|
| 1 | + |
| 2 | +## Building a Real Time Chat Application with Spring Boot and Websocket |
| 3 | + |
| 4 | +## What is Websocket? |
| 5 | +> WebSocket is a computer communications protocol, providing full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection. |
| 6 | +> WebSocket is distinct from HTTP. The protocol enables interaction between a web browser (or other client application) and a web server with lower overhead than half-duplex alternatives such as HTTP polling, facilitating real-time data transfer from and to the server. |
| 7 | +
|
| 8 | + |
| 9 | + |
| 10 | +Once a websocket connection is established between a client and a server, both can exchange information until the connection is closed by any of the parties. |
| 11 | + |
| 12 | +This is the main reasion which websocket is preferred over the HTTP protocol when building a chat-like communication service that operates at high frequencies with low latency. |
| 13 | + |
| 14 | +## What is STOMP? |
| 15 | +> Simple (or Streaming) Text Oriented Message Protocol (STOMP), formerly known as TTMP, is a simple text-based protocol, designed for working with message-oriented middleware (MOM). It provides an interoperable wire format that allows STOMP clients to talk with any message broker supporting the protocol. |
| 16 | +
|
| 17 | +Since websocket is just a communication protocol, it doesn’t know how to send a message to a particular user. STOMP is basically a messaging protocol which is useful for these functionalities. |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +## Setting up the application |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +Our application will have the following configuration which can be set using [Spring Initializr](https://start.spring.io/) : |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +* Java version : 11 |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +* Type : Maven Project |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +* Dependencies : Websocket |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +* Spring Boot version : 2.4.2 |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +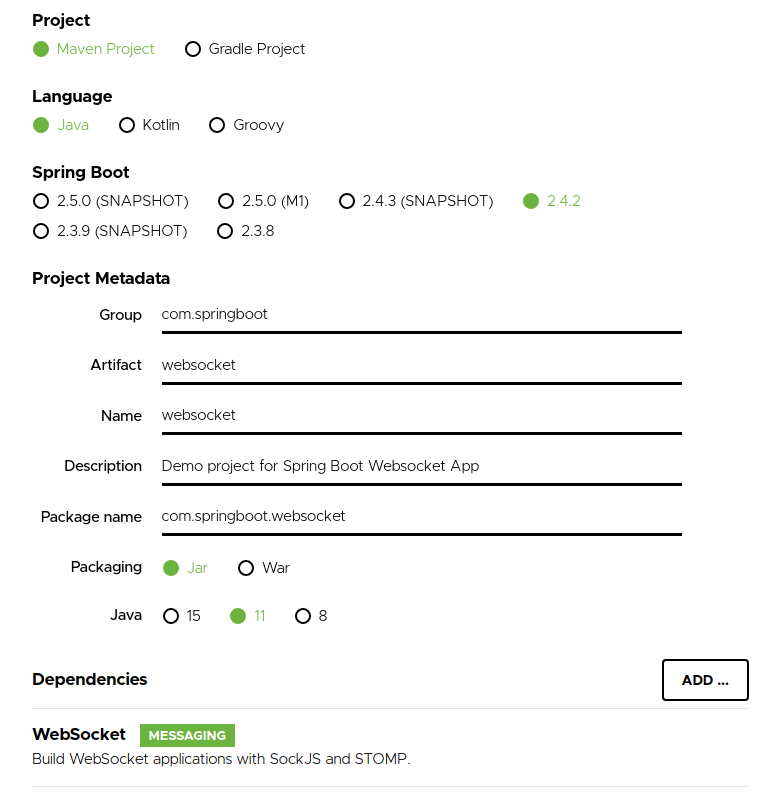 |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +## Project structure |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +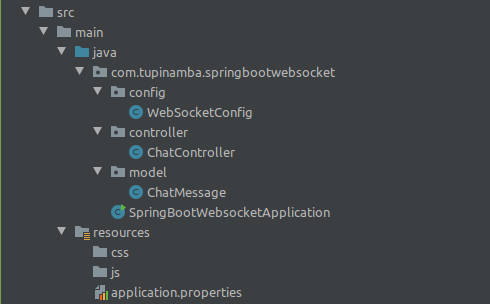 |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +## Configuring WebSocket |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | +Configuring our websocket endpoint and message broker is fairly simple. |
| 40 | + |
| 41 | + @Configuration |
| 42 | + @EnableWebSocketMessageBroker |
| 43 | + public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer { |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | + @Override |
| 46 | + public void registerStompEndpoints(StompEndpointRegistry registry) { |
| 47 | + registry.addEndpoint("/websocket").withSockJS(); |
| 48 | + } |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | + @Override |
| 51 | + public void configureMessageBroker(MessageBrokerRegistry registry) { |
| 52 | + registry.enableSimpleBroker("/topic"); |
| 53 | + registry.setApplicationDestinationPrefixes("/app"); |
| 54 | + } |
