|
| 1 | +## Artboard |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +The artboard component is responsible for controllling all the graphics management. It creates turtles, canvases for each turtle, control the turtle(sprite) movements, communicate a particular turtle to draw on canvas. Any change to the background canvas can be done by manipulating this component. |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +Artboard is composed of three components. |
| 6 | +<ol> |
| 7 | + <li> Underlay </li> |
| 8 | + <li> Manager </li> |
| 9 | + <li> Interactor </li> |
| 10 | +</ol> |
| 11 | + |
| 12 | +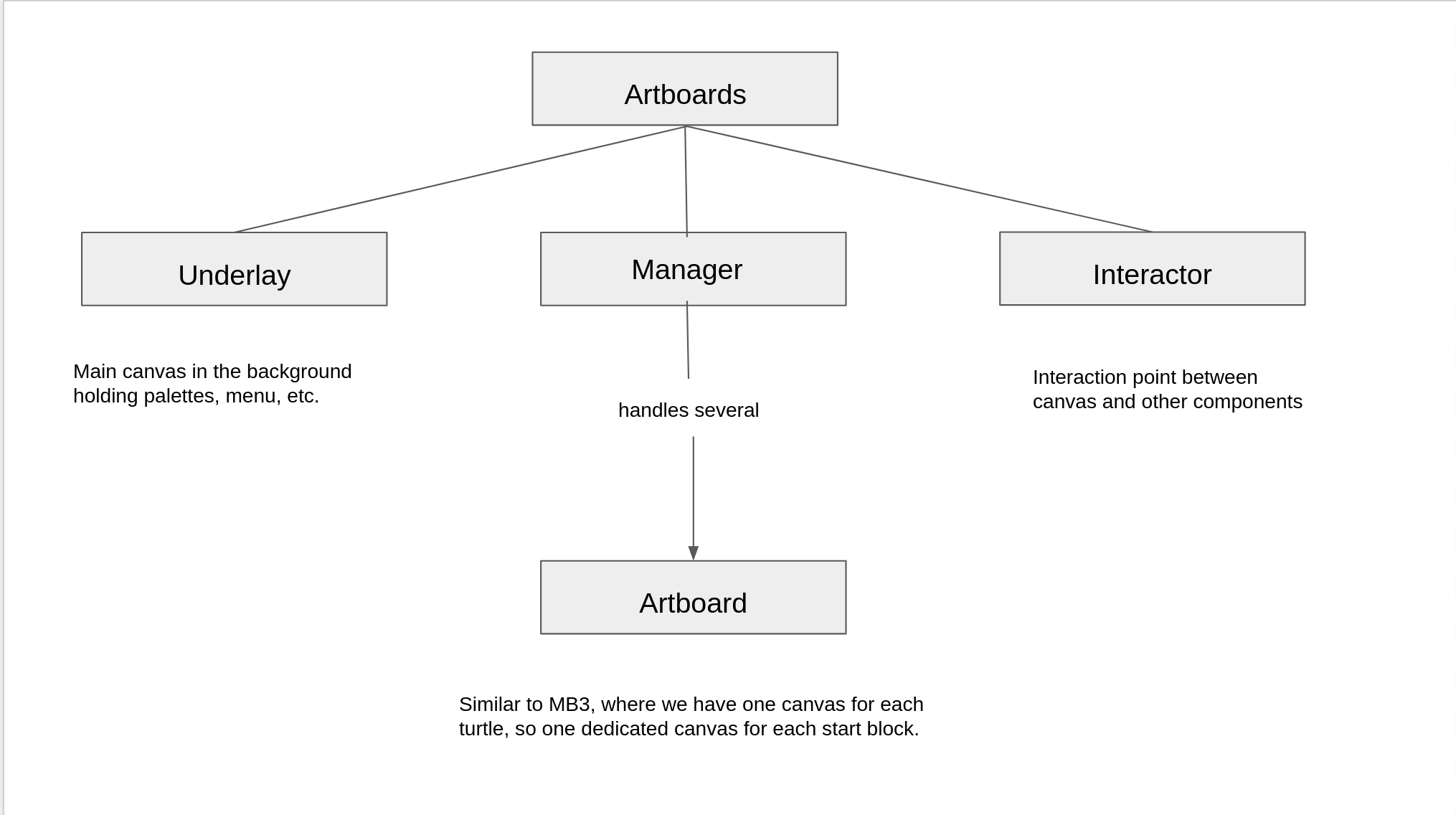 |
| 13 | + |
| 14 | +### Underlay |
| 15 | +This refers to main canvas in the background which holds the palettes, menus and blocks. It will be present even if there are no turtles (sprite). |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +### Interactor |
| 18 | +It is the interaction point between the canvases and other components. |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +#### Manager |
| 21 | +This is the main sub component of artboard as it is responsible for handling all artboards.For e.g. it can add a new artboard(canvas), remove an existing artboard, renders a particular turtle to draw on artboard, etc. It receives signals from monitor component to do a change in a particular artboard. It maintains a list of artboards which are currently present in the program. Before knowing how it handles several artboards let us take a look at the overall design structure of artboard and turtle. |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +#### Turtle and Artboard |
| 24 | +There is a dedicated canvas for each turtle and all drawings corresponding to the its turtle reside in it. We can say there is one-to-one relationship between artboard and turtle. Artboard is designed based on MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel). The model of an artboard contains properties specific to its artboard like line parameters, arc parameters, etc. The ViewModel contains a reference to the corresponding DOM element. e.g. - canvas and turtle positions, style etc.The view component is basically a HTML canvas generated by p5 library and all the functions to draw line, arcs, clear, etc are written using p5 library. See the below figure for more clarity. |
| 25 | + |
| 26 | +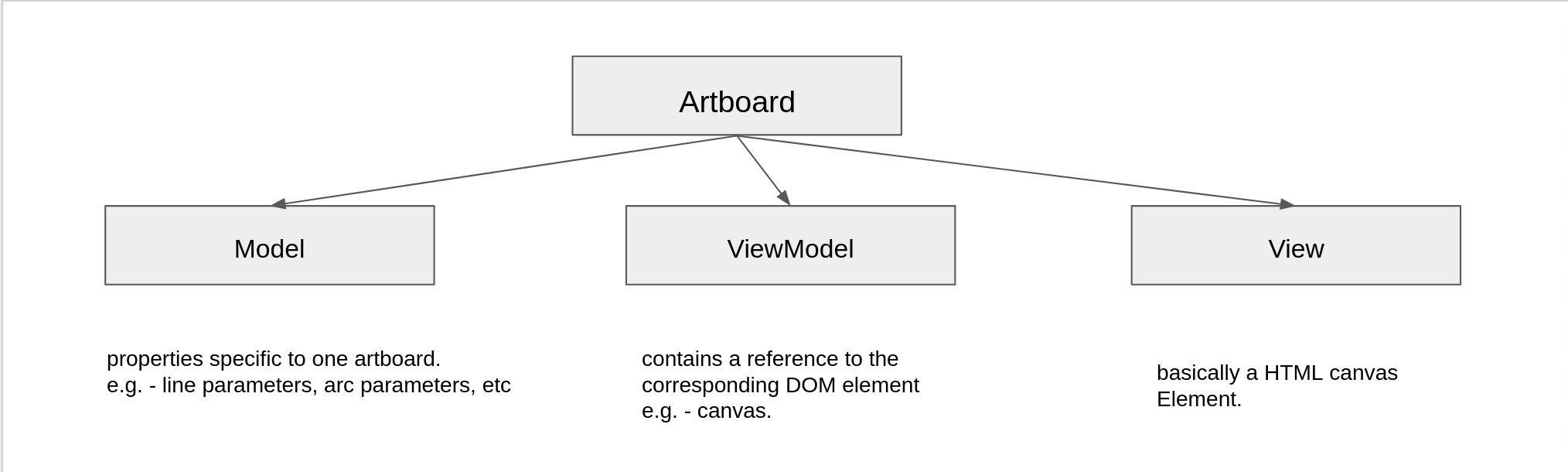 |
| 27 | + |
| 28 | +### File Structure |
| 29 | + |
| 30 | +All relevant folders and files of artboard are listed down - |
| 31 | +<ul> |
| 32 | + <li>Types |
| 33 | + <ul> |
| 34 | + <li>artboard.d.ts</li> |
| 35 | + <li>context.d.ts</li> |
| 36 | + </ul> |
| 37 | + </li> |
| 38 | + <li>Components |
| 39 | + <ul> |
| 40 | + <li>artboard |
| 41 | + <ul> |
| 42 | + <li>Artboard.tsx</li> |
| 43 | + <li>Manager.tsx</li> |
