You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
<td><a href="https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/how-to-build-a-diy-gnss-reference-station">How to build a DIY GNSS reference station</a></td>
27
27
</tr>
28
28
</table>
29
29
30
30
31
31
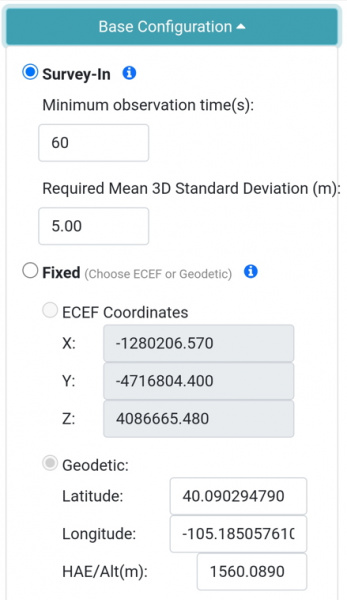
The Base Menu allows the user to select between Survey-In or Fixed Base setups.
32
32
33
-
[](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/1/4/6/3/RTK_Surveyor_-_WiFi_Config_-_Base_Config1.jpg)
33
+

34
34
35
35
*Controlling the type of Base from WiFi AP Config*
36
36
@@ -42,7 +42,13 @@ The Base Menu allows the user to select between Survey-In or Fixed Base setups.
42
42
43
43
In **Survey-In** mode, the minimum observation time and Mean 3D Standard Deviation can be set. The defaults are 60 seconds and 5 meters as directed by u-blox. The device will wait for the position accuracy to be better than 1 meter before a Survey-In is started. Don't be fooled; setting the observation time to 4 hours or an initial positional accuracy of 0.3m is not going to significantly improve the accuracy of the survey - use [PPP](https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/how-to-build-a-diy-gnss-reference-station#gather-raw-gnss-data) instead.
44
44
45
-
In **Fixed** mode, the coordinates of the antenna need to be sent. These can be entered in ECEF or Geographic coordinates. Whenever a user enters Base mode by pressing the SETUP button the GNSS receiver will immediately go into Base mode with these coordinates and immediately begin outputting RTCM correction data.
45
+

46
+
47
+
*Fixed base coordinate input*
48
+
49
+
In **Fixed** mode, the coordinates of the antenna need to be set. These can be entered in ECEF or Geographic coordinates. Whenever a user enters Base mode by pressing the SETUP button the GNSS receiver will immediately go into Base mode with these coordinates and immediately begin outputting RTCM correction data.
50
+
51
+
**Note:** The 'Paste Current XYZ' button will copy the current base coordinates and paste them into the X/Y/Z boxes. This shortcut allows the user to skip writing down coordinates just to re-enter them. However, taking a snap-shot of the unit's position in time is a very inaccurate way to assign the unit's base position.
46
52
47
53
[](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/1/8/5/7/SparkFun_RTK_Express_-_Display_-_Survey-In.jpg)
48
54
@@ -98,6 +104,14 @@ Every second a few hundred bytes, up to ~2k, will be transmitted to your mount p
98
104
99
105
Note: During NTRIP transmission WiFi is turned on and Bluetooth is turned off. You should not need to know the location information of the base so Bluetooth should not be needed. If necessary, USB can be connected to view detailed location information using the [System Report](https://sparkfun.github.io/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/system_status_report/) command.
100
106
107
+
## Commonly Use Coordinates
108
+
109
+

110
+
111
+
*A list of common coordinates*
112
+
113
+
For users who return to the same base position or monument, the coordinates can be saved to a 'Commonly Used Coordinates' list. A nickname and the X/Y/Z positions are saved to the list. Any record on the list can be loaded from the list into the X/Y/Z fields allowing quick switching without the need to hand record or re-enter coordinates from day-to-day repositioning of the base.
114
+
101
115
## Assisted Base
102
116
103
117
An Assisted Base is where a temporary base is set up to Survey-In its location but is simultaneously provided RTCM corrections so that its Survey-In is done with very precise readings. An assisted base running a Survey-In removes much of the relative inaccuracies from a Rover-Base system.
Because of the nature of these controls, the AP config page is different than the terminal menu.
8
8
9
-

