You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
You receive a bunch of brand new rack-mount ProLiant servers and want to get them up and running as soon as possible. Ansible, Chef, Puppet, Ironic, Python, PowerShell are your friends but, before being able to use those powerful and flexible tools to fully deploy the servers, you need one little thing: An access to the iLO to configure low level system parameters (i.e. iLO network, BIOS, storage…).
15
19
16
-
This blog proposes a simple, quick and modern method to modify the factory randomly generated Administrator iLO password without knowing it. It can be used on one or several thousands of rack-mount ProLiant servers starting at Gen9 models. This problem does not exist for blades or Synergy compute modules because their embedded management modules (respectively OA and Composer) have the ability to perform those tasks without any credentials.
20
+
This blog proposes a simple, quick and modern method to modify the factory randomly generated Administrator iLO password without knowing it. It can be used on one or several thousands of rack-mount ProLiant servers starting at Gen9 models. This problem does not exist for blades or Synergy compute modules because their embedded management modules (respectively OA and Composer) have the ability to perform those tasks without any credentials.
17
21
18
22
## In-band management with `ilorest` does the trick
19
23
@@ -23,31 +27,33 @@ Instead, I will use an in-band management access method with the [ilorest(8)](ht
23
27
24
28
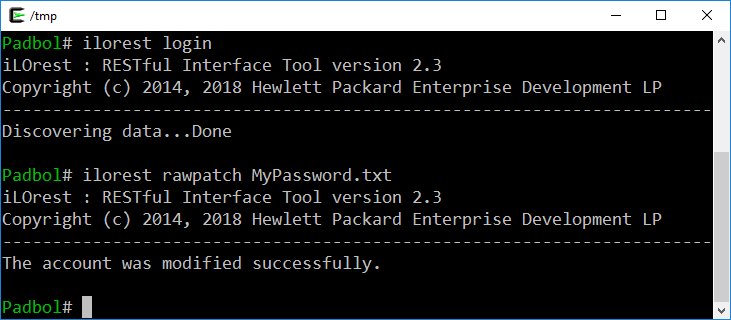
To set the iLO 4/5 Administrator password, when logged in to the OS as a privileged user (root or Administrator), I just need to create a text file (i.e. `MyPassword.txt`) with the following content:
25
29
26
-
27
-
~~~
30
+
```
28
31
{
29
32
"path": "/redfish/v1/AccountService/Accounts/1/",
30
33
"body": {
31
34
"Password": "MyPassword"
32
35
}
33
36
}
34
-
~~~
37
+
```
35
38
36
39
Then, using the `ilorest` tool, I connect to the iLO via an internal path (no credential required here) and send the password request modification:
37
40
38
-
41
+

39
42
40
43
# Data model clean crawling
41
44
42
45
But are you sure you changed the Administrator password and not another password account? What if the Administrator account is not located at position “1” in this collection of object?
43
46
44
47
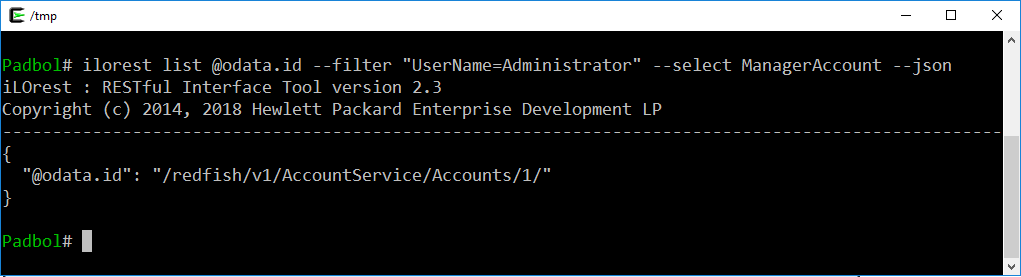
`ilorest` can help you isolate the exact location of the Administrator account. The following command returns in JSON format what you need:
45
48
46
-
49
+

47
50
48
51
With a simple parsing of the output of this command, you can create an error prone script to change the desired password.
49
52
50
53
Should you need to perform more complex digging to retrieve objects from this data model, the [Managing HP Servers Using the HP RESTful API](http://h20564.www2.hpe.com/hpsc/doc/public/display?docId=c04423967) manual explains very well with pseudo code examples how to crawl the data model without making bad assumptions.
51
54
52
55
# Building the complete solution
56
+
53
57
Using this in-band management feature you can easily foresee an entire solution starting with a PXE boot of the servers on a minimal WinPE or PE-Linux operating system containing the `ilorest(8)` tool and an automatic trigger of a script performing the iLO password change and other tasks if desired.
58
+
59
+
Don't forget to check out some of my other <ahref="https://developer.hpe.com/search/?term=donze"target="_blank">blog posts</a> on the HPE Developer portal to learn more about Redfish tips and tricks.
0 commit comments