OpenAI generative services, including text, images, videos, and other generation.
API home page: Ace Data Cloud - OpenAI generation
OpenAI ChatGPT is a very powerful AI dialogue system that can generate smooth and natural responses in just a few seconds by inputting prompts. ChatGPT stands out in the industry with its excellent language understanding and generation capabilities, and today, ChatGPT has been widely applied across various industries and fields, with its influence becoming increasingly significant. Whether for daily conversations, creative writing, or professional consulting and coding, ChatGPT can provide astonishing intelligent assistance, greatly enhancing human work efficiency and creativity.
This document mainly introduces the usage process of the OpenAI Chat Completion API, allowing us to easily utilize the dialogue function of the official OpenAI ChatGPT.
To use the OpenAI Chat Completion API, you can first visit the OpenAI Chat Completion API page and click the "Acquire" button to obtain the credentials needed for the request:
If you are not logged in or registered, you will be automatically redirected to the login page inviting you to register and log in. After logging in or registering, you will be automatically returned to the current page.
When applying for the first time, there will be a free quota available for you to use the API for free.
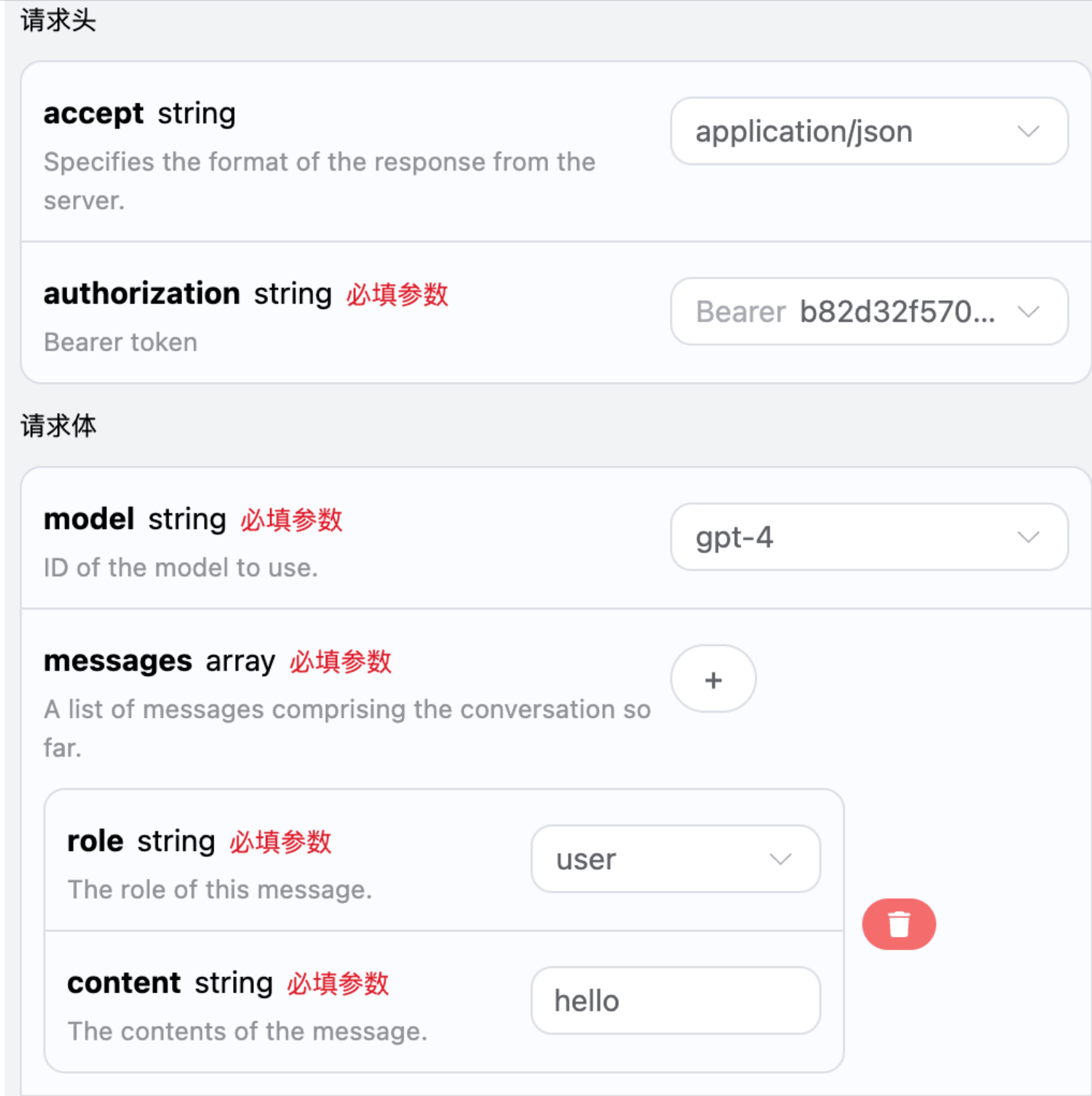
Next, you can fill in the corresponding content on the interface, as shown in the figure:
When using this interface for the first time, we need to fill in at least three pieces of information: one is authorization, which can be selected directly from the dropdown list. The other parameter is model, which is the category of the OpenAI ChatGPT model we choose to use. Here we mainly have 20 types of models; details can be found in the models we provide. The last parameter is messages, which is an array of our input questions. It is an array that allows multiple questions to be uploaded simultaneously, with each question containing role and content. The role indicates the role of the questioner, and we provide three identities: user, assistant, and system. The other content is the specific content of our question.
