index:only`. If it returns no results, the repository has not been indexed.
-
-### Sourcegraph is making unauthorized requests to the git server
-
-This is normal and happens whenever git is used over HTTP. To avoid unnecessarily sending a password over HTTP, git first
-makes a request without the password included. If a 401 Unauthorized is returned, git sends the request with the password.
-
-More information can be found [here](https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucketserverkb/two-401-responses-for-every-git-opperation-938854756.html).
-
-If this behaviour is undesired, the `gitURLType` in the [external service configuration](/admin/code_hosts/github#configuration)
-should be set to `ssh` instead of `http`. This will also require [ssh keys to be set up](/admin/repo/auth#repositories-that-need-http-s-or-ssh-authentication).
diff --git a/docs/admin/updates/grpc/index.mdx b/docs/admin/updates/grpc/index.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index 0fd599411..000000000
--- a/docs/admin/updates/grpc/index.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,115 +0,0 @@
-import { CURRENT_VERSION_STRING_NO_V, CURRENT_VERSION_STRING } from 'src/components/PreCodeBlock'
-
-# Sourcegraph 5.3 gRPC Configuration Guide
-
-## Overview
-
-As part of our continuous effort to enhance performance and reliability, in Sourcegraph 5.3 we’ve fully transitioned to using [gRPC](https://grpc.io/) as the primary communication method for our internal services.
-
-This guide will help you understand this change and its implications for your setup.
-
-## Quick Overview
-
-- **What’s changing?** In Sourcegraph `5.3`, we've transitioned to [gRPC](https://grpc.io/) for internal communication between Sourcegraph services.
-- **Why?** gRPC, a high-performance Remote Procedure Call (RPC) framework by Google, brings about several benefits like a more efficient serialization format, faster speeds, and a better development experience.
-- **Is any action needed?** If you don’t have restrictions on Sourcegraph’s **internal** (service to service) traffic, you shouldn't need to take any action—the change should be invisible. If you do have restrictions, some firewall or security configurations may be necessary. See the ["Who needs to Act"](#who-needs-to-act) section for more details.
-- **Can I disable gRPC if something goes wrong?** In Sourcegraph `5.3.X`, gRPC can no longer be disabled. However, if you run into an issue it is possible to downgrade to Sourcegraph `5.2.X`, which includes a [toggle to enable/disable gRPC](#sourcegraph-52x-only-enabling--disabling-grpc) while you troubleshoot the issue. Contact our customer support team for more information.
-
-## gRPC: A Brief Intro
-
-[gRPC](https://grpc.io/) is an open-source [RPC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Remote_procedure_call) framework developed by Google. Compared to [REST](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/REST), gRPC is faster, more efficient, has built-in backwards compatibility support, and offers a superior development experience.
-
-## Key Changes
-
-### 1. Internal Service Communication
-
-For Sourcegraph version `5.3.X` onwards, our microservices like `repo-updater` and `gitserver` will use mainly gRPC instead of REST for their internal traffic. This affects only communication *between* our services. Interactions you have with Sourcegraph's UI and external APIs remain unchanged.
-
-### 2. Rollout Plan
-
-| Version | gRPC Status |
-|---------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| `5.2.X` (Released on October 4th, 2023) | On by default but can be disabled via a feature flag. |
-| `5.3.X` (Releasing Feburary 15th, 2024)| Fully integrated and can't be turned off. Able to temporarily downgrade to `5.2.X` if there are any issues. |
-
-## Preparing for the Change
-
-### Who Needs to Act?
-
-Our use of gRPC only affects traffic **_between_** our microservices (e.x. `searcher` ↔ `gitserver`). Traffic between the Sourcegraph Web UI and the rest of the application is unaffected (e.x. `sourcegraph.example.com` ↔ `frontend`’s GraphQL API).
-
-**If Sourcegraph's internal traffic faces no security restrictions in your environment, no action is required.**
-
-However, if you’ve applied security measures or have firewall restrictions on this traffic, adjustments might be needed to accommodate gRPC communication. The following is a more technical description of the protocol that can help you configure your security settings:
-
-### gRPC Technical Details
-
-- **Protocol Description**: gRPC runs on-top of [HTTP/2](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP/2) (which, in turn, runs on top of [TCP](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_Control_Protocol). It transfers (binary-encoded, not human-readable plain-text) [Protocol Buffer](https://protobuf.dev/) payloads. Our current gRPC implementation does not use any encryption.
-
-- **List of services**: The following services will now _speak mainly gRPC in addition_ to their previous traffic:
- - [frontend](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/frontend/sourcegraph-frontend.Service.yaml)
- - [gitserver](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/gitserver/gitserver.Service.yaml)
- - [searcher](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/searcher/searcher.StatefulSet.yaml)
- - [zoekt-webserver](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/indexed-search/indexed-search.StatefulSet.yaml)
- - [zoekt-indexserver](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/indexed-search/indexed-search.StatefulSet.yaml)
-
-- The following aspects about Sourcegraph’s networking configuration **aren’t changing**:
- - **Ports**: all Sourcegraph services will use the same ports as they were in the **5.1.X** release.
- - **External traffic**: gRPC only affects how Sourcegraph’s microservices communicate amongst themselves - **no new external traffic is sent via gRPC**.
- - **Service dependencies:** each Sourcegraph service will communicate with the same set of services regardless of whether gRPC is enabled.
- - Example: `searcher` will still need to communicate with `gitserver` to fetch repository data. Whether gRPC is enabled doesn’t matter.
-
-### Sourcegraph `5.2.X` only: enabling / disabling GRPC
-
-In the `5.2.x` release, you are able to use the following methods to enable / disable gRPC if a problem occurs.
-
- In the `5.3.X` release, these options are removed and gRPC is always enabled. However, if you run into an issue it is possible to downgrade to Sourcegraph `5.2.X` and use the configuration below to temporarily disable gRPC while you troubleshoot the issue. Contact our customer support team for more assistance with downgrading.
-
-#### All services besides `zoekt-indexserver`
-
-Disabling gRPC on any service that is not `zoekt-indexserver` can be done by one of these options:
-
-##### Option 1: disable via site-configuration
-
-Set the `enableGRPC` experimental feature to `false` in the site configuration file:
-
-```json
-{
- "experimentalFeatures": {
- "enableGRPC": false // disabled
- }
-}
-```
-
-##### Option 2: disable via environment variables
-
-Set the environment variable `SG_FEATURE_FLAG_GRPC="false"` for every service.
-
-#### `zoekt-indexserver` service: disable via environment variable
-
-Set the environment variable `GRPC_ENABLED="false"` on the `zoekt-indexserver` container. (See [indexed-search.StatefulSet.yaml](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/indexed-search/indexed-search.StatefulSet.yaml) for the configuration):
-
-```yaml
-- name: zoekt-indexserver
- env:
- - name: GRPC_ENABLED
- value: 'false'
- image: docker.io/sourcegraph/search-indexer:{CURRENT_VERSION_NO_V}
-```
-
-_zoekt-indexserver can’t read from Sourcegraph’s site configuration, so we can only use environment variables to communicate this setting._
-
-If any issues arise with gRPC, admins have the option to disable it in version `5.2.X`. This will be phased out in `5.3.X`.
-
-## Monitoring gRPC
-
-To ensure the smooth operation of gRPC, we offer:
-
-- **gRPC Grafana Dashboards**: For every gRPC service, we provide dedicated dashboards. These boards present request and error rates for every method, aiding in performance tracking. See our [dashboard documentation](/admin/observability/dashboards).
-
-
-- **Internal Error Reporter**: For certain errors specifically from gRPC libraries or configurations, we've integrated an "internal error" reporter. Logs prefixed with `grpc.internal.error.reporter` signal issues with our gRPC execution and should be reported to customer support for more assistance.
-
-## Need Help?
-
-For any queries or concerns, reach out to our customer support team. We’re here to assist!
diff --git a/docs/admin/updates/index.mdx b/docs/admin/updates/index.mdx
index 023eb51d2..258510c02 100644
--- a/docs/admin/updates/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/admin/updates/index.mdx
@@ -132,4 +132,3 @@ If your instance has schema drift or unfinished oob migrations you may need to a
- [Upgrading Early Versions](/admin/updates/migrator/upgrading-early-versions)
- [Troubleshooting upgrades](/admin/updates/migrator/troubleshooting-upgrades)
- [Downgrading](/admin/updates/migrator/downgrading)
-- [Sourcegraph 5.2 gRPC Configuration Guide](/admin/updates/grpc/)
diff --git a/docs/admin/validation.mdx b/docs/admin/validation.mdx
index 24bec457f..8abaca66a 100644
--- a/docs/admin/validation.mdx
+++ b/docs/admin/validation.mdx
@@ -2,7 +2,6 @@
Sourcegraph Validation is currently experimental.
-
## Validate Sourcegraph Installation
Installation validation provides a quick way to check that a Sourcegraph installation functions properly after a fresh install
diff --git a/docs/cloud/index.mdx b/docs/cloud/index.mdx
index 9e90562b2..c8e28b2a7 100644
--- a/docs/cloud/index.mdx
+++ b/docs/cloud/index.mdx
@@ -242,7 +242,7 @@ Sourcegraph Cloud instances are single-tenant, limiting exposure to outages and
### Is data safe with Sourcegraph Cloud?
-Sourcegraph Cloud utilizes a single-tenant architecture. Each customer's data is isolated and stored in a dedicated GCP project. Data is [encrypted in transit](https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/encryption-in-transit) and [at rest](https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/encryption/default-encryption) and is backed up daily. Such data includes but is not limited to, customer source code, repository metadata, code host connection configuration, and user profile. Sourcegraph Cloud also has [4 supported regions](#multiple-region-availability) on GCP to meet data sovereignty requirements.
+Sourcegraph Cloud utilizes a single-tenant architecture. Each customer's data is isolated and stored in a dedicated GCP project. Data is [encrypted in transit](https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/encryption-in-transit) and [at rest](https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/encryption/default-encryption) and is backed up daily. Such data includes but is not limited to, customer source code, repository metadata, code host connection configuration, and user profile. Sourcegraph Cloud also has [5 supported regions](#multiple-region-availability) on GCP to meet data sovereignty requirements.
Sourcegraph continuously monitors Cloud instances for security vulnerability using manual reviews and automated tools. Third-party auditors regularly perform testing to ensure maximum protection against vulnerabilities and are automatically upgraded to fix any vulnerability in third-party dependencies. In addition, GCP’s managed offering regularly patches any vulnerability in the underlying infrastructure. Any infrastructure changes must pass security checks, which are tested against industry-standard controls.
diff --git a/docs/code_insights/references/common_reasons_code_insights_may_not_match_search_results.mdx b/docs/code_insights/references/common_reasons_code_insights_may_not_match_search_results.mdx
index 76cb28ea9..1f5d147fc 100644
--- a/docs/code_insights/references/common_reasons_code_insights_may_not_match_search_results.mdx
+++ b/docs/code_insights/references/common_reasons_code_insights_may_not_match_search_results.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Because code insights historical search defaults to `fork:yes` and `archived:yes
All repositories in a historical search are unindexed, but a manual Sourcegraph search only includes indexed repositories. It's possible your manual searches are missing results from unindexed repositories.
-To investigate this, one can compare the list of repositories in the manual search (use a `select:repository` filter) with the list of repositories in the insight `series_points` database table. To see why a repository may not be indexing, refer to [this guide](/admin/troubleshooting#sourcegraph-is-not-returning-results-from-a-repository-unless-repo-is-included).
+To investigate this, one can compare the list of repositories in the manual search (use a `select:repository` filter) with the list of repositories in the insight `series_points` database table. To see why a repository may not be indexing, refer to [this guide](/admin/faq#sourcegraph-is-not-returning-results-from-a-repository-unless-repo-is-included).
## If the chart data point shows *lower* counts than a manual search
diff --git a/docs/pricing/faqs.mdx b/docs/pricing/faqs.mdx
index 5197afd8a..3c740a97f 100644
--- a/docs/pricing/faqs.mdx
+++ b/docs/pricing/faqs.mdx
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# FAQs
-Learn about some of the most commonly asked questions about Sourcegraph.
+Learn about some of the most commonly asked questions about Sourcegraph.
## What's the difference between Free, Enterprise Starter, and Enterprise plans?
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ For Enterprise customers, Sourcegraph will not train on your company's data unle
## How are active users counted and billed for Cody?
-This only applies to Cody Enterprise contracts.
+This only applies to Cody Enterprise contracts.
A billable user is one who is signed in to their Enterprise account and actively interacts with the product (e.g., they see suggested autocompletions, run commands or chat with Cody, start new discussions, clear chat history, or copy text from chats, change settings, and more). Simply having Cody installed is not enough to be considered a billable user.
diff --git a/public/llms.txt b/public/llms.txt
index dfe8044ea..97feee713 100644
--- a/public/llms.txt
+++ b/public/llms.txt
@@ -13,6 +13,8 @@ Currently supported versions of Sourcegraph:
| **Release** | **General Availability Date** | **Supported** | **Release Notes** | **Install** |
|--------------|-------------------------------|---------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------|
+| 6.6 Patch 1 | June 2025 | ✅ | [Notes](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/technical-changelog#v66868) | [Install](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/admin/deploy) |
+| 6.6 Patch 0 | June 2025 | ✅ | [Notes](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/technical-changelog#v660) | [Install](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/admin/deploy) |
| 6.5 Patch 2 | June 2025 | ✅ | [Notes](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/technical-changelog#v652654) | [Install](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/admin/deploy) |
| 6.5 Patch 1 | June 2025 | ✅ | [Notes](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/technical-changelog#v651211) | [Install](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/admin/deploy) |
| 6.5 Patch 0 | June 2025 | ✅ | [Notes](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/technical-changelog#v650) | [Install](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/admin/deploy) |
@@ -521,7 +523,7 @@ Slack Support provides access to creating tickets directly from Slack, allowing
| Role-based access control | - | - | ✓ |
| Analytics | - | Basic | ✓ |
| Audit logs | - | - | ✓ |
-| Guardrails | - | - | Beta |
+| Guardrails (*Deprecated*) | - | - | Beta |
| Indexed code | - | Private | Private |
| Context Filters | - | - | ✓ |
| **Compatibility** | | | |
@@ -538,7 +540,7 @@ Slack Support provides access to creating tickets directly from Slack, allowing
# FAQs
-Learn about some of the most commonly asked questions about Sourcegraph.
+Learn about some of the most commonly asked questions about Sourcegraph.
## What's the difference between Free, Enterprise Starter, and Enterprise plans?
@@ -568,7 +570,7 @@ For Enterprise customers, Sourcegraph will not train on your company's data unle
## How are active users counted and billed for Cody?
-This only applies to Cody Enterprise contracts.
+This only applies to Cody Enterprise contracts.
A billable user is one who is signed in to their Enterprise account and actively interacts with the product (e.g., they see suggested autocompletions, run commands or chat with Cody, start new discussions, clear chat history, or copy text from chats, change settings, and more). Simply having Cody installed is not enough to be considered a billable user.
@@ -702,7 +704,7 @@ Here's a detailed breakdown of features included in the different Enterprise pla
| **AI features** | - Cody AI Assistant | - Cody AI Assistant
- Bring your own LLM key |
| **Code Search features** | - Everything in Enterprise Starter, plus:
- Batch Changes
- Code Insights
- Code Navigation | - Everything in Enterprise Starter, plus:
- Batch Changes
- Code Insights
- Code Navigation |
| **Deployment types** | - Single-tenant Coud | - Self- Hosted |
-| **Compatibility** | - Everything in Enterprise Starter, plus:
- Enterprise admin and security features
- All major code hosts
- Guardrails
- Context Filters | - Everything in Enterprise Starter, plus:
- Enterprise admin and security features
- All major code hosts
- Guardrails
- Context Filters |
+| **Compatibility** | - Everything in Enterprise Starter, plus:
- Enterprise admin and security features
- All major code hosts
- Guardrails (Deprecated)
- Context Filters | - Everything in Enterprise Starter, plus:
- Enterprise admin and security features
- All major code hosts
- Guardrails (Deprecated)
- Context Filters |
| **Support** | - 24x5 support with options like:
- TA support
- Premium Support Offerings
- Forward Deployed Engineer (FDE) | - Enterprise support with options like:
- Dedicated TA support
- Premium Support Offerings
- Forward Deployed Engineer (FDE) |
@@ -741,17 +743,17 @@ The Enterprise Starter plan supports a variety of search-based features like:
| ------------------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------- |
| Indexed Code Search | Simplified admin experience with UI‑based repo‑management | Support with limited SLAs |
| Indexed Symbol Search | User management | - |
-| Searched‑based code‑navigation | GitHub code host integration | - |
+| Searched‑based code‑navigation | Code host integrations (GitHub, GitLab.com, Bitbucket Cloud) | - |
## Limits
Sourcegraph Enterprise Starter offers the following limits:
-- Max 50 users per workspace
+- Max 500 users per workspace
- Max 100 repos per workspace
-- Starts with 5 GB of storage
-- 1 GB storage per seat added
-- 10 GB max total storage
+- Starts with 25 GB of storage
+- 5 GB storage per seat added
+- 50 GB max total storage
## Workspace settings
@@ -767,9 +769,11 @@ After creating a new workspace, you can switch views between your personal and w
## Getting started with workspace
-A workspace admin can invite new members to their workspace using their team member's email address. Once the team member accepts the invitation, they will be added to the workspace and assigned the member role. Next, the member is asked to connect and authorize the code host (GitHub) to access the private repositories indexed in your Sourcegraph account.
+A workspace admin can invite new members to their workspace using their team member's email address. Once the team member accepts the invitation, they will be added to the workspace and assigned the member role.
-If you skip this step, the member won't be able to access any of the private repositories they have access to. However, they can still use the public search via the Sourcegraph code search bar.
+If the workspace includes GitHub repositories, the member will be asked to connect and authorize GitHub to access those private repositories. This authorization step is only required for GitHub repositories. For GitLab.com and Bitbucket Cloud repositories, no additional authorization is needed.
+
+Without GitHub authorization, members cannot access private GitHub repositories but can access all other repositories (GitLab.com, Bitbucket Cloud) and use the public search via the Sourcegraph code search bar.

@@ -777,7 +781,12 @@ If you skip this step, the member won't be able to access any of the private rep
From the Repository Management settings, workspace admins can configure various settings for connecting code hosts and indexing repositories in their workspace. You can index up to 100 repos per workspace.
-
+**Repository permissions**:
+
+- **GitHub** provides repository-level permissions that are reflected in Sourcegraph.
+- **GitLab.com** and **Bitbucket Cloud** repositories are accessible to all workspace members regardless of the member's permissions on the external code host.
