diff --git a/CycleGAN.ipynb b/CycleGAN.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..590a2a174a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/CycleGAN.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+{
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "colab": {
+ "name": "CycleGAN",
+ "provenance": [],
+ "collapsed_sections": [],
+ "include_colab_link": true
+ },
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "name": "python3",
+ "display_name": "Python 3"
+ },
+ "accelerator": "GPU"
+ },
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "view-in-github",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ " "
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "5VIGyIus8Vr7",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "Take a look at the [repository](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix) for more information"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "7wNjDKdQy35h",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Install"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "TRm-USlsHgEV",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "Pt3igws3eiVp",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import os\n",
+ "os.chdir('pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/')"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "z1EySlOXwwoa",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!pip install -r requirements.txt"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "8daqlgVhw29P",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Datasets\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Download one of the official datasets with:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh [apple2orange, orange2apple, summer2winter_yosemite, winter2summer_yosemite, horse2zebra, zebra2horse, monet2photo, style_monet, style_cezanne, style_ukiyoe, style_vangogh, sat2map, map2sat, cityscapes_photo2label, cityscapes_label2photo, facades_photo2label, facades_label2photo, iphone2dslr_flower]`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Or use your own dataset by creating the appropriate folders and adding in the images.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- Create a dataset folder under `/dataset` for your dataset.\n",
+ "- Create subfolders `testA`, `testB`, `trainA`, and `trainB` under your dataset's folder. Place any images you want to transform from a to b (cat2dog) in the `testA` folder, images you want to transform from b to a (dog2cat) in the `testB` folder, and do the same for the `trainA` and `trainB` folders."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "vrdOettJxaCc",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh horse2zebra"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "gdUz4116xhpm",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Pretrained models\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Download one of the official pretrained models with:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `bash ./scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh [apple2orange, orange2apple, summer2winter_yosemite, winter2summer_yosemite, horse2zebra, zebra2horse, monet2photo, style_monet, style_cezanne, style_ukiyoe, style_vangogh, sat2map, map2sat, cityscapes_photo2label, cityscapes_label2photo, facades_photo2label, facades_label2photo, iphone2dslr_flower]`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Or add your own pretrained model to `./checkpoints/{NAME}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pt`"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "B75UqtKhxznS",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!bash ./scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh horse2zebra"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "yFw1kDQBx3LN",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Training\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/horse2zebra --name horse2zebra --model cycle_gan`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Change the `--dataroot` and `--name` to your own dataset's path and model's name. Use `--gpu_ids 0,1,..` to train on multiple GPUs and `--batch_size` to change the batch size. I've found that a batch size of 16 fits onto 4 V100s and can finish training an epoch in ~90s.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Once your model has trained, copy over the last checkpoint to a format that the testing model can automatically detect:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Use `cp ./checkpoints/horse2zebra/latest_net_G_A.pth ./checkpoints/horse2zebra/latest_net_G.pth` if you want to transform images from class A to class B and `cp ./checkpoints/horse2zebra/latest_net_G_B.pth ./checkpoints/horse2zebra/latest_net_G.pth` if you want to transform images from class B to class A.\n"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "0sp7TCT2x9dB",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/horse2zebra --name horse2zebra --model cycle_gan"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "9UkcaFZiyASl",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Testing\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --name horse2zebra_pretrained --model test --no_dropout`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Change the `--dataroot` and `--name` to be consistent with your trained model's configuration.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> from https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix:\n",
+ "> The option --model test is used for generating results of CycleGAN only for one side. This option will automatically set --dataset_mode single, which only loads the images from one set. On the contrary, using --model cycle_gan requires loading and generating results in both directions, which is sometimes unnecessary. The results will be saved at ./results/. Use --results_dir {directory_path_to_save_result} to specify the results directory.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> For your own experiments, you might want to specify --netG, --norm, --no_dropout to match the generator architecture of the trained model."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "uCsKkEq0yGh0",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --name horse2zebra_pretrained --model test --no_dropout"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "OzSKIPUByfiN",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Visualize"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "9Mgg8raPyizq",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
+ "\n",
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/horse2zebra_pretrained/test_latest/images/n02381460_1010_fake.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "0G3oVH9DyqLQ",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
+ "\n",
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/horse2zebra_pretrained/test_latest/images/n02381460_1010_real.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ }
+ ]
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index e9b50da76ad..b514174f649 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -4,40 +4,53 @@
# CycleGAN and pix2pix in PyTorch
-This is our PyTorch implementation for both unpaired and paired image-to-image translation. It is still under active development.
+We provide PyTorch implementations for both unpaired and paired image-to-image translation.
-The code was written by [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://github.com/junyanz) and [Taesung Park](https://github.com/taesung89), and supported by [Tongzhou Wang](https://ssnl.github.io/).
+The code was written by [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://github.com/junyanz) and [Taesung Park](https://github.com/taesung), and supported by [Tongzhou Wang](https://ssnl.github.io/).
-This PyTorch implementation produces results comparable to or better than our original Torch software. If you would like to reproduce the exact same results as in the papers, check out the original [CycleGAN Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) and [pix2pix Torch](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix) code
+This PyTorch implementation produces results comparable to or better than our original Torch software. If you would like to reproduce the same results as in the papers, check out the original [CycleGAN Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) and [pix2pix Torch](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix) code
-**Note**: The current software works well with PyTorch 0.4. Check out the older [branch](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/tree/pytorch0.3.1) that supports PyTorch 0.1-0.3.
+**Note**: The current software works well with PyTorch 0.41+. Check out the older [branch](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/tree/pytorch0.3.1) that supports PyTorch 0.1-0.3.
-#### CycleGAN: [[Project]](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN)
-
"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "5VIGyIus8Vr7",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "Take a look at the [repository](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix) for more information"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "7wNjDKdQy35h",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Install"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "TRm-USlsHgEV",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "Pt3igws3eiVp",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import os\n",
+ "os.chdir('pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/')"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "z1EySlOXwwoa",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!pip install -r requirements.txt"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "8daqlgVhw29P",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Datasets\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Download one of the official datasets with:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh [apple2orange, orange2apple, summer2winter_yosemite, winter2summer_yosemite, horse2zebra, zebra2horse, monet2photo, style_monet, style_cezanne, style_ukiyoe, style_vangogh, sat2map, map2sat, cityscapes_photo2label, cityscapes_label2photo, facades_photo2label, facades_label2photo, iphone2dslr_flower]`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Or use your own dataset by creating the appropriate folders and adding in the images.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- Create a dataset folder under `/dataset` for your dataset.\n",
+ "- Create subfolders `testA`, `testB`, `trainA`, and `trainB` under your dataset's folder. Place any images you want to transform from a to b (cat2dog) in the `testA` folder, images you want to transform from b to a (dog2cat) in the `testB` folder, and do the same for the `trainA` and `trainB` folders."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "vrdOettJxaCc",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh horse2zebra"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "gdUz4116xhpm",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Pretrained models\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Download one of the official pretrained models with:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `bash ./scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh [apple2orange, orange2apple, summer2winter_yosemite, winter2summer_yosemite, horse2zebra, zebra2horse, monet2photo, style_monet, style_cezanne, style_ukiyoe, style_vangogh, sat2map, map2sat, cityscapes_photo2label, cityscapes_label2photo, facades_photo2label, facades_label2photo, iphone2dslr_flower]`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Or add your own pretrained model to `./checkpoints/{NAME}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pt`"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "B75UqtKhxznS",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!bash ./scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh horse2zebra"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "yFw1kDQBx3LN",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Training\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/horse2zebra --name horse2zebra --model cycle_gan`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Change the `--dataroot` and `--name` to your own dataset's path and model's name. Use `--gpu_ids 0,1,..` to train on multiple GPUs and `--batch_size` to change the batch size. I've found that a batch size of 16 fits onto 4 V100s and can finish training an epoch in ~90s.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Once your model has trained, copy over the last checkpoint to a format that the testing model can automatically detect:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Use `cp ./checkpoints/horse2zebra/latest_net_G_A.pth ./checkpoints/horse2zebra/latest_net_G.pth` if you want to transform images from class A to class B and `cp ./checkpoints/horse2zebra/latest_net_G_B.pth ./checkpoints/horse2zebra/latest_net_G.pth` if you want to transform images from class B to class A.\n"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "0sp7TCT2x9dB",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/horse2zebra --name horse2zebra --model cycle_gan"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "9UkcaFZiyASl",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Testing\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --name horse2zebra_pretrained --model test --no_dropout`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Change the `--dataroot` and `--name` to be consistent with your trained model's configuration.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> from https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix:\n",
+ "> The option --model test is used for generating results of CycleGAN only for one side. This option will automatically set --dataset_mode single, which only loads the images from one set. On the contrary, using --model cycle_gan requires loading and generating results in both directions, which is sometimes unnecessary. The results will be saved at ./results/. Use --results_dir {directory_path_to_save_result} to specify the results directory.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> For your own experiments, you might want to specify --netG, --norm, --no_dropout to match the generator architecture of the trained model."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "uCsKkEq0yGh0",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --name horse2zebra_pretrained --model test --no_dropout"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "OzSKIPUByfiN",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Visualize"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "9Mgg8raPyizq",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
+ "\n",
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/horse2zebra_pretrained/test_latest/images/n02381460_1010_fake.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "0G3oVH9DyqLQ",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
+ "\n",
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/horse2zebra_pretrained/test_latest/images/n02381460_1010_real.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ }
+ ]
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index e9b50da76ad..b514174f649 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -4,40 +4,53 @@
# CycleGAN and pix2pix in PyTorch
-This is our PyTorch implementation for both unpaired and paired image-to-image translation. It is still under active development.
+We provide PyTorch implementations for both unpaired and paired image-to-image translation.
-The code was written by [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://github.com/junyanz) and [Taesung Park](https://github.com/taesung89), and supported by [Tongzhou Wang](https://ssnl.github.io/).
+The code was written by [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://github.com/junyanz) and [Taesung Park](https://github.com/taesung), and supported by [Tongzhou Wang](https://ssnl.github.io/).
-This PyTorch implementation produces results comparable to or better than our original Torch software. If you would like to reproduce the exact same results as in the papers, check out the original [CycleGAN Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) and [pix2pix Torch](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix) code
+This PyTorch implementation produces results comparable to or better than our original Torch software. If you would like to reproduce the same results as in the papers, check out the original [CycleGAN Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) and [pix2pix Torch](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix) code
-**Note**: The current software works well with PyTorch 0.4. Check out the older [branch](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/tree/pytorch0.3.1) that supports PyTorch 0.1-0.3.
+**Note**: The current software works well with PyTorch 0.41+. Check out the older [branch](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/tree/pytorch0.3.1) that supports PyTorch 0.1-0.3.
-#### CycleGAN: [[Project]](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN)
-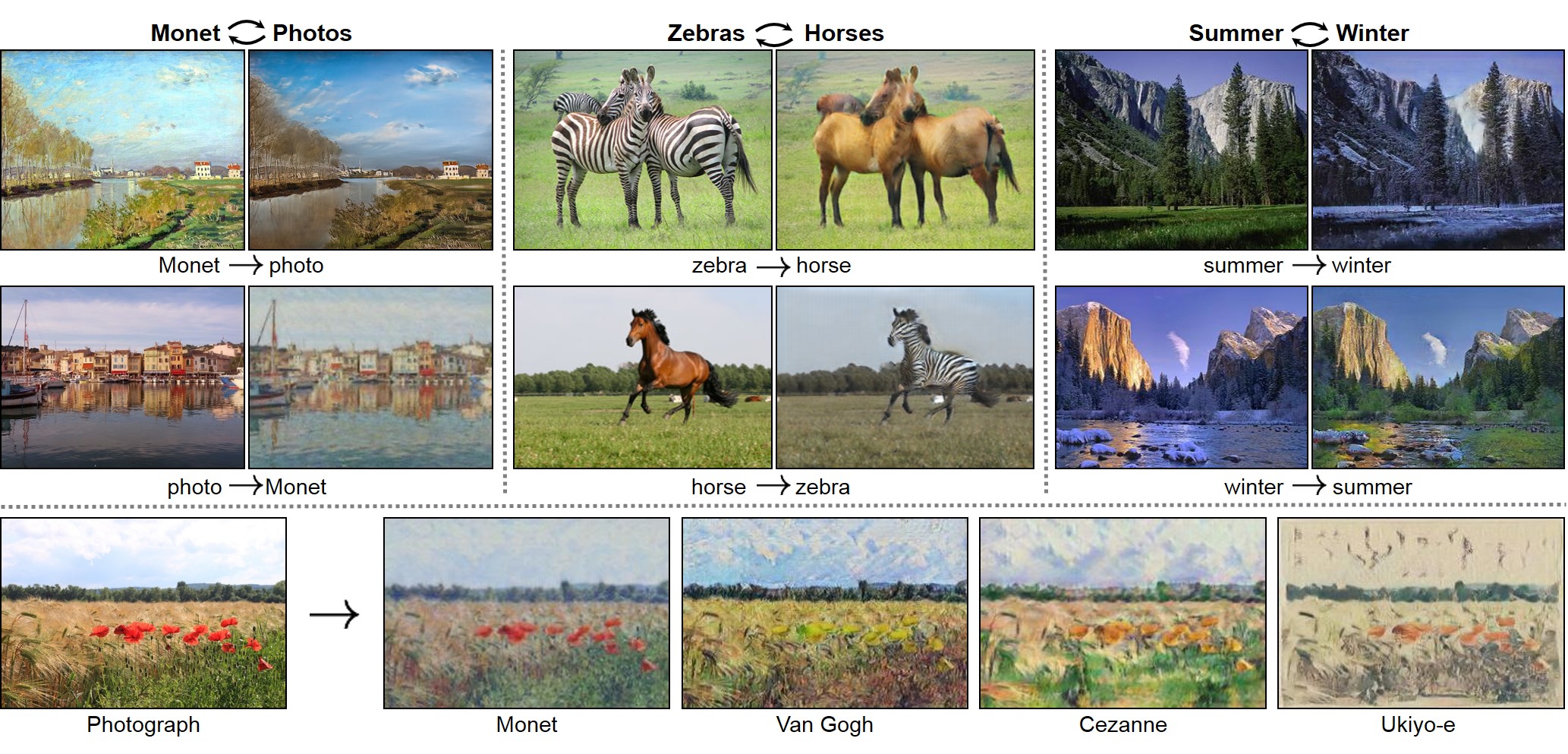 +You may find useful information in [training/test tips](docs/tips.md) and [frequently asked questions](docs/qa.md). To implement custom models and datasets, check out our [templates](#custom-model-and-dataset). To help users better understand and adapt our codebase, we provide an [overview](docs/overview.md) of the code structure of this repository.
-#### Pix2pix: [[Project]](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004v1.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix)
+**CycleGAN: [Project](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf) | [Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) |
+[Tensorflow Core Tutorial](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/generative/cyclegan) | [PyTorch Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/CycleGAN.ipynb)**
-
+You may find useful information in [training/test tips](docs/tips.md) and [frequently asked questions](docs/qa.md). To implement custom models and datasets, check out our [templates](#custom-model-and-dataset). To help users better understand and adapt our codebase, we provide an [overview](docs/overview.md) of the code structure of this repository.
-#### Pix2pix: [[Project]](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004v1.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix)
+**CycleGAN: [Project](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf) | [Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) |
+[Tensorflow Core Tutorial](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/generative/cyclegan) | [PyTorch Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/CycleGAN.ipynb)**
- +
+ -#### [[EdgesCats Demo]](https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/) [[pix2pix-tensorflow]](https://github.com/affinelayer/pix2pix-tensorflow)
-Written by [Christopher Hesse](https://twitter.com/christophrhesse)
+**Pix2pix: [Project](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004.pdf) | [Torch](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix) |
+[Tensorflow Core Tutorial](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/generative/cyclegan) | [PyTorch Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/pix2pix.ipynb)**
-
-#### [[EdgesCats Demo]](https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/) [[pix2pix-tensorflow]](https://github.com/affinelayer/pix2pix-tensorflow)
-Written by [Christopher Hesse](https://twitter.com/christophrhesse)
+**Pix2pix: [Project](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004.pdf) | [Torch](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix) |
+[Tensorflow Core Tutorial](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/generative/cyclegan) | [PyTorch Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/pix2pix.ipynb)**
- +
+ +
+
+**[EdgesCats Demo](https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/) | [pix2pix-tensorflow](https://github.com/affinelayer/pix2pix-tensorflow) | by [Christopher Hesse](https://twitter.com/christophrhesse)**
+
+
+
+
+**[EdgesCats Demo](https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/) | [pix2pix-tensorflow](https://github.com/affinelayer/pix2pix-tensorflow) | by [Christopher Hesse](https://twitter.com/christophrhesse)**
+
+ If you use this code for your research, please cite:
-Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
-[Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/)\*, [Taesung Park](https://taesung.me/)\*, [Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola/), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
-In ICCV 2017. (* equal contributions)
+Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks.
If you use this code for your research, please cite:
-Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
-[Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/)\*, [Taesung Park](https://taesung.me/)\*, [Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola/), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
-In ICCV 2017. (* equal contributions)
+Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks.
+[Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/)\*, [Taesung Park](https://taesung.me/)\*, [Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola/), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros). In ICCV 2017. (* equal contributions) [[Bibtex]](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/CycleGAN.txt)
+
+Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks.
+[Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola), [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz), [Tinghui Zhou](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros). In CVPR 2017. [[Bibtex]](http://people.csail.mit.edu/junyanz/projects/pix2pix/pix2pix.bib)
-Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks
-[Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola), [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz), [Tinghui Zhou](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
-In CVPR 2017.
+## Talks and Course
+pix2pix slides: [keynote](http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/CVPR18_slides/pix2pix.key) | [pdf](http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/CVPR18_slides/pix2pix.pdf),
+CycleGAN slides: [pptx](http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/CVPR18_slides/CycleGAN.pptx) | [pdf](http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/CVPR18_slides/CycleGAN.pdf)
-## Course
CycleGAN course assignment [code](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rgrosse/courses/csc321_2018/assignments/a4-code.zip) and [handout](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rgrosse/courses/csc321_2018/assignments/a4-handout.pdf) designed by Prof. [Roger Grosse](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rgrosse/) for [CSC321](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rgrosse/courses/csc321_2018/) "Intro to Neural Networks and Machine Learning" at University of Toronto. Please contact the instructor if you would like to adopt it in your course.
+## Colab Notebook
+TensorFlow Core CycleGAN Tutorial: [Google Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/generative/cyclegan.ipynb) | [Code](https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/generative/cyclegan.ipynb)
+
+TensorFlow Core pix2pix Tutorial: [Google Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/generative/cyclegan.ipynb) | [Code](https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/generative/cyclegan.ipynb)
+
+PyTorch Colab notebook: [CycleGAN](https://colab.research.google.com/github/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/CycleGAN.ipynb) and [pix2pix](https://colab.research.google.com/github/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/pix2pix.ipynb)
+
## Other implementations
### CycleGAN
[Tensorflow] (by Harry Yang),
@@ -49,7 +62,9 @@ CycleGAN course assignment [code](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rgrosse/courses/csc
[Chainer] (by Yanghua Jin),
[Minimal PyTorch] (by yunjey),
[Mxnet] (by Ldpe2G),
-[lasagne/keras] (by tjwei)
+[lasagne/Keras] (by tjwei),
+[Keras] (by Simon Karlsson)
+
### pix2pix
@@ -66,77 +81,69 @@ CycleGAN course assignment [code](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rgrosse/courses/csc
## Prerequisites
- Linux or macOS
-- Python 2 or 3
+- Python 3
- CPU or NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN
## Getting Started
### Installation
-- Install PyTorch 0.4 and dependencies from http://pytorch.org
-- Install Torch vision from the source.
-```bash
-git clone https://github.com/pytorch/vision
-cd vision
-python setup.py install
-```
-- Install python libraries [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom) and [dominate](https://github.com/Knio/dominate).
-```bash
-pip install visdom
-pip install dominate
-```
-- Alternatively, all dependencies can be installed by
-```bash
-pip install -r requirements.txt
-```
+
- Clone this repo:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
cd pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
```
+- Install [PyTorch](http://pytorch.org and) 0.4+ and other dependencies (e.g., torchvision, [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom) and [dominate](https://github.com/Knio/dominate)).
+ - For pip users, please type the command `pip install -r requirements.txt`.
+ - For Conda users, we provide a installation script `./scripts/conda_deps.sh`. Alternatively, you can create a new Conda environment using `conda env create -f environment.yml`.
+ - For Docker users, we provide the pre-built Docker image and Dockerfile. Please refer to our [Docker](docs/docker.md) page.
+
### CycleGAN train/test
- Download a CycleGAN dataset (e.g. maps):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh maps
```
+- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097.
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_cyclegan.sh
-python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --no_dropout
+python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan
```
-- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/maps_cyclegan/web/index.html`
+To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/maps_cyclegan/web/index.html`.
- Test the model:
```bash
#!./scripts/test_cyclegan.sh
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --phase test --no_dropout
+python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan
```
-The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/maps_cyclegan/latest_test/index.html`.
+- The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/maps_cyclegan/latest_test/index.html`.
### pix2pix train/test
-- Download a pix2pix dataset (e.g.facades):
+- Download a pix2pix dataset (e.g.[facades](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade/)):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades
```
+- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097.
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
-python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch --pool_size 0
+python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA
```
-- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/facades_pix2pix/web/index.html`
+To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/facades_pix2pix/web/index.html`.
+
- Test the model (`bash ./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh`):
```bash
#!./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
+python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA
```
-The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/facades_pix2pix/latest_val/index.html`.
-
-More example scripts can be found at `scripts` directory.
+- The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/facades_pix2pix/test_latest/index.html`. You can find more scripts at `scripts` directory.
+- To train and test pix2pix-based colorization models, please add `--model colorization` and `--dataset_mode colorization`. See our training [tips](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/tips.md#notes-on-colorization) for more details.
### Apply a pre-trained model (CycleGAN)
- You can download a pretrained model (e.g. horse2zebra) with the following script:
```bash
-bash pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh horse2zebra
+bash ./scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh horse2zebra
```
-The pretrained model is saved at `./checkpoints/{name}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth`.
+- The pretrained model is saved at `./checkpoints/{name}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth`. Check [here](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh#L3) for all the available CycleGAN models.
- To test the model, you also need to download the horse2zebra dataset:
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh horse2zebra
@@ -144,88 +151,54 @@ bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh horse2zebra
- Then generate the results using
```bash
-python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --checkpoints_dir ./checkpoints/ --name horse2zebra_pretrained --no_dropout --model test --dataset_mode single --loadSize 256
+python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --name horse2zebra_pretrained --model test --no_dropout
```
-The results will be saved at `./results/`. Use `--results_dir {directory_path_to_save_result}` to specify the results directory.
-- Note: The models trained using Torch and PyTorch produce slightly different results, although we were not able to decide which result is better. If you would like to reproduce the same results in our paper, we recommend using the pretrained models in the Torch codebase.
+- The option `--model test` is used for generating results of CycleGAN only for one side. This option will automatically set `--dataset_mode single`, which only loads the images from one set. On the contrary, using `--model cycle_gan` requires loading and generating results in both directions, which is sometimes unnecessary. The results will be saved at `./results/`. Use `--results_dir {directory_path_to_save_result}` to specify the results directory.
-- If you would like to apply a pre-trained model to a collection of input images (rather than image pairs), please use `--dataset_mode single` and `--model test` options. Here is a script to apply a model to Facade label maps (stored in the directory `facades/testB`).
-``` bash
-#!./scripts/test_single.sh
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name {your_trained_model_name} --model test --dataset_mode single
-```
-You might want to specify `--which_model_netG` to match the generator architecture of the trained model.
+- For your own experiments, you might want to specify `--netG`, `--norm`, `--no_dropout` to match the generator architecture of the trained model.
### Apply a pre-trained model (pix2pix)
+Download a pre-trained model with `./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh`.
-Download a pre-trained model with `./pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh`.
-
-- For example, if you would like to download label2photo model on the Facades dataset,
+- Check [here](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh#L3) for all the available pix2pix models. For example, if you would like to download label2photo model on the Facades dataset,
```bash
-bash pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh facades_label2photo
+bash ./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh facades_label2photo
```
-
-- Download the pix2pix facades datasets
+- Download the pix2pix facades datasets:
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades
```
- Then generate the results using
```bash
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/ --which_direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_label2photo_pretrained --dataset_mode aligned --which_model_netG unet_256 --norm batch
+python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/ --direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_label2photo_pretrained
```
-Note that we specified `--which_direction BtoA` as Facades dataset's A to B direction is photos to labels.
-
-- See a list of currently available models at `bash pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh`
+- Note that we specified `--direction BtoA` as Facades dataset's A to B direction is photos to labels.
-## Training/test Details
-- Flags: see `options/train_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for all the training flags; see `options/test_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for all the test flags.
-- CPU/GPU (default `--gpu_ids 0`): set`--gpu_ids -1` to use CPU mode; set `--gpu_ids 0,1,2` for multi-GPU mode. You need a large batch size (e.g. `--batchSize 32`) to benefit from multiple GPUs.
-- Visualization: during training, the current results can be viewed using two methods. First, if you set `--display_id` > 0, the results and loss plot will appear on a local graphics web server launched by [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom). To do this, you should have `visdom` installed and a server running by the command `python -m visdom.server`. The default server URL is `http://localhost:8097`. `display_id` corresponds to the window ID that is displayed on the `visdom` server. The `visdom` display functionality is turned on by default. To avoid the extra overhead of communicating with `visdom` set `--display_id 0`. Second, the intermediate results are saved to `[opt.checkpoints_dir]/[opt.name]/web/` as an HTML file. To avoid this, set `--no_html`.
-- Preprocessing: images can be resized and cropped in different ways using `--resize_or_crop` option. The default option `'resize_and_crop'` resizes the image to be of size `(opt.loadSize, opt.loadSize)` and does a random crop of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`. `'crop'` skips the resizing step and only performs random cropping. `'scale_width'` resizes the image to have width `opt.fineSize` while keeping the aspect ratio. `'scale_width_and_crop'` first resizes the image to have width `opt.loadSize` and then does random cropping of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`.
-- Fine-tuning/Resume training: to fine-tune a pre-trained model, or resume the previous training, use the `--continue_train` flag. The program will then load the model based on `which_epoch`. By default, the program will initialize the epoch count as 1. Set `--epoch_count ` to specify a different starting epoch count.
-- For Conda users, we include a script `./scripts/conda_deps.sh` to install PyTorch and other libraries.
-
-### CycleGAN Datasets
-Download the CycleGAN datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
-```bash
-bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh dataset_name
-```
-- `facades`: 400 images from the [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
-- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
-- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps.
-- `horse2zebra`: 939 horse images and 1177 zebra images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `wild horse` and `zebra`
-- `apple2orange`: 996 apple images and 1020 orange images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `apple` and `navel orange`.
-- `summer2winter_yosemite`: 1273 summer Yosemite images and 854 winter Yosemite images were downloaded using Flickr API. See more details in our paper.
-- `monet2photo`, `vangogh2photo`, `ukiyoe2photo`, `cezanne2photo`: The art images were downloaded from [Wikiart](https://www.wikiart.org/). The real photos are downloaded from Flickr using the combination of the tags *landscape* and *landscapephotography*. The training set size of each class is Monet:1074, Cezanne:584, Van Gogh:401, Ukiyo-e:1433, Photographs:6853.
-- `iphone2dslr_flower`: both classes of images were downlaoded from Flickr. The training set size of each class is iPhone:1813, DSLR:3316. See more details in our paper.
+- If you would like to apply a pre-trained model to a collection of input images (rather than image pairs), please use `--model test` option. See `./scripts/test_single.sh` for how to apply a model to Facade label maps (stored in the directory `facades/testB`).
-To train a model on your own datasets, you need to create a data folder with two subdirectories `trainA` and `trainB` that contain images from domain A and B. You can test your model on your training set by setting `--phase train` in `test.py`. You can also create subdirectories `testA` and `testB` if you have test data.
+- See a list of currently available models at `./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh`
-You should **not** expect our method to work on just any random combination of input and output datasets (e.g. `cats<->keyboards`). From our experiments, we find it works better if two datasets share similar visual content. For example, `landscape painting<->landscape photographs` works much better than `portrait painting <-> landscape photographs`. `zebras<->horses` achieves compelling results while `cats<->dogs` completely fails.
+## [Docker](docs/docker.md)
+We provide the pre-built Docker image and Dockerfile that can run this code repo. See [docker](docs/docker.md).
-### pix2pix datasets
-Download the pix2pix datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
-```bash
-bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh dataset_name
-```
-- `facades`: 400 images from [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
-- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
-- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps
-- `edges2shoes`: 50k training images from [UT Zappos50K dataset](http://vision.cs.utexas.edu/projects/finegrained/utzap50k). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/shoes.tex)]
-- `edges2handbags`: 137K Amazon Handbag images from [iGAN project](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/handbags.tex)]
+## [Datasets](docs/datasets.md)
+Download pix2pix/CycleGAN datasets and create your own datasets.
-We provide a python script to generate pix2pix training data in the form of pairs of images {A,B}, where A and B are two different depictions of the same underlying scene. For example, these might be pairs {label map, photo} or {bw image, color image}. Then we can learn to translate A to B or B to A:
+## [Training/Test Tips](docs/tips.md)
+Best practice for training and testing your models.
-Create folder `/path/to/data` with subfolders `A` and `B`. `A` and `B` should each have their own subfolders `train`, `val`, `test`, etc. In `/path/to/data/A/train`, put training images in style A. In `/path/to/data/B/train`, put the corresponding images in style B. Repeat same for other data splits (`val`, `test`, etc).
+## [Frequently Asked Questions](docs/qa.md)
+Before you post a new question, please first look at the above Q & A and existing GitHub issues.
-Corresponding images in a pair {A,B} must be the same size and have the same filename, e.g., `/path/to/data/A/train/1.jpg` is considered to correspond to `/path/to/data/B/train/1.jpg`.
+## Custom Model and Dataset
+If you plan to implement custom models and dataset for your new applications, we provide a dataset [template](data/template_dataset.py) and a model [template](models/template_model.py) as a starting point.
-Once the data is formatted this way, call:
-```bash
-python datasets/combine_A_and_B.py --fold_A /path/to/data/A --fold_B /path/to/data/B --fold_AB /path/to/data
-```
+## [Code structure](docs/overview.md)
+To help users better understand and use our code, we briefly overview the functionality and implementation of each package and each module.
-This will combine each pair of images (A,B) into a single image file, ready for training.
+## Pull Request
+You are always welcome to contribute to this repository by sending a [pull request](https://help.github.com/articles/about-pull-requests/).
+Please run `flake8 --ignore E501 .` and `python ./scripts/test_before_push.py` before you commit the code. Please also update the code structure [overview](docs/overview.md) accordingly if you add or remove files.
## Citation
If you use this code for your research, please cite our papers.
@@ -244,17 +217,18 @@ If you use this code for your research, please cite our papers.
booktitle={Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017 IEEE Conference on},
year={2017}
}
-
```
+
+
## Related Projects
-[CycleGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN): Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
-[pix2pix](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix): Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial nets
-[iGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN): Interactive Image Generation via Generative Adversarial Networks
+**[CycleGAN-Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) |
+[pix2pix-Torch](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix) | [pix2pixHD](https://github.com/NVIDIA/pix2pixHD)|
+[BicycleGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/BicycleGAN) | [vid2vid](https://tcwang0509.github.io/vid2vid/) | [SPADE/GauGAN](https://github.com/NVlabs/SPADE)**
+**[iGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN) | [GAN Dissection](https://github.com/CSAILVision/GANDissect) | [GAN Paint](http://ganpaint.io/)**
## Cat Paper Collection
-If you love cats, and love reading cool graphics, vision, and learning papers, please check out the Cat Paper Collection:
-[[Github]](https://github.com/junyanz/CatPapers) [[Webpage]](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/cat/cat_papers.html)
+If you love cats, and love reading cool graphics, vision, and learning papers, please check out the Cat Paper [Collection](https://github.com/junyanz/CatPapers).
## Acknowledgments
-Code is inspired by [pytorch-DCGAN](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/dcgan).
+Our code is inspired by [pytorch-DCGAN](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/dcgan).
diff --git a/data/__init__.py b/data/__init__.py
index 341281d548f..8cb618618fc 100644
--- a/data/__init__.py
+++ b/data/__init__.py
@@ -1,54 +1,93 @@
+"""This package includes all the modules related to data loading and preprocessing
+
+ To add a custom dataset class called 'dummy', you need to add a file called 'dummy_dataset.py' and define a subclass 'DummyDataset' inherited from BaseDataset.
+ You need to implement four functions:
+ -- <__init__>: initialize the class, first call BaseDataset.__init__(self, opt).
+ -- <__len__>: return the size of dataset.
+ -- <__getitem__>: get a data point from data loader.
+ -- : (optionally) add dataset-specific options and set default options.
+
+Now you can use the dataset class by specifying flag '--dataset_mode dummy'.
+See our template dataset class 'template_dataset.py' for more details.
+"""
+import importlib
import torch.utils.data
-from data.base_data_loader import BaseDataLoader
+from data.base_dataset import BaseDataset
-def CreateDataLoader(opt):
- data_loader = CustomDatasetDataLoader()
- print(data_loader.name())
- data_loader.initialize(opt)
- return data_loader
+def find_dataset_using_name(dataset_name):
+ """Import the module "data/[dataset_name]_dataset.py".
+ In the file, the class called DatasetNameDataset() will
+ be instantiated. It has to be a subclass of BaseDataset,
+ and it is case-insensitive.
+ """
+ dataset_filename = "data." + dataset_name + "_dataset"
+ datasetlib = importlib.import_module(dataset_filename)
-def CreateDataset(opt):
dataset = None
- if opt.dataset_mode == 'aligned':
- from data.aligned_dataset import AlignedDataset
- dataset = AlignedDataset()
- elif opt.dataset_mode == 'unaligned':
- from data.unaligned_dataset import UnalignedDataset
- dataset = UnalignedDataset()
- elif opt.dataset_mode == 'single':
- from data.single_dataset import SingleDataset
- dataset = SingleDataset()
- else:
- raise ValueError("Dataset [%s] not recognized." % opt.dataset_mode)
-
- print("dataset [%s] was created" % (dataset.name()))
- dataset.initialize(opt)
+ target_dataset_name = dataset_name.replace('_', '') + 'dataset'
+ for name, cls in datasetlib.__dict__.items():
+ if name.lower() == target_dataset_name.lower() \
+ and issubclass(cls, BaseDataset):
+ dataset = cls
+
+ if dataset is None:
+ raise NotImplementedError("In %s.py, there should be a subclass of BaseDataset with class name that matches %s in lowercase." % (dataset_filename, target_dataset_name))
+
+ return dataset
+
+
+def get_option_setter(dataset_name):
+ """Return the static method of the dataset class."""
+ dataset_class = find_dataset_using_name(dataset_name)
+ return dataset_class.modify_commandline_options
+
+
+def create_dataset(opt):
+ """Create a dataset given the option.
+
+ This function wraps the class CustomDatasetDataLoader.
+ This is the main interface between this package and 'train.py'/'test.py'
+
+ Example:
+ >>> from data import create_dataset
+ >>> dataset = create_dataset(opt)
+ """
+ data_loader = CustomDatasetDataLoader(opt)
+ dataset = data_loader.load_data()
return dataset
-class CustomDatasetDataLoader(BaseDataLoader):
- def name(self):
- return 'CustomDatasetDataLoader'
+class CustomDatasetDataLoader():
+ """Wrapper class of Dataset class that performs multi-threaded data loading"""
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize this class
- def initialize(self, opt):
- BaseDataLoader.initialize(self, opt)
- self.dataset = CreateDataset(opt)
+ Step 1: create a dataset instance given the name [dataset_mode]
+ Step 2: create a multi-threaded data loader.
+ """
+ self.opt = opt
+ dataset_class = find_dataset_using_name(opt.dataset_mode)
+ self.dataset = dataset_class(opt)
+ print("dataset [%s] was created" % type(self.dataset).__name__)
self.dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
self.dataset,
- batch_size=opt.batchSize,
+ batch_size=opt.batch_size,
shuffle=not opt.serial_batches,
- num_workers=int(opt.nThreads))
+ num_workers=int(opt.num_threads))
def load_data(self):
return self
def __len__(self):
+ """Return the number of data in the dataset"""
return min(len(self.dataset), self.opt.max_dataset_size)
def __iter__(self):
+ """Return a batch of data"""
for i, data in enumerate(self.dataloader):
- if i * self.opt.batchSize >= self.opt.max_dataset_size:
+ if i * self.opt.batch_size >= self.opt.max_dataset_size:
break
yield data
diff --git a/data/aligned_dataset.py b/data/aligned_dataset.py
index f153f26c58f..cce2be3e608 100644
--- a/data/aligned_dataset.py
+++ b/data/aligned_dataset.py
@@ -1,64 +1,60 @@
import os.path
-import random
-import torchvision.transforms as transforms
-import torch
-from data.base_dataset import BaseDataset
+from data.base_dataset import BaseDataset, get_params, get_transform
from data.image_folder import make_dataset
from PIL import Image
class AlignedDataset(BaseDataset):
- def initialize(self, opt):
- self.opt = opt
- self.root = opt.dataroot
- self.dir_AB = os.path.join(opt.dataroot, opt.phase)
- self.AB_paths = sorted(make_dataset(self.dir_AB))
- assert(opt.resize_or_crop == 'resize_and_crop')
+ """A dataset class for paired image dataset.
+
+ It assumes that the directory '/path/to/data/train' contains image pairs in the form of {A,B}.
+ During test time, you need to prepare a directory '/path/to/data/test'.
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize this dataset class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class) -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ """
+ BaseDataset.__init__(self, opt)
+ self.dir_AB = os.path.join(opt.dataroot, opt.phase) # get the image directory
+ self.AB_paths = sorted(make_dataset(self.dir_AB, opt.max_dataset_size)) # get image paths
+ assert(self.opt.load_size >= self.opt.crop_size) # crop_size should be smaller than the size of loaded image
+ self.input_nc = self.opt.output_nc if self.opt.direction == 'BtoA' else self.opt.input_nc
+ self.output_nc = self.opt.input_nc if self.opt.direction == 'BtoA' else self.opt.output_nc
def __getitem__(self, index):
+ """Return a data point and its metadata information.