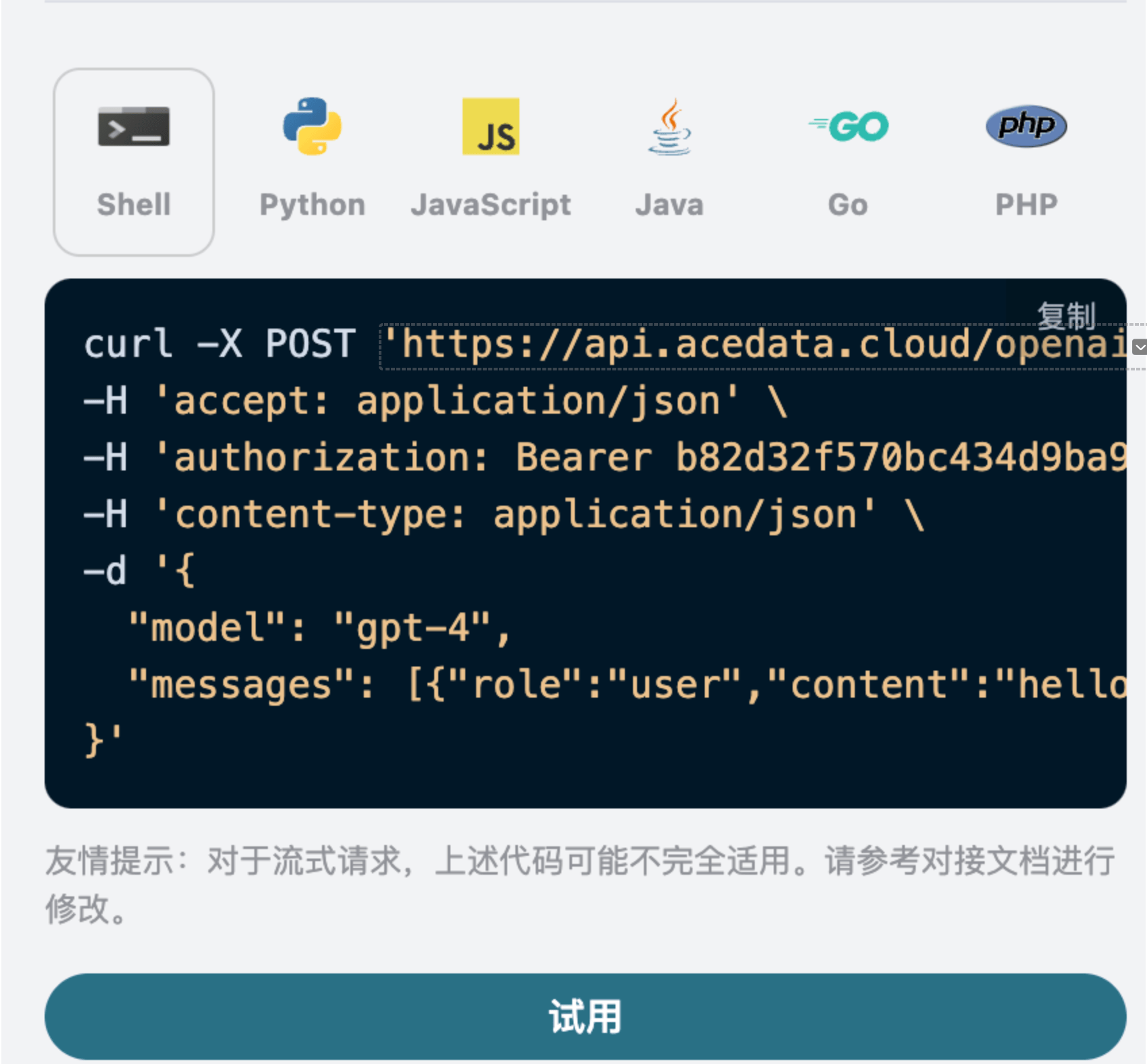
You can also notice that there is corresponding code generation on the right side; you can copy the code to run directly or click the "Try" button for testing.