9
+

10
10
11
11
*System Config Menu on WiFi AP Config Page*
12
12
13
+
### System Initial State
14
+
15
+
At power on, the device will enter either Rover or Base state.
16
+
13
17
### Log to SD
14
18
15
19
If a microSD card is detected, all messages will be logged.
@@ -22,6 +26,16 @@ Once the max log time is achieved, logging will cease. This is useful for limiti
22
26
23
27
Every 'max long length' amount of time the current log will be closed and a new log will be started. This is known as cyclic logging and is convenient on *very* long surveys (ie, months or years) to prevent logs from getting too unwieldy and helps limit the risk of log corruption. This will continue until the unit is powered down or the *max logging time* is reached.
24
28
29
+
### Start New Log
30
+
31
+
Pressing the 'Start New Log' button will close the current log. A new log will be opened when the AP Config page is closed and the unit restarts. This can be helpful in the field when a certain set of coordinates or feature marks need to be recorded in close proximity to one another. By dividing up the logs, the work can be more easily identified.
32
+
33
+
### Bluetooth Protocol
34
+
35
+
By default, the RTK products use Bluetooth v2.0 SPP (Serial Port Profile) to connect to data collectors. Nearly all data collectors support this protocol. The RTK product line also supports BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy). The BLE protocol has a variety of improvements but very few data collectors support it.
36
+
37
+
**Note:** Bluetooth SPP cannot operate concurrently with ESP-Now radio transmissions. Therefore, if you plan to use the ESP-Now radio system to connect RTK products, the BLE protocol must be used to communicate over Bluetooth to data collectors. Alternatively, ESP-Now works concurrently with WiFi so connecting to a data collector over WiFi can be used.
38
+
25
39
### Enable Factory Defaults
26
40
27
41
Factory Defaults will erase any user settings and reset the internal receiver to stock settings. Any logs on SD are maintained. To prevent accidental reset the checkbox must first be checked before the button is pressed.
@@ -32,11 +46,11 @@ Various stats for the SD card are shown.
32
46
33
47
### Update Firmware
34
48
35
-
New firmware may be uploaded via WiFi to the unit. See [Updating Firmware from the SD Card](https://sparkfun.github.io/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/firmware_update/#updating-firmware-from-the-sd-card) for more information.
49
+
New firmware may be uploaded via WiFi to the unit. See [Updating Firmware from WiFi](https://docs.sparkfun.com/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/firmware_update/#updating-firmware-from-wifi) for more information.
36
50
37
51
### Reset Counter
38
52
39
-
A counter is displayed indicating the number of non-power-on-resets since the last poweron.
53
+
A counter is displayed indicating the number of non-power-on-resets since the last power-on.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: docs/configure_ports.md
+50-3Lines changed: 50 additions & 3 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ By default, the **Radio** port is set to 57600bps to match the [Serial Telemetry
19
19
The **Data** port on the RTK Facet, Express, and Express Plus is very flexible. Internally the **Data** connector is connected to a digital mux allowing one of four software-selectable setups. By default, the Data port will be connected to the UART1 of the ZED-F9P and output any messages via serial.
20
20
21
21
***NMEA** - The TX pin outputs any enabled messages (NMEA, UBX, and RTCM) at a default of 460,800bps (configurable 9600 to 921600bps). The RX pin can receive RTCM for RTK and can also receive UBX configuration commands if desired.
22
-
***PPS/Trigger** - The TX pin outputs the pulse-per-second signal that is accurate to 30ns RMS. This pin can be configured as an extremely accurate time base. The pulse length and time between pulses are configurable down to 1us. The RX pin is connected to the EXTINT pin on the ZED-F9P allowing for events to be measured with incredibly accurate nano-second resolution. Useful for things like audio triangulation. See the Timemark section of the [ZED-F9P Integration Manual](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/1/8/5/7/ZED-F9P_IntegrationManual__UBX-18010802_.pdf) for more information.
22
+
***PPS/Trigger** - The TX pin outputs the pulse-per-second signal that is accurate to 30ns RMS. This pin can be configured as an extremely accurate time base. The pulse length and time between pulses are configurable down to 1us. The RX pin is connected to the EXTINT pin on the ZED-F9P allowing for events to be measured with incredibly accurate nano-second resolution. Useful for things like audio triangulation. See the [External Event Logging](#surveyor-data-port) section below and the Timemark section of the [ZED-F9P Integration Manual](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/1/8/5/7/ZED-F9P_IntegrationManual__UBX-18010802_.pdf) for more information.
23
23
***I2C** - The TX pin operates as SCL, RX pin as SDA on the I2C bus. This allows additional sensors to be connected to the I2C bus.
24
24
***GPIO** - The TX pin operates as a DAC-capable GPIO on the ESP32. The RX pin operates as an ADC-capable input on the ESP32. This is useful for custom applications.
25
25
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ The **Data** port on the RTK Facet, Express, and Express Plus is very flexible.
33
33
34
34
## Data Port
35
35
36
-
By default, the **Data** port is set to 460800bps and can be configured from 4800bps to 921600bps. The 460800bps baud rate was chosen to support applications where a large number of messages are enabled and a large amount of data is being sent. If you need to decrease the baud rate to 115200bps or other, be sure to monitor the MON-COMM message within u-center for buffer overruns. A baud rate of 115200bps and the NMEA+RXM default configuration at 4Hz *will* cause buffer overruns.
36
+
By default, the **Data** port is set to 460800bps and can be configured from 4800bps to 921600bps. The 460800bps baud rate was chosen to support applications where a large number of messages are enabled and a large amount of data is sent. If you need to decrease the baud rate to 115200bps or other, be sure to monitor the MON-COMM message within u-center for buffer overruns. A baud rate of 115200bps and the NMEA+RXM default configuration at 4Hz *will* cause buffer overruns.
37
37
38
38
[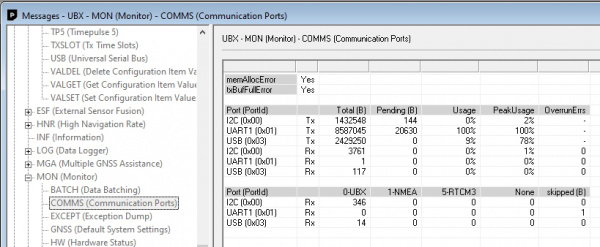](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/1/8/5/7/SparkFun_RTK_Express_-_Ports_Menu_MON-COMM_Overrun.jpg)
39
39
@@ -47,4 +47,51 @@ Most applications do not need to plug anything into the **Data** port. Most user
47
47
48
48
By default, the Data port is set to 460800bps and can be configured from 4800bps to 921600bps.
49
49
50
-
Note: The Data port does not output NMEA by default. The unit must be opened and the *Serial NMEA Connection* switch must be moved to 'Ext Connector'. See [Hardware Overview - Advanced Features](https://sparkfun.github.io/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/hardware_rtk_surveyor/#advanced-features) for the location of the switch.
50
+
Note: The Data port does not output NMEA by default. The unit must be opened and the *Serial NMEA Connection* switch must be moved to 'Ext Connector'. See [Hardware Overview - Advanced Features](https://sparkfun.github.io/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/hardware_rtk_surveyor/#advanced-features) for the location of the switch.
51
+
52
+
## External Event Logging
53
+
54
+

