diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 37d2d46..0342336 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,8 +1,1047 @@
-# Distributed Systems Practice
-Notes from learning about distributed systems in [GW CS 6421](https://gwdistsys18.github.io/) with [Prof. Wood](https://faculty.cs.gwu.edu/timwood/)
+Notes Contents
+=================
-## Area 1
-> Include notes here about each of the links
+ * [Big Data and Machine Learning -(Beginner level + Intermediate Level)](#bigDataAndMachineLearning)
+ * [ Video: Hadoop Intro](#introduction)
+ * [ AWS Tutorial: Analyze Big Data with Hadoop](#Analyze-Big-Data-with-Hadoop)
+ * [QwikLab: Intro to S3](#Intro-to-S3)
+ * [QwikLab: Intro to Amazon Redshift](#Intro-to-Amazon-Redshift)
+ * [Video: Short AWS Machine Learning Overview](#Short-AWS-Machine-Learning-Overview)
+ * [Video Tutorial: Overview of AWS SageMaker](#Overview-of-AWS-SageMaker)
+ * [AWS Tutorial: Analyze Big Data with Hadoop](#AWS-Tutorial-Analyze-Big-Data-with-Hadoop)
+ * [QwikLab: Intro to Amazon Machine Learning](#QwikLab-Intro-to-Amazon-Machine-Learning)
+ * [AWS Tutorial: Build a Machine Learning Model](#AWS-Tutorial-Build-a-Machine-Learning-Model)
+ * [Video Tutorial: Overview of AWS SageMaker](#VideoTutorialOverviewofAWSSageMaker)
+ * [Build a Serverless Real-Time Data Processing App](#BuildaServerlessReal-TimeDataProcessingApp)
+
+ * [Cloud Web Apps(Beginner level + Intermediate Level)](#cloud-web-apps)
+ * [AWS Tutorial: Launch a VM](#AWS-Tutorial-Launch-a-VM)
+ * [Video: Virtualization](#VideoVirtualization)
+ * [AWS Tutorial: Install a LAMP Web Server on Amazon Linux 2](#AWSTutorialInstallaLAMPWebServeronAmazonLinux2)
+ * [AWS Tutorial: Deploy a Scalable Node.js Web App](#AWSTutorialDeployaScalableNodejsWebApp)
+ * [QwikLab: Intro to DynamoDB](#QwikLabIntrotoDynamoDB)
+ * [QwikLab: Intro to AWS Lambda](#QwikLabIntrotoAWSLambda)
+ * [QwikLab: Intro to Amazon API Gateway](#QwikLabIntrotoAmazonAPIGateway)
+ * [AWS Tutorial: Build a Serverless Web Application](#AWSTutorialBuildaServerlessWebApplication)
+ * [AWS Tutorial: Build a Modern Web Application](#AWSTutorialBuildaModernWebApplication)
+
+ * [Docker and Container(Beginner Level)](DockerandContainerBeginnerLevel)
+ * [Video: Why Docker?](#VideoWhyDocker?)
+ * [Lab: DevOps Docker Beginners Guide](#LabDevOpsDockerBeginnersGuide)
-## Area 2
-> Include notes here about each of the links
+
+
+
+## Big Data and Machine Learning (Beginner level + Intermediate Level)
+
+
+## [Video: Hadoop Intro](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jKCj4BxGTi8&feature=youtu.be)
+
+Time: it takes 35 minutes to learn it.
+
+* The video tutorial gives basic ideas of Hadoop framework. After 2000, the solution which uses the computation power provided by available computers to process data could not help. In recent years, there is an incredible explosion in the volume of data. IBM reported that 2.5 billion gigabytes of data was generated every day in 2012. 40000 search queries were done on Google every second. Therefore, we need computers with larger memories and faster processors or other more advanced solutions. The idea distributed system is using multiple computers to do the processing work which has much better performance. There are also challenges for this. There are high chances of failure since a distributed system uses multiple computers. There is also limit on bandwidth. Because it is difficult to synchronize data and process, the programming complexity is also high. The solution is Hadoop. Hadoop is a framework that allows for distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of commodity computers using simple programming models. The four key characters of Hadoop are economical, scalable, reliable and flexible. Compared to traditional DBMS, Hadoop distributes the data to multiple systems and later runs the computation wherever the data is located. The Hadoop has an ecosystem which is evolved from its three core components, data processing, resource management and Hadoop distributed file system. It is now comprised of 12 components including Hadoop distributed file system, HBase, scoop, flume, spark, Hadoop MapReduce, Pig, Impala, Hive, Cloudera Search, Oozie, Hue.
+
+
+## [AWS Tutorial: Analyze Big Data with Hadoop](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/projects/analyze-big-data/?trk=gs_card)
+
+Time: it takes me more than one hour to learn and write up a summary.
+
+* I have acquired how to create Amazon S3 bucket store my log files and output data, Launch a fully functional Hadoop cluster using Amazon EMR, define the schema, create a table for sample log data stored in Amazon S3, analyze the data using a HiveQL script and write the results back to Amazon S3. It is interesting to learn.
+
+
+## [QwikLab: Intro to S3](https://awseducate.qwiklabs.com/focuses/30?parent=catalog)
+
+Time: it takes 50 minutes.
+
+* In this lab, I learned:
+ * Create a bucket in Amazon S3 service
+ * Add an object for example a picture to the bucket
+ * Manage access permissions on an object: change from private to public and see the access difference
+ * Create a bucket policy by using the AWS policy generator which require the Amazon Resource Name.
+ * Use bucket versioning to get access the picture with same name but uploaded at different time by changing the bucket policy
+
+ * The bucket is a really useful service and the versioning feature is quite cool.
+
+
+## [QwikLab: Intro to Amazon Redshift](https://awseducate.qwiklabs.com/focuses/28?parent=catalog)
+
+Time: it takes me 60 minutes. In this lab, it covers
+
+* Launch a Redshift cluster: a cluster is a fully managed data warehouse that consists of a set of compute nodes; when launching a cluster, you have to specify the node type which determines the CPU, RAM, storage capacity and storage drive type.
+* Connect an SQL client called Pgweb to the Amazon Redshift cluster: we can write and run queries in Pgweb and also view the database information and structure.
+* Load sample data from an S3 bucket into the Amazon Redshift cluster which will hold the data for querying.
+* Run queries against data stored in Amazon Redshift: we could use SQL to query the data we need.
+
+
+## [Video: Short AWS Machine Learning Overview](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=soG1B4jMl2s)
+
+Time: it takes me 10 minutes
+
+* it talks about the Machine learning on AWS. Machine learning has three layers, framework interfaces for expert, ML platforms for developers and data scientists and application services for machine learning API calls in the application. Amazon Deep Learning AMI is for the frameworks layer and Zillow uses it. Amazon SageMaker is a good for ML platform layer.
+
+
+## [Overview of AWS SageMaker](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ym7NEYEx9x4&index=12&list=RDMWhrLw7YK38)
+
+Time: it takes me 35 minutes.
+
+* The AWS SageMaker has four parts, including the notebook instance, jobs, models and endpoints. Notebook instance is about using algorithms to create model via training jobs. Training jobs are instances to train the model. We create models for hosting from job outputs, or import externally trained models into Amazon SageMaker. Endpoints are for developers to use the SageMaker in production. The tutor elaborate on xgboost, kmeans, scikit . He talks about setting up the training parameters. We can train it on single or multiple instances. Then we import models into hosts. The last step is build endpoint configuration and create endpoint for developers to call.
+
+
+## [AWS Tutorial: Analyze Big Data with Hadoop](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/projects/analyze-big-data/?trk=gs_card)
+
+Time: it takes me 80 minutes.
+
+I followed the following steps to finish the tutorial:
+
+* 1: Set Up Prerequisites: you have to have a personal AWS account; create an Amazon S3 Bucket and folder to store the output data from a Hive query; create an Amazon EC2 Key Pair to to connect to the nodes in your cluster over a secure channel using the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol.
+* 2: Launch The Cluster: user launches sample Amazon EMR cluster by using Quick Options in the Amazon EMR console and leaving most options to their default values; Amazon EMR is a managed cluster platform that simplifies running big data frameworks, such as Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark, on AWS to process and analyze vast amounts of data. By using these frameworks and related open-source projects, such as Apache Hive and Apache Pig, you can process data for analytics purposes and business intelligence workloads. Additionally, you can use Amazon EMR to transform and move large amounts of data into and out of other AWS data stores and databases, such as Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and Amazon DynamoDB.
+* 3: Allow SSH Connections to the Cluster From Your Client: Security groups act as virtual firewalls to control inbound and outbound traffic to your cluster. The default Amazon EMR-managed security groups associated with cluster instances do not allow inbound SSH connections as a security precaution. To connect to cluster nodes using SSH so that you can use the command line and view web interfaces that are hosted on the cluster, you need to add inbound rules that allow SSH traffic from trusted clients.
+* 4: Run a Hive Script to Process Data: The sample data is a series of Amazon CloudFront access log files; The sample script calculates the total number of requests per operating system over a specified time frame. The script uses HiveQL, which is a SQL-like scripting language for data warehousing and analysis
+* 5:Terminate the resources you do not need to save for the future
+
+terminating your cluster terminates the associated Amazon EC2 instances and stops the accrual of Amazon EMR charges. Amazon EMR preserves metadata information about completed clusters for your reference, at no charge, for two months. The console does not provide a way to delete terminated clusters so that they aren't viewable in the console. Terminated clusters are removed from the cluster when the metadata is removed
+There is more information on how to plan and configure clusters in your custom way, set up the security, manage clusters and trouble shoot cluster if it is performing in a wrong way.
+
+
+## [QwikLab: Intro to Amazon Machine Learning](https://awseducate.qwiklabs.com/focuses/27?parent=catalog)
+
+Time : it takes me 75 minutes.
+
+The lab tutorial consists of several parts:
+* Part 1- Upload training data : we put restaurant customer reviews data into Amazon S3 bucket and save it for analyzing
+* Part2- Create a datasource: configure Amazon ML to use the restaurant data set; we set customer review data as the data source for Amazon ML model
+* Part3- Create an ML Model from the Datasource: we will use data source to train and validate the model created in this part; the data source also contains metadata, such as the column data types and target variable which will also be used by the model algorithm; the ML modeling process will take 5 to 10 minutes to complete and we can see that in message section
+* Evaluate an ML model: the Amazon Machine Learning service evaluate the model automatically as part of the model creation process; it takes 70 percent of the data source to train the model and 30 percent to evaluate it.
+* Generate predictions from ML model: batch mode and real-time mode are two ways to generate predictions from ML model; batch mode is asynchronous while the real-time mode is real time.
