diff --git a/libraries/BLE/README.md b/libraries/BLE/README.md
index 759c8526f0f..b89d556dcc9 100644
--- a/libraries/BLE/README.md
+++ b/libraries/BLE/README.md
@@ -1,12 +1,467 @@
-# ESP32 BLE for Arduino
-The Arduino IDE provides an excellent library package manager where versions of libraries can be downloaded and installed. This Github project provides the repository for the ESP32 BLE support for Arduino.
+# BLE for ESP32 Arduino Core
+
+A comprehensive reference for ESP32 Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) pairing and security implementation using the ESP32 Arduino BLE library.
+
+## Overview
+
+This guide provides ESP32 developers with comprehensive information about BLE security implementation using the ESP32 Arduino BLE library. It covers both Bluedroid (ESP32) and NimBLE (other SoCs) implementations with realistic scenarios and troubleshooting guidance.
+
+Issues and questions should be raised here: https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/issues
(please don't use https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/issues or https://github.com/h2zero/NimBLE-Arduino/issues)
+
+## Security
+
+### Quick Start
+
+1. **Choose your ESP32's IO capabilities** using `ESP_IO_CAP_*` constants
+2. **Configure authentication requirements** with properties or permissions
+3. **Set up security** using `BLESecurity` class methods
+4. **Handle stack differences** between Bluedroid (ESP32) and NimBLE (other SoCs)
+5. **Test with NVS clearing** during development
+
+### Understanding BLE Pairing
+
+#### Pairing vs Bonding
+- **Pairing**: The process of establishing encryption keys between devices
+- **Bonding**: Storing those keys for future reconnections (persistent pairing)
+
+#### Pairing Types
+- **Legacy Pairing**: Original BLE pairing (Bluetooth 4.0/4.1)
+- **Secure Connections**: Enhanced security (Bluetooth 4.2+) using FIPS-approved algorithms
+
+#### Security Levels
+- **Just Works**: Encryption without user verification (vulnerable to passive eavesdropping)
+- **MITM Protected**: User verification prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
+
+### IO Capabilities Explained
+
+The ESP32 BLE library defines the following IO capabilities:
+
+| Capability | Library Constant | Can Display | Can Input | Can Confirm | Example Devices |
+|------------|-----------------|-------------|-----------|-------------|-----------------|
+| **No Input No Output** | `ESP_IO_CAP_NONE` | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | Sensor nodes, beacons, simple actuators |
+| **Display Only** | `ESP_IO_CAP_OUT` | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | E-ink displays, LED matrix displays |
+| **Keyboard Only** | `ESP_IO_CAP_IN` | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | Button-only devices, rotary encoders |
+| **Display Yes/No** | `ESP_IO_CAP_IO` | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Devices with display + confirmation button |
+| **Keyboard Display** | `ESP_IO_CAP_KBDISP` | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Full-featured ESP32 devices with UI |
+
+### Pairing Methods Explained
+
+#### 🔓 Just Works
+- **Security**: Encryption only (no MITM protection)
+- **User Experience**: Automatic, no user interaction
+- **Use Case**: Convenience over security (fitness trackers, mice)
+- **Vulnerability**: Susceptible to passive eavesdropping during pairing
+
+#### 🔐 Passkey Entry
+- **Security**: Full MITM protection
+- **User Experience**: One device shows 6-digit code, other inputs it
+- **Use Case**: Keyboards pairing to computers
+- **Process**:
+ 1. Display device shows random 6-digit number (000000-999999)
+ 2. Input device user types the number
+ 3. Pairing succeeds if numbers match
+
+#### 🔐 Numeric Comparison (Secure Connections Only)
+- **Security**: Full MITM protection
+- **User Experience**: Both devices show same number, user confirms match
+- **Use Case**: Two smartphones/tablets pairing
+- **Process**:
+ 1. Both devices display identical 6-digit number
+ 2. User verifies numbers match on both screens
+ 3. User confirms "Yes" on both devices
+
+#### 🔐 Out-of-Band (OOB) (Not supported by this library)
+- **Security**: Highest security level
+- **User Experience**: Uses external channel (NFC, QR code)
+- **Use Case**: High-security applications
+- **Priority**: Always used when OOB data is available
+
+### Pairing Methods Compatibility Matrix
+
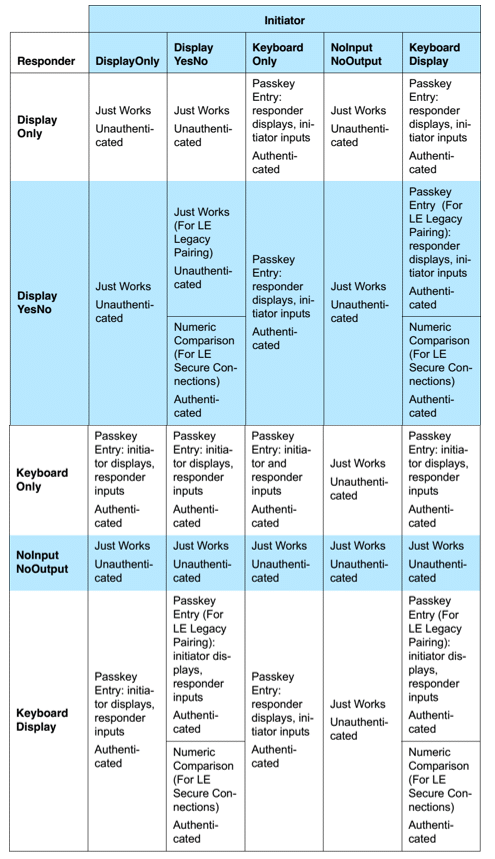
+Here is the compatibility matrix for the pairing methods depending on the IO capabilities of the devices.
