You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: docs/TESTS.md
+8-18Lines changed: 8 additions & 18 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -10,8 +10,7 @@ You should also install the following `pytest` plugins:
10
10
We also recommend using the code linting program [pylint][pylint], as it is part of our automated feedback on the website and can be a very useful static code analysis tool.
11
11
For ease-of-use, the [pytest-pylint][pytest-pylint] plugin for `pytest` will allow you to run `pylint` via `pytest` on the command line.
12
12
13
-
Pylint configuration can be a bit much, so this [tutorial from pycqa.org][tutorial from pycqa.org] can be helpful for getting started, as can this overview of [Code Quality: Tools and Best Practices][Code Quality: Tools and Best Practices] from Real Python.
14
-
13
+
Pylint configuration can be a bit much, so this [tutorial from pylint.readthedocs.io][tutorial from pylint.readthedocs.io] can be helpful for getting started, as can this overview of [Code Quality: Tools and Best Practices][Code Quality: Tools and Best Practices] from Real Python.
@@ -85,7 +82,6 @@ More information on pytest marks can be found in the `pytest` documentation on [
85
82
86
83
_More information on customizing pytest configurations can be found in the pytest documentation on [configuration file formats][configuration file formats]_
87
84
88
-
89
85
### Test Failures
90
86
91
87
When tests fail, `pytest` prints the text of each failed test, along with the expected and actual `return` values of each to the terminal.
If you really want to be specific about what pytest returns on your screen, here are some handy command-line arguments that allows you to configure its behavior.
112
108
113
-
114
109
#### Return All Details [`-v`]
115
110
116
111
Adding the `-v` (_verbose_) flag will return both environment information and a test summary in addition to test failures:
The `pytest-cache` plugin remembers which tests failed last time you ran `pytest`, so using the flag `--ff` will tell `pytest` to run previously failed tests **first**, then continue with the remainder of the tests.
167
162
This might speed up your testing if you are making a lot of smaller fixes around one particular task or set of inputs.
==================== 7 passed in 503s ====================
@@ -192,7 +186,6 @@ This will test your solution.
192
186
When `pytest` encounters a failed test, the program will stop and tell you which test failed.
193
187
When you make fixes and run the test again, `pytest` will first run the previous test that failed, then continue with the remaining tests.
194
188
195
-
196
189
### Using PDB, the Python Debugger, with pytest
197
190
198
191
If you want to "debug like a pro", you can use the `--pdb` argument after the `pytest` command, and drop into the built-in [Python debugger][pdb], `PDB`.
@@ -206,13 +199,11 @@ When a test fails, dropping into `PDB` will allow you to step through your code
206
199
More details on the `PDB` module can be found in the [Python documentation on PDB][pdb].
207
200
Additionally, the [pytest docs on PDB][pytest-pdb] and [this guide from Real Python](https://realpython.com/python-debugging-pdb/) are extremely helpful.
208
201
209
-
210
202
## Extending your IDE
211
203
212
204
If you'd like to extend your IDE with some tools that will help you with testing and improving your code, check the [tools](./tools) page.
213
205
We explore multiple IDEs, editors and some useful extensions for linting and debugging there.
214
206
215
-
216
207
## Additional information
217
208
218
209
### Adding python to your PATH
@@ -245,7 +236,6 @@ Then add a new line, as shown in the picture, replacing `{python_directory}` wit
245
236
246
237
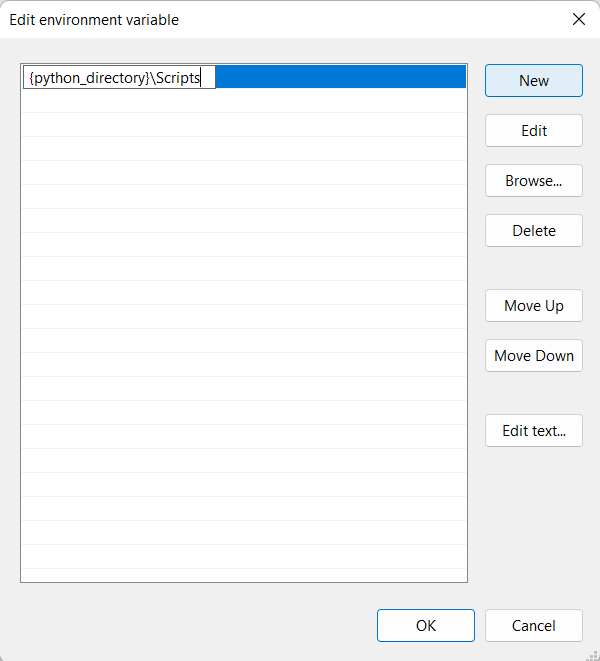
247
238
248
-
249
239
#### MacOS/Linux
250
240
251
241
The below should work for most Linux and MacOS flavors with a `bash` shell.
0 commit comments