions]
-
-To track the real-time percentage of CPU, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
-```
-
-
-##### Compare the data [compare-the-data]
-
-To compare two data sets, add another series, and offset the data back by one hour, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct'),
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
-```
-
-
-##### Add label names [add-label-names]
-
-To easily distinguish between the two data sets, add label names, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('last hour'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('current hour')
-```
-
-
-##### Add a title [add-a-title]
-
-To make is easier for unfamiliar users to understand the purpose of the visualization, add a title, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('last hour'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('current hour')
- .title('CPU usage over time')
-```
-
-
-##### Change the appearance of the chart lines [change-the-chart-type]
-
-To differentiate between the current hour and the last hour, change the appearance of the chart lines, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('last hour')
- .lines(fill=1,width=0.5),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('current hour')
- .title('CPU usage over time')
-```
-
-
-##### Change the line colors [change-the-line-colors]
-
-**Timelion** supports standard color names, hexadecimal values, or a color schema for grouped data.
-
-To make the first data series stand out, change the line colors, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('last hour')
- .lines(fill=1,width=0.5)
- .color(gray),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('current hour')
- .title('CPU usage over time')
- .color(#1E90FF)
-```
-
-
-##### Adjust the legend [make-adjustments-to-the-legend]
-
-Move the legend to the north west position with two columns, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(offset=-1h,
- index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('last hour')
- .lines(fill=1,width=0.5)
- .color(gray),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
- .label('current hour')
- .title('CPU usage over time')
- .color(#1E90FF)
- .legend(columns=2, position=nw)
-```
-
-:::{image} ../../images/kibana-timelion-customize04.png
-:alt: Final time series visualization
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-
-
-##### Save and add the panel [save-the-timelion-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-
-### Visualize the inbound and outbound network traffic [timelion-tutorial-create-visualizations-with-mathematical-functions]
-
-To create a visualization for inbound and outbound network traffic, use mathematical functions.
-
-
-#### Define the functions [mathematical-functions-define-functions]
-
-To start tracking the inbound and outbound network traffic, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
-```
-
-
-#### Plot the rate of change [mathematical-functions-plot-change]
-
-To easily monitor the inbound traffic, plots the change in values over time, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
- .derivative()
-```
-
-Add a similar calculation for outbound traffic, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
- .derivative(),
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .multiply(-1) <1>
-```
-
-1. `.multiply(-1)` converts the outbound network traffic to a negative value since the outbound network traffic is leaving your machine. `.multiply()` multiplies the data series by a number, the result of a data series, or a list of data series.
-
-
-
-#### Change the data metric [mathematical-functions-convert-data]
-
-To make the data easier to analyze, change the data metric from `bytes` to `megabytes`, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .divide(1048576),
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .multiply(-1)
- .divide(1048576) <1>
-```
-
-1. `.divide()` accepts the same input as `.multiply()`, then divides the data series by the defined divisor.
-
-
-
-#### Customize and format the visualization [mathematical-functions-add-labels]
-
-Customize and format the visualization using the following functions, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .divide(1048576)
- .lines(fill=2, width=1)
- .color(green)
- .label("Inbound traffic")
- .title("Network traffic (MB/s)"),
-.es(index=metricbeat*,
- timefield=@timestamp,
- metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
- .derivative()
- .multiply(-1)
- .divide(1048576)
- .lines(fill=2, width=1)
- .color(blue)
- .label("Outbound traffic")
- .legend(columns=2, position=nw)
-```
-
-:::{image} ../../images/kibana-timelion-math05.png
-:alt: Final visualization that displays inbound and outbound network traffic
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-
-
-##### Save and add the panel [save-the-network-timelion-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-
-#### Detect outliers and discover patterns over time [timelion-tutorial-create-visualizations-withconditional-logic-and-tracking-trends]
-
-To easily detect outliers and discover patterns over time, modify the time series data with conditional logic and create a trend with a moving average.
-
-With **Timelion** conditional logic, you can use the following operator values to compare your data:
-
-`eq`
-: equal
-
-`ne`
-: not equal
-
-`lt`
-: less than
-
-`lte`
-: less than or equal to
-
-`gt`
-: greater than
-
-`gte`
-: greater than or equal to
-
-
-##### Define the functions [conditional-define-functions]
-
-To chart the maximum value of `system.memory.actual.used.bytes`, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
-```
-
-
-##### Track used memory [conditional-track-memory]
-
-To track the amount of memory used, create two thresholds, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt, <1>
- 11300000000, <2>
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('warning')
- .color('#FFCC11'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,
- 11375000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('severe')
- .color('red')
-```
-
-1. `if()` compares each point to a number. When the condition is `true`, adjust the styling. When the condition is `false`, use the default styling.
-2. **Timelion** conditional logic for the *greater than* operator. In this example, the warning threshold is 11.3GB (`11300000000`), and the severe threshold is 11.375GB (`11375000000`). If the threshold values are too high or low for your machine, adjust the values.
-
-
-
-##### Determine the trend [conditional-determine-trend]
-
-To determine the trend, create a new data series, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,11300000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('warning')
- .color('#FFCC11'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,11375000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null).
- label('severe')
- .color('red'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .mvavg(10) <1>
-```
-
-1. `mvavg()` calculates the moving average over a specified period of time. In this example, `.mvavg(10)` creates a moving average with a window of 10 data points.
-
-
-
-##### Customize and format the visualization [conditional-format-visualization]
-
-Customize and format the visualization using the following functions, then click **Update**:
-
-```text
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .label('max memory')
- .title('Memory consumption over time'),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,
- 11300000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('warning')
- .color('#FFCC11')
- .lines(width=5),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .if(gt,
- 11375000000,
- .es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
- null)
- .label('severe')
- .color('red')
- .lines(width=5),
-.es(index=metricbeat-*,
- timefield='@timestamp',
- metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
- .mvavg(10)
- .label('mvavg')
- .lines(width=2)
- .color(#5E5E5E)
- .legend(columns=4, position=nw)
-```
-
-:::{image} ../../images/kibana-timelion-conditional04.png
-:alt: Final visualization that displays outliers and patterns over time
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-
-
-##### Save and add the panel [save-the-outlier-timelion-panel]
-
-Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
-
-To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
-
-1. Click **Save to library**.
-2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../find-and-organize/tags.md).
-3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
-4. Click **Save and return**.
-
-To save the panel to the dashboard:
-
-1. Click **Save and return**.
-2. Add an optional title to the panel.
-
- 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
- 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
- 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
-
-
-For more information about **Timelion** conditions, refer to [I have but one .condition()](https://www.elastic.co/blog/timeseries-if-then-else-with-timelion).
+- [Aggregation-based](legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md)
+- [TSVB](legacy-editors/tsvb.md)
+- [Timelion](legacy-editors/timelion.md)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d5a9573488
--- /dev/null
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md
@@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
+# Aggregation-based [add-aggregation-based-visualization-panels]
+
+Aggregation-based visualizations are the core {{kib}} panels, and are not optimized for a specific use case.
+
+With aggregation-based visualizations, you can:
+
+* Split charts up to three aggregation levels, which is more than **Lens** and **TSVB**
+* Create visualization with non-time series data
+* Use a [Discover session](../../discover/save-open-search.md) as an input
+* Sort data tables and use the summary row and percentage column features
+* Assign colors to data series
+* Extend features with plugins
+
+Aggregation-based visualizations include the following limitations:
+
+* Limited styling options
+* Math is unsupported
+* Multiple indices is unsupported
+
+
+## Types of aggregation-based visualizations [types-of-visualizations]
+
+{{kib}} supports the following types of aggregation-based visualizations.
+
+| | |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Area**: Displays data points, connected by a line, where the area between the line and axes are shaded.Use area charts to compare two or more categories over time, and display the magnitude of trends. |  |
+| **Data table**: Displays your aggregation results in a tabular format. Use data tables to display server configuration details, track counts, min,or max values for a specific field, and monitor the status of key services. |  |
+| **Gauge**: Displays your data along a scale that changes color according to where your data falls on the expected scale. Use the gauge to show how metricvalues relate to reference threshold values, or determine how a specified field is performing versus how it is expected to perform. |  |
+| **Goal**: Displays how your metric progresses toward a fixed goal. Use the goal to display an easy to read visual of the status of your goal progression. |  |
+| **Heat map**: Displays graphical representations of data where the individual values are represented by colors. Use heat maps when your data set includescategorical data. For example, use a heat map to see the flights of origin countries compared to destination countries using the sample flight data. |  |
+| **Horizontal Bar**: Displays bars side-by-side where each bar represents a category. Use bar charts to compare data across alarge number of categories, display data that includes categories with negative values, and easily identifythe categories that represent the highest and lowest values. {{kib}} also supports vertical bar charts. |  |
+| **Line**: Displays data points that are connected by a line. Use line charts to visualize a sequence of values, discovertrends over time, and forecast future values. |  |
+| **Metric**: Displays a single numeric value for an aggregation. Use the metric visualization when you have a numeric value that is powerful enough to tella story about your data. |  |
+| **Pie**: Displays slices that represent a data category, where the slice size is proportional to the quantity it represents.Use pie charts to show comparisons between multiple categories, illustrate the dominance of one category over others,and show percentage or proportional data. |  |
+| **Tag cloud**: Graphical representations of how frequently a word appears in the source text. Use tag clouds to easily produce a summary of large documents andcreate visual art for a specific topic. |  |
+
+
+## Create an aggregation-based visualization panel [create-aggregation-based-panel]
+
+Choose the type of visualization you want to create, then use the editor to configure the options.
+
+1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**.
+
+ 1. Select the visualization type you want to create.
+ 2. Select the data source you want to visualize.
+
+ ::::{note}
+ There is no performance impact on the data source you select. For example, saved Discover sessions perform the same as {{data-sources}}.
+ ::::
+
+2. Add the [aggregations](../supported-chart-types.md#aggregation-reference) you want to visualize using the editor, then click **Update**.
+
+ ::::{note}
+ For the **Date Histogram** to use an **auto interval**, the date field must match the primary time field of the {{data-source}}.
+ ::::
+
+3. To change the order, drag and drop the aggregations in the editor.
+
+ 
+
+4. To customize the series colors, click the series in the legend, then select the color you want to use.
+
+ 
+
+
+
+## Try it: Create an aggregation-based bar chart [try-it-aggregation-based-panel]
+
+You collected data from your web server, and you want to visualize and analyze the data on a dashboard. To create a dashboard panel of the data, create a bar chart that displays the top five log traffic sources for every three hours.
+
+
+### Add the data and create the dashboard [_add_the_data_and_create_the_dashboard]
+
+Add the sample web logs data that you’ll use to create the bar chart, then create the dashboard.
+
+1. [Install the web logs sample data set](../../overview/kibana-quickstart.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana).
+2. Go to **Dashboards**.
+3. On the **Dashboards** page, click **Create dashboard**.
+
+
+### Open and set up the aggregation-based bar chart [_open_and_set_up_the_aggregation_based_bar_chart]
+
+Open the **Aggregation based** editor and change the time range.
+
+1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**, select **Vertical bar**, then select **Kibana Sample Data Logs**.
+2. Make sure the [time filter](../../query-filter/filtering.md) is **Last 7 days**.
+
+
+### Create the bar chart [tutorial-configure-the-bar-chart]
+
+To create the bar chart, add a [bucket aggregation](../supported-chart-types.md#bucket-aggregations), then add the terms sub-aggregation to display the top values.
+
+1. Add a **Buckets** aggregation.
+
+ 1. Click **Add**, then select **X-axis**.
+ 2. From the **Aggregation** dropdown, select **Date Histogram**.
+ 3. Click **Update**.
+
+ 
+
+2. To show the top five log traffic sources, add a sub-bucket aggregation.
+
+ 1. Click **Add**, then select **Split series**.
+
+ ::::{tip}
+ Aggregation-based panels support a maximum of three **Split series**.
+ ::::
+
+ 2. From the **Sub aggregation** dropdown, select **Terms**.
+ 3. From the **Field** dropdown, select **geo.src**.
+ 4. Click **Update**.
+ 
+
+
+
+## Open and edit aggregation-based visualizations in Lens [edit-agg-based-visualizations-in-lens]
+
+When you open aggregation-based visualizations in **Lens**, all configuration options appear in the **Lens** visualization editor.
+
+You can open the following aggregation-based visualizations in **Lens**:
+
+* Area
+* Data table
+* Gauge
+* Goal
+* Heat map
+* Horizontal bar
+* Line
+* Metric
+* Pie
+* Vertical bar
+
+To get started, click **Edit visualization in Lens** in the toolbar.
+
+For more information, check out [Create visualizations with Lens](../lens.md).
+
+
+### Save and add the panel [save-the-aggregation-based-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f65c40dd35
--- /dev/null
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md
@@ -0,0 +1,553 @@
+# Timelion [timelion]
+
+To use **Timelion**, you define a graph by chaining functions together, using the **Timelion**-specific syntax. The syntax enables some features that classical point series charts don’t offer, such as pulling data from different indices or data sources into one graph.
+
+**Timelion** is driven by a simple expression language that you use to:
+
+* Retrieve time series data from one or more indices
+* Perform math across two or more time series
+* Visualize the results
+
+
+
+
+## Timelion expressions [_timelion_expressions]
+
+Timelion functions always start with a dot, followed by the function name, followed by parentheses containing all the parameters to the function.
+
+The `.es` (or `.elasticsearch` if you are a fan of typing long words) function gathers data from {{es}} and draws it over time. By default the .es function will just count the number of documents, resulting in a graph showing the amount of documents over time.
+
+
+## Function parameters [_function_parameters]
+
+Functions can have multiple parameters, and so does the `.es` function. Each parameter has a name, that you can use inside the parentheses to set its value. The parameters also have an order, which is shown by the autocompletion or the documentation (using the Docs button in the top menu).
+
+If you don’t specify the parameter name, timelion assigns the values to the parameters in the order, they are listed in the documentation.
+
+The fist parameter of the .es function is the parameter q (for query), which is a Query String used to filter the data for this series. You can also explicitly reference this parameter by its name, and I would always recommend doing so as soon as you are passing more than one parameter to the function. The following two expressions are thus equivalent:
+
+Multiple parameters are separated by a comma. The .es function has another parameter called index, that can be used to specify a {{data-source}} for this series, so the query won’t be executed against all indexes (or whatever you changed the setting to).
+
+If the value of your parameter contains spaces or commas you have to put the value in single or double quotes. You can omit these quotes otherwise.
+
+
+### .yaxis() function [customize-data-series-y-axis]
+
+{{kib}} supports many y-axis scales and ranges for your data series.
+
+The `.yaxis()` function supports the following parameters:
+
+* **yaxis** — The numbered y-axis to plot the series on. For example, use `.yaxis(2)` to display a second y-axis.
+* **min** — The minimum value for the y-axis range.
+* **max** — The maximum value for the y-axis range.
+* **position** — The location of the units. Values include `left` or `right`.
+* **label** — The label for the axis.
+* **color** — The color of the axis label.
+* **units** — The function to use for formatting the y-axis labels. Values include `bits`, `bits/s`, `bytes`, `bytes/s`, `currency(:ISO 4217 currency code)`, `percent`, and `custom(:prefix:suffix)`.
+* **tickDecimals** — The tick decimal precision.
+
+Example:
+
+```text
+.es(index= kibana_sample_data_logs,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:bytes')
+ .label('Average Bytes for request')
+ .title('Memory consumption over time in bytes').yaxis(1,units=bytes,position=left), <1>
+.es(index= kibana_sample_data_logs,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric=avg:machine.ram)
+ .label('Average Machine RAM amount').yaxis(2,units=bytes,position=right) <2>
+```
+
+1. `.yaxis(1,units=bytes,position=left)` — Specifies the first y-axis for the first data series, and changes the units on the left.
+2. `.yaxis(2,units=bytes,position=left)` — Specifies the second y-axis for the second data series, and changes the units on the right.
+
+
+
+## Tutorial: Create visualizations with Timelion [_tutorial_create_visualizations_with_timelion]
+
+You collected data from your operating system using Metricbeat, and you want to visualize and analyze the data on a dashboard. To create panels of the data, use **Timelion** to create a time series visualization,
+
+
+## Add the data and create the dashboard [_add_the_data_and_create_the_dashboard_2]
+
+Set up Metricbeat, then create the dashboard.
+
+1. To set up Metricbeat, go to [Metricbeat quick start: installation and configuration](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/metricbeat/current/metricbeat-installation-configuration.html)
+2. Go to **Dashboards**.
+3. On the **Dashboards** page, click **Create dashboard**.
+
+
+## Open and set up Timelion [_open_and_set_up_timelion]
+
+Open **Timelion** and change the time range.
+
+1. On the dashboard, click **All types > Aggregation based**, then select **Timelion**.
+2. Make sure the [time filter](../../query-filter/filtering.md) is **Last 7 days**.
+
+
+## Create a time series visualization [timelion-tutorial-create-time-series-visualizations]
+
+To compare the real-time percentage of CPU time spent in user space to the results offset by one hour, create a time series visualization.
+
+
+### Define the functions [define-the-functions]
+
+To track the real-time percentage of CPU, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+```
+
+
+### Compare the data [compare-the-data]
+
+To compare two data sets, add another series, and offset the data back by one hour, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct'),
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+```
+
+
+### Add label names [add-label-names]
+
+To easily distinguish between the two data sets, add label names, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('last hour'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('current hour')
+```
+
+
+### Add a title [add-a-title]
+
+To make is easier for unfamiliar users to understand the purpose of the visualization, add a title, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('last hour'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('current hour')
+ .title('CPU usage over time')
+```
+
+
+### Change the appearance of the chart lines [change-the-chart-type]
+
+To differentiate between the current hour and the last hour, change the appearance of the chart lines, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('last hour')
+ .lines(fill=1,width=0.5),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('current hour')
+ .title('CPU usage over time')
+```
+
+
+### Change the line colors [change-the-line-colors]
+
+**Timelion** supports standard color names, hexadecimal values, or a color schema for grouped data.
+
+To make the first data series stand out, change the line colors, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('last hour')
+ .lines(fill=1,width=0.5)
+ .color(gray),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('current hour')
+ .title('CPU usage over time')
+ .color(#1E90FF)
+```
+
+
+### Adjust the legend [make-adjustments-to-the-legend]
+
+Move the legend to the north west position with two columns, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(offset=-1h,
+ index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('last hour')
+ .lines(fill=1,width=0.5)
+ .color(gray),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
+ .label('current hour')
+ .title('CPU usage over time')
+ .color(#1E90FF)
+ .legend(columns=2, position=nw)
+```
+
+:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-timelion-customize04.png
+:alt: Final time series visualization
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+
+
+### Save and add the panel [save-the-timelion-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
+
+## Visualize the inbound and outbound network traffic [timelion-tutorial-create-visualizations-with-mathematical-functions]
+
+To create a visualization for inbound and outbound network traffic, use mathematical functions.
+
+
+## Define the functions [mathematical-functions-define-functions]
+
+To start tracking the inbound and outbound network traffic, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+```
+
+
+## Plot the rate of change [mathematical-functions-plot-change]
+
+To easily monitor the inbound traffic, plots the change in values over time, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+```
+
+Add a similar calculation for outbound traffic, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+ .derivative(),
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .multiply(-1) <1>
+```
+
+1. `.multiply(-1)` converts the outbound network traffic to a negative value since the outbound network traffic is leaving your machine. `.multiply()` multiplies the data series by a number, the result of a data series, or a list of data series.
+
+
+
+## Change the data metric [mathematical-functions-convert-data]
+
+To make the data easier to analyze, change the data metric from `bytes` to `megabytes`, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .divide(1048576),
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .multiply(-1)
+ .divide(1048576) <1>
+```
+
+1. `.divide()` accepts the same input as `.multiply()`, then divides the data series by the defined divisor.
+
+
+
+## Customize and format the visualization [mathematical-functions-add-labels]
+
+Customize and format the visualization using the following functions, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .divide(1048576)
+ .lines(fill=2, width=1)
+ .color(green)
+ .label("Inbound traffic")
+ .title("Network traffic (MB/s)"),
+.es(index=metricbeat*,
+ timefield=@timestamp,
+ metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
+ .derivative()
+ .multiply(-1)
+ .divide(1048576)
+ .lines(fill=2, width=1)
+ .color(blue)
+ .label("Outbound traffic")
+ .legend(columns=2, position=nw)
+```
+
+:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-timelion-math05.png
+:alt: Final visualization that displays inbound and outbound network traffic
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+
+
+### Save and add the panel [save-the-network-timelion-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
+
+## Detect outliers and discover patterns over time [timelion-tutorial-create-visualizations-withconditional-logic-and-tracking-trends]
+
+To easily detect outliers and discover patterns over time, modify the time series data with conditional logic and create a trend with a moving average.
+
+With **Timelion** conditional logic, you can use the following operator values to compare your data:
+
+`eq`
+: equal
+
+`ne`
+: not equal
+
+`lt`
+: less than
+
+`lte`
+: less than or equal to
+
+`gt`
+: greater than
+
+`gte`
+: greater than or equal to
+
+
+### Define the functions [conditional-define-functions]
+
+To chart the maximum value of `system.memory.actual.used.bytes`, enter the following in the **Timelion Expression** field, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+```
+
+
+### Track used memory [conditional-track-memory]
+
+To track the amount of memory used, create two thresholds, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt, <1>
+ 11300000000, <2>
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('warning')
+ .color('#FFCC11'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,
+ 11375000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('severe')
+ .color('red')
+```
+
+1. `if()` compares each point to a number. When the condition is `true`, adjust the styling. When the condition is `false`, use the default styling.
+2. **Timelion** conditional logic for the *greater than* operator. In this example, the warning threshold is 11.3GB (`11300000000`), and the severe threshold is 11.375GB (`11375000000`). If the threshold values are too high or low for your machine, adjust the values.
+
+
+
+### Determine the trend [conditional-determine-trend]
+
+To determine the trend, create a new data series, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,11300000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('warning')
+ .color('#FFCC11'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,11375000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null).
+ label('severe')
+ .color('red'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .mvavg(10) <1>
+```
+
+1. `mvavg()` calculates the moving average over a specified period of time. In this example, `.mvavg(10)` creates a moving average with a window of 10 data points.
+
+
+
+### Customize and format the visualization [conditional-format-visualization]
+
+Customize and format the visualization using the following functions, then click **Update**:
+
+```text
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .label('max memory')
+ .title('Memory consumption over time'),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,
+ 11300000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('warning')
+ .color('#FFCC11')
+ .lines(width=5),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .if(gt,
+ 11375000000,
+ .es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
+ null)
+ .label('severe')
+ .color('red')
+ .lines(width=5),
+.es(index=metricbeat-*,
+ timefield='@timestamp',
+ metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
+ .mvavg(10)
+ .label('mvavg')
+ .lines(width=2)
+ .color(#5E5E5E)
+ .legend(columns=4, position=nw)
+```
+
+:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-timelion-conditional04.png
+:alt: Final visualization that displays outliers and patterns over time
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+
+
+### Save and add the panel [save-the-outlier-timelion-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
+For more information about **Timelion** conditions, refer to [I have but one .condition()](https://www.elastic.co/blog/timeseries-if-then-else-with-timelion).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3813988427
--- /dev/null
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md
@@ -0,0 +1,257 @@
+# TSVB [tsvb-panel]
+
+**TSVB** is a set of visualization types that you configure and display on dashboards.
+
+With **TSVB**, you can:
+
+* Combine an infinite number of [aggregations](../supported-chart-types.md#aggregation-reference) to display your data.
+* Annotate time series data with timestamped events from an {{es}} index.
+* View the data in several types of visualizations, including charts, data tables, and markdown panels.
+* Display multiple [data views](../../find-and-organize/data-views.md) in each visualization.
+* Use custom functions and some math on aggregations.
+* Customize the data with labels and colors.
+
+:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-tsvb-screenshot.png
+:alt: TSVB overview
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+## Open and set up TSVB [tsvb-data-view-mode]
+
+Open **TSVB**, then configure the required settings. You can create **TSVB** visualizations with only {{data-sources}}, or {{es}} index strings.
+
+When you use only {{data-sources}}, you are able to:
+
+* Create visualizations with runtime fields
+* Add URL drilldowns
+* Add interactive filters for time series visualizations
+* Improve performance
+
+::::{important}
+:name: tsvb-index-patterns-mode
+
+Creating **TSVB** visualizations with an {{es}} index string is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. By default, you create **TSVB** visualizations with only {{data-sources}}. To use an {{es}} index string, contact your administrator, or go to [Advanced Settings](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/advanced-options.html) and set `metrics:allowStringIndices` to `true`.
+::::
+
+
+1. On the dashboard, click **Select type**, then select **TSVB**.
+2. In **TSVB**, click **Panel options**, then specify the **Data** settings.
+3. Open the **Data view mode** options next to the **Data view** dropdown.
+4. Select **Use only {{kib}} {data-sources}**.
+5. From the **Data view** dropdown, select the {{data-source}}, then select the **Time field** and **Interval**.
+6. Select a **Drop last bucket** option.
+
+ By default, **TSVB** drops the last bucket because the time filter intersects the time range of the last bucket. To view the partial data, select **No**.
+
+7. To view a filtered set of documents, enter [KQL filters](../../query-filter/languages/kql.md) in the **Panel filter** field.
+
+
+## Configure the series [tsvb-function-reference]
+
+Each **TSVB** visualization shares the same options to create a **Series**. Each series can be thought of as a separate {{es}} aggregation. The **Options** control the styling and {{es}} options, and are inherited from **Panel options**. When you have separate options for each series, you can compare different {{es}} indices, and view two time ranges from the same index.
+
+To configure the value of each series, select the function, then configure the function inputs. Only the last function is displayed.
+
+1. From the **Aggregation** dropdown, select the function for the series. **TSVB** provides you with shortcuts for some frequently-used functions:
+
+ **Filter Ratio**
+ : Returns a percent value by calculating a metric on two sets of documents. For example, calculate the error rate as a percentage of the overall events over time.
+
+ **Counter Rate**
+ : Used when dealing with monotonically increasing counters. Shortcut for **Max**, **Derivative**, and **Positive Only**.
+
+ **Positive Only**
+ : Removes any negative values from the results, which can be used as a post-processing step after a derivative.
+
+ **Series Agg**
+ : Applies a function to all of the **Group by** series to reduce the values to a single number. This function must always be the last metric in the series. For example, if the **Time Series** visualization shows 10 series, the sum **Series Agg** calculates the sum of all 10 bars and outputs a single Y value per X value. This is often confused with the overall sum function, which outputs a single Y value per unique series.
+
+ **Math**
+ : For each series, apply simple and advanced calculations. Only use **Math** for the last function in a series.
+
+2. To display each group separately, select one of the following options from the **Group by** dropdown:
+
+ * **Filters** — Groups the data into the specified filters. To differentiate the groups, assign a color to each filter.
+ * **Terms** — Displays the top values of the field. The color is only configurable in the **Time Series** chart. To configure, click **Options**, then select an option from the **Split color theme** dropdown.
+
+3. Click **Options**, then configure the inputs for the function. For example, to use a different field format, make a selection from the **Data formatter** dropdown.
+
+
+## TSVB visualization options [configure-the-visualizations]
+
+The configuration options differ for each **TSVB** visualization.
+
+
+### Time Series [tsvb-time-series]
+
+By default, the y-axis displays the full range of data, including zero. To automatically scale the y-axis from the minimum to maximum values of the data, click **Data > Options > Fill**, then enter `0` in the **Fill** field. You can add annotations to the x-axis based on timestamped documents in a separate {{es}} index.
+
+
+### All chart types except Time Series [all-chart-types-except-time-series]
+
+The **Data timerange mode** dropdown in **Panel options** controls the timespan that **TSVB** uses to match documents. **Last value** is unable to match all documents, only the specific interval. **Entire timerange** matches all documents specified in the time filter.
+
+
+### Metric, Top N, and Gauge [metric-topn-gauge]
+
+**Color rules** in **Panel options** contains conditional coloring based on the values.
+
+
+### Top N and Table [topn-table]
+
+When you click a series, **TSVB** applies a filter based on the series name. To change this behavior, click **Panel options**, then specify a URL in the **Item URL** field, which opens a URL instead of applying a filter on click.
+
+
+### Markdown [tsvb-markdown]
+
+The **Markdown** visualization supports Markdown with Handlebar (mustache) syntax to insert dynamic data, and supports custom CSS.
+
+
+## Open and edit TSVB visualizations in Lens [edit-visualizations-in-lens]
+
+When you open **TSVB** visualizations in **Lens**, all configuration options and annotations appear in the **Lens** visualization editor.
+
+You can open the following **TSVB** visualizations in **Lens**:
+
+* Time Series
+* Metric
+* Top N
+* Gauge
+* Table
+
+To get started, click **Edit visualization in Lens** in the toolbar.
+
+For more information, check out [Create visualizations with Lens](../lens.md).
+
+
+## View the visualization data requests [view-data-and-requests-tsvb]
+
+View the requests that collect the visualization data.
+
+1. In the toolbar, click **Inspect**.
+2. From the **Request** dropdown, select the series you want to view.
+
+
+## Save and add the panel [save-the-tsvb-panel]
+
+Save the panel to the **Visualize Library** and add it to the dashboard, or add it to the dashboard without saving.
+
+To save the panel to the **Visualize Library**:
+
+1. Click **Save to library**.
+2. Enter the **Title** and add any applicable [**Tags**](../../find-and-organize/tags.md).
+3. Make sure that **Add to Dashboard after saving** is selected.
+4. Click **Save and return**.
+
+To save the panel to the dashboard:
+
+1. Click **Save and return**.
+2. Add an optional title to the panel.
+
+ 1. In the panel header, click **No Title**.
+ 2. On the **Panel settings** window, select **Show title**.
+ 3. Enter the **Title**, then click **Save**.
+
+
+
+## Frequently asked questions [tsvb-faq]
+
+For answers to frequently asked **TSVB** question, review the following.
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I create dashboard drilldowns for Top N and Table visualizations?
+:name: how-do-i-create-dashboard-drilldowns
+
+You can create dashboard drilldowns that include the specified time range for **Top N** and **Table** visualizations.
+
+1. Open the dashboard that you want to link to, then copy the URL.
+2. Open the dashboard with the **Top N** and **Table** visualization panel, then click **Edit** in the toolbar.
+3. Open the **Top N** or **Table** panel menu, then select **Edit visualization**.
+4. Click **Panel options**.
+5. In the **Item URL** field, enter the URL.
+
+ For example `dashboards#/view/f193ca90-c9f4-11eb-b038-dd3270053a27`.
+
+6. Click **Save and return**.
+7. In the toolbar, click **Save as**, then make sure **Store time with dashboard** is deselected.
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I base drilldown URLs on my data?
+:name: how-do-i-base-drilldowns-on-data
+
+You can build drilldown URLs dynamically with your visualization data.
+
+Do this by adding the `{{key}}` placeholder to your URL
+
+For example `https://example.org/{{key}}`
+
+This instructs TSVB to substitute the value from your visualization wherever it sees `{{key}}`.
+
+If your data contain reserved or invalid URL characters such as "#" or "&", you should apply a transform to URL-encode the key like this `{{encodeURIComponent key}}`. If you are dynamically constructing a drilldown to another location in Kibana (for example, clicking a table row takes to you a value-scoped Discover session), you will likely want to Rison-encode your key as it may contain invalid Rison characters. ([Rison](https://github.com/Nanonid/rison#rison---compact-data-in-uris) is the serialization format many parts of Kibana use to store information in their URL.)
+
+For example: `discover#/view/0ac50180-82d9-11ec-9f4a-55de56b00cc0?_a=(filters:!((query:(match_phrase:(foo.keyword:{{rison key}})))))`
+
+If both conditions apply, you can cover all cases by applying both transforms: `{{encodeURIComponent (rison key)}}`.
+
+Technical note: TSVB uses [Handlebars](https://handlebarsjs.com/) to perform these interpolations. `rison` and `encodeURIComponent` are custom Handlebars helpers provided by Kibana.
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} Why is my TSVB visualization missing data?
+:name: why-is-my-tsvb-visualiztion-missing-data
+
+It depends, but most often there are two causes:
+
+* For **Time series** visualizations with a derivative function, the time interval can be too small. Derivatives require sequential values.
+* For all other **TSVB** visualizations, the cause is probably the **Data timerange mode**, which is controlled by **Panel options > Data timerange mode > Entire time range**. By default, **TSVB** displays the last whole bucket. For example, if the time filter is set to **Last 24 hours**, and the current time is 9:41, **TSVB** displays only the last 10 minutes — from 9:30 to 9:40.
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I calculate the difference between two data series?
+:name: how-do-i-calculate-the-difference-between-two-data-series
+
+Performing math across data series is unsupported in **TSVB**. To calculate the difference between two data series, use [**Timelion**](timelion.md) or [**Vega**](../custom-visualizations-with-vega.md).
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I compare the current versus previous month?
+:name: how-do-i-compare-the-current-versus-previous-month
+
+**TSVB** can display two series with time offsets, but it can’t perform math across series. To add a time offset:
+
+1. Click **Clone Series**, then choose a color for the new series.
+
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-tsvb_clone_series.png
+ :alt: Clone Series action
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
+
+2. Click **Options**, then enter the offset value in the **Offset series time by** field.
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I calculate a month over month change?
+:name: how-do-i-calculate-a-month-over-month-change
+
+The ability to calculate a month over month change is not fully supported in **TSVB**, but there is a special case that is supported *if* the time filter is set to 3 months or more *and* the **Interval** is `1m`. Use the **Derivative** to get the absolute monthly change. To convert to a percent, add the **Math** function with the `params.current / (params.current - params.derivative)` formula, then select **Percent** from the **Data Formatter** dropdown.
+
+For other types of month over month calculations, use [**Timelion**](timelion.md) or [**Vega**](../custom-visualizations-with-vega.md).
+
+::::
+
+
+::::{dropdown} How do I calculate the duration between the start and end of an event?
+:name: calculate-duration-start-end
+
+Calculating the duration between the start and end of an event is unsupported in **TSVB** because **TSVB** requires correlation between different time periods. **TSVB** requires that the duration is pre-calculated.
+
+::::
+
+
+
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md
index c5003774ba..c6c8906ba3 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md
@@ -63,10 +63,8 @@ Change the fields list to display a different {{data-source}}, different time ra
* If the fields list is empty, change the [time filter](../query-filter/filtering.md).
* To add fields, open the {{data-source}} dropdown, then select **Add a field to this {{data-source}}**.
-
- 
-
- For more information about adding fields to {{data-sources}} and examples, refer to [Explore your data with runtime fields](../find-and-organize/data-views.md#runtime-fields).
+ 
+ For more information about adding fields to {{data-sources}} and examples, refer to [Explore your data with runtime fields](../find-and-organize/data-views.md#runtime-fields).
@@ -118,10 +116,10 @@ To use a keyboard instead of a mouse, use the **Lens** fully accessible and cont
1. Select the field in the fields list or layer pane. Most fields have an inner and outer select state. The inner state opens a panel with detailed information or options. The outer state allows you to drag the field. Tab through the fields until you get the outer state on the field.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_drag_drop_2.png
- :alt: Lens drag and drop focus state
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_drag_drop_2.png
+ :alt: Lens drag and drop focus state
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
2. Complete the following actions:
@@ -130,10 +128,10 @@ To use a keyboard instead of a mouse, use the **Lens** fully accessible and cont
* To reorder the fields on the layer pane, use the Up and Down arrows.
* To duplicate an action, use the Left and Right arrows, then select the **Drop a field or click to add** field you want to use.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_drag_drop_3.gif
- :alt: Using drag and drop to reorder
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-lens_drag_drop_3.gif
+ :alt: Using drag and drop to reorder
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
3. To confirm the action, press Space bar. To cancel, press Esc.
@@ -453,7 +451,7 @@ To save the panel to the dashboard:
For answers to common **Lens** questions, review the following.
-::::{dropdown} **When should I normalize the data by unit or use a custom interval?**
+::::{dropdown} When should I normalize the data by unit or use a custom interval?
:name: when-should-i-normalize-the-data-by-unit-or-use-a-custom-interval
* **Normalize by unit** — Calculates the average for the interval. When you normalize the data by unit, the data appears less granular, but **Lens** is able to calculate the data faster.
@@ -474,7 +472,7 @@ To create a custom interval:
::::
-::::{dropdown} **What data is categorized as Other?**
+::::{dropdown} What data is categorized as Other?
:name: what-is-the-other-category
The **Other** category contains all of the documents that do not match the specified criteria or filters. Use **Other** when you want to compare a value, or multiple values, to a whole.
@@ -486,7 +484,7 @@ To disable **Group other values as "Other"**, click a field in the layer pane, c
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I add documents without a field?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I add documents without a field?
:name: how-can-i-include-documents-without-the-field-in-the-operation
By default, **Lens** retrieves only the documents from the fields. For bucket aggregations, such as **Top values**, you can add documents that do not contain the fields, which is helpful when you want to make a comparison to the whole documentation set.
@@ -497,7 +495,7 @@ By default, **Lens** retrieves only the documents from the fields. For bucket ag
::::
-::::{dropdown} **When do I use runtime fields vs. formula?**
+::::{dropdown} When do I use runtime fields vs. formula?
:name: when-do-i-use-runtime-fields-vs-formula
Use runtime fields to format, concatenate, and extract document-level fields. Runtime fields work across all of {{kib}} and are best used for smaller computations without compromising performance.
@@ -507,7 +505,7 @@ Use formulas to compare multiple {{es}} aggregations that can be filtered or shi
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Can I add more than one y-axis scale?**
+::::{dropdown} Can I add more than one y-axis scale?
:name: is-it-possible-to-have-more-than-one-Y-axis-scale
For each y-axis, you can select **Left** and **Right**, and configure a different scale.
@@ -515,7 +513,7 @@ For each y-axis, you can select **Left** and **Right**, and configure a differen
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Why is my value the incorrect color when I use value-based coloring?**
+::::{dropdown} Why is my value the incorrect color when I use value-based coloring?
:name: why-is-my-value-with-the-right-color-using-value-based-coloring
Here’s a short list of few different aspects to check:
@@ -532,7 +530,7 @@ Here’s a short list of few different aspects to check:
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I sort by multiple columns?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I sort by multiple columns?
:name: can-i-sort-by-multiple-columns
Multiple column sorting is unsupported, but is supported in **Discover**. For information on how to sort multiple columns in **Discover**, refer to [Explore the fields in your data](../discover/discover-get-started.md#explore-fields-in-your-data).
@@ -540,7 +538,7 @@ Multiple column sorting is unsupported, but is supported in **Discover**. For in
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Why is my field missing from the fields list?**
+::::{dropdown} Why is my field missing from the fields list?
:name: why-my-field-is-missing-from-the-fields-list
The following field types do not appear in the **Available fields** list:
@@ -555,7 +553,7 @@ Verify if the field appears in the **Empty fields** list. **Lens** uses heuristi
::::
-::::{dropdown} **What do I do with gaps in time series visualizations?**
+::::{dropdown} What do I do with gaps in time series visualizations?
:name: how-to-handle-gaps-in-time-series-visualizations
When you create **Area** and **Line** charts with sparse time series data, open **Visual options** in the editor toolbar, then select a **Missing values** option.
@@ -563,7 +561,7 @@ When you create **Area** and **Line** charts with sparse time series data, open
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Can I statically define the y-axis scale?**
+::::{dropdown} Can I statically define the y-axis scale?
:name: is-it-possible-to-change-the-scale-of-Y-axis
You can set the scale, or *bounds*, for area, bar, and line charts. You can configure the bounds for all functions, except **Percentile**. Logarithmic scales are unsupported.
@@ -573,7 +571,7 @@ To configure the bounds, use the menus in the editor toolbar. Bar and area chart
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Is it possible to display icons in data tables?**
+::::{dropdown} Is it possible to display icons in data tables?
:name: is-it-possible-to-show-icons-in-datatable
You can display icons with [field formatters](../find-and-organize/data-views.md) in data tables.
@@ -581,7 +579,7 @@ You can display icons with [field formatters](../find-and-organize/data-views.md
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I inspect {{es}} queries in visualizations?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I inspect {{es}} queries in visualizations?
:name: is-it-possible-to-inspect-the-elasticsearch-queries-in-Lens
You can inspect the requests sent by the visualization to {{es}} using the Inspector. It can be accessed within the editor or in the dashboard.
@@ -589,7 +587,7 @@ You can inspect the requests sent by the visualization to {{es}} using the Inspe
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I isolate a single series in a chart?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I isolate a single series in a chart?
:name: how-to-isolate-a-single-series-in-a-chart
For area, line, and bar charts, press Shift, then click the series in the legend. All other series are automatically deselected.
@@ -597,7 +595,7 @@ For area, line, and bar charts, press Shift, then click the series in the legend
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I visualize saved Discover sessions?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I visualize saved Discover sessions?
:name: is-it-possible-to-use-saved-serches-in-lens
Visualizing saved Discover sessions is unsupported.
@@ -605,7 +603,7 @@ Visualizing saved Discover sessions is unsupported.
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I change the number of suggestions?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I change the number of suggestions?
:name: is-it-possible-to-decrease-or-increase-the-number-of-suggestions
Configuring the **Suggestions** is unsupported.
@@ -613,15 +611,15 @@ Configuring the **Suggestions** is unsupported.
::::
-::::{dropdown} **Is it possible to have pagination in a data table?**
+::::{dropdown} Is it possible to have pagination in a data table?
:name: is-it-possible-to-have-pagination-for-datatable
-Pagination in a data table is unsupported. To use pagination in data tables, create an [aggregation-based data table](legacy-editors.md#types-of-visualizations).
+Pagination in a data table is unsupported. To use pagination in data tables, create an [aggregation-based data table](legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md#types-of-visualizations).
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How do I change the color for a single data point?**
+::::{dropdown} How do I change the color for a single data point?
:name: is-it-possible-to-select-color-for-specific-bar-or-point
Specifying the color for a single data point, such as a single bar or line, is unsupported.
@@ -629,7 +627,7 @@ Specifying the color for a single data point, such as a single bar or line, is u
::::
-::::{dropdown} **How does dynamic coloring work for the metric visualization?**
+::::{dropdown} How does dynamic coloring work for the metric visualization?
:name: dynamic-metric-coloring
In the color palette editor, if you select **Value type: Number** the colors are applied based on the **Primary metric** value.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md
index fb4c6ac02b..e894ecaa61 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md
@@ -51,10 +51,10 @@ To edit links panels:
1. Hover over the panel and click  to edit the link. The **Edit links panel** flyout appears.
2. Click  next to the link.
- :::{image} ../../images/kibana-edit-links-panel.png
- :alt: A screenshot displaying the Edit icon next to the link
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../images/kibana-edit-links-panel.png
+ :alt: A screenshot displaying the Edit icon next to the link
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
3. Edit the link as needed and then click **Update link**.
4. Click **Save**.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md
index 2d0f51e3e4..6854eb74d7 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md
@@ -4,11 +4,77 @@ mapped_urls:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/serverless/current/maps.html
---
-# Maps
+# Maps [maps]
% What needs to be done: Align serverless/stateful
% Use migrated content from existing pages that map to this page:
% - [ ] ./raw-migrated-files/kibana/kibana/maps.md
-% - [ ] ./raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md
\ No newline at end of file
+% - [ ] ./raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md
+
+
+Create beautiful maps from your geographical data. With **Maps**, you can:
+
+* Build maps with multiple layers and indices.
+* Animate spatial temporal data.
+* Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles.
+* Embed your map in dashboards.
+* Symbolize features using data values.
+* Focus on only the data that’s important to you.
+
+On Elastic Cloud Serverless, Maps is only available for Security projects [](../../solutions/security/elastic-security-serverless.md).
+
+
+## Build maps with multiple layers and indices [_build_maps_with_multiple_layers_and_indices]
+
+Use multiple layers and indices to show all your data in a single map. Show how data sits relative to physical features like weather patterns, human-made features like international borders, and business-specific features like sales regions. Plot individual documents or use aggregations to plot any data set, no matter how large.
+
+:::{image} ../../images/kibana-sample_data_ecommerce.png
+:alt: sample data ecommerce
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+To learn about specific types of layers, check out [Heat map layer](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/heatmap-layer.md), [Tile layer](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/tile-layer.md), and [Vector layer](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-layer.md).
+
+
+## Animate spatial temporal data [_animate_spatial_temporal_data]
+
+Data comes to life with animation. Hard to detect patterns in static data pop out with movement. Use time slider to animate your data and gain deeper insights.
+
+This animated map uses the time slider to show Portland buses over a period of 15 minutes. The routes come alive as the bus locations update with time.
+
+:::{image} ../../images/kibana-timeslider.gif
+:alt: timeslider
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+To create this type of map, check out [Track, visualize, and alert assets in real time](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md).
+
+## Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles [_upload_geojson_files_and_shapefiles]
+
+Use **Maps** to drag and drop your GeoJSON and shapefile data into Elasticsearch, and then use them as layers in your map.
+
+
+## Embed your map in dashboards [_embed_your_map_in_dashboards]
+
+Viewing data from different angles provides better insights. Dimensions that are obscured in one visualization might be illuminated in another. Add your map to a [Dashboard](../../explore-analyze/dashboards.md) and view your geospatial data alongside bar charts, pie charts, tag clouds, and more.
+
+This choropleth map shows the density of non-emergency service requests in San Diego by council district. The map is embedded in a dashboard, so users can better understand when services are requested and gain insight into the top requested services.
+
+:::{image} ../../images/kibana-embed_in_dashboard.jpeg
+:alt: embed in dashboard
+:class: screenshot
+:::
+
+
+## Symbolize features using data values [_symbolize_features_using_data_values]
+
+Customize each layer to highlight meaningful dimensions in your data. For example, use dark colors to symbolize areas with more web log traffic, and lighter colors to symbolize areas with less traffic.
+
+
+## Focus on only the data that’s important to you [_focus_on_only_the_data_thats_important_to_you]
+
+Search across the layers in your map to focus on just the data you want. Combine free text search with field-based search using the [{{kib}} Query Language](../../explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/kql.md). Set the time filter to restrict layers by time. Draw a polygon on the map or use the shape from features to create spatial filters. Filter individual layers to compares facets.
+
+Check out [Search geographic data](../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search.md).
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md
index 168d82a385..135e52949f 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md
@@ -565,10 +565,10 @@ Add a layer that uses attributes in the data to set the style and orientation of
4. Set **Border width** to 0.
5. Change **Symbol orientation** to use **By value** and the `trimet.bearing` field.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-top_hits_layer_style.png
- :alt: top hits layer style
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-top_hits_layer_style.png
+ :alt: top hits layer style
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
7. Click **Keep changes**.
8. Open the [time filter](../../query-filter/filtering.md), and set **Refresh every** to 10 seconds, and click **Start**.
@@ -738,10 +738,10 @@ With the alert configured and running, in a few minutes your `trimet_alerts` ind
* Enable the **Label** option with the `vehicleId` field
* Add the `vehicleId`, `boundaryId`, `detectionTime`, and `vehicleTime` fields to the tooltip configuration to allow viewing alert details on the map.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-vehicle_alerts.png
- :alt: vehicle alerts
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-vehicle_alerts.png
+ :alt: vehicle alerts
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
Congratulations! You have completed the tutorial and have the recipe for tracking assets. You can now try replicating this same analysis with your own data.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md
index 69c4dd872e..ec8c2b1201 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md
@@ -30,12 +30,12 @@ The data represents two real airports, two fictitious flight routes, and fictiti
1. [Create a new map](maps-getting-started.md#maps-create).
2. Zoom in on the New England area in the northeast United States.
- You’re adding flight paths to this area, and this sets up the map for a good view of the data.
+ You’re adding flight paths to this area, and this sets up the map for a good view of the data.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_new_england_map.png
- :alt: fu gs new england map
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_new_england_map.png
+ :alt: fu gs new england map
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -58,12 +58,12 @@ For each GeoJSON file you downloaded, complete the following steps:
7. Click **Keep changes**.
8. Once you’ve added all of the sample files, [save your map](maps-getting-started.md#maps-save).
- At this point, you could consider the map complete, but there are a few additions and tweaks that you can make to tell a better story with your data.
+ At this point, you could consider the map complete, but there are a few additions and tweaks that you can make to tell a better story with your data.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_flight_paths.png
- :alt: fu gs flight paths
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_flight_paths.png
+ :alt: fu gs flight paths
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -87,12 +87,12 @@ Looking at the `Lightning detected` layer, it’s clear where lightning has stru
6. When you’re finished modifying settings, click **Keep changes**.
- With your new lightning heat map layer, your map should look like this:
+ With your new lightning heat map layer, your map should look like this:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_lightning_intensity.png
- :alt: fu gs lightning intensity
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-fu_gs_lightning_intensity.png
+ :alt: fu gs lightning intensity
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md
index 8617d56c74..72f6f8655e 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md
@@ -481,9 +481,9 @@ If you cannot connect to Elastic Maps Service from the {{kib}} server or browser
1. Pull the {{hosted-ems}} Docker image.
- ::::{warning}
- Version 9.0.0-beta1 of {{hosted-ems}} has not yet been released. No Docker image is currently available for this version.
- ::::
+ ::::{warning}
+ Version 9.0.0-beta1 of {{hosted-ems}} has not yet been released. No Docker image is currently available for this version.
+ ::::
```bash
@@ -516,10 +516,10 @@ If you cannot connect to Elastic Maps Service from the {{kib}} server or browser
Once {{hosted-ems}} is running, follow instructions from the webpage at `localhost:8080` to define a configuration file and optionally download a more detailed basemaps database.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-elastic-maps-server-instructions.png
- :alt: Set-up instructions
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-elastic-maps-server-instructions.png
+ :alt: Set-up instructions
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md
index 4fa4130643..db4ec8bb93 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md
@@ -68,12 +68,12 @@ The first layer you’ll add is a choropleth layer to shade world countries by w
8. Click **Keep changes**.
- Your map now looks like this:
+ Your map now looks like this:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_add_cloropeth_layer.png
- :alt: Map showing the Total Requests by Destination layer
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_add_cloropeth_layer.png
+ :alt: Map showing the Total Requests by Destination layer
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -100,12 +100,12 @@ This layer displays web log documents as points. The layer is only visible when
7. In **Layer style**, set **Fill color** to **#2200FF**.
8. Click **Keep changes**.
- Your map will look like this from zoom level 9 to 24:
+ Your map will look like this from zoom level 9 to 24:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_add_es_document_layer.png
- :alt: Map showing what zoom level looks like a level 9
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_add_es_document_layer.png
+ :alt: Map showing what zoom level looks like a level 9
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -135,12 +135,12 @@ You’ll create a layer for [aggregated data](../../aggregations.md) and make it
7. Click **Keep changes** button.
- Your map will look like this between zoom levels 0 and 9:
+ Your map will look like this between zoom levels 0 and 9:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-sample_data_web_logs.png
- :alt: Map showing what zoom level 3 looks like
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-sample_data_web_logs.png
+ :alt: Map showing what zoom level 3 looks like
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
@@ -158,10 +158,10 @@ View your geospatial data alongside a heat map and pie chart, and then filter th
1. Click **Add from library** to open a list of panels that you can add to the dashboard.
2. Add **[Logs] Unique Destination Heatmap** and **[Logs] Bytes distribution** to the dashboard.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_dashboard_with_map.png
- :alt: Map in a dashboard with 2 other panels
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_dashboard_with_map.png
+ :alt: Map in a dashboard with 2 other panels
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
3. To filter for documents with unusually high byte values, click and drag in the **Bytes distribution** chart.
4. Remove the filter by clicking **x** next to its name in the filter bar.
@@ -170,17 +170,17 @@ View your geospatial data alongside a heat map and pie chart, and then filter th
1. Open a tooltip by clicking anywhere in the United States vector.
2. To show only documents where **geo.src** is **US**, click the filter icon in the row for **ISO 3066-1 alpha-2**.
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_tooltip_filter.png
- :alt: Tooltip on map
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_tooltip_filter.png
+ :alt: Tooltip on map
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
- Your filtered map should look similar to this:
+ Your filtered map should look similar to this:
- :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_map_filtered.png
- :alt: Map showing filtered data
- :class: screenshot
- :::
+ :::{image} ../../../images/kibana-gs_map_filtered.png
+ :alt: Map showing filtered data
+ :class: screenshot
+ :::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md
index 37298b5c40..5860301916 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md
@@ -63,9 +63,9 @@ $$$aggregation-reference$$$
| Function | **Lens** | **TSVB** |
| --- | --- | --- |
| Counter rate | ✓ | ✓ |
-| [Filter ratio](legacy-editors.md#tsvb-function-reference) | Use [formula](lens.md#lens-formulas) | ✓ |
-| [Positive only](legacy-editors.md#tsvb-function-reference) | | ✓ |
-| [Series agg](legacy-editors.md#tsvb-function-reference) | Use [formula](lens.md#lens-formulas) | ✓ |
+| [Filter ratio](legacy-editors/tsvb.md#tsvb-function-reference) | Use [formula](lens.md#lens-formulas) | ✓ |
+| [Positive only](legacy-editors/tsvb.md#tsvb-function-reference) | | ✓ |
+| [Series agg](legacy-editors/tsvb.md#tsvb-function-reference) | Use [formula](lens.md#lens-formulas) | ✓ |
| Static value | ✓ | ✓ |
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md
index c2bfd74b71..57d0bd74d4 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md
@@ -5,8 +5,6 @@ mapped_pages:
# Visualize Library [visualize-library]
-This content applies to: [](../../solutions/search.md) [](../../solutions/observability.md) [](../../solutions/security/elastic-security-serverless.md)
-
The **Visualize Library** is a space where you can save visualization panels that you may want to use across multiple dashboards. The **Visualize Library** consists of two pages:
* **Visualizations**
@@ -15,7 +13,7 @@ The **Visualize Library** is a space where you can save visualization panels tha
## Visualizations [visualize-library-visualizations]
-By default the **Visualizations** page opens first. Here you can create new visualizations, or select from a list of previously created visualizations. To learn more, refer to [save to the Visualize Library](../../explore-analyze/index.md#elasticsearch-explore-your-data-visualizations-save-to-the-visualize-library).
