-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
Ground Station
The ground station is a collection of APIs, interfaces, and team-written processing code that serves as a bridge between iridium packets sent to/from the Alpha CubeSat and the front-end/back-end interfaces that make the bytes of data user-centric and understandable. The diagram below details different parts of the ground station and how they interact with each other.
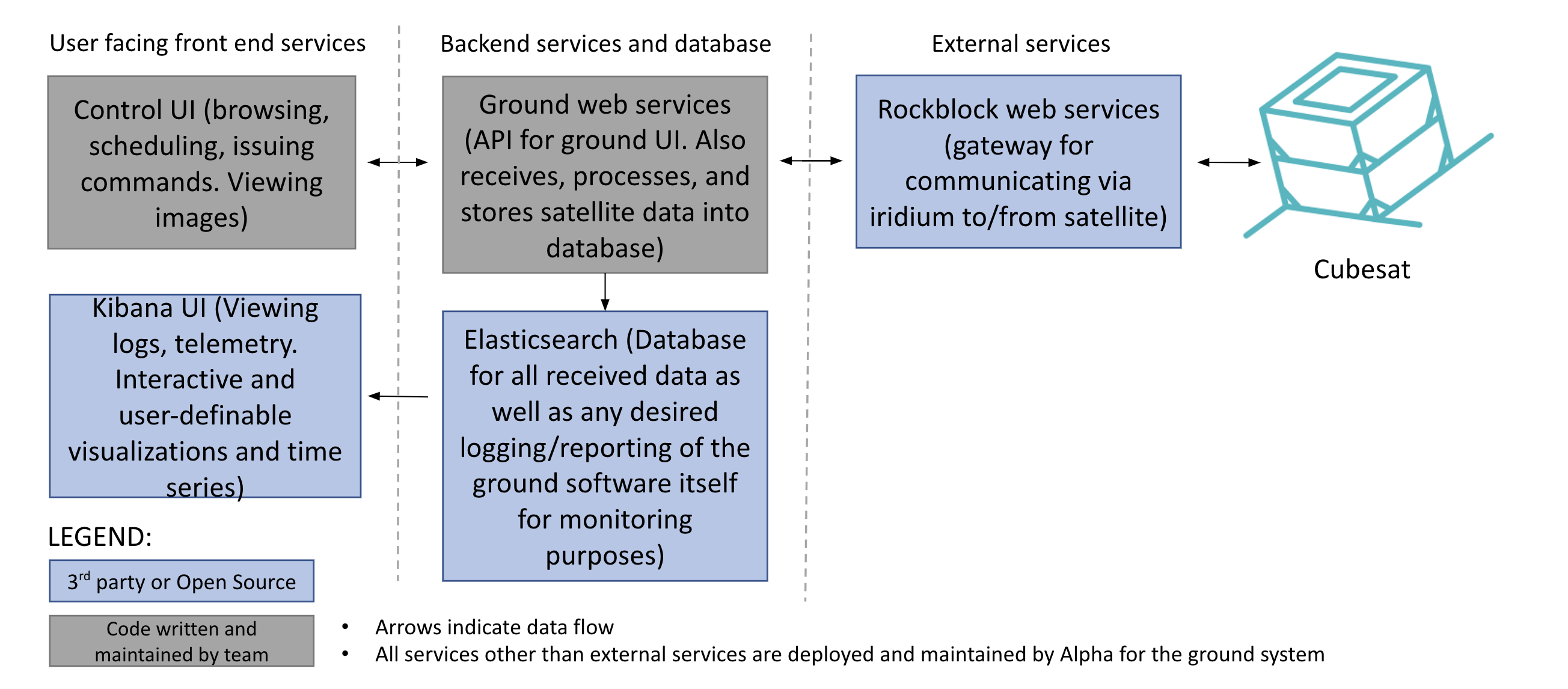
Orginal creator of diagram: Maxwell Anderson
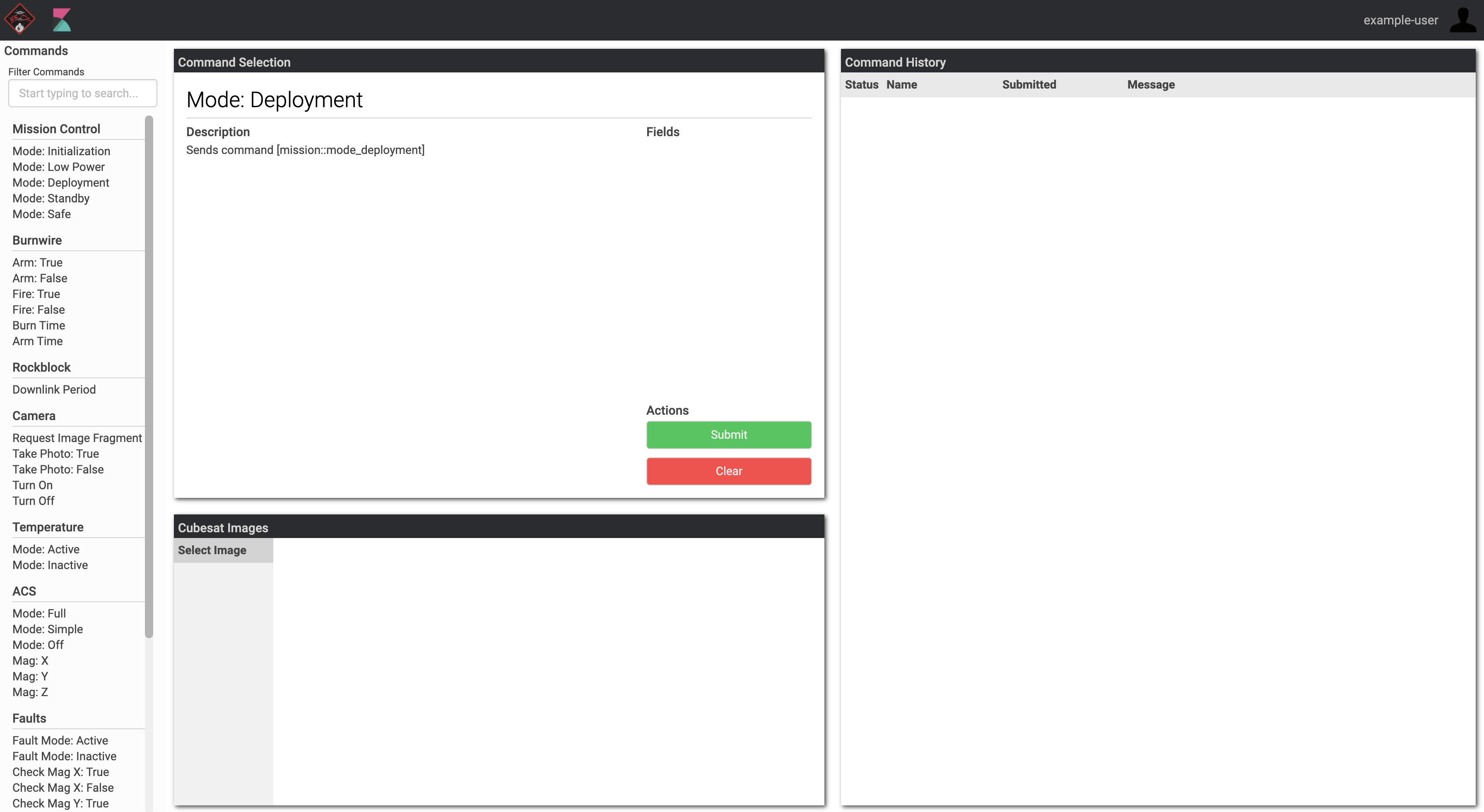
The Control UI is a tool developed by the Alpha Software team members (current and former). It allows for uplinking commands to the CubeSat and changing values. A screenshot of this interface is shown below.
