|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +title: Python Data Types Explained - A Visual Guide for Beginners |
| 3 | +description: This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Python's built-in data types, their characteristics, and use cases. |
| 4 | +date: Jul 20, 2025 |
| 5 | +updated: Jul 20, 2025 |
| 6 | +tags: python, intermediate, data types |
| 7 | +socialImage: /blog/python-data-types.jpg |
| 8 | +--- |
| 9 | + |
| 10 | +<route lang="yaml"> |
| 11 | +meta: |
| 12 | + layout: article |
| 13 | + title: Python Data Types Explained - A Visual Guide for Beginners |
| 14 | + description: This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Python's built-in data types, their characteristics, and use cases. |
| 15 | + date: Jul 20, 2025 |
| 16 | + updated: Jul 20, 2025 |
| 17 | + socialImage: /blog/python-data-types.jpg |
| 18 | + tags: python, intermediate, data types |
| 19 | +</route> |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +<blog-title-header :frontmatter="frontmatter" title="Python data types: A visual guide for beginners" /> |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +Python comes with just eight core data types, yet choosing the right one makes code clearer, faster, and safer. The cheat-sheet below shows how each type works, when to reach for it, and where its limitations hide. |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +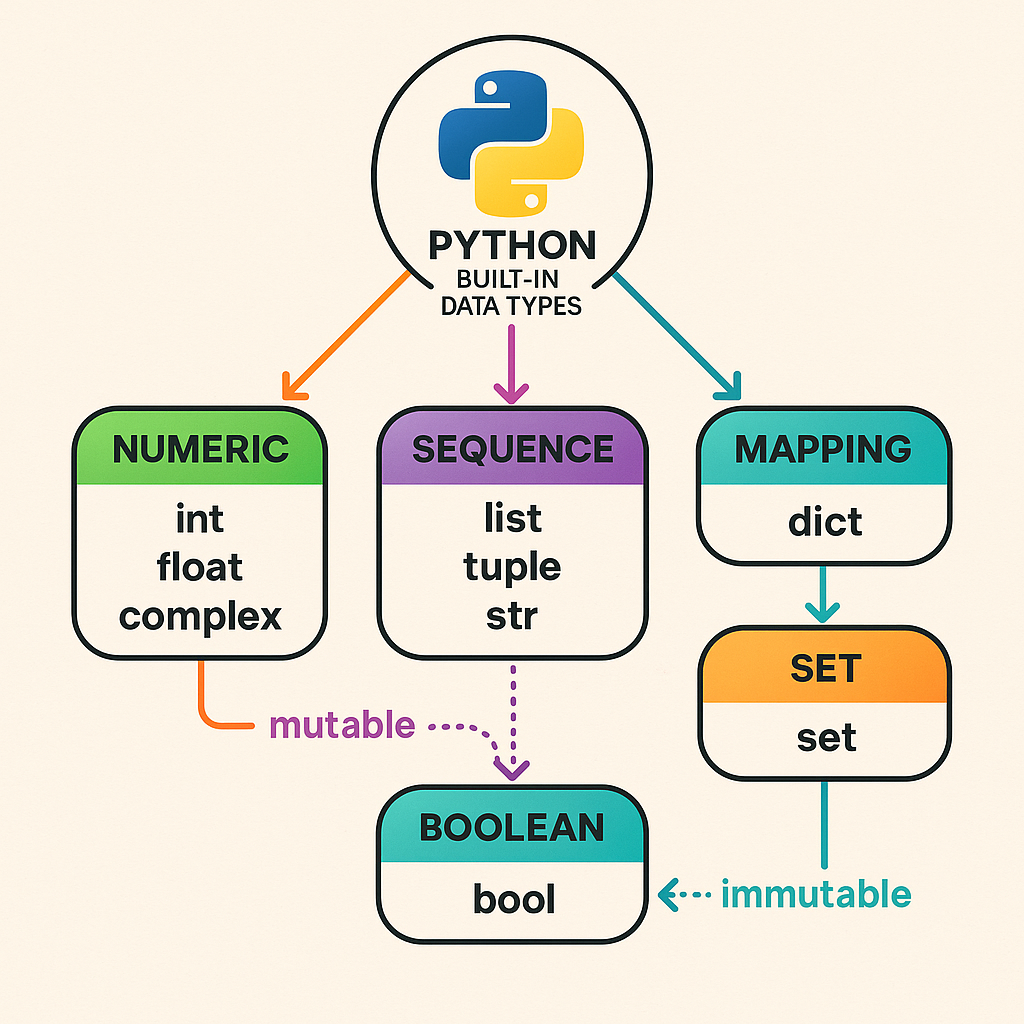 |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +Diagram of Python built-in data type categories and mutability. |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +## 1. Numbers – `int`, `float`, `complex` |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +Python groups pure numeric types under one family but gives each a specialty. |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +| Type | Typical literal | Key traits | When to use | Handy methods/ops | |
| 34 | +| :-------- | :--------------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------- | :-------------------------------------- | |
| 35 | +| `int` | `42`, `0xFF` | Unlimited precision whole numbers; supports binary `0b`, octal `0o`, hex `0x` literals[^1] | Counting, indexing, money amounts (with `decimal` for cents) | `bit_length()`, `to_bytes()`[^2] | |
| 36 | +| `float` | `3.14`, `1.2e3` | 64-bit IEEE-754 float; rounding error possible[^3][^4] | Scientific data, averages, continuous measures | `.is_integer()`, `.hex()`, math module | |
| 37 | +| `complex` | `2+3j`, `complex(a,b)` | Real + imag part; full arithmetic, `.real`, `.imag`, `.conjugate()`[^5][^6] | DSP, fractals, impedance math | All arithmetic, `abs()` gives magnitude | |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | +### Quick demo |
| 40 | + |
| 41 | +```python |
| 42 | +radius = 2.5 # float |
| 43 | +area = 3.1416 * radius**2 |
| 44 | +z = complex(2, 3) # (2+3j) |
| 45 | +polar_r = abs(z) # 3.605… |
| 46 | +``` |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | +## 2. Strings – `str` |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +Immutable sequences of Unicode code points. |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +- Creation: quotes `'hi'` or `"hi"`, triple quotes for multi-line. |
| 53 | +- Formatting: f-strings `f"{name=}"` (fast), older `str.format`, `%` operator. |
| 54 | +- Common methods: `split`, `join`, `replace`, `strip`, `startswith`, `casefold` for case-insensitive compares[^7][^8][^9]. |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +Why immutability? Fast hashing (dictionary keys) and thread-safety. |
| 57 | + |
| 58 | +## 3. Booleans – `bool` |
