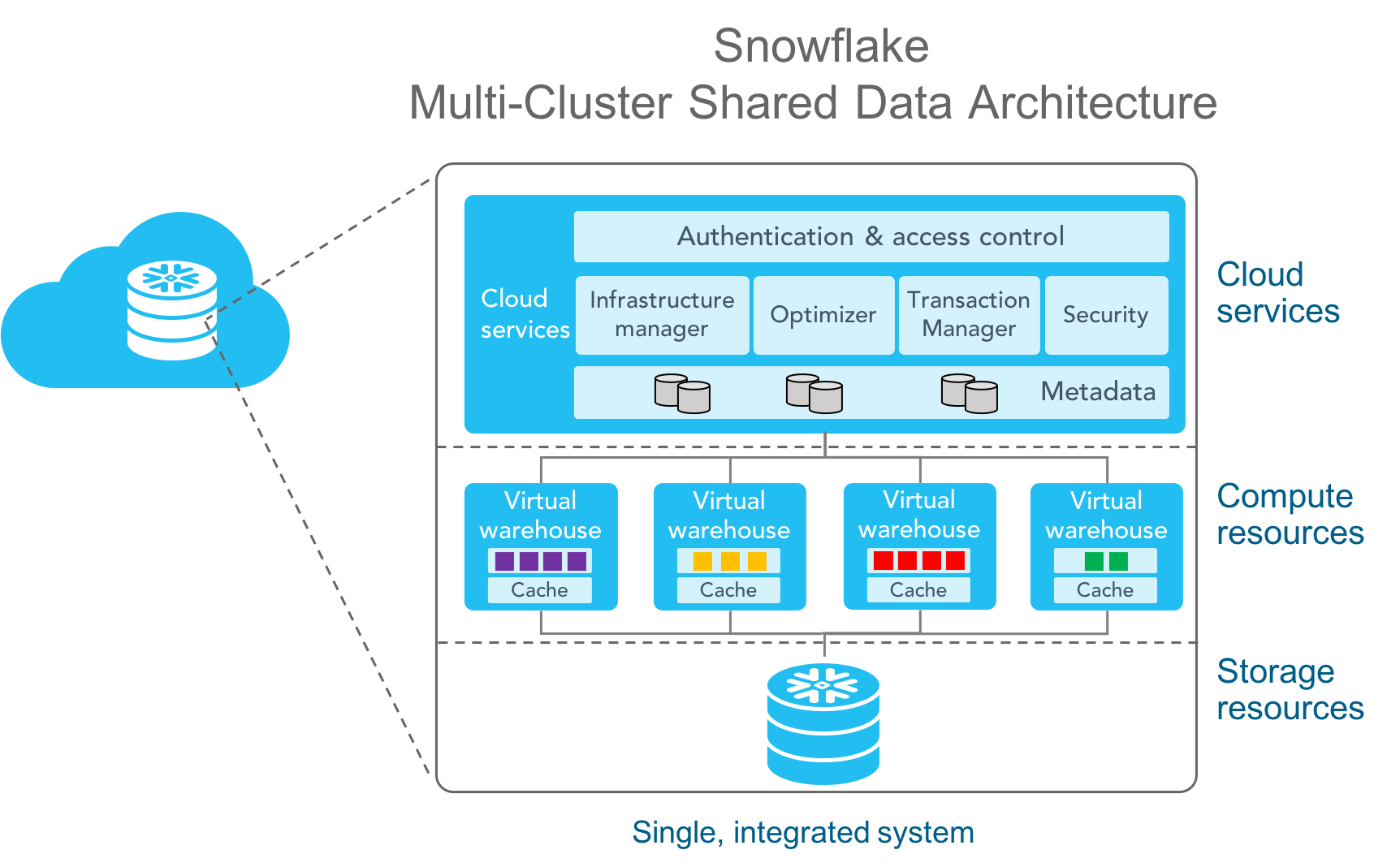
A virtual warehouse in Snowflake is a cluster of compute resources that you can use to execute queries and process data. It's called a "virtual" warehouse because you don't manage the underlying hardware or infrastructure. Instead, you create a virtual warehouse and then use it to process your data. A virtual warehouse is available in two types:
-
Standard
A warehouse provides the required resources, such as CPU, memory, and temporary storage, to perform the following operations in a Snowflake session:
-
Executing SQL SELECT statements that require compute resources (e.g. retrieving rows from tables and views).
-
Performing DML (Data Manipulation Language) operations, such as:
- Updating rows in tables (DELETE , INSERT , UPDATE).
- Loading data into tables (COPY INTO <table>).
- Unloading data from tables (COPY INTO <location>).
Warehouses can be started and stopped at any time. They can also be resized at any time, even while running, to accommodate the need for more or less compute resources, based on the type of operations being performed by the warehouse.
| Warehouse Size | Credits / Hour | Credits / Second | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-Small | 1 | 0.0003 | Default size for warehouses created in Snowsight and using CREATE WAREHOUSE. |
| Small | 2 | 0.0006 | |
| Medium | 4 | 0.0011 | |
| Large | 8 | 0.0022 | |
| X-Large | 16 | 0.0044 | Default size for warehouses created using the Classic Console. |
| 2X-Large | 32 | 0.0089 | |
| 3X-Large | 64 | 0.0178 | |
| 4X-Large | 128 | 0.0356 | |
| 5X-Large | 256 | 0.0711 | Generally available in Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure regions, and in preview in US Government regions. |
| 6X-Large | 512 | 0.1422 | Generally available in Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure regions, and in preview in US Government regions. |
Note
For a multi-cluster warehouse, the number of credits billed is calculated based on the warehouse size and the number of clusters that run within the time period.
For example, if a 3X-Large multi-cluster warehouse runs 1 cluster for one full hour and then runs 2 clusters for the next full hour, the total number of credits billed would be 192 (i.e. 64 + 128).
Multi-cluster warehouses are an Enterprise Edition feature
Snowpark-optimized warehouses which provide 16x memory per node compared to a standard Snowflake virtual warehouse.
Snowpark workloads can be run on both Standard and Snowpark-optimized warehouses. Snowpark-optimized warehouses are recommended for workloads that have large memory requirements such as ML training use cases using a stored procedure on a single virtual warehouse node. Initial creation and resumption of a Snowpark-optimized virtual warehouse may take longer than standard warehouses. Additionally, Snowpark workloads, utilizing UDF or UDTF, may also benefit from Snowpark-optimized warehouses.
Creating a Snowpark-optimized warehouse
Use the warehouse_type property in the CREATE WAREHOUSE command to create a new Snowpark-optimized warehouse.
- Create a new Snowpark-optimized warehouse snowpark_opt_wh:
CREATE OR REPLACE WAREHOUSE snowpark_opt_wh WITH WAREHOUSE_SIZE = 'MEDIUM' WAREHOUSE_TYPE = 'SNOWPARK-OPTIMIZED';