You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: content/blog/storage-management-with-redfish.md
+11-10Lines changed: 11 additions & 10 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -15,23 +15,25 @@ tags:
15
15
- ProLiant
16
16
- iLO5
17
17
---
18
-
Updated: June, 2022
18
+
Updated: July 26, 2023
19
19
20
20
## Introduction
21
21
22
22
Integrated Lights-Out ([iLO](https://www.hpe.com/info/ilo)) is an HPE ProLiant and Synergy server-embedded technology that delivers the core foundation for server intelligence along with out-of-band and in-band management facilities. This technology is a combination of the iLO ASIC that is part of the server board and the firmware that powers the ASIC. Out of the box, HPE iLO simplifies server setup, provides access to server health information, and enables server management at scale, including basic remote administration. Different generations of ProLiant Servers carry different versions of the iLO ASIC.
23
23
24
24
In HPE ProLiant and Synergy Gen10 servers, HPE iLO 5 introduced the management of storage controllers via its graphical user interface and via the [Redfish](http://www.dmtf.org/redfish) RESTful API standard. Although [videos](https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCIZhrIYcNh3wHLiY4ola5ew/search?query=logicaldrive) already exist that cover the graphical user interface, I wanted to address this feature with a pure Redfish API approach, bypassing the `ilorest`[interface tool](http://www.hpe.com/info/resttool) and its Smart Array macro commands.
25
25
26
-
In this article you start by learning how to cleanup and prepare a SmartRAID (SR) storage Controller for receiving a configuration with one or more logical drives using an HPE proprietary OEM process. Then, on this fresh environment, you will learn how to create a simple RAID array configuration prior to more complex ones to complement the [API reference documentation](https://hewlettpackard.github.io/ilo-rest-api-docs/ilo5/?python#smartstorageconfig).
26
+
In this article you start by learning how to cleanup and prepare a SmartRAID (SR) storage Controller for receiving a configuration with one or more logical drives using an HPE proprietary OEM process. Then, on this fresh environment, you will learn how to create a simple RAID array configuration prior to more complex ones.
27
+
28
+
**NOTE**: The HPE proprietary `SmartStorageConfig` introduced with HPE iLO 5 has been [deprecated](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/redfishservices/ilos/ilo6/ilo6_adaptation/#hpe-smart-storage-model-oem-deprecated) in iLO 6 based servers (Gen11) in favor of the standard [DMTF storage model](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/redfishservices/ilos/supplementdocuments/storage/). For backward compatibility, HPE iLO 5 implements both models.
27
29
28
30
## Foreword
29
31
30
32
I've used the [Postman](https://www.getpostman.com/) API development to illustrate our examples. This should give you the ability to implement these raw examples using your own preferred language.
31
33
32
34
The reader should have the knowledge of HTTP [request methods](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertext_Transfer_Protocol#Request_methods) like `GET`, `PUT` and `PATCH`.
33
35
34
-
Moreover, it is assumed that the reader knows how to manage Redfish sessions as described in the [Redfish API Reference documentation](https://hewlettpackard.github.io/ilo-rest-api-docs/ilo5/#authentication-and-sessions). More hints for managing iLO sessions with Redfish can be found in this [article](/blog/managing-ilo-sessions-with-redfish).
36
+
Moreover, it is assumed that the reader knows how to manage Redfish sessions as described in the [Redfish API Reference documentation](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/concepts/redfishauthentication/). More hints for managing iLO sessions with Redfish can be found in this [article](/blog/managing-ilo-sessions-with-redfish).
35
37
36
38
## Storage data models
37
39
@@ -70,15 +72,15 @@ Upon reboot, and once the server has finished its Pre-OS Tasks (POST), you shoul
70
72
71
73
## The `DataGuard` property
72
74
73
-
The management of HPE Smart Storage devices requires a proper understanding of the `DataGuard` property part of the `SmartStorageConfig` sub-tree. The value of this attribute "_indicates whether or not data destructive actions are allowed_" as explained in the [API Reference documentation](https://hewlettpackard.github.io/ilo-rest-api-docs/ilo5/#dataguard).