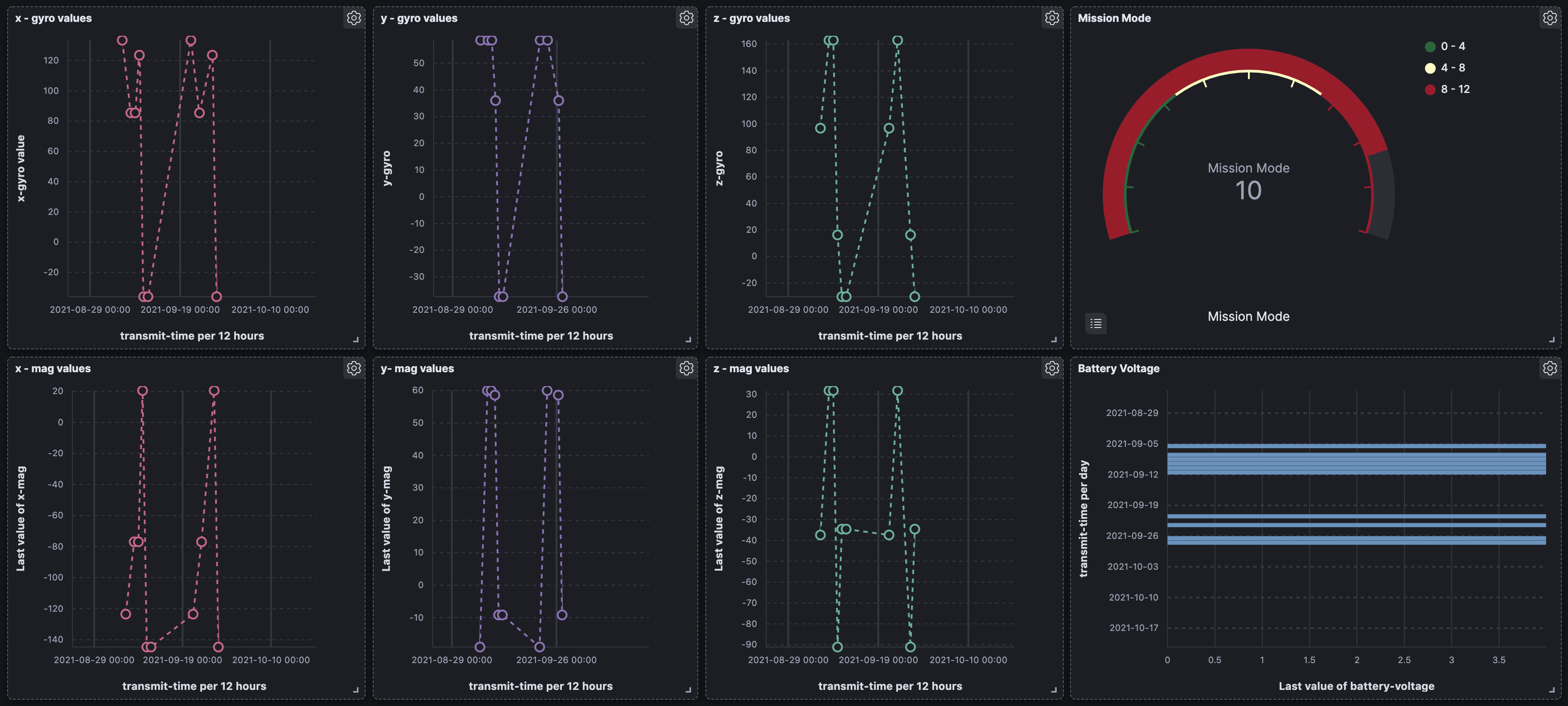
The front end of the ground station has two main components. One is the Kibana dashboard which shows downlinked data from the Cubesat. This includes data such as plots of gyroscope values, the current mission mode, and battery voltage among other characteristics. The Kibana UI also allows for viewing raw data for reports in a JSON format. A screenshot of the current interface is shown below.