+
+ Parameters:
+ index - - a random integer for data indexing
+
+ Returns a dictionary that contains A, B, A_paths and B_paths
+ A (tensor) - - an image in the input domain
+ B (tensor) - - its corresponding image in the target domain
+ A_paths (str) - - image paths
+ B_paths (str) - - image paths (same as A_paths)
+ """
+ # read a image given a random integer index
AB_path = self.AB_paths[index]
AB = Image.open(AB_path).convert('RGB')
+ # split AB image into A and B
w, h = AB.size
w2 = int(w / 2)
- A = AB.crop((0, 0, w2, h)).resize((self.opt.loadSize, self.opt.loadSize), Image.BICUBIC)
- B = AB.crop((w2, 0, w, h)).resize((self.opt.loadSize, self.opt.loadSize), Image.BICUBIC)
- A = transforms.ToTensor()(A)
- B = transforms.ToTensor()(B)
- w_offset = random.randint(0, max(0, self.opt.loadSize - self.opt.fineSize - 1))
- h_offset = random.randint(0, max(0, self.opt.loadSize - self.opt.fineSize - 1))
-
- A = A[:, h_offset:h_offset + self.opt.fineSize, w_offset:w_offset + self.opt.fineSize]
- B = B[:, h_offset:h_offset + self.opt.fineSize, w_offset:w_offset + self.opt.fineSize]
+ A = AB.crop((0, 0, w2, h))
+ B = AB.crop((w2, 0, w, h))
- A = transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))(A)
- B = transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))(B)
+ # apply the same transform to both A and B
+ transform_params = get_params(self.opt, A.size)
+ A_transform = get_transform(self.opt, transform_params, grayscale=(self.input_nc == 1))
+ B_transform = get_transform(self.opt, transform_params, grayscale=(self.output_nc == 1))
- if self.opt.which_direction == 'BtoA':
- input_nc = self.opt.output_nc
- output_nc = self.opt.input_nc
- else:
- input_nc = self.opt.input_nc
- output_nc = self.opt.output_nc
+ A = A_transform(A)
+ B = B_transform(B)
- if (not self.opt.no_flip) and random.random() < 0.5:
- idx = [i for i in range(A.size(2) - 1, -1, -1)]
- idx = torch.LongTensor(idx)
- A = A.index_select(2, idx)
- B = B.index_select(2, idx)
-
- if input_nc == 1: # RGB to gray
- tmp = A[0, ...] * 0.299 + A[1, ...] * 0.587 + A[2, ...] * 0.114
- A = tmp.unsqueeze(0)
-
- if output_nc == 1: # RGB to gray
- tmp = B[0, ...] * 0.299 + B[1, ...] * 0.587 + B[2, ...] * 0.114
- B = tmp.unsqueeze(0)
-
- return {'A': A, 'B': B,
- 'A_paths': AB_path, 'B_paths': AB_path}
+ return {'A': A, 'B': B, 'A_paths': AB_path, 'B_paths': AB_path}
def __len__(self):
+ """Return the total number of images in the dataset."""
return len(self.AB_paths)
-
- def name(self):
- return 'AlignedDataset'
diff --git a/data/base_data_loader.py b/data/base_data_loader.py
deleted file mode 100644
index ae5a1689caf..00000000000
--- a/data/base_data_loader.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
-class BaseDataLoader():
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- def initialize(self, opt):
- self.opt = opt
- pass
-
- def load_data():
- return None
diff --git a/data/base_dataset.py b/data/base_dataset.py
index 359f6949b31..ae434b7fe0b 100644
--- a/data/base_dataset.py
+++ b/data/base_dataset.py
@@ -1,48 +1,157 @@
+"""This module implements an abstract base class (ABC) 'BaseDataset' for datasets.
+
+It also includes common transformation functions (e.g., get_transform, __scale_width), which can be later used in subclasses.
+"""
+import random
+import numpy as np
import torch.utils.data as data
from PIL import Image
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
+from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
+
+
+class BaseDataset(data.Dataset, ABC):
+ """This class is an abstract base class (ABC) for datasets.
+
+ To create a subclass, you need to implement the following four functions:
+ -- <__init__>: initialize the class, first call BaseDataset.__init__(self, opt).
+ -- <__len__>: return the size of dataset.
+ -- <__getitem__>: get a data point.
+ -- : (optionally) add dataset-specific options and set default options.
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize the class; save the options in the class
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class)-- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ """
+ self.opt = opt
+ self.root = opt.dataroot
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train):
+ """Add new dataset-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.
+
+ Parameters:
+ parser -- original option parser
+ is_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
+ Returns:
+ the modified parser.
+ """
+ return parser
-class BaseDataset(data.Dataset):
- def __init__(self):
- super(BaseDataset, self).__init__()
+ @abstractmethod
+ def __len__(self):
+ """Return the total number of images in the dataset."""
+ return 0
- def name(self):
- return 'BaseDataset'
+ @abstractmethod
+ def __getitem__(self, index):
+ """Return a data point and its metadata information.
- def initialize(self, opt):
+ Parameters:
+ index - - a random integer for data indexing
+
+ Returns:
+ a dictionary of data with their names. It ususally contains the data itself and its metadata information.
+ """
pass
-def get_transform(opt):
+def get_params(opt, size):
+ w, h = size
+ new_h = h
+ new_w = w
+ if opt.preprocess == 'resize_and_crop':
+ new_h = new_w = opt.load_size
+ elif opt.preprocess == 'scale_width_and_crop':
+ new_w = opt.load_size
+ new_h = opt.load_size * h // w
+
+ x = random.randint(0, np.maximum(0, new_w - opt.crop_size))
+ y = random.randint(0, np.maximum(0, new_h - opt.crop_size))
+
+ flip = random.random() > 0.5
+
+ return {'crop_pos': (x, y), 'flip': flip}
+
+
+def get_transform(opt, params=None, grayscale=False, method=Image.BICUBIC, convert=True):
transform_list = []
- if opt.resize_or_crop == 'resize_and_crop':
- osize = [opt.loadSize, opt.loadSize]
- transform_list.append(transforms.Resize(osize, Image.BICUBIC))
- transform_list.append(transforms.RandomCrop(opt.fineSize))
- elif opt.resize_or_crop == 'crop':
- transform_list.append(transforms.RandomCrop(opt.fineSize))
- elif opt.resize_or_crop == 'scale_width':
- transform_list.append(transforms.Lambda(
- lambda img: __scale_width(img, opt.fineSize)))
- elif opt.resize_or_crop == 'scale_width_and_crop':
- transform_list.append(transforms.Lambda(
- lambda img: __scale_width(img, opt.loadSize)))
- transform_list.append(transforms.RandomCrop(opt.fineSize))
-
- if opt.isTrain and not opt.no_flip:
- transform_list.append(transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip())
-
- transform_list += [transforms.ToTensor(),
- transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5),
- (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]
+ if grayscale:
+ transform_list.append(transforms.Grayscale(1))
+ if 'resize' in opt.preprocess:
+ osize = [opt.load_size, opt.load_size]
+ transform_list.append(transforms.Resize(osize, method))
+ elif 'scale_width' in opt.preprocess:
+ transform_list.append(transforms.Lambda(lambda img: __scale_width(img, opt.load_size, method)))
+
+ if 'crop' in opt.preprocess:
+ if params is None:
+ transform_list.append(transforms.RandomCrop(opt.crop_size))
+ else:
+ transform_list.append(transforms.Lambda(lambda img: __crop(img, params['crop_pos'], opt.crop_size)))
+
+ if opt.preprocess == 'none':
+ transform_list.append(transforms.Lambda(lambda img: __make_power_2(img, base=4, method=method)))
+
+ if not opt.no_flip:
+ if params is None:
+ transform_list.append(transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip())
+ elif params['flip']:
+ transform_list.append(transforms.Lambda(lambda img: __flip(img, params['flip'])))
+
+ if convert:
+ transform_list += [transforms.ToTensor()]
+ if grayscale:
+ transform_list += [transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))]
+ else:
+ transform_list += [transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]
return transforms.Compose(transform_list)
-def __scale_width(img, target_width):
+def __make_power_2(img, base, method=Image.BICUBIC):
+ ow, oh = img.size
+ h = int(round(oh / base) * base)
+ w = int(round(ow / base) * base)
+ if (h == oh) and (w == ow):
+ return img
+
+ __print_size_warning(ow, oh, w, h)
+ return img.resize((w, h), method)
+
+
+def __scale_width(img, target_width, method=Image.BICUBIC):
ow, oh = img.size
if (ow == target_width):
return img
w = target_width
h = int(target_width * oh / ow)
- return img.resize((w, h), Image.BICUBIC)
+ return img.resize((w, h), method)
+
+
+def __crop(img, pos, size):
+ ow, oh = img.size
+ x1, y1 = pos
+ tw = th = size
+ if (ow > tw or oh > th):
+ return img.crop((x1, y1, x1 + tw, y1 + th))
+ return img
+
+
+def __flip(img, flip):
+ if flip:
+ return img.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
+ return img
+
+
+def __print_size_warning(ow, oh, w, h):
+ """Print warning information about image size(only print once)"""
+ if not hasattr(__print_size_warning, 'has_printed'):
+ print("The image size needs to be a multiple of 4. "
+ "The loaded image size was (%d, %d), so it was adjusted to "
+ "(%d, %d). This adjustment will be done to all images "
+ "whose sizes are not multiples of 4" % (ow, oh, w, h))
+ __print_size_warning.has_printed = True
diff --git a/data/colorization_dataset.py b/data/colorization_dataset.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2616c61b649
--- /dev/null
+++ b/data/colorization_dataset.py
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+import os.path
+from data.base_dataset import BaseDataset, get_transform
+from data.image_folder import make_dataset
+from skimage import color # require skimage
+from PIL import Image
+import numpy as np
+import torchvision.transforms as transforms
+
+
+class ColorizationDataset(BaseDataset):
+ """This dataset class can load a set of natural images in RGB, and convert RGB format into (L, ab) pairs in Lab color space.
+
+ This dataset is required by pix2pix-based colorization model ('--model colorization')
+ """
+ @staticmethod
+ def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train):
+ """Add new dataset-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.
+
+ Parameters:
+ parser -- original option parser
+ is_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
+
+ Returns:
+ the modified parser.
+
+ By default, the number of channels for input image is 1 (L) and
+ the nubmer of channels for output image is 2 (ab). The direction is from A to B
+ """
+ parser.set_defaults(input_nc=1, output_nc=2, direction='AtoB')
+ return parser
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize this dataset class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class) -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ """
+ BaseDataset.__init__(self, opt)
+ self.dir = os.path.join(opt.dataroot, opt.phase)
+ self.AB_paths = sorted(make_dataset(self.dir, opt.max_dataset_size))
+ assert(opt.input_nc == 1 and opt.output_nc == 2 and opt.direction == 'AtoB')
+ self.transform = get_transform(self.opt, convert=False)
+
+ def __getitem__(self, index):
+ """Return a data point and its metadata information.
+
+ Parameters:
+ index - - a random integer for data indexing
+
+ Returns a dictionary that contains A, B, A_paths and B_paths
+ A (tensor) - - the L channel of an image
+ B (tensor) - - the ab channels of the same image
+ A_paths (str) - - image paths
+ B_paths (str) - - image paths (same as A_paths)
+ """
+ path = self.AB_paths[index]
+ im = Image.open(path).convert('RGB')
+ im = self.transform(im)
+ im = np.array(im)
+ lab = color.rgb2lab(im).astype(np.float32)
+ lab_t = transforms.ToTensor()(lab)
+ A = lab_t[[0], ...] / 50.0 - 1.0
+ B = lab_t[[1, 2], ...] / 110.0
+ return {'A': A, 'B': B, 'A_paths': path, 'B_paths': path}
+
+ def __len__(self):
+ """Return the total number of images in the dataset."""
+ return len(self.AB_paths)
diff --git a/data/image_folder.py b/data/image_folder.py
index 898200b2274..a9cea74d7e7 100644
--- a/data/image_folder.py
+++ b/data/image_folder.py
@@ -1,9 +1,8 @@
-###############################################################################
-# Code from
-# https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/datasets/folder.py
-# Modified the original code so that it also loads images from the current
-# directory as well as the subdirectories
-###############################################################################
+"""A modified image folder class
+
+We modify the official PyTorch image folder (https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/datasets/folder.py)
+so that this class can load images from both current directory and its subdirectories.
+"""
import torch.utils.data as data
@@ -21,7 +20,7 @@ def is_image_file(filename):
return any(filename.endswith(extension) for extension in IMG_EXTENSIONS)
-def make_dataset(dir):
+def make_dataset(dir, max_dataset_size=float("inf")):
images = []
assert os.path.isdir(dir), '%s is not a valid directory' % dir
@@ -30,8 +29,7 @@ def make_dataset(dir):
if is_image_file(fname):
path = os.path.join(root, fname)
images.append(path)
-
- return images
+ return images[:min(max_dataset_size, len(images))]
def default_loader(path):
diff --git a/data/single_dataset.py b/data/single_dataset.py
index 12083b15dde..9a5c3232f2f 100644
--- a/data/single_dataset.py
+++ b/data/single_dataset.py
@@ -1,38 +1,40 @@
-import os.path
from data.base_dataset import BaseDataset, get_transform
from data.image_folder import make_dataset
from PIL import Image
class SingleDataset(BaseDataset):
- def initialize(self, opt):
- self.opt = opt
- self.root = opt.dataroot
- self.dir_A = os.path.join(opt.dataroot)
+ """This dataset class can load a set of images specified by the path --dataroot /path/to/data.
- self.A_paths = make_dataset(self.dir_A)
+ It can be used for generating CycleGAN results only for one side with the model option '-model test'.
+ """
- self.A_paths = sorted(self.A_paths)
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize this dataset class.
- self.transform = get_transform(opt)
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class) -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ """
+ BaseDataset.__init__(self, opt)
+ self.A_paths = sorted(make_dataset(opt.dataroot, opt.max_dataset_size))
+ input_nc = self.opt.output_nc if self.opt.direction == 'BtoA' else self.opt.input_nc
+ self.transform = get_transform(opt, grayscale=(input_nc == 1))
def __getitem__(self, index):
+ """Return a data point and its metadata information.
+
+ Parameters:
+ index - - a random integer for data indexing
+
+ Returns a dictionary that contains A and A_paths
+ A(tensor) - - an image in one domain
+ A_paths(str) - - the path of the image
+ """
A_path = self.A_paths[index]
A_img = Image.open(A_path).convert('RGB')
A = self.transform(A_img)
- if self.opt.which_direction == 'BtoA':
- input_nc = self.opt.output_nc
- else:
- input_nc = self.opt.input_nc
-
- if input_nc == 1: # RGB to gray
- tmp = A[0, ...] * 0.299 + A[1, ...] * 0.587 + A[2, ...] * 0.114
- A = tmp.unsqueeze(0)
-
return {'A': A, 'A_paths': A_path}
def __len__(self):
+ """Return the total number of images in the dataset."""
return len(self.A_paths)
-
- def name(self):
- return 'SingleImageDataset'
diff --git a/data/template_dataset.py b/data/template_dataset.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bfdf16be2a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/data/template_dataset.py
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+"""Dataset class template
+
+This module provides a template for users to implement custom datasets.
+You can specify '--dataset_mode template' to use this dataset.
+The class name should be consistent with both the filename and its dataset_mode option.
+The filename should be _dataset.py
+The class name should be Dataset.py
+You need to implement the following functions:
+ -- : Add dataset-specific options and rewrite default values for existing options.
+ -- <__init__>: Initialize this dataset class.
+ -- <__getitem__>: Return a data point and its metadata information.
+ -- <__len__>: Return the number of images.
+"""
+from data.base_dataset import BaseDataset, get_transform
+# from data.image_folder import make_dataset
+# from PIL import Image
+
+
+class TemplateDataset(BaseDataset):
+ """A template dataset class for you to implement custom datasets."""
+ @staticmethod
+ def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train):
+ """Add new dataset-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.
+
+ Parameters:
+ parser -- original option parser
+ is_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
+
+ Returns:
+ the modified parser.
+ """
+ parser.add_argument('--new_dataset_option', type=float, default=1.0, help='new dataset option')
+ parser.set_defaults(max_dataset_size=10, new_dataset_option=2.0) # specify dataset-specific default values
+ return parser
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize this dataset class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class) -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+
+ A few things can be done here.
+ - save the options (have been done in BaseDataset)
+ - get image paths and meta information of the dataset.
+ - define the image transformation.
+ """
+ # save the option and dataset root
+ BaseDataset.__init__(self, opt)
+ # get the image paths of your dataset;
+ self.image_paths = [] # You can call sorted(make_dataset(self.root, opt.max_dataset_size)) to get all the image paths under the directory self.root
+ # define the default transform function. You can use ; You can also define your custom transform function
+ self.transform = get_transform(opt)
+
+ def __getitem__(self, index):
+ """Return a data point and its metadata information.
+
+ Parameters:
+ index -- a random integer for data indexing
+
+ Returns:
+ a dictionary of data with their names. It usually contains the data itself and its metadata information.
+
+ Step 1: get a random image path: e.g., path = self.image_paths[index]
+ Step 2: load your data from the disk: e.g., image = Image.open(path).convert('RGB').
+ Step 3: convert your data to a PyTorch tensor. You can use helpder functions such as self.transform. e.g., data = self.transform(image)
+ Step 4: return a data point as a dictionary.
+ """
+ path = 'temp' # needs to be a string
+ data_A = None # needs to be a tensor
+ data_B = None # needs to be a tensor
+ return {'data_A': data_A, 'data_B': data_B, 'path': path}
+
+ def __len__(self):
+ """Return the total number of images."""
+ return len(self.image_paths)
diff --git a/data/unaligned_dataset.py b/data/unaligned_dataset.py
index 2f59b2ae20d..832bc88cdcb 100644
--- a/data/unaligned_dataset.py
+++ b/data/unaligned_dataset.py
@@ -6,53 +6,66 @@
class UnalignedDataset(BaseDataset):
- def initialize(self, opt):
- self.opt = opt
- self.root = opt.dataroot
- self.dir_A = os.path.join(opt.dataroot, opt.phase + 'A')
- self.dir_B = os.path.join(opt.dataroot, opt.phase + 'B')
+ """
+ This dataset class can load unaligned/unpaired datasets.
- self.A_paths = make_dataset(self.dir_A)
- self.B_paths = make_dataset(self.dir_B)
+ It requires two directories to host training images from domain A '/path/to/data/trainA'
+ and from domain B '/path/to/data/trainB' respectively.
+ You can train the model with the dataset flag '--dataroot /path/to/data'.
+ Similarly, you need to prepare two directories:
+ '/path/to/data/testA' and '/path/to/data/testB' during test time.
+ """
- self.A_paths = sorted(self.A_paths)
- self.B_paths = sorted(self.B_paths)
- self.A_size = len(self.A_paths)
- self.B_size = len(self.B_paths)
- self.transform = get_transform(opt)
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize this dataset class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class) -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ """
+ BaseDataset.__init__(self, opt)
+ self.dir_A = os.path.join(opt.dataroot, opt.phase + 'A') # create a path '/path/to/data/trainA'
+ self.dir_B = os.path.join(opt.dataroot, opt.phase + 'B') # create a path '/path/to/data/trainB'
+
+ self.A_paths = sorted(make_dataset(self.dir_A, opt.max_dataset_size)) # load images from '/path/to/data/trainA'
+ self.B_paths = sorted(make_dataset(self.dir_B, opt.max_dataset_size)) # load images from '/path/to/data/trainB'
+ self.A_size = len(self.A_paths) # get the size of dataset A
+ self.B_size = len(self.B_paths) # get the size of dataset B
+ btoA = self.opt.direction == 'BtoA'
+ input_nc = self.opt.output_nc if btoA else self.opt.input_nc # get the number of channels of input image
+ output_nc = self.opt.input_nc if btoA else self.opt.output_nc # get the number of channels of output image
+ self.transform_A = get_transform(self.opt, grayscale=(input_nc == 1))
+ self.transform_B = get_transform(self.opt, grayscale=(output_nc == 1))
def __getitem__(self, index):
- A_path = self.A_paths[index % self.A_size]
- if self.opt.serial_batches:
+ """Return a data point and its metadata information.
+
+ Parameters:
+ index (int) -- a random integer for data indexing
+
+ Returns a dictionary that contains A, B, A_paths and B_paths
+ A (tensor) -- an image in the input domain
+ B (tensor) -- its corresponding image in the target domain
+ A_paths (str) -- image paths
+ B_paths (str) -- image paths
+ """
+ A_path = self.A_paths[index % self.A_size] # make sure index is within then range
+ if self.opt.serial_batches: # make sure index is within then range
index_B = index % self.B_size
- else:
+ else: # randomize the index for domain B to avoid fixed pairs.
index_B = random.randint(0, self.B_size - 1)
B_path = self.B_paths[index_B]
- # print('(A, B) = (%d, %d)' % (index_A, index_B))
A_img = Image.open(A_path).convert('RGB')
B_img = Image.open(B_path).convert('RGB')
+ # apply image transformation
+ A = self.transform_A(A_img)
+ B = self.transform_B(B_img)
- A = self.transform(A_img)
- B = self.transform(B_img)
- if self.opt.which_direction == 'BtoA':
- input_nc = self.opt.output_nc
- output_nc = self.opt.input_nc
- else:
- input_nc = self.opt.input_nc
- output_nc = self.opt.output_nc
-
- if input_nc == 1: # RGB to gray
- tmp = A[0, ...] * 0.299 + A[1, ...] * 0.587 + A[2, ...] * 0.114
- A = tmp.unsqueeze(0)
-
- if output_nc == 1: # RGB to gray
- tmp = B[0, ...] * 0.299 + B[1, ...] * 0.587 + B[2, ...] * 0.114
- B = tmp.unsqueeze(0)
- return {'A': A, 'B': B,
- 'A_paths': A_path, 'B_paths': B_path}
+ return {'A': A, 'B': B, 'A_paths': A_path, 'B_paths': B_path}
def __len__(self):
- return max(self.A_size, self.B_size)
+ """Return the total number of images in the dataset.
- def name(self):
- return 'UnalignedDataset'
+ As we have two datasets with potentially different number of images,
+ we take a maximum of
+ """
+ return max(self.A_size, self.B_size)
diff --git a/datasets/bibtex/transattr.tex b/datasets/bibtex/transattr.tex
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..05858499616
--- /dev/null
+++ b/datasets/bibtex/transattr.tex
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+@article {Laffont14,
+ title = {Transient Attributes for High-Level Understanding and Editing of Outdoor Scenes},
+ author = {Pierre-Yves Laffont and Zhile Ren and Xiaofeng Tao and Chao Qian and James Hays},
+ journal = {ACM Transactions on Graphics (proceedings of SIGGRAPH)},
+ volume = {33},
+ number = {4},
+ year = {2014}
+}
diff --git a/datasets/combine_A_and_B.py b/datasets/combine_A_and_B.py
index 70907adbec6..2eebdafba01 100644
--- a/datasets/combine_A_and_B.py
+++ b/datasets/combine_A_and_B.py
@@ -7,12 +7,12 @@
parser.add_argument('--fold_A', dest='fold_A', help='input directory for image A', type=str, default='../dataset/50kshoes_edges')
parser.add_argument('--fold_B', dest='fold_B', help='input directory for image B', type=str, default='../dataset/50kshoes_jpg')
parser.add_argument('--fold_AB', dest='fold_AB', help='output directory', type=str, default='../dataset/test_AB')
-parser.add_argument('--num_imgs', dest='num_imgs', help='number of images',type=int, default=1000000)
-parser.add_argument('--use_AB', dest='use_AB', help='if true: (0001_A, 0001_B) to (0001_AB)',action='store_true')
+parser.add_argument('--num_imgs', dest='num_imgs', help='number of images', type=int, default=1000000)
+parser.add_argument('--use_AB', dest='use_AB', help='if true: (0001_A, 0001_B) to (0001_AB)', action='store_true')
args = parser.parse_args()
for arg in vars(args):
- print('[%s] = ' % arg, getattr(args, arg))
+ print('[%s] = ' % arg, getattr(args, arg))
splits = os.listdir(args.fold_A)
@@ -40,9 +40,9 @@
if os.path.isfile(path_A) and os.path.isfile(path_B):
name_AB = name_A
if args.use_AB:
- name_AB = name_AB.replace('_A.', '.') # remove _A
+ name_AB = name_AB.replace('_A.', '.') # remove _A
path_AB = os.path.join(img_fold_AB, name_AB)
- im_A = cv2.imread(path_A, cv2.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR)
- im_B = cv2.imread(path_B, cv2.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR)
+ im_A = cv2.imread(path_A, 1) # python2: cv2.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR; python3: cv2.IMREAD_COLOR
+ im_B = cv2.imread(path_B, 1) # python2: cv2.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR; python3: cv2.IMREAD_COLOR
im_AB = np.concatenate([im_A, im_B], 1)
cv2.imwrite(path_AB, im_AB)
diff --git a/datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh b/datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh
index 1f0b1631855..5cae4479bc8 100755
--- a/datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh
+++ b/datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh
@@ -1,10 +1,17 @@
FILE=$1
-if [[ $FILE != "ae_photos" && $FILE != "apple2orange" && $FILE != "summer2winter_yosemite" && $FILE != "horse2zebra" && $FILE != "monet2photo" && $FILE != "cezanne2photo" && $FILE != "ukiyoe2photo" && $FILE != "vangogh2photo" && $FILE != "maps" && $FILE != "cityscapes" && $FILE != "facades" && $FILE != "iphone2dslr_flower" && $FILE != "ae_photos" ]]; then
+if [[ $FILE != "ae_photos" && $FILE != "apple2orange" && $FILE != "summer2winter_yosemite" && $FILE != "horse2zebra" && $FILE != "monet2photo" && $FILE != "cezanne2photo" && $FILE != "ukiyoe2photo" && $FILE != "vangogh2photo" && $FILE != "maps" && $FILE != "cityscapes" && $FILE != "facades" && $FILE != "iphone2dslr_flower" && $FILE != "mini" && $FILE != "mini_pix2pix" && $FILE != "mini_colorization" ]]; then
echo "Available datasets are: apple2orange, summer2winter_yosemite, horse2zebra, monet2photo, cezanne2photo, ukiyoe2photo, vangogh2photo, maps, cityscapes, facades, iphone2dslr_flower, ae_photos"
exit 1
fi
+if [[ $FILE == "cityscapes" ]]; then
+ echo "Due to license issue, we cannot provide the Cityscapes dataset from our repository. Please download the Cityscapes dataset from https://cityscapes-dataset.com, and use the script ./datasets/prepare_cityscapes_dataset.py."
+ echo "You need to download gtFine_trainvaltest.zip and leftImg8bit_trainvaltest.zip. For further instruction, please read ./datasets/prepare_cityscapes_dataset.py"
+ exit 1
+fi
+
+echo "Specified [$FILE]"
URL=https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~taesung_park/CycleGAN/datasets/$FILE.zip
ZIP_FILE=./datasets/$FILE.zip
TARGET_DIR=./datasets/$FILE/
diff --git a/datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh b/datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh
index 2d28e4f38eb..4cfbfb1fb00 100755
--- a/datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh
+++ b/datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh
@@ -1,8 +1,22 @@
FILE=$1
-URL=https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz/projects/pix2pix/datasets/$FILE.tar.gz
+
+if [[ $FILE != "cityscapes" && $FILE != "night2day" && $FILE != "edges2handbags" && $FILE != "edges2shoes" && $FILE != "facades" && $FILE != "maps" ]]; then
+ echo "Available datasets are cityscapes, night2day, edges2handbags, edges2shoes, facades, maps"
+ exit 1
+fi
+
+if [[ $FILE == "cityscapes" ]]; then
+ echo "Due to license issue, we cannot provide the Cityscapes dataset from our repository. Please download the Cityscapes dataset from https://cityscapes-dataset.com, and use the script ./datasets/prepare_cityscapes_dataset.py."
+ echo "You need to download gtFine_trainvaltest.zip and leftImg8bit_trainvaltest.zip. For further instruction, please read ./datasets/prepare_cityscapes_dataset.py"
+ exit 1
+fi
+
+echo "Specified [$FILE]"
+
+URL=http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/pix2pix/datasets/$FILE.tar.gz
TAR_FILE=./datasets/$FILE.tar.gz
TARGET_DIR=./datasets/$FILE/
wget -N $URL -O $TAR_FILE
-mkdir $TARGET_DIR
+mkdir -p $TARGET_DIR
tar -zxvf $TAR_FILE -C ./datasets/
-rm $TAR_FILE
\ No newline at end of file
+rm $TAR_FILE
diff --git a/datasets/prepare_cityscapes_dataset.py b/datasets/prepare_cityscapes_dataset.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..20791398df4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/datasets/prepare_cityscapes_dataset.py
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+import os
+import glob
+from PIL import Image
+
+help_msg = """
+The dataset can be downloaded from https://cityscapes-dataset.com.
+Please download the datasets [gtFine_trainvaltest.zip] and [leftImg8bit_trainvaltest.zip] and unzip them.
+gtFine contains the semantics segmentations. Use --gtFine_dir to specify the path to the unzipped gtFine_trainvaltest directory.
+leftImg8bit contains the dashcam photographs. Use --leftImg8bit_dir to specify the path to the unzipped leftImg8bit_trainvaltest directory.
+The processed images will be placed at --output_dir.
+
+Example usage:
+
+python prepare_cityscapes_dataset.py --gitFine_dir ./gtFine/ --leftImg8bit_dir ./leftImg8bit --output_dir ./datasets/cityscapes/
+"""
+
+def load_resized_img(path):
+ return Image.open(path).convert('RGB').resize((256, 256))
+
+def check_matching_pair(segmap_path, photo_path):
+ segmap_identifier = os.path.basename(segmap_path).replace('_gtFine_color', '')
+ photo_identifier = os.path.basename(photo_path).replace('_leftImg8bit', '')
+
+ assert segmap_identifier == photo_identifier, \
+ "[%s] and [%s] don't seem to be matching. Aborting." % (segmap_path, photo_path)
+
+
+def process_cityscapes(gtFine_dir, leftImg8bit_dir, output_dir, phase):
+ save_phase = 'test' if phase == 'val' else 'train'
+ savedir = os.path.join(output_dir, save_phase)
+ os.makedirs(savedir, exist_ok=True)
+ os.makedirs(savedir + 'A', exist_ok=True)
+ os.makedirs(savedir + 'B', exist_ok=True)
+ print("Directory structure prepared at %s" % output_dir)
+
+ segmap_expr = os.path.join(gtFine_dir, phase) + "/*/*_color.png"
+ segmap_paths = glob.glob(segmap_expr)
+ segmap_paths = sorted(segmap_paths)
+
+ photo_expr = os.path.join(leftImg8bit_dir, phase) + "/*/*_leftImg8bit.png"
+ photo_paths = glob.glob(photo_expr)
+ photo_paths = sorted(photo_paths)
+
+ assert len(segmap_paths) == len(photo_paths), \
+ "%d images that match [%s], and %d images that match [%s]. Aborting." % (len(segmap_paths), segmap_expr, len(photo_paths), photo_expr)
+
+ for i, (segmap_path, photo_path) in enumerate(zip(segmap_paths, photo_paths)):
+ check_matching_pair(segmap_path, photo_path)
+ segmap = load_resized_img(segmap_path)
+ photo = load_resized_img(photo_path)
+
+ # data for pix2pix where the two images are placed side-by-side
+ sidebyside = Image.new('RGB', (512, 256))
+ sidebyside.paste(segmap, (256, 0))
+ sidebyside.paste(photo, (0, 0))
+ savepath = os.path.join(savedir, "%d.jpg" % i)
+ sidebyside.save(savepath, format='JPEG', subsampling=0, quality=100)
+
+ # data for cyclegan where the two images are stored at two distinct directories
+ savepath = os.path.join(savedir + 'A', "%d_A.jpg" % i)
+ photo.save(savepath, format='JPEG', subsampling=0, quality=100)
+ savepath = os.path.join(savedir + 'B', "%d_B.jpg" % i)
+ segmap.save(savepath, format='JPEG', subsampling=0, quality=100)
+
+ if i % (len(segmap_paths) // 10) == 0:
+ print("%d / %d: last image saved at %s, " % (i, len(segmap_paths), savepath))
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ import argparse
+ parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
+ parser.add_argument('--gtFine_dir', type=str, required=True,
+ help='Path to the Cityscapes gtFine directory.')
+ parser.add_argument('--leftImg8bit_dir', type=str, required=True,
+ help='Path to the Cityscapes leftImg8bit_trainvaltest directory.')
+ parser.add_argument('--output_dir', type=str, required=True,
+ default='./datasets/cityscapes',
+ help='Directory the output images will be written to.')
+ opt = parser.parse_args()
+
+ print(help_msg)
+
+ print('Preparing Cityscapes Dataset for val phase')
+ process_cityscapes(opt.gtFine_dir, opt.leftImg8bit_dir, opt.output_dir, "val")
+ print('Preparing Cityscapes Dataset for train phase')
+ process_cityscapes(opt.gtFine_dir, opt.leftImg8bit_dir, opt.output_dir, "train")
+
+ print('Done')
+
+
+
diff --git a/docs/Dockerfile b/docs/Dockerfile
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..99cb43db64c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/Dockerfile
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+FROM nvidia/cuda:9.0-base
+
+RUN apt update && apt install -y wget unzip curl bzip2 git
+RUN curl -LO http://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
+RUN bash Miniconda-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh -p /miniconda -b
+RUN rm Miniconda-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
+ENV PATH=/miniconda/bin:${PATH}
+RUN conda update -y conda
+
+RUN conda install -y pytorch torchvision -c pytorch
+RUN mkdir /workspace/ && cd /workspace/ && git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix.git && cd pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix && pip install -r requirements.txt
+
+WORKDIR /workspace
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/datasets.md b/docs/datasets.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b53c7db4b6d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/datasets.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+
+
+### CycleGAN Datasets
+Download the CycleGAN datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
+```bash
+bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh dataset_name
+```
+- `facades`: 400 images from the [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](../datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
+- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](../datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]. Note: Due to license issue, we cannot directly provide the Cityscapes dataset. Please download the Cityscapes dataset from [https://cityscapes-dataset.com](https://cityscapes-dataset.com) and use the script `./datasets/prepare_cityscapes_dataset.py`.
+- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps.
+- `horse2zebra`: 939 horse images and 1177 zebra images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `wild horse` and `zebra`
+- `apple2orange`: 996 apple images and 1020 orange images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `apple` and `navel orange`.
+- `summer2winter_yosemite`: 1273 summer Yosemite images and 854 winter Yosemite images were downloaded using Flickr API. See more details in our paper.
+- `monet2photo`, `vangogh2photo`, `ukiyoe2photo`, `cezanne2photo`: The art images were downloaded from [Wikiart](https://www.wikiart.org/). The real photos are downloaded from Flickr using the combination of the tags *landscape* and *landscapephotography*. The training set size of each class is Monet:1074, Cezanne:584, Van Gogh:401, Ukiyo-e:1433, Photographs:6853.
+- `iphone2dslr_flower`: both classes of images were downlaoded from Flickr. The training set size of each class is iPhone:1813, DSLR:3316. See more details in our paper.
+
+To train a model on your own datasets, you need to create a data folder with two subdirectories `trainA` and `trainB` that contain images from domain A and B. You can test your model on your training set by setting `--phase train` in `test.py`. You can also create subdirectories `testA` and `testB` if you have test data.
+
+You should **not** expect our method to work on just any random combination of input and output datasets (e.g. `cats<->keyboards`). From our experiments, we find it works better if two datasets share similar visual content. For example, `landscape painting<->landscape photographs` works much better than `portrait painting <-> landscape photographs`. `zebras<->horses` achieves compelling results while `cats<->dogs` completely fails.
+
+### pix2pix datasets
+Download the pix2pix datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
+```bash
+bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh dataset_name
+```
+- `facades`: 400 images from [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](../datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
+- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](../datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
+- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps
+- `edges2shoes`: 50k training images from [UT Zappos50K dataset](http://vision.cs.utexas.edu/projects/finegrained/utzap50k). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/shoes.tex)]
+- `edges2handbags`: 137K Amazon Handbag images from [iGAN project](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/handbags.tex)]
+- `night2day`: around 20K natural scene images from [Transient Attributes dataset](http://transattr.cs.brown.edu/) [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/transattr.tex)]. To train a `day2night` pix2pix model, you need to add `--direction BtoA`.
+
+We provide a python script to generate pix2pix training data in the form of pairs of images {A,B}, where A and B are two different depictions of the same underlying scene. For example, these might be pairs {label map, photo} or {bw image, color image}. Then we can learn to translate A to B or B to A:
+
+Create folder `/path/to/data` with subfolders `A` and `B`. `A` and `B` should each have their own subfolders `train`, `val`, `test`, etc. In `/path/to/data/A/train`, put training images in style A. In `/path/to/data/B/train`, put the corresponding images in style B. Repeat same for other data splits (`val`, `test`, etc).
+
+Corresponding images in a pair {A,B} must be the same size and have the same filename, e.g., `/path/to/data/A/train/1.jpg` is considered to correspond to `/path/to/data/B/train/1.jpg`.
+
+Once the data is formatted this way, call:
+```bash
+python datasets/combine_A_and_B.py --fold_A /path/to/data/A --fold_B /path/to/data/B --fold_AB /path/to/data
+```
+
+This will combine each pair of images (A,B) into a single image file, ready for training.
diff --git a/docs/docker.md b/docs/docker.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..74043e3a37e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/docker.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+# Docker image with pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
+
+We provide both Dockerfile and pre-built Docker container that can run this code repo.
+
+## Prerequisite
+
+- Install [docker-ce](https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/ubuntu/)
+- Install [nvidia-docker](https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker#quickstart)
+
+## Running pre-built Dockerfile
+
+- Pull the pre-built docker file
+
+```bash
+docker pull taesungp/pytorch-cyclegan-and-pix2pix
+```
+
+- Start an interactive docker session. `-p 8097:8097` option is needed if you want to run `visdom` server on the Docker container.
+
+```bash
+nvidia-docker run -it -p 8097:8097 taesungp/pytorch-cyclegan-and-pix2pix
+```
+
+- Now you are in the Docker environment. Go to our code repo and start running things.
+```bash
+cd /workspace/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
+bash datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades
+python -m visdom.server &
+bash scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
+```
+
+## Running with Dockerfile
+
+We also posted the [Dockerfile](Dockerfile). To generate the pre-built file, download the Dockerfile in this directory and run
+```bash
+docker build -t [target_tag] .
+```
+in the directory that contains the Dockerfile.
diff --git a/docs/overview.md b/docs/overview.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5db2ae9c1ec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/overview.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+## Overview of Code Structure
+To help users better understand and use our codebase, we briefly overview the functionality and implementation of each package and each module. Please see the documentation in each file for more details. If you have questions, you may find useful information in [training/test tips](tips.md) and [frequently asked questions](qa.md).
+
+[train.py](../train.py) is a general-purpose training script. It works for various models (with option `--model`: e.g., `pix2pix`, `cyclegan`, `colorization`) and different datasets (with option `--dataset_mode`: e.g., `aligned`, `unaligned`, `single`, `colorization`). See the main [README](.../README.md) and [training/test tips](tips.md) for more details.