+Note that the initiator is the device that starts the pairing process (usually the client) and the responder is
+the device that accepts the pairing request (usually the server).
+
+
+
+### Bluedroid vs NimBLE
+
+Bluedroid and NimBLE are two different Bluetooth stack implementations.
+
+#### Bluedroid
+
+Bluedroid is the default Bluetooth stack in ESP-IDF. It supports both Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth LE. It is used by the ESP32 in the Arduino Core.
+
+Bluedroid requires more flash and RAM than NimBLE and access permissions for characteristics and descriptors are set using a specific API through the `setAccessPermissions()` function.
The original source of the Bluedroid project, **which is not maintained anymore**, can be found here: https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets
-Some parts of the NimBLE implementation are based on the work of h2zero, which can be found here: https://github.com/h2zero/NimBLE-Arduino
+**Bluedroid will be replaced by NimBLE in version 4.0.0 of the Arduino Core. Bluetooth Classic and Bluedroid will no longer be supported but can be used by using Arduino as an ESP-IDF component.**
+
+#### NimBLE
+
+NimBLE is a lightweight Bluetooth stack for Bluetooth LE only. It is used by all SoCs that are not the ESP32.
+
+NimBLE requires less flash and RAM than Bluedroid. Access permissions for characteristics are set using exclusive properties in the characteristic creation. Access permissions for descriptors are set using the `setAccessPermissions()` function just like in Bluedroid.
+
+Some parts of the NimBLE implementation are based on the work of h2zero, which can be found here: https://github.com/h2zero/NimBLE-Arduino. For a more customizable and feature-rich implementation of the NimBLE stack, you can use the [NimBLE-Arduino](https://github.com/h2zero/NimBLE-Arduino) library.
+
+### Common Scenarios
+
+Here are some common scenarios for the pairing methods depending on the IO capabilities of the devices. Check also the secure BLE examples in the ESP32 Arduino Core for more detailed usage examples.
+
+#### Scenario 1: Mobile App ↔ ESP32 Sensor Node
+- **Devices**: Mobile (`ESP_IO_CAP_IO`) ↔ ESP32 Sensor (`ESP_IO_CAP_NONE`)
+- **MITM**: Not achievable with this IO combination (falls back to Just Works)
+- **Characteristic Authentication**: Bonding only
+- **Result**: Just Works with bonding for reconnection
+- **Use Case**: Weather stations, environmental monitors
+
+#### Scenario 2: ESP32 Smart Lock ↔ Mobile App
+- **Devices**: ESP32 Lock (`ESP_IO_CAP_OUT`) ↔ Mobile (`ESP_IO_CAP_KBDISP`)
+- **MITM**: Required for security
+- **Characteristic Authentication**: Bonding + Secure Connection + MITM
+- **Result**: Passkey Entry (ESP32 displays, mobile enters)
+- **Implementation**: Static passkey or dynamic display
+
+#### Scenario 3: ESP32 Configuration Device ↔ Admin Tool
+- **Devices**: ESP32 (`ESP_IO_CAP_KBDISP`) ↔ Admin Tool (`ESP_IO_CAP_KBDISP`)
+- **MITM**: Required for configuration security
+- **Characteristic Authentication**: Bonding + Secure Connection + MITM
+- **Result**:
+ - Legacy: Passkey Entry
+ - Secure Connections: Numeric Comparison
+- **Use Case**: Industrial IoT configuration, network setup
+
+#### Scenario 4: ESP32 Beacon ↔ Scanner App
+- **Devices**: ESP32 Beacon (`ESP_IO_CAP_NONE`) ↔ Scanner (`ESP_IO_CAP_IO`)
+- **MITM**: Not required (broadcast only)
+- **Characteristic Authentication**: None
+- **Result**: No pairing required
+- **Use Case**: Asset tracking, proximity detection
+
+#### Scenario 5: ESP32 Smart Home Hub ↔ Multiple Devices
+- **Devices**: ESP32 Hub (`ESP_IO_CAP_IO`) ↔ Various sensors (`ESP_IO_CAP_NONE`)
+- **MITM**: Not possible when any of the peers are `ESP_IO_CAP_NONE`
+- **Characteristic Authentication**: Bonding only (no MITM possible with `ESP_IO_CAP_NONE`)
+- **Result**: Just Works only
+- **Use Case**: Centralized home automation controller
+
+### Implementation Guidelines
+
+#### For ESP32 Device Developers
+
+##### Choosing IO Capabilities
+```cpp
+#include
+
+// Conservative approach - limits pairing methods but ensures compatibility
+pSecurity->setCapability(ESP_IO_CAP_NONE); // Just Works only
+
+// Balanced approach - good UX with optional security
+pSecurity->setCapability(ESP_IO_CAP_IO); // Just Works or Numeric Comparison
+
+// Maximum security - supports all methods
+pSecurity->setCapability(ESP_IO_CAP_KBDISP); // All pairing methods available
+```
+
+##### Authentication Configuration
+```cpp
+BLESecurity *pSecurity = new BLESecurity();
+
+// Low security applications (sensors, environmental monitoring)
+pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(ESP_LE_AUTH_NO_BOND);
+
+// Standard security with bonding (smart home devices)
+pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(ESP_LE_AUTH_BOND);
+
+// MITM protection required (access control, payments)
+pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(ESP_LE_AUTH_REQ_MITM | ESP_LE_AUTH_BOND);
+
+// Maximum security with Secure Connections (critical systems)
+pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(ESP_LE_AUTH_REQ_SC_MITM_BOND);
+
+// Alternative syntax (more readable for complex requirements)
+pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(true, true, true); // Bonding, MITM, Secure Connections
