|
| 1 | +# Using MCP with Local and Open Source Models |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +In this section, we'll connect MCP with local and open-source models using |
| 4 | +Continue, a tool for building AI coding assistants that works with local tools |
| 5 | +like Ollama. |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +## Setup Continue |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +You can install Continue from the VS Code marketplace. |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +<Tip> |
| 12 | +*Continue also has an extension for [JetBrains](https://plugins.jetbrains.com/plugin/22707-continue).* |
| 13 | +</Tip> |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +### VS Code extension |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +1. Click `Install` on the [Continue extension page in the Visual Studio Marketplace](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=Continue.continue) |
| 18 | +2. This will open the Continue extension page in VS Code, where you will need to click `Install` again |
| 19 | +3. The Continue logo will appear on the left sidebar. For a better experience, move Continue to the right sidebar |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +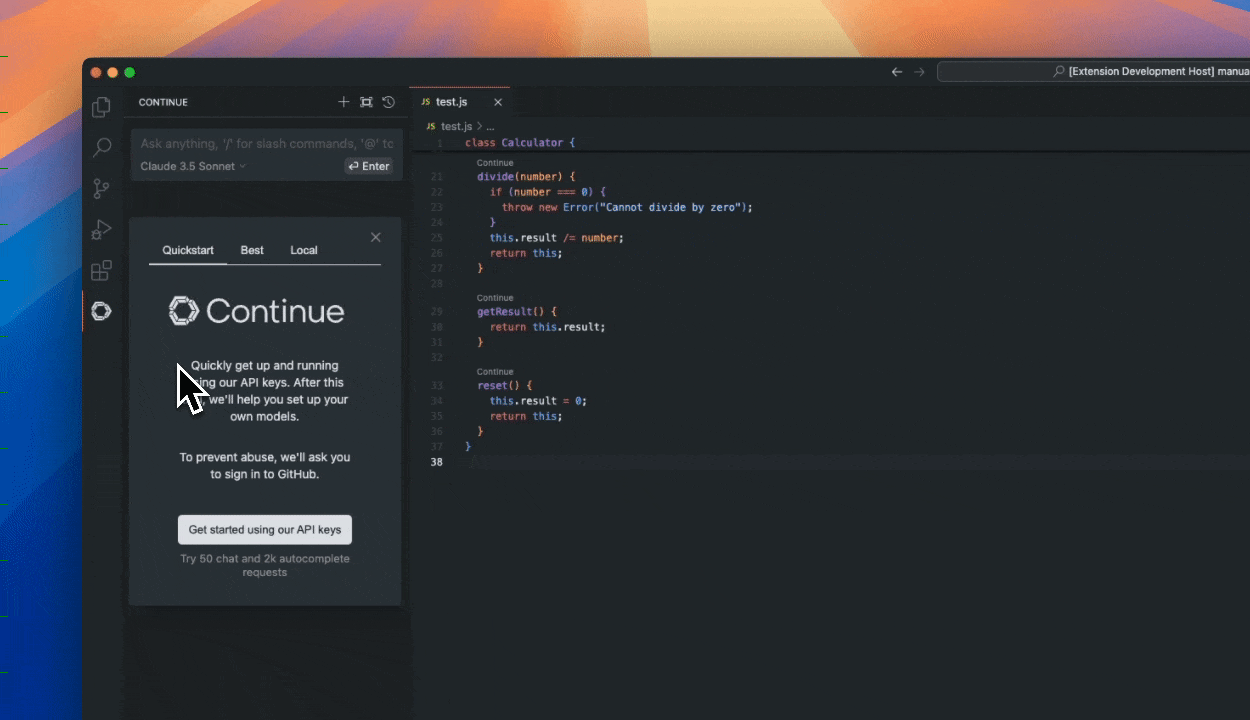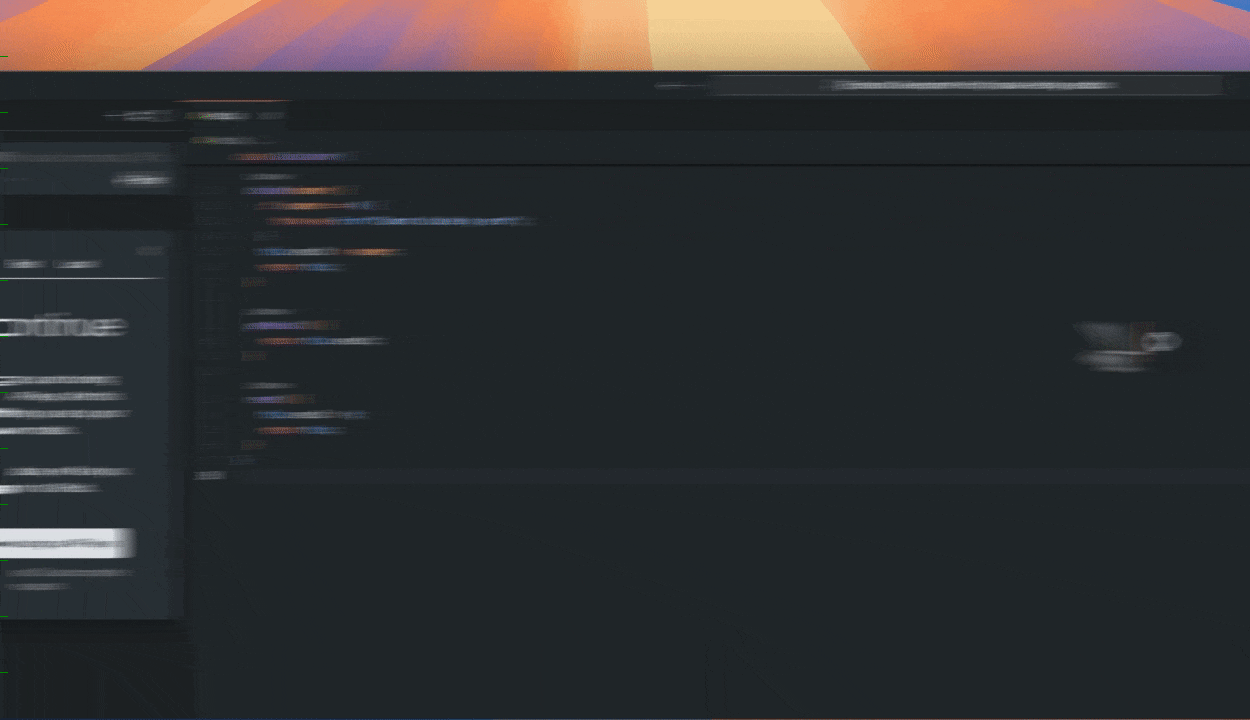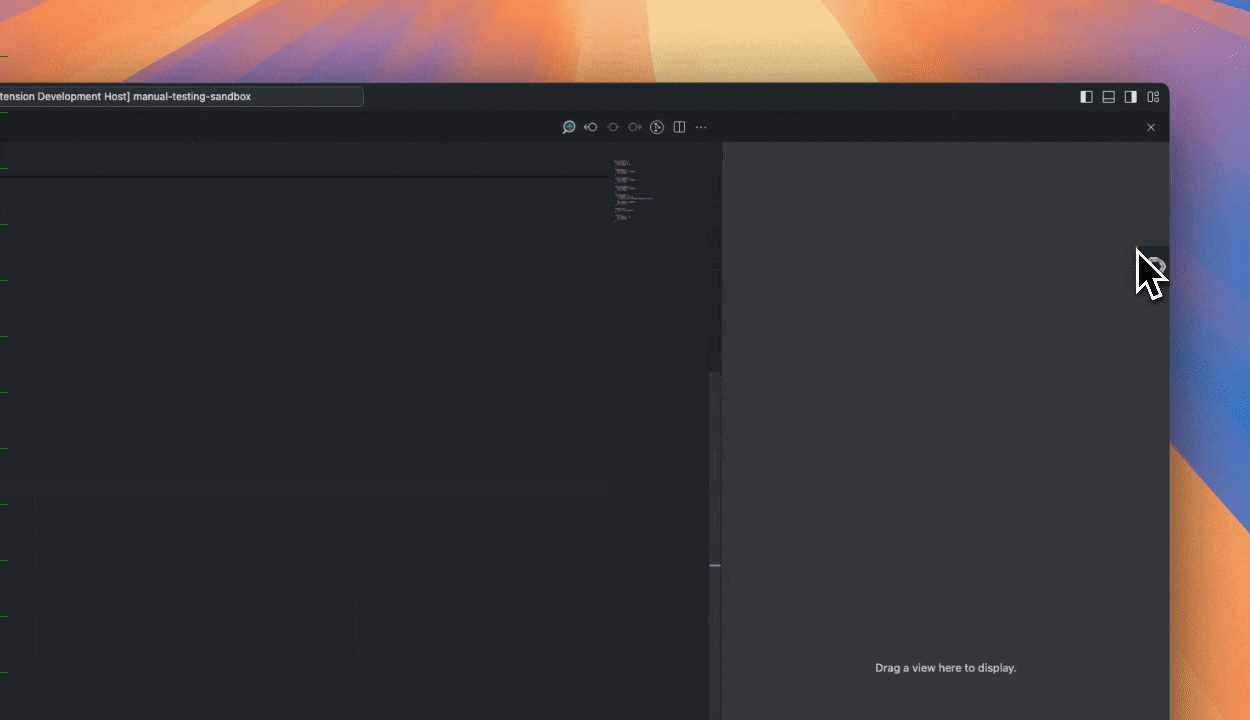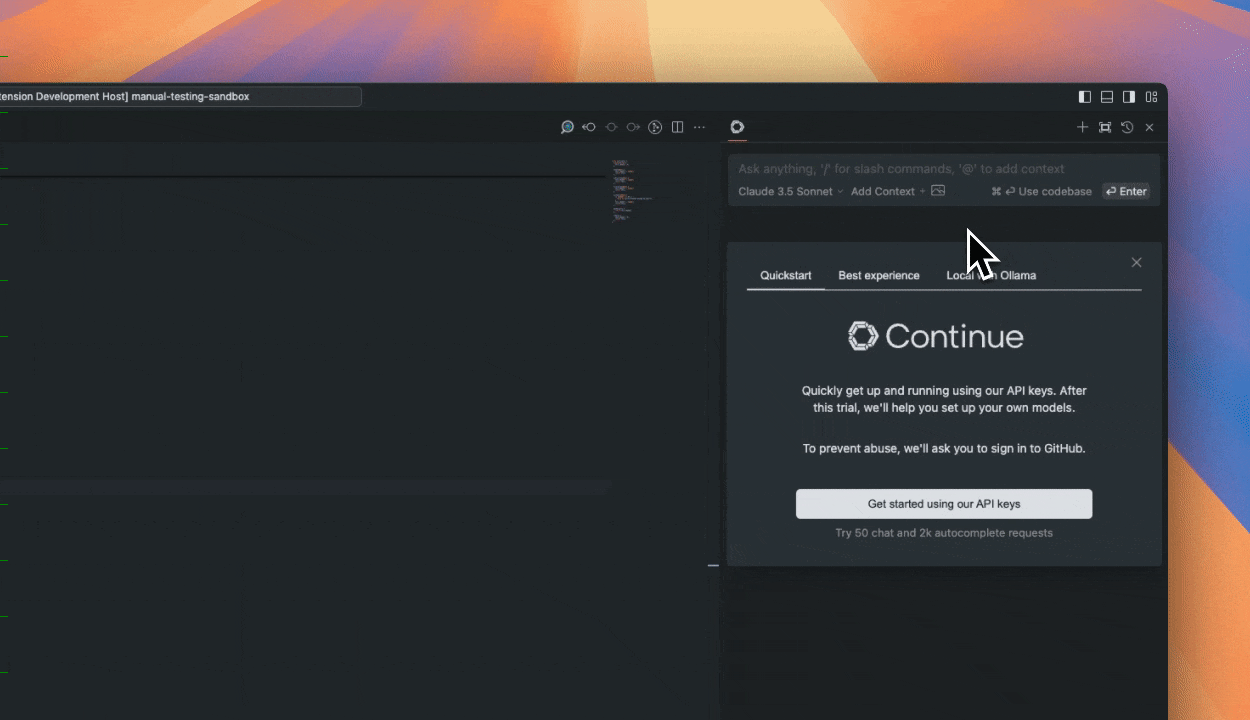 |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +With Continue configured, we'll move on to setting up Ollama to pull local models. |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +### Ollama local models |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +Ollama is an open-source tool that allows users to run large language models (LLMs) |