+
+## [AWS Tutorial: Build a Machine Learning Model](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/projects/build-machine-learning-model/?trk=gs_card)
+
+Time: it takes me 50 minutes. It is about using Amazon ML to Predict Responses to a Marketing Offer:
+* Step 1: Prepare Your Data: In machine learning, you typically obtain the data and ensure that it is well formatted before starting the training process; we use customer purchase history to predict if this customer will subscribe to my new product
+* Step 2: Create a Training Datasource using the Amazon S3 service
+* Step 3: Create an ML Model: After you've created the training datasource, you use it to create an ML model, train the model, and then evaluate the results
+* Step 4: Review the ML Model's Predictive Performance and Set a Score Threshold
+* Step 5: Use the ML Model to Generate Predictions
+
+
+## [Video Tutorial: Overview of AWS SageMaker](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ym7NEYEx9x4&index=12&list=RDMWhrLw7YK38)
+
+Time:it takes me 40 minutes
+
+The AWS SageMaker has four parts, including the notebook instance, jobs, models and endpoints. Notebook instance is about using algorithms to create model via training jobs. Training jobs are instances to train the model. We create models for hosting from job outputs, or import externally trained models into Amazon SageMaker. Endpoints are for developers to use the SageMaker in production. The tutor elaborate on xgboost, kmeans, scikit . He talks about setting up the training parameters. We can train it on single or multiple instances. Then we import models into hosts. The last step is build endpoint configuration and create endpoint for developers to call
+For AWS Tutorial: AWS SageMaker, it takes me 80 minutes.
+Step 1: Setting Up
+Step 2: Create an Amazon SageMaker Notebook Instance
+Step 3: Train and Deploy a Model
+Step 4: Clean up
+Step 5: Additional Considerations
+
+
+## [Build a Serverless Real-Time Data Processing App](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/projects/build-serverless-real-time-data-processing-app-lambda-kinesis-s3-dynamodb-cognito-athena/?trk=gs_card)
+
+Time: it takes 150 minutes,
+
+Cloud web application
+For QwikLab: Intro to S3, it takes 50 minutes. In this lab, I learned:
+• Create a bucket in Amazon S3 service
+• Add an object for example a picture to the bucket
+• Manage access permissions on an object: change from private to public and see the access difference
+• Create a bucket policy by using the AWS policy generator which require the Amazon Resource Name.
+• Use bucket versioning to get access the picture with same name but uploaded at different time by changing the bucket policy
+The bucket is a really useful service and the versioning feature is quite cool.
+
+## Cloud Web Apps(Beginner level + Intermediate Level)
+
+## [AWS Tutorial: Launch a VM](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/tutorials/launch-a-virtual-machine/)
+
+Time Spent: 40 min
+
+### 1. Sign-up for AWS
+* You could use your only personal account to register and you could also choose to set up IAM user for better management
+
+### 2. Launch an Amazon EC2 Instance
+ a. Enter the Amazon EC2 Console
+ Open the AWS Management Console, so you can keep this step-by-step guide open. When the screen loads, enter your user name and password to get started. Then type EC2 in the search bar and select Amazon EC2 to open the service console.
+
+b. Launch an Instance
+Select Launch Instance to create and configure your virtual machine.
+
+
+### 3. Configure your Instance
+ You are now in the EC2 Launch Instance Wizard, which will help you configure and launch your instance.
+ #### a. In this screen, you are shown options to choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI). AMIs are preconfigured server templates you can use to launch an instance. Each AMI includes an operating system, and can also include applications and application servers. For this tutorial, find Amazon Linux AMI and click Select.
+
+b. You will now choose an instance type. Instance types comprise of varying combinations of CPU, memory, storage, and networking capacity so you can choose the appropriate mix for your applications.
+The default option of t2.micro should already be checked. This instance type is covered within the Free Tier and offers enough compute capacity to tackle simple workloads. Click Review and Launch at the bottom of the page.
+c. You can review the configuration, storage, tagging, and security settings that have been selected for your instance. While you have the option to customize these settings, we recommend accepting the default values for this tutorial.
+Click Launch at the bottom of the page.
+
+d. On the next screen you will be asked to choose an existing key pair or create a new key pair. A key pair is used to securely access your Linux instance using SSH. AWS stores the public part of the key pair which is just like a house lock. You download and use the private part of the key pair which is just like a house key.
+Select Create a new key pair and give it the name MyKeyPair. Next click the Download Key Pair button.
+After you download the MyKeyPair key, you will want to store your key in a secure location. If you lose your key, you won't be able to access your instance. If someone else gets access to your key, they will be able to access your instance.
+Windows users: We recommend saving your key pair in your user directory in a sub-directory called .ssh (ex. C:\user\{yourusername}\.ssh\MyKeyPair.pem).
+
+Tip: You can't use Windows Explorer to create a folder with a name that begins with a period unless you also end the folder name with a period. After you enter the name (.ssh.), the final period is removed automatically.
+Mac/Linux users: We recommend saving your key pair in the .ssh sub-directory from your home directory (ex. ~/.ssh/MyKeyPair.pem).
+
+Tip: On MacOS, the key pair is downloaded to your Downloads directory by default. To move the key pair into the .ssh sub-directory, enter the following command in a terminal window: mv ~/Downloads/MyKeyPair.pem ~/.ssh/MyKeyPair.pem
+After you have stored your key pair, click Launch Instance to start your Linux instance.
+e. Click View Instances on the next screen to view your instances and see the status of the instance you have just started.
+f. In a few minutes, the Instance State column on your instance will change to "running" and a Public IP address will be shown. You can refresh these Instance State columns by pressing the refresh button on the right just above the table. Copy the Public IP address of your AWS instance, so you can use it when we connect to the instance using SSH in Step 4.
+
+
+### 4. Connect to your Instance
+After launching your instance, it's time to connect to it using SSH.
+Mac/Linux user: Select Mac / Linux below to see instructions for opening a terminal window.
+* Windows
+
+* Mac
+* a. Your Mac or Linux computer most likely includes an SSH client by default. You can check for an SSH client by typing ssh at the command line. If your computer doesn't recognize the command, the OpenSSH project provides a free implementation of the full suite of SSH tools that you can download.
+Mac users: Open a terminal window first. Then press enter to open the terminal window.
+Linux users: Open a terminal window.
+b. Use the chmod command to make sure your private key file is not publicly viewable by entering the following command to restrict permissions to your private SSH key:
+chmod 400 ~/.ssh/mykeypair.pem
+You do not need to do this every time you connect to you instance, you only need to set this once per SSH key that you have.
+c. Use SSH to connect to your instance. In this case the user name is ec2-user, the SSH key is stored in the directory we saved it to in step 3 part d, and the IP address is from step 3 part f. The format is:
+ssh -i {full path of your .pem file} ec2-user@{instance IP address}
+Enter the following:
+ssh -i ~/.ssh/MyKeyPair.pem ec2-user@{IP_Address}
+Example: ssh -i ~/.ssh/MyKeyPair.pem ec2-user@52.27.212.125
+You'll see a response similar to the following:
+The authenticity of host 'ec2-198-51-100-1.compute-1.amazonaws.com (10.254.142.33)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is 1f:51:ae:28:df:63:e9:d8:cf:38:5d:87:2d:7b:b8:ca:9f:f5:b1:6f. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
+Type yes and press enter.
+d. You'll see a response similar to the following:
+Warning: Permanently added 'ec2-198-51-100-1.compute-1.amazonaws.com' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
+You should then see the welcome screen for your instance and you are now connected to your AWS Linux virtual machine in the cloud.
+
+### 5. Terminate Your Instance
+You can easily terminate the instance from the EC2 console. In fact, it is a best practice to terminate instances you are no longer using so you don’t keep getting charged for them.
+a. Back on the EC2 Console, select the box next to the instance you created. Then click the Actions button, navigate to Instance State, and click Terminate.
+b. You will be asked to confirm your termination - select Yes, Terminate.
+Note: This process can take several seconds to complete. Once your instance has been terminated, the Instance State will change to terminated on your EC2 Console.
+
+
+[Video: Virtualization](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GIdVRB5yNsk)
+
+Cloud computing is booming thus we need virtualization to meet the needs. Virtualization first emerged in the 1970s and brought out by IBM since there were different computer with different systems.
+
+It starts with VMWare with a bunch of students in Stanford wanted to do software emulation of virtual machines. We often have two levels of privileges to run computer software. We run operating System and our applications. The OS part is called ring 0 and application part is called ring 3.
+
+Since X86 processor is not easy to be virtualized by VMWare, the Xen is developed. It is a hypervisor using a microkernel design, providing services that allow multiple operating systems to execute on the same computer hardware concurrently. But it has some drawbacks like high overheads which means that an instruction was executed on hypervisor means more instructions on the operating system.
+
+The Intel realized they have to do the virtualization itself thus the VT technology was developed and released into nearly all intel processors.
+
+In summary, the cloud computing companies just utilizes the software virtualization of the processors and other hardware resources they have to rent it the customer and gives the results they want back.
+
+
+## [AWS Tutorial: Install a LAMP Web Server on Amazon Linux 2](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ec2-lamp-amazon-linux-2.html)
+
+Time: 80 minutes
+
+### 1: Prepare the LAMP Server
+#### Prerequisites:
+*Create an IAM User:
+https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/get-set-up-for-amazon-ec2.html#create-an-iam-user
+
+
+
+* Create a Key Pair:
+Amazon EC2 uses public–key cryptography to encrypt and decrypt login information. Public–key cryptography uses a public key to encrypt a piece of data, such as a password, then the recipient uses the private key to decrypt the data. The public and private keys are known as a key pair.
+
+
+* Create a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC):
+Amazon VPC enables you to launch AWS resources into a virtual network that you've defined, known as a virtual private cloud (VPC). The newer EC2 instance types require that you launch your instances in a VPC
+
+
+
+* Create a Security Group:
+Security groups act as a firewall for associated instances, controlling both inbound and outbound traffic at the instance level. You must add rules to a security group that enable you to connect to your instance from your IP address using SSH. You can also add rules that allow inbound and outbound HTTP and HTTPS access from anywhere.
+
+*Launch an Instance
+1. Open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/.
+2. From the console dashboard, choose Launch Instance.
+3. The Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) page displays a list of basic configurations, called Amazon Machine Images (AMIs), that serve as templates for your instance. Select an HVM version of Amazon Linux 2. Notice that these AMIs are marked "Free tier eligible."
+4. On the Choose an Instance Type page, you can select the hardware configuration of your instance. Select the t2.micro type, which is selected by default. Notice that this instance type is eligible for the free tier.
+5. Choose Review and Launch to let the wizard complete the other configuration settings for you.
+6. On the Review Instance Launch page, under Security Groups, you'll see that the wizard created and selected a security group for you. You can use this security group, or alternatively you can select the security group that you created when getting set up using the following steps:
+a. Choose Edit security groups.
+b. On the Configure Security Group page, ensure that Select an existing security group is selected.
+c. Select your security group from the list of existing security groups, and then choose Review and Launch.
+7. On the Review Instance Launch page, choose Launch.
+8. When prompted for a key pair, select Choose an existing key pair, then select the key pair that you created when getting set up.