+```
+
+##### Static Passkey Example (from secure examples)
+```cpp
+// Set a static passkey for consistent pairing experience
+#define DEVICE_PASSKEY 123456
+pSecurity->setPassKey(true, DEVICE_PASSKEY); // static=true, passkey=123456
+pSecurity->setCapability(ESP_IO_CAP_KBDISP); // Required for MITM even with static passkey
+```
+
+### Security Considerations
+
+#### When to Require MITM
+- **Always**: Payment systems, medical devices, access control
+- **Usually**: File transfers, personal data sync, keyboards
+- **Optional**: Fitness trackers, environmental sensors, mice
+- **Never**: Beacons, broadcast-only devices
+
+#### Legacy vs Secure Connections
+- **Legacy**: Compatible with all BLE devices (2010+)
+- **Secure Connections**: Better security but requires Bluetooth 4.2+ (2014+)
+- **Recommendation**: Support both, prefer Secure Connections when available
+
+#### Implementation Differences
+```cpp
+// Basic characteristic properties (both stacks)
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ | BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE;
+
+// NimBLE: Add authentication properties (ignored by Bluedroid)
+properties |= BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHEN | BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_AUTHEN;
+
+BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(CHAR_UUID, properties);
+
+// Bluedroid: Set access permissions (ignored by NimBLE)
+pCharacteristic->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENC_MITM | ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENC_MITM);
+
+// Check which stack is running
+String stackType = BLEDevice::getBLEStackString();
+Serial.println("Using BLE stack: " + stackType);
+```
+
+#### Known Vulnerabilities
+1. **Just Works**: Vulnerable to passive eavesdropping during initial pairing
+2. **Legacy Pairing**: Uses weaker cryptographic algorithms
+3. **Passkey Brute Force**: 6-digit passkeys have only 1M combinations
+4. **Physical Security**: Displayed passkeys can be shoulder-surfed
+
+### Troubleshooting
+
+#### Common Issues
+
+##### Pairing Always Uses Just Works
+```cpp
+// ❌ Problem: Missing MITM flag
+pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(ESP_LE_AUTH_REQ_SC_BOND);
+
+// ✅ Solution: Add MITM protection
+pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(ESP_LE_AUTH_REQ_SC_MITM_BOND);
+```
+
+##### Static passkey not being requested / Nothing happens when trying to read secure characteristic
+```cpp
+// ❌ Problem: Wrong IO capability for MITM
+pSecurity->setCapability(ESP_IO_CAP_NONE); // Can't support MITM
+
+// ✅ Solution: Set proper capability even for static passkey
+pSecurity->setCapability(ESP_IO_CAP_KBDISP); // Required for MITM
+pSecurity->setPassKey(true, 123456);
+```
+
+##### Secure Characteristic Access Fails
+```cpp
+// ❌ Problem: Wrong security method for stack
+// Bluedroid approach (won't work on NimBLE)
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ;
+pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(uuid, properties);
+pCharacteristic->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENC_MITM); // Ignored by NimBLE!
+
+// ✅ Solution: Use both methods for cross-compatibility
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHEN; // For NimBLE
+pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(uuid, properties);
+pCharacteristic->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENC_MITM); // For Bluedroid
+```
+
+##### Pairing Works Once, Then Fails (NVS Cache Issue)
+```cpp
+// ✅ Solution: Clear NVS for testing/development
+Serial.println("Clearing NVS pairing data for testing...");
+nvs_flash_erase();
+nvs_flash_init();
+```
+
+##### Default Passkey Warning
+```
+*WARNING* Using default passkey: 123456
+*WARNING* Please use a random passkey or set a different static passkey
+```
+```cpp
+// ✅ Solution: Change from default
+#define CUSTOM_PASSKEY 567890 // Your unique passkey
+pSecurity->setPassKey(true, CUSTOM_PASSKEY);
+```
+
+##### Connection drops during pairing
+```cpp
+// ✅ Solution: Implement security callbacks for better error handling
+class MySecurityCallbacks : public BLESecurityCallbacks {
+ void onAuthenticationComplete(esp_ble_auth_cmpl_t param) override {
+ if (param.success) {
+ Serial.println("Pairing successful!");
+ } else {
+ Serial.printf("Pairing failed, reason: %d\n", param.fail_reason);
+ }
+ }
+};
+
+BLEDevice::setSecurityCallbacks(new MySecurityCallbacks());
+```
+
+#### Cross-Platform Best Practice
+```cpp
+// Always use both methods for maximum compatibility
+uint32_t secure_properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHEN | // NimBLE
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_AUTHEN; // NimBLE
+
+BLECharacteristic *pChar = pService->createCharacteristic(uuid, secure_properties);
+
+// Bluedroid permissions (ignored by NimBLE, but doesn't hurt)
+pChar->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENC_MITM | ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENC_MITM);
+```
+
+### Complete Properties and Permissions Reference
+
+#### Bluedroid
+
+Bluedroid uses properties to define the capabilities of a characteristic and permissions to define the access permissions. NimBLE will ignore the access permissions.
