There are two models provided in the main.ipynb file. First is the model trained from scratch, and the second is a model utilizing transfer learning.
The first model implements a CNN (Convolutional Neural Network). It is best described with the following picture. 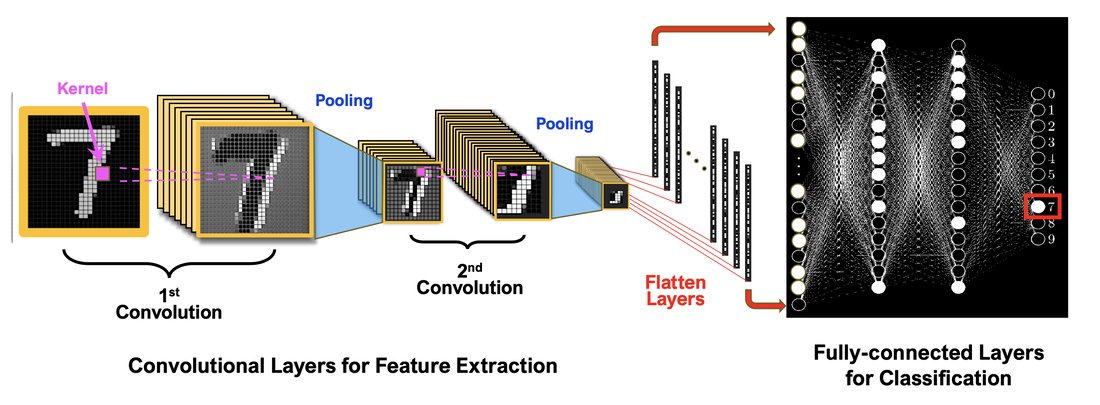
The second model uses transfer learning from imagenet to assist the learning process. It is much more accurate because of the experienced base model. The picture below illustrates the process well. 
- Download dataset from Kaggle
- Install libraries via
pip install requirements.txt - Train the model
- Test images (256x256) by uploading images from the internet and linking them through the path directory
test_img1 = cv2.imread('chee.jpg') # modify chee.jpg
result = int(model.predict(np.expand_dims(test_img1/255,0)) > 0.5)
result