+
+
From here, you can:
@@ -795,7 +804,7 @@ When you add a new organization, you must authorize access and permission for al
As you add more repos, you get logs for the number of repos added, storage used, and their status. To remove any repo from your workspace, click the repo name that changes the repo status **TO BE REMOVED**. Click the **Save Changes** button to confirm it.
-
+
@@ -6241,6 +6250,8 @@ Site administrators can set the duration of access tokens for users connecting C
## Guardrails
+Guardrails has been deprecated and is no longer recommended for use.
+
Guardrails for public code is only supported on VS Code, JetBrains IDEs extension, and Sourcegraph Web app for Cody Enterprise customers using [Cody Gateway](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/cody/core-concepts/cody-gateway#sourcegraph-cody-gateway). It is not supported for any BYOK (Bring Your Own Key) deployments.
Open source attribution guardrails for public code, commonly called copyright guardrails, reduce the exposure to copyrighted code. This involves implementing a verification mechanism within Cody to ensure that any code generated by the platform does not replicate open source code.
@@ -7766,7 +7777,7 @@ git diff | cody chat -m 'Write a commit message for this diff' -
| Single-repo context | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Multi-repo context | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Local context | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| Guardrails | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
+| Guardrails (*Deprecated*) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Repo-based context filters | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| **Prompts** | | | | | |
| Access to prompts and Prompt library | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
@@ -9082,86 +9093,117 @@ Since MCP is an open protocol and servers can be created by anyone, your mileage
-
-# Quickstart for code monitoring
+
+# Code monitoring
-## Introduction
+
+ Supported on [Enterprise](/pricing/enterprise) plans.
+
+ Currently available via the Web app.
+
+
-In this tutorial, we will create a new code monitor that monitors new appearances of the word "TODO" in your codebase.
+Keep on top of events in your codebase. Watch your code with code monitors and trigger actions to run automatically in response to events.
-## Creating a code monitor
+Code monitors allow you to keep track of and get notified about changes in your code. Some use cases for code monitors include getting notifications for potential secrets, anti-patterns, or common typos committed to your codebase.
-Prerequisite: Ensure [email notifications](/admin/observability/alerting#email) are configured in site configuration.
+Here are some starting points for your first code monitor:
-1. On your Sourcegraph instance, click the **Code monitoring** menu item at the top right of your page. Alternatively, go to `https://sourcegraph.example.com/code-monitoring` (where sourcegraph.example.com represents your unique Sourcegraph url).
-2. Click the **Create new code monitor** button at the top right of the page.
-3. Fill out the **Name** input with: "TODOs".
-4. Under the **Trigger** section, click **When there are new search results**.
-5. In the **Search query** input, enter the following search query:
-`TODO type:diff patternType:keyword`.
-(Note that `type:` and `patternType:` are required as part of the search query for code monitoring.)
-1. You can click **Preview results** to see all previous additions or removals of TODO to your codebase.
-2. Back in the code monitor form, click **Continue**.
-3. Click **Send email notifications** under the **Actions** section.
-4. Click **Done**.
-5. Click **Create code monitor**.
+**Watch for consumers of deprecated endpoints**
-You should now be on `https://sourcegraph.example.com/code-monitoring`, and be able to see the TODO code monitor on the page.
+```
+f:\.tsx?$ patterntype:regexp fetch\(['"`]/deprecated-endpoint
+```
-## Sending a test email notification
+If you’re deprecating an API or an endpoint, you may find it useful to set up a code monitor watching for new consumers. As an example, the above query will surface fetch() calls to `/deprecated-endpoint` within TypeScript files. Replace `/deprecated-endpoint` with the actual path of the endpoint being deprecated.
-If you want to preview the email notification alerting you of a new result with TODO, follow these steps:
+**Get notified when a file changes**
-1. In the **Send email notifications** action, click "Send test email".
-1. Within a few minutes, you should receive a test email from Sourcegraph with a preview of the email notification.
+```
+patterntype:regexp repo:^github\.com/sourcegraph/sourcegraph$ file:SourcegraphWebApp\.tsx$ type:diff
+```
-If you want to test receiving an email with a real new result, follow these steps:
+You may want to get notified when a given file is changed, regardless of the diff contents of the change: the above query will return all changes to the `SourcegraphWebApp.tsx` file on the `github.com/sourcegraph/sourcegraph` repo.
-1. In any repository that's on your Sourcegraph instance (for purposes of this tutorial, we recommend a dummy or test repo that's not used), add `TODO` to any file.
-1. Commit the change, and push it to your code host.
-1. Within a few minutes, you should see an email from Sourcegraph with a link to the new result you just pushed.
+**Get notified when a specific function call is added**
-
+```
+repo:^github\.com/sourcegraph/sourcegraph$ type:diff select:commit.diff.added Sprintf
+```
-
-# Code monitoring
+You may want to monitor new additions of a specific function call, for example a deprecated function or a function that introduces a security concern. This query will notify you whenever a new addition of `Sprintf` is added to the `sourcegraph/sourcegraph` repository. This query selects all diff additions marked as "+". If a call of `Sprintf` is both added and removed from a file, this query will still notify due to the addition.
-
- Supported on [Enterprise](/pricing/enterprise) plans.
-
- Currently available via the Web app.
-
-
+Code monitors are made up of two main elements: **Triggers** and **Actions**.
-Keep on top of events in your codebase
+## Triggers
-Watch your code with code monitors and trigger actions to run automatically in response to events.
+A _trigger_ is an event which causes execution of an action. Currently, code monitoring supports one kind of trigger: "When new search results are detected" for a particular search query. When creating a code monitor, users will be asked to specify a query as part of the trigger.
-## Getting started
+Sourcegraph will run the search query over every new commit for the searched repositories, and when new results for the query are detected, a trigger event is emitted. In response to the trigger event, any _actions_ attached to the code monitor will be executed.
-
-
-
-
+A query used in a "When new search results are detected" trigger must be a `type:commit` or `type:diff` search. This allows Sourcegraph to detect new search results periodically.
-## Questions & Feedback
+## Actions
-We want to hear your feedback! [Share your thoughts](mailto:feedback@sourcegraph.com)
+An _action_ is executed in response to a trigger event. Currently, code monitoring supports three different actions:
-
+### Sending a notification email to the owner of the code monitor
+
+Prerequisite: Ensure [email notifications](/admin/observability/alerting#email) are configured in site configuration.
+
+1. Click the _Code monitoring_ menu item at the top right of your page.
+2. Click the _Create new code monitor_ button at the top right of the page.
+3. Fill out the _Name_ input with: "TODOs".
+4. Under the _Trigger_ section, click _When there are new search results_.
+5. In the _Search query_ input, enter the following search query:
+`TODO type:diff patternType:keyword`.
+(Note that `type:` and `patternType:` are required as part of the search query for code monitoring.)
+1. You can click _Preview results_ to see all previous additions or removals of TODO to your codebase.
+2. Back in the code monitor form, click _Continue_.
+3. Click _Send email notifications_ under the _Actions_ section. You can use "Send test email" to verify you can properly receive notifications and to lean more about the format.
+4. Click _Done_.
+5. Click _Create code monitor_.
+
+You should now see the TODO code monitor on the page, and you will receive email notifications whenever the trigger fires.
+
+### Sending a Slack message to a channel
+
+You can set up code monitors to send notifications about new matching search results to Slack channels.
+
+#### Usage
-
-# Setting up Webhook notifications
+1. In Sourcegraph, click on the "Code Monitoring" nav item at the top of the page.
+1. Create a new code monitor or edit an existing monitor by clicking on the "Edit" button next to it.
+1. Under actions, select **Send Slack message to channel**.
+1. Paste your webhook URL into the "Webhook URL" field. (See "[Creating a Slack incoming webhook URL](#creating-a-slack-incoming-webhook-url)" below for detailed instructions.)
+1. Click on the "Continue" button, and then the "Save" button.
+
+##### Creating a Slack incoming webhook URL
+
+1. You must have permission to create apps in your organization's Slack workspace.
+1. Go to https://api.slack.com/apps and sign in to your Slack account if necessary.
+1. Click on the "Create an app" button.
+1. Create your app "From scratch".
+1. Give your app a name and select the workplace you want notifications sent to.
+
+1. Once your app is created, click on the "Incoming Webhooks" in the sidebar, under "Features".
+1. Click the toggle button to activate incoming webhooks.
+1. Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on "Add New Webhook to Workspace".
+1. Select the channel you want notifications sent to, then click on the "Allow" button.
+1. Your webhook URL is now created! Click the copy button to copy it to your clipboard.
+
+
+### Sending a webhook event to an endpoint of your choosing
Webhook notifications provide a way to execute custom responses to a code monitor notification.
They are implemented as a POST request to a URL of your choice. The body of the request is defined
by Sourcegraph, and contains all the information available about the cause of the notification.
-## Prerequisites
+#### Prerequisites
- You must have a service running that can accept the POST request triggered by the webhook notification
-## Creating a webhook receiver
+#### Creating a webhook receiver
A webhook receiver is a service that can accept an HTTP POST request with the contents of the webhook notification.
The receiver must be reachable from the Sourcegraph cluster using the URL that is configured below.
@@ -9179,7 +9221,8 @@ The HTTP POST request sent to the receiver will have a JSON-encoded body with th
- `message`: The matching commit message. Only set if the result is a commit match.
- `matchedMessageRanges`: The character ranges of `message` that matched `query`. Only set if the result is a commit match.
-Example payload:
+
+
```json
{
"monitorDescription": "My test monitor",
@@ -9207,155 +9250,37 @@ Example payload:
}
```
-## Configuring a code monitor to send Webhook notifications
-
-1. In Sourcegraph, click on the "Code Monitoring" nav item at the top of the page.
-1. Create a new code monitor or edit an existing monitor by clicking on the "Edit" button next to it.
-1. Go through the standard configuration steps for a code monitor and select action "Call a webhook".
-1. Paste your webhook URL into the "Webhook URL" field.
-1. Click on the "Continue" button, and then the "Save" button.
-
-
-
-
-# Start monitoring your code
-
-This page lists code monitors that are commonly used and can be used across most codebases.
-
-
-## Watch for consumers of deprecated endpoints
-
-```
-f:\.tsx?$ patterntype:regexp fetch\(['"`]/deprecated-endpoint
-```
-
-If you’re deprecating an API or an endpoint, you may find it useful to set up a code monitor watching for new consumers. As an example, the above query will surface fetch() calls to `/deprecated-endpoint` within TypeScript files. Replace `/deprecated-endpoint` with the actual path of the endpoint being deprecated.
-
-## Get notified when a file changes
-
-```
-patterntype:regexp repo:^github\.com/sourcegraph/sourcegraph$ file:SourcegraphWebApp\.tsx$ type:diff
-```
-
-You may want to get notified when a given file is changed, regardless of the diff contents of the change: the above query will return all changes to the `SourcegraphWebApp.tsx` file on the `github.com/sourcegraph/sourcegraph` repo.
-
-## Get notified when a specific function call is added
-
-```
-repo:^github\.com/sourcegraph/sourcegraph$ type:diff select:commit.diff.added Sprintf
-```
-
-You may want to monitor new additions of a specific function call, for example a deprecated function or a function that introduces a security concern. This query will notify you whenever a new addition of `Sprintf` is added to the `sourcegraph/sourcegraph` repository. This query selects all diff additions marked as "+". If a call of `Sprintf` is both added and removed from a file, this query will still notify due to the addition.
-
-
-
-
-# Slack notifications for code monitors
-
-You can set up [code monitors](/code_monitoring) to send notifications about new matching search results to Slack channels.
-
-## Requirements
-
-- You must have permission to create apps in your organization's Slack workspace.
-
-## Usage
-
-1. In Sourcegraph, click on the "Code Monitoring" nav item at the top of the page.
-1. Create a new code monitor or edit an existing monitor by clicking on the "Edit" button next to it.
-1. Go through the standard steps for a code monitor (if it's a new one) and select the action **Send Slack message to channel**.
-1. Paste your webhook URL into the "Webhook URL" field. (See "[Creating a Slack incoming webhook URL](#creating-a-slack-incoming-webhook-url)" below for detailed instructions.)
-1. Click on the "Continue" button, and then the "Save" button.
-
-### Creating a Slack incoming webhook URL
-
-1. Go to https://api.slack.com/apps and sign in to your Slack account if necessary.
-1. Click on the "Create an app" button.
-1. Create your app "From scratch".
-1. Give your app a name and select the workplace you want notifications sent to.
-
-1. Once your app is created, click on the "Incoming Webhooks" in the sidebar, under "Features".
-1. Click the toggle button to activate incoming webhooks.
-1. Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on "Add New Webhook to Workspace".
-1. Select the channel you want notifications sent to, then click on the "Allow" button.
-1. Your webhook URL is now created! Click the copy button to copy it to your clipboard.
-
-
-
-
-
-# How-tos
-
-* [Starting points](/code_monitoring/how-tos/starting_points)
-* [Setting up Slack notifications](/code_monitoring/how-tos/slack)
-* [Setting up Webhook notifications](/code_monitoring/how-tos/webhook)
-
-
-
-
-# Explanations
-
-* [Core concepts](/code_monitoring/explanations/core_concepts)
-* [Best practices](/code_monitoring/explanations/best_practices)
-
-
-
-
-# Core concepts
-
-Code monitors allow you to keep track of and get notified about changes in your code. Some use cases for code monitors include getting notifications for potential secrets, anti-patterns, or common typos committed to your codebase.
-
-Code monitors are made up of two main elements: **Triggers** and **Actions**.
-
-## Triggers
-
-A _trigger_ is an event which causes execution of an action. Currently, code monitoring supports one kind of trigger: "When new search results are detected" for a particular search query. When creating a code monitor, users will be asked to specify a query as part of the trigger.
-
-Sourcegraph will run the search query over every new commit for the searched repositories, and when new results for the query are detected, a trigger event is emitted. In response to the trigger event, any _actions_ attached to the code monitor will be executed.
-
-**Query requirements**
-
-A query used in a "When new search results are detected" trigger must be a diff or commit search. In other words, the query must contain `type:commit` or `type:diff`. This allows Sourcegraph to detect new search results periodically.
-
-## Actions
-
-An _action_ is executed in response to a trigger event. Currently, code monitoring supports three different actions:
-
-* Sending a notification email to the owner of the code monitor
-* Sending a Slack message to a preconfigured channel (Beta)
-* Sending a webhook event to an endpoint of your choosing (Beta)
+
-## Current flow
+### Current flow
To put it all together, a code monitor has a flow similar to the following:
A user creates a code monitor, which consists of:
- * a name for the monitor
- * a trigger, which consists of a search query to run periodically,
- * and an action, which is sending an email, sending a Slack message, or sending a webhook event
+- a name for the monitor
+- a trigger, which consists of a search query to run periodically,
+- and an action, which is sending an email, sending a Slack message, or sending a webhook event
Sourcegraph runs the query periodically over new commits. When new results are detected, a notification will be sent with the configured action. It will either contain a link to the search that provided new results, or if the "Include results" setting is enabled, it will include the result contents.
-
-
-
-# Best practices
+## Best practices
There are some best practices we recommend when creating code monitors.
-## Privacy and visibility
+### Privacy and visibility
-### Do not include confidential information in monitor names
+#### Do not include confidential information in monitor names
Every code monitor has a name that will be shown wherever the monitor is referenced. In notification actions this name is likely to be the only information about the event, so it’s important for identifying what was triggered, but also has to be “safe” to expose in plain text emails.
-### Do not include results when the notification destination is untrusted
+#### Do not include results when the notification destination is untrusted
Each code monitor action has the ability to include the result contents when sending a notification. This is often convenient because it lets you immediately see which results triggered the notification. However, because the result contents include the code that matched the search query, they may contain sensitive information. Care should be taken to only send result contents if the destination is secure.
For example, if sending the results to a Slack channel, every user that can view that channel will also be able to view the notification messages. The channel should be properly restricted to users who should be able to view that code.
-## Scale
+### Scale
Code monitors have been designed to be performant even for large Sourcegraph instances. There are no hard limits on the number of monitors or the volume of code monitored. However, depending on a number of factors such as the number of code monitors, the number of repos monitored, the frequency of commits, and the resources allocated to your instance, it's still possible to hit soft limits. If this happens, your code monitor will continue to work reliably, but it may execute more infrequently.
@@ -10464,7 +10389,7 @@ Because code insights historical search defaults to `fork:yes` and `archived:yes
All repositories in a historical search are unindexed, but a manual Sourcegraph search only includes indexed repositories. It's possible your manual searches are missing results from unindexed repositories.
-To investigate this, one can compare the list of repositories in the manual search (use a `select:repository` filter) with the list of repositories in the insight `series_points` database table. To see why a repository may not be indexing, refer to [this guide](/admin/troubleshooting#sourcegraph-is-not-returning-results-from-a-repository-unless-repo-is-included).
+To investigate this, one can compare the list of repositories in the manual search (use a `select:repository` filter) with the list of repositories in the insight `series_points` database table. To see why a repository may not be indexing, refer to [this guide](/admin/faq#sourcegraph-is-not-returning-results-from-a-repository-unless-repo-is-included).
## If the chart data point shows *lower* counts than a manual search
@@ -16103,25 +16028,35 @@ If the repository contains both a `lsif-java.json` file as well as `*.java`, `*.
-# Private Resources on on-prem data center via Sourcegraph Connect agent
+# Private Resources in On-Prem Data Centers via Sourcegraph Connect Agent
-This feature is in the Experimental stage. Please contact Sourcegraph directly via [preferred contact method](https://about.sourcegraph.com/contact) for more information.
+This feature is in the Experimental stage. [Contact us](https://about.sourcegraph.com/contact) for more information.
-As part of the [Enterprise tier](https://sourcegraph.com/pricing), Sourcegraph Cloud supports connecting private resources on any on-prem private network by running Sourcegraph Connect tunnel agent in customer infrastructure.
+As part of the [Enterprise tier](https://sourcegraph.com/pricing), Sourcegraph Cloud supports connecting to private code hosts and artifact registries in the customer's network by deploying the Sourcegraph Connect tunnel agent in the customer's network.
## How it works
-Sourcegraph will set up a tunnel server in a customer dedicated GCP project. Customer will start the tunnel agent provided by Sourcegraph with the provided credential. After start, the agent will authenticate and establish a secure connection with Sourcegraph tunnel server.
+Sourcegraph Connect consists of three components:
+
+### Tunnel Clients
+
+Forward proxy clients for the Sourcegraph Cloud instance's containers to reach the customer's private code hosts and artifact registries, through the tunnel server.
-Sourcegraph Connect consists of three major components:
+Managed by Sourcegraph, and deployed in the customer's Sourcegraph Cloud instance's VPC.