+Alternatively, you can create a new key pair. Select Create a new key pair, enter a name for the key pair, and then choose Download Key Pair. This is the only chance for you to save the private key file, so be sure to download it. Save the private key file in a safe place. You'll need to provide the name of your key pair when you launch an instance and the corresponding private key each time you connect to the instance.
+Warning
+Don't select the Proceed without a key pair option. If you launch your instance without a key pair, then you can't connect to it.
+When you are ready, select the acknowledgement check box, and then choose Launch Instances.
+9. A confirmation page lets you know that your instance is launching. Choose View Instances to close the confirmation page and return to the console.
+10. On the Instances screen, you can view the status of the launch. It takes a short time for an instance to launch. When you launch an instance, its initial state is pending. After the instance starts, its state changes to running and it receives a public DNS name. (If the Public DNS (IPv4) column is hidden, choose Show/Hide Columns (the gear-shaped icon) in the top right corner of the page and then select Public DNS (IPv4).) Note: if you use a VPC for the security group, you have to assign elastic IP and associate it with the instance to get the Public DNS else you do not have one automatically
+11. It can take a few minutes for the instance to be ready so that you can connect to it. Check that your instance has passed its status checks; you can view this information in the Status Checks column.
+
+*Now since we are done with the prerequisites, we are gonna prepare the LEMP server
+
+1. Connect to my instance using SSH
+Before you connect to your Linux instance, complete the following prerequisites:
+• Install an SSH client
+Your Linux computer most likely includes an SSH client by default. You can check for an SSH client by typing ssh at the command line. If your computer doesn't recognize the command, the OpenSSH project provides a free implementation of the full suite of SSH tools. For more information, see http://www.openssh.com.
+• Install the AWS CLI Tools
+(Optional) If you're using a public AMI from a third party, you can use the command line tools to verify the fingerprint. For more information about installing the AWS CLI, see Getting Set Up in the AWS Command Line Interface User Guide.
+• Get the ID of the instance
+You can get the ID of your instance using the Amazon EC2 console (from the Instance ID column). If you prefer, you can use the describe-instances (AWS CLI) or Get-EC2Instance (AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell) command.
+• Get the public DNS name of the instance
+You can get the public DNS for your instance using the Amazon EC2 console. Check the Public DNS (IPv4) column. If this column is hidden, choose the Show/Hide icon and select Public DNS (IPv4). If you prefer, you can use the describe-instances (AWS CLI) or Get-EC2Instance (AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell) command.
+• (IPv6 only) Get the IPv6 address of the instance
+If you've assigned an IPv6 address to your instance, you can optionally connect to the instance using its IPv6 address instead of a public IPv4 address or public IPv4 DNS hostname. Your local computer must have an IPv6 address and must be configured to use IPv6. You can get the IPv6 address of your instance using the Amazon EC2 console. Check the IPv6 IPs field. If you prefer, you can use the describe-instances (AWS CLI) or Get-EC2Instance(AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell) command. For more information about IPv6, see IPv6 Addresses.
+• Locate the private key and verify permissions
+Get the fully-qualified path to the location on your computer of the .pem file for the key pair that you specified when you launched the instance. Verify that the .pem file has permissions of 0400, not 0777. For more information, see Error: Unprotected Private Key File.
+• Get the default user name for the AMI that you used to launch your instance
+o For Amazon Linux 2 or the Amazon Linux AMI, the user name is ec2-user.
+o For a Centos AMI, the user name is centos.
+o For a Debian AMI, the user name is admin or root.
+o For a Fedora AMI, the user name is ec2-user or fedora.
+o For a RHEL AMI, the user name is ec2-user or root.
+o For a SUSE AMI, the user name is ec2-user or root.
+o For an Ubuntu AMI, the user name is ubuntu.
+o Otherwise, if ec2-user and root don't work, check with the AMI provider.
+• Enable inbound SSH traffic from your IP address to your instance
+Ensure that the security group associated with your instance allows incoming SSH traffic from your IP address. The default security group for the VPC does not allow incoming SSH traffic by default. The security group created by the launch wizard enables SSH traffic by default. For more information, see Authorizing Inbound Traffic for Your Linux Instances.
+
+1) (Optional) You can verify the RSA key fingerprint on your running instance by using one of the following commands on your local system (not on the instance). This is useful if you've launched your instance from a public AMI from a third party. Locate the SSH HOST KEY FINGERPRINTS section, and note the RSA fingerprint (for example, 1f:51:ae:28:bf:89:e9:d8:1f:25:5d:37:2d:7d:b8:ca:9f:f5:f1:6f) and compare it to the fingerprint of the instance.
+aws ec2 get-console-output --instance-id instance_id
+2) In a command-line shell, change directories to the location of the private key file that you created when you launched the instance.
+
+3) Use the following command to set the permissions of your private key file so that only you can read it.
+chmod 400 /path/my-key-pair.pem
+4) Use the ssh command to connect to the instance. You specify the private key (.pem) file anduser_name@public_dns_name. For example, if you used Amazon Linux 2 or the Amazon Linux AMI, the user name is ec2-user.
+ssh -i /path/my-key-pair.pem ec2-user@ec2-198-51-100-1.compute-1.amazonaws.com
+5) Enter yes.
+You see a response like the following:
+Warning: Permanently added 'ec2-***-**-***-*.compute-1.amazonaws.com' (RSA)
+to the list of known hosts.
+2. To ensure that all of your software packages are up to date, perform a quick software update on your instance. This process may take a few minutes, but it is important to make sure that you have the latest security updates and bug fixes.
+The -y option installs the updates without asking for confirmation. If you would like to examine the updates before installing, you can omit this option.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo yum update -y
+
+3. Install the lamp-mariadb10.2-php7.2 and php7.2 Amazon Linux Extras repositories to get the latest versions of the LAMP MariaDB and PHP packages for Amazon Linux 2.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo amazon-linux-extras install -y lamp-mariadb10.2-php7.2 php7.2
+Note
+If you receive an error stating sudo: amazon-linux-extras: command not found, then your instance was not launched with an Amazon Linux 2 AMI (perhaps you are using the Amazon Linux AMI instead). You can view your version of Amazon Linux with the following command.
+cat /etc/system-release
+4. Now that your instance is current, you can install the Apache web server, MariaDB, and PHP software packages.
+Use the yum install command to install multiple software packages and all related dependencies at the same time.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo yum install -y httpd mariadb-server
+Note
+You can view the current versions of these packages with the following command:
+yum info package_name
+5. Start the Apache web server.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl start httpd
+6. Use the systemctl command to configure the Apache web server to start at each system boot.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl enable httpd
+You can verify that httpd is on by running the following command:
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl is-enabled httpd
+7. Add a security rule to allow inbound HTTP (port 80) connections to your instance if you have not already done so. By default, a launch-wizard-N security group was set up for your instance during initialization. This group contains a single rule to allow SSH connections.
+8. Test your web server. In a web browser, type the public DNS address (or the public IP address) of your instance. If there is no content in /var/www/html, you should see the Apache test page. You can get the public DNS for your instance using the Amazon EC2 console (check the Public DNS column; if this column is hidden, chooseShow/Hide Columns (the gear-shaped icon) and choose Public DNS).
+
+Apache httpd serves files that are kept in a directory called the Apache document root. The Amazon Linux Apache document root is /var/www/html, which by default is owned by root.
+
+To allow the ec2-user account to manipulate files in this directory, you must modify the ownership and permissions of the directory. There are many ways to accomplish this task. In this tutorial, you add ec2-user to the apache group, to give the apache group ownership of the /var/www directory and assign write permissions to the group.
+
+ To set file permissions
+1. Add your user (in this case, ec2-user) to the apache group.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo usermod -a -G apache ec2-user
+2. Log out and then log back in again to pick up the new group, and then verify your membership.
+a. Log out of the ec2 (use the exit command or close the terminal window):
+[ec2-user ~]$ exit
+b. To verify your membership in the apache group, reconnect to your instance, and then run the following command:
+[ec2-user ~]$ groups
+ec2-user adm wheel apache systemd-journal
+3. Change the group ownership of /var/www and its contents to the apache group.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo chown -R ec2-user:apache /var/www
+4. To add group write permissions and to set the group ID on future subdirectories, change the directory permissions of /var/www and its subdirectories.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo chmod 2775 /var/www && find /var/www -type d -exec sudo chmod 2775 {} \;
+5. To add group write permissions, recursively change the file permissions of /var/www and its subdirectories:
+[ec2-user ~]$ find /var/www -type f -exec sudo chmod 0664 {} \;
+Now, ec2-user (and any future members of the apache group) can add, delete, and edit files in the Apache document root, enabling you to add content, such as a static website or a PHP application.
+Step 2: Test Your LAMP Server
+1. Create a PHP file in the Apache document root.
+[ec2-user ~]$ echo "" > /var/www/html/phpinfo.php
+If you get a "Permission denied" error when trying to run this command, try logging out and logging back in again to pick up the proper group permissions that you configured in To set file permissions.
+2. In a web browser, type the URL of the file that you just created. This URL is the public DNS address of your instance followed by a forward slash and the file name. For example:
+http://my.public.dns.amazonaws.com/phpinfo.php
+You should see the PHP information page:
+
+Note
+If you do not see this page, verify that the /var/www/html/phpinfo.php file was created properly in the previous step. You can also verify that all of the required packages were installed with the following command.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo yum list installed httpd mariadb-server php-mysqlnd
+If any of the required packages are not listed in your output, install them with the sudo yum installpackage command. Also verify that the php7.2 and lamp-mariadb10.2-php7.2 extras are enabled in the out put of the amazon-linux-extras command.
+3. Delete the phpinfo.php file. Although this can be useful information, it should not be broadcast to the internet for security reasons.
+[ec2-user ~]$ rm /var/www/html/phpinfo.php
+You should now have a fully functional LAMP web server. If you add content to the Apache document root at /var/www/html, you should be able to view that content at the public DNS address for your instance.
+Step 3: Secure the Database Server
+To secure the MariaDB server
+1. Start the MariaDB server.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl start mariadb
+2. Run mysql_secure_installation.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
+a. When prompted, type a password for the root account.
+i. Type the current root password. By default, the root account does not have a password set. Press Enter.
+ii. Type Y to set a password, and type a secure password twice. For more information about creating a secure password, see https://identitysafe.norton.com/password-generator/. Make sure to store this password in a safe place.
+Note
+Setting a root password for MariaDB is only the most basic measure for securing your database. When you build or install a database-driven application, you typically create a database service user for that application and avoid using the root account for anything but database administration.
+b. Type Y to remove the anonymous user accounts.
+c. Type Y to disable the remote root login.
+d. Type Y to remove the test database.
+e. Type Y to reload the privilege tables and save your changes.