+
+[test.py](../test.py) is a general-purpose test script. Once you have trained your model with `train.py`, you can use this script to test the model. It will load a saved model from `--checkpoints_dir` and save the results to `--results_dir`. See the main [README](.../README.md) and [training/test tips](tips.md) for more details.
+
+
+[data](../data) directory contains all the modules related to data loading and preprocessing. To add a custom dataset class called `dummy`, you need to add a file called `dummy_dataset.py` and define a subclass `DummyDataset` inherited from `BaseDataset`. You need to implement four functions: `__init__` (initialize the class, you need to first call `BaseDataset.__init__(self, opt)`), `__len__` (return the size of dataset), `__getitem__` (get a data point), and optionally `modify_commandline_options` (add dataset-specific options and set default options). Now you can use the dataset class by specifying flag `--dataset_mode dummy`. See our template dataset [class](../data/template_dataset.py) for an example. Below we explain each file in details.
+
+* [\_\_init\_\_.py](../data/__init__.py) implements the interface between this package and training and test scripts. `train.py` and `test.py` call `from data import create_dataset` and `dataset = create_dataset(opt)` to create a dataset given the option `opt`.
+* [base_dataset.py](../data/base_dataset.py) implements an abstract base class ([ABC](https://docs.python.org/3/library/abc.html)) for datasets. It also includes common transformation functions (e.g., `get_transform`, `__scale_width`), which can be later used in subclasses.
+* [image_folder.py](../data/image_folder.py) implements an image folder class. We modify the official PyTorch image folder [code](https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/datasets/folder.py) so that this class can load images from both the current directory and its subdirectories.
+* [template_dataset.py](../data/template_dataset.py) provides a dataset template with detailed documentation. Check out this file if you plan to implement your own dataset.
+* [aligned_dataset.py](../data/aligned_dataset.py) includes a dataset class that can load image pairs. It assumes a single image directory `/path/to/data/train`, which contains image pairs in the form of {A,B}. See [here](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/tips.md#prepare-your-own-datasets-for-pix2pix) on how to prepare aligned datasets. During test time, you need to prepare a directory `/path/to/data/test` as test data.
+* [unaligned_dataset.py](../data/unaligned_dataset.py) includes a dataset class that can load unaligned/unpaired datasets. It assumes that two directories to host training images from domain A `/path/to/data/trainA` and from domain B `/path/to/data/trainB` respectively. Then you can train the model with the dataset flag `--dataroot /path/to/data`. Similarly, you need to prepare two directories `/path/to/data/testA` and `/path/to/data/testB` during test time.
+* [single_dataset.py](../data/single_dataset.py) includes a dataset class that can load a set of single images specified by the path `--dataroot /path/to/data`. It can be used for generating CycleGAN results only for one side with the model option `-model test`.
+* [colorization_dataset.py](../data/colorization_dataset.py) implements a dataset class that can load a set of nature images in RGB, and convert RGB format into (L, ab) pairs in [Lab](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CIELAB_color_space) color space. It is required by pix2pix-based colorization model (`--model colorization`).
+
+
+[models](../models) directory contains modules related to objective functions, optimizations, and network architectures. To add a custom model class called `dummy`, you need to add a file called `dummy_model.py` and define a subclass `DummyModel` inherited from `BaseModel`. You need to implement four functions: `__init__` (initialize the class; you need to first call `BaseModel.__init__(self, opt)`), `set_input` (unpack data from dataset and apply preprocessing), `forward` (generate intermediate results), `optimize_parameters` (calculate loss, gradients, and update network weights), and optionally `modify_commandline_options` (add model-specific options and set default options). Now you can use the model class by specifying flag `--model dummy`. See our template model [class](../models/template_model.py) for an example. Below we explain each file in details.
+
+* [\_\_init\_\_.py](../models/__init__.py) implements the interface between this package and training and test scripts. `train.py` and `test.py` call `from models import create_model` and `model = create_model(opt)` to create a model given the option `opt`. You also need to call `model.setup(opt)` to properly initialize the model.
+* [base_model.py](../models/base_model.py) implements an abstract base class ([ABC](https://docs.python.org/3/library/abc.html)) for models. It also includes commonly used helper functions (e.g., `setup`, `test`, `update_learning_rate`, `save_networks`, `load_networks`), which can be later used in subclasses.
+* [template_model.py](../models/template_model.py) provides a model template with detailed documentation. Check out this file if you plan to implement your own model.
+* [pix2pix_model.py](../models/pix2pix_model.py) implements the pix2pix [model](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/), for learning a mapping from input images to output images given paired data. The model training requires `--dataset_mode aligned` dataset. By default, it uses a `--netG unet256` [U-Net](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1505.04597.pdf) generator, a `--netD basic` discriminator (PatchGAN), and a `--gan_mode vanilla` GAN loss (standard cross-entropy objective).
+* [colorization_model.py](../models/colorization_model.py) implements a subclass of `Pix2PixModel` for image colorization (black & white image to colorful image). The model training requires `-dataset_model colorization` dataset. It trains a pix2pix model, mapping from L channel to ab channels in [Lab](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CIELAB_color_space) color space. By default, the `colorization` dataset will automatically set `--input_nc 1` and `--output_nc 2`.
+* [cycle_gan_model.py](../models/cycle_gan_model.py) implements the CycleGAN [model](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/), for learning image-to-image translation without paired data. The model training requires `--dataset_mode unaligned` dataset. By default, it uses a `--netG resnet_9blocks` ResNet generator, a `--netD basic` discriminator (PatchGAN introduced by pix2pix), and a least-square GANs [objective](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.04076) (`--gan_mode lsgan`).
+* [networks.py](../models/networks.py) module implements network architectures (both generators and discriminators), as well as normalization layers, initialization methods, optimization scheduler (i.e., learning rate policy), and GAN objective function (`vanilla`, `lsgan`, `wgangp`).
+* [test_model.py](../models/test_model.py) implements a model that can be used to generate CycleGAN results for only one direction. This model will automatically set `--dataset_mode single`, which only loads the images from one set. See the test [instruction](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix#apply-a-pre-trained-model-cyclegan) for more details.
+
+[options](../options) directory includes our option modules: training options, test options, and basic options (used in both training and test). `TrainOptions` and `TestOptions` are both subclasses of `BaseOptions`. They will reuse the options defined in `BaseOptions`.
+* [\_\_init\_\_.py](../options/__init__.py) is required to make Python treat the directory `options` as containing packages,
+* [base_options.py](../options/base_options.py) includes options that are used in both training and test. It also implements a few helper functions such as parsing, printing, and saving the options. It also gathers additional options defined in `modify_commandline_options` functions in both dataset class and model class.
+* [train_options.py](../options/train_options.py) includes options that are only used during training time.
+* [test_options.py](../options/test_options.py) includes options that are only used during test time.
+
+
+[util](../util) directory includes a miscellaneous collection of useful helper functions.
+ * [\_\_init\_\_.py](../util/__init__.py) is required to make Python treat the directory `util` as containing packages,
+ * [get_data.py](../util/get_data.py) provides a Python script for downloading CycleGAN and pix2pix datasets. Alternatively, You can also use bash scripts such as [download_pix2pix_model.sh](../scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh) and [download_cyclegan_model.sh](../scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh).
+ * [html.py](../util/html.py) implements a module that saves images into a single HTML file. It consists of functions such as `add_header` (add a text header to the HTML file), `add_images` (add a row of images to the HTML file), `save` (save the HTML to the disk). It is based on Python library `dominate`, a Python library for creating and manipulating HTML documents using a DOM API.
+ * [image_pool.py](../util/image_pool.py) implements an image buffer that stores previously generated images. This buffer enables us to update discriminators using a history of generated images rather than the ones produced by the latest generators. The original idea was discussed in this [paper](http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/papers/Shrivastava_Learning_From_Simulated_CVPR_2017_paper.pdf). The size of the buffer is controlled by the flag `--pool_size`.
+ * [visualizer.py](../util/visualizer.py) includes several functions that can display/save images and print/save logging information. It uses a Python library `visdom` for display and a Python library `dominate` (wrapped in `HTML`) for creating HTML files with images.
+ * [util.py](../util/util.py) consists of simple helper functions such as `tensor2im` (convert a tensor array to a numpy image array), `diagnose_network` (calculate and print the mean of average absolute value of gradients), and `mkdirs` (create multiple directories).
diff --git a/docs/qa.md b/docs/qa.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8d858547f1f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/qa.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+## Frequently Asked Questions
+Before you post a new question, please first look at the following Q & A and existing GitHub issues. You may also want to read [Training/Test tips](docs/tips.md) for more suggestions.
+
+#### Connection Error:HTTPConnectionPool ([#230](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/230), [#24](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/24), [#38](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/38))
+Similar error messages include “Failed to establish a new connection/Connection refused”.
+
+Please start the visdom server before starting the training:
+```bash
+python -m visdom.server
+```
+To install the visdom, you can use the following command:
+```bash
+pip install visdom
+```
+You can also disable the visdom by setting `--display_id 0`.
+
+#### My PyTorch errors on CUDA related code.
+Try to run the following code snippet to make sure that CUDA is working (assuming using PyTorch >= 0.4):
+```python
+import torch
+torch.cuda.init()
+print(torch.randn(1, device='cuda'))
+```
+
+If you met an error, it is likely that your PyTorch build does not work with CUDA, e.g., it is installl from the official MacOS binary, or you have a GPU that is too old and not supported anymore. You may run the the code with CPU using `--gpu_ids -1`.
+
+#### TypeError: Object of type 'Tensor' is not JSON serializable ([#258](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/258))
+Similar errors: AttributeError: module 'torch' has no attribute 'device' ([#314](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/314))
+
+The current code only works with PyTorch 0.4+. An earlier PyTorch version can often cause the above errors.
+
+#### ValueError: empty range for randrange() ([#390](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/390), [#376](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/376), [#194](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/194))
+Similar error messages include "ConnectionRefusedError: [Errno 111] Connection refused"
+
+It is related to data augmentation step. It often happens when you use `--preprocess crop`. The program will crop random `crop_size x crop_size` patches out of the input training images. But if some of your image sizes (e.g., `256x384`) are smaller than the `crop_size` (e.g., 512), you will get this error. A simple fix will be to use other data augmentation methods such as `resize_and_crop` or `scale_width_and_crop`. Our program will automatically resize the images according to `load_size` before apply `crop_size x crop_size` cropping. Make sure that `load_size >= crop_size`.
+
+
+#### Can I continue/resume my training? ([#350](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/350), [#275](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/275), [#234](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/234), [#87](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/87))
+You can use the option `--continue_train`. Also set `--epoch_count` to specify a different starting epoch count. See more discussion in [training/test tips](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/tips.md#trainingtest-tips).
+
+#### Why does my training loss not converge? ([#335](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/335), [#164](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/164), [#30](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/30))
+Many GAN losses do not converge (exception: WGAN, WGAN-GP, etc. ) due to the nature of minimax optimization. For DCGAN and LSGAN objective, it is quite normal for the G and D losses to go up and down. It should be fine as long as they do not blow up.
+
+#### How can I make it work for my own data (e.g., 16-bit png, tiff, hyperspectral images)? ([#309](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/309), [#320](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/), [#202](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/202))
+The current code only supports RGB and grayscale images. If you would like to train the model on other data types, please follow the following steps:
+
+- change the parameters `--input_nc` and `--output_nc` to the number of channels in your input/output images.
+- Write your own custom data loader (It is easy as long as you know how to load your data with python). If you write a new data loader class, you need to change the flag `--dataset_mode` accordingly. Alternatively, you can modify the existing data loader. For aligned datasets, change this [line](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/data/aligned_dataset.py#L41); For unaligned datasets, change these two [lines](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/data/unaligned_dataset.py#L57).
+
+- If you use visdom and HTML to visualize the results, you may also need to change the visualization code.
+
+#### Multi-GPU Training ([#327](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/327), [#292](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/292), [#137](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/137), [#35](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/35))
+You can use Multi-GPU training by setting `--gpu_ids` (e.g., `--gpu_ids 0,1,2,3` for the first four GPUs on your machine.) To fully utilize all the GPUs, you need to increase your batch size. Try `--batch_size 4`, `--batch_size 16`, or even a larger batch_size. Each GPU will process batch_size/#GPUs images. The optimal batch size depends on the number of GPUs you have, GPU memory per GPU, and the resolution of your training images.
+
+We also recommend that you use the instance normalization for multi-GPU training by setting `--norm instance`. The current batch normalization might not work for multi-GPUs as the batchnorm parameters are not shared across different GPUs. Advanced users can try [synchronized batchnorm](https://github.com/vacancy/Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch).
+
+
+#### Can I run the model on CPU? ([#310](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/310))
+Yes, you can set `--gpu_ids -1`. See [training/test tips](tips.md) for more details.
+
+
+#### Are pre-trained models available? ([#10](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/10))
+Yes, you can download pretrained models with the bash script `./scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh`. See [here](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix#apply-a-pre-trained-model-cyclegan) for more details. We are slowly adding more models to the repo.
+
+#### Out of memory ([#174](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/174))
+CycleGAN is more memory-intensive than pix2pix as it requires two generators and two discriminators. If you would like to produce high-resolution images, you can do the following.
+
+- During training, train CycleGAN on cropped images of the training set. Please be careful not to change the aspect ratio or the scale of the original image, as this can lead to the training/test gap. You can usually do this by using `--preprocess crop` option, or `--preprocess scale_width_and_crop`.
+
+- Then at test time, you can load only one generator to produce the results in a single direction. This greatly saves GPU memory as you are not loading the discriminators and the other generator in the opposite direction. You can probably take the whole image as input. You can do this using `--model test --dataroot [path to the directory that contains your test images (e.g., ./datasets/horse2zebra/trainA)] --model_suffix _A --preprocess none`. You can use either `--preprocess none` or `--preprocess scale_width --crop_size [your_desired_image_width]`. Please see the [model_suffix](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/models/test_model.py#L16) and [preprocess](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/data/base_dataset.py#L24) for more details.
+
+#### What is the identity loss? ([#322](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/322), [#373](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/373), [#362](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/pull/362))
+We use the identity loss for our photo to painting application. The identity loss can regularize the generator to be close to an identity mapping when fed with real samples from the *target* domain. If something already looks like from the target domain, you should preserve the image without making additional changes. The generator trained with this loss will often be more conservative for unknown content. Please see more details in Sec 5.2 ''Photo generation from paintings'' and Figure 12 in the CycleGAN [paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf). The loss was first proposed in the Equation 6 of the prior work [[Taigman et al., 2017]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.02200.pdf).
+
+#### The color gets inverted from the beginning of training ([#249](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/249))
+The authors also observe that the generator unnecessarily inverts the color of the input image early in training, and then never learns to undo the inversion. In this case, you can try two things.
+
+- First, try using identity loss `--lambda_identity 1.0` or `--lambda_identity 0.1`. We observe that the identity loss makes the generator to be more conservative and make fewer unnecessary changes. However, because of this, the change may not be as dramatic.
+
+- Second, try smaller variance when initializing weights by changing `--init_gain`. We observe that smaller variance in weight initialization results in less color inversion.
+
+#### For labels2photo Cityscapes evaluation, why does the pretrained FCN-8s model not work well on the original Cityscapes input images? ([#150](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/150))
+The model was trained on 256x256 images that are resized/upsampled to 1024x2048, so expected input images to the network are very blurry. The purpose of the resizing was to 1) keep the label maps in the original high resolution untouched and 2) avoid the need of changing the standard FCN training code for Cityscapes.
+
+#### How do I get the `ground-truth` numbers on the labels2photo Cityscapes evaluation? ([#150](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/150))
+You need to resize the original Cityscapes images to 256x256 before running the evaluation code.
+
+
+#### Using resize-conv to reduce checkerboard artifacts ([#190](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/190), [#64](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/64))
+This Distill [blog](https://distill.pub/2016/deconv-checkerboard/) discussed one of the potential causes of the checkerboard artifacts. You can fix that issue by switching from "deconvolution" to nearest-neighbor upsampling followed by regular convolution. Here is one implementation provided by [@SsnL](https://github.com/SsnL). You can replace the ConvTranspose2d with the following layers.
+```python
+nn.Upsample(scale_factor = 2, mode='bilinear'),
+nn.ReflectionPad2d(1),
+nn.Conv2d(ngf * mult, int(ngf * mult / 2), kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0),
+```
+We have also noticed that sometimes the checkboard artifacts will go away if you train long enough. Maybe you can try training your model a bit longer.
+
+#### pix2pix/CycleGAN has no random noise z ([#152](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/152))
+The current pix2pix/CycleGAN model does not take z as input. In both pix2pix and CycleGAN, we tried to add z to the generator: e.g., adding z to a latent state, concatenating with a latent state, applying dropout, etc., but often found the output did not vary significantly as a function of z. Conditional GANs do not need noise as long as the input is sufficiently complex so that the input can kind of play the role of noise. Without noise, the mapping is deterministic.
+
+Please check out the following papers that show ways of getting z to actually have a substantial effect: e.g., [BicycleGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/BicycleGAN), [AugmentedCycleGAN](https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.10151), [MUNIT](https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.04732), [DRIT](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1808.00948.pdf), etc.
+
+#### Experiment details (e.g., BW->color) ([#306](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/issues/306))
+You can find more training details and hyperparameter settings in the appendix of [CycleGAN](https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.10593) and [pix2pix](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004) papers.
+
+#### Results with [Cycada](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.03213.pdf)
+We generated the [result of translating GTA images to Cityscapes-style images](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/) using our Torch repo. Our PyTorch and Torch implementation seemed to produce a little bit different results, although we have not measured the FCN score using the pytorch-trained model. To reproduce the result of Cycada, please use the Torch repo for now.
diff --git a/docs/tips.md b/docs/tips.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..182ded2ebdf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/tips.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+## Training/test Tips
+#### Training/test options
+Please see `options/train_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for the training flags; see `options/test_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for the test flags. There are some model-specific flags as well, which are added in the model files, such as `--lambda_A` option in `model/cycle_gan_model.py`. The default values of these options are also adjusted in the model files.
+#### CPU/GPU (default `--gpu_ids 0`)
+Please set`--gpu_ids -1` to use CPU mode; set `--gpu_ids 0,1,2` for multi-GPU mode. You need a large batch size (e.g., `--batch_size 32`) to benefit from multiple GPUs.
+
+#### Visualization
+During training, the current results can be viewed using two methods. First, if you set `--display_id` > 0, the results and loss plot will appear on a local graphics web server launched by [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom). To do this, you should have `visdom` installed and a server running by the command `python -m visdom.server`. The default server URL is `http://localhost:8097`. `display_id` corresponds to the window ID that is displayed on the `visdom` server. The `visdom` display functionality is turned on by default. To avoid the extra overhead of communicating with `visdom` set `--display_id -1`. Second, the intermediate results are saved to `[opt.checkpoints_dir]/[opt.name]/web/` as an HTML file. To avoid this, set `--no_html`.
+
+#### Preprocessing
+ Images can be resized and cropped in different ways using `--preprocess` option. The default option `'resize_and_crop'` resizes the image to be of size `(opt.load_size, opt.load_size)` and does a random crop of size `(opt.crop_size, opt.crop_size)`. `'crop'` skips the resizing step and only performs random cropping. `'scale_width'` resizes the image to have width `opt.crop_size` while keeping the aspect ratio. `'scale_width_and_crop'` first resizes the image to have width `opt.load_size` and then does random cropping of size `(opt.crop_size, opt.crop_size)`. `'none'` tries to skip all these preprocessing steps. However, if the image size is not a multiple of some number depending on the number of downsamplings of the generator, you will get an error because the size of the output image may be different from the size of the input image. Therefore, `'none'` option still tries to adjust the image size to be a multiple of 4. You might need a bigger adjustment if you change the generator architecture. Please see `data/base_datset.py` do see how all these were implemented.
+
+#### Fine-tuning/resume training
+To fine-tune a pre-trained model, or resume the previous training, use the `--continue_train` flag. The program will then load the model based on `epoch`. By default, the program will initialize the epoch count as 1. Set `--epoch_count ` to specify a different starting epoch count.
+
+
+#### Prepare your own datasets for CycleGAN
+You need to create two directories to host images from domain A `/path/to/data/trainA` and from domain B `/path/to/data/trainB`. Then you can train the model with the dataset flag `--dataroot /path/to/data`. Optionally, you can create hold-out test datasets at `/path/to/data/testA` and `/path/to/data/testB` to test your model on unseen images.
+
+#### Prepare your own datasets for pix2pix
+Pix2pix's training requires paired data. We provide a python script to generate training data in the form of pairs of images {A,B}, where A and B are two different depictions of the same underlying scene. For example, these might be pairs {label map, photo} or {bw image, color image}. Then we can learn to translate A to B or B to A:
+
+Create folder `/path/to/data` with subdirectories `A` and `B`. `A` and `B` should each have their own subdirectories `train`, `val`, `test`, etc. In `/path/to/data/A/train`, put training images in style A. In `/path/to/data/B/train`, put the corresponding images in style B. Repeat same for other data splits (`val`, `test`, etc).
+
+Corresponding images in a pair {A,B} must be the same size and have the same filename, e.g., `/path/to/data/A/train/1.jpg` is considered to correspond to `/path/to/data/B/train/1.jpg`.
+
+Once the data is formatted this way, call:
+```bash
+python datasets/combine_A_and_B.py --fold_A /path/to/data/A --fold_B /path/to/data/B --fold_AB /path/to/data
+```
+
+This will combine each pair of images (A,B) into a single image file, ready for training.
+
+
+#### About image size
+ Since the generator architecture in CycleGAN involves a series of downsampling / upsampling operations, the size of the input and output image may not match if the input image size is not a multiple of 4. As a result, you may get a runtime error because the L1 identity loss cannot be enforced with images of different size. Therefore, we slightly resize the image to become multiples of 4 even with `--preprocess none` option. For the same reason, `--crop_size` needs to be a multiple of 4.
+
+#### Training/Testing with high res images
+CycleGAN is quite memory-intensive as four networks (two generators and two discriminators) need to be loaded on one GPU, so a large image cannot be entirely loaded. In this case, we recommend training with cropped images. For example, to generate 1024px results, you can train with `--preprocess scale_width_and_crop --load_size 1024 --crop_size 360`, and test with `--preprocess scale_width --load_size 1024`. This way makes sure the training and test will be at the same scale. At test time, you can afford higher resolution because you don’t need to load all networks.
+
+#### About loss curve
+Unfortunately, the loss curve does not reveal much information in training GANs, and CycleGAN is no exception. To check whether the training has converged or not, we recommend periodically generating a few samples and looking at them.
+
+#### About batch size
+For all experiments in the paper, we set the batch size to be 1. If there is room for memory, you can use higher batch size with batch norm or instance norm. (Note that the default batchnorm does not work well with multi-GPU training. You may consider using [synchronized batchnorm](https://github.com/vacancy/Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch) instead). But please be aware that it can impact the training. In particular, even with Instance Normalization, different batch sizes can lead to different results. Moreover, increasing `--crop_size` may be a good alternative to increasing the batch size.
+
+
+#### Notes on Colorization
+No need to run `combine_A_and_B.py` for colorization. Instead, you need to prepare natural images and set `--dataset_mode colorization` and `--model colorization` in the script. The program will automatically convert each RGB image into Lab color space, and create `L -> ab` image pair during the training. Also set `--input_nc 1` and `--output_nc 2`. The training and test directory should be organized as `/your/data/train` and `your/data/test`. See example scripts `scripts/train_colorization.sh` and `scripts/test_colorization` for more details.
+
+#### Notes on Extracting Edges
+We provide python and Matlab scripts to extract coarse edges from photos. Run `scripts/edges/batch_hed.py` to compute [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edges. Run `scripts/edges/PostprocessHED.m` to simplify edges with additional post-processing steps. Check the code documentation for more details.
+
+#### Evaluating Labels2Photos on Cityscapes
+We provide scripts for running the evaluation of the Labels2Photos task on the Cityscapes **validation** set. We assume that you have installed `caffe` (and `pycaffe`) in your system. If not, see the [official website](http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/installation.html) for installation instructions. Once `caffe` is successfully installed, download the pre-trained FCN-8s semantic segmentation model (512MB) by running
+```bash
+bash ./scripts/eval_cityscapes/download_fcn8s.sh
+```
+Then make sure `./scripts/eval_cityscapes/` is in your system's python path. If not, run the following command to add it
+```bash
+export PYTHONPATH=${PYTHONPATH}:./scripts/eval_cityscapes/
+```
+Now you can run the following command to evaluate your predictions:
+```bash
+python ./scripts/eval_cityscapes/evaluate.py --cityscapes_dir /path/to/original/cityscapes/dataset/ --result_dir /path/to/your/predictions/ --output_dir /path/to/output/directory/
+```
+Images stored under `--result_dir` should contain your model predictions on the Cityscapes **validation** split, and have the original Cityscapes naming convention (e.g., `frankfurt_000001_038418_leftImg8bit.png`). The script will output a text file under `--output_dir` containing the metric.
+
+**Further notes**: The pre-trained model is **not** supposed to work on Cityscapes in the original resolution (1024x2048) as it was trained on 256x256 images that are upsampled to 1024x2048. The purpose of the resizing was to 1) keep the label maps in the original high resolution untouched and 2) avoid the need of changing the standard FCN training code for Cityscapes. To get the *ground-truth* numbers in the paper, you need to resize the original Cityscapes images to 256x256 before running the evaluation code.
diff --git a/environment.yml b/environment.yml
index 116d0521c02..12ed68cfb0c 100644
--- a/environment.yml
+++ b/environment.yml
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ channels:
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.5.5
-- pytorch=0.3.1
+- pytorch=0.4.1
- scipy
- pip:
- dominate==2.3.1
diff --git a/imgs/edges2cats.jpg b/imgs/edges2cats.jpg
index c9586bcfb31..be5c1412eb0 100644
Binary files a/imgs/edges2cats.jpg and b/imgs/edges2cats.jpg differ
diff --git a/models/__init__.py b/models/__init__.py
index 27a4cc1bb29..fc01113da66 100644
--- a/models/__init__.py
+++ b/models/__init__.py
@@ -1,19 +1,67 @@
-def create_model(opt):
+"""This package contains modules related to objective functions, optimizations, and network architectures.
+
+To add a custom model class called 'dummy', you need to add a file called 'dummy_model.py' and define a subclass DummyModel inherited from BaseModel.
+You need to implement the following five functions:
+ -- <__init__>: initialize the class; first call BaseModel.__init__(self, opt).
+ -- : unpack data from dataset and apply preprocessing.
+ -- : produce intermediate results.
+ -- : calculate loss, gradients, and update network weights.
+ -- : (optionally) add model-specific options and set default options.
+
+In the function <__init__>, you need to define four lists:
+ -- self.loss_names (str list): specify the training losses that you want to plot and save.
+ -- self.model_names (str list): define networks used in our training.
+ -- self.visual_names (str list): specify the images that you want to display and save.
+ -- self.optimizers (optimizer list): define and initialize optimizers. You can define one optimizer for each network. If two networks are updated at the same time, you can use itertools.chain to group them. See cycle_gan_model.py for an usage.
+
+Now you can use the model class by specifying flag '--model dummy'.
+See our template model class 'template_model.py' for more details.
+"""
+
+import importlib
+from models.base_model import BaseModel
+
+
+def find_model_using_name(model_name):
+ """Import the module "models/[model_name]_model.py".
+
+ In the file, the class called DatasetNameModel() will
+ be instantiated. It has to be a subclass of BaseModel,
+ and it is case-insensitive.
+ """
+ model_filename = "models." + model_name + "_model"
+ modellib = importlib.import_module(model_filename)
model = None
- if opt.model == 'cycle_gan':
- assert(opt.dataset_mode == 'unaligned')
- from .cycle_gan_model import CycleGANModel
- model = CycleGANModel()
- elif opt.model == 'pix2pix':
- assert(opt.dataset_mode == 'aligned')
- from .pix2pix_model import Pix2PixModel
- model = Pix2PixModel()
- elif opt.model == 'test':
- assert(opt.dataset_mode == 'single')
- from .test_model import TestModel
- model = TestModel()
- else:
- raise NotImplementedError('model [%s] not implemented.' % opt.model)
- model.initialize(opt)
- print("model [%s] was created" % (model.name()))
+ target_model_name = model_name.replace('_', '') + 'model'
+ for name, cls in modellib.__dict__.items():
+ if name.lower() == target_model_name.lower() \
+ and issubclass(cls, BaseModel):
+ model = cls
+
+ if model is None:
+ print("In %s.py, there should be a subclass of BaseModel with class name that matches %s in lowercase." % (model_filename, target_model_name))
+ exit(0)
+
return model
+
+
+def get_option_setter(model_name):
+ """Return the static method of the model class."""
+ model_class = find_model_using_name(model_name)
+ return model_class.modify_commandline_options
+
+
+def create_model(opt):
+ """Create a model given the option.
+
+ This function warps the class CustomDatasetDataLoader.
+ This is the main interface between this package and 'train.py'/'test.py'
+
+ Example:
+ >>> from models import create_model
+ >>> model = create_model(opt)
+ """
+ model = find_model_using_name(opt.model)
+ instance = model(opt)
+ print("model [%s] was created" % type(instance).__name__)
+ return instance
diff --git a/models/base_model.py b/models/base_model.py
index 0564bf05671..307c2ba3132 100644
--- a/models/base_model.py
+++ b/models/base_model.py
@@ -1,90 +1,154 @@
import os
import torch
from collections import OrderedDict
+from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from . import networks
-class BaseModel():
- def name(self):
- return 'BaseModel'
-
- def initialize(self, opt):
+class BaseModel(ABC):
+ """This class is an abstract base class (ABC) for models.
+ To create a subclass, you need to implement the following five functions:
+ -- <__init__>: initialize the class; first call BaseModel.__init__(self, opt).
+ -- : unpack data from dataset and apply preprocessing.
+ -- : produce intermediate results.
+ -- : calculate losses, gradients, and update network weights.
+ -- : (optionally) add model-specific options and set default options.
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize the BaseModel class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class)-- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+
+ When creating your custom class, you need to implement your own initialization.
+ In this fucntion, you should first call
+ Then, you need to define four lists:
+ -- self.loss_names (str list): specify the training losses that you want to plot and save.
+ -- self.model_names (str list): specify the images that you want to display and save.
+ -- self.visual_names (str list): define networks used in our training.
+ -- self.optimizers (optimizer list): define and initialize optimizers. You can define one optimizer for each network. If two networks are updated at the same time, you can use itertools.chain to group them. See cycle_gan_model.py for an example.
+ """
self.opt = opt
self.gpu_ids = opt.gpu_ids
self.isTrain = opt.isTrain
- self.device = torch.device('cuda:{}'.format(self.gpu_ids[0])) if self.gpu_ids else torch.device('cpu')
- self.save_dir = os.path.join(opt.checkpoints_dir, opt.name)
- if opt.resize_or_crop != 'scale_width':
+ self.device = torch.device('cuda:{}'.format(self.gpu_ids[0])) if self.gpu_ids else torch.device('cpu') # get device name: CPU or GPU
+ self.save_dir = os.path.join(opt.checkpoints_dir, opt.name) # save all the checkpoints to save_dir
+ if opt.preprocess != 'scale_width': # with [scale_width], input images might have different sizes, which hurts the performance of cudnn.benchmark.
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
self.loss_names = []
self.model_names = []
self.visual_names = []
+ self.optimizers = []
self.image_paths = []
+ self.metric = 0 # used for learning rate policy 'plateau'
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train):
+ """Add new model-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.
+
+ Parameters:
+ parser -- original option parser
+ is_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
+
+ Returns:
+ the modified parser.
+ """
+ return parser
+ @abstractmethod
def set_input(self, input):
- self.input = input
+ """Unpack input data from the dataloader and perform necessary pre-processing steps.
+ Parameters:
+ input (dict): includes the data itself and its metadata information.
+ """
+ pass
+
+ @abstractmethod
def forward(self):
+ """Run forward pass; called by both functions and ."""
+ pass
+
+ @abstractmethod
+ def optimize_parameters(self):
+ """Calculate losses, gradients, and update network weights; called in every training iteration"""
pass
- # load and print networks; create shedulars
def setup(self, opt):
+ """Load and print networks; create schedulers
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class) -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ """
if self.isTrain:
self.schedulers = [networks.get_scheduler(optimizer, opt) for optimizer in self.optimizers]
-
if not self.isTrain or opt.continue_train:
- self.load_networks(opt.which_epoch)
+ load_suffix = 'iter_%d' % opt.load_iter if opt.load_iter > 0 else opt.epoch
+ self.load_networks(load_suffix)
self.print_networks(opt.verbose)
- # make models eval mode during test time
def eval(self):
+ """Make models eval mode during test time"""
for name in self.model_names:
if isinstance(name, str):
net = getattr(self, 'net' + name)
net.eval()
- # used in test time, wrapping `forward` in no_grad() so we don't save
- # intermediate steps for backprop
def test(self):
+ """Forward function used in test time.
+
+ This function wraps function in no_grad() so we don't save intermediate steps for backprop
+ It also calls to produce additional visualization results
+ """
with torch.no_grad():
self.forward()
+ self.compute_visuals()
+
+ def compute_visuals(self):
+ """Calculate additional output images for visdom and HTML visualization"""
+ pass
- # get image paths
def get_image_paths(self):
+ """ Return image paths that are used to load current data"""
return self.image_paths
- def optimize_parameters(self):
- pass
-
- # update learning rate (called once every epoch)
def update_learning_rate(self):
+ """Update learning rates for all the networks; called at the end of every epoch"""
for scheduler in self.schedulers:
- scheduler.step()
+ if self.opt.lr_policy == 'plateau':
+ scheduler.step(self.metric)
+ else:
+ scheduler.step()
+
lr = self.optimizers[0].param_groups[0]['lr']
print('learning rate = %.7f' % lr)
- # return visualization images. train.py will display these images, and save the images to a html
def get_current_visuals(self):
+ """Return visualization images. train.py will display these images with visdom, and save the images to a HTML"""
visual_ret = OrderedDict()
for name in self.visual_names:
if isinstance(name, str):
visual_ret[name] = getattr(self, name)
return visual_ret
- # return traning losses/errors. train.py will print out these errors as debugging information
def get_current_losses(self):
+ """Return traning losses / errors. train.py will print out these errors on console, and save them to a file"""
errors_ret = OrderedDict()
for name in self.loss_names:
if isinstance(name, str):
- # float(...) works for both scalar tensor and float number
- errors_ret[name] = float(getattr(self, 'loss_' + name))
+ errors_ret[name] = float(getattr(self, 'loss_' + name)) # float(...) works for both scalar tensor and float number
return errors_ret
- # save models to the disk
- def save_networks(self, which_epoch):
+ def save_networks(self, epoch):
+ """Save all the networks to the disk.
+
+ Parameters:
+ epoch (int) -- current epoch; used in the file name '%s_net_%s.pth' % (epoch, name)
+ """
for name in self.model_names:
if isinstance(name, str):
- save_filename = '%s_net_%s.pth' % (which_epoch, name)
+ save_filename = '%s_net_%s.pth' % (epoch, name)
save_path = os.path.join(self.save_dir, save_filename)
net = getattr(self, 'net' + name)
@@ -95,34 +159,50 @@ def save_networks(self, which_epoch):
torch.save(net.cpu().state_dict(), save_path)
def __patch_instance_norm_state_dict(self, state_dict, module, keys, i=0):
+ """Fix InstanceNorm checkpoints incompatibility (prior to 0.4)"""
key = keys[i]
if i + 1 == len(keys): # at the end, pointing to a parameter/buffer
if module.__class__.__name__.startswith('InstanceNorm') and \
(key == 'running_mean' or key == 'running_var'):
if getattr(module, key) is None:
state_dict.pop('.'.join(keys))
+ if module.__class__.__name__.startswith('InstanceNorm') and \
+ (key == 'num_batches_tracked'):
+ state_dict.pop('.'.join(keys))
else:
self.__patch_instance_norm_state_dict(state_dict, getattr(module, key), keys, i + 1)
- # load models from the disk
- def load_networks(self, which_epoch):
+ def load_networks(self, epoch):
+ """Load all the networks from the disk.
+
+ Parameters:
+ epoch (int) -- current epoch; used in the file name '%s_net_%s.pth' % (epoch, name)
+ """
for name in self.model_names:
if isinstance(name, str):
- save_filename = '%s_net_%s.pth' % (which_epoch, name)
- save_path = os.path.join(self.save_dir, save_filename)
+ load_filename = '%s_net_%s.pth' % (epoch, name)
+ load_path = os.path.join(self.save_dir, load_filename)
net = getattr(self, 'net' + name)
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.DataParallel):
net = net.module
+ print('loading the model from %s' % load_path)
# if you are using PyTorch newer than 0.4 (e.g., built from
# GitHub source), you can remove str() on self.device
- state_dict = torch.load(save_path, map_location=str(self.device))
+ state_dict = torch.load(load_path, map_location=str(self.device))
+ if hasattr(state_dict, '_metadata'):
+ del state_dict._metadata
+
# patch InstanceNorm checkpoints prior to 0.4
for key in list(state_dict.keys()): # need to copy keys here because we mutate in loop
self.__patch_instance_norm_state_dict(state_dict, net, key.split('.'))
net.load_state_dict(state_dict)
- # print network information
def print_networks(self, verbose):
+ """Print the total number of parameters in the network and (if verbose) network architecture
+
+ Parameters:
+ verbose (bool) -- if verbose: print the network architecture
+ """
print('---------- Networks initialized -------------')
for name in self.model_names:
if isinstance(name, str):
@@ -134,3 +214,16 @@ def print_networks(self, verbose):
print(net)
print('[Network %s] Total number of parameters : %.3f M' % (name, num_params / 1e6))
print('-----------------------------------------------')
+
+ def set_requires_grad(self, nets, requires_grad=False):
+ """Set requies_grad=Fasle for all the networks to avoid unnecessary computations
+ Parameters:
+ nets (network list) -- a list of networks
+ requires_grad (bool) -- whether the networks require gradients or not
+ """
+ if not isinstance(nets, list):
+ nets = [nets]
+ for net in nets:
+ if net is not None:
+ for param in net.parameters():
+ param.requires_grad = requires_grad
diff --git a/models/colorization_model.py b/models/colorization_model.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2b4a12722e5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/models/colorization_model.py
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+from .pix2pix_model import Pix2PixModel
+import torch
+from skimage import color # used for lab2rgb
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class ColorizationModel(Pix2PixModel):
+ """This is a subclass of Pix2PixModel for image colorization (black & white image -> colorful images).
+
+ The model training requires '-dataset_model colorization' dataset.
+ It trains a pix2pix model, mapping from L channel to ab channels in Lab color space.
+ By default, the colorization dataset will automatically set '--input_nc 1' and '--output_nc 2'.
+ """
+ @staticmethod
+ def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train=True):
+ """Add new dataset-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.
+
+ Parameters:
+ parser -- original option parser
+ is_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
+
+ Returns:
+ the modified parser.
