-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 25
HLD Removing mcrypt and adding libsodium
Three (3) specific goals that have to be accomplished in order for our code base to be considered cryptographically secure
- Fix all encryption weaknesses.
- Improve overall hashing, including password storing mechanism.
- Use strong Cryptographically Secure Pseudo-Random Number Generator (CSPRNG), and replace current ones.
- It should have high-level (not low-level) authentication functions, so that easily deployable/used by developers.
- It should have authenticated encryption. (like AES-OCB or AES-GCM or HMAC)
- It should use AES-256 or better algorithm, not any variant of this algorithms (currently Magento uses a variant of AES-256).
- It should use CBC (layered, not divided) cipher mode by default (not ECB at all), and of course with a strong and unpredictable initialization vector (IV). IV is a block of bits that is used by several modes to randomize the encryption and hence to produce distinct ciphertexts even if the same plaintext is encrypted multiple times, without the need for a slower re-keying process.
- No weak entropy (random number generation). The library should have strong Cryptographically Secure Pseudo-Random Number Generator (CSPRNG).
In PHP 7.2 Sodium replaced Mcrypt as their inherent crypto security library. Not only is that a major factor in the decision to use the library, it fulfills all the Magento requirements as a trusted cryptographic security solution. Below are the reasons why it is the clear solution for our security needs.
- All details about this library: https://paragonie.com/book/pecl-libsodium
- Pros: uses authenticated encryption.
- Pros: uses AES-GCM.
- Pros: good for both symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
- Pros: good for cryptographic hash functions.
- Pros: super easy to use.
- Pros: constantly updating/releasing (https://pecl.php.net/package/libsodium)
- Cons: probably not good for SSL/TLS (which actually we don’t require in our case for Magento)
When PHP 7.2 came out the mcrypt library was removed as a bundled extension because the code is no longer being maintained by its creators. This has caused it to fall behind from a security standpoint and is no longer considered cryptographically secure. Due to this problem PHP decided to bundle libsodium into PHP as their encryption and hashing library.
In order for Magento to support PHP 7.2 changes have to be made to our crypt security. One school of thought would be to leave the current code in place for PHP 7.1 installations and acknowledge this is a less secure platform choice. If a client decides to upgrade their environment to PHP 7.2 then they would receive the benefit of newer, more secure dependencies that provide a cryptographically secure data utility.
The problems with this theory are we ship a half baked security update. If you decide to upgrade your environment to PHP 7.2 your data is protected. If you don’t then we can’t guarantee our code will secure your data.
The school of thought should be that if you upgrade your Magento instance we will fill the security gaps exposed by previous versions. By using dependency injection for the nonce we won’t need to modify the interface. This will keep us from causing BIC which is the goal of any solution at Magento.
Two problems exist that have to be resolved in order for us to deliver an effective upgrade strategy:
- Php 7.1 ships with mcrypt but doesn’t include sodium.
- Php 7.2 ships with sodium but doesn’t include mcrypt.
By tying Magento’s dependencies to PHP’s dependencies we break most rules defined by the SOLID principals. The requirements are take what has been cryptographically modified using legacy techniques, validate it, and cryptographically modify it using cryptographically secure techniques. If we rely on PHP’s dependency choices the solution becomes convoluted and highly susceptible to backwards incompatible changes.
Instead of relying on the bundled php libraries we should use composer to load both libraries and inject them accordingly. Then you don’t have to worry about what version of PHP is running on the web instance. Removing the dependency on the PHP extensions allows us to give the same amount of security to clients running PHP 7.1 and 7.2.
Below are the Composer repositories for the libraries we need.
**paragonie/sodium_compat ** Pure PHP implementation of libsodium; uses the PHP extension if it exists phpseclib/mcrypt_compat PHP 7.1 polyfill for the mcrypt extension from PHP
- If a 3rd party developer wants their code to be compatible with PHP 7.2 they already know their crypto security code has to be refactored now that mcrypt has been removed.
- 3rd party developers should follow the vision described by this document for converting data secured by inferior cryptographic techniques to cryptographically secure techniques.
