📚 Welcome to the interview questions repository!
🌟 Here, you'll find a curated list of interview questions collected from various reputable sources. This compilation provides a comprehensive resource for preparing technical interviews.
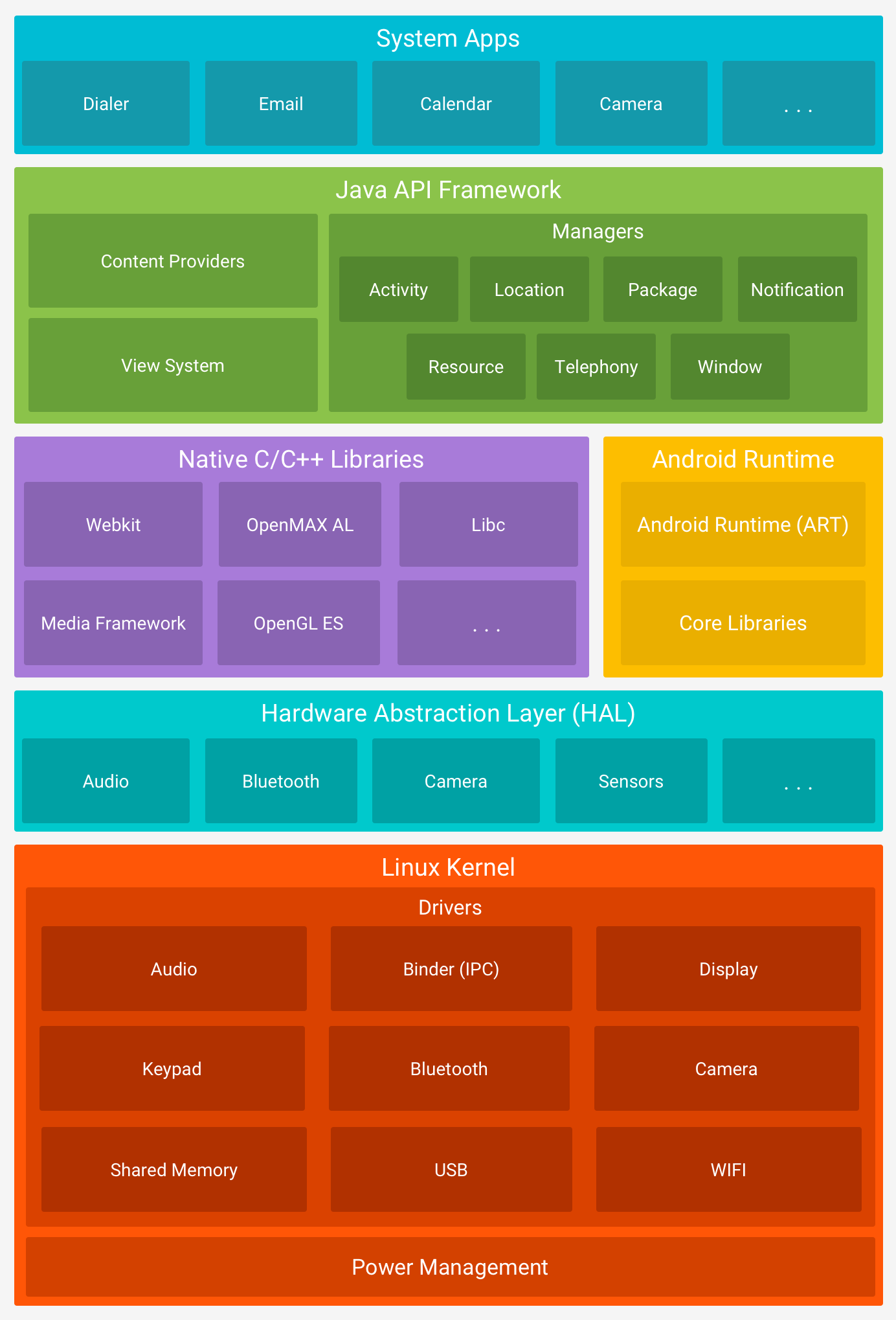
- Android
- OOPS
- List of Android Interview questions
- Android Jetpack
- Kotlin
- Jetpack Compose Design
- Android Roadmap 2024
- 10 Android interview question answers for Freshers
- 20 Essential Android Interview Questions from Toptal
- 25 Essential Android Interview Questions from Adeva
- A couple of Android questions posted by Quora users
- A great list of Android interview questions covering all the aspects of this career
- Collection of Android and Java related questions and topics, including general developer questions, Java core, Data structures, Build Tools, Programming Paradigms, Core Android, Databases and etc
- Collection of Android and Java questions divided by experience
- RocketSkill App Android Interview Questions
- Android cheat sheet: Coding program, Data structure, Android and Java interview questions with answers and categorized by topics
- Android Interview Questions And Answers From Beginner To Advanced
- Interview Questions for Senior Android Developers
- 35+ Android Interview Questions
- Top 50 Android Interview Questions and Answers in 2024
- Difference Between abstraction and polymorphism
- Access Providers OOP
- Virtual functions
- Can an Interface implement another Interface?