+3. (Optional) If you do not plan to use the MariaDB server right away, stop it. You can restart it when you need it again.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl stop mariadb
+4. (Optional) If you want the MariaDB server to start at every boot, type the following command.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl enable mariadb
+
+Step 4: (Optional) Install phpMyAdmin
+phpMyAdmin is a web-based database management tool that you can use to view and edit the MySQL databases on your EC2 instance. Follow the steps below to install and configure phpMyAdmin on your Amazon Linux instance.
+Important
+We do not recommend using phpMyAdmin to access a LAMP server unless you have enabled SSL/TLS in Apache; otherwise, your database administrator password and other data are transmitted insecurely across the internet. For security recommendations from the developers, see Securing your phpMyAdmin installation. For general information about securing a web server on an EC2 instance, see Tutorial: Configure Apache Web Server on Amazon Linux to use SSL/TLS.
+To install phpMyAdmin
+1. Install the required dependencies.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo yum install php-mbstring -y
+2. Restart Apache.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl restart httpd
+3. Restart php-fpm.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
+4. Navigate to the Apache document root at /var/www/html.
+[ec2-user ~]$ cd /var/www/html
+5. Select a source package for the latest phpMyAdmin release from https://www.phpmyadmin.net/downloads. To download the file directly to your instance, copy the link and paste it into a wget command, as in this example:
+[ec2-user html]$ wget https://www.phpmyadmin.net/downloads/phpMyAdmin-latest-all-languages.tar.gz
+6. Create a phpMyAdmin folder and extract the package into it with the following command.
+[ec2-user html]$ mkdir phpMyAdmin && tar -xvzf phpMyAdmin-latest-all-languages.tar.gz -C phpMyAdmin --strip-components 1
+7. Delete the phpMyAdmin-latest-all-languages.tar.gz tarball.
+[ec2-user html]$ rm phpMyAdmin-latest-all-languages.tar.gz
+8. (Optional) If the MySQL server is not running, start it now.
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl start mariadb
+9. In a web browser, type the URL of your phpMyAdmin installation. This URL is the public DNS address (or the public IP address) of your instance followed by a forward slash and the name of your installation directory. For example:
+http://my.public.dns.amazonaws.com/phpMyAdmin
+You should see the phpMyAdmin login page:
+
+10. Log in to your phpMyAdmin installation with the root user name and the MySQL root password you created earlier.
+Your installation must still be configured before you put it into service. To configure phpMyAdmin, you can manually create a configuration file, use the setup console, or combine both approaches.
+For information about using phpMyAdmin, see the phpMyAdmin User Guide.
+Troubleshooting
+This section offers suggestions for resolving common problems you may encounter while setting up a new LAMP server.
+I can't connect to my server using a web browser.
+Perform the following checks to see if your Apache web server is running and accessible.
+• Check the status of the web server
+You can verify that httpd is on by running the following command:
+[ec2-user ~]$ sudo systemctl is-enabled httpd
+If the httpd process is not running, repeat the steps described in To prepare the LAMP server.
+• Check the firewall configuration
+If you are unable to see the Apache test page, check that the security group you are using contains a rule to allow HTTP (port 80) traffic. For information about adding an HTTP rule to your security group, see Adding Rules to a Security Group.
+
+
+[QwikLab: Intro to DynamoDB](https://awseducate.qwiklabs.com/focuses/23?parent=catalog)
+
+Time spent: 30 min
+Introduction: Amazon DynamoDB is a fast and flexible NoSQL database service for all applications that need consistent, single-digit millisecond latency at any scale. It is a fully managed database and supports both document and key-value data models. This lab is for creating a table in Amazon DynamoDB to store information about a music library and execute some queries and finally delete the table.
+
+Task 1: create the music library table
+Use the Music as the library name to create the NoSQL table and set it up.
+
+Task 2: Add data to the music table.
+In NoSQL database, a table is a collection of data on a particular topic. Each table contains multiple items and an item is a group of attributes that is uniquely identifiable among all of the other items. An attribute is a fundamental data element.
+
+Task 3: Modify an existing item
+You can edit an item after creation if you find something wrong with it which is convenient
+
+Task 4: Query the table
+I learned that there are two ways to query a DynamoDB table, one is Query and another is Scan. A query is the most efficient way to retrieve data from a DynamoDB table. A scan will look through every item in the table which is less efficient.
+
+
+Task 5: Delete the table.
+
+
+
+[AWS Tutorial: Deploy a Scalable Node.js Web App](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/projects/deploy-nodejs-web-app/?trk=gs_card)
+
+![]() add image
+
+## Learning Steps
+
+### 1. Create Elastic Beanstalk App and Launch
+
+- Choose __Platform__ as _Node.js_
+
add image
+
+## Learning Steps
+
+### 1. Create Elastic Beanstalk App and Launch
+
+- Choose __Platform__ as _Node.js_
+![]() add image
+- Choose __Application code__ as _Sample application_
+- Create app and Launch, it should look like below,
+
add image
+- Choose __Application code__ as _Sample application_
+- Create app and Launch, it should look like below,
+![]() add image
+
+- I learned that Elastic Beanstalk creates the environment with the following resources: EC2 instance, instance security group, load balancer, load balancer security group, auto Scaling group, amazon S3 bucket, Amazon CloudWatch alarms, AWS CloudFormation stack, Domain name
+
+
+### 2. Add Permissions to Your Environment's Instances
+
+- Open the [Roles page](https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/home#roles) in the IAM console.
+- Choose __aws-elasticbeanstalk-ec2-role__
+- Attach Policies
+ - _AmazonSNSFullAccess_
+ - _AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess_
+
+### 3. Deploy the Sample Application
+
+- Download the [source bundle](https://github.com/awslabs/eb-node-express-sample/releases/download/v1.1/eb-node-express-sample-v1.1.zip) from Github
+- Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
+- Choose __Upload and Deploy__, select the source bundle
+
+
add image
+
+- I learned that Elastic Beanstalk creates the environment with the following resources: EC2 instance, instance security group, load balancer, load balancer security group, auto Scaling group, amazon S3 bucket, Amazon CloudWatch alarms, AWS CloudFormation stack, Domain name
+
+
+### 2. Add Permissions to Your Environment's Instances
+
+- Open the [Roles page](https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/home#roles) in the IAM console.
+- Choose __aws-elasticbeanstalk-ec2-role__
+- Attach Policies
+ - _AmazonSNSFullAccess_
+ - _AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess_
+
+### 3. Deploy the Sample Application
+
+- Download the [source bundle](https://github.com/awslabs/eb-node-express-sample/releases/download/v1.1/eb-node-express-sample-v1.1.zip) from Github
+- Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
+- Choose __Upload and Deploy__, select the source bundle
+
+![]() add image
+
+### 4. Create a DynamoDB Table outside Elastic Beanstalk
+
+- Table name: _nodejs-tutorial_
+- Primary key: _email_
+- Primary key type: _String_
+
+### 5. Update the Application's Configuration Files
+
+- Unzip the source file bundle
+- Open _.ebextensions/options.config_ and change the values of the following settings:
+ - NewSignupEmail: _YOUR EMAIL_
+ - STARTUP-SIGNUP-TABLE: _nodejs-tutorial_
+
+This configures the application to use the __nodejs-tutorial__ table instead of the one created by
+_.ebextensions/create-dynamodb-table.config_, and sets the email address that the Amazon SNS topic uses for notifications.
+
+- Remove _.ebextensions/create-dynamodb-table.config_, so that the next time you deploy the application,
+the table created by this configuration file will be deleted
+
+```bash
+~/nodejs-tutorial$ rm .ebextensions/create-dynamodb-table.config
+```
+
+- Zip the modified source bundle and deploy again
+
+### 6.Configure Your Environment for High Availability
+
+- Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
+- Choose __Configuration__
+- On the __Capacity__ configuration card, choose Modify
+- In the __Auto Scaling Group__ section, set __Min instances__ to 2.
+
+
add image
+
+### 4. Create a DynamoDB Table outside Elastic Beanstalk
+
+- Table name: _nodejs-tutorial_
+- Primary key: _email_
+- Primary key type: _String_
+
+### 5. Update the Application's Configuration Files
+
+- Unzip the source file bundle
+- Open _.ebextensions/options.config_ and change the values of the following settings:
+ - NewSignupEmail: _YOUR EMAIL_
+ - STARTUP-SIGNUP-TABLE: _nodejs-tutorial_
+
+This configures the application to use the __nodejs-tutorial__ table instead of the one created by
+_.ebextensions/create-dynamodb-table.config_, and sets the email address that the Amazon SNS topic uses for notifications.
+
+- Remove _.ebextensions/create-dynamodb-table.config_, so that the next time you deploy the application,
+the table created by this configuration file will be deleted
+
+```bash
+~/nodejs-tutorial$ rm .ebextensions/create-dynamodb-table.config
+```
+
+- Zip the modified source bundle and deploy again
+
+### 6.Configure Your Environment for High Availability
+
+- Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
+- Choose __Configuration__
+- On the __Capacity__ configuration card, choose Modify
+- In the __Auto Scaling Group__ section, set __Min instances__ to 2.
+
+![]() add image
+
+### 7. Cleanup
+
+- Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
+- Choose __Actions__, and then choose __Terminate Environment__
+- Delete DynamoDB table __nodejs-tutorial__
+
+
+[QwikLab: Intro to AWS Lambda](https://awseducate.qwiklabs.com/focuses/36?parent=catalog)
+
+> AWS Lambda is a compute service that runs your code in response to events and automatically manages the compute resources for you, making it easy to build applications that respond quickly to new information.
+This lab creates a Lambda function to handle S3 image uploads by resizing them to thumbnails
+and storing the thumbnails in another S3 bucket.
+
+
+## Learning process
+
+### 1. Create 2 Amazon S3 Buckets as Input and Output Destination
+
+- On the __Services__ menu, select __S3__
+- Create bucket, with name _images-1234_, as the source bucket for original uploads
+- Create another bucket, with name _images-1234-resized_, as the output bucket for thumbnails
+- Upload the _HappyFace.jpg_ to source bucket
+
+### 2. Create an AWS Lambda Function
+
+- On the __Services__ menu, select __Lambda__
+- Create function and configure
+ - Name: Create-Thumbnail
+ - Runtime: Python 3.6
+ - Existing role: lambda-execution-role
+
+ This role grants permission to the Lambda function to read and write images in S3
+- Finish the rest of configuration by providing the url of the zipped Python script, which handles upload event, creates
+thumbnail in output bucket
+
+### 3. Trigger Your Function by Uploads
+
+- Click _Test_ button and configure
+ - Event template: Amazon S3 put
+ - Event name: Upload
+- Modify the template
+ - replace _example-bucket_ with _images-1234_
+ - replace _test.key_ with _HappyFace.jpg_
+- Save and run
+- If success, the thumbnail image could be found in output bucket
+
+
+### 4. Monitoring and Logging
+- __Monitoring__ tab displays graphs showing:
+ - Invocations: The number of times the function has been invoked.
+ - Duration: How long the function took to execute (in milliseconds).
