You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: views/md/introduction.md
+11-6Lines changed: 11 additions & 6 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -3,7 +3,9 @@
3
3
## What is JSON Web Token?
4
4
JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard ([RFC 7519](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7519)) that defines a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed. JWTs can be signed using a secret (with the **HMAC** algorithm) or a public/private key pair using **RSA**.
5
5
6
-
Let's explain some concepts of this definition further.
6
+
Although JWTs can be encrypted to also provide secrecy between parties, we will focus on *signed* tokens. Signed tokens can verify the *integrity* of the claims contained within it, while encrypted tokens *hide* those claims from other parties. When tokens are signed using public/private key pairs, the signature also certifies that only the party holding the private key is the one that signed it.
7
+
8
+
Let's explain some concepts further.
7
9
8
10
-**Compact**: Because of their smaller size, JWTs can be sent through a URL, POST parameter, or inside an HTTP header. Additionally, the smaller size means transmission is fast.
9
11
@@ -17,7 +19,7 @@ Here are some scenarios where JSON Web Tokens are useful:
17
19
-**Information Exchange**: JSON Web Tokens are a good way of securely transmitting information between parties. Because JWTs can be signed—for example, using public/private key pairs—you can be sure the senders are who they say they are. Additionally, as the signature is calculated using the header and the payload, you can also verify that the content hasn't been tampered with.
18
20
19
21
## What is the JSON Web Token structure?
20
-
JSON Web Tokens consist of three parts separated by dots (`.`), which are:
22
+
In its compact form, JSON Web Tokens consist of three parts separated by dots (`.`), which are:
21
23
22
24
- Header
23
25
- Payload
@@ -69,6 +71,8 @@ An example payload could be:
69
71
70
72
The payload is then **Base64Url** encoded to form the second part of the JSON Web Token.
71
73
74
+
> Do note that for signed tokens this information, though protected against tampering, is readable by anyone. Do not put secret information in the payload or header elements of a JWT unless it is encrypted.
75
+
72
76
### Signature
73
77
To create the signature part you have to take the encoded header, the encoded payload, a secret, the algorithm specified in the header, and sign that.
74
78
@@ -81,18 +85,18 @@ HMACSHA256(
81
85
secret)
82
86
```
83
87
84
-
The signature is used to verify that the sender of the JWT is who it says it is and to ensure that the message wasn't changed along the way.
88
+
The signature is used to verify the message wasn't changed along the way, and, in the case of tokens signed with a private key, it can also verify that the sender of the JWT is who it says it is.
85
89
86
90
### Putting all together
87
91
88
-
The output is three Base64 strings separated by dots that can be easily passed in HTML and HTTP environments, while being more compact when compared to XML-based standards such as SAML.
92
+
The output is three Base64-URL strings separated by dots that can be easily passed in HTML and HTTP environments, while being more compact when compared to XML-based standards such as SAML.
89
93
90
94
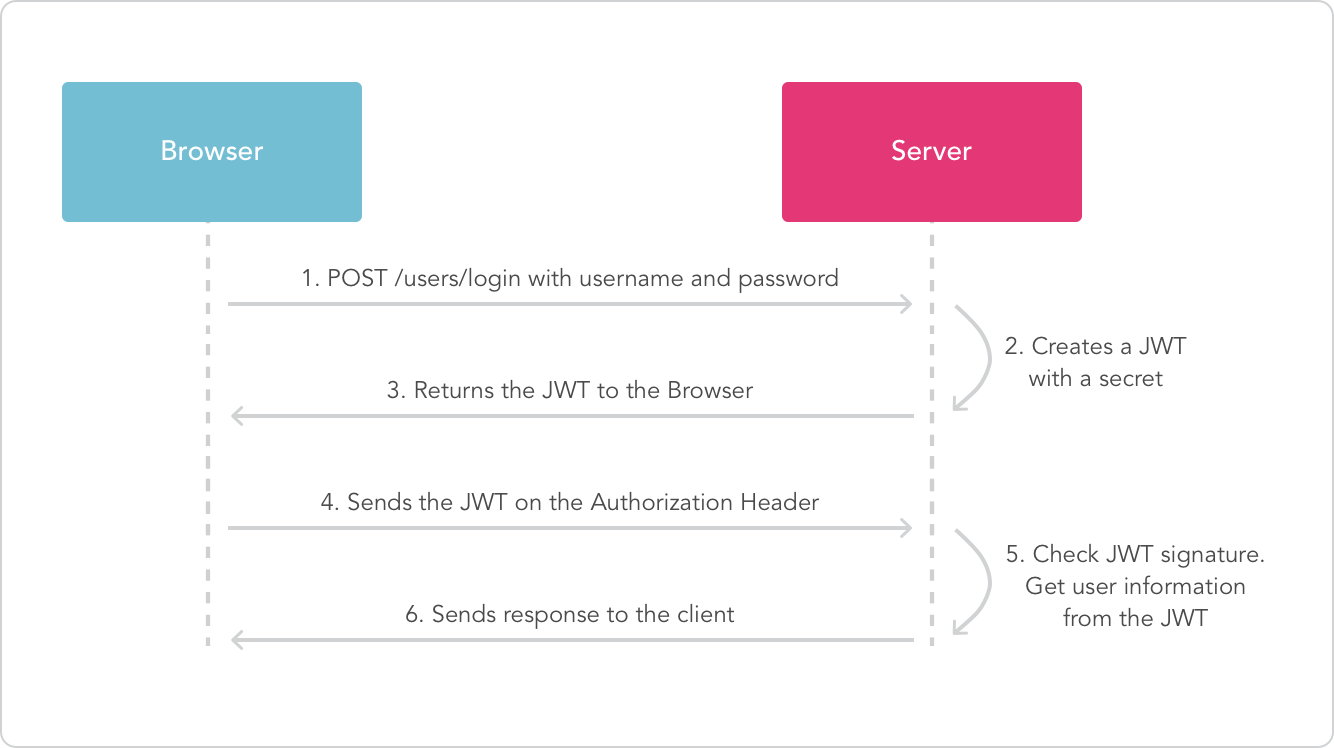
The following shows a JWT that has the previous header and payload encoded, and it is signed with a secret.