| 55 | + } |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +* @EnableWebSocketMessageBroker annotation is used to enable our WebSocket server. |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +* WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer interface is used to provide implementation for some of its methods to configure the websocket connection. |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +* registerStompEndpoints method is used to register a websocket endpoint that the clients will use to connect to the server. |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | +* configureMessageBroker method is used to configure our message broker which will be used to route messages from one client to another. |
| 64 | + |
| 65 | +SockJS is also being used to enable fallback options for browsers that don’t support websocket. |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | +## Creating a Chat Model |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +Our chat model is the message payload which will be exchanged between the client side and server side of the application. |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | + public class ChatMessage { |
| 72 | + private String content; |
| 73 | + private String sender; |
| 74 | + private MessageType type; |
| 75 | + |
| 76 | + public enum MessageType { |
| 77 | + *CHAT*, *LEAVE*, *JOIN |
| 78 | + *} |
| 79 | + |
| 80 | + public String getContent() { |
| 81 | + return content; |
| 82 | + } |
| 83 | + |
| 84 | + public void setContent(String content) { |
| 85 | + this.content = content; |
| 86 | + } |
| 87 | + |
| 88 | + public String getSender() { |
| 89 | + return sender; |
| 90 | + } |
| 91 | + |
| 92 | + public void setSender(String sender) { |
| 93 | + this.sender = sender; |
| 94 | + } |
| 95 | + |
| 96 | + public MessageType getType() { |
| 97 | + return type; |
| 98 | + } |
| 99 | + |
| 100 | + public void setType(MessageType type) { |
| 101 | + this.type = type; |
| 102 | + } |
| 103 | + } |
| 104 | + |
| 105 | +## Creating our Chat Controller |
| 106 | + |
| 107 | +Our controller will be responsible for handling all message methods present in our chat application which will basically receive messages from one client and then broadcast it to others. |
| 108 | + |
| 109 | + @Controller |
| 110 | + public class ChatController { |
| 111 | + |
| 112 | + @MessageMapping("/chat.register") |
| 113 | + @SendTo("/topic/public") |
| 114 | + public ChatMessage register(@Payload ChatMessage chatMessage, SimpMessageHeaderAccessor headerAccessor) { |
| 115 | + headerAccessor.getSessionAttributes().put("username", chatMessage.getSender()); |
| 116 | + return chatMessage; |
| 117 | + } |
| 118 | + |
| 119 | + @MessageMapping("/chat.send") |
| 120 | + @SendTo("/topic/public") |
| 121 | + public ChatMessage sendMessage(@Payload ChatMessage chatMessage) { |
| 122 | + return chatMessage; |
| 123 | + } |
| 124 | + } |
| 125 | + |
| 126 | +The use of /app as a destination point is because of our websocket configuration file which says that all messages will be routed to these handling methods annotated with @MessageMapping. |
| 127 | + |
| 128 | +## Creating a front-end UI |
| 129 | + |
| 130 | + |
| 131 | + |
| 132 | +Our UI is a simple cardbox built using HTML and CSS that runs some JS functions to send and receive messages. |
| 133 | + |
| 134 | +* index.html is a HTML file which contains some basic structure a S*ock.js* to enable fallback options to those that can’t run JS on their browsers and a *STOMP* library to serve as a message broker. |
| 135 | +* main.css is a CSS file that styles our HTML. |
| 136 | +* main.js is a Javascript file which connects the websocket endpoint to send and receive messages. It also displays and format the messages on the screen. |
| 137 | + |
| 138 | +## End result |
| 139 | + |
| 140 | + |
| 141 | + |
| 142 | +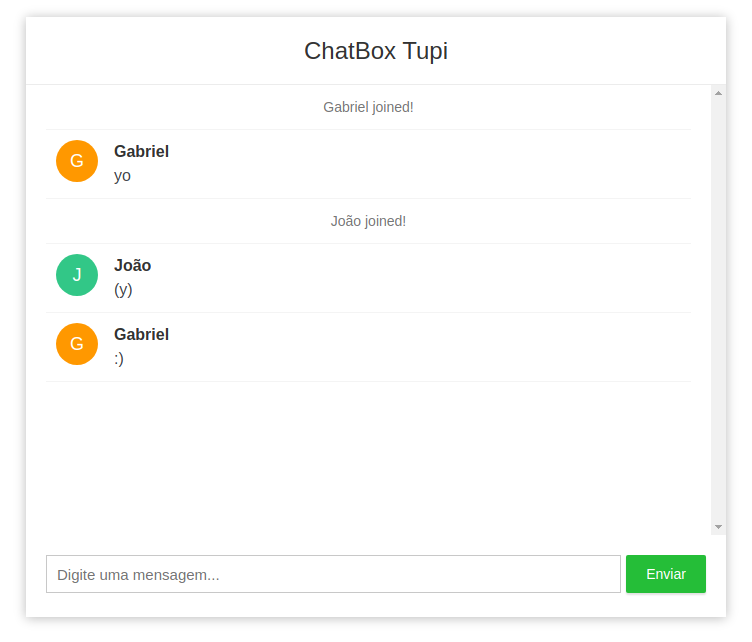 |
0 commit comments