You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
The concept of deferred / pending settings in the [Bios](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/concepts/biosdatamodel/#bios-current-and-pending-areas) and `SmartStorageConfig` subsystems of HPE iLO 5 is briefly presented in the [HPE Reference API](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/) documentation. With two examples, this document illustrates what is happening when properties are modified in those subsystems using the Redfish REST API against HPE servers.
18
+
Updated March 5, 2024
19
19
20
-
**NOTE**: The `SmartStorageConfig`[data type](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/concepts/datatypesandcollections/) is [deprecated in HPE iLO 6](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/redfishservices/ilos/ilo6/ilo6_adaptation/#hpe-smart-storage-model-oem-deprecated) based servers.
20
+
The concept of deferred / pending settings in the <ahref="https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/concepts/biosdatamodel/#bios-current-and-pending-areas"target="_blank">Bios</a> and `SmartStorageConfig` subsystems of HPE iLO 5 is briefly presented in the <ahref="https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/"target="_blank">HPE Reference API</a> documentation. With two examples, this document illustrates what is happening when properties are modified in those subsystems using the Redfish REST API against HPE servers.
21
21
22
-
**NOTE**: The latest versions of iLO 5 firmware support both the HPE `SmartStorageConfig`and the DMTF standard storage models. Volume management with controllers implementing the DMTF storage model is described in the [HPE server management portal](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/redfishservices/ilos/supplementdocuments/storage/).
22
+
**NOTE**: The `SmartStorageConfig`<ahref="https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/concepts/datatypesandcollections/"target="_blank">data type</a> is <ahref="https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/redfishservices/ilos/ilo6/ilo6_adaptation/#hpe-smart-storage-model-oem-deprecated"target="_blank">deprecated in HPE iLO 6</a> based servers.
23
23
24
-
We assume that the reader is familiar with REST APIs in general and Redfish in particular. A good entry point for developers to grasp the power of Redfish is the [iLO RESTful API Ecosystem](https://www.hpe.com/us/en/servers/restful-api.html#).
24
+
**NOTE**: The latest versions of iLO 5 firmware support both the HPE `SmartStorageConfig` and the DMTF standard storage models. Volume management with controllers implementing the DMTF storage model is described in the <ahref="https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/redfishservices/ilos/supplementdocuments/storage/"target="_blank">HPE server management portal</a>.
25
+
26
+
We assume that the reader is familiar with REST APIs in general and Redfish in particular. A good entry point for developers to grasp the power of Redfish is the <ahref="https://www.hpe.com/us/en/servers/restful-api.html#"target="_blank">iLO RESTful API Ecosystem</a>.
25
27
26
28
## Foreword
27
29
28
-
For didactic purposes, we use direct URIs to targets instead of crawling the Redfish tree to discover the target URIs, as explained in the [Getting Started with the Redfish(c) API Part 2](/blog/getting-started-with-the-redfish-api-part-2) document.
30
+
For didactic purposes, we use direct URIs to targets instead of crawling the Redfish tree to discover the target URIs, as explained in the <ahref="https://developer.hpe.com/blog/getting-started-with-the-redfish-api-part-2/"target="_blank">Getting Started with the Redfish® API Part 2</a> blog post.
29
31
30
32
In the following paragraphs, `{{Subsystem-URI}}` refers to an URI like `https://<ilo-IP>/redfish/v1/<subsystem>/` where `<subsystem>` represents either `Bios` or `SmartStorageConfig`. These subsystems contains the currently used properties.
31
33
@@ -34,9 +36,7 @@ Each of them has a pending sub-zone called `Settings/` and explained in the next
34
36
## Deferred / pending high level concept description
35
37
36
38
1. Modifications in these subsystems are performed using HTTP `PATCH` or HTTP `PUT` against `{{Subsystem-URI}}/`**`Settings/`**.
37
-
38
39
2. Upon a successful transaction, the HTTP return code is `200 OK` with the associated message: `One or more properties were changed and will not take effect until the system is reset`.
39
-
40
40
3. During the next system reset, the content of `{{Subsystem-URI}}/Settings/` is transferred one level up, in `{{Subsystem-URI}}/`. The return status of this transfer is present in `{{Subsystem-URI}}` with an associated message.
41
41
42
42
The important thing to note in this flow is that the final status code and associated message of a property setting is visible **after the system reset**.
@@ -45,56 +45,58 @@ The important thing to note in this flow is that the final status code and assoc
45
45
46
46
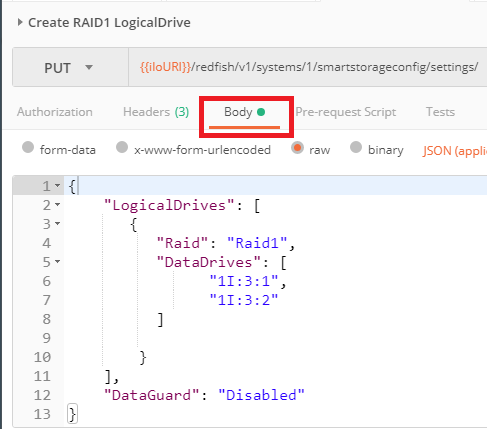
In this example, we create a Raid1 storage array of two physical disks using Postman. To achieve this goal, we have to issue a `PUT` to `{{iloURI}}/redfish/v1/Systems/1/SmartStorageConfig/Settings/` with a body (aka payload) similar to the example shown below:
47
47
48
-
48
+