- If a client wants to upgrade to PHP 7.2 and their 3rd party component dependencies haven't released a compatible version they are pinned to their current version.
- The inclusion of modules that haven't been updated to use Sodium are not cryptographically secure.
- If a module hasn't been updated to use Sodium they will continue to use the bundled mcrypt library which will not cause backward incompatible changes.
For encryption and hashing, this is the current interface in Magento we need to modify the method bodies of: lib/internal/Magento/Framework/Encryption/EncryptorInterface. We also need to inject a new interface into the classes that implement EncryptorInterface for the nonce that is required by Sodium. For overall random number generation and hashing, those are calling Magento FW's hash functions currently, we need to refactor them throughout Magento code base to leverage libsodium's corresponding functions.
6.1.1. Authenticated Encryption
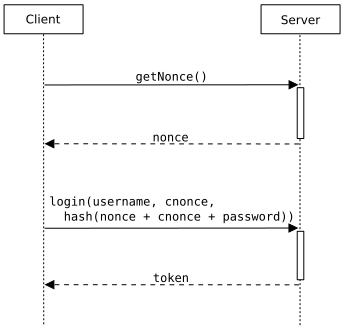
Authenticated encryption is a form of encryption which simultaneously provides confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity assurances on the data that is sent from a client to a server. Currently Magento doesn't have a secure authenticated encryption protocol and it needs to be added to make sure we provide our clients a mechanism to secure themselves from replay attacks and semantic url attacks. The good news is we don't have to modify the existing EncryptorInterface methods. We simply need to create a two new methods for generating a nonce and validating the nonce once the message is received from the client.
The following is a diagram of a typical authenticated encryption workflow.
In order for us to support this workflow the AuthenticatedEncryptionInterface needs to be created with the following two new methods.
<?php
/**
* Copyright © Magento, Inc. All rights reserved.
* See COPYING.txt for license details.
*/
namespace Magento\Framework\Encryption;
/**
* Authenticated Encryption Interface
*
* @api
*/
interface AuthenticatedEncryptionInterface
{
/**
* Create a unique nonce and store it for future validation
*
* @return string
* @throws \Exception
*/
public function getNonce();
/**
* Validate encrypted text using a nonce to make sure the ciphertext hasn't been tampered with.
* The method returns the decrypted text.
* If the nonce validation fails a SecurityViolationException will be thrown.
*
* @param string $cipherText
* @param string $nonce
* @return string
* @throws SecurityViolationException
*/
public function validateEncryption($cipherText, $nonce);
}An example implementation of the AuthenticatedEncryptionInterface would be the following:
<?php
/**
* Copyright © Magento, Inc. All rights reserved.
* See COPYING.txt for license details.
*/
namespace Magento\Framework\Encryption;
/**
* Authenticated Encryption
*
* @api
*/
class AuthenticatedEncryption implements AuthenticatedEncryptionInterface
{
/**
* Cryptographic key for instance
*
* @var string
*/
private string $key;
/**
* @param DeploymentConfig $deploymentConfig
*/
public function __construct(
DeploymentConfig $deploymentConfig
) {
// Load the cryptographic key from env.php
$this->key = $deploymentConfig->get('crypt/key')));
}
/**
* Create a unique nonce and store it for future validation
*
* @return string
*/
public function getNonce()
{
unsigned char $nonce[crypto_secretbox_NONCEBYTES];
randombytes_buf($nonce, sizeof $nonce);
activateNonce($nonce);
return $nonce;
}
/**
* Validate encrypted text using a nonce to make sure the ciphertext hasn't been tampered with.
* The method returns the decrypted text.
* If the nonce validation fails a SecurityViolationException will be thrown.
*
* @param string $cipherText
* @param string $nonce
* @return string
* @throws SecurityViolationException
*/
public function validateEncryption(
string $cipherText,
string $nonce
) {
unsigned char $decrypted[MESSAGE_LEN];
if (crypto_secretbox_open_easy(
$decrypted,
$ciphertext,
sizeof $cipherText,
$nonce,
$key
) != 0) {
/* message forged! */
return new \Magento\Framework\Exception\SecurityViolationException(
__("This message has been tampered with.")
);
}
deactivateNonce($nonce);
return $decrypted;
}
/**
* Store the nonce so that it can be referenced later for validation
*
* @param string $nonce
*/
private function activateNonce(
string $nonce
) {
/* Store the nonce in persistent storage
...