| 44 | + <li>Underlay.tsx</li> |
| 45 | + </ul> |
| 46 | + </li> |
| 47 | + <li>Monitor.ts</li> |
| 48 | + </ul> |
| 49 | + </li> |
| 50 | + <li>Context |
| 51 | + <ul> |
| 52 | + <li>ArtBoardContext.ts</li> |
| 53 | + </ul> |
| 54 | + </li> |
| 55 | + <li>Models |
| 56 | + <ul>artboard |
| 57 | + <li>ArtBoardDraw.ts</li> |
| 58 | + <li>Artboard.ts</li> |
| 59 | + <li>ArtboardManager.ts</li> |
| 60 | + <li>Turtle.ts</li> |
| 61 | + </ul> |
| 62 | + </li> |
| 63 | + <li>Views |
| 64 | + <ul> |
| 65 | + <li>artboard |
| 66 | + <ul> |
| 67 | + <li>Artboard.scss</li> |
| 68 | + <li>Artboard.tsx</li> |
| 69 | + <li>ArtboardHandler.tsx</li> |
| 70 | + <li>ArtboardSketch.tsx</li> |
| 71 | + <li>ArtboardTurtle.tsx</li> |
| 72 | + </ul> |
| 73 | + </li> |
| 74 | + </ul> |
| 75 | + </li> |
| 76 | +</ul> |
| 77 | + |
| 78 | +## p5 Library and Artboard |
| 79 | +[p5](https://p5js.org/) library is used to create and handle canvases. p5 provides many inbuilt functions to draw graphics and control over the canvas.p5.js has a number of predefined functions which we can use to draw anything we want. The most basic (and necessary) functions are the setup() and draw() functions. A simple canvas using p5 in react can be created like this. |
| 80 | + |
| 81 | +[`p5 Canvas is created in instance mode.`](https://github.com/processing/p5.js/wiki/Global-and-instance-mode) |
| 82 | + |
| 83 | + |
| 84 | + const Sketch = (sketch: P5Instance): void => { |
| 85 | + let demoCanvas: p5.Element; |
| 86 | + |
| 87 | + /** This is a setup function */ |
| 88 | + sketch.setup = () => { |
| 89 | + demoCanvas = sketch.createCanvas(1200, 600); |
| 90 | + }; |
| 91 | + |
| 92 | + /** This is a draw function */ |
| 93 | + sketch.draw = () => { |
| 94 | + sketch.background(220); |
| 95 | + sketch.ellipse(50, 50, 80, 80); |
| 96 | + }; |
| 97 | + }; |
| 98 | + |
| 99 | +It creates a canvas as p5 element with a circle on top of it. There are two important functions `setup` and `draw`. The code inside the `draw()` function runs continuously from top to bottom until the program is stopped. The setup function runs only once in the beginning. |
| 100 | + |
| 101 | +### Integration p5 Sketches with React |
| 102 | + |
| 103 | +By using React we get all the advantages of declarative code with clean, reusable and reactive components. All the while still maintaining the easy to use abstractions exposed by p5. The above sketch defintion is called inside a react component. |
| 104 | + |
| 105 | +### How Do We Add A Sketch In React? |
| 106 | + |
| 107 | +The sample sketch above is written in plain javascript and we can’t just write the same code in react. We have to add it using a few manipulations. |
| 108 | + |
| 109 | +Adding a sketch in react is fairly simple, we need to do three basic things: |
| 110 | +<ol> |