-Tunnel agent: deployed inside the customer network, which uses its own identity and encrypts traffic between the customer code host and client. Agent can only communicate with permitted customer code hosts inside the customer network. Only agents are allowed to establish secure connections with tunnel server, the server can only accept connections if agent identity is approved.
+### Tunnel Server
-Tunnel server: a centralized broker between client and agent managed by Sourcegraph. Its purpose is to set up mTLS, proxy encrypted traffic between clients and agents and enforce ACL.
+The broker between agents and clients, it authenticates agents and clients, enforces ACLs, sets up mTLS, and proxies encrypted traffic between agents and clients.
-Tunnel client: forward proxy clients managed by sourcegraph. Every client has its own identity and it cannot establish a direct connection with the customer agent, and has to go through tunnel server.
+Managed by Sourcegraph, and deployed in the customer's Sourcegraph Cloud instance's VPC.
-[link](https://link.excalidraw.com/readonly/453uvY8infI8wskSecGJ)
+### Tunnel Agents
+
+Deployed by the customer inside their network, agents proxy and encrypt traffic between the customer's private resources and the Sourcegraph Cloud tunnel clients.
+
+The agent has its own identity, and using credentials provided to the customer during deployment, the agent authenticates and establishes a secure connection with the tunnel server. Only agents are allowed to establish secure connections with the tunnel server, and the server only accepts a connection if the agent's identity is approved.
+
+Agents can only communicate with permitted code hosts and artifact registries.
+[Diagram link](https://link.excalidraw.com/readonly/453uvY8infI8wskSecGJ)
## Steps
### Initiate the process
-Customer should reach out to their account manager to initiate the process. The account manager will work with the customer to collect the required information and initiate the process, including but not limited to:
+The customer reaches out to their account manager to request this feature be enabled on their Sourcegraph Cloud instance.
-- The DNS name of the private code host, e.g. `gitlab.internal.company.net` or private artifact registry, e.g. `artifactory.internal.company.net`.
-- The port of the private code host, e.g., `443`, `80`, `22`.
-- The type of TLS certificate used by the private resource: either self-signed by an internal private CA or issued by a public CA.
+The account manager collects the required information from the customer, including but not limited to:
-Finally, Sourcegraph will provide the following:
+- The DNS names of the needed private resources (e.g. `gitlab.internal.company.net`, `artifactory.internal.company.net`)
+- The ports of the private resources (e.g. `443`, `80`, `22`)
+- The type of TLS certificates used by the private resources (e.g. self-signed, internal PKI, or issued by a public CA)
-- Instruction to run the agent along with credentials, and endpoint to allowlist egress traffic if needed.
+Sourcegraph provides:
+- The instructions, config file, and credentials to run the agent
+- The tunnel server's static public IPs and ports
### Create the connection
-Customer can follow the provided instructions and install the tunnel agent in the private network. At a high level:
+The customer installs the agent in their private network, following the instructions provided. At a high level:
-- Permit egress to the internet to a set of static IP addresses and corresponding ports to be provided by Sourcegraph.
-- Permit egress to the private resources at the given port.
-- Run the tunnel agent binary or docker images with the provided config files and credentials.
+- Configure internet egress to the provided tunnel server's static public IPs and ports
+- Configure intranet egress to the needed private resources
+- Deploy the tunnel agent via Docker container or binary, with the provided config file and credentials
-### Create the code host connection
+### Configure the code host connection
-Once the connection to private code host is established, the customer can create the [code host connection](/admin/code_hosts/) on their Sourcegraph Cloud instance.
+Once the tunnel is established between the agent and server, the customer can configure the [code host connection](/admin/code_hosts/) on their Sourcegraph Cloud instance.
## FAQ
+### Why TCP over gRPC?
+
+The tunnel between the client and agent is built using TCP over gRPC. gRPC is a high-performant and battle-tested framework, with built-in support for mTLS for a trusted secure connection. TCP and HTTP/2 are widely supported in the majority of customer environments. Compared to traditional VPN solutions, such as OpenVPN, IPSec, and SSH over bastion hosts, gRPC allows us to design our own protocol, and the programmable interface allows us to implement advanced features, such as fine-grained access control at a per-connection level, audit logging with effective metadata, etc.
+
### How are connections encrypted? Can anyone else inspect the traffic?
-Connections between the tunnel agent inside customer network and a tunnel server inside customer dedicated Sourcegraph GCP VPC use mTLS. Both agents, server and Sourcegraph clients have their own certificates and encrypt/decrypt traffic over TCP. mTLS enforce that both the client and the agent has to have a private key and present valid signed certificate from a trusted CA, which is not shared and this protects from [on-paths and spoofing attacks](https://www.cloudflare.com/en-gb/learning/access-management/what-is-mutual-tls/).
+Tunnel connections use mTLS between the agent in the customer's network and the clients in the customer's Sourcegraph Cloud instance's VPC. Agents, clients, and the server all have their own certificates and encrypt / decrypt traffic over TCP. mTLS requires agents and clients to have a private key, and present a valid signed certificate from a trusted CA, which is not shared. This protects customers and Sourcegraph from [on-path and spoofing attacks](https://www.cloudflare.com/en-gb/learning/access-management/what-is-mutual-tls/).
### How do you authenticate requests?
-Both tunnel clients and agents are assigned an identity corresponding to a GCP Service Account, and they are provided credentials to prove such identity. For tunnel agents, a Service Account key is distributed to the customer. For tunnel clients, it will utilize Workload Identity to prove its identity. They use them to authenticate against tunnel server by sending signed JWT tokens and public key. JWT token contains information about GCP service account credential public key required to validate signature and confirm identity of requestor. The server will then sign the requestor public key and respond with a signed certificate containing GCP Service Account email as a Subject Alternative Name (SAN).
+Both tunnel agents and clients are assigned an identity corresponding to a GCP Service Account, and they are provided credentials to prove this identity. Agents use the Service Account key provided to the customer during deployment, and clients use Workload Identity to prove their identity. They use these credentials to authenticate to the tunnel server, by sending signed JWT tokens and public keys. JWT tokens contain details to specify the GCP Service Account credential public key required to validate their signature to confirm the identity of the requestor. The server then signs the requestor's public key and responds with a signed certificate containing the GCP Service Account email as a Subject Alternative Name (SAN).
-Finally, if the customer NAT Gateway/Exit Gateway has stable CIDRs, we can provision firewall rules to restrict access to the tunnel server from the provided IP ranges only for an added layer of security.
+For an added layer of security, if the customer network's NAT / internet gateway uses public IPs in a stable CIDR range, Sourcegraph can provision firewall rules to restrict access to the tunnel server from the provided IP ranges.
-### How do you enforce authorization to restrict what requests can reach the private code host?
+### How do you enforce authorization to restrict which requests can reach private resources?
-The tunnel server is configured with ACLs. With mTLS every entity in the network has its own identity. The client's identity is used as a source for accessing customer private code hosts, while the agent's identity is used for destination. Tunnel server ensures that only clients with proven identity can communicate with customer tunnel agents.
+With mTLS, every entity in the network has its own identity. The tunnel server is configured with ACLs, using the client's identity as the source, and the agent's identity as the destination. This ensures only clients with a proven identity can communicate with agents.
-### Do you rotate the encryption keys?
+### How do you manage keys and certificates?
-Encryption keys are short-lived and both tunnel agents and clients have to refresh certificates every 24h. The customer may also manually rotate it by restarting the tunnel agent.
+We utilize GCP Certificate Authority Service (CAS), a managed Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) service. It is responsible for the storage of root and intermediate CA signing keys, and the signing of client certificates. Access to GCP CAS is governed by GCP IAM, and only necessary individuals and services can access CAS, with audit trails in GCP Logging.
-### How do you manage keys or certificates?
+The TLS private keys in the agents and clients only exist in memory, and are never transmitted or shared. Only the public key is sent to the tunnel server, to issue a signed certificate, to establish the mTLS connection.
-We utilize GCP Certificate Authority Service (CAS), a managed Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) service. It is responsible for the storage of all signing keys (e.g., root CAs, immediate CAs), and the signing of client certificates. Access to GCP CAS is governed by GCP IAM service and only necessary services or individuals will have access to the service with audit trails in GCP Logging.
+### How often do you rotate the encryption keys?
-The TLS private key on the tunnel agent or tunnel clients only exist in memory, and are never shared with other parties. Only the public key is sent to the tunnel server to issue a signed certificate to establish mTLS connection.
+Encryption keys are short-lived, and both tunnel agents and clients refresh their certificates every 24h. The customer may also manually rotate the agent's certificate by restarting the agent.
### How do you audit access?
-Tunnel server will log all critical operations with sufficient metadata to identify the requester to GCP Logging with a default 30-day retention policy. We will also be monitoring unauthorized access events to watch out for potential attackers.
+Tunnel server logs operations to GCP Logging, with sufficient metadata to identify the requester, and a 30-day retention policy. We also monitor unauthorized access events to watch for potential attacks.
-### Why TCP over gRPC?
+### What if an attacker gains access to the Sourcegraph Cloud instance?
-The tunnel is built using TCP over gRPC. gRPC is a high-performant and battle-tested framework, e.g., built-in support for mTLS for a trusted secure connection. We believe TCP and HTTP/2 are widely supported in majority of environments. Moreover, the simplicity of having a single endpoint for connection between customer environment and their Cloud instance greatly simplifies the work required for customer IT admin. Compared to traditional VPN solutions, such as OpenVPN, IPSec, and SSH over bastion hosts, gRPC allows us to design our own protocol, and the programmable interface allows us to implement advanced features, e.g., fine-grained access control at a per connection level, audit logging with rich metadata.
+If an attacker gains access to the Sourcegraph Cloud instance's containers, this would be a security breach, and trigger our Incident Response process. However, we have many controls in place to prevent this from happening, where Cloud infrastructure access always requires approval, and the Security team is on-call for unexpected usage patterns. Learn more in our [security portal](https://security.sourcegraph.com/).
-### How many agents can a customer start?
+Please reach out to us if you have any specific questions regarding our Cloud security posture, we are happy to provide more detail to address your concerns.
-To obtain high availability, customers can start multiple tunnel agents. Each of the agents will use the same GCP Service Account credentials, authenticate with the tunnel server and establish connection to it. Tunnel client will randomly select an available agent to forward the traffic.
+### How do I need to configure my network for the agent to work?
-### How does the customer configure the network to make the agent work?
+The tunnel agent needs to connect to the tunnel server, and your private resources. Sourcegraph provides dedicated static IPs and ports to connect to the tunnel server. The customer must configure network egress to allow TCP (HTTP/2) traffic access to these IPs and ports.
-The customer tunnel agent has to authenticate and establish connection with the tunnel server. Sourcegraph will provide a single dedicated static IP from customer dedicated GCP VPC which is used to connect with the tunnel server. Customer has to configure network egress to allow TCP (HTTP/2) traffic access to this static IP.
+### How can I restrict access to my private resources?
-### How can I restrict access to my private code host connection?
+The customer has full control of their network where they deploy the tunnel agent, and can configure, monitor, and terminate connections at will.
-The customer has full control over the tunnel agent configuration and they can terminate the connection at any time.
-What if the attacker gains access to the frontend?
+We recommend implementing an allowlist to restrict the egress traffic of the agent to the IP addresses provided by Sourcegraph and to the specific private resources your Sourcegraph Cloud instance needs to access, and configuring your firewall to alert you if this ACL is hit.
-In the event of an attacker gaining access to the Sourcegraph containers, we consider this to be a security breach and we have Incident response processes in place that we will follow. However, we have many controls in place to prevent this from happening where Cloud infrastructure access always requires approval and the Security team is on-call for unexpected usage patterns. You may learn more from our [Security Portal](https://security.sourcegraph.com/).
+If your code hosts or registries use DNS names, the agent needs access to the DNS server configured on its host.
-Please reach out to us if you have any specific questions regarding our Cloud security posture, and we are happy to provide more detail to address your concerns.
+### How can I harden the tunnel agent deployment?
-### How to harden the tunnel agent deployment?
+The tunnel agent is designed and built with a minimal footprint and attack surface, and is scanned for vulnerabilities.
-We recommend using an allowlist to limit the egress traffic of the agent to IP addresses provided by Sourcegraph and specific private resources you would like to permit access. This will prevent the agent to talk to arbitrary services, and reduce the blast radius in the event of a security event.
+You can:
-### How can I audit the data Sourcegraph has access to in my environment?
+- Deploy the agent on a hardened container platform
+- Store the agent credential and config content in a secrets management system and mount these secrets to the container
+- Forward the agent's logs to your log management system
-The tunnel is secured and authenticated by mTLS over gRPC, and everything is encrypted over transit. If a customer is looking to perform an audit, such as TLS inspection, on the connection between the private resources and Sourcegraph Cloud, we recommend only intercepting and inspecting traffic between the tunnel agent and private resources. The connection between the tunnel agent and Sourcegraph Cloud is using a custom protocol, and the decrypted payload has very little value.
+### How can I inspect the agent's traffic, and audit the data the agent is accessing in my environment?
-### Can I use self-signed TLS certificate for my private resources?
+If a customer needs to inspect and audit traffic, such as performing TLS inspection on the connection between the private resources and Sourcegraph Cloud, we recommend inspecting traffic on the connections between the tunnel agent and internal resources, as this traffic uses the protocols and encryption of the internal resources.
+
+The tunnel from the agent to the server is encrypted and authenticated by mTLS over gRPC, and uses a custom protocol, so the decrypted payload isn't usable for traffic inspection.
+
+### Can I use Internal PKI or self-signed TLS certificates for my private resources?
+
+Yes. Please work with your account team to add the public certificate chain of your internal CAs, and / or your private resources' self-signed certs, under `experimentalFeatures.tls.external.certificates` in your instance's [site configuration](/admin/config/site_config#experimentalFeatures).
+
+### Is this connection highly available?
-Yes. Please work with your account team to add the certificate chain of your internal CA to [site configuration](/admin/config/site_config#experimentalFeatures) at `experimentalFeatures.tls.external.certificates`
+To achieve high availability, customers can run multiple tunnel agents across their network. Each agent uses the same GCP Service Account credentials, authenticates with the tunnel server, and establishes their own connection to it. Tunnel clients randomly select an available agent to forward traffic through.
@@ -16571,9 +16522,10 @@ As part of this service you will receive a number of benefits from our team, inc
All of Sourcegraph's features are available on Sourcegraph Cloud instances out-of-the-box, including but not limited to:
- [Cody](/cody)
+- [Deep Search](/deep-search)
- [Server-side Batch Changes](/batch-changes/server-side)
- [Precise code navigation powered by auto-indexing](/code-search/code-navigation/auto_indexing)
-- [Code Monitoring](/code_monitoring/) (including [email delivery](#managed-smtp) of notifications)
+- [Code Monitoring](/code_monitoring/)
- [Code Insights](/code_insights/)
### Access restrictions
@@ -16778,7 +16730,7 @@ Sourcegraph Cloud instances are single-tenant, limiting exposure to outages and
### Is data safe with Sourcegraph Cloud?
-Sourcegraph Cloud utilizes a single-tenant architecture. Each customer's data is isolated and stored in a dedicated GCP project. Data is [encrypted in transit](https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/encryption-in-transit) and [at rest](https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/encryption/default-encryption) and is backed up daily. Such data includes but is not limited to, customer source code, repository metadata, code host connection configuration, and user profile. Sourcegraph Cloud also has [4 supported regions](#multiple-region-availability) on GCP to meet data sovereignty requirements.
+Sourcegraph Cloud utilizes a single-tenant architecture. Each customer's data is isolated and stored in a dedicated GCP project. Data is [encrypted in transit](https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/encryption-in-transit) and [at rest](https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/encryption/default-encryption) and is backed up daily. Such data includes but is not limited to, customer source code, repository metadata, code host connection configuration, and user profile. Sourcegraph Cloud also has [5 supported regions](#multiple-region-availability) on GCP to meet data sovereignty requirements.
Sourcegraph continuously monitors Cloud instances for security vulnerability using manual reviews and automated tools. Third-party auditors regularly perform testing to ensure maximum protection against vulnerabilities and are automatically upgraded to fix any vulnerability in third-party dependencies. In addition, GCP’s managed offering regularly patches any vulnerability in the underlying infrastructure. Any infrastructure changes must pass security checks, which are tested against industry-standard controls.
@@ -21262,6 +21214,43 @@ curl \
+
+# Viewing Batch Changes
+
+Learn how to view, search, and filter your Batch Changes.
+
+## Viewing batch changes
+
+You can view a list of Batch Changes by clicking the **Batch Changes** icon in the top navigation bar:
+
+
+
+### Title-based search
+
+You can search through your previously created batch changes by title. This search experience makes it easier to find the batch change you're looking for, especially when you have large volumes of batch changes to monitor.
+
+Start typing the keywords that match the batch change's title, and you will see a list of relevant results.
+
+
+
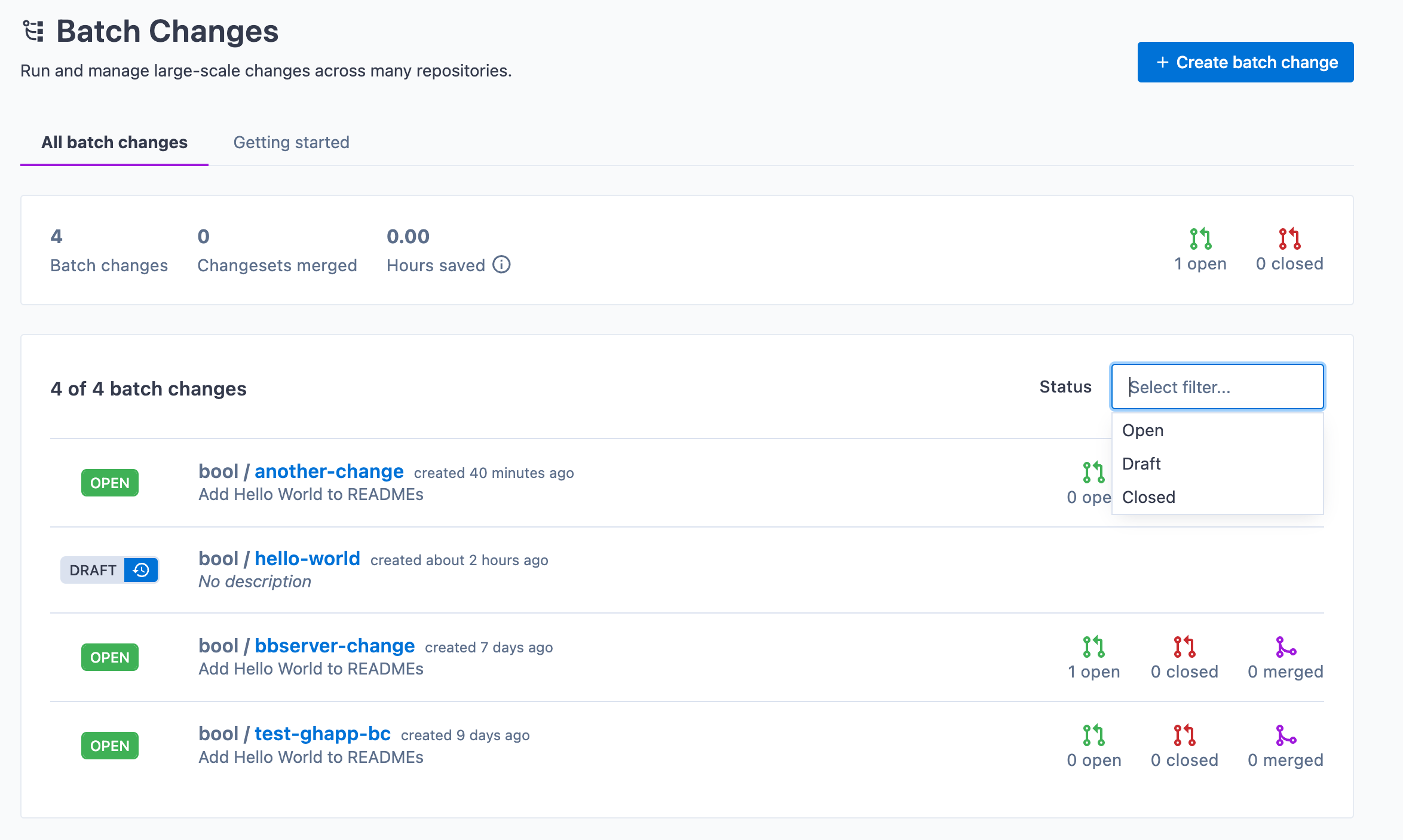
+## Filtering Batch Changes
+
+You can also use filters to switch between showing all open or closed Batch Changes.
