Export DXF with matplotlib #582
-
|
Hello! First of all, thank you for this great library! Highly appreciate your work and use it in my hobby projects. Exporting DXF file (AC1015) of 75 KB size with matplotlib approach results in a 320KB output pdf. Exporting the same file with AutoCAD "DWG to PDF" default printer results with 15KB output pdf file. This is how the file looks: I have noticed that AutoCAD output has embedded .ttf font and matplotlib output has no embedded fonts. I tried to export with .shx fonts and it makes no difference. As long as pdf is vector file format, I wonder why the pdf files rendered by matplotlib are so huge? What I have tried so far is converting dxf to svg with Inkscape, but it is not possibly to install on my headless Raspberry Pi. Ghostscript converting to PostScript file and back to PDF produces ~220KB file, which is no acceptable for my purposes. May be you or somebody could give me advice on how to solve this problem. |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
Replies: 3 comments 12 replies
-
|
A simple script to create an example PDF by import ezdxf
from ezdxf.addons.drawing.matplotlib import qsave
doc = ezdxf.new()
msp = doc.modelspace()
msp.add_text("TEXT")
qsave(msp, "text.pdf")If you open the PDF with a PDF editor or a vector graphic editor, you will see that |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
I tried to understand Matplotlib scaling and learned nothing :( def new_doc(width, height):
doc = ezdxf.new()
msp = doc.modelspace()
w, h = width, height
text_size = 10
msp.add_lwpolyline([(0, 0), (w, 0), (w, h), (0, h)], close=True)
for y in range(1, 10):
msp.add_line((0, y), (10, y))
msp.add_line((0, text_size), (w, text_size))
msp.add_text("A LINE OF TEXT", dxfattribs={"height": text_size}).set_pos(
(10, 0)
)
return doc
def main(width, height, dpi=300):
doc = new_doc(width, height)
layout = doc.modelspace()
scale = 10 * 50.0 / height
fig: plt.Figure = plt.figure()
ax: plt.Axes = fig.add_axes((0, 0, 1, 1))
ctx = RenderContext(layout.doc)
layout_properties = LayoutProperties.from_layout(layout)
out = FixedSizedTextMatplotlibBackend(ax, text_size_scale=scale)
config = Configuration.defaults()
Frontend(
ctx, out, config=config.with_changes(lineweight_scaling=0.01)
).draw_layout(
layout,
finalize=True,
layout_properties=layout_properties,
)
paper_width = 10
fig.set_size_inches(paper_width, (height / width) * paper_width)
name = rf"C:\Users\manfred\Desktop\Outbox\{width}x{height}.pdf"
fig.savefig(
name,
dpi=dpi,
facecolor=ax.get_facecolor(),
transparent=True,
)
print(f"{name} saved")
plt.close(fig)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(200, 50)
main(200, 100)
main(200, 150)
main(200, 200)
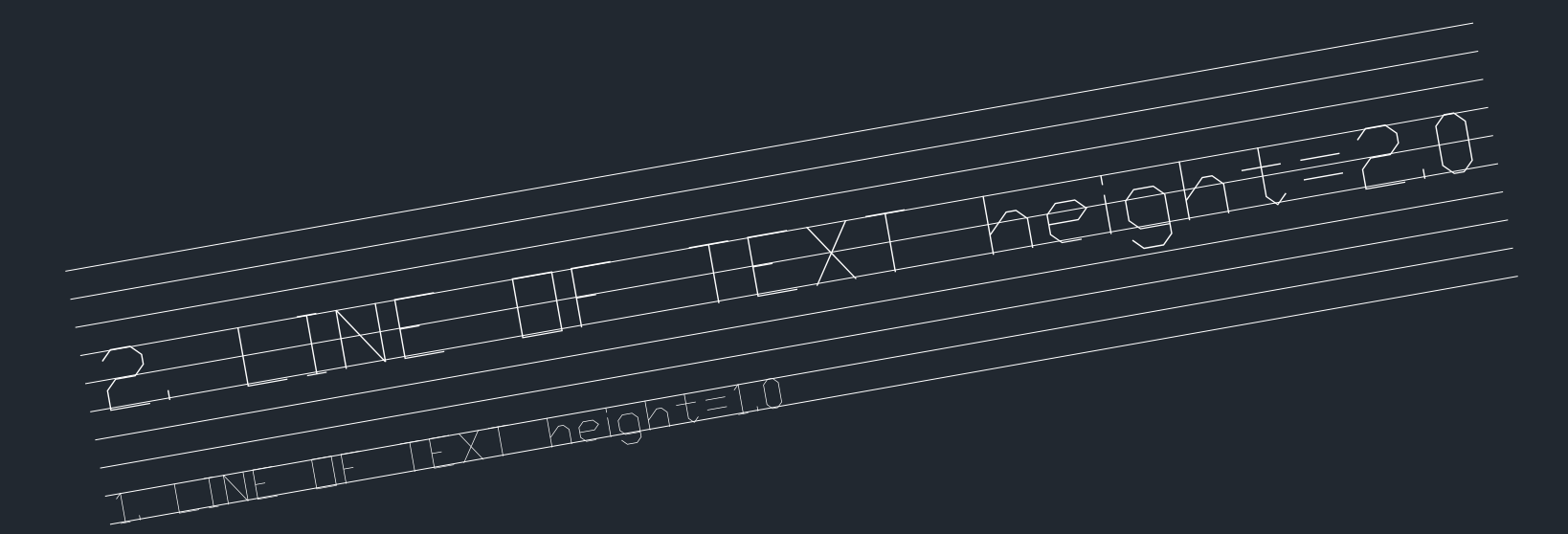
main(200, 300)At least I can set the paper size in inches now :) The Line weight scaling seems not to work for the Matplotlib backend. |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.





A simple script to create an example PDF by
Matplotlib:If you open the PDF with a PDF editor or a vector graphic editor, you will see that
Matplotlib(as we use it) exports text as path objects. This takes up more space, but also does not require embedding font files. This is the current status of implementation and it will not change in the future either.