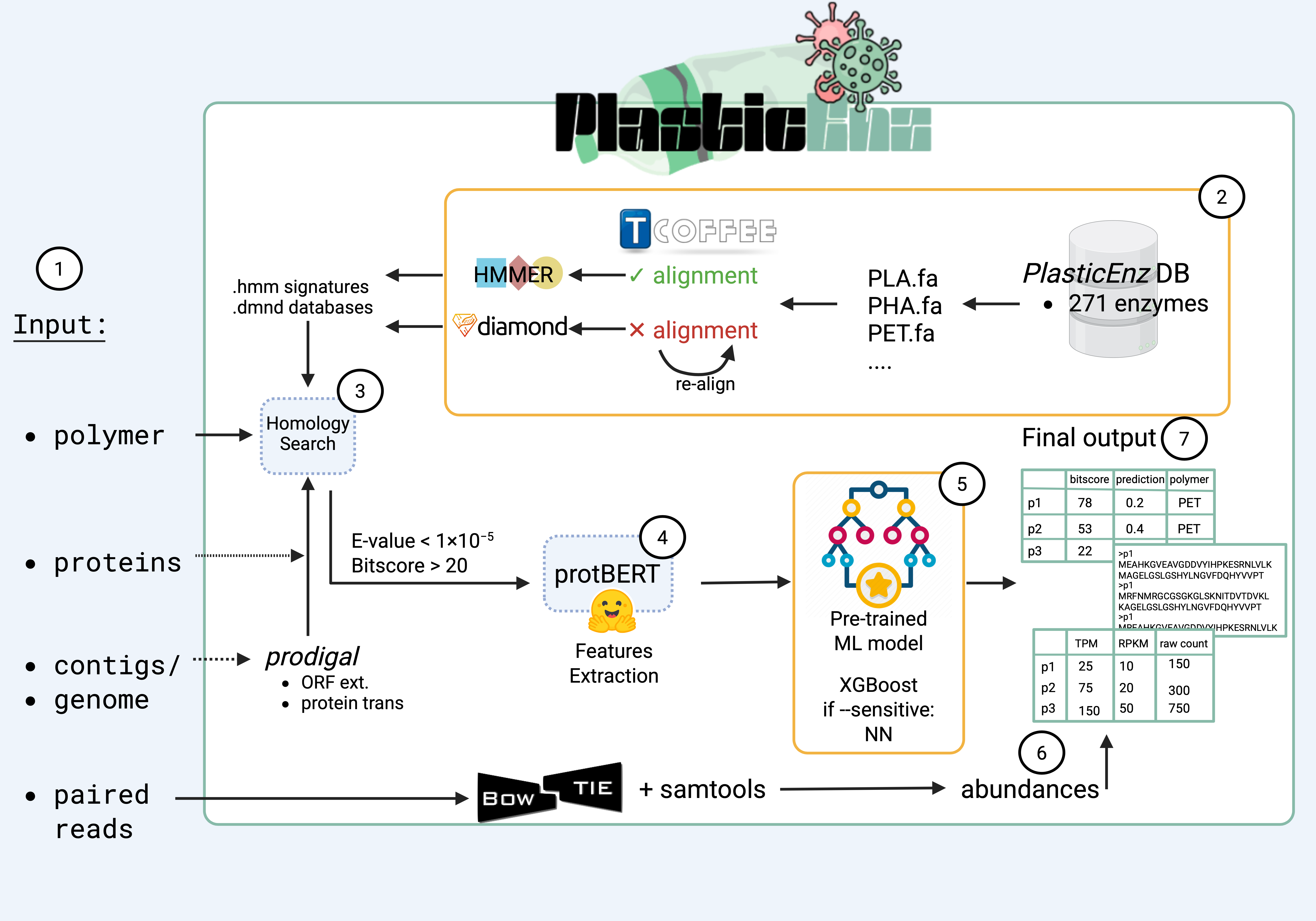
PlasticEnz offers a streamlined and accessible solution for identifying plastic-degrading enzymes in metagenomic data by combining homology-based and machine learning approaches. It accepts contigs, genomes, MAGs and proteins and screens them for potential plastic degrading homologous enzymes.
Figure 1. Overview of the PlasticEnz workflow.git clone https://github.com/msysbio/PlasticEnz.gitconda create -n plasticenz_env --no-channel-priority -c bioconda -c conda-forge -c defaults python=3.11 libffi=3.4.2 prodigal hmmer diamond bowtie2 samtoolsconda activate plasticenz_envWith your conda environment activated, navigate to the package folder and install the remaining python packages:
cd PlasticEnz
pip install -r requirements.txtpip install .PlasticEnz can be built and run using either Docker or Podman.
In the commands below, replace docker with podman if applicable.
After cloning the repository and navigating inside it, build the image like this:
docker build -t plasticenz .Before using the PlasticEnz on your dataset run the test-case (data included within the package) to ensure all is sound. To do so run:
plasticenz --test --outdir .When running inside a container:
docker run --rm plasticenz --test --outdir .Wait until you see "✅PlasticEnz analysis completed successfully!" and check the outdir folder for output files.
If you see three these files there:
Abundances_table.tsv
Proteins_unique.fa
Summary_table.tsv.