+
+
+
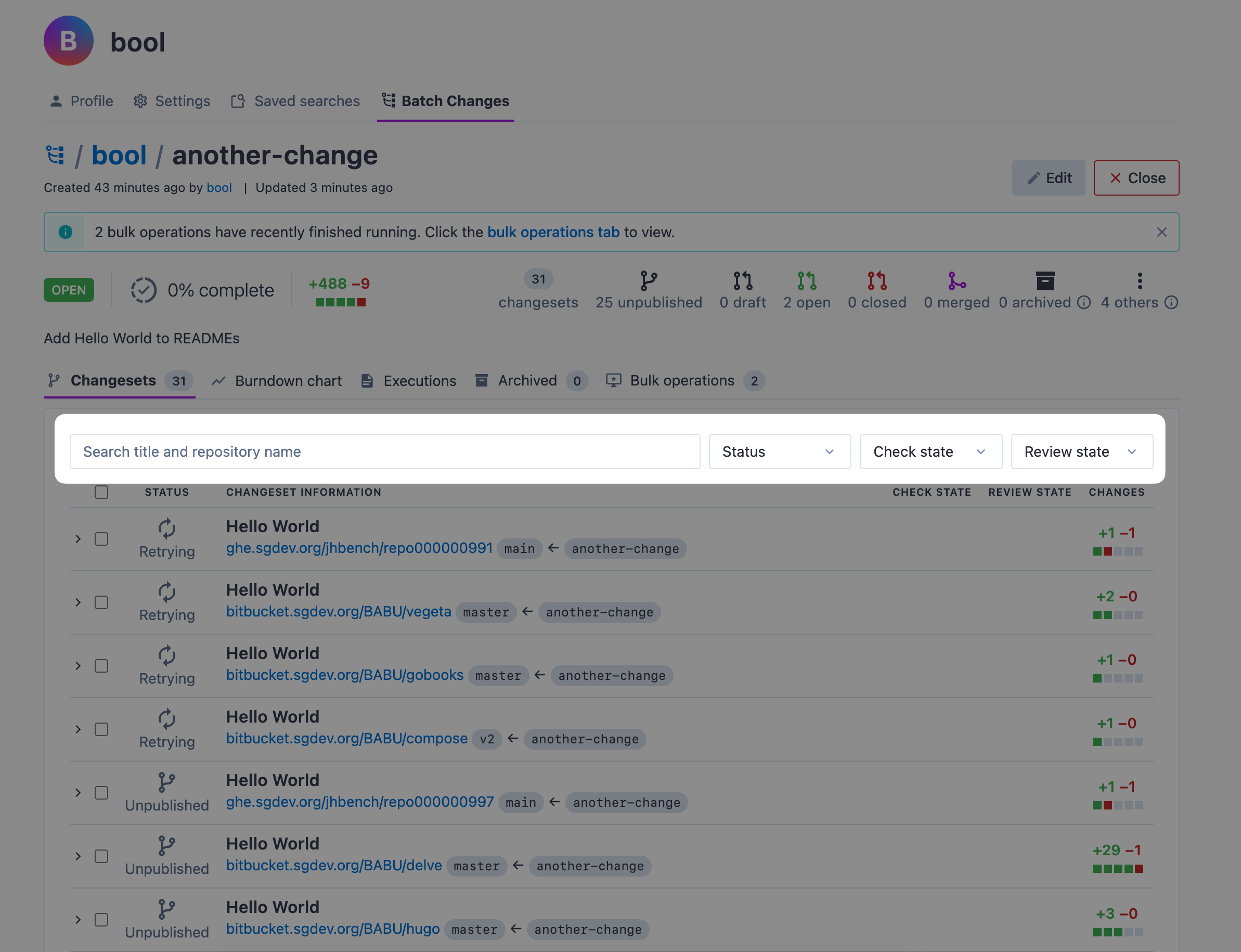
+## Filtering changesets
+
+When looking at a batch change, you can search and filter the list of changesets with the controls at the top of the list:
+
+
+
+## Administration
+
+Once a batch change is open, any Sourcegraph user can view it. However, the namespace determines who can administer it, such as editing or deleting it. When a batch change is created in a user namespace, only that user (and site admins) can administer it. When a batch change is created in an organization namespace, all members of that organization (and site admins) can administer it.
+
+
+
# Updating Go Import Statements using Comby
@@ -23817,14 +23806,91 @@ If the repository containing the workspaces is really large and it's not feasibl
Batch Changes are created by writing a [batch spec](/batch-changes/batch-spec-yaml-reference) and executing that batch spec with the [Sourcegraph CLI](https://github.com/sourcegraph/src-cli) `src`.
+There are two ways of creating a batch change:
+
+1. On your Sourcegraph instance, with [server-side execution](#on-your-sourcegraph-instance)
+2. On your local machine, with the [Sourcegraph CLI](#using-the-sourcegraph-cli)
+
+## On your Sourcegraph instance
+
+Here, you'll learn how to create and run a batch change via server-side execution.
+
+To get started, click the **Batch Changes** icon in the top navigation or navigate to `/batch-changes`.
+
+### Create a batch change
+
+Click the **Create batch change** button on the Batch Changes page, or go to `/batch-changes/create`.
+
+
+
+You will be redirected to a page showing you a list of curated templates.
+
+### Choosing a template
+
+Templates is a feature available in Sourcegraph 6.6 and later.
+
+From the template selection page, you can either:
+
+- **Pick a template** from the list of curated templates that best matches your use case
+- **Click "Start from Scratch"** if you prefer to continue without a template
+
+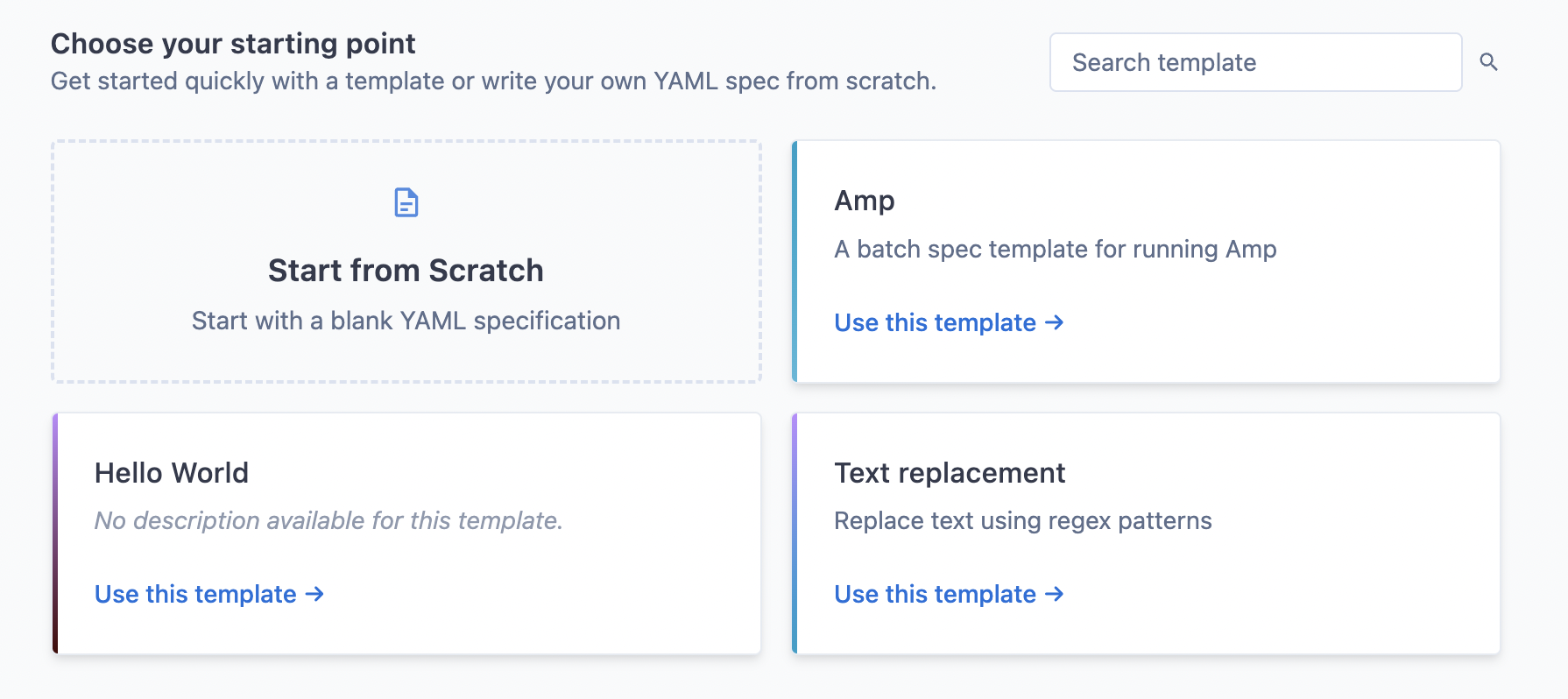
+
+Your site admin can curate the list of available templates to match your organization's specific needs and use cases.
+
+### Filling out template fields
+
+If you selected a template, you will need to fill out the form fields specific to that template. These fields will customize the batch spec to your specific requirements.
+
+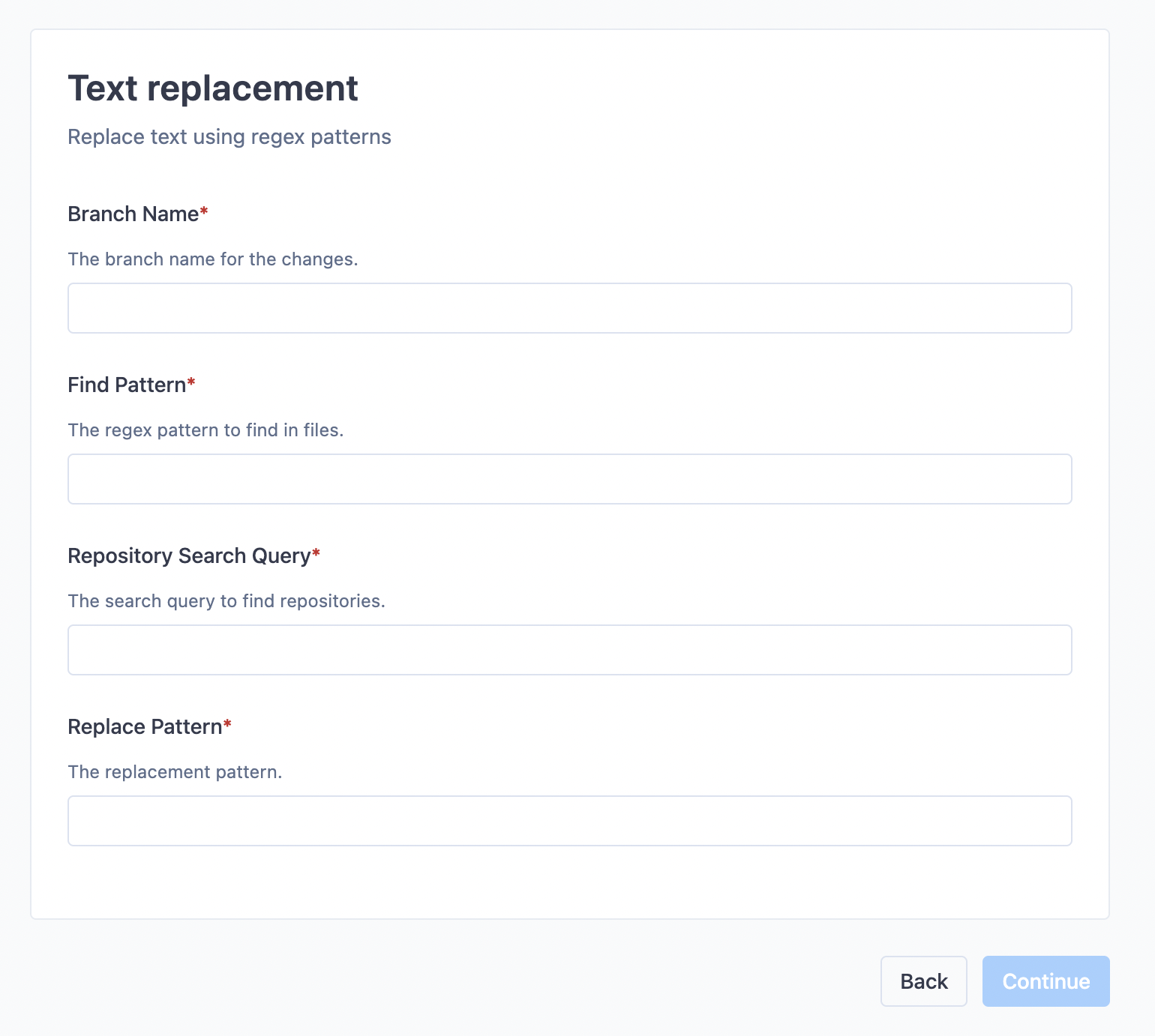
+
+The form fields are validated by regular expressions. If the validation fails, look at the description of that field to see what kind of value is required.
+
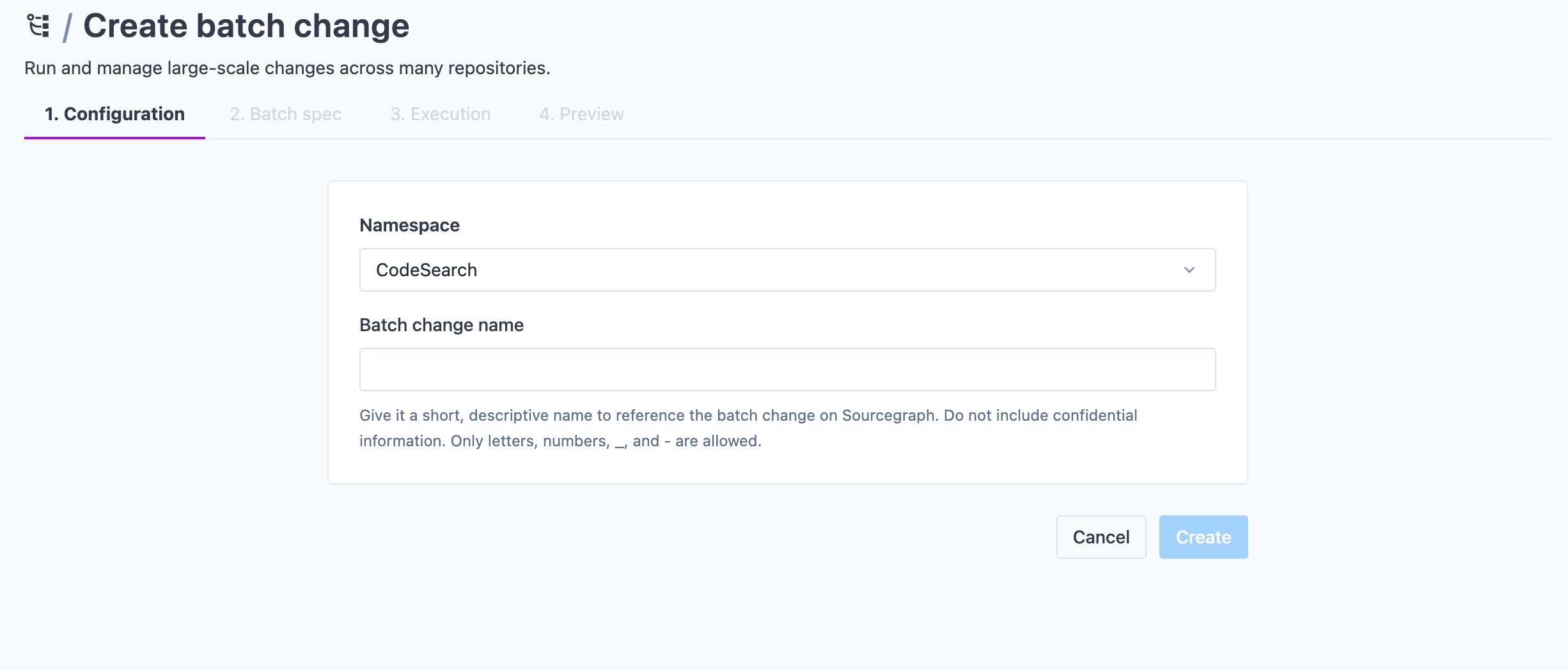
+### Choose a name for your batch change
+
+After you've filled out the template form fields, or after you've clicked "Start from Scratch", you will be prompted to choose a name for your namespace and optionally define a custom namespace to put your batch change in.
+
+
+
+Once done, click **Create**.
