-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 175
Debugpy with Webassembly (proposal)
This page seeks to describe WebAssembly and how Debugpy might be modified to support debugging CPython running with WebAssembly.
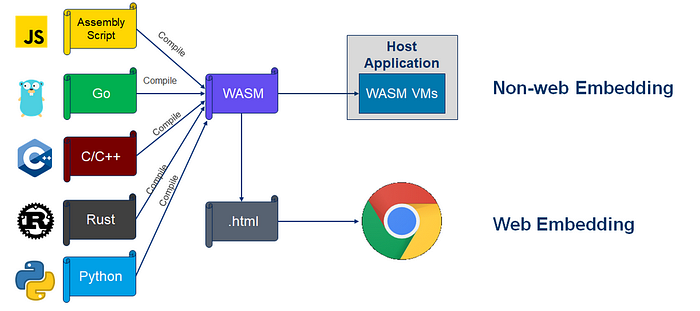
WebAssembly (abbreviated Wasm) is a binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine. Wasm is designed as a portable compilation target for programming languages, enabling deployment on the web for client and server applications.
source: https://megaease.com/blog/2021/09/17/extend-backend-application-with-webassembly/
How does this code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}get turned into something like so?

The first step is something called WebAssembly.instantiate.
Javascript code loads the 'wasm' module and calls WebAssembly.instantiate (or WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming) on it.
const instance = await WebAssembly.instantiate(wasmModule, imports);This call loads the WASM into the web page.
Javascript can now do things like so:
instance.export.main();Which would call the 'main' function on the wasm.
When the C code is built, it has external dependencies. This is indicated in the WASM file like so:
(import "wasi_snapshot_preview1" "proc_exit" (func $wasi_snapshot_preview1.proc_exit (type $t4)))
(import "wasi_snapshot_preview1" "fd_write" (func $wasi_snapshot_preview1.fd_write (type $t11)))
(import "wasi_snapshot_preview1" "fd_close" (func $wasi_snapshot_preview1.fd_close (type $t1)))
(import "wasi_snapshot_preview1" "fd_seek" (func $wasi_snapshot_preview1.fd_seek (type $t12)))This is the list of imports required by the simple hello world.
-
proc_exitto be called for cleanup -
fd_writeto write to stdout -
fd_closeto finish using stdout -
fd_seekto seek to the beginning of stdout
When the javascript code does this:
const instance = await WebAssembly.instantiate(wasmModule, imports);The list of imports can be setup like so:
var heapu32;
var heapu8;
var stdout = console.log.bind(console);
var stderr = console.warn.bind(console);
var streams = ['', '', ''];
function printChar(stream, curr) {
var dest = stream === 1 ? stdout : stderr;
if (curr === 0 || curr === 10) {
var str = streams[stream];
dest(str);
streams[stream] = '';
} else {
streams[stream] += String.fromCharCode(curr);
}
}
function _fd_write(fd, iov, iovcnt, pnum) {
var num = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < iovcnt; i++) {
var ptr = heapu32[((iov) >> 2)];
var len = heapu32[(((iov) + (4)) >> 2)];
iov += 8;
for (var j = 0; j < len; j++) {
printChar(fd, heapu8[ptr + j]);
}
num += len;
}
heapu32[((pnum) >> 2)] = num;
return 0;
}
function _fd_close(fd) {
return 0;
}
function _fd_fdstat_get(fd, iov) {
return 0;
}
function _fd_seek(fd, offset, where) {
return 0;
}
function _proc_exit() {
return 0;
}
const imports = {};
imports.wasi_snapshot_preview1 = {};
imports.wasi_snapshot_preview1.fd_write = _fd_write;
imports.wasi_snapshot_preview1.fd_close = _fd_close;
imports.wasi_snapshot_preview1.fd_fdstat_get = _fd_fdstat_get;
imports.wasi_snapshot_preview1.fd_seek = _fd_seek;
imports.wasi_snapshot_preview1.proc_exit = _proc_exit;
fetch("hello_world_wasi.wasm")
.then(resp => WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming(resp, imports))
.then(result => {
console.log(`Starting wasm`);
heapu32 = new Uint32Array(result.instance.exports.memory.buffer);
heapu8 = new Uint8Array(result.instance.exports.memory.buffer);
result.instance.exports._start();
})There's some interesting things to note here:
- When writing using
fd_write, the data is passed in as a pointer to memory. This is why after the wasm is loaded, theheapis captured from thememoryexport. - The
memoryexport is how the WASM exports its memory to the Javascript layer. -
fd_writeneeds to treat things as pointers to memory, reading one byte at a time. There is no string that's passed through, it's the raw bytes of the data written to stdout. Basically implementing the writev from POSIX.
Thankfully the answer to this is no.
Table of options