+ - Errors: How many times the function failed.
+ - Throttles: When too many functions are invoked simultaneously, they will be throttled. The default is 1000 concurrent executions.
+ - Iterator Age: Measures the age of the last record processed from streaming triggers (Amazon Kinesis and Amazon DynamoDB Streams).
+ - Dead Letter Errors: Failures when sending messages to the Dead Letter Queue.
+- __Amazon CloudWatch Logs__ have detailed log messages in stream
+
+
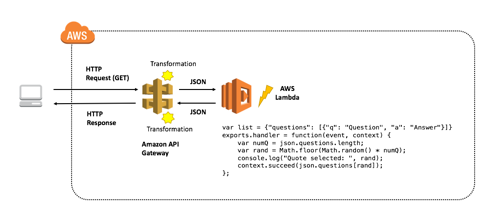
+[QwikLab: Intro to Amazon API Gateway](https://awseducate.qwiklabs.com/focuses/21?parent=catalog)
+
+> API Gateway is a managed service provided by AWS that makes creating, deploying and maintaining APIs easy.
+The lab creates a Lambda function and triggers it by accessing API Gateway endpoint url.
+The lab also introduced the best practices of building a RESTful API and the use of micro-service.
+
+## API Gateway includes features to:
+
+- Transform the body and headers of incoming API requests to match backend systems
+- Transform the body and headers of the outgoing API responses to match API requirements
+- Control API access via Amazon Identity and Access Management
+- Create and apply API keys for third-party development
+- Enable Amazon CloudWatch integration for API monitoring
+- Cache API responses via Amazon CloudFront for faster response times
+- Deploy an API to multiple stages, allowing easy differentiation between development, test, production as well as versioning
+- Connect custom domains to an API
+- Define models to help standardize your API request and response transformations
+
+## Amazon API Gateway and AWS Lambda Terminology:
+
+- __Resource__: Represented as a URL endpoint and path.
+For example, _api.mysite.com/questions_.
+You can associate HTTP methods with resources and define different backend targets for each method.
+In a microservices architecture, a resource would represent a single microservice within your system.
+
+- __Method__: In API Gateway, a method is identified by the combination of a resource path and an HTTP verb,
+such as GET, POST, and DELETE.
+
+- __Method Request__: The method request settings in API gateway store the methods authorization settings
+and define the URL Query String parameters and HTTP Request Headers that are received from the client.
+
+- __Integration Request__: The integration request settings define the backend target used with the method.
+It is also where you can define mapping templates, to transform the incoming request to match what the backend target is expecting.
+
+- __Integration Response__: The integration response settings is where the mappings are defined
+between the response from the backend target and the method response in API Gateway.
+You can also transform the data that is returned from your backend target to fit what your end users and applications are expecting.
+
+- __Method Response__: The method response settings define the method response types, their headers and content types.
+
+- __Model__: In API Gateway, a model defines the format, also known as the schema or shape, of some data.
+You create and use models to make it easier to create mapping templates.
+Because API Gateway is designed to work primarily with JavaScript Object Notation (JSON)-formatted data,
+API Gateway uses JSON Schema to define the expected schema of the data.
+
+- __Stage__: In API Gateway, a stage defines the path through which an API deployment is accessible.
+This is commonly used to deviate between versions, as well as development vs production endpoints, etc.
+
+- __Blueprint__: A Lambda blueprint is an example lambda function that can be used as a base to build out new Lambda functions.
+
+## useful resources
+- [White House RESTful API Standards](https://github.com/WhiteHouse/api-standards#pragmatic-rest)
+- [Spotify RESTful API Standards](https://developer.spotify.com/web-api/)
+
+
+
+## Learning Notes
+
+### 1. Create a Lambda Function on API Gateway
+
+- Same as [the last Lambda tutorial]((../cloud-web-apps-lab-aws-lambda)), use _Author from Scratch_, and configure:
+ - __Name__: FAQ
+ - __Runtime__: Node.js 8.10
+ - __Existing Role__: lambda-basic-execution
+
+- Create function and replace the event handling script, which performs:
+ - Define a list of FAQs
+ - Return a random FAQ
+
+- Add an API Gateway Trigger, the Lambda function is triggered whenever a call is made to API Gateway:
+ - __API__: Create a new API
+ - __Security__: Open
+ - __API name__: FAQ-API
+ - __Deployment stage__: myDeployment
+
+
+### 2. Trigger Lambda Function by API Gateway URL
+
+- Access API Gateway endpoint url in browser, a random JSON object will be returned
+- Create a test by configuring:
+ - __Event name__: BasicTest
+ - Replace keys and values with an empty JSON object
+ - Save, run and check logs
+
+
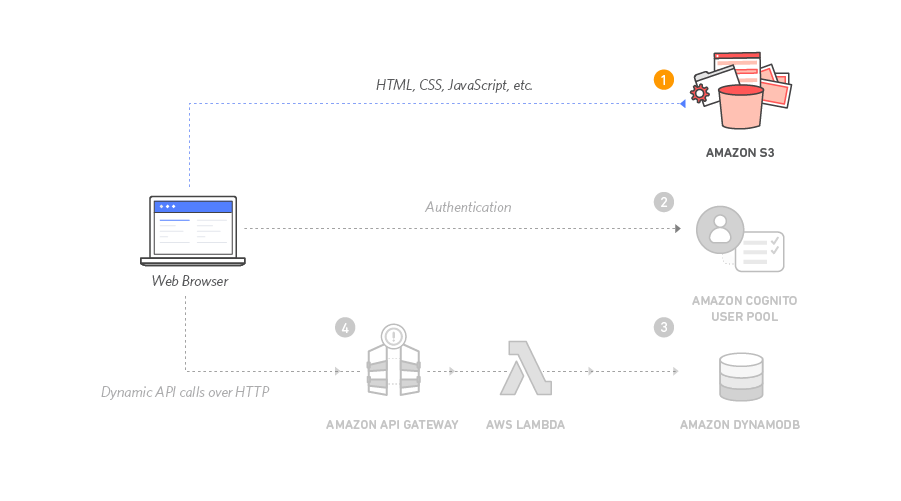
+[AWS Tutorial: Build a Serverless Web Application](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/projects/build-serverless-web-app-lambda-apigateway-s3-dynamodb-cognito/?trk=gs_card)
+
+> In this lab I build a simple serverless (AWS Lambda) web application that enables users to request unicorn rides from the Wild Rydes fleet. The application present users with an HTML based user interface for indicating the location
+where they would like to be picked up and will interface on the backend with a RESTful web service
+to submit the request and dispatch a nearby unicorn.
+The application will also provide facilities for users to register with the service and log in before requesting rides.
+
+
+### Static Web Hosting on S3
+
+Amazon S3 hosts static web resources including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and image files which are loaded in the user's browser.
+
+
+
+- [Download the zip that has everything of the static site](https://github.com/awslabs/aws-serverless-workshops/archive/master.zip)
+- Create an S3 bucket with name _wildrydes-FIRSTNAME-LASTNAME_ as suggested
+- Unzip and upload everything in folder */WebApplication/1_StaticWebHosting/website/*
+- Make bucket content public by setting up policy
+```json
+{
+ "Version": "2012-10-17",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": "*",
+ "Action": "s3:GetObject",
+ "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::wildrydes-warren/*"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+- Enable __Static website hosting__ under __Properties__ tab, and set _index.html_ for the Index document
+- Save and [see static website](http://wildrydes-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/)
+
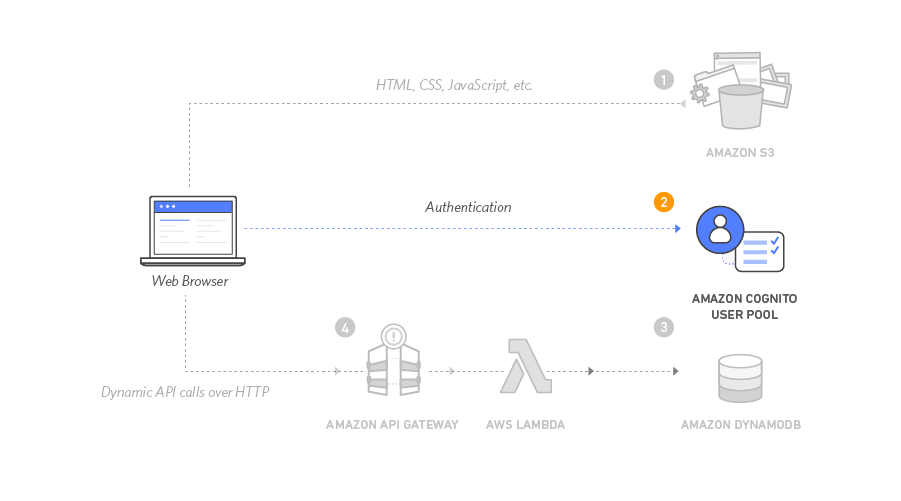
+### User Management on Cognito
+
+Amazon Cognito provides user management and authentication functions to secure the backend API.
+
+
+
+- Create a Cognito user pool with name _WildRydes_, then get __Pool Id__
+- Add app client to pool with name _WildRydesWebApp_, uncheck the __Generate client secret__ option, since client secrets aren't
+currently supported for use with browser-based applications, then get __App client id__
+
+
+
+- Modify __/js/config.js__ by filling in __Pool Id__, __App client id__, and region
+```javascript
+window._config = {
+ cognito: {
+ userPoolId: 'us-east-1_65cLrZQkK', // e.g. us-east-2_uXboG5pAb
+ userPoolClientId: '3m1t3bi2d9p62qa79pj930r65p', // e.g. 25ddkmj4v6hfsfvruhpfi7n4hv
+ region: 'us-east-1' // e.g. us-east-2
+ },
+ api: {
+ invokeUrl: '' // e.g. https://rc7nyt4tql.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/prod',
+ }
+};
+```
+
+- Visit [register.html](http://wildrydes-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/register.html) to create an account,
+either with a real mailbox or a dummy one
+
+- Visit [verify.html](http://wildrydes-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/verify.html), fill in the verification code
+or __confirm__ user in Cognito console (General settings/Users and groups) manually
+
+- Visit [ride.html](http://wildrydes-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/ride.html), log in with email and password,
+you should see
+
+
+
+### Serverless Backend with AWS Lambda
+
+Amazon DynamoDB provides a persistence layer where data can be stored by the API's Lambda function.
+
+
+- Create DynamoDB table with name __Rides__, and __RideId__ for partition key
+- Create an IAM role for Your Lambda function, name it _WildRydesLambda_
+
+ Every Lambda function has an IAM role associated with it.
+ This role defines what other AWS services the function is allowed to interact with.
+
+- Grant IAM role _WildRydesLambda_ to write DynamoDB
+
+
+
+- Specify table to the role with table ARN
+
+
+
+
+- Create a Lambda Function for Handling Requests, name it _RequestUnicorn_
+
+- Choose an existing role for function _RequestUnicorn_ as _WildRydesLambda_, so that the function
+is able to write DynamoDB
+
+
+
+- Test the function
+
+
+
+### RESTful APIs with API Gateway
+
+In this module you'll use Amazon API Gateway to expose the Lambda function _RequestUnicorn_ as a RESTful API.
+This API will be accessible on the public Internet.
+It will be secured using the Amazon Cognito user pool you created in the previous module.
+
+
+
+- Create a New REST API in API Gateway, name it _WildRydes_
+- Create a Cognito User Pools Authorizer, name it _WildRydes_, then test with the __Authorization Token__
+
+
+
+
+- Create a new resource, name it __ride__ and create a _POST_ method for it
+- Use Lambda function _RequestUnicorn_ to handle the _POST_ method
+- Deploy API in stage _prod_
+- Update _config.js_ in S3 with the _invokeUrl_
+- Login and request a unicorn pickup on white house south lawn :)
+
+
+
+[AWS Tutorial: Build a Modern Web Application](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/projects/build-modern-app-fargate-lambda-dynamodb-python/?trk=gs_card)
+
+> Due to the web application builds up with a rather complex architecture, the CD/CI configuration
+is not included, please refer to Module 2 tutorial. This article mainly focuses on implementing the features of app
+with AWS-CLI commands.
+
+## Application Architecture
+
+
add image
+
+### 7. Cleanup
+
+- Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
+- Choose __Actions__, and then choose __Terminate Environment__
+- Delete DynamoDB table __nodejs-tutorial__
+
+
+[QwikLab: Intro to AWS Lambda](https://awseducate.qwiklabs.com/focuses/36?parent=catalog)
+
+> AWS Lambda is a compute service that runs your code in response to events and automatically manages the compute resources for you, making it easy to build applications that respond quickly to new information.
+This lab creates a Lambda function to handle S3 image uploads by resizing them to thumbnails
+and storing the thumbnails in another S3 bucket.
+
+
+## Learning process
+
+### 1. Create 2 Amazon S3 Buckets as Input and Output Destination
+
+- On the __Services__ menu, select __S3__
+- Create bucket, with name _images-1234_, as the source bucket for original uploads
+- Create another bucket, with name _images-1234-resized_, as the output bucket for thumbnails
+- Upload the _HappyFace.jpg_ to source bucket
+
+### 2. Create an AWS Lambda Function
+
+- On the __Services__ menu, select __Lambda__
+- Create function and configure
+ - Name: Create-Thumbnail
+ - Runtime: Python 3.6
+ - Existing role: lambda-execution-role
+
+ This role grants permission to the Lambda function to read and write images in S3
+- Finish the rest of configuration by providing the url of the zipped Python script, which handles upload event, creates
+thumbnail in output bucket
+
+### 3. Trigger Your Function by Uploads
+
+- Click _Test_ button and configure
+ - Event template: Amazon S3 put
+ - Event name: Upload
+- Modify the template
+ - replace _example-bucket_ with _images-1234_
+ - replace _test.key_ with _HappyFace.jpg_
+- Save and run
+- If success, the thumbnail image could be found in output bucket
+
+
+### 4. Monitoring and Logging
+- __Monitoring__ tab displays graphs showing:
+ - Invocations: The number of times the function has been invoked.
+ - Duration: How long the function took to execute (in milliseconds).
+ - Errors: How many times the function failed.
+ - Throttles: When too many functions are invoked simultaneously, they will be throttled. The default is 1000 concurrent executions.
+ - Iterator Age: Measures the age of the last record processed from streaming triggers (Amazon Kinesis and Amazon DynamoDB Streams).
+ - Dead Letter Errors: Failures when sending messages to the Dead Letter Queue.
+- __Amazon CloudWatch Logs__ have detailed log messages in stream
+
+
+[QwikLab: Intro to Amazon API Gateway](https://awseducate.qwiklabs.com/focuses/21?parent=catalog)
+
+> API Gateway is a managed service provided by AWS that makes creating, deploying and maintaining APIs easy.
+The lab creates a Lambda function and triggers it by accessing API Gateway endpoint url.
+The lab also introduced the best practices of building a RESTful API and the use of micro-service.
+
+## API Gateway includes features to:
+
+- Transform the body and headers of incoming API requests to match backend systems
+- Transform the body and headers of the outgoing API responses to match API requirements
+- Control API access via Amazon Identity and Access Management
+- Create and apply API keys for third-party development
+- Enable Amazon CloudWatch integration for API monitoring
+- Cache API responses via Amazon CloudFront for faster response times
+- Deploy an API to multiple stages, allowing easy differentiation between development, test, production as well as versioning
+- Connect custom domains to an API
+- Define models to help standardize your API request and response transformations
+
+## Amazon API Gateway and AWS Lambda Terminology:
+
+- __Resource__: Represented as a URL endpoint and path.
+For example, _api.mysite.com/questions_.
+You can associate HTTP methods with resources and define different backend targets for each method.
+In a microservices architecture, a resource would represent a single microservice within your system.
+
+- __Method__: In API Gateway, a method is identified by the combination of a resource path and an HTTP verb,
+such as GET, POST, and DELETE.
+
+- __Method Request__: The method request settings in API gateway store the methods authorization settings
+and define the URL Query String parameters and HTTP Request Headers that are received from the client.
+
+- __Integration Request__: The integration request settings define the backend target used with the method.
+It is also where you can define mapping templates, to transform the incoming request to match what the backend target is expecting.
+
+- __Integration Response__: The integration response settings is where the mappings are defined
+between the response from the backend target and the method response in API Gateway.
+You can also transform the data that is returned from your backend target to fit what your end users and applications are expecting.
+
+- __Method Response__: The method response settings define the method response types, their headers and content types.
+
+- __Model__: In API Gateway, a model defines the format, also known as the schema or shape, of some data.
+You create and use models to make it easier to create mapping templates.
+Because API Gateway is designed to work primarily with JavaScript Object Notation (JSON)-formatted data,
+API Gateway uses JSON Schema to define the expected schema of the data.
+
+- __Stage__: In API Gateway, a stage defines the path through which an API deployment is accessible.
+This is commonly used to deviate between versions, as well as development vs production endpoints, etc.
+
+- __Blueprint__: A Lambda blueprint is an example lambda function that can be used as a base to build out new Lambda functions.
+
+## useful resources
+- [White House RESTful API Standards](https://github.com/WhiteHouse/api-standards#pragmatic-rest)
+- [Spotify RESTful API Standards](https://developer.spotify.com/web-api/)
+
+
+
+## Learning Notes
+
+### 1. Create a Lambda Function on API Gateway
+
+- Same as [the last Lambda tutorial]((../cloud-web-apps-lab-aws-lambda)), use _Author from Scratch_, and configure:
+ - __Name__: FAQ
+ - __Runtime__: Node.js 8.10
+ - __Existing Role__: lambda-basic-execution
+
+- Create function and replace the event handling script, which performs:
+ - Define a list of FAQs
+ - Return a random FAQ
+
+- Add an API Gateway Trigger, the Lambda function is triggered whenever a call is made to API Gateway:
+ - __API__: Create a new API
+ - __Security__: Open
+ - __API name__: FAQ-API
+ - __Deployment stage__: myDeployment
+
+
+### 2. Trigger Lambda Function by API Gateway URL
+
+- Access API Gateway endpoint url in browser, a random JSON object will be returned
+- Create a test by configuring:
+ - __Event name__: BasicTest
+ - Replace keys and values with an empty JSON object
+ - Save, run and check logs
+
+
+[AWS Tutorial: Build a Serverless Web Application](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/projects/build-serverless-web-app-lambda-apigateway-s3-dynamodb-cognito/?trk=gs_card)
+
+> In this lab I build a simple serverless (AWS Lambda) web application that enables users to request unicorn rides from the Wild Rydes fleet. The application present users with an HTML based user interface for indicating the location
+where they would like to be picked up and will interface on the backend with a RESTful web service
+to submit the request and dispatch a nearby unicorn.
+The application will also provide facilities for users to register with the service and log in before requesting rides.
+
+
+### Static Web Hosting on S3
+
+Amazon S3 hosts static web resources including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and image files which are loaded in the user's browser.
+
+
+
+- [Download the zip that has everything of the static site](https://github.com/awslabs/aws-serverless-workshops/archive/master.zip)
+- Create an S3 bucket with name _wildrydes-FIRSTNAME-LASTNAME_ as suggested
+- Unzip and upload everything in folder */WebApplication/1_StaticWebHosting/website/*
+- Make bucket content public by setting up policy
+```json
+{
+ "Version": "2012-10-17",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": "*",
+ "Action": "s3:GetObject",
+ "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::wildrydes-warren/*"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+- Enable __Static website hosting__ under __Properties__ tab, and set _index.html_ for the Index document
+- Save and [see static website](http://wildrydes-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/)
+
+### User Management on Cognito
+
+Amazon Cognito provides user management and authentication functions to secure the backend API.
+
+
+
+- Create a Cognito user pool with name _WildRydes_, then get __Pool Id__
+- Add app client to pool with name _WildRydesWebApp_, uncheck the __Generate client secret__ option, since client secrets aren't
+currently supported for use with browser-based applications, then get __App client id__
+
+
+
+- Modify __/js/config.js__ by filling in __Pool Id__, __App client id__, and region
+```javascript
+window._config = {
+ cognito: {
+ userPoolId: 'us-east-1_65cLrZQkK', // e.g. us-east-2_uXboG5pAb
+ userPoolClientId: '3m1t3bi2d9p62qa79pj930r65p', // e.g. 25ddkmj4v6hfsfvruhpfi7n4hv
+ region: 'us-east-1' // e.g. us-east-2
+ },
+ api: {
+ invokeUrl: '' // e.g. https://rc7nyt4tql.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/prod',
+ }
+};
+```
+
+- Visit [register.html](http://wildrydes-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/register.html) to create an account,
+either with a real mailbox or a dummy one
+
+- Visit [verify.html](http://wildrydes-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/verify.html), fill in the verification code
+or __confirm__ user in Cognito console (General settings/Users and groups) manually
+
+- Visit [ride.html](http://wildrydes-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/ride.html), log in with email and password,
+you should see
+
+
+
+### Serverless Backend with AWS Lambda
+
+Amazon DynamoDB provides a persistence layer where data can be stored by the API's Lambda function.
+
+
+- Create DynamoDB table with name __Rides__, and __RideId__ for partition key
+- Create an IAM role for Your Lambda function, name it _WildRydesLambda_
+
+ Every Lambda function has an IAM role associated with it.
+ This role defines what other AWS services the function is allowed to interact with.
+
+- Grant IAM role _WildRydesLambda_ to write DynamoDB
+
+
+
+- Specify table to the role with table ARN
+
+
+
+
+- Create a Lambda Function for Handling Requests, name it _RequestUnicorn_
+
+- Choose an existing role for function _RequestUnicorn_ as _WildRydesLambda_, so that the function
+is able to write DynamoDB
+
+
+
+- Test the function
+
+
+
+### RESTful APIs with API Gateway
+
+In this module you'll use Amazon API Gateway to expose the Lambda function _RequestUnicorn_ as a RESTful API.
+This API will be accessible on the public Internet.
+It will be secured using the Amazon Cognito user pool you created in the previous module.
+
+
+
+- Create a New REST API in API Gateway, name it _WildRydes_
+- Create a Cognito User Pools Authorizer, name it _WildRydes_, then test with the __Authorization Token__
+
+
+
+
+- Create a new resource, name it __ride__ and create a _POST_ method for it
+- Use Lambda function _RequestUnicorn_ to handle the _POST_ method
+- Deploy API in stage _prod_
+- Update _config.js_ in S3 with the _invokeUrl_
+- Login and request a unicorn pickup on white house south lawn :)
+
+
+
+[AWS Tutorial: Build a Modern Web Application](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/projects/build-modern-app-fargate-lambda-dynamodb-python/?trk=gs_card)
+
+> Due to the web application builds up with a rather complex architecture, the CD/CI configuration
+is not included, please refer to Module 2 tutorial. This article mainly focuses on implementing the features of app
+with AWS-CLI commands.
+
+## Application Architecture
+
+![]() add image
+
+The Mythical Mysfits website serves its static content directly from __Amazon S3__,
+provides a microservice API backend deployed as a container through __AWS Fargate__ on __Amazon ECS__,
+stores data in a managed NoSQL database provided by __Amazon DynamoDB__,
+with authentication and authorization for the application enabled through __AWS API Gateway__ and its integration with __AWS Cognito__.
+The user website clicks will be sent as records to an __Amazon Kinesis Firehose Delivery stream__
+where those records will be processed by serverless __AWS Lambda__ functions and then stored in __Amazon S3__.
+
+## Learning Notes
+
+### Module 1: IDE Setup and Static Website Hosting
+
+- AWS Cloud9 IDE ships with a _t2.micro_ EC2 instance for free tier, the whole environment resembles _CodeAnywhere_ we
+have used for project 1
+
+
add image
+
+The Mythical Mysfits website serves its static content directly from __Amazon S3__,
+provides a microservice API backend deployed as a container through __AWS Fargate__ on __Amazon ECS__,
+stores data in a managed NoSQL database provided by __Amazon DynamoDB__,
+with authentication and authorization for the application enabled through __AWS API Gateway__ and its integration with __AWS Cognito__.
+The user website clicks will be sent as records to an __Amazon Kinesis Firehose Delivery stream__
+where those records will be processed by serverless __AWS Lambda__ functions and then stored in __Amazon S3__.
+
+## Learning Notes
+
+### Module 1: IDE Setup and Static Website Hosting
+
+- AWS Cloud9 IDE ships with a _t2.micro_ EC2 instance for free tier, the whole environment resembles _CodeAnywhere_ we
+have used for project 1
+
+![]() add image
+
+- Several aws-cli commands
+ - Create S3 bucket
+ ```bash
+ aws s3 mb s3://REPLACE_ME_BUCKET_NAME
+ ```
+ - Set website homepage in bucket
+ ```bash
+ aws s3 website s3://REPLACE_ME_BUCKET_NAME --index-document index.html
+ ```
+ - Set bucket access policy to public
+ ```bash
+ aws s3api put-bucket-policy
+ --bucket REPLACE_ME_BUCKET_NAME
+ --policy file://~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-1/aws-cli/website-bucket-policy.json
+ ```
+ - Publish website on S3
+ ```bash
+ aws s3 cp
+ ~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-1/web/index.html
+ s3://REPLACE_ME_BUCKET_NAME/index.html
+ ```
+
+- Visit static website [s3 index](http://mythical-bucket-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/)
+
+### Module 2: Creating a Service with AWS Fargate
+AWS Fargate is a deployment option in Amazon ECS that allows you to deploy containers without having to manage any clusters or servers.
+For our Mythical Mysfits backend, we will use Python and create a Flask app in a Docker container behind a Network Load Balancer.
+These will form the microservice backend for the frontend website to integrate with.
+
+- Create the Core Infrastructure stack on cloud using AWS CloudFormation in 10 minutes, including
+ - An Amazon VPC
+ - Two NAT Gateways (cost $1 per day)
+ - A DynamoDB VPC Endpoint
+ - A Security Group
+ - IAM Roles
+
+```bash
+aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name MythicalMysfitsCoreStack --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
+--template-body file://~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-2/cfn/core.yml
+```
+
+Stack components are specified in _core.yml_.
+
+- Save stack information when creation completes
+
+```bash
+aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name MythicalMysfitsCoreStack >
+~/environment/cloudformation-core-output.json
+```
+
+- Dockerize backend Flask webservice
+ - Change directory, where _Dockerfile_ that tells Docker all of the instructions
+ that should take place when the build command is executed.
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-2/app
+ ```
+ - Build Docker image
+ ```bash
+ docker build . -t REPLACE_ME_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.REPLACE_ME_REGION.amazonaws.com/mythicalmysfits/service:latest
+ ```
+ - Run image locally
+ ```bash
+ docker run -p 8080:8080 REPLACE_ME_WITH_DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG
+ ```
+ 
+ - Push the Docker Image to Amazon ECR (Amazon Elastic Container Registry)
+ ```bash
+ aws ecr create-repository --repository-name mythicalmysfits/service
+ $(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email)
+ docker push REPLACE_ME_WITH_DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG
+ ```
+- Deploy container on Cluster in the Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
+ - Create cluster
+ ```bash
+ aws ecs create-cluster --cluster-name MythicalMysfits-Cluster
+ ```
+ - Create an AWS CloudWatch Logs Group
+ ```bash
+ aws logs create-log-group --log-group-name mythicalmysfits-logs
+ ```
+
+__AWS Fargate__ allows you to specify that your containers be deployed to a cluster without having to actually provision or manage any servers yourself.
+
+
+
+- Enabling a Load Balanced Fargate Service
+
+ - Create a Network Load Balancer
+ ```bash
+ aws elbv2 create-load-balancer --name mysfits-nlb --scheme internet-facing --type network
+ --subnets REPLACE_ME_PUBLIC_SUBNET_ONE REPLACE_ME_PUBLIC_SUBNET_TWO > ~/environment/nlb-output.json
+ ```
+
+ - Create a Load Balancer Target Group
+
+ A target group allows AWS resources to register themselves as targets for requests that the load balancer receives to forward.
+
+ ```bash
+ aws elbv2 create-target-group --name MythicalMysfits-TargetGroup --port 8080 --protocol TCP --target-type ip
+ --vpc-id REPLACE_ME_VPC_ID --health-check-interval-seconds 10 --health-check-path /
+ --health-check-protocol HTTP --healthy-threshold-count 3 --unhealthy-threshold-count 3 >
+ ~/environment/target-group-output.json
+ ```
+
+ - Create a Load Balancer Listener
+
+ This informs that load balancer that for requests received on a specific port,
+ they should be forwarded to targets that have registered to the above target group.
+
+ ```bash
+ aws elbv2 create-listener --default-actions TargetGroupArn=REPLACE_ME_NLB_TARGET_GROUP_ARN,
+ Type=forward --load-balancer-arn REPLACE_ME_NLB_ARN --port 80 --protocol TCP
+ ```
+
+- Visit website [s3 index](http://mythical-bucket-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/) again, website is accessing
+load balancer to retrieve data
+
+
+### Module 3 - Adding a Data Tier with Amazon DynamoDB
+
+Rather than have all of the Mysfits be stored in a static JSON file,
+we will store them in a database to make the websites future more extensible and scalable.
+
+- Create a DynamoDB Table
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb create-table --cli-input-json
+file://~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-3/aws-cli/dynamodb-table.json
+```
+
+- Populate the Table
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb batch-write-item
+--request-items file://~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-3/aws-cli/populate-dynamodb.json
+```
+
+- Update Flask code to read data from DynamoDB
+
+- Visit website [s3 index](http://mythical-bucket-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/) again, website now displays
+data from DynamoDB.
+
+### Module 4: Adding User and API features with Amazon API Gateway and AWS Cognito
+
+To make sure that only registered users are authorized to like or adopt mysfits on the website,
+we will deploy an REST API with Amazon API Gateway to sit in front of our NLB.
+
+- Adding a User Pool for Website Users
+ - Create the Cognito User Pool
+ ```bash
+ aws cognito-idp create-user-pool --pool-name MysfitsUserPool --auto-verified-attributes email
+ ```
+ - Create a Cognito User Pool Client
+ ```bash
+ aws cognito-idp create-user-pool-client --user-pool-id REPLACE_ME --client-name MysfitsUserPoolClient
+ ```
+- Adding a new REST API with Amazon API Gateway
+ - Create an API Gateway VPC Link
+ ```bash
+ aws apigateway create-vpc-link --name MysfitsApiVpcLink --target-arns REPLACE_ME_NLB_ARN >
+ ~/environment/api-gateway-link-output.json
+ ```
+ In order for API Gateway to privately integrate with our NLB,
+ we will configure an API Gateway VPC Link that enables API Gateway APIs to directly integrate with backend web services
+ that are privately hosted inside a VPC.
+
+ - Create the REST API using Swagger
+ REST API and all of its resources, methods, and configuration are defined within a JSON file.
+
+ - Deploy the API
+ A stage is a named reference to a deployment, which is a snapshot of the API.
+ You can use a Stage to manage and optimize a particular deployment.
+
+- Updating the Mythical Mysfits Website
+ - Update the Flask Service Backend
+
+ Provide new Flask service to keep up with the newly defined API in Gateway
+
+ - Update the Mythical Mysfits Website in S3
+
+ Switch API endpoint to API Gateway from NLB, see [API gateway health check](https://jigpafa4ti.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod/mysfits)
+
+### Module 5: Capturing User Behavior
+To help us gather more insights of user activity,
+we will implement the ability for the website frontend to submit a tiny request,
+each time a mysfit profile is clicked by a user,
+to a new microservice API we'll create.
+Those records will be processed in real-time by a serverless code function,
+aggregated, and stored for any future analysis that you may want to perform.
+
+- Creating the Streaming Service Stack
+ - Create an S3 Bucket for Lambda Function Code Packages
+ - Use the SAM CLI to Package your Code for Lambda
+ - Deploy the Stack using AWS CloudFormation
+
+- Sending Mysfit Profile Clicks to the Service
+ - Update the Website Content
+ - Push the New Site Version to S3
+
+- Login and click on website items, check user behavior data gathered in bucket
+
+
+- Workshop Clean-Up
+
+Clean up the workshop to avoid additional charging
+
+```bash
+aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name STACK-NAME-HERE
+```
+
+## Docker and Containers(Beginner Level)
+
+
+### [Video: Why Docker?](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RYDHUTHLf8U&t=0s&list=PLBmVKD7o3L8tQzt8QPCINK9wXmKecTHlM&index=23)
+
+Time Spent: 20 min
+* This video talked about the trend of advancements in computer science it acknowledged that Docker and containerization in general is a trend that many people are moving towards because it is easy to set up and the speed associated with spinning up a new container.
+
+
+### [Lab: DevOps Docker Beginners Guide](https://training.play-with-docker.com/ops-s1-hello/)
+
+Time Spent : 60 min
+
+* This tutorial started with a few simple commands and explained what docker is doing when those commands are run.
+* This tutorial then uses a lightweight version of linux to run somemore basic commands in while continuing to explain Docker infrastructure further.
+* The tutorial explains a lot on differences between VMs and containers. Primarily the focus is on the speed with which a contianer can be spun up and killed. Fast enough to run a single command and get an output within a reasonable amount of time.
+* Security is inforced through the separate instances of contianers. although n contiars can be run using the same instance they all have isolation ensure because they are executing in different contexts while sharing the same image.
diff --git a/Technical Report.md b/Technical Report.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5def935
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Technical Report.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+
add image
+
+- Several aws-cli commands
+ - Create S3 bucket
+ ```bash
+ aws s3 mb s3://REPLACE_ME_BUCKET_NAME
+ ```
+ - Set website homepage in bucket
+ ```bash
+ aws s3 website s3://REPLACE_ME_BUCKET_NAME --index-document index.html
+ ```
+ - Set bucket access policy to public
+ ```bash
+ aws s3api put-bucket-policy
+ --bucket REPLACE_ME_BUCKET_NAME
+ --policy file://~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-1/aws-cli/website-bucket-policy.json
+ ```
+ - Publish website on S3
+ ```bash
+ aws s3 cp
+ ~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-1/web/index.html
+ s3://REPLACE_ME_BUCKET_NAME/index.html
+ ```
+
+- Visit static website [s3 index](http://mythical-bucket-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/)
+
+### Module 2: Creating a Service with AWS Fargate
+AWS Fargate is a deployment option in Amazon ECS that allows you to deploy containers without having to manage any clusters or servers.
+For our Mythical Mysfits backend, we will use Python and create a Flask app in a Docker container behind a Network Load Balancer.
+These will form the microservice backend for the frontend website to integrate with.
+
+- Create the Core Infrastructure stack on cloud using AWS CloudFormation in 10 minutes, including
+ - An Amazon VPC
+ - Two NAT Gateways (cost $1 per day)
+ - A DynamoDB VPC Endpoint
+ - A Security Group
+ - IAM Roles
+
+```bash
+aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name MythicalMysfitsCoreStack --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
+--template-body file://~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-2/cfn/core.yml
+```
+
+Stack components are specified in _core.yml_.
+
+- Save stack information when creation completes
+
+```bash
+aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name MythicalMysfitsCoreStack >
+~/environment/cloudformation-core-output.json
+```
+
+- Dockerize backend Flask webservice
+ - Change directory, where _Dockerfile_ that tells Docker all of the instructions
+ that should take place when the build command is executed.
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-2/app
+ ```
+ - Build Docker image
+ ```bash
+ docker build . -t REPLACE_ME_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.REPLACE_ME_REGION.amazonaws.com/mythicalmysfits/service:latest
+ ```
+ - Run image locally
+ ```bash
+ docker run -p 8080:8080 REPLACE_ME_WITH_DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG
+ ```
+ 
+ - Push the Docker Image to Amazon ECR (Amazon Elastic Container Registry)
+ ```bash
+ aws ecr create-repository --repository-name mythicalmysfits/service
+ $(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email)
+ docker push REPLACE_ME_WITH_DOCKER_IMAGE_TAG
+ ```
+- Deploy container on Cluster in the Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
+ - Create cluster
+ ```bash
+ aws ecs create-cluster --cluster-name MythicalMysfits-Cluster
+ ```
+ - Create an AWS CloudWatch Logs Group
+ ```bash
+ aws logs create-log-group --log-group-name mythicalmysfits-logs
+ ```
+
+__AWS Fargate__ allows you to specify that your containers be deployed to a cluster without having to actually provision or manage any servers yourself.
+
+
+
+- Enabling a Load Balanced Fargate Service
+
+ - Create a Network Load Balancer
+ ```bash
+ aws elbv2 create-load-balancer --name mysfits-nlb --scheme internet-facing --type network
+ --subnets REPLACE_ME_PUBLIC_SUBNET_ONE REPLACE_ME_PUBLIC_SUBNET_TWO > ~/environment/nlb-output.json
+ ```
+
+ - Create a Load Balancer Target Group
+
+ A target group allows AWS resources to register themselves as targets for requests that the load balancer receives to forward.
+
+ ```bash
+ aws elbv2 create-target-group --name MythicalMysfits-TargetGroup --port 8080 --protocol TCP --target-type ip
+ --vpc-id REPLACE_ME_VPC_ID --health-check-interval-seconds 10 --health-check-path /
+ --health-check-protocol HTTP --healthy-threshold-count 3 --unhealthy-threshold-count 3 >
+ ~/environment/target-group-output.json
+ ```
+
+ - Create a Load Balancer Listener
+
+ This informs that load balancer that for requests received on a specific port,
+ they should be forwarded to targets that have registered to the above target group.
+
+ ```bash
+ aws elbv2 create-listener --default-actions TargetGroupArn=REPLACE_ME_NLB_TARGET_GROUP_ARN,
+ Type=forward --load-balancer-arn REPLACE_ME_NLB_ARN --port 80 --protocol TCP
+ ```
+
+- Visit website [s3 index](http://mythical-bucket-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/) again, website is accessing
+load balancer to retrieve data
+
+
+### Module 3 - Adding a Data Tier with Amazon DynamoDB
+
+Rather than have all of the Mysfits be stored in a static JSON file,
+we will store them in a database to make the websites future more extensible and scalable.
+
+- Create a DynamoDB Table
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb create-table --cli-input-json
+file://~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-3/aws-cli/dynamodb-table.json
+```
+
+- Populate the Table
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb batch-write-item
+--request-items file://~/environment/aws-modern-application-workshop/module-3/aws-cli/populate-dynamodb.json
+```
+
+- Update Flask code to read data from DynamoDB
+
+- Visit website [s3 index](http://mythical-bucket-warren.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/) again, website now displays
+data from DynamoDB.
+
+### Module 4: Adding User and API features with Amazon API Gateway and AWS Cognito
+
+To make sure that only registered users are authorized to like or adopt mysfits on the website,
+we will deploy an REST API with Amazon API Gateway to sit in front of our NLB.
+
+- Adding a User Pool for Website Users
+ - Create the Cognito User Pool
+ ```bash
+ aws cognito-idp create-user-pool --pool-name MysfitsUserPool --auto-verified-attributes email
+ ```
+ - Create a Cognito User Pool Client
+ ```bash
+ aws cognito-idp create-user-pool-client --user-pool-id REPLACE_ME --client-name MysfitsUserPoolClient
+ ```
+- Adding a new REST API with Amazon API Gateway
+ - Create an API Gateway VPC Link
+ ```bash
+ aws apigateway create-vpc-link --name MysfitsApiVpcLink --target-arns REPLACE_ME_NLB_ARN >
+ ~/environment/api-gateway-link-output.json
+ ```
+ In order for API Gateway to privately integrate with our NLB,
+ we will configure an API Gateway VPC Link that enables API Gateway APIs to directly integrate with backend web services
+ that are privately hosted inside a VPC.
+
+ - Create the REST API using Swagger
+ REST API and all of its resources, methods, and configuration are defined within a JSON file.
+
+ - Deploy the API
+ A stage is a named reference to a deployment, which is a snapshot of the API.
+ You can use a Stage to manage and optimize a particular deployment.
+
+- Updating the Mythical Mysfits Website
+ - Update the Flask Service Backend
+
+ Provide new Flask service to keep up with the newly defined API in Gateway
+
+ - Update the Mythical Mysfits Website in S3
+
+ Switch API endpoint to API Gateway from NLB, see [API gateway health check](https://jigpafa4ti.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod/mysfits)
+
+### Module 5: Capturing User Behavior
+To help us gather more insights of user activity,
+we will implement the ability for the website frontend to submit a tiny request,
+each time a mysfit profile is clicked by a user,
+to a new microservice API we'll create.
+Those records will be processed in real-time by a serverless code function,
+aggregated, and stored for any future analysis that you may want to perform.
+
+- Creating the Streaming Service Stack
+ - Create an S3 Bucket for Lambda Function Code Packages
+ - Use the SAM CLI to Package your Code for Lambda
+ - Deploy the Stack using AWS CloudFormation
+
+- Sending Mysfit Profile Clicks to the Service
+ - Update the Website Content
+ - Push the New Site Version to S3
+
+- Login and click on website items, check user behavior data gathered in bucket
+
+
+- Workshop Clean-Up
+
+Clean up the workshop to avoid additional charging
+
+```bash
+aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name STACK-NAME-HERE
+```
+
+## Docker and Containers(Beginner Level)
+
+
+### [Video: Why Docker?](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RYDHUTHLf8U&t=0s&list=PLBmVKD7o3L8tQzt8QPCINK9wXmKecTHlM&index=23)
+
+Time Spent: 20 min
+* This video talked about the trend of advancements in computer science it acknowledged that Docker and containerization in general is a trend that many people are moving towards because it is easy to set up and the speed associated with spinning up a new container.
+
+
+### [Lab: DevOps Docker Beginners Guide](https://training.play-with-docker.com/ops-s1-hello/)
+
+Time Spent : 60 min
+
+* This tutorial started with a few simple commands and explained what docker is doing when those commands are run.
+* This tutorial then uses a lightweight version of linux to run somemore basic commands in while continuing to explain Docker infrastructure further.
+* The tutorial explains a lot on differences between VMs and containers. Primarily the focus is on the speed with which a contianer can be spun up and killed. Fast enough to run a single command and get an output within a reasonable amount of time.
+* Security is inforced through the separate instances of contianers. although n contiars can be run using the same instance they all have isolation ensure because they are executing in different contexts while sharing the same image.
diff --git a/Technical Report.md b/Technical Report.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5def935
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Technical Report.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+
+
+## Introduction to Hadoop Mapreduce, Spark and Comparison Between Them
+
+
+### Introduction to Hadoop MapReduce
+MapReduce started to get popular as a programming model in 2004 used by Google. Google used the MapReduce to collect and analyze website data for better search performance for users. Google ran it on its private file system which is called GFS, of course. At the same time, Apache also used the MapReduce for its own web search engine.
+
+
+Hadoop MapReduce is a very important part of distributed system. It is a software framework for processing large amounts of data which could be provided by the Hadoop Distributed File System. The data could be either stuctured or unstructured and can be in terabytes or petabytes. The MapReduce algorithms consists of two important tasks, one is Map and another is Reduce..
+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
 +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+