49
49
50
50
Upon successful completion of this `PUT` request, the HTTP status return code is `200 OK`, which means that the remote Web server understood what to do with this well-formed payload.
51
51
52
52
The Body of the HTTP response contains an `error` property with a `SystemResetRequired` message. This property is a Redfish object sent by the Redfish server. It is there to give details about the next step to perform to finish the modification process.
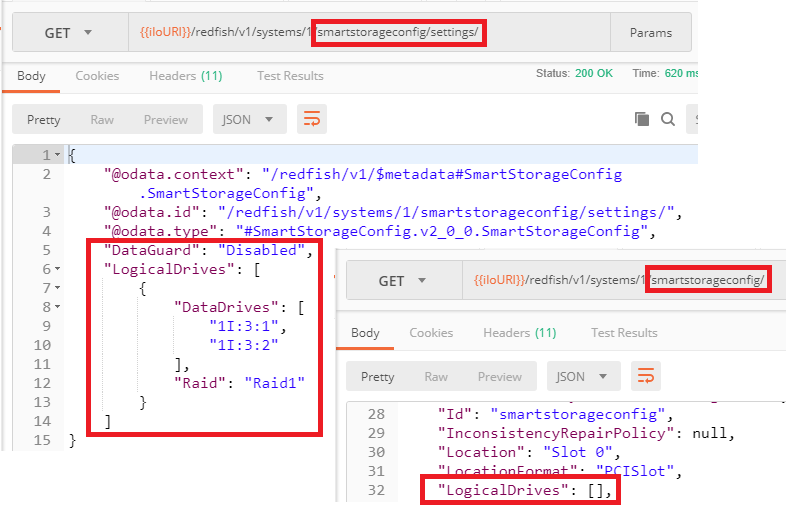
At this stage of the process, only the staging / "pending zone" of the Smart Array has changed and contains the `PUT` payload. We can verify this assertion by comparing the content of `{{Subsystem-URI}}/Settings/` with the content of `{{Subsystem-URI/}}`.
57
57
58
58
In the pending zone (`.../SmartStorageConfig/Settings/`) we can see the payload we sent to the Redfish server. However, in the "running zone" (`.../SmartStorageConfig/`) the `LogicalDrives` array is still empty:
59
59
60
-
60
+

61
61
62
62
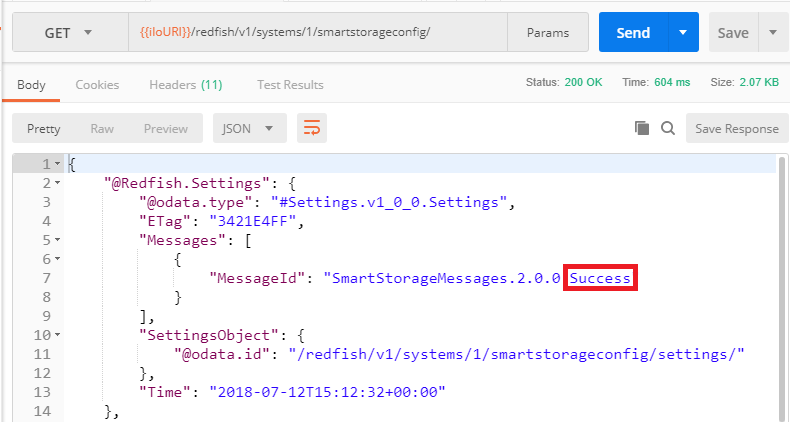
It is now time to reset the server and perform a `GET` of the running zone. In the response body of this operation, the first Redfish object is a `@Redfish.Settings` collection containing a single `MessageID` mentioning `Success`. This single message is synonym of a successful transfer of the "pending zone" in to the "running zone". We will see later in this document what we get in case of an un-successful transfer.
63
63
64
-
64
+

65
65
66
66
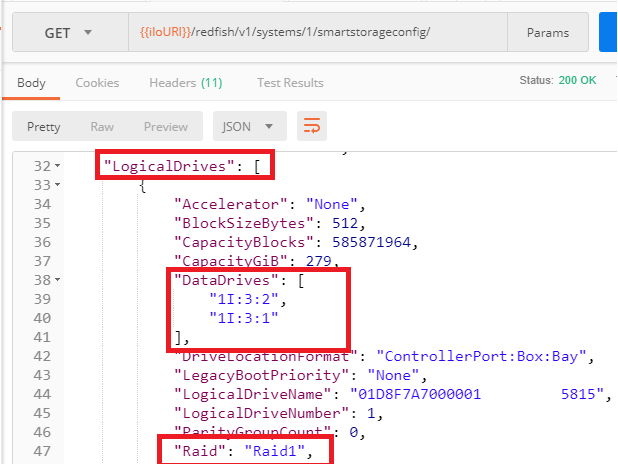
Further down in this response we find the `LogicalDrives` array containing the Raid1 disk array:
67
67
68
-
68
+

