-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 22
Home
Developing enterprise services for access to data (CRUD) can be deceptively simple. Just write something that gives access to the data you need. Done!
Well...not quite. The challenge arises as the business grows and with it the number applications and services built to support the growth. How do you avoid duplicating the data access layer for every service or web app you write? How do you keep track of application and service inter-dependencies? How do you audit and manage access to your enterprise data? How do you continue supporting the growth while building systems to scale?
There are many projects for lightblue corresponding to the flexibility depected above. They are each documented here.
Cloud focused data services with dynamic querying, versioned schemas, and robust security.
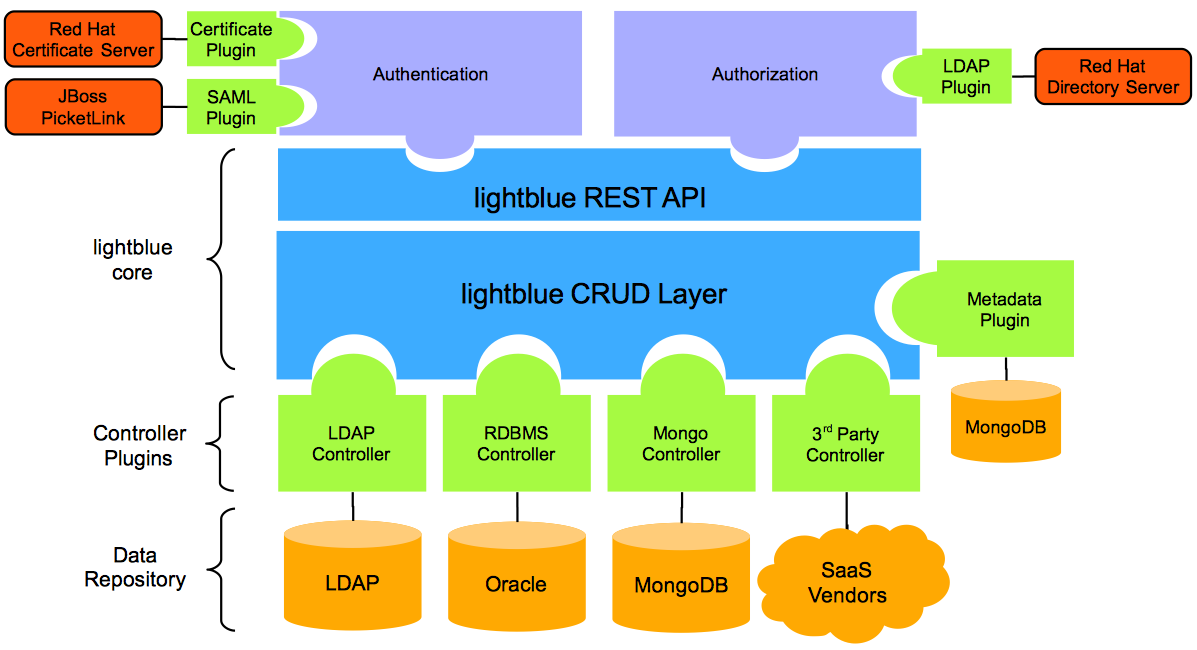
Lightblue is an open source project built from the ground up to be very flexible. This plugin based component architecture enables deployment of lightblue in virtually any environment and with only the plugins needed enabled. This bascially means you can deploy lightblue where you want and plug in the puzzle pieces you want!
All documentation is moving to gitbook.io, please check out these links. We decided to do this to better manage documentation that really spans multiple repositories, meaning multiple wiki's.
Cloud focused data services with dynamic querying, versioned schemas, and robust security.