After the call, we find that the returned result is as follows:
{
"id": "chatcmpl-9k1idCCQuteN6Zu7Kv35TrG6DHKNt",
"object": "chat.completion.chunk",
"created": 1720756723,
"model": "gpt-4",
"system_fingerprint": "fp_abc28019ad",
"choices": [
{
"index": 0,
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Hello! How can I assist you today?"
},
"finish_reason": "stop"
}
],
"recipient": "all",
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 8,
"completion_tokens": 9,
"total_tokens": 17
}
}The returned result contains multiple fields, described as follows:
id, the ID generated for this dialogue task, used to uniquely identify this dialogue task.model, the selected OpenAI ChatGPT model.choices, the response information provided by ChatGPT for the question.usage: statistics on token usage for this Q&A.
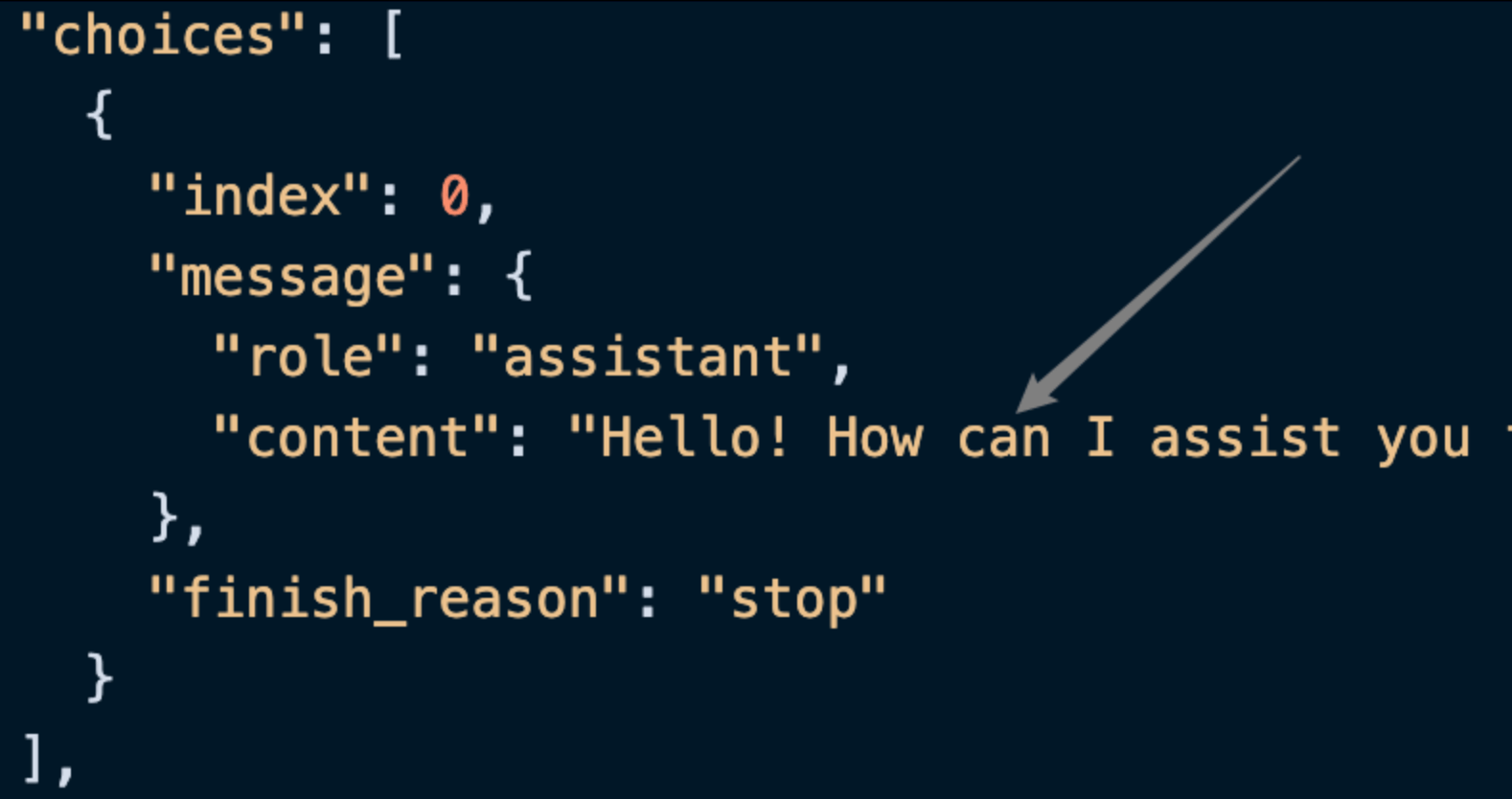
Among them, choices contains the response information from ChatGPT, and the choices inside it can be seen as shown in the figure.
It can be seen that the content field inside choices contains the specific content of ChatGPT's reply.
This interface also supports streaming responses, which is very useful for web integration, allowing the webpage to achieve a word-by-word display effect.
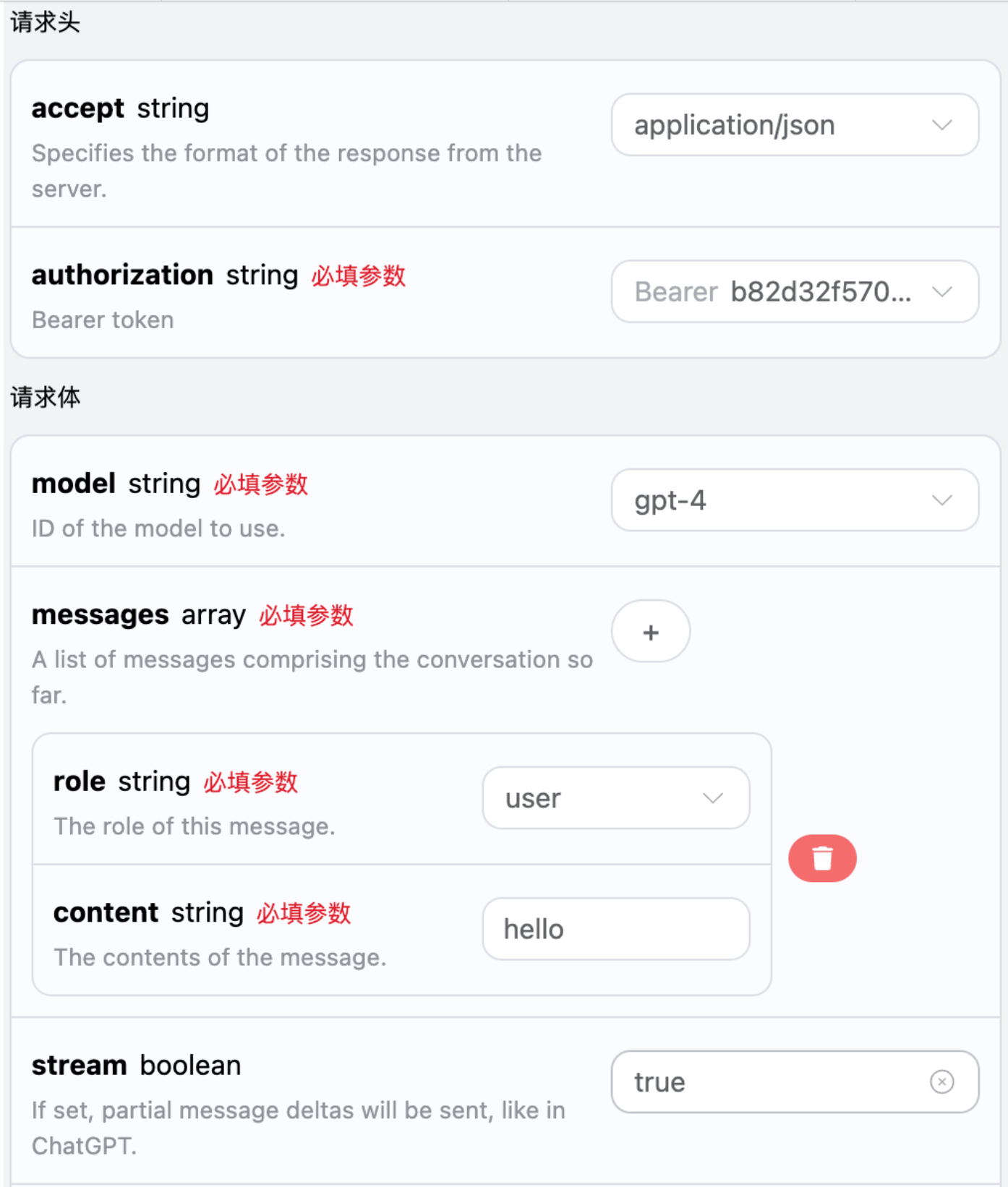
If you want to return responses in a streaming manner, you can change the stream parameter in the request header to true.