55
+
56
+
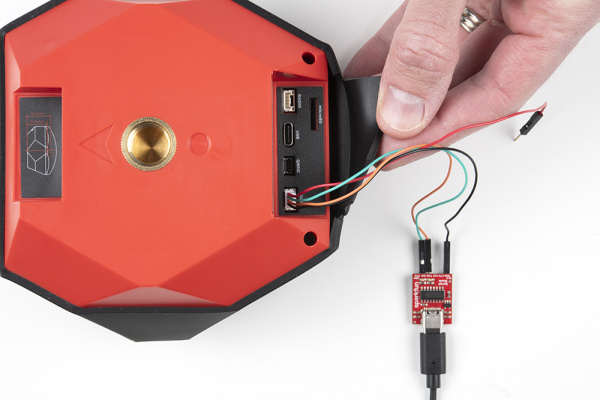
*Three RTK Expresses wired with external microphones*
57
+
58
+
The external triggering system is a powerful feature enabling a variety of scientific applications. Above is three RTK Expresses wired with external microphones used in a 'popped balloon' audio triangulation experiment.
59
+
60
+
The ZED-F9P has the ability to mark a detected event with +/-30 *nanosecond accuracy*. When enabled, an event on the RX pin (a low-to-high or high-to-low transition) on the DATA port, will trigger a message in the log with a very accurate timestamp.
61
+
62
+
***Red** - 3.3V
63
+
***Green** - TX (output from the RTK device)
64
+
***Orange** - RX (input into the RTK device)
65
+
***Black** - GND
66
+
67
+
[](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/2/1/8/8/SparkFun_RTK_Facet_-_Data_Port_to_USB.jpg)
68
+
69
+
For event logging, only the Black and Orange wires are needed. If you need to provide 3.3V to your system, the red wire can supply up to 600mA but we do not recommend sourcing more than 300mA.
70
+
71
+