+
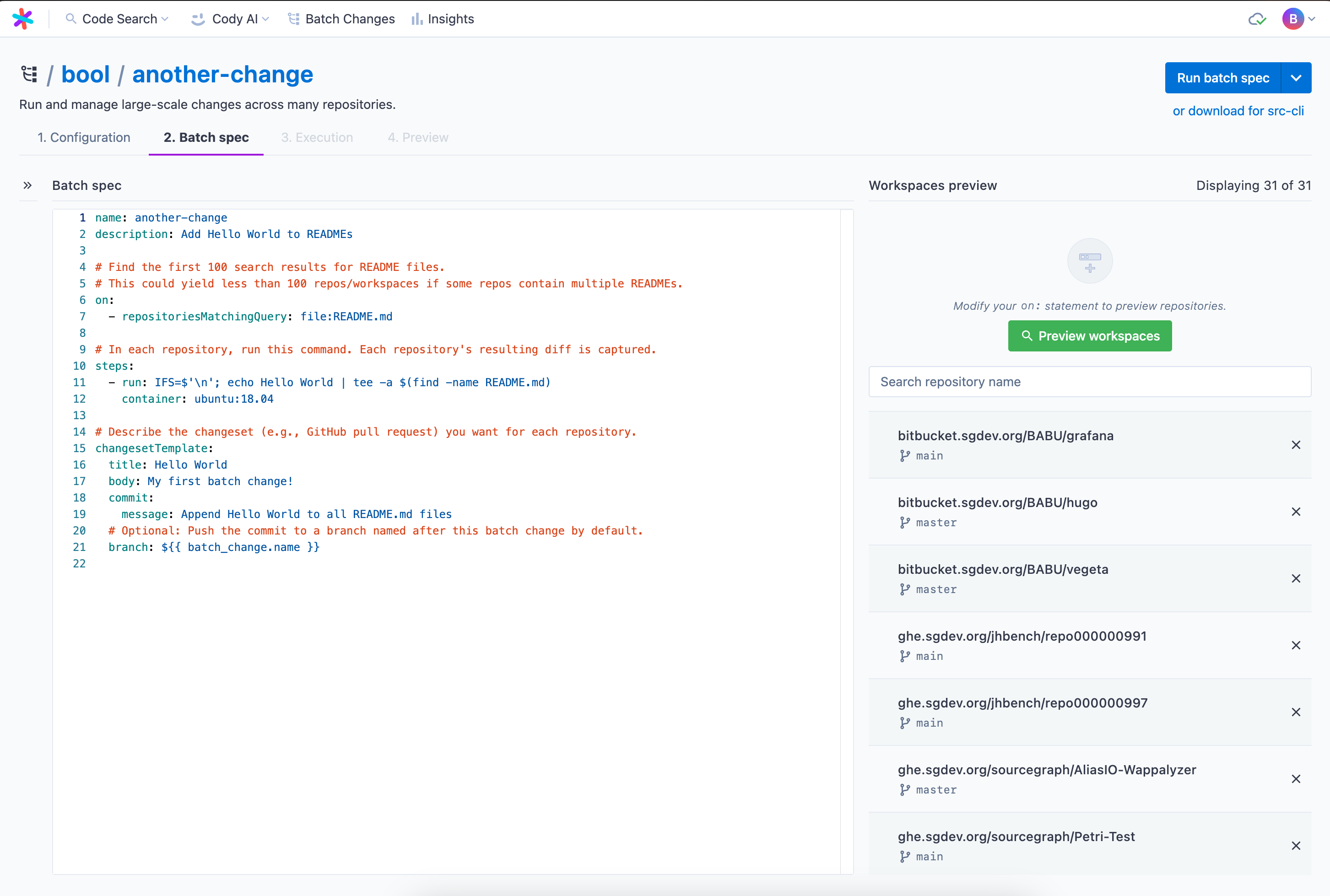
+### Previewing batch spec and workspaces
+
+You can now see the batch spec and run a preview of the affected repositories and workspaces from the right-hand side panel. After resolution, it will show all the workspaces in repositories that match the given `on` statements. You can search through them and determine if your query is satisfying before starting execution. You can also exclude single workspaces from this list.
+
Batch Changes can also be used on [multiple projects within a monorepo](/batch-changes/creating-changesets-per-project-in-monorepos) by using the `workspaces` key in your batch spec.
-There are two ways of creating a batch change:
+The library contains examples that you can apply right into your batch spec if you need inspiration. Your site admin can manage the library of examples.
+
+
+
+### Executing your batch spec
+
+When the spec is ready to run, ensure the [preview](/batch-changes/create-a-batch-change#previewing-workspaces) is up to date and then click **Run batch spec**. This takes you to the execution screen. On this page, you see:
+
+- Run statistics at the top
+- All the workspaces, including status and diff stat, in the left panel
+- Details on a particular workspace on the right-hand side panel where you can see steps with:
+ - Logs
+ - Results
+ - Command
+ - Per-step diffs
+ - Output variables
+ - Execution timelines for debugging
+
+Once finished, you can proceed to the batch spec preview, as you know it from before.
-1. On your local machine, with the [Sourcegraph CLI](#create-a-batch-change-with-the-sourcegraph-cli)
-2. Remotely, with [server-side execution](/batch-changes/server-side)
+
+
+### Previewing and applying the batch spec
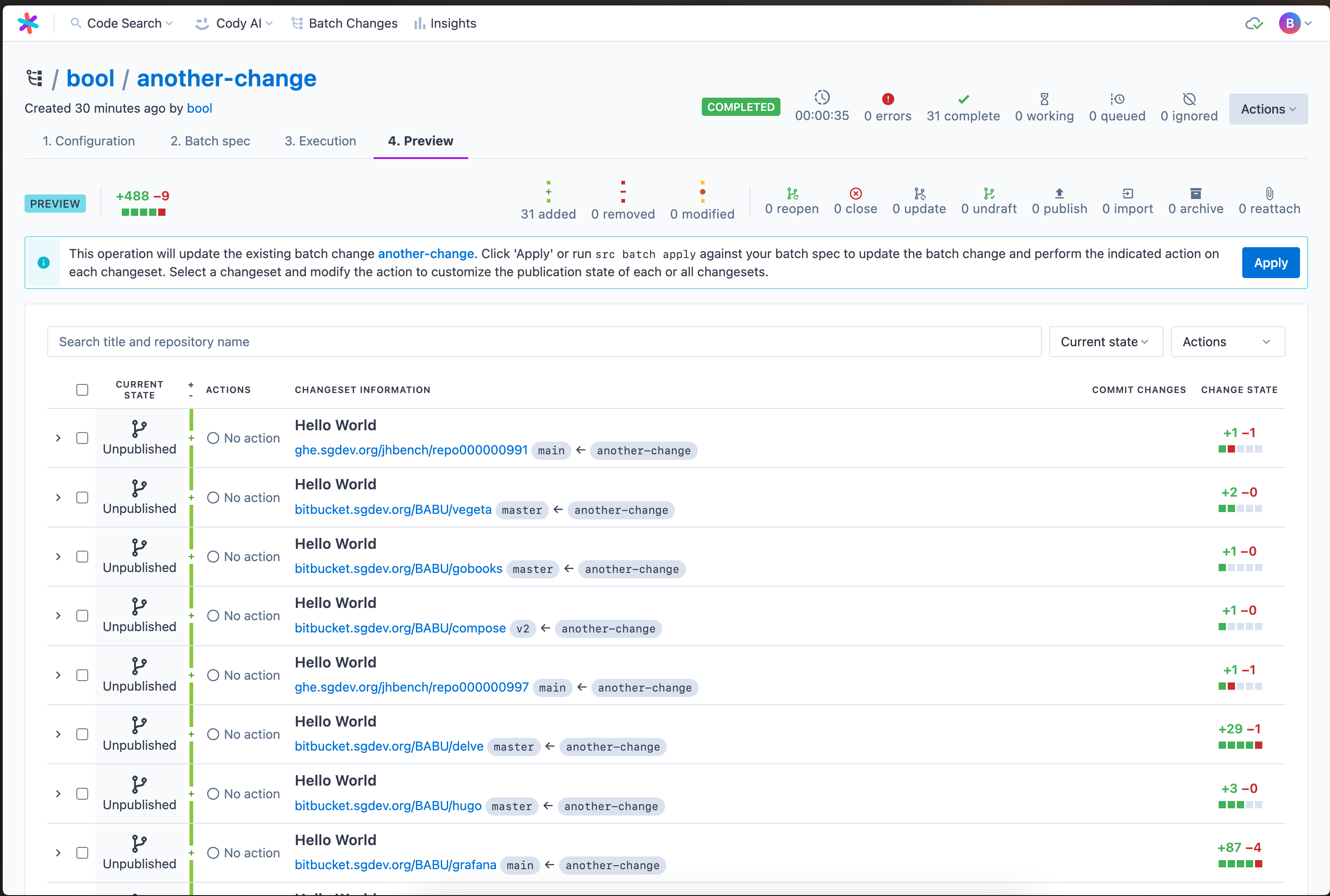
+
+On this page, you can review the proposed changes. Once satisfied, click **Apply**.
+
+Congratulations, you ran your first batch change server-side 🎊
+
+
-## Create a batch change with the Sourcegraph CLI
+## Using the Sourcegraph CLI
This part of the guide will walk you through creating a batch change on your local machine with the Sourcegraph CLI.
@@ -23896,7 +23962,7 @@ src batch preview -f YOUR_BATCH_SPEC.yaml
After you've applied a batch spec, you can [publish changesets](/batch-changes/publishing-changesets) to the code host when you're ready. This will turn the patches into commits, branches, and changesets (such as GitHub pull requests) for others to review and merge.
-You can share the link to your batch change with other users if you want their help. Any user on your Sourcegraph instance can [view it in the batch changes list](/batch-changes/create-a-batch-change#viewing-batch-changes).
+You can share the link to your batch change with other users if you want their help. Any user on your Sourcegraph instance can [view it in the batch changes list](/batch-changes/view-batch-changes).
If a user viewing the batch change lacks read access to a repository in the batch change, they can only see [limited information about the changes to that repository](/batch-changes/permissions-in-batch-changes#repository-permissions-for-batch-changes) (and not the repository name, file paths, or diff).
@@ -23928,91 +23994,6 @@ src batch preview -f your_batch_spec.yaml -namespace
@@ -26900,10 +26881,10 @@ Learn more about how we think about [the ROI of Sourcegraph in our blog](https:/
### Overview metrics
-| **Metric** | **Description** |
-| ------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
-| Percent of code written by Cody | Percentage of code written by Cody out of all code written during the selected time. [Learn more about this metric.](/analytics/pcw) |
-| Lines of code written by Cody | Total lines of code written by Cody during the selected time |
+| **Metric** | **Description** |
+| ---------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| Percent of code written by Cody | Percentage of code written by Cody out of all code written during the selected time. [Learn more about this metric.](/analytics/pcw) |
+| Characters of code written by Cody | Total characters of code written by Cody during the selected time |
### User metrics
@@ -27044,9 +27025,9 @@ The Sourcegraph Analytics API is an API that provides programmatic access to you
For Sourcegraph Analytics, you can generate an access token for programmatic access. Tokens are long-lived with an optional expiry and have the same permissions to access instance data as the user who created them.
-### Token management APIs
+### Getting Started
-Token management is currently only available via the Sourcegraph Analytics API. Token management APIs are authenticated via the `cas` session cookie.
+Access tokens are created using the `cas` cookie for authentication to the token creation endpoint. Access tokens are longer lived than the `cas` cookie making them more suitable for programmatic access to the Sourcegraph Analytics API.
- Sign in to [Sourcegraph Analytics](https://analytics.sourcegraph.com).
- Retrieve your session cookie, `cas`, from your browser's developer tools.
@@ -27433,7 +27414,6 @@ Here is a snapshot of an unhealthy dashboard, where no active instance is runnin
Sourcegraph Validation is currently experimental.
-
## Validate Sourcegraph Installation
Installation validation provides a quick way to check that a Sourcegraph installation functions properly after a fresh install
@@ -27782,126 +27762,6 @@ When that is done, update your DNS records to point to your gateway's external I
-
-# Administration troubleshooting
-
-### Docker Toolbox on Windows: `New state of 'nil' is invalid`
-
-If you are using Docker Toolbox on Windows to run Sourcegraph, you may see an error in the `frontend` log output:
-
-```bash
-frontend |
-frontend |
-frontend |
-frontend | New state of 'nil' is invalid.
-```
-
-After this error, no more `frontend` log output is printed.
-
-This problem is caused by [docker/toolbox#695](https://github.com/docker/toolbox/issues/695#issuecomment-356218801) in Docker Toolbox on Windows. To work around it, set the environment variable `LOGO=false`, as in:
-
-```bash
-docker container run -e LOGO=false ... sourcegraph/server
-```
-
-> WARNING: Running Sourcegraph on Docker Toolbox for Windows is not supported for production deployments.
-
-### Submitting a metrics dump
-
-If you encounter performance or instability issues with Sourcegraph, we may ask you to submit a metrics dump to us. This allows us to inspect the performance and health of various parts of your Sourcegraph instance in the past and can often be the most effective way for us to identify the cause of your issue.
-
-The metrics dump includes non-sensitive aggregate statistics of Sourcegraph like CPU & memory usage, number of successful and error requests between Sourcegraph services, and more. It does NOT contain sensitive information like code, repository names, user names, etc.
-
-In the process of troubleshooting, we may also ask that you perform other tasks from the command line to help us assist you. Our [command line generator](https://sourcegraph.github.io/support-generator/) is a tool we've created to help users generate commands for various functions (i.e. retrieving logs from specific containers, port forwarding, checking dirty databases, etc.).
-
-#### Docker Compose deployments
-
-To create a metrics dump from a docker-compose deployment, follow these steps:
-
-* Open a shell to the running `prometheus` container:
-
-```sh
-docker exec -it prometheus /bin/sh
-```
-
-* Inside the container bash shell trigger the creation of a Prometheus snapshot:
-
-```sh
-wget --post-data "" http://localhost:9090/api/v1/admin/tsdb/snapshot
-```
-
-* Find the created snapshot's name:
-
-```sh
-ls /prometheus/snapshots/
-```
-
-* Tar up the created snapshot
-
-```sh
-cd /prometheus/snapshots && tar -czvf /tmp/sourcegraph-metrics-dump.tgz
-```
-
-* Switch back to local shell (`exit`) and copy the metrics dump file to the host machine:
-
-```sh
-docker cp prometheus:/tmp/sourcegraph-metrics-dump.tgz sourcegraph-metrics-dump.tgz
-```
-
-Please then upload the `sourcegraph-metrics-dump.tgz` file to Sourcegraph support so we can inspect it.
-
-#### Single-container Sourcegraph deployments
-
-To create a metrics dump from a [single-container `sourcegraph/server` deployment](/admin/deploy/docker-single-container/), follow these steps:
-
-* Open a shell to the running container:
- 1. Run `docker ps` to get the name of the Sourcegraph server container.
- 1. Run `docker exec -it /bin/bash` to open a bash shell.
-* Inside the container bash shell trigger the creation of a Prometheus snapshot:
-
-```sh
-wget --post-data "" http://localhost:9090/api/v1/admin/tsdb/snapshot
-```
-
-* Tar up the created snapshot
-
-```sh
-cd ~/.sourcegraph/data/prometheus/snapshots && tar -czvf /tmp/sourcegraph-metrics-dump.tgz
-```
-
-* If needed, you can download the metrics dump to your local machine (current directory) using `scp`:
-
-```sh
-scp -r username@hostname:/tmp/sourcegraph-metrics-dump.tgz .
-```
-
-Please then upload the `sourcegraph-metrics-dump.tgz` for Sourcegraph support to access it. If desired, we can send you a shared private Google Drive folder for the upload as it can sometimes be a few gigabytes.
-
-### Generating pprof profiles
-
-Please follow [these instructions](/admin/pprof) to generate pprof profiles.
-
-### Sourcegraph is not returning results from a repository unless "repo:" is included
-
-If you can get repository results when you explicitly include `repo:{your repository}` in your search, but don't see any results from that repository when you don't, there are a few possible causes:
-
-- The repository is a fork repository (excluded from search results by default) and `fork:yes` is not specified in the search query.
-- The repository is an archived repository (excluded from search results by default) and `archived:yes` is not specified in the search query.
-- There is an issue indexing the repository: check the logs of worker and/or search-indexer.
-- The search index is unavailable for some reason: try the search query `repo: index:only`. If it returns no results, the repository has not been indexed.
-
-### Sourcegraph is making unauthorized requests to the git server
-
-This is normal and happens whenever git is used over HTTP. To avoid unnecessarily sending a password over HTTP, git first
-makes a request without the password included. If a 401 Unauthorized is returned, git sends the request with the password.
-
-More information can be found [here](https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucketserverkb/two-401-responses-for-every-git-opperation-938854756.html).
-
-If this behaviour is undesired, the `gitURLType` in the [external service configuration](/admin/code_hosts/github#configuration)
-should be set to `ssh` instead of `http`. This will also require [ssh keys to be set up](/admin/repo/auth#repositories-that-need-http-s-or-ssh-authentication).
-
-
-
# Securing a Sourcegraph instance with TLS/SSL
@@ -29344,13 +29204,6 @@ To automatically join all users on your instance to a specific organization, cre
-
-# Sourcegraph Nginx HTTP and HTTPS/SSL configuration
-
-This documentation page has been moved to "[Sourcegraph HTTP and HTTPS/SSL configuration](/admin/http_https_configuration)".
-
-
-
# Using Sourcegraph with a monorepo
@@ -29369,16 +29222,6 @@ Sourcegraph uses the standard `git` binary to interact with repositories, but st
Sourcegraph's code search index scales horizontally with the number of files being indexed for search. Multiple shards may be allocated for one repository, and the index is agnostic to whether the code exists in one massive repository or many smaller ones. Sourcegraph has been used to index both large monorepos and tens of thousands of smaller repositories.
-### Known Limitations
-
-- Sourcegraph will inspect the full tree for language detection. It incrementally caches and builds the language statistics to reuse information across commits. However, this has been shown to create too much load in monorepos. You can disable this feature by setting the environment variable `USE_ENHANCED_LANGUAGE_DETECTION=false` on `sourcegraph-frontend`.
-
-## Custom git binaries
-
-Sourcegraph clones code from your code host via the usual `git clone` or `git fetch` commands. Some organisations use custom `git` binaries or commands to speed up these operations. Sourcegraph supports using alternative git binaries to allow cloning. This can be done by inheriting from the `gitserver` docker image and installing the custom `git` onto the `$PATH`.
-
-Some monorepos use a custom command for `git fetch` to speed up fetch. Sourcegraph provides the `experimentalFeatures.customGitFetch` site setting to specify the custom command.
-
## Statistics
You can help the Sourcegraph developers understand the scale of your monorepo by sharing some statistics with the team. The bash script [`git-stats`](https://github.com/sourcegraph/sourcegraph-public-snapshot/blob/main/dev/git-stats) when run in your git repository will calculate these statistics.