| 111 | + <li>Create a function which encapsulates our sketch </li> |
| 112 | + <li>Create a p5 object using the p5 package that we installed earlier </li> |
| 113 | + <li>Pass our sketch to the p5 object as an argument</li> |
| 114 | +</ol> |
| 115 | +The canvas is wrapped inside a react component so that we can use some of the lifecycle to manipulate it accordingly. |
| 116 | + |
| 117 | + |
| 118 | + const DemoSketch: React.FC<P5WrapperProps> = ({ sketch, children, ...props }) => { |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | + /** Sketch takes a P5Instance of canvas, props contains attributes like bg color, etc*/ |
| 121 | + const demoSketch = createRef<HTMLDivElement>(); |
| 122 | + const [instance, setInstance] = useState<P5Instance>(); |
| 123 | + const id = `demo-sketch`; |
| 124 | + useEffect(() => { |
| 125 | + instance?.updateWithProps?.(props); |
| 126 | + }, [props]); |
| 127 | + |
| 128 | + useEffect(() => { |
| 129 | + if (demoSketch.current === null) return; |
| 130 | + instance?.remove(); |
| 131 | + const canvas = new p5(Sketch, document.getElementById(id) as HTMLElement) as P5Instance; |
| 132 | + canvas.updateWithProps?.(props); |
| 133 | + setInstance(canvas); |
| 134 | + }, [sketch, demoSketch.current]); |
| 135 | + |
| 136 | + return ( |
| 137 | + <div id={id} ref={demoSketch}> |
| 138 | + {children} |
| 139 | + </div> |
| 140 | + ); |
| 141 | + }; |
| 142 | + |
| 143 | +For more information on the integration of p5 sketches with react, please read this [post](https://levelup.gitconnected.com/integrating-p5-sketches-into-your-react-app-de44a8c74e91). |
| 144 | + |
| 145 | +## Artboard and react hooks |
| 146 | + |
| 147 | + sketch.updateWithProps = (props: SketchProps) => { |
| 148 | + if (props.color) { |
| 149 | + bgcolor = parseInt(props.color, 10); |
| 150 | + } |
| 151 | + }; |
| 152 | + |
| 153 | + useEffect(() => { |
| 154 | + instance?.updateWithProps?.(props); |
| 155 | + }, [props]); |
| 156 | + |
| 157 | + |
| 158 | +We declare a reference variable called "demoSketch" using React's useRef hook. This just let's our other libraries have a node or reference insertion point. It's important that we pass "domSketch.current" into DOM because ".current" gives the actual HTML node we want. And finally, we return some jsx of a div that has the ref attribute equal to the value of our useRef hook variable. |
| 159 | + |
| 160 | +Similarly, useEffect hook is used to reflect the change on the canvas. In the above example we see the `updateWithProps()` function, which is called when the properties of a wrapper component are changed. Read more [here](https://github.com/jamesrweb/react-p5-wrapper). |
| 161 | + |
| 162 | +### Monitor and Manager |
| 163 | + |
| 164 | +### Manager and Artboard |
| 165 | + |
| 166 | +### Artboard and Turtles |
| 167 | + |
| 168 | + |
0 commit comments