In authentication, when the user successfully logs in using their credentials, a JSON Web Token will be returned and must be saved locally (typically in local storage, but cookies can be also used), instead of the traditional approach of creating a session in the server and returning a cookie.
@@ -112,6 +116,8 @@ The following diagram shows this process:
112
116
113
117
114
118
119
+
Do note that with signed tokens, all the information contained within the token is exposed to users or other parties, even though they are unable to change it. This means you should not put secret information within the token.
120
+
115
121
## Why should we use JSON Web Tokens?
116
122
117
123
Let's talk about the benefits of **JSON Web Tokens (JWT)** when compared to **Simple Web Tokens (SWT)** and **Security Assertion Markup Language Tokens (SAML)**.
@@ -127,5 +133,4 @@ Regarding usage, JWT is used at Internet scale. This highlights the ease of clie
127
133
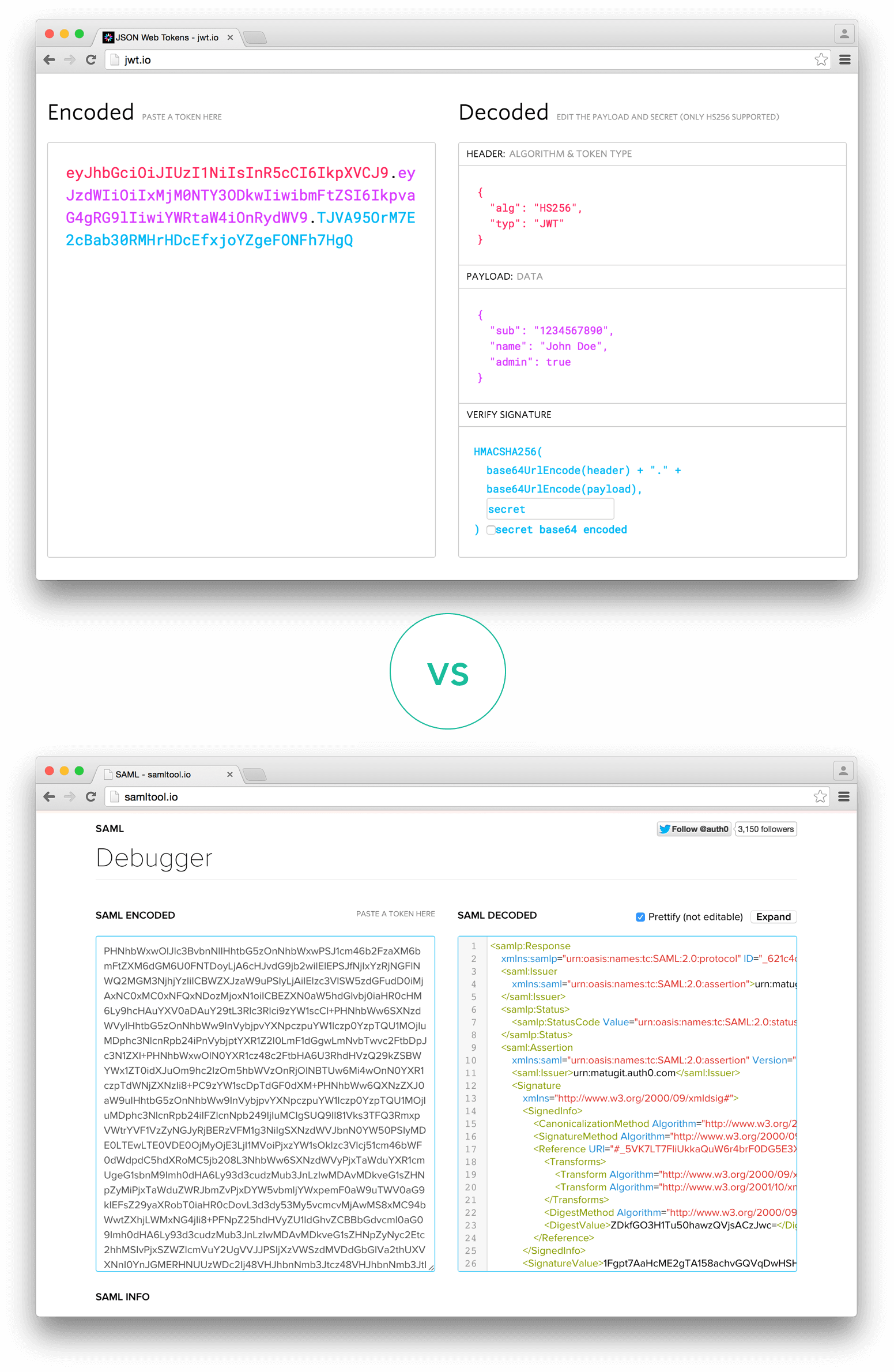
128
134
_Comparison of the length of an encoded JWT and an encoded SAML_
129
135
130
-
131
136
If you want to read more about JSON Web Tokens and even start using them to perform authentication in your own applications, browse to the [JSON Web Token landing page](http://auth0.com/learn/json-web-tokens) at Auth0.
0 commit comments