+
+ By default, we use 'colorization' dataset for this model.
+ See the original pix2pix paper (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004.pdf) and colorization results (Figure 9 in the paper)
+ """
+ Pix2PixModel.modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train)
+ parser.set_defaults(dataset_mode='colorization')
+ return parser
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize the class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class)-- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+
+ For visualization, we set 'visual_names' as 'real_A' (input real image),
+ 'real_B_rgb' (ground truth RGB image), and 'fake_B_rgb' (predicted RGB image)
+ We convert the Lab image 'real_B' (inherited from Pix2pixModel) to a RGB image 'real_B_rgb'.
+ we convert the Lab image 'fake_B' (inherited from Pix2pixModel) to a RGB image 'fake_B_rgb'.
+ """
+ # reuse the pix2pix model
+ Pix2PixModel.__init__(self, opt)
+ # specify the images to be visualized.
+ self.visual_names = ['real_A', 'real_B_rgb', 'fake_B_rgb']
+
+ def lab2rgb(self, L, AB):
+ """Convert an Lab tensor image to a RGB numpy output
+ Parameters:
+ L (1-channel tensor array): L channel images (range: [-1, 1], torch tensor array)
+ AB (2-channel tensor array): ab channel images (range: [-1, 1], torch tensor array)
+
+ Returns:
+ rgb (RGB numpy image): rgb output images (range: [0, 255], numpy array)
+ """
+ AB2 = AB * 110.0
+ L2 = (L + 1.0) * 50.0
+ Lab = torch.cat([L2, AB2], dim=1)
+ Lab = Lab[0].data.cpu().float().numpy()
+ Lab = np.transpose(Lab.astype(np.float64), (1, 2, 0))
+ rgb = color.lab2rgb(Lab) * 255
+ return rgb
+
+ def compute_visuals(self):
+ """Calculate additional output images for visdom and HTML visualization"""
+ self.real_B_rgb = self.lab2rgb(self.real_A, self.real_B)
+ self.fake_B_rgb = self.lab2rgb(self.real_A, self.fake_B)
diff --git a/models/cycle_gan_model.py b/models/cycle_gan_model.py
index 5d837d5cfd5..15bb72d8ddc 100644
--- a/models/cycle_gan_model.py
+++ b/models/cycle_gan_model.py
@@ -6,105 +6,159 @@
class CycleGANModel(BaseModel):
- def name(self):
- return 'CycleGANModel'
-
- def initialize(self, opt):
- BaseModel.initialize(self, opt)
-
- # specify the training losses you want to print out. The program will call base_model.get_current_losses
+ """
+ This class implements the CycleGAN model, for learning image-to-image translation without paired data.
+
+ The model training requires '--dataset_mode unaligned' dataset.
+ By default, it uses a '--netG resnet_9blocks' ResNet generator,
+ a '--netD basic' discriminator (PatchGAN introduced by pix2pix),
+ and a least-square GANs objective ('--gan_mode lsgan').
+
+ CycleGAN paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf
+ """
+ @staticmethod
+ def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train=True):
+ """Add new dataset-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.
+
+ Parameters:
+ parser -- original option parser
+ is_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
+
+ Returns:
+ the modified parser.
+
+ For CycleGAN, in addition to GAN losses, we introduce lambda_A, lambda_B, and lambda_identity for the following losses.
+ A (source domain), B (target domain).
+ Generators: G_A: A -> B; G_B: B -> A.
+ Discriminators: D_A: G_A(A) vs. B; D_B: G_B(B) vs. A.
+ Forward cycle loss: lambda_A * ||G_B(G_A(A)) - A|| (Eqn. (2) in the paper)
+ Backward cycle loss: lambda_B * ||G_A(G_B(B)) - B|| (Eqn. (2) in the paper)
+ Identity loss (optional): lambda_identity * (||G_A(B) - B|| * lambda_B + ||G_B(A) - A|| * lambda_A) (Sec 5.2 "Photo generation from paintings" in the paper)
+ Dropout is not used in the original CycleGAN paper.
+ """
+ parser.set_defaults(no_dropout=True) # default CycleGAN did not use dropout
+ if is_train:
+ parser.add_argument('--lambda_A', type=float, default=10.0, help='weight for cycle loss (A -> B -> A)')
+ parser.add_argument('--lambda_B', type=float, default=10.0, help='weight for cycle loss (B -> A -> B)')
+ parser.add_argument('--lambda_identity', type=float, default=0.5, help='use identity mapping. Setting lambda_identity other than 0 has an effect of scaling the weight of the identity mapping loss. For example, if the weight of the identity loss should be 10 times smaller than the weight of the reconstruction loss, please set lambda_identity = 0.1')
+
+ return parser
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize the CycleGAN class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class)-- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ """
+ BaseModel.__init__(self, opt)
+ # specify the training losses you want to print out. The training/test scripts will call
self.loss_names = ['D_A', 'G_A', 'cycle_A', 'idt_A', 'D_B', 'G_B', 'cycle_B', 'idt_B']
- # specify the images you want to save/display. The program will call base_model.get_current_visuals
+ # specify the images you want to save/display. The training/test scripts will call
visual_names_A = ['real_A', 'fake_B', 'rec_A']
visual_names_B = ['real_B', 'fake_A', 'rec_B']
- if self.isTrain and self.opt.lambda_identity > 0.0:
- visual_names_A.append('idt_A')
- visual_names_B.append('idt_B')
+ if self.isTrain and self.opt.lambda_identity > 0.0: # if identity loss is used, we also visualize idt_B=G_A(B) ad idt_A=G_A(B)
+ visual_names_A.append('idt_B')
+ visual_names_B.append('idt_A')
- self.visual_names = visual_names_A + visual_names_B
- # specify the models you want to save to the disk. The program will call base_model.save_networks and base_model.load_networks
+ self.visual_names = visual_names_A + visual_names_B # combine visualizations for A and B
+ # specify the models you want to save to the disk. The training/test scripts will call and .
if self.isTrain:
self.model_names = ['G_A', 'G_B', 'D_A', 'D_B']
else: # during test time, only load Gs
self.model_names = ['G_A', 'G_B']
- # load/define networks
- # The naming conversion is different from those used in the paper
- # Code (paper): G_A (G), G_B (F), D_A (D_Y), D_B (D_X)
- self.netG_A = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc,
- opt.ngf, opt.which_model_netG, opt.norm, not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, self.gpu_ids)
- self.netG_B = networks.define_G(opt.output_nc, opt.input_nc,
- opt.ngf, opt.which_model_netG, opt.norm, not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, self.gpu_ids)
+ # define networks (both Generators and discriminators)
+ # The naming is different from those used in the paper.
+ # Code (vs. paper): G_A (G), G_B (F), D_A (D_Y), D_B (D_X)
+ self.netG_A = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG, opt.norm,
+ not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
+ self.netG_B = networks.define_G(opt.output_nc, opt.input_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG, opt.norm,
+ not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
- if self.isTrain:
- use_sigmoid = opt.no_lsgan
- self.netD_A = networks.define_D(opt.output_nc, opt.ndf,
- opt.which_model_netD,
- opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, use_sigmoid, opt.init_type, self.gpu_ids)
- self.netD_B = networks.define_D(opt.input_nc, opt.ndf,
- opt.which_model_netD,
- opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, use_sigmoid, opt.init_type, self.gpu_ids)
+ if self.isTrain: # define discriminators
+ self.netD_A = networks.define_D(opt.output_nc, opt.ndf, opt.netD,
+ opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
+ self.netD_B = networks.define_D(opt.input_nc, opt.ndf, opt.netD,
+ opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
if self.isTrain:
- self.fake_A_pool = ImagePool(opt.pool_size)
- self.fake_B_pool = ImagePool(opt.pool_size)
+ if opt.lambda_identity > 0.0: # only works when input and output images have the same number of channels
+ assert(opt.input_nc == opt.output_nc)
+ self.fake_A_pool = ImagePool(opt.pool_size) # create image buffer to store previously generated images
+ self.fake_B_pool = ImagePool(opt.pool_size) # create image buffer to store previously generated images
# define loss functions
- self.criterionGAN = networks.GANLoss(use_lsgan=not opt.no_lsgan).to(self.device)
+ self.criterionGAN = networks.GANLoss(opt.gan_mode).to(self.device) # define GAN loss.
self.criterionCycle = torch.nn.L1Loss()
self.criterionIdt = torch.nn.L1Loss()
- # initialize optimizers
- self.optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.netG_A.parameters(), self.netG_B.parameters()),
- lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
- self.optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.netD_A.parameters(), self.netD_B.parameters()),
- lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
- self.optimizers = []
+ # initialize optimizers; schedulers will be automatically created by function .
+ self.optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.netG_A.parameters(), self.netG_B.parameters()), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
+ self.optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.netD_A.parameters(), self.netD_B.parameters()), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_G)
self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_D)
def set_input(self, input):
- AtoB = self.opt.which_direction == 'AtoB'
+ """Unpack input data from the dataloader and perform necessary pre-processing steps.
+
+ Parameters:
+ input (dict): include the data itself and its metadata information.
+
+ The option 'direction' can be used to swap domain A and domain B.
+ """
+ AtoB = self.opt.direction == 'AtoB'
self.real_A = input['A' if AtoB else 'B'].to(self.device)
self.real_B = input['B' if AtoB else 'A'].to(self.device)
self.image_paths = input['A_paths' if AtoB else 'B_paths']
def forward(self):
- self.fake_B = self.netG_A(self.real_A)
- self.rec_A = self.netG_B(self.fake_B)
-
- self.fake_A = self.netG_B(self.real_B)
- self.rec_B = self.netG_A(self.fake_A)
+ """Run forward pass; called by both functions and ."""
+ self.fake_B = self.netG_A(self.real_A) # G_A(A)
+ self.rec_A = self.netG_B(self.fake_B) # G_B(G_A(A))
+ self.fake_A = self.netG_B(self.real_B) # G_B(B)
+ self.rec_B = self.netG_A(self.fake_A) # G_A(G_B(B))
def backward_D_basic(self, netD, real, fake):
+ """Calculate GAN loss for the discriminator
+
+ Parameters:
+ netD (network) -- the discriminator D
+ real (tensor array) -- real images
+ fake (tensor array) -- images generated by a generator
+
+ Return the discriminator loss.
+ We also call loss_D.backward() to calculate the gradients.
+ """
# Real
pred_real = netD(real)
loss_D_real = self.criterionGAN(pred_real, True)
# Fake
pred_fake = netD(fake.detach())
loss_D_fake = self.criterionGAN(pred_fake, False)
- # Combined loss
+ # Combined loss and calculate gradients
loss_D = (loss_D_real + loss_D_fake) * 0.5
- # backward
loss_D.backward()
return loss_D
def backward_D_A(self):
+ """Calculate GAN loss for discriminator D_A"""
fake_B = self.fake_B_pool.query(self.fake_B)
self.loss_D_A = self.backward_D_basic(self.netD_A, self.real_B, fake_B)
def backward_D_B(self):
+ """Calculate GAN loss for discriminator D_B"""
fake_A = self.fake_A_pool.query(self.fake_A)
self.loss_D_B = self.backward_D_basic(self.netD_B, self.real_A, fake_A)
def backward_G(self):
+ """Calculate the loss for generators G_A and G_B"""
lambda_idt = self.opt.lambda_identity
lambda_A = self.opt.lambda_A
lambda_B = self.opt.lambda_B
# Identity loss
if lambda_idt > 0:
- # G_A should be identity if real_B is fed.
+ # G_A should be identity if real_B is fed: ||G_A(B) - B||
self.idt_A = self.netG_A(self.real_B)
self.loss_idt_A = self.criterionIdt(self.idt_A, self.real_B) * lambda_B * lambda_idt
- # G_B should be identity if real_A is fed.
+ # G_B should be identity if real_A is fed: ||G_B(A) - A||
self.idt_B = self.netG_B(self.real_A)
self.loss_idt_B = self.criterionIdt(self.idt_B, self.real_A) * lambda_A * lambda_idt
else:
@@ -113,28 +167,28 @@ def backward_G(self):
# GAN loss D_A(G_A(A))
self.loss_G_A = self.criterionGAN(self.netD_A(self.fake_B), True)
-
# GAN loss D_B(G_B(B))
self.loss_G_B = self.criterionGAN(self.netD_B(self.fake_A), True)
-
- # Forward cycle loss
+ # Forward cycle loss || G_B(G_A(A)) - A||
self.loss_cycle_A = self.criterionCycle(self.rec_A, self.real_A) * lambda_A
-
- # Backward cycle loss
+ # Backward cycle loss || G_A(G_B(B)) - B||
self.loss_cycle_B = self.criterionCycle(self.rec_B, self.real_B) * lambda_B
- # combined loss
+ # combined loss and calculate gradients
self.loss_G = self.loss_G_A + self.loss_G_B + self.loss_cycle_A + self.loss_cycle_B + self.loss_idt_A + self.loss_idt_B
self.loss_G.backward()
def optimize_parameters(self):
+ """Calculate losses, gradients, and update network weights; called in every training iteration"""
# forward
- self.forward()
+ self.forward() # compute fake images and reconstruction images.
# G_A and G_B
- self.optimizer_G.zero_grad()
- self.backward_G()
- self.optimizer_G.step()
+ self.set_requires_grad([self.netD_A, self.netD_B], False) # Ds require no gradients when optimizing Gs
+ self.optimizer_G.zero_grad() # set G_A and G_B's gradients to zero
+ self.backward_G() # calculate gradients for G_A and G_B
+ self.optimizer_G.step() # update G_A and G_B's weights
# D_A and D_B
- self.optimizer_D.zero_grad()
- self.backward_D_A()
- self.backward_D_B()
- self.optimizer_D.step()
+ self.set_requires_grad([self.netD_A, self.netD_B], True)
+ self.optimizer_D.zero_grad() # set D_A and D_B's gradients to zero
+ self.backward_D_A() # calculate gradients for D_A
+ self.backward_D_B() # calculate graidents for D_B
+ self.optimizer_D.step() # update D_A and D_B's weights
diff --git a/models/networks.py b/models/networks.py
index 20167bf5c1d..ae088f6e78e 100644
--- a/models/networks.py
+++ b/models/networks.py
@@ -4,172 +4,358 @@
import functools
from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
+
###############################################################################
# Helper Functions
###############################################################################
+class Identity(nn.Module):
+ def forward(self, x):
+ return x
+
+
def get_norm_layer(norm_type='instance'):
+ """Return a normalization layer
+
+ Parameters:
+ norm_type (str) -- the name of the normalization layer: batch | instance | none
+
+ For BatchNorm, we use learnable affine parameters and track running statistics (mean/stddev).
+ For InstanceNorm, we do not use learnable affine parameters. We do not track running statistics.
+ """
if norm_type == 'batch':
- norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, affine=True)
+ norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
elif norm_type == 'instance':
- norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.InstanceNorm2d, affine=False)
+ norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.InstanceNorm2d, affine=False, track_running_stats=False)
elif norm_type == 'none':
- norm_layer = None
+ norm_layer = lambda x: Identity()
else:
raise NotImplementedError('normalization layer [%s] is not found' % norm_type)
return norm_layer
def get_scheduler(optimizer, opt):
- if opt.lr_policy == 'lambda':
+ """Return a learning rate scheduler
+
+ Parameters:
+ optimizer -- the optimizer of the network
+ opt (option class) -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions.
+ opt.lr_policy is the name of learning rate policy: linear | step | plateau | cosine
+
+ For 'linear', we keep the same learning rate for the first epochs
+ and linearly decay the rate to zero over the next epochs.
+ For other schedulers (step, plateau, and cosine), we use the default PyTorch schedulers.
+ See https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/optim.html for more details.
+ """
+ if opt.lr_policy == 'linear':
def lambda_rule(epoch):
- lr_l = 1.0 - max(0, epoch + 1 + opt.epoch_count - opt.niter) / float(opt.niter_decay + 1)
+ lr_l = 1.0 - max(0, epoch + opt.epoch_count - opt.niter) / float(opt.niter_decay + 1)
return lr_l
scheduler = lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lambda_rule)
elif opt.lr_policy == 'step':
scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=opt.lr_decay_iters, gamma=0.1)
elif opt.lr_policy == 'plateau':
scheduler = lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='min', factor=0.2, threshold=0.01, patience=5)
+ elif opt.lr_policy == 'cosine':
+ scheduler = lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=opt.niter, eta_min=0)
else:
return NotImplementedError('learning rate policy [%s] is not implemented', opt.lr_policy)
return scheduler
-def init_weights(net, init_type='normal', gain=0.02):
- def init_func(m):
+def init_weights(net, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02):
+ """Initialize network weights.
+
+ Parameters:
+ net (network) -- network to be initialized
+ init_type (str) -- the name of an initialization method: normal | xavier | kaiming | orthogonal
+ init_gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
+
+ We use 'normal' in the original pix2pix and CycleGAN paper. But xavier and kaiming might
+ work better for some applications. Feel free to try yourself.
+ """
+ def init_func(m): # define the initialization function
classname = m.__class__.__name__
if hasattr(m, 'weight') and (classname.find('Conv') != -1 or classname.find('Linear') != -1):
if init_type == 'normal':
- init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, gain)
+ init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, init_gain)
elif init_type == 'xavier':
- init.xavier_normal_(m.weight.data, gain=gain)
+ init.xavier_normal_(m.weight.data, gain=init_gain)
elif init_type == 'kaiming':
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight.data, a=0, mode='fan_in')
elif init_type == 'orthogonal':
- init.orthogonal_(m.weight.data, gain=gain)
+ init.orthogonal_(m.weight.data, gain=init_gain)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('initialization method [%s] is not implemented' % init_type)
if hasattr(m, 'bias') and m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)
- elif classname.find('BatchNorm2d') != -1:
- init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, gain)
+ elif classname.find('BatchNorm2d') != -1: # BatchNorm Layer's weight is not a matrix; only normal distribution applies.
+ init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, init_gain)
init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)
print('initialize network with %s' % init_type)
- net.apply(init_func)
+ net.apply(init_func) # apply the initialization function
+
+def init_net(net, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):
+ """Initialize a network: 1. register CPU/GPU device (with multi-GPU support); 2. initialize the network weights
+ Parameters:
+ net (network) -- the network to be initialized
+ init_type (str) -- the name of an initialization method: normal | xavier | kaiming | orthogonal
+ gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
+ gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2
-def init_net(net, init_type='normal', gpu_ids=[]):
+ Return an initialized network.
+ """
if len(gpu_ids) > 0:
assert(torch.cuda.is_available())
net.to(gpu_ids[0])
- net = torch.nn.DataParallel(net, gpu_ids)
- init_weights(net, init_type)
+ net = torch.nn.DataParallel(net, gpu_ids) # multi-GPUs
+ init_weights(net, init_type, init_gain=init_gain)
return net
-def define_G(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, which_model_netG, norm='batch', use_dropout=False, init_type='normal', gpu_ids=[]):
- netG = None
+def define_G(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, netG, norm='batch', use_dropout=False, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):
+ """Create a generator
+
+ Parameters:
+ input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
+ output_nc (int) -- the number of channels in output images
+ ngf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
+ netG (str) -- the architecture's name: resnet_9blocks | resnet_6blocks | unet_256 | unet_128
+ norm (str) -- the name of normalization layers used in the network: batch | instance | none
+ use_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers.
+ init_type (str) -- the name of our initialization method.
+ init_gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
+ gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2
+
+ Returns a generator
+
+ Our current implementation provides two types of generators:
+ U-Net: [unet_128] (for 128x128 input images) and [unet_256] (for 256x256 input images)
+ The original U-Net paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597
+
+ Resnet-based generator: [resnet_6blocks] (with 6 Resnet blocks) and [resnet_9blocks] (with 9 Resnet blocks)
+ Resnet-based generator consists of several Resnet blocks between a few downsampling/upsampling operations.
+ We adapt Torch code from Justin Johnson's neural style transfer project (https://github.com/jcjohnson/fast-neural-style).
+
+
+ The generator has been initialized by . It uses RELU for non-linearity.
+ """
+ net = None
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm)
- if which_model_netG == 'resnet_9blocks':
- netG = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=9)
- elif which_model_netG == 'resnet_6blocks':
- netG = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=6)
- elif which_model_netG == 'unet_128':
- netG = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 7, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
- elif which_model_netG == 'unet_256':
- netG = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 8, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
+ if netG == 'resnet_9blocks':
+ net = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=9)
+ elif netG == 'resnet_6blocks':
+ net = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=6)
+ elif netG == 'unet_128':
+ net = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 7, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
+ elif netG == 'unet_256':
+ net = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 8, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
else:
- raise NotImplementedError('Generator model name [%s] is not recognized' % which_model_netG)
- return init_net(netG, init_type, gpu_ids)
+ raise NotImplementedError('Generator model name [%s] is not recognized' % netG)
+ return init_net(net, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids)
+
+
+def define_D(input_nc, ndf, netD, n_layers_D=3, norm='batch', init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):
+ """Create a discriminator
+
+ Parameters:
+ input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
+ ndf (int) -- the number of filters in the first conv layer
+ netD (str) -- the architecture's name: basic | n_layers | pixel
+ n_layers_D (int) -- the number of conv layers in the discriminator; effective when netD=='n_layers'
+ norm (str) -- the type of normalization layers used in the network.
+ init_type (str) -- the name of the initialization method.
+ init_gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
+ gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2
+
+ Returns a discriminator
+
+ Our current implementation provides three types of discriminators:
+ [basic]: 'PatchGAN' classifier described in the original pix2pix paper.
+ It can classify whether 70×70 overlapping patches are real or fake.
+ Such a patch-level discriminator architecture has fewer parameters
+ than a full-image discriminator and can work on arbitrarily-sized images
+ in a fully convolutional fashion.
+
+ [n_layers]: With this mode, you cna specify the number of conv layers in the discriminator
+ with the parameter (default=3 as used in [basic] (PatchGAN).)
+ [pixel]: 1x1 PixelGAN discriminator can classify whether a pixel is real or not.
+ It encourages greater color diversity but has no effect on spatial statistics.
-def define_D(input_nc, ndf, which_model_netD,
- n_layers_D=3, norm='batch', use_sigmoid=False, init_type='normal', gpu_ids=[]):
- netD = None
+ The discriminator has been initialized by . It uses Leakly RELU for non-linearity.
+ """
+ net = None
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm)
- if which_model_netD == 'basic':
- netD = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers=3, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_sigmoid=use_sigmoid)
- elif which_model_netD == 'n_layers':
- netD = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers_D, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_sigmoid=use_sigmoid)
- elif which_model_netD == 'pixel':
- netD = PixelDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_sigmoid=use_sigmoid)
+ if netD == 'basic': # default PatchGAN classifier
+ net = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers=3, norm_layer=norm_layer)
+ elif netD == 'n_layers': # more options
+ net = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers_D, norm_layer=norm_layer)
+ elif netD == 'pixel': # classify if each pixel is real or fake
+ net = PixelDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, norm_layer=norm_layer)
else:
- raise NotImplementedError('Discriminator model name [%s] is not recognized' %
- which_model_netD)
- return init_net(netD, init_type, gpu_ids)
+ raise NotImplementedError('Discriminator model name [%s] is not recognized' % netD)
+ return init_net(net, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids)
##############################################################################
# Classes
##############################################################################
+class GANLoss(nn.Module):
+ """Define different GAN objectives.
+ The GANLoss class abstracts away the need to create the target label tensor
+ that has the same size as the input.
+ """
-# Defines the GAN loss which uses either LSGAN or the regular GAN.
-# When LSGAN is used, it is basically same as MSELoss,
-# but it abstracts away the need to create the target label tensor
-# that has the same size as the input
-class GANLoss(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, use_lsgan=True, target_real_label=1.0, target_fake_label=0.0):
+ def __init__(self, gan_mode, target_real_label=1.0, target_fake_label=0.0):
+ """ Initialize the GANLoss class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ gan_mode (str) - - the type of GAN objective. It currently supports vanilla, lsgan, and wgangp.
+ target_real_label (bool) - - label for a real image
+ target_fake_label (bool) - - label of a fake image
+
+ Note: Do not use sigmoid as the last layer of Discriminator.
+ LSGAN needs no sigmoid. vanilla GANs will handle it with BCEWithLogitsLoss.
+ """
super(GANLoss, self).__init__()
self.register_buffer('real_label', torch.tensor(target_real_label))
self.register_buffer('fake_label', torch.tensor(target_fake_label))
- if use_lsgan:
+ self.gan_mode = gan_mode
+ if gan_mode == 'lsgan':
self.loss = nn.MSELoss()
+ elif gan_mode == 'vanilla':
+ self.loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
+ elif gan_mode in ['wgangp']:
+ self.loss = None
else:
- self.loss = nn.BCELoss()
+ raise NotImplementedError('gan mode %s not implemented' % gan_mode)
+
+ def get_target_tensor(self, prediction, target_is_real):
+ """Create label tensors with the same size as the input.
+
+ Parameters:
+ prediction (tensor) - - tpyically the prediction from a discriminator
+ target_is_real (bool) - - if the ground truth label is for real images or fake images
+
+ Returns:
+ A label tensor filled with ground truth label, and with the size of the input
+ """
- def get_target_tensor(self, input, target_is_real):
if target_is_real:
target_tensor = self.real_label
else:
target_tensor = self.fake_label
- return target_tensor.expand_as(input)
-
- def __call__(self, input, target_is_real):
- target_tensor = self.get_target_tensor(input, target_is_real)
- return self.loss(input, target_tensor)
+ return target_tensor.expand_as(prediction)
+
+ def __call__(self, prediction, target_is_real):
+ """Calculate loss given Discriminator's output and grount truth labels.
+
+ Parameters:
+ prediction (tensor) - - tpyically the prediction output from a discriminator
+ target_is_real (bool) - - if the ground truth label is for real images or fake images
+
+ Returns:
+ the calculated loss.
+ """
+ if self.gan_mode in ['lsgan', 'vanilla']:
+ target_tensor = self.get_target_tensor(prediction, target_is_real)
+ loss = self.loss(prediction, target_tensor)
+ elif self.gan_mode == 'wgangp':
+ if target_is_real:
+ loss = -prediction.mean()
+ else:
+ loss = prediction.mean()
+ return loss
+
+
+def cal_gradient_penalty(netD, real_data, fake_data, device, type='mixed', constant=1.0, lambda_gp=10.0):
+ """Calculate the gradient penalty loss, used in WGAN-GP paper https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.00028
+
+ Arguments:
+ netD (network) -- discriminator network
+ real_data (tensor array) -- real images
+ fake_data (tensor array) -- generated images from the generator
+ device (str) -- GPU / CPU: from torch.device('cuda:{}'.format(self.gpu_ids[0])) if self.gpu_ids else torch.device('cpu')
+ type (str) -- if we mix real and fake data or not [real | fake | mixed].
+ constant (float) -- the constant used in formula ( | |gradient||_2 - constant)^2
+ lambda_gp (float) -- weight for this loss
+
+ Returns the gradient penalty loss
+ """
+ if lambda_gp > 0.0:
+ if type == 'real': # either use real images, fake images, or a linear interpolation of two.
+ interpolatesv = real_data
+ elif type == 'fake':
+ interpolatesv = fake_data
+ elif type == 'mixed':
+ alpha = torch.rand(real_data.shape[0], 1, device=device)
+ alpha = alpha.expand(real_data.shape[0], real_data.nelement() // real_data.shape[0]).contiguous().view(*real_data.shape)
+ interpolatesv = alpha * real_data + ((1 - alpha) * fake_data)
+ else:
+ raise NotImplementedError('{} not implemented'.format(type))
+ interpolatesv.requires_grad_(True)
+ disc_interpolates = netD(interpolatesv)
+ gradients = torch.autograd.grad(outputs=disc_interpolates, inputs=interpolatesv,
+ grad_outputs=torch.ones(disc_interpolates.size()).to(device),
+ create_graph=True, retain_graph=True, only_inputs=True)
+ gradients = gradients[0].view(real_data.size(0), -1) # flat the data
+ gradient_penalty = (((gradients + 1e-16).norm(2, dim=1) - constant) ** 2).mean() * lambda_gp # added eps
+ return gradient_penalty, gradients
+ else:
+ return 0.0, None
-# Defines the generator that consists of Resnet blocks between a few
-# downsampling/upsampling operations.
-# Code and idea originally from Justin Johnson's architecture.
-# https://github.com/jcjohnson/fast-neural-style/
class ResnetGenerator(nn.Module):
+ """Resnet-based generator that consists of Resnet blocks between a few downsampling/upsampling operations.
+
+ We adapt Torch code and idea from Justin Johnson's neural style transfer project(https://github.com/jcjohnson/fast-neural-style)
+ """
+
def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, ngf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False, n_blocks=6, padding_type='reflect'):
+ """Construct a Resnet-based generator
+
+ Parameters:
+ input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
+ output_nc (int) -- the number of channels in output images
+ ngf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
+ norm_layer -- normalization layer
+ use_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers
+ n_blocks (int) -- the number of ResNet blocks
+ padding_type (str) -- the name of padding layer in conv layers: reflect | replicate | zero
+ """
assert(n_blocks >= 0)
super(ResnetGenerator, self).__init__()
- self.input_nc = input_nc
- self.output_nc = output_nc
- self.ngf = ngf
if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial:
use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2d
else:
use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d
model = [nn.ReflectionPad2d(3),
- nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ngf, kernel_size=7, padding=0,
- bias=use_bias),
+ nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ngf, kernel_size=7, padding=0, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ngf),
nn.ReLU(True)]
n_downsampling = 2
- for i in range(n_downsampling):
- mult = 2**i
- model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf * mult, ngf * mult * 2, kernel_size=3,
- stride=2, padding=1, bias=use_bias),
+ for i in range(n_downsampling): # add downsampling layers
+ mult = 2 ** i
+ model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf * mult, ngf * mult * 2, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ngf * mult * 2),
nn.ReLU(True)]
- mult = 2**n_downsampling
- for i in range(n_blocks):
+ mult = 2 ** n_downsampling
+ for i in range(n_blocks): # add ResNet blocks
+
model += [ResnetBlock(ngf * mult, padding_type=padding_type, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, use_bias=use_bias)]
- for i in range(n_downsampling):
- mult = 2**(n_downsampling - i)
+ for i in range(n_downsampling): # add upsampling layers
+ mult = 2 ** (n_downsampling - i)
model += [nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * mult, int(ngf * mult / 2),
kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, output_padding=1,
@@ -183,16 +369,36 @@ def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, ngf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_d
self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)
def forward(self, input):
+ """Standard forward"""
return self.model(input)
-# Define a resnet block
class ResnetBlock(nn.Module):
+ """Define a Resnet block"""
+
def __init__(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias):
+ """Initialize the Resnet block
+
+ A resnet block is a conv block with skip connections
+ We construct a conv block with build_conv_block function,
+ and implement skip connections in function.
+ Original Resnet paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf
+ """
super(ResnetBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv_block = self.build_conv_block(dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias)
def build_conv_block(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias):
+ """Construct a convolutional block.
+
+ Parameters:
+ dim (int) -- the number of channels in the conv layer.
+ padding_type (str) -- the name of padding layer: reflect | replicate | zero
+ norm_layer -- normalization layer
+ use_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers.
+ use_bias (bool) -- if the conv layer uses bias or not
+
+ Returns a conv block (with a conv layer, a normalization layer, and a non-linearity layer (ReLU))
+ """
conv_block = []
p = 0
if padding_type == 'reflect':
@@ -204,9 +410,7 @@ def build_conv_block(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('padding [%s] is not implemented' % padding_type)
- conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p, bias=use_bias),
- norm_layer(dim),
- nn.ReLU(True)]
+ conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p, bias=use_bias), norm_layer(dim), nn.ReLU(True)]
if use_dropout:
conv_block += [nn.Dropout(0.5)]
@@ -219,46 +423,68 @@ def build_conv_block(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias)
p = 1
else:
raise NotImplementedError('padding [%s] is not implemented' % padding_type)
- conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p, bias=use_bias),
- norm_layer(dim)]
+ conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p, bias=use_bias), norm_layer(dim)]
return nn.Sequential(*conv_block)
def forward(self, x):
- out = x + self.conv_block(x)
+ """Forward function (with skip connections)"""
+ out = x + self.conv_block(x) # add skip connections
return out
-# Defines the Unet generator.
-# |num_downs|: number of downsamplings in UNet. For example,
-# if |num_downs| == 7, image of size 128x128 will become of size 1x1
-# at the bottleneck
class UnetGenerator(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, num_downs, ngf=64,
- norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False):
+ """Create a Unet-based generator"""
+
+ def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, num_downs, ngf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False):
+ """Construct a Unet generator
+ Parameters:
+ input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
+ output_nc (int) -- the number of channels in output images
+ num_downs (int) -- the number of downsamplings in UNet. For example, # if |num_downs| == 7,
+ image of size 128x128 will become of size 1x1 # at the bottleneck
+ ngf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
+ norm_layer -- normalization layer
+
+ We construct the U-Net from the innermost layer to the outermost layer.
+ It is a recursive process.
+ """
super(UnetGenerator, self).__init__()
-
# construct unet structure
- unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 8, ngf * 8, input_nc=None, submodule=None, norm_layer=norm_layer, innermost=True)
- for i in range(num_downs - 5):
+ unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 8, ngf * 8, input_nc=None, submodule=None, norm_layer=norm_layer, innermost=True) # add the innermost layer
+ for i in range(num_downs - 5): # add intermediate layers with ngf * 8 filters
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 8, ngf * 8, input_nc=None, submodule=unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
+ # gradually reduce the number of filters from ngf * 8 to ngf
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 4, ngf * 8, input_nc=None, submodule=unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer)
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 2, ngf * 4, input_nc=None, submodule=unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer)
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf, ngf * 2, input_nc=None, submodule=unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer)
- unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(output_nc, ngf, input_nc=input_nc, submodule=unet_block, outermost=True, norm_layer=norm_layer)
-
- self.model = unet_block
+ self.model = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(output_nc, ngf, input_nc=input_nc, submodule=unet_block, outermost=True, norm_layer=norm_layer) # add the outermost layer
def forward(self, input):
+ """Standard forward"""
return self.model(input)
-# Defines the submodule with skip connection.
-# X -------------------identity---------------------- X
-# |-- downsampling -- |submodule| -- upsampling --|
class UnetSkipConnectionBlock(nn.Module):
+ """Defines the Unet submodule with skip connection.
+ X -------------------identity----------------------
+ |-- downsampling -- |submodule| -- upsampling --|
+ """
+
def __init__(self, outer_nc, inner_nc, input_nc=None,
submodule=None, outermost=False, innermost=False, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False):
+ """Construct a Unet submodule with skip connections.
+
+ Parameters:
+ outer_nc (int) -- the number of filters in the outer conv layer
+ inner_nc (int) -- the number of filters in the inner conv layer
+ input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images/features
+ submodule (UnetSkipConnectionBlock) -- previously defined submodules
+ outermost (bool) -- if this module is the outermost module
+ innermost (bool) -- if this module is the innermost module
+ norm_layer -- normalization layer
+ user_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers.
+ """
super(UnetSkipConnectionBlock, self).__init__()
self.outermost = outermost
if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial:
@@ -305,62 +531,71 @@ def __init__(self, outer_nc, inner_nc, input_nc=None,
def forward(self, x):
if self.outermost:
return self.model(x)
- else:
+ else: # add skip connections
return torch.cat([x, self.model(x)], 1)
-# Defines the PatchGAN discriminator with the specified arguments.
class NLayerDiscriminator(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, n_layers=3, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_sigmoid=False):
+ """Defines a PatchGAN discriminator"""
+
+ def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, n_layers=3, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d):
+ """Construct a PatchGAN discriminator
+
+ Parameters:
+ input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
+ ndf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
+ n_layers (int) -- the number of conv layers in the discriminator
+ norm_layer -- normalization layer
+ """
super(NLayerDiscriminator, self).__init__()
- if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial:
+ if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial: # no need to use bias as BatchNorm2d has affine parameters
use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2d
else:
use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d
kw = 4
padw = 1
- sequence = [
- nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw),
- nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
- ]
-
+ sequence = [nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)]
nf_mult = 1
nf_mult_prev = 1
- for n in range(1, n_layers):
+ for n in range(1, n_layers): # gradually increase the number of filters
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
- nf_mult = min(2**n, 8)
+ nf_mult = min(2 ** n, 8)
sequence += [
- nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult,
- kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),
+ nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
- nf_mult = min(2**n_layers, 8)
+ nf_mult = min(2 ** n_layers, 8)
sequence += [
- nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult,
- kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),
+ nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
- sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult, 1, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw)]
-
- if use_sigmoid:
- sequence += [nn.Sigmoid()]
-
+ sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult, 1, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw)] # output 1 channel prediction map
self.model = nn.Sequential(*sequence)
def forward(self, input):
+ """Standard forward."""
return self.model(input)
class PixelDiscriminator(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_sigmoid=False):
+ """Defines a 1x1 PatchGAN discriminator (pixelGAN)"""
+
+ def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d):
+ """Construct a 1x1 PatchGAN discriminator
+
+ Parameters:
+ input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
+ ndf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
+ norm_layer -- normalization layer
+ """
super(PixelDiscriminator, self).__init__()
- if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial:
+ if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial: # no need to use bias as BatchNorm2d has affine parameters
use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2d
else:
use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d
@@ -373,10 +608,8 @@ def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_sigmoid=Fals
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True),
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, 1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=use_bias)]
- if use_sigmoid:
- self.net.append(nn.Sigmoid())
-
self.net = nn.Sequential(*self.net)
def forward(self, input):
+ """Standard forward."""
return self.net(input)
diff --git a/models/pix2pix_model.py b/models/pix2pix_model.py
index 9cddf0b533b..939eb887ee3 100644
--- a/models/pix2pix_model.py
+++ b/models/pix2pix_model.py
@@ -1,96 +1,127 @@
import torch
-from util.image_pool import ImagePool
from .base_model import BaseModel
from . import networks
class Pix2PixModel(BaseModel):
- def name(self):
- return 'Pix2PixModel'
-
- def initialize(self, opt):
- BaseModel.initialize(self, opt)
- self.isTrain = opt.isTrain
- # specify the training losses you want to print out. The program will call base_model.get_current_losses
+ """ This class implements the pix2pix model, for learning a mapping from input images to output images given paired data.
+
+ The model training requires '--dataset_mode aligned' dataset.
+ By default, it uses a '--netG unet256' U-Net generator,
+ a '--netD basic' discriminator (PatchGAN),
+ and a '--gan_mode' vanilla GAN loss (the cross-entropy objective used in the orignal GAN paper).
+
+ pix2pix paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004.pdf
+ """
+ @staticmethod
+ def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train=True):
+ """Add new dataset-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.
+
+ Parameters:
+ parser -- original option parser
+ is_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
+
+ Returns:
+ the modified parser.