75
+
The management of HPE Smart Storage devices requires a proper understanding of the `DataGuard` property part of the `SmartStorageConfig` sub-tree. The value of this attribute "_indicates whether or not data destructive actions are allowed_" as explained in the [API Reference documentation](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/redfishservices/ilos/ilo5/ilo5_290/ilo5_other_resourcedefns290/#dataguard).
74
76
75
77
This property is set in the pending settings (`SmartStorageConfig/Settings`) along with the directives to be performed by the Smart Storage device (i.e. Logical Volume Creation, Deletion...). During the next POST, the firmware checks its value and performs, or does not perform, the requested directives.
76
78
77
79
If the value is `Strict`, which is the default value when not changed in the pending settings, the firmware denies any destructive data action (create/delete logical drives or clear drive metadata....).
78
80
79
81
If the value is set to `Disabled`, destructive data actions are allowed. Finally, when the value is `Permissive`, only destructive data actions are allowed on the specified objects.
80
82
81
-
Refer to the [iLO RESTful API documentation](https://hewlettpackard.github.io/ilo-rest-api-docs/ilo5/#delete-logical-drives) for more information.
83
+
Refer to the [iLO RESTful API documentation](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/redfishservices/ilos/supplementdocuments/storage/) for more information.
82
84
83
85
## Storage controller and physical disks preparation
84
86
@@ -130,12 +132,11 @@ To delete a specific logical drive you have to send a `PUT` request to the `Smar
130
132
131
133
### Sanitizing / disk drives
132
134
133
-
In addition to the removal of logical drives and the meta data cleanup of physical drives, you may want to [erase / sanitize](https://hewlettpackard.github.io/ilo-rest-api-docs/ilo5/#sanitize-drives) a list of physical drives. To perform this (long) operation, send the following `PATCH` action with the correct list of the drives to erase, separated by a comma. Don't forget to disabled the `DataGuard` property as well:
135
+
In addition to the removal of logical drives and the meta data cleanup of physical drives, you may want to erase / sanitize a list of physical drives. To perform this (long) operation, send the following `PATCH` action with the correct list of the drives to erase, separated by a comma. Don't forget to disabled the `DataGuard` property as well:
134
136
135
137
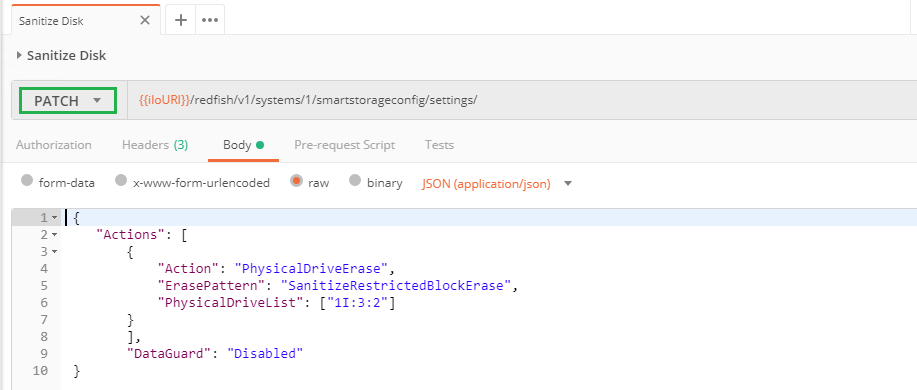
136
138
137
-
The `ErasePattern` property supports the following [values](https://hewlettpackard.github.io/ilo-rest-api-docs/ilo5/#actions-array):
138
-
139
+
The `ErasePattern` property supports the following [values](https://servermanagementportal.ext.hpe.com/docs/redfishservices/ilos/ilo5/ilo5_290/ilo5_other_resourcedefns290/#actions-array):
139
140
140
141
````text
141
142
SanitizeRestrictedBlockErase
@@ -157,7 +158,7 @@ As mentioned above, the sanitize process is extremely long and you can retrieve
157
158
158
159
Logical drives can be created using the `PUT` method. In some circumstances a `PATCH` can be used. To keep things simple, I'll only use the `PUT` method.