72
+
73
+
*Configuring the External Pulse and External Events over WiFi*
74
+
75
+
Be sure to select 'Enable External Event Logging' through the ports menu.
* 02: sentenceType - Externally triggered events are type 0x02
91
+
* 5: triggerCount
92
+
* 494326906: towMsR - Time Of Week of rising edge (ms)
93
+
* 136292: towSubMsR - Millisecond fraction of Time Of Week of rising edge (ns)
94
+
* 31: accEst - Accuracy estimate (ns)
95
+
* 74: NMEA CRC
96
+
97
+
The event timestamps can be analyzed to precisely coordinate or triangulate a past event. In the case of the three RTK Expresses with microphones, the three units' locations were known with RTK 14mm accuracy. The air temperature was taken to obtain the speed of sound. From these data points, we can solve for the location of a sound such as a popped balloon.

6
+
7
+
*Configuration menu via Bluetooth*
8
+
9
+
Starting with firmware v2.7, Bluetooth-based configuration is supported. For more information about updating the firmware on your device, please see [Updating RTK Firmware](https://sparkfun.github.io/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/firmware_update/).
10
+
11
+
The RTK device will be a discoverable Bluetooth device (both BT SPP and BLE are supported). For information about Bluetooth pairing, please see [Connecting Bluetooth](/docs/connecting_bluetooth.md).
12
+
13
+
## Entering Bluetooth Echo Mode
14
+
15
+

16
+
17
+
Once connected, the RTK device will report a large amount of NMEA data over the link. To enter Bluetooth Echo Mode send the characters +++.
18
+
19
+
**Note:** There must be a 2 second gap between any serial sent from a phone to the RTK device, and any escape characters. In almost all cases this is not a problem. Just be sure it's been 2 seconds since an NTRIP source has been turned off and attempting to enter Bluetooth Echo Mode.
20
+
21
+

22
+
23
+
*The GNSS Messages menu shown over Bluetooth Echo Mode*
24
+
25
+
Once in Bluetooth Echo Mode, any character sent from the RTK unit will be shown in the Bluetooth app, and any character sent from the connected device (cell phone, laptop, etc) will be received by the RTK device. This allows the opening of the config menu as well as the viewing of all regular system output.
26
+
27
+
For more information about the Serial Config menu please see [Configure with Serial](/docs/configure_with_serial.md).
28
+
29
+

30
+
31
+
*Exit from the Serial Config Menu*
32
+
33
+
Bluetooth can also be used to view system status and output. Simply exit the config menu using option 'x' and the system output can be seen.
34
+
35
+
## Exit Bluetooth Echo Mode
36
+
37
+
To exit Bluetooth Echo Mode simply disconnect Bluetooth. In the Bluetooth Serial Terminal app, this is done by pressing the 'two plugs' icon in the upper right corner.
38
+
39
+

40
+
41
+
*Menu option 'b' for exiting Bluetooth Echo Mode*
42
+
43
+
Alternatively, if you wish to stay connected over Bluetooth but need to exit Bluetooth Echo Mode, use the 'b' menu option from the main menu.
44
+
45
+
## Serial Bluetooth Terminal Settings
46
+
47
+
Here we provide some settings recommendations to make the terminal navigation of the RTK device a bit easier.
48
+
49
+

50
+
51
+
*Terminal Settings with Timestamps disabled*
52
+
53
+
Disable timestamps to make the window a bit wider, allowing the display of longer menu items without wrapping.
54
+
55
+

56
+
57
+
*Clear on send and echo off*
58
+
59
+
Clearing the input box when sending is very handy as well as turning off local echo.

6
+
7
+
*Configuration page via WiFi*
8
+
5
9
Starting with firmware v1.7, WiFi-based configuration is supported. For more information about updating the firmware on your device, please see [Updating RTK Firmware](https://sparkfun.github.io/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/firmware_update/).
6
10
7
11
The RTK device will present a webpage that is viewable from either a desktop/laptop with WiFi or a cell phone. For advanced configurations, a desktop is recommended. For quick in-field changes, a cell phone works great.
0 commit comments