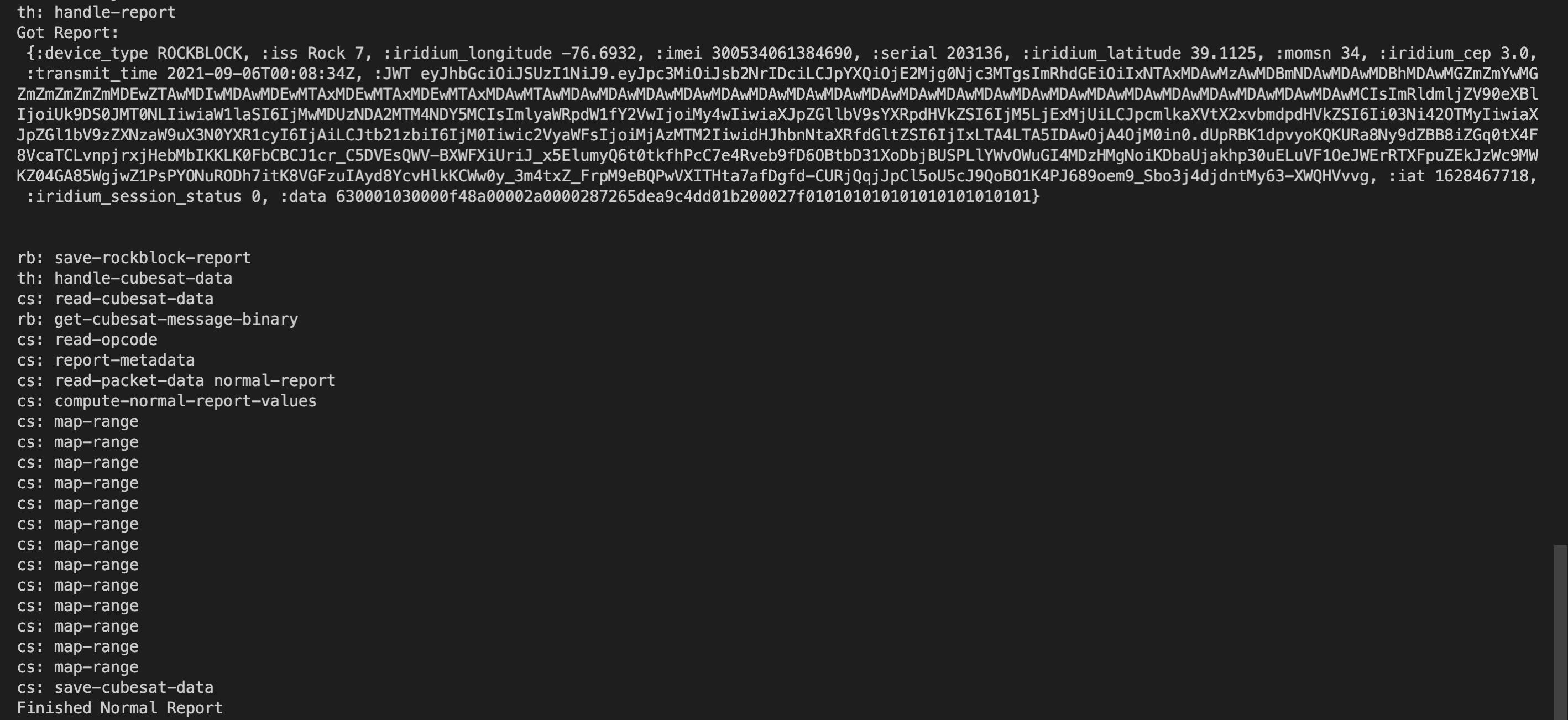
This part of the back-end unit has been developed by Alpha Software team members. It connects with the RockBlock API as well as Elasticsearch. The ground station code processes report as they are downlinked and first appear in the RockBlock portal. From there, once the stream of bits has been transformed into a more user-friendly format -- the code is pushed to the ElasticSearch database.
Elasticsearch is the database used to store report data that has been downlinked from the CubeSat. It connects to the Kibana dashboard leading to seamless updates whenever a new time range is selected.
Below is a diagram showing how reports are processed in the ground station backend.