159
160
160
-
For this section, start with the clean infrastructure generated previously to create a 100GB RAID1 logical drive with a [`Roaming`](https://hewlettpackard.github.io/ilo-rest-api-docs/ilo5/#sparerebuildmode) spare drive.
161
+
For this section, start with the clean infrastructure generated previously to create a 100GB RAID1 logical drive with a `Roaming` spare drive.
161
162
162
163
Then, add a RAID0 Logical drive located on a single hard disk without spare drive and spanning the entire disk (300GB).
163
164
@@ -204,7 +205,7 @@ The following screenshot shows the characteristics of the added RAID0 logical dr
204
205
205
206
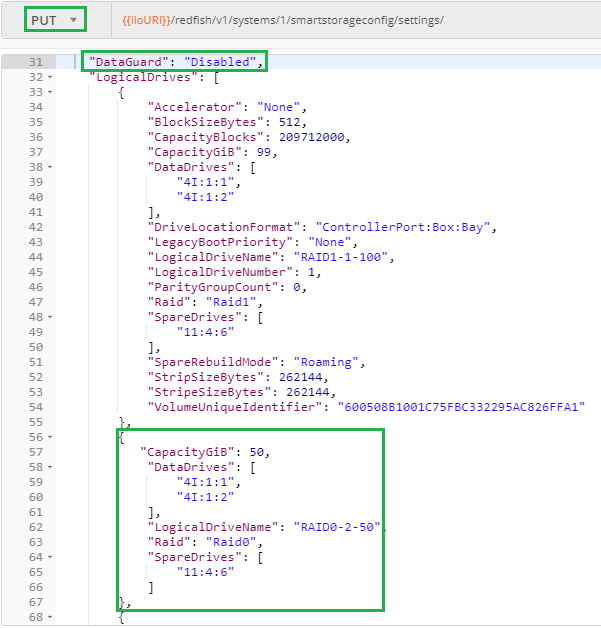
206
207
207
-
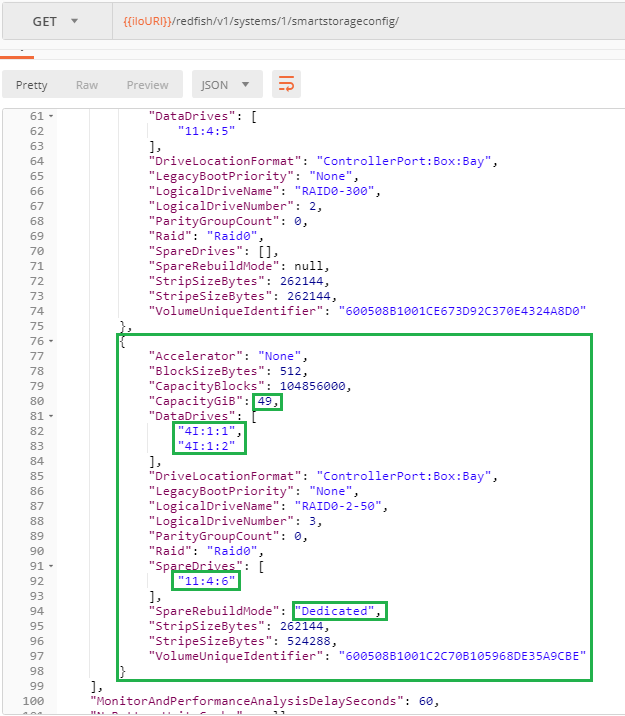
After reboot, the requested RAID0 logical drive is visible in the current configuration. Note that the `SpareRebuildMode` has been automatically adjusted to [`Dedicated`](https://hewlettpackard.github.io/ilo-rest-api-docs/ilo5/#sparerebuildmode) since `Roaming` is not a valid value anymore.
208
+
After reboot, the requested RAID0 logical drive is visible in the current configuration. Note that the `SpareRebuildMode` has been automatically adjusted to `Dedicated` since `Roaming` is not a valid value anymore.
208
209
209
210
0 commit comments