417. Pacific Atlantic Water Flow #2250
-
|
Topics: There is an The island is partitioned into a grid of square cells. You are given an The island receives a lot of rain, and the rain water can flow to neighboring cells directly north, south, east, and west if the neighboring cell's height is less than or equal to the current cell's height. Water can flow from any cell adjacent to an ocean into the ocean. Return a 2D list of grid coordinates Example 1:
Example 2:
Constraints:
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
Replies: 1 comment 2 replies
-
|
We need to determine which cells in a given grid can allow rainwater to flow to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The Pacific Ocean borders the top and left edges of the grid, while the Atlantic Ocean borders the bottom and right edges. Water can flow from a cell to neighboring cells in the four cardinal directions if the neighboring cell's height is less than or equal to the current cell's height. Approach
Let's implement this solution in PHP: 417. Pacific Atlantic Water Flow <?php
/**
* @param Integer[][] $heights
* @return Integer[][]
*/
function pacificAtlantic($heights) {
$m = count($heights);
$n = count($heights[0]);
$pacific = array_fill(0, $m, array_fill(0, $n, false));
$atlantic = array_fill(0, $m, array_fill(0, $n, false));
for ($i = 0; $i < $m; $i++) {
dfs($heights, $pacific, $i, 0, $m, $n);
dfs($heights, $atlantic, $i, $n - 1, $m, $n);
}
for ($j = 0; $j < $n; $j++) {
dfs($heights, $pacific, 0, $j, $m, $n);
dfs($heights, $atlantic, $m - 1, $j, $m, $n);
}
$result = [];
for ($i = 0; $i < $m; $i++) {
for ($j = 0; $j < $n; $j++) {
if ($pacific[$i][$j] && $atlantic[$i][$j]) {
$result[] = [$i, $j];
}
}
}
return $result;
}
/**
* @param $heights
* @param $visited
* @param $i
* @param $j
* @param $m
* @param $n
* @return void
*/
function dfs($heights, &$visited, $i, $j, $m, $n) {
$visited[$i][$j] = true;
$directions = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]];
foreach ($directions as $dir) {
$x = $i + $dir[0];
$y = $j + $dir[1];
if ($x >= 0 && $x < $m && $y >= 0 && $y < $n &&
!$visited[$x][$y] && $heights[$x][$y] >= $heights[$i][$j]) {
dfs($heights, $visited, $x, $y, $m, $n);
}
}
}
// Test cases
$heights1 = [
[1,2,2,3,5],
[3,2,3,4,4],
[2,4,5,3,1],
[6,7,1,4,5],
[5,1,1,2,4]
];
print_r(pacificAtlantic($heights1));
// Expected: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
$heights2 = [[1]];
print_r(pacificAtlantic($heights2));
// Expected: [[0,0]]
?>Explanation:
This approach efficiently narrows down the solution by leveraging reverse traversal from the ocean borders, ensuring optimal performance even for the upper constraint limits. |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
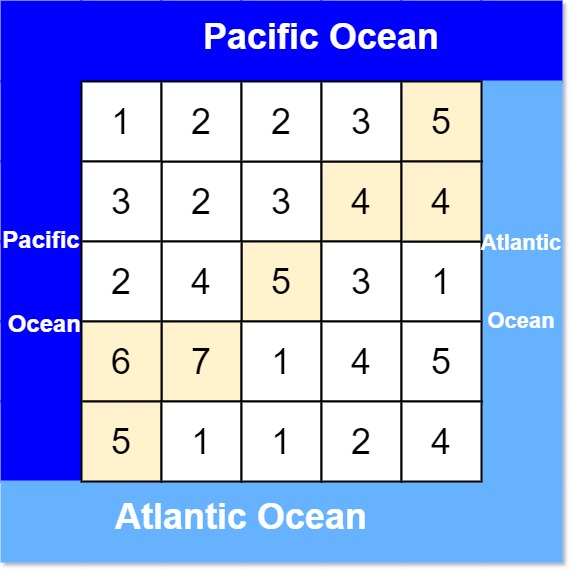
We need to determine which cells in a given grid can allow rainwater to flow to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The Pacific Ocean borders the top and left edges of the grid, while the Atlantic Ocean borders the bottom and right edges. Water can flow from a cell to neighboring cells in the four cardinal directions if the neighboring cell's height is less than or equal to the current cell's height.
Approach