| 28 | +locally on their own computers. To use Ollama, you can [install](https://ollama.com/download) it and |
| 29 | +download the model you want to run with the `ollama pull` command. |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +For example, you can download the [llama 3.1:8b](https://ollama.com/models/llama-3:1b) model with: |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +```bash |
| 34 | +ollama pull llama3.1:8b |
| 35 | +``` |
| 36 | +<Tip> |
| 37 | +It is possible |
| 38 | +to use other local model provides, like [Llama.cpp](https://docs.continue.dev/customize/model-providers/more/llamacpp), and [LLmstudio](https://docs.continue.dev/customize/model-providers/more/lmstudio) by updating the |
| 39 | +model provider in the configuration files below. However, Continue has been |
| 40 | +tested with Ollama and it is recommended to use it for the best experience. |
| 41 | + |
| 42 | +Details on all available model providers can be found in the [Continue documentation](https://docs.continue.dev/customize/model-providers). |
| 43 | +</Tip> |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | +It is important that we use models that have tool calling as a built-in feature, i.e. Codestral Qwen and Llama 3.1x. |
| 46 | + |
| 47 | +1. Create a folder called `.continue/models` at the top level of your workspace |
| 48 | +2. Add a file called `llama-max.yaml` to this folder |
| 49 | +3. Write the following contents to `llama-max.yaml` and save |
| 50 | + |
| 51 | +```yaml |
| 52 | +name: Ollama Llama model |
| 53 | +version: 0.0.1 |
| 54 | +schema: v1 |
| 55 | +models: |
| 56 | + - provider: ollama |
| 57 | + model: llama3.1:8b |
| 58 | + defaultCompletionOptions: |
| 59 | + contextLength: 128000 |
| 60 | + name: a llama3.1:8b max |
| 61 | + roles: |
| 62 | + - chat |
| 63 | + - edit |
| 64 | +``` |
| 65 | +
|
| 66 | +By default, each model has a max context length, in this case it is `128000` tokens. This setup includes a larger use of |
| 67 | +that context window to perform multiple MCP requests and needs to be able to handle more tokens. |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +## How it works |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | +### The tool handshake |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | +Tools provide a powerful way for models to interface with the external world. |
| 74 | +They are provided to the model as a JSON object with a name and an arguments |
| 75 | +schema. For example, a `read_file` tool with a `filepath` argument will give the |
| 76 | +model the ability to request the contents of a specific file. |
| 77 | + |
| 78 | + |
| 79 | + |
| 80 | +The following handshake describes how the Agent uses tools: |
| 81 | + |
| 82 | +1. In Agent mode, available tools are sent along with `user` chat requests |
| 83 | +2. The model can choose to include a tool call in its response |
