Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to people through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. It is preventable and curable. According to WHO there are 212 Million malaria cases and 435000 deaths. Early diagnostics and treatment of malaria can prevent deaths. Malaria is prevalent across the world especially in tropical regions the severity of malaria varies based on the species of plasmodium. Symptoms are chills, fever and sweating, usually occurring a few weeks after being bitten. If efficient detection of malaria is made then deaths can be avoided which will ave families and communities from downward spiral of poverty. Most of the 435000 who died of Malaria were children, mainly in Africa, which is hyperendemic for malaria.When severe malaria does occur, malnourished children have a higher morbidity and mortality.when severe malaria does occur, malnourished children have a higher morbidity and mortality.when severe malaria does occur, malnourished children have a higher morbidity and mortality. Malaria causes Renal failure,Pulmonary oedema,Jaundice,Anemia,Pre-treatment hypoglycemia and Convulsions.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to help tackle some of the world’s most challenging problems and when coupled with popular tools and technologies for development and betterment of our society, what the point of technology when it can't help the needy and save lives. Deep learning helps us to build robust, scalable and effective solutions which can be adopted by everyone even in remote corners of the world and detection of Malaria is one of the problems which Deep learning has help to tackle.
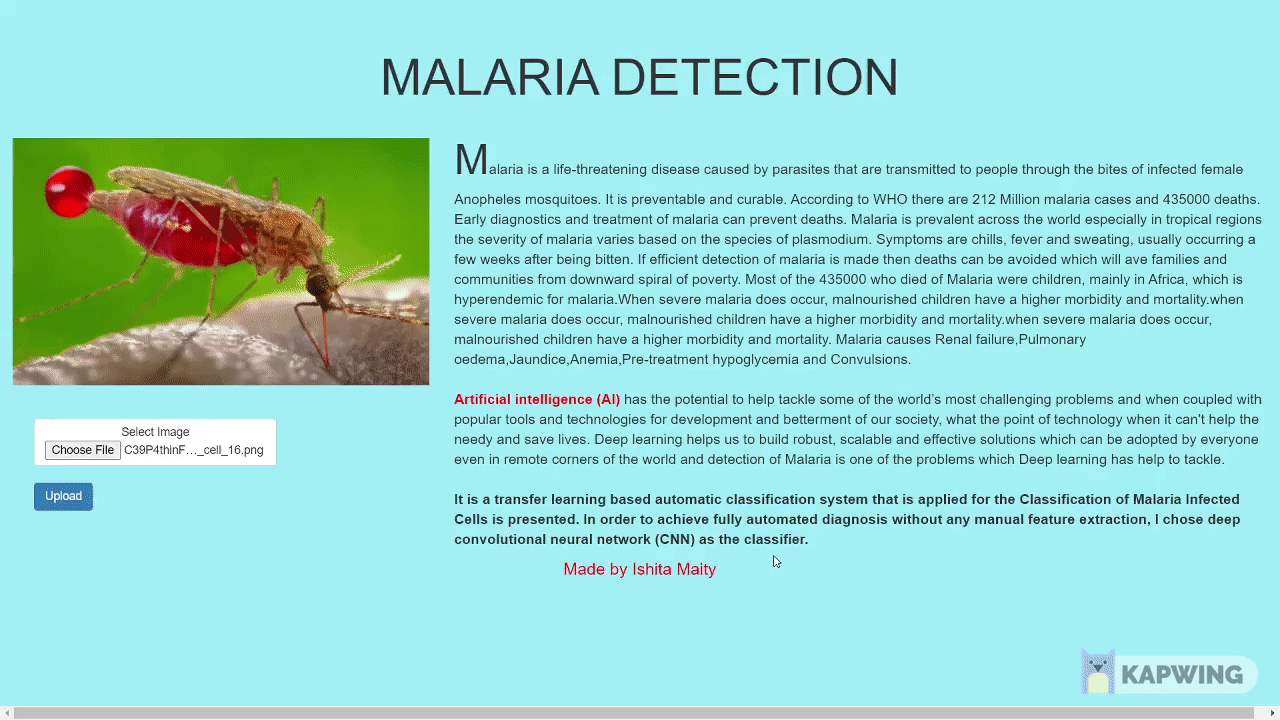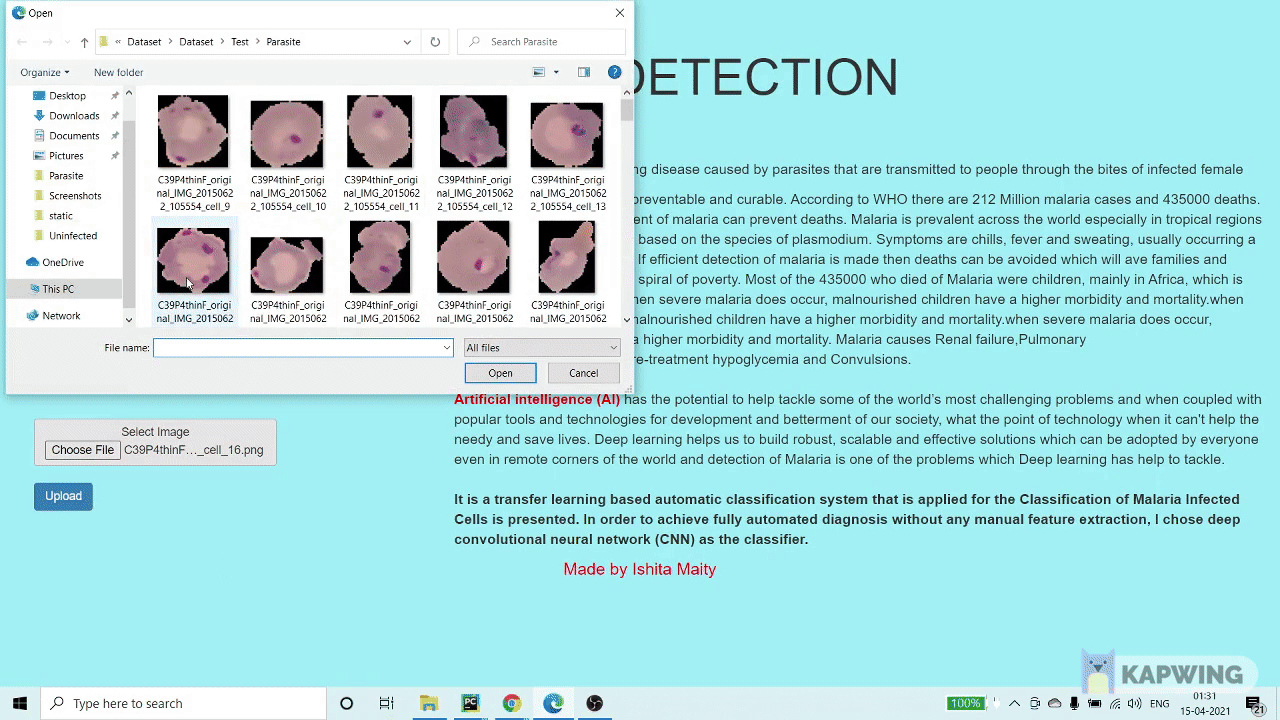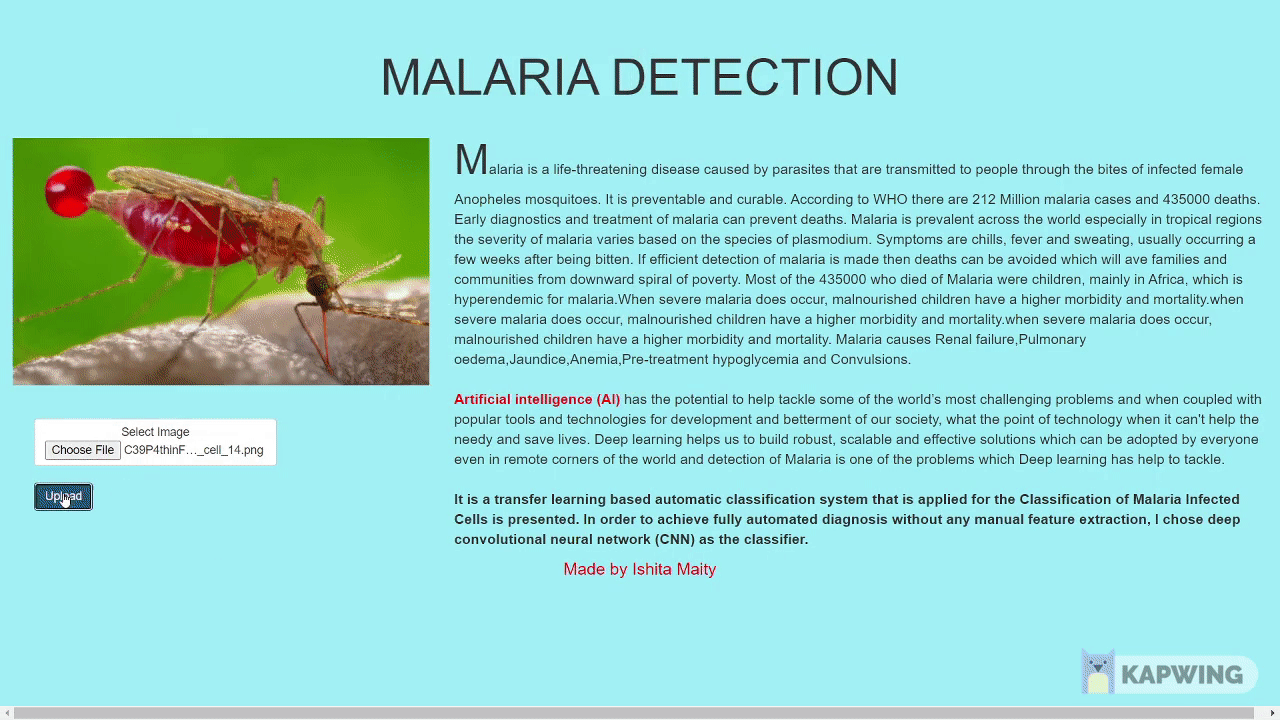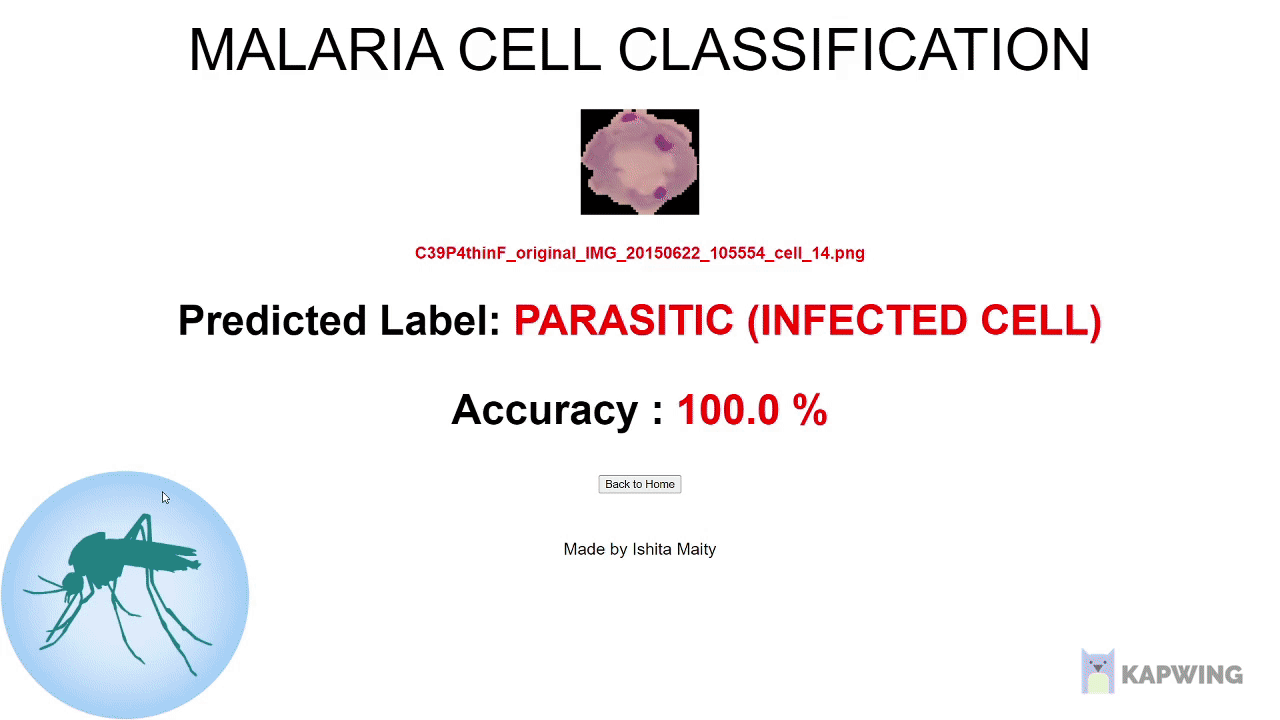
It is a transfer learning based automatic classification system that is applied for the Classification of Malaria Infected Cells is presented. In order to achieve fully automated diagnosis without any manual feature extraction, I chose deep convolutional neural network (CNN) as the classifier.
- Detection of malarial parasites from thin Blood Smear images. Images were collected from Malaria screening research activity by National Institutes of Health (NIH).
- Employed Inception V3 Deep Learning (Convolutional Neural Network) and fine-tuned the model weights in the entire network to distinguish infected from uninfected images. Used Tensorflow 2.4 for model training. Incrementally unfroze and tuned all layers in the network.
- Image augmentation and resizing of images were done on the fly during the training process.
- Attained a loss (categorical crossentropy) and an accuracy 97% on the test data.
.png)
.png)
.png)