+
+##### Supported Properties
+```cpp
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ // Read operation
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE // Write operation
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_NR // Write without response
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_NOTIFY // Notifications
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_INDICATE // Indications
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_BROADCAST // Broadcast
+```
+
+##### Characteristic and Descriptor Access Permissions
+```cpp
+// Basic permissions
+ESP_GATT_PERM_READ // Read allowed
+ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE // Write allowed
+
+// Encryption required
+ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENCRYPTED // Read requires encryption
+ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENCRYPTED // Write requires encryption
+
+// Authentication required (MITM protection)
+ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENC_MITM // Read requires encryption + MITM
+ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENC_MITM // Write requires encryption + MITM
+
+// Authorization required
+ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_AUTHORIZATION // Read requires authorization callback
+ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_AUTHORIZATION // Write requires authorization callback
+```
+
+#### NimBLE
+
+NimBLE uses properties to define both the capabilities of a characteristic and the access permissions. Bluedroid will ignore the NimBLE exclusive properties.
+
+##### Supported Properties
+```cpp
+// Basic properties
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ // Read operation
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE // Write operation
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_NR // Write without response
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_NOTIFY // Notifications
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_INDICATE // Indications
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_BROADCAST // Broadcast
+
+// NimBLE specific properties
+
+// Encryption required
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_ENC // Read requires encryption
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_ENC // Write requires encryption
+
+// Authentication required (MITM protection)
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHEN // Read requires encryption + MITM protection
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_AUTHEN // Write requires encryption + MITM protection
+
+// Authorization required
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHOR // Read requires authorization callback
+BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_AUTHOR // Write requires authorization callback
+```
+
+##### Descriptor Access Permissions
+```cpp
+// Basic permissions
+ESP_GATT_PERM_READ // Read allowed
+ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE // Write allowed
+
+// Encryption required
+ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENCRYPTED // Read requires encryption
+ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENCRYPTED // Write requires encryption
+
+// Authentication required (MITM protection)
+ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENC_MITM // Read requires encryption + MITM
+ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENC_MITM // Write requires encryption + MITM
+
+// Authorization required
+ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_AUTHORIZATION // Read requires authorization callback
+ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_AUTHORIZATION // Write requires authorization callback
+```
+
+#### Usage Examples by Security Level
+
+##### No Security (Both Stacks)
+```cpp
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE;
+```
+
+##### Encryption Only
+```cpp
+// NimBLE
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_ENC |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_ENC;
+
+// Bluedroid
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE;
+pChar->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENCRYPTED | ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENCRYPTED);
+```
+
+##### MITM Protection (Authentication)
+```cpp
+// NimBLE
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHEN |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_AUTHEN;
+
+// Bluedroid
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE;
+pChar->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENC_MITM | ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENC_MITM);
+```
+
+##### Authorization Required
+```cpp
+// NimBLE
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHOR |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_AUTHOR;
+
+// Bluedroid
+uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
+ BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE;
+pChar->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_AUTHORIZATION | ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_AUTHORIZATION);
+```
+
+#### Debug Tips
+1. **Log pairing features** exchanged between devices
+2. **Monitor pairing method** selected by the stack
+3. **Check timeout values** for user input methods
+4. **Verify key distribution** flags match on both sides
+
+### Standards References
-Issues and questions should be raised here: https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/issues
(please don't use https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/issues or https://github.com/h2zero/NimBLE-Arduino/issues!)
+- **Bluetooth Core Specification v5.4**: Volume 3, Part H (Security Manager)
+- **Bluetooth Assigned Numbers**: IO Capability values
+- **FIPS-140-2**: Cryptographic standards for Secure Connections
-Documentation for using the library can be found here: https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/tree/master/Documentation
+---
-For a more customizable and feature-rich implementation of the NimBLE stack, you can use the [NimBLE-Arduino](https://github.com/h2zero/NimBLE-Arduino) library.
+*This guide is based on the ESP32 Arduino BLE library implementation and the official Bluetooth Core Specification. For the latest API documentation, refer to the ESP32 Arduino BLE library source code and examples.*
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/examples/Client_secure_static_passkey/Client_secure_static_passkey.ino b/libraries/BLE/examples/Client_secure_static_passkey/Client_secure_static_passkey.ino
index c6e20b58bbb..2ee503efa5d 100644
--- a/libraries/BLE/examples/Client_secure_static_passkey/Client_secure_static_passkey.ino
+++ b/libraries/BLE/examples/Client_secure_static_passkey/Client_secure_static_passkey.ino
@@ -12,9 +12,9 @@
This means that in NimBLE you can read the insecure characteristic without entering
the passkey. This is not possible in Bluedroid.
