video.mp4
Driving stress test: Closed-loop execution of TransFuser v6, the latest iteration of the TransFuser family, demonstrating stable control in a complex urban scenario under degraded perception and adversarial traffic.
We release the complete pipeline (covering routes description, expert driver, data preprocessing, training, and evaluation) required to achieve state-of-the-art closed-loop performance on the Bench2Drive benchmark. Built around the CARLA simulator, the stack features a data-centric design with:
- Extensive visualization suite and runtime type validation for easier debugging.
- Optimized storage format, packs 72 hours of driving in ~200GB.
- Native support for real-world datasets, including NAVSIM and Waymo Vision-based E2E.
- Roadmap
- Updates
- Quick Start (Get Driving in 20 Minutes)
- Further Documentation
- External Resources
- Acknowledgements
- Citation
- License
- ✅ Checkpoints and inference code (stable)
- 🚧 Documentation, training pipeline and expert code (partial release)
- Full dataset release on HuggingFace
- Cross-dataset training tools and documentation
Status: Active development. Core code and checkpoints are released; remaining components coming soon.
2025/12/24Arxiv paper and code release
1. Environment initialization
Clone the repository and map the project root to your environment
git clone https://github.com/autonomousvision/lead.git
cd lead
# Set the project root directory and configure paths for CARLA, datasets, and dependencies.
{
echo -e "export LEAD_PROJECT_ROOT=$(pwd)" # Set project root variable
echo "source $(pwd)/scripts/main.sh" # Persist more environment variables
} >> ~/.bashrc # Append to bash config to persist across sessions
source ~/.bashrc # Reload config to apply changes immediatelyNote
Please verify that ~/.bashrc reflects these paths correctly.
2. Setup experiment infrastructure
We utilize Miniconda and conda-lock for a more deterministic build:
# Install conda-lock and create conda environment
pip install conda-lock && conda-lock install -n lead conda-lock.yml
# Activate conda environment
conda activate lead
# Install dependencies and setup git hooks
pip install uv && uv pip install -r requirements.txt && uv pip install -e .
# Install other tools needed for development
conda install conda-forge::ffmpeg conda-forge::parallel conda-forge::tree conda-forge::gcc
# Optional: Activate git hooks
pre-commit installWhile waiting for dependencies installation, we recommend CARLA setup on parallel:
bash scripts/setup_carla.sh # Download and setup CARLA at 3rd_party/CARLA_09153. Model zoo
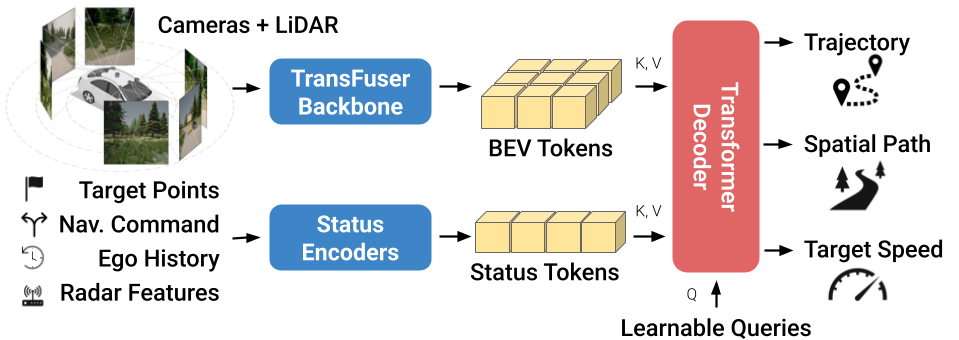
Pre-trained driving policies are hosted on HuggingFace for reproducibility. These checkpoints follow the TFv6 architecture (detailed in Fig. 1), but differ in their sensor configurations, vision backbones or dataset composition.
Figure 1: TFv6 architecture.
Tab. 1 shows available checkpoints with their performance on three major CARLA benchmarks. As first step, we recommend tfv6_resnet34 as it provides a good balance between performance and resource usage.
| Checkpoint | Description | Bench2Drive | Longest6 v2 | Town13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tfv6_regnety032 | TFv6 | 95.2 | 62 | 5.01 |
| tfv6_resnet34 | ResNet34 Backbone | 94.7 | 57 | 3.31 |
| 4cameras_resnet34 | Additional rear camera | 95.1 | 53 | - |
| noradar_resnet34 | No radar sensor | 94.7 | 52 | - |
| visiononly_resnet34 | Vision-only driving model | 91.6 | 43 | - |
| town13heldout_resnet34 | Generalization evaluation | 93.1 | 52 | 2.65 |
Table 1: Performance of pre-trained checkpoints. We report Driving Score, for which higher is better.
To download one checkpoint:
bash scripts/download_one_checkpoint.shOr download all checkpoints at once with git lfs
git clone https://huggingface.co/ln2697/TFv6 outputs/checkpoints
cd outputs/checkpoints
git lfs pull4. Verify driving stack
To initiate closed-loop evaluation and verify the integration of the driving stack, execute the following:
# Start driving environment
bash scripts/start_carla.sh
# Start policy on one route
bash scripts/eval_bench2drive.shDriving logs will be saved to outputs/local_evaluation with the following structure:
outputs/local_evaluation
├── 23687
│ ├── checkpoint_endpoint.json
│ ├── debug_images
│ ├── demo_images
│ └── metric_info.json
├── 23687_debug.mp4
└── 23687_demo.mp4Tip
- Disable video recording in config_closed_loop by turning off
produce_demo_videoandproduce_debug_video. - If memory is limited, modify the file prefixes to load only the first checkpoint seed. By default, the pipeline loads all three seeds as an ensemble.
5. Verify autopilot
Verify the expert policy and data acquisition pipeline by executing a test run on a sample route:
# Start CARLA if not done already
bash scripts/start_carla.sh
# Run expert on one route
bash scripts/run_expert.shData collected will be stored at data/expert_debug and should have following structure:
data/expert_debug
├── data
│ └── BlockedIntersection
│ └── 999_Rep-1_Town06_13_route0_12_22_22_34_45
│ ├── bboxes
│ ├── depth
│ ├── depth_perturbated
│ ├── hdmap
│ ├── hdmap_perturbated
│ ├── lidar
│ ├── metas
│ ├── radar
│ ├── radar_perturbated
│ ├── results.json
│ ├── rgb
│ ├── rgb_perturbated
│ ├── semantics
│ └── semantics_perturbated
└── results
└── Town06_13_result.jsonFor more detailed instructions, see the full documentation. In particular:
Special thanks to carla_garage for the foundational codebase. We also thank the creators of the numerous open-source projects we use:
Other helpful repositories:
Long Nguyen led development of the project. Kashyap Chitta, Bernhard Jaeger, and Andreas Geiger contributed through technical discussion and advisory feedback. Daniel Dauner provided guidance with NAVSIM.
If you find this work useful, please consider giving this repository a star ⭐ and citing our work in your research:
@article{Nguyen2025ARXIV,
title={LEAD: Minimizing Learner-Expert Asymmetry in End-to-End Driving},
author={Nguyen, Long and Fauth, Micha and Jaeger, Bernhard and Dauner, Daniel and Igl, Maximilian and Geiger, Andreas and Chitta, Kashyap},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2512.20563},
year={2025}
}This project is released under the MIT License. See LICENSE for details.