Simple and easy to use text logger.
The logger must be initialized then can be called with one of the four log levels:
traceinfowarnerror
import Logger from 'project-logger';
const logger = Logger('context');
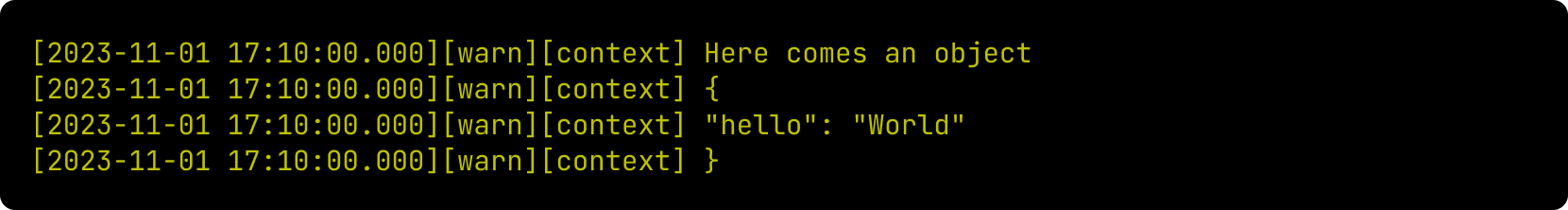
logger.warn('Here comes an object');
logger.warn({
hello: 'World',
});Output:
The Logger module exports a factory function that is used to generate loggers instances.
Logger([context], [options])
Logger([options])
The factory generates logger instances, it can be initialized with a context and with options.
If no context is provided, the logger will take the current file location as context.
Examples:
import Logger from 'logger';
// Simple initialization with a context
const simple = Logger('my-context');
// No context provided, the file location will be used
const noContext = Logger();
// The logger instance can be initialized with some options
const withOptions = Logger('my-context', {
trim: false,
});The options attribute is an object that can contains :
- colors (
object): Object defining the colors used for each kind of log levels:trace,info,warn,error. Each attribute of the color option must be a function that will receive an input and returns it colorized. Internally,chalkdo the default colorization. If null, colorization is disabled. - dateFormat (
string): Date format used to display the dates. The formater being [dayjs][days], the format must follow their own format described here. If null or empty, no date will be displayed. - trim (
boolean): Option to toggle the trim of each strings to log. It does not affect objects and errors. - ignoreEmpty (
boolean): Option to toggle the empty lines removal. - output (
function): Output method called for each line to display. Defaults toprocess.stdout.write. - logLevel (
string): Minimum log level to diplay. Can be eitherTRACE,INFO,WARNorERROR. Defaults toprocess.env.LOG_LEVELorWARNif it does not exists.
configure(options)
The module also export a method overriding the global configuration of all the Logger instances.
It takes the same arguments as the Factory options.
Each instance consist of 4 methods: trace, info, warn, error:
logger.trace(content)
logger.info(content)
logger.warn(content)
logger.error(content)
The attribute content can be a string, object or error. The log only outputs if the
configured log level is equal or "inferior" of the log method.
getLogLevel()
You can retrieve the current log level with the method getLogLevel. It can be useful if you need
to conditionnaly start heavy log loops on your processes.