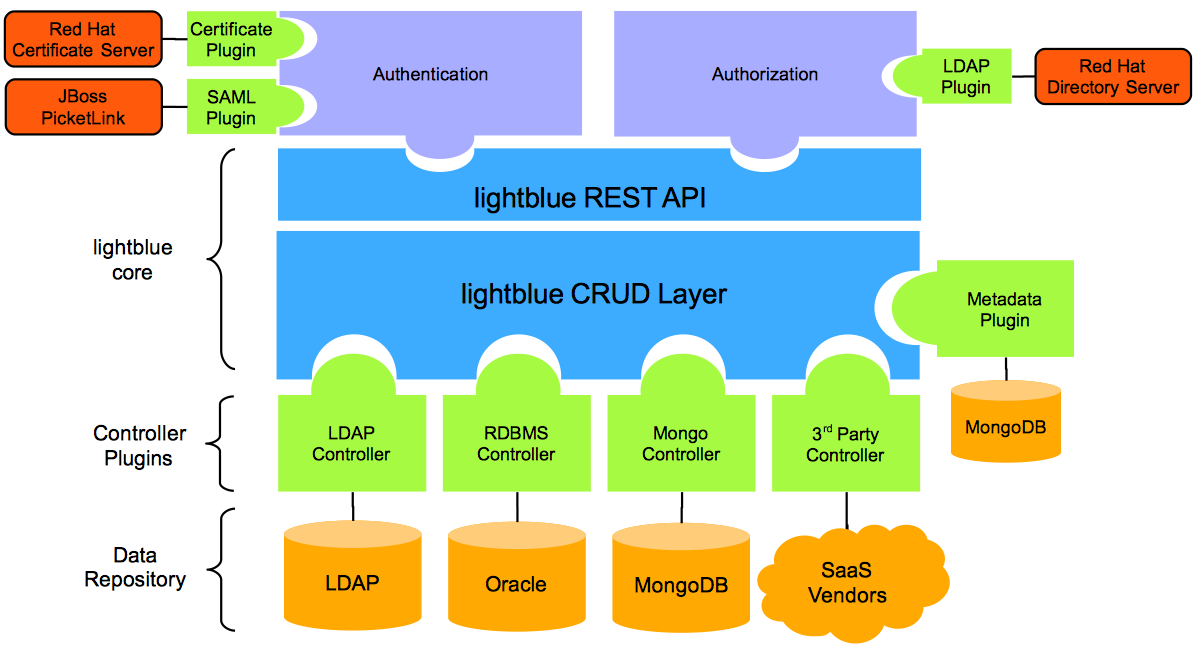
Developing enterprise services for access to data (CRUD) can be deceptively simple. Just write something that gives access to the data you need. Done! Well...not quite. The challenge arises as the business grows and with it the number applications and services built to support the growth. How do you avoid duplicating the data access layer for every service or web app you write? How do you keep track of application and service inter-dependencies? How do you audit and manage access to your enterprise data? And finally, how do you continue supporting the growth while building systems to scale?
lightblue enables development teams focus on the core business logic by providing a consistent, query based CRUD layer for data access. lightblue abstracts developers from the underlying data store, be it a NoSQL, RDBMS, LDAP or SaaS based repository, and provides a unified view of the data. It also has the ability to provide SAML or certificate based authentication and fine grained authorization at an individual attribute/column level with a backing LDAP store. What's great is you can pick and chose the modules you need for your specific purposes. lightblue stays true to SOA principles and is modular in structure. If there isn't a plugin readily available, lightblue provides well defined interfaces to write a custom plugin.
- Adding a field may break backwards compatibility for clients.
- Updating all clients is not easy to schedule.
- Creating new APIs on the service solves the above problems but leads to sprawling APIs and inconsistency.
- Migrating from one type of tech to another is not trivial, such as RDBMS to NoSQL.
- Moving some proprietary database technologies outside of a traditional datastore can be very costly.
- Changes in underlying datastore will lead to optimized ways accessing the data. This changes APIs!
- When you control your data and application tier hardware it is easy to be lax with security.
- Moving data and applications off of hardware you control requires robust security.
- Enabling the move to public API access to even sensitive data requires a lot of rigor.
- IT budgets are shrinking while business demands continue to rise. Any place cost can be reduced relative to gains is great!
One of the time sinks for developers is adding new features for clients of their software. To address this for data access, lightblue provides a robust and very capable API, supports a growing number of datastores, and enables changes to data models without impacting existing clients through the use of versioned metadata.