| 59 | + |
| 60 | +Subclass of `int` with only two singletons: `True`, `False`. |
| 61 | +Python evaluates _truthiness_: any non-zero number, non-empty sequence, or custom object with `__bool__` → `True`; zero, empty, or `None` → `False`[^10][^11][^12]. |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | +```python |
| 64 | +items = [] |
| 65 | +if items: # empty list is falsey |
| 66 | + ... |
| 67 | +``` |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +## 4. Lists – `list` |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | +Mutable, ordered, heterogeneous collection. |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | +- Square-bracket syntax: `nums = [^13][^14][^15]`[^16]. |
| 74 | +- Operations: `append`, `extend`, `insert`, `remove`, `pop`, slicing, list comprehension[^17][^18][^19]. |
| 75 | +- When: ordered data you’ll mutate, stack/queue prototypes, accumulating results. |
| 76 | + Performance tip: prefer `deque` for heavy pops from the left. |
| 77 | + |
| 78 | +## 5. Dictionaries – `dict` |
| 79 | + |
| 80 | +Hash-table mapping of _immutable_ keys to values; insertion-ordered since 3.7. |
| 81 | + |
| 82 | +- Literal: `movie = {"title": "Dune", "year": 2021}` |
| 83 | +- Methods: `get`, `items`, `keys`, `update`, `setdefault`, `pop`[^20][^21]. |
| 84 | +- When: lookup by key (id → row), counting, memoization. |
| 85 | + Use `defaultdict` or `Counter` from `collections` for common patterns. |
| 86 | + |
| 87 | +## 6. Tuples – `tuple` |
| 88 | + |
| 89 | +Immutable, ordered sequence. |
| 90 | + |
| 91 | +- Parentheses optional: `pt = 10, 20` |
| 92 | +- Supports unpacking: `x, y = pt` |
| 93 | +- Why immutable? Makes tuples hashable → usable as dict/set keys, guarantees fixed structure[^22][^23]. |
| 94 | + Typical roles: return multiple values, coordinates, config constants. |
| 95 | + |
| 96 | +## 7. Sets – `set`, `frozenset` |
| 97 | + |
| 98 | +Unordered collection of unique, hashable elements. |
| 99 | + |
| 100 | +```python |
| 101 | +tags = {"python", "ai", "flask"} |
| 102 | +if "ai" in tags: ... |
| 103 | +``` |
| 104 | + |
| 105 | +- Operations: union `|`, intersection `&`, difference `-`, symmetric difference `^`[^13]. |
| 106 | +- Mutable `set`; immutable `frozenset` for dictionary keys. |
| 107 | + Use cases: membership testing, deduplication, relation algebra. |
| 108 | + |
| 109 | +## Picking the right type – real-world tips |
| 110 | + |
| 111 | +| Scenario | Best type | Rationale | |
| 112 | +| :---------------------------------- | :--------------------------------------------- | :--------------------------------------- | |
| 113 | +| Logging unique visitor IDs | `set` | O(1) membership, duplicates auto-ignored | |
| 114 | +| JSON payload representing an object | `dict` | Key–value mirrors JSON, order preserved | |
| 115 | +| Constant RGB triplet | `tuple` | Fixed size, prevents accidental edits | |
| 116 | +| Editable shopping cart items | `list` | Needs ordering and mutation | |
| 117 | +| Switch/feature flags | `bool` in a `dict` | Clear true/false semantics | |
| 118 | +| Polynomial coefficients | `list` or `tuple` depending on mutability need | | |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | +## Cheat-sheet for mutability \& hashability |
| 121 | + |
| 122 | +| Type | Mutable? | Hashable? | Can be dict key? | |
| 123 | +| :---------------------------- | :------- | :-------- | :--------------- | |
| 124 | +| `int`, `float`, `complex` | No | Yes | ✔ | |
| 125 | +| `str` | No | Yes | ✔ | |
| 126 | +| `bool` | No | Yes | ✔ | |
| 127 | +| `tuple` (all immutable items) | No | Yes | ✔ | |
| 128 | +| `list` | Yes | No | ✘ | |
| 129 | +| `dict` | Yes | No | ✘ | |
| 130 | +| `set` | Yes | No | ✘ | |
| 131 | +| `frozenset` | No | Yes | ✔ | |
| 132 | + |
| 133 | +## Takeaways |
| 134 | + |
| 135 | +1. Start with the high-level question “Will this collection change?”—that single answer often narrows the choice. |
| 136 | +2. Prefer immutables for safety and speed; fall back to mutables only when modification is required. |
| 137 | +3. Knowing the built-ins saves dependencies: many “utility” libraries duplicate what core types already provide. |
| 138 | + |
| 139 | +<div style="text-align: center">⁂</div> |
| 140 | + |
| 141 | +[^1]: https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/python/python-number-type |
| 142 | + |
| 143 | +[^2]: https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html |
| 144 | + |
| 145 | +[^3]: https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/python-tutorial/float-in-python |
| 146 | + |
| 147 | +[^4]: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/python-float-type-and-its-methods/ |
| 148 | + |
| 149 | +[^5]: https://www.codesansar.com/python-programming/complex-data-type.htm |
| 150 | + |
| 151 | +[^6]: https://www.prepbytes.com/blog/python/complex-data-type-in-python/ |
| 152 | + |
| 153 | +[^7]: https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_ref_string.asp |
| 154 | + |
| 155 | +[^8]: https://developers.google.com/edu/python/strings |
| 156 | + |
| 157 | +[^9]: https://www.pythonmorsels.com/string-methods/ |
| 158 | + |
| 159 | +[^10]: https://www.pythonmorsels.com/truthiness/ |
| 160 | + |
| 161 | +[^11]: https://www.uvm.edu/~cbcafier/cs1210/book/08_branching/truthiness_and_falsiness.html |
| 162 | + |
| 163 | +[^12]: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/truthy-in-python/ |
| 164 | + |
| 165 | +[^13]: https://www.pythoncheatsheet.org/blog/python-sets-what-why-how |
| 166 | + |
| 167 | +[^14]: https://www.pythoncheatsheet.org/blog/python-uv-package-manager |
| 168 | + |
| 169 | +[^15]: https://www.pythoncheatsheet.org/blog/python-projects-with-poetry-and-vscode-part-2 |
| 170 | + |
| 171 | +[^16]: https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_lists.asp |
| 172 | + |
| 173 | +[^17]: https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/datastructures.html |
| 174 | + |
| 175 | +[^18]: https://www.programiz.com/python-programming/list |
| 176 | + |
| 177 | +[^19]: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/list-methods-python/ |
| 178 | + |
| 179 | +[^20]: https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_ref_dictionary.asp |
| 180 | + |
| 181 | +[^21]: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/python-dictionary-methods/ |
| 182 | + |
| 183 | +[^22]: https://dev.to/iraycd/tuple-immutability-2038 |
| 184 | + |
| 185 | +[^23]: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/are-tuples-immutable-in-python/ |
| 186 | + |
| 187 | +[^24]: https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_numbers.asp |
| 188 | + |
| 189 | +[^25]: https://realpython.com/python-data-types/ |
| 190 | + |
| 191 | +[^26]: https://www.pytut.com/int/ |
| 192 | + |
| 193 | +[^27]: https://jakevdp.github.io/PythonDataScienceHandbook/02.01-understanding-data-types.html |
| 194 | + |
| 195 | +[^28]: https://www.pythoncheatsheet.org/blog/python-3-14-breaking-free-from-gil |
| 196 | + |
| 197 | +[^29]: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/python-string-methods/ |
| 198 | + |
| 199 | +[^30]: https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html |
| 200 | + |
| 201 | +[^31]: https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/python-string-functions |