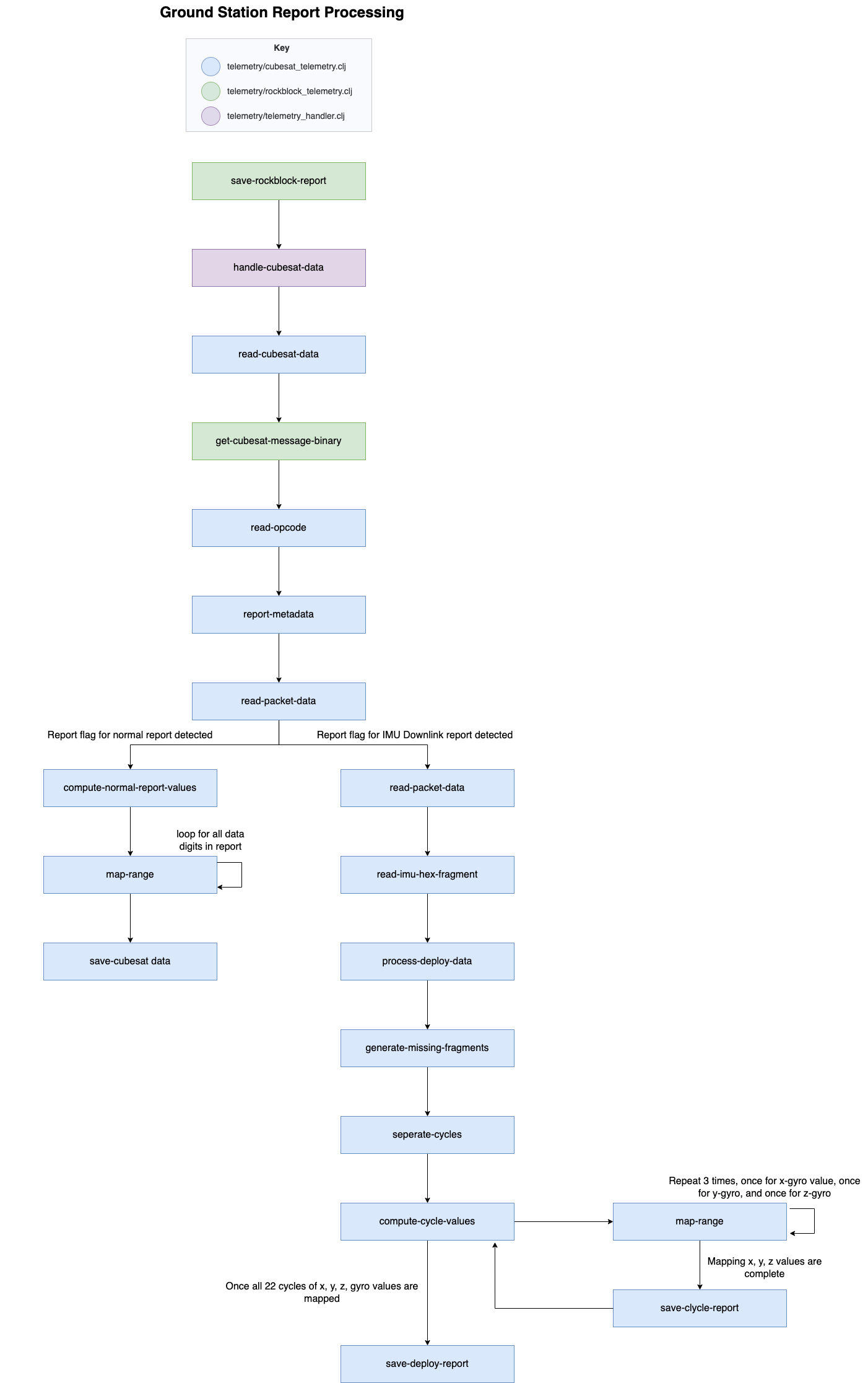
There are 3 main types of reports that the Ground Web Services part of the ground station currently processes.
- Normal Report
- IMU Downlink Report
- Camera Report
The Normal report downlinks a variety of satellite-specific general data.
Format for downlinked data.
| Index | Data | Min (if applicable) | Max (if applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 99 (normel report flag) | N/A | N/A |
| 1 | photoresistor covered | ||
| 2 | button pressed | ||
| 3 | mission mode | ||
| 4 | burn wire fire | ||
| 5 | burn wire arm | ||
| 6 | burn wire time | 0 | 60000 |
| 7 | burn wire armed time | 0 | 86400000 |
| 8 | burn wire mode | ||
| 9 | burn wire attempts | 10 | |
| 10 | downlink period | 1000 | 172800000 |
| 11 | waiting message | ||
| 12 | waiting command | ||
| 13 | mag_x | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 14 | mag_y | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 15 | mag_z | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 16 | gyro_x | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 17 | gryo_y | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 18 | gyro_z | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 19 | light val | ||
| 20 | temperature | 200 | |
| 21 | solar current | 500 | |
| 22 | in sun | ||
| 23 | acs mode | ||
| 24 | voltage | 3 | 5 |
| 25 | fault mode | ||
| 26 | fault1 | ||
| 27 | fault2 | ||
| 28 | fault3 | ||
| 29 | take photo | ||
| 30 | camera powered | ||
| ... | opcodes of received commands | ||
| report.size() - 2 | 254 (end flag 1) | ||
| report.size() - 1 | 255 (end flag 2) |
The IMU downlink report downlink a series of x, y, and z gyro values. These values help determine what the movement of the CubeSat is looking like in space and are a vital part of determining if the CubeSat is stable. There are 22 cycles of x, y, z, gyro values. Read further here.