+
+ For pix2pix, we do not use image buffer
+ The training objective is: GAN Loss + lambda_L1 * ||G(A)-B||_1
+ By default, we use vanilla GAN loss, UNet with batchnorm, and aligned datasets.
+ """
+ # changing the default values to match the pix2pix paper (https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/)
+ parser.set_defaults(norm='batch', netG='unet_256', dataset_mode='aligned')
+ if is_train:
+ parser.set_defaults(pool_size=0, gan_mode='vanilla')
+ parser.add_argument('--lambda_L1', type=float, default=100.0, help='weight for L1 loss')
+
+ return parser
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize the pix2pix class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class)-- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ """
+ BaseModel.__init__(self, opt)
+ # specify the training losses you want to print out. The training/test scripts will call
self.loss_names = ['G_GAN', 'G_L1', 'D_real', 'D_fake']
- # specify the images you want to save/display. The program will call base_model.get_current_visuals
+ # specify the images you want to save/display. The training/test scripts will call
self.visual_names = ['real_A', 'fake_B', 'real_B']
- # specify the models you want to save to the disk. The program will call base_model.save_networks and base_model.load_networks
+ # specify the models you want to save to the disk. The training/test scripts will call and
if self.isTrain:
self.model_names = ['G', 'D']
- else: # during test time, only load Gs
+ else: # during test time, only load G
self.model_names = ['G']
- # load/define networks
- self.netG = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc, opt.ngf,
- opt.which_model_netG, opt.norm, not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, self.gpu_ids)
+ # define networks (both generator and discriminator)
+ self.netG = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG, opt.norm,
+ not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
- if self.isTrain:
- use_sigmoid = opt.no_lsgan
- self.netD = networks.define_D(opt.input_nc + opt.output_nc, opt.ndf,
- opt.which_model_netD,
- opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, use_sigmoid, opt.init_type, self.gpu_ids)
+ if self.isTrain: # define a discriminator; conditional GANs need to take both input and output images; Therefore, #channels for D is input_nc + output_nc
+ self.netD = networks.define_D(opt.input_nc + opt.output_nc, opt.ndf, opt.netD,
+ opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
if self.isTrain:
- self.fake_AB_pool = ImagePool(opt.pool_size)
# define loss functions
- self.criterionGAN = networks.GANLoss(use_lsgan=not opt.no_lsgan).to(self.device)
+ self.criterionGAN = networks.GANLoss(opt.gan_mode).to(self.device)
self.criterionL1 = torch.nn.L1Loss()
-
- # initialize optimizers
- self.optimizers = []
- self.optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(self.netG.parameters(),
- lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
- self.optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(self.netD.parameters(),
- lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
+ # initialize optimizers; schedulers will be automatically created by function .
+ self.optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(self.netG.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
+ self.optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(self.netD.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_G)
self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_D)
def set_input(self, input):
- AtoB = self.opt.which_direction == 'AtoB'
+ """Unpack input data from the dataloader and perform necessary pre-processing steps.
+
+ Parameters:
+ input (dict): include the data itself and its metadata information.
+
+ The option 'direction' can be used to swap images in domain A and domain B.
+ """
+ AtoB = self.opt.direction == 'AtoB'
self.real_A = input['A' if AtoB else 'B'].to(self.device)
self.real_B = input['B' if AtoB else 'A'].to(self.device)
self.image_paths = input['A_paths' if AtoB else 'B_paths']
def forward(self):
- self.fake_B = self.netG(self.real_A)
+ """Run forward pass; called by both functions and ."""
+ self.fake_B = self.netG(self.real_A) # G(A)
def backward_D(self):
- # Fake
- # stop backprop to the generator by detaching fake_B
- fake_AB = self.fake_AB_pool.query(torch.cat((self.real_A, self.fake_B), 1))
+ """Calculate GAN loss for the discriminator"""
+ # Fake; stop backprop to the generator by detaching fake_B
+ fake_AB = torch.cat((self.real_A, self.fake_B), 1) # we use conditional GANs; we need to feed both input and output to the discriminator
pred_fake = self.netD(fake_AB.detach())
self.loss_D_fake = self.criterionGAN(pred_fake, False)
-
# Real
real_AB = torch.cat((self.real_A, self.real_B), 1)
pred_real = self.netD(real_AB)
self.loss_D_real = self.criterionGAN(pred_real, True)
-
- # Combined loss
+ # combine loss and calculate gradients
self.loss_D = (self.loss_D_fake + self.loss_D_real) * 0.5
-
self.loss_D.backward()
def backward_G(self):
+ """Calculate GAN and L1 loss for the generator"""
# First, G(A) should fake the discriminator
fake_AB = torch.cat((self.real_A, self.fake_B), 1)
pred_fake = self.netD(fake_AB)
self.loss_G_GAN = self.criterionGAN(pred_fake, True)
-
# Second, G(A) = B
- self.loss_G_L1 = self.criterionL1(self.fake_B, self.real_B) * self.opt.lambda_A
-
+ self.loss_G_L1 = self.criterionL1(self.fake_B, self.real_B) * self.opt.lambda_L1
+ # combine loss and calculate gradients
self.loss_G = self.loss_G_GAN + self.loss_G_L1
-
self.loss_G.backward()
def optimize_parameters(self):
- self.forward()
-
- self.optimizer_D.zero_grad()
- self.backward_D()
- self.optimizer_D.step()
-
- self.optimizer_G.zero_grad()
- self.backward_G()
- self.optimizer_G.step()
+ self.forward() # compute fake images: G(A)
+ # update D
+ self.set_requires_grad(self.netD, True) # enable backprop for D
+ self.optimizer_D.zero_grad() # set D's gradients to zero
+ self.backward_D() # calculate gradients for D
+ self.optimizer_D.step() # update D's weights
+ # update G
+ self.set_requires_grad(self.netD, False) # D requires no gradients when optimizing G
+ self.optimizer_G.zero_grad() # set G's gradients to zero
+ self.backward_G() # calculate graidents for G
+ self.optimizer_G.step() # udpate G's weights
diff --git a/models/template_model.py b/models/template_model.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..68cdaf6a9a2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/models/template_model.py
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+"""Model class template
+
+This module provides a template for users to implement custom models.
+You can specify '--model template' to use this model.
+The class name should be consistent with both the filename and its model option.
+The filename should be _dataset.py
+The class name should be Dataset.py
+It implements a simple image-to-image translation baseline based on regression loss.
+Given input-output pairs (data_A, data_B), it learns a network netG that can minimize the following L1 loss:
+ min_ ||netG(data_A) - data_B||_1
+You need to implement the following functions:
+ : Add model-specific options and rewrite default values for existing options.
+ <__init__>: Initialize this model class.
+ : Unpack input data and perform data pre-processing.
+ : Run forward pass. This will be called by both and .
+ : Update network weights; it will be called in every training iteration.
+"""
+import torch
+from .base_model import BaseModel
+from . import networks
+
+
+class TemplateModel(BaseModel):
+ @staticmethod
+ def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train=True):
+ """Add new model-specific options and rewrite default values for existing options.
+
+ Parameters:
+ parser -- the option parser
+ is_train -- if it is training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
+
+ Returns:
+ the modified parser.
+ """
+ parser.set_defaults(dataset_mode='aligned') # You can rewrite default values for this model. For example, this model usually uses aligned dataset as its dataset.
+ if is_train:
+ parser.add_argument('--lambda_regression', type=float, default=1.0, help='weight for the regression loss') # You can define new arguments for this model.
+
+ return parser
+
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize this model class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt -- training/test options
+
+ A few things can be done here.
+ - (required) call the initialization function of BaseModel
+ - define loss function, visualization images, model names, and optimizers
+ """
+ BaseModel.__init__(self, opt) # call the initialization method of BaseModel
+ # specify the training losses you want to print out. The program will call base_model.get_current_losses to plot the losses to the console and save them to the disk.
+ self.loss_names = ['loss_G']
+ # specify the images you want to save and display. The program will call base_model.get_current_visuals to save and display these images.
+ self.visual_names = ['data_A', 'data_B', 'output']
+ # specify the models you want to save to the disk. The program will call base_model.save_networks and base_model.load_networks to save and load networks.
+ # you can use opt.isTrain to specify different behaviors for training and test. For example, some networks will not be used during test, and you don't need to load them.
+ self.model_names = ['G']
+ # define networks; you can use opt.isTrain to specify different behaviors for training and test.
+ self.netG = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG, gpu_ids=self.gpu_ids)
+ if self.isTrain: # only defined during training time
+ # define your loss functions. You can use losses provided by torch.nn such as torch.nn.L1Loss.
+ # We also provide a GANLoss class "networks.GANLoss". self.criterionGAN = networks.GANLoss().to(self.device)
+ self.criterionLoss = torch.nn.L1Loss()
+ # define and initialize optimizers. You can define one optimizer for each network.
+ # If two networks are updated at the same time, you can use itertools.chain to group them. See cycle_gan_model.py for an example.
+ self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.netG.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
+ self.optimizers = [self.optimizer]
+
+ # Our program will automatically call to define schedulers, load networks, and print networks
+
+ def set_input(self, input):
+ """Unpack input data from the dataloader and perform necessary pre-processing steps.
+
+ Parameters:
+ input: a dictionary that contains the data itself and its metadata information.
+ """
+ AtoB = self.opt.direction == 'AtoB' # use to swap data_A and data_B
+ self.data_A = input['A' if AtoB else 'B'].to(self.device) # get image data A
+ self.data_B = input['B' if AtoB else 'A'].to(self.device) # get image data B
+ self.image_paths = input['A_paths' if AtoB else 'B_paths'] # get image paths
+
+ def forward(self):
+ """Run forward pass. This will be called by both functions and ."""
+ self.output = self.netG(self.data_A) # generate output image given the input data_A
+
+ def backward(self):
+ """Calculate losses, gradients, and update network weights; called in every training iteration"""
+ # caculate the intermediate results if necessary; here self.output has been computed during function
+ # calculate loss given the input and intermediate results
+ self.loss_G = self.criterionLoss(self.output, self.data_B) * self.opt.lambda_regression
+ self.loss_G.backward() # calculate gradients of network G w.r.t. loss_G
+
+ def optimize_parameters(self):
+ """Update network weights; it will be called in every training iteration."""
+ self.forward() # first call forward to calculate intermediate results
+ self.optimizer.zero_grad() # clear network G's existing gradients
+ self.backward() # calculate gradients for network G
+ self.optimizer.step() # update gradients for network G
diff --git a/models/test_model.py b/models/test_model.py
index f51ea90d66a..fe15f40176e 100644
--- a/models/test_model.py
+++ b/models/test_model.py
@@ -3,30 +3,67 @@
class TestModel(BaseModel):
- def name(self):
- return 'TestModel'
+ """ This TesteModel can be used to generate CycleGAN results for only one direction.
+ This model will automatically set '--dataset_mode single', which only loads the images from one collection.
- def initialize(self, opt):
- assert(not opt.isTrain)
- BaseModel.initialize(self, opt)
+ See the test instruction for more details.
+ """
+ @staticmethod
+ def modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train=True):
+ """Add new dataset-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.
+
+ Parameters:
+ parser -- original option parser
+ is_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.
+
+ Returns:
+ the modified parser.
+
+ The model can only be used during test time. It requires '--dataset_mode single'.
+ You need to specify the network using the option '--model_suffix'.
+ """
+ assert not is_train, 'TestModel cannot be used during training time'
+ parser.set_defaults(dataset_mode='single')
+ parser.add_argument('--model_suffix', type=str, default='', help='In checkpoints_dir, [epoch]_net_G[model_suffix].pth will be loaded as the generator.')
+
+ return parser
- # specify the training losses you want to print out. The program will call base_model.get_current_losses
+ def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize the pix2pix class.
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt (Option class)-- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ """
+ assert(not opt.isTrain)
+ BaseModel.__init__(self, opt)
+ # specify the training losses you want to print out. The training/test scripts will call
self.loss_names = []
- # specify the images you want to save/display. The program will call base_model.get_current_visuals
- self.visual_names = ['real_A', 'fake_B']
- # specify the models you want to save to the disk. The program will call base_model.save_networks and base_model.load_networks
- self.model_names = ['G']
+ # specify the images you want to save/display. The training/test scripts will call
+ self.visual_names = ['real', 'fake']
+ # specify the models you want to save to the disk. The training/test scripts will call and
+ self.model_names = ['G' + opt.model_suffix] # only generator is needed.
+ self.netG = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG,
+ opt.norm, not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)
- self.netG = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc,
- opt.ngf, opt.which_model_netG,
- opt.norm, not opt.no_dropout,
- opt.init_type,
- self.gpu_ids)
+ # assigns the model to self.netG_[suffix] so that it can be loaded
+ # please see
+ setattr(self, 'netG' + opt.model_suffix, self.netG) # store netG in self.
def set_input(self, input):
- # we need to use single_dataset mode
- self.real_A = input['A'].to(self.device)
+ """Unpack input data from the dataloader and perform necessary pre-processing steps.
+
+ Parameters:
+ input: a dictionary that contains the data itself and its metadata information.
+
+ We need to use 'single_dataset' dataset mode. It only load images from one domain.
+ """
+ self.real = input['A'].to(self.device)
self.image_paths = input['A_paths']
def forward(self):
- self.fake_B = self.netG(self.real_A)
+ """Run forward pass."""
+ self.fake = self.netG(self.real) # G(real)
+
+ def optimize_parameters(self):
+ """No optimization for test model."""
+ pass
diff --git a/options/__init__.py b/options/__init__.py
index e69de29bb2d..e7eedebe54a 100644
--- a/options/__init__.py
+++ b/options/__init__.py
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+"""This package options includes option modules: training options, test options, and basic options (used in both training and test)."""
diff --git a/options/base_options.py b/options/base_options.py
index aaf28d71700..afb5d0852d1 100644
--- a/options/base_options.py
+++ b/options/base_options.py
@@ -2,84 +2,135 @@
import os
from util import util
import torch
+import models
+import data
class BaseOptions():
+ """This class defines options used during both training and test time.
+
+ It also implements several helper functions such as parsing, printing, and saving the options.
+ It also gathers additional options defined in functions in both dataset class and model class.
+ """
+
def __init__(self):
- self.parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter)
+ """Reset the class; indicates the class hasn't been initailized"""
self.initialized = False
- def initialize(self):
- self.parser.add_argument('--dataroot', required=True, help='path to images (should have subfolders trainA, trainB, valA, valB, etc)')
- self.parser.add_argument('--batchSize', type=int, default=1, help='input batch size')
- self.parser.add_argument('--loadSize', type=int, default=286, help='scale images to this size')
- self.parser.add_argument('--fineSize', type=int, default=256, help='then crop to this size')
- self.parser.add_argument('--input_nc', type=int, default=3, help='# of input image channels')
- self.parser.add_argument('--output_nc', type=int, default=3, help='# of output image channels')
- self.parser.add_argument('--ngf', type=int, default=64, help='# of gen filters in first conv layer')
- self.parser.add_argument('--ndf', type=int, default=64, help='# of discrim filters in first conv layer')
- self.parser.add_argument('--which_model_netD', type=str, default='basic', help='selects model to use for netD')
- self.parser.add_argument('--which_model_netG', type=str, default='resnet_9blocks', help='selects model to use for netG')
- self.parser.add_argument('--n_layers_D', type=int, default=3, help='only used if which_model_netD==n_layers')
- self.parser.add_argument('--gpu_ids', type=str, default='0', help='gpu ids: e.g. 0 0,1,2, 0,2. use -1 for CPU')
- self.parser.add_argument('--name', type=str, default='experiment_name', help='name of the experiment. It decides where to store samples and models')
- self.parser.add_argument('--dataset_mode', type=str, default='unaligned', help='chooses how datasets are loaded. [unaligned | aligned | single]')
- self.parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default='cycle_gan',
- help='chooses which model to use. cycle_gan, pix2pix, test')
- self.parser.add_argument('--which_direction', type=str, default='AtoB', help='AtoB or BtoA')
- self.parser.add_argument('--nThreads', default=4, type=int, help='# threads for loading data')
- self.parser.add_argument('--checkpoints_dir', type=str, default='./checkpoints', help='models are saved here')
- self.parser.add_argument('--norm', type=str, default='instance', help='instance normalization or batch normalization')
- self.parser.add_argument('--serial_batches', action='store_true', help='if true, takes images in order to make batches, otherwise takes them randomly')
- self.parser.add_argument('--display_winsize', type=int, default=256, help='display window size')
- self.parser.add_argument('--display_id', type=int, default=1, help='window id of the web display')
- self.parser.add_argument('--display_server', type=str, default="http://localhost", help='visdom server of the web display')
- self.parser.add_argument('--display_port', type=int, default=8097, help='visdom port of the web display')
- self.parser.add_argument('--no_dropout', action='store_true', help='no dropout for the generator')
- self.parser.add_argument('--max_dataset_size', type=int, default=float("inf"),
- help='Maximum number of samples allowed per dataset. If the dataset directory contains more than max_dataset_size, only a subset is loaded.')
- self.parser.add_argument('--resize_or_crop', type=str, default='resize_and_crop', help='scaling and cropping of images at load time [resize_and_crop|crop|scale_width|scale_width_and_crop]')
- self.parser.add_argument('--no_flip', action='store_true', help='if specified, do not flip the images for data augmentation')
- self.parser.add_argument('--init_type', type=str, default='normal', help='network initialization [normal|xavier|kaiming|orthogonal]')
- self.parser.add_argument('--verbose', action='store_true', help='if specified, print more debugging information')
- self.parser.add_argument('--suffix', default='', type=str, help='customized suffix: opt.name = opt.name + suffix: e.g., {model}_{which_model_netG}_size{loadSize}')
+ def initialize(self, parser):
+ """Define the common options that are used in both training and test."""
+ # basic parameters
+ parser.add_argument('--dataroot', required=True, help='path to images (should have subfolders trainA, trainB, valA, valB, etc)')
+ parser.add_argument('--name', type=str, default='experiment_name', help='name of the experiment. It decides where to store samples and models')
+ parser.add_argument('--gpu_ids', type=str, default='0', help='gpu ids: e.g. 0 0,1,2, 0,2. use -1 for CPU')
+ parser.add_argument('--checkpoints_dir', type=str, default='./checkpoints', help='models are saved here')
+ # model parameters
+ parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default='cycle_gan', help='chooses which model to use. [cycle_gan | pix2pix | test | colorization]')
+ parser.add_argument('--input_nc', type=int, default=3, help='# of input image channels: 3 for RGB and 1 for grayscale')
+ parser.add_argument('--output_nc', type=int, default=3, help='# of output image channels: 3 for RGB and 1 for grayscale')
+ parser.add_argument('--ngf', type=int, default=64, help='# of gen filters in the last conv layer')
+ parser.add_argument('--ndf', type=int, default=64, help='# of discrim filters in the first conv layer')
+ parser.add_argument('--netD', type=str, default='basic', help='specify discriminator architecture [basic | n_layers | pixel]. The basic model is a 70x70 PatchGAN. n_layers allows you to specify the layers in the discriminator')
+ parser.add_argument('--netG', type=str, default='resnet_9blocks', help='specify generator architecture [resnet_9blocks | resnet_6blocks | unet_256 | unet_128]')
+ parser.add_argument('--n_layers_D', type=int, default=3, help='only used if netD==n_layers')
+ parser.add_argument('--norm', type=str, default='instance', help='instance normalization or batch normalization [instance | batch | none]')
+ parser.add_argument('--init_type', type=str, default='normal', help='network initialization [normal | xavier | kaiming | orthogonal]')
+ parser.add_argument('--init_gain', type=float, default=0.02, help='scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.')
+ parser.add_argument('--no_dropout', action='store_true', help='no dropout for the generator')
+ # dataset parameters
+ parser.add_argument('--dataset_mode', type=str, default='unaligned', help='chooses how datasets are loaded. [unaligned | aligned | single | colorization]')
+ parser.add_argument('--direction', type=str, default='AtoB', help='AtoB or BtoA')
+ parser.add_argument('--serial_batches', action='store_true', help='if true, takes images in order to make batches, otherwise takes them randomly')
+ parser.add_argument('--num_threads', default=4, type=int, help='# threads for loading data')
+ parser.add_argument('--batch_size', type=int, default=1, help='input batch size')
+ parser.add_argument('--load_size', type=int, default=286, help='scale images to this size')
+ parser.add_argument('--crop_size', type=int, default=256, help='then crop to this size')
+ parser.add_argument('--max_dataset_size', type=int, default=float("inf"), help='Maximum number of samples allowed per dataset. If the dataset directory contains more than max_dataset_size, only a subset is loaded.')
+ parser.add_argument('--preprocess', type=str, default='resize_and_crop', help='scaling and cropping of images at load time [resize_and_crop | crop | scale_width | scale_width_and_crop | none]')
+ parser.add_argument('--no_flip', action='store_true', help='if specified, do not flip the images for data augmentation')
+ parser.add_argument('--display_winsize', type=int, default=256, help='display window size for both visdom and HTML')
+ # additional parameters
+ parser.add_argument('--epoch', type=str, default='latest', help='which epoch to load? set to latest to use latest cached model')
+ parser.add_argument('--load_iter', type=int, default='0', help='which iteration to load? if load_iter > 0, the code will load models by iter_[load_iter]; otherwise, the code will load models by [epoch]')
+ parser.add_argument('--verbose', action='store_true', help='if specified, print more debugging information')
+ parser.add_argument('--suffix', default='', type=str, help='customized suffix: opt.name = opt.name + suffix: e.g., {model}_{netG}_size{load_size}')
self.initialized = True
+ return parser
+
+ def gather_options(self):
+ """Initialize our parser with basic options(only once).
+ Add additional model-specific and dataset-specific options.
+ These options are defined in the function
+ in model and dataset classes.
+ """
+ if not self.initialized: # check if it has been initialized
+ parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter)
+ parser = self.initialize(parser)
+
+ # get the basic options
+ opt, _ = parser.parse_known_args()
+
+ # modify model-related parser options
+ model_name = opt.model
+ model_option_setter = models.get_option_setter(model_name)
+ parser = model_option_setter(parser, self.isTrain)
+ opt, _ = parser.parse_known_args() # parse again with new defaults
+
+ # modify dataset-related parser options
+ dataset_name = opt.dataset_mode
+ dataset_option_setter = data.get_option_setter(dataset_name)
+ parser = dataset_option_setter(parser, self.isTrain)
+
+ # save and return the parser
+ self.parser = parser
+ return parser.parse_args()
+
+ def print_options(self, opt):
+ """Print and save options
+
+ It will print both current options and default values(if different).
+ It will save options into a text file / [checkpoints_dir] / opt.txt
+ """
+ message = ''
+ message += '----------------- Options ---------------\n'
+ for k, v in sorted(vars(opt).items()):
+ comment = ''
+ default = self.parser.get_default(k)
+ if v != default:
+ comment = '\t[default: %s]' % str(default)
+ message += '{:>25}: {:<30}{}\n'.format(str(k), str(v), comment)
+ message += '----------------- End -------------------'
+ print(message)
+
+ # save to the disk
+ expr_dir = os.path.join(opt.checkpoints_dir, opt.name)
+ util.mkdirs(expr_dir)
+ file_name = os.path.join(expr_dir, '{}_opt.txt'.format(opt.phase))
+ with open(file_name, 'wt') as opt_file:
+ opt_file.write(message)
+ opt_file.write('\n')
def parse(self):
- if not self.initialized:
- self.initialize()
- opt = self.parser.parse_args()
+ """Parse our options, create checkpoints directory suffix, and set up gpu device."""
+ opt = self.gather_options()
opt.isTrain = self.isTrain # train or test
+ # process opt.suffix
+ if opt.suffix:
+ suffix = ('_' + opt.suffix.format(**vars(opt))) if opt.suffix != '' else ''
+ opt.name = opt.name + suffix
+
+ self.print_options(opt)
+
+ # set gpu ids
str_ids = opt.gpu_ids.split(',')
opt.gpu_ids = []
for str_id in str_ids:
id = int(str_id)
if id >= 0:
opt.gpu_ids.append(id)
-
- # set gpu ids
if len(opt.gpu_ids) > 0:
torch.cuda.set_device(opt.gpu_ids[0])
- args = vars(opt)
-
- print('------------ Options -------------')
- for k, v in sorted(args.items()):
- print('%s: %s' % (str(k), str(v)))
- print('-------------- End ----------------')
-
- if opt.suffix:
- suffix = ('_' + opt.suffix.format(**vars(opt))) if opt.suffix != '' else ''
- opt.name = opt.name + suffix
- # save to the disk
- expr_dir = os.path.join(opt.checkpoints_dir, opt.name)
- util.mkdirs(expr_dir)
- file_name = os.path.join(expr_dir, 'opt.txt')
- with open(file_name, 'wt') as opt_file:
- opt_file.write('------------ Options -------------\n')
- for k, v in sorted(args.items()):
- opt_file.write('%s: %s\n' % (str(k), str(v)))
- opt_file.write('-------------- End ----------------\n')
self.opt = opt
return self.opt
diff --git a/options/test_options.py b/options/test_options.py
index 6b79860fd50..c85c99601cb 100644
--- a/options/test_options.py
+++ b/options/test_options.py
@@ -2,12 +2,23 @@
class TestOptions(BaseOptions):
- def initialize(self):
- BaseOptions.initialize(self)
- self.parser.add_argument('--ntest', type=int, default=float("inf"), help='# of test examples.')
- self.parser.add_argument('--results_dir', type=str, default='./results/', help='saves results here.')
- self.parser.add_argument('--aspect_ratio', type=float, default=1.0, help='aspect ratio of result images')
- self.parser.add_argument('--phase', type=str, default='test', help='train, val, test, etc')
- self.parser.add_argument('--which_epoch', type=str, default='latest', help='which epoch to load? set to latest to use latest cached model')
- self.parser.add_argument('--how_many', type=int, default=50, help='how many test images to run')
+ """This class includes test options.
+
+ It also includes shared options defined in BaseOptions.
+ """
+
+ def initialize(self, parser):
+ parser = BaseOptions.initialize(self, parser) # define shared options
+ parser.add_argument('--ntest', type=int, default=float("inf"), help='# of test examples.')
+ parser.add_argument('--results_dir', type=str, default='./results/', help='saves results here.')
+ parser.add_argument('--aspect_ratio', type=float, default=1.0, help='aspect ratio of result images')
+ parser.add_argument('--phase', type=str, default='test', help='train, val, test, etc')
+ # Dropout and Batchnorm has different behavioir during training and test.
+ parser.add_argument('--eval', action='store_true', help='use eval mode during test time.')
+ parser.add_argument('--num_test', type=int, default=50, help='how many test images to run')
+ # rewrite devalue values
+ parser.set_defaults(model='test')
+ # To avoid cropping, the load_size should be the same as crop_size
+ parser.set_defaults(load_size=parser.get_default('crop_size'))
self.isTrain = False
+ return parser
diff --git a/options/train_options.py b/options/train_options.py
index 345b3f78220..8b8ebfba6cb 100644
--- a/options/train_options.py
+++ b/options/train_options.py
@@ -2,31 +2,39 @@
class TrainOptions(BaseOptions):
- def initialize(self):
- BaseOptions.initialize(self)
- self.parser.add_argument('--display_freq', type=int, default=400, help='frequency of showing training results on screen')
- self.parser.add_argument('--display_ncols', type=int, default=4, help='if positive, display all images in a single visdom web panel with certain number of images per row.')
- self.parser.add_argument('--update_html_freq', type=int, default=1000, help='frequency of saving training results to html')
- self.parser.add_argument('--print_freq', type=int, default=100, help='frequency of showing training results on console')
- self.parser.add_argument('--save_latest_freq', type=int, default=5000, help='frequency of saving the latest results')
- self.parser.add_argument('--save_epoch_freq', type=int, default=5, help='frequency of saving checkpoints at the end of epochs')
- self.parser.add_argument('--continue_train', action='store_true', help='continue training: load the latest model')
- self.parser.add_argument('--epoch_count', type=int, default=1, help='the starting epoch count, we save the model by , +, ...')
- self.parser.add_argument('--phase', type=str, default='train', help='train, val, test, etc')
- self.parser.add_argument('--which_epoch', type=str, default='latest', help='which epoch to load? set to latest to use latest cached model')
- self.parser.add_argument('--niter', type=int, default=100, help='# of iter at starting learning rate')
- self.parser.add_argument('--niter_decay', type=int, default=100, help='# of iter to linearly decay learning rate to zero')
- self.parser.add_argument('--beta1', type=float, default=0.5, help='momentum term of adam')
- self.parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.0002, help='initial learning rate for adam')
- self.parser.add_argument('--no_lsgan', action='store_true', help='do *not* use least square GAN, if false, use vanilla GAN')
- self.parser.add_argument('--lambda_A', type=float, default=10.0, help='weight for cycle loss (A -> B -> A)')
- self.parser.add_argument('--lambda_B', type=float, default=10.0, help='weight for cycle loss (B -> A -> B)')
- self.parser.add_argument('--lambda_identity', type=float, default=0.5,
- help='use identity mapping. Setting lambda_identity other than 0 has an effect of scaling the weight of the identity mapping loss.'
- 'For example, if the weight of the identity loss should be 10 times smaller than the weight of the reconstruction loss, please set lambda_identity = 0.1')
- self.parser.add_argument('--pool_size', type=int, default=50, help='the size of image buffer that stores previously generated images')
- self.parser.add_argument('--no_html', action='store_true', help='do not save intermediate training results to [opt.checkpoints_dir]/[opt.name]/web/')
- self.parser.add_argument('--lr_policy', type=str, default='lambda', help='learning rate policy: lambda|step|plateau')
- self.parser.add_argument('--lr_decay_iters', type=int, default=50, help='multiply by a gamma every lr_decay_iters iterations')
+ """This class includes training options.
+
+ It also includes shared options defined in BaseOptions.
+ """
+
+ def initialize(self, parser):
+ parser = BaseOptions.initialize(self, parser)
+ # visdom and HTML visualization parameters
+ parser.add_argument('--display_freq', type=int, default=400, help='frequency of showing training results on screen')
+ parser.add_argument('--display_ncols', type=int, default=4, help='if positive, display all images in a single visdom web panel with certain number of images per row.')
+ parser.add_argument('--display_id', type=int, default=1, help='window id of the web display')
+ parser.add_argument('--display_server', type=str, default="http://localhost", help='visdom server of the web display')
+ parser.add_argument('--display_env', type=str, default='main', help='visdom display environment name (default is "main")')
+ parser.add_argument('--display_port', type=int, default=8097, help='visdom port of the web display')
+ parser.add_argument('--update_html_freq', type=int, default=1000, help='frequency of saving training results to html')
+ parser.add_argument('--print_freq', type=int, default=100, help='frequency of showing training results on console')
+ parser.add_argument('--no_html', action='store_true', help='do not save intermediate training results to [opt.checkpoints_dir]/[opt.name]/web/')
+ # network saving and loading parameters
+ parser.add_argument('--save_latest_freq', type=int, default=5000, help='frequency of saving the latest results')
+ parser.add_argument('--save_epoch_freq', type=int, default=5, help='frequency of saving checkpoints at the end of epochs')
+ parser.add_argument('--save_by_iter', action='store_true', help='whether saves model by iteration')
+ parser.add_argument('--continue_train', action='store_true', help='continue training: load the latest model')
+ parser.add_argument('--epoch_count', type=int, default=1, help='the starting epoch count, we save the model by , +, ...')
+ parser.add_argument('--phase', type=str, default='train', help='train, val, test, etc')
+ # training parameters
+ parser.add_argument('--niter', type=int, default=100, help='# of iter at starting learning rate')
+ parser.add_argument('--niter_decay', type=int, default=100, help='# of iter to linearly decay learning rate to zero')
+ parser.add_argument('--beta1', type=float, default=0.5, help='momentum term of adam')
+ parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.0002, help='initial learning rate for adam')
+ parser.add_argument('--gan_mode', type=str, default='lsgan', help='the type of GAN objective. [vanilla| lsgan | wgangp]. vanilla GAN loss is the cross-entropy objective used in the original GAN paper.')
+ parser.add_argument('--pool_size', type=int, default=50, help='the size of image buffer that stores previously generated images')
+ parser.add_argument('--lr_policy', type=str, default='linear', help='learning rate policy. [linear | step | plateau | cosine]')
+ parser.add_argument('--lr_decay_iters', type=int, default=50, help='multiply by a gamma every lr_decay_iters iterations')
self.isTrain = True
+ return parser
diff --git a/pix2pix.ipynb b/pix2pix.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bb7030dafec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pix2pix.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,265 @@
+{
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "colab": {
+ "name": "pix2pix",
+ "provenance": [],
+ "collapsed_sections": [],
+ "include_colab_link": true
+ },
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "name": "python3",
+ "display_name": "Python 3"
+ },
+ "accelerator": "GPU"
+ },
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "view-in-github",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ " "
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "7wNjDKdQy35h",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Install"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "TRm-USlsHgEV",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "Pt3igws3eiVp",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import os\n",
+ "os.chdir('pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/')"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "z1EySlOXwwoa",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!pip install -r requirements.txt"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "8daqlgVhw29P",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Datasets\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Download one of the official datasets with:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh [cityscapes, night2day, edges2handbags, edges2shoes, facades, maps]`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Or use your own dataset by creating the appropriate folders and adding in the images. Follow the instructions [here](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/datasets.md#pix2pix-datasets)."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "vrdOettJxaCc",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "gdUz4116xhpm",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Pretrained models\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Download one of the official pretrained models with:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `bash ./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh [edges2shoes, sat2map, map2sat, facades_label2photo, and day2night]`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Or add your own pretrained model to `./checkpoints/{NAME}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pt`"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "GC2DEP4M0OsS",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!bash ./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh facades_label2photo"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "yFw1kDQBx3LN",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Training\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Change the `--dataroot` and `--name` to your own dataset's path and model's name. Use `--gpu_ids 0,1,..` to train on multiple GPUs and `--batch_size` to change the batch size. Add `--direction BtoA` if you want to train a model to transfrom from class B to A."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "0sp7TCT2x9dB",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "9UkcaFZiyASl",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Testing\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_pix2pix`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Change the `--dataroot`, `--name`, and `--direction` to be consistent with your trained model's configuration and how you want to transform images.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> from https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix:\n",
+ "> Note that we specified --direction BtoA as Facades dataset's A to B direction is photos to labels.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> If you would like to apply a pre-trained model to a collection of input images (rather than image pairs), please use --model test option. See ./scripts/test_single.sh for how to apply a model to Facade label maps (stored in the directory facades/testB).\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> See a list of currently available models at ./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "mey7o6j-0368",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!ls checkpoints/"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "uCsKkEq0yGh0",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_label2photo_pretrained"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "OzSKIPUByfiN",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Visualize"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "9Mgg8raPyizq",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
+ "\n",
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/facades_label2photo_pretrained/test_latest/images/100_fake_B.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "0G3oVH9DyqLQ",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/facades_label2photo_pretrained/test_latest/images/100_real_A.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "ErK5OC1j1LH4",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/facades_label2photo_pretrained/test_latest/images/100_real_B.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ }
+ ]
+}
diff --git a/pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh b/pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh
deleted file mode 100644
index 91f002144d5..00000000000
--- a/pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
-FILE=$1
-
-echo "Note: available models are horse2zebra, zebra2horse"
-
-echo "Specified [$FILE]"
-
-mkdir -p ./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained
-MODEL_FILE=./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth
-URL=https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~taesung_park/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/models/$FILE.pth
-
-wget -N $URL -O $MODEL_FILE
-
-
diff --git a/pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh b/pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh
deleted file mode 100644
index ee51a43450a..00000000000
--- a/pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
-FILE=$1
-
-echo "Note: available models are edges2shoes, sat2map, and facades_label2photo"
-
-echo "Specified [$FILE]"
-
-mkdir -p ./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained
-MODEL_FILE=./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth
-URL=https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~taesung_park/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/pix2pix_models/$FILE.pth
-
-wget -N $URL -O $MODEL_FILE
-
-
diff --git a/requirements.txt b/requirements.txt
index 072d027a2b0..a3561a19a03 100644
--- a/requirements.txt
+++ b/requirements.txt
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-torch>=0.4.0
+torch>=0.4.1
torchvision>=0.2.1
dominate>=2.3.1
visdom>=0.1.8.3
diff --git a/scripts/check_all.sh b/scripts/check_all.sh
deleted file mode 100644
index f13a64766e0..00000000000
--- a/scripts/check_all.sh
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
-set -ex
-DOWNLOAD=${1}
-echo 'apply a pretrained cyclegan model'
-if [ ${DOWNLOAD} -eq 1 ]
-then
- bash pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh horse2zebra
- bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh horse2zebra
-fi
-python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --checkpoints_dir ./checkpoints/ --name horse2zebra_pretrained --no_dropout --model test --dataset_mode single --loadSize 256
-
-echo 'apply a pretrained pix2pix model'
-if [ ${DOWNLOAD} -eq 1 ]
-then
- bash pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh facades_label2photo
- bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades
-fi
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/ --which_direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_label2photo_pretrained --dataset_mode aligned --which_model_netG unet_256 --norm batch
-
-
-echo 'cyclegan train (1 epoch) and test'
-if [ ${DOWNLOAD} -eq 1 ]
-then
- bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh maps
-fi
-python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --no_dropout --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --max_dataset_size 100 --save_latest_freq 100
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --phase test --no_dropout
-
-
-echo 'pix2pix train (1 epoch) and test'
-python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch --pool_size 0 --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --save_latest_freq 400
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
diff --git a/scripts/conda_deps.sh b/scripts/conda_deps.sh
index accac640541..72df436f0e9 100644
--- a/scripts/conda_deps.sh
+++ b/scripts/conda_deps.sh
@@ -1,6 +1,4 @@
set -ex
conda install numpy pyyaml mkl mkl-include setuptools cmake cffi typing
-conda install -c pytorch magma-cuda80 # or magma-cuda90 if CUDA 9
-conda install pytorch torchvision -c pytorch # install pytorch; if you want to use cuda90, add cuda90
-conda install -c conda-forge dominate # install dominate
-conda install -c conda-forge visdom # install visdom
+conda install pytorch torchvision -c pytorch # add cuda90 if CUDA 9
+conda install visdom dominate -c conda-forge # install visdom and dominate
diff --git a/scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh b/scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..26e198a44aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+FILE=$1
+
+echo "Note: available models are apple2orange, orange2apple, summer2winter_yosemite, winter2summer_yosemite, horse2zebra, zebra2horse, monet2photo, style_monet, style_cezanne, style_ukiyoe, style_vangogh, sat2map, map2sat, cityscapes_photo2label, cityscapes_label2photo, facades_photo2label, facades_label2photo, iphone2dslr_flower"
+
+echo "Specified [$FILE]"
+
+mkdir -p ./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained
+MODEL_FILE=./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth
+URL=http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/cyclegan/pretrained_models/$FILE.pth
+
+wget -N $URL -O $MODEL_FILE
diff --git a/scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh b/scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6b21232f074
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+FILE=$1
+
+echo "Note: available models are edges2shoes, sat2map, map2sat, facades_label2photo, and day2night"
+echo "Specified [$FILE]"
+
+mkdir -p ./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained
+MODEL_FILE=./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth
+URL=http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/pix2pix/models-pytorch/$FILE.pth
+
+wget -N $URL -O $MODEL_FILE
diff --git a/scripts/edges/PostprocessHED.m b/scripts/edges/PostprocessHED.m
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..78a99106ea6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/edges/PostprocessHED.m
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+%%% Prerequisites
+% You need to get the cpp file edgesNmsMex.cpp from https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pdollar/edges/master/private/edgesNmsMex.cpp
+% and compile it in Matlab: mex edgesNmsMex.cpp
+% You also need to download and install Piotr's Computer Vision Matlab Toolbox: https://pdollar.github.io/toolbox/
+
+%%% parameters
+% hed_mat_dir: the hed mat file directory (the output of 'batch_hed.py')
+% edge_dir: the output HED edges directory
+% image_width: resize the edge map to [image_width, image_width]
+% threshold: threshold for image binarization (default 25.0/255.0)
+% small_edge: remove small edges (default 5)
+
+function [] = PostprocessHED(hed_mat_dir, edge_dir, image_width, threshold, small_edge)
+
+if ~exist(edge_dir, 'dir')
+ mkdir(edge_dir);
+end
+fileList = dir(fullfile(hed_mat_dir, '*.mat'));
+nFiles = numel(fileList);
+fprintf('find %d mat files\n', nFiles);
+
+for n = 1 : nFiles
+ if mod(n, 1000) == 0
+ fprintf('process %d/%d images\n', n, nFiles);
+ end
+ fileName = fileList(n).name;
+ filePath = fullfile(hed_mat_dir, fileName);
+ jpgName = strrep(fileName, '.mat', '.jpg');
+ edge_path = fullfile(edge_dir, jpgName);
+
+ if ~exist(edge_path, 'file')
+ E = GetEdge(filePath);
+ E = imresize(E,[image_width,image_width]);
+ E_simple = SimpleEdge(E, threshold, small_edge);
+ E_simple = uint8(E_simple*255);
+ imwrite(E_simple, edge_path, 'Quality',100);
+ end
+end
+end
+
+
+
+
+function [E] = GetEdge(filePath)
+load(filePath);
+E = 1-edge_predict;
+end
+
+function [E4] = SimpleEdge(E, threshold, small_edge)
+if nargin <= 1
+ threshold = 25.0/255.0;
+end
+
+if nargin <= 2
+ small_edge = 5;
+end
+
+if ndims(E) == 3
+ E = E(:,:,1);
+end
+
+E1 = 1 - E;
+E2 = EdgeNMS(E1);
+E3 = double(E2>=max(eps,threshold));
+E3 = bwmorph(E3,'thin',inf);
+E4 = bwareaopen(E3, small_edge);
+E4=1-E4;
+end
+
+function [E_nms] = EdgeNMS( E )
+E=single(E);
+[Ox,Oy] = gradient2(convTri(E,4));
+[Oxx,~] = gradient2(Ox);
+[Oxy,Oyy] = gradient2(Oy);
+O = mod(atan(Oyy.*sign(-Oxy)./(Oxx+1e-5)),pi);
+E_nms = edgesNmsMex(E,O,1,5,1.01,1);
+end
diff --git a/scripts/edges/batch_hed.py b/scripts/edges/batch_hed.py
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..6de60e05721
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/edges/batch_hed.py
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+# HED batch processing script; modified from https://github.com/s9xie/hed/blob/master/examples/hed/HED-tutorial.ipynb
+# Step 1: download the hed repo: https://github.com/s9xie/hed
+# Step 2: download the models and protoxt, and put them under {caffe_root}/examples/hed/
+# Step 3: put this script under {caffe_root}/examples/hed/
+# Step 4: run the following script:
+# python batch_hed.py --images_dir=/data/to/path/photos/ --hed_mat_dir=/data/to/path/hed_mat_files/
+# The code sometimes crashes after computation is done. Error looks like "Check failed: ... driver shutting down". You can just kill the job.
+# For large images, it will produce gpu memory issue. Therefore, you better resize the images before running this script.
+# Step 5: run the MATLAB post-processing script "PostprocessHED.m"
+
+
+import caffe
+import numpy as np
+from PIL import Image
+import os
+import argparse
+import sys
+import scipy.io as sio
+
+
+def parse_args():
+ parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='batch proccesing: photos->edges')
+ parser.add_argument('--caffe_root', dest='caffe_root', help='caffe root', default='../../', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--caffemodel', dest='caffemodel', help='caffemodel', default='./hed_pretrained_bsds.caffemodel', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--prototxt', dest='prototxt', help='caffe prototxt file', default='./deploy.prototxt', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--images_dir', dest='images_dir', help='directory to store input photos', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--hed_mat_dir', dest='hed_mat_dir', help='directory to store output hed edges in mat file', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--border', dest='border', help='padding border', type=int, default=128)
+ parser.add_argument('--gpu_id', dest='gpu_id', help='gpu id', type=int, default=1)
+ args = parser.parse_args()
+ return args
+
+
+args = parse_args()
+for arg in vars(args):
+ print('[%s] =' % arg, getattr(args, arg))
+# Make sure that caffe is on the python path:
+caffe_root = args.caffe_root # this file is expected to be in {caffe_root}/examples/hed/
+sys.path.insert(0, caffe_root + 'python')
+
+
+if not os.path.exists(args.hed_mat_dir):
+ print('create output directory %s' % args.hed_mat_dir)
+ os.makedirs(args.hed_mat_dir)
+
+imgList = os.listdir(args.images_dir)
+nImgs = len(imgList)
+print('#images = %d' % nImgs)
+
+caffe.set_mode_gpu()
+caffe.set_device(args.gpu_id)
+# load net
+net = caffe.Net(args.prototxt, args.caffemodel, caffe.TEST)
+# pad border
+border = args.border
+
+for i in range(nImgs):
+ if i % 500 == 0:
+ print('processing image %d/%d' % (i, nImgs))
+ im = Image.open(os.path.join(args.images_dir, imgList[i]))
+
+ in_ = np.array(im, dtype=np.float32)
+ in_ = np.pad(in_, ((border, border), (border, border), (0, 0)), 'reflect')
+
+ in_ = in_[:, :, 0:3]
+ in_ = in_[:, :, ::-1]
+ in_ -= np.array((104.00698793, 116.66876762, 122.67891434))
+ in_ = in_.transpose((2, 0, 1))
+ # remove the following two lines if testing with cpu
+
+ # shape for input (data blob is N x C x H x W), set data
+ net.blobs['data'].reshape(1, *in_.shape)
+ net.blobs['data'].data[...] = in_
+ # run net and take argmax for prediction
+ net.forward()
+ fuse = net.blobs['sigmoid-fuse'].data[0][0, :, :]
+ # get rid of the border
+ fuse = fuse[border:-border, border:-border]
+ # save hed file to the disk
+ name, ext = os.path.splitext(imgList[i])
+ sio.savemat(os.path.join(args.hed_mat_dir, name + '.mat'), {'edge_predict': fuse})
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/deploy.prototxt b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/deploy.prototxt
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..f4d7e71e924
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/deploy.prototxt
@@ -0,0 +1,769 @@
+layer {
+ name: "data"
+ type: "Input"
+ top: "data"
+ input_param {
+ shape {
+ dim: 1
+ dim: 3
+ dim: 500
+ dim: 500
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv1_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "data"
+ top: "conv1_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 64
+ pad: 100
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu1_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv1_1"
+ top: "conv1_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv1_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv1_1"
+ top: "conv1_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 64
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu1_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv1_2"
+ top: "conv1_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool1"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv1_2"
+ top: "pool1"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv2_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool1"
+ top: "conv2_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 128
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu2_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv2_1"
+ top: "conv2_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv2_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv2_1"
+ top: "conv2_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 128
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu2_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv2_2"
+ top: "conv2_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool2"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv2_2"
+ top: "pool2"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv3_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool2"
+ top: "conv3_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 256
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu3_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv3_1"
+ top: "conv3_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv3_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv3_1"
+ top: "conv3_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 256
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu3_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv3_2"
+ top: "conv3_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv3_3"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv3_2"
+ top: "conv3_3"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 256
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu3_3"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv3_3"
+ top: "conv3_3"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool3"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv3_3"
+ top: "pool3"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv4_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool3"
+ top: "conv4_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu4_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv4_1"
+ top: "conv4_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv4_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv4_1"
+ top: "conv4_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu4_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv4_2"
+ top: "conv4_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv4_3"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv4_2"
+ top: "conv4_3"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu4_3"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv4_3"
+ top: "conv4_3"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool4"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv4_3"
+ top: "pool4"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv5_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool4"
+ top: "conv5_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu5_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv5_1"
+ top: "conv5_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv5_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv5_1"
+ top: "conv5_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu5_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv5_2"
+ top: "conv5_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv5_3"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv5_2"
+ top: "conv5_3"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu5_3"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv5_3"
+ top: "conv5_3"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool5"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv5_3"
+ top: "pool5"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "fc6_cs"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool5"
+ top: "fc6_cs"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 4096
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 7
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu6_cs"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "fc6_cs"
+ top: "fc6_cs"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "fc7_cs"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "fc6_cs"
+ top: "fc7_cs"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 4096
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 1
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu7_cs"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "fc7_cs"
+ top: "fc7_cs"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_fr"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "fc7_cs"
+ top: "score_fr"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "upscore2"
+ type: "Deconvolution"
+ bottom: "score_fr"
+ top: "upscore2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ bias_term: false
+ kernel_size: 4
+ stride: 2
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_pool4"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool4"
+ top: "score_pool4"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_pool4c"
+ type: "Crop"
+ bottom: "score_pool4"
+ bottom: "upscore2"
+ top: "score_pool4c"
+ crop_param {
+ axis: 2
+ offset: 5
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "fuse_pool4"
+ type: "Eltwise"
+ bottom: "upscore2"
+ bottom: "score_pool4c"
+ top: "fuse_pool4"
+ eltwise_param {
+ operation: SUM
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "upscore_pool4"
+ type: "Deconvolution"
+ bottom: "fuse_pool4"
+ top: "upscore_pool4"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ bias_term: false
+ kernel_size: 4
+ stride: 2
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_pool3"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool3"
+ top: "score_pool3"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_pool3c"
+ type: "Crop"
+ bottom: "score_pool3"
+ bottom: "upscore_pool4"
+ top: "score_pool3c"
+ crop_param {
+ axis: 2
+ offset: 9
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "fuse_pool3"
+ type: "Eltwise"
+ bottom: "upscore_pool4"
+ bottom: "score_pool3c"
+ top: "fuse_pool3"
+ eltwise_param {
+ operation: SUM
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "upscore8"
+ type: "Deconvolution"
+ bottom: "fuse_pool3"
+ top: "upscore8"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ bias_term: false
+ kernel_size: 16
+ stride: 8
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score"
+ type: "Crop"
+ bottom: "upscore8"
+ bottom: "data"
+ top: "score"
+ crop_param {
+ axis: 2
+ offset: 31
+ }
+}
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/cityscapes.py b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/cityscapes.py
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..05b14715d3b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/cityscapes.py
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
+# The following code is modified from https://github.com/shelhamer/clockwork-fcn
+import sys
+import os
+import glob
+import numpy as np
+from PIL import Image
+
+
+class cityscapes:
+ def __init__(self, data_path):
+ # data_path something like /data2/cityscapes
+ self.dir = data_path
+ self.classes = ['road', 'sidewalk', 'building', 'wall', 'fence',
+ 'pole', 'traffic light', 'traffic sign', 'vegetation', 'terrain',
+ 'sky', 'person', 'rider', 'car', 'truck',
+ 'bus', 'train', 'motorcycle', 'bicycle']
+ self.mean = np.array((72.78044, 83.21195, 73.45286), dtype=np.float32)
+ # import cityscapes label helper and set up label mappings
+ sys.path.insert(0, '{}/scripts/helpers/'.format(self.dir))
+ labels = __import__('labels')
+ self.id2trainId = {label.id: label.trainId for label in labels.labels} # dictionary mapping from raw IDs to train IDs
+ self.trainId2color = {label.trainId: label.color for label in labels.labels} # dictionary mapping train IDs to colors as 3-tuples
+
+ def get_dset(self, split):
+ '''
+ List images as (city, id) for the specified split
+
+ TODO(shelhamer) generate splits from cityscapes itself, instead of
+ relying on these separately made text files.
+ '''
+ if split == 'train':
+ dataset = open('{}/ImageSets/segFine/train.txt'.format(self.dir)).read().splitlines()
+ else:
+ dataset = open('{}/ImageSets/segFine/val.txt'.format(self.dir)).read().splitlines()
+ return [(item.split('/')[0], item.split('/')[1]) for item in dataset]
+
+ def load_image(self, split, city, idx):
+ im = Image.open('{}/leftImg8bit_sequence/{}/{}/{}_leftImg8bit.png'.format(self.dir, split, city, idx))
+ return im
+
+ def assign_trainIds(self, label):
+ """
+ Map the given label IDs to the train IDs appropriate for training
+ Use the label mapping provided in labels.py from the cityscapes scripts
+ """
+ label = np.array(label, dtype=np.float32)
+ if sys.version_info[0] < 3:
+ for k, v in self.id2trainId.iteritems():
+ label[label == k] = v
+ else:
+ for k, v in self.id2trainId.items():
+ label[label == k] = v
+ return label
+
+ def load_label(self, split, city, idx):
+ """
+ Load label image as 1 x height x width integer array of label indices.
+ The leading singleton dimension is required by the loss.
+ """
+ label = Image.open('{}/gtFine/{}/{}/{}_gtFine_labelIds.png'.format(self.dir, split, city, idx))
+ label = self.assign_trainIds(label) # get proper labels for eval
+ label = np.array(label, dtype=np.uint8)
+ label = label[np.newaxis, ...]
+ return label
+
+ def preprocess(self, im):
+ """
+ Preprocess loaded image (by load_image) for Caffe:
+ - cast to float
+ - switch channels RGB -> BGR
+ - subtract mean
+ - transpose to channel x height x width order
+ """
+ in_ = np.array(im, dtype=np.float32)
+ in_ = in_[:, :, ::-1]
+ in_ -= self.mean
+ in_ = in_.transpose((2, 0, 1))
+ return in_
+
+ def palette(self, label):
+ '''
+ Map trainIds to colors as specified in labels.py
+ '''
+ if label.ndim == 3:
+ label = label[0]
+ color = np.empty((label.shape[0], label.shape[1], 3))
+ if sys.version_info[0] < 3:
+ for k, v in self.trainId2color.iteritems():
+ color[label == k, :] = v
+ else:
+ for k, v in self.trainId2color.items():
+ color[label == k, :] = v
+ return color
+
+ def make_boundaries(label, thickness=None):
+ """
+ Input is an image label, output is a numpy array mask encoding the boundaries of the objects
+ Extract pixels at the true boundary by dilation - erosion of label.
+ Don't just pick the void label as it is not exclusive to the boundaries.
+ """
+ assert(thickness is not None)
+ import skimage.morphology as skm
+ void = 255
+ mask = np.logical_and(label > 0, label != void)[0]
+ selem = skm.disk(thickness)
+ boundaries = np.logical_xor(skm.dilation(mask, selem),
+ skm.erosion(mask, selem))
+ return boundaries
+
+ def list_label_frames(self, split):
+ """
+ Select labeled frames from a split for evaluation
+ collected as (city, shot, idx) tuples
+ """
+ def file2idx(f):
+ """Helper to convert file path into frame ID"""
+ city, shot, frame = (os.path.basename(f).split('_')[:3])
+ return "_".join([city, shot, frame])
+ frames = []
+ cities = [os.path.basename(f) for f in glob.glob('{}/gtFine/{}/*'.format(self.dir, split))]
+ for c in cities:
+ files = sorted(glob.glob('{}/gtFine/{}/{}/*labelIds.png'.format(self.dir, split, c)))
+ frames.extend([file2idx(f) for f in files])
+ return frames
+
+ def collect_frame_sequence(self, split, idx, length):
+ """
+ Collect sequence of frames preceding (and including) a labeled frame
+ as a list of Images.
+
+ Note: 19 preceding frames are provided for each labeled frame.
+ """
+ SEQ_LEN = length
+ city, shot, frame = idx.split('_')
+ frame = int(frame)
+ frame_seq = []
+ for i in range(frame - SEQ_LEN, frame + 1):
+ frame_path = '{0}/leftImg8bit_sequence/val/{1}/{1}_{2}_{3:0>6d}_leftImg8bit.png'.format(
+ self.dir, city, shot, i)
+ frame_seq.append(Image.open(frame_path))
+ return frame_seq
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/download_fcn8s.sh b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/download_fcn8s.sh
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..f45af158e94
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/download_fcn8s.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
+URL=http://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz/projects/pix2pix/fcn-8s-cityscapes/fcn-8s-cityscapes.caffemodel
+OUTPUT_FILE=./scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/fcn-8s-cityscapes.caffemodel
+wget -N $URL -O $OUTPUT_FILE
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/evaluate.py b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/evaluate.py
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..500c20f7007
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/evaluate.py
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+import os
+import caffe
+import argparse
+import numpy as np
+import scipy.misc
+from PIL import Image
+from util import segrun, fast_hist, get_scores
+from cityscapes import cityscapes
+
+parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
+parser.add_argument("--cityscapes_dir", type=str, required=True, help="Path to the original cityscapes dataset")
+parser.add_argument("--result_dir", type=str, required=True, help="Path to the generated images to be evaluated")
+parser.add_argument("--output_dir", type=str, required=True, help="Where to save the evaluation results")
+parser.add_argument("--caffemodel_dir", type=str, default='./scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/', help="Where the FCN-8s caffemodel stored")
+parser.add_argument("--gpu_id", type=int, default=0, help="Which gpu id to use")
+parser.add_argument("--split", type=str, default='val', help="Data split to be evaluated")
+parser.add_argument("--save_output_images", type=int, default=0, help="Whether to save the FCN output images")
+args = parser.parse_args()
+
+
+def main():
+ if not os.path.isdir(args.output_dir):
+ os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
+ if args.save_output_images > 0:
+ output_image_dir = args.output_dir + 'image_outputs/'
+ if not os.path.isdir(output_image_dir):
+ os.makedirs(output_image_dir)
+ CS = cityscapes(args.cityscapes_dir)
+ n_cl = len(CS.classes)
+ label_frames = CS.list_label_frames(args.split)
+ caffe.set_device(args.gpu_id)
+ caffe.set_mode_gpu()
+ net = caffe.Net(args.caffemodel_dir + '/deploy.prototxt',
+ args.caffemodel_dir + 'fcn-8s-cityscapes.caffemodel',
+ caffe.TEST)
+
+ hist_perframe = np.zeros((n_cl, n_cl))
+ for i, idx in enumerate(label_frames):
+ if i % 10 == 0:
+ print('Evaluating: %d/%d' % (i, len(label_frames)))
+ city = idx.split('_')[0]
+ # idx is city_shot_frame
+ label = CS.load_label(args.split, city, idx)
+ im_file = args.result_dir + '/' + idx + '_leftImg8bit.png'
+ im = np.array(Image.open(im_file))
+ im = scipy.misc.imresize(im, (label.shape[1], label.shape[2]))
+ out = segrun(net, CS.preprocess(im))
+ hist_perframe += fast_hist(label.flatten(), out.flatten(), n_cl)
+ if args.save_output_images > 0:
+ label_im = CS.palette(label)
+ pred_im = CS.palette(out)
+ scipy.misc.imsave(output_image_dir + '/' + str(i) + '_pred.jpg', pred_im)
+ scipy.misc.imsave(output_image_dir + '/' + str(i) + '_gt.jpg', label_im)
+ scipy.misc.imsave(output_image_dir + '/' + str(i) + '_input.jpg', im)
+
+ mean_pixel_acc, mean_class_acc, mean_class_iou, per_class_acc, per_class_iou = get_scores(hist_perframe)
+ with open(args.output_dir + '/evaluation_results.txt', 'w') as f:
+ f.write('Mean pixel accuracy: %f\n' % mean_pixel_acc)
+ f.write('Mean class accuracy: %f\n' % mean_class_acc)
+ f.write('Mean class IoU: %f\n' % mean_class_iou)
+ f.write('************ Per class numbers below ************\n')
+ for i, cl in enumerate(CS.classes):
+ while len(cl) < 15:
+ cl = cl + ' '
+ f.write('%s: acc = %f, iou = %f\n' % (cl, per_class_acc[i], per_class_iou[i]))
+
+
+main()
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/util.py b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/util.py
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..8fce27fd6eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/util.py
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+# The following code is modified from https://github.com/shelhamer/clockwork-fcn
+import numpy as np
+
+
+def get_out_scoremap(net):
+ return net.blobs['score'].data[0].argmax(axis=0).astype(np.uint8)
+
+
+def feed_net(net, in_):
+ """
+ Load prepared input into net.
+ """
+ net.blobs['data'].reshape(1, *in_.shape)
+ net.blobs['data'].data[...] = in_
+
+
+def segrun(net, in_):
+ feed_net(net, in_)
+ net.forward()
+ return get_out_scoremap(net)
+
+
+def fast_hist(a, b, n):
+ k = np.where((a >= 0) & (a < n))[0]
+ bc = np.bincount(n * a[k].astype(int) + b[k], minlength=n**2)
+ if len(bc) != n**2:
+ # ignore this example if dimension mismatch
+ return 0
+ return bc.reshape(n, n)
+
+
+def get_scores(hist):
+ # Mean pixel accuracy
+ acc = np.diag(hist).sum() / (hist.sum() + 1e-12)
+
+ # Per class accuracy
+ cl_acc = np.diag(hist) / (hist.sum(1) + 1e-12)
+
+ # Per class IoU
+ iu = np.diag(hist) / (hist.sum(1) + hist.sum(0) - np.diag(hist) + 1e-12)
+
+ return acc, np.nanmean(cl_acc), np.nanmean(iu), cl_acc, iu
diff --git a/scripts/test_before_push.py b/scripts/test_before_push.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a68746421aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/test_before_push.py
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+# Simple script to make sure basic usage
+# such as training, testing, saving and loading
+# runs without errors.
+import os
+
+
+def run(command):
+ print(command)
+ exit_status = os.system(command)
+ if exit_status > 0:
+ exit(1)
+
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ # download mini datasets
+ if not os.path.exists('./datasets/mini'):
+ run('bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh mini')
+
+ if not os.path.exists('./datasets/mini_pix2pix'):
+ run('bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh mini_pix2pix')
+
+ # pretrained cyclegan model
+ if not os.path.exists('./checkpoints/horse2zebra_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth'):
+ run('bash ./scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh horse2zebra')
+ run('python test.py --model test --dataroot ./datasets/mini --name horse2zebra_pretrained --no_dropout --num_test 1 --no_dropout')
+
+ # pretrained pix2pix model
+ if not os.path.exists('./checkpoints/facades_label2photo_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth'):
+ run('bash ./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh facades_label2photo')
+ if not os.path.exists('./datasets/facades'):
+ run('bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades')
+ run('python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/ --direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_label2photo_pretrained --num_test 1')
+
+ # cyclegan train/test
+ run('python train.py --model cycle_gan --name temp_cyclegan --dataroot ./datasets/mini --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --save_latest_freq 10 --print_freq 1 --display_id -1')
+ run('python test.py --model test --name temp_cyclegan --dataroot ./datasets/mini --num_test 1 --model_suffix "_A" --no_dropout')
+
+ # pix2pix train/test
+ run('python train.py --model pix2pix --name temp_pix2pix --dataroot ./datasets/mini_pix2pix --niter 1 --niter_decay 5 --save_latest_freq 10 --display_id -1')
+ run('python test.py --model pix2pix --name temp_pix2pix --dataroot ./datasets/mini_pix2pix --num_test 1')
+
+ # template train/test
+ run('python train.py --model template --name temp2 --dataroot ./datasets/mini_pix2pix --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --save_latest_freq 10 --display_id -1')
+ run('python test.py --model template --name temp2 --dataroot ./datasets/mini_pix2pix --num_test 1')
+
+ # colorization train/test (optional)
+ if not os.path.exists('./datasets/mini_colorization'):
+ run('bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh mini_colorization')
+
+ run('python train.py --model colorization --name temp_color --dataroot ./datasets/mini_colorization --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --save_latest_freq 5 --display_id -1')
+ run('python test.py --model colorization --name temp_color --dataroot ./datasets/mini_colorization --num_test 1')
diff --git a/scripts/test_colorization.sh b/scripts/test_colorization.sh
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9837fd5fffa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/test_colorization.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+set -ex
+python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/colorization --name color_pix2pix --model colorization
diff --git a/scripts/test_pix2pix.sh b/scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
index 2cc311e4b26..589599b4c16 100755
--- a/scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
+++ b/scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
@@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
set -ex
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
+python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --netG unet_256 --direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
diff --git a/scripts/test_single.sh b/scripts/test_single.sh
index f1570ccf583..eada640276b 100755
--- a/scripts/test_single.sh
+++ b/scripts/test_single.sh
@@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
set -ex
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name facades_pix2pix --model test --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode single --norm batch
+python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name facades_pix2pix --model test --netG unet_256 --direction BtoA --dataset_mode single --norm batch
diff --git a/scripts/train_colorization.sh b/scripts/train_colorization.sh
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e6c06801209
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/train_colorization.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+set -ex
+python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/colorization --name color_pix2pix --model colorization
diff --git a/scripts/train_pix2pix.sh b/scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
index e9f703e1998..0171001c554 100755
--- a/scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
+++ b/scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
@@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
set -ex
-python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch --pool_size 0
+python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --netG unet_256 --direction BtoA --lambda_L1 100 --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch --pool_size 0
diff --git a/test.py b/test.py
index 51e7f929d9d..9281a992d50 100644
--- a/test.py
+++ b/test.py
@@ -1,35 +1,69 @@
+"""General-purpose test script for image-to-image translation.
+
+Once you have trained your model with train.py, you can use this script to test the model.
+It will load a saved model from --checkpoints_dir and save the results to --results_dir.
+
+It first creates model and dataset given the option. It will hard-code some parameters.
+It then runs inference for --num_test images and save results to an HTML file.
+
+Example (You need to train models first or download pre-trained models from our website):
+ Test a CycleGAN model (both sides):
+ python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan
+
+ Test a CycleGAN model (one side only):
+ python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --name horse2zebra_pretrained --model test --no_dropout
+
+ The option '--model test' is used for generating CycleGAN results only for one side.
+ This option will automatically set '--dataset_mode single', which only loads the images from one set.
+ On the contrary, using '--model cycle_gan' requires loading and generating results in both directions,
+ which is sometimes unnecessary. The results will be saved at ./results/.
+ Use '--results_dir ' to specify the results directory.
+
+ Test a pix2pix model:
+ python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA
+
+See options/base_options.py and options/test_options.py for more test options.
+See training and test tips at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/tips.md
+See frequently asked questions at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/qa.md
+"""
import os
from options.test_options import TestOptions
-from data import CreateDataLoader
+from data import create_dataset
from models import create_model
from util.visualizer import save_images
from util import html
if __name__ == '__main__':
- opt = TestOptions().parse()
- opt.nThreads = 1 # test code only supports nThreads = 1
- opt.batchSize = 1 # test code only supports batchSize = 1
- opt.serial_batches = True # no shuffle
- opt.no_flip = True # no flip
- opt.display_id = -1 # no visdom display
- data_loader = CreateDataLoader(opt)
- dataset = data_loader.load_data()
- model = create_model(opt)
- model.setup(opt)
- # create website
- web_dir = os.path.join(opt.results_dir, opt.name, '%s_%s' % (opt.phase, opt.which_epoch))
- webpage = html.HTML(web_dir, 'Experiment = %s, Phase = %s, Epoch = %s' % (opt.name, opt.phase, opt.which_epoch))
- # test
+ opt = TestOptions().parse() # get test options
+ # hard-code some parameters for test
+ opt.num_threads = 0 # test code only supports num_threads = 1
+ opt.batch_size = 1 # test code only supports batch_size = 1
+ opt.serial_batches = True # disable data shuffling; comment this line if results on randomly chosen images are needed.
+ opt.no_flip = True # no flip; comment this line if results on flipped images are needed.
+ opt.display_id = -1 # no visdom display; the test code saves the results to a HTML file.
+ dataset = create_dataset(opt) # create a dataset given opt.dataset_mode and other options
+ model = create_model(opt) # create a model given opt.model and other options
+ model.setup(opt) # regular setup: load and print networks; create schedulers
+ # create a website
+ web_dir = os.path.join(opt.results_dir, opt.name, '{}_{}'.format(opt.phase, opt.epoch)) # define the website directory
+ if opt.load_iter > 0: # load_iter is 0 by default
+ web_dir = '{:s}_iter{:d}'.format(web_dir, opt.load_iter)
+ print('creating web directory', web_dir)
+ webpage = html.HTML(web_dir, 'Experiment = %s, Phase = %s, Epoch = %s' % (opt.name, opt.phase, opt.epoch))
+ # test with eval mode. This only affects layers like batchnorm and dropout.
+ # For [pix2pix]: we use batchnorm and dropout in the original pix2pix. You can experiment it with and without eval() mode.
+ # For [CycleGAN]: It should not affect CycleGAN as CycleGAN uses instancenorm without dropout.
+ if opt.eval:
+ model.eval()
for i, data in enumerate(dataset):
- if i >= opt.how_many:
+ if i >= opt.num_test: # only apply our model to opt.num_test images.
break
- model.set_input(data)
- model.test()
- visuals = model.get_current_visuals()
- img_path = model.get_image_paths()
- if i % 5 == 0:
+ model.set_input(data) # unpack data from data loader
+ model.test() # run inference
+ visuals = model.get_current_visuals() # get image results
+ img_path = model.get_image_paths() # get image paths
+ if i % 5 == 0: # save images to an HTML file
print('processing (%04d)-th image... %s' % (i, img_path))
save_images(webpage, visuals, img_path, aspect_ratio=opt.aspect_ratio, width=opt.display_winsize)
-
- webpage.save()
+ webpage.save() # save the HTML
diff --git a/train.py b/train.py
index 0877a35f9a7..73982310101 100644
--- a/train.py
+++ b/train.py
@@ -1,59 +1,78 @@
+"""General-purpose training script for image-to-image translation.
+
+This script works for various models (with option '--model': e.g., pix2pix, cyclegan, colorization) and
+different datasets (with option '--dataset_mode': e.g., aligned, unaligned, single, colorization).
+You need to specify the dataset ('--dataroot'), experiment name ('--name'), and model ('--model').
+
+It first creates model, dataset, and visualizer given the option.
+It then does standard network training. During the training, it also visualize/save the images, print/save the loss plot, and save models.
+The script supports continue/resume training. Use '--continue_train' to resume your previous training.
+
+Example:
+ Train a CycleGAN model:
+ python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan
+ Train a pix2pix model:
+ python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA
+
+See options/base_options.py and options/train_options.py for more training options.
+See training and test tips at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/tips.md
+See frequently asked questions at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/qa.md
+"""
import time
from options.train_options import TrainOptions
-from data import CreateDataLoader
+from data import create_dataset
from models import create_model
from util.visualizer import Visualizer
if __name__ == '__main__':
- opt = TrainOptions().parse()
- data_loader = CreateDataLoader(opt)
- dataset = data_loader.load_data()
- dataset_size = len(data_loader)
- print('#training images = %d' % dataset_size)
-
- model = create_model(opt)
- model.setup(opt)
- visualizer = Visualizer(opt)
- total_steps = 0
-
- for epoch in range(opt.epoch_count, opt.niter + opt.niter_decay + 1):
- epoch_start_time = time.time()
- iter_data_time = time.time()
- epoch_iter = 0
-
- for i, data in enumerate(dataset):
- iter_start_time = time.time()
- if total_steps % opt.print_freq == 0:
+ opt = TrainOptions().parse() # get training options
+ dataset = create_dataset(opt) # create a dataset given opt.dataset_mode and other options
+ dataset_size = len(dataset) # get the number of images in the dataset.
+ print('The number of training images = %d' % dataset_size)
+
+ model = create_model(opt) # create a model given opt.model and other options
+ model.setup(opt) # regular setup: load and print networks; create schedulers
+ visualizer = Visualizer(opt) # create a visualizer that display/save images and plots
+ total_iters = 0 # the total number of training iterations
+
+ for epoch in range(opt.epoch_count, opt.niter + opt.niter_decay + 1): # outer loop for different epochs; we save the model by , +
+ epoch_start_time = time.time() # timer for entire epoch
+ iter_data_time = time.time() # timer for data loading per iteration
+ epoch_iter = 0 # the number of training iterations in current epoch, reset to 0 every epoch
+ visualizer.reset() # reset the visualizer: make sure it saves the results to HTML at least once every epoch
+
+ for i, data in enumerate(dataset): # inner loop within one epoch
+ iter_start_time = time.time() # timer for computation per iteration
+ if total_iters % opt.print_freq == 0:
t_data = iter_start_time - iter_data_time
- visualizer.reset()
- total_steps += opt.batchSize
- epoch_iter += opt.batchSize
- model.set_input(data)
- model.optimize_parameters()
-
- if total_steps % opt.display_freq == 0:
- save_result = total_steps % opt.update_html_freq == 0
+
+ total_iters += opt.batch_size
+ epoch_iter += opt.batch_size
+ model.set_input(data) # unpack data from dataset and apply preprocessing
+ model.optimize_parameters() # calculate loss functions, get gradients, update network weights
+
+ if total_iters % opt.display_freq == 0: # display images on visdom and save images to a HTML file
+ save_result = total_iters % opt.update_html_freq == 0
+ model.compute_visuals()
visualizer.display_current_results(model.get_current_visuals(), epoch, save_result)
- if total_steps % opt.print_freq == 0:
+ if total_iters % opt.print_freq == 0: # print training losses and save logging information to the disk
losses = model.get_current_losses()
- t = (time.time() - iter_start_time) / opt.batchSize
- visualizer.print_current_losses(epoch, epoch_iter, losses, t, t_data)
+ t_comp = (time.time() - iter_start_time) / opt.batch_size
+ visualizer.print_current_losses(epoch, epoch_iter, losses, t_comp, t_data)
if opt.display_id > 0:
- visualizer.plot_current_losses(epoch, float(epoch_iter) / dataset_size, opt, losses)
+ visualizer.plot_current_losses(epoch, float(epoch_iter) / dataset_size, losses)
- if total_steps % opt.save_latest_freq == 0:
- print('saving the latest model (epoch %d, total_steps %d)' %
- (epoch, total_steps))
- model.save_networks('latest')
+ if total_iters % opt.save_latest_freq == 0: # cache our latest model every iterations
+ print('saving the latest model (epoch %d, total_iters %d)' % (epoch, total_iters))
+ save_suffix = 'iter_%d' % total_iters if opt.save_by_iter else 'latest'
+ model.save_networks(save_suffix)
iter_data_time = time.time()
- if epoch % opt.save_epoch_freq == 0:
- print('saving the model at the end of epoch %d, iters %d' %
- (epoch, total_steps))
+ if epoch % opt.save_epoch_freq == 0: # cache our model every epochs
+ print('saving the model at the end of epoch %d, iters %d' % (epoch, total_iters))
model.save_networks('latest')
model.save_networks(epoch)
- print('End of epoch %d / %d \t Time Taken: %d sec' %
- (epoch, opt.niter + opt.niter_decay, time.time() - epoch_start_time))
- model.update_learning_rate()
+ print('End of epoch %d / %d \t Time Taken: %d sec' % (epoch, opt.niter + opt.niter_decay, time.time() - epoch_start_time))
+ model.update_learning_rate() # update learning rates at the end of every epoch.
diff --git a/util/__init__.py b/util/__init__.py
index e69de29bb2d..ae36f63d885 100644
--- a/util/__init__.py
+++ b/util/__init__.py
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+"""This package includes a miscellaneous collection of useful helper functions."""
diff --git a/util/get_data.py b/util/get_data.py
index 6325605bc68..97edc3ce3c3 100644
--- a/util/get_data.py
+++ b/util/get_data.py
@@ -9,26 +9,24 @@
class GetData(object):
- """
-
- Download CycleGAN or Pix2Pix Data.
+ """A Python script for downloading CycleGAN or pix2pix datasets.
- Args:
- technique : str
- One of: 'cyclegan' or 'pix2pix'.
- verbose : bool
- If True, print additional information.
+ Parameters:
+ technique (str) -- One of: 'cyclegan' or 'pix2pix'.
+ verbose (bool) -- If True, print additional information.
Examples:
>>> from util.get_data import GetData
>>> gd = GetData(technique='cyclegan')
>>> new_data_path = gd.get(save_path='./datasets') # options will be displayed.
+ Alternatively, You can use bash scripts: 'scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh'
+ and 'scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh'.
"""
def __init__(self, technique='cyclegan', verbose=True):
url_dict = {
- 'pix2pix': 'https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz/projects/pix2pix/datasets',
+ 'pix2pix': 'http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/pix2pix/datasets/',
'cyclegan': 'https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~taesung_park/CycleGAN/datasets'
}
self.url = url_dict.get(technique.lower())
@@ -83,18 +81,15 @@ def get(self, save_path, dataset=None):
Download a dataset.
- Args:
- save_path : str
- A directory to save the data to.
- dataset : str, optional
- A specific dataset to download.
- Note: this must include the file extension.
- If None, options will be presented for you
- to choose from.
+ Parameters:
+ save_path (str) -- A directory to save the data to.
+ dataset (str) -- (optional). A specific dataset to download.
+ Note: this must include the file extension.
+ If None, options will be presented for you
+ to choose from.
Returns:
- save_path_full : str
- The absolute path to the downloaded data.
+ save_path_full (str) -- the absolute path to the downloaded data.
"""
if dataset is None:
diff --git a/util/html.py b/util/html.py
index c7956f1353f..cc3262a1eaf 100644
--- a/util/html.py
+++ b/util/html.py
@@ -1,10 +1,24 @@
import dominate
-from dominate.tags import *
+from dominate.tags import meta, h3, table, tr, td, p, a, img, br
import os
class HTML:
- def __init__(self, web_dir, title, reflesh=0):
+ """This HTML class allows us to save images and write texts into a single HTML file.
+
+ It consists of functions such as (add a text header to the HTML file),
+ (add a row of images to the HTML file), and (save the HTML to the disk).
+ It is based on Python library 'dominate', a Python library for creating and manipulating HTML documents using a DOM API.
