diff --git a/.gitignore b/.gitignore
index 102aa91b50..a54c00dcc0 100644
--- a/.gitignore
+++ b/.gitignore
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ AGENTS.md
.github/instructions/**.instructions.md
CLAUDE.md
GEMINI.md
-.cursor
-# VS code settings
+# Editor settings
+.cursor
.vscode
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md
index 6f6d8da6d9..83ccda65f2 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/add-controls.html
+description: Add interactive filter controls to dashboards with options lists, range sliders, and time sliders. Help viewers dynamically filter data and focus on specific segments.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,9 +11,17 @@ products:
# Add filter controls [add-controls]
-**Controls** are interactive panels that you add to your dashboards to help viewers filter and display only the data they want to explore quicker. Controls apply to all relevant panels in a dashboard.
+Filter controls enable dashboard viewers to interactively narrow down displayed data without editing the dashboard itself. When viewers select values in a control, the filters apply across all relevant panels, making it easier to focus on specific data segments or time ranges.
-There are three types of controls:
+You can add filter controls to your dashboards:
+
+- **Options list**: Dropdown selections for one or more field values
+- **Range slider**: Numeric range filtering for continuous data
+- **Time slider**: Time range navigation and animation
+
+Before adding controls, make sure you have edit permissions for the dashboard and understand which fields your viewers need to filter by.
+
+## Control types
* [**Options list**](#create-and-add-options-list-and-range-slider-controls) — Adds a dropdown that allows to filter data by selecting one or more values.
For example, if you are using the **[Logs] Web Traffic** dashboard from the sample web logs data, you can add an options list for the `machine.os.keyword` field that allows you to display only the logs generated from `osx` and `ios` operating systems.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/arrange-panels.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/arrange-panels.md
index bb0c24d804..081950f3b2 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/arrange-panels.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/arrange-panels.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/arrange-panels.html
+description: Organize dashboard panels with collapsible sections, resize layouts, and reposition visualizations. Improve readability and load performance with structured arrangements.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Organize dashboard panels [arrange-panels]
-Customize your dashboard layout by arranging panels into logical groups and adjusting their size and position. When panels are well organized, it makes your dashboard easier to read, faster to load, and helps its viewers locate important information quicker.
+Well-organized dashboard layouts help viewers find information quickly and improve overall performance. You can arrange panels into collapsible sections, resize and reposition them, and use keyboard controls for precise placement.
+
+This guide shows you how to create collapsible sections, move and resize panels using mouse or keyboard, and duplicate panels across dashboards.
## Arrange panels in collapsible sections [collapsible-sections]
```{applies_to}
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/building.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/building.md
index 82ade8cdf6..d25389d3a2 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/building.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/building.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/create-dashboards.html
+description: Build dashboards in Kibana with visualizations, charts, maps, and controls to track key metrics and enable data exploration across Elasticsearch data.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,22 +9,19 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Building dashboards [create-dashboards]
+# Build dashboards [create-dashboards]
-{{kib}} offers many ways to build powerful dashboards that will help you visualize and keep track of the most important information contained in your {{es}} data.
+Dashboards in {{product.kibana}} combine multiple visualizations, metrics, and controls into a single view that tells a story about your data. You can create dashboards from scratch, start with templates, or assemble panels from the Visualize Library.
-* Create and assemble visualizations such as charts or maps, and enrich them with helpful legends containing key data.
-* Extract and show key indicators and metrics to keep them visible and highlighted at all times.
-* Add text, images, and links to help viewers make the most of your dashboard.
-* Include additional controls to facilitate filtering and browsing the data.
+This section covers the key concepts and requirements for building dashboards. To get started, you need indexed data in {{product.elasticsearch}} and a {{data-source}} that defines which data to analyze.
$$$dashboard-minimum-requirements$$$
To create or edit dashboards, you first need to:
-* have [data indexed into {{es}}](/manage-data/ingest.md) and a [data view](../find-and-organize/data-views.md). A data view is a subset of your {{es}} data, and allows you to load the right data when building a visualization or exploring it.
+* have [data indexed into {{product.elasticsearch}}](/manage-data/ingest.md) and a [data view](../find-and-organize/data-views.md). A data view is a subset of your {{product.elasticsearch}} data, and allows you to load the right data when building a visualization or exploring it.
::::{tip}
If you don’t have data at hand and still want to explore dashboards, you can import one of the [sample data sets](../../manage-data/ingest/sample-data.md) available.
::::
-* have sufficient permissions on the **Dashboard** feature. If that’s not the case, you might get a read-only indicator. A {{kib}} administrator can [grant you the required privileges](../../deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/kibana-privileges.md).
+* have sufficient permissions on the **Dashboard** feature. If that’s not the case, you might get a read-only indicator. A {{product.kibana}} administrator can [grant you the required privileges](../../deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/kibana-privileges.md).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md
index b1cc51eaa7..9405d1e45a 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/create-a-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.html
+description: Step-by-step tutorial for building a time series dashboard with e-commerce data, including custom intervals, percentiles, and multi-layer visualizations.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,9 +11,14 @@ products:
# Create a dashboard with time series charts [create-a-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data]
-In this tutorial, you’ll use the ecommerce sample data to analyze sales trends, but you can use any type of data to complete the tutorial.
+In this tutorial, you'll learn how to build time series visualizations that reveal patterns in your data over time. You'll explore techniques for customizing date intervals, calculating percentiles, comparing multiple data series, and analyzing percentage changes. By the end, you'll understand the core workflows for creating effective time series dashboards.
-When you’re done, you’ll have a complete overview of the sample web logs data.
+The tutorial uses ecommerce sample data, but you can apply these techniques to any time-based data set.
+
+**Prerequisites:**
+
+- Access to {{product.kibana}} (version 8.0 or later)
+- Ecommerce sample data installed (instructions below)
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-lens_timeSeriesDataTutorialDashboard_8.3.png
:alt: Final dashboard with eCommerce sample data
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md
index 13e0e4de0b..d49de55fef 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/create-a-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.html
+description: Step-by-step tutorial for building log monitoring dashboards with web server data, covering metrics, traffic analysis, and common Lens visualization patterns.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,11 +9,16 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Create a simple dashboard to monitor website logs [create-a-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data]
+# Create a dashboard to monitor website logs [create-a-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data]
-Learn the most common ways to create a dashboard from your own data. The tutorial will use sample data from the perspective of an analyst looking at website logs, but this type of dashboard works on any type of data.
+In this tutorial, you'll learn the most common visualization patterns for creating dashboards in {{product.kibana}}. You'll explore how to build metric panels, line charts, tables, pie charts, and other visualizations using Lens, the default visualization editor. By the end, you'll understand the fundamental workflows for transforming raw data into meaningful dashboards.
-When you’re done, you’ll have a complete overview of the sample web logs data.
+The tutorial uses web server log data from the analyst perspective, but these techniques apply to any data set.
+
+**Prerequisites:**
+
+- Access to {{product.kibana}} (version 8.0 or later)
+- Web logs sample data installed (instructions below)
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-lens_logsDashboard_8.4.0.png
:alt: Logs dashboard
@@ -38,7 +44,7 @@ Open the visualization editor, then make sure the correct fields appear.
* {applies_to}`stack: ga 9.2` Select **Add** > **Visualization** in the toolbar.
* {applies_to}`stack: ga 9.0` Click **Create visualization**.
-2. Make sure the **{{kib}} Sample Data Logs** {{data-source}} appears.
+2. Make sure the **{{product.kibana}} Sample Data Logs** {{data-source}} appears.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-lens_dataViewDropDown_8.4.0.png
:alt: Data view dropdown
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard.md
index 8b93bf5c02..eb9880900a 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/create-dashboard.html
+description: Create dashboards with visualizations, controls, and content from the library. Configure settings, organize panels, and save custom analytics views for data exploration.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,16 +9,22 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Create a dashboard [create-dashboard]
+# Create dashboards [create-dashboard]
-1. Open the **Dashboards** page in {{kib}}.
+Creating a dashboard involves assembling visualizations, controls, and other panel types into a cohesive view that tells a story about your data. You can start from scratch, add content from the Visualize Library, or combine both approaches.
+
+This guide walks through the process of creating a new dashboard, adding content, configuring settings, and saving your work.
+
+To create a dashboard:
+
+1. Open the **Dashboards** page in {{product.kibana}}.
2. Select **Create dashboard** to start with an empty dashboard.
When you create a dashboard, you are automatically in edit mode and can make changes to the dashboard.
3. Populate your dashboard with the content that you need. You can:
- * [**Add new visualizations**](../visualize.md#panels-editors). Create a chart using [Lens](../visualize/lens.md), the default visualization editor in {{kib}}, or other visualizations such as [Maps](../visualize/maps.md).
+ * [**Add new visualizations**](../visualize.md#panels-editors). Create a chart using [Lens](../visualize/lens.md), the default visualization editor in {{product.kibana}}, or other visualizations such as [Maps](../visualize/maps.md).
* [**Add existing content from the library**](../visualize/visualize-library.md). Select existing visualizations or Discover sessions that have already been configured and saved to the **Visualize Library**.
* [**Add annotations or navigation panels**](../visualize.md#panels-editors). Make your dashboard more informative and easier to read with sections, text, and images.
* [**Add controls**](add-controls.md). Define a set of interactive filters (options lists, range or time sliders) that you and future users of this dashboard can use to explore its data.
@@ -25,7 +32,7 @@ products:
4. Organize your dashboard by [organizing the various panels](arrange-panels.md).
5. Define the main settings of your dashboard from the **Settings** menu located in the toolbar.
- 1. A meaningful title, description, and [tags](../find-and-organize/tags.md) allow you to find the dashboard quickly later when browsing your list of dashboards or using the {{kib}} search bar.
+ 1. A meaningful title, description, and [tags](../find-and-organize/tags.md) allow you to find the dashboard quickly later when browsing your list of dashboards or using the {{product.kibana}} search bar.
2. Additional display options allow you unify the look and feel of the dashboard’s panels:
* **Store time with dashboard** — Saves the specified time filter.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/drilldowns.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/drilldowns.md
index 1bb4e5fca1..82b27c0573 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/drilldowns.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/drilldowns.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/drilldowns.html
+description: Create interactive drilldowns in dashboards to navigate between dashboards, external URLs, or Discover. Maintain context with filters and time ranges during exploration.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,9 +11,9 @@ products:
# Add drilldowns [drilldowns]
-Panels have built-in interactive capabilities that apply filters to the dashboard data. For example, when you drag a time range or click a pie slice, a filter for the time range or pie slice is applied. Drilldowns let you customize the interactive behavior while keeping the context of the interaction.
+Drilldowns extend the built-in interactivity of dashboard panels by letting you define custom actions that users can trigger by clicking on data points. Unlike basic click interactions that only apply filters, drilldowns can navigate to other dashboards, open external websites, or jump to Discover while preserving filters, time ranges, and other context.
-There are three types of drilldowns you can add to dashboards:
+You can add three types of drilldowns to dashboard panels:
* **Dashboard** — Navigates you from one dashboard to another dashboard. For example, create a drilldown for a **Lens** panel that navigates you from a summary dashboard to a dashboard with a filter for a specific host name.
* **URL** — Navigates you from a dashboard to an external website. For example, a website with the specific host name as a parameter.
@@ -113,13 +114,13 @@ For example, if you have a dashboard that shows data from a Github repository, y
1. Give the drilldown a name. For example, `Show on Github`.
2. For the **Trigger**, select **Single click**.
- 3. To navigate to the {{kib}} repository Github issues, enter the following in the **Enter URL** field:
+ 3. To navigate to the {{product.kibana}} repository Github issues, enter the following in the **Enter URL** field:
```bash
https://github.com/elastic/kibana/issues?q=is:issue+is:open+{{event.value}}
```
- {{kib}} substitutes `{{event.value}}` with a value associated with the selected pie slice.
+ {{product.kibana}} substitutes `{{event.value}}` with a value associated with the selected pie slice.
4. Click **Create drilldown**.
@@ -128,7 +129,7 @@ For example, if you have a dashboard that shows data from a Github repository, y

-9. In the list of {{kib}} repository issues, verify that the slice value appears.
+9. In the list of {{product.kibana}} repository issues, verify that the slice value appears.

@@ -212,7 +213,7 @@ Example:
**rison**
-Serialize variables in [rison](https://github.com/w33ble/rison-node) format. Rison is a common format for {{kib}} apps for storing state in the URL.
+Serialize variables in [rison](https://github.com/w33ble/rison-node) format. Rison is a common format for {{product.kibana}} apps for storing state in the URL.
Example:
@@ -346,11 +347,11 @@ To ensure that the configured URL drilldown works as expected with your data, yo
| Source | Variable | Description |
| --- | --- | --- |
-| **Global** | kibanaUrl | {{kib}} base URL. Useful for creating URL drilldowns that navigate within {{kib}}. |
+| **Global** | kibanaUrl | {{product.kibana}} base URL. Useful for creating URL drilldowns that navigate within {{product.kibana}}. |
| **Context** | context.panel | Context provided by current dashboard panel. |
| | context.panel.id | ID of a panel. |
| | context.panel.title | Title of a panel. |
-| | context.panel.filters | List of {{kib}} filters applied to a panel.
Tip: Use in combination with [rison](#helpers) helper forinternal {{kib}} navigations with carrying over current filters. |
+| | context.panel.filters | List of {{product.kibana}} filters applied to a panel.
Tip: Use in combination with [rison](#helpers) helper forinternal {{product.kibana}} navigations with carrying over current filters. |
| | context.panel.query.query | Current query string. |
| | context.panel.query.language | Current query language. |
| | context.panel.timeRange.from
context.panel.timeRange.to | Current time picker values.
Tip: Use in combination with [date](#helpers) helper to format date. |
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
index dc687891e7..c8279941ee 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/duplicate-dashboards.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/duplicate-dashboards.html
+description: Duplicate dashboards to create copies with identical panels and configurations. Modify duplicates independently while preserving original dashboard settings.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,7 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Duplicate a dashboard [duplicate-dashboards]
+# Duplicate dashboards [duplicate-dashboards]
+
+Duplicating a dashboard creates an exact copy with all panels, filters, and settings intact. This is useful when you want to experiment with changes without affecting the original dashboard, or when you need similar dashboards for different data sets or audiences.
+
+To duplicate a dashboard:
1. Open the dashboard you want to duplicate.
2. Exit the edit mode, and click **Duplicate** in the toolbar.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/import-dashboards.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/import-dashboards.md
index 75f587f5fe..89be838954 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/import-dashboards.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/import-dashboards.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/_import_dashboards.html
+description: Import dashboards with related objects from saved object files. Configure import behavior for data views, visualizations, and handle object conflicts during migration.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,11 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Import a dashboard [_import_dashboards]
+# Import dashboards [_import_dashboards]
-You can import dashboards from the [Saved Objects](../find-and-organize/saved-objects.md) page under **Stack Management**.
+To move dashboards between {{product.kibana}} instances or restore dashboards from backup, use the import feature. Import works with NDJSON files that contain dashboard definitions and their dependencies.
-When importing dashboards, you also import their related objects, such as data views and visualizations. Import options allow you to define how the import should behave with these related objects.
+When you import a dashboard, {{product.kibana}} also imports related objects like {{data-sources}} and visualizations. You can control whether to overwrite existing objects or create new ones with random IDs to avoid conflicts.
* **Check for existing objects**: When selected, objects are not imported when another object with the same ID already exists in this space or cluster. For example, if you import a dashboard that uses a data view which already exists, the data view is not imported and the dashboard uses the existing data view instead. You can also chose to select manually which of the imported or the existing objects are kept by selecting **Request action on conflict**.
* **Create new objects with random IDs**: All related objects are imported and are assigned a new ID to avoid conflicts.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md
index 78b9084ce7..caebc0f35d 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/managing.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/_manage_dashboards.html
+description: Manage Kibana dashboards by searching, filtering by tags and creators, and tracking favorites to monitor usage statistics and organize collections.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,8 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Managing dashboards [_manage_dashboards]
+# Manage dashboards [_manage_dashboards]
+As your collection of dashboards grows, you need efficient ways to find, organize, and track them. {{product.kibana}} provides search, filtering, and tagging capabilities to help you locate specific dashboards quickly, plus favorites and usage tracking to monitor which dashboards your team relies on most.
+
+This guide shows you how to search dashboards by name or tag, filter by creator, mark favorites, and view usage statistics.
## Browse dashboards [find-dashboards]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md
index 731b3c14c6..4f0a2e4f08 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/open-dashboard.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/open-the-dashboard.html
+description: Edit dashboard content, settings, and layout with Edit mode. Adjust panels, controls, and configurations to maintain and update visualizations for viewers.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,15 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Edit a dashboard [open-the-dashboard]
+# Edit dashboards [open-the-dashboard]
-1. Open the **Dashboards** page in {{kib}}.
+To modify an existing dashboard, you need to switch to Edit mode where you can add or remove panels, adjust settings, modify controls, and reorganize the layout. Changes you make are not visible to other viewers until you save the dashboard.
+
+This guide shows you how to open a dashboard for editing, make modifications, and save or reset your changes.
+
+To edit a dashboard:
+
+1. Open the **Dashboards** page in {{product.kibana}}.
2. Locate the dashboard you want to edit.
::::{tip}
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
index 0011a4e396..8d29556260 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/share-the-dashboard.html
+description: Share dashboards with links, reports, or exports. Generate shareable URLs with current filters and time ranges, or export dashboard configurations as NDJSON.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,15 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Sharing dashboards [share-the-dashboard]
+# Share dashboards [share-the-dashboard]
-To share a dashboard with a larger audience, click {icon}`share` **Share** in the toolbar. For detailed information about the sharing options and time ranges, refer to [Reporting and sharing](../report-and-share.md).
+You can share dashboards with colleagues, stakeholders, or external audiences using shareable links, scheduled reports, or exported files. When sharing with a link, you can include the current filters, queries, and time range to provide context.
+
+This page covers generating shareable links and exporting dashboard configurations. For detailed information about scheduling reports and other sharing options, refer to [Reporting and sharing](../report-and-share.md).
+
+## Generate shareable links
+
+To share a dashboard with a larger audience, click {icon}`share` **Share** in the toolbar.
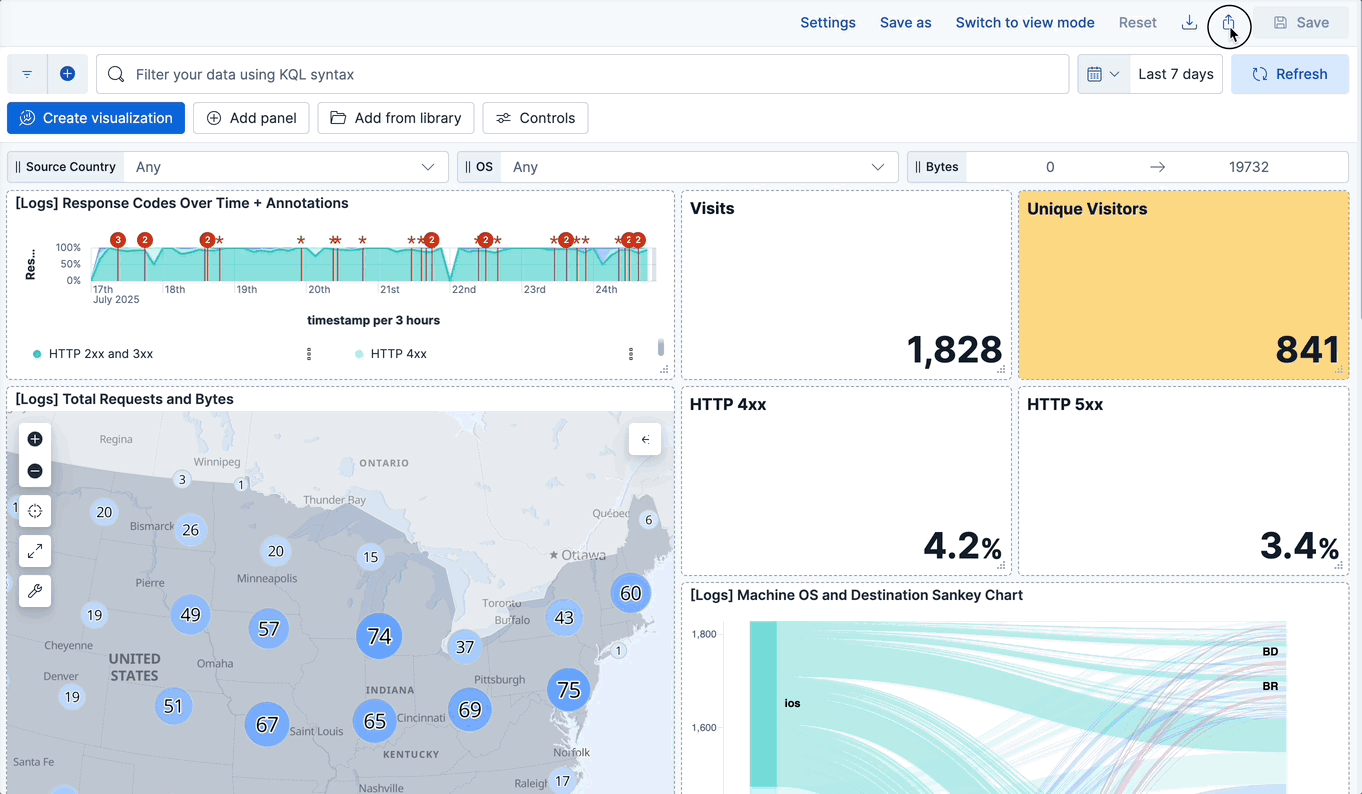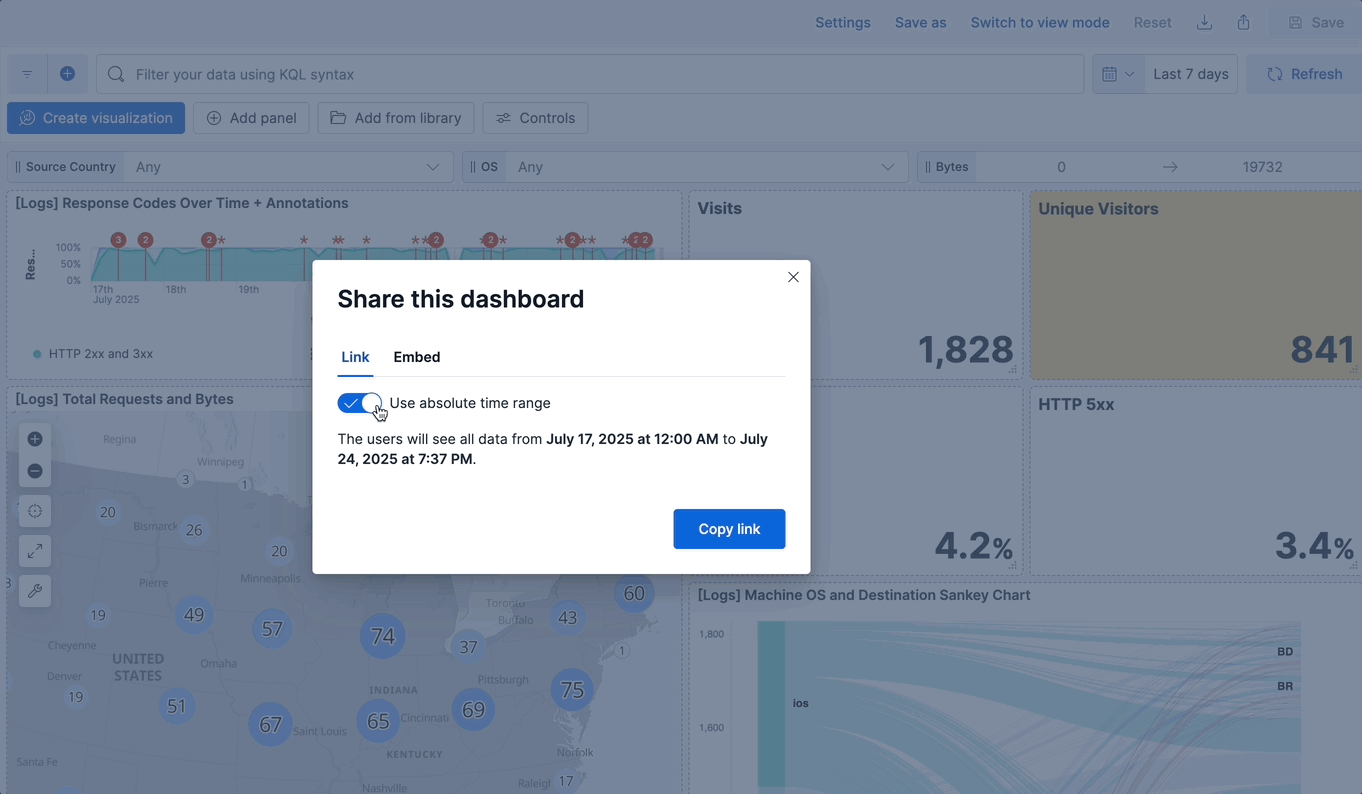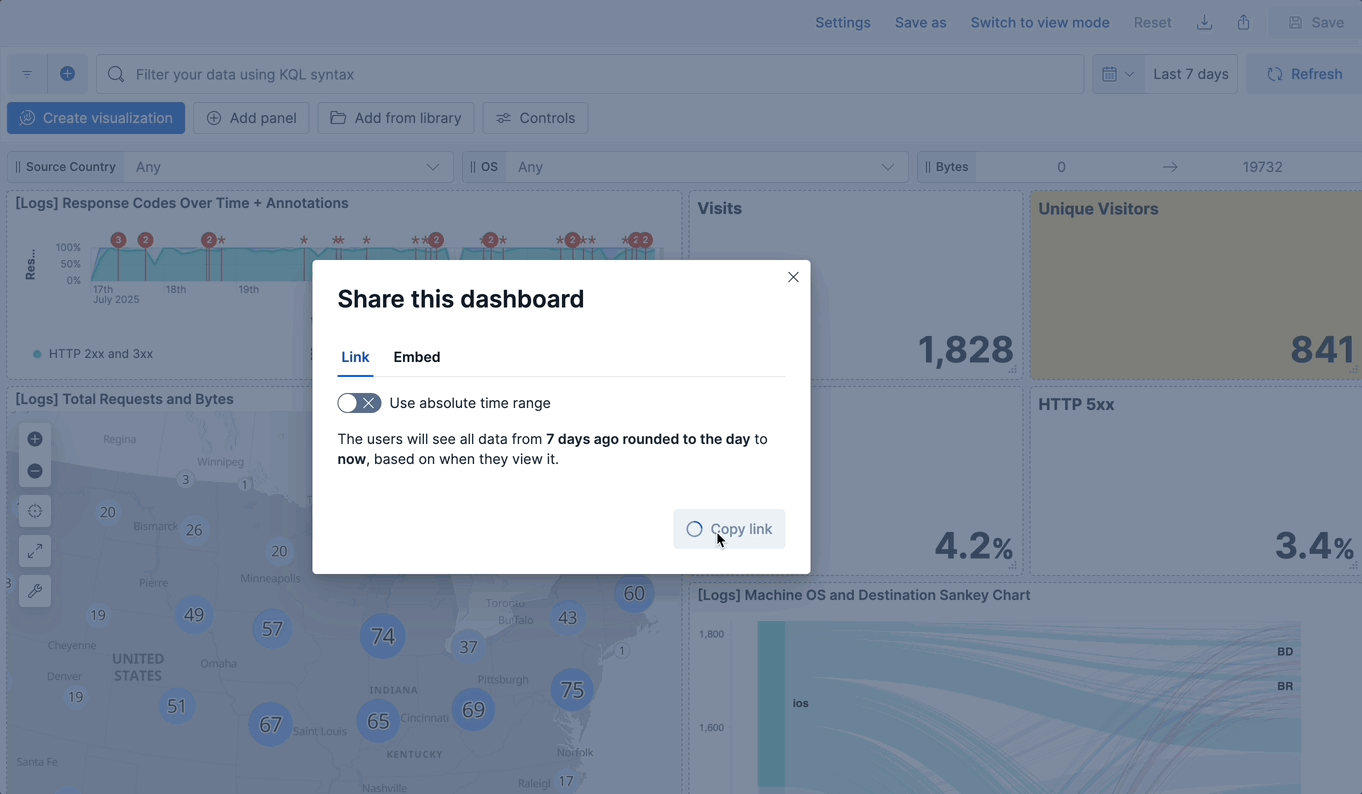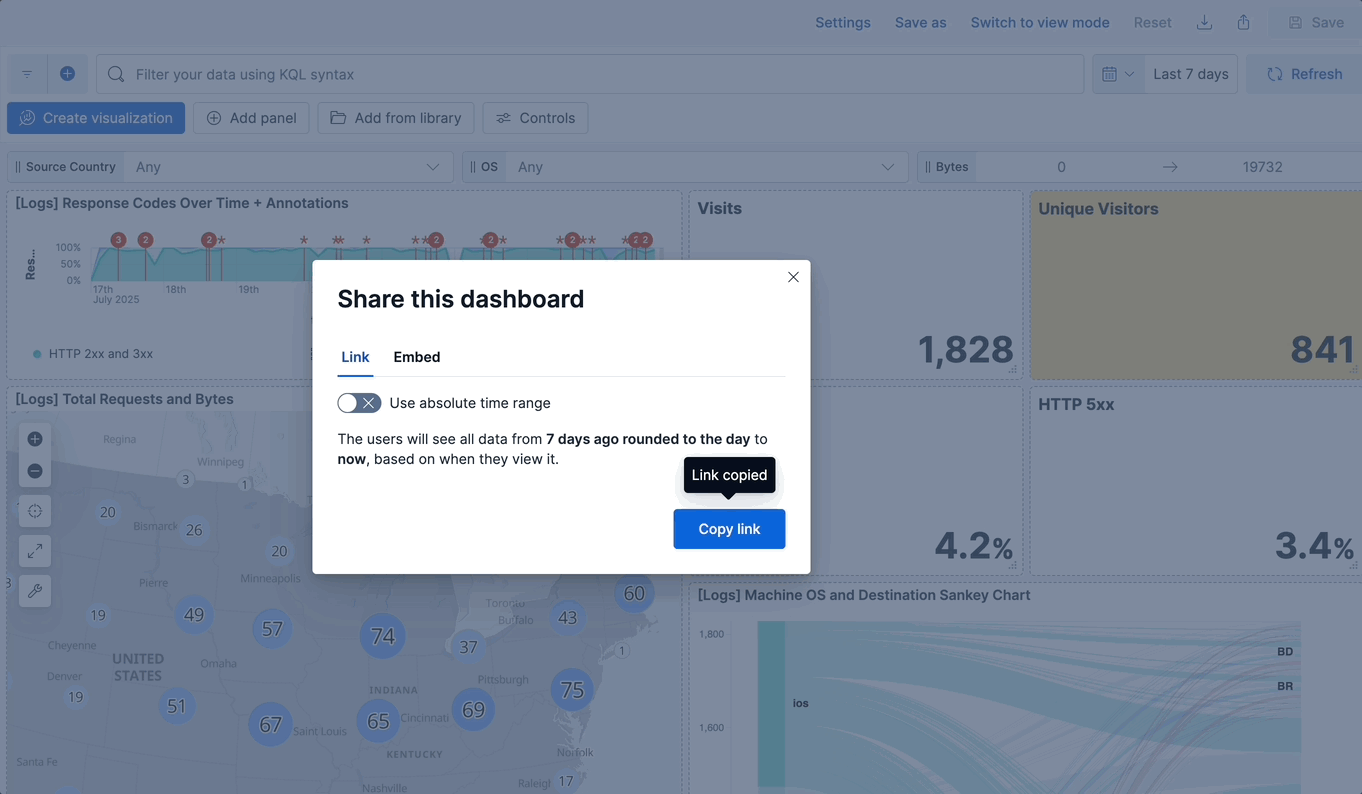
@@ -30,4 +37,4 @@ You can export dashboards from **Stack Management** > **Saved Objects**. To conf

-To automate {{kib}}, you can export dashboards as NDJSON using the [Export saved objects API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/kibana/group/endpoint-saved-objects). It is important to export dashboards with all necessary references.
+To automate {{product.kibana}}, you can export dashboards as NDJSON using the [Export saved objects API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/kibana/group/endpoint-saved-objects). It is important to export dashboards with all necessary references.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/tutorials.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/tutorials.md
index 243e753685..636de88066 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/tutorials.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/tutorials.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/_tutorials.html
+description: Collection of step-by-step Kibana dashboard tutorials with sample data, covering visualization techniques and analytical workflows applicable to any dataset.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,11 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Tutorials [_tutorials]
+# Dashboard tutorials [_tutorials]
-Learn more about building dashboards and creating visualizations with the following tutorials.
+These step-by-step tutorials walk you through building complete dashboards from start to finish. Each tutorial demonstrates specific visualization techniques and analytical workflows that you can apply to your own data.
-These tutorials use [sample data](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana) available in {{kib}} as a way to get started more easily, but you can apply and adapt these instructions to your own data as well.
+While the tutorials use {{product.kibana}} sample data sets for convenience, the techniques and approaches work with any compatible data source. Choose a tutorial based on the type of analysis you want to perform.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
index 55337cb814..6cc1a58f33 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/_use_and_filter_dashboards.html
-description: Learn how to explore and interact with Kibana dashboards using filters, time ranges, and controls to uncover insights in your data.
+description: Explore data with Kibana dashboards using KQL queries, filter pills, time ranges, and controls to view panel data and apply custom filters.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -9,17 +9,17 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Exploring dashboards [_use_and_filter_dashboards]
+# Explore dashboards [_use_and_filter_dashboards]
-Kibana dashboards support filtering, time range adjustments, and interactive controls that let you focus on specific data segments or time periods.
+When viewing a dashboard, you can refine what data appears by applying filters, adjusting time ranges, and using interactive controls. These techniques help you drill down into specific data patterns, compare different time periods, or isolate particular segments of your data set.
-This page covers the main ways to explore dashboard data: using KQL queries, filter pills, time ranges, and dashboard controls. You'll also learn how to view underlying data and switch between different display modes.
+This guide shows you how to filter dashboard data with {{product.kibana}} Query Language queries, create and manage filter pills, adjust time ranges globally or per panel, use control elements, and inspect the underlying data behind visualizations.
## Search and filter your dashboard data [search-or-filter-your-data]
-{{kib}} supports several ways to explore the data displayed in a dashboard more in depth:
+{{product.kibana}} supports several ways to explore the data displayed in a dashboard more in depth:
* The **query bar**, using KQL expressions by default.
* The **time range**, that allows you to display data only for the period that you want to focus on. You can set a global time range for the entire dashboard, or specify a custom time range for each panel.
@@ -27,11 +27,11 @@ This page covers the main ways to explore dashboard data: using KQL queries, fil
* **Filter pills**, that you can add and combine by clicking on specific parts of the dashboard visualizations, or by defining conditions manually from the filter editor. The filter editor is a good alternative if you’re not comfortable with using KQL expressions in the main query bar.
* View the data of a panel and the requests used to build it.
-This section shows the most common ways for you to filter dashboard data. For more information about {{kib}} and {{es}} filtering capabilities, refer to [](/explore-analyze/query-filter.md).
+This section shows the most common ways for you to filter dashboard data. For more information about {{product.kibana}} and {{product.elasticsearch}} filtering capabilities, refer to [](/explore-analyze/query-filter.md).
### Filter dashboards using the KQL query bar [_filter_dashboards_using_the_kql_query_bar]
-The query bar lets you build filters using [{{kib}} Query Language (KQL)](../query-filter/languages/kql.md). When typing, it dynamically suggests matching fields, operators, and values to help you get the exact results that you want.
+The query bar lets you build filters using [{{product.kibana}} Query Language (KQL)](../query-filter/languages/kql.md). When typing, it dynamically suggests matching fields, operators, and values to help you get the exact results that you want.
You can use KQL to create complex queries that filter your dashboard data. For example:
- `status:error` to show only error records
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ As an alternative to the main query bar, you can filter dashboard data by defini
### Filter dashboards using the KQL query bar [_filter_dashboards_using_the_kql_query_bar]
-The query bar lets you build filters using [{{kib}} Query Language (KQL)](../query-filter/languages/kql.md). When typing, it dynamically suggests matching fields, operators, and values to help you get the exact results that you want.
+The query bar lets you build filters using [{{product.kibana}} Query Language (KQL)](../query-filter/languages/kql.md). When typing, it dynamically suggests matching fields, operators, and values to help you get the exact results that you want.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-dashboard-filter-kql.png
:alt: KQL filter dynamically suggesting values
@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ The data visible in a dashboard highly depends on the time range that is applied
#### Apply a global time range to an entire dashboard [_apply_a_global_time_range_to_an_entire_dashboard]
-The global time range menu is located right next to the query bar, in the dashboard’s header. With this menu, you can select the time range to apply, and set the frequency for refreshing the dashboard data. Setting the time range is a common action in {{kib}}. Refer to [Set the time range](../query-filter/filtering.md) for more details.
+The global time range menu is located right next to the query bar, in the dashboard’s header. With this menu, you can select the time range to apply, and set the frequency for refreshing the dashboard data. Setting the time range is a common action in {{product.kibana}}. Refer to [Set the time range](../query-filter/filtering.md) for more details.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-dashboard-global-time-range.png
:alt: Time range menu with multiple time range suggestions
@@ -230,7 +230,7 @@ When viewing a dashboard with read-only permissions, certain visualization panel
## Full screen mode and maximized panel views [_full_screen_mode_and_maximized_panel_views]
-You can display dashboards in full screen mode to gain visual space and view or show visualizations without the rest of the {{kib}} interface.
+You can display dashboards in full screen mode to gain visual space and view or show visualizations without the rest of the {{product.kibana}} interface.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-dashboard-full-screen.png
:alt: A dashboard in full screen mode
diff --git a/explore-analyze/discover/background-search.md b/explore-analyze/discover/background-search.md
index ecb741cfa4..408e9f03e1 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/discover/background-search.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/discover/background-search.md
@@ -7,23 +7,21 @@ applies_to:
serverless: unavailable
products:
- id: kibana
-description: Send your long-running queries to run in the background with background searches and search sessions, and focus on your other tasks while they complete.
+description: Run long-running searches with background search in Discover and Dashboards when analyzing large datasets. Continue working on your data while queries complete, then review results.
---
# Run Discover and Dashboards queries in the background
+When searching through years of historical data or running complex queries on large datasets, you can send long-running queries to run in the background. This lets you continue your work in other applications, explore different data, or even close your browser while the search runs. Return anytime to check progress or view completed results.
+
+**Technical summary**: Start a query, click **Send to background** once it begins running, and manage background searches from the {icon}`background_task` toolbar icon. Searches expire after 7 days (configurable through `data.search.sessions.defaultExpiration`). Requires the Background search subfeature permission.
+
::::{important} - Background search replaces Search sessions
Background search is a feature introduced in version 9.2. It replaces the deprecated **Search sessions** feature.
If you have been using search sessions and upgrade to 9.2, your search sessions aren't lost and become background searches.
::::
-Sometimes you might need to search through large amounts of data, no matter how long the search takes. Consider a threat hunting scenario, where you need to search through years of data.
-
-You can send your long-running searches to the background from **Discover** or **Dashboards** and let them run while you continue your work.
-
-You can access your list of background searches at any time to check their status and manage them from the {icon}`background_task` **Background searches** button in the toolbar.
-

@@ -81,7 +79,7 @@ From the list of background searches, you can reopen and edit any searches, but
:::{tip}
From **Discover**, you can only view Discover background searches. And from **Dashboards**, you can only see Dashboards background searches.
:::
- - Open the **Background Search** management page in {{kib}}.
+ - Open the **Background Search** management page in {{product.kibana}}.
1. Find the background search that you want to interact with using the search or status filter options.
- To open it to view its results and continue your explorations, select its name. Relative dates are converted to absolute dates.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/discover/discover-get-started.md b/explore-analyze/discover/discover-get-started.md
index 4392fd27a4..fe7453db6b 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/discover/discover-get-started.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/discover/discover-get-started.md
@@ -6,25 +6,22 @@ applies_to:
serverless: ga
products:
- id: kibana
+description: Explore Elasticsearch data with Kibana Discover. Select data views, filter and search documents, analyze field values, add runtime fields, and visualize findings to understand patterns.
---
-# Explore fields and data with Discover [discover-get-started]
+# Get started with Discover [discover-get-started]
-Learn how to use **Discover** to:
-
-* **Select** and **filter** your {{es}} data.
-* **Explore** the fields and content of your data in depth.
-* **Present** your findings in a visualization.
+Discover is your starting point for exploring data in {{product.elasticsearch}}. Whether you're investigating an issue, learning about your data's structure, or building insights, Discover provides an interactive environment to search, filter, and analyze documents. This tutorial helps you learn the essential workflows and features that make data exploration effective.
**Prerequisites:**
-* If you don’t already have {{kib}}, [start a free trial](https://www.elastic.co/cloud/elasticsearch-service/signup?baymax=docs-body&elektra=docs) on Elastic Cloud.
-* You must have data in {{es}}. Examples on this page use the [ecommerce sample data set](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana), but you can use your own data.
-* You should have an understanding of [{{es}} documents and indices](../../manage-data/data-store/index-basics.md).
+* If you don't already have {{product.kibana}}, [start a free trial](https://www.elastic.co/cloud/elasticsearch-service/signup?baymax=docs-body&elektra=docs) on {{ecloud}}.
+* You must have data in {{product.elasticsearch}}. The examples on this page use the [ecommerce sample data set](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana), but you can use your own data.
+* You should have an understanding of [{{product.elasticsearch}} documents and indices](../../manage-data/data-store/index-basics.md).
## Context-aware data exploration [context-aware-discover]
-**Discover** provides tailored interfaces and features for the following data types when accessed from Observability or Security project types or {{kib}} solution views:
+**Discover** provides tailored interfaces and features for the following data types when accessed from Observability or Security project types or {{product.kibana}} solution views:
* Observability:
* **[Logs exploration](/solutions/observability/logs/discover-logs.md)**
@@ -59,9 +56,9 @@ Select the data you want to explore, and then specify the time range in which to
1. Find **Discover** in the navigation menu or by using the [global search field](../../explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md).
2. Select the data view that contains the data you want to explore.
::::{tip}
- By default, {{kib}} requires a [{{data-source}}](../find-and-organize/data-views.md) to access your Elasticsearch data. A {{data-source}} can point to one or more indices, [data streams](../../manage-data/data-store/data-streams.md), or [index aliases](/manage-data/data-store/aliases.md). When adding data to {{es}} using one of the many integrations available, sometimes data views are created automatically, but you can also create your own.
+ By default, {{product.kibana}} requires a [{{data-source}}](../find-and-organize/data-views.md) to access your Elasticsearch data. A {{data-source}} can point to one or more indices, [data streams](../../manage-data/data-store/data-streams.md), or [index aliases](/manage-data/data-store/aliases.md). When adding data to {{product.elasticsearch}} using one of the many integrations available, sometimes data views are created automatically, but you can also create your own.
- You can also [try {{esql}}](try-esql.md), that lets you query any data you have in {{es}} without specifying a {{data-source}} first.
+ You can also [try {{esql}}](try-esql.md), that lets you query any data you have in {{product.elasticsearch}} without specifying a {{data-source}} first.
::::
If you’re using sample data, data views are automatically created and are ready to use.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-discover-data-view.png
@@ -157,14 +154,14 @@ In the following example, we’re adding 2 fields: A simple "Hello world" field,
### Visualize aggregated fields [_visualize_aggregated_fields]
-If a field can be [aggregated](../query-filter/aggregations.md), you can quickly visualize it in detail by opening it in **Lens** from **Discover**. **Lens** is the default visualization editor in {{kib}}.
+If a field can be [aggregated](../query-filter/aggregations.md), you can quickly visualize it in detail by opening it in **Lens** from **Discover**. **Lens** is the default visualization editor in {{product.kibana}}.
1. In the list of fields, find an aggregatable field. For example, with the sample data, you can look for `day_of_week`.

2. In the popup, click **Visualize**.
- {{kib}} creates a **Lens** visualization best suited for this field.
+ {{product.kibana}} creates a **Lens** visualization best suited for this field.
3. In **Lens**, from the **Available fields** list, drag and drop more fields to refine the visualization. In this example, we’re adding the `manufacturer.keyword` field onto the workspace, which automatically adds a breakdown of the top values to the visualization.

@@ -374,7 +371,7 @@ From **Discover**, you can create a rule to periodically check when data goes ab
1. Ensure that your data view, query, and filters fetch the data for which you want an alert.
2. In the application menu bar, click **Alerts > Create search threshold rule**.
- The **Create rule** form is pre-filled with the latest query sent to {{es}}.
+ The **Create rule** form is pre-filled with the latest query sent to {{product.elasticsearch}}.
3. [Configure your query](../alerts-cases/alerts/rule-type-es-query.md) and [select a connector type](../../deploy-manage/manage-connectors.md).
4. Click **Save**.
@@ -396,5 +393,5 @@ This section references common questions and issues encountered when using Disco
This can happen in several cases:
-* With runtime fields and regular keyword fields, when the string exceeds the value set for the [ignore_above](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/mapping-reference/ignore-above.md) setting used when indexing the data into {{es}}.
+* With runtime fields and regular keyword fields, when the string exceeds the value set for the [ignore_above](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/mapping-reference/ignore-above.md) setting used when indexing the data into {{product.elasticsearch}}.
* Due to the structure of nested fields, a leaf field added to the table as a column will not contain values in any of its cells. Instead, add the root field as a column to view a JSON representation of its values. Learn more in [this blog post](https://www.elastic.co/de/blog/discover-uses-fields-api-in-7-12).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/discover/discover-search-for-relevance.md b/explore-analyze/discover/discover-search-for-relevance.md
index 18dcc5bb2b..46cf1ef678 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/discover/discover-search-for-relevance.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/discover/discover-search-for-relevance.md
@@ -6,17 +6,24 @@ applies_to:
serverless: ga
products:
- id: kibana
+description: Sort Discover results with relevance scoring to surface documents that best match search queries. Focus exploration on the most pertinent results for faster data insights.
---
-# Search for relevance [discover-search-for-relevance]
+# Sort Discover results by relevance score [discover-search-for-relevance]
-{{es}} assigns a relevancy, or score to each document, so you can can narrow your search to the documents with the most relevant results. The higher the score, the better it matches your query.
+When searching large datasets, you want the most relevant documents to appear first. {{product.elasticsearch}} assigns a relevance score to each document based on how well it matches your query. This guide shows you how to sort results by relevance score in Discover to surface the most pertinent matches.
-This example shows how to use **Discover** to list your documents from most relevant to least relevant. This example uses the [sample flights data set](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana), or you can use your own data.
+**Technical summary**: Add the `_score` meta field to your document table, clear the default time-based sort, and sort by `_score` in descending order to show most relevant results first.
+
+**Prerequisites:**
+
+* You need a {{data-source}} with searchable text fields
+* Works best with text search queries (not filters or time range queries alone)
+* This example uses the [sample flights data set](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana), or you can use your own data
1. In **Discover**, open the {{data-source}} dropdown, and select the data that you want to work with.
- For the sample flights data, set the {{data-source}} to **Kibana Sample Data Flights**.
+ For the sample flights data, set the {{data-source}} to **{{kib}} Sample Data Flights**.
2. Run your search. For the sample data, try:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/discover/document-explorer.md b/explore-analyze/discover/document-explorer.md
index e36d513104..ffa2eca7c1 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/discover/document-explorer.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/discover/document-explorer.md
@@ -6,14 +6,22 @@ applies_to:
serverless: ga
products:
- id: kibana
+description: Customize data exploration with Discover's table controls. Arrange columns, adjust density and row height, control sample size, sort by multiple fields, and filter documents.
---
# Customize the Discover view [document-explorer]
-Fine tune your explorations by customizing **Discover** to bring out the the best view of your documents.
+Discover provides extensive customization options for the document table and interface layout. You can adjust table density, row height, column layout, sample size, and sorting to optimize your data exploration workflow. These settings persist across sessions and carry over when you create dashboard panels.
+
+This page covers:
+- Hiding and resizing interface areas (chart, fields list, document table)
+- Customizing the document table (columns, density, row height, sample size)
+- Sorting by single or multiple fields
+- Filtering documents and comparing field values
+- Editing field display formats
:::{tip}
-Discover provides default [context-aware experiences](/explore-analyze/discover/discover-get-started.md#context-aware-discover) tailored to the type of data that you're exploring, and you can further customize your Discover view on top of them.
+Discover provides default [context-aware experiences](/explore-analyze/discover/discover-get-started.md#context-aware-discover) tailored to the type of data you're exploring. You can further customize your Discover view on top of these experiences.
:::
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-hello-field.png
@@ -90,9 +98,9 @@ To sort by multiple fields:
### Edit a field [document-explorer-edit-field]
-Change how {{kib}} displays a field.
+Change how {{product.kibana}} displays a field.
-1. Click the column header for the field, and then select **Edit data view field.**
+1. Click the column header for the field, and then select **Edit {{data-source}} field.**
2. In the **Edit field** form, change the field name and format.
For detailed information on formatting options, refer to [Format data fields](../find-and-organize/data-views.md#managing-fields).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/discover/run-pattern-analysis-discover.md b/explore-analyze/discover/run-pattern-analysis-discover.md
index 127922d84c..6af394375d 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/discover/run-pattern-analysis-discover.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/discover/run-pattern-analysis-discover.md
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
---
+navigation_title: "Pattern analysis"
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/run-pattern-analysis-discover.html
applies_to:
@@ -6,18 +7,23 @@ applies_to:
serverless: ga
products:
- id: kibana
+description: Detect patterns in unstructured logs with Discover's pattern analysis. Categorize log messages, identify common structures, and filter out noise during troubleshooting.
---
-# Run a pattern analysis on your log data [run-pattern-analysis-discover]
+# Analyze log patterns in Discover [run-pattern-analysis-discover]
-Log pattern analysis helps you to find patterns in unstructured log messages and makes it easier to examine your data. It performs categorization analysis on a selected field of a {{data-source}}, creates categories based on the data and displays them together with a chart that shows the distribution of each category and an example document that matches the category.
+When troubleshooting with unstructured log data, manually identifying patterns is time-consuming. Pattern analysis automatically categorizes log messages to help you find common structures and filter out noise during investigation. This guide shows you how to run pattern analysis in Discover.
-Log pattern analysis works on every text field.
+**Technical summary**: Open the **Patterns** tab in Discover, select a text field for analysis, adjust the minimum time range if needed, and filter or exclude patterns to focus on actionable data.
-This example uses the [sample web logs data](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana), or you can use your own data.
+**Prerequisites:**
+
+* You need a {{data-source}} with text fields containing log data
+* Pattern analysis works on any text field in your data
+* This example uses the [sample web logs data](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana), or you can use your own data
1. Go to **Discover**.
-2. Expand the {{data-source}} dropdown, and select **Kibana Sample Data Logs**.
+2. Expand the {{data-source}} dropdown, and select **{{product.kibana}} Sample Data Logs**.
3. If you don’t see any results, expand the time range, for example, to **Last 15 days**.
4. Click the **Patterns** tab next to **Documents** and **Field statistics**. The pattern analysis starts. The results are displayed under the chart. You can change the analyzed field by using the field selector. In the **Pattern analysis menu**, you can change the **Minimum time range**. This option enables you to widen the time range for calculating patterns which improves accuracy. The patterns, however, are still displayed by the time range you selected in step 3.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/discover/save-open-search.md b/explore-analyze/discover/save-open-search.md
index dc485a0f03..93e599e82c 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/discover/save-open-search.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/discover/save-open-search.md
@@ -7,16 +7,23 @@ applies_to:
serverless: ga
products:
- id: kibana
+description: Preserve exploration work with saved Discover sessions that store queries, filters, column selections, and data views. Reuse explorations, share with teams, or add to dashboards.
---
-# Discover sessions: Save a search for reuse [save-open-search]
+# Save and reuse Discover searches [save-open-search]
-A saved Discover session is a convenient way to reuse a search that you’ve created in **Discover**. Discover sessions are good for saving a configured view of Discover to use later or adding search results to a dashboard, and can also serve as a foundation for building visualizations.
+After configuring a search with specific queries, filters, and column selections, you can save your work as a Discover session. This lets you reopen the exact view later, share it with team members, or add the results to a dashboard. Saved sessions preserve all aspects of your exploration for future use.
+**Technical summary**: Click **Save** in the toolbar, name your session, and optionally store time range and tags. Saved sessions preserve query text, filters, selected {{data-source}}, columns, sort order, and document table configuration.
+
+**Prerequisites:**
+
+* You need privileges to save Discover sessions (refer to [Granting access to {{product.kibana}}](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/roles.md))
+* If a read-only indicator appears, you can view but not save sessions
## Read-only access [discover-read-only-access]
-If you don’t have sufficient privileges to save Discover sessions, the following indicator is displayed and the **Save** button is not visible. For more information, refer to [Granting access to {{kib}}](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/roles.md).
+If you don't have sufficient privileges to save Discover sessions, the following indicator is displayed and the **Save** button is not visible.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-read-only-badge.png
:alt: Example of Discover's read only access indicator in Kibana's header
diff --git a/explore-analyze/discover/show-field-statistics.md b/explore-analyze/discover/show-field-statistics.md
index a26e5b0141..c89ea59d91 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/discover/show-field-statistics.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/discover/show-field-statistics.md
@@ -6,24 +6,28 @@ applies_to:
serverless: ga
products:
- id: kibana
+description: Examine field distributions and value ranges with Discover's Field statistics view. Identify data quality issues, understand cardinality, and create visualizations from field data.
---
-# View field statistics [show-field-statistics]
+# View field statistics in Discover [show-field-statistics]
-Explore the fields in your data with the **Field statistics** view in **Discover** and answer such questions as:
+Field statistics view in Discover shows distribution patterns, cardinality, and value ranges for fields in your data. Use this view to assess data quality, understand field usage, identify outliers, and create quick visualizations from field distributions. Statistics vary by field type. Numeric fields show ranges and distributions, while geo fields display coordinate maps.
-* What does the latency look like when one of the containers is down on a Sunday?
-* Is the field type and format in the data view appropriate for the data and its cardinality?
+Field statistics help you answer questions like:
+* What's the distribution of values across a field?
+* Are there unexpected patterns or outliers in the data?
+* Is the field format appropriate for its cardinality?
+* What does latency look like when one of the containers is down on a specific day?
-:::{note}
-Field statistics aren't available when **Discover** is in {{esql}} mode.
-:::
+**Prerequisites:**
-This example explores the fields in the [sample web logs data](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana), or you can use your own data.
+* You need a {{data-source}} with data to explore
+* Field statistics aren't available when Discover is in {{esql}} mode
+* This example uses [sample web logs data](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana), or you can use your own data
1. Go to **Discover**.
-2. Expand the {{data-source}} dropdown, and select **Kibana Sample Data Logs**.
-3. If you don’t see any results, expand the time range, for example, to **Last 7 days**.
+2. Expand the {{data-source}} dropdown, and select **{{kib}} Sample Data Logs**.
+3. If you don't see any results, expand the time range, for example, to **Last 7 days**.
4. Click **Field statistics**.
The table summarizes how many documents in the sample contain each field for the selected time period the number of distinct values, and the distribution.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/discover/try-esql.md b/explore-analyze/discover/try-esql.md
index 053350650f..f0b8f7efae 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/discover/try-esql.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/discover/try-esql.md
@@ -6,26 +6,24 @@ applies_to:
serverless: ga
products:
- id: kibana
+description: Query Elasticsearch data with ES|QL in Discover to explore any indices without predefining data views. Filter, aggregate, sort results, and build dynamic visualizations.
---
-# Using ES|QL [try-esql]
+# Get started with {{esql}} in Discover [try-esql]
-The Elasticsearch Query Language, {{esql}}, makes it easier to explore your data without leaving Discover.
+{{esql}} brings a powerful piped query language directly into Discover, letting you work with your data more flexibly. Unlike traditional searches that require predefined {{data-sources}}, {{esql}} queries can target any index and reshape results on the fly. This tutorial helps you learn {{esql}} syntax fundamentals by progressively building queries that filter, sort, and aggregate data.
-The examples on this page use the {{kib}} sample web logs in Discover and Lens to explore the data and create visualizations. You can also install it by following [Add sample data](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana).
+**Prerequisites:**
-::::{tip}
-For the complete {{esql}} documentation, including all supported commands, functions, and operators, refer to the [{{esql}} reference](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/esql/esql-syntax-reference.md). For a more detailed overview of {{esql}} in {{kib}}, refer to [Use {{esql}} in Kibana](../query-filter/languages/esql-kibana.md).
+* You need access to {{product.kibana}} (version 8.11 or later for {{esql}} support)
+* The `enableESQL` setting must be enabled from {{product.kibana}}'s **Advanced Settings**. It is enabled by default.
+* The examples use the [sample web logs data](../index.md#gs-get-data-into-kibana). Install it or use your own data.
+::::{tip}
+For the complete {{esql}} documentation, including all supported commands, functions, and operators, refer to the [{{esql}} reference](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/esql/esql-syntax-reference.md). For a more detailed overview of {{esql}} in {{product.kibana}}, refer to [Use {{esql}} in {{product.kibana}}](../query-filter/languages/esql-kibana.md).
::::
-
-## Prerequisite [prerequisite]
-
-To view the {{esql}} option in **Discover**, the `enableESQL` setting must be enabled from Kibana’s **Advanced Settings**. It is enabled by default.
-
-
## Use {{esql}} [tutorial-try-esql]
To load the sample data:
@@ -142,7 +140,7 @@ In **Discover**, LOOKUP JOIN commands include interactive options that let you c
You can create a lookup index directly from the ES|QL editor. To populate this index, you can type in data manually or upload a CSV file up to 500 MB.
-To create lookup indices, you need the [`create_index`](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/security-privileges.md#privileges-list-indices) {{es}} privilege on the corresponding pattern.
+To create lookup indices, you need the [`create_index`](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/security-privileges.md#privileges-list-indices) {{product.elasticsearch}} privilege on the corresponding pattern.
1. In your {{esql}} query, add a `LOOKUP JOIN` command. For example:
```esql
@@ -173,8 +171,8 @@ Your new index is automatically added to your query. You can then specify the fi
#### View or edit a lookup index from the editor
You can view and modify existing lookup indices referenced in an {{esql}} query directly from the editor, depending on your privileges:
-- To edit lookup indices, you need the [`write`](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/security-privileges.md#privileges-list-indices) {{es}} privilege.
-- To view lookup indices in read-only mode, you need the [`view_index_metadata`](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/security-privileges.md#privileges-list-indices) {{es}} privilege.
+- To edit lookup indices, you need the [`write`](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/security-privileges.md#privileges-list-indices) {{product.elasticsearch}} privilege.
+- To view lookup indices in read-only mode, you need the [`view_index_metadata`](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/security-privileges.md#privileges-list-indices) {{product.elasticsearch}} privilege.
To view or edit an index:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/data-views.md b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/data-views.md
index ad0ce607e9..ada0f89a6f 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/data-views.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/data-views.md
@@ -9,29 +9,32 @@ applies_to:
products:
- id: kibana
- id: cloud-serverless
+description: Create and manage data views to access Elasticsearch data in Kibana analytics features. Add runtime fields, format data fields, and configure patterns for indices, data streams, and aliases.
---
# Data views [data-views]
-By default, analytics features such as Discover require a {{data-source}} to access the {{es}} data that you want to explore. A {{data-source}} can point to one or more indices, [data streams](../../manage-data/data-store/data-streams.md), or [index aliases](/manage-data/data-store/aliases.md). For example, a {{data-source}} can point to your log data from yesterday, or all indices that contain your data.
+{{data-sources-cap}} define which {{product.elasticsearch}} indices, data streams, or index aliases are accessible to {{product.kibana}} analytics features like Discover, Lens, and Maps. A {{data-source}} can target a single index or use patterns to match multiple indices, allowing you to analyze data across related sources.
+
+Each {{data-source}} includes field definitions, formatting options, and a timestamp field for time-based filtering. You can also add runtime fields that calculate values on the fly without modifying your indexed data.
::::{note}
-In certain apps, you can also query your {{es}} data using [{{esql}}](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/esql.md). With {{esql}}, data views aren't required.
+Some {{product.kibana}} features support {{esql}} queries, which don't require {{data-sources}}. Refer to [{{esql}}](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/esql.md) for details.
::::
## Permissions [data-views-read-only-access]
* Creating and managing data views requires [a role](../../deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/defining-roles.md) with the following permissions:
- - `Data View Management` {{kib}} privilege.
- - `view_index_metadata` {{es}} privilege.
+ - `Data View Management` {{product.kibana}} privilege.
+ - `view_index_metadata` {{product.elasticsearch}} privilege.
* If a read-only indicator appears, you have insufficient privileges to create or save {{data-sources}}. In addition, the buttons to create {{data-sources}} or save existing {{data-sources}} are not visible.
* {applies_to}`stack: ga 9.2` Some data views are exclusively configured and **managed** by Elastic. You can view and use these managed data views, but you can't edit them. If you'd like to use a modified version of a managed data view, you can [duplicate it](#duplicate-managed-data-view) and edit that new copy as needed.
## Create a data view [settings-create-pattern]
-If you collected data using one of the {{kib}} [ingest options](../../manage-data/ingest.md), uploaded a file, or added sample data, you get a {{data-source}} created automatically, and can start exploring your data. If you loaded your own data, follow these steps to create a {{data-source}}.
+If you collected data using one of the {{product.kibana}} [ingest options](../../manage-data/ingest.md), uploaded a file, or added sample data, you get a {{data-source}} created automatically, and can start exploring your data. If you loaded your own data, follow these steps to create a {{data-source}}.
1. Open **Lens** or **Discover**, and then open the data view menu.
@@ -43,7 +46,7 @@ If you collected data using one of the {{kib}} [ingest options](../../manage-dat
2. Click **Create a {{data-source}}**.
3. Give your {{data-source}} a name.
-4. Start typing in the **Index pattern** field, and {{kib}} looks for the names of indices, data streams, and aliases that match your input. You can view all available sources or only the sources that the data view targets.
+4. Start typing in the **Index pattern** field, and {{product.kibana}} looks for the names of indices, data streams, and aliases that match your input. You can view all available sources or only the sources that the data view targets.

* To match multiple sources, use a wildcard (*). `filebeat-*` matches `filebeat-apache-a`, `filebeat-apache-b`, and so on.
@@ -58,9 +61,9 @@ If you collected data using one of the {{kib}} [ingest options](../../manage-dat
6. Click **Show advanced settings** to:
* Display hidden and system indices.
- * Specify your own {{data-source}} name. For example, enter your {{es}} index alias name.
+ * Specify your own {{data-source}} name. For example, enter your {{product.elasticsearch}} index alias name.
-7. $$$reload-fields$$$ Click **Save {{data-source}} to {{kib}}**.
+7. $$$reload-fields$$$ Click **Save {{data-source}} to {{product.kibana}}**.
You can manage your data views from the **Management** menu.
@@ -68,7 +71,7 @@ If you collected data using one of the {{kib}} [ingest options](../../manage-dat
### Create a temporary {{data-source}} [_create_a_temporary_data_source]
-Want to explore your data or create a visualization without saving it as a data view? Select **Use without saving** in the **Create {{data-source}}** form in **Discover** or **Lens**. With a temporary {{data-source}}, you can add fields and create an {{es}} query alert, just like you would a regular {{data-source}}. Your work won’t be visible to others in your space.
+Want to explore your data or create a visualization without saving it as a data view? Select **Use without saving** in the **Create {{data-source}}** form in **Discover** or **Lens**. With a temporary {{data-source}}, you can add fields and create an {{product.elasticsearch}} query alert, just like you would a regular {{data-source}}. Your work won’t be visible to others in your space.
A temporary {{data-source}} remains in your space until you change apps, or until you save it.
@@ -111,13 +114,13 @@ serverless: unavailable
stack: ga
```
-If your {{es}} clusters are configured for [{{ccs}}](../../solutions/search/cross-cluster-search.md), you can create a {{data-source}} to search across the clusters of your choosing. Specify data streams, indices, and aliases in a remote cluster using the following syntax:
+If your {{product.elasticsearch}} clusters are configured for [{{ccs}}](../../solutions/search/cross-cluster-search.md), you can create a {{data-source}} to search across the clusters of your choosing. Specify data streams, indices, and aliases in a remote cluster using the following syntax:
```ts
:
```
-To query {{ls}} indices across two {{es}} clusters that you set up for {{ccs}}, named `cluster_one` and `cluster_two`:
+To query {{ls}} indices across two {{product.elasticsearch}} clusters that you set up for {{ccs}}, named `cluster_one` and `cluster_two`:
```ts
cluster_one:logstash-*,cluster_two:logstash-*
@@ -129,7 +132,7 @@ Use wildcards in your cluster names to match any number of clusters. To search {
cluster_*:logstash-*
```
-To query across all {{es}} clusters that have been configured for {{ccs}}, use a standalone wildcard for your cluster name:
+To query across all {{product.elasticsearch}} clusters that have been configured for {{ccs}}, use a standalone wildcard for your cluster name:
```ts
*:logstash-*
@@ -147,14 +150,14 @@ Excluding a cluster avoids sending any network calls to that cluster. To exclude
cluster_*:logstash-*,-cluster_one:*
```
-Once you configure a {{data-source}} to use the {{ccs}} syntax, all searches and aggregations using that {{data-source}} in {{kib}} take advantage of {{ccs}}.
+Once you configure a {{data-source}} to use the {{ccs}} syntax, all searches and aggregations using that {{data-source}} in {{product.kibana}} take advantage of {{ccs}}.
For more information, refer to [Excluding clusters or indicies from cross-cluster search](../../solutions/search/cross-cluster-search.md#exclude-problematic-clusters).
## Delete a {{data-source}} [delete-data-view]
-When you delete a {{data-source}}, you cannot recover the associated field formatters, runtime fields, source filters, and field popularity data. Deleting a {{data-source}} does not remove any indices or data documents from {{es}}.
+When you delete a {{data-source}}, you cannot recover the associated field formatters, runtime fields, source filters, and field popularity data. Deleting a {{data-source}} does not remove any indices or data documents from {{product.elasticsearch}}.
::::{warning}
Deleting a {{data-source}} breaks all visualizations, saved Discover sessions, and other saved objects that reference the data view.
@@ -167,13 +170,13 @@ Deleting a {{data-source}} breaks all visualizations, saved Discover sessions, a
## Data view field cache [data-view-field-cache]
-The browser caches {{data-source}} field lists for increased performance. This is particularly impactful for {{data-sources}} with a high field count that span a large number of indices and clusters. The field list is updated every couple of minutes in typical {{kib}} usage. Alternatively, use the refresh button on the {{data-source}} management detail page to get an updated field list. A force reload of {{kib}} has the same effect.
+The browser caches {{data-source}} field lists for increased performance. This is particularly impactful for {{data-sources}} with a high field count that span a large number of indices and clusters. The field list is updated every couple of minutes in typical {{product.kibana}} usage. Alternatively, use the refresh button on the {{data-source}} management detail page to get an updated field list. A force reload of {{product.kibana}} has the same effect.
The field list may be impacted by changes in indices and user permissions.
## Manage data views [managing-data-views]
-To customize the fields in your data view, you can add runtime fields to the existing documents, add scripted fields to compute data on the fly, and change how {{kib}} displays the data view fields.
+To customize the fields in your data view, you can add runtime fields to the existing documents, add scripted fields to compute data on the fly, and change how {{product.kibana}} displays the data view fields.
### Explore your data with runtime fields [runtime-fields]
@@ -188,11 +191,11 @@ With runtime fields, you can:
* Add fields to existing documents without reindexing your data.
::::{warning}
-Runtime fields can impact {{kib}} performance. When you run a query, {{es}} uses the fields you index first to shorten the response time. Index the fields that you commonly search for and filter on, such as `timestamp`, then use runtime fields to limit the number of fields {{es}} uses to calculate values.
+Runtime fields can impact {{product.kibana}} performance. When you run a query, {{product.elasticsearch}} uses the fields you index first to shorten the response time. Index the fields that you commonly search for and filter on, such as `timestamp`, then use runtime fields to limit the number of fields {{product.elasticsearch}} uses to calculate values.
::::
-For detailed information on how to use runtime fields with {{es}}, refer to [Runtime fields](../../manage-data/data-store/mapping/runtime-fields.md).
+For detailed information on how to use runtime fields with {{product.elasticsearch}}, refer to [Runtime fields](../../manage-data/data-store/mapping/runtime-fields.md).
#### Add runtime fields [create-runtime-fields]
@@ -213,7 +216,7 @@ To add runtime fields to your data views, open the data view you want to change,
7. Click **Create field**.
:::{warning}
-Runtime fields created against a data view are not applied to the underlying index mapping in {{es}}.
+Runtime fields created against a data view are not applied to the underlying index mapping in {{product.elasticsearch}}.
:::
@@ -318,14 +321,14 @@ Use [runtime fields](../../manage-data/data-store/mapping/runtime-fields.md) ins
::::
-Scripted fields compute data on the fly from the data in your {{es}} indices. The data is shown on the Discover tab as part of the document data, and you can use scripted fields in your visualizations. You query scripted fields with the [{{kib}} query language](../../explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/kql.md), and can filter them using the filter bar. The scripted field values are computed at query time, so they aren’t indexed and cannot be searched using the {{kib}} default query language.
+Scripted fields compute data on the fly from the data in your {{product.elasticsearch}} indices. The data is shown on the Discover tab as part of the document data, and you can use scripted fields in your visualizations. You query scripted fields with the [{{product.kibana}} query language](../../explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/kql.md), and can filter them using the filter bar. The scripted field values are computed at query time, so they aren’t indexed and cannot be searched using the {{product.kibana}} default query language.
::::{warning}
-Computing data on the fly with scripted fields can be very resource intensive and can have a direct impact on {{kib}} performance. Keep in mind that there’s no built-in validation of a scripted field. If your scripts are buggy, you’ll get exceptions whenever you try to view the dynamically generated data.