Format for downlinked data.
| Index | Data |
|---|---|
| 0 | 24 (flag in decimal) |
| 2 | fragment number |
| 4 | x-gyro value |
| 6 | y-gyro value |
| 8 | z-gyro value |
| 10 | x-gyro value |
| 12 | y-gyro value |
| 14 | z-gyro value |
| ... | |
| 130 | x-gyro value |
| 132 | y-gyro value |
| 134 | z-gyro value |
The Camera report downlinks image fragments. The Ground station then assembles these image fragments and creates a full image.
Format for downlinked data.
| Index | Data |
|---|---|
| 0 | 42 (flag in decimal). |
| 1 | Image Serial Number |
| 2-5 | Fragment Number |
| 6-report.size()-1. | Fragment Content |
Steps below are adapted from the original documentation by Eric Zhang
The ground station code is run on a DigitalOcean server. To run the ground station back end code follow the following steps.
- Make sure the ground station repository is cloned on your device
- Run the following command to access the DigitalOcean droplet:
ssh: root@xx-xxxx-xxxx - When prompted, enter the password
- Complete steps 1 through 3 in two separate terminals
In terminal #1 complete the following to run the backend
5. cd ~/Alpha-Cubesat-Ground-Station/cubesat-backend/target
6. java -jar cubesat.jar
In terminal #2 complete the following to run the frontend
7. cd ~/Alpha-Cubesat-Ground-Station/control-frontend/target
8. java -jar cubesat-control.jar
Once the .jar files are running type in the urls for the Kibana UI and Control UI in the browser to access them.
Every time the ground station code is changed and pushed to GitHub, the droplet must be updated to run code with the new changes. The process of updating the code in the droplet and creating new jar files is outlined below.
Adapted from the original documentation written by Eric Zhang
- Push updated code to the private Gound Station GitHub repository
cd ~/Alpha-Cubesat-Ground-Station-
git pullYou will be prompted to enter your GitHub credentials. In the password section, if you get Authentication errors use a Personal Access Token instead of your GitHub password.
Now we want to stop running the previous jar files that may have been running.
5. ps -ef | grep java
6. sudo kill -9 <pid for frontend>
7. sudo kill -9 <pid for backend>
Now we compile the new backend code
8. cd ~/Alpha-Cubesat-Ground-Station/cubesat-backend
9. lein do clean, ring uberjar (this may take a while)
10. cp config.edn ~/Alpha-Cubesat-Ground-Station/cubesat-backend/target
11. cp users-example.edn ~/Alpha-Cubesat-Ground-Station/cubesat-backend/target
Now we compile the new frontend code
12. cd ~/Alpha-Cubesat-Ground-Station/control-frontend
13. lein prod
Finally, we want to make sure Kibana and Elasticsearch services are running.
14. Check Kibana with service kibana status and restart if needed with service restart kibana
15. Check Elasticsearch with service elasticsearch status and restart if needed with service restart elasticsearch
The current testing file in the CubeSat back end is called test2.clj. There are examples of "sample reports" written in the file. To run the file complete the following tasks
- Make sure you are connected to the Digital Ocean Droplet with the correct credentials.
- Cd into the following directory
Alpha-Cubesat-Ground-Station/cubesat-backend/src/cubesat_clj - Run following command
lein repl - A line should pop up with the following text
cubesat-clj.test2=>. Type in (-main) next to the ">" character and press enter to run the tests.
The backend has logging implemented so it will print out the names of the functions (detailed flowchart above) as they are executed. The output data should appear in the "discover" section of Elastic Search. An example output with Ground Station logging is shown below: