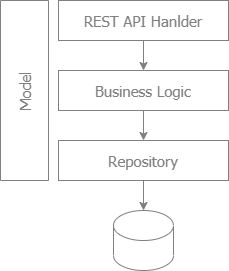
go run main.go- Build the search model at http handler
- Build dynamic SQL for search
- Build SQL for paging by page index (page) and page size (limit)
- Build SQL to count total of records
In the below sample, search users with these criteria:
- get users of page "1", with page size "20"
- email="tony": get users with email starting with "tony"
- dateOfBirth between "min" and "max" (between 1953-11-16 and 1976-11-16)
- sort by phone ascending, id descending
{
"page": 1,
"limit": 20,
"sort": "phone,-id",
"email": "tony",
"dateOfBirth": {
"min": "1953-11-16T00:00:00+07:00",
"max": "1976-11-16T00:00:00+07:00"
}
}GET /users/search?page=1&limit=2&email=tony&dateOfBirth.min=1953-11-16T00:00:00+07:00&dateOfBirth.max=1976-11-16T00:00:00+07:00&sort=phone,-id
In this sample, search users with these criteria:
- get users of page "1", with page size "20"
- email="tony": get users with email starting with "tony"
- dateOfBirth between "min" and "max" (between 1953-11-16 and 1976-11-16)
- sort by phone ascending, id descending
- total: total of users, which is used to calculate numbers of pages at client
- list: list of users
{
"list": [
{
"id": "ironman",
"username": "tony.stark",
"email": "[email protected]",
"phone": "0987654321",
"dateOfBirth": "1963-03-24T17:00:00Z"
}
],
"total": 1
}- GET: retrieve a representation of the resource
- POST: create a new resource
- PUT: update the resource
- PATCH: perform a partial update of a resource, refer to core-go/core and core-go/sql
- DELETE: delete a resource
To check if the service is available.
{
"status": "UP",
"details": {
"sql": {
"status": "UP"
}
}
}[
{
"id": "spiderman",
"username": "peter.parker",
"email": "[email protected]",
"phone": "0987654321",
"dateOfBirth": "1962-08-25T16:59:59.999Z"
},
{
"id": "wolverine",
"username": "james.howlett",
"email": "[email protected]",
"phone": "0987654321",
"dateOfBirth": "1974-11-16T16:59:59.999Z"
}
]GET /users/wolverine{
"id": "wolverine",
"username": "james.howlett",
"email": "[email protected]",
"phone": "0987654321",
"dateOfBirth": "1974-11-16T16:59:59.999Z"
}{
"id": "wolverine",
"username": "james.howlett",
"email": "[email protected]",
"phone": "0987654321",
"dateOfBirth": "1974-11-16T16:59:59.999Z"
}1PUT /users/wolverine{
"username": "james.howlett",
"email": "[email protected]",
"phone": "0987654321",
"dateOfBirth": "1974-11-16T16:59:59.999Z"
}1Perform a partial update of user. For example, if you want to update 2 fields: email and phone, you can send the request body of below.
PATCH /users/wolverine{
"email": "[email protected]",
"phone": "0987654321"
}1If we pass a struct as a parameter, we cannot control what fields we need to update. So, we must pass a map as a parameter.
type UserService interface {
Update(ctx context.Context, user *User) (int64, error)
Patch(ctx context.Context, user map[string]interface{}) (int64, error)
}We must solve 2 problems:
- At http handler layer, we must convert the user struct to map, with json format, and make sure the nested data types are passed correctly.
- At repository layer, from json format, we must convert the json format to database format (in this case, we must convert to column)
At http handler layer, we use core-go/core, to convert the user struct to map, to make sure we just update the fields we need to update
import "github.com/core-go/core"
func (h *UserHandler) Patch(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
var user User
userType := reflect.TypeOf(user)
_, jsonMap := core.BuildMapField(userType)
body, _ := core.BuildMapAndStruct(r, &user)
json, er1 := core.BodyToJson(r, user, body, ids, jsonMap, nil)
result, er2 := h.service.Patch(r.Context(), json)
if er2 != nil {
http.Error(w, er2.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
respond(w, result)
}DELETE /users/wolverine1- core-go/health: include HealthHandler, HealthChecker, SqlHealthChecker
- core-go/config: to load the config file, and merge with other environments (SIT, UAT, ENV)
- core-go/log: logging
- core-go/middleware: middleware log tracing
To check if the service is available, refer to core-go/health
{
"status": "UP",
"details": {
"sql": {
"status": "UP"
}
}
}To create health checker, and health handler
db, err := sql.Open(conf.Driver, conf.DataSourceName)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
sqlChecker := s.NewSqlHealthChecker(db)
healthHandler := health.NewHealthHandler(sqlChecker)To handler routing
r := mux.NewRouter()
r.HandleFunc("/health", healthHandler.Check).Methods("GET")To load the config from "config.yml", in "configs" folder
package main
import "github.com/core-go/config"
type Root struct {
DB DatabaseConfig `mapstructure:"db"`
}
type DatabaseConfig struct {
Driver string `mapstructure:"driver"`
DataSourceName string `mapstructure:"data_source_name"`
}
func main() {
var conf Root
err := config.Load(&conf, "configs/config")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}import (
"github.com/core-go/config"
"github.com/core-go/log"
mid "github.com/core-go/middleware"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
)
func main() {
var cfg app.Root
config.Load(&cfg, "configs/config")
r := mux.NewRouter()
log.Initialize(cfg.Log)
r.Use(mid.BuildContext)
logger := mid.NewLogger()
r.Use(mid.Logger(cfg.MiddleWare, log.InfoFields, logger))
r.Use(mid.Recover(log.ErrorMsg))
}To configure to ignore the health check, use "skips":
middleware:
skips: /health