+Computing data on the fly with scripted fields can be very resource intensive and can have a direct impact on {{product.kibana}} performance. Keep in mind that there’s no built-in validation of a scripted field. If your scripts are buggy, you’ll get exceptions whenever you try to view the dynamically generated data.
::::
-When you define a scripted field in {{kib}}, you have a choice of the [Lucene expressions](../../explore-analyze/scripting/modules-scripting-expression.md) or the [Painless](../../explore-analyze/scripting/modules-scripting-painless.md) scripting language.
+When you define a scripted field in {{product.kibana}}, you have a choice of the [Lucene expressions](../../explore-analyze/scripting/modules-scripting-expression.md) or the [Painless](../../explore-analyze/scripting/modules-scripting-painless.md) scripting language.
You can reference any single value numeric field in your expressions, for example:
@@ -333,7 +336,7 @@ You can reference any single value numeric field in your expressions, for exampl
doc['field_name'].value
```
-For more information on scripted fields and additional examples, refer to [Using Painless in {{kib}} scripted fields](https://www.elastic.co/blog/using-painless-kibana-scripted-fields)
+For more information on scripted fields and additional examples, refer to [Using Painless in {{product.kibana}} scripted fields](https://www.elastic.co/blog/using-painless-kibana-scripted-fields)
#### Migrate to runtime fields or {{esql}} queries [migrate-off-scripted-fields]
@@ -444,7 +447,7 @@ The ability to create new scripted fields has been removed from the **Data Views
2. Select the data view that contains the scripted field you want to manage.
3. Select the **Scripted fields** tab, then open the scripted field edit options or delete the scripted field.
-For more information about scripted fields in {{es}}, refer to [Scripting](../../explore-analyze/scripting.md).
+For more information about scripted fields in {{product.elasticsearch}}, refer to [Scripting](../../explore-analyze/scripting.md).
::::{warning}
Built-in validation is unsupported for scripted fields. When your scripts contain errors, you receive exceptions when you view the dynamically generated data.
@@ -454,7 +457,7 @@ Built-in validation is unsupported for scripted fields. When your scripts contai
### Format data view fields [managing-fields]
-{{kib}} uses the same field types as {{es}}, however, some {{es}} field types are unsupported in {{kib}}. To customize how {{kib}} displays data view fields, use the formatting options.
+{{product.kibana}} uses the same field types as {{product.elasticsearch}}. However, some {{product.elasticsearch}} field types are unsupported in {{product.kibana}}. To customize how {{product.kibana}} displays data view fields, use the formatting options.
1. Go to the **Data Views** management page using the navigation menu or the [global search field](../../explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md).
2. Click the data view that contains the field you want to change.
@@ -598,7 +601,7 @@ Supported transformations include:
Numeric fields support **Bytes and Bits**, **Color**, **Duration**, **Histogram**, **Number**, **Percentage**, **String**, and **Url** formatters.
-The **Bytes and Bits**, **Number**, and **Percentage** formatters enable you to choose the display formats of numbers in the field using the [Elastic numeral pattern](../../explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md) syntax that {{kib}} maintains.
+The **Bytes and Bits**, **Number**, and **Percentage** formatters enable you to choose the display formats of numbers in the field using the [Elastic numeral pattern](../../explore-analyze/numeral-formatting.md) syntax that {{product.kibana}} maintains.
The **Histogram** formatter is used only for the [histogram field type](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/mapping-reference/histogram.md). When you use the **Histogram** formatter, you can apply the **Bytes and Bits**, **Number**, or **Percentage** format to aggregated data.
@@ -675,7 +678,7 @@ stack: ga 9.2
Some data views are exclusively configured and **managed** by Elastic. You can view and use these managed data views, but you can't edit them. If you'd like to use a modified version of a managed data view, you can duplicate it and edit that new copy as needed. To do this:
-1. Open the {{kib}} application where you want to use the data view. For example, **Discover** or **Lens**.
+1. Open the {{product.kibana}} application where you want to use the data view. For example, **Discover** or **Lens**.
:::{note}
The duplication operation isn't available from the **Data Views** management page.
:::
@@ -688,4 +691,4 @@ Some data views are exclusively configured and **managed** by Elastic. You can v
4. Select **Duplicate**. A Similar flyout opens where you can adjust the settings of the new copy of the managed data view.
-5. Finalize your edits, then select **Save data view to Kibana** or **Use without saving**, depending on your needs. By saving it to {{kib}}, you can retrieve it and use it again later.
+5. Finalize your edits, then select **Save data view to Kibana** or **Use without saving**, depending on your needs. By saving it to {{product.kibana}}, you can retrieve it and use it again later.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/files.md b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/files.md
index a3abc1ac62..72858b85dc 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/files.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/files.md
@@ -5,14 +5,16 @@ applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
products:
+ - id: kibana
- id: cloud-serverless
+description: Access and manage files uploaded to Kibana from features like cases and Image panels. View, organize, and delete stored files from a centralized management page.
---
# Files [files]
-Several features let you upload files. For example, you can add files to [cases](../../solutions/observability/incident-management/cases.md) or upload a logo to an [Image panel](../visualize/image-panels.md) in a dashboard.
+The Files management page provides a centralized view of all files uploaded to {{product.kibana}}, including images added to dashboards, attachments in cases, and other uploaded assets. From this page, you can view file metadata, download files, or remove them to manage storage.
-You can access and manage all of the files currently stored in {{kib}} from the **Files** page.
+Files uploaded through different {{product.kibana}} features appear here regardless of where they were originally added, making it easier to audit file usage and maintain your {{product.kibana}} instance.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/serverless-file-management.png
:alt: Files UI
diff --git a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md
index e335f5a1a2..f21107e63f 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md
@@ -6,11 +6,14 @@ applies_to:
serverless: ga
products:
- id: kibana
+description: Find apps and saved objects quickly using the global search field. Search by type, name, and tag with keyboard shortcuts and advanced syntax for efficient navigation.
---
# Find apps and objects [kibana-navigation-search]
-To quickly find apps and the objects you create, use the search field in the global header. Search suggestions include deep links into applications, allowing you to directly navigate to the views you need most.
+The global search field in the {{product.kibana}} header provides instant access to applications, dashboards, visualizations, and other saved objects. As you type, search suggestions appear with deep links that take you directly to specific views or objects.
+
+Use advanced search syntax to filter by object type or tag, and keyboard shortcuts to access search without using your mouse.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-app-navigation-search.png
:alt: Example of searching for apps
diff --git a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/reports.md b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/reports.md
index 9a04311e54..9dc18d681b 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/reports.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/reports.md
@@ -5,16 +5,16 @@ applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
products:
+ - id: kibana
- id: cloud-serverless
+description: View and manage generated reports for saved searches, dashboards, and visualizations. Download CSV reports from Discover and track reporting history.
---
# Reports [reports]
-{{kib}} provides you with several options to share saved searches, dashboards, and visualizations.
+The {{reports-app}} management page displays a history of generated reports from Discover searches, dashboards, and visualizations. From this page, you can download completed reports, view report details, or remove old reports to manage storage.
-For example, in **Discover**, you can create and download comma-separated values (CSV) reports for saved searches.
-
-To view and manage reports, go to **Management** > **Reporting**.
+Reports are typically generated as CSV files for Discover searches or PDFs for dashboards and visualizations. The management interface shows report status, creation time, and file size.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/serverless-reports-management.png
:alt: {{reports-app}}
diff --git a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md
index fa144c9e88..0efaf6482d 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md
@@ -9,18 +9,22 @@ applies_to:
products:
- id: cloud-serverless
- id: kibana
+description: Manage saved objects including dashboards, visualizations, and data views. Import, export, copy between spaces, and understand globally unique IDs.
---
# Saved objects [saved-objects]
+Saved objects in {{product.kibana}} include dashboards, visualizations, {{data-sources}}, searches, maps, and other reusable assets. You can organize saved objects with names and tags, import and export them between {{product.kibana}} instances, and copy them between spaces to share with different teams.
+
+This guide covers managing, importing, exporting, and understanding saved object IDs across {{product.kibana}} versions.
+
$$$managing-saved-objects-copy-to-space$$$
$$$managing-saved-objects-export-objects$$$
$$$managing-saved-objects-share-to-space$$$
-
-{{kib}} lets you save objects for your own future use or for sharing with others. Each saved object type has different abilities. For example, you can save your search queries made with **Discover**, which lets you:
+Each saved object type provides different capabilities. For example, saved Discover searches let you:
* Share a link to your search
* Download the full search results in CSV form
@@ -42,10 +46,10 @@ You can find the **Saved Objects** page using the navigation menu or the [global
## Permissions [_required_permissions_5]
-To access **Saved Objects**, you must have a role with the `Saved Objects Management` {{kib}} privilege.
+To access **Saved Objects**, you must have a role with the `Saved Objects Management` {{product.kibana}} privilege.
::::{note}
-Granting access to `Saved Objects Management` authorizes users to manage all saved objects in {{kib}}, including objects that are managed by applications they may not otherwise be authorized to access.
+Granting access to `Saved Objects Management` authorizes users to manage all saved objects in {{product.kibana}}, including objects that are managed by applications they may not otherwise be authorized to access.
::::
@@ -58,9 +62,9 @@ Granting access to `Saved Objects Management` authorizes users to manage all sav
## Import and export [saved-objects-import-and-export]
-Use import and export to move objects between different {{kib}} instances. These actions are useful when you have multiple environments for development and production. Import and export also work well when you have a large number of objects to update and want to batch the process.
+Use import and export to move objects between different {{product.kibana}} instances. These actions are useful when you have multiple environments for development and production. Import and export also work well when you have a large number of objects to update and want to batch the process.
-{{kib}} also provides import and export saved objects APIs for your [Elastic Stack deployments](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/kibana/group/endpoint-saved-objects) and [serverless projects](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/serverless/group/endpoint-saved-objects) to automate this process.
+{{product.kibana}} also provides import and export saved objects APIs for your [Elastic Stack deployments](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/kibana/group/endpoint-saved-objects) and [serverless projects](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/serverless/group/endpoint-saved-objects) to automate this process.
### Import [saved-objects-import]
@@ -69,7 +73,7 @@ Import multiple objects in a single operation.
1. In the toolbar, click **Import**.
2. Select the NDJSON file that includes the objects you want to import.
-3. Select the import options. By default, saved objects already in {{kib}} are overwritten.
+3. Select the import options. By default, saved objects already in {{product.kibana}} are overwritten.
4. Click **Import**.
::::{note}
@@ -84,7 +88,7 @@ Export objects by selection or type.
* To export specific objects, select them in the table, and then click **Export**.
* To export objects by type, click **Export objects** in the toolbar.
-{{kib}} creates an NDJSON with all your saved objects. By default, the NDJSON includes child objects related to the saved objects. Exported dashboards include their associated {{data-sources}}.
+{{product.kibana}} creates an NDJSON with all your saved objects. By default, the NDJSON includes child objects related to the saved objects. Exported dashboards include their associated {{data-sources}}.
::::{note}
The [`savedObjects.maxImportExportSize`](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#savedobjects-maximportexportsize) configuration setting limits the number of saved objects that you can export.
@@ -105,9 +109,9 @@ The copy operation automatically includes child objects that are related to the
## Compatibility across versions [_compatibility_across_versions]
-With each release, {{kib}} introduces changes to the way saved objects are stored. When importing a saved object, {{kib}} runs the necessary migrations to ensure that the imported saved objects are compatible with the current version.
+With each release, {{product.kibana}} introduces changes to the way saved objects are stored. When importing a saved object, {{product.kibana}} runs the necessary migrations to ensure that the imported saved objects are compatible with the current version.
-However, saved objects can only be imported into the same version, a newer minor on the same major, or the next major. Exported saved objects are not backward compatible and cannot be imported into an older version of {{kib}}. For example:
+However, saved objects can only be imported into the same version, a newer minor on the same major, or the next major. Exported saved objects are not backward compatible and cannot be imported into an older version of {{product.kibana}}. For example:
| Exporting version | Importing version | Compatible? |
| --- | --- | --- |
@@ -122,42 +126,42 @@ However, saved objects can only be imported into the same version, a newer minor
stack:
```
-In the past, many saved object types could have the same ID in different [spaces](/deploy-manage/manage-spaces.md). For example, if you copied dashboard "123" from the one space to another space, the second dashboard would also have an ID of "123". While the saved object ID is not something that users would interact with directly, many aspects of {{kib}} rely on it, notably URLs. If you have a "deep link" URL to a saved dashboard, that URL includes the saved object ID.
+In the past, many saved object types could have the same ID in different [spaces](/deploy-manage/manage-spaces.md). For example, if you copied dashboard "123" from the one space to another space, the second dashboard would also have an ID of "123". While the saved object ID is not something that users would interact with directly, many aspects of {{product.kibana}} rely on it, notably URLs. If you have a "deep link" URL to a saved dashboard, that URL includes the saved object ID.
-**Since version 8.0**, {{kib}} requires most saved objects to have *globally unique* IDs. This is a change that we needed to make to support sharing saved objects to multiple spaces. Most saved objects cannot be shared to multiple spaces *yet*, but we needed to start enforcing globally unique object IDs first.
+**Since version 8.0**, {{product.kibana}} requires most saved objects to have *globally unique* IDs. This is a change that we needed to make to support sharing saved objects to multiple spaces. Most saved objects cannot be shared to multiple spaces *yet*, but we needed to start enforcing globally unique object IDs first.
We have made several enhancements to minimize the impact, and this document describes what you need to know about the changes and how it will affect you.
### Impact upon upgrading to version 8.x or later [saved-object-ids-impact-upon-upgrading]
-Every time you upgrade {{kib}}, [saved objects are migrated to a new format](/deploy-manage/upgrade/deployment-or-cluster/saved-object-migrations.md). When you first upgrade to version 8.x or later, this migration process will start enforcing globally unique saved object IDs.
+Every time you upgrade {{product.kibana}}, [saved objects are migrated to a new format](/deploy-manage/upgrade/deployment-or-cluster/saved-object-migrations.md). When you first upgrade to version 8.x or later, this migration process will start enforcing globally unique saved object IDs.
In practical terms, **any old saved objects that exist in a custom space will have their IDs changed to a new UUID**, while saved objects in the Default space will be unchanged. This is how we can ensure that every saved object ID is unique. For example: if you had dashboard "123" in the Default space and dashboard "123" in Another space, after the upgrade you would have dashboard "123" in the Default space and dashboard "456" in Another space.
### Impact when using version 8.x or later [saved-object-ids-impact-when-using]
-After you upgrade, or if you set up a new {{kib}} instance using version 8.x or later, there are a few more things that behave differently.
+After you upgrade, or if you set up a new {{product.kibana}} instance using version 8.x or later, there are a few more things that behave differently.
#### Accessing saved objects using old URLs [saved-object-ids-impact-when-using-legacy-urls]
-When you upgrade {{kib}} and saved object IDs change, the "deep link" URLs to access those saved objects will also change. To reduce the impact, each existing URL is preserved with a special [legacy URL alias](kibana://extend/legacy-url-aliases.md). This means that if you use a bookmark for a saved object ID that was changed, you’ll be redirected to the new URL for that saved object.
+When you upgrade {{product.kibana}} and saved object IDs change, the "deep link" URLs to access those saved objects will also change. To reduce the impact, each existing URL is preserved with a special [legacy URL alias](kibana://extend/legacy-url-aliases.md). This means that if you use a bookmark for a saved object ID that was changed, you’ll be redirected to the new URL for that saved object.
#### Importing and copying saved objects [saved-object-ids-impact-when-using-import-and-copy]
-When you [copy a saved object to another space](/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md#saved-objects-copy-to-other-spaces), {{kib}} effectively [exports it and imports it into that space](/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md#saved-objects-export). In this way, copying a saved object has always behaved like an import. In this document when we say "import", it applies to both features.
+When you [copy a saved object to another space](/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md#saved-objects-copy-to-other-spaces), {{product.kibana}} effectively [exports it and imports it into that space](/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md#saved-objects-export). In this way, copying a saved object has always behaved like an import. In this document when we say "import", it applies to both features.
-Historically, whether you imported or copied a saved object, {{kib}} would create *at most* one copy of a saved object in that space. If you imported the saved object multiple times, {{kib}} would overwrite the existing object, because it used the same ID. Since saved object IDs are now globally unique, {{kib}} maintains this functionality by tracking each saved object’s *origin*. When you import an object in version 8.x or later, {{kib}} uses either the saved object ID *or* the origin to determine its destination.
+Historically, whether you imported or copied a saved object, {{product.kibana}} would create *at most* one copy of a saved object in that space. If you imported the saved object multiple times, {{product.kibana}} would overwrite the existing object, because it used the same ID. Since saved object IDs are now globally unique, {{product.kibana}} maintains this functionality by tracking each saved object’s *origin*. When you import an object in version 8.x or later, {{product.kibana}} uses either the saved object ID *or* the origin to determine its destination.
-If you import a saved object using the "Check for existing objects" option, {{kib}} will take the following steps:
+If you import a saved object using the "Check for existing objects" option, {{product.kibana}} will take the following steps:
-1. If {{kib}} finds a matching saved object with the exact same ID in the target space, that will be the import destination — you can **overwrite** that destination or **skip** it.
-2. Otherwise, if {{kib}} finds a matching saved object with a *different* ID that has the same origin, that will be the import destination — again, you can **overwrite** that destination or **skip** it.
-3. Otherwise, if a saved object with the exact same ID exists in a *different* space, then {{kib}} will generate a random ID for the import destination, preserving the saved object’s origin.
-4. Otherwise, {{kib}} creates the saved object with the given ID.
+1. If {{product.kibana}} finds a matching saved object with the exact same ID in the target space, that will be the import destination — you can **overwrite** that destination or **skip** it.
+2. Otherwise, if {{product.kibana}} finds a matching saved object with a *different* ID that has the same origin, that will be the import destination — again, you can **overwrite** that destination or **skip** it.
+3. Otherwise, if a saved object with the exact same ID exists in a *different* space, then {{product.kibana}} will generate a random ID for the import destination, preserving the saved object’s origin.
+4. Otherwise, {{product.kibana}} creates the saved object with the given ID.
-For example, you have a saved object in an `export.ndjson` file, and you set up a brand new {{kib}} instance. You attempt to import the saved object using the "Check for existing objects" and "Automatically overwrite conflicts" options. The first time you import the saved object, {{kib}} will create a new object with the same ID (step 4 above). If you import it again, {{kib}} will find that object and overwrite it (step 1 above). If you then create a *different* space and import it there, {{kib}} will create a new object with a random ID (step 3 above). Finally, if you import it into the second space again, {{kib}} will find the second object with a matching origin and overwrite it (step 2 above).
+For example, you have a saved object in an `export.ndjson` file, and you set up a brand new {{product.kibana}} instance. You attempt to import the saved object using the "Check for existing objects" and "Automatically overwrite conflicts" options. The first time you import the saved object, {{product.kibana}} will create a new object with the same ID (step 4 above). If you import it again, {{product.kibana}} will find that object and overwrite it (step 1 above). If you then create a *different* space and import it there, {{product.kibana}} will create a new object with a random ID (step 3 above). Finally, if you import it into the second space again, {{product.kibana}} will find the second object with a matching origin and overwrite it (step 2 above).
::::{warning}
When you import a saved object and it is created with a different ID, if 1. it contains weak links to other saved objects (such as a dashboard with a Markdown URL to navigate to another dashboard) and 2. the object’s ID has changed (step 3 above), those weak links will be broken. For more information, refer to [the changelog](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/8.0/release-notes-8.0.0.html#known-issue-8.0.0).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/tags.md b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/tags.md
index 0d87cdb48b..e60ebd5edd 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/tags.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/tags.md
@@ -8,12 +8,14 @@ applies_to:
products:
- id: cloud-serverless
- id: kibana
+description: Categorize and organize saved objects with tags. Create color-coded tags, assign them to dashboards and visualizations, and filter objects by shared tags in global search.
---
# Tags [managing-tags]
+Tags help you organize and find saved objects by categorizing them into groups. You can create color-coded tags, assign them to multiple objects like dashboards and visualizations, and then use tags to quickly filter and locate related content in the global search or {{manage-app}} pages.
-Use tags to categorize your saved objects, then filter for related objects based on shared tags.
+This guide shows you how to create tags, assign them to objects, and manage tag assignments across your saved objects.
To get started, go to the **Tags** management page using the navigation menu or the [global search field](../../explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md).
@@ -32,7 +34,7 @@ To create tags, you must meet the minimum requirements.
* The `write` privilege allows to create, edit, and delete tags.
::::{note}
-Having the `Tag Management` {{kib}} privilege is not required to view tags assigned on objects you have `read` access to, or to filter objects by tags from the global search.
+Having the `Tag Management` {{product.kibana}} privilege is not required to view tags assigned on objects you have `read` access to, or to filter objects by tags from the global search.
::::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/automating-report-generation.md b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/automating-report-generation.md
index a25b48137c..bb940a35f3 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/automating-report-generation.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/automating-report-generation.md
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
---
+description: Generate reports automatically using {{watcher}}, scripts, or scheduled tasks. Configure recurring exports and share PDF, PNG, or CSV reports by email.
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/automating-report-generation.html
applies_to:
@@ -10,11 +11,23 @@ products:
# Automatically generate reports [automating-report-generation]
-To automatically generate PDF and CSV reports, generate a POST URL, then submit an HTTP `POST` request using {{watcher}} or a script. In {{stack}} 9.1 and Serverless, you can use {{kib}} to generate reports on a recurring schedule and share them with a list of emails that you specify.
+Automate report generation to share dashboards, visualizations, and data exports on a regular schedule. You can use {{watcher}} or scripts to trigger report generation through a POST URL, or set up recurring schedules directly in {{product.kibana}} to generate and email reports automatically.
+
+Several approaches are available for automating reports:
+
+* **{{watcher}}**: Configure watches that generate and email reports based on schedules or conditions
+* **Scripts**: Use HTTP POST requests to programmatically generate reports on demand
+* **Scheduled exports**: {applies_to}`stack: preview 9.1` {applies_to}`serverless: preview` Set up recurring tasks in {{product.kibana}} that automatically generate and share reports by email
+
+**Prerequisites:**
+
+* Appropriate {{product.kibana}} privileges to create reports
+* {applies_to}`stack: ga` API key or user credentials with reporting permissions
+* {applies_to}`stack: preview 9.1` {applies_to}`serverless: preview` For scheduled email sharing, a configured email connector
:::{note}
:applies_to: {stack: ga, serverless: unavailable}
-API keys are used to authenticate requests to generate reports. If you have a cross-cluster search environment and want to generate reports from remote clusters, you must have the appropriate cluster and index privileges on the remote cluster and local cluster. For example, if requests are authenticated with an API key, the API key requires certain privileges on the local cluster that contains the leader index, instead of the remote. For more information and examples, refer to [Configure roles and users for remote clusters](../../deploy-manage/remote-clusters/remote-clusters-cert.md#remote-clusters-privileges-cert).
+{{api-keys-app}} are used to authenticate requests to generate reports. If you have a {{ccs}} environment and want to generate reports from remote clusters, you must have the appropriate cluster and index privileges on the remote cluster and local cluster. For example, if requests are authenticated with an API key, the API key requires certain privileges on the local cluster that contains the leader index, instead of the remote. For more information and examples, refer to [Configure roles and users for remote clusters](../../deploy-manage/remote-clusters/remote-clusters-cert.md#remote-clusters-privileges-cert).
:::
## Create a POST URL [create-a-post-url]
@@ -88,7 +101,7 @@ PUT _watcher/watch/error_report
2. An example POST URL. You can copy and paste the URL for any report.
3. Optional, default is `40`.
4. Optional, default is `15s`.
-5. User credentials for a user with permission to access {{kib}} and the {{report-features}}. For more information, refer to [Configure reporting](../report-and-share.md).
+5. User credentials for a user with permission to access {{product.kibana}} and the {{report-features}}. For more information, refer to [Configure reporting](../report-and-share.md).
::::{note}
@@ -117,8 +130,8 @@ curl \
```
1. The required `POST` method.
-2. The user credentials for a user with permission to access {{kib}} and {{report-features}}.
-3. The required `kbn-xsrf` header for all `POST` requests to {{kib}}. For more information, refer to [API Request Headers](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/kibana/).
+2. The user credentials for a user with permission to access {{product.kibana}} and {{report-features}}.
+3. The required `kbn-xsrf` header for all `POST` requests to {{product.kibana}}. For more information, refer to [API Request Headers](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/kibana/).
4. The POST URL. You can copy and paste the URL for any report.
@@ -139,7 +152,7 @@ An example response for a successfully queued report:
}
```
-1. The relative path on the {{kib}} host for downloading the report.
+1. The relative path on the {{product.kibana}} host for downloading the report.
2. (Not included in the example) Internal representation of the reporting job, as found in the `.reporting-*` storage.
@@ -161,14 +174,14 @@ The response payload of a request to generate a report includes the path to down
## Deprecated report URLs [deprecated-report-urls]
-If you experience issues with the deprecated report URLs after you upgrade {{kib}}, regenerate the POST URL for your reports.
+If you experience issues with the deprecated report URLs after you upgrade {{product.kibana}}, regenerate the POST URL for your reports.
* **Dashboard** reports: `/api/reporting/generate/dashboard/`
* **Visualize Library** reports: `/api/reporting/generate/visualization/`
* **Discover** reports: `/api/reporting/generate/search/`
:::{important}
-In earlier {{kib}} versions, you could use the `&sync` parameter to append to report URLs that held the request open until the document was fully generated. The `&sync` parameter is now unsupported. If you use the `&sync` parameter in Watcher, you must update the parameter.
+In earlier {{product.kibana}} versions, you could use the `&sync` parameter to append to report URLs that held the request open until the document was fully generated. The `&sync` parameter is now unsupported. If you use the `&sync` parameter in Watcher, you must update the parameter.
:::
## Schedule and share reports [schedule-report-generation]
@@ -182,23 +195,23 @@ Save time by setting up a recurring task that automatically generates reports an
### Prerequisites [scheduled-reports-reqs]
-* To generate PDF and PNG reports, your {{kib}} instance needs a minimum of 2GB of RAM. There is no minimum requirement for CSV reports.
+* To generate PDF and PNG reports, your {{product.kibana}} instance needs a minimum of 2GB of RAM. There is no minimum requirement for CSV reports.
* To use the scheduled reports feature, your role needs [access to reporting](../../deploy-manage/kibana-reporting-configuration.md#grant-user-access).
-* (Optional) To view and manage other users’ reports and schedules, your role needs `All` privileges for the **Manage Scheduled Reports** feature. You can set this by configuring your role's {{kib}} privileges. If your role doesn't have the **Manage Scheduled Reporting** feature privilege, you can only share reports with yourself.
-* Sharing reports outside of {{kib}} requires a default preconfigured email connector.
+* (Optional) To view and manage other users’ reports and schedules, your role needs `All` privileges for the **Manage Scheduled Reports** feature. You can set this by configuring your role's {{product.kibana}} privileges. If your role doesn't have the **Manage Scheduled Reporting** feature privilege, you can only share reports with yourself.
+* Sharing reports outside of {{product.kibana}} requires a default preconfigured email connector.
* **{{ech}} or {{serverless-short}} users**: You do not need to set up a default preconfigured email connector. Kibana provides you with a built-in preconfigured email connector that uses the SMTP protocol to send emails. To view it, go to the **Connectors** page and find the Elastic-Cloud-SMTP connector.
- * **Self-managed users**: You must set up a default preconfigured email connector to send notifications outside of {{kib}}. To do this:
+ * **Self-managed users**: You must set up a default preconfigured email connector to send notifications outside of {{product.kibana}}. To do this:
1. Open your `kibana.yml` file.
- 2. Add the `xpack.actions.preconfigured` {{kib}} setting. This setting specifies configuration details for the preconfigured connector that you're defining.
+ 2. Add the `xpack.actions.preconfigured` {{product.kibana}} setting. This setting specifies configuration details for the preconfigured connector that you're defining.
3. Under the `xpack.actions.preconfigured` setting, define the email connector. Refer to [Email connectors](kibana://reference/connectors-kibana/pre-configured-connectors.md#preconfigured-email-configuration) to learn about requirements for different email services and providers.
:::{note}
- You must define preconfigured email connector details in the `kibana.yml` file. You cannot create a preconfigured email connector from the {{kib}} UI.
+ You must define preconfigured email connector details in the `kibana.yml` file. You cannot create a preconfigured email connector from the {{product.kibana}} UI.
:::
- 4. Add the `notifications.connectors.default.email` {{kib}} setting, and provide the name of your email connector. The `notifications.connectors.default.email` setting specifies the default email connector to use when sending notifications. This is especially useful if you have multiple email connectors and want to set a default one.
+ 4. Add the `notifications.connectors.default.email` {{product.kibana}} setting, and provide the name of your email connector. The `notifications.connectors.default.email` setting specifies the default email connector to use when sending notifications. This is especially useful if you have multiple email connectors and want to set a default one.
The following example shows a modified `kibana.yml` file with a preconfigured email connector that's set as the default connector for email notifications:
@@ -221,7 +234,7 @@ Save time by setting up a recurring task that automatically generates reports an
notifications.connectors.default.email: my-email
```
-* (Optional) To control who can receive email notifications from {{kib}}, add the [`xpack.actions.email.domain_allowlist` setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/alerting-settings.md) to your `kibana.yml` file. To learn more about configuring this setting, refer to [Notifications domain allowlist](../alerts-cases/alerts/notifications-domain-allowlist.md).
+* (Optional) To control who can receive email notifications from {{product.kibana}}, add the [`xpack.actions.email.domain_allowlist` setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/alerting-settings.md) to your `kibana.yml` file. To learn more about configuring this setting, refer to [Notifications domain allowlist](../alerts-cases/alerts/notifications-domain-allowlist.md).
### Create a schedule [create-scheduled-report]
@@ -255,8 +268,8 @@ To stop a scheduled report, you can take the following actions from the **Schedu
The feature enables analysis of data in external tools, but it is not intended for bulk export or to backup Elasticsearch data. Issues with report generation and sharing are likely to happen in the following scenarios:
-* The limit for email attachments is 10 MB. {{kib}} might fail to attach reports that are larger than this size.
-* Scheduling too many reports at the same time might cause reports to be shared late or at an inconsistent schedule. {{kib}} Task Manager runs reporting tasks one at a time.
+* The limit for email attachments is 10 MB. {{product.kibana}} might fail to attach reports that are larger than this size.
+* Scheduling too many reports at the same time might cause reports to be shared late or at an inconsistent schedule. {{product.kibana}} Task Manager runs reporting tasks one at a time.
* If your cluster is running many tasks in general, reports may be delayed.
* Scheduling reports of Canvas workpads is not supported since Canvas workpads are in maintenance mode.
* Scheduling CSV reports of Lens visualizations is not supported.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md
index 69bcafed57..c2b932baee 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
---
+description: Troubleshoot common CSV export issues including timeouts, socket errors, token expiration, and scroll API configuration.
navigation_title: CSV
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/reporting-troubleshooting-csv.html
@@ -13,31 +14,34 @@ products:
# CSV [reporting-troubleshooting-csv]
+CSV export in {{product.kibana}} queries {{product.elasticsearch}} and formats the results as downloadable CSV files. While this works well for moderate data exports, issues can occur with large datasets, slow storage, network latency, or authentication timeouts. This page helps you diagnose and resolve common CSV export problems.
+
+Common issues include:
+
+* Report timeouts when exporting more than 250 MB of data
+* Incomplete data when shards are unavailable or using {{ccs}}
+* Socket hangup errors during long-running exports
+* Token expiration for SAML-authenticated deployments
+
+For general troubleshooting guidance, refer to [Troubleshooting](reporting-troubleshooting.md).
::::{note}
-We recommend using CSV reports to export moderate amounts of data only. The feature enables analysis of data in external tools, but it is not intended for bulk export or to backup Elasticsearch data. Report timeout and incomplete data issues are likely if you are exporting data where:
+CSV export is designed for moderate data amounts only. It enables data analysis in external tools but is not intended for bulk export or {{product.elasticsearch}} backups. Report timeout and incomplete data issues are likely when exporting data where:
* More than 250 MB of data is being exported
* Data is stored on slow storage tiers
* Any shard needed for the search is unavailable
* Network latency between nodes is high
-* Cross-cluster search is used
-* ES|QL is used and result row count exceeds the limits of ES|QL queries
-
-To work around the limitations, use filters to create multiple smaller reports, or extract the data you need directly with the Elasticsearch APIs.
+* {{ccs}} is used
+* {{esql}} is used and result row count exceeds the limits of {{esql}} queries
-For more information on using Elasticsearch APIs directly, see [Scroll API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-scroll), [Point in time API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-open-point-in-time), [ES|QL](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/esql/esql-rest.md) or [SQL](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/sql/sql-rest-format.md#_csv) with CSV response data format. We recommend that you use an official Elastic language client: details for each programming language library that Elastic provides are in the [{{es}} Client documentation](/reference/elasticsearch-clients/index.md).
+To work around these limitations, use filters to create multiple smaller reports, or extract data directly with {{product.elasticsearch}} APIs. For information on using {{product.elasticsearch}} APIs directly, refer to [Scroll API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-scroll), [Point in time API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-open-point-in-time), [{{esql}}](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/esql/esql-rest.md), or [SQL](elasticsearch://reference/query-languages/sql/sql-rest-format.md#_csv) with CSV response data format. Consider using an official {{product.elasticsearch}} client: refer to [{{product.elasticsearch}} Client documentation](/reference/elasticsearch-clients/index.md).
-[Reporting parameters](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/reporting-settings.md) can be adjusted to overcome some of these limiting scenarios. Results are dependent on data size, availability, and latency factors and are not guaranteed.
+You can adjust [Reporting parameters](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/reporting-settings.md) to overcome some limiting scenarios. Results depend on data size, availability, and latency factors and are not guaranteed.
::::
-The CSV export feature in Kibana makes queries to Elasticsearch and formats the results into CSV. This feature offers a solution that attempts to provide the most benefit to the most use cases. However, things could go wrong during export. Elasticsearch can stop responding, repeated querying can take so long that authentication tokens can time out, and the format of exported data can be too complex for spreadsheet applications to handle. Such situations are outside of the control of Kibana. If the use case becomes complex enough, it’s recommended that you create scripts that query Elasticsearch directly, using a scripting language like Python and the public {{es}} APIs.
-
-For advice about common problems, refer to [Troubleshooting](reporting-troubleshooting.md).
-
-
## Configuring CSV export to use the scroll API [reporting-troubleshooting-csv-configure-scan-api]
The Kibana CSV export feature collects all of the data from Elasticsearch by using multiple requests to page over all of the documents. Internally, the feature uses the [Point in time API and `search_after` parameters in the queries](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-open-point-in-time) to do so. There are some limitations related to the point in time API:
@@ -101,4 +105,4 @@ You can use the following workarounds for this error:
* Create smaller reports. Instead of creating one report that covers a large time range, create multiple reports that cover segmented time ranges.
* Increase `xpack.security.authc.token.timeout`, which is set to `20m` by default.
-* To avoid token expirations completely, use a type of authentication that doesn’t expire (such as Basic auth), or run the export using scripts that query {{es}} directly.
+* To avoid token expirations completely, use a type of authentication that doesn’t expire (such as Basic auth), or run the export using scripts that query {{product.elasticsearch}} directly.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-pdf.md b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-pdf.md
index 2fc7833422..24b94f79b2 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-pdf.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-pdf.md
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
---
+description: Troubleshoot PDF and PNG export issues including browser dependencies, sandbox requirements, font rendering, connection errors, and system requirements.
navigation_title: PDF/PNG
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/reporting-troubleshooting-pdf.html
@@ -13,21 +14,31 @@ products:
# PDF/PNG [reporting-troubleshooting-pdf]
+PDF and PNG reporting in {{product.kibana}} uses a headless Chromium browser to capture screenshots of dashboards and visualizations. Issues can occur due to missing system dependencies, sandbox restrictions, font problems, or resource constraints. This page helps you diagnose and resolve common PDF and PNG export problems.
-::::{note}
-We recommend using PNG/PDF reports to export moderate amounts of data only. The feature enables a high-level export capability, but it’s not intended for bulk export. If you need to export several pages of image data, consider using multiple report jobs to export a small number of pages at a time. If the screenshot of exported dashboard contains a large number of pixels, consider splitting the large dashboard into smaller artifacts to use less memory and CPU resources.
+Common issues include:
-For the most reliable configuration of PDF/PNG {{report-features}}, consider installing {{kib}} using [Docker](../../deploy-manage/deploy/self-managed/install-kibana-with-docker.md) or using [Elastic Cloud](https://cloud.elastic.co).
+* Missing Network Security Service (NSS) libraries
+* Chromium sandbox requirements and user namespace restrictions
+* Text rendering incorrectly due to missing fonts
+* Connection refused errors with server host settings
+* Memory limitations causing page crashes
-::::
+**Technical summary**: Use the built-in reporting diagnostics tool at **{{reports-app}} > Run reporting diagnostics** to identify common configuration issues. For Docker or {{ecloud}} deployments, most dependencies are preconfigured.
+
+For general troubleshooting guidance, refer to [Troubleshooting](reporting-troubleshooting.md).
+::::{note}
+PDF and PNG reports work best with moderate amounts of visual data. The feature provides high-level export capability but is not intended for bulk export. If you need to export several pages of image data, use multiple report jobs to export a small number of pages at a time. If exported dashboard screenshots contain a large number of pixels, split large dashboards into smaller artifacts to reduce memory and CPU usage.
+
+For the most reliable configuration of PDF/PNG {{report-features}}, install {{product.kibana}} using [Docker](../../deploy-manage/deploy/self-managed/install-kibana-with-docker.md) or use [{{ecloud}}](https://cloud.elastic.co).
-For more advice about common problems, refer to [Troubleshooting](reporting-troubleshooting.md).
+::::
## Reporting diagnostics [reporting-diagnostics]
-Reporting comes with a built-in utility to try to automatically find common issues. When {{kib}} is running, navigate to the **Report Listing** page, and click **Run reporting diagnostics**. This will open up a diagnostic tool that checks various parts of the {{kib}} deployment and comes up with any relevant recommendations.
+Reporting comes with a built-in utility to try to automatically find common issues. When {{product.kibana}} is running, navigate to the **Report Listing** page, and click **Run reporting diagnostics**. This will open up a diagnostic tool that checks various parts of the {{product.kibana}} deployment and comes up with any relevant recommendations.
If the diagnostic information doesn’t reveal the problem, you can troubleshoot further by starting the Kibana server with an environment variable for revealing additional debugging logs. Refer to [Puppeteer debug logs](#reporting-troubleshooting-puppeteer-debug-logs).
@@ -74,7 +85,7 @@ The Chromium binary is located in the Kibana installation directory as `data/hea
## Puppeteer debug logs [reporting-troubleshooting-puppeteer-debug-logs]
-The Chromium browser that {{kib}} launches on the server is driven by a NodeJS library for Chromium called Puppeteer. The Puppeteer library has its own command-line method to generate its own debug logs, which can sometimes be helpful, particularly to figure out if a problem is caused by Kibana or Chromium. Learn more [debugging tips](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v1.19.0/README.md#debugging-tips).
+The Chromium browser that {{product.kibana}} launches on the server is driven by a NodeJS library for Chromium called Puppeteer. The Puppeteer library has its own command-line method to generate its own debug logs, which can sometimes be helpful, particularly to figure out if a problem is caused by Kibana or Chromium. Learn more [debugging tips](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v1.19.0/README.md#debugging-tips).
Using Puppeteer’s debug method when launching Kibana would look like:
@@ -89,30 +100,30 @@ The Puppeteer logs are very verbose and could possibly contain sensitive informa
## System requirements [reporting-troubleshooting-system-requirements]
-In Elastic Cloud, the {{kib}} instances that most configurations provide by default is for 1GB of RAM for the instance. That is enough for {{kib}} {{report-features}} when the visualization or dashboard is relatively simple, such as a single pie chart or a dashboard with a few visualizations. However, certain visualization types incur more load than others. For example, a TSVB panel has a lot of network requests to render.
+In Elastic Cloud, the {{product.kibana}} instances that most configurations provide by default is for 1GB of RAM for the instance. That is enough for {{product.kibana}} {{report-features}} when the visualization or dashboard is relatively simple, such as a single pie chart or a dashboard with a few visualizations. However, certain visualization types incur more load than others. For example, a TSVB panel has a lot of network requests to render.
-If the {{kib}} instance doesn’t have enough memory to run the report, the report fails with an error such as `Error: Page crashed!`. In this case, try increasing the memory for the {{kib}} instance to 2GB.
+If the {{product.kibana}} instance doesn’t have enough memory to run the report, the report fails with an error such as `Error: Page crashed!`. In this case, try increasing the memory for the {{product.kibana}} instance to 2GB.
## Unable to connect to Elastic Maps Service [reporting-troubleshooting-maps-ems]
-[Elastic Maps Service ({{ems-init}})](https://www.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service) is a service that hosts tile layers and vector shapes of administrative boundaries. If a report contains a map with a missing basemap layer or administrative boundary, the {{kib}} server does not have access to {{ems-init}}. Refer to [*Connect to Elastic Maps Service*](../visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md) for information about how to connect your {{kib}} server to {{ems-init}}.
+[Elastic Maps Service ({{ems-init}})](https://www.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service) is a service that hosts tile layers and vector shapes of administrative boundaries. If a report contains a map with a missing basemap layer or administrative boundary, the {{product.kibana}} server does not have access to {{ems-init}}. Refer to [*Connect to Elastic Maps Service*](../visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md) for information about how to connect your {{product.kibana}} server to {{ems-init}}.
## Manually install the Chromium browser for Darwin [reporting-manual-chromium-install]
-Chromium is not embedded into {{kib}} for the Darwin (Mac OS) architecture. When running {{kib}} on Darwin, {{report-features}} will download Chromium into the proper area of the {{kib}} installation path the first time the server starts. If the server does not have access to the internet, you must download the Chromium browser and install it into the {{kib}} installation path.
+Chromium is not embedded into {{product.kibana}} for the Darwin (Mac OS) architecture. When running {{product.kibana}} on Darwin, {{report-features}} will download Chromium into the proper area of the {{product.kibana}} installation path the first time the server starts. If the server does not have access to the internet, you must download the Chromium browser and install it into the {{product.kibana}} installation path.
1. Download the Chromium zip file:
* For [x64](https://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/chromium-browser-snapshots/Mac/901912/chrome-mac.zip) systems
* For [ARM](https://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/chromium-browser-snapshots/Mac_Arm/901913/chrome-mac.zip) systems
-2. Copy the zip file into the holding area. Relative to the root directory of {{kib}}, the path is:
+2. Copy the zip file into the holding area. Relative to the root directory of {{product.kibana}}, the path is:
* `.chromium/x64` for x64 systems
* `.chromium/arm64` for ARM systems
-When {{kib}} starts, it will automatically extract the browser from the zip file and is then ready for PNG and PDF reports.
+When {{product.kibana}} starts, it will automatically extract the browser from the zip file and is then ready for PNG and PDF reports.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting.md b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting.md
index 5f8b288472..66c3d3c29e 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting.md
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
---
+description: Diagnose and resolve common reporting errors including version conflicts, max attempts reached, and timeout issues. Enable verbose logging for troubleshooting.
navigation_title: Troubleshoot reporting
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/reporting-troubleshooting.html
@@ -11,12 +12,17 @@ products:
-# Troubleshoot report errors and logs in {{kib}} [reporting-troubleshooting]
+# Troubleshoot report errors and logs in {{product.kibana}} [reporting-troubleshooting]
+{{report-features}} in {{product.kibana}} are designed for simple data exports and visualizations, not bulk data export or large-scale operations. When you encounter issues generating reports, understanding common error messages and enabling verbose logging can help you diagnose and resolve problems quickly.
-Kibana excels as a data visualization tool. The {{report-features}} exist to export data as simple reports, however Kibana is not a data export tool. To export data at a large scale, there are better ways and better architectures for exporting data at scale from Elasticsearch.
+Common issues include:
-If you have trouble creating simple reports, there are some general solutions to common problems you might encounter while using {{report-features}}. For tips related to specific types of reports, refer to [CSV](reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md) and [PDF/PNG](reporting-troubleshooting-pdf.md).
+* Version conflict exceptions in clustered environments
+* "Max attempts reached" errors due to timeouts or configuration issues
+* Report failures with large datasets or complex visualizations
+
+For issues specific to report formats, refer to [CSV troubleshooting](reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md) and [PDF/PNG troubleshooting](reporting-troubleshooting-pdf.md).
## Error messages [reporting-troubleshooting-error-messages]
@@ -26,7 +32,7 @@ There are some common solutions for error messages that you might encounter in {
### Version conflict engine exceptions [reporting-troubleshooting-version-conflict-exception]
-If you are running multiple instances of {{kib}} in a cluster, the instances share the work of running report jobs to evenly distribute the workload. Each instance searches the reporting index for "pending" jobs that the user has requested. It is possible for multiple instances to find the same job in these searches. Only the instance that successfully updated the job status to "processing" will actually run the report job. The other instances that unsuccessfully tried to make the same update will log something similar to this:
+If you are running multiple instances of {{product.kibana}} in a cluster, the instances share the work of running report jobs to evenly distribute the workload. Each instance searches the reporting index for "pending" jobs that the user has requested. It is possible for multiple instances to find the same job in these searches. Only the instance that successfully updated the job status to "processing" will actually run the report job. The other instances that unsuccessfully tried to make the same update will log something similar to this:
```text
StatusCodeError: [version_conflict_engine_exception] [...]: version conflict, required seqNo [6124], primary term [1]. current document has seqNo [6125] and primary term [1], with { ... }
@@ -58,7 +64,7 @@ Create a Markdown visualization and then create a PDF report. If this succeeds,
## Verbose logging [reporting-troubleshooting-verbose-logs]
-{{kib}} server logs have a lot of useful information for troubleshooting and understanding how things work. The full logs from {{report-features}} are a good place to look when you encounter problems. In [`kibana.yml`](/deploy-manage/stack-settings.md):
+{{product.kibana}} server logs have a lot of useful information for troubleshooting and understanding how things work. The full logs from {{report-features}} are a good place to look when you encounter problems. In [`kibana.yml`](/deploy-manage/stack-settings.md):
```yaml
logging.root.level: all
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/alert-panels.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/alert-panels.md
index 29c5861299..ac6c97b586 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/alert-panels.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/alert-panels.md
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
---
+description: Display Observability or Security alerts in dashboard panels filtered by rule tags and types. View alert details, track status, and take actions directly from dashboards.
applies_to:
stack: ga 9.1
serverless: ga
@@ -8,7 +9,9 @@ products:
# Alert panels
-To view alerts in a dashboard, add **Alerts** panels that show selected alerts. Each panel can display either **Observability** or **Security** alerts with the rule tags and rule types that you select.
+Alert panels display {{product.observability}} or {{product.security}} alerts directly in your dashboards, providing quick visibility into active issues without switching to dedicated alert views. You can filter alerts by rule tags and types to focus on specific categories relevant to each dashboard.
+
+This guide shows you how to create alert panels, configure filters, and take actions on alerts from within your dashboard.
## Create an alerts panel
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md
index 5f74a05997..bef3cf2164 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/canvas.html
+description: Design pixel-perfect presentations in Kibana Canvas with live Elasticsearch data. Create multi-page workpads combining visualizations, images, and text.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -14,7 +15,7 @@ products:
Canvas is only available for upgraded installations with existing workpads.
:::
-**Canvas** is a data visualization and presentation tool that allows you to pull live data from {{es}}, then combine the data with colors, images, text, and your imagination to create dynamic, multi-page, pixel-perfect displays. If you are a little bit creative, a little bit technical, and a whole lot curious, then **Canvas** is for you.
+Canvas provides pixel-perfect control over dashboard layouts, letting you create custom presentations that combine live {{es}} data with images, text, and precise styling. Unlike standard dashboards, Canvas gives you complete freedom to position elements exactly where you want them, making it ideal for presentations, reports, and infographics.
With **Canvas**, you can:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-function-reference.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-function-reference.md
index 0f34d74f7c..63aca0fc71 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-function-reference.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-function-reference.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/canvas-function-reference.html
+description: Complete reference of Canvas expression language functions for data transforms, type casting, and sub-expressions. Build powerful workpad visualizations with function documentation.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,9 +11,9 @@ products:
# Canvas function reference [canvas-function-reference]
-Behind the scenes, Canvas is driven by a powerful expression language, with dozens of functions and other capabilities, including table transforms, type casting, and sub-expressions.
+The Canvas expression language provides dozens of functions for transforming data, manipulating element properties, and controlling workpad behavior. Each function accepts specific arguments and returns values that can be passed to other functions through chaining or sub-expressions.
-The Canvas expression language also supports [TinyMath functions](canvas-tinymath-functions.md), which perform complex math calculations.
+This reference documents all available Canvas functions, organized alphabetically. Functions marked with * have required arguments, while † indicates arguments that can be passed multiple times. For mathematical operations, see the [TinyMath functions](canvas-tinymath-functions.md) reference.
A **\*** denotes a required argument.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-present-workpad.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-present-workpad.md
index 7a0876edb8..1b713f7462 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-present-workpad.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-present-workpad.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/canvas-present-workpad.html
+description: Present Canvas workpads with autoplay and fullscreen modes. Configure cycling intervals and presentation settings for dynamic data storytelling.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Present your workpad [canvas-present-workpad]
+# Present workpads [canvas-present-workpad]
-When you are ready to present your workpad, use and enable the presentation options.
+Canvas workpads support presentation features including autoplay to cycle through pages, fullscreen mode for distraction-free viewing, and customizable auto-refresh intervals to keep data current. These features work together to create effective presentations and live monitoring displays.
+
+This guide shows you how to configure autoplay timing, enable fullscreen mode, adjust zoom levels, and control data refresh intervals.
1. Configure the autoplay options.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tinymath-functions.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tinymath-functions.md
index 38fe657dd4..b06619c41d 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tinymath-functions.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tinymath-functions.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/canvas-tinymath-functions.html
+description: Complete reference of TinyMath functions for complex math calculations in Canvas expressions. Perform array operations and apply JavaScript Math methods to data.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,9 +11,9 @@ products:
# TinyMath functions [canvas-tinymath-functions]
-TinyMath provides a set of functions that can be used with the Canvas expression language to perform complex math calculations. Read on for detailed information about the functions available in TinyMath, including what parameters each function accepts, the return value of that function, and examples of how each function behaves.
+TinyMath functions enable complex mathematical calculations within Canvas expressions. These functions operate on numbers and arrays, applying standard JavaScript Math methods element-wise to array inputs. When multiple arrays are provided, calculations occur index by index.
-Most of the functions accept arrays and apply JavaScript Math methods to each element of that array. For the functions that accept multiple arrays as parameters, the function generally does the calculation index by index.
+This reference provides detailed documentation for each TinyMath function, including parameters, return values, and practical examples. Functions can be nested, with inner function return types matching the parameter types expected by outer functions.
Any function can be wrapped by another function as long as the return type of the inner function matches the acceptable parameter type of the outer function.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md
index 3e93918a19..f3628e61ee 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/canvas-tutorial.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/canvas-tutorial.html
+description: Step-by-step tutorial for creating Canvas workpads with ecommerce data. Learn to build sales monitoring dashboards with custom elements and data visualizations.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,14 @@ products:
# Tutorial: Create a workpad for monitoring sales [canvas-tutorial]
-To familiarize yourself with **Canvas**, add the Sample eCommerce orders data, then use the data to create a workpad for monitoring sales at an eCommerce store.
+In this tutorial, you'll learn the fundamentals of building Canvas workpads by creating a sales monitoring dashboard. You'll explore how to add images, create metric displays, build data tables, and apply time range controls. By the end, you'll understand the core workflows for creating custom presentations with live data.
+
+The tutorial uses eCommerce sample data to demonstrate these techniques, but you can apply the same approaches to any data set.
+
+**Prerequisites:**
+
+- Access to {{kib}} (version 8.0 or later)
+- eCommerce sample data installed (instructions below)
## Open and set up Canvas [_open_and_set_up_canvas]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md
index 8cd23c0b82..4ad6ccfed3 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/canvas/edit-workpads.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/edit-workpads.html
+description: Customize Canvas workpads with variables, format settings, and element styling. Create reusable patterns and apply consistent formatting across workpad components.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Edit workpads [edit-workpads]
-To create the look and feel that you want, apply format settings to the entire workpad, or individual elements.
+Customizing Canvas workpads involves creating variables for reusable patterns, applying formatting to elements and entire workpads, and styling components to achieve your desired appearance. Variables are particularly useful when cloning workpads or updating multiple elements that share common properties.
+
+This guide covers creating and using variables, applying workpad-level formatting, and customizing individual element styles.
## Create variables [create-variables]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md
index 90ea1799f8..300d809425 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/custom-visualizations-with-vega.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/vega.html
+description: Build custom visualizations with Vega and Vega-Lite grammars for advanced use cases. Create scatter charts, sankey diagrams, and custom maps with Elasticsearch queries.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Custom visualizations with Vega [vega]
-**Vega** and **Vega-Lite** are both grammars for creating custom visualizations. They are recommended for advanced users who are comfortable writing {{es}} queries manually. **Vega-Lite** is a good starting point for users who are new to both grammars, but they are not compatible.
+Vega and Vega-Lite provide declarative grammar for building custom visualizations beyond what standard {{kib}} editors support. Vega-Lite offers a simpler, high-level syntax for common charts, while Vega provides more control for complex visualizations like sankey diagrams, scatter charts, and custom maps.
+
+These grammars are designed for advanced users comfortable with writing {{es}} queries and JSON specifications. Note that Vega and Vega-Lite use different syntaxes and are not compatible with each other.
**Vega** and **Vega-Lite** panels can display one or more data sources, including {{es}}, Elastic Map Service, URL, or static data, and support [{{kib}} extensions](#reference-for-kibana-extensions) that allow you to embed the panels on your dashboard and add interactive tools.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md
index 6361815a91..cbf290cf19 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/esorql.md
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
navigation_title: ES|QL
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/esql-visualizations.html
+description: Create visualizations with ES|QL queries from Discover or dashboards. Generate charts dynamically from query results with automatic visualization type suggestions.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -11,7 +12,9 @@ products:
# ES|QL visualizations [esql-visualizations]
-You can add {{esql}} visualizations to a dashboard directly from queries in Discover, or you can start from a dashboard.
+{{esql}} visualizations let you create charts directly from {{esql}} queries without needing to configure {{data-sources}} or aggregations. The visualization type is automatically determined based on your query results, and you can customize the appearance and chart type as needed.
+
+You can create {{esql}} visualizations from Discover by writing queries and saving the results, or start from a dashboard and build the query and visualization together. This approach works well when you need query flexibility beyond what {{data-sources}} provide.
## Edit and add from Discover [_edit_and_add_from_discover]
@@ -85,7 +88,7 @@ serverless:
security: unavailable
```
-Once you've created an {{esql}} panel, you can create an {{es}} threshold rule directly from the visualization panel, based on the data it displays. When you do this, the rule query is automatically generated and either describes the data and sets a specific threshold, or describes the data without setting a specific threshold.
+Once you've created an {{esql}} panel, you can create an {{product.elasticsearch}} threshold rule directly from the visualization panel, based on the data it displays. When you do this, the rule query is automatically generated and either describes the data and sets a specific threshold, or describes the data without setting a specific threshold.
::::{note}
{{elastic-sec}} rule types are not supported.
@@ -93,11 +96,11 @@ Once you've created an {{esql}} panel, you can create an {{es}} threshold rule d
To create a rule with the threshold pre-specified:
- Right-click a data point in the visualization and click **Add alert rule**. This opens the **Create rule** flyout. The generated query will define a threshold that corresponds to the data point you selected.
-- [Configure](/solutions/observability/incident-management/create-an-elasticsearch-query-rule.md) your {{es}} rule.
+- [Configure](/solutions/observability/incident-management/create-an-elasticsearch-query-rule.md) your {{product.elasticsearch}} rule.
To create a rule without the threshold pre-specified:
- Open the **More actions** (three dots) menu in the upper right of the panel and select **Add alert rule**. This opens the **Create rule** flyout. The generated query will define a threshold that corresponds to the data point you selected.
-- [Configure](/solutions/observability/incident-management/create-an-elasticsearch-query-rule.md) your {{es}} rule.
+- [Configure](/solutions/observability/incident-management/create-an-elasticsearch-query-rule.md) your {{product.elasticsearch}} rule.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md
index 5076fc3418..e7b75118f5 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/xpack-graph.html
+description: Explore relationships in Elasticsearch data with Kibana Graph. Discover connections between indexed terms to detect fraud patterns and power recommendation engines.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: unavailable
@@ -10,11 +11,9 @@ products:
# Graph [xpack-graph]
-The {{graph-features}} enable you to discover how items in an {{es}} index are related. You can explore the connections between indexed terms and see which connections are the most meaningful. This can be useful in a variety of applications, from fraud detection to recommendation engines.
+Graph explores relationships between terms in your {{es}} indices to reveal meaningful connections in your data. It works by analyzing which terms frequently appear together in documents, using relevance scoring to identify significant connections rather than simple co-occurrence counts.
-For example, graph exploration could help you uncover website vulnerabilities that hackers are targeting so you can harden your website. Or, you might provide graph-based personalized recommendations to your e-commerce customers.
-
-The {{graph-features}} provide a simple, yet powerful [graph exploration API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/group/endpoint-graph), and an interactive graph visualization app for {{kib}}. Both work out of the box with existing {{es}} indices—you don’t need to store any additional data to use these features.
+Graph applications include fraud detection (identifying patterns in suspicious behavior), security analysis (uncovering attack vectors), and recommendation systems (suggesting related products or content). The feature works with existing indices without requiring additional data storage or special index configuration.
## How Graph works [how-graph-works]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
index 977e6a8b89..638677e9de 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-configuration.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/graph-configuration.html
+description: Configure Graph workspace settings for data views, fields, colors, icons, and data storage. Control how graph visualizations are saved and displayed.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: unavailable
@@ -10,7 +11,13 @@ products:
# Configure Graph [graph-configuration]
-When a user saves a graph workspace in Kibana, it is stored in the `.kibana` index along with other saved objects like visualizations and dashboards. By default, both the configuration and data are saved for the workspace:
+Graph configuration controls how workspaces are saved and what access users have to Graph features. The primary configuration concern is managing the save policy, which determines whether users can save workspace data, configuration, or both. This matters because saved workspace data represents a snapshot that bypasses normal security policies.
+
+This reference covers Graph save policies, security configuration, and how to disable specific features like drilldown configuration.
+
+## Save policies
+
+When a user saves a graph workspace in {{kib}}, it is stored in the `.kibana` index along with other saved objects like visualizations and dashboards. By default, both the configuration and data are saved for the workspace:
**configuration**
: The selected data view, fields, colors, icons, and settings.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-troubleshooting.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-troubleshooting.md
index c709111125..881f0fc306 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-troubleshooting.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/graph/graph-troubleshooting.md
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
navigation_title: Troubleshooting and limitations
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/graph-troubleshooting.html
+description: Troubleshooting guide for Graph API issues including missing results, slow performance, and noisy connections. Understand sampling strategies and limitations.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: unavailable
@@ -13,6 +14,10 @@ products:
# Troubleshooting and limitations of the Graph API [graph-troubleshooting]
+When Graph exploration returns unexpected results, performance issues, or missing connections, understanding the underlying sampling and filtering strategies helps you adjust settings appropriately. Graph uses statistical significance and sampling to filter noise from large data sets, but these defaults can sometimes exclude relevant details.
+
+This guide explains common issues like missing results, slow performance, and noisy connections, plus the limitations of multi-index exploration. Use these troubleshooting steps to balance performance with the level of detail you need.
+
## Why are results missing? [_why_are_results_missing]
The default settings in Graph API requests are configured to tune out noisy results by using the following strategies:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/image-panels.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/image-panels.md
index 86a720458b..b8e19e0e74 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/image-panels.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/image-panels.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/add-image.html
+description: Personalize dashboards with image panels for logos and graphics. Upload images from computer, reuse uploaded files, or add images from external URLs.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,11 +11,10 @@ products:
# Image panels [add-image]
-To personalize your dashboards, add your own logos and graphics with the **Image** panel.
+Image panels let you add logos, diagrams, and other graphics to dashboards for branding or visual context. You can upload images directly from your computer, select from previously uploaded files, or link to images hosted at external URLs.
::::{important}
-Image uploads are limited to 10 MiB.
-
+Image uploads are limited to 10 MiB. Uploaded images are stored in {{kib}} and can be reused across multiple dashboards.
::::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md
index 1d2b8353d7..276cf4304f 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/legacy-editors.html
+description: Access legacy visualization editors including aggregation-based, TSVB, and Timelion. Available for existing panels; new visualizations should use Lens instead.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,9 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Legacy editors [legacy-editors]
+# Legacy visualization editors [legacy-editors]
-Legacy editors are still available but have been replaced by better alternatives. Consider using one of the [modern editors](../visualize.md) offered in Elastic such as **Lens**.
+Legacy visualization editors including aggregation-based, TSVB, and Timelion remain available for existing visualizations but are no longer recommended for new work. Lens provides equivalent or superior functionality with a more intuitive interface.
:::{note}
Legacy panel types only appear in the **Add panel** dashboard menu if you already have such panels in your dashboards. If you have never used these panel types, use Lens instead.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md
index 070ff56c9b..f512731d96 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/aggregation-based.md
@@ -1,12 +1,17 @@
---
+description: Create visualizations with aggregation-based editor for multi-level splits and non-time series data. Access classic Kibana chart types with plugin extensibility.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
+products:
+ - id: kibana
---
-# Aggregation-based [add-aggregation-based-visualization-panels]
+# Aggregation-based visualizations [add-aggregation-based-visualization-panels]
-Aggregation-based visualizations are the core {{kib}} panels, and are not optimized for a specific use case.
+Aggregation-based visualizations represent the original {{kib}} visualization editor, offering classic chart types like pie charts, data tables, and gauges. While Lens now provides a more intuitive interface for most use cases, aggregation-based visualizations remain available for specific scenarios where their features are still needed.
+
+These visualizations support deeper aggregation splits (up to three levels), non-time series data, and plugin extensibility. However, they lack some modern features like easy styling options and mathematical operations.
With aggregation-based visualizations, you can:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md
index 32c69cf7b6..e643e26f92 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/timelion.md
@@ -1,12 +1,17 @@
---
+description: Query time series data with Timelion expression language. Pull data from multiple indices, perform cross-series math, and visualize results with chained functions.
applies_to:
stack: deprecated 7.10
serverless: unavailable
+products:
+ - id: kibana
---
# Timelion [timelion]
-To use **Timelion**, you define a graph by chaining functions together, using the **Timelion**-specific syntax. The syntax enables some features that classical point series charts don’t offer, such as pulling data from different indices or data sources into one graph.
+Timelion is a time series visualization tool that uses an expression language to define charts through chained functions. While deprecated since version 7.10, it remains available in some deployments for existing visualizations. For new work, use Lens or TSVB instead.
+
+Timelion's expression language lets you query multiple indices, perform mathematical operations across time series, and combine data sources in ways that standard visualizations don't support. You build visualizations by chaining functions together with a simple dot notation.
**Timelion** is driven by a simple expression language that you use to:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md
index 00fa2971fa..085bc6d3aa 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/legacy-editors/tsvb.md
@@ -1,12 +1,17 @@
---
+description: Build time series visualizations with TSVB editor combining infinite aggregations. Annotate data, display multiple data views, and create markdown panels.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
+products:
+ - id: kibana
---
# TSVB [tsvb-panel]
-**TSVB** is a set of visualization types that you configure and display on dashboards.
+TSVB (Time Series Visual Builder) is a legacy visualization editor specialized for time series data. While Lens now provides equivalent functionality with a more intuitive interface, TSVB remains available for existing visualizations and specific use cases where its advanced features are needed.
+
+TSVB excels at complex time series scenarios involving custom aggregation chains, annotations, and multiple {{data-sources}} in a single visualization. It supports unlimited aggregation combinations and custom mathematical functions.
With **TSVB**, you can:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md
index b2dd70a42f..36e357a11a 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/lens.md
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
navigation_title: Lens
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/lens.html
+description: Build visualizations in Kibana with Lens drag-and-drop editor. Create charts, tables, and metrics without writing queries using intelligent field suggestions.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -13,14 +14,12 @@ products:
# Lens [lens]
-**Lens** is {{kib}}'s drag-and-drop visualization builder. It lets you create charts without writing queries: You drag fields onto the canvas, and {{kib}} suggests the best visualization types for your data.
+Lens is the default visualization editor in {{product.kibana}}, designed to make creating charts as simple as dragging fields onto a canvas. It automatically suggests appropriate visualization types based on your data and lets you switch between chart types with a single click.
-These fields come from your data indices stored in {{es}}. When you bring data into {{es}}, like logs, metrics, or business data, each piece of information becomes a field: timestamps, user names, error codes, sales amounts, and so on.
-
-Lens doesn't directly look into your {{es}} indices. You first need to specify a [data view](/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/data-views.md) that tells {{kib}} which indices to look at. When you open Lens and select a data view, you see all the fields from that data as a list you can drag and drop to build visualizations.
+To use Lens, you need a {{data-source}} that defines which {{product.elasticsearch}} indices to visualize. Once you select a {{data-source}}, Lens presents all available fields, and you can drag them into different areas to build your visualization. The editor handles aggregations and formatting automatically, though you can customize them when needed.
:::{tip}
-If you collected data using one of the {{kib}} [ingest options](/manage-data/ingest.md), uploaded a file, or added sample data, you likely have a {{data-source}} created automatically, and can start exploring your data. If not, you must create one yourself.
+If you collected data using one of the {{product.kibana}} [ingest options](/manage-data/ingest.md), uploaded a file, or added sample data, you likely have a {{data-source}} created automatically, and can start exploring your data. If not, you must create one yourself.
:::
With **Lens**, you can:
@@ -139,8 +138,8 @@ To assign colors to terms in your visualization:
4. Click the **Edit colors** icon. In the menu that opens, keep **Use legacy palettes** turned off to be able to assign colors to specific terms
5. Select a color palette from the available options:
* **Elastic**: The default and most recent palette. It is intentionally built from a color spectrum designed for flexibility and consistency, while being suited for future accessibility improvements.
- * **{{kib}} 7.0**: A palette that matches the {{kib}} 7.0 color theme for visualizations
- * **{{kib}} 4.0**: A palette that matches the {{kib}} 4.0 color theme for visualizations
+ * **{{product.kibana}} 7.0**: A palette that matches the {{product.kibana}} 7.0 color theme for visualizations
+ * **{{product.kibana}} 4.0**: A palette that matches the {{product.kibana}} 4.0 color theme for visualizations
* **Elastic classic**: A palette made of classic Elastic brand colors
6. Select the color mode you'd like to use with this palette:
* **Categorical**: Assign a distinct color to each term
@@ -351,7 +350,7 @@ Annotations allow you to call out specific points in your visualizations that ar
Annotations support two placement types:
* **Static date** — Displays annotations for specific times or time ranges.
-* **Custom query** — Displays annotations based on custom {{es}} queries. For detailed information about queries, check [Semi-structured search](/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/kql.md#semi-structured-search).
+* **Custom query** — Displays annotations based on custom {{product.elasticsearch}} queries. For detailed information about queries, check [Semi-structured search](/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/kql.md#semi-structured-search).
Any annotation layer can be saved as an annotation group to the **Visualize Library** in order to reuse it in other visualizations. Any changes made to the annotation group will be reflected in all visualizations to which it is added.
@@ -630,7 +629,7 @@ To make your legends as informative as possible, you can show some additional **
* **Std Deviation**: Standard deviation of all data points plotted in the chart
* **Current or last value**: The exact value of the current or last data point moused over
-All statistics are computed based on the selected time range and the aggregated data points shown in the chart, rather than the original data coming from {{es}}.
+All statistics are computed based on the selected time range and the aggregated data points shown in the chart, rather than the original data coming from {{product.elasticsearch}}.
For example, if the metric plotted in the chart is `Median(system.memory)` and the time range is **last 24 hours**, when you show the **Max** statistic in the Legend, the value that shows corresponds to the `Max[Median(system.memory)]` for the last 24 hours.
@@ -738,9 +737,9 @@ By default, **Lens** retrieves only the documents from the fields. For bucket ag
::::{dropdown} When do I use runtime fields vs. formula?
:name: when-do-i-use-runtime-fields-vs-formula
-Use runtime fields to format, concatenate, and extract document-level fields. Runtime fields work across all of {{kib}} and are best used for smaller computations without compromising performance.
+Use runtime fields to format, concatenate, and extract document-level fields. Runtime fields work across all of {{product.kibana}} and are best used for smaller computations without compromising performance.
-Use formulas to compare multiple {{es}} aggregations that can be filtered or shifted in time. Formulas apply only to **Lens** panels and are computationally intensive.
+Use formulas to compare multiple {{product.elasticsearch}} aggregations that can be filtered or shifted in time. Formulas apply only to **Lens** panels and are computationally intensive.
::::
@@ -819,10 +818,10 @@ You can display icons with [field formatters](../find-and-organize/data-views.md
::::
-::::{dropdown} How do I inspect {{es}} queries in visualizations?
+::::{dropdown} How do I inspect {{product.elasticsearch}} queries in visualizations?
:name: is-it-possible-to-inspect-the-elasticsearch-queries-in-Lens
-You can inspect the requests sent by the visualization to {{es}} using the Inspector. It can be accessed within the editor or in the dashboard.
+You can inspect the requests sent by the visualization to {{product.elasticsearch}} using the Inspector. It can be accessed within the editor or in the dashboard.
::::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md
index dbc2994b09..002baa8f13 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/link-panels.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/dashboard-links.html
+description: Add link panels to dashboards for navigation between dashboards or external URLs. Carry time ranges, filters, and queries to maintain exploration context.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Link panels [dashboard-links]
-You can use **Links** panels to create links to other dashboards or external websites. When creating links to other dashboards, you have the option to carry the time range, query, and filters to apply over to the linked dashboard. Links to external websites follow the [`externalUrl.policy`](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/url-drilldown-settings.md#external-url-policy) settings. **Links** panels support vertical and horizontal layouts and may be saved to the **Library** for use in other dashboards.
+Link panels provide navigation between dashboards or to external websites, helping users discover related content or access supporting documentation. When linking to other dashboards, you can preserve the current time range, filters, and queries to maintain context as users navigate.
+
+Links panels support vertical or horizontal layouts and can be saved to the Visualize Library for reuse. External links respect the [`externalUrl.policy`](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/url-drilldown-settings.md#external-url-policy) security settings.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-dashboard_links_panel.png
:alt: A screenshot displaying the new links panel
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/manage-panels.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/manage-panels.md
index 19e6b161be..5b8c6406cf 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/manage-panels.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/manage-panels.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/manage-panels.html
+description: Save panels to Visualize Library for reuse across dashboards or save locally. Configure panel options, manage sharing, and control visualization updates.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,9 +11,9 @@ products:
# Manage panels [manage-panels]
-When creating a panel, you can choose to add it to a dashboard, or to save it to the Visualize Library so it can be added to multiple dashboards later.
+Panels can be saved in two ways: locally to a single dashboard, or to the Visualize Library for reuse across multiple dashboards. Library panels stay synchronized across dashboards, so updating one instance updates all others. Local panels are independent and changes only affect that specific dashboard.
-There are also some common options that you can configure on the various types of panels to make a dashboard easier to navigate and analyze.
+This guide covers saving panels to the library or dashboard, editing existing panels, linking panels to Discover for data exploration, and unlinking library panels to make independent copies.
### Save to the Visualize Library [save-to-visualize-library]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md
index 0790bb0c7a..7c64cdfeff 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps.md
@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@ mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps.html
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/serverless/current/maps.html
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-visualizations.html
+description: Create geospatial visualizations in Kibana Maps with multi-layer mapping, animations, and GeoJSON uploads. Visualize location data with custom styling and dashboard embedding.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -13,14 +14,9 @@ products:
# Maps [maps]
-Create beautiful maps from your geographical data. With **Maps**, you can:
+Maps visualizes geospatial data from {{es}} indices, uploaded files, or external sources. You can combine multiple data layers, animate temporal changes, apply custom styling based on data values, and embed maps in dashboards alongside other visualizations.
-* Build maps with multiple layers and indices.
-* Animate spatial temporal data.
-* Upload GeoJSON files and shapefiles.
-* Embed your map in dashboards.
-* Symbolize features using data values.
-* Focus on only the data that’s important to you.
+Maps supports various data sources including {{es}} documents with geo fields, GeoJSON files, shapefiles, tile services, and web mapping services. Use Maps to display location data, analyze spatial patterns, track assets in real time, or create choropleth visualizations.
## Build maps with multiple layers and indices [_build_maps_with_multiple_layers_and_indices]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md
index bfc5c2a488..e94951f85e 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/asset-tracking-tutorial.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/asset-tracking-tutorial.html
+description: Step-by-step tutorial for tracking real-time asset locations with Maps. Visualize transit data, create alerts for geofences, and monitor vehicle movements.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,9 +11,9 @@ products:
# Track, visualize, and alert on assets in real time [asset-tracking-tutorial]
-Are you interested in asset tracking? Good news! Visualizing and analyzing data that moves is easy with **Maps**. You can track the location of an IoT device and monitor a package or vehicle in transit.
+In this tutorial, you'll learn how to track moving assets using Maps with live data streams. You'll explore techniques for visualizing vehicle tracks, displaying last-known positions, styling movement direction, and creating geofence alerts to monitor when assets enter specific zones. By the end, you'll understand the workflows for building real-time asset tracking applications.
-In this tutorial, you’ll look at live urban transit data from the city of Portland, Oregon. You’ll watch the city buses, tram, and trains, use the data to visualize congestion, and notify a dispatch team when a vehicle enters a construction zone.
+The tutorial uses live transit data from Portland, Oregon to demonstrate tracking buses, trams, and trains, but these techniques apply to any moving assets like IoT devices, delivery vehicles, or mobile equipment.
You’ll learn to:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/heatmap-layer.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/heatmap-layer.md
index 3b7ddeb487..1183bad692 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/heatmap-layer.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/heatmap-layer.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/heatmap-layer.html
+description: Add heat map layers to Maps for visualizing point density clusters. Show geographic locations with higher data concentrations using geo_point or geo_shape fields.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Heat map layer [heatmap-layer]
-Heat map layers cluster point data to show locations with higher densities.
+Heat map layers visualize point density by clustering geographic data and displaying concentration patterns with color gradients. Use heat maps to identify hotspots, understand geographic distribution patterns, and reveal areas with higher or lower activity levels.
+
+Heat map layers work with geo_point or geo_shape fields and support count, sum, and unique count aggregations. The layer automatically blends nearby values to create smooth density visualizations.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-heatmap_layer.png
:alt: heatmap layer
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/import-geospatial-data.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/import-geospatial-data.md
index e6ead2eada..9ac3acfd86 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/import-geospatial-data.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/import-geospatial-data.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/import-geospatial-data.html
+description: Import geospatial data into Elasticsearch as geo_point or geo_shape. Upload GeoJSON files, shapefiles, or use coordinate pairs for map visualization.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Import geospatial data [import-geospatial-data]
-To import geospatical data into the Elastic Stack, the data must be indexed as [geo_point](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/mapping-reference/geo-point.md) or [geo_shape](elasticsearch://reference/elasticsearch/mapping-reference/geo-shape.md). Geospatial data comes in many formats. Choose an import tool based on the format of your geospatial data.
+Before visualizing geospatial data in Maps, you must index it in {{es}} as geo_point or geo_shape fields. The import method depends on your data format: you can upload GeoJSON files or shapefiles directly through the Maps interface, use the {{data-viz}} for delimited files with coordinate pairs, or programmatically index data using {{es}} APIs or {{product.logstash}}.
+
+This guide covers import options for different geospatial data formats, required permissions, and best practices for indexing location data.
## Security privileges [import-geospatial-privileges]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md
index 0d18a94ba1..7500fc8da1 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/indexing-geojson-data-tutorial.html
+description: Step-by-step tutorial for importing and indexing GeoJSON files into Elasticsearch. Build multi-layer maps displaying flight paths and geographic points.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,10 +11,14 @@ products:
# Tutorial: Index GeoJSON data [indexing-geojson-data-tutorial]
-In this tutorial, you’ll build a customized map that shows the flight path between two airports, and the lightning hot spots on that route. You’ll learn to:
+In this tutorial, you'll learn how to import and index GeoJSON files into {{product.elasticsearch}} for visualization in Maps. You'll explore uploading vector data files, indexing them as geo_shape fields, and building multi-layer maps that combine different geographic features. By the end, you'll understand the workflow for working with custom GeoJSON data.
+
+The tutorial creates a map showing airport locations, flight paths, and lightning detection zones, but these techniques apply to any GeoJSON vector data.
+
+You'll learn to:
* Import GeoJSON files into Kibana
-* Index the files in {{es}}
+* Index the files in {{product.elasticsearch}}
* Display the data in a multi-layer map
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-aggregations.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-aggregations.md
index da52ec2a8d..8132d268f6 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-aggregations.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-aggregations.md
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
navigation_title: Plot big data
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-aggregations.html
+description: Visualize large datasets in Maps with aggregations to avoid overwhelming networks. Plot document groups with calculated metrics for efficient data visualization.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -13,8 +14,9 @@ products:
# Plot big data [maps-aggregations]
+When visualizing large data sets, aggregations prevent network congestion and browser slowdowns by keeping documents in {{es}} and returning only calculated group metrics. Instead of transferring thousands or millions of individual documents, Maps receives summary statistics for each geographic bucket or region.
-Use [aggregations](../../query-filter/aggregations.md) to plot large data sets without overwhelming your network or your browser. When using aggregations, the documents stay in Elasticsearch and only the calculated values for each group are returned to your computer.
+Aggregations group documents into buckets and calculate metrics like count, average, or sum for each bucket. Use these metrics for data-driven styling or to display statistical patterns across geographic areas.
Aggregations group your documents into buckets and calculate metrics for each bucket. Use metric aggregations for [data driven styling](vector-style.md#maps-vector-style-data-driven). For example, use the count aggregation to shade world countries by web log traffic.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-clean-data.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-clean-data.md
index 269fbd273a..9cce301ab8 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-clean-data.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-clean-data.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-clean-your-data.html
+description: Troubleshoot and prepare geospatial data for Elasticsearch upload. Convert formats, fix invalid geometries, and address field restrictions before indexing.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Clean your data [maps-clean-your-data]
+# Clean geospatial data [maps-clean-your-data]
-Geospatial fields in {{es}} have certain restrictions that need to be addressed before upload. On this section a few recipes will be presented to help troubleshooting common issues on this type of data.
+Before uploading geospatial data to {{es}}, you may need to address format incompatibilities, geometry errors, or field restrictions. Common issues include unsupported file formats, invalid geometries, and field names that conflict with {{es}} reserved words.
+
+This guide provides recipes for converting formats, fixing geometry problems, and preparing data to meet {{es}} geospatial field requirements.
## Convert to GeoJSON or Shapefile [_convert_to_geojson_or_shapefile]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md
index a80f05627e..0bcdf762d6 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-connect-to-ems.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-connect-to-ems.html
+description: Configure Maps connection to Elastic Maps Service for base maps and administrative boundaries. Set up custom tile servers or disable EMS connections.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,9 +11,9 @@ products:
# Connect to Elastic Maps Service [maps-connect-to-ems]
-[Elastic Maps Service (EMS)](https://www.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service) is a service that hosts tile layers and vector shapes of administrative boundaries. If you are using Kibana’s out-of-the-box settings, Maps is already configured to use EMS.
+{{ems}} provides base map tiles and administrative boundary vectors that Maps uses by default. In restricted or air-gapped environments, you'll need to configure firewall rules to allow {{ems-init}} connections, set up custom tile servers, or disable {{ems-init}} entirely.
-If you are on a restricted or fully air-gapped environment, you may need to configure your firewall to enable access to EMS resources. Find below details on the domains and HTTP headers used by Elastic Maps Service. Alternatively, Elastic Maps Service can be [disabled](#disable-ems) or [installed locally](#elastic-maps-server).
+This reference covers {{ems-init}} domain requirements, connection configuration, custom tile server setup, and local {{ems-init}} installation for offline environments.
## Domains [_domains]
@@ -480,9 +481,9 @@ Find more details about installing Elastic components in an air-gapped environme
::::
-If you cannot connect to Elastic Maps Service from the {{kib}} server or browser clients, and your cluster has the appropriate license level, you can opt to host the service on your own infrastructure.
+If you cannot connect to Elastic Maps Service from the {{product.kibana}} server or browser clients, and your cluster has the appropriate license level, you can opt to host the service on your own infrastructure.
-{{hosted-ems}} is a self-managed version of Elastic Maps Service offered as a Docker image that provides both the EMS basemaps and EMS boundaries. The image is bundled with basemaps up to zoom level 8. After connecting it to your {{es}} cluster for license validation, you have the option to download and configure a more detailed basemaps database.
+{{hosted-ems}} is a self-managed version of Elastic Maps Service offered as a Docker image that provides both the EMS basemaps and EMS boundaries. The image is bundled with basemaps up to zoom level 8. After connecting it to your {{product.elasticsearch}} cluster for license validation, you have the option to download and configure a more detailed basemaps database.
1. Pull the {{hosted-ems}} Docker image.
@@ -490,7 +491,7 @@ If you cannot connect to Elastic Maps Service from the {{kib}} server or browser
docker pull docker.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service/elastic-maps-server:{{version.stack}}
```
-2. Optional: Install [Cosign](https://docs.sigstore.dev/system_config/installation/) for your environment. Then use Cosign to verify the {{es}} image’s signature.
+2. Optional: Install [Cosign](https://docs.sigstore.dev/system_config/installation/) for your environment. Then use Cosign to verify the {{product.elasticsearch}} image’s signature.
```sh subs=true
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/cosign.pub
@@ -531,32 +532,32 @@ If you cannot connect to Elastic Maps Service from the {{kib}} server or browser
| | |
| --- | --- |
-| $$$ems-host$$$`host` | Specifies the host of the backend server. To allow remote users to connect, set the value to the IP address or DNS name of the {{hosted-ems}} container. **Default: _your-hostname_**. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-host). |
-| `port` | Specifies the port used by the backend server. Default: **`8080`**. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-port). |
-| `basePath` | Specify a path at which to mount the server if you are running behind a proxy. This setting cannot end in a slash (`/`). [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-basepath). |
+| $$$ems-host$$$`host` | Specifies the host of the backend server. To allow remote users to connect, set the value to the IP address or DNS name of the {{hosted-ems}} container. **Default: _your-hostname_**. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-host). |
+| `port` | Specifies the port used by the backend server. Default: **`8080`**. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-port). |
+| `basePath` | Specify a path at which to mount the server if you are running behind a proxy. This setting cannot end in a slash (`/`). [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-basepath). |
| `ui` | Controls the display of the status page and the layer preview. **Default: `true`** |
| `logging.level` | Verbosity of {{hosted-ems}} logs. Valid values are `trace`, `debug`, `info`, `warn`, `error`, `fatal`, and `silent`. **Default: `info`** |
| `path.planet` | Path of the basemaps database. **Default: `/usr/src/app/data/planet.mbtiles`** |
-**{{es}} connection and security settings**
+**{{product.elasticsearch}} connection and security settings**
| | |
| --- | --- |
-| `elasticsearch.host` | URL of the {{es}} instance to use for license validation. |
+| `elasticsearch.host` | URL of the {{product.elasticsearch}} instance to use for license validation. |
| `elasticsearch.username` and `elasticsearch.password` | Credentials of a user with at least the `monitor` role. |
-| `elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities` | Paths to one or more PEM-encoded X.509 certificate authority (CA) certificates that make up a trusted certificate chain for {{hosted-ems}}. This chain is used by {{hosted-ems}} to establish trust when connecting to your {{es}} cluster. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#elasticsearch-ssl-certificateauthorities). |
-| `elasticsearch.ssl.certificate` and `elasticsearch.ssl.key`, and `elasticsearch.ssl.keyPassphrase` | Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files and the key password. These files are used to verify the identity of {{hosted-ems}} to {{es}} and are required when `xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication` in {{es}} is set to `required`. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#elasticsearch-ssl-cert-key). |
-| `elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode` | Controls the verification of the server certificate that {{hosted-ems}} receives when making an outbound SSL/TLS connection to {{es}}. Valid values are "`full`", "`certificate`", and "`none`". Using "`full`" performs hostname verification, using "`certificate`" skips hostname verification, and using "`none`" skips verification entirely. **Default: `full`**. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#elasticsearch-ssl-verificationmode). |
+| `elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities` | Paths to one or more PEM-encoded X.509 certificate authority (CA) certificates that make up a trusted certificate chain for {{hosted-ems}}. This chain is used by {{hosted-ems}} to establish trust when connecting to your {{product.elasticsearch}} cluster. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#elasticsearch-ssl-certificateauthorities). |
+| `elasticsearch.ssl.certificate` and `elasticsearch.ssl.key`, and `elasticsearch.ssl.keyPassphrase` | Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files and the key password. These files are used to verify the identity of {{hosted-ems}} to {{product.elasticsearch}} and are required when `xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication` in {{product.elasticsearch}} is set to `required`. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#elasticsearch-ssl-cert-key). |
+| `elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode` | Controls the verification of the server certificate that {{hosted-ems}} receives when making an outbound SSL/TLS connection to {{product.elasticsearch}}. Valid values are "`full`", "`certificate`", and "`none`". Using "`full`" performs hostname verification, using "`certificate`" skips hostname verification, and using "`none`" skips verification entirely. **Default: `full`**. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#elasticsearch-ssl-verificationmode). |
**Server security settings**
| | |
| --- | --- |
-| `ssl.enabled` | Enables SSL/TLS for inbound connections to {{hosted-ems}}. When set to `true`, a certificate and its corresponding private key must be provided. **Default: `false`**. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-enabled). |
-| `ssl.certificateAuthorities` | Paths to one or more PEM-encoded X.509 certificate authority (CA) certificates that make up a trusted certificate chain for {{hosted-ems}}. This chain is used by the {{hosted-ems}} to establish trust when receiving inbound SSL/TLS connections from end users. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-certificateauthorities). |
-| `ssl.key`, `ssl.certificate`, and `ssl.keyPassphrase` | Location of yor SSL key and certificate files and the password that decrypts the private key that is specified via `ssl.key`. This password is optional, as the key may not be encrypted. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-cert-key). |
-| `ssl.supportedProtocols` | An array of supported protocols with versions.Valid protocols: `TLSv1`, `TLSv1.1`, `TLSv1.2`. **Default: `TLSv1.1`, `TLSv1.2`**. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-supportedprotocols). |
-| `ssl.cipherSuites` | Details on the format, and the valid options, are available via the[OpenSSL cipher list format documentation](https://www.openssl.org/docs/man1.1.1/man1/ciphers.html#CIPHER-LIST-FORMAT).**Default: `TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256, DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256, ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384, DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384, ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256, DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256, HIGH,!aNULL, !eNULL, !EXPORT, !DES, !RC4, !MD5, !PSK, !SRP, !CAMELLIA`**. [Equivalent {{kib}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-ciphersuites). |
+| `ssl.enabled` | Enables SSL/TLS for inbound connections to {{hosted-ems}}. When set to `true`, a certificate and its corresponding private key must be provided. **Default: `false`**. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-enabled). |
+| `ssl.certificateAuthorities` | Paths to one or more PEM-encoded X.509 certificate authority (CA) certificates that make up a trusted certificate chain for {{hosted-ems}}. This chain is used by the {{hosted-ems}} to establish trust when receiving inbound SSL/TLS connections from end users. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-certificateauthorities). |
+| `ssl.key`, `ssl.certificate`, and `ssl.keyPassphrase` | Location of yor SSL key and certificate files and the password that decrypts the private key that is specified via `ssl.key`. This password is optional, as the key may not be encrypted. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-cert-key). |
+| `ssl.supportedProtocols` | An array of supported protocols with versions.Valid protocols: `TLSv1`, `TLSv1.1`, `TLSv1.2`. **Default: `TLSv1.1`, `TLSv1.2`**. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-supportedprotocols). |
+| `ssl.cipherSuites` | Details on the format, and the valid options, are available via the[OpenSSL cipher list format documentation](https://www.openssl.org/docs/man1.1.1/man1/ciphers.html#CIPHER-LIST-FORMAT).**Default: `TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256, DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256, ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384, DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384, ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256, DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256, HIGH,!aNULL, !eNULL, !EXPORT, !DES, !RC4, !MD5, !PSK, !SRP, !CAMELLIA`**. [Equivalent {{product.kibana}} setting](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md#server-ssl-ciphersuites). |
#### Bind-mounted configuration [elastic-maps-server-bind-mount-config]
@@ -611,7 +612,7 @@ The available basemaps and boundaries can be explored from the `/maps` endpoint
### Kibana configuration [elastic-maps-server-kibana]
-With {{hosted-ems}} running, add the `map.emsUrl` configuration key in your [kibana.yml](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md) file pointing to the root of the service. This setting will point {{kib}} to request EMS basemaps and boundaries from {{hosted-ems}}. Typically this will be the URL to the [host and port](#ems-host) of {{hosted-ems}}. For example, `map.emsUrl: https://my-ems-server:8080`.
+With {{hosted-ems}} running, add the `map.emsUrl` configuration key in your [kibana.yml](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md) file pointing to the root of the service. This setting will point {{product.kibana}} to request EMS basemaps and boundaries from {{hosted-ems}}. Typically this will be the URL to the [host and port](#ems-host) of {{hosted-ems}}. For example, `map.emsUrl: https://my-ems-server:8080`.
### Status check [elastic-maps-server-check]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-create-filter-from-map.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-create-filter-from-map.md
index 9ee119f139..24f3b947a9 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-create-filter-from-map.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-create-filter-from-map.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-create-filter-from-map.html
+description: Create filters from Maps by drawing shapes or selecting features. Focus analysis on specific geographic regions with interactive spatial filtering.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Create filters from a map [maps-create-filter-from-map]
+# Create filters from maps [maps-create-filter-from-map]
-Create filters from your map to focus in on just the data you want. **Maps** provides three ways to create filters:
+Maps supports interactive filtering that lets you select geographic areas or features to focus your analysis. You can filter by map bounds as you pan and zoom, draw custom shapes to create spatial filters, or click features to filter by specific values.
+
+Maps provides three filtering approaches:
* [Filter dashboard by map bounds](#maps-map-extent-filter)
* [Spatial filters](#maps-spatial-filters)
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md
index b38d5c2c8a..0078974b68 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-getting-started.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-getting-started.html
+description: Step-by-step tutorial for building Maps to compare metrics by country or region. Create multi-layer maps with styled data, labels, and dashboard integration.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,7 @@ products:
# Build a map to compare metrics by country or region [maps-getting-started]
-If you are new to **Maps**, this tutorial is a good place to start. It guides you through the common steps for working with your location data.
+In this tutorial, you'll learn the fundamentals of creating maps in {{kib}} by building a multi-layer visualization that compares web traffic metrics across countries. You'll explore how to add layers, style data with colors and labels, and embed maps in dashboards. By the end, you'll understand the core workflows for building effective geographic visualizations.
You will learn to:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-grid-aggregation.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-grid-aggregation.md
index b02a46efa7..7dfdf2cbd2 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-grid-aggregation.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-grid-aggregation.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-grid-aggregation.html
+description: Visualize data with grid aggregations in Maps using geohash, geotile, or geohex grids. Group documents into geographic buckets for density analysis.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Clusters [maps-grid-aggregation]
+# Clusters and grid aggregations [maps-grid-aggregation]
-Clusters use [Geotile grid aggregation](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/search-aggregations-bucket-geotilegrid-aggregation.md) or [Geohex grid aggregation](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/search-aggregations-bucket-geohexgrid-aggregation.md) to group your documents into grids. You can calculate metrics for each gridded cell.
+Grid aggregations group documents into geographic cells and calculate metrics for each cell, enabling efficient visualization of large data sets. Maps supports geotile and geohex grid aggregations, which you can visualize as cluster symbols, bounding box grids, or heat maps.
+
+Grid aggregations work well for density analysis, identifying geographic patterns, and displaying summary statistics across geographic areas.
Symbolize cluster metrics as:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-layer-based-filtering.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-layer-based-filtering.md
index d22531e471..fdb006907b 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-layer-based-filtering.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-layer-based-filtering.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-layer-based-filtering.html
+description: Apply filters to individual layers in Maps without affecting other layers. Create focused visualizations with layer-specific data filters and queries.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Filter a single layer [maps-layer-based-filtering]
+# Filter individual layers [maps-layer-based-filtering]
-You can apply a search request to individual layers by setting `Filters` in the layer details panel. Click the **Add filter** button to add a filter to a layer.
+Layer-specific filters let you apply different filter criteria to each layer without affecting other layers on the map. This approach enables focused visualizations where each layer displays a different subset or view of the data.
+
+To add layer-specific filters, use the layer details panel's filter controls. Note that layer filters don't apply to the right side of term joins.
::::{note}
Layer filters are not applied to the right side of **term joins**. You can apply a search request to the right side of **term joins** by setting the **where** clause in the join definition. For example, suppose you have a layer with a term join where the left side is roads and the right side is traffic volume measurements. A layer filter of `roadType is "highway"` is applied to the roads index, but not to the traffic volume measurements index.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search-across-multiple-indices.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search-across-multiple-indices.md
index 394ee45631..4a6f422347 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search-across-multiple-indices.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search-across-multiple-indices.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-search-across-multiple-indices.html
+description: Query data from multiple Elasticsearch indices in Maps to visualize combined datasets. Build maps with layers from different data sources and indices.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,9 +11,9 @@ products:
# Search across multiple indices [maps-search-across-multiple-indices]
-Your map might contain multiple {{es}} indices. This can occur when your map contains two or more layers with {{es}} sources from different indices. This can also occur with a single layer with an {{es}} source and a [Term join](terms-join.md).
+When maps contain layers from different {{product.elasticsearch}} indices, global searches may produce unexpected results or empty layers. This occurs when search queries reference fields that exist in some indices but not others.
-Searching across multiple indices might sometimes result in empty layers. The most common cause for empty layers are searches for a field that exists in one index, but does not exist in other indices.
+Understanding how to handle multi-index scenarios helps you avoid empty layers and create effective search strategies across diverse data sources.
## Disable global search for a layer [maps-disable-search-for-layer]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search.md
index 0c2e9e4a65..0dde77f185 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-search.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-search.html
+description: Search and filter map data with queries and time ranges. Control data visibility across layers using global or layer-specific search parameters.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Search geographic data [maps-search]
-Search across the layers in your map to focus on just the data you want. Combine free text search with field-based search using the [{{kib}} Query Language](../../query-filter/languages/kql.md). Set the time filter to restrict layers by time.
+Global search and time filters in Maps narrow data across all {{product.elasticsearch}}-backed layers simultaneously. You can use KQL queries for field-based searches, combine multiple filters, and set time ranges to focus on specific data subsets.
+
+This guide covers global search behavior, layer-specific search options, and strategies for controlling which layers respond to search criteria.
This image shows an example of global search and global time narrowing results.
@@ -19,7 +22,7 @@ This image shows an example of global search and global time narrowing results.
:screenshot:
:::
-Only layers requesting data from {{es}} are narrowed by global search and global time. To add a layer that requests data from {{es}} to your map, click **Add layer**, then select one of the following:
+Only layers requesting data from {{product.elasticsearch}} are narrowed by global search and global time. To add a layer that requests data from {{product.elasticsearch}} to your map, click **Add layer**, then select one of the following:
* Documents
* Choropleth
@@ -32,7 +35,7 @@ Only layers requesting data from {{es}} are narrowed by global search and global
## Narrow layers by global search [maps-narrow-layer-by-global-search]
-Layers that request data from {{es}} are narrowed when you submit a search. Layers narrowed by semi-structured search and filters contain the filter icon  next to the layer name in the legend.
+Layers that request data from {{product.elasticsearch}} are narrowed when you submit a search. Layers narrowed by semi-structured search and filters contain the filter icon  next to the layer name in the legend.
To prevent the global search from applying to a layer, configure the following:
@@ -42,7 +45,7 @@ To prevent the global search from applying to a layer, configure the following:
## Narrow layers by global time [maps-narrow-layer-by-global-time]
-Layers that request data from {{es}} using a [data view](../../find-and-organize/data-views.md) with a configured time field are narrowed by the [global time](../../query-filter/filtering.md). These layers contain the clock icon  next to the layer name in the legend.
+Layers that request data from {{product.elasticsearch}} using a [data view](../../find-and-organize/data-views.md) with a configured time field are narrowed by the [global time](../../query-filter/filtering.md). These layers contain the clock icon  next to the layer name in the legend.
Use the time slider to quickly select time slices within the global time range:
@@ -58,7 +61,7 @@ To prevent the global time filter from applying to a layer, configure the follow
## Refresh layer data [maps-refresh-layer]
-Layers that request data from {{es}} re-fetch data when [automatic refresh](../../query-filter/filtering.md) fires and when you click **Refresh**.
+Layers that request data from {{product.elasticsearch}} re-fetch data when [automatic refresh](../../query-filter/filtering.md) fires and when you click **Refresh**.
To prevent refreshing layer data, configure the following:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-settings.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-settings.md
index bfbbc077c1..c51fa97917 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-settings.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-settings.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-settings.html
+description: Configure Maps display settings for auto-fit bounds, browser location, initial view, and tooltip behavior. Customize map interaction and default appearance.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Configure map settings [maps-settings]
-Maps offers settings that let you configure how a map is displayed. To access these settings, click **Settings** in the application toolbar.
+Map settings control display behavior, initial view positioning, tooltip preferences, and custom icon management. These settings determine how maps appear when opened and how users interact with layers and features.
+
+This reference covers all available map configuration options, including background colors, zoom behavior, browser location access, and custom icon management.
## Custom icons [maps-settings-custom-icons]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-top-hits-aggregation.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-top-hits-aggregation.md
index 3bcbc0c156..93e30d02d4 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-top-hits-aggregation.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-top-hits-aggregation.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-top-hits-aggregation.html
+description: Display most recent or highest-ranked documents in Maps with top hits aggregation. Show latest GPS positions and track entity movements over time.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Display the most relevant documents per entity [maps-top-hits-aggregation]
-Use **Top hits per entity** to display the most relevant documents per entity, for example, the most recent GPS tracks per flight route. To get this data, {{es}} first groups your data using a [terms aggregation](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/search-aggregations-bucket-terms-aggregation.md), then accumulates the most relevant documents based on sort order for each entry using a [top hits metric aggregation](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/search-aggregations-metrics-top-hits-aggregation.md).
+Top hits per entity displays the most recent or highest-ranked documents for each unique entity, such as the latest GPS position per vehicle or most recent transaction per customer. This layer type combines terms aggregation to group by entity with top hits metric aggregation to select the most relevant documents from each group.
+
+Use top hits layers for asset tracking, displaying current states, or showing the most significant event per entity on a map.
To enable top hits:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-troubleshooting.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-troubleshooting.md
index 48d9556d35..c8c419ef4b 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-troubleshooting.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-troubleshooting.md
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
navigation_title: Troubleshoot
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-troubleshooting.html
+description: Troubleshooting guide for Maps issues including Elasticsearch request inspection, polygon display problems, and layer configuration errors.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -11,15 +12,16 @@ products:
-# Troubleshoot [maps-troubleshooting]
+# Troubleshoot Maps [maps-troubleshooting]
+When Maps displays unexpected results or encounters errors, inspecting {{product.elasticsearch}} requests and understanding common configuration issues helps identify root causes. The Maps inspector shows both vector tile and search API requests, revealing how layers query data and why certain features might not display.
-Use the information in this section to inspect Elasticsearch requests and find solutions to common problems.
+This guide covers inspecting {{product.elasticsearch}} requests, troubleshooting missing or incorrect polygon displays, and resolving common layer configuration problems.
## Inspect Elasticsearch requests [_inspect_elasticsearch_requests]
-Maps uses the [{{es}} vector tile search API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-search-mvt) and the [{{es}} search API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-search) to get documents and aggregation results from {{es}}. Use **Vector tiles** inspector to view {{es}} vector tile search API requests. Use **Requests** inspector to view {{es}} search API requests.
+Maps uses the [{{product.elasticsearch}} vector tile search API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-search-mvt) and the [{{product.elasticsearch}} search API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-search) to get documents and aggregation results from {{product.elasticsearch}}. Use **Vector tiles** inspector to view {{product.elasticsearch}} vector tile search API requests. Use **Requests** inspector to view {{product.elasticsearch}} search API requests.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-vector_tile_inspector.png
:alt: vector tile inspector
@@ -54,7 +56,7 @@ Maps uses the [{{es}} vector tile search API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/do
### Features are not displayed [_features_are_not_displayed]
-* Use Inspector to view {{es}} responses. Ensure the response is not empty.
+* Use Inspector to view {{product.elasticsearch}} responses. Ensure the response is not empty.
* Ensure geometry uses the correct latitude and longitude ordering.
* Geo-points expressed as strings are ordered as `"latitude,longitude"`. Geo-points expressed as arrays are ordered as the reverse: `[longitude, latitude]`.
@@ -70,6 +72,6 @@ Maps uses the [{{es}} vector tile search API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/do
### Custom tiles are not displayed [_custom_tiles_are_not_displayed]
-* When using a custom tile service, ensure your tile server has configured [Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CORS) so tile requests from your {{kib}} domain have permission to access your tile server domain.
+* When using a custom tile service, ensure your tile server has configured [Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CORS) so tile requests from your {{product.kibana}} domain have permission to access your tile server domain.
* Ensure custom vector and tile services have the required coordinate system. Vector data must use EPSG:4326 and tiles must use EPSG:3857.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-vector-style-properties.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-vector-style-properties.md
index 21195282ec..56b19e0fa1 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-vector-style-properties.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/maps-vector-style-properties.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/maps-vector-style-properties.html
+description: Customize vector layer appearance in Maps with fill colors, border styles, label formatting, and icon settings. Apply data-driven or static styling properties.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Vector style properties [maps-vector-style-properties]
-Point, polygon, and line features support different styling properties.
+Vector layer styling properties differ based on feature geometry type. Points support icon and label styling, polygons support fill and border styling, and lines support stroke properties. Each property can use static values or data-driven expressions that change appearance based on field values.
+
+This reference documents all available style properties for point, polygon, and line features, including label positioning, color options, size controls, and icon customization.
## Point style properties [point-style-properties]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/point-to-point.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/point-to-point.md
index 5161e13a90..07d017f9b9 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/point-to-point.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/point-to-point.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/point-to-point.html
+description: Visualize connections between geographic locations with point-to-point layers. Display origin-destination relationships and directional flows on maps.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Point to point [point-to-point]
+# Point-to-point layers [point-to-point]
-A point-to-point connection plots aggregated data paths between the source and the destination. Thicker, darker lines symbolize more connections between a source and destination, and thinner, lighter lines symbolize less connections.
+Point-to-point layers visualize origin-destination relationships by drawing lines between source and destination locations. Line thickness and color intensity represent connection volume or frequency, with thicker, darker lines showing higher traffic and thinner, lighter lines showing lower traffic.
+
+Point-to-point layers work well for network traffic visualization, flight routes, migration patterns, and delivery logistics.
Point to point uses an {{es}} [terms aggregation](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/search-aggregations-bucket-terms-aggregation.md) to group your documents by destination. Then, a nested [GeoTile grid aggregation](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/search-aggregations-bucket-geotilegrid-aggregation.md) groups sources for each destination into grids. A line connects each source grid centroid to each destination.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/reverse-geocoding-tutorial.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/reverse-geocoding-tutorial.md
index fad7683681..32e6d71c17 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/reverse-geocoding-tutorial.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/reverse-geocoding-tutorial.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/reverse-geocoding-tutorial.html
+description: Step-by-step tutorial for converting coordinates to human-readable location names with reverse geocoding. Enrich geospatial data with place names and addresses.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,16 +11,16 @@ products:
# Map custom regions with reverse geocoding [reverse-geocoding-tutorial]
-**Maps** comes with [predefined regions](https://maps.elastic.co/#file) that allow you to quickly visualize regions by metrics. **Maps** also offers the ability to map your own regions. You can use any region data you’d like, as long as your source data contains an identifier for the corresponding region.
+In this tutorial, you'll learn how to map custom geographic regions when your data contains coordinates but not region identifiers. You'll explore uploading custom region boundaries, using {{product.elasticsearch}} enrich processors for reverse geocoding, and visualizing metrics by region. By the end, you'll understand how to assign region identifiers to data based on geographic location.
-But how can you map regions when your source data does not contain a region identifier? This is where reverse geocoding comes in. Reverse geocoding is the process of assigning a region identifier to a feature based on its location.
+Reverse geocoding converts coordinates into region identifiers by determining which region boundary contains each point. This tutorial demonstrates the technique using US Census Bureau Combined Statistical Areas, but it applies to any custom regional boundaries.
In this tutorial, you’ll use reverse geocoding to visualize United States Census Bureau Combined Statistical Area (CSA) regions by web traffic.
You’ll learn to:
* Upload custom regions.
-* Reverse geocode with the {{es}} [enrich processor](elasticsearch://reference/enrich-processor/enrich-processor.md).
+* Reverse geocode with the {{product.elasticsearch}} [enrich processor](elasticsearch://reference/enrich-processor/enrich-processor.md).
* Create a map and visualize CSA regions by web traffic.
When you complete this tutorial, you’ll have a map that looks like this:
@@ -77,7 +78,7 @@ Looking at the map, you get a sense of what constitutes a metro area in the eyes
## Step 3: Reverse geocoding [_step_3_reverse_geocoding]
-To visualize CSA regions by web log traffic, the web log traffic must contain a CSA region identifier. You’ll use {{es}} [enrich processor](elasticsearch://reference/enrich-processor/enrich-processor.md) to add CSA region identifiers to the web logs sample data set. You can skip this step if your source data already contains region identifiers.
+To visualize CSA regions by web log traffic, the web log traffic must contain a CSA region identifier. You’ll use {{product.elasticsearch}} [enrich processor](elasticsearch://reference/enrich-processor/enrich-processor.md) to add CSA region identifiers to the web logs sample data set. You can skip this step if your source data already contains region identifiers.
1. Go to **Developer tools** using the navigation menu or the [global search field](/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/find-apps-and-objects.md).
2. In **Console**, create a [geo_match enrichment policy](../../../manage-data/ingest/transform-enrich/example-enrich-data-based-on-geolocation.md):
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/terms-join.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/terms-join.md
index dc2fcc741e..6bd0aa2526 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/terms-join.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/terms-join.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/terms-join.html
+description: Enrich map layers with terms joins to combine metrics from Elasticsearch with vector boundaries. Calculate and visualize aggregated statistics by region.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -8,9 +9,11 @@ products:
- id: kibana
---
-# Term join [terms-join]
+# Term joins [terms-join]
-Use term joins to augment vector features with properties for [data driven styling](vector-style.md#maps-vector-style-data-driven) and richer tooltip content.
+Term joins enrich vector layer features with metrics calculated from {{product.elasticsearch}} aggregations, enabling data-driven styling and detailed tooltips. A term join matches vector features to aggregated metrics using a common field value, allowing you to visualize statistics like traffic counts, sales totals, or error rates on geographic boundaries.
+
+Term joins work with Documents, Configured GeoJSON, and {{ems-init}} Boundaries vector layers, providing flexibility for combining boundary data with your metrics.
Term joins are available for the following [vector layers](vector-layer.md):
@@ -29,7 +32,7 @@ The [choropleth layer example](maps-getting-started.md#maps-add-choropleth-layer
### How a term join works [_how_a_term_join_works]
-A term join uses a shared key to combine vector features, the left source, with the results of an {{es}} terms aggregation, the right source.
+A term join uses a shared key to combine vector features, the left source, with the results of an {{product.elasticsearch}} terms aggregation, the right source.
The cloropeth example uses the shared key, [ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code](https://wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_3166-1_alpha-2), to join world countries and web log traffic. ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code is an international standard that identifies countries by a two-letter country code. For example, **Sweden** has an ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code of **SE**.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/tile-layer.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/tile-layer.md
index aacaf6d671..d05e78a648 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/tile-layer.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/tile-layer.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/tile-layer.html
+description: Add tile layers to Maps for base map backgrounds and overlays. Configure Elastic Maps Service, custom tile servers, and Web Map Services.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Tile layer [tile-layer]
-Tile layers display image tiles served from a tile server.
+Tile layers provide base map imagery and overlays from tile servers. You can add street maps, satellite imagery, topographic maps, or custom styled base maps from various tile services including {{ems}}, standard tile servers, vector tile services, and Web Map Services.
+
+Tile layers typically serve as the background for your map, providing geographic context for the data layers displayed above them.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-tile_layer.png
:alt: tile layer
@@ -20,7 +23,7 @@ Tile layers display image tiles served from a tile server.
To add a tile layer to your map, click **Add layer**, then select one of the following:
**Configured Tile Map Service**
-: Tile map service configured in kibana.yml. See map.tilemap.url in [*Configure {{kib}}*](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md) for details.
+: Tile map service configured in kibana.yml. See map.tilemap.url in [*Configure {{product.kibana}}*](kibana://reference/configuration-reference/general-settings.md) for details.
**EMS Basemaps**
: Tile map service from [Elastic Maps Service](https://www.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-layer.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-layer.md
index 1cf0672669..3363738a66 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-layer.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-layer.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/vector-layer.html
+description: Add vector layers to Maps for displaying points, lines, and polygons from Elasticsearch data. Visualize documents, clusters, and geospatial features.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Vector layer [vector-layer]
-Vector layers display points, lines, and polygons.
+Vector layers display geographic features as points, lines, and polygons from your {{product.elasticsearch}} data. These layers support various visualization modes including individual documents, clustered aggregations, choropleth maps for statistical comparisons, and custom-drawn shapes.
+
+Vector layers are the primary way to visualize your data on maps, offering flexible scaling options to handle data sets of any size.
:::{image} /explore-analyze/images/kibana-vector_layer.png
:alt: vector layer
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-style.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-style.md
index 402f602e89..d8b1cfe830 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-style.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-style.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/vector-style.html
+description: Style vector layers in Maps with data-driven or static properties. Apply colors, sizes, and symbols based on field values for meaningful visualizations.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Vector styling [vector-style]
-When styling a vector layer, you can customize your data by property, such as size and color. For each property, you can specify whether to use a constant or data driven value for the style.
+Vector layer styling controls the visual appearance of points, lines, and polygons through properties like color, size, opacity, and icons. Each style property can use static values that apply uniformly to all features, or data-driven values that change appearance based on field values.
+
+Data-driven styling enables choropleth maps, proportional symbols, and other visualizations that encode data values through visual variables.
## Static styling [maps-vector-style-static]
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-tooltip.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-tooltip.md
index b70dc79691..48627b2625 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-tooltip.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/maps/vector-tooltip.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/vector-tooltip.html
+description: Configure tooltips for vector layers to display field values on hover. Customize tooltip content and formatting for better data exploration in Maps.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Vector tooltips [vector-tooltip]
-Vector tooltips display attributes for the features at your mouse location. These tooltips give users an in-depth insight into what’s going on in the map.
+Vector layer tooltips display feature attributes when hovering over map elements. You can customize which fields appear, their formatting, and their display order. When multiple features overlap at a location, the tooltip shows attributes from the top feature and indicates how many additional features exist at that point.
+
+Tooltips provide essential context for understanding map data without cluttering the visualization with permanent labels.
If more than one feature exists at a location, the tooltip displays the attributes for the top feature, and notes the number of features at that location. The following image has a tooltip with three features at the current location: a green circle from the **Total Sales Revenue** layer, a blue New York State polygon from **United States** layer, and a red United States Country polygon from the **World Countries** layer. The tooltip displays attributes for the top feature, the green circle, from the **Total Sales Revenue** layer.
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md
index d9dbfb2164..b61d3ab607 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/supported-chart-types.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/chart-types.html
+description: Compare visualization capabilities across Lens, TSVB, aggregation-based editors, Vega, and Timelion. Reference tables list supported chart types, features, and aggregations.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,6 +11,10 @@ products:
# Supported chart types [chart-types]
+{{product.kibana}} offers multiple visualization editors, each with different capabilities and supported chart types. Use this reference to compare which visualization types, features, and aggregations are available in Lens, TSVB, aggregation-based editors, Vega, and Timelion.
+
+Choose your editor based on which features you need for your specific use case. Lens provides the broadest support for standard chart types with an intuitive drag-and-drop interface, while Vega offers maximum flexibility for custom visualizations.
+
$$$aggregation-reference$$$
| Panel type | **Lens** | **TSVB** | **Aggregation-based** | **Vega** | **Timelion** |
@@ -47,7 +52,7 @@ $$$aggregation-reference$$$
| Math across indices | | | ✓ | ✓ |
| Visualize two indices | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Time shift | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
-| Custom {{es}} queries | | | ✓ | |
+| Custom {{product.elasticsearch}} queries | | | ✓ | |
| Normalize by time | ✓ | ✓ | | |
| Automatically generated suggestions | ✓ | | | |
| Annotations | ✓ | ✓ | | |
@@ -91,7 +96,7 @@ Metric aggregations are calculated from the values in the aggregated documents.
| Value count | ✓ | | ✓ | ✓ |
| Variance | ✓ | ✓ | | ✓ |
-For information about {{es}} metrics aggregations, refer to [Metrics aggregations](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/metrics.md).
+For information about {{product.elasticsearch}} metrics aggregations, refer to [Metrics aggregations](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/metrics.md).
## Bucket aggregations [bucket-aggregations]
@@ -112,7 +117,7 @@ Bucket aggregations group, or bucket, documents based on the aggregation type. T
| Terms | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Significant terms | ✓ | | ✓ | ✓ |
-For information about {{es}} bucket aggregations, refer to [Bucket aggregations](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/bucket.md).
+For information about {{product.elasticsearch}} bucket aggregations, refer to [Bucket aggregations](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/bucket.md).
## Pipeline aggregations [pipeline-aggregations]
@@ -132,5 +137,5 @@ Pipeline aggregations are dependent on the outputs calculated from other aggrega
| Bucket selector | | | | ✓ |
| Serial differencing | | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
-For information about {{es}} pipeline aggregations, refer to [Pipeline aggregations](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/pipeline.md).
+For information about {{product.elasticsearch}} pipeline aggregations, refer to [Pipeline aggregations](elasticsearch://reference/aggregations/pipeline.md).
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/text-panels.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/text-panels.md
index 5316c325ea..32e176e26b 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/text-panels.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/text-panels.md
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/add-text.html
+description: Add Markdown text panels to dashboards for context and instructions. Display formatted text, images, and links using GitHub-flavored Markdown syntax.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
@@ -10,7 +11,9 @@ products:
# Text panels [add-text]
-To provide context to your dashboard panels, add **Text** panels that display important information, instructions, images, and more. You can create **Text** panels using GitHub-flavored Markdown text.
+Text panels add context to dashboards by displaying formatted text, instructions, images, and links. You write content using GitHub-flavored Markdown, which supports headings, lists, code blocks, tables, and more.
+
+Use text panels to explain dashboard purpose, provide usage instructions, document data sources, or add important notes for dashboard viewers.
:::::{applies-switch}
diff --git a/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md b/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md
index ac9a294381..8e4a0b2025 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/visualize/visualize-library.md
@@ -1,19 +1,20 @@
---
mapped_pages:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/serverless/current/visualize-library.html
+description: Store and reuse visualizations in Kibana Visualize Library. Manage shared panels, annotation groups, and visualization assets across multiple dashboards.
applies_to:
stack: ga
serverless: ga
products:
+ - id: kibana
- id: cloud-serverless
---
# Visualize Library [visualize-library]
-The **Visualize Library** is a space where you can save visualization panels that you may want to use across multiple dashboards. The **Visualize Library** consists of two pages:
+The Visualize Library serves as a centralized repository for managing reusable visualization assets in {{product.kibana}}. When you save a panel to the library, you can add it to multiple dashboards, and any updates to the library version automatically propagate to all dashboards using that panel.
-* **Visualizations**
-* **Annotation groups**
+The library contains two main sections: **Visualizations** for charts and data panels, and **Annotation groups** for reusable annotations that mark events or milestones across time series visualizations.
## Visualizations [visualize-library-visualizations]