You are good to go!
plasticenz or plasticenz --help
After PlasticEnz has been run, the user may want to conduct extra steps to check whether the predicted plastizymes are secretory proteins. PlasticEnz includes a wrapper function that allows it post-analysis using SignalP 6 package:
Teufel, F., Almagro Armenteros, J.J., Johansen, A.R. et al. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat Biotechnol 40, 1023–1025 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-021-01156-3
- Create a clean conda env (OPTIONAL):
We recommend setting up a clean python environment to install the package in in order to avoid conflicts.
conda create -n signalp6_env python=3.11
conda activate signalp6_env
python -m pip install pandas- Download the latest version of SignalP 6.0 (v. 6.0h, Fast).
- Unpack the downlaoded
tar.gzfile. - Open the directory containing the downloaded package, and install it by executing the following command.
pip install .- Copy the model files to the location at which the signalp module got installed. The model weight files are large, so this might take a while.
cd ..
SIGNALP_DIR=$(python -c "import signalp; import os; print(os.path.dirname(signalp.__file__))" )
cp -r signalp-6-package/models/* $SIGNALP_DIR/model_weights/-
The installer created a command
signalp6on your system that is available within the python environment in which you ran step 1. -
To run SignalP on your PlasticEnz output: Navigate to the
extra/folder inside PlasticEnz and run the provided wrapper script:
cd PlasticEnz/extra
conda activate signalp6_env
python signalp6_post.py \
--in /path/to/Summary_table.tsv \
--out /path/to/Summary_table.signalp6.tsv- Output
The new file Summary_table.signalp6.tsv contains all original PlasticEnz results plus one additional column:
signalp6_pred → shows whether each predicted plastizyme is classified as secretory or not.
___ _ _ _ __
/ _ | | __ _ ___| |_(_) ___ /___ __ ____
/ /_)| |/ _` / __| __| |/ __|/_\| '_ \|_ /
/ ___/| | (_| \__ | |_| | (__//__| | | |/ /
\/ |_|\__,_|___/\__|_|\___\__/|_| |_/___|
PlasticEnz - Plastic-Degrading Enzyme Detection Pipeline
Please remember to cite these references when using PlasticEnz:
- Prodigal: Hyatt et al., 2010. BMC Bioinformatics. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-119
- HMMER: Eddy, 2011. PLoS Comput Biol. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195
- DIAMOND: Buchfink et al., 2015. Nat Methods. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3176
- Bowtie2: Langmead & Salzberg, 2012. Nat Methods. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1923
- Samtools: Danecek et al., 2021. Gigascience. DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giab008
- ProtTrans: Elnaggar et al., 2022. IEEE TPAMI. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3095381
usage: plasticenz [-h] [-c CONTIGS] [-1 READS_FORWARD] [-2 READS_REVERSE] [-p PROTEINS] [-g GENOME] [--polymer POLYMER] [--outdir OUTDIR] [--cores CORES] [--use_gpu] [--sensitive] [--evalue_hmmer EVALUE_HMMER]
[--bitscore_hmmer BITSCORE_HMMER] [--evalue_diamond EVALUE_DIAMOND] [--bitscore_diamond BITSCORE_DIAMOND] [--test]
PlasticEnz: A tool for detecting plastic-degrading enzymes from sequence data.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--test Run the tool with a predefined test dataset. (default: False)
Input Files:
-c CONTIGS, --contigs CONTIGS
Path to contigs file (FASTA). (default: None)
-1 READS_FORWARD, --reads_forward READS_FORWARD
Path to forward reads file (FASTQ). (default: None)
-2 READS_REVERSE, --reads_reverse READS_REVERSE
Path to reverse reads file (FASTQ). (default: None)
-p PROTEINS, --proteins PROTEINS
Path to protein file (FASTA). (default: None)
-g GENOME, --genome GENOME
Path to genome or MAG file (FASTA). (default: None)
Analysis Parameters:
--polymer POLYMER Polymer(s) to screen for: LDPE,PBSA,PBS,PCL,PES,PHBV,PLA,P3HP,PBAT,PEA,PET,PHA,PHB. Use 'all' for all available. (default: None)
--outdir OUTDIR Output directory. (default: None)
--cores CORES Number of CPU cores to use. (default: 1)
Performance Options:
--use_gpu Attempt to use GPU for accelerated computations. (default: False)
--sensitive Use neural network model (nn_model.pkl) for sensitive predictions. (default: False)
Search Thresholds:
--evalue_hmmer EVALUE_HMMER
E-value threshold for HMMER search. (default: 1e-05)
--bitscore_hmmer BITSCORE_HMMER
Bitscore value for HMMER search. (default: 20)
--evalue_diamond EVALUE_DIAMOND
E-value threshold for DIAMOND search. (default: 1e-05)
--bitscore_diamond BITSCORE_DIAMOND
Minimum alignment quality for DIAMOND search. (default: 20)
PlasticEnz requires several external tools. If you encounter issues with Conda installation, you can install them manually within the plasticenz_env:
conda install -c bioconda prodigal=2.6.3
conda install -c bioconda hmmer=3.4
conda install -c bioconda diamond=2.1.8
conda install -c bioconda bowtie2=2.5.4
conda install -c bioconda samtools=1.21Krzynowek, A., Snoeks, J. and Faust, K. (2026). PlasticEnz: An integrated database and screening tool combining homology and machine learning to identify plastic-degrading enzymes in meta-omics datasets. PLoS Computational Biology, Version 2, published 26 January. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1013892