- Difference between method overloading and overriding.
- Singleton class java
- @JvmStatic, @JvmField, @JvmOverload
- MVVM design pattern
- Data binding
- Difference between one way and two-way data binding
- Rxjava
- What is activity
- What is fragment
- Life cycle of activity and fragment
- Fragment backstack
- How to share activity viewmodel with its fragments
- How to load image using data binding
- Android proguard
- Android proguard rules
- Types of Permissions
- Android manifest file
- Broadcast receivers
- Types of services
- Difference between sticky intent and pending intents
- Implicit and explicit intents
- Difference between service and intent service
- What is ANR
- R8, delvik
- Dependency Injection
- Relationship between activity and fragment life cycle
- Type of activity launch modes
- Content Providers
- foreground service vs Background service
- AsyncTask vs Thread vs Service
- AsyncTask life cycle during activity rotation
- Alternative of AsncTask(Deprecated in api level 30)
- What is Android Jetpack and why to use this?
- What is a ViewModel and how is it useful?
- What are Android Architecture Components?
- What is LiveData in Android?
- How LiveData is different from ObservableField?
- What is the difference between setValue and postValue in LiveData?
- How to share ViewModel between Fragments in Android?
- Explain WorkManager and its use cases.
- How does ViewModel work internally?
- What is kotlin
- What is the difference between ?. and !!
- Difference between lateinit and lazy.
- Kotlin inline function
- Kotlin scope functions
- What are Higher-Order functions in Kotlin?
- Kotlin high level and lambda function
- What are Data Classes in Kotlin?
- Kotlin delegates
- What is the difference between var and val?
- Kotlin val Vs constant
- Kotlin Sealed Classes
- Design pattern
- Architecture patterns
- SOLID principles
- extension function
- coroutines vs Rxjava
- Explain Coroutine LifecycleScope.
- Serialisation vs parcelable
- Kotlin unified
- Room vs Realm? Why not Realm?
- Explain the use-case of let, run, with, also, apply in Kotlin
-
Jetpack Compose is a modern Android UI toolkit that simplifies UI development through a declarative syntax. Unlike the traditional View system, Compose allows developers to define UI using functions (@Composable) that describe the UI's current state, making it more intuitive and concise.
-
The @Composable annotation is used to define functions that describe UI components. These functions are responsible for rendering UI elements based on their current state. When the state changes, Compose automatically recomposes and updates only the affected UI components.
-
State management in Jetpack Compose involves using state variables annotated with remember or rememberSaveable. Common state types include mutableStateOf for basic state, mutableStateListOf for lists, and derivedStateOf for computed state based on other state variables.
-
If you are working with Material Design icons and want to use the built-in system icons provided by the Material Design guidelines, you should use the Icon composable. If you have custom image assets or graphics that are not part of the standard Material Design icons, you should use the Image composable. Image allows you to load and display bitmap images or other custom drawable resources.
-
Box allows you to position its children elements absolutely. If you need to place elements at specific coordinates within the container, Box is the appropriate choice and If you have elements that need to overlap, Box provides a straightforward way to layer components on top of each other. Column is designed for vertical stacking of elements. If you want to arrange elements in a single column, use Column and When you need a simple linear vertical layout, Column provides an easy and concise way to arrange your UI elements.
-
The Modifier is used to customize and apply transformations to UI elements in Jetpack Compose. It allows you to specify properties such as size, padding, alignment, background color, and more. Modifiers can be chained together to apply multiple transformations to a single UI element.
-
Jetpack Compose can be integrated with existing Android frameworks and libraries by using interoperability features. Compose provides compatibility libraries to bridge the gap between Compose and existing View-based UI components. Additionally, Compose supports the embedding of traditional View-based components within Composable functions using the AndroidView or ComposeView APIs.
-
Navigation in Jetpack Compose is handled using the Navigation Compose library. It introduces the concept of navigation graphs, where each screen or destination is represented by a composable function. The navigation graph defines the connections between destinations, and navigation actions can be triggered using predefined navigation methods.
-
Some best practices for performance optimization in Jetpack Compose include: Minimize unnecessary recompositions by using immutable state objects and avoiding excessive state changes. Use the remember function to cache expensive computations and avoid unnecessary recomputations. Use the key parameter to explicitly control the identity of Composable functions and optimize the diffing algorithm. Use LaunchedEffect and other coroutine-based APIs to perform asynchronous operations off the main thread and ensure smooth and responsive user interfaces in Jetpack Compose.
Feel free to contribute additional questions or improvements via pull requests.
💻 Happy coding and good luck with your interviews! 🚀