+By default the **Visualizations** page opens first. Here you can create new visualizations, or select from a list of previously created visualizations. To learn more, refer to [save to the Visualize Library](../../explore-analyze/visualize/manage-panels.md).
## Annotation groups [visualize-library-annotation-groups]
diff --git a/images/kibana-dashboard_add_content_to_dashboard_8.15.0.png b/images/kibana-dashboard_add_content_to_dashboard_8.15.0.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8a8b9b9d5d
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/kibana-dashboard_add_content_to_dashboard_8.15.0.png differ
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md b/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3b1c20cd6e..0000000000
--- a/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/maps.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-# {{maps-app}} [maps]
-
-This content applies to: [](../../../solutions/security/elastic-security-serverless.md)
-
-In **{{project-settings}} → {{maps-app}}** you can:
-
-* Build maps with multiple layers and indices.
-* Animate spatial temporal data.
-* Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles.
-* Embed your map in dashboards.
-* Focus on only the data that’s important to you.
-
-
-## Build maps with multiple layers and indices [maps-build-maps-with-multiple-layers-and-indices]
-
-Use multiple layers and indices to show all your data in a single map. Show how data sits relative to physical features like weather patterns, human-made features like international borders, and business-specific features like sales regions. Plot individual documents or use aggregations to plot any data set, no matter how large.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/serverless-sample_data_ecommerce_map.png
-:alt: A world map with country and revenue layers
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-Go to **{{project-settings}} → {{maps-app}}** and click **Add layer**. To learn about specific types of layers, check out [Heat map layer](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/heatmap-layer.md), [Tile layer](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/tile-layer.md), and [Vector layer](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-layer.md).
-
-
-## Animate spatial temporal data [maps-animate-spatial-temporal-data]
-
-Data comes to life with animation. Hard to detect patterns in static data pop out with movement. Use time slider to animate your data and gain deeper insights.
-
-This animated map uses the time slider to show Portland buses over a period of 15 minutes. The routes come alive as the bus locations update with time.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/serverless-timeslider_map.gif
-:alt: An animated city map of Portland with changing bus locations
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-To create this type of map, check out [Track, visualize, and alert assets in real time](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md).
-
-
-## Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles [maps-upload-geojson-files-and-shapefiles]
-
-Use **{{maps-app}}** to drag and drop your GeoJSON and shapefile data and then use them as layers in your map. Check out [Import geospatial data](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/import-geospatial-data.md).
-
-
-## Embed your map in dashboards [maps-embed-your-map-in-dashboards]
-
-Viewing data from different angles provides better insights. Dimensions that are obscured in one visualization might be illuminated in another. Add your map to a [Dashboard](../../../explore-analyze/dashboards.md) and view your geospatial data alongside bar charts, pie charts, tag clouds, and more.
-
-This choropleth map shows the density of non-emergency service requests in San Diego by council district. The map is embedded in a dashboard, so users can better understand when services are requested and gain insight into the top requested services.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/serverless-embed_dashboard_map.jpeg
-:alt: A dashboard with a map
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-For a detailed example, check out [Build a map to compare metrics by country or region](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md).
-
-
-## Focus on only the data that’s important to you [maps-focus-on-only-the-data-thats-important-to-you]
-
-Search across the layers in your map to focus on just the data you want. Combine free text search with field-based search using the {{kib}} Query Language (KQL) Set the time filter to restrict layers by time. Draw a polygon on the map or use the shape from features to create spatial filters. Filter individual layers to compares facets.
-
-Check out [Search geographic data](../../../explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search.md).
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/kibana/kibana/maps.md b/raw-migrated-files/kibana/kibana/maps.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 797488c84c..0000000000
--- a/raw-migrated-files/kibana/kibana/maps.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-# Maps [maps]
-
-Create beautiful maps from your geographical data. With **Maps**, you can:
-
-* Build maps with multiple layers and indices.
-* Animate spatial temporal data.
-* Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles.
-* Embed your map in dashboards.
-* Symbolize features using data values.
-* Focus on only the data that’s important to you.
-
-
-## Build maps with multiple layers and indices [_build_maps_with_multiple_layers_and_indices]
-
-Use multiple layers and indices to show all your data in a single map. Show how data sits relative to physical features like weather patterns, human-made features like international borders, and business-specific features like sales regions. Plot individual documents or use aggregations to plot any data set, no matter how large.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-sample_data_ecommerce.png
-:alt: sample data ecommerce
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-## Animate spatial temporal data [_animate_spatial_temporal_data]
-
-Data comes to life with animation. Hard to detect patterns in static data pop out with movement. Use time slider to animate your data and gain deeper insights.
-
-This animated map uses the time slider to show Portland buses over a period of 15 minutes. The routes come alive as the bus locations update with time.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-timeslider.gif
-:alt: timeslider
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-## Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles [_upload_geojson_files_and_shapefiles]
-
-Use **Maps** to drag and drop your GeoJSON and shapefile data into Elasticsearch, and then use them as layers in your map.
-
-
-## Embed your map in dashboards [_embed_your_map_in_dashboards]
-
-Viewing data from different angles provides better insights. Dimensions that are obscured in one visualization might be illuminated in another. Add your map to a dashboard and view your geospatial data alongside bar charts, pie charts, tag clouds, and more.
-
-This choropleth map shows the density of non-emergency service requests in San Diego by council district. The map is embedded in a dashboard, so users can better understand when services are requested and gain insight into the top requested services.
-
-:::{image} ../../../images/kibana-embed_in_dashboard.jpeg
-:alt: embed in dashboard
-:class: screenshot
-:::
-
-
-## Symbolize features using data values [_symbolize_features_using_data_values]
-
-Customize each layer to highlight meaningful dimensions in your data. For example, use dark colors to symbolize areas with more web log traffic, and lighter colors to symbolize areas with less traffic.
-
-
-## Focus on only the data that’s important to you [_focus_on_only_the_data_thats_important_to_you]
-
-Search across the layers in your map to focus on just the data you want. Combine free text search with field-based search using the [{{kib}} Query Language](../../../explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/kql.md). Set the time filter to restrict layers by time. Draw a polygon on the map or use the shape from features to create spatial filters. Filter individual layers to compares facets.
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/toc.yml b/raw-migrated-files/toc.yml
index 200c9814b1..aec7104527 100644
--- a/raw-migrated-files/toc.yml
+++ b/raw-migrated-files/toc.yml
@@ -306,7 +306,6 @@ toc:
- file: docs-content/serverless/ingest-wiz-data.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/intro.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/maintenance-windows.md
- - file: docs-content/serverless/maps.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/monitor-k8s-otel-edot.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/observability-add-logs-service-name.md
- file: docs-content/serverless/observability-aggregationOptions.md
@@ -690,7 +689,6 @@ toc:
- file: kibana/kibana/managing-data-views.md
- file: kibana/kibana/managing-saved-objects.md
- file: kibana/kibana/managing-tags.md
- - file: kibana/kibana/maps.md
- file: kibana/kibana/osquery.md
- file: kibana/kibana/playground.md
- file: kibana/kibana/reporting-getting-started.md