69
69
70
70
## Unsuccessful example
71
71
72
72
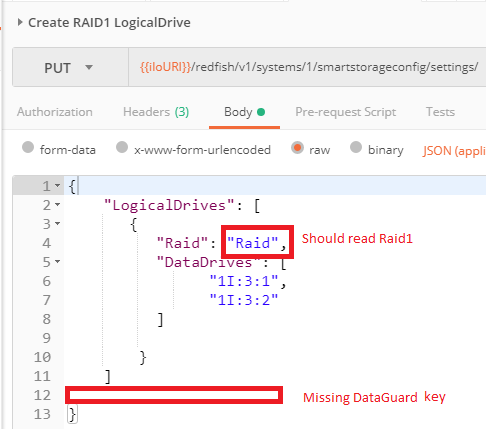
In order to emphasize the fact that the modification status of properties in the `Bios` and `SmartStorage` subsystems must be done after a system reset, we will study a case where the JSON `PUT` payload is syntactically correct but embedding a value typo (`Raid` instead of `Raid1`) and missing a required key-value (`DataGuard=Disabled`):
73
73
74
-
74
+

75
75
76
76
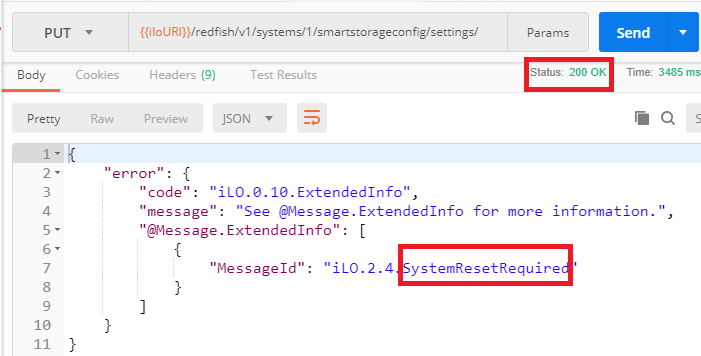
Sending this request returns an HTTP `200 OK` status and a `SystemResetRequired` Redfish message just like in the previous example:
77
77
78
-
78
+

79
79
80
80
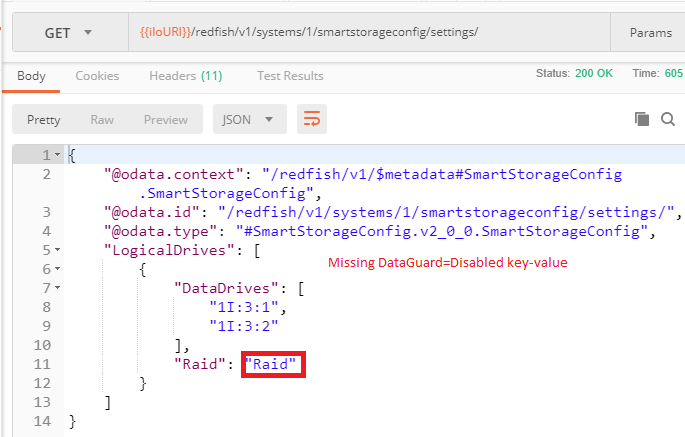
The pending zone contains the faulty payload:
81
81
82
-
82
+

83
83
84
84
After the server reset, a `GET` of the running zone responds with a `MessageArgs=[DataGuard]` object and two `MessageID`keys. The first one mentions `DataGuard` as a missing property and the second one (`Success`) means that the analysis of the transfer from the pending zone to the running zone has successfully ended. This `Success` message does not means that the transfer has occurred.
85
85
86
86
Moreover, note that there is nothing mentioning the `Raid` typo. It means that analysis of the payload to transfer stops at the first error found.
If we `PUT` a new payload with the `DataGuard=Disabled` property but still without correct Raid level and reset the server, we notice an `InvalidRAIDLevel` message explaining the problem.
Understanding the pending / deferred process when modifying Bios and SmartStorage properties using the Redfish API as well as the different types of return codes (HTTP, MessageID...) should ease program development and troubleshooting sessions.
100
+
Understanding the pending / deferred process when modifying Bios and SmartStorage properties using the Redfish API as well as the different types of return codes (HTTP, MessageID...) should ease program development and troubleshooting sessions.
101
+
102
+
Don't forget to check out some of my other <ahref="https://developer.hpe.com/search/?term=donze"target="_blank">blog posts</a> on the HPE Developer portal to learn more about Redfish tips and tricks.
0 commit comments