}
/**
* Remove the nonce so that it can't be used again
*
* @param string $nonce
*/
private function deactivateNonce(
string $nonce
) {
/* Remove the nonce from storage to indicate it has been used
...
}
}For clients that want to use this added security benefit they will need to refactor their code to get the nonce from the Magento API and then use the nonce, cryptographic key and payload to generate the ciphertext that will be sent to the server API along with the nonce. Then when the server validates the ciphertext with the nonce the action will be allowed to continue. If the nonce has been used or the cipher text cannot be decrypted with the nonce and key the action will fail.
6.1.2 Normal Encryption
For data that needs to be stored in persistent storage the nonce is needed as an argument to the encryption function, however, we don't want to make the caller keep track of the data because it will force them to refactor the encryption code to store the nonce. If the nonce is prepended to the ciphertext the decryption code can extract the nonce from the stored data and successfully decrypt the stored data. This will enable us to remove mcrypt and implement the advanced security features of libsodium without causing backwards incompatible changes. This means we can upgrade Magento cryptographic security without making 3rd party modules modify their code.
Below is an example of how we can refactor the encrypt and decrypt methods on the EncryptorInterface without causing backwards incompatible changes:
<?php
/**
* Copyright © Magento, Inc. All rights reserved.
* See COPYING.txt for license details.
*/
namespace Magento\Framework\Encryption;
use Magento\Framework\App\DeploymentConfig;
use Magento\Framework\Encryption\Helper\Security;
use Magento\Framework\Math\Random;
/**
* Class Encryptor provides basic logic for hashing strings and encrypting/decrypting misc data
*/
class Encryptor implements EncryptorInterface
{
/**
* Cryptographic key for instance
*
* @var string
*/
private string $key;
/**
* @param DeploymentConfig $deploymentConfig
*/
public function __construct(
DeploymentConfig $deploymentConfig
) {
// Load the cryptographic key from env.php
$this->key = $deploymentConfig->get('crypt/key')));
}
/**
* Encrypt a message
*
* @param string $message - message to encrypt
* @return string
*/
function encrypt(
string $message
) {
$nonce = \Sodium\randombytes_buf(
\Sodium\CRYPTO_SECRETBOX_NONCEBYTES
);
$cipher = base64_encode(
$nonce.
\Sodium\crypto_secretbox(
$message,
$nonce,
$key
)
);
\Sodium\memzero($message);
\Sodium\memzero($key);
return $cipher;
}
/**
* Decrypt a message
*
* @param string $encrypted - message encrypted with encrypt()
* @return string
* @throws SecurityViolationException
*/
function decrypt(
string $encrypted,
) {
$decoded = base64_decode($encrypted);
if ($decoded === false) {
throw new \Exception('Scream bloody murder, the encoding failed');
}
if (mb_strlen($decoded, '8bit') < (\Sodium\CRYPTO_SECRETBOX_NONCEBYTES + \Sodium\CRYPTO_SECRETBOX_MACBYTES)) {
throw new \Exception('Scream bloody murder, the message was truncated');
}
$nonce = mb_substr($decoded, 0, \Sodium\CRYPTO_SECRETBOX_NONCEBYTES, '8bit');
$ciphertext = mb_substr($decoded, \Sodium\CRYPTO_SECRETBOX_NONCEBYTES, null, '8bit');
$plain = \Sodium\crypto_secretbox_open(
$ciphertext,
$nonce,
$key
);
if ($plain === false) {
throw new \SecurityViolationException('This message has been tampered with.');
}
\Sodium\memzero($ciphertext);
\Sodium\memzero($key);
return $plain;
}
}-
Design Document
- Discussion: Encryption with Libsodium
- Info
- ZenHub board
-
Weekly calls(on pause): - Slack: #feature-php-72