@@ -29831,9 +29674,24 @@ You can then access your dashboards directly through your Grafana instance URL.
This error is expected if your instance was not [deployed with Kubernetes](/admin/deploy/kubernetes/). The Instrumentation page is currently only available for Kubernetes instances.
-## Troubleshooting
+## Sourcegraph is making unauthorized requests to the git server
+
+This is normal and happens whenever git is used over HTTP. To avoid unnecessarily sending a password over HTTP, git first
+makes a request without the password included. If a 401 Unauthorized is returned, git sends the request with the password.
+
+More information can be found [here](https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucketserverkb/two-401-responses-for-every-git-opperation-938854756.html).
+
+If this behaviour is undesired, the `gitURLType` in the [external service configuration](/admin/code_hosts/github#configuration)
+should be set to `ssh` instead of `http`. This will also require [ssh keys to be set up](/admin/repo/auth#repositories-that-need-http-s-or-ssh-authentication).
+
+## Sourcegraph is not returning results from a repository unless "repo:" is included
-Please refer to our [dedicated troubleshooting page](/admin/troubleshooting).
+If you can get repository results when you explicitly include `repo:{your repository}` in your search, but don't see any results from that repository when you don't, there are a few possible causes:
+
+- The repository is a fork repository (excluded from search results by default) and `fork:yes` is not specified in the search query.
+- The repository is an archived repository (excluded from search results by default) and `archived:yes` is not specified in the search query.
+- There is an issue indexing the repository: check the logs of worker and/or search-indexer.
+- The search index is unavailable for some reason: try the search query `repo: index:only`. If it returns no results, the repository has not been indexed.
@@ -31672,7 +31530,6 @@ If your instance has schema drift or unfinished oob migrations you may need to a
- [Upgrading Early Versions](/admin/updates/migrator/upgrading-early-versions)
- [Troubleshooting upgrades](/admin/updates/migrator/troubleshooting-upgrades)
- [Downgrading](/admin/updates/migrator/downgrading)
-- [Sourcegraph 5.2 gRPC Configuration Guide](/admin/updates/grpc/)
@@ -32730,125 +32587,6 @@ You can rollback by resetting your `release` branch to the old state before rede
-
-import { CURRENT_VERSION_STRING_NO_V, CURRENT_VERSION_STRING } from 'src/components/PreCodeBlock'
-
-# Sourcegraph 5.3 gRPC Configuration Guide
-
-## Overview
-
-As part of our continuous effort to enhance performance and reliability, in Sourcegraph 5.3 we’ve fully transitioned to using [gRPC](https://grpc.io/) as the primary communication method for our internal services.
-
-This guide will help you understand this change and its implications for your setup.
-
-## Quick Overview
-
-- **What’s changing?** In Sourcegraph `5.3`, we've transitioned to [gRPC](https://grpc.io/) for internal communication between Sourcegraph services.
-- **Why?** gRPC, a high-performance Remote Procedure Call (RPC) framework by Google, brings about several benefits like a more efficient serialization format, faster speeds, and a better development experience.
-- **Is any action needed?** If you don’t have restrictions on Sourcegraph’s **internal** (service to service) traffic, you shouldn't need to take any action—the change should be invisible. If you do have restrictions, some firewall or security configurations may be necessary. See the ["Who needs to Act"](#who-needs-to-act) section for more details.
-- **Can I disable gRPC if something goes wrong?** In Sourcegraph `5.3.X`, gRPC can no longer be disabled. However, if you run into an issue it is possible to downgrade to Sourcegraph `5.2.X`, which includes a [toggle to enable/disable gRPC](#sourcegraph-52x-only-enabling--disabling-grpc) while you troubleshoot the issue. Contact our customer support team for more information.
-
-## gRPC: A Brief Intro
-
-[gRPC](https://grpc.io/) is an open-source [RPC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Remote_procedure_call) framework developed by Google. Compared to [REST](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/REST), gRPC is faster, more efficient, has built-in backwards compatibility support, and offers a superior development experience.
-
-## Key Changes
-
-### 1. Internal Service Communication
-
-For Sourcegraph version `5.3.X` onwards, our microservices like `repo-updater` and `gitserver` will use mainly gRPC instead of REST for their internal traffic. This affects only communication *between* our services. Interactions you have with Sourcegraph's UI and external APIs remain unchanged.
-
-### 2. Rollout Plan
-
-| Version | gRPC Status |
-|---------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| `5.2.X` (Released on October 4th, 2023) | On by default but can be disabled via a feature flag. |
-| `5.3.X` (Releasing Feburary 15th, 2024)| Fully integrated and can't be turned off. Able to temporarily downgrade to `5.2.X` if there are any issues. |
-
-## Preparing for the Change
-
-### Who Needs to Act?
-
-Our use of gRPC only affects traffic **_between_** our microservices (e.x. `searcher` ↔ `gitserver`). Traffic between the Sourcegraph Web UI and the rest of the application is unaffected (e.x. `sourcegraph.example.com` ↔ `frontend`’s GraphQL API).
-
-**If Sourcegraph's internal traffic faces no security restrictions in your environment, no action is required.**
-
-However, if you’ve applied security measures or have firewall restrictions on this traffic, adjustments might be needed to accommodate gRPC communication. The following is a more technical description of the protocol that can help you configure your security settings:
-
-### gRPC Technical Details
-
-- **Protocol Description**: gRPC runs on-top of [HTTP/2](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP/2) (which, in turn, runs on top of [TCP](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_Control_Protocol). It transfers (binary-encoded, not human-readable plain-text) [Protocol Buffer](https://protobuf.dev/) payloads. Our current gRPC implementation does not use any encryption.
-
-- **List of services**: The following services will now _speak mainly gRPC in addition_ to their previous traffic:
- - [frontend](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/frontend/sourcegraph-frontend.Service.yaml)
- - [gitserver](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/gitserver/gitserver.Service.yaml)
- - [searcher](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/searcher/searcher.StatefulSet.yaml)
- - [zoekt-webserver](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/indexed-search/indexed-search.StatefulSet.yaml)
- - [zoekt-indexserver](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/indexed-search/indexed-search.StatefulSet.yaml)
-
-- The following aspects about Sourcegraph’s networking configuration **aren’t changing**:
- - **Ports**: all Sourcegraph services will use the same ports as they were in the **5.1.X** release.
- - **External traffic**: gRPC only affects how Sourcegraph’s microservices communicate amongst themselves - **no new external traffic is sent via gRPC**.
- - **Service dependencies:** each Sourcegraph service will communicate with the same set of services regardless of whether gRPC is enabled.
- - Example: `searcher` will still need to communicate with `gitserver` to fetch repository data. Whether gRPC is enabled doesn’t matter.
-
-### Sourcegraph `5.2.X` only: enabling / disabling GRPC
-
-In the `5.2.x` release, you are able to use the following methods to enable / disable gRPC if a problem occurs.
-
- In the `5.3.X` release, these options are removed and gRPC is always enabled. However, if you run into an issue it is possible to downgrade to Sourcegraph `5.2.X` and use the configuration below to temporarily disable gRPC while you troubleshoot the issue. Contact our customer support team for more assistance with downgrading.
-
-#### All services besides `zoekt-indexserver`
-
-Disabling gRPC on any service that is not `zoekt-indexserver` can be done by one of these options:
-
-##### Option 1: disable via site-configuration
-
-Set the `enableGRPC` experimental feature to `false` in the site configuration file:
-
-```json
-{
- "experimentalFeatures": {
- "enableGRPC": false // disabled
- }
-}
-```
-
-##### Option 2: disable via environment variables
-
-Set the environment variable `SG_FEATURE_FLAG_GRPC="false"` for every service.
-
-#### `zoekt-indexserver` service: disable via environment variable
-
-Set the environment variable `GRPC_ENABLED="false"` on the `zoekt-indexserver` container. (See [indexed-search.StatefulSet.yaml](https://github.com/sourcegraph/deploy-sourcegraph-k8s/blob/main/base/sourcegraph/indexed-search/indexed-search.StatefulSet.yaml) for the configuration):
-
-```yaml
-- name: zoekt-indexserver
- env:
- - name: GRPC_ENABLED
- value: 'false'
- image: docker.io/sourcegraph/search-indexer:{CURRENT_VERSION_NO_V}
-```
-
-_zoekt-indexserver can’t read from Sourcegraph’s site configuration, so we can only use environment variables to communicate this setting._
-
-If any issues arise with gRPC, admins have the option to disable it in version `5.2.X`. This will be phased out in `5.3.X`.
-
-## Monitoring gRPC
-
-To ensure the smooth operation of gRPC, we offer:
-
-- **gRPC Grafana Dashboards**: For every gRPC service, we provide dedicated dashboards. These boards present request and error rates for every method, aiding in performance tracking. See our [dashboard documentation](/admin/observability/dashboards).
-
-
-- **Internal Error Reporter**: For certain errors specifically from gRPC libraries or configurations, we've integrated an "internal error" reporter. Logs prefixed with `grpc.internal.error.reporter` signal issues with our gRPC execution and should be reported to customer support for more assistance.
-
-## Need Help?
-
-For any queries or concerns, reach out to our customer support team. We’re here to assist!
-
-
-
# Telemetry
@@ -32914,7 +32652,7 @@ After hitting create, you will be redirected to the team page where you can add
### From the CLI
-If you prefer a command line based approach, or would like to integrate an external system of record for teams into Sourcegraph, [src-cli](https://github.com/sourcegraph/src-cli) (v5.0+) provides commands to manage teams:
+If you prefer a command line based approach, or would like to integrate an external system of record for teams into Sourcegraph, [src-cli](https://github.com/sourcegraph/src-cli) provides commands to manage teams:
```bash
# List configured teams. Lists root teams, using -parent-team can read child teams.
@@ -32944,6 +32682,7 @@ src teams members remove -team-name= [-email=] [-username=
-export ORG
-
-if [[ -z "${ORG}" ]]; then
- echo "ORG environment variable is required."
- exit 1
-fi
-
-SRC_ENDPOINT=
-export SRC_ENDPOINT
-
-if [[ -z "${GITHUB_TOKEN}" ]]; then
- echo "GITHUB_TOKEN environment variable is required."
- exit 1
-fi
-
-if [[ -z "${SRC_ACCESS_TOKEN}" ]]; then
- echo "SRC_ACCESS_TOKEN environment variable is required."
- exit 1
-fi
-
-# get_json_property parses the first argument string as JSON and returns the
-# path passed as the second argument. Empty strings and null are truncated.
-function get_json_property() {
- val="$(jq -r ".${2} | select (.!=null)" <<<"${1}")"
- if [[ -z "$val" || "$val" == "null" ]]; then
- echo -n
- return
- fi
- echo -n "$val"
-}
-
-# fetch_teams_paginated reads teams from the GitHub API in the configured organization.
-# It reads all teams until pagination indicates all results have been fetched.
-function fetch_teams_paginated() {
- query=$(cat < NOTE: GitLab teams are not globally unique in name, only within their parent team. This is different to how teams work in Sourcegraph, where names are globally unique. You have to choose globally unique names when ingesting GitLab teams. This can affect name matching in code ownership.
-
-```
-TODO: Script here that scrapes the GitLab API for teams and converts them into Sourcegraph teams.
-```
-
@@ -33650,7 +33184,7 @@ With this setting, Sourcegraph will ignore any rules with a host other than `*`,
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/perforce.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:36Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:40Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
// If non-null, enforces Perforce depot permissions.
@@ -81797,420 +81331,6 @@ Let us know how we can help! [Contact us directly](https://sourcegraph.com/conta
- [Migrating from Oracle OpenGrok to Sourcegraph for code search](/admin/migration/opengrok)
- [Back up or migrate to a new Sourcegraph instance](/admin/deploy/migrate-backup)
- [Update notes](/admin/updates/)
-- [Migrating from Sourcegraph 3.30.0, 3.30.1, and 3.30.2](/admin/migration/3_30)
-- [Migrating to Sourcegraph 3.31.x](/admin/migration/3_31)
-- [Migrating to Sourcegraph 5.1.x](/admin/migration/5_1)
-
-## Legacy guides
-
-- [Migrating from Sourcegraph 2.13 to 3.0.0](/admin/migration/3_0)
-- [Migrating from Sourcegraph 3.x to 3.7.2+](/admin/migration/3_7)
-- [Migrating from Sourcegraph 3.x to 3.11](/admin/migration/3_11)
-
-
-
-
-# Migrating to Sourcegraph 5.1.x
-
-> NOTE: The following applies only deployments that use our [Docker Single Container Deployment](/admin/deploy/docker-single-container) with the default built-in database. Deployments that use the Single Container Deployment with external databases (e.g. Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, etc.), and users of other deployment methods (Docker Compose, Kubernetes, Machine Images, Sourcegraph Cloud) are **not affected**, and can ignore this page.
-
-In Sourcegraph 5.1.x, the container image used for Docker Single Container Deployments has switched from an Alpine-based image to a Wolfi-base image in order to provide a more secure container. Upon upgrading, Sourcegraph will need to re-index the entire database. This process is automatic but requires user interation to start as it can take up to several hours to complete. It is strongly recommended to review and follow the instructions on this page prior to upgrading.
-
-## Determine whether you are affected
-
-Only instances which fit the following criteria are affected:
-
-* Using the [Docker Single Container Deployment](/admin/deploy/docker-single-container)
-* Using the default built-in database (i.e. not
-connecting to an external database like Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, etc.)
-* Upgrading from any release prior to Sourcegraph 5.1
-
-If you are unsure whether you are affected by this migration, please contact either customer support or your Customer Engineer for further advice.
-
-## Preparations
-
-### Determine how long the migration will take
-
-You can estimate the duration of the migration by looking at the size of the instance's Postgres directory, which can be found under `data/postgresql` on the host, or mounted as `/var/opt/sourcegraph/postgresql` on the instance.
-
-Based on Sourcegraph's testing, you should allow 15-20 minutes per 100GB of data in this directory.
-
-### Provision additional resources for the server instance
-
-Ensure that the instance has sufficient free disk space, as reindexing can temporarily require up to 25% additional disk space beyond the size of the existing Postgres data directory.
-
-> The following is an optional step, but can help reduce the downtime needed during the migration.
-
-Postgres reindexing speed is primarily affected by:
-
-* The amount of RAM available
-* The speed of the underlying storage (SSD recommended)
-
-Temporarily provisioning additional RAM and faster storage can help reduce the time needed for reindexing.
-
-As the Postgres reindexing process is single-threaded, provisioning more CPU cores beyond 2 will not significantly help speed up reindexing.
-
-### Back up data volumes
-
-As with all migrations, you should take the precaution of backing up both the `data` and `config` volumes from the existing instance prior to upgrading.
-
-### Ensure that the instance will not be terminated during the migration
-
-As the migration process can take up to several hours, ensure that any health check systems which may terminate unavailable instances are disabled for the duration of the migration.
-
-## Migrating
-
-Once the preceded preparation steps have been followed, start up the instance using a 5.1 or later container image, with the following environment variable set:
-
-`SOURCEGRAPH_5_1_DB_MIGRATION=true`
-
-> If you start up the instance without this variable set, the instance will not start and instead display a message referring to this migration guide.
-
-The migration will then run automatically. During this time, information about the reindexing process will be written to the container's log.
-
-Once the migration has completed, you can start up the instance as usual without this environment variable set.
-
-If the migration fails to complete due to an error or takes significantly longer than estimated, please contact either customer support or your Customer Engineer with this information and we'll advise further.
-
-## Rolling back to Sourcegraph 5.0 (or earlier) prior to running the migration
-
-If you have not performed the "Migrating" step above, you can roll back to Sourcegraph 5.0 (or earlier) by switching back to the previously-used image.
-
-## Rolling back to Sourcegraph 5.0 (or earlier) after running the migration
-
-If you have performed the "Migrating" step above but need to roll back to Sourcegraph 5.0 (or earlier), you should restore a backup of the `data` volume taken prior to the migration step.
-
-If you did not take a backup of this volume prior to migrating, please contact either customer support or your Customer Engineer and we'll advise further.
-
-
-
-
-# Migrating to Sourcegraph 3.7.2+
-
-Sourcegraph 3.7.2+ includes much faster indexed symbol search ([on large searches, up to 20x faster](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1oPzePjD8YLrnppLm3nk46h48_Cxipz4_QqRMBYaIOYQ/edit?usp=sharing)). However, there are some aspects you should be aware of when upgrading an existing Sourcegraph instance:
-
-Upgrading and downgrading is safe, reindexing will occur in the background seamlessly with no downtime or harm to search performance.
-
-**Please read this document in full before upgrading to 3.7.**
-
-## Increased disk space requirements
-
-With indexed symbol search comes an **increase in the required disk space. Please ensure you have enough free space before upgrading.**
-
-Run the command below for your deployment to determine how much disk space the indexed search indexes are taking currently. Then, multiply the number you get times 1.3 to determine how much free space you need before upgrading.
-
-For example, in the below examples we see 126 GiB is currently in use. Multiplying 126 GiB * 1.3 gives us 163.8 GiB (the amount we should ensure is free before upgrading).
-
-### Single-container Docker deployment
-
-Run the following on the host machine:
-
-```bash
-$ du -sh ~/.sourcegraph/data/zoekt/index/
-126G /Users/jane/.sourcegraph/data
-```
-
-
-### Kubernetes cluster deployment
-Run the following, but replace the value of `$POD_NAME` with your `indexed-search` pod name from `kubectl get pods`:
-
-```
-$ POD_NAME='indexed-search-974c74498-6jngm' kubectl --namespace=prod exec -it $POD_NAME -c zoekt-indexserver -- du -sh /data/index
-126G /data/index
-```
-
-### Pure-Docker cluster Deployment
-
-Run the following against the `zoekt-shared-disk` directory on the host machine:
-
-```bash
-$ du -sh ~/sourcegraph-docker/zoekt-shared-disk/
-126G /home/ec2-user/sourcegraph-docker/zoekt-shared-disk/
-```
-
-
-## Background indexing
-
-Sourcegraph will reindex all repositories in the background seamlessly. In the meantime, it will serve searches just as fast from the old search index.
-
-This process happens at a rate of about 1,400 repositories/hr, depending on repository size and available resources.
-
-**Until this process has completed, search performance will be the same as the prior version.**
-
-If you're eager or want to confirm, here's how to check the process has finished:
-
-### Single-container Docker deployment
-The following command ran on the host machine shows how many repositories have been reindexed:
-
-```bash
-$ ls ~/.sourcegraph/data/zoekt/index/*_v16* | wc -l
- 12583
-```
-
-When it is equal to the number of repositories on your instance, the process has finished!