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self, web_dir, title, refresh=0):
+ """Initialize the HTML classes
+
+ Parameters:
+ web_dir (str) -- a directory that stores the webpage. HTML file will be created at /index.html; images will be saved at 0:
+ if refresh > 0:
with self.doc.head:
- meta(http_equiv="reflesh", content=str(reflesh))
+ meta(http_equiv="refresh", content=str(refresh))
def get_image_dir(self):
+ """Return the directory that stores images"""
return self.img_dir
- def add_header(self, str):
- with self.doc:
- h3(str)
+ def add_header(self, text):
+ """Insert a header to the HTML file
- def add_table(self, border=1):
- self.t = table(border=border, style="table-layout: fixed;")
- self.doc.add(self.t)
+ Parameters:
+ text (str) -- the header text
+ """
+ with self.doc:
+ h3(text)
def add_images(self, ims, txts, links, width=400):
- self.add_table()
+ """add images to the HTML file
+
+ Parameters:
+ ims (str list) -- a list of image paths
+ txts (str list) -- a list of image names shown on the website
+ links (str list) -- a list of hyperref links; when you click an image, it will redirect you to a new page
+ """
+ self.t = table(border=1, style="table-layout: fixed;") # Insert a table
+ self.doc.add(self.t)
with self.t:
with tr():
for im, txt, link in zip(ims, txts, links):
@@ -43,19 +66,18 @@ def add_images(self, ims, txts, links, width=400):
p(txt)
def save(self):
+ """save the current content to the HMTL file"""
html_file = '%s/index.html' % self.web_dir
f = open(html_file, 'wt')
f.write(self.doc.render())
f.close()
-if __name__ == '__main__':
+if __name__ == '__main__': # we show an example usage here.
html = HTML('web/', 'test_html')
html.add_header('hello world')
- ims = []
- txts = []
- links = []
+ ims, txts, links = [], [], []
for n in range(4):
ims.append('image_%d.png' % n)
txts.append('text_%d' % n)
diff --git a/util/image_pool.py b/util/image_pool.py
index 52413e0f8a4..6d086f882bc 100644
--- a/util/image_pool.py
+++ b/util/image_pool.py
@@ -3,30 +3,52 @@
class ImagePool():
+ """This class implements an image buffer that stores previously generated images.
+
+ This buffer enables us to update discriminators using a history of generated images
+ rather than the ones produced by the latest generators.
+ """
+
def __init__(self, pool_size):
+ """Initialize the ImagePool class
+
+ Parameters:
+ pool_size (int) -- the size of image buffer, if pool_size=0, no buffer will be created
+ """
self.pool_size = pool_size
- if self.pool_size > 0:
+ if self.pool_size > 0: # create an empty pool
self.num_imgs = 0
self.images = []
def query(self, images):
- if self.pool_size == 0:
+ """Return an image from the pool.
+
+ Parameters:
+ images: the latest generated images from the generator
+
+ Returns images from the buffer.
+
+ By 50/100, the buffer will return input images.
+ By 50/100, the buffer will return images previously stored in the buffer,
+ and insert the current images to the buffer.
+ """
+ if self.pool_size == 0: # if the buffer size is 0, do nothing
return images
return_images = []
for image in images:
image = torch.unsqueeze(image.data, 0)
- if self.num_imgs < self.pool_size:
+ if self.num_imgs < self.pool_size: # if the buffer is not full; keep inserting current images to the buffer
self.num_imgs = self.num_imgs + 1
self.images.append(image)
return_images.append(image)
else:
p = random.uniform(0, 1)
- if p > 0.5:
+ if p > 0.5: # by 50% chance, the buffer will return a previously stored image, and insert the current image into the buffer
random_id = random.randint(0, self.pool_size - 1) # randint is inclusive
tmp = self.images[random_id].clone()
self.images[random_id] = image
return_images.append(tmp)
- else:
+ else: # by another 50% chance, the buffer will return the current image
return_images.append(image)
- return_images = torch.cat(return_images, 0)
+ return_images = torch.cat(return_images, 0) # collect all the images and return
return return_images
diff --git a/util/util.py b/util/util.py
index ba7b083ca18..b050c13e1d6 100644
--- a/util/util.py
+++ b/util/util.py
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
+"""This module contains simple helper functions """
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import numpy as np
@@ -5,21 +6,34 @@
import os
-# Converts a Tensor into an image array (numpy)
-# |imtype|: the desired type of the converted numpy array
def tensor2im(input_image, imtype=np.uint8):
- if isinstance(input_image, torch.Tensor):
- image_tensor = input_image.data
- else:
- return input_image
- image_numpy = image_tensor[0].cpu().float().numpy()
- if image_numpy.shape[0] == 1:
- image_numpy = np.tile(image_numpy, (3, 1, 1))
- image_numpy = (np.transpose(image_numpy, (1, 2, 0)) + 1) / 2.0 * 255.0
+ """"Converts a Tensor array into a numpy image array.
+
+ Parameters:
+ input_image (tensor) -- the input image tensor array
+ imtype (type) -- the desired type of the converted numpy array
+ """
+ if not isinstance(input_image, np.ndarray):
+ if isinstance(input_image, torch.Tensor): # get the data from a variable
+ image_tensor = input_image.data
+ else:
+ return input_image
+ image_numpy = image_tensor[0].cpu().float().numpy() # convert it into a numpy array
+ if image_numpy.shape[0] == 1: # grayscale to RGB
+ image_numpy = np.tile(image_numpy, (3, 1, 1))
+ image_numpy = (np.transpose(image_numpy, (1, 2, 0)) + 1) / 2.0 * 255.0 # post-processing: tranpose and scaling
+ else: # if it is a numpy array, do nothing
+ image_numpy = input_image
return image_numpy.astype(imtype)
def diagnose_network(net, name='network'):
+ """Calculate and print the mean of average absolute(gradients)
+
+ Parameters:
+ net (torch network) -- Torch network
+ name (str) -- the name of the network
+ """
mean = 0.0
count = 0
for param in net.parameters():
@@ -32,12 +46,31 @@ def diagnose_network(net, name='network'):
print(mean)
-def save_image(image_numpy, image_path):
+def save_image(image_numpy, image_path, aspect_ratio=1.0):
+ """Save a numpy image to the disk
+
+ Parameters:
+ image_numpy (numpy array) -- input numpy array
+ image_path (str) -- the path of the image
+ """
+
image_pil = Image.fromarray(image_numpy)
+ h, w, _ = image_numpy.shape
+
+ if aspect_ratio > 1.0:
+ image_pil = image_pil.resize((h, int(w * aspect_ratio)), Image.BICUBIC)
+ if aspect_ratio < 1.0:
+ image_pil = image_pil.resize((int(h / aspect_ratio), w), Image.BICUBIC)
image_pil.save(image_path)
def print_numpy(x, val=True, shp=False):
+ """Print the mean, min, max, median, std, and size of a numpy array
+
+ Parameters:
+ val (bool) -- if print the values of the numpy array
+ shp (bool) -- if print the shape of the numpy array
+ """
x = x.astype(np.float64)
if shp:
print('shape,', x.shape)
@@ -48,6 +81,11 @@ def print_numpy(x, val=True, shp=False):
def mkdirs(paths):
+ """create empty directories if they don't exist
+
+ Parameters:
+ paths (str list) -- a list of directory paths
+ """
if isinstance(paths, list) and not isinstance(paths, str):
for path in paths:
mkdir(path)
@@ -56,5 +94,10 @@ def mkdirs(paths):
def mkdir(path):
+ """create a single empty directory if it didn't exist
+
+ Parameters:
+ path (str) -- a single directory path
+ """
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
diff --git a/util/visualizer.py b/util/visualizer.py
index ffbf298173c..9736b5c3049 100644
--- a/util/visualizer.py
+++ b/util/visualizer.py
@@ -1,14 +1,30 @@
import numpy as np
import os
+import sys
import ntpath
import time
-from . import util
-from . import html
-from scipy.misc import imresize
+from . import util, html
+from subprocess import Popen, PIPE
+
+
+if sys.version_info[0] == 2:
+ VisdomExceptionBase = Exception
+else:
+ VisdomExceptionBase = ConnectionError
-# save image to the disk
def save_images(webpage, visuals, image_path, aspect_ratio=1.0, width=256):
+ """Save images to the disk.
+
+ Parameters:
+ webpage (the HTML class) -- the HTML webpage class that stores these imaegs (see html.py for more details)
+ visuals (OrderedDict) -- an ordered dictionary that stores (name, images (either tensor or numpy) ) pairs
+ image_path (str) -- the string is used to create image paths
+ aspect_ratio (float) -- the aspect ratio of saved images
+ width (int) -- the images will be resized to width x width
+
+ This function will save images stored in 'visuals' to the HTML file specified by 'webpage'.
+ """
image_dir = webpage.get_image_dir()
short_path = ntpath.basename(image_path[0])
name = os.path.splitext(short_path)[0]
@@ -20,13 +36,7 @@ def save_images(webpage, visuals, image_path, aspect_ratio=1.0, width=256):
im = util.tensor2im(im_data)
image_name = '%s_%s.png' % (name, label)
save_path = os.path.join(image_dir, image_name)
- h, w, _ = im.shape
- if aspect_ratio > 1.0:
- im = imresize(im, (h, int(w * aspect_ratio)), interp='bicubic')
- if aspect_ratio < 1.0:
- im = imresize(im, (int(h / aspect_ratio), w), interp='bicubic')
- util.save_image(im, save_path)
-
+ util.save_image(im, save_path, aspect_ratio=aspect_ratio)
ims.append(image_name)
txts.append(label)
links.append(image_name)
@@ -34,42 +44,75 @@ def save_images(webpage, visuals, image_path, aspect_ratio=1.0, width=256):
class Visualizer():
+ """This class includes several functions that can display/save images and print/save logging information.
+
+ It uses a Python library 'visdom' for display, and a Python library 'dominate' (wrapped in 'HTML') for creating HTML files with images.
+ """
+
def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize the Visualizer class
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ Step 1: Cache the training/test options
+ Step 2: connect to a visdom server
+ Step 3: create an HTML object for saveing HTML filters
+ Step 4: create a logging file to store training losses
+ """
+ self.opt = opt # cache the option
self.display_id = opt.display_id
self.use_html = opt.isTrain and not opt.no_html
self.win_size = opt.display_winsize
self.name = opt.name
- self.opt = opt
+ self.port = opt.display_port
self.saved = False
- if self.display_id > 0:
+ if self.display_id > 0: # connect to a visdom server given and
import visdom
self.ncols = opt.display_ncols
- self.vis = visdom.Visdom(server=opt.display_server, port=opt.display_port)
+ self.vis = visdom.Visdom(server=opt.display_server, port=opt.display_port, env=opt.display_env)
+ if not self.vis.check_connection():
+ self.create_visdom_connections()
- if self.use_html:
+ if self.use_html: # create an HTML object at /web/; images will be saved under /web/images/
self.web_dir = os.path.join(opt.checkpoints_dir, opt.name, 'web')
self.img_dir = os.path.join(self.web_dir, 'images')
print('create web directory %s...' % self.web_dir)
util.mkdirs([self.web_dir, self.img_dir])
+ # create a logging file to store training losses
self.log_name = os.path.join(opt.checkpoints_dir, opt.name, 'loss_log.txt')
with open(self.log_name, "a") as log_file:
now = time.strftime("%c")
log_file.write('================ Training Loss (%s) ================\n' % now)
def reset(self):
+ """Reset the self.saved status"""
self.saved = False
- # |visuals|: dictionary of images to display or save
+ def create_visdom_connections(self):
+ """If the program could not connect to Visdom server, this function will start a new server at port < self.port > """
+ cmd = sys.executable + ' -m visdom.server -p %d &>/dev/null &' % self.port
+ print('\n\nCould not connect to Visdom server. \n Trying to start a server....')
+ print('Command: %s' % cmd)
+ Popen(cmd, shell=True, stdout=PIPE, stderr=PIPE)
+
def display_current_results(self, visuals, epoch, save_result):
- if self.display_id > 0: # show images in the browser
+ """Display current results on visdom; save current results to an HTML file.
+
+ Parameters:
+ visuals (OrderedDict) - - dictionary of images to display or save
+ epoch (int) - - the current epoch
+ save_result (bool) - - if save the current results to an HTML file
+ """
+ if self.display_id > 0: # show images in the browser using visdom
ncols = self.ncols
- if ncols > 0:
+ if ncols > 0: # show all the images in one visdom panel
ncols = min(ncols, len(visuals))
h, w = next(iter(visuals.values())).shape[:2]
table_css = """""" % (w, h)
+ table {border-collapse: separate; border-spacing: 4px; white-space: nowrap; text-align: center}
+ table td {width: % dpx; height: % dpx; padding: 4px; outline: 4px solid black}
+ """ % (w, h) # create a table css
+ # create a table of images.
title = self.name
label_html = ''
label_html_row = ''
@@ -90,28 +133,36 @@ def display_current_results(self, visuals, epoch, save_result):
idx += 1
if label_html_row != '':
label_html += '
"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "7wNjDKdQy35h",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Install"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "TRm-USlsHgEV",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "Pt3igws3eiVp",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import os\n",
+ "os.chdir('pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/')"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "z1EySlOXwwoa",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!pip install -r requirements.txt"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "8daqlgVhw29P",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Datasets\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Download one of the official datasets with:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh [cityscapes, night2day, edges2handbags, edges2shoes, facades, maps]`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Or use your own dataset by creating the appropriate folders and adding in the images. Follow the instructions [here](https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/datasets.md#pix2pix-datasets)."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "vrdOettJxaCc",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "gdUz4116xhpm",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Pretrained models\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Download one of the official pretrained models with:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `bash ./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh [edges2shoes, sat2map, map2sat, facades_label2photo, and day2night]`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Or add your own pretrained model to `./checkpoints/{NAME}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pt`"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "GC2DEP4M0OsS",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!bash ./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh facades_label2photo"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "yFw1kDQBx3LN",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Training\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Change the `--dataroot` and `--name` to your own dataset's path and model's name. Use `--gpu_ids 0,1,..` to train on multiple GPUs and `--batch_size` to change the batch size. Add `--direction BtoA` if you want to train a model to transfrom from class B to A."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "0sp7TCT2x9dB",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "9UkcaFZiyASl",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Testing\n",
+ "\n",
+ "- `python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_pix2pix`\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Change the `--dataroot`, `--name`, and `--direction` to be consistent with your trained model's configuration and how you want to transform images.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> from https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix:\n",
+ "> Note that we specified --direction BtoA as Facades dataset's A to B direction is photos to labels.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> If you would like to apply a pre-trained model to a collection of input images (rather than image pairs), please use --model test option. See ./scripts/test_single.sh for how to apply a model to Facade label maps (stored in the directory facades/testB).\n",
+ "\n",
+ "> See a list of currently available models at ./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "mey7o6j-0368",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!ls checkpoints/"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "uCsKkEq0yGh0",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "!python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_label2photo_pretrained"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "OzSKIPUByfiN",
+ "colab_type": "text"
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Visualize"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "9Mgg8raPyizq",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
+ "\n",
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/facades_label2photo_pretrained/test_latest/images/100_fake_B.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "0G3oVH9DyqLQ",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/facades_label2photo_pretrained/test_latest/images/100_real_A.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "metadata": {
+ "id": "ErK5OC1j1LH4",
+ "colab_type": "code",
+ "colab": {}
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "img = plt.imread('./results/facades_label2photo_pretrained/test_latest/images/100_real_B.png')\n",
+ "plt.imshow(img)"
+ ],
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "outputs": []
+ }
+ ]
+}
diff --git a/pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh b/pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh
deleted file mode 100644
index 91f002144d5..00000000000
--- a/pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
-FILE=$1
-
-echo "Note: available models are horse2zebra, zebra2horse"
-
-echo "Specified [$FILE]"
-
-mkdir -p ./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained
-MODEL_FILE=./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth
-URL=https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~taesung_park/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/models/$FILE.pth
-
-wget -N $URL -O $MODEL_FILE
-
-
diff --git a/pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh b/pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh
deleted file mode 100644
index ee51a43450a..00000000000
--- a/pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
-FILE=$1
-
-echo "Note: available models are edges2shoes, sat2map, and facades_label2photo"
-
-echo "Specified [$FILE]"
-
-mkdir -p ./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained
-MODEL_FILE=./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth
-URL=https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~taesung_park/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/pix2pix_models/$FILE.pth
-
-wget -N $URL -O $MODEL_FILE
-
-
diff --git a/requirements.txt b/requirements.txt
index 072d027a2b0..a3561a19a03 100644
--- a/requirements.txt
+++ b/requirements.txt
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-torch>=0.4.0
+torch>=0.4.1
torchvision>=0.2.1
dominate>=2.3.1
visdom>=0.1.8.3
diff --git a/scripts/check_all.sh b/scripts/check_all.sh
deleted file mode 100644
index f13a64766e0..00000000000
--- a/scripts/check_all.sh
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
-set -ex
-DOWNLOAD=${1}
-echo 'apply a pretrained cyclegan model'
-if [ ${DOWNLOAD} -eq 1 ]
-then
- bash pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh horse2zebra
- bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh horse2zebra
-fi
-python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --checkpoints_dir ./checkpoints/ --name horse2zebra_pretrained --no_dropout --model test --dataset_mode single --loadSize 256
-
-echo 'apply a pretrained pix2pix model'
-if [ ${DOWNLOAD} -eq 1 ]
-then
- bash pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh facades_label2photo
- bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades
-fi
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/ --which_direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_label2photo_pretrained --dataset_mode aligned --which_model_netG unet_256 --norm batch
-
-
-echo 'cyclegan train (1 epoch) and test'
-if [ ${DOWNLOAD} -eq 1 ]
-then
- bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh maps
-fi
-python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --no_dropout --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --max_dataset_size 100 --save_latest_freq 100
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --phase test --no_dropout
-
-
-echo 'pix2pix train (1 epoch) and test'
-python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch --pool_size 0 --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --save_latest_freq 400
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
diff --git a/scripts/conda_deps.sh b/scripts/conda_deps.sh
index accac640541..72df436f0e9 100644
--- a/scripts/conda_deps.sh
+++ b/scripts/conda_deps.sh
@@ -1,6 +1,4 @@
set -ex
conda install numpy pyyaml mkl mkl-include setuptools cmake cffi typing
-conda install -c pytorch magma-cuda80 # or magma-cuda90 if CUDA 9
-conda install pytorch torchvision -c pytorch # install pytorch; if you want to use cuda90, add cuda90
-conda install -c conda-forge dominate # install dominate
-conda install -c conda-forge visdom # install visdom
+conda install pytorch torchvision -c pytorch # add cuda90 if CUDA 9
+conda install visdom dominate -c conda-forge # install visdom and dominate
diff --git a/scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh b/scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..26e198a44aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+FILE=$1
+
+echo "Note: available models are apple2orange, orange2apple, summer2winter_yosemite, winter2summer_yosemite, horse2zebra, zebra2horse, monet2photo, style_monet, style_cezanne, style_ukiyoe, style_vangogh, sat2map, map2sat, cityscapes_photo2label, cityscapes_label2photo, facades_photo2label, facades_label2photo, iphone2dslr_flower"
+
+echo "Specified [$FILE]"
+
+mkdir -p ./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained
+MODEL_FILE=./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth
+URL=http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/cyclegan/pretrained_models/$FILE.pth
+
+wget -N $URL -O $MODEL_FILE
diff --git a/scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh b/scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6b21232f074
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+FILE=$1
+
+echo "Note: available models are edges2shoes, sat2map, map2sat, facades_label2photo, and day2night"
+echo "Specified [$FILE]"
+
+mkdir -p ./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained
+MODEL_FILE=./checkpoints/${FILE}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth
+URL=http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/pix2pix/models-pytorch/$FILE.pth
+
+wget -N $URL -O $MODEL_FILE
diff --git a/scripts/edges/PostprocessHED.m b/scripts/edges/PostprocessHED.m
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..78a99106ea6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/edges/PostprocessHED.m
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+%%% Prerequisites
+% You need to get the cpp file edgesNmsMex.cpp from https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pdollar/edges/master/private/edgesNmsMex.cpp
+% and compile it in Matlab: mex edgesNmsMex.cpp
+% You also need to download and install Piotr's Computer Vision Matlab Toolbox: https://pdollar.github.io/toolbox/
+
+%%% parameters
+% hed_mat_dir: the hed mat file directory (the output of 'batch_hed.py')
+% edge_dir: the output HED edges directory
+% image_width: resize the edge map to [image_width, image_width]
+% threshold: threshold for image binarization (default 25.0/255.0)
+% small_edge: remove small edges (default 5)
+
+function [] = PostprocessHED(hed_mat_dir, edge_dir, image_width, threshold, small_edge)
+
+if ~exist(edge_dir, 'dir')
+ mkdir(edge_dir);
+end
+fileList = dir(fullfile(hed_mat_dir, '*.mat'));
+nFiles = numel(fileList);
+fprintf('find %d mat files\n', nFiles);
+
+for n = 1 : nFiles
+ if mod(n, 1000) == 0
+ fprintf('process %d/%d images\n', n, nFiles);
+ end
+ fileName = fileList(n).name;
+ filePath = fullfile(hed_mat_dir, fileName);
+ jpgName = strrep(fileName, '.mat', '.jpg');
+ edge_path = fullfile(edge_dir, jpgName);
+
+ if ~exist(edge_path, 'file')
+ E = GetEdge(filePath);
+ E = imresize(E,[image_width,image_width]);
+ E_simple = SimpleEdge(E, threshold, small_edge);
+ E_simple = uint8(E_simple*255);
+ imwrite(E_simple, edge_path, 'Quality',100);
+ end
+end
+end
+
+
+
+
+function [E] = GetEdge(filePath)
+load(filePath);
+E = 1-edge_predict;
+end
+
+function [E4] = SimpleEdge(E, threshold, small_edge)
+if nargin <= 1
+ threshold = 25.0/255.0;
+end
+
+if nargin <= 2
+ small_edge = 5;
+end
+
+if ndims(E) == 3
+ E = E(:,:,1);
+end
+
+E1 = 1 - E;
+E2 = EdgeNMS(E1);
+E3 = double(E2>=max(eps,threshold));
+E3 = bwmorph(E3,'thin',inf);
+E4 = bwareaopen(E3, small_edge);
+E4=1-E4;
+end
+
+function [E_nms] = EdgeNMS( E )
+E=single(E);
+[Ox,Oy] = gradient2(convTri(E,4));
+[Oxx,~] = gradient2(Ox);
+[Oxy,Oyy] = gradient2(Oy);
+O = mod(atan(Oyy.*sign(-Oxy)./(Oxx+1e-5)),pi);
+E_nms = edgesNmsMex(E,O,1,5,1.01,1);
+end
diff --git a/scripts/edges/batch_hed.py b/scripts/edges/batch_hed.py
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..6de60e05721
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/edges/batch_hed.py
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+# HED batch processing script; modified from https://github.com/s9xie/hed/blob/master/examples/hed/HED-tutorial.ipynb
+# Step 1: download the hed repo: https://github.com/s9xie/hed
+# Step 2: download the models and protoxt, and put them under {caffe_root}/examples/hed/
+# Step 3: put this script under {caffe_root}/examples/hed/
+# Step 4: run the following script:
+# python batch_hed.py --images_dir=/data/to/path/photos/ --hed_mat_dir=/data/to/path/hed_mat_files/
+# The code sometimes crashes after computation is done. Error looks like "Check failed: ... driver shutting down". You can just kill the job.
+# For large images, it will produce gpu memory issue. Therefore, you better resize the images before running this script.
+# Step 5: run the MATLAB post-processing script "PostprocessHED.m"
+
+
+import caffe
+import numpy as np
+from PIL import Image
+import os
+import argparse
+import sys
+import scipy.io as sio
+
+
+def parse_args():
+ parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='batch proccesing: photos->edges')
+ parser.add_argument('--caffe_root', dest='caffe_root', help='caffe root', default='../../', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--caffemodel', dest='caffemodel', help='caffemodel', default='./hed_pretrained_bsds.caffemodel', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--prototxt', dest='prototxt', help='caffe prototxt file', default='./deploy.prototxt', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--images_dir', dest='images_dir', help='directory to store input photos', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--hed_mat_dir', dest='hed_mat_dir', help='directory to store output hed edges in mat file', type=str)
+ parser.add_argument('--border', dest='border', help='padding border', type=int, default=128)
+ parser.add_argument('--gpu_id', dest='gpu_id', help='gpu id', type=int, default=1)
+ args = parser.parse_args()
+ return args
+
+
+args = parse_args()
+for arg in vars(args):
+ print('[%s] =' % arg, getattr(args, arg))
+# Make sure that caffe is on the python path:
+caffe_root = args.caffe_root # this file is expected to be in {caffe_root}/examples/hed/
+sys.path.insert(0, caffe_root + 'python')
+
+
+if not os.path.exists(args.hed_mat_dir):
+ print('create output directory %s' % args.hed_mat_dir)
+ os.makedirs(args.hed_mat_dir)
+
+imgList = os.listdir(args.images_dir)
+nImgs = len(imgList)
+print('#images = %d' % nImgs)
+
+caffe.set_mode_gpu()
+caffe.set_device(args.gpu_id)
+# load net
+net = caffe.Net(args.prototxt, args.caffemodel, caffe.TEST)
+# pad border
+border = args.border
+
+for i in range(nImgs):
+ if i % 500 == 0:
+ print('processing image %d/%d' % (i, nImgs))
+ im = Image.open(os.path.join(args.images_dir, imgList[i]))
+
+ in_ = np.array(im, dtype=np.float32)
+ in_ = np.pad(in_, ((border, border), (border, border), (0, 0)), 'reflect')
+
+ in_ = in_[:, :, 0:3]
+ in_ = in_[:, :, ::-1]
+ in_ -= np.array((104.00698793, 116.66876762, 122.67891434))
+ in_ = in_.transpose((2, 0, 1))
+ # remove the following two lines if testing with cpu
+
+ # shape for input (data blob is N x C x H x W), set data
+ net.blobs['data'].reshape(1, *in_.shape)
+ net.blobs['data'].data[...] = in_
+ # run net and take argmax for prediction
+ net.forward()
+ fuse = net.blobs['sigmoid-fuse'].data[0][0, :, :]
+ # get rid of the border
+ fuse = fuse[border:-border, border:-border]
+ # save hed file to the disk
+ name, ext = os.path.splitext(imgList[i])
+ sio.savemat(os.path.join(args.hed_mat_dir, name + '.mat'), {'edge_predict': fuse})
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/deploy.prototxt b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/deploy.prototxt
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..f4d7e71e924
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/deploy.prototxt
@@ -0,0 +1,769 @@
+layer {
+ name: "data"
+ type: "Input"
+ top: "data"
+ input_param {
+ shape {
+ dim: 1
+ dim: 3
+ dim: 500
+ dim: 500
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv1_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "data"
+ top: "conv1_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 64
+ pad: 100
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu1_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv1_1"
+ top: "conv1_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv1_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv1_1"
+ top: "conv1_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 64
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu1_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv1_2"
+ top: "conv1_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool1"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv1_2"
+ top: "pool1"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv2_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool1"
+ top: "conv2_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 128
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu2_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv2_1"
+ top: "conv2_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv2_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv2_1"
+ top: "conv2_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 128
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu2_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv2_2"
+ top: "conv2_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool2"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv2_2"
+ top: "pool2"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv3_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool2"
+ top: "conv3_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 256
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu3_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv3_1"
+ top: "conv3_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv3_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv3_1"
+ top: "conv3_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 256
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu3_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv3_2"
+ top: "conv3_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv3_3"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv3_2"
+ top: "conv3_3"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 256
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu3_3"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv3_3"
+ top: "conv3_3"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool3"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv3_3"
+ top: "pool3"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv4_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool3"
+ top: "conv4_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu4_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv4_1"
+ top: "conv4_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv4_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv4_1"
+ top: "conv4_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu4_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv4_2"
+ top: "conv4_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv4_3"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv4_2"
+ top: "conv4_3"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu4_3"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv4_3"
+ top: "conv4_3"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool4"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv4_3"
+ top: "pool4"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv5_1"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool4"
+ top: "conv5_1"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu5_1"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv5_1"
+ top: "conv5_1"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv5_2"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv5_1"
+ top: "conv5_2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu5_2"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv5_2"
+ top: "conv5_2"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "conv5_3"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "conv5_2"
+ top: "conv5_3"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 512
+ pad: 1
+ kernel_size: 3
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu5_3"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "conv5_3"
+ top: "conv5_3"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "pool5"
+ type: "Pooling"
+ bottom: "conv5_3"
+ top: "pool5"
+ pooling_param {
+ pool: MAX
+ kernel_size: 2
+ stride: 2
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "fc6_cs"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool5"
+ top: "fc6_cs"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 4096
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 7
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu6_cs"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "fc6_cs"
+ top: "fc6_cs"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "fc7_cs"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "fc6_cs"
+ top: "fc7_cs"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 4096
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 1
+ stride: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "gaussian"
+ std: 0.01
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ value: 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "relu7_cs"
+ type: "ReLU"
+ bottom: "fc7_cs"
+ top: "fc7_cs"
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_fr"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "fc7_cs"
+ top: "score_fr"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "upscore2"
+ type: "Deconvolution"
+ bottom: "score_fr"
+ top: "upscore2"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ bias_term: false
+ kernel_size: 4
+ stride: 2
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_pool4"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool4"
+ top: "score_pool4"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_pool4c"
+ type: "Crop"
+ bottom: "score_pool4"
+ bottom: "upscore2"
+ top: "score_pool4c"
+ crop_param {
+ axis: 2
+ offset: 5
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "fuse_pool4"
+ type: "Eltwise"
+ bottom: "upscore2"
+ bottom: "score_pool4c"
+ top: "fuse_pool4"
+ eltwise_param {
+ operation: SUM
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "upscore_pool4"
+ type: "Deconvolution"
+ bottom: "fuse_pool4"
+ top: "upscore_pool4"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ bias_term: false
+ kernel_size: 4
+ stride: 2
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_pool3"
+ type: "Convolution"
+ bottom: "pool3"
+ top: "score_pool3"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ decay_mult: 1
+ }
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 2
+ decay_mult: 0
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ pad: 0
+ kernel_size: 1
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score_pool3c"
+ type: "Crop"
+ bottom: "score_pool3"
+ bottom: "upscore_pool4"
+ top: "score_pool3c"
+ crop_param {
+ axis: 2
+ offset: 9
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "fuse_pool3"
+ type: "Eltwise"
+ bottom: "upscore_pool4"
+ bottom: "score_pool3c"
+ top: "fuse_pool3"
+ eltwise_param {
+ operation: SUM
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "upscore8"
+ type: "Deconvolution"
+ bottom: "fuse_pool3"
+ top: "upscore8"
+ param {
+ lr_mult: 1
+ }
+ convolution_param {
+ num_output: 20
+ bias_term: false
+ kernel_size: 16
+ stride: 8
+ weight_filler {
+ type: "xavier"
+ }
+ bias_filler {
+ type: "constant"
+ }
+ }
+}
+layer {
+ name: "score"
+ type: "Crop"
+ bottom: "upscore8"
+ bottom: "data"
+ top: "score"
+ crop_param {
+ axis: 2
+ offset: 31
+ }
+}
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/cityscapes.py b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/cityscapes.py
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..05b14715d3b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/cityscapes.py
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
+# The following code is modified from https://github.com/shelhamer/clockwork-fcn
+import sys
+import os
+import glob
+import numpy as np
+from PIL import Image
+
+
+class cityscapes:
+ def __init__(self, data_path):
+ # data_path something like /data2/cityscapes
+ self.dir = data_path
+ self.classes = ['road', 'sidewalk', 'building', 'wall', 'fence',
+ 'pole', 'traffic light', 'traffic sign', 'vegetation', 'terrain',
+ 'sky', 'person', 'rider', 'car', 'truck',
+ 'bus', 'train', 'motorcycle', 'bicycle']
+ self.mean = np.array((72.78044, 83.21195, 73.45286), dtype=np.float32)
+ # import cityscapes label helper and set up label mappings
+ sys.path.insert(0, '{}/scripts/helpers/'.format(self.dir))
+ labels = __import__('labels')
+ self.id2trainId = {label.id: label.trainId for label in labels.labels} # dictionary mapping from raw IDs to train IDs
+ self.trainId2color = {label.trainId: label.color for label in labels.labels} # dictionary mapping train IDs to colors as 3-tuples
+
+ def get_dset(self, split):
+ '''
+ List images as (city, id) for the specified split
+
+ TODO(shelhamer) generate splits from cityscapes itself, instead of
+ relying on these separately made text files.
+ '''
+ if split == 'train':
+ dataset = open('{}/ImageSets/segFine/train.txt'.format(self.dir)).read().splitlines()
+ else:
+ dataset = open('{}/ImageSets/segFine/val.txt'.format(self.dir)).read().splitlines()
+ return [(item.split('/')[0], item.split('/')[1]) for item in dataset]
+
+ def load_image(self, split, city, idx):
+ im = Image.open('{}/leftImg8bit_sequence/{}/{}/{}_leftImg8bit.png'.format(self.dir, split, city, idx))
+ return im
+
+ def assign_trainIds(self, label):
+ """
+ Map the given label IDs to the train IDs appropriate for training
+ Use the label mapping provided in labels.py from the cityscapes scripts
+ """
+ label = np.array(label, dtype=np.float32)
+ if sys.version_info[0] < 3:
+ for k, v in self.id2trainId.iteritems():
+ label[label == k] = v
+ else:
+ for k, v in self.id2trainId.items():
+ label[label == k] = v
+ return label
+
+ def load_label(self, split, city, idx):
+ """
+ Load label image as 1 x height x width integer array of label indices.
+ The leading singleton dimension is required by the loss.
+ """
+ label = Image.open('{}/gtFine/{}/{}/{}_gtFine_labelIds.png'.format(self.dir, split, city, idx))
+ label = self.assign_trainIds(label) # get proper labels for eval
+ label = np.array(label, dtype=np.uint8)
+ label = label[np.newaxis, ...]
+ return label
+
+ def preprocess(self, im):
+ """
+ Preprocess loaded image (by load_image) for Caffe:
+ - cast to float
+ - switch channels RGB -> BGR
+ - subtract mean
+ - transpose to channel x height x width order
+ """
+ in_ = np.array(im, dtype=np.float32)
+ in_ = in_[:, :, ::-1]
+ in_ -= self.mean
+ in_ = in_.transpose((2, 0, 1))
+ return in_
+
+ def palette(self, label):
+ '''
+ Map trainIds to colors as specified in labels.py
+ '''
+ if label.ndim == 3:
+ label = label[0]
+ color = np.empty((label.shape[0], label.shape[1], 3))
+ if sys.version_info[0] < 3:
+ for k, v in self.trainId2color.iteritems():
+ color[label == k, :] = v
+ else:
+ for k, v in self.trainId2color.items():
+ color[label == k, :] = v
+ return color
+
+ def make_boundaries(label, thickness=None):
+ """
+ Input is an image label, output is a numpy array mask encoding the boundaries of the objects
+ Extract pixels at the true boundary by dilation - erosion of label.
+ Don't just pick the void label as it is not exclusive to the boundaries.
+ """
+ assert(thickness is not None)
+ import skimage.morphology as skm
+ void = 255
+ mask = np.logical_and(label > 0, label != void)[0]
+ selem = skm.disk(thickness)
+ boundaries = np.logical_xor(skm.dilation(mask, selem),
+ skm.erosion(mask, selem))
+ return boundaries
+
+ def list_label_frames(self, split):
+ """
+ Select labeled frames from a split for evaluation
+ collected as (city, shot, idx) tuples
+ """
+ def file2idx(f):
+ """Helper to convert file path into frame ID"""
+ city, shot, frame = (os.path.basename(f).split('_')[:3])
+ return "_".join([city, shot, frame])
+ frames = []
+ cities = [os.path.basename(f) for f in glob.glob('{}/gtFine/{}/*'.format(self.dir, split))]
+ for c in cities:
+ files = sorted(glob.glob('{}/gtFine/{}/{}/*labelIds.png'.format(self.dir, split, c)))
+ frames.extend([file2idx(f) for f in files])
+ return frames
+
+ def collect_frame_sequence(self, split, idx, length):
+ """
+ Collect sequence of frames preceding (and including) a labeled frame
+ as a list of Images.
+
+ Note: 19 preceding frames are provided for each labeled frame.
+ """
+ SEQ_LEN = length
+ city, shot, frame = idx.split('_')
+ frame = int(frame)
+ frame_seq = []
+ for i in range(frame - SEQ_LEN, frame + 1):
+ frame_path = '{0}/leftImg8bit_sequence/val/{1}/{1}_{2}_{3:0>6d}_leftImg8bit.png'.format(
+ self.dir, city, shot, i)
+ frame_seq.append(Image.open(frame_path))
+ return frame_seq
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/download_fcn8s.sh b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/download_fcn8s.sh
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..f45af158e94
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/download_fcn8s.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
+URL=http://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz/projects/pix2pix/fcn-8s-cityscapes/fcn-8s-cityscapes.caffemodel
+OUTPUT_FILE=./scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/fcn-8s-cityscapes.caffemodel
+wget -N $URL -O $OUTPUT_FILE
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/evaluate.py b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/evaluate.py
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..500c20f7007
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/evaluate.py
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+import os
+import caffe
+import argparse
+import numpy as np
+import scipy.misc
+from PIL import Image
+from util import segrun, fast_hist, get_scores
+from cityscapes import cityscapes
+
+parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
+parser.add_argument("--cityscapes_dir", type=str, required=True, help="Path to the original cityscapes dataset")
+parser.add_argument("--result_dir", type=str, required=True, help="Path to the generated images to be evaluated")
+parser.add_argument("--output_dir", type=str, required=True, help="Where to save the evaluation results")
+parser.add_argument("--caffemodel_dir", type=str, default='./scripts/eval_cityscapes/caffemodel/', help="Where the FCN-8s caffemodel stored")
+parser.add_argument("--gpu_id", type=int, default=0, help="Which gpu id to use")
+parser.add_argument("--split", type=str, default='val', help="Data split to be evaluated")
+parser.add_argument("--save_output_images", type=int, default=0, help="Whether to save the FCN output images")
+args = parser.parse_args()
+
+
+def main():
+ if not os.path.isdir(args.output_dir):
+ os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
+ if args.save_output_images > 0:
+ output_image_dir = args.output_dir + 'image_outputs/'
+ if not os.path.isdir(output_image_dir):
+ os.makedirs(output_image_dir)
+ CS = cityscapes(args.cityscapes_dir)
+ n_cl = len(CS.classes)
+ label_frames = CS.list_label_frames(args.split)
+ caffe.set_device(args.gpu_id)
+ caffe.set_mode_gpu()
+ net = caffe.Net(args.caffemodel_dir + '/deploy.prototxt',
+ args.caffemodel_dir + 'fcn-8s-cityscapes.caffemodel',
+ caffe.TEST)
+
+ hist_perframe = np.zeros((n_cl, n_cl))
+ for i, idx in enumerate(label_frames):
+ if i % 10 == 0:
+ print('Evaluating: %d/%d' % (i, len(label_frames)))
+ city = idx.split('_')[0]
+ # idx is city_shot_frame
+ label = CS.load_label(args.split, city, idx)
+ im_file = args.result_dir + '/' + idx + '_leftImg8bit.png'
+ im = np.array(Image.open(im_file))
+ im = scipy.misc.imresize(im, (label.shape[1], label.shape[2]))
+ out = segrun(net, CS.preprocess(im))
+ hist_perframe += fast_hist(label.flatten(), out.flatten(), n_cl)
+ if args.save_output_images > 0:
+ label_im = CS.palette(label)
+ pred_im = CS.palette(out)
+ scipy.misc.imsave(output_image_dir + '/' + str(i) + '_pred.jpg', pred_im)
+ scipy.misc.imsave(output_image_dir + '/' + str(i) + '_gt.jpg', label_im)
+ scipy.misc.imsave(output_image_dir + '/' + str(i) + '_input.jpg', im)
+
+ mean_pixel_acc, mean_class_acc, mean_class_iou, per_class_acc, per_class_iou = get_scores(hist_perframe)
+ with open(args.output_dir + '/evaluation_results.txt', 'w') as f:
+ f.write('Mean pixel accuracy: %f\n' % mean_pixel_acc)
+ f.write('Mean class accuracy: %f\n' % mean_class_acc)
+ f.write('Mean class IoU: %f\n' % mean_class_iou)
+ f.write('************ Per class numbers below ************\n')
+ for i, cl in enumerate(CS.classes):
+ while len(cl) < 15:
+ cl = cl + ' '
+ f.write('%s: acc = %f, iou = %f\n' % (cl, per_class_acc[i], per_class_iou[i]))
+
+
+main()
diff --git a/scripts/eval_cityscapes/util.py b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/util.py
new file mode 100755
index 00000000000..8fce27fd6eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/eval_cityscapes/util.py
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+# The following code is modified from https://github.com/shelhamer/clockwork-fcn
+import numpy as np
+
+
+def get_out_scoremap(net):
+ return net.blobs['score'].data[0].argmax(axis=0).astype(np.uint8)
+
+
+def feed_net(net, in_):
+ """
+ Load prepared input into net.
+ """
+ net.blobs['data'].reshape(1, *in_.shape)
+ net.blobs['data'].data[...] = in_
+
+
+def segrun(net, in_):
+ feed_net(net, in_)
+ net.forward()
+ return get_out_scoremap(net)
+
+
+def fast_hist(a, b, n):
+ k = np.where((a >= 0) & (a < n))[0]
+ bc = np.bincount(n * a[k].astype(int) + b[k], minlength=n**2)
+ if len(bc) != n**2:
+ # ignore this example if dimension mismatch
+ return 0
+ return bc.reshape(n, n)
+
+
+def get_scores(hist):
+ # Mean pixel accuracy
+ acc = np.diag(hist).sum() / (hist.sum() + 1e-12)
+
+ # Per class accuracy
+ cl_acc = np.diag(hist) / (hist.sum(1) + 1e-12)
+
+ # Per class IoU
+ iu = np.diag(hist) / (hist.sum(1) + hist.sum(0) - np.diag(hist) + 1e-12)
+
+ return acc, np.nanmean(cl_acc), np.nanmean(iu), cl_acc, iu
diff --git a/scripts/test_before_push.py b/scripts/test_before_push.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a68746421aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/test_before_push.py
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+# Simple script to make sure basic usage
+# such as training, testing, saving and loading
+# runs without errors.
+import os
+
+
+def run(command):
+ print(command)
+ exit_status = os.system(command)
+ if exit_status > 0:
+ exit(1)
+
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ # download mini datasets
+ if not os.path.exists('./datasets/mini'):
+ run('bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh mini')
+
+ if not os.path.exists('./datasets/mini_pix2pix'):
+ run('bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh mini_pix2pix')
+
+ # pretrained cyclegan model
+ if not os.path.exists('./checkpoints/horse2zebra_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth'):
+ run('bash ./scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh horse2zebra')
+ run('python test.py --model test --dataroot ./datasets/mini --name horse2zebra_pretrained --no_dropout --num_test 1 --no_dropout')
+
+ # pretrained pix2pix model
+ if not os.path.exists('./checkpoints/facades_label2photo_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth'):
+ run('bash ./scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh facades_label2photo')
+ if not os.path.exists('./datasets/facades'):
+ run('bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades')
+ run('python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/ --direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_label2photo_pretrained --num_test 1')
+
+ # cyclegan train/test
+ run('python train.py --model cycle_gan --name temp_cyclegan --dataroot ./datasets/mini --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --save_latest_freq 10 --print_freq 1 --display_id -1')
+ run('python test.py --model test --name temp_cyclegan --dataroot ./datasets/mini --num_test 1 --model_suffix "_A" --no_dropout')
+
+ # pix2pix train/test
+ run('python train.py --model pix2pix --name temp_pix2pix --dataroot ./datasets/mini_pix2pix --niter 1 --niter_decay 5 --save_latest_freq 10 --display_id -1')
+ run('python test.py --model pix2pix --name temp_pix2pix --dataroot ./datasets/mini_pix2pix --num_test 1')
+
+ # template train/test
+ run('python train.py --model template --name temp2 --dataroot ./datasets/mini_pix2pix --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --save_latest_freq 10 --display_id -1')
+ run('python test.py --model template --name temp2 --dataroot ./datasets/mini_pix2pix --num_test 1')
+
+ # colorization train/test (optional)
+ if not os.path.exists('./datasets/mini_colorization'):
+ run('bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh mini_colorization')
+
+ run('python train.py --model colorization --name temp_color --dataroot ./datasets/mini_colorization --niter 1 --niter_decay 0 --save_latest_freq 5 --display_id -1')
+ run('python test.py --model colorization --name temp_color --dataroot ./datasets/mini_colorization --num_test 1')
diff --git a/scripts/test_colorization.sh b/scripts/test_colorization.sh
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9837fd5fffa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/test_colorization.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+set -ex
+python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/colorization --name color_pix2pix --model colorization
diff --git a/scripts/test_pix2pix.sh b/scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
index 2cc311e4b26..589599b4c16 100755
--- a/scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
+++ b/scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
@@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
set -ex
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
+python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --netG unet_256 --direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
diff --git a/scripts/test_single.sh b/scripts/test_single.sh
index f1570ccf583..eada640276b 100755
--- a/scripts/test_single.sh
+++ b/scripts/test_single.sh
@@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
set -ex
-python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name facades_pix2pix --model test --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode single --norm batch
+python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name facades_pix2pix --model test --netG unet_256 --direction BtoA --dataset_mode single --norm batch
diff --git a/scripts/train_colorization.sh b/scripts/train_colorization.sh
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e6c06801209
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/train_colorization.sh
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+set -ex
+python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/colorization --name color_pix2pix --model colorization
diff --git a/scripts/train_pix2pix.sh b/scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
index e9f703e1998..0171001c554 100755
--- a/scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
+++ b/scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
@@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
set -ex
-python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch --pool_size 0
+python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --netG unet_256 --direction BtoA --lambda_L1 100 --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch --pool_size 0
diff --git a/test.py b/test.py
index 51e7f929d9d..9281a992d50 100644
--- a/test.py
+++ b/test.py
@@ -1,35 +1,69 @@
+"""General-purpose test script for image-to-image translation.
+
+Once you have trained your model with train.py, you can use this script to test the model.
+It will load a saved model from --checkpoints_dir and save the results to --results_dir.
+
+It first creates model and dataset given the option. It will hard-code some parameters.
+It then runs inference for --num_test images and save results to an HTML file.
+
+Example (You need to train models first or download pre-trained models from our website):
+ Test a CycleGAN model (both sides):
+ python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan
+
+ Test a CycleGAN model (one side only):
+ python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --name horse2zebra_pretrained --model test --no_dropout
+
+ The option '--model test' is used for generating CycleGAN results only for one side.
+ This option will automatically set '--dataset_mode single', which only loads the images from one set.
+ On the contrary, using '--model cycle_gan' requires loading and generating results in both directions,
+ which is sometimes unnecessary. The results will be saved at ./results/.
+ Use '--results_dir ' to specify the results directory.
+
+ Test a pix2pix model:
+ python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA
+
+See options/base_options.py and options/test_options.py for more test options.
+See training and test tips at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/tips.md
+See frequently asked questions at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/qa.md
+"""
import os
from options.test_options import TestOptions
-from data import CreateDataLoader
+from data import create_dataset
from models import create_model
from util.visualizer import save_images
from util import html
if __name__ == '__main__':
- opt = TestOptions().parse()
- opt.nThreads = 1 # test code only supports nThreads = 1
- opt.batchSize = 1 # test code only supports batchSize = 1
- opt.serial_batches = True # no shuffle
- opt.no_flip = True # no flip
- opt.display_id = -1 # no visdom display
- data_loader = CreateDataLoader(opt)
- dataset = data_loader.load_data()
- model = create_model(opt)
- model.setup(opt)
- # create website
- web_dir = os.path.join(opt.results_dir, opt.name, '%s_%s' % (opt.phase, opt.which_epoch))
- webpage = html.HTML(web_dir, 'Experiment = %s, Phase = %s, Epoch = %s' % (opt.name, opt.phase, opt.which_epoch))
- # test
+ opt = TestOptions().parse() # get test options
+ # hard-code some parameters for test
+ opt.num_threads = 0 # test code only supports num_threads = 1
+ opt.batch_size = 1 # test code only supports batch_size = 1
+ opt.serial_batches = True # disable data shuffling; comment this line if results on randomly chosen images are needed.
+ opt.no_flip = True # no flip; comment this line if results on flipped images are needed.
+ opt.display_id = -1 # no visdom display; the test code saves the results to a HTML file.
+ dataset = create_dataset(opt) # create a dataset given opt.dataset_mode and other options
+ model = create_model(opt) # create a model given opt.model and other options
+ model.setup(opt) # regular setup: load and print networks; create schedulers
+ # create a website
+ web_dir = os.path.join(opt.results_dir, opt.name, '{}_{}'.format(opt.phase, opt.epoch)) # define the website directory
+ if opt.load_iter > 0: # load_iter is 0 by default
+ web_dir = '{:s}_iter{:d}'.format(web_dir, opt.load_iter)
+ print('creating web directory', web_dir)
+ webpage = html.HTML(web_dir, 'Experiment = %s, Phase = %s, Epoch = %s' % (opt.name, opt.phase, opt.epoch))
+ # test with eval mode. This only affects layers like batchnorm and dropout.
+ # For [pix2pix]: we use batchnorm and dropout in the original pix2pix. You can experiment it with and without eval() mode.
+ # For [CycleGAN]: It should not affect CycleGAN as CycleGAN uses instancenorm without dropout.
+ if opt.eval:
+ model.eval()
for i, data in enumerate(dataset):
- if i >= opt.how_many:
+ if i >= opt.num_test: # only apply our model to opt.num_test images.
break
- model.set_input(data)
- model.test()
- visuals = model.get_current_visuals()
- img_path = model.get_image_paths()
- if i % 5 == 0:
+ model.set_input(data) # unpack data from data loader
+ model.test() # run inference
+ visuals = model.get_current_visuals() # get image results
+ img_path = model.get_image_paths() # get image paths
+ if i % 5 == 0: # save images to an HTML file
print('processing (%04d)-th image... %s' % (i, img_path))
save_images(webpage, visuals, img_path, aspect_ratio=opt.aspect_ratio, width=opt.display_winsize)
-
- webpage.save()
+ webpage.save() # save the HTML
diff --git a/train.py b/train.py
index 0877a35f9a7..73982310101 100644
--- a/train.py
+++ b/train.py
@@ -1,59 +1,78 @@
+"""General-purpose training script for image-to-image translation.
+
+This script works for various models (with option '--model': e.g., pix2pix, cyclegan, colorization) and
+different datasets (with option '--dataset_mode': e.g., aligned, unaligned, single, colorization).
+You need to specify the dataset ('--dataroot'), experiment name ('--name'), and model ('--model').
+
+It first creates model, dataset, and visualizer given the option.
+It then does standard network training. During the training, it also visualize/save the images, print/save the loss plot, and save models.
+The script supports continue/resume training. Use '--continue_train' to resume your previous training.
+
+Example:
+ Train a CycleGAN model:
+ python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan
+ Train a pix2pix model:
+ python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoA
+
+See options/base_options.py and options/train_options.py for more training options.
+See training and test tips at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/tips.md
+See frequently asked questions at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/qa.md
+"""
import time
from options.train_options import TrainOptions
-from data import CreateDataLoader
+from data import create_dataset
from models import create_model
from util.visualizer import Visualizer
if __name__ == '__main__':
- opt = TrainOptions().parse()
- data_loader = CreateDataLoader(opt)
- dataset = data_loader.load_data()
- dataset_size = len(data_loader)
- print('#training images = %d' % dataset_size)
-
- model = create_model(opt)
- model.setup(opt)
- visualizer = Visualizer(opt)
- total_steps = 0
-
- for epoch in range(opt.epoch_count, opt.niter + opt.niter_decay + 1):
- epoch_start_time = time.time()
- iter_data_time = time.time()
- epoch_iter = 0
-
- for i, data in enumerate(dataset):
- iter_start_time = time.time()
- if total_steps % opt.print_freq == 0:
+ opt = TrainOptions().parse() # get training options
+ dataset = create_dataset(opt) # create a dataset given opt.dataset_mode and other options
+ dataset_size = len(dataset) # get the number of images in the dataset.
+ print('The number of training images = %d' % dataset_size)
+
+ model = create_model(opt) # create a model given opt.model and other options
+ model.setup(opt) # regular setup: load and print networks; create schedulers
+ visualizer = Visualizer(opt) # create a visualizer that display/save images and plots
+ total_iters = 0 # the total number of training iterations
+
+ for epoch in range(opt.epoch_count, opt.niter + opt.niter_decay + 1): # outer loop for different epochs; we save the model by , +
+ epoch_start_time = time.time() # timer for entire epoch
+ iter_data_time = time.time() # timer for data loading per iteration
+ epoch_iter = 0 # the number of training iterations in current epoch, reset to 0 every epoch
+ visualizer.reset() # reset the visualizer: make sure it saves the results to HTML at least once every epoch
+
+ for i, data in enumerate(dataset): # inner loop within one epoch
+ iter_start_time = time.time() # timer for computation per iteration
+ if total_iters % opt.print_freq == 0:
t_data = iter_start_time - iter_data_time
- visualizer.reset()
- total_steps += opt.batchSize
- epoch_iter += opt.batchSize
- model.set_input(data)
- model.optimize_parameters()
-
- if total_steps % opt.display_freq == 0:
- save_result = total_steps % opt.update_html_freq == 0
+
+ total_iters += opt.batch_size
+ epoch_iter += opt.batch_size
+ model.set_input(data) # unpack data from dataset and apply preprocessing
+ model.optimize_parameters() # calculate loss functions, get gradients, update network weights
+
+ if total_iters % opt.display_freq == 0: # display images on visdom and save images to a HTML file
+ save_result = total_iters % opt.update_html_freq == 0
+ model.compute_visuals()
visualizer.display_current_results(model.get_current_visuals(), epoch, save_result)
- if total_steps % opt.print_freq == 0:
+ if total_iters % opt.print_freq == 0: # print training losses and save logging information to the disk
losses = model.get_current_losses()
- t = (time.time() - iter_start_time) / opt.batchSize
- visualizer.print_current_losses(epoch, epoch_iter, losses, t, t_data)
+ t_comp = (time.time() - iter_start_time) / opt.batch_size
+ visualizer.print_current_losses(epoch, epoch_iter, losses, t_comp, t_data)
if opt.display_id > 0:
- visualizer.plot_current_losses(epoch, float(epoch_iter) / dataset_size, opt, losses)
+ visualizer.plot_current_losses(epoch, float(epoch_iter) / dataset_size, losses)
- if total_steps % opt.save_latest_freq == 0:
- print('saving the latest model (epoch %d, total_steps %d)' %
- (epoch, total_steps))
- model.save_networks('latest')
+ if total_iters % opt.save_latest_freq == 0: # cache our latest model every iterations
+ print('saving the latest model (epoch %d, total_iters %d)' % (epoch, total_iters))
+ save_suffix = 'iter_%d' % total_iters if opt.save_by_iter else 'latest'
+ model.save_networks(save_suffix)
iter_data_time = time.time()
- if epoch % opt.save_epoch_freq == 0:
- print('saving the model at the end of epoch %d, iters %d' %
- (epoch, total_steps))
+ if epoch % opt.save_epoch_freq == 0: # cache our model every epochs
+ print('saving the model at the end of epoch %d, iters %d' % (epoch, total_iters))
model.save_networks('latest')
model.save_networks(epoch)
- print('End of epoch %d / %d \t Time Taken: %d sec' %
- (epoch, opt.niter + opt.niter_decay, time.time() - epoch_start_time))
- model.update_learning_rate()
+ print('End of epoch %d / %d \t Time Taken: %d sec' % (epoch, opt.niter + opt.niter_decay, time.time() - epoch_start_time))
+ model.update_learning_rate() # update learning rates at the end of every epoch.
diff --git a/util/__init__.py b/util/__init__.py
index e69de29bb2d..ae36f63d885 100644
--- a/util/__init__.py
+++ b/util/__init__.py
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+"""This package includes a miscellaneous collection of useful helper functions."""
diff --git a/util/get_data.py b/util/get_data.py
index 6325605bc68..97edc3ce3c3 100644
--- a/util/get_data.py
+++ b/util/get_data.py
@@ -9,26 +9,24 @@
class GetData(object):
- """
-
- Download CycleGAN or Pix2Pix Data.
+ """A Python script for downloading CycleGAN or pix2pix datasets.
- Args:
- technique : str
- One of: 'cyclegan' or 'pix2pix'.
- verbose : bool
- If True, print additional information.
+ Parameters:
+ technique (str) -- One of: 'cyclegan' or 'pix2pix'.
+ verbose (bool) -- If True, print additional information.
Examples:
>>> from util.get_data import GetData
>>> gd = GetData(technique='cyclegan')
>>> new_data_path = gd.get(save_path='./datasets') # options will be displayed.
+ Alternatively, You can use bash scripts: 'scripts/download_pix2pix_model.sh'
+ and 'scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh'.
"""
def __init__(self, technique='cyclegan', verbose=True):
url_dict = {
- 'pix2pix': 'https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz/projects/pix2pix/datasets',
+ 'pix2pix': 'http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/pix2pix/datasets/',
'cyclegan': 'https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~taesung_park/CycleGAN/datasets'
}
self.url = url_dict.get(technique.lower())
@@ -83,18 +81,15 @@ def get(self, save_path, dataset=None):
Download a dataset.
- Args:
- save_path : str
- A directory to save the data to.
- dataset : str, optional
- A specific dataset to download.
- Note: this must include the file extension.
- If None, options will be presented for you
- to choose from.
+ Parameters:
+ save_path (str) -- A directory to save the data to.
+ dataset (str) -- (optional). A specific dataset to download.
+ Note: this must include the file extension.
+ If None, options will be presented for you
+ to choose from.
Returns:
- save_path_full : str
- The absolute path to the downloaded data.
+ save_path_full (str) -- the absolute path to the downloaded data.
"""
if dataset is None:
diff --git a/util/html.py b/util/html.py
index c7956f1353f..cc3262a1eaf 100644
--- a/util/html.py
+++ b/util/html.py
@@ -1,10 +1,24 @@
import dominate
-from dominate.tags import *
+from dominate.tags import meta, h3, table, tr, td, p, a, img, br
import os
class HTML:
- def __init__(self, web_dir, title, reflesh=0):
+ """This HTML class allows us to save images and write texts into a single HTML file.
+
+ It consists of functions such as (add a text header to the HTML file),
+ (add a row of images to the HTML file), and (save the HTML to the disk).
+ It is based on Python library 'dominate', a Python library for creating and manipulating HTML documents using a DOM API.
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self, web_dir, title, refresh=0):
+ """Initialize the HTML classes
+
+ Parameters:
+ web_dir (str) -- a directory that stores the webpage. HTML file will be created at /index.html; images will be saved at 0:
+ if refresh > 0:
with self.doc.head:
- meta(http_equiv="reflesh", content=str(reflesh))
+ meta(http_equiv="refresh", content=str(refresh))
def get_image_dir(self):
+ """Return the directory that stores images"""
return self.img_dir
- def add_header(self, str):
- with self.doc:
- h3(str)
+ def add_header(self, text):
+ """Insert a header to the HTML file
- def add_table(self, border=1):
- self.t = table(border=border, style="table-layout: fixed;")
- self.doc.add(self.t)
+ Parameters:
+ text (str) -- the header text
+ """
+ with self.doc:
+ h3(text)
def add_images(self, ims, txts, links, width=400):
- self.add_table()
+ """add images to the HTML file
+
+ Parameters:
+ ims (str list) -- a list of image paths
+ txts (str list) -- a list of image names shown on the website
+ links (str list) -- a list of hyperref links; when you click an image, it will redirect you to a new page
+ """
+ self.t = table(border=1, style="table-layout: fixed;") # Insert a table
+ self.doc.add(self.t)
with self.t:
with tr():
for im, txt, link in zip(ims, txts, links):
@@ -43,19 +66,18 @@ def add_images(self, ims, txts, links, width=400):
p(txt)
def save(self):
+ """save the current content to the HMTL file"""
html_file = '%s/index.html' % self.web_dir
f = open(html_file, 'wt')
f.write(self.doc.render())
f.close()
-if __name__ == '__main__':
+if __name__ == '__main__': # we show an example usage here.
html = HTML('web/', 'test_html')
html.add_header('hello world')
- ims = []
- txts = []
- links = []
+ ims, txts, links = [], [], []
for n in range(4):
ims.append('image_%d.png' % n)
txts.append('text_%d' % n)
diff --git a/util/image_pool.py b/util/image_pool.py
index 52413e0f8a4..6d086f882bc 100644
--- a/util/image_pool.py
+++ b/util/image_pool.py
@@ -3,30 +3,52 @@
class ImagePool():
+ """This class implements an image buffer that stores previously generated images.
+
+ This buffer enables us to update discriminators using a history of generated images
+ rather than the ones produced by the latest generators.
+ """
+
def __init__(self, pool_size):
+ """Initialize the ImagePool class
+
+ Parameters:
+ pool_size (int) -- the size of image buffer, if pool_size=0, no buffer will be created
+ """
self.pool_size = pool_size
- if self.pool_size > 0:
+ if self.pool_size > 0: # create an empty pool
self.num_imgs = 0
self.images = []
def query(self, images):
- if self.pool_size == 0:
+ """Return an image from the pool.
+
+ Parameters:
+ images: the latest generated images from the generator
+
+ Returns images from the buffer.
+
+ By 50/100, the buffer will return input images.
+ By 50/100, the buffer will return images previously stored in the buffer,
+ and insert the current images to the buffer.
+ """
+ if self.pool_size == 0: # if the buffer size is 0, do nothing
return images
return_images = []
for image in images:
image = torch.unsqueeze(image.data, 0)
- if self.num_imgs < self.pool_size:
+ if self.num_imgs < self.pool_size: # if the buffer is not full; keep inserting current images to the buffer
self.num_imgs = self.num_imgs + 1
self.images.append(image)
return_images.append(image)
else:
p = random.uniform(0, 1)
- if p > 0.5:
+ if p > 0.5: # by 50% chance, the buffer will return a previously stored image, and insert the current image into the buffer
random_id = random.randint(0, self.pool_size - 1) # randint is inclusive
tmp = self.images[random_id].clone()
self.images[random_id] = image
return_images.append(tmp)
- else:
+ else: # by another 50% chance, the buffer will return the current image
return_images.append(image)
- return_images = torch.cat(return_images, 0)
+ return_images = torch.cat(return_images, 0) # collect all the images and return
return return_images
diff --git a/util/util.py b/util/util.py
index ba7b083ca18..b050c13e1d6 100644
--- a/util/util.py
+++ b/util/util.py
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
+"""This module contains simple helper functions """
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import numpy as np
@@ -5,21 +6,34 @@
import os
-# Converts a Tensor into an image array (numpy)
-# |imtype|: the desired type of the converted numpy array
def tensor2im(input_image, imtype=np.uint8):
- if isinstance(input_image, torch.Tensor):
- image_tensor = input_image.data
- else:
- return input_image
- image_numpy = image_tensor[0].cpu().float().numpy()
- if image_numpy.shape[0] == 1:
- image_numpy = np.tile(image_numpy, (3, 1, 1))
- image_numpy = (np.transpose(image_numpy, (1, 2, 0)) + 1) / 2.0 * 255.0
+ """"Converts a Tensor array into a numpy image array.
+
+ Parameters:
+ input_image (tensor) -- the input image tensor array
+ imtype (type) -- the desired type of the converted numpy array
+ """
+ if not isinstance(input_image, np.ndarray):
+ if isinstance(input_image, torch.Tensor): # get the data from a variable
+ image_tensor = input_image.data
+ else:
+ return input_image
+ image_numpy = image_tensor[0].cpu().float().numpy() # convert it into a numpy array
+ if image_numpy.shape[0] == 1: # grayscale to RGB
+ image_numpy = np.tile(image_numpy, (3, 1, 1))
+ image_numpy = (np.transpose(image_numpy, (1, 2, 0)) + 1) / 2.0 * 255.0 # post-processing: tranpose and scaling
+ else: # if it is a numpy array, do nothing
+ image_numpy = input_image
return image_numpy.astype(imtype)
def diagnose_network(net, name='network'):
+ """Calculate and print the mean of average absolute(gradients)
+
+ Parameters:
+ net (torch network) -- Torch network
+ name (str) -- the name of the network
+ """
mean = 0.0
count = 0
for param in net.parameters():
@@ -32,12 +46,31 @@ def diagnose_network(net, name='network'):
print(mean)
-def save_image(image_numpy, image_path):
+def save_image(image_numpy, image_path, aspect_ratio=1.0):
+ """Save a numpy image to the disk
+
+ Parameters:
+ image_numpy (numpy array) -- input numpy array
+ image_path (str) -- the path of the image
+ """
+
image_pil = Image.fromarray(image_numpy)
+ h, w, _ = image_numpy.shape
+
+ if aspect_ratio > 1.0:
+ image_pil = image_pil.resize((h, int(w * aspect_ratio)), Image.BICUBIC)
+ if aspect_ratio < 1.0:
+ image_pil = image_pil.resize((int(h / aspect_ratio), w), Image.BICUBIC)
image_pil.save(image_path)
def print_numpy(x, val=True, shp=False):
+ """Print the mean, min, max, median, std, and size of a numpy array
+
+ Parameters:
+ val (bool) -- if print the values of the numpy array
+ shp (bool) -- if print the shape of the numpy array
+ """
x = x.astype(np.float64)
if shp:
print('shape,', x.shape)
@@ -48,6 +81,11 @@ def print_numpy(x, val=True, shp=False):
def mkdirs(paths):
+ """create empty directories if they don't exist
+
+ Parameters:
+ paths (str list) -- a list of directory paths
+ """
if isinstance(paths, list) and not isinstance(paths, str):
for path in paths:
mkdir(path)
@@ -56,5 +94,10 @@ def mkdirs(paths):
def mkdir(path):
+ """create a single empty directory if it didn't exist
+
+ Parameters:
+ path (str) -- a single directory path
+ """
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
diff --git a/util/visualizer.py b/util/visualizer.py
index ffbf298173c..9736b5c3049 100644
--- a/util/visualizer.py
+++ b/util/visualizer.py
@@ -1,14 +1,30 @@
import numpy as np
import os
+import sys
import ntpath
import time
-from . import util
-from . import html
-from scipy.misc import imresize
+from . import util, html
+from subprocess import Popen, PIPE
+
+
+if sys.version_info[0] == 2:
+ VisdomExceptionBase = Exception
+else:
+ VisdomExceptionBase = ConnectionError
-# save image to the disk
def save_images(webpage, visuals, image_path, aspect_ratio=1.0, width=256):
+ """Save images to the disk.
+
+ Parameters:
+ webpage (the HTML class) -- the HTML webpage class that stores these imaegs (see html.py for more details)
+ visuals (OrderedDict) -- an ordered dictionary that stores (name, images (either tensor or numpy) ) pairs
+ image_path (str) -- the string is used to create image paths
+ aspect_ratio (float) -- the aspect ratio of saved images
+ width (int) -- the images will be resized to width x width
+
+ This function will save images stored in 'visuals' to the HTML file specified by 'webpage'.
+ """
image_dir = webpage.get_image_dir()
short_path = ntpath.basename(image_path[0])
name = os.path.splitext(short_path)[0]
@@ -20,13 +36,7 @@ def save_images(webpage, visuals, image_path, aspect_ratio=1.0, width=256):
im = util.tensor2im(im_data)
image_name = '%s_%s.png' % (name, label)
save_path = os.path.join(image_dir, image_name)
- h, w, _ = im.shape
- if aspect_ratio > 1.0:
- im = imresize(im, (h, int(w * aspect_ratio)), interp='bicubic')
- if aspect_ratio < 1.0:
- im = imresize(im, (int(h / aspect_ratio), w), interp='bicubic')
- util.save_image(im, save_path)
-
+ util.save_image(im, save_path, aspect_ratio=aspect_ratio)
ims.append(image_name)
txts.append(label)
links.append(image_name)
@@ -34,42 +44,75 @@ def save_images(webpage, visuals, image_path, aspect_ratio=1.0, width=256):
class Visualizer():
+ """This class includes several functions that can display/save images and print/save logging information.
+
+ It uses a Python library 'visdom' for display, and a Python library 'dominate' (wrapped in 'HTML') for creating HTML files with images.
+ """
+
def __init__(self, opt):
+ """Initialize the Visualizer class
+
+ Parameters:
+ opt -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions
+ Step 1: Cache the training/test options
+ Step 2: connect to a visdom server
+ Step 3: create an HTML object for saveing HTML filters
+ Step 4: create a logging file to store training losses
+ """
+ self.opt = opt # cache the option
self.display_id = opt.display_id
self.use_html = opt.isTrain and not opt.no_html
self.win_size = opt.display_winsize
self.name = opt.name
- self.opt = opt
+ self.port = opt.display_port
self.saved = False
- if self.display_id > 0:
+ if self.display_id > 0: # connect to a visdom server given and
import visdom
self.ncols = opt.display_ncols
- self.vis = visdom.Visdom(server=opt.display_server, port=opt.display_port)
+ self.vis = visdom.Visdom(server=opt.display_server, port=opt.display_port, env=opt.display_env)
+ if not self.vis.check_connection():
+ self.create_visdom_connections()
- if self.use_html:
+ if self.use_html: # create an HTML object at /web/; images will be saved under /web/images/
self.web_dir = os.path.join(opt.checkpoints_dir, opt.name, 'web')
self.img_dir = os.path.join(self.web_dir, 'images')
print('create web directory %s...' % self.web_dir)
util.mkdirs([self.web_dir, self.img_dir])
+ # create a logging file to store training losses
self.log_name = os.path.join(opt.checkpoints_dir, opt.name, 'loss_log.txt')
with open(self.log_name, "a") as log_file:
now = time.strftime("%c")
log_file.write('================ Training Loss (%s) ================\n' % now)
def reset(self):
+ """Reset the self.saved status"""
self.saved = False
- # |visuals|: dictionary of images to display or save
+ def create_visdom_connections(self):
+ """If the program could not connect to Visdom server, this function will start a new server at port < self.port > """
+ cmd = sys.executable + ' -m visdom.server -p %d &>/dev/null &' % self.port
+ print('\n\nCould not connect to Visdom server. \n Trying to start a server....')
+ print('Command: %s' % cmd)
+ Popen(cmd, shell=True, stdout=PIPE, stderr=PIPE)
+
def display_current_results(self, visuals, epoch, save_result):
- if self.display_id > 0: # show images in the browser
+ """Display current results on visdom; save current results to an HTML file.
+
+ Parameters:
+ visuals (OrderedDict) - - dictionary of images to display or save
+ epoch (int) - - the current epoch
+ save_result (bool) - - if save the current results to an HTML file
+ """
+ if self.display_id > 0: # show images in the browser using visdom
ncols = self.ncols
- if ncols > 0:
+ if ncols > 0: # show all the images in one visdom panel
ncols = min(ncols, len(visuals))
h, w = next(iter(visuals.values())).shape[:2]
table_css = """""" % (w, h)
+ table {border-collapse: separate; border-spacing: 4px; white-space: nowrap; text-align: center}
+ table td {width: % dpx; height: % dpx; padding: 4px; outline: 4px solid black}
+ """ % (w, h) # create a table css
+ # create a table of images.
title = self.name
label_html = ''
label_html_row = ''
@@ -90,28 +133,36 @@ def display_current_results(self, visuals, epoch, save_result):
idx += 1
if label_html_row != '':
label_html += '%s
' % label_html_row
- # pane col = image row
- self.vis.images(images, nrow=ncols, win=self.display_id + 1,
- padding=2, opts=dict(title=title + ' images'))
- label_html = '' % label_html
- self.vis.text(table_css + label_html, win=self.display_id + 2,
- opts=dict(title=title + ' labels'))
- else:
+ try:
+ self.vis.images(images, nrow=ncols, win=self.display_id + 1,
+ padding=2, opts=dict(title=title + ' images'))
+ label_html = '' % label_html
+ self.vis.text(table_css + label_html, win=self.display_id + 2,
+ opts=dict(title=title + ' labels'))
+ except VisdomExceptionBase:
+ self.create_visdom_connections()
+
+ else: # show each image in a separate visdom panel;
idx = 1
- for label, image in visuals.items():
- image_numpy = util.tensor2im(image)
- self.vis.image(image_numpy.transpose([2, 0, 1]), opts=dict(title=label),
- win=self.display_id + idx)
- idx += 1
+ try:
+ for label, image in visuals.items():
+ image_numpy = util.tensor2im(image)
+ self.vis.image(image_numpy.transpose([2, 0, 1]), opts=dict(title=label),
+ win=self.display_id + idx)
+ idx += 1
+ except VisdomExceptionBase:
+ self.create_visdom_connections()
- if self.use_html and (save_result or not self.saved): # save images to a html file
+ if self.use_html and (save_result or not self.saved): # save images to an HTML file if they haven't been saved.
self.saved = True
+ # save images to the disk
for label, image in visuals.items():
image_numpy = util.tensor2im(image)
img_path = os.path.join(self.img_dir, 'epoch%.3d_%s.png' % (epoch, label))
util.save_image(image_numpy, img_path)
+
# update website
- webpage = html.HTML(self.web_dir, 'Experiment name = %s' % self.name, reflesh=1)
+ webpage = html.HTML(self.web_dir, 'Experiment name = %s' % self.name, refresh=1)
for n in range(epoch, 0, -1):
webpage.add_header('epoch [%d]' % n)
ims, txts, links = [], [], []
@@ -125,28 +176,46 @@ def display_current_results(self, visuals, epoch, save_result):
webpage.add_images(ims, txts, links, width=self.win_size)
webpage.save()
- # losses: dictionary of error labels and values
- def plot_current_losses(self, epoch, counter_ratio, opt, losses):
+ def plot_current_losses(self, epoch, counter_ratio, losses):
+ """display the current losses on visdom display: dictionary of error labels and values
+
+ Parameters:
+ epoch (int) -- current epoch
+ counter_ratio (float) -- progress (percentage) in the current epoch, between 0 to 1
+ losses (OrderedDict) -- training losses stored in the format of (name, float) pairs
+ """
if not hasattr(self, 'plot_data'):
self.plot_data = {'X': [], 'Y': [], 'legend': list(losses.keys())}
self.plot_data['X'].append(epoch + counter_ratio)
self.plot_data['Y'].append([losses[k] for k in self.plot_data['legend']])
- self.vis.line(
- X=np.stack([np.array(self.plot_data['X'])] * len(self.plot_data['legend']), 1),
- Y=np.array(self.plot_data['Y']),
- opts={
- 'title': self.name + ' loss over time',
- 'legend': self.plot_data['legend'],
- 'xlabel': 'epoch',
- 'ylabel': 'loss'},
- win=self.display_id)
+ try:
+ self.vis.line(
+ X=np.stack([np.array(self.plot_data['X'])] * len(self.plot_data['legend']), 1),
+ Y=np.array(self.plot_data['Y']),
+ opts={
+ 'title': self.name + ' loss over time',
+ 'legend': self.plot_data['legend'],
+ 'xlabel': 'epoch',
+ 'ylabel': 'loss'},
+ win=self.display_id)
+ except VisdomExceptionBase:
+ self.create_visdom_connections()
# losses: same format as |losses| of plot_current_losses
- def print_current_losses(self, epoch, i, losses, t, t_data):
- message = '(epoch: %d, iters: %d, time: %.3f, data: %.3f) ' % (epoch, i, t, t_data)
+ def print_current_losses(self, epoch, iters, losses, t_comp, t_data):
+ """print current losses on console; also save the losses to the disk
+
+ Parameters:
+ epoch (int) -- current epoch
+ iters (int) -- current training iteration during this epoch (reset to 0 at the end of every epoch)
+ losses (OrderedDict) -- training losses stored in the format of (name, float) pairs
+ t_comp (float) -- computational time per data point (normalized by batch_size)
+ t_data (float) -- data loading time per data point (normalized by batch_size)
+ """
+ message = '(epoch: %d, iters: %d, time: %.3f, data: %.3f) ' % (epoch, iters, t_comp, t_data)
for k, v in losses.items():
message += '%s: %.3f ' % (k, v)
- print(message)
+ print(message) # print the message
with open(self.log_name, "a") as log_file:
- log_file.write('%s\n' % message)
+ log_file.write('%s\n' % message) # save the message
 +You may find useful information in [training/test tips](docs/tips.md) and [frequently asked questions](docs/qa.md). To implement custom models and datasets, check out our [templates](#custom-model-and-dataset). To help users better understand and adapt our codebase, we provide an [overview](docs/overview.md) of the code structure of this repository.
-#### Pix2pix: [[Project]](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004v1.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix)
+**CycleGAN: [Project](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf) | [Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) |
+[Tensorflow Core Tutorial](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/generative/cyclegan) | [PyTorch Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/CycleGAN.ipynb)**
-
+You may find useful information in [training/test tips](docs/tips.md) and [frequently asked questions](docs/qa.md). To implement custom models and datasets, check out our [templates](#custom-model-and-dataset). To help users better understand and adapt our codebase, we provide an [overview](docs/overview.md) of the code structure of this repository.
-#### Pix2pix: [[Project]](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004v1.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix)
+**CycleGAN: [Project](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf) | [Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) |
+[Tensorflow Core Tutorial](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/generative/cyclegan) | [PyTorch Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/CycleGAN.ipynb)**
- +
+ +
+