Modify as shown in the figure, but the calling code needs to have corresponding changes to support streaming responses.
After changing stream to true, the API will return the corresponding JSON data line by line, and we need to make corresponding modifications in the code to obtain the line-by-line results.
Python sample calling code:
import requests
url = "https://api.acedata.cloud/openai/chat/completions"
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"authorization": "Bearer {token}",
"content-type": "application/json"
}
payload = {
"model": "gpt-4",
"messages": [{"role":"user","content":"hello"}],
"stream": True
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(response.text)The output effect is as follows:
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": "Hi", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": " there", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": "!", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": " How", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": " can", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": " I", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": " assist", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": " you", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": " today", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"content": "?", "role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"role": "assistant"}, "index": 0}], "created": 1721007348, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: {"choices": [{"delta": {"role": "assistant", "finish_reason": "stop", "index": 0}], "created": 1721007349, "id": "chatcmpl-YzczYjVhNjhjMzMwNDQ5MDkyNGYzOGZjZGE1ZGQ5OGU", "model": "gpt-4", "object": "chat.completion.chunk", "recipient": "all"}
data: [DONE]
It can be seen that there are many data in the response, and the choices in data are the latest response content, consistent with the content introduced above. The choices are the newly added response content, and you can interface it with your system based on the results. At the same time, the end of the streaming response is determined by the content of data. If the content is [DONE], it indicates that the streaming response has completely ended. The returned data result has multiple fields, which are described as follows:
id, the ID generated for this dialogue task, used to uniquely identify this dialogue task.model, the OpenAI ChatGPT model selected.choices, the response information provided by ChatGPT to the query.
JavaScript is also supported, for example, the streaming call code for Node.js is as follows:
const options = {
method: "post",
headers: {
accept: "application/json",
authorization: "Bearer {token}",
"content-type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
model: "gpt-4",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "hello" }],
stream: true,
}),
};
fetch("https://api.acedata.cloud/openai/chat/completions", options)
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((response) => console.log(response))
.catch((err) => console.error(err));Java sample code:
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("model", "gpt-4");
jsonObject.put("messages", [{"role":"user","content":"hello"}]);
jsonObject.put("stream", true);
MediaType mediaType = "application/json; charset=utf-8".toMediaType();
RequestBody body = jsonObject.toString().toRequestBody(mediaType);
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("https://api.acedata.cloud/openai/chat/completions")
.post(body)
.addHeader("accept", "application/json")
.addHeader("authorization", "Bearer {token}")
.addHeader("content-type", "application/json")
.build();
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
System.out.print(response.body!!.string())Other languages can be rewritten accordingly; the principle is the same.
For more info, please check below APIs and integration documents.
| API | Path | Integration Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| OpenAI Chat Completions API | /openai/chat/completions |
OpenAI Chat Completion API Integration Guide |
| $t(document_title_openai_v1_responses_api) | /openai/responses |
$t(document_title_openai_v1_responses) |
| $t(document_title_openai_embeddings_api) | /openai/embeddings |
|
| OpenAI Images Generations API | /openai/images/generations |
OpenAI Images Generations API Integration Guide |
/openai/images/generations |
Base URL: https://api.acedata.cloud
If you meet any issue, check our from support info.