-
-
-### Kubernetes cluster deployment
-The following command will show how many repositories have been reindexed. Replace the value of `$POD_NAME` with your `indexed-search` pod name from `kubectl get pods`:
-
-```bash
-$ kubectl --namespace=prod exec -it indexed-search-974c74498-6jngm -c zoekt-indexserver -- sh -c 'ls /data/index/*_v16* | wc -l'
-12583
-```
-
-When it is equal to the number of repositories on your instance, the process has finished!
-
-
-### Pure-Docker cluster deployment
-The following command ran on the host machine against the `zoekt-shared-disk` directory will show how many repositories have been reindexed.
-
-```bash
-$ ls ~/sourcegraph-docker/zoekt-shared-disk/*_v16* | wc -l
-12583
-```
-
-When it is equal to the number of repositories on your instance, the process has finished!
-
-
-## Downgrading
-
-As guaranteed by our compatibility promise, it is always safe to downgrade to a previous minor version. e.g. 3.7.2 to 3.6.x. There will be no downtime, and search speed will not be impacted.
-
-Please do *not* downgrade or upgrade to 3.7.0 or 3.7.1, though, as those versions will incur a reindex and search performance will be harmed in the meantime.
-
-## Memory and CPU requirements (no substantial change compared to v3.5)
-
-- In v3.7, the `indexed-search` / `zoekt-indexserver` container will use 28% more memory on average compared to v3.6. However, please take note that v3.6 reduced memory consumption of the same container by about 41% -- so the net change from v3.5 -> v3.7 is still less memory usage overall.
-- CPU usage may increase depending on the amount of symbol queries your users run now that it is much faster. We suggest not changing any CPU resources and instead checking resource usage after the upgrade and reindexing has finished.
-
-
-
-
-# Migrating to Sourcegraph 3.31.x
-
-> NOTE: The following applies only users that use our built-in databases. Users that use external databases (e.x: Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, etc.) are not affected, and can ignore this page.
-
-In Sourcegraph 3.31.x, both the **built-in** main Postgres (`pgsql`) and codeintel (`codeintel-db`) databases have switched to an Alpine-based Docker image—this has been done to resolve vulnerabilities found in Debian but not Alpine. Upon upgrading, Sourcegraph will need to re-index the entire database. This process requires some preparation, so please read through **all** of the instructions on the rest of the page beforehand.
-
-For customers who previously upgraded to 3.27, there is a possibility that upgrade inadvertently introduced a major glibc change. This may have caused corruption in some indexes. While this is unlikely to have been noticeable up til now, upgrading to 3.31 (or more specifically the subsequent reindexing) will fail unless certain steps are taken before hand. Customers who have installed fresh from 3.27 or later should be unaffected by this potential data corruption, but are still likely to see the delay caused by the reindexing following upgrade.
-
-> WARNING: We advise all customers upgrading to 3.31 to check for corruption prior to upgrading to 3.31, and allow for greater than normal downtime. See below for more detailed advice.
-
-## Preparations
-
-### Check for prior index corruption before upgrading
-
-There is a possibility that prior Sourcegraph upgrades inadvertently introduced a major glibc change. This can cause corruption in indexes that have collatable key columns (e.g. any index with a `text` column). Read more about this [here](https://postgresql.verite.pro/blog/2018/08/27/glibc-upgrade.html).
-
-If your indexes are corrupted, then there is also a possibility that there is bad data in your databases that would cause the re-indexing process (and thus the 3.31.x upgrade) to fail. In order to do a first-pass check for corrupt indexes, please run the following SQL query against **both** of the following instances **before** upgrading to 3.31.x:
-
-1. `pgsql`
-2. `codeintel-db`
-
-*For more information about how to access a database container and run queries via `psql` see our admin documentation for [kubernetes](/admin/deploy/kubernetes/operations#access-the-database), [docker-compose](/admin/deploy/docker-compose/#access-the-database) or [single-container docker](/admin/deploy/docker-single-container/#access-the-database)*
-
-```sql
-create extension amcheck;
-
-select bt_index_parent_check(c.oid, true), c.relname, c.relpages
-from pg_index i
-join pg_opclass op ON i.indclass[0] = op.oid
-join pg_am am ON op.opcmethod = am.oid
-join pg_class c ON i.indexrelid = c.oid
-join pg_namespace n ON c.relnamespace = n.oid
-where am.amname = 'btree'
--- Don't check temp tables, which may be from another session:
-and c.relpersistence != 't'
--- Function may throw an error when this is omitted:
-and i.indisready AND i.indisvalid;
-```
-
-#### If no errors are reported
-
-It is probable that your indexes are fine (and thus no bad data is in your databases). You can proceed to ["Prepare for downtime"](#prepare-for-downtime).
-
-#### If any errors are reported
-
-You will need to repair the corrupt Postgres database indexes prior to upgrading by following the steps in [How to rebuild corrupt Postgres indexes.](/admin/how-to/rebuild-corrupt-postgres-indexes) Contact customer support with any questions.
-
-### Prepare for downtime
-
-**Sourcegraph will be unavailable until the re-indexing process has completed.** If the database containers are restarted/killed during the re-indexing process (for example, as a result of automated deployments), re-indexing will have to start over from scratch. Please plan accordingly, and communicate this downtime to your users.
-
-For systems with large datasets, re-indexing can take **1-2+ hours**.
-
-To validate the size of your dataset relative to these estimates, we can help estimate your potential downtime with some additional information.
-
-In order to check your dataset size, please run the following SQL query against **both** of the following instances:
-
-1. `pgsql`
-2. `codeintel-db`
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- table_name,
- pg_size_pretty(total_bytes) AS total,
- pg_size_pretty(index_bytes) AS index,
- pg_size_pretty(toast_bytes) AS toast,
- pg_size_pretty(table_bytes) AS table
-FROM
- (
- SELECT
- *,
- total_bytes - index_bytes - coalesce(toast_bytes, 0) AS table_bytes
- FROM
- (
- SELECT
- relname AS table_name,
- pg_total_relation_size(c.oid) AS total_bytes,
- pg_indexes_size(c.oid) AS index_bytes,
- pg_total_relation_size(reltoastrelid) AS toast_bytes
- FROM
- pg_class c
- LEFT JOIN
- pg_namespace n
- ON n.oid = c.relnamespace
- WHERE
- relkind = 'r'
- )
- a
- )
- a
-ORDER BY
- total_bytes DESC;
-```
-
-Please contact either customer support or your Customer Engineer with this information and we'll advise further.
-
-
-
-
-# Migrating from 3.30.0, 3.30.1, and 3.30.2
-
-The Sourcegraph 3.30 release introduced a change that caused corruption in certain indexes, breaking a number of Sourcegraph features. **This issue affects Sourcegraph 3.30.0, 3.30.1, and 3.30.2**, and was fixed in 3.30.3.
-
-- Users on 3.29.x are advised to upgrade directly to 3.30.3.
-- Users that have already upgraded to one of the affected releases must fix the already corrupt databases manually by following this guide: [**How to rebuild corrupt Postgres indexes**](/admin/how-to/rebuild-corrupt-postgres-indexes).
-
-> WARNING: If you have already upgraded to one of the affected releases, **do not upgrade to 3.30.3** after applying the above fix. Instead, [please upgrade directly to 3.31](/admin/migration/3_31).
-
-If you need any additional assistance, please reach out to `support@sourcegraph.com`.
-
-## Background
-
-The 3.30 release introduced a `pgsql` and `codeinteldb` base image change from debian to alpine which changed the default OS locale.
-This caused corruption in indexes that have collatable key columns (e.g. any index with a `text` column).
-Read more about this [here](https://postgresql.verite.pro/blog/2018/08/27/glibc-upgrade.html).
-
-After we found the root-cause of the issues many customers were seeing, we cut [a patch release, 3.30.3](/technical-changelog#3-30-3), that reverted the images to be based on debian, buying us time to change the alpine based version of the images to reindex affected indexes on startup, before accepting new connections.
-
-However, this means that after fixing the corrupt indexes on the alpine images in the affected releases, upgrading to debian based images in 3.30.3 will cause index corruption again. For this reason, **do not upgrade to 3.30.3** after fixing corrupt Postgres indexes. Instead, [please upgrade directly to 3.31](/admin/migration/3_31).
-
-
-
-
-# Migration notes for Sourcegraph 3.11+
-
-### Management console removal
-
-In Sourcegraph v3.11, the management console has been removed and all of its configuration properties have been moved into the **Site admin** > **Configuration** page. Upon upgrading, your management console configuration will automatically be merged into your site configuration.
-
-### Users of SITE_CONFIG_FILE and CRITICAL_CONFIG_FILE
-
-If you are making use of `SITE_CONFIG_FILE` or `CRITICAL_CONFIG_FILE` environment variables please:
-
-1. Simply copy all properties from `CRITICAL_CONFIG_FILE` and paste them into `SITE_CONFIG_FILE`.
-2. Upgrade to the latest Sourcegraph version.
-3. Delete and remove the `CRITICAL_CONFIG_FILE`, as it will no longer be used.
-
-If you have already upgraded without doing the above, simply copy the merged configuration from `https://sourcegraph.example.com/site-admin/configuration` back into your `SITE_CONFIG_FILE`, delete and remove the `CRITICAL_CONFIG_FILE`.
-
-### Downgrading
-
-If you intend to downgrade from v3.11 back to v3.10 or earlier, please note that you will need to restore your management console configuration after downgrading. To safely downgrade, please perform the following steps:
-
-1. Make a copy of your site configuration.
-2. Change the Docker image tag(s) to 3.10 or earlier and restart the server.
-3. Visit the management console, your critical configuration will be just `{"migrated": true}`.
-4. Copy the relevant properties from your site configuration into the management console.
-
-If you have any questions or concerns, please reach out to us `support@sourcegraph.com`.
-
-
-
-
-# Migrating to Sourcegraph 3.0.1+
-
-3.0 includes a few major product and configuration changes that you should be aware of if you are upgrading an existing instance.
-
-## PostgreSQL upgrade
-
-> WARNING: ⚠️ Because `3.0.1` [upgrades the PostgreSQL version](/admin/postgres):
->
->* Anyone upgrading from `2.x` to `3.0.1+`, or from `3.0.0` to `3.0.1+` MUST follow the [Upgrading PostgreSQL](/admin/postgres) instructions below.
->* It will not be possible to downgrade from `3.0.1+` to `2.x` unless you also restore your PostgreSQL database from a `2.x` snapshot.
-
-The version of PostgreSQL that ships with Sourcegraph `3.0.1` has been upgraded to `11.1` for all deployments.
-
-👉 Follow the [upgrade instructions](/admin/postgres) to safely migrate your data.
-
-If you are connecting Sourcegraph to an external PostgreSQL database, the minimum supported version is `12`.
-
-## Zero configuration code navigation is on by default for 10 languages
-
-The [sourcegraph/basic-code-intel](https://sourcegraph.com/extensions/sourcegraph/basic-code-intel) extension has been deprecated and split into one extension per language, with the top 10 [programming language extensions](https://sourcegraph.com/extensions?query=category%3A"Programming+languages") enabled by default.
-
-If you have [sourcegraph/basic-code-intel](https://sourcegraph.com/extensions/sourcegraph/basic-code-intel) enabled, disable it and enable any additional extensions for languages you use.
-
-If you were running language servers with 2.x from the `https://sourcegraph.example.com/site-admin/code-intelligence` page, you will need to enable the corresponding [Sourcegraph language extensions](https://sourcegraph.com/extensions?query=category%3A"Programming+languages") and follow the READMEs to set up language servers and to point the extensions to those language servers.
-
-## Repositories are managed by configuring external services
-
-Top level configuration options for code hosts (e.g. "github", "gitlab", "phabricator", "awscodecommit", "bitbucket", "gitolite") have been removed from [site configuration](/admin/config/site_config/).
-
-The configuration of code hosts and repositories has moved to the external services UI at `https://sourcegraph.example.com/site-admin/external-services`.
-
-The data from your existing site configuration will be automatically migrated when you upgrade to 3.0, so **no action is required**.
-
-## `repos.list` was removed from site configuration
-
-The top-level `repos.list` site configuration was removed in favour of each code-host's equivalent options, now configured via [external services](#Repositories-are-managed-by-configuring-external-services). Equivalent options in code hosts configuration:
- - GitHub via `github.repos`
- - GitLab via `gitlab.projectQuery`
- - Phabricator via `phabricator.repos`
- - Other external services
-
-## Configuration is now stored in the database, not in a config.json file
-
-Sourcegraph configuration is now stored in the PostgreSQL database, not in a configuration file. Editing the configuration is now only possible through the web UI (even in cluster deployments). Critical Sourcegraph configuration is stored in the management console.
-
-When you first start 3.0, the old configuration file will be copied into the database to populate the site configuration and management console. After this, you should delete that file as it will no longer be respected.
-
-For single-node deployments (`sourcegraph/server`), this file is `/etc/sourcegraph/sourcegraph-config.json` inside the Docker container.
-
-For Kubernetes cluster deployments, this is your `config-file` config map (`deploy-sourcegraph/base/config-file.ConfigMap.yaml`).
-
-## Some site configuration options have moved to the new management console
-
-The following options have moved into the management console:
-
-```
-auth.providers
-auth.public
-auth.sessionExpiry
-auth.userOrgMap
-externalURL
-htmlBodyBottom
-htmlBodyTop
-htmlHeadBottom
-htmlHeadTop
-licenseKey
-lightstepAccessToken
-lightstepProject
-log
-update.channel
-useJaeger
-```
@@ -85134,49 +84254,6 @@ See the following guides to use an external or managed version of each service t
-
-# Native Execution
-
-This feature is in beta and is available in Sourcegraph 5.1.0 and later.
-
-
-Native Execution is an image that runs Batch Changes without
-requiring [`src-cli`](https://github.com/sourcegraph/src-cli) to be installed on the Executor machine.
-
-Native Execution is required when running Batch Changes in Kubernetes. No docker-in-docker or privileged
-containers are required.
-
-This is also useful for environments where it is difficult to install `src-cli` on the Executor machine, e.g. air-gap
-environments.
-
-## Enable
-
-Native Execution is configured using a feature flag. To enable it,
-
-1. Go to **Site admin**
-2. Under **Configuration** select **Feature flags**
-3. Select **Create feature flag**
-4. Enter `native-ssbc-execution` as the **Name**
-5. Select `Boolean` as the **Type**
-6. Set the **Value** to `True`
-
-## Docker Image
-
-The Native Execution Docker image is available on Docker Hub
-at [`sourcegraph/batcheshelper`](https://hub.docker.com/r/sourcegraph/batcheshelper/tags).
-
-The default image (`sourcegraph/batcheshelper:${VERSION}`) can be overridden by updating the following in the **Site configuration**
-
-- `executors.batcheshelperImage`
-- `executors.batcheshelperImageTag`
-
-## Requirements
-
-The Docker Images that execute the actual Batch Change step require `tee` to be available on the image. Without `tee`,
-the output of the step cannot be captured properly for template variable rendering.
-
-
-
# Executors
@@ -85219,7 +84296,7 @@ Deciding how to deploy the executor depends on your use case. For users that wis
## How it works
-Executor instances are capable of being deployed in a variety of ways. Each runtime varies in _how_ jobs are executed.
+Executor instances are capable of being deployed in a variety of ways. Each runtime varies in how jobs are executed.
### Locally with src-cli
@@ -85313,11 +84390,8 @@ Executor instances are capable of being deployed in a variety of ways. Each runt
> NOTE: This is an experimental feature.
-
-
 -
1. The executor image is started as a pod in a Kubernetes node
2. The executor pulls for available Jobs from a Sourcegraph API
3. A user initiates a process that creates executor Jobs.
@@ -85332,10 +84406,6 @@ Executor instances are capable of being deployed in a variety of ways. Each runt
9. Logs are streamed from the executor to a Sourcegraph API
10. The executor calls a Sourcegraph API to that "complete" the Job.
-### Native execution
-
-Read more in [Native execution](/admin/executors/native_execution).
-
### Docker-in-Docker Kubernetes
> NOTE: This is an experimental feature.
@@ -85360,6 +84430,7 @@ Read more in [Native execution](/admin/executors/native_execution).
10. The executor calls a Sourcegraph API to that "complete" the Job.
## Troubleshooting
+
Refer to the [Troubleshooting Executors](/admin/executors/executors_troubleshooting) document for common debugging operations.
@@ -85745,7 +84816,7 @@ The following environment variables are specific to the native Kubernetes Execut
| `KUBERNETES_JOB_POD_ANNOTATIONS` | N/A | The JSON encoded annotations to add to the Kubernetes Job Pods. e.g. `{"foo": "bar", "faz": "baz"}` |
| `KUBERNETES_IMAGE_PULL_SECRETS` | N/A | The names of Kubernetes image pull secrets to use for pulling images. e.g. my-secret,my-other-secret |
-Note: `EXECUTOR_KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE` should be set to either "default" or the specific namespace where your Executor is deployed.
+`EXECUTOR_KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE` should be set to either "default" or the specific namespace where your Executor is deployed.
@@ -87165,6 +86236,7 @@ If you're deploying a new Enterprise instance, this page covers our most frequen
## Admin articles
### General
+
- [Deployment overview](/admin/deploy/)
- [Resource estimator](/admin/deploy/resource_estimator)
- [SAML config](/admin/auth/saml/)
@@ -87181,12 +86253,14 @@ If you're deploying a new Enterprise instance, this page covers our most frequen
- [Changelog](https://sourcegraph.com/changelog) to track releases and updates
### Docker-compose
+
- [Basic installation guide](/admin/deploy/docker-compose/)
- [AWS installation](/admin/deploy/docker-compose/aws)
- [Digital Ocean installation](/admin/deploy/docker-compose/digitalocean)
- [Google Cloud installlation](/admin/deploy/docker-compose/google_cloud)
## User articles
+
- [Search syntax](/code-search/queries)
- [Search filters](/code-search/queries#filters-all-searches)
- [Example batch changes](/batch-changes/examples)
@@ -88758,8 +87832,6 @@ Choose an AWS Region in the launcher below and click **Launch Stack**. When prom
-If you're running into any problem, see our [Troubleshooting guide](/admin/troubleshooting).
-
### Confirm you can access Sourcegraph
Find the URL of your Sourcegraph instance in the **Outputs** section of the AWS Stack. On first launch, Sourcegraph may take ~5 minutes to start and may display a `404 not found` page temporarily.
@@ -95950,7 +95022,7 @@ All site configuration options and their default values are shown below.
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/config/site.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:25Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:28Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
@@ -97305,7 +96377,7 @@ Settings options and their default values are shown below.
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/config/settings.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:26Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:29Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
@@ -97349,6 +96421,9 @@ Settings options and their default values are shown below.
// Whether to enable trace logging on the extension.