The REST API of lightblue is designed to do everything a client could want. There are some key points that the API addresses:
- Query: a very rich query language
- Projection: return only the data a client wants
- Bulk Operations: ability execute CRUD operations against many records or entire collections
Clients do not care where data is stored as long as it is available and secure. With lightblue we have controller implementations for:
- MongoDB (1.9.0 and higher)
- RDBMS (ANSI SQL92)
Not seeing a contoller you need? We welcome new implementations and contributions in general! From opening a request for enhancement to writing code, your ideas and help are greatly appricated.
All data in lightblue is controlled by its metadata. Think of this as all the DDL for a table in a relational database.
Data structures are maintained by metadata. A specific version of this metadata provides a window to the stored data. You can have many versions of metadata active at a time, providing different clients with different windows to this data. Key points to remember:
- all data structures are captured as metadata
- each data stucture can have multiple versions active at a time
- each client views data with a specific version
- clients using different versions are seeing the same data, just viewed through a different window
<insert example, something simple that anybody can relate to>
One of the challenges with maintaining enterprise applications is ensuring they are always on. When any change to a data structure requires application deployments it requires operations resources and can require outages to execute. With lightblue any changes to a data structure is simply a change to metadata.
- metadata updates are not software changes
- metadata updates are guarenteed backwards compatible
Example workflow to update a single field without lightblue:
Example workflow to update a single field with lightblue:
Some other benefits beyond simply reducing operations overhead are:
- lightblue is designed to be deployed anywhere
- lightblue employes a flexible component architecture that enables components to be deployed and scaled independently
- lightblue is built to be both latency and fault tollerant
- lightblue works with your preference of authentication and authorization
If lightblue enables data access across many datasources and technologies we also need to provide tools to support that stack! Enter the management applications:
- Metadata Management Application
- Data Management Application
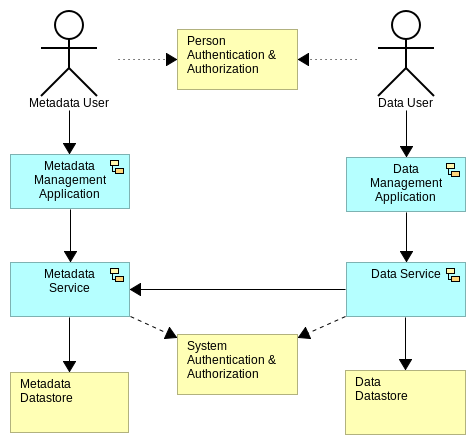
Each of the applications provides access to the corresponding service layer. The point of them is provide a nicer interface to the service layer without having to deal with the service directly. Each application can be secured independent of the service tier, as noted in the diagram.
- Deploy lightblue on OpenShift: openshift-lightblue-all
- Deploy lightblue with basic-auth:
- Deploy lightblue with SAML 2.0:
The license of lightblue is GPLv3. See COPYING in root of project for the full text.
| Dependency | Why | License |
|---|---|---|
| Jackson | Java library for processing JSON documents. Use in complicated cases where processing is required on the JSON document. | Apache License, Version 2.0 |
| Gson | Convert Java to and from JSON. Used in simple cases where processing is 1:1 between Java and the JSON document. | Apache License, Version 2.0 |
| JSONassert | Used in unit tests to compare JSON documents before and after processing. Useful for verifying parsing and type conversions (JSON -> Java -> JSON for example) | Apache License, Version 2.0 |
| json-schema-validator | Validation of JSON documents against a JSON schema. Similar to XML Schema validation. | LGPLv3 or later |
| Flapdoodle Embedded MongoDB | In memory MongoDB used in unit tests to test against a real database. | Apache License, Version 2.0 |
| mongo-java-driver | MongoDB driver for Java. Used for all interactions with MongoDB from Java. | Apache License, Version 2.0 |
| hystrix et al. | Hystrix core is a java framework to build a Distributed/Cloud-enabled Systems. It's "... is a latency and fault tolerance library designed to isolate points. .., stop cascading failure and enable resilience ...". | Apache License, Version 2.0 |
| pyresttest | Python utility for testing and benchmarking RESTful services. | Apache License, Version 2.0 |

