-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 42
Proposal of spatial navigation on TPAC 2017
Hyojin and Jihye proposed spatial navigation at TPAC 2017. (Slide of the presentation)
The Proposal assumed that the browser supports spatial navigation by default. Main purpose of the proposal was to handle edge cases which cannot be covered by the default behavior, such as
- Unreachable elements
- The group of elements based on their functions or behaviors (e.g., main, menu, dialog, etc.)
- The list of elements with a long scroll
The following properties have been suggested to provide ways for customization of the spatial navigation. We prefer focusing on the base functionality for the moment, offering author the ability to add their behavior via Javascript APIs.
If experience shows that authors often use the JavaScript APIs to create solutions similar to the features described below, they could be considered for standardization at a later stage.
- This property can customize the spatial navigation of the group of elements in response to pressing the arrow keys.
nav-rule: auto | projection | direction | nearest-
The meaning of
nav-rulevalues- auto: The UA automatically determines which element to navigate the focus.
- projection: Moves the focus to the first element encountered when projecting the edge of the currently focused element to the edge of the applied element in the direction of navigation.
- direction : Moves the focus to the first element encountered when projecting the edge of the applied element from the currently focused element in the direction of navigation.
- nearest: Moves the focus to the closest element based on the shortest 2D distance and the distance is measured depending on the center of each element.
-
Note
- Able to use if the heuristic spatial navigation is enabled by default.
- Applied to the containing block, so all focusable elements in the DOM subtree rooted at the applied element follow the specified rule for the spatial navigation.
- Overridden by nav-left/right/top/bottom properties.
- Override the Heuristic Spatial Navigation if it is supported.
-
If the
nav-ruleproperty is applied to the element E, the focus moves in the DOM subtree rooted at E in the scrollable area created by E as below.// HTML <div id="E"> <div id="A" tabindex="1" style="top: 100px; left: 50px;">A</div> <div id="B" tabindex="1" style="top: 250px; left: 150px;">B</div> <div id="C" tabindex="1" style="top: 50px; left: 200px;">C</div> <div id="D" tabindex="1" style="top: 100px; left: 300px;">D</div> </div>
// CSS #E { width: 400px; height: 300px; } #A, #B, #C, #D { width: 50px; height: 50px; }
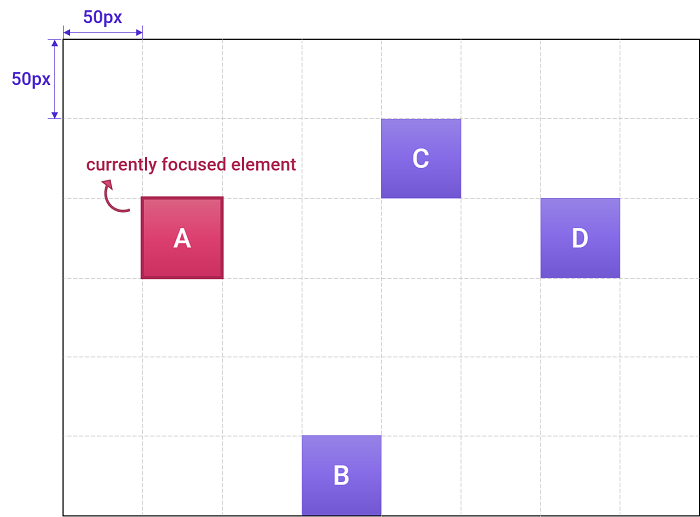
- If the currently focused element is A and there is input from the ➡️ (right-arrow key),
- If
nav-rule: projectionis applied to the element E, the focus moves to D. - If
nav-rule: directionis applied to the element E, the focus moves to B. - Otherwise
nav-rule: nearestis applied to the element E, the focus moves to C.
- If
- If the currently focused element is A and there is input from the ➡️ (right-arrow key),
- This property enables the ability about the focus looping (moving the focus when the focus reaches the end of the page).
- The sequential focus navigation by tab key supports the focus looping, but the heuristic spatial navigation implemented in blink does not support it.
- It would be useful to have the focus looping feature in the spatial navigation, especially for the single page with long-scroll.
nav-loop: auto | no-repeat | repeat-
The meaning of
nav-loopvalues- auto: The UA automatically determines where to move the focus when the focus reaches the end of the page.
- no-repeat: Disables the focus looping
- repeat: Enables the focus looping
-
If
nav-loop: repeatis applied to the element E, the DOM subtree rooted at E is eligible to participate in the focus looping for any scrollable area created by E.- Let the element A is the first child node, and the element Z is the last child node in the DOM subtree rooted at E.
- If the currently focused element is Z and there is an input from the ⬇️ (down-arrow key), the focus is moved to A.