- Also, the SoC stores the authentication info in the NVS memory. After a successful
- connection it is possible that a passkey change will be ineffective.
- To avoid this, clear the memory of the SoC's between security tests.
+ IMPORTANT: MITM (Man-In-The-Middle protection) must be enabled for password prompts
+ to work. Without MITM, the BLE stack assumes no user interaction is needed and will use
+ "Just Works" pairing method (with encryption if secure connection is enabled).
Based on examples from Neil Kolban and h2zero.
Created by lucasssvaz.
@@ -22,6 +22,7 @@
#include "BLEDevice.h"
#include "BLESecurity.h"
+#include "nvs_flash.h"
// The remote service we wish to connect to.
static BLEUUID serviceUUID("4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b");
@@ -116,7 +117,7 @@ bool connectToServer() {
// For Bluedroid, we need to set the authentication request type for the secure characteristic
// This is not needed for NimBLE and will be ignored.
- pRemoteSecureCharacteristic->setAuth(ESP_GATT_AUTH_REQ_NO_MITM);
+ pRemoteSecureCharacteristic->setAuth(ESP_GATT_AUTH_REQ_MITM);
// Try to read the secure characteristic (this will trigger security negotiation in NimBLE)
if (pRemoteSecureCharacteristic->canRead()) {
@@ -167,6 +168,12 @@ void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Starting Secure BLE Client application...");
+ // Clear NVS to remove any cached pairing information
+ // This ensures fresh authentication for testing
+ Serial.println("Clearing NVS pairing data...");
+ nvs_flash_erase();
+ nvs_flash_init();
+
BLEDevice::init("Secure BLE Client");
// Set up security with the same passkey as the server
@@ -177,7 +184,7 @@ void setup() {
// - IO capability is set to NONE
// - Initiator and responder key distribution flags are set to both encryption and identity keys.
// - Passkey is set to BLE_SM_DEFAULT_PASSKEY (123456). It will warn if you don't change it.
- // - Max key size is set to 16 bytes
+ // - Key size is set to 16 bytes
// Set the same static passkey as the server
// The first argument defines if the passkey is static or random.
@@ -185,8 +192,8 @@ void setup() {
pSecurity->setPassKey(true, CLIENT_PIN);
// Set authentication mode to match server requirements
- // Enable secure connection only for this example
- pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(false, false, true);
+ // Enable secure connection and MITM (for password prompts) for this example
+ pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(false, true, true);
// Retrieve a Scanner and set the callback we want to use to be informed when we
// have detected a new device. Specify that we want active scanning and start the
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_authorization/Server_secure_authorization.ino b/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_authorization/Server_secure_authorization.ino
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b1ab9cd5931
--- /dev/null
+++ b/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_authorization/Server_secure_authorization.ino
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+/*
+ Simple BLE Server Authorization Example
+
+ This example demonstrates how to create a BLE server with authorization
+ requirements. It shows the essential setup for:
+ - Authorization with static passkey
+ - Secure connection
+ - MITM (Man-In-The-Middle) protection
+
+ The server creates a single characteristic that requires authorization
+ to access. Clients must provide the correct passkey (123456) to read
+ or write to the characteristic.
+
+ Note that ESP32 uses Bluedroid by default and the other SoCs use NimBLE.
+ Bluedroid initiates security on-connect, while NimBLE initiates security on-demand.
+
+ Due to a bug in ESP-IDF's Bluedroid, this example will currently not work with ESP32.
+
+ IMPORTANT: MITM (Man-In-The-Middle protection) must be enabled for password prompts
+ to work. Without MITM, the BLE stack assumes no user interaction is needed and will use
+ "Just Works" pairing method (with encryption if secure connection is enabled).
+
+ Created by lucasssvaz.
+*/
+
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include
+
+// See the following for generating UUIDs:
+// https://www.uuidgenerator.net/
+
+#define SERVICE_UUID "4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b"
+#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID "beb5483e-36e1-4688-b7f5-ea07361b26a8"
+
+// Example passkey - change this for production use
+#define AUTH_PASSKEY 123456
+
+static int s_readCount = 0;
+static BLECharacteristic *s_pCharacteristic;
+
+class MySecurityCallbacks : public BLESecurityCallbacks {
+ bool onAuthorizationRequest(uint16_t connHandle, uint16_t attrHandle, bool isRead) {
+ Serial.println("Authorization request received");
+ if (isRead) {
+ s_readCount++;
+ // Keep value length <= (MTU - 1) to avoid a follow-up read request
+ uint16_t maxLen = BLEDevice::getServer()->getPeerMTU(connHandle) - 1;
+ String msg = "Authorized #" + String(s_readCount);
+ if (msg.length() > maxLen) {
+ msg = msg.substring(0, maxLen);
+ }
+ s_pCharacteristic->setValue(msg);
+ // Grant authorization to the first 3 reads
+ if (s_readCount <= 3) {
+ Serial.println("Authorization granted");
+ return true;
+ } else {
+ Serial.println("Authorization denied, read count exceeded");
+ Serial.println("Please reset the read counter to continue");
+ return false;
+ }
+ }
+ // Fallback to deny
+ Serial.println("Authorization denied");
+ return false;
+ }
+};
+
+void setup() {
+ Serial.begin(115200);
+ Serial.println("Starting BLE Authorization Example!");
+
+ // Initialize the BOOT pin for resetting the read count
+ pinMode(BOOT_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
+
+ // Clear NVS to remove any cached pairing information
+ // This ensures fresh authentication for testing
+ Serial.println("Clearing NVS pairing data...");
+ nvs_flash_erase();
+ nvs_flash_init();
+
+ Serial.print("Using BLE stack: ");
+ Serial.println(BLEDevice::getBLEStackString());
+
+ BLEDevice::init("BLE Auth Server");
+
+ // Set MTU to 517 to avoid a follow-up read request
+ BLEDevice::setMTU(517);
+
+ // Configure BLE Security
+ BLESecurity *pSecurity = new BLESecurity();
+
+ // Set static passkey for authentication
+ pSecurity->setPassKey(true, AUTH_PASSKEY);
+
+ // Set IO capability to DisplayOnly for MITM authentication
+ pSecurity->setCapability(ESP_IO_CAP_OUT);
+
+ // Enable authorization requirements:
+ // - bonding: true (for persistent storage of the keys)
+ // - MITM: true (enables Man-In-The-Middle protection for password prompts)
+ // - secure connection: true (enables secure connection for encryption)
+ pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(true, true, true);
+
+ // Set the security callbacks
+ BLEDevice::setSecurityCallbacks(new MySecurityCallbacks());
+
+ // Create BLE Server
+ BLEServer *pServer = BLEDevice::createServer();
+ pServer->advertiseOnDisconnect(true);
+
+ // Create BLE Service
+ BLEService *pService = pServer->createService(SERVICE_UUID);
+
+ // Create characteristic with read and write properties
+ uint32_t properties = BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ;
+
+ // For NimBLE: Add authentication properties
+ // These properties ensure the characteristic requires authorization
+ // (ignored by Bluedroid but harmless)
+ properties |= BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHEN | BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHOR;
+
+ s_pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(CHARACTERISTIC_UUID, properties);
+
+ // For Bluedroid: Set access permissions that require encryption and MITM
+ // This ensures authorization is required (ignored by NimBLE)
+ s_pCharacteristic->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENC_MITM | ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_AUTHORIZATION);
+
+ // Set initial value
+ s_pCharacteristic->setValue("Hello! You needed authorization to read this!");
+
+ // Start the service
+ pService->start();
+
+ // Configure and start advertising
+ BLEAdvertising *pAdvertising = BLEDevice::getAdvertising();
+ pAdvertising->addServiceUUID(SERVICE_UUID);
+ pAdvertising->setScanResponse(true);
+ pAdvertising->setMinPreferred(0x06); // helps with iPhone connections
+ pAdvertising->setMinPreferred(0x12);
+
+ BLEDevice::startAdvertising();
+
+ Serial.println("BLE Server is running!");
+ Serial.println("Authorization is required to access the characteristic.");
+ Serial.printf("Use passkey: %d when prompted\n", AUTH_PASSKEY);
+}
+
+void loop() {
+ // Reset the read count if the BOOT pin is pressed
+ if (digitalRead(BOOT_PIN) == LOW) {
+ s_readCount = 0;
+ Serial.println("Read count reset");
+ }
+
+ delay(100);
+}
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_authorization/ci.json b/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_authorization/ci.json
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1e2d20da791
--- /dev/null
+++ b/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_authorization/ci.json
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+{
+ "targets": {
+ "esp32": false
+ },
+ "fqbn_append": "PartitionScheme=huge_app",
+ "requires": [
+ "CONFIG_SOC_BLE_SUPPORTED=y"
+ ]
+}
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_static_passkey/Server_secure_static_passkey.ino b/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_static_passkey/Server_secure_static_passkey.ino
index 2f1189d5cf3..79b73695202 100644
--- a/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_static_passkey/Server_secure_static_passkey.ino
+++ b/libraries/BLE/examples/Server_secure_static_passkey/Server_secure_static_passkey.ino
@@ -15,9 +15,9 @@
This means that in NimBLE you can read the insecure characteristic without entering
the passkey. This is not possible in Bluedroid.
- Also, the SoC stores the authentication info in the NVS memory. After a successful
- connection it is possible that a passkey change will be ineffective.
- To avoid this, clear the memory of the SoC's between security tests.
+ IMPORTANT: MITM (Man-In-The-Middle protection) must be enabled for password prompts
+ to work. Without MITM, the BLE stack assumes no user interaction is needed and will use
+ "Just Works" pairing method (with encryption if secure connection is enabled).
Based on examples from Neil Kolban and h2zero.
Created by lucasssvaz.
@@ -27,13 +27,14 @@
#include
#include
#include
+#include
#include
// See the following for generating UUIDs:
// https://www.uuidgenerator.net/
#define SERVICE_UUID "4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b"
-#define Insecure_CHARACTERISTIC_UUID "beb5483e-36e1-4688-b7f5-ea07361b26a8"
+#define INSECURE_CHARACTERISTIC_UUID "beb5483e-36e1-4688-b7f5-ea07361b26a8"
#define SECURE_CHARACTERISTIC_UUID "ff1d2614-e2d6-4c87-9154-6625d39ca7f8"
// This is an example passkey. You should use a different or random passkey.
@@ -43,6 +44,12 @@ void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Starting BLE work!");
+ // Clear NVS to remove any cached pairing information
+ // This ensures fresh authentication for testing
+ Serial.println("Clearing NVS pairing data...");
+ nvs_flash_erase();
+ nvs_flash_init();
+
Serial.print("Using BLE stack: ");
Serial.println(BLEDevice::getBLEStackString());
@@ -55,16 +62,22 @@ void setup() {
// - IO capability is set to NONE
// - Initiator and responder key distribution flags are set to both encryption and identity keys.
// - Passkey is set to BLE_SM_DEFAULT_PASSKEY (123456). It will warn if you don't change it.
- // - Max key size is set to 16 bytes
+ // - Key size is set to 16 bytes
// Set static passkey
// The first argument defines if the passkey is static or random.
// The second argument is the passkey (ignored when using a random passkey).
pSecurity->setPassKey(true, SERVER_PIN);
+ // Set IO capability to DisplayOnly
+ // We need the proper IO capability for MITM authentication even
+ // if the passkey is static and won't be shown to the user
+ // See https://www.bluetooth.com/blog/bluetooth-pairing-part-2-key-generation-methods/
+ pSecurity->setCapability(ESP_IO_CAP_OUT);
+
// Set authentication mode
- // Require secure connection only for this example
- pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(false, false, true);
+ // Require secure connection and MITM (for password prompts) for this example
+ pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(false, true, true);
BLEServer *pServer = BLEDevice::createServer();
pServer->advertiseOnDisconnect(true);
@@ -78,16 +91,16 @@ void setup() {
// These special permission properties are not supported by Bluedroid and will be ignored.
// This can be removed if only using Bluedroid (ESP32).
// Check the BLECharacteristic.h file for more information.
- secure_properties |= BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_ENC | BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_ENC;
+ secure_properties |= BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ_AUTHEN | BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE_AUTHEN;
BLECharacteristic *pSecureCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(SECURE_CHARACTERISTIC_UUID, secure_properties);
- BLECharacteristic *pInsecureCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(Insecure_CHARACTERISTIC_UUID, insecure_properties);
+ BLECharacteristic *pInsecureCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(INSECURE_CHARACTERISTIC_UUID, insecure_properties);
// Bluedroid uses permissions to secure characteristics.
// This is the same as using the properties above.
// NimBLE does not use permissions and will ignore these calls.
// This can be removed if only using NimBLE (any SoC except ESP32).
- pSecureCharacteristic->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENCRYPTED | ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENCRYPTED);
+ pSecureCharacteristic->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ_ENC_MITM | ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE_ENC_MITM);
pInsecureCharacteristic->setAccessPermissions(ESP_GATT_PERM_READ | ESP_GATT_PERM_WRITE);
// Set value for secure characteristic
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/src/BLECharacteristic.cpp b/libraries/BLE/src/BLECharacteristic.cpp
index c41cd9fcded..d410c94ec72 100644
--- a/libraries/BLE/src/BLECharacteristic.cpp
+++ b/libraries/BLE/src/BLECharacteristic.cpp
@@ -923,7 +923,6 @@ int BLECharacteristic::handleGATTServerEvent(uint16_t conn_handle, uint16_t attr
if (ctxt->om->om_pkthdr_len > 8) {
rc = ble_gap_conn_find(conn_handle, &desc);
assert(rc == 0);
- pCharacteristic->m_pCallbacks->onRead(pCharacteristic);
pCharacteristic->m_pCallbacks->onRead(pCharacteristic, &desc);
}
@@ -957,7 +956,6 @@ int BLECharacteristic::handleGATTServerEvent(uint16_t conn_handle, uint16_t attr
rc = ble_gap_conn_find(conn_handle, &desc);
assert(rc == 0);
pCharacteristic->setValue(buf, len);
- pCharacteristic->m_pCallbacks->onWrite(pCharacteristic);
pCharacteristic->m_pCallbacks->onWrite(pCharacteristic, &desc);
return 0;
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/src/BLEClient.cpp b/libraries/BLE/src/BLEClient.cpp
index 39c21a49584..d1b5d8d5338 100644
--- a/libraries/BLE/src/BLEClient.cpp
+++ b/libraries/BLE/src/BLEClient.cpp
@@ -536,6 +536,8 @@ void BLEClient::gattClientEventHandler(esp_gattc_cb_event_t event, esp_gatt_if_t
m_semaphoreRssiCmplEvt.give();
m_semaphoreSearchCmplEvt.give(1);
BLEDevice::removePeerDevice(m_appId, true);
+ // Reset security state on disconnect
+ BLESecurity::resetSecurity();
if (m_wasConnected && m_pClientCallbacks != nullptr) {
m_pClientCallbacks->onDisconnect(this);
}
@@ -981,6 +983,8 @@ int BLEClient::handleGAPEvent(struct ble_gap_event *event, void *arg) {
BLEDevice::removePeerDevice(client->m_appId, true);
client->m_isConnected = false;
+ // Reset security state on disconnect
+ BLESecurity::resetSecurity();
if (client->m_pClientCallbacks != nullptr) {
client->m_pClientCallbacks->onDisconnect(client);
}
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/src/BLESecurity.cpp b/libraries/BLE/src/BLESecurity.cpp
index ae47aea533f..a481d569765 100644
--- a/libraries/BLE/src/BLESecurity.cpp
+++ b/libraries/BLE/src/BLESecurity.cpp
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ bool BLESecurity::m_securityStarted = false;
bool BLESecurity::m_passkeySet = false;
bool BLESecurity::m_staticPasskey = true;
bool BLESecurity::m_regenOnConnect = false;
-uint8_t BLESecurity::m_iocap = 0;
+uint8_t BLESecurity::m_iocap = ESP_IO_CAP_NONE;
uint8_t BLESecurity::m_authReq = 0;
uint8_t BLESecurity::m_initKey = 0;
uint8_t BLESecurity::m_respKey = 0;
@@ -188,6 +188,12 @@ void BLESecurity::regenPassKeyOnConnect(bool enable) {
m_regenOnConnect = enable;
}
+// This function resets the security state on disconnect.
+void BLESecurity::resetSecurity() {
+ log_d("resetSecurity: Resetting security state");
+ m_securityStarted = false;
+}
+
// This function sets the authentication mode with bonding, MITM, and secure connection options.
void BLESecurity::setAuthenticationMode(bool bonding, bool mitm, bool sc) {
log_d("setAuthenticationMode: bonding=%d, mitm=%d, sc=%d", bonding, mitm, sc);
@@ -270,6 +276,7 @@ void BLESecurity::setEncryptionLevel(esp_ble_sec_act_t level) {
bool BLESecurity::startSecurity(esp_bd_addr_t bd_addr, int *rcPtr) {
#ifdef CONFIG_BLE_SMP_ENABLE
+ log_d("startSecurity: bd_addr=%s", BLEAddress(bd_addr).toString().c_str());
if (m_securityStarted) {
log_w("Security already started for bd_addr=%s", BLEAddress(bd_addr).toString().c_str());
if (rcPtr) {
@@ -333,6 +340,7 @@ void BLESecurityCallbacks::onAuthenticationComplete(esp_ble_auth_cmpl_t param) {
#if defined(CONFIG_NIMBLE_ENABLED)
// This function initiates security for a given connection handle.
bool BLESecurity::startSecurity(uint16_t connHandle, int *rcPtr) {
+ log_d("startSecurity: connHandle=%d", connHandle);
if (m_securityStarted) {
log_w("Security already started for connHandle=%d", connHandle);
if (rcPtr) {
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/src/BLESecurity.h b/libraries/BLE/src/BLESecurity.h
index 79fb99f544b..d3a1679df8f 100644
--- a/libraries/BLE/src/BLESecurity.h
+++ b/libraries/BLE/src/BLESecurity.h
@@ -104,6 +104,7 @@ class BLESecurity {
static uint32_t getPassKey();
static uint32_t generateRandomPassKey();
static void regenPassKeyOnConnect(bool enable = false);
+ static void resetSecurity();
/***************************************************************************
* Bluedroid public declarations *
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/src/BLEServer.cpp b/libraries/BLE/src/BLEServer.cpp
index 896e25f3ffc..5f0a4b71047 100644
--- a/libraries/BLE/src/BLEServer.cpp
+++ b/libraries/BLE/src/BLEServer.cpp
@@ -460,6 +460,9 @@ void BLEServer::handleGATTServerEvent(esp_gatts_cb_event_t event, esp_gatt_if_t
m_connectedCount--; // Decrement the number of connected devices count.
}
+ // Reset security state on disconnect
+ BLESecurity::resetSecurity();
+
// Start advertising again if enabled
if (m_advertiseOnDisconnect) {
log_i("Start advertising again after disconnect");
@@ -676,6 +679,9 @@ int BLEServer::handleGATTServerEvent(struct ble_gap_event *event, void *arg) {
server->m_pServerCallbacks->onDisconnect(server, &event->disconnect.conn);
}
+ // Reset security state on disconnect
+ BLESecurity::resetSecurity();
+
#if !defined(CONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_EXT_ADV)
if (server->m_advertiseOnDisconnect) {
log_i("Start advertising again after disconnect");
diff --git a/libraries/BLE/src/BLEUtils.cpp b/libraries/BLE/src/BLEUtils.cpp
index 7d6f7a18e7d..bce66df4cb2 100644
--- a/libraries/BLE/src/BLEUtils.cpp
+++ b/libraries/BLE/src/BLEUtils.cpp
@@ -2170,6 +2170,9 @@ const char *BLEUtils::gapEventToString(uint8_t eventType) {
case BLE_GAP_EVENT_EXT_DISC: //19
return "BLE_GAP_EVENT_EXT_DISC";
+
+ case BLE_GAP_EVENT_AUTHORIZE: //32
+ return "BLE_GAP_EVENT_AUTHORIZE";
#ifdef BLE_GAP_EVENT_PERIODIC_SYNC // IDF 4.0 does not support these
case BLE_GAP_EVENT_PERIODIC_SYNC: //20
return "BLE_GAP_EVENT_PERIODIC_SYNC";