| 84 | +3. The user gives permission. This step is skipped if the policy for that tool is set to `Automatic` |
| 85 | +4. Continue calls the tool using built-in functionality or the MCP server that offers that particular tool |
| 86 | +5. Continue sends the result back to the model |
| 87 | +6. The model responds, potentially with another tool call, and step 2 begins again |
| 88 | + |
| 89 | +Continue supports multiple local model providers. You can use different models |
| 90 | +for different tasks or switch models as needed. This section focuses on |
| 91 | +local-first solutions, but Continue does work with popular providers |
| 92 | +like OpenAI, Anthropic, Microsoft/Azure, Mistral, and more. You can also run |
| 93 | +your own model provider. |
| 94 | + |
| 95 | +### Local Model Integration with MCP |
| 96 | + |
| 97 | +Now that we have everything set up, let's add an existing MCP server. Below is a quick example of setting up a new MCP server for use in your assistant: |
| 98 | + |
| 99 | +1. Create a folder called `.continue/mcpServers` at the top level of your workspace |
| 100 | +2. Add a file called `playwright-mcp.yaml` to this folder |
| 101 | +3. Write the following contents to `playwright-mcp.yaml` and save |
| 102 | + |
| 103 | +```yaml |
| 104 | +name: Playwright mcpServer |
| 105 | +version: 0.0.1 |
| 106 | +schema: v1 |
| 107 | +mcpServers: |
| 108 | + - name: Browser search |
| 109 | + command: npx |
| 110 | + args: |
| 111 | + - "@playwright/mcp@latest" |
| 112 | +``` |
| 113 | + |
| 114 | +Now test your MCP server by prompting the following command: |