"codeIntel.traceExtension": false,
+ // Whether the cody chat code snippets should be code highlighted.
+ "cody.chatCodeSyntaxHighlightingEnabled": true,
+
// Custom informational messages to display to users at Cody clients locations.
// Usually this setting is used in global and organization settings. If set in user settings, the message will only be displayed to that single user.
"cody.notices": null,
@@ -98109,7 +97184,6 @@ A few helpful tips:
## Sending a test email
-(Added in Sourcegraph v3.38)
To verify email sending is working correctly, visit the GraphQL API console at e.g. `https://sourcegraph.example.com/api/console` and then run the following query replacing `test@example.com` with your personal email address:
@@ -98141,6 +97215,45 @@ Otherwise, you should see an error with more information:
If you need further assistance, please let us know at `mailto:support@sourcegraph.com`.
+## Email templates
+
+Customize email templates sent by Sourcegraph via the `email.templates` configuration option.
+
+Navigate to your site configuration (e.g. `https://sourcegraph.com/site-admin/configuration`) and add:
+
+```jsonc
+{
+ // [...]
+ "email.templates": {
+ "resetPassword": {
+ "subject": "Reset your password on {{.Host}}",
+ "html": "
-
1. The executor image is started as a pod in a Kubernetes node
2. The executor pulls for available Jobs from a Sourcegraph API
3. A user initiates a process that creates executor Jobs.
@@ -85332,10 +84406,6 @@ Executor instances are capable of being deployed in a variety of ways. Each runt
9. Logs are streamed from the executor to a Sourcegraph API
10. The executor calls a Sourcegraph API to that "complete" the Job.
-### Native execution
-
-Read more in [Native execution](/admin/executors/native_execution).
-
### Docker-in-Docker Kubernetes
> NOTE: This is an experimental feature.
@@ -85360,6 +84430,7 @@ Read more in [Native execution](/admin/executors/native_execution).
10. The executor calls a Sourcegraph API to that "complete" the Job.
## Troubleshooting
+
Refer to the [Troubleshooting Executors](/admin/executors/executors_troubleshooting) document for common debugging operations.
@@ -85745,7 +84816,7 @@ The following environment variables are specific to the native Kubernetes Execut
| `KUBERNETES_JOB_POD_ANNOTATIONS` | N/A | The JSON encoded annotations to add to the Kubernetes Job Pods. e.g. `{"foo": "bar", "faz": "baz"}` |
| `KUBERNETES_IMAGE_PULL_SECRETS` | N/A | The names of Kubernetes image pull secrets to use for pulling images. e.g. my-secret,my-other-secret |
-Note: `EXECUTOR_KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE` should be set to either "default" or the specific namespace where your Executor is deployed.
+`EXECUTOR_KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE` should be set to either "default" or the specific namespace where your Executor is deployed.
@@ -87165,6 +86236,7 @@ If you're deploying a new Enterprise instance, this page covers our most frequen
## Admin articles
### General
+
- [Deployment overview](/admin/deploy/)
- [Resource estimator](/admin/deploy/resource_estimator)
- [SAML config](/admin/auth/saml/)
@@ -87181,12 +86253,14 @@ If you're deploying a new Enterprise instance, this page covers our most frequen
- [Changelog](https://sourcegraph.com/changelog) to track releases and updates
### Docker-compose
+
- [Basic installation guide](/admin/deploy/docker-compose/)
- [AWS installation](/admin/deploy/docker-compose/aws)
- [Digital Ocean installation](/admin/deploy/docker-compose/digitalocean)
- [Google Cloud installlation](/admin/deploy/docker-compose/google_cloud)
## User articles
+
- [Search syntax](/code-search/queries)
- [Search filters](/code-search/queries#filters-all-searches)
- [Example batch changes](/batch-changes/examples)
@@ -88758,8 +87832,6 @@ Choose an AWS Region in the launcher below and click **Launch Stack**. When prom
-If you're running into any problem, see our [Troubleshooting guide](/admin/troubleshooting).
-
### Confirm you can access Sourcegraph
Find the URL of your Sourcegraph instance in the **Outputs** section of the AWS Stack. On first launch, Sourcegraph may take ~5 minutes to start and may display a `404 not found` page temporarily.
@@ -95950,7 +95022,7 @@ All site configuration options and their default values are shown below.
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/config/site.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:25Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:28Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
@@ -97305,7 +96377,7 @@ Settings options and their default values are shown below.
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/config/settings.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:26Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:29Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
@@ -97349,6 +96421,9 @@ Settings options and their default values are shown below.
// Whether to enable trace logging on the extension.
"codeIntel.traceExtension": false,
+ // Whether the cody chat code snippets should be code highlighted.
+ "cody.chatCodeSyntaxHighlightingEnabled": true,
+
// Custom informational messages to display to users at Cody clients locations.
// Usually this setting is used in global and organization settings. If set in user settings, the message will only be displayed to that single user.
"cody.notices": null,
@@ -98109,7 +97184,6 @@ A few helpful tips:
## Sending a test email
-(Added in Sourcegraph v3.38)
To verify email sending is working correctly, visit the GraphQL API console at e.g. `https://sourcegraph.example.com/api/console` and then run the following query replacing `test@example.com` with your personal email address:
@@ -98141,6 +97215,45 @@ Otherwise, you should see an error with more information:
If you need further assistance, please let us know at `mailto:support@sourcegraph.com`.
+## Email templates
+
+Customize email templates sent by Sourcegraph via the `email.templates` configuration option.
+
+Navigate to your site configuration (e.g. `https://sourcegraph.com/site-admin/configuration`) and add:
+
+```jsonc
+{
+ // [...]
+ "email.templates": {
+ "resetPassword": {
+ "subject": "Reset your password on {{.Host}}",
+ "html": "To reset your password on {{.Host}}, please click the link below:
Reset Password
If you did not request a password reset, please ignore this email.
"
+ },
+ "setPassword": {
+ "subject": "Set your password on {{.Host}}",
+ "html": "To set your password on {{.Host}} and complete your account registration, please click the link below:
Set Password
Your username is: {{.Username}}
"
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Available template types:
+
+* `resetPassword` - Email sent on password resets
+* `setPassword` - Email sent on account creation, if a password reset URL is created
+
+Template variables:
+
+* `{{.Host}}` - The hostname of your Sourcegraph instance
+* `{{.URL}}` - The action URL (password reset/set link)
+* `{{.Username}}` - The recipient's username
+
+Template fields:
+
+* `subject` - The email subject line (required)
+* `html` - The HTML email body content (required)
+* `text` - Optional plain-text email body. If not provided, a plain-text body will be automatically generated from the HTML template
+
@@ -98490,12 +97603,37 @@ However, if the user deletion is permanent, deleting both account and data, then
## Batch Spec Library
- Batch Spec Library is currently in Experimental.
+The Batch Spec Library offers curated examples and guided templates that make large-scale code modifications accessible to developers at every skill level. As a site admin you can manage the library.
+
+The library distinguishes between [templates](#templates) and [examples](#library-examples). Examples are batch specs that are meant to be modified by power users who are comfortable with the batch spec syntax. Templates, on the other hand, are batch specs that contain variables that the user can provide data for through form fields without having to modify the batch spec code.
+
+Sourcegraph instances come with a couple of examples out of the box. You can use the GraphQL APIs to [manage the Batch Spec Library](#managing-the-batch-spec-library).
+
+As a site admin, you can [feature records](#featured-records) to highlight the most useful templates and examples for your organization.
+
+### Examples
+
+Examples are complete batch specs intended for advanced users who are comfortable working with YAML and writing code. These examples serve as inspiration and starting points for custom batch changes.
+
+Examples are visible in the library pane when you are in the batch spec editor. They are not displayed by default in the templates list which is the entry point for users creating a batch change. See [choosing a template](/batch-changes/create-a-batch-change#choosing-a-template) for more details.
-The Batch Spec Library is a collection of Batch Specs that can be used to create Batch Changes. Sourcegraph provides a few Batch Specs out of the box.
+### Templates
+
+Templates are supported in Sourcegraph v6.6 and more.
+
+Templates are like examples, but with variables for easy reuse across multiple batch changes. Templates provide the simplest path for users to create batch changes without needing to learn Batch Spec YAML syntax. Users select from a curated list of templates and complete a form with the required parameters, making batch change creation accessible to all team members regardless of their technical background.
+
+An example becomes a template once it has at least one [variable](#variables) defined. It will then be displayed in the list of templates that a user sees when they click on [create a batch change](/batch-changes/create-a-batch-change).
+
+Variables can be used to replace any text in the batch spec except the batch change's name.
+
+### Managing the Batch Spec Library
+
+Site admins can manage the Batch Spec library in Sourcegraph v6.4 and more.
Site admins can manage the library through the GraphQL mutations `createBatchSpecLibraryRecord`, `updateBatchSpecLibraryRecord`, and `deleteBatchSpecLibraryRecord`. Use the query `batchSpecLibrary` to list all available Batch Spec examples.
+
```graphql
createBatchSpecLibraryRecord(name: "example", spec: "version: 2\nname: example") {
id
@@ -98517,20 +97655,15 @@ batchSpecLibrary(first: 100) {
}
```
-### Featured Templates
-
-Featured templates are supported in Sourcegraph v6.4 and more.
+### Featured Records
-Site-admins can mark a template as featured by either clicking the star button next to the list of library records. Featured records will automatically move to a section atop the remaining library records.
+Site-admins can mark a record as featured by either clicking the star button next to the list of library records or adding the `"featured"` [label](#labels) label with a GraphQL mutation. Featured records will automatically move to a section atop the remaining library records.
### Labels
-Labels are supported in Sourcegraph v6.4 and more.
+Library records support an optional `labels` field for categorization and filtering.
-Batch Spec Library records support an optional `labels` field for categorization and filtering. Common labels include:
-
-- `"featured"` - Marks popular or recommended batch specs that are displayed in a "Featured Templates" section above the remaining examples
-- Custom labels for organizational categorization (not exposed to Batch Changes users yet)
+The `"featured"` label marks popular or recommended batch specs that are displayed in a featured section above the remaining examples and templates.
To remove the featured status, you can update the library record with an empty list of labels (`[]`).
@@ -98556,6 +97689,41 @@ batchSpecLibrary(first: 100, labels: ["featured"]) {
}
```
+### Variables
+
+Variables are supported in Sourcegraph v6.6 and more.
+
+When creating a template, you can define placeholders for values that will vary between different uses of the template. Users filling out the template see these variables as form fields where they can enter specific values like repository names, file paths, or commit messages.
+
+You cannot use a variable for the batch change name.
+
+The `libraryVariables` field accepts an array of variable objects, each with the following configuration options:
+
+- **Name**: The variable identifier used in the template
+- **Display name**: Optional human-readable name shown in the form interface
+- **Pattern**: Regular expression for input validation
+- **Description**: Help text shown to users explaining what the variable is for
+- **Mandatory**: Boolean field indicating whether the variable is required
+- **Level**: Validation message severity level (`INFO`, `WARNING`, or `ERROR`)
+
+You can create templates by adding the `libraryVariables` field to the `createBatchSpecLibraryRecord` mutation. Here's an example that creates a simple template:
+
+```graphql
+createBatchSpecLibraryRecord(name:"Hello World Template",
+libraryVariables: [{
+ name:"REPOSITORY_QUERY",
+ displayName:"Repository Search Query",
+ pattern: ".+",
+ description:"The search query to find repositories.",
+ mandatory:true,
+ level:ERROR
+ }], spec: "version: 2\nname: hello-world\ndescription: Add Hello World to READMEs\n\non:\n - repositoriesMatchingQuery: $REPOSITORY_QUERY\n\nsteps:\n - run: echo Hello World | tee -a README.md\n container: alpine:3\n\nchangesetTemplate:\n title: Hello World\n body: Add Hello World to README\n branch: hello-world\n commit:\n message: Add Hello World to README") {
+ id
+ }
+```
+
+To update or remove variables from an existing template, you will need to recreate the record using the `deleteBatchSpecLibraryRecord` and `createBatchSpecLibraryRecord` mutations.
+
@@ -99790,7 +98958,7 @@ The Sourcegraph instance's site admin must [update the `corsOrigin` site config
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/phabricator.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:34Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:38Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
// SSH cipher to use when cloning via SSH. Must be a valid choice from `ssh -Q cipher`.
@@ -99892,7 +99060,7 @@ Repositories must be listed individually:
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/other_external_service.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:35Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:39Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
// A list of repositories to never mirror by name after applying repositoryPathPattern. Supports excluding by exact name ({"name": "myrepo"}) or regular expression ({"pattern": ".*secret.*"}).
@@ -100198,7 +99366,7 @@ To connect Gitolite to Sourcegraph:
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/gitolite.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:33Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:37Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
// A list of repositories to never mirror from this Gitolite instance. Supports excluding by exact name ({"name": "foo"}).
@@ -100439,7 +99607,7 @@ See [Internal rate limits](/admin/code_hosts/rate_limits#internal-rate-limits).
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/gitlab.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:28Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:31Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
// If non-null, enforces GitLab repository permissions. This requires that there be an item in the `auth.providers` field of type "gitlab" with the same `url` field as specified in this `GitLabConnection`.
@@ -101066,7 +100234,7 @@ GitHub connections support the following configuration options, which are specif
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/github.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:27Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:30Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
// Authentication alternatives: token OR gitHubAppDetails OR externalAccount OR useRandomExternalAccount
@@ -101349,7 +100517,7 @@ Gerrit connections support the following configuration options, which are specif
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/gerrit.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:32Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:36Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
// If non-null, enforces Gerrit repository permissions. This requires that there is an item in the [site configuration json](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/admin/config/site_config#auth-providers) `auth.providers` field, of type "gerrit" with the same `url` field as specified in this `GerritConnection`.
@@ -101638,7 +100806,7 @@ Bitbucket Server / Bitbucket Data Center connections support the following confi
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/bitbucket_server.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:28Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:32Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
// Authentication alternatives: token OR password
@@ -101906,20 +101074,22 @@ Bitbucket Cloud connections support the following configuration options, which a
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/bitbucket_cloud.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:29Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:33Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
- // Authentication alternatives: username + appPassword
-
{
// The workspace access token to use when authenticating with Bitbucket Cloud.
"accessToken": null,
+ // The API token to use when authenticating with Bitbucket Cloud.
+ "apiToken": null,
+
// The API URL of Bitbucket Cloud, such as https://api.bitbucket.org. Generally, admin should not modify the value of this option because Bitbucket Cloud is a public hosting platform.
// Other example values:
// - "https://api.bitbucket.org"
"apiURL": null,
// The app password to use when authenticating to the Bitbucket Cloud. Also set the corresponding "username" field.
+ // 🚨 NOTE 🚨: Please use the "apiToken" field instead of this field, since Bitbucket Cloud is deprecating app passwords as of June 9, 2026. See https://www.atlassian.com/blog/bitbucket/bitbucket-cloud-transitions-to-api-tokens-enhancing-security-with-app-password-deprecation for more details.
"appPassword": null,
// If non-null, enforces Bitbucket Cloud repository permissions. This requires that there is an item in the [site configuration json](https://sourcegraph.com/docs/admin/config/site_config#auth-providers) `auth.providers` field, of type "bitbucketcloud" with the same `url` field as specified in this `BitbucketCloudConnection`.
@@ -102093,7 +101263,7 @@ Azure DevOps connections support the following configuration options, which are
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/azuredevops.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:30Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:34Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
// Authentication alternatives: token OR windowsPassword
@@ -102260,7 +101430,7 @@ AWS CodeCommit connections support the following configuration options, which ar
{/* SCHEMA_SYNC_START: admin/code_hosts/aws_codecommit.schema.json */}
{/* WARNING: This section is auto-generated during releases. Do not edit manually. */}
-{/* Last updated: 2025-07-10T00:07:31Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.5.2654 */}
+{/* Last updated: 2025-07-28T21:25:35Z via sourcegraph/sourcegraph@v6.6.868 */}
```json
{
// REQUIRED:
diff --git a/src/data/navigation.ts b/src/data/navigation.ts
index b0fcd9134..e10320de7 100644
--- a/src/data/navigation.ts
+++ b/src/data/navigation.ts
@@ -467,7 +467,6 @@ export const navigation: NavigationItem[] = [
{ title: 'Analytics', href: '/admin/analytics' },
{ title: 'Executors', href: '/admin/executors' },
{ title: 'FAQs', href: '/admin/faq' },
- { title: 'Troubleshooting', href: '/admin/troubleshooting' },
{ title: 'How-to Guides', href: '/admin/how-to' },
{
title: 'Enterprise Getting Started',
diff --git a/src/data/redirects.ts b/src/data/redirects.ts
index 3ba2e5e18..8b4ac5ce4 100644
--- a/src/data/redirects.ts
+++ b/src/data/redirects.ts
@@ -6923,6 +6923,11 @@ const redirectsData = [
destination: '/code_monitoring',
permanent: true
},
+ {
+ source: '/admin/nginx',
+ destination: '/admin/http_https_configuration',
+ permanent: true
+ },
];
const updatedRedirectsData = redirectsData.map(redirect => {
 -
1. The executor image is started as a pod in a Kubernetes node
2. The executor pulls for available Jobs from a Sourcegraph API
3. A user initiates a process that creates executor Jobs.
@@ -85332,10 +84406,6 @@ Executor instances are capable of being deployed in a variety of ways. Each runt
9. Logs are streamed from the executor to a Sourcegraph API
10. The executor calls a Sourcegraph API to that "complete" the Job.
-### Native execution
-
-Read more in [Native execution](/admin/executors/native_execution).
-
### Docker-in-Docker Kubernetes
> NOTE: This is an experimental feature.
@@ -85360,6 +84430,7 @@ Read more in [Native execution](/admin/executors/native_execution).
10. The executor calls a Sourcegraph API to that "complete" the Job.
## Troubleshooting
+
Refer to the [Troubleshooting Executors](/admin/executors/executors_troubleshooting) document for common debugging operations.
-
1. The executor image is started as a pod in a Kubernetes node
2. The executor pulls for available Jobs from a Sourcegraph API
3. A user initiates a process that creates executor Jobs.
@@ -85332,10 +84406,6 @@ Executor instances are capable of being deployed in a variety of ways. Each runt
9. Logs are streamed from the executor to a Sourcegraph API
10. The executor calls a Sourcegraph API to that "complete" the Job.
-### Native execution
-
-Read more in [Native execution](/admin/executors/native_execution).
-
### Docker-in-Docker Kubernetes
> NOTE: This is an experimental feature.
@@ -85360,6 +84430,7 @@ Read more in [Native execution](/admin/executors/native_execution).
10. The executor calls a Sourcegraph API to that "complete" the Job.
## Troubleshooting
+
Refer to the [Troubleshooting Executors](/admin/executors/executors_troubleshooting) document for common debugging operations.