| 202 | + |
| 203 | +[^32]: https://www.programiz.com/python-programming/methods/string |
| 204 | + |
| 205 | +[^33]: https://www.pythoncheatsheet.org/blog/python-easy-args-kwargs |
| 206 | + |
| 207 | +[^34]: https://www.pythoncheatsheet.org/blog/python-comprehensions-step-by-step |
| 208 | + |
| 209 | +[^35]: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/python-lists/ |
| 210 | + |
| 211 | +[^36]: https://www.linkedin.com/posts/brijpandeyji_i-created-this-fun-guide-to-python-list-operations-activity-7243582307918319616-VYv1 |
| 212 | + |
| 213 | +[^37]: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/python-data-types/ |
| 214 | + |
| 215 | +[^38]: https://realpython.com/ref/builtin-types/float/ |
| 216 | + |
| 217 | +[^39]: https://www.scaler.com/topics/complex-in-python/ |
| 218 | + |
| 219 | +[^40]: https://realpython.com/ref/builtin-types/int/ |
| 220 | + |
| 221 | +[^41]: https://www.pytut.com/float/ |
| 222 | + |
| 223 | +[^42]: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/python-complex-function/ |
| 224 | + |
| 225 | +[^43]: https://discovery.cs.illinois.edu/guides/Python-Fundamentals/Python-data-types/ |
| 226 | + |
| 227 | +[^44]: https://builtin.com/data-science/how-to-use-make-float-in-python |
| 228 | + |
| 229 | +[^45]: https://www.w3schools.com/python/ref_func_complex.asp |
| 230 | + |
| 231 | +[^46]: https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html |
| 232 | + |
| 233 | +[^47]: https://mathspp.com/blog/pydonts/truthy-falsy-and-bool |
| 234 | + |
| 235 | +[^48]: https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_strings.asp |
| 236 | + |
| 237 | +[^49]: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/49021823/understanding-the-truthiness-of-strings |
| 238 | + |
| 239 | +[^50]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn_web_development/Core/Scripting/Useful_string_methods |
| 240 | + |
| 241 | +[^51]: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/truthy-and-falsy-values-in-python/ |
| 242 | + |
| 243 | +[^52]: https://www.thepythoncodingstack.com/p/telling-the-truthy-python-truthiness-falsiness |
| 244 | + |
| 245 | +[^53]: https://realpython.com/python-boolean/ |
| 246 | + |
| 247 | +[^54]: https://www.learnpython.dev/02-introduction-to-python/090-boolean-logic/10-truthiness/ |
| 248 | + |
| 249 | +[^55]: https://dev.to/icncsx/what-determines-the-truthiness-of-an-object-in-python-2e99 |
| 250 | + |
| 251 | +[^56]: https://developers.google.com/edu/python/lists |
| 252 | + |
| 253 | +[^57]: https://dev.to/usooldatascience/a-quick-guide-to-python-dictionary-methods-with-examples-2gfb |
| 254 | + |
| 255 | +[^58]: http://inventwithpython.com/blog/python-tuples-are-immutable-except-when-theyre-mutable.html |
| 256 | + |
| 257 | +[^59]: https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_ref_list.asp |
| 258 | + |
| 259 | +[^60]: https://pages.di.unipi.it/marino/python/Dictionaries/Dictionarymethods.html |
| 260 | + |
| 261 | +[^61]: https://winterflower.github.io/2015/01/18/why-are-tuples-immutable/ |
| 262 | + |
| 263 | +[^62]: https://www.programiz.com/python-programming/methods/dictionary |
| 264 | + |
| 265 | +[^63]: https://www.thepythoncodingstack.com/p/mutating-the-immutable-python-tuples |
| 266 | + |
| 267 | +[^64]: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-dictionary-methods-dictionaries-in-python/ |
| 268 | + |
| 269 | +[^65]: https://eng.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Computer_Science/Programming_Languages/Making_Games_with_Python_and_Pygame_(Sweigart)/04:_Memory_Puzzle/4.12:_Tuples_vs._Lists,_Immutable_vs._Mutable |
0 commit comments