| 115 | + |
| 116 | +``` |
| 117 | +1. Using playwright, navigate to https://news.ycombinator.com. |
| 118 | +
|
| 119 | +2. Extract the titles and URLs of the top 4 posts on the homepage. |
| 120 | +
|
| 121 | +3. Create a file named hn.txt in the root directory of the project. |
| 122 | +
|
| 123 | +4. Save this list as plain text in the hn.txt file, with each line containing the title and URL separated by a hyphen. |
| 124 | +
|
| 125 | +Do not output code or instructions—just complete the task and confirm when it is done. |
| 126 | +``` |
| 127 | + |
| 128 | +The result will be a generated file called `hn.txt` in the current working directory. |
| 129 | + |
| 130 | +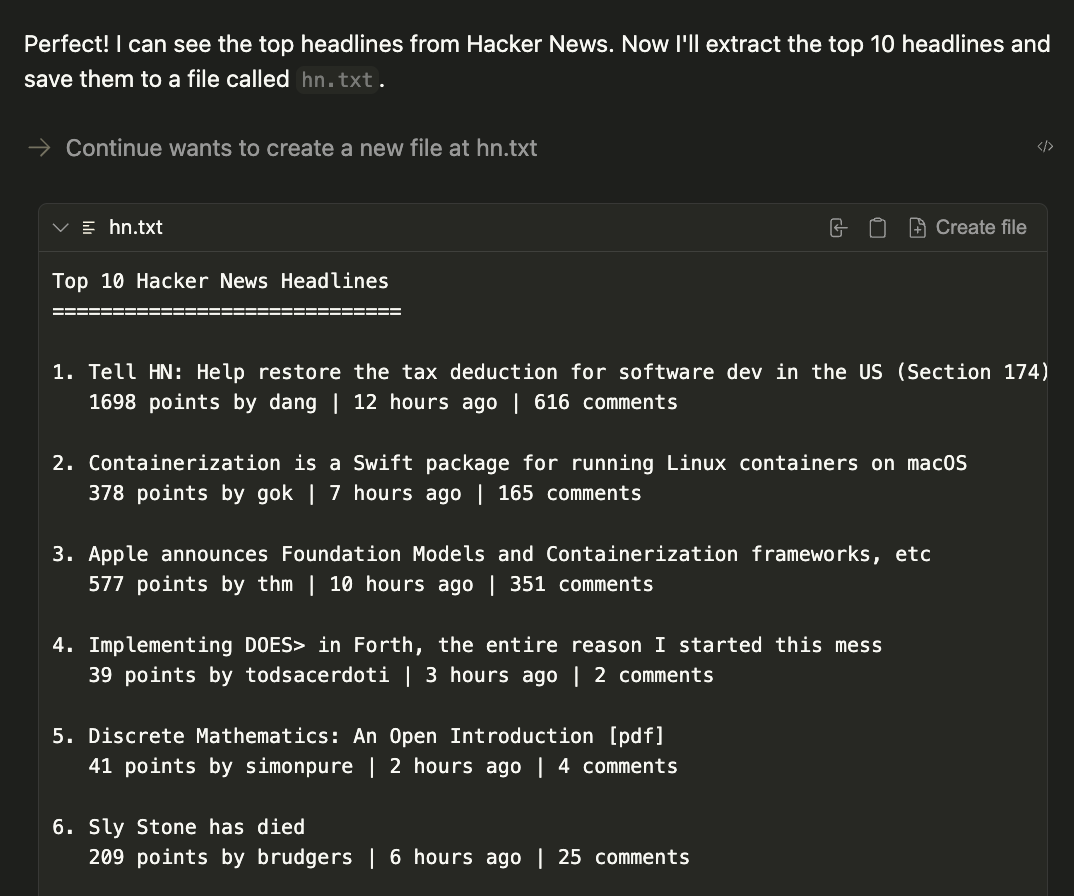 |
| 131 | + |
| 132 | +## Conclusion |
| 133 | + |
| 134 | +By combining Continue with local models like Llama 3.1 and MCP servers, you've |
| 135 | +unlocked a powerful development workflow that keeps your code and data private |
| 136 | +while leveraging cutting-edge AI capabilities. |
| 137 | + |
| 138 | +This setup gives you the flexibility to customize your AI assistant with |
| 139 | +specialized tools, from web automation to file management, all running entirely |
| 140 | +on your local machine. Ready to take your development workflow to the next |
| 141 | +level? Start by experimenting with different MCP servers from the [Continue Hub |
| 142 | +MCP explore page](https://hub.continue.dev/explore/mcp) and discover how |
| 143 